Unconventional Monetary Policy and Valuations of Risk Financial Assets, Recovery without Hiring, Ten Million Fewer Full-time Jobs, Youth and Middle Age Unemployment, United States International Trade, United States Producer Prices, Collapse of United States Dynamism of Income Growth and Employment Creation, World Cyclical Slow Growth and Global Recession Risk
Carlos M. Pelaez
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017
IA Unconventional Monetary Policy and Valuations of Risk Financial Assets
I Recovery without Hiring
IA1 Hiring Collapse
IA2 Labor Underutilization
ICA3 Ten Million Fewer Full-time Jobs
IA4 Theory and Reality of Cyclical Slow Growth Not Secular Stagnation: Youth and Middle-Age Unemployment
II United States International Trade
IIB United States Producer Prices
II IB Collapse of United States Dynamism of Income Growth and Employment Creation
III World Financial Turbulence
IIIA Financial Risks
IIIE Appendix Euro Zone Survival Risk
IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation
IV Global Inflation
V World Economic Slowdown
VA United States
VB Japan
VC China
VD Euro Area
VE Germany
VF France
VG Italy
VH United Kingdom
VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets
VII Economic Indicators
VIII Interest Rates
IX Conclusion
References
Appendixes
Appendix I The Great Inflation
IIIB Appendix on Safe Haven Currencies
IIIC Appendix on Fiscal Compact
IIID Appendix on European Central Bank Large Scale Lender of Last Resort
IIIG Appendix on Deficit Financing of Growth and the Debt Crisis
IIIGA Monetary Policy with Deficit Financing of Economic Growth
IIIGB Adjustment during the Debt Crisis of the 1980s
IA Unconventional Monetary Policy and Valuations of Risk Financial Assets. Unconventional monetary policy since 2003 has consisted of near zero nominal interest rates, negative real rates of interest, massive purchases of securities for the balance sheet of the Fed and intervention in allocation of credit. Professor John B. Taylor (2016Dec 7, 2016Dec20), in Testimony to the Subcommittee on Monetary Policy and Trade Committee on Financial Services, on Dec 7, 2016, analyzes the adverse effects of unconventional monetary policy:
“My research and that of others over the years shows that these policies were not effective, and may have been counterproductive. Economic growth was consistently below the Fed’s forecasts with the policies, and was much weaker than in earlier U.S. recoveries from deep recessions. Job growth has been insufficient to raise the percentage of the population that is working above pre-recession levels. There is a growing consensus that the extra low interest rates and unconventional monetary policy have reached diminishing or negative returns. Many have argued that these policies widen the income distribution, adversely affect savers, and increase the volatility of the dollar exchange rate. Experienced market participants have expressed concerns about bubbles, imbalances, and distortions caused by the policies. The unconventional policies have also raised public policy concerns about the Fed being transformed into a multipurpose institution, intervening in particular sectors and allocating credit, areas where Congress may have a role, but not a limited-purpose independent agency of government.”
A counterfactual consists of theory and measurements of what would have occurred otherwise if economic policies or institutional arrangements had been different. This task is quite difficult because economic data are observed with all effects as they actually occurred while the counterfactual attempts to evaluate how data would differ had policies and institutional arrangements been different (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. I (2008b), 125, 136; Pelaez 1979, 26-8). Counterfactual data are unobserved and must be calculated using theory and measurement methods. The measurement of costs and benefits of projects or applied welfare economics (Harberger 1971, 1997) specifies and attempts to measure projects such as what would be economic welfare with or without a bridge or whether markets would be more or less competitive in the absence of antitrust and regulation laws (Winston 2006). The “new economic history” of the United States used counterfactuals to measure the economy with or without railroads (Fishlow 1965, Fogel 1964) and in analyzing slavery (Fogel and Engerman 1974). A critical counterfactual in economic history is how Britain surged ahead of France (North and Weingast 1989). There is similarly path-breaking research on railroads in Latin America by Coastworth (1981) and Summerhill (1997, 1998, 2003). Coastworth (2006, 176) argues that: “We already have so many history books that tells us so much about what really occurred in the past, that what we need now are books about what did not happen—but might have, or perhaps even should have happened: Counterfactual History, that is, history that is contrary to fact.”
The counterfactual of avoidance of deeper and more prolonged contraction by fiscal and monetary policies is not the critical issue. As Professor John B. Taylor (2012Oct25) argues, the critically important counterfactual is that the financial crisis and global recession would have not occurred in the first place if different economic policies had been followed. The counterfactual intends to verify that a combination of housing policies and discretionary monetary policies instead of rules (Taylor 1993) caused, deepened and prolonged the financial crisis (Taylor 2007, 2008Nov, 2009, 2012FP, 2012Mar27, 2012Mar28, 2012JMCB, 2015, 2012 Oct 25; 2013Oct28, 2014 Jan01, 2014Jan3, 2014Jun26, 2014Jul15, 2015, 2016Dec7, 2016Dec20 http://www.johnbtaylor.com/; see http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2017/01/rules-versus-discretionary-authorities.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/rules-versus-discretionary-authorities.html). The experience resembles that of the Great Inflation of the 1960s and 1970s with stop-and-go growth/inflation that coined the term stagflation (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/rules-versus-discretionary-authorities.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/05/slowing-growth-global-inflation-great.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/04/new-economics-of-rose-garden-turned.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/03/is-there-second-act-of-us-great.html and Appendix I).
Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. US economic growth has been at only 2.1 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 29 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2016. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the third estimate of GDP for IIIQ2016 (https://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2016/pdf/gdp3q16_3rd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,745.9 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,355.6 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,745.9/$14,355.6 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1989, 4.5 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1989. 4.5 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1990 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2016 would have accumulated to 29.5 percent. GDP in IIIQ2016 would be $19,414.4 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2687.4 billion than actual $16,727.0 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 24.2 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 14.4 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2017/01/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). US GDP in IIIQ2016 is 13.8 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,727.0 billion in IIIQ2016 or 11.6 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.3 percent. Professor John H. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. Cochrane (2016May02) measures GDP growth in the US at average 3.5 percent per year from 1950 to 2000 and only at 1.76 percent per year from 2000 to 2015 with only at 2.0 percent annual equivalent in the current expansion. Cochrane (2016May02) proposes drastic changes in regulation and legal obstacles to private economic activity. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth of manufacturing at average 3.1 percent per year from Nov 1919 to Nov 2016. Growth at 3.1 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 108.2316 in Dec 2007 to 142.1081 in Nov 2016. The actual index NSA in Nov 2016 is 103.0759, which is 27.5 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.1 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2015. Using trend growth of 2.1 percent per year, the index would increase to 130.3109 in Nov 2016. The output of manufacturing at 103.0759 in Nov 2016 is 20.9 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
There is socio-economic stress in the combination of adverse events and cyclical performance:
- Mediocre economic growth below potential and long-term trend, resulting in idle productive resources with GDP two trillion dollars below trend (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). US GDP grew at the average rate of 3.2 percent per year from 1929 to 2015, with similar performance in whole cycles of contractions and expansions, but only at 1.2 percent per year on average from 2007 to 2015. GDP in IIIQ2016 is 13.8 percent lower than what it would have been had it grown at trend of 3.0 percent
- Private fixed investment stagnating at increase of 7.5 percent in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2016 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html)
- Twenty four million or 14.4 percent of the effective labor force unemployed or underemployed in involuntary part-time jobs with stagnating or declining real wages (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2017/01/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/the-case-for-increase-in-federal-funds.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/10/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/09/interest-rates-and-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/08/global-competitive-easing-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/fluctuating-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/financial-turbulence-twenty-four.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/proceeding-cautiously-in-monetary.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets-in.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/weakening-equities-with-exchange-rate.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/liftoff-of-fed-funds-rate-followed-by.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/live-possibility-of-interest-rates.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/labor-market-uncertainty-and-interest.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-policy-dependent-on-what.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/turbulence-of-financial-asset.html)
- Stagnating real disposable income per person or income per person after inflation and taxes (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/the-case-for-increase-in-federal-funds.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/the-case-for-increase-in-federal-funds.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/10/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/09/interest-rates-and-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/08/global-competitive-easing-or.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/financial-asset-values-rebound-from.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/financial-turbulence-twenty-four.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/proceeding-cautiously-in-monetary.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets-in.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/dollar-revaluation-and-decreasing.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/dollar-revaluation-constraining.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/dollar-revaluation-constraining.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/live-possibility-of-interest-rates.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/labor-market-uncertainty-and-interest.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-policy-dependent-on-what.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/international-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/dollar-devaluation-and-carry-trade.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/volatility-of-valuations-of-financial.html)
- Depressed hiring that does not afford an opportunity for reducing unemployment/underemployment and moving to better-paid jobs (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-values-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/dollar-revaluation-and-valuations-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/10/imf-view-of-world-economy-and-finance.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/09/interest-rate-uncertainty-and-valuation.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/08/rising-valuations-of-risk-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/oscillating-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/considerable-uncertainty-about-economic.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/recovery-without-hiring-ten-million.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/proceeding-cautiously-in-reducing.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/contraction-of-united-states-corporate.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/subdued-foreign-growth-and-dollar.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/unconventional-monetary-policy-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/liftoff-of-interest-rates-with-volatile_17.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/interest-rate-policy-conundrum-recovery.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/impact-of-monetary-policy-on-exchange.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-policy-dependent-on-what_13.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/exchange-rate-and-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/oscillating-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/volatility-of-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/volatility-of-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/fluctuating-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/dollar-revaluation-recovery-without.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/global-exchange-rate-struggle-recovery.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/02/g20-monetary-policy-recovery-without.html)
- Productivity growth fell from 2.2 percent per year on average from 1947 to 2015 and average 2.3 percent per year from 1947 to 2007 to 1.3 percent per year on average from 2007 to 2015, deteriorating future growth and prosperity (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-values-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/the-case-for-increase-in-federal-funds.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/09/interest-rates-and-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/08/rising-valuations-of-risk-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/considerable-uncertainty-about-economic.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/closely-monitoring-global-economic-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/liftoff-of-fed-funds-rate-followed-by.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/live-possibility-of-interest-rates.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-policy-dependent-on-what.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/exchange-rate-and-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/quite-high-equity-valuations-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/global-competitive-devaluation-rules.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/02/job-creation-and-monetary-policy-twenty.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/financial-risks-twenty-six-million.html)
- Output of manufacturing in Nov 2016 at 27.5 percent below long-term trend since 1919 and at 20.9 percent below trend since 1986 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/of-course-economic-outlook-is-highly.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/interest-rate-increase-could-well.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/10/dollar-revaluation-world-inflation.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/09/interest-rates-and-volatility-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/08/interest-rate-policy-uncertainty-and.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/unresolved-us-balance-of-payments.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/fomc-projections-world-inflation-waves.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/most-fomc-participants-judged-that-if.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/contracting-united-states-industrial.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/monetary-policy-and-competitive.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/unconventional-monetary-policy-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/liftoff-of-interest-rates-with-monetary.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/interest-rate-liftoff-followed-by.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/interest-rate-policy-quagmire-world.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-increase-on-hold-because.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/exchange-rate-and-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/fluctuating-financial-asset-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/fluctuating-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/global-portfolio-reallocations-squeeze.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/impatience-with-monetary-policy-of.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/02/world-financial-turbulence-squeeze-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/01/exchange-rate-conflicts-squeeze-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/10/imf-view-squeeze-of-economic-activity.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html)
- Unsustainable government deficit/debt and balance of payments deficit (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2017/01/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/unresolved-us-balance-of-payments.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/proceeding-cautiously-in-reducing.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/weakening-equities-and-dollar.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/monetary-policy-designed-on-measurable.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/fluctuating-financial-asset-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/impatience-with-monetary-policy-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/irrational-exuberance-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/monetary-policy-world-inflation-waves.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/06/valuation-risks-world-inflation-waves.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/02/theory-and-reality-of-cyclical-slow.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/interest-rate-risks-world-inflation.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/tapering-quantitative-easing-mediocre.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/09/duration-dumping-and-peaking-valuations.html)
- Worldwide waves of inflation (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/of-course-economic-outlook-is-highly.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/interest-rate-increase-could-well.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/10/dollar-revaluation-world-inflation.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/09/interest-rates-and-volatility-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/08/interest-rate-policy-uncertainty-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/oscillating-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/fomc-projections-world-inflation-waves.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/most-fomc-participants-judged-that-if.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/contracting-united-states-industrial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/monetary-policy-and-competitive.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/uncertainty-of-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/liftoff-of-interest-rates-with-monetary.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/interest-rate-liftoff-followed-by.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/interest-rate-policy-quagmire-world.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-increase-on-hold-because.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/global-decline-of-values-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/fluctuating-financial-asset-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/interest-rate-policy-and-dollar.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/global-portfolio-reallocations-squeeze.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/dollar-revaluation-and-financial-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/irrational-exuberance-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/01/competitive-currency-conflicts-world.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/10/financial-oscillations-world-inflation.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/monetary-policy-world-inflation-waves.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/world-inflation-waves-united-states.html)
- Deteriorating terms of trade and net revenue margins of production across countries in squeeze of economic activity by carry trades induced by zero interest rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/of-course-economic-outlook-is-highly.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/interest-rate-increase-could-well.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/10/dollar-revaluation-world-inflation.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/09/interest-rates-and-volatility-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/unresolved-us-balance-of-payments.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/fomc-projections-world-inflation-waves.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/most-fomc-participants-judged-that-if.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/imf-view-of-world-economy-and-finance.html and earlier) (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/monetary-policy-and-competitive.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/uncertainty-of-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/liftoff-of-interest-rates-with-monetary.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/interest-rate-liftoff-followed-by.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/interest-rate-policy-quagmire-world.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-increase-on-hold-because.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/global-decline-of-values-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/fluctuating-financial-asset-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/global-portfolio-reallocations-squeeze.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/impatience-with-monetary-policy-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/02/world-financial-turbulence-squeeze-of.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/01/exchange-rate-conflicts-squeeze-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/10/imf-view-squeeze-of-economic-activity.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html
- Financial repression of interest rates and credit affecting the most people without means and access to sophisticated financial investments with likely adverse effects on income distribution and wealth disparity (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/the-case-for-increase-in-federal-funds.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/the-case-for-increase-in-federal-funds.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/10/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/09/interest-rates-and-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/08/global-competitive-easing-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/financial-asset-values-rebound-from.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/financial-turbulence-twenty-four.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/proceeding-cautiously-in-monetary.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/closely-monitoring-global-economic-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/dollar-revaluation-and-decreasing.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/dollar-revaluation-constraining.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/live-possibility-of-interest-rates.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/labor-market-uncertainty-and-interest.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-policy-dependent-on-what.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/international-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/dollar-devaluation-and-carry-trade.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/volatility-of-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/global-competitive-devaluation-rules.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/02/job-creation-and-monetary-policy-twenty.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/growth-uncertainties-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/10/world-financial-turbulence-twenty-seven.html)
- 43 million in poverty and 29 million without health insurance with family income adjusted for inflation regressing to 1999 levels (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/09/the-economic-outlook-is-inherently.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/interest-rate-policy-uncertainty-imf.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/financial-volatility-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/09/duration-dumping-and-peaking-valuations.html)
- Net worth of households and nonprofits organizations increasing by 18.1 percent after adjusting for inflation in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIQ2016 when it would have grown over 30.6 percent at trend of 3.1 percent per year in real terms from IVQ1945 to IIIQ2016 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2017/01/rules-versus-discretionary-authorities.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/09/the-economic-outlook-is-inherently.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/of-course-considerable-uncertainty.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/monetary-policy-and-fluctuations-of_13.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/weakening-equities-and-dollar.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/monetary-policy-designed-on-measurable.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/fluctuating-financial-asset-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/dollar-revaluation-and-financial-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/financial-volatility-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/06/financial-indecision-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/global-financial-risks-recovery-without.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/collapse-of-united-states-dynamism-of.html). Financial assets increased $20.4 trillion while nonfinancial assets increased $3.9 trillion with likely concentration of wealth in those with access to sophisticated financial investments. Real estate assets adjusted for inflation fell 2.4 percent.
Valuations of risk financial assets have reached extremely high levels in markets with fluctuating volumes. For example, the DJIA has increased 105.3 percent since the trough of the sovereign debt crisis in Europe on Jul 2, 2010 to Jan 13, 2016; S&P 500 has gained 122.4 percent and DAX 105.1 percent. The overwhelming risk factor is the unsustainable Treasury deficit/debt of the United States (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2017/01/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/unresolved-us-balance-of-payments.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/proceeding-cautiously-in-reducing.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/weakening-equities-and-dollar.html). A competing event is the high level of valuations of risk financial assets (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/unconventional-monetary-policy-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/01/peaking-valuations-of-risk-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/01/theory-and-reality-of-secular.html). Matt Jarzemsky, writing on “Dow industrials set record,” on Mar 5, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887324156204578275560657416332.html), analyzes that the DJIA broke the closing high of 14,164.53 set on Oct 9, 2007, and subsequently also broke the intraday high of 14,198.10 reached on Oct 11, 2007. The DJIA closed at 19,885.73 on Jan 13, 2017, which is higher by 40.4 percent than the value of 14,164.53 reached on Oct 9, 2007 and higher by 40.1 percent than the value of 14,198.10 reached on Oct 11, 2007. Values of risk financial assets have been approaching or exceeding historical highs.
The financial crisis and global recession were caused by interest rate and housing subsidies and affordability policies that encouraged high leverage and risks, low liquidity and unsound credit (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 157-66, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 217-27, International Financial Architecture (2005), 15-18, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 221-5, Globalization and the State Vol. II (2008b), 197-213, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 182-4). Several past comments of this blog elaborate on these arguments, among which: http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/07/causes-of-2007-creditdollar-crisis.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/professor-mckinnons-bubble-economy.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/world-inflation-quantitative-easing.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/treasury-yields-valuation-of-risk.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/11/quantitative-easing-theory-evidence-and.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/12/is-fed-printing-money-what-are.html
Table VI-1 shows the phenomenal impulse to valuations of risk financial assets originating in the initial shock of near zero interest rates in 2003-2004 with the fed funds rate at 1 percent, in fear of deflation that never materialized, and quantitative easing in the form of suspension of the auction of 30-year Treasury bonds to lower mortgage rates. World financial markets were dominated by monetary and housing policies in the US. Between 2002 and 2008, the DJ UBS Commodity Index rose 165.5 percent largely because of unconventional monetary policy encouraging carry trades from low US interest rates to long leveraged positions in commodities, exchange rates and other risk financial assets. The charts of risk financial assets show sharp increase in valuations leading to the financial crisis and then profound drops that are captured in Table VI-1 by percentage changes of peaks and troughs. The first round of quantitative easing and near zero interest rates depreciated the dollar relative to the euro by 39.3 percent between 2003 and 2008, with revaluation of the dollar by 25.1 percent from 2008 to 2010 in the flight to dollar-denominated assets in fear of world financial risks. The dollar revalued 10.7 percent by Fri Jan 13, 2017. Dollar devaluation is a major vehicle of monetary policy in reducing the output gap that is implemented in the probably erroneous belief that devaluation will not accelerate inflation, misallocating resources toward less productive economic activities and disrupting financial markets. The last row of Table VI-1 shows CPI inflation in the US rising from 1.9 percent in 2003 to 4.1 percent in 2007 even as monetary policy increased the fed funds rate from 1 percent in Jun 2004 to 5.25 percent in Jun 2006.
Table VI-1, Volatility of Assets
| DJIA | 10/08/02-10/01/07 | 10/01/07-3/4/09 | 3/4/09- 4/6/10 | |
| ∆% | 87.8 | -51.2 | 60.3 | |
| NYSE Financial | 1/15/04- 6/13/07 | 6/13/07- 3/4/09 | 3/4/09- 4/16/07 | |
| ∆% | 42.3 | -75.9 | 121.1 | |
| Shanghai Composite | 6/10/05- 10/15/07 | 10/15/07- 10/30/08 | 10/30/08- 7/30/09 | |
| ∆% | 444.2 | -70.8 | 85.3 | |
| STOXX EUROPE 50 | 3/10/03- 7/25/07 | 7/25/07- 3/9/09 | 3/9/09- 4/21/10 | |
| ∆% | 93.5 | -57.9 | 64.3 | |
| UBS Com. | 1/23/02- 7/1/08 | 7/1/08- 2/23/09 | 2/23/09- 1/6/10 | |
| ∆% | 165.5 | -56.4 | 41.4 | |
| 10-Year Treasury | 6/10/03 | 6/12/07 | 12/31/08 | 4/5/10 |
| % | 3.112 | 5.297 | 2.247 | 3.986 |
| USD/EUR | 6/26/03 | 7/14/08 | 6/07/10 | 01/13/2017 |
| Rate | 1.1423 | 1.5914 | 1.192 | 1.0645 |
| CNY/USD | 01/03 | 07/21 | 7/15 | 01/13/ 2017 |
| Rate | 8.2798 | 8.2765 | 6.8211 | 6.8998 |
| New House | 1963 | 1977 | 2005 | 2009 |
| Sales 1000s | 560 | 819 | 1283 | 375 |
| New House | 2000 | 2007 | 2009 | 2010 |
| Median Price $1000 | 169 | 247 | 217 | 222 |
| 2003 | 2005 | 2007 | 2010 | |
| CPI | 2.3 | 3.4 | 2.8 | 1.6 |
Sources: http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_hps_marketdata
http://www.census.gov/const/www/newressalesindex_excel.html
http://federalreserve.gov/releases/h10/Hist/dat00_eu.htm
There are collateral effects of unconventional monetary policy. Chart VIII-1 of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System provides the rate on the overnight fed funds rate and the yields of the 10-year constant maturity Treasury and the Baa seasoned corporate bond. Table VIII-3 provides the data for selected points in Chart VIII-1. There are two important economic and financial events, illustrating the ease of inducing carry trade with extremely low interest rates and the resulting financial crash and recession of abandoning extremely low interest rates.
- The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) lowered the target of the fed funds rate from 7.03 percent on Jul 3, 2000, to 1.00 percent on Jun 22, 2004, in pursuit of non-existing deflation (Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), 18-28, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 83-85). Central bank commitment to maintain the fed funds rate at 1.00 percent induced adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMS) linked to the fed funds rate. Lowering the interest rate near the zero bound in 2003-2004 caused the illusion of permanent increases in wealth or net worth in the balance sheets of borrowers and also of lending institutions, securitized banking and every financial institution and investor in the world. The discipline of calculating risks and returns was seriously impaired. The objective of monetary policy was to encourage borrowing, consumption and investment. The exaggerated stimulus resulted in a financial crisis of major proportions as the securitization that had worked for a long period was shocked with policy-induced excessive risk, imprudent credit, high leverage and low liquidity by the incentive to finance everything overnight at interest rates close to zero, from adjustable rate mortgages (ARMS) to asset-backed commercial paper of structured investment vehicles (SIV). The consequences of inflating liquidity and net worth of borrowers were a global hunt for yields to protect own investments and money under management from the zero interest rates and unattractive long-term yields of Treasuries and other securities. Monetary policy distorted the calculations of risks and returns by households, business and government by providing central bank cheap money. Short-term zero interest rates encourage financing of everything with short-dated funds, explaining the SIVs created off-balance sheet to issue short-term commercial paper with the objective of purchasing default-prone mortgages that were financed in overnight or short-dated sale and repurchase agreements (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession, 50-1, Regulation of Banks and Finance, 59-60, Globalization and the State Vol. I, 89-92, Globalization and the State Vol. II, 198-9, Government Intervention in Globalization, 62-3, International Financial Architecture, 144-9). ARMS were created to lower monthly mortgage payments by benefitting from lower short-dated reference rates. Financial institutions economized in liquidity that was penalized with near zero interest rates. There was no perception of risk because the monetary authority guaranteed a minimum or floor price of all assets by maintaining low interest rates forever or equivalent to writing an illusory put option on wealth. Subprime mortgages were part of the put on wealth by an illusory put on house prices. The housing subsidy of $221 billion per year created the impression of ever-increasing house prices. The suspension of auctions of 30-year Treasuries was designed to increase demand for mortgage-backed securities, lowering their yield, which was equivalent to lowering the costs of housing finance and refinancing. Fannie and Freddie purchased or guaranteed $1.6 trillion of nonprime mortgages and worked with leverage of 75:1 under Congress-provided charters and lax oversight. The combination of these policies resulted in high risks because of the put option on wealth by near zero interest rates, excessive leverage because of cheap rates, low liquidity by the penalty in the form of low interest rates and unsound credit decisions. The put option on wealth by monetary policy created the illusion that nothing could ever go wrong, causing the credit/dollar crisis and global recession (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession, 157-66, Regulation of Banks, and Finance, 217-27, International Financial Architecture, 15-18, The Global Recession Risk, 221-5, Globalization and the State Vol. II, 197-213, Government Intervention in Globalization, 182-4). The FOMC implemented increments of 25 basis points of the fed funds target from Jun 2004 to Jun 2006, raising the fed funds rate to 5.25 percent on Jul 3, 2006, as shown in Chart VIII-1. The gradual exit from the first round of unconventional monetary policy from 1.00 percent in Jun 2004 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/boarddocs/press/monetary/2004/20040630/default.htm) to 5.25 percent in Jun 2006 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20060629a.htm) caused the financial crisis and global recession.
- On Dec 16, 2008, the policy determining committee of the Fed decided (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20081216b.htm): “The Federal Open Market Committee decided today to establish a target range for the federal funds rate of 0 to 1/4 percent.” Policymakers emphasize frequently that there are tools to exit unconventional monetary policy at the right time. At the confirmation hearing on nomination for Chair of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Vice Chair Yellen (2013Nov14 http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20131114a.htm), states that: “The Federal Reserve is using its monetary policy tools to promote a more robust recovery. A strong recovery will ultimately enable the Fed to reduce its monetary accommodation and reliance on unconventional policy tools such as asset purchases. I believe that supporting the recovery today is the surest path to returning to a more normal approach to monetary policy.” Perception of withdrawal of $2671 billion, or $2.7 trillion, of bank reserves (http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h41/current/h41.htm#h41tab1), would cause Himalayan increase in interest rates that would provoke another recession. There is no painless gradual or sudden exit from zero interest rates because reversal of exposures created on the commitment of zero interest rates forever.
In his classic restatement of the Keynesian demand function in terms of “liquidity preference as behavior toward risk,” James Tobin (http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/economic-sciences/laureates/1981/tobin-bio.html) identifies the risks of low interest rates in terms of portfolio allocation (Tobin 1958, 86):
“The assumption that investors expect on balance no change in the rate of interest has been adopted for the theoretical reasons explained in section 2.6 rather than for reasons of realism. Clearly investors do form expectations of changes in interest rates and differ from each other in their expectations. For the purposes of dynamic theory and of analysis of specific market situations, the theories of sections 2 and 3 are complementary rather than competitive. The formal apparatus of section 3 will serve just as well for a non-zero expected capital gain or loss as for a zero expected value of g. Stickiness of interest rate expectations would mean that the expected value of g is a function of the rate of interest r, going down when r goes down and rising when r goes up. In addition to the rotation of the opportunity locus due to a change in r itself, there would be a further rotation in the same direction due to the accompanying change in the expected capital gain or loss. At low interest rates expectation of capital loss may push the opportunity locus into the negative quadrant, so that the optimal position is clearly no consols, all cash. At the other extreme, expectation of capital gain at high interest rates would increase sharply the slope of the opportunity locus and the frequency of no cash, all consols positions, like that of Figure 3.3. The stickier the investor's expectations, the more sensitive his demand for cash will be to changes in the rate of interest (emphasis added).”
Tobin (1969) provides more elegant, complete analysis of portfolio allocation in a general equilibrium model. The major point is equally clear in a portfolio consisting of only cash balances and a perpetuity or consol. Let g be the capital gain, r the rate of interest on the consol and re the expected rate of interest. The rates are expressed as proportions. The price of the consol is the inverse of the interest rate, (1+re). Thus, g = [(r/re) – 1]. The critical analysis of Tobin is that at extremely low interest rates there is only expectation of interest rate increases, that is, dre>0, such that there is expectation of capital losses on the consol, dg<0. Investors move into positions combining only cash and no consols. Valuations of risk financial assets would collapse in reversal of long positions in carry trades with short exposures in a flight to cash. There is no exit from a central bank created liquidity trap without risks of financial crash and another global recession. The net worth of the economy depends on interest rates. In theory, “income is generally defined as the amount a consumer unit could consume (or believe that it could) while maintaining its wealth intact” (Friedman 1957, 10). Income, Y, is a flow that is obtained by applying a rate of return, r, to a stock of wealth, W, or Y = rW (Friedman 1957). According to a subsequent statement: “The basic idea is simply that individuals live for many years and that therefore the appropriate constraint for consumption is the long-run expected yield from wealth r*W. This yield was named permanent income: Y* = r*W” (Darby 1974, 229), where * denotes permanent. The simplified relation of income and wealth can be restated as:
W = Y/r (1)
Equation (1) shows that as r goes to zero, r→0, W grows without bound, W→∞. Unconventional monetary policy lowers interest rates to increase the present value of cash flows derived from projects of firms, creating the impression of long-term increase in net worth. An attempt to reverse unconventional monetary policy necessarily causes increases in interest rates, creating the opposite perception of declining net worth. As r→∞, W = Y/r →0. There is no exit from unconventional monetary policy without increasing interest rates with resulting pain of financial crisis and adverse effects on production, investment and employment.
Dan Strumpf and Pedro Nicolaci da Costa, writing on “Fed’s Yellen: Stock Valuations ‘Generally are Quite High,’” on May 6, 2015, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/feds-yellen-cites-progress-on-bank-regulation-1430918155?tesla=y ), quote Chair Yellen at open conversation with Christine Lagarde, Managing Director of the IMF, finding “equity-market valuations” as “quite high” with “potential dangers” in bond valuations. The DJIA fell 0.5 percent on May 6, 2015, after the comments and then increased 0.5 percent on May 7, 2015 and 1.5 percent on May 8, 2015.
| Fri May 1 | Mon 4 | Tue 5 | Wed 6 | Thu 7 | Fri 8 |
| DJIA 18024.06 -0.3% 1.0% | 18070.40 0.3% 0.3% | 17928.20 -0.5% -0.8% | 17841.98 -1.0% -0.5% | 17924.06 -0.6% 0.5% | 18191.11 0.9% 1.5% |
There are two approaches in theory considered by Bordo (2012Nov20) and Bordo and Lane (2013). The first approach is in the classical works of Milton Friedman and Anna Jacobson Schwartz (1963a, 1987) and Karl Brunner and Allan H. Meltzer (1973). There is a similar approach in Tobin (1969). Friedman and Schwartz (1963a, 66) trace the effects of expansionary monetary policy into increasing initially financial asset prices: “It seems plausible that both nonbank and bank holders of redundant balances will turn first to securities comparable to those they have sold, say, fixed-interest coupon, low-risk obligations. But as they seek to purchase these they will tend to bid up the prices of those issues. Hence they, and also other holders not involved in the initial central bank open-market transactions, will look farther afield: the banks, to their loans; the nonbank holders, to other categories of securities-higher risk fixed-coupon obligations, equities, real property, and so forth.”
The second approach is by the Austrian School arguing that increases in asset prices can become bubbles if monetary policy allows their financing with bank credit. Professor Michael D. Bordo provides clear thought and empirical evidence on the role of “expansionary monetary policy” in inflating asset prices (Bordo2012Nov20, Bordo and Lane 2013). Bordo and Lane (2013) provide revealing narrative of historical episodes of expansionary monetary policy. Bordo and Lane (2013) conclude that policies of depressing interest rates below the target rate or growth of money above the target influences higher asset prices, using a panel of 18 OECD countries from 1920 to 2011. Bordo (2012Nov20) concludes: “that expansionary money is a significant trigger” and “central banks should follow stable monetary policies…based on well understood and credible monetary rules.” Taylor (2007, 2009) explains the housing boom and financial crisis in terms of expansionary monetary policy. Professor Martin Feldstein (2016), at Harvard University, writing on “A Federal Reserve oblivious to its effects on financial markets,” on Jan 13, 2016, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/a-federal-reserve-oblivious-to-its-effect-on-financial-markets-1452729166), analyzes how unconventional monetary policy drove values of risk financial assets to high levels. Quantitative easing and zero interest rates distorted calculation of risks with resulting vulnerabilities in financial markets.
Another hurdle of exit from zero interest rates is “competitive easing” that Professor Raghuram Rajan, governor of the Reserve Bank of India, characterizes as disguised “competitive devaluation” (http://www.centralbanking.com/central-banking-journal/interview/2358995/raghuram-rajan-on-the-dangers-of-asset-prices-policy-spillovers-and-finance-in-india). The fed has been considering increasing interest rates. The European Central Bank (ECB) announced, on Mar 5, 2015, the beginning on Mar 9, 2015 of its quantitative easing program denominated as Public Sector Purchase Program (PSPP), consisting of “combined monthly purchases of EUR 60 bn [billion] in public and private sector securities” (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/mopo/liq/html/pspp.en.html). Expectation of increasing interest rates in the US together with euro rates close to zero or negative cause revaluation of the dollar (or devaluation of the euro and of most currencies worldwide). US corporations suffer currency translation losses of their foreign transactions and investments (http://www.fasb.org/jsp/FASB/Pronouncement_C/SummaryPage&cid=900000010318) while the US becomes less competitive in world trade (Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. I (2008a), Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c)). The DJIA fell 1.5 percent on Mar 6, 2015 and the dollar revalued 2.2 percent from Mar 5 to Mar 6, 2015. The euro has devalued 49.4 percent relative to the dollar from the high on Jul 15, 2008 to Jan 13, 2017.
| Fri 27 Feb | Mon 3/2 | Tue 3/3 | Wed 3/4 | Thu 3/5 | Fri 3/6 |
| USD/ EUR 1.1197 1.6% 0.0% | 1.1185 0.1% 0.1% | 1.1176 0.2% 0.1% | 1.1081 1.0% 0.9% | 1.1030 1.5% 0.5% | 1.0843 3.2% 1.7% |
Chair Yellen explained the removal of the word “patience” from the advanced guidance at the press conference following the FOMC meeting on Mar 18, 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20150318.pdf):
“In other words, just because we removed the word “patient” from the statement doesn’t mean we are going to be impatient. Moreover, even after the initial increase in the target funds rate, our policy is likely to remain highly accommodative to support continued progress toward our objectives of maximum employment and 2 percent inflation.”
Exchange rate volatility is increasing in response of “impatience” in financial markets with monetary policy guidance and measures:
| Fri Mar 6 | Mon 9 | Tue 10 | Wed 11 | Thu 12 | Fri 13 |
| USD/ EUR 1.0843 3.2% 1.7% | 1.0853 -0.1% -0.1% | 1.0700 1.3% 1.4% | 1.0548 2.7% 1.4% | 1.0637 1.9% -0.8% | 1.0497 3.2% 1.3% |
| Fri Mar 13 | Mon 16 | Tue 17 | Wed 18 | Thu 19 | Fri 20 |
| USD/ EUR 1.0497 3.2% 1.3% | 1.0570 -0.7% -0.7% | 1.0598 -1.0% -0.3% | 1.0864 -3.5% -2.5% | 1.0661 -1.6% 1.9% | 1.0821 -3.1% -1.5% |
| Fri Apr 24 | Mon 27 | Tue 28 | Wed 29 | Thu 30 | May Fri 1 |
| USD/ EUR 1.0874 -0.6% -0.4% | 1.0891 -0.2% -0.2% | 1.0983 -1.0% -0.8% | 1.1130 -2.4% -1.3% | 1.1223 -3.2% -0.8% | 1.1199 -3.0% 0.2% |
In a speech at Brown University on May 22, 2015, Chair Yellen stated (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20150522a.htm):
“For this reason, if the economy continues to improve as I expect, I think it will be appropriate at some point this year to take the initial step to raise the federal funds rate target and begin the process of normalizing monetary policy. To support taking this step, however, I will need to see continued improvement in labor market conditions, and I will need to be reasonably confident that inflation will move back to 2 percent over the medium term. After we begin raising the federal funds rate, I anticipate that the pace of normalization is likely to be gradual. The various headwinds that are still restraining the economy, as I said, will likely take some time to fully abate, and the pace of that improvement is highly uncertain.”
The US dollar appreciated 3.8 percent relative to the euro in the week of May 22, 2015:
| Fri May 15 | Mon 18 | Tue 19 | Wed 20 | Thu 21 | Fri 22 |
| USD/ EUR 1.1449 -2.2% -0.3% | 1.1317 1.2% 1.2% | 1.1150 2.6% 1.5% | 1.1096 3.1% 0.5% | 1.1113 2.9% -0.2% | 1.1015 3.8% 0.9% |
The Managing Director of the International Monetary Fund (IMF), Christine Lagarde, warned on Jun 4, 2015, that: (http://blog-imfdirect.imf.org/2015/06/04/u-s-economy-returning-to-growth-but-pockets-of-vulnerability/):
“The Fed’s first rate increase in almost 9 years is being carefully prepared and telegraphed. Nevertheless, regardless of the timing, higher US policy rates could still result in significant market volatility with financial stability consequences that go well beyond US borders. I weighing these risks, we think there is a case for waiting to raise rates until there are more tangible signs of wage or price inflation than are currently evident. Even after the first rate increase, a gradual rise in the federal fund rates will likely be appropriate.”
The President of the European Central Bank (ECB), Mario Draghi, warned on Jun 3, 2015 that (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pressconf/2015/html/is150603.en.html):
“But certainly one lesson is that we should get used to periods of higher volatility. At very low levels of interest rates, asset prices tend to show higher volatility…the Governing Council was unanimous in its assessment that we should look through these developments and maintain a steady monetary policy stance.”
The Chair of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Janet L. Yellen, stated on Jul 10, 2015 that (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20150710a.htm):
“Based on my outlook, I expect that it will be appropriate at some point later this year to take the first step to raise the federal funds rate and thus begin normalizing monetary policy. But I want to emphasize that the course of the economy and inflation remains highly uncertain, and unanticipated developments could delay or accelerate this first step. I currently anticipate that the appropriate pace of normalization will be gradual, and that monetary policy will need to be highly supportive of economic activity for quite some time. The projections of most of my FOMC colleagues indicate that they have similar expectations for the likely path of the federal funds rate. But, again, both the course of the economy and inflation are uncertain. If progress toward our employment and inflation goals is more rapid than expected, it may be appropriate to remove monetary policy accommodation more quickly. However, if progress toward our goals is slower than anticipated, then the Committee may move more slowly in normalizing policy.”
There is essentially the same view in the Testimony of Chair Yellen in delivering the Semiannual Monetary Policy Report to the Congress on Jul 15, 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20150715a.htm).
At the press conference after the meeting of the FOMC on Sep 17, 2015, Chair Yellen states (http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20150917.pdf 4):
“The outlook abroad appears to have become more uncertain of late, and heightened concerns about growth in China and other emerging market economies have led to notable volatility in financial markets. Developments since our July meeting, including the drop in equity prices, the further appreciation of the dollar, and a widening in risk spreads, have tightened overall financial conditions to some extent. These developments may restrain U.S. economic activity somewhat and are likely to put further downward pressure on inflation in the near term. Given the significant economic and financial interconnections between the United States and the rest of the world, the situation abroad bears close watching.”
Some equity markets fell on Fri Sep 18, 2015:
| Fri Sep 11 | Mon 14 | Tue 15 | Wed 16 | Thu 17 | Fri 18 |
| DJIA 16433.09 2.1% 0.6% | 16370.96 -0.4% -0.4% | 16599.85 1.0% 1.4% | 16739.95 1.9% 0.8% | 16674.74 1.5% -0.4% | 16384.58 -0.3% -1.7% |
| Nikkei 225 18264.22 2.7% -0.2% | 17965.70 -1.6% -1.6% | 18026.48 -1.3% 0.3% | 18171.60 -0.5% 0.8% | 18432.27 0.9% 1.4% | 18070.21 -1.1% -2.0% |
| DAX 10123.56 0.9% -0.9% | 10131.74 0.1% 0.1% | 10188.13 0.6% 0.6% | 10227.21 1.0% 0.4% | 10229.58 1.0% 0.0% | 9916.16 -2.0% -3.1% |
Frank H. Knight (1963, 233), in Risk, uncertainty and profit, distinguishes between measurable risk and unmeasurable uncertainty. Chair Yellen, in a lecture on “Inflation dynamics and monetary policy,” on Sep 24, 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20150924a.htm), states that (emphasis added):
· “The economic outlook, of course, is highly uncertain”
· “Considerable uncertainties also surround the outlook for economic activity”
· “Given the highly uncertain nature of the outlook…”
Is there a “science” or even “art” of central banking under this extreme uncertainty in which policy does not generate higher volatility of money, income, prices and values of financial assets?
Lingling Wei, writing on Oct 23, 2015, on China’s central bank moves to spur economic growth,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/chinas-central-bank-cuts-rates-1445601495), analyzes the reduction by the People’s Bank of China (http://www.pbc.gov.cn/ http://www.pbc.gov.cn/english/130437/index.html) of borrowing and lending rates of banks by 50 basis points and reserve requirements of banks by 50 basis points. Paul Vigna, writing on Oct 23, 2015, on “Stocks rally out of correction territory on latest central bank boost,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://blogs.wsj.com/moneybeat/2015/10/23/stocks-rally-out-of-correction-territory-on-latest-central-bank-boost/), analyzes the rally in financial markets following the statement on Oct 22, 2015, by the President of the European Central Bank (ECB) Mario Draghi of consideration of new quantitative measures in Dec 2015 (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0814riKW25k&rel=0) and the reduction of bank lending/deposit rates and reserve requirements of banks by the People’s Bank of China on Oct 23, 2015. The dollar revalued 2.8 percent from Oct 21 to Oct 23, 2015, following the intended easing of the European Central Bank. The DJIA rose 2.8 percent from Oct 21 to Oct 23 and the DAX index of German equities rose 5.4 percent from Oct 21 to Oct 23, 2015.
| Fri Oct 16 | Mon 19 | Tue 20 | Wed 21 | Thu 22 | Fri 23 |
| USD/ EUR 1.1350 0.1% 0.3% | 1.1327 0.2% 0.2% | 1.1348 0.0% -0.2% | 1.1340 0.1% 0.1% | 1.1110 2.1% 2.0% | 1.1018 2.9% 0.8% |
| DJIA 17215.97 0.8% 0.4% | 17230.54 0.1% 0.1% | 17217.11 0.0% -0.1% | 17168.61 -0.3% -0.3% | 17489.16 1.6% 1.9% | 17646.70 2.5% 0.9% |
| Dow Global 2421.58 0.3% 0.6% | 2414.33 -0.3% -0.3% | 2411.03 -0.4% -0.1% | 2411.27 -0.4% 0.0% | 2434.79 0.5% 1.0% | 2458.13 1.5% 1.0% |
| DJ Asia Pacific 1402.31 1.1% 0.3% | 1398.80 -0.3% -0.3% | 1395.06 -0.5% -0.3% | 1402.68 0.0% 0.5% | 1396.03 -0.4% -0.5% | 1415.50 0.9% 1.4% |
| Nikkei 225 18291.80 -0.8% 1.1% | 18131.23 -0.9% -0.9% | 18207.15 -0.5% 0.4% | 18554.28 1.4% 1.9% | 18435.87 0.8% -0.6% | 18825.30 2.9% 2.1% |
| Shanghai 3391.35 6.5% 1.6% | 3386.70 -0.1% -0.1% | 3425.33 1.0% 1.1% | 3320.68 -2.1% -3.1% | 3368.74 -0.7% 1.4% | 3412.43 0.6% 1.3% |
| DAX 10104.43 0.1% 0.4% | 10164.31 0.6% 0.6% | 10147.68 0.4% -0.2% | 10238.10 1.3% 0.9% | 10491.97 3.8% 2.5% | 10794.54 6.8% 2.9% |
Ben Leubsdorf, writing on “Fed’s Yellen: December is “Live Possibility” for First Rate Increase,” on Nov 4, 2015, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/feds-yellen-december-is-live-possibility-for-first-rate-increase-1446654282) quotes Chair Yellen that a rate increase in “December would be a live possibility.” The remark of Chair Yellen was during a hearing on supervision and regulation before the Committee on Financial Services, US House of Representatives (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20151104a.htm) and a day before the release of the employment situation report for Oct 2015 (Section I). The dollar revalued 2.4 percent during the week. The euro has devalued 49.4 percent relative to the dollar from the high on Jul 15, 2008 to Jan 13, 2016.
| Fri Oct 30 | Mon 2 | Tue 3 | Wed 4 | Thu 5 | Fri 6 |
| USD/ EUR 1.1007 0.1% -0.3% | 1.1016 -0.1% -0.1% | 1.0965 0.4% 0.5% | 1.0867 1.3% 0.9% | 1.0884 1.1% -0.2% | 1.0742 2.4% 1.3% |
The release on Nov 18, 2015 of the minutes of the FOMC (Federal Open Market Committee) meeting held on Oct 28, 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/fomcminutes20151028.htm) states:
“Most participants anticipated that, based on their assessment of the current economic situation and their outlook for economic activity, the labor market, and inflation, these conditions [for interest rate increase] could well be met by the time of the next meeting. Nonetheless, they emphasized that the actual decision would depend on the implications for the medium-term economic outlook of the data received over the upcoming intermeeting period… It was noted that beginning the normalization process relatively soon would make it more likely that the policy trajectory after liftoff could be shallow.”
Markets could have interpreted a symbolic increase in the fed funds rate at the meeting of the FOMC on Dec 15-16, 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/fomccalendars.htm) followed by “shallow” increases, explaining the sharp increase in stock market values and appreciation of the dollar after the release of the minutes on Nov 18, 2015:
| Fri Nov 13 | Mon 16 | Tue 17 | Wed 18 | Thu 19 | Fri 20 |
| USD/ EUR 1.0774 -0.3% 0.4% | 1.0686 0.8% 0.8% | 1.0644 1.2% 0.4% | 1.0660 1.1% -0.2% | 1.0735 0.4% -0.7% | 1.0647 1.2% 0.8% |
| DJIA 17245.24 -3.7% -1.2% | 17483.01 1.4% 1.4% | 17489.50 1.4% 0.0% | 17737.16 2.9% 1.4% | 17732.75 2.8% 0.0% | 17823.81 3.4% 0.5% |
| DAX 10708.40 -2.5% -0.7% | 10713.23 0.0% 0.0% | 10971.04 2.5% 2.4% | 10959.95 2.3% -0.1% | 11085.44 3.5% 1.1% | 11119.83 3.8% 0.3% |
In testimony before The Joint Economic Committee of Congress on Dec 3, 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20151203a.htm), Chair Yellen reiterated that the FOMC (Federal Open Market Committee) “anticipates that even after employment and inflation are near mandate-consistent levels, economic condition may, for some time, warrant keeping the target federal funds rate below the Committee views as normal in the longer run.” Todd Buell and Katy Burne, writing on “Draghi says ECB could step up stimulus efforts if necessary,” on Dec 4, 2015, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/draghi-says-ecb-could-step-up-stimulus-efforts-if-necessary-1449252934), analyze that the President of the European Central Bank (ECB), Mario Draghi, reassured financial markets that the ECB will increase stimulus if required to raise inflation the euro area to targets. The USD depreciated 3.1 percent on Thu Dec 3, 2015 after weaker than expected measures by the European Central Bank. DJIA fell 1.4 percent on Dec 3 and increased 2.1 percent on Dec 4. DAX fell 3.6 percent on Dec 3.
| Fri Nov 27 | Mon 30 | Tue 1 | Wed 2 | Thu 3 | Fri 4 |
| USD/ EUR 1.0594 0.5% 0.2% | 1.0565 0.3% 0.3% | 1.0634 -0.4% -0.7% | 1.0616 -0.2% 0.2% | 1.0941 -3.3% -3.1% | 1.0885 -2.7% 0.5% |
| DJIA 17798.49 -0.1% -0.1% | 17719.92 -0.4% -0.4% | 17888.35 0.5% 1.0% | 17729.68 -0.4% -0.9% | 17477.67 -1.8% -1.4% | 17847.63 0.3% 2.1% |
| DAX 11293.76 1.6% -0.2% | 11382.23 0.8% 0.8% | 11261.24 -0.3% -1.1% | 11190.02 -0.9% -0.6% | 10789.24 -4.5% -3.6% | 10752.10 -4.8% -0.3% |
At the press conference following the meeting of the FOMC on Dec 16, 2015, Chair Yellen states (http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20151216.pdf page 8):
“And we recognize that monetary policy operates with lags. We would like to be able to move in a prudent, and as we've emphasized, gradual manner. It's been a long time since the Federal Reserve has raised interest rates, and I think it's prudent to be able to watch what the impact is on financial conditions and spending in the economy and moving in a timely fashion enables us to do this.”
The implication of this statement is that the state of the art is not accurate in analyzing the effects of monetary policy on financial markets and economic activity. The US dollar appreciated and equities fluctuated:
| Fri Dec 11 | Mon 14 | Tue 15 | Wed 16 | Thu 17 | Fri 18 |
| USD/ EUR 1.0991 -1.0% -0.4% | 1.0993 0.0% 0.0% | 1.0932 0.5% 0.6% | 1.0913 0.7% 0.2% | 1.0827 1.5% 0.8% | 1.0868 1.1% -0.4% |
| DJIA 17265.21 -3.3% -1.8% | 17368.50 0.6% 0.6% | 17524.91 1.5% 0.9% | 17749.09 2.8% 1.3% | 17495.84 1.3% -1.4% | 17128.55 -0.8% -2.1% |
| DAX 10340.06 -3.8% -2.4% | 10139.34 -1.9% -1.9% | 10450.38 -1.1% 3.1% | 10469.26 1.2% 0.2% | 10738.12 3.8% 2.6% | 10608.19 2.6% -1.2% |
On January 29, 2016, the Policy Board of the Bank of Japan introduced a new policy to attain the “price stability target of 2 percent at the earliest possible time” (https://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2016/k160129a.pdf). The new framework consists of three dimensions: quantity, quality and interest rate. The interest rate dimension consists of rates paid to current accounts that financial institutions hold at the Bank of Japan of three tiers zero, positive and minus 0.1 percent. The quantitative dimension consists of increasing the monetary base at the annual rate of 80 trillion yen. The qualitative dimension consists of purchases by the Bank of Japan of Japanese government bonds (JGBs), exchange traded funds (ETFs) and Japan real estate investment trusts (J-REITS). The yen devalued sharply relative to the dollar and world equity markets soared after the new policy announced on Jan 29, 2016:
| Fri 22 | Mon 25 | Tue 26 | Wed 27 | Thu 28 | Fri 29 |
| JPY/ USD 118.77 -1.5% -0.9% | 118.30 0.4% 0.4% | 118.42 0.3% -0.1% | 118.68 0.1% -0.2% | 118.82 0.0% -0.1% | 121.13 -2.0% -1.9% |
| DJIA 16093.51 0.7% 1.3% | 15885.22 -1.3% -1.3% | 16167.23 0.5% 1.8% | 15944.46 -0.9% -1.4% | 16069.64 -0.1% 0.8% | 16466.30 2.3% 2.5% |
| Nikkei 16958.53 -1.1% 5.9% | 17110.91 0.9% 0.9% | 16708.90 -1.5% -2.3% | 17163.92 1.2% 2.7% | 17041.45 0.5% -0.7% | 17518.30 3.3% 2.8% |
| Shanghai 2916.56 0.5% 1.3 | 2938.51 0.8% 0.8% | 2749.79 -5.7% -6.4% | 2735.56 -6.2% -0.5% | 2655.66 -8.9% -2.9% | 2737.60 -6.1% 3.1% |
| DAX 9764.88 2.3% 2.0% | 9736.15 -0.3% -0.3% | 9822.75 0.6% 0.9% | 9880.82 1.2% 0.6% | 9639.59 -1.3% -2.4% | 9798.11 0.3% 1.6% |
In testimony on the Semiannual Monetary Policy Report to the Congress on Feb 10-11, 2016, Chair Yellen (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20160210a.htm) states: “U.S. real gross domestic product is estimated to have increased about 1-3/4 percent in 2015. Over the course of the year, subdued foreign growth and the appreciation of the dollar restrained net exports. In the fourth quarter of last year, growth in the gross domestic product is reported to have slowed more sharply, to an annual rate of just 3/4 percent; again, growth was held back by weak net exports as well as by a negative contribution from inventory investment.”
Jon Hilsenrath, writing on “Yellen Says Fed Should Be Prepared to Use Negative Rates if Needed,” on Feb 11, 2016, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/yellen-reiterates-concerns-about-risks-to-economy-in-senate-testimony-1455203865), analyzes the statement of Chair Yellen in Congress that the FOMC (Federal Open Market Committee) is considering negative interest rates on bank reserves. The Wall Street Journal provides yields of two and ten-year sovereign bonds with negative interest rates on shorter maturities where central banks pay negative interest rates on excess bank reserves:
| Sovereign Yields 2/12/16 | Japan | Germany | USA |
| 2 Year | -0.168 | -0.498 | 0.694 |
| 10 Year | 0.076 | 0.262 | 1.744 |
On Mar 10, 2016, the European Central Bank (ECB) announced (1) reduction of the refinancing rate by 5 basis points to 0.00 percent; decrease the marginal lending rate to 0.25 percent; reduction of the deposit facility rate to 0,40 percent; increase of the monthly purchase of assets to €80 billion; include nonbank corporate bonds in assets eligible for purchases; and new long-term refinancing operations (https://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pr/date/2016/html/pr160310.en.html). The President of the ECB, Mario Draghi, stated in the press conference (https://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pressconf/2016/html/is160310.en.html): “How low can we go? Let me say that rates will stay low, very low, for a long period of time, and well past the horizon of our purchases…We don’t anticipate that it will be necessary to reduce rates further. Of course, new facts can change the situation and the outlook.”
The dollar devalued relative to the euro and open stock markets traded lower after the announcement on Mar 10, 2016, but stocks rebounded on Mar 11:
| Fri 4 | Mon 7 | Tue 8 | Wed 9 | Thu10 | Fri 11 |
| USD/ EUR 1.1006 -0.7% -0.4% | 1.1012 -0.1% -0.1% | 1.1013 -0.1% 0.0% | 1.0999 0.1% 0.1% | 1.1182 -1.6% -1.7% | 1.1151 -1.3% 0.3% |
| DJIA 17006.77 2.2% 0.4% | 17073.95 0.4% 0.4% | 16964.10 -0.3% -0.6% | 17000.36 0.0% 0.2% | 16995.13 -0.1% 0.0% | 17213.31 1.2% 1.3% |
| DAX 9824.17 3.3% 0.7% | 9778.93 -0.5% 0.5% | 9692.82 -1.3% -0.9% | 9723.09 -1.0% 0.3% | 9498.15 -3.3% -2.3% | 9831.13 0.1% 3.5% |
At the press conference after the FOMC meeting on Sep 21, 2016, Chair Yellen states (http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20160921.pdf ): “However, the economic outlook is inherently uncertain.” In the address to the Jackson Hole symposium on Aug 26, 2016, Chair Yellen states: “I believe the case for an increase in in federal funds rate has strengthened in recent months…And, as ever, the economic outlook is uncertain, and so monetary policy is not on a preset course” (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20160826a.htm). In a speech at the World Affairs Council of Philadelphia, on Jun 6, 2016 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20160606a.htm), Chair Yellen finds that “there is considerable uncertainty about the economic outlook.” There are fifteen references to this uncertainty in the text of 18 pages double-spaced. In the Semiannual Monetary Policy Report to the Congress on Jun 21, 2016, Chair Yellen states (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20160621a.htm), “Of course, considerable uncertainty about the economic outlook remains.” Frank H. Knight (1963, 233), in Risk, uncertainty and profit, distinguishes between measurable risk and unmeasurable uncertainty. Is there a “science” or even “art” of central banking under this extreme uncertainty in which policy does not generate higher volatility of money, income, prices and values of financial assets?
Chart VIII-1, Fed Funds Rate and Yields of Ten-year Treasury Constant Maturity and Baa Seasoned Corporate Bond, Jan 2, 2001 to Oct 6, 2016
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/
Chart VIII-1A, Fed Funds Rate and Yields of Ten-year Treasury Constant Maturity, Jan 2, 2001 to Jan 12, 2016
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/
Table VIII-3, Selected Data Points in Chart VIII-1, % per Year
| Fed Funds Overnight Rate | 10-Year Treasury Constant Maturity | Seasoned Baa Corporate Bond | |
| 1/2/2001 | 6.67 | 4.92 | 7.91 |
| 10/1/2002 | 1.85 | 3.72 | 7.46 |
| 7/3/2003 | 0.96 | 3.67 | 6.39 |
| 6/22/2004 | 1.00 | 4.72 | 6.77 |
| 6/28/2006 | 5.06 | 5.25 | 6.94 |
| 9/17/2008 | 2.80 | 3.41 | 7.25 |
| 10/26/2008 | 0.09 | 2.16 | 8.00 |
| 10/31/2008 | 0.22 | 4.01 | 9.54 |
| 4/6/2009 | 0.14 | 2.95 | 8.63 |
| 4/5/2010 | 0.20 | 4.01 | 6.44 |
| 2/4/2011 | 0.17 | 3.68 | 6.25 |
| 7/25/2012 | 0.15 | 1.43 | 4.73 |
| 5/1/13 | 0.14 | 1.66 | 4.48 |
| 9/5/13 | 0.089 | 2.98 | 5.53 |
| 11/21/2013 | 0.09 | 2.79 | 5.44 |
| 11/26/13 | 0.09 | 2.74 | 5.34 (11/26/13) |
| 12/5/13 | 0.09 | 2.88 | 5.47 |
| 12/11/13 | 0.09 | 2.89 | 5.42 |
| 12/18/13 | 0.09 | 2.94 | 5.36 |
| 12/26/13 | 0.08 | 3.00 | 5.37 |
| 1/1/2014 | 0.08 | 3.00 | 5.34 |
| 1/8/2014 | 0.07 | 2.97 | 5.28 |
| 1/15/2014 | 0.07 | 2.86 | 5.18 |
| 1/22/2014 | 0.07 | 2.79 | 5.11 |
| 1/30/2014 | 0.07 | 2.72 | 5.08 |
| 2/6/2014 | 0.07 | 2.73 | 5.13 |
| 2/13/2014 | 0.06 | 2.73 | 5.12 |
| 2/20/14 | 0.07 | 2.76 | 5.15 |
| 2/27/14 | 0.07 | 2.65 | 5.01 |
| 3/6/14 | 0.08 | 2.74 | 5.11 |
| 3/13/14 | 0.08 | 2.66 | 5.05 |
| 3/20/14 | 0.08 | 2.79 | 5.13 |
| 3/27/14 | 0.08 | 2.69 | 4.95 |
| 4/3/14 | 0.08 | 2.80 | 5.04 |
| 4/10/14 | 0.08 | 2.65 | 4.89 |
| 4/17/14 | 0.09 | 2.73 | 4.89 |
| 4/24/14 | 0.10 | 2.70 | 4.84 |
| 5/1/14 | 0.09 | 2.63 | 4.77 |
| 5/8/14 | 0.08 | 2.61 | 4.79 |
| 5/15/14 | 0.09 | 2.50 | 4.72 |
| 5/22/14 | 0.09 | 2.56 | 4.81 |
| 5/29/14 | 0.09 | 2.45 | 4.69 |
| 6/05/14 | 0.09 | 2.59 | 4.83 |
| 6/12/14 | 0.09 | 2.58 | 4.79 |
| 6/19/14 | 0.10 | 2.64 | 4.83 |
| 6/26/14 | 0.10 | 2.53 | 4.71 |
| 7/2/14 | 0.10 | 2.64 | 4.84 |
| 7/10/14 | 0.09 | 2.55 | 4.75 |
| 7/17/14 | 0.09 | 2.47 | 4.69 |
| 7/24/14 | 0.09 | 2.52 | 4.72 |
| 7/31/14 | 0.08 | 2.58 | 4.75 |
| 8/7/14 | 0.09 | 2.43 | 4.71 |
| 8/14/14 | 0.09 | 2.40 | 4.69 |
| 8/21/14 | 0.09 | 2.41 | 4.69 |
| 8/28/14 | 0.09 | 2.34 | 4.57 |
| 9/04/14 | 0.09 | 2.45 | 4.70 |
| 9/11/14 | 0.09 | 2.54 | 4.79 |
| 9/18/14 | 0.09 | 2.63 | 4.91 |
| 9/25/14 | 0.09 | 2.52 | 4.79 |
| 10/02/14 | 0.09 | 2.44 | 4.76 |
| 10/09/14 | 0.08 | 2.34 | 4.68 |
| 10/16/14 | 0.09 | 2.17 | 4.64 |
| 10/23/14 | 0.09 | 2.29 | 4.71 |
| 11/13/14 | 0.09 | 2.35 | 4.82 |
| 11/20/14 | 0.10 | 2.34 | 4.86 |
| 11/26/14 | 0.10 | 2.24 | 4.73 |
| 12/04/14 | 0.12 | 2.25 | 4.78 |
| 12/11/14 | 0.12 | 2.19 | 4.72 |
| 12/18/14 | 0.13 | 2.22 | 4.78 |
| 12/23/14 | 0.13 | 2.26 | 4.79 |
| 12/30/14 | 0.06 | 2.20 | 4.69 |
| 1/8/15 | 0.12 | 2.03 | 4.57 |
| 1/15/15 | 0.12 | 1.77 | 4.42 |
| 1/22/15 | 0.12 | 1.90 | 4.49 |
| 1/29/15 | 0.11 | 1.77 | 4.35 |
| 2/05/15 | 0.12 | 1.83 | 4.43 |
| 2/12/15 | 0.12 | 1.99 | 4.53 |
| 2/19/15 | 0.12 | 2.11 | 4.64 |
| 2/26/15 | 0.11 | 2.03 | 4.47 |
| 3/5/215 | 0.11 | 2.11 | 4.58 |
| 3/12/15 | 0.11 | 2.10 | 4.56 |
| 3/19/15 | 0.12 | 1.98 | 4.48 |
| 3/26/15 | 0.11 | 2.01 | 4.56 |
| 4/03/15 | 0.12 | 1.92 | 4.47 |
| 4/9/15 | 0.12 | 1.97 | 4.50 |
| 4/16/15 | 0.13 | 1.90 | 4.45 |
| 4/23/15 | 0.13 | 1.96 | 4.50 |
| 5/1/15 | 0.08 | 2.05 | 4.65 |
| 5/7/15 | 0.13 | 2.18 | 4.82 |
| 5/14/15 | 0.13 | 2.23 | 4.97 |
| 5/21/15 | 0.12 | 2.19 | 4.94 |
| 5/28/15 | 0.12 | 2.13 | 4.88 |
| 6/04/15 | 0.13 | 2.31 | 5.03 |
| 6/11/15 | 0.13 | 2.39 | 5.10 |
| 6/18/15 | 0.14 | 2.35 | 5.17 |
| 6/25/15 | 0.13 | 2.40 | 5.20 |
| 7/1/15 | 0.13 | 2.43 | 5.26 |
| 7/9/15 | 0.13 | 2.32 | 5.20 |
| 7/16/15 | 0.14 | 2.36 | 5.24 |
| 7/23/15 | 0.13 | 2.28 | 5.13 |
| 7/30/15 | 0.14 | 2.28 | 5.16 |
| 8/06/15 | 0.14 | 2.23 | 5.15 |
| 8/20/15 | 0.15 | 2.09 | 5.13 |
| 8/27/15 | 0.14 | 2.18 | 5.33 |
| 9/03/15 | 0.14 | 2.18 | 5.35 |
| 9/10/15 | 0.14 | 2.23 | 5.35 |
| 9/17/15 | 0.14 | 2.21 | 5.39 |
| 9/25/15 | 0.14 | 2.13 | 5.29 |
| 10/01/15 | 0.13 | 2.05 | 5.36 |
| 10/08/15 | 0.13 | 2.12 | 5.40 |
| 10/15/15 | 0.13 | 2.04 | 5.33 |
| 10/22/15 | 0.12 | 2.04 | 5.30 |
| 10/29/15 | 0.12 | 2.19 | 5.40 |
| 11/05/15 | 0.12 | 2.26 | 5.44 |
| 11/12/15 | 0.12 | 2.32 | 5.51 |
| 11/19/15 | 0.12 | 2.24 | 5.44 |
| 11/25/15 | 0.12 | 2.23 | 5.44 |
| 12/03/15 | 0.13 | 2.33 | 5.51 |
| 12/10/15 | 0.14 | 2.24 | 5.43 |
| 12/17/15 | 0.37 | 2.24 | 5.45 |
| 12/23/15 | 0.36 | 2.27 | 5.53 |
| 12/30/15 | 0.35 | 2.31 | 5.54 |
| 1/07/2016 | 0.36 | 2.16 | 5.44 |
| 01/14/16 | 0.36 | 2.10 | 5.46 |
| 01/20/16 | 0.37 | 2.01 | 5.41 |
| 01/29/16 | 0.38 | 2.00 | 5.48 |
| 02/04/16 | 0.38 | 1.87 | 5.40 |
| 02/11/16 | 0.38 | 1.63 | 5.26 |
| 02/18/16 | 0.38 | 1.75 | 5.37 |
| 02/25/16 | 0.37 | 1.71 | 5.27 |
| 03/03/16 | 0.37 | 1.83 | 5.30 |
| 03/10/16 | 0.36 | 1.93 | 5.23 |
| 03/17/16 | 0.37 | 1.91 | 5.11 |
| 03/24/16 | 0.37 | 1.91 | 4.97 |
| 03/31/16 | 0.25 | 1.78 | 4.90 |
| 04/07/16 | 0.37 | 1.70 | 4.76 |
| 04/14/16 | 0.37 | 1.80 | 4.79 |
| 04/21/16 | 0.37 | 1.88 | 4.79 |
| 04/28/16 | 0.37 | 1.84 | 4.73 |
| 05/05/16 | 0.37 | 1.76 | 4.62 |
| 05/12/16 | 0.37 | 1.75 | 4.66 |
| 05/19/16 | 0.37 | 1.85 | 4.70 |
| 05/26/16 | 0.37 | 1.83 | 4.69 |
| 06/02/16 | 0.37 | 1.81 | 4.64 |
| 06/09/16 | 0.37 | 1.68 | 4.53 |
| 06/16/16 | 0.38 | 1.57 | 4.47 |
| 06/23/16 | 0.39 | 1.74 | 4.60 |
| 06/30/16 | 0.36 | 1.49 | 4.41 |
| 07/07/16 | 0.40 | 1.40 | 4.19 |
| 07/14/16 | 0.40 | 1.53 | 4.23 |
| 07/21/16 | 0.40 | 1.57 | 4.25 |
| 07/28/16 | 0.40 | 1.52 | 4.20 |
| 08/04/16 | 0.40 | 1.51 | 4.27 |
| 08/11/16 | 0.40 | 1.57 | 4.27 |
| 08/18/16 | 0.40 | 1.53 | 4.23 |
| 08/25/16 | 0.40 | 1.58 | 4.21 |
| 09/01/16 | 0.40 | 1.57 | 4.19 |
| 09/08/16 | 0.40 | 1.61 | 4.28 |
| 09/15/16 | 0.40 | 1.71 | 4.43 |
| 09/22/16 | 0.40 | 1.63 | 4.32 |
| 09/29/16 | 0.40 | 1.56 | 4.23 |
| 10/06/16 | 0.40 | 1.75 | 4.36 |
| 10/13/16 | 0.40 | 1.75 | NA* |
| 10/20/16 | 0.41 | 1.76 | NA* |
| 10/27/16 | 0.41 | 1.85 | NA* |
| 11/03/16 | 0.41 | 1.82 | NA* |
| 11/09/16 | 0.41 | 2.07 | NA* |
| 11/17/16 | 0.41 | 2.29 | NA* |
| 11/23/16 | 0.40 | 2.36 | NA* |
| 12/01/16 | 0.40 | 2.45 | NA* |
| 12/08/16 | 0.41 | 2.40 | NA* |
| 12/15/16 | 0.66 | 2.60 | NA* |
| 12/22/16 | 0.66 | 2.55 | NA* |
| 12/29/16 | 0.66 | 2.49 | NA* |
| 01/05/17 | 0.66 | 2.37 | NA* |
| 01/12/17 | 0.66 | 2.36 | NA* |
*Note: the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System discontinued the publication of the BAA bond yield.
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/
Chart VIII-2 of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System provides the rate of US dollars (USD) per euro (EUR), USD/EUR. The rate appreciated from USD 1.0860/EUR on Jan 6, 2016 to USD 1.0560/EUR on Jan 6, 2017 or 2.8 percent. The euro has devalued 49.4 percent relative to the dollar from the high on Jul 15, 2008 to Jan 13, 2017. US corporations with foreign transactions and net worth experience losses in their balance sheets in converting revenues from depreciated currencies to the dollar. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA fell at $127.9 billion in IVQ2015 with decrease of domestic industries at $149.8 billion, mostly because of decrease of nonfinancial business at $131.7 billion, and increase of profits from operations in the rest of the world at $22.0 billion. Receipts from the rest of the world fell at $19.9 billion. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased at $66.0 billion in IQ2016 with increase of domestic industries at $92.9 billion. Profits from operations from the rest of the world fell at $26.9 billion and payments to the rest of the world increased at $35.6 billion. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA decreased at $12.5 billion in IIQ2016. Profits from domestic industries fell at $50.5 billion and profits from nonfinancial business fell at $56.1 billion. Profits from the rest of the world increased at $38.0 billion. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased at $117.8 billion in IIIQ2016. Profits from domestic industries increased at $116.5 billion and profits from nonfinancial business increased at $66.4 billion. Profits from the rest of the world increased at $1.3 billion. Total corporate profits with IVA and CCA were $2138.8 billion in IIIQ2016 of which $1729.9 billion from domestic industries, or 80.9 percent of the total, and $408.9 billion, or 19.1 percent, from the rest of the world. Nonfinancial corporate profits of $1236.9 billion account for 57.8 percent of the total. Uncertainty originating in fiscal, regulatory and monetary policy causes wide swings in expectations and decisions by the private sector with adverse effects on investment, real economic activity and employment. There is increase in corporate profits from devaluing the dollar with unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates and decrease of corporate profits in revaluing the dollar with attempts at “normalization” or increases in interest rates. Conflicts arise while other central banks differ in their adjustment process. The current account deficit seasonally adjusted decreases from 2.7 percent of GDP in IIIQ2015 to 2.5 percent in IVQ2015. The current account deficit increases to 2.9 percent of GDP in IQ2016. The deficit decreases to 2.6 percent in IIQ2016 and decreases to 2.4 percent in IIIQ2016. The net international investment position increases from minus $7.2 trillion in IIIQ2015 to minus $7.3 trillion in IVQ2015, increasing at minus $7.6 trillion in IQ2016. The net international investment position increases to minus $8.0 trillion in IIQ2016 and decreases to minus $7.8 trillion in IIIQ2016. The BEA explains as follows (https://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/international/intinv/2016/pdf/intinv316.pdf):
“The U.S. net international investment position increased to −$7,781.1 billion (preliminary) at the end of the third quarter of 2016 from −$8,026.9 billion (revised) at the end of the second quarter, according to statistics released today by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA). The $245.8 billion increase in the net investment position reflected a $346.2 billion increase in U.S. assets and a $100.5 billion increase in U.S. liabilities. The net investment position increased 3.1 percent in the third quarter, compared with a decrease of 5.9 percent in the second quarter and an average quarterly decrease of 6.0 percent from the first quarter of 2011 through the first quarter of 2016.”
The BEA explains further (https://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/international/intinv/2016/pdf/intinv316.pdf): “U.S. assets increased $346.2 billion to $24,861.2 billion at the end of the third quarter, reflecting an increase in assets excluding financial derivatives that was partly offset by a decrease in financial derivatives. Assets excluding financial derivatives increased $794.9 billion to $22,086.1 billion, mostly reflecting increases in portfolio investment and direct investment assets due to increases in foreign equity prices. Financial derivatives decreased $448.7 billion to $2,775.1 billion, mostly in single-currency interest rate contracts and in foreign exchange contracts. U.S. liabilities increased $100.5 billion to $32,642.3 billion at the end of the third quarter, reflecting an increase in liabilities excluding financial derivatives that was partly offset by a decrease in financial derivatives. Liabilities excluding financial derivatives increased $546.3 billion to $29,922.5 billion, reflecting increases in portfolio investment and direct investment liabilities due to financial transactions and increases in U.S. equity prices. Financial derivatives decreased $445.8 billion to $2,719.9 billion, mostly in single-currency interest rate contracts and in foreign exchange contracts.”
Chart VIII-2, Exchange Rate of US Dollars (USD) per Euro (EUR), Jan 6, 2016 to Jan 6, 2017
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/H10/default.htm
Chart VIII-3 of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System provides the yield of the 10-year Treasury constant maturity note from 1.79 percent on Oct 12, 2016 to 2.36 percent on Jan 12, 2017. There is turbulence in financial markets originating in a combination of intentions of normalizing or increasing US policy fed funds rate, quantitative easing in Europe and Japan and increasing perception of financial/economic risks.
Chart VIII-3, Yield of Ten-year Constant Maturity Treasury, Oct 12, 2016 to Jan 12, 2017
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/H15/default.htm
Percentage changes of risk financial assets from the last day of the year relative to the last day of the earlier year are in Table I-1 from 2007 to 2016. Risk financial assets mostly increased in 2016. DJIA increased 13.4 percent and S&P increased 9.5 percent while the NYSE gained 10.4 percent. Dow Global increased 8.4 percent with Dow Asia Pacific increasing 2.4 percent. NIKKEI Average increased 0.4 percent while Shanghai Composite fell 12.3 percent. The US dollar appreciated 3.1 percent relative to the euro and the ten-year Treasury yield increased to 2.447 percent. There is mixed performance in 2015 with declines of 2.2 for DJIA, 0.7 percent for S&P 500, 6.0 percent for NYSE Financial, 6.6 percent for Dow Global and 2.5 percent for Dow Asia Pacific. There were increases of 9.1 percent for the Nikkei Average, 9.4 percent for Shanghai Composite and 9.6 percent for DAX of Germany. The US dollar appreciated 10.2 percent relative to the euro. Calendar year 2014 was satisfactory for most equity indexes but not as excellent as 2013. Shanghai Composite outperformed all equity indexes in Table I-1 in 2014 with increase of 52.9 percent after falling 6.7 percent in 2013. The second highest increase is 11.4 percent for the Standard and Poor’s 500 (S&P 500). DAX of Germany gained 2.7 percent. NYSE Financial increased 5.6 percent and Dow Global gained 0.6 percent. Dow Asia Pacific decreased 1.6 percent while the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) increased 7.5 percent. The USD appreciated 12.0 percent relative to the EUR. Equities also outperformed in calendar year 2012. DAX gained 29.1 percent and NYSE Financial 25.9 percent. Equities soared in 2013. The Nikkei Average increased 56.7 percent. DJIA gained 26.5 percent and S&P 500 29.6 percent. DAX of Germany increased 25.5 percent. The dollar depreciated 4.2 percent relative to the euro. DJ UBS Commodities index fell 9.6 percent. Equities enjoyed a good year in 2012. Nikkei Average gained 22.9 percent in 2012. S&P increased 13.4 percent and DJIA 7.3 percent. Shanghai Composite increased 3.2 percent. Dow Global increased 10.7 percent and Dow Asia Pacific 13.1 percent. DJ UBS Commodities fell 1.8 percent. The only gain for a major equity index in Table I-1 for 2011 is 5.5 percent for the DJIA. S&P 500 is better than other equity markets by remaining flat for 2011. With the exception of a drop of 8.4 percent of the European equity index STOXX 50, all declines of equity markets in 2011 are in excess of 10 percent. China’s Shanghai Composite lost 21.7 percent. The equity index of Germany DAX fell 14.7 percent. The DJ UBS Commodities Index dropped 13.4 percent. Robin Wigglesworth, writing on Dec 30, 2011, on “$6.3tn wiped off markets in 2011,” published in the Financial Times (http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/483069d8-32f3-11e1-8e0d-00144feabdc0.html#axzz1i2BE7OPa), provides an estimate of $6.3 trillion erased from equity markets globally in 2011. The Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) estimates US nominal GDP in 2011 at $15,517.9 billion (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). The loss in equity markets worldwide in 2011 of $6.3 trillion is equivalent to about 40.6 percent of US GDP or economic activity in 2011. Table I-1 also provides the exchange rate of number of US dollars (USD) required in buying a unit of euro (EUR), USD/EUR. The dollar appreciated 3.1 percent on the last day of trading in 2011 relative to the last day of trading in 2010, suggesting risk aversion. Depreciation of the dollar by 1.8 percent in 2012 and 4.2 percent in 2013 suggests more favorable environment of risk appetite for carry trades from zero interest rates into risk financial assets. The final row of Table I-1 provides the yield of the ten-year Treasury, decreasing to 2.172 percent in 2014 and 2.269 percent in 2015. The yield of the ten-year Treasury increased to 3.030 percent in 2013, which is the highest since 3.292 percent in 2010 and 3.844 percent in 2008. The yield at year-end 2007 was 4.077 percent.
Table I-1, Percentage Change of Year-end Values of Financial Assets Relative to Earlier Year-end Values 2007-2016 and Year-end Yield of 10-Year Treasury Note
| ∆% | 2015 | 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 |
| DJIA | -2.2 | 7.5 | 26.5 | 7.3 | 5.5 | 11.0 | 18.8 | -33.8 | 6.4 |
| S&P 500 | -0.7 | 11.4 | 29.6 | 13.4 | 0.0 | 12.8 | 23.5 | -38.5 | 3.5 |
| NYSE Fin | -6.0 | 5.6 | 24.2 | 25.9 | -18.1 | 5.0 | 22.7 | -53.6 | -13.1 |
| Dow Global | -6.6 | 0.6 | 24.5 | 10.7 | -13.6 | 5.2 | 30.0 | -45.4 | 30.5 |
| Dow Asia-Pacific | -2.5 | -1.6 | 10.2 | 13.1 | -17.6 | 16.0 | 36.4 | -44.2 | 14.0 |
| Nikkei Av | 9.1 | 7.1 | 56.7 | 22.9 | -17.3 | -3.0 | 19.0 | -42.1 | -11.1 |
| Shanghai | 9.4 | 52.9 | -6.7 | 3.2 | -21.7 | -14.3 | 80.0 | -65.4 | 96.7 |
| DAX | 9.6 | 2.7 | 25.5 | 29.1 | -14.7 | 16.1 | 23.8 | -40.4 | 22.3 |
| USD/ EUR* | 10.2 | 12.0 | -4.2 | -1.8 | 3.1 | 6.6 | -2.5 | 4.3 | -10.6 |
| DJ UBS** Com | NA | -9.6 | -1.1 | -13.4 | 16.7 | 18.7 | -36.6 | 11.2 | |
| Year-end Yield 10-Year Treasury % | 2.269 | 2.172 | 3.030 | 1.758 | 2.027 | 3.292 | 3.844 | 2.157 | 4.077 |
| ∆% | 2016 |
| DJIA | 13.4 |
| S&P 500 | 9.5 |
| NYSE Financial | 10.4 |
| Dow Global | 8.4 |
| Dow Asia Pacific | 2.4 |
| Nikkei Average | 0.4 |
| Shanghai Composite | -12.3 |
| DAX | 6.9 |
| USD/EUR* | 3.1 |
| DJ UBS Commodities** | NA |
| Year-end Yield 10 Year Treasury | 2.447 |
*Negative sign is dollar devaluation; positive sign is dollar appreciation
**DJ UBS available only for 2013 and earlier years
Sources: http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_PRO_hps_marketdata
The other yearly percentage changes in Table I-2 are also revealing wide fluctuations in valuations of risk financial assets. To be sure, economic conditions and perceptions of the future do influence valuations of risk financial assets. It is also valid to contend that unconventional monetary policy magnifies fluctuations in these valuations by inducing carry trades from zero interest rates to exposures with high leverage in risk financial assets such as equities, emerging equities, currencies, high-yield structured products and commodities futures and options. In fact, one of the alleged channels of transmission of unconventional monetary policy is through higher consumption induced by increases in wealth resulting from higher valuations of stock markets. Bernanke (2010WP) and Yellen (2011AS) reveal the emphasis of monetary policy on the impact of the rise of stock market valuations in stimulating consumption by wealth effects on household confidence. Unconventional monetary policy could also result in magnification of values of risk financial assets beyond actual discounted future cash flows, creating financial instability. Separating all these effects in practice may be quite difficult because they are observed simultaneously. Conclusive evidence would require contrasting what actually happened with the counterfactual of what would have happened in the absence of unconventional monetary policy and other effects (on counterfactuals see Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State Vol I (2008a), 125, 136, Harberger (1971, 1997), Fishlow 1965, Fogel 1964, Fogel and Engerman 1974, North and Weingast 1989, Coastworth 1981, 2006, Summerhill 1997, 1998, 2003,Pelaez 1979, 26-7). There is no certainty or evidence that unconventional policies attain their intended effects without risks of costly side effects. Yearly fluctuations of financial assets in Table I-1 are quite wide. In 2007, for example, the equity index Dow Global increased 30.5 percent while DAX gained 22.3 percent and the Shanghai Composite jumped 96.7 percent. The DJIA gained only 6.4 percent as recession began in IVQ2007. The flight to government obligations in 2008 (Cochrane and Zingales 2009, Cochrane 2011Jan) was equivalent to the astronomical declines of world equity markets and commodities. The flight from risk is also in evidence in the appreciation of the dollar by 4.3 percent in 2008 with unwinding carry trades and with renewed carry trades in the depreciation of the dollar by 2.5 percent in 2009. Recovery still continued in 2010 with shocks of the European debt crisis in the spring and in Nov 2010. The flight from risk exposures dominated declines of valuations of risk financial assets in 2011.
Table I-2 is designed to provide a comparison of valuations of risk financial assets at the end of 2015 relative to valuations at the end of every year from 2007 to 2016. There were increases in major indexes in 2016: 13.4 percent for DJIA, 9.5 percent for S&P 500, 10.4 percent for NYSE Financial, 8.4 percent for Dow Global and 2.4 percent for Dow Asia Pacific. There are increases in major indexes: 0.4 percent for Nikkei and 6.9 percent for DAX of Germany. Shanghai Composite fell 12.3 percent. The DJIA index is 10.9 percent higher at the end of 2016 relative to the valuation at the end of 2014, 49.0 percent above the valuation at the end of 2007 and 58.6 percent higher relative to the valuation at the end of 2006. DJIA is higher by 125.2 percent at the end of 2016 relative to the depressed valuation at the end of 2008. Several indexes are still lower at the end of 2016 relative to the values at the end of 2007 with exception of gains of 49.0 for DJIA, 52.5 percent for S&P 500, 24.9 percent for Nikkei Average and 42.3 percent for DAX. Some equity indexes are higher at the end of 2016 relative to the end of 2006: DJIA by 58.6 percent, S&P by 57.9 percent, Dow Global by 18.3 percent, Nikkei Average by 11.0 percent, Shanghai Composite by 16.0 percent and DAX by 74.0 percent. The USD is 27.9 stronger at the end of 2016 relative to 2007 and 20.3 percent stronger relative to 2006. Zero interest rates do not devalue the dollar during prolonged bouts of relative risk aversion and portfolio reallocations. Low valuations of risk financial assets are intimately related to risk aversion in international financial markets because of the European debt crisis, weakness and unemployment in advanced economies, fiscal imbalances and slowing growth worldwide. Valuations of stock indexes for the US and Germany are peaking at the turn of 2014 into 2015 relative to 2007 and 2006 with recent sharp declines into 2016.
Table I-2, Percentage Change of Year-end 2015 Values of Financial Assets Relative to Year-end Values 2006-2014
| ∆% 16/ 14 | ∆% 16/ 13 | ∆% 16/ 12 | ∆% 16/ 11 | ∆% 16/ 10 | ∆% 16/ 09 | ∆% 16/ 08 | ∆% 16/ 07 | |
| DJIA | 10.9 | 19.2 | 50.8 | 61.8 | 70.7 | 89.5 | 125.2 | 49.0 |
| S&P 500 | 8.7 | 21.1 | 57.0 | 78.0 | 78.0 | 100.8 | 147.9 | 52.5 |
| NYSE Fin | 3.8 | 9.6 | 36.1 | 71.3 | 40.4 | 47.5 | 80.9 | -16.1 |
| Dow Global | 1.2 | 1.8 | 26.8 | 40.4 | 21.3 | 27.6 | 65.9 | -9.4 |
| Dow Asia-Pacific | -0.2 | -1.8 | 8.3 | 22.4 | 0.9 | 17.0 | 59.6 | -11.0 |
| Nikkei Av | 9.5 | 17.3 | 83.9 | 126.1 | 86.9 | 81.2 | 115.7 | 24.9 |
| Shanghai | -4.1 | 46.7 | 36.8 | 41.1 | 10.5 | -5.3 | 70.5 | -41.0 |
| DAX | 17.1 | 20.2 | 50.8 | 94.6 | 66.1 | 92.7 | 138.7 | 42.3 |
| USD/EUR* | 13.1 | 23.5 | 20.3 | 18.8 | 21.3 | 26.5 | 24.7 | 27.9 |
| DJ UBS** Com | NA | -9.6 | -10.6 | -22.6 | -9.7 | 7.3 | -32.0 | -24.4 |
| ∆% 16/15 | |
| DJIA | 13.4 |
| S&P 500 | 9.5 |
| NYSE Fin | 10.4 |
| Dow Global | 8.4 |
| Dow Asia Pacific | 2.4 |
| Nikkei Average | 0.4 |
| Shanghai Composite | -12.3 |
| DAX | 6.9 |
| USD/EUR* | 3.1 |
| DJ UBS Commodities** | NA |
*Negative sign is dollar devaluation; positive sign is dollar appreciation
**DJ UBS available only for 2013 and earlier years; percentage change is to 2013.
Sources: http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_PRO_hps_marketdata
The carry trade from zero interest rates to leveraged positions in risk financial assets had proved strongest for commodity exposures but US equities have regained leadership. The DJIA has increased 105.3 percent since the trough of the sovereign debt crisis in Europe on Jul 16, 2010 to Jan 13, 2017; S&P 500 has gained 122.4 percent and DAX 105.1 percent. Before the current round of risk aversion, almost all assets in the column “∆% Trough to 1/13/17” in Table VI-4 had double digit gains relative to the trough around Jul 2, 2010 followed by negative performance but now some valuations of equity indexes show varying behavior. China’s Shanghai Composite is 30.6 percent above the trough. Japan’s Nikkei Average is 118.6 percent above the trough. DJ Asia Pacific TSM is 28.9 percent above the trough. Dow Global is 52.6 percent above the trough. STOXX 50 of 50 blue-chip European equities (http://www.stoxx.com/indices/index_information.html?symbol=sx5E) is 32.7 percent above the trough. NYSE Financial Index is 66.7 percent above the trough. DAX index of German equities (http://www.bloomberg.com/quote/DAX:IND) is 105.1 percent above the trough. Japan’s Nikkei Average is 118.6 percent above the trough on Aug 31, 2010 and 69.3 percent above the peak on Apr 5, 2010. The Nikkei Average closed at 19,287.28 on Jan 13, 2017 (http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_PRO_hps_marketdata), which is 88.1 percent higher than 10,254.43 on Mar 11, 2011, on the date of the Tōhoku or Great East Japan Earthquake/tsunami. Global risk aversion erased the earlier gains of the Nikkei. The dollar appreciated 10.7 percent relative to the euro. The dollar devalued before the new bout of sovereign risk issues in Europe. The column “∆% week to 1/13/17” in Table VI-4 shows
decrease of 1.3 percent in the week for China’s Shanghai Composite. The Nikkei decreased 0.9 percent. DJ Asia Pacific increased 1.3 percent. NYSE Financial decreased 0.2 percent in the week. Dow Global increased 0.6 percent in the week of Jan 13, 2017. The DJIA decreased 0.4 percent and S&P 500 decreased 0.1 percent. DAX of Germany increased 0.3 percent. STOXX 50 decreased 0.1 percent. The USD depreciated 1.1 percent. There are still high uncertainties on European sovereign risks and banking soundness, US and world growth slowdown and China’s growth tradeoffs. Sovereign problems in the “periphery” of Europe and fears of slower growth in Asia and the US cause risk aversion with trading caution instead of more aggressive risk exposures. There is a fundamental change in Table VI-4 from the relatively upward trend with oscillations since the sovereign risk event of Apr-Jul 2010. Performance is best assessed in the column “∆% Peak to 1/13/17” that provides the percentage change from the peak in Apr 2010 before the sovereign risk event to Jan 13, 2017. Most risk financial assets had gained not only relative to the trough as shown in column “∆% Trough to 1/13/17” but also relative to the peak in column “∆% Peak to 1/13/17.” There are now several equity indexes above the peak in Table VI-4: DJIA 77.5 percent, S&P 500 86.9 percent, DAX 83.7 percent, Dow Global 24.5 percent, NYSE Financial Index (http://www.nyse.com/about/listed/nykid.shtml) 32.8 percent, Nikkei Average 69.3 percent, STOXX 50 12.4 percent. Shanghai Composite is 1.6 percent below the peak and DJ Asia Pacific TSM is 12.8 percent above the peak. The Shanghai Composite increased 57.7 percent from March 12, 2014, to Jan 13, 2017. The US dollar strengthened 29.6 percent relative to the peak. The factors of risk aversion have adversely affected the performance of risk financial assets. The performance relative to the peak in Apr 2010 is more important than the performance relative to the trough around early Jul 2010 because improvement could signal that conditions have returned to normal levels before European sovereign doubts in Apr 2010. Sharp and continuing strengthening of the dollar is affecting balance sheets of US corporations with foreign operations (http://www.fasb.org/jsp/FASB/Pronouncement_C/SummaryPage&cid=900000010318). The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) is following “financial and international developments” as part of the process of framing interest rate policy (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20150128a.htm). Kate Linebaugh, writing on “Corporate profits set to shrink for fourth consecutive quarter,” on Jul 17, 2016, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/corporate-profits-set-to-shrink-for-fourth-consecutive-quarter-1468799278), quotes forecasts of Thomson Reuters of 4.7 decline of adjusted earnings per share in the S&P 500 index in IIQ2016 relative to a year earlier. That would be the fourth consecutive quarterly decline. Theo Francis and Kate Linebaugh, writing on “US corporate profits on pace for third straight decline,” on Apr 28, 2016, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/u-s-corporate-profits-on-pace-for-third-straight-decline-1461872242), analyze three consecutive quarters of decline of corporate earnings and revenue in companies in S&P 500. They quote Thomson Reuters on expected decline of earnings of 6.1 percent in IQ2016 based on 55 percent of reporting companies. Weakness of economic activity shows in decline of revenues in IQ2016 of 1.4 percent, increasing 1.7 percent excluding energy, and contraction of profits of 0.5 percent. Justin Lahart, writing on “S&P 500 Earnings: far worse than advertised,” on Feb 24, 2016, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/s-p-500-earnings-far-worse-than-advertised-1456344483), analyzes S&P 500 earnings in 2015. Under data provided by companies, earnings increased 0.4 percent in 2015 relative to 2014 but under GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles), earnings fell 12.7 percent, which is the worst decrease since 2008. Theo Francis e Kate Linebaugh, writing on Oct 25, 2015, on “US Companies Warn of Slowing Economy, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/u-s-companies-warn-of-slowing-economy-1445818298) analyze the first contraction of earnings and revenue of big US companies. Production, sales and employment are slowing in a large variety of companies with some contracting. Corporate profits also suffer from revaluation of the dollar that constrains translation of foreign profits into dollar balance sheets. Francis and Linebaugh quote Thomson Reuters that analysts expect decline of earnings per share of 2.8 percent in IIIQ2015 relative to IIIQ2014 based on reports by one third of companies in the S&P 500. Sales would decline 4.0% in a third quarter for the first joint decline of earnings per share and revenue in the same quarter since IIIQ2009. Dollar revaluation also constrains corporate results.
Inyoung Hwang, writing on “Fed optimism spurs record bets against stock volatility,” on Aug 21, 2014, published in Bloomberg.com (http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2014-08-21/fed-optimism-spurs-record-bets-against-stock-voalitlity.html), informs that the S&P 500 is trading at 16.6 times estimated earnings, which is higher than the five-year average of 14.3 Tom Lauricella, writing on Mar 31, 2014, on “Stock investors see hints of a stronger quarter,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702304157204579473513864900656?mod=WSJ_smq0314_LeadStory&mg=reno64-wsj), finds views of stronger earnings among many money managers with positive factors for equity markets in continuing low interest rates and US economic growth. There is important information in the Quarterly Markets review of the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/public/page/quarterly-markets-review-03312014.html) for IQ2014. Alexandra Scaggs, writing on “Tepid profits, roaring stocks,” on May 16, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887323398204578487460105747412.html), analyzes stabilization of earnings growth: 70 percent of 458 reporting companies in the S&P 500 stock index reported earnings above forecasts but sales fell 0.2 percent relative to forecasts of increase of 0.5 percent. Paul Vigna, writing on “Earnings are a margin story but for how long,” on May 17, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://blogs.wsj.com/moneybeat/2013/05/17/earnings-are-a-margin-story-but-for-how-long/), analyzes that corporate profits increase with stagnating sales while companies manage costs tightly. More than 90 percent of S&P components reported moderate increase of earnings of 3.7 percent in IQ2013 relative to IQ2012 with decline of sales of 0.2 percent. Earnings and sales have been in declining trend. In IVQ2009, growth of earnings reached 104 percent and sales jumped 13 percent. Net margins reached 8.92 percent in IQ2013, which is almost the same at 8.95 percent in IIIQ2006. Operating margins are 9.58 percent. There is concern by market participants that reversion of margins to the mean could exert pressure on earnings unless there is more accelerated growth of sales. Vigna (op. cit.) finds sales growth limited by weak economic growth. Kate Linebaugh, writing on “Falling revenue dings stocks,” on Oct 20, 2012, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10000872396390444592704578066933466076070.html?mod=WSJPRO_hpp_LEFTTopStories), identifies a key financial vulnerability: falling revenues across markets for United States reporting companies. Global economic slowdown is reducing corporate sales and squeezing corporate strategies. Linebaugh quotes data from Thomson Reuters that 100 companies of the S&P 500 index have reported declining revenue only 1 percent higher in Jun-Sep 2012 relative to Jun-Sep 2011 but about 60 percent of the companies are reporting lower sales than expected by analysts with expectation that revenue for the S&P 500 will be lower in Jun-Sep 2012 for the entities represented in the index. Results of US companies are likely repeated worldwide. Future company cash flows derive from investment projects. Future company cash flows derive from investment projects. In IQ1980, real gross private domestic investment in the US was $951.6 billion of chained 2009 dollars, growing to $1,270.0 billion in IQ1990 or 33.5 percent. Real gross private domestic investment in the US increased 7.7 percent from $2605.2 billion in IVQ2007 to $2,804.7 billion in IIIQ2016. As shown in Table IAI-2, real private fixed investment increased 7.5 percent from $2,586.3 billion of chained 2009 dollars in IVQ2007 to $2,779.3 billion in IIIQ2016. Private fixed investment fell relative to IVQ2007 in all quarters preceding IQ2014 and changed 0.0 percent in IIIQ2016, declining 0.3 percent in IIQ2016 and falling 0.2 percent in IQ2016. Growth of real private investment in Table IA1-2 is mediocre for all but four quarters from IIQ2011 to IQ2012. The investment decision of United States corporations is fractured in the current economic cycle in preference of cash. There are three aspects. First, there is fluctuation in corporate profits. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA decreased at $127.9 billion in IVQ2015 and increased at $66.0 billion in IQ2016. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA fell at $12.5 billion in IIQ2016 and increased at $117.8 billion in IIIQ2016. Profits after tax with IVA and CCA fell at $172.7 billion in IVQ2015 and increased at $113.4 billion in IQ2016. Profits after tax with IVA and CCA fell at $28.9 billion in IIQ2016 and increased at $98.3 billion in IIIQ2016. Net dividends fell at $20.8 billion in IVQ2015 and increased at $7.3 billion in IQ2016. Net dividends fell at $9.3 billion in IIQ2016. Net dividends increased at $18.5 billion in IIIQ2016. Undistributed corporate profits with IVA and CCA fell at $152.0 billion in IVQ2015. Undistributed profits with IVA and CCA increased at $106.1 billion in IQ2016. Undistributed corporate profits fell at $19.6 billion in IIQ2016. Undistributed corporate profits increased at $79.8 billion in IIIQ2016. Undistributed corporate profits swelled 238.8 percent from $107.7 billion in IQ2007 to $364.9 billion in IIIQ2016 and changed signs from minus $55.9 billion in current dollars in IVQ2007. Uncertainty originating in fiscal, regulatory and monetary policy causes wide swings in expectations and decisions by the private sector with adverse effects on investment, real economic activity and employment. Second, sharp and continuing strengthening of the dollar is affecting balance sheets of US corporations with foreign operations (http://www.fasb.org/jsp/FASB/Pronouncement_C/SummaryPage&cid=900000010318) and the overall US economy. The bottom part of Table IA1-9 provides the breakdown of corporate profits with IVA and CCA in domestic industries and the rest of the world. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA fell at $127.9 billion in IVQ2015 with decrease of domestic industries at $149.8 billion, mostly because of decrease of nonfinancial business at $131.7 billion, and increase of profits from operations in the rest of the world at $22.0 billion. Receipts from the rest of the world fell at $19.9 billion. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased at $66.0 billion in IQ2016 with increase of domestic industries at $92.9 billion. Profits from operations from the rest of the world fell at $26.9 billion and payments to the rest of the world increased at $35.6 billion. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA decreased at $12.5 billion in IIQ2016. Profits from domestic industries fell at $50.5 billion and profits from nonfinancial business fell at $56.1 billion. Profits from the rest of the world increased at $38.0 billion. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased at $117.8 billion in IIIQ2016. Profits from domestic industries increased at $116.5 billion and profits from nonfinancial business increased at $66.4 billion. Profits from the rest of the world increased at $1.3 billion. Total corporate profits with IVA and CCA were $2138.8 billion in IIIQ2016 of which $1729.9 billion from domestic industries, or 80.9 percent of the total, and $408.9 billion, or 19.1 percent, from the rest of the world. Nonfinancial corporate profits of $1236.9 billion account for 57.8 percent of the total. Third, there is reduction in the use of corporate cash for investment. Vipal Monga, David Benoit and Theo Francis, writing on “Companies send more cash back to shareholders,” published on May 26, 2015 in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/companies-send-more-cash-back-to-shareholders-1432693805?tesla=y), use data of a study by Capital IQ conducted for the Wall Street Journal. This study shows that companies in the S&P 500 reduced investment in plant and equipment to median 29 percent of operating cash flow in 2013 from 33 percent in 2003 while increasing dividends and buybacks to median 36 percent in 2013 from 18 percent in 2003.
The basic valuation equation that is also used in capital budgeting postulates that the value of stocks or of an investment project is given by:
Where Rτ is expected revenue in the time horizon from τ =1 to T; Cτ denotes costs; and ρ is an appropriate rate of discount. In words, the value today of a stock or investment project is the net revenue, or revenue less costs, in the investment period from τ =1 to T discounted to the present by an appropriate rate of discount. In the current weak economy, revenues have been increasing more slowly than anticipated in investment plans. An increase in interest rates would affect discount rates used in calculations of present value, resulting in frustration of investment decisions. If V represents value of the stock or investment project, as ρ → ∞, meaning that interest rates increase without bound, then V → 0, or
declines. Equally, decline in expected revenue from the stock or project, Rτ, causes decline in valuation.
An intriguing issue is the difference in performance of valuations of risk financial assets and economic growth and employment. Paul A. Samuelson (http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/economics/laureates/1970/samuelson-bio.html) popularized the view of the elusive relation between stock markets and economic activity in an often-quoted phrase “the stock market has predicted nine of the last five recessions.” In the presence of zero interest rates forever, valuations of risk financial assets are likely to differ from the performance of the overall economy. The interrelations of financial and economic variables prove difficult to analyze and measure.
Table VI-4, Stock Indexes, Commodities, Dollar and 10-Year Treasury
| Peak | Trough | ∆% to Trough | ∆% Peak to 01/13/ /17 | ∆% Week 01/13/17 | ∆% Trough to 01/13/ 17 | |
| DJIA | 4/26/ | 7/2/10 | -13.6 | 77.5 | -0.4 | 105.3 |
| S&P 500 | 4/23/ | 7/20/ | -16.0 | 86.9 | -0.1 | 122.4 |
| NYSE Finance | 4/15/ | 7/2/10 | -20.3 | 32.8 | -0.2 | 66.7 |
| Dow Global | 4/15/ | 7/2/10 | -18.4 | 24.5 | 0.6 | 52.6 |
| Asia Pacific | 4/15/ | 7/2/10 | -12.5 | 12.8 | 1.3 | 28.9 |
| Japan Nikkei Aver. | 4/05/ | 8/31/ | -22.5 | 69.3 | -0.9 | 118.6 |
| China Shang. | 4/15/ | 7/02 | -24.7 | -1.6 | -1.3 | 30.6 |
| STOXX 50 | 4/15/10 | 7/2/10 | -15.3 | 12.4 | -0.1 | 32.7 |
| DAX | 4/26/ | 5/25/ | -10.5 | 83.7 | 0.3 | 105.1 |
| Dollar | 11/25 2009 | 6/7 | 21.2 | 29.6 | -1.1 | 10.7 |
| DJ UBS Comm. | 1/6/ | 7/2/10 | -14.5 | NA | NA | NA |
| 10-Year T Note | 4/5/ | 4/6/10 | 3.986 | 2.784 | 2.381 |
T: trough; Dollar: positive sign appreciation relative to euro (less dollars paid per euro), negative sign depreciation relative to euro (more dollars paid per euro)
Source: http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_hps_marketdata
Appendix on the Monetary History of Brazil. According to an influential school of thought, the interrelation of growth and inflation in Latin America is complex, preventing analysis of whether inflation promotes or restricts economic growth (Seers 1962, 191). In this view, there are multiple structural factors of inflation. Successful economic policy requires a development program that ameliorates structural weaknesses. Policy measures in developed countries are not transferable to developing economies.
In extensive research and analysis, Kahil (1973) finds no evidence of the role of structural factors in Brazilian inflation from 1947 to 1963. In fact, Kahil (1973, 329) concludes:
“The immediate causes of the persistent and often violent rise in prices, with which Brazil was plagued from the last month of 1948 to the early months of 1964, are pretty obvious: large and generally growing public deficits, together with too rapid an expansion of bank credit in the first years and, later, exaggerated and more and more frequent increases in the legal minimum wages.”
Kahil (1973, 334) analyzes the impact of inflation on the economy and society of Brazil:
“The real incomes of the various social classes alternately suffered increasingly frequent and sharp fluctuations: no sooner had a group succeeded in its struggle to restore its real income to some previous peak than it witnessed its erosion with accelerated speed; and it soon became apparent to all that the success of any important group in raising its real income, through government actions or by other means, was achieved only by reducing theirs. Social harmony, the general climate of euphoria, and also enthusiasm for government policies, which had tended to prevail until the last months of 1958, gave way in the following years of galloping inflation to intense political and social conflict and to profound disillusionment with public policies. By 1963 when inflation reached its runaway stage, the economy had ceased to grow, industry and transport were convulsed by innumerable strikes, and peasants were invading land in the countryside; and the situation further worsened in the first months of 1964.”
Professor Nathiel H. Leff (1975) at Columbia University identified another important contribution of Kahil (1975, Chapter IV “The supply of capital,” 127-185) of key current relevance to current proposals to promote economic growth and employment by raising inflation targets:
“Contrary to the assertions of some earlier writers on this topic, Kahil concludes that inflation did not lead to accelerated capital formation in Brazil.”
In econometric analysis of Brazil’s inflation from 1947 to 1980, Barbosa (1987) concludes:
“The most important result, based on the empirical evidence presented here, is that in the long run inflation is a monetary phenomenon. It follows that the most challenging task for Brazilian society in the near future is to shape a monetary-fiscal constitution that precludes financing much of the budget deficits through the inflation tax.”
Experience with continuing fiscal deficits and money creation tend to show accelerating inflation. Table III-10 provides average yearly rates of growth of two definitions of the money stock, M1, and M2 that adds also interest-paying deposits. The data were part of a research project on the monetary history of Brazil using the NBER framework of Friedman and Schwartz (1963, 1970) and Cagan (1965) as well as the institutional framework of Rondo E. Cameron (1967, 1972) who inspired the research (Pelaez 1974, 1975, 1976a,b, 1977, 1979, Pelaez and Suzigan 1978, 1981). The data were also used to test the correct specification of money and income following Sims (1972; see also Williams et al. 1976) as well as another test of orthogonality of money demand and supply using covariance analysis. Sims (1972, 541) finds that: “If and only if causality runs one way from current and past values of some list of exogenous variables to a given endogenous variable, then in a regression of the endogenous variable on past, current, and future values of the exogenous variables, the future values of the exogenous variables should have zero coefficients.” The objective of research was to verify the quantity theory of money of Friedman and Schwartz (1963, 1970) for the economy of Brazil from 1862 to 1976. The Granger-Sims test postulates that causality runs from money into nominal income if and only if in a regression of nominal income on past, current and future values of money, future coefficients are zero. The results show that the Sims F coefficients are zero for the regressions of nominal income on money and 38 for the coefficients of money on income (Pelaez and Suzigan 1978, Pelaez 1979, 106). There also covariance tests verifying orthogonality of money demand and money supply and orthogonality of base money and the money multiplier. The quantity theory of money explains money, income and prices in the historical period of Brazil 1862 to 1976. There are two important conclusions.
- Models of Keynesian multipliers in historical Brazil are inconsistent with these findings
- Pelaez (1979, 121) concludes following Friedman that for the case of Brazil “in historical perspective, it appears that a system of rules, instead of authorities, would have best promoted the interests of the Nation.”
Hill (2007, 763) develops “a simple parametric recursion for VAR coefficients that, for trivariate processes with one scalar auxiliary variable, always allows for sequential linear parametric conditions for non-causality up to horizon h ≥ 1. An empirical analysis of the money-income relationship reveals significant evidence in favor of linear causation of money to income, either directly when we control for cointegration, or indirectly after a delay of 1-3 months in models of first differences.” Shikida, Araujo Jr. and Figueiredo (2014) apply Hill (2007) to the historical experience of Brazil. They conclude that base money influences nominal output but not real output. Their results are consistent with the unpleasant monetarist arithmetic of Sargent and Wallace (1981) that uses base money instead of the stock of money. Because of restrictions on banking and finance (Summerhill 2015, Pelaez 1975), base money should have been more important in influencing nominal income in historical Brazil. It is still valid to conclude that monetary policy rules instead of discretionary authorities would have best promoted national interests in historical Brazil.
The average yearly rates of inflation are high for almost any period in 1861-1970, even when prices were declining at 1 percent in 19th century England, and accelerated to 27.1 percent in 1945-1970. There may be concern in an uncontrolled deficit monetized by sharp increases in base money. The Fed may have desired to control inflation at 2 percent after lowering the fed funds rate to 1 percent in 2003 but inflation rose to 4.1 percent in 2007. There is not “one hundred percent” confidence in controlling inflation because of the lags in effects of monetary policy impulses and the equally important lags in realization of the need for action and taking of action and also the inability to forecast any economic variable. Romer and Romer (2004) find that a one percentage point tightening of monetary policy is associated with a 4.3 percent decline in industrial production. There is no change in inflation in the first 22 months after monetary policy tightening when it begins to decline steadily, with decrease by 6 percent after 48 months (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 102). Even if there were one hundred percent confidence in reducing inflation by monetary policy, it could take a prolonged period with adverse effects on economic activity. Certainty does not occur in economic policy, which is characterized by costs that cannot be anticipated.
Table III-10, Brazil, Yearly Growth Rates of M1, M2, Nominal Income (Y), Real Income (y), Real Income per Capita (y/n) and Prices (P)
| M1 | M2 | Y | y | y/N | P | |
| 1861-1970 | 9.3 | 6.2 | 10.2 | 4.6 | 2.4 | 5.8 |
| 1861-1900 | 5.4 | 5.9 | 5.9 | 4.4 | 2.6 | 1.6 |
| 1861-1913 | 4.7 | 4.7 | 5.3 | 4.4 | 2.4 | 0.1 |
| 1861-1929 | 5.5 | 5.6 | 6.4 | 4.3 | 2.3 | 2.1 |
| 1900-1970 | 13.9 | 13.9 | 15.2 | 4.9 | 2.6 | 10.3 |
| 1900-1929 | 8.9 | 8.9 | 10.8 | 4.2 | 2.1 | 6.6 |
| 1900-1945 | 8.6 | 9.1 | 9.2 | 4.3 | 2.2 | 4.9 |
| 1920-1970 | 17.8 | 17.3 | 19.4 | 5.3 | 2.8 | 14.1 |
| 1920-1945 | 8.3 | 8.7 | 7.5 | 4.3 | 2.2 | 3.2 |
| 1920-1929 | 5.4 | 6.9 | 11.1 | 5.3 | 3.3 | 5.8 |
| 1929-1939 | 8.9 | 8.1 | 11.7 | 6.3 | 4.1 | 5.4 |
| 1945-1970 | 30.3 | 29.2 | 33.2 | 6.1 | 3.1 | 27.1 |
Note: growth rates are obtained by regressions of the natural logarithms on time. M1 and M2 definitions of the money stock; Y nominal GDP; y real GDP; y/N real GDP per capita; P prices.
Source: See Pelaez and Suzigan (1978), 143; M1 and M2 from Pelaez and Suzigan (1981); money income and real income from Contador and Haddad (1975) and Haddad (1974); prices by the exchange rate adjusted by British wholesale prices until 1906 and then from Villela and Suzigan (1973); national accounts after 1947 from Fundação Getúlio Vargas.
Chart III-1 shows in semi-logarithmic scale from 1861 to 1970 in descending order two definitions of income velocity, money income, M1, M2, an indicator of prices and real income.
Chart III-1, Brazil, Money, Income and Prices 1861-1970.
Source: © Carlos Manuel Pelaez and Wilson Suzigan. 1981. História Monetária do Brasil Segunda Edição. Coleção Temas Brasileiros. Brasília: Universidade de Brasília, 21.
Table III-11 provides yearly percentage changes of GDP, GDP per capita, base money, prices and the current account in millions of dollars during the acceleration of inflation after 1947. There was an explosion of base money or the issue of money and three waves of inflation identified by Kahil (1973). Inflation accelerated together with issue of money and political instability from 1960 to 1964. There must be a role for expectations in inflation but there is not much sound knowledge and measurement as Rajan (2012May8) argues. There have been inflation waves documented in periodic comments in this blog (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/of-course-economic-outlook-is-highly.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/interest-rate-increase-could-well.html). The risk is ignition of adverse expectations at the crest of one of worldwide inflation waves. Lack of credibility of the commitment by the FOMC to contain inflation could ignite such perverse expectations. Deficit financing of economic growth can lead to inflation and financial instability.
Table III-11, Brazil, GDP, GDP per Capita, Base Money, Prices and Current Account of the Balance of Payments, ∆% and USD Millions, 1947-1971
| GDP ∆% | GDP per Capita ∆% | Base Money ∆% | Prices ∆% | Current USD Millions | |
| 1947 | 2.4 | 0.1 | -1.4 | 14.0 | 162 |
| 1948 | 7.4 | 4.9 | 4.6 | 7.6 | -24 |
| 1949 | 6.6 | 4.2 | 14.5 | 4.0 | -74 |
| 1950 | 6.5 | 4.0 | 23.0 | 10.0 | 52 |
| 1951 | 5.9 | 2.9 | 15.3 | 21.9 | -291 |
| 1952 | 8.7 | 5.6 | 17.7 | 10.2 | -615 |
| 1953 | 2.5 | -0.5 | 15.5 | 12.1 | 16 |
| 1954 | 10.1 | 6.9 | 23.4 | 31.0 | -203 |
| 1955 | 6.9 | 3.8 | 18.0 | 14.0 | 17 |
| 1956 | 3.2 | 0.2 | 16.9 | 21.6 | 194 |
| 1957 | 8.1 | 4.9 | 30.5 | 13.9 | -180 |
| 1958 | 7.7 | 4.6 | 26.1 | 10.4 | -253 |
| 1959 | 5.6 | 2.5 | 32.3 | 37.7 | -154 |
| 1960 | 9.7 | 6.5 | 42.4 | 27.6 | -410 |
| 1961 | 10.3 | 7.1 | 54.4 | 36.1 | 115 |
| 1962 | 5.3 | 2.2 | 66.4 | 54.1 | -346 |
| 1963 | 1.6 | -1.4 | 78.4 | 75.2 | -244 |
| 1964 | 2.9 | -0.1 | 82.5 | 89.7 | 40 |
| 1965 | 2.7 | -0.6 | 67.6 | 62.0 | 331 |
| 1966 | 4.4 | 1.5 | 25.8 | 37.9 | 153 |
| 1967 | 4.9 | 2.0 | 33.9 | 28.7 | -245 |
| 1968 | 11.2 | 8.1 | 31.4 | 25.2 | 32 |
| 1969 | 9.9 | 6.9 | 22.4 | 18.2 | 549 |
| 1970 | 8.9 | 5.8 | 20.2 | 20.7 | 545 |
| 1971 | 13.3 | 10.2 | 29.8 | 22.0 | 530 |
Sources: Fundação Getúlio Vargas, Banco Central do Brasil and Pelaez and Suzigan (1981). Carlos Manuel Pelaez, História Econômica do Brasil: Um Elo entre a Teoria e a Realidade Econômica. São Paulo: Editora Atlas, 1979, 94.
I Recovery without Hiring. Professor Edward P. Lazear (2012Jan19) at Stanford University finds that recovery of hiring in the US to peaks attained in 2007 requires an increase of hiring by 30 percent while hiring levels increased by only 4 percent from Jan 2009 to Jan 2012. The high level of unemployment with low level of hiring reduces the statistical probability that the unemployed will find a job. According to Lazear (2012Jan19), the probability of finding a new job in early 2012 is about one third of the probability of finding a job in 2007. Improvements in labor markets have not increased the probability of finding a new job. Lazear (2012Jan19) quotes an essay coauthored with James R. Spletzer in the American Economic Review (Lazear and Spletzer 2012Mar, 2012May) on the concept of churn. A dynamic labor market occurs when a similar amount of workers is hired as those who are separated. This replacement of separated workers is called churn, which explains about two-thirds of total hiring. Typically, wage increases received in a new job are higher by 8 percent. Lazear (2012Jan19) argues that churn has declined 35 percent from the level before the recession in IVQ2007. Because of the collapse of churn, there are no opportunities in escaping falling real wages by moving to another job. As this blog argues, there are meager chances of escaping unemployment because of the collapse of hiring and those employed cannot escape falling real wages by moving to another job (Section I and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-values-of-risk-financial-assets.html). Lazear and Spletzer (2012Mar, 1) argue that reductions of churn reduce the operational effectiveness of labor markets. Churn is part of the allocation of resources or in this case labor to occupations of higher marginal returns. The decline in churn can harm static and dynamic economic efficiency. Losses from decline of churn during recessions can affect an economy over the long-term by preventing optimal growth trajectories because resources are not used in the occupations where they provide highest marginal returns. Lazear and Spletzer (2012Mar 7-8) conclude that: “under a number of assumptions, we estimate that the loss in output during the recession [of 2007 to 2009] and its aftermath resulting from reduced churn equaled $208 billion. On an annual basis, this amounts to about .4% of GDP for a period of 3½ years.”
There are two additional facts discussed below: (1) there are about ten million fewer full-time jobs currently than before the recession of 2008 and 2009; and (2) the extremely high and rigid rate of youth unemployment is denying an early start to young people ages 16 to 24 years while unemployment of ages 45 years or over has swelled. There are four subsections. IA1 Hiring Collapse provides the data and analysis on the weakness of hiring in the United States economy. IA2 Labor Underutilization provides the measures of labor underutilization of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). Statistics on the decline of full-time employment are in IA3 Ten Million Fewer Full-time Jobs. IA4 Theory and Reality of Cyclical Slow Growth Not Secular Stagnation: Youth and Middle-Age Unemployment provides the data on high unemployment of ages 16 to 24 years and of ages 45 years or over.
IA1 Hiring Collapse. An important characteristic of the current fractured labor market of the US is the closing of the avenue for exiting unemployment and underemployment normally available through dynamic hiring. Another avenue that is closed is the opportunity for advancement in moving to new jobs that pay better salaries and benefits again because of the collapse of hiring in the United States. Those who are unemployed or underemployed cannot find a new job even accepting lower wages and no benefits. The employed cannot escape declining inflation-adjusted earnings because there is no hiring. The objective of this section is to analyze hiring and labor underutilization in the United States.
Blanchard and Katz (1997, 53 consider an appropriate measure of job stress:
“The right measure of the state of the labor market is the exit rate from unemployment, defined as the number of hires divided by the number unemployed, rather than the unemployment rate itself. What matters to the unemployed is not how many of them there are, but how many of them there are in relation to the number of hires by firms.”
The natural rate of unemployment and the similar NAIRU are quite difficult to estimate in practice (Ibid; see Ball and Mankiw 2002).
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) created the Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey (JOLTS) with the purpose that (http://www.bls.gov/jlt/jltover.htm#purpose):
“These data serve as demand-side indicators of labor shortages at the national level. Prior to JOLTS, there was no economic indicator of the unmet demand for labor with which to assess the presence or extent of labor shortages in the United States. The availability of unfilled jobs—the jobs opening rate—is an important measure of tightness of job markets, parallel to existing measures of unemployment.”
The BLS collects data from about 16,000 US business establishments in nonagricultural industries through the 50 states and DC. The data are released monthly and constitute an important complement to other data provided by the BLS (see also Lazear and Spletzer 2012Mar, 6-7).
There is socio-economic stress in the combination of adverse events and cyclical performance:
- Mediocre economic growth below potential and long-term trend, resulting in idle productive resources with GDP two trillion dollars below trend (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). US GDP grew at the average rate of 3.2 percent per year from 1929 to 2015, with similar performance in whole cycles of contractions and expansions, but only at 1.2 percent per year on average from 2007 to 2015. GDP in IIIQ2016 is 13.8 percent lower than what it would have been had it grown at trend of 3.0 percent
- Private fixed investment stagnating at increase of 7.5 percent in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2016 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html)
- Twenty four million or 14.4 percent of the effective labor force unemployed or underemployed in involuntary part-time jobs with stagnating or declining real wages (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2017/01/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/the-case-for-increase-in-federal-funds.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/10/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/09/interest-rates-and-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/08/global-competitive-easing-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/fluctuating-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/financial-turbulence-twenty-four.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/proceeding-cautiously-in-monetary.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets-in.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/weakening-equities-with-exchange-rate.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/liftoff-of-fed-funds-rate-followed-by.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/live-possibility-of-interest-rates.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/labor-market-uncertainty-and-interest.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-policy-dependent-on-what.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/turbulence-of-financial-asset.html)
- Stagnating real disposable income per person or income per person after inflation and taxes (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/the-case-for-increase-in-federal-funds.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/the-case-for-increase-in-federal-funds.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/10/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/09/interest-rates-and-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/08/global-competitive-easing-or.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/financial-asset-values-rebound-from.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/financial-turbulence-twenty-four.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/proceeding-cautiously-in-monetary.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets-in.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/dollar-revaluation-and-decreasing.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/dollar-revaluation-constraining.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/dollar-revaluation-constraining.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/live-possibility-of-interest-rates.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/labor-market-uncertainty-and-interest.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-policy-dependent-on-what.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/international-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/dollar-devaluation-and-carry-trade.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/volatility-of-valuations-of-financial.html)
- Depressed hiring that does not afford an opportunity for reducing unemployment/underemployment and moving to better-paid jobs (Section I and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-values-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/dollar-revaluation-and-valuations-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/10/imf-view-of-world-economy-and-finance.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/09/interest-rate-uncertainty-and-valuation.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/08/rising-valuations-of-risk-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/oscillating-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/considerable-uncertainty-about-economic.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/recovery-without-hiring-ten-million.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/proceeding-cautiously-in-reducing.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/contraction-of-united-states-corporate.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/subdued-foreign-growth-and-dollar.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/unconventional-monetary-policy-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/liftoff-of-interest-rates-with-volatile_17.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/interest-rate-policy-conundrum-recovery.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/impact-of-monetary-policy-on-exchange.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-policy-dependent-on-what_13.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/exchange-rate-and-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/oscillating-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/volatility-of-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/volatility-of-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/fluctuating-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/dollar-revaluation-recovery-without.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/global-exchange-rate-struggle-recovery.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/02/g20-monetary-policy-recovery-without.html)
- Productivity growth fell from 2.2 percent per year on average from 1947 to 2015 and average 2.3 percent per year from 1947 to 2007 to 1.3 percent per year on average from 2007 to 2015, deteriorating future growth and prosperity (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-values-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/the-case-for-increase-in-federal-funds.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/09/interest-rates-and-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/08/rising-valuations-of-risk-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/considerable-uncertainty-about-economic.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/closely-monitoring-global-economic-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/liftoff-of-fed-funds-rate-followed-by.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/live-possibility-of-interest-rates.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-policy-dependent-on-what.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/exchange-rate-and-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/quite-high-equity-valuations-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/global-competitive-devaluation-rules.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/02/job-creation-and-monetary-policy-twenty.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/financial-risks-twenty-six-million.html)
- Output of manufacturing in Nov 2016 at 27.5 percent below long-term trend since 1919 and at 20.9 percent below trend since 1986 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/of-course-economic-outlook-is-highly.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/interest-rate-increase-could-well.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/10/dollar-revaluation-world-inflation.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/09/interest-rates-and-volatility-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/08/interest-rate-policy-uncertainty-and.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/unresolved-us-balance-of-payments.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/fomc-projections-world-inflation-waves.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/most-fomc-participants-judged-that-if.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/contracting-united-states-industrial.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/monetary-policy-and-competitive.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/unconventional-monetary-policy-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/liftoff-of-interest-rates-with-monetary.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/interest-rate-liftoff-followed-by.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/interest-rate-policy-quagmire-world.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-increase-on-hold-because.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/exchange-rate-and-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/fluctuating-financial-asset-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/fluctuating-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/global-portfolio-reallocations-squeeze.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/impatience-with-monetary-policy-of.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/02/world-financial-turbulence-squeeze-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/01/exchange-rate-conflicts-squeeze-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/10/imf-view-squeeze-of-economic-activity.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html)
- Unsustainable government deficit/debt and balance of payments deficit (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2017/01/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/unresolved-us-balance-of-payments.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/proceeding-cautiously-in-reducing.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/weakening-equities-and-dollar.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/monetary-policy-designed-on-measurable.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/fluctuating-financial-asset-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/impatience-with-monetary-policy-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/irrational-exuberance-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/monetary-policy-world-inflation-waves.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/06/valuation-risks-world-inflation-waves.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/02/theory-and-reality-of-cyclical-slow.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/interest-rate-risks-world-inflation.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/tapering-quantitative-easing-mediocre.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/09/duration-dumping-and-peaking-valuations.html)
- Worldwide waves of inflation (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/of-course-economic-outlook-is-highly.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/interest-rate-increase-could-well.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/10/dollar-revaluation-world-inflation.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/09/interest-rates-and-volatility-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/08/interest-rate-policy-uncertainty-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/oscillating-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/fomc-projections-world-inflation-waves.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/most-fomc-participants-judged-that-if.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/contracting-united-states-industrial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/monetary-policy-and-competitive.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/uncertainty-of-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/liftoff-of-interest-rates-with-monetary.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/interest-rate-liftoff-followed-by.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/interest-rate-policy-quagmire-world.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-increase-on-hold-because.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/global-decline-of-values-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/fluctuating-financial-asset-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/interest-rate-policy-and-dollar.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/global-portfolio-reallocations-squeeze.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/dollar-revaluation-and-financial-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/irrational-exuberance-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/01/competitive-currency-conflicts-world.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/10/financial-oscillations-world-inflation.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/monetary-policy-world-inflation-waves.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/world-inflation-waves-united-states.html)
- Deteriorating terms of trade and net revenue margins of production across countries in squeeze of economic activity by carry trades induced by zero interest rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/of-course-economic-outlook-is-highly.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/interest-rate-increase-could-well.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/10/dollar-revaluation-world-inflation.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/09/interest-rates-and-volatility-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/unresolved-us-balance-of-payments.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/fomc-projections-world-inflation-waves.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/most-fomc-participants-judged-that-if.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/imf-view-of-world-economy-and-finance.html and earlier) (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/monetary-policy-and-competitive.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/uncertainty-of-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/liftoff-of-interest-rates-with-monetary.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/interest-rate-liftoff-followed-by.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/interest-rate-policy-quagmire-world.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-increase-on-hold-because.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/global-decline-of-values-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/fluctuating-financial-asset-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/global-portfolio-reallocations-squeeze.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/impatience-with-monetary-policy-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/02/world-financial-turbulence-squeeze-of.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/01/exchange-rate-conflicts-squeeze-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/10/imf-view-squeeze-of-economic-activity.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html
- Financial repression of interest rates and credit affecting the most people without means and access to sophisticated financial investments with likely adverse effects on income distribution and wealth disparity (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/the-case-for-increase-in-federal-funds.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/the-case-for-increase-in-federal-funds.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/10/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/09/interest-rates-and-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/08/global-competitive-easing-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/financial-asset-values-rebound-from.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/financial-turbulence-twenty-four.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/proceeding-cautiously-in-monetary.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/closely-monitoring-global-economic-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/dollar-revaluation-and-decreasing.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/dollar-revaluation-constraining.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/live-possibility-of-interest-rates.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/labor-market-uncertainty-and-interest.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-policy-dependent-on-what.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/international-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/dollar-devaluation-and-carry-trade.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/volatility-of-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/global-competitive-devaluation-rules.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/02/job-creation-and-monetary-policy-twenty.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/growth-uncertainties-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/10/world-financial-turbulence-twenty-seven.html)
- 43 million in poverty and 29 million without health insurance with family income adjusted for inflation regressing to 1999 levels (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/09/the-economic-outlook-is-inherently.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/interest-rate-policy-uncertainty-imf.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/financial-volatility-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/09/duration-dumping-and-peaking-valuations.html)
- Net worth of households and nonprofits organizations increasing by 18.1 percent after adjusting for inflation in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIQ2016 when it would have grown over 30.6 percent at trend of 3.1 percent per year in real terms from IVQ1945 to IIIQ2016 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2017/01/rules-versus-discretionary-authorities.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/09/the-economic-outlook-is-inherently.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/of-course-considerable-uncertainty.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/monetary-policy-and-fluctuations-of_13.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/weakening-equities-and-dollar.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/monetary-policy-designed-on-measurable.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/fluctuating-financial-asset-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/dollar-revaluation-and-financial-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/financial-volatility-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/06/financial-indecision-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/global-financial-risks-recovery-without.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/collapse-of-united-states-dynamism-of.html). Financial assets increased $20.4 trillion while nonfinancial assets increased $3.9 trillion with likely concentration of wealth in those with access to sophisticated financial investments. Real estate assets adjusted for inflation fell 2.4 percent.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) revised on Mar 17, 2016 “With the release of January 2016 data on March 17, job openings, hires, and separations data have been revised from December 2000 forward to incorporate annual updates to the Current Employment Statistics employment estimates and the Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey (JOLTS) seasonal adjustment factors. In addition, all data series are now available on a seasonally adjusted basis. Tables showing the revisions from 2000 through 2015 can be found using this link:http://www.bls.gov/jlt/revisiontables.htm.” (http://www.bls.gov/jlt/). Hiring in the nonfarm sector (HNF) has declined from 63.327 million in 2006 to 61.680 million in 2015 or by 1.647 million while hiring in the private sector (HP) has declined from 59.128 million in 2006 to 57.557 million in 2015 or by 1.571 million, as shown in Table I-1. The ratio of nonfarm hiring to employment (RNF) has fallen from 47.0 in 2005 to 43.5 in 2015 and in the private sector (RHP) from 52.7 in 2005 to 48.0 in 2015. Hiring has not recovered as in previous cyclical expansions because of the low rate of economic growth in the current cyclical expansion. The civilian noninstitutional population or those in condition to work increased from 228.815 million in 2006 to 250.801 million in 2015 or by 21.986 million. Hiring has not recovered prerecession levels while needs of hiring multiplied because of growth of population by more than 21 million. Private hiring of 59.128 million in 2006 was equivalent to 25.8 percent of the civilian noninstitutional population of 228.815, or those in condition of working, falling to 57.557 million in 2015 or 22.9 percent of the civilian noninstitutional population of 250.801 million in 2015. The percentage of hiring in civilian noninstitutional population of 25.9 percent in 2006 would correspond to 64.957 million of hiring in 2015, which would be 7.400 million higher than actual 57.557 million in 2015. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. US economic growth has been at only 2.1 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 29 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2016. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the third estimate of GDP for IIIQ2016 (https://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2016/pdf/gdp3q16_3rd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,745.9 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,355.6 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,745.9/$14,355.6 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1989, 4.5 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1989. 4.5 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1990 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2016 would have accumulated to 29.5 percent. GDP in IIIQ2016 would be $19,414.4 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2687.4 billion than actual $16,727.0 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 24.2 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 14.4 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2017/01/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). US GDP in IIIQ2016 is 13.8 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,727.0 billion in IIIQ2016 or 11.6 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.3 percent. Professor John H. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. Cochrane (2016May02) measures GDP growth in the US at average 3.5 percent per year from 1950 to 2000 and only at 1.76 percent per year from 2000 to 2015 with only at 2.0 percent annual equivalent in the current expansion. Cochrane (2016May02) proposes drastic changes in regulation and legal obstacles to private economic activity. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth of manufacturing at average 3.1 percent per year from Nov 1919 to Nov 2016. Growth at 3.1 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 108.2316 in Dec 2007 to 142.1081 in Nov 2016. The actual index NSA in Nov 2016 is 103.0759, which is 27.5 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.1 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2015. Using trend growth of 2.1 percent per year, the index would increase to 130.3109 in Nov 2016. The output of manufacturing at 103.0759 in Nov 2016 is 20.9 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Table I-1, US, Annual Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF) and Total Private Hiring (HP) in the US in Thousands and Percentage of Total Employment
| HNF | Rate RNF | HP | Rate HP | |
| 2001 | 62,633 | 47.4 | 58,501 | 52.7 |
| 2002 | 58,479 | 44.8 | 54,665 | 50.1 |
| 2003 | 56,949 | 43.7 | 53,584 | 49.3 |
| 2004 | 60,263 | 45.7 | 56,573 | 51.4 |
| 2005 | 62,951 | 47.0 | 59,179 | 52.7 |
| 2006 | 63,327 | 46.4 | 59,128 | 51.7 |
| 2007 | 62,104 | 45.0 | 57,797 | 49.9 |
| 2008 | 54,745 | 39.9 | 51,316 | 44.8 |
| 2009 | 45,931 | 35.0 | 42,703 | 39.3 |
| 2010 | 48,740 | 37.4 | 44,903 | 41.7 |
| 2011 | 50,283 | 38.1 | 47,179 | 43.0 |
| 2012 | 52,367 | 39.0 | 48,916 | 43.6 |
| 2013 | 54,241 | 39.8 | 50,787 | 44.3 |
| 2014 | 58,657 | 42.2 | 55,048 | 47.0 |
| 2015 | 61,680 | 43.5 | 57,557 | 48.0 |
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-1 shows the annual level of total nonfarm hiring (HNF) that collapsed during the global recession after 2007 in contrast with milder decline in the shallow recession of 2001. Nonfarm hiring has not recovered, remaining at a depressed level. The civilian noninstitutional population or those in condition to work increased from 228.815 million in 2006 to 250.801 million in 2015 or by 21.986 million. Hiring has not recovered precession levels while needs of hiring multiplied because of growth of population by more than 21 million.
Chart I-1, US, Level Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF), Annual, 2001-2015
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-2 shows the ratio or rate of nonfarm hiring to employment (RNF) that also fell much more in the recession of 2007 to 2009 than in the shallow recession of 2001. Recovery is weak in the current environment of cyclical slow growth.
Chart I-2, US, Rate Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF), Annual, 2001-2015
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Yearly percentage changes of total nonfarm hiring (HNF) are provided in Table I-2. There were much milder declines in 2002 of 6.6 percent and 2.6 percent in 2003 followed by strong rebounds of 5.8 percent in 2004 and 4.5 percent in 2005. In contrast, the contractions of nonfarm hiring in the recession after 2007 were much sharper in percentage points: 1.9 in 2007, 11.8 in 2008 and 16.1 percent in 2009. On a yearly basis, nonfarm hiring grew 6.1 percent in 2010 relative to 2009, 3.2 percent in 2011, 4.1 percent in 2012 and 3.6 percent in 2013. Nonfarm hiring grew 8.1 percent in 2014 and increased 5.2 percent in 2015. The relatively large length of 27 quarters of the current expansion reduces the likelihood of significant recovery of hiring levels in the United States because lower rates of growth and hiring in the final phase of expansions.
Table I-2, US, Annual Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF), Annual Percentage Change, 2002-2015
| Year | Annual ∆% |
| 2002 | -6.6 |
| 2003 | -2.6 |
| 2004 | 5.8 |
| 2005 | 4.5 |
| 2006 | 0.6 |
| 2007 | -1.9 |
| 2008 | -11.8 |
| 2009 | -16.1 |
| 2010 | 6.1 |
| 2011 | 3.2 |
| 2012 | 4.1 |
| 2013 | 3.6 |
| 2014 | 8.1 |
| 2015 | 5.2 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Total private hiring (HP) 12-month percentage changes of annual data are in Chart I-3. There has been sharp contraction of total private hiring in the US and only milder recovery from 2010 to 2015.
Chart I-3, US, Total Nonfarm Hiring Level, Annual, ∆%, 2001-2015
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Total private hiring (HP) annual data are in Chart I-5. There has been sharp contraction of total private hiring in the US and only milder recovery from 2010 to 2015.
Chart I-5, US, Total Private Hiring, Annual, 2001-2015
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-5A plots the rate of total private hiring relative to employment (RHP). The rate collapsed during the global recession after 2007 with insufficient recovery.
Chart I-5A, US, Rate Total Private Hiring, Annual, 2001-2015
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Total nonfarm hiring (HNF), total private hiring (HP) and their respective rates are in Table I-3 for the month of Nov in the years from 2001 to 2016. Hiring numbers are in thousands. There is recovery in HNF from 3541 thousand (or 4.0 million) in Nov 2009 to 3657 thousand in Nov 2010, 3814 thousand in Nov 2011, 4001 thousand in Nov 2012, 4257 thousand in Nov 2013, 4674 thousand in Nov 2014, 4873 thousand in Nov 2015 and 4850 thousand in Nov 2016 for cumulative gain of 37.0 percent at average rate of 4.6 percent per year. HP rose from 3338 thousand in Nov 2009 to 3436 thousand in Nov 2010, 31613 thousand in Nov 2011, 3791 thousand in Nov 2012, 4029 thousand in Nov 2013, 4432 thousand in Nov 2014, 4599 in Nov 2015 and 4563 thousand in Nov 2016 for cumulative gain of 37.0 percent at the average yearly rate of 4.6 percent. HNF has decreased from 4915 thousand in Nov 2006 to 4850 thousand in Nov 2016 or by 1.3 percent. HP has decreased from 4654 thousand in Nov 2006 to 4563 thousand in Nov 2016 or by 2.0 percent. The civilian noninstitutional population of the US, or those in condition of working, rose from 229.905 million in Nov 2006 to 254.540 million in Nov 2016, by 24.635 million or 10.7 percent. There is often ignored ugly fact that hiring decreased by around 2.0 percent while population available for working increased around 10.7 percent. Private hiring of 59.128 million in 2006 was equivalent to 25.8 percent of the civilian noninstitutional population of 228.815, or those in condition of working, falling to 57.557 million in 2015 or 22.9 percent of the civilian noninstitutional population of 250.801 million in 2015. The percentage of hiring in civilian noninstitutional population of 25.9 percent in 2006 would correspond to 64.957 million of hiring in 2015, which would be 7.400 million higher than actual 57.557 million in 2015. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. Cyclical slow growth over the entire business cycle from IVQ2007 to the present in comparison with earlier cycles and long-term trend (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html) explains the fact that there are many million fewer hires in the US than before the global recession. The labor market continues to be fractured, failing to provide an opportunity to exit from unemployment/underemployment or to find an opportunity for advancement away from declining inflation-adjusted earnings.
Table I-3, US, Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF) and Total Private Hiring (HP) in the US in
Thousands and in Percentage of Total Employment Not Seasonally Adjusted
| HNF | Rate RNF | HP | Rate HP | |
| 2001 Nov | 4253 | 3.2 | 3998 | 3.6 |
| 2002 Nov | 4274 | 3.2 | 3998 | 3.6 |
| 2003 Nov | 4125 | 3.1 | 3914 | 3.6 |
| 2004 Nov | 4591 | 3.4 | 4326 | 3.9 |
| 2005 Nov | 4682 | 3.4 | 4423 | 3.9 |
| 2006 Nov | 4915 | 3.6 | 4654 | 4.0 |
| 2007 Nov | 4616 | 3.3 | 4368 | 3.7 |
| 2008 Nov | 3499 | 2.6 | 3301 | 2.9 |
| 2009 Nov | 3541 | 2.7 | 3338 | 3.1 |
| 2010 Nov | 3657 | 2.8 | 3436 | 3.1 |
| 2011 Nov | 3814 | 2.8 | 3613 | 3.2 |
| 2012 Nov | 4001 | 2.9 | 3791 | 3.3 |
| 2013 Nov | 4257 | 3.1 | 4029 | 3.5 |
| 2014 Nov | 4674 | 3.3 | 4432 | 3.7 |
| 2015 Nov | 4873 | 3.4 | 4599 | 3.8 |
| 2016 Nov | 4850 | 3.3 | 4563 | 3.7 |
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-6 provides total nonfarm hiring on a monthly basis from 2001 to 2016. Nonfarm hiring rebounded in early 2010 but then fell and stabilized at a lower level than the early peak not-seasonally adjusted (NSA) of 4815 in May 2010 until it surpassed it with 5006 in Jun 2011 but declined to 3092 in Dec 2012. Nonfarm hiring fell to 2997 in Dec 2011 from 3814 in Nov 2011 and to revised 3629 in Feb 2012, increasing to 4197 in Mar 2012, 3092 in Dec 2012 and 4238 in Jan 2013 and declining to 3690 in Feb 2013. Nonfarm hires not seasonally adjusted increased to 4257 in Nov 2013 and 3223 in Dec 2013. Nonfarm hires reached 3730 in Dec 2014, 3919 in Dec 2015 and 4850 in Dec 2016. Chart I-6 provides seasonally adjusted (SA) monthly data. The number of seasonally-adjusted hires in Oct 2011 was 4239 thousand, increasing to revised 4470 thousand in Feb 2012, or 5.4 percent, moving to 4345 in Dec 2012 for cumulative increase of 2.6 percent from 4234 in Dec 2011 and 4488 in Dec 2013 for increase of 3.3 percent relative to 4345 in Dec 2012. The number of hires not seasonally adjusted was 5006 in Jun 2011, falling to 2997 in Dec 2011 but increasing to 4110 in Jan 2012 and declining to 3092 in Dec 2012. The number of nonfarm hiring not seasonally adjusted fell by 40.1 percent from 5006 in Jun 2011 to 2997 in Dec 2011 and fell 40.1 percent from 5162 in Jun 2012 to 3092 in Dec 2012 in a yearly-repeated seasonal pattern. The number of nonfarm hires not seasonally adjusted fell from 5114 in Jun 2013 to 3223 in Dec 2013, or decline of 37.0 percent, showing strong seasonality. The number of nonfarm hires not seasonally adjusted fell from 5570 in Jun 2014 to 3730 in Dec 2014 or 33.0 percent. The level of nonfarm hires fell from 5918 in Jun 2015 to 3919 in Dec 2015 or 33.8 percent.
Chart I-6, US, Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF), 2001-2016 Month SA
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Similar behavior occurs in the rate of nonfarm hiring in Chart I-7. Recovery in early 2010 was followed by decline and stabilization at a lower level but with stability in monthly SA estimates of 3.2 in Aug 2011 to 3.2 in Jan 2012, increasing to 3.3 in May 2012 and stabilizing to 3.3 in Jun 2012. The rate stabilized at 3.2 in Jul 2012, increasing to 3.3 in Aug 2012 but falling to 3.2 in Dec 2012 and 3.3 in Dec 2013. The rate not seasonally adjusted fell from 3.8 in Jun 2011 to 2.2 in Dec 2011, climbing to 3.8 in Jun 2012 but falling to 2.3 in Dec 2012. The rate of nonfarm hires not seasonally adjusted fell from 3.7 in Jun 2013 to 2.3 in Dec 2013. The NSA rate of nonfarm hiring fell from 4.0 in Jun 2014 to 2.6 in Dec 2014. The NSA rate fell from 4.1 in Jun 2015 to 2.7 in Dec 2015. Rates of nonfarm hiring NSA were in the range of 2.7 (Dec) to 4.4 (Jun) in 2006. The rate of nonfarm hiring SA stood at 3.6 in Nov 2016 and at 3.3 NSA.
Chart I-7, US, Rate Total Nonfarm Hiring, Month SA 2001-2016
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
There is only milder improvement in total private hiring shown in Chart I-8. Hiring private (HP) rose in 2010 with stability and renewed increase in 2011 followed by almost stationary series in 2012. The number of private hiring seasonally adjusted fell from 4043 thousand in Sep 2011 to 3933 in Dec 2011 or by 2.7 percent, decreasing to 4015 in Jan 2012 or decline by 0.7 percent relative to the level in Sep 2011. Private hiring fell to 3961 in Sep 2012 or lower by 2.0 percent relative to Sep 2011, moving to 4049 in Dec 2012 for increase of 0.8 percent relative to 4015 in Jan 2012. The number of private hiring not seasonally adjusted fell from 4626 in Jun 2011 to 2817 in Dec 2011 or by 39.1 percent, reaching 3855 in Jan 2012 or decline of 16.7 percent relative to Jun 2011 and moving to 2911 in Dec 2012 or 38.8 percent lower relative to 4757 in Jun 2012. Hires not seasonally adjusted fell from 4761 in Jun 2013 to 3059 in Dec 2013. The level of private hiring NSA fell from 5151 in Jun 2014 to 3532 in Dec 2014 or 31.4 percent. The level of private hiring fell from 5475 in Jun 2015 to 3697 in Dec 2015 or 32.5 percent. Companies reduce hiring in the latter part of the year that explains the high seasonality in year-end employment data. For example, NSA private hiring fell from 5614 in Jun 2006 to 3579 in Dec 2006 or by 36.2 percent. Private hiring NSA data are useful in showing the huge declines from the period before the global recession. Hiring in the nonfarm sector (HNF) has declined from 63.327 million in 2006 to 61.680 million in 2015 or by 1.647 million while hiring in the private sector (HP) has declined from 59.128 million in 2006 to 57.557 million in 2015 or by 1.571 million, as shown in Table I-1. The ratio of nonfarm hiring to employment (RNF) has fallen from 47.0 in 2005 to 43.5 in 2015 and in the private sector (RHP) from 52.7 in 2005 to 48.0 in 2015. Hiring has not recovered as in previous cyclical expansions because of the low rate of economic growth in the current cyclical expansion. The civilian noninstitutional population or those in condition to work increased from 228.815 million in 2006 to 250.801 million in 2015 or by 21.986 million. Hiring has not recovered prerecession levels while needs of hiring multiplied because of growth of population by more than 21 million. Private hiring of 59.128 million in 2006 was equivalent to 25.8 percent of the civilian noninstitutional population of 228.815, or those in condition of working, falling to 57.557 million in 2015 or 22.9 percent of the civilian noninstitutional population of 250.801 million in 2015. The percentage of hiring in civilian noninstitutional population of 25.9 percent in 2006 would correspond to 64.957 million of hiring in 2015, which would be 7.400 million higher than actual 57.557 million in 2015.
Chart I-8, US, Total Private Hiring Month SA 2001-2016
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-9 shows similar behavior in the rate of private hiring. The rate in 2011 in monthly SA data did not rise significantly above the peak in 2010. The rate seasonally adjusted fell from 3.7 in Sep 2011 to 3.5 in Dec 2011 and reached 3.6 in Dec 2012 and 3.6 in Dec 2013. The rate not seasonally adjusted (NSA) fell from 3.7 in Sep 2011 to 2.5 in Dec 2011, increasing to 3.8 in Oct 2012 but falling to 2.6 in Dec 2012 and 3.4 in Mar 2013. The NSA rate of private hiring fell from 4.8 in Jul 2006 to 3.4 in Aug 2009 but recovery was insufficient to only 3.9 in Aug 2012, 2.6 in Dec 2012 and 2.6 in Dec 2013. The NSA rate increased to 3.0 in Dec 2015 and 3.7 in Nov
2016.
Chart I-9, US, Rate Total Private Hiring Month SA 2001-2016
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
The JOLTS report of the Bureau of Labor Statistics also provides total nonfarm job openings (TNF JOB), TNF JOB rate and TNF LD (layoffs and discharges) shown in Table I-4 for the month of Nov from 2001 to 2016. The final column provides annual TNF LD for the years from 2001 to 2015. Nonfarm job openings (TNF JOB) increased from a peak of 4113 in Nov 2006 to 5246 in Nov 2016 or by 27.5 percent while the rate increased from 2.9 to 3.5. This was mediocre performance because the civilian noninstitutional population of the US, or those in condition of working rose from 229.905 million in Nov 2006 to 254.540 million in Nov 2016, by 24.635 million or 10.7 percent. Nonfarm layoffs and discharges (TNF LD) rose from 1872 in Nov 2006 to 2224 in Nov 2008 or by 18.8 percent. The annual data show layoffs and discharges rising from 20.9 million in 2006 to 26.4 million in 2009 or by 26.6 percent. Business pruned payroll jobs to survive the global recession but there has not been hiring because of the low rate of GDP growth. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions.
Table I-4, US, Total Nonfarm Job Openings and Total Nonfarm Layoffs and Discharges, Thousands NSA
| TNF JOB | TNF JOB | TNF LD | TNF LD | |
| Nov 2001 | 3132 | 2.3 | 2130 | 24138 |
| Nov 2002 | 3157 | 2.3 | 1897 | 22706 |
| Nov 2003 | 2924 | 2.2 | 1797 | 23490 |
| Nov 2004 | 3005 | 2.2 | 1867 | 22668 |
| Nov 2005 | 3989 | 2.8 | 1656 | 22243 |
| Nov 2006 | 4113 | 2.9 | 1872 | 20896 |
| Nov 2007 | 3943 | 2.7 | 1914 | 21958 |
| Nov 2008 | 2769 | 2.0 | 2224 | 24028 |
| Nov 2009 | 2164 | 1.6 | 1858 | 26444 |
| Nov 2010 | 2710 | 2.0 | 1762 | 21827 |
| Nov 2011 | 2935 | 2.1 | 1753 | 20801 |
| Nov 2012 | 3316 | 2.4 | 1771 | 20872 |
| Nov 2013 | 3627 | 2.6 | 1487 | 19889 |
| Nov 2014 | 4454 | 3.1 | 1626 | 20418 |
| Nov 2015 | 4897 | 3.3 | 1624 | 20942 |
| Nov 2016 | 5246 | 3.5 | 1563 |
Notes: TNF JOB: Total Nonfarm Job Openings; LD: Layoffs and Discharges
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-10 shows monthly job openings rising from the trough in 2009 to a high in the beginning of 2010. Job openings then stabilized into 2011 but have surpassed the peak of 3220 seasonally adjusted in Apr 2010 with 3576 seasonally adjusted in Dec 2012, which is higher by 11.1 percent relative to Apr 2010 but higher by 0.6 percent relative to 3556 in Nov 2012 and lower by 7.2 percent than 3852 in Mar 2012. Nonfarm job openings increased from 3576 in Dec 2012 to 3742 in Dec 2013 or by 4.6 percent and to 4815 in Dec 2014 or 28.7 percent relative to 2013. The high of job openings not seasonally adjusted was 3408 in Apr 2010 that was surpassed by 3647 in Jul 2011, increasing to 3905 in Oct 2012 but declining to 3218 in Dec 2012 and increasing to 3369 in Dec 2013. The level of job opening NSA increased to 4844 in Dec 2015. The level of job opening NSA increased to 5246 in Nov 2016. The level of job openings not seasonally adjusted fell to 3218 in Dec 2012 or by 17.3 percent relative to 3891 in Apr 2012. There is here again the strong seasonality of year-end labor data. Job openings fell from 4199 in Apr 2013 to 3369 in Dec 2013 and from 4829 in Apr 2014 to 44033 in Dec 2014, showing strong seasonal effects. The level of nonfarm job openings decreased from 5862 in Apr 2015 to 4844 in Dec 2015 or by 17.4 percent. Nonfarm job openings (TNF JOB) increased from a peak of 4113 in Nov 2006 to 5246 in Nov 2016 or by 27.5 percent while the rate increased from 2.9 to 3.5. This was mediocre performance because the civilian noninstitutional population of the US, or those in condition of working rose from 229.905 million in Nov 2006 to 254.540 million in Nov 2016, by 24.635 million or 10.7 percent.
Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions.
Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. US economic growth has been at only 2.1 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 29 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2016. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the third estimate of GDP for IIIQ2016 (https://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2016/pdf/gdp3q16_3rd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,745.9 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,355.6 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,745.9/$14,355.6 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1989, 4.5 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1989. 4.5 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1990 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2016 would have accumulated to 29.5 percent. GDP in IIIQ2016 would be $19,414.4 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2687.4 billion than actual $16,727.0 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 24.2 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 14.4 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2017/01/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). US GDP in IIIQ2016 is 13.8 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,727.0 billion in IIIQ2016 or 11.6 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.3 percent. Professor John H. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. Cochrane (2016May02) measures GDP growth in the US at average 3.5 percent per year from 1950 to 2000 and only at 1.76 percent per year from 2000 to 2015 with only at 2.0 percent annual equivalent in the current expansion. Cochrane (2016May02) proposes drastic changes in regulation and legal obstacles to private economic activity. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth of manufacturing at average 3.1 percent per year from Nov 1919 to Nov 2016. Growth at 3.1 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 108.2316 in Dec 2007 to 142.1081 in Nov 2016. The actual index NSA in Nov 2016 is 103.0759, which is 27.5 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.1 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2015. Using trend growth of 2.1 percent per year, the index would increase to 130.3109 in Nov 2016. The output of manufacturing at 103.0759 in Nov 2016 is 20.9 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Chart I-10, US Job Openings, Thousands NSA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The rate of job openings in Chart I-11 shows similar behavior. The rate seasonally adjusted increased from 2.2 in Jan 2011 to 2.5 in Dec 2011, 2.6 in Dec 2012, 2.7 in Dec 2013 and 3.3 in Dec 2014. The rate seasonally adjusted stood at 3.6 in Dec 2015 and 3.7 in Nov 2016. The rate not seasonally adjusted rose from the high of 2.6 in Apr 2010 to 3.0 in Apr 2013, easing to 2.4 in Dec 2013. The rate of job openings NSA fell from 3.3 in Jul 2007 to 1.6 in Nov-Dec 2009, recovering to 3.3 in Dec 2015. The rate of job opening NSA stood at 3.5 in Nov 2016.
Chart I-11, US, Rate of Job Openings, NSA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Total separations are in Chart I-12. Separations are lower in 2012-16 than before the global recession but hiring has not recovered.
Chart I-12, US, Total Nonfarm Separations, Month Thousands SA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-13 provides annual total separations. Separations fell sharply during the global recession but hiring has not recovered relative to population growth.
Chart I-13, US, Total Separations, Annual, Thousands, 2001-2015
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Table I-5 provides total nonfarm total separations from 2001 to 2015. Separations fell from 61.1 million in 2006 to 47.8 million in 2010 or by 13.4 million and 48.2 million in 2011 or by 12.9 million. Total separations increased from 48.2 million in 2011 to 51.8 million in 2013 or by 3.6 million and to 55.5 million in 2014 or by 7.3 million relative to 2011. Total separations increased to 58.943 million in 2015 or by 10.7 million relative to 2011.
Table I-5, US, Total Nonfarm Total Separations, Thousands, 2001-2015
| Year | Annual Thousands |
| 2001 | 64472 |
| 2002 | 59003 |
| 2003 | 56970 |
| 2004 | 58238 |
| 2005 | 60494 |
| 2006 | 61117 |
| 2007 | 60838 |
| 2008 | 58227 |
| 2009 | 51127 |
| 2010 | 47752 |
| 2011 | 48227 |
| 2012 | 50047 |
| 2013 | 51783 |
| 2014 | 55524 |
| 2015 | 58943 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Monthly data of layoffs and discharges reach a peak in early 2009, as shown in Chart I-14. Layoffs and discharges dropped sharply with the recovery of the economy in 2010 and 2011 once employers reduced their job count to what was required for cost reductions and loss of business. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth. Growth rates have been unusually low in the expansion of the current economic cycle.
Chart I-14, US, Total Nonfarm Layoffs and Discharges, Monthly Thousands SA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Layoffs and discharges in Chart I-15 rose sharply to a peak in 2009. There was pronounced drop into 2010 and 2011 with mild increase into 2012 and renewed decline into 2013. There is mild increase into 2014-2015.
Chart I-15, US, Total Nonfarm Layoffs and Discharges, Annual, 2001-2015
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Annual layoff and discharges are in Table I-6. Layoffs and discharges increased sharply from 20.896 million in 2006 to 26.444 million in 2009 or 26.6 percent. Layoff and discharges fell to 19.889 million in 2013 or 24.8 percent relative to 2009 and increased to 20.418 million in 2014 or 2.7 percent relative to 2013. Layoffs and discharges increased to 20.942 million in 2015 or 2.6 percent relative to 2014.
Table I-6, US, Total Nonfarm Layoffs and Discharges, Thousands, 2001-2015
| Year | Annual Thousands |
| 2001 | 24138 |
| 2002 | 22706 |
| 2003 | 23490 |
| 2004 | 22668 |
| 2005 | 22243 |
| 2006 | 20896 |
| 2007 | 21958 |
| 2008 | 24028 |
| 2009 | 26444 |
| 2010 | 21827 |
| 2011 | 20801 |
| 2012 | 20872 |
| 2013 | 19889 |
| 2014 | 20418 |
| 2015 | 20942 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
IA2 Labor Underutilization. The Bureau of Labor Statistics also provides alternative measures of labor underutilization shown in Table I-7. The most comprehensive measure is U6 that consists of total unemployed plus total employed part time for economic reasons plus all marginally attached workers as percent of the labor force. U6 not seasonally adjusted has risen from 8.2 percent in 2006 to 9.1 percent in Dec 2016.
Table I-7, US, Alternative Measures of Labor Underutilization NSA %
| U1 | U2 | U3 | U4 | U5 | U6 | |
| 2016 | ||||||
| Dec | 1.9 | 2.3 | 4.5 | 4.8 | 5.5 | 9.1 |
| Nov | 1.8 | 2.1 | 4.4 | 4.8 | 5.6 | 9.0 |
| Oct | 1.9 | 2.1 | 4.7 | 5.0 | 5.7 | 9.2 |
| Sep | 1.9 | 2.2 | 4.8 | 5.1 | 5.9 | 9.3 |
| Aug | 1.8 | 2.4 | 5.0 | 5.3 | 6.0 | 9.7 |
| Jul | 1.9 | 2.4 | 5.1 | 5.5 | 6.3 | 10.1 |
| Jun | 1.9 | 2.3 | 5.1 | 5.4 | 6.1 | 9.9 |
| May | 2.0 | 2.1 | 4.5 | 4.9 | 5.6 | 9.4 |
| Apr | 2.2 | 2.3 | 4.7 | 5.0 | 5.7 | 9.3 |
| Mar | 2.3 | 2.6 | 5.1 | 5.5 | 6.1 | 9.9 |
| Feb | 2.2 | 2.7 | 5.2 | 5.6 | 6.3 | 10.1 |
| Jan | 2.1 | 2.7 | 5.3 | 5.7 | 6.5 | 10.5 |
| 2015 | ||||||
| Dec | 2.1 | 2.4 | 4.8 | 5.2 | 5.9 | 9.8 |
| Nov | 2.1 | 2.3 | 4.8 | 5.2 | 5.8 | 9.6 |
| Oct | 2.1 | 2.3 | 4.8 | 5.2 | 6.0 | 9.5 |
| Sep | 2.0 | 2.2 | 4.9 | 5.3 | 6.0 | 9.6 |
| Aug | 2.1 | 2.5 | 5.2 | 5.6 | 6.3 | 10.3 |
| Jul | 2.0 | 2.7 | 5.6 | 6.0 | 6.7 | 10.7 |
| Jun | 2.1 | 2.5 | 5.5 | 5.8 | 6.6 | 10.8 |
| May | 2.4 | 2.5 | 5.3 | 5.6 | 6.4 | 10.4 |
| Apr | 2.4 | 2.5 | 5.1 | 5.5 | 6.4 | 10.4 |
| Mar | 2.6 | 2.9 | 5.6 | 6.0 | 6.8 | 11.0 |
| Feb | 2.7 | 3.0 | 5.8 | 6.3 | 7.1 | 11.4 |
| Jan | 2.7 | 3.1 | 6.1 | 6.5 | 7.4 | 12.0 |
| 2014 | ||||||
| Dec | 2.5 | 2.8 | 5.4 | 5.8 | 6.7 | 11.1 |
| Nov | 2.7 | 2.7 | 5.5 | 5.9 | 6.8 | 11.0 |
| Oct | 2.7 | 2.6 | 5.5 | 6.0 | 6.8 | 11.1 |
| Sep | 2.7 | 2.7 | 5.7 | 6.2 | 7.1 | 11.3 |
| Aug | 2.8 | 3.0 | 6.3 | 6.7 | 7.5 | 12.0 |
| Jul | 2.8 | 3.1 | 6.5 | 7.0 | 7.8 | 12.6 |
| Jun | 2.8 | 3.0 | 6.3 | 6.7 | 7.5 | 12.4 |
| May | 3.1 | 3.0 | 6.1 | 6.5 | 7.3 | 11.7 |
| Apr | 3.3 | 3.2 | 5.9 | 6.3 | 7.2 | 11.8 |
| Mar | 3.7 | 3.7 | 6.8 | 7.2 | 8.1 | 12.8 |
| Feb | 3.6 | 3.9 | 7.0 | 7.5 | 8.4 | 13.1 |
| Jan | 3.5 | 4.0 | 7.0 | 7.5 | 8.6 | 13.5 |
| 2013 | ||||||
| Dec | 3.5 | 3.5 | 6.5 | 7.0 | 7.9 | 13.0 |
| Nov | 3.7 | 3.5 | 6.6 | 7.1 | 7.9 | 12.7 |
| Oct | 3.7 | 3.6 | 7.0 | 7.4 | 8.3 | 13.2 |
| Sep | 3.7 | 3.5 | 7.0 | 7.5 | 8.4 | 13.1 |
| Aug | 3.7 | 3.8 | 7.3 | 7.9 | 8.7 | 13.6 |
| Jul | 3.7 | 3.8 | 7.7 | 8.3 | 9.1 | 14.3 |
| Jun | 3.9 | 3.8 | 7.8 | 8.4 | 9.3 | 14.6 |
| May | 4.1 | 3.7 | 7.3 | 7.7 | 8.5 | 13.4 |
| Apr | 4.3 | 3.9 | 7.1 | 7.6 | 8.5 | 13.4 |
| Mar | 4.3 | 4.3 | 7.6 | 8.1 | 9.0 | 13.9 |
| Feb | 4.3 | 4.6 | 8.1 | 8.6 | 9.6 | 14.9 |
| Jan | 4.3 | 4.9 | 8.5 | 9.0 | 9.9 | 15.4 |
| 2012 | ||||||
| Dec | 4.2 | 4.3 | 7.6 | 8.3 | 9.2 | 14.4 |
| Nov | 4.2 | 3.9 | 7.4 | 7.9 | 8.8 | 13.9 |
| Oct | 4.3 | 3.9 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 9.0 | 13.9 |
| Sep | 4.2 | 4.0 | 7.6 | 8.0 | 9.0 | 14.2 |
| Aug | 4.3 | 4.4 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 9.7 | 14.6 |
| Jul | 4.3 | 4.6 | 8.6 | 9.1 | 10.0 | 15.2 |
| Jun | 4.5 | 4.4 | 8.4 | 8.9 | 9.9 | 15.1 |
| May | 4.7 | 4.3 | 7.9 | 8.4 | 9.3 | 14.3 |
| Apr | 4.8 | 4.3 | 7.7 | 8.3 | 9.1 | 14.1 |
| Mar | 4.9 | 4.8 | 8.4 | 8.9 | 9.7 | 14.8 |
| Feb | 4.9 | 5.1 | 8.7 | 9.3 | 10.2 | 15.6 |
| Jan | 4.9 | 5.4 | 8.8 | 9.4 | 10.5 | 16.2 |
| 2011 | ||||||
| Dec | 4.8 | 5.0 | 8.3 | 8.8 | 9.8 | 15.2 |
| Nov | 4.9 | 4.7 | 8.2 | 8.9 | 9.7 | 15.0 |
| Oct | 5.0 | 4.8 | 8.5 | 9.1 | 10.0 | 15.3 |
| Sep | 5.2 | 5.0 | 8.8 | 9.4 | 10.2 | 15.7 |
| Aug | 5.2 | 5.1 | 9.1 | 9.6 | 10.6 | 16.1 |
| Jul | 5.2 | 5.2 | 9.3 | 10.0 | 10.9 | 16.3 |
| Jun | 5.1 | 5.1 | 9.3 | 9.9 | 10.9 | 16.4 |
| May | 5.5 | 5.1 | 8.7 | 9.2 | 10.0 | 15.4 |
| Apr | 5.5 | 5.2 | 8.7 | 9.2 | 10.1 | 15.5 |
| Mar | 5.7 | 5.8 | 9.2 | 9.7 | 10.6 | 16.2 |
| Feb | 5.6 | 6.0 | 9.5 | 10.1 | 11.1 | 16.7 |
| Jan | 5.6 | 6.2 | 9.8 | 10.4 | 11.4 | 17.3 |
| Dec 2010 | 5.4 | 5.9 | 9.1 | 9.9 | 10.7 | 16.6 |
| Annual | ||||||
| 2016 | 2.0 | 2.3 | 4.9 | 5.2 | 5.9 | 9.6 |
| 2015 | 2.3 | 2.6 | 5.3 | 5.7 | 6.4 | 10.4 |
| 2014 | 3.0 | 3.1 | 6.2 | 6.6 | 7.5 | 12.0 |
| 2013 | 3.9 | 3.9 | 7.4 | 7.9 | 8.8 | 13.8 |
| 2012 | 4.5 | 4.4 | 8.1 | 8.6 | 9.5 | 14.7 |
| 2011 | 5.3 | 5.3 | 8.9 | 9.5 | 10.4 | 15.9 |
| 2010 | 5.7 | 6.0 | 9.6 | 10.3 | 11.1 | 16.7 |
| 2009 | 4.7 | 5.9 | 9.3 | 9.7 | 10.5 | 16.2 |
| 2008 | 2.1 | 3.1 | 5.8 | 6.1 | 6.8 | 10.5 |
| 2007 | 1.5 | 2.3 | 4.6 | 4.9 | 5.5 | 8.3 |
| 2006 | 1.5 | 2.2 | 4.6 | 4.9 | 5.5 | 8.2 |
| 2005 | 1.8 | 2.5 | 5.1 | 5.4 | 6.1 | 8.9 |
| 2004 | 2.1 | 2.8 | 5.5 | 5.8 | 6.5 | 9.6 |
| 2003 | 2.3 | 3.3 | 6.0 | 6.3 | 7.0 | 10.1 |
| 2002 | 2.0 | 3.2 | 5.8 | 6.0 | 6.7 | 9.6 |
| 2001 | 1.2 | 2.4 | 4.7 | 4.9 | 5.6 | 8.1 |
| 2000 | 0.9 | 1.8 | 4.0 | 4.2 | 4.8 | 7.0 |
Note: LF: labor force; U1, persons unemployed 15 weeks % LF; U2, job losers and persons who completed temporary jobs %LF; U3, total unemployed % LF; U4, total unemployed plus discouraged workers, plus all other marginally attached workers; % LF plus discouraged workers; U5, total unemployed, plus discouraged workers, plus all other marginally attached workers % LF plus all marginally attached workers; U6, total unemployed, plus all marginally attached workers, plus total employed part time for economic reasons % LF plus all marginally attached workers
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Monthly seasonally adjusted measures of labor underutilization are provided in Table I-8. U6 climbed from 16.1 percent in Aug 2011 to 16.4 percent in Sep 2011 and then fell to 14.5 percent in Mar 2012, reaching 9.2 percent in Dec 2016. Unemployment is an incomplete measure of the stress in US job markets. A different calculation in this blog is provided by using the participation rate in the labor force before the global recession. This calculation shows 24.2 million in job stress of unemployment/underemployment in Nov 2016, not seasonally adjusted, corresponding to 14.4 percent of the labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2017/01/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html).
Table I-8, US, Alternative Measures of Labor Underutilization SA %
| U1 | U2 | U3 | U4 | U5 | U6 | |
| Dec | 1.9 | 2.3 | 4.7 | 5.0 | 5.7 | 9.2 |
| Nov | 1.8 | 2.2 | 4.6 | 5.0 | 5.8 | 9.3 |
| Oct | 2.0 | 2.3 | 4.8 | 5.1 | 5.9 | 9.5 |
| Sep | 2.0 | 2.5 | 4.9 | 5.3 | 6.0 | 9.7 |
| Aug | 1.9 | 2.4 | 4.9 | 5.3 | 5.9 | 9.7 |
| Jul | 2.0 | 2.3 | 4.9 | 5.2 | 6.0 | 9.7 |
| Jun | 2.0 | 2.4 | 4.9 | 5.2 | 6.0 | 9.6 |
| May | 1.9 | 2.3 | 4.7 | 5.0 | 5.7 | 9.7 |
| Apr | 2.1 | 2.4 | 5.0 | 5.3 | 6.0 | 9.7 |
| Mar | 2.1 | 2.4 | 5.0 | 5.4 | 6.0 | 9.8 |
| Feb | 2.1 | 2.4 | 4.9 | 5.3 | 6.0 | 9.7 |
| Jan | 2.0 | 2.3 | 4.9 | 5.3 | 6.2 | 9.9 |
| Dec 2015 | 2.1 | 2.4 | 5.0 | 5.4 | 6.1 | 9.9 |
| Nov | 2.1 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 5.4 | 6.1 | 9.9 |
| Oct | 2.1 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 5.4 | 6.2 | 9.8 |
| Sep | 2.1 | 2.4 | 5.0 | 5.4 | 6.2 | 10.0 |
| Aug | 2.2 | 2.5 | 5.1 | 5.5 | 6.2 | 10.2 |
| Jul | 2.1 | 2.6 | 5.2 | 5.6 | 6.4 | 10.3 |
| Jun | 2.2 | 2.6 | 5.3 | 5.6 | 6.4 | 10.5 |
| May | 2.4 | 2.7 | 5.5 | 5.8 | 6.6 | 10.7 |
| Apr | 2.3 | 2.6 | 5.4 | 5.9 | 6.7 | 10.8 |
| Mar | 2.4 | 2.7 | 5.4 | 5.9 | 6.7 | 10.9 |
| Feb | 2.5 | 2.7 | 5.5 | 6.0 | 6.8 | 11.0 |
| Jan | 2.7 | 2.7 | 5.7 | 6.1 | 7.0 | 11.3 |
| Dec 2014 | 2.6 | 2.8 | 5.6 | 6.0 | 6.9 | 11.2 |
| Nov | 2.7 | 2.9 | 5.8 | 6.2 | 7.0 | 11.4 |
| Oct | 2.8 | 2.8 | 5.7 | 6.2 | 7.0 | 11.5 |
| Sep | 2.8 | 2.9 | 5.9 | 6.3 | 7.3 | 11.8 |
| Aug | 2.9 | 3.0 | 6.2 | 6.6 | 7.4 | 12.0 |
| July | 2.9 | 3.1 | 6.2 | 6.6 | 7.5 | 12.2 |
| Jun | 3.0 | 3.1 | 6.1 | 6.5 | 7.3 | 12.0 |
| May | 3.1 | 3.2 | 6.3 | 6.7 | 7.5 | 12.1 |
| Apr | 3.2 | 3.3 | 6.2 | 6.7 | 7.5 | 12.3 |
| Mar | 3.4 | 3.5 | 6.7 | 7.1 | 7.9 | 12.6 |
| Feb | 3.4 | 3.5 | 6.7 | 7.1 | 8.0 | 12.6 |
| Jan | 3.4 | 3.5 | 6.6 | 7.1 | 8.1 | 12.7 |
| Dec 2013 | 3.6 | 3.5 | 6.7 | 7.3 | 8.1 | 13.1 |
| Nov | 3.7 | 3.7 | 6.9 | 7.4 | 8.2 | 13.1 |
| Oct | 3.8 | 4.0 | 7.2 | 7.7 | 8.5 | 13.6 |
| Sep | 3.8 | 3.8 | 7.2 | 7.7 | 8.6 | 13.7 |
| Aug | 3.9 | 3.7 | 7.3 | 7.8 | 8.6 | 13.6 |
| Jul | 3.9 | 3.8 | 7.3 | 7.9 | 8.7 | 13.8 |
| Jun | 4.0 | 3.9 | 7.5 | 8.1 | 9.0 | 14.2 |
| May | 4.1 | 3.9 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 8.8 | 13.8 |
| Apr | 4.1 | 4.1 | 7.6 | 8.1 | 8.9 | 14.0 |
| Mar | 4.1 | 4.1 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 8.9 | 13.8 |
| Feb | 4.1 | 4.2 | 7.7 | 8.2 | 9.2 | 14.4 |
| Jan | 4.2 | 4.3 | 8.0 | 8.5 | 9.4 | 14.5 |
| Dec 2012 | 4.3 | 4.2 | 7.9 | 8.5 | 9.4 | 14.4 |
| Nov | 4.2 | 4.2 | 7.7 | 8.3 | 9.2 | 14.4 |
| Oct | 4.4 | 4.2 | 7.8 | 8.3 | 9.2 | 14.4 |
| Sep | 4.4 | 4.2 | 7.8 | 8.3 | 9.3 | 14.8 |
| Aug | 4.5 | 4.4 | 8.1 | 8.6 | 9.6 | 14.6 |
| Jul | 4.5 | 4.6 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 9.6 | 14.8 |
| Jun | 4.7 | 4.6 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 9.6 | 14.8 |
| May | 4.6 | 4.5 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 9.6 | 14.7 |
| Apr | 4.6 | 4.4 | 8.2 | 8.8 | 9.6 | 14.6 |
| Mar | 4.6 | 4.5 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 9.6 | 14.5 |
| Feb | 4.7 | 4.6 | 8.3 | 8.9 | 9.8 | 15.0 |
| Jan | 4.8 | 4.7 | 8.3 | 8.9 | 9.9 | 15.2 |
| Dec 2011 | 4.9 | 4.9 | 8.5 | 9.1 | 10.0 | 15.2 |
| Nov | 5.0 | 5.0 | 8.6 | 9.3 | 10.1 | 15.5 |
| Oct | 5.1 | 5.1 | 8.8 | 9.4 | 10.3 | 15.8 |
| Sep | 5.4 | 5.2 | 9.0 | 9.7 | 10.5 | 16.4 |
| Aug | 5.4 | 5.2 | 9.0 | 9.6 | 10.5 | 16.1 |
| Jul | 5.3 | 5.3 | 9.0 | 9.6 | 10.6 | 15.9 |
| Jun | 5.3 | 5.3 | 9.1 | 9.7 | 10.7 | 16.1 |
| May | 5.3 | 5.4 | 9.0 | 9.5 | 10.3 | 15.8 |
| Apr | 5.2 | 5.4 | 9.1 | 9.7 | 10.5 | 16.1 |
| Mar | 5.3 | 5.4 | 9.0 | 9.5 | 10.4 | 15.9 |
| Feb | 5.3 | 5.5 | 9.0 | 9.6 | 10.6 | 16.0 |
| Jan | 5.5 | 5.5 | 9.1 | 9.7 | 10.8 | 16.2 |
Note: LF: labor force; U1, persons unemployed 15 weeks % LF; U2, job losers and persons who completed temporary jobs %LF; U3, total unemployed % LF; U4, total unemployed plus discouraged workers, plus all other marginally attached workers; % LF plus discouraged workers; U5, total unemployed, plus discouraged workers, plus all other marginally attached workers % LF plus all marginally attached workers; U6, total unemployed, plus all marginally attached workers, plus total employed part time for economic reasons % LF plus all marginally attached workers
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-16 provides U6 on a monthly basis from 2001 to 2016. There was a steep climb from 2007 into 2009 and then this measure of unemployment and underemployment stabilized at that high level but declined into 2012. The low of U6 SA was 8.0 percent in Mar 2007 and the peak was 17.1 percent in Apr 2010. The low NSA was 7.6 percent in Oct 2006 and the peak was 18.0 percent in Jan 2010.
Chart I-16, US, U6, total unemployed, plus all marginally attached workers, plus total employed Part-Time for Economic Reasons, Month, SA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-17 provides the number employed part-time for economic reasons or who cannot find full-time employment. There are sharp declines at the end of 2009, 2010 and 2011 but an increase in 2012 followed by relative stability in 2013-2016.
Chart I-17, US, Working Part-time for Economic Reasons
Thousands, Month SA 2001-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
ICA3 Ten Million Fewer Full-time Jobs. There is strong seasonality in US labor markets around the end of the year.
- Seasonally adjusted part-time for economic reasons. The number employed part-time for economic reasons because they could not find full-time employment fell from 9.166 million in Sep 2011 to 7.775 million in Mar 2012, seasonally adjusted, or decline of 1.391 million in six months, as shown in Table I-9. The number employed part-time for economic reasons rebounded to 8.671 million in Sep 2012 for increase of 697,000 in one month from Aug to Sep 2012. The number employed part-time for economic reasons declined to 8.203 million in Oct 2012 or by 468,000 again in one month, further declining to 8.166 million in Nov 2012 for another major one-month decline of 37,000 and 7.943 million in Dec 2012 or fewer 223,000 in just one month. The number employed part-time for economic reasons increased to 8.074 million in Jan 2013 or 131,000 more than in Dec 2012 and to 8.119 million in Feb 2013, declining to 7.864 million in May 2013 but increasing to 8.096 million in Jun 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 7.804 million in Aug 2013 for decline of 279,000 in one month from 8.083 million in Jul 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons increased 207,000 from 7.804 million in Aug 2013 to 8.011 million in Sep 2013. The number part-time for economic reasons rose to 7.995 million in Oct 2013, falling by 265,000 to 7.730 million in Nov 2013. The number part-time for economic reasons increased to 7.792 million in Dec 2013, decreasing to 7.298 million in Jan 2014. The number employed part-time for economic reasons fell from 7.298 million in Jan 2014 to 7.262 million in Feb 2014. The number employed part-time for economic reasons increased to 7.403 million in Mar 2014 and 7.466 million in Apr 2014. The number employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 7.170 million in May 2014, increasing to 7.469 million in Jun 2014. The level employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 7.430 million in Jul 2014 and 7.173 million in Aug 2014. The level employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 7.123 million in Sep 2014, 7.033 million in Oct 2014 and 6.870 million in Nov 2014. The level employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 6.819 million in Dec 2014, increasing to 6.836 million in Jan 2015. The level employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 6.664 million in Feb 2015, increasing to 6.646 million in Mar 2015. The level of employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 6.563 million in Apr 2015, increasing to 6.544 million in May 2015. The level employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 6.463 million in Jun 2015 and 6.292 million in Jul 2015. The level employed part-time for economic reasons increased to 6.438 million in Aug 2015, declining to 6.031 million in Sep 2015. The level employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 5.734 million in Oct 2015, increasing to 6.113 million in Nov 2015. The level of part-time for economic reasons fell to 6.057 million in Dec 2015, decreasing to 6.035 million in Jan 2016. The level employed part-time for economic reasons decreased to 6.019 million in Feb 2016 and increased to 6.120 million in Mar 2016. The level employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 5.970 million in Apr 2016 and increased to 6.409 million in May 2016. The level of part-time for economic reasons fell to 5.820 million in Jun 2016, increasing to 5.936 million in Jul 2016. The level of part-time for economic reasons increased to 6.027 million in Aug 2016, decreasing to 5.874 million in Sep 2016. The level of part-time for economic reasons reached 5.850 million in Oct 2016, decreasing to 5.659 million in Nov 2016 and 5.598 million in Dec 2016.
- Seasonally adjusted full-time. The number employed full-time increased from 112.923 million in Oct 2011 to 115.024 million in Mar 2012 or 2.101 million but then fell to 114.233 million in May 2012 or 0.791 million fewer full-time employed than in Mar 2012. The number employed full-time increased from 114.736 million in Aug 2012 to 115.570 million in Oct 2012 or increase of 0.834 million full-time jobs in two months and further to 115.724 million in Jan 2013 or increase of 0.988 million more full-time jobs in five months from Aug 2012 to Jan 2013. The number of full time jobs decreased slightly to 115.674 million in Feb 2013, increasing to 116.247 million in May 2013 and 116.126 million in Jun 2013. Then number of full-time jobs increased to 116.155 million in Jul 2013, 116.435 million in Aug 2013 and 116.895 million in Sep 2013. The number of full-time jobs fell to 116.362 million in Oct 2013 and increased to 117.046 in Nov 2013. The level of full-time jobs increased to 117.351 million in Dec 2013, increasing to 117.504 million in Jan 2014 and 117.747 million in Feb 2014. The level of employment full-time increased to 117.941 million in Mar 2014 and 118.516 million in Apr 2014. The level of full-time employment reached 118.816 million in May 2014, decreasing to 118.238 million in Jun 2014. The level of full-time jobs increased to 118.450 million in Jul 2014 and 118.707 million in Aug 2014. The level of full-time jobs increased to 119.338 million in Sep 2014, 119.763 million in Oct 2014 and 119.645 million in Nov 2014. The level of full-time jobs increased to 120.075 million in Dec 2014 and 120.575 million in Jan 2015. The level of full-time jobs increased to 120.776 million in Feb 2015 and 120.963 million in Mar 2015. The level of full-time jobs decreased to 120.870 million in Apr 2015, increasing to 121.523 million in May 2015 and decreasing to 121.066 million in Jun 2015. The level of full-time jobs increased to 121.629 million in Jul 2015 and increased to 121.934 million in Aug 2015, decreasing to 121.829 million in Sep 2015. The level of full-time jobs increased to 122.071 million in Oct 2015 and increased to 122.110 million in Nov 2015. The level of full-time jobs increased to 122.700 million in Dec 2015 and 123.116 million in Jan 2016. The level of full-time jobs increased to 123.210 million in Feb 2016 and increased to 123.513 million in Mar 2016. The level of full-time jobs decreased to 123.259 million in Apr 2016 and 123.232 million in May 2016. The level of full-time jobs increased to 123.618 million in Jun 2016, increasing to 123.888 million in Jul 2016. The level of full-time jobs increased to 124.256 million in Aug 2016, decreasing to 124.253 million in Sep 2016 and 124.190 million in Oct 2016. The level of full-time jobs increased to 124.213 million in Nov 2016 and 124.248 million in Dec 2016. Adjustments of benchmark and seasonality-factors at the turn of every year could affect comparability of labor market indicators (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets-in.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/02/job-creation-and-monetary-policy-twenty.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/02/financial-instability-rules.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/02/thirty-one-million-unemployed-or.html).
- Not seasonally adjusted part-time for economic reasons. The number of employed part-time for economic reasons actually increased without seasonal adjustment from 8.271 million in Nov 2011 to 8.428 million in Dec 2011 or by 157,000 and then to 8.918 million in Jan 2012 or by an additional 490,000 for cumulative increase from Nov 2011 to Jan 2012 of 647,000. The level of employed part-time for economic reasons then fell from 8.918 million in Jan 2012 to 7.867 million in Mar 2012 or by 1.051 million and to 7.694 million in Apr 2012 or 1.224 million fewer relative to Jan 2012. In Aug 2012, the number employed part-time for economic reasons reached 7.842 million NSA or 148,000 more than in Apr 2012. The number employed part-time for economic reasons increased from 7.842 million in Aug 2012 to 8.110 million in Sep 2012 or by 3.4 percent. The number part-time for economic reasons fell from 8.110 million in Sep 2012 to 7.870 million in Oct 2012 or by 240.000 in one month. The number employed part-time for economic reasons NSA increased to 8.628 million in Jan 2013 or 758,000 more than in Oct 2012. The number employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 8.298 million in Feb 2013, which is lower by 330,000 relative to 8.628 million in Jan 2013 but higher by 428,000 relative to 7.870 million in Oct 2012. The number employed part time for economic reasons fell to 7.734 million in Mar 2013 or 564,000 fewer than in Feb 2013 and fell to 7.709 million in Apr 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons reached 7.618 million in May 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons jumped from 7.618 million in May 2013 to 8.440 million in Jun 2013 or 822,000 in one month. The number employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 8.324 million in Jul 2013 and 7.690 million in Aug 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons NSA fell to 7.522 million in Sep 2013, increasing to 7.700 million in Oct 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 7.563 million in Nov 2013 and increased to 7.990 million in Dec 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 7.771 million in Jan 2014 and 7.397 million in Feb 2014. The level of part-time for economic reasons increased to 7.455 million in Mar 2014 and fell to 7.243 million in Apr 2014. The number of part-time for economic reasons fell to 6.960 million in May 2014, increasing to 7.805 million in Jun 2014. The level of part-time for economic reasons fell to 7.665 million in Jul 2014 and 7.083 million in Aug 2014. The level of part-time for economic reasons fell to 6.711 million in Sep 2014 and increased to 6.787 million in Oct 2014. The level of part-time for economic reasons reached 6.713 million in Nov 2014 and 6.970 million in Dec 2014, increasing to 7.269 million in Jan 2015. The level of part-time for economic reasons fell to 6.772 million in Feb 2015 and 6.672 million in Mar 2015, falling to 6.356 million in Apr 2015. The level of part-time for economic reasons increased to 6.363 million in May 2015 and to 6.776 million in Jun 2015, decreasing to 6.511 million in Jul 2015. The level of part-time for economic reasons fell to 6.361 million in Aug 2015 and 5.693 million in Sep 2015. The level of part-time for economic reasons fell to 5.536 million in Oct 2015, increasing to 5.967 million in Nov 2015. The level of part-time for economic reasons increased to 6.179 million in Dec 2015, increasing to 6.406 million in Jan 2016. The level of part-time for economic reasons decreased to 6.106 million in Feb 2016 and increased to 6.138 million in Mar 2016. The level of part-time for economic reasons decreased to 5.771 million in Apr 2016 and increased to 6.238 million in May 2016. The level of part-time for economic reasons decreased to 6.119 million in Jun 2016, increasing to 6.157 million in Jul 2016. The level of part-time for economic reasons fell to 5.963 million in Aug 2016, decreasing to 5.550 million in Sep 2016. The level of part-time for economic reasons increased to 5.648 million in Oct 2016, decreasing to 5.518 million in Nov 2016 and increasing to 5.707 million in Dec 2016.
- Not seasonally adjusted full-time. The number employed full time without seasonal adjustment fell from 113.138 million in Nov 2011 to 113.050 million in Dec 2011 or by 88,000 and fell further to 111.879 in Jan 2012 for cumulative decrease of 1.259 million. The number employed full-time not seasonally adjusted fell from 113.138 million in Nov 2011 to 112.587 million in Feb 2012 or by 551.000 but increased to 116.214 million in Aug 2012 or 3.076 million more full-time jobs than in Nov 2011. The number employed full-time not seasonally adjusted decreased from 116.214 million in Aug 2012 to 115.678 million in Sep 2012 for loss of 536,000 full-time jobs and rose to 116.045 million in Oct 2012 or by 367,000 full-time jobs in one month relative to Sep 2012. The number employed full-time NSA fell from 116.045 million in Oct 2012 to 115.515 million in Nov 2012 or decline of 530.000 in one month. The number employed full-time fell from 115.515 in Nov 2012 to 115.079 million in Dec 2012 or decline by 436,000 in one month. The number employed full time fell from 115.079 million in Dec 2012 to 113.868 million in Jan 2013 or decline of 1.211 million in one month. The number of full time jobs increased to 114.191 in Feb 2012 or by 323,000 in one month and increased to 114.796 million in Mar 2013 for cumulative increase from Jan by 928,000 full-time jobs but decrease of 283,000 from Dec 2012. The number employed full time reached 117.400 million in Jun 2013 and increased to 117.688 in Jul 2013 or by 288,000. The number employed full-time reached 117.868 million in Aug 2013 for increase of 180,000 in one month relative to Jul 2013. The number employed full-time fell to 117.308 million in Sep 2013 or by 560,000. The number employed full-time fell to 116.798 million in Oct 2013 or decline of 510.000 in one month. The number employed full-time rose to 116.875 million in Nov 2013, falling to 116.661 million in Dec 2013. The number employed full-time fell to 115.744 million in Jan 2014 but increased to 116.323 million in Feb 2014. The level of full-time jobs increased to 116.985 in Mar 2014 and 118.073 million in Apr 2014. The number of full-time jobs increased to 119.179 million in May 2014, increasing to 119.472 million in Jun 2014. The level of full-time jobs increased to 119.900 million in Jul 2014. Comparisons over long periods require use of NSA data. The number with full-time jobs fell from a high of 123.219 million in Jul 2007 to 108.777 million in Jan 2010 or by 14.442 million. The number with full-time jobs in Dec 2016 is 123.570 million, which is higher by 0.351 million relative to the peak of 123.219 million in Jul 2007.
- Loss of full-time jobs. The magnitude of the stress in US labor markets is magnified by the increase in the civilian noninstitutional population of the United States from 231.958 million in Jul 2007 to 254.742 million in Dec 2016 or by 22.784 million (http://www.bls.gov/data/). The number with full-time jobs in Dec 2016 is 123.570 million, which is higher by 0.351 million relative to the peak of 123.219 million in Jul 2007. The ratio of full-time jobs of 123.219 million in Jul 2007 to civilian noninstitutional population of 231.958 million was 53.1 percent. If that ratio had remained the same, there would be 135.268 million full-time jobs with population of 254.742 million in Dec 2016 (0.531 x 254.742) or 11.698 million fewer full-time jobs relative to actual 123.570 million. There appear to be around 10 million fewer full-time jobs in the US than before the global recession while population increased around 20 million. Mediocre GDP growth is the main culprit of the fractured US labor market. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. US economic growth has been at only 2.1 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 29 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2016. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the third estimate of GDP for IIIQ2016 (https://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2016/pdf/gdp3q16_3rd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,745.9 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,355.6 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,745.9/$14,355.6 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1989, 4.5 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1989. 4.5 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1990 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2016 would have accumulated to 29.5 percent. GDP in IIIQ2016 would be $19,414.4 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2687.4 billion than actual $16,727.0 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 24.2 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 14.4 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2017/01/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). US GDP in IIIQ2016 is 13.8 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,727.0 billion in IIIQ2016 or 11.6 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.3 percent. Professor John H. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. Cochrane (2016May02) measures GDP growth in the US at average 3.5 percent per year from 1950 to 2000 and only at 1.76 percent per year from 2000 to 2015 with only at 2.0 percent annual equivalent in the current expansion. Cochrane (2016May02) proposes drastic changes in regulation and legal obstacles to private economic activity. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth of manufacturing at average 3.1 percent per year from Nov 1919 to Nov 2016. Growth at 3.1 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 108.2316 in Dec 2007 to 142.1081 in Nov 2016. The actual index NSA in Nov 2016 is 103.0759, which is 27.5 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.1 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2015. Using trend growth of 2.1 percent per year, the index would increase to 130.3109 in Nov 2016. The output of manufacturing at 103.0759 in Nov 2016 is 20.9 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Table I-9, US, Employed Part-time for Economic Reasons, Thousands, and Full-time, Millions
| Part-time Thousands | Full-time Millions | |
| Seasonally Adjusted | ||
| Dec 2016 | 5,598 | 124.248 |
| Nov 2016 | 5,659 | 124.213 |
| Oct 2016 | 5,850 | 124.190 |
| Sep 2016 | 5,874 | 124.253 |
| Aug 2016 | 6,027 | 124.256 |
| Jul 2016 | 5,936 | 123.888 |
| Jun 2016 | 5,820 | 123.618 |
| May 2016 | 6,409 | 123.232 |
| Apr 2016 | 5,970 | 123.259 |
| Mar 2016 | 6,120 | 123.513 |
| Feb 2016 | 6,019 | 123.210 |
| Jan 2016 | 6,035 | 123.116 |
| Dec 2015 | 6,057 | 122.700 |
| Nov 2015 | 6,113 | 122.110 |
| Oct 2015 | 5,734 | 122.071 |
| Sep 2015 | 6,031 | 121.829 |
| Aug 2015 | 6,438 | 121.934 |
| Jul 2015 | 6,292 | 121.629 |
| Jun 2015 | 6,463 | 121.066 |
| May 2015 | 6,544 | 121.523 |
| Apr 2015 | 6,563 | 120.870 |
| Mar 2015 | 6,646 | 120.963 |
| Feb 2015 | 6,664 | 120.776 |
| Jan 2015 | 6,836 | 120.575 |
| Dec 2014 | 6,819 | 120.075 |
| Nov 2014 | 6,870 | 119.645 |
| Oct 2014 | 7,033 | 119.763 |
| Sep 2014 | 7,123 | 119.338 |
| Aug 2014 | 7,173 | 118.707 |
| Jul 2014 | 7,430 | 118.450 |
| Jun 2014 | 7,469 | 118.238 |
| May 2014 | 7,170 | 118.816 |
| Apr 2014 | 7,466 | 118.516 |
| Mar 2014 | 7,403 | 117.941 |
| Feb 2014 | 7,262 | 117.747 |
| Jan 2014 | 7,298 | 117.504 |
| Dec 2013 | 7,792 | 117.351 |
| Nov 2013 | 7,730 | 117.046 |
| Oct 2013 | 7,995 | 116.362 |
| Sep 2013 | 8,011 | 116.895 |
| Aug 2013 | 7,804 | 116.435 |
| Jul 2013 | 8,083 | 116.155 |
| Jun 2013 | 8,096 | 116.126 |
| May 2013 | 7,864 | 116.247 |
| Apr 2013 | 7,936 | 116.044 |
| Mar 2013 | 7,658 | 115.785 |
| Feb 2013 | 8,119 | 115.674 |
| Jan 2013 | 8,074 | 115.724 |
| Dec 2012 | 7,943 | 115.791 |
| Nov 2012 | 8,166 | 115.655 |
| Oct 2012 | 8,203 | 115.570 |
| Sep 2012 | 8,671 | 115.252 |
| Aug 2012 | 7,974 | 114.736 |
| Jul 2012 | 8,082 | 114.575 |
| Jun 2012 | 8,072 | 114.749 |
| May 2012 | 8,101 | 114.233 |
| Apr 2012 | 7,913 | 114.371 |
| Mar 2012 | 7,775 | 115.024 |
| Feb 2012 | 8,238 | 114.141 |
| Jan 2012 | 8,305 | 113.755 |
| Dec 2011 | 8,171 | 113.774 |
| Nov 2011 | 8,447 | 113.213 |
| Oct 2011 | 8,657 | 112.923 |
| Sep 2011 | 9,166 | 112.544 |
| Aug 2011 | 8,788 | 112.723 |
| Jul 2011 | 8,281 | 112.193 |
| Not Seasonally Adjusted | ||
| Dec 2016 | 5,707 | 123.570 |
| Nov 2016 | 5,518 | 123.960 |
| Oct 2016 | 5,648 | 124.588 |
| Sep 2016 | 5,550 | 124.278 |
| Aug 2016 | 5,963 | 125.892 |
| Jul 2016 | 6,157 | 125.507 |
| Jun 2016 | 6,119 | 124.903 |
| May 2016 | 6,238 | 123.548 |
| Apr 2016 | 5,771 | 122.742 |
| Mar 2016 | 6,138 | 122.522 |
| Feb 2016 | 6,106 | 121.757 |
| Jan 2016 | 6,406 | 121.411 |
| Dec 2015 | 6,179 | 122.013 |
| Nov 2015 | 5,967 | 121.897 |
| Oct 2015 | 5,536 | 122.466 |
| Sep 2015 | 5,693 | 122.303 |
| Aug 2015 | 6,361 | 123.420 |
| Jul 2015 | 6,511 | 123.142 |
| Jun 2015 | 6,776 | 122.268 |
| May 2015 | 6,363 | 121.863 |
| Apr 2015 | 6,356 | 120.402 |
| Mar 2015 | 6,672 | 119.981 |
| Feb 2015 | 6,772 | 119.313 |
| Jan 2015 | 7,269 | 118.840 |
| Dec 2014 | 6,970 | 119.394 |
| Nov 2014 | 6,713 | 119.441 |
| Oct 2014 | 6,787 | 120.176 |
| Sep 2014 | 6,711 | 119.791 |
| Aug 2014 | 7,083 | 120.110 |
| Jul 2014 | 7,665 | 119.900 |
| Jun 2014 | 7,805 | 119.472 |
| May 2014 | 6,960 | 119.179 |
| Apr 2014 | 7,243 | 118.073 |
| Mar 2014 | 7,455 | 116.985 |
| Feb 2014 | 7,397 | 116.323 |
| Jan 2014 | 7,771 | 115.774 |
| Dec 2013 | 7,990 | 116.661 |
| Nov 2013 | 7,563 | 116.875 |
| Oct 2013 | 7,700 | 116.798 |
| Sep 2013 | 7,522 | 117.308 |
| Aug 2013 | 7,690 | 117.868 |
| Jul 2013 | 8,324 | 117.688 |
| Jun 2013 | 8,440 | 117.400 |
| May 2013 | 7,618 | 116.643 |
| Apr 2013 | 7,709 | 115.674 |
| Mar 2013 | 7,734 | 114.796 |
| Feb 2013 | 8,298 | 114.191 |
| Jan 2013 | 8,628 | 113.868 |
| Dec 2012 | 8,166 | 115.079 |
| Nov 2012 | 7,994 | 115.515 |
| Oct 2012 | 7,870 | 116.045 |
| Sep 2012 | 8,110 | 115.678 |
| Aug 2012 | 7,842 | 116.214 |
| Jul 2012 | 8,316 | 116.131 |
| Jun 2012 | 8,394 | 116.024 |
| May 2012 | 7,837 | 114.634 |
| Apr 2012 | 7,694 | 113.999 |
| Mar 2012 | 7,867 | 113.916 |
| Feb 2012 | 8,455 | 112.587 |
| Jan 2012 | 8,918 | 111.879 |
| Dec 2011 | 8,428 | 113.050 |
| Nov 2011 | 8,271 | 113.138 |
| Oct 2011 | 8,258 | 113.456 |
| Sep 2011 | 8,541 | 112.980 |
| Aug 2011 | 8,604 | 114.286 |
| Jul 2011 | 8,514 | 113.759 |
| Jun 2011 | 8,738 | 113.255 |
| May 2011 | 8,270 | 112.618 |
| Apr 2011 | 8,425 | 111.844 |
| Mar 2011 | 8,737 | 111.186 |
| Feb 2011 | 8,749 | 110.731 |
| Jan 2011 | 9,187 | 110.373 |
| Dec 2010 | 9,205 | 111.207 |
| Nov 2010 | 8,670 | 111.348 |
| Oct 2010 | 8,408 | 112.342 |
| Sep 2010 | 8,628 | 112.385 |
| Aug 2010 | 8,628 | 113.508 |
| Jul 2010 | 8,737 | 113.974 |
| Jun 2010 | 8,867 | 113.856 |
| May 2010 | 8,513 | 112.809 |
| Apr 2010 | 8,921 | 111.391 |
| Mar 2010 | 9,343 | 109.877 |
| Feb 2010 | 9,282 | 109.100 |
| Jan 2010 | 9,290 | 108.777 (low) |
| Dec 2009 | 9,354 (high) | 109.875 |
| Nov 2009 | 8,894 | 111.274 |
| Oct 2009 | 8,474 | 111.599 |
| Sep 2009 | 8,255 | 111.991 |
| Aug 2009 | 8,835 | 113.863 |
| Jul 2009 | 9,103 | 114.184 |
| Jun 2009 | 9,301 | 114.014 |
| May 2009 | 8,785 | 113.083 |
| Apr 2009 | 8,648 | 112.746 |
| Mar 2009 | 9,305 | 112.215 |
| Feb 2009 | 9,170 | 112.947 |
| Jan 2009 | 8,829 | 113.815 |
| Dec 2008 | 8,250 | 116.422 |
| Nov 2008 | 7,135 | 118.432 |
| Oct 2008 | 6,267 | 120.020 |
| Sep 2008 | 5,701 | 120.213 |
| Aug 2008 | 5,736 | 121.556 |
| Jul 2008 | 6,054 | 122.378 |
| Jun 2008 | 5,697 | 121.845 |
| May 2008 | 5,096 | 120.809 |
| Apr 2008 | 5,071 | 120.027 |
| Mar 2008 | 5,038 | 119.875 |
| Feb 2008 | 5,114 | 119.452 |
| Jan 2008 | 5,340 | 119.332 |
| Dec 2007 | 4,750 | 121.042 |
| Nov 2007 | 4,374 | 121.846 |
| Oct 2007 | 4,028 | 122.006 |
| Sep 2007 | 4,137 | 121.728 |
| Aug 2007 | 4,494 | 122.870 |
| Jul 2007 | 4,516 | 123.219 (high) |
| Jun 2007 | 4,469 | 122.150 |
| May 2007 | 4,315 | 120.846 |
| Apr 2007 | 4,205 | 119.609 |
| Mar 2007 | 4,384 | 119.640 |
| Feb 2007 | 4,417 | 119.041 |
| Jan 2007 | 4,726 | 119.094 |
| Dec 2006 | 4,281 | 120.371 |
| Nov 2006 | 4,054 | 120.507 |
| Oct 2006 | 4,010 | 121.199 |
| Sep 2006 | 3,735 (low) | 120.780 |
| Aug 2006 | 4,104 | 121.979 |
| Jul 2006 | 4,450 | 121.951 |
| Jun 2006 | 4,456 | 121.070 |
| May 2006 | 3,968 | 118.925 |
| Apr 2006 | 3,787 | 118.559 |
| Mar 2006 | 4,097 | 117.693 |
| Feb 2006 | 4,403 | 116.823 |
| Jan 2006 | 4,597 | 116.395 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
People lose their marketable job skills after prolonged unemployment and face increasing difficulty in finding another job. Chart I-18 shows the sharp rise in unemployed over 27 weeks and stabilization at an extremely high level.
Chart I-18, US, Number Unemployed for 27 Weeks or Over, Thousands SA Month 2001-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Another segment of U6 consists of people marginally attached to the labor force who continue to seek employment but less frequently on the frustration there may not be a job for them. Chart I-19 shows the sharp rise in people marginally attached to the labor force after 2007 and subsequent stabilization.
Chart I-19, US, Marginally Attached to the Labor Force, NSA Month, Thousands, 2001-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-20 provides the level of full-time jobs from 2001 to 2016. The magnitude of the stress in US labor markets is magnified by the increase in the civilian noninstitutional population of the United States from 231.958 million in Jul 2007 to 254.742 million in Dec 2016 or by 22.784 million (http://www.bls.gov/data/). The number with full-time jobs in Dec 2016 is 123.570 million, which is higher by 0.351 million relative to the peak of 123.219 million in Jul 2007. The ratio of full-time jobs of 123.219 million in Jul 2007 to civilian noninstitutional population of 231.958 million was 53.1 percent. If that ratio had remained the same, there would be 135.268 million full-time jobs with population of 254.742 million in Dec 2016 (0.531 x 254.742) or 11.698 million fewer full-time jobs relative to actual 123.570 million. There appear to be around 10 million fewer full-time jobs in the US than before the global recession while population increased around 20 million. Mediocre GDP growth is the main culprit of the fractured US labor market.
There is current interest in past theories of “secular stagnation.” Alvin H. Hansen (1939, 4, 7; see Hansen 1938, 1941; for an early critique see Simons 1942) argues:
“Not until the problem of full employment of our productive resources from the long-run, secular standpoint was upon us, were we compelled to give serious consideration to those factors and forces in our economy which tend to make business recoveries weak and anaemic (sic) and which tend to prolong and deepen the course of depressions. This is the essence of secular stagnation-sick recoveries which die in their infancy and depressions which feed on them-selves and leave a hard and seemingly immovable core of unemployment. Now the rate of population growth must necessarily play an important role in determining the character of the output; in other words, the com-position of the flow of final goods. Thus a rapidly growing population will demand a much larger per capita volume of new residential building construction than will a stationary population. A stationary population with its larger proportion of old people may perhaps demand more personal services; and the composition of consumer demand will have an important influence on the quantity of capital required. The demand for housing calls for large capital outlays, while the demand for personal services can be met without making large investment expenditures. It is therefore not unlikely that a shift from a rapidly growing population to a stationary or declining one may so alter the composition of the final flow of consumption goods that the ratio of capital to output as a whole will tend to decline.”
The argument that anemic population growth causes “secular stagnation” in the US (Hansen 1938, 1939, 1941) is as misplaced currently as in the late 1930s (for early dissent see Simons 1942). This is merely another case of theory without reality with dubious policy proposals.
Inferior performance of the US economy and labor markets, during cyclical slow growth not secular stagnation, is the critical current issue of analysis and policy design.
Chart I-20, US, Full-time Employed, Thousands, NSA, 2001-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-20A provides the noninstitutional civilian population of the United States from 2001 to 2016. There is clear trend of increase of the population while the number of full-time jobs collapsed after 2008 without sufficient recovery as shown in the preceding Chart I-20.
Chart I-20A, US, Noninstitutional Civilian Population, Thousands, 2001-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-20B provides number of full-time jobs in the US from 1968 to 2016. There were multiple recessions followed by expansions without contraction of full-time jobs and without recovery as during the period after 2008. The problem is specific of the current cycle and not secular.
Chart I-20B, US, Full-time Employed, Thousands, NSA, 1968-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-20C provides the noninstitutional civilian population of the United States from 1968 to 2016. Population expanded at a relatively constant rate of increase with the assurance of creation of full-time jobs that has been broken since 2008.
Chart I-20C, US, Noninstitutional Civilian Population, Thousands, 1968-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
IA4 Theory and Reality of Secular Stagnation: Youth and Middle-Age Unemployment. Three tables support the argument that the proper comparison of the business cycle is between the recessions of the 1980s and the global recession after IVQ2007 and not as argued erroneously with the Great Depression of the 1930s. Table I-9A provides percentage change of real GDP in the United States in the 1930s, 1980s and 2000s. The recession in 1981-1982 is quite similar on its own to the 2007-2009 recession. In contrast, during the Great Depression in the four years of 1930 to 1933, GDP in constant dollars fell 26.4 percent cumulatively and fell 45.3 percent in current dollars (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 150-2, Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2009b), 205-7 and revisions in http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). Data are available for the 1930s only on a yearly basis. US GDP fell 4.7 percent in the two recessions (1) from IQ1980 to IIIQ1980 and (2) from III1981 to IVQ1982 and 4.2 percent cumulatively in the recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. It is instructive to compare the first years of the expansions in the 1980s and the current expansion. GDP grew at 4.6 percent in 1983, 7.3 percent in 1984, 4.2 percent in 1985, 3.5 percent in 1986, 3.5 percent in 1987, 4.2 percent in 1988 and 3.7 percent in 1989. In contrast, GDP grew 2.5 percent in 2010, 1.6 percent in 2011, 2.2 percent in 2012, 1.7 percent in 2013, 2.4 percent in 2014 and 2.6 percent in 2015. Actual annual equivalent GDP growth in the four quarters of 2012, twelve quarters from IQ2013 to IVQ2015, IQ2016, IIQ2016 and IIIQ2016 is 2.1 percent and 1.7 percent in the four quarters ending in IIIQ2016. GDP grew at 4.2 percent in 1985, 3.5 percent in 1986, 3.5 percent in 1987, 4.2 percent in 1988 and 3.7 percent in 1989. The forecasts of the central tendency of participants of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) are in the range of 1.9 to 2.3 percent in 2017 (https://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20161214.pdf) with less reliable forecast of 1.8 to 2.2 percent in 2017 (https://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20161214.pdf). Growth of GDP in the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2016 has been at average 2.1 percent in annual equivalent.
Table I-9A, US, Percentage Change of GDP in the 1930s, 1980s and 2000s, ∆%
| Year | GDP ∆% | Year | GDP ∆% | Year | GDP ∆% |
| 1930 | -8.5 | 1980 | -0.2 | 2000 | 4.1 |
| 1931 | -6.4 | 1981 | 2.6 | 2001 | 1.0 |
| 1932 | -12.9 | 1982 | -1.9 | 2002 | 1.8 |
| 1933 | -1.3 | 1983 | 4.6 | 2003 | 2.8 |
| 1934 | 10.8 | 1984 | 7.3 | 2004 | 3.8 |
| 1935 | 8.9 | 1985 | 4.2 | 2005 | 3.3 |
| 1936 | 12.9 | 1986 | 3.5 | 2006 | 2.7 |
| 1937 | 5.1 | 1987 | 3.5 | 2007 | 1.8 |
| 1938 | -3.3 | 1988 | 4.2 | 2008 | -0.3 |
| 1939 | 8.0 | 1989 | 3.7 | 2009 | -2.8 |
| 1940 | 8.8 | 1990 | 1.9 | 2010 | 2.5 |
| 1941 | 17.7 | 1991 | -0.1 | 2011 | 1.6 |
| 1942 | 18.9 | 1992 | 3.6 | 2012 | 2.2 |
| 1943 | 17.0 | 1993 | 2.7 | 2013 | 1.7 |
| 1944 | 8.0 | 1994 | 4.0 | 2014 | 2.4 |
| 1945 | -1.0 | 1995 | 2.7 | 2015 | 2.6 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Characteristics of the four cyclical contractions are in Table I-9B with the first column showing the number of quarters of contraction; the second column the cumulative percentage contraction; and the final column the average quarterly rate of contraction. There were two contractions from IQ1980 to IIIQ1980 and from IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 separated by three quarters of expansion. The drop of output combining the declines in these two contractions is 4.7 percent, which is almost equal to the decline of 4.2 percent in the contraction from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. In contrast, during the Great Depression in the four years of 1930 to 1933, GDP in constant dollars fell 26.4 percent cumulatively and fell 45.3 percent in current dollars (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 150-2, Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2009b), 205-7 and revisions in http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). The comparison of the global recession after 2007 with the Great Depression is entirely misleading.
Table I-9B, US, Number of Quarters, GDP Cumulative Percentage Contraction and Average Percentage Annual Equivalent Rate in Cyclical Contractions
| Number of Quarters | Cumulative Percentage Contraction | Average Percentage Rate | |
| IIQ1953 to IIQ1954 | 3 | -2.4 | -0.8 |
| IIIQ1957 to IIQ1958 | 3 | -3.0 | -1.0 |
| IVQ1973 to IQ1975 | 5 | -3.1 | -0.6 |
| IQ1980 to IIIQ1980 | 2 | -2.2 | -1.1 |
| IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 | 4 | -2.5 | -0.64 |
| IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 | 6 | -4.2 | -0.72 |
Sources: Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table I-9C shows the mediocre average annual equivalent growth rate of 2.1 percent of the US economy in the twenty-nine quarters of the current cyclical expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2016. In sharp contrast, the average growth rate of GDP was:
- 5.7 percent in the first thirteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1986
- 5.4 percent in the first fifteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986
- 5.2 percent in the first sixteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1986
- 5.0 percent in the first seventeen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1987
- 5.0 percent in the first eighteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIQ1987
- 4.9 percent in the first nineteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987
- 5.0 percent in the first twenty quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1987
- 4.9 percent in the first twenty-first quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1988
- 4.9 percent in the first twenty-two quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIQ1988
- 4.8 percent in the first twenty-three quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988
- 4.8 percent in the first twenty-four quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1988
- 4.8 percent in the first twenty-five quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1989
- 4.7 percent in the first twenty-six quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIQ1989
- 4.7 percent in the first twenty-seven quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIIQ1989
- 4.5 percent in the first twenty-eight quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1989
- 4.5 percent in the first twenty-nine quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1990
The line “average first four quarters in four expansions” provides the average growth rate of 7.7 percent with 7.8 percent from IIIQ1954 to IIQ1955, 9.2 percent from IIIQ1958 to IIQ1959, 6.1 percent from IIIQ1975 to IIQ1976 and 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983. The United States missed this opportunity of high growth in the initial phase of recovery. BEA data show the US economy in standstill with annual growth of 2.5 percent in 2010 decelerating to 1.6 percent annual growth in 2011, 2.2 percent in 2012, 1.7 percent in 2013, 2.4 percent in 2014 and 2.6 percent in 2015 (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). The expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1986 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.7 percent, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1988, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988. 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1989. 4.5 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1989, 4.5 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1990 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983. GDP grew 2.7 percent in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010. GDP growth in the four quarters of 2012, the four quarters of 2013, the four quarters of 2014, the four quarters of Q2015, IQ2016, IIQ2016 and IIIQ2016 accumulated to 10.0 percent. This growth is equivalent to 2.1 percent per year, obtained by dividing GDP in IIIQ2016 of $16,727.0 billion by GDP in IVQ2011 of $15,190.3 billion and compounding by 4/19: {[($16,727.0/$15,190.3)4/19 -1]100 = 2.1 percent}.
Table I-9C shows that GDP grew 16.5 percent in the first twenty-nine quarters of expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2016 at the annual equivalent rate of 2.1 percent.
Table I-9C, US, Number of Quarters, Cumulative Growth and Average Annual Equivalent Growth Rate in Cyclical Expansions
| Number | Cumulative Growth ∆% | Average Annual Equivalent Growth Rate | |
| IIIQ 1954 to IQ1957 | 11 | 12.8 | 4.5 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ1954 to IIQ1955 | 4 | 7.8 | |
| IIQ1958 to IIQ1959 | 5 | 10.0 | 7.9 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ1958 to IIQ1959 | 4 | 9.2 | |
| IIQ1975 to IVQ1976 | 8 | 8.3 | 4.1 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ1975 to IIQ1976 | 4 | 6.1 | |
| IQ1983-IQ1986 IQ1983-IIIQ1986 IQ1983-IVQ1986 IQ1983-IQ1987 IQ1983-IIQ1987 IQ1983 to IIIQ1987 IQ1983 to IVQ1987 IQ1983 to IQ1988 IQ1983 to IIQ1988 IQ1983 to IIIQ1988 IQ1983 to IVQ1988 IQ1983 to IQ1989 IQ1983 to IIQ1989 IQ1983 to IIIQ1989 IQ1983 to IVQ1989 IQ1983 to IQ1990 | 13 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 | 19.9 21.6 22.3 23.1 24.5 25.6 27.7 28.4 30.1 30.9 32.6 34.0 35.0 36.0 36.3 37.8 | 5.7 5.4 5.2 5.0 5.0 4.9 5.0 4.9 4.9 4.8 4.8 4.8 4.7 4.7 4.5 4.5 |
| First Four Quarters IQ1983 to IVQ1983 | 4 | 7.8 | |
| Average First Four Quarters in Four Expansions* | 7.7 | ||
| IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2016 | 29 | 16.5 | 2.1 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 | 2.7 |
*First Four Quarters: 7.8% IIIQ1954-IIQ1955; 9.2% IIIQ1958-IIQ1959; 6.1% IIIQ1975-IQ1976; 7.8% IQ1983-IVQ1983
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table EMP provides the comparison between the labor market in the current whole cycle from 2007 to 2016 and the whole cycle from 1979 to 1989. In the entire cycle from 2007 to 2016, the number employed increased 5.389 million, full-time employed increased 2.670 million, part-time for economic reasons increased 1.542 million and population increased 21.491 million. The number employed increased 3.7 percent, full-time employed increased 2.2 percent, part-time for economic reasons increased 35.0 percent and population increased 9.3 percent. There is sharp contrast with the contractions of the 1980s and with most economic history of the United States. In the whole cycle from 1979 to 1989, the number employed increased 18.518 million, full-time employed increased 14.715 million, part-time for economic reasons increased 1.317 million and population increased 21.530 million. In the entire cycle from 1979 to 1989, the number employed increased 18.7 percent, full-time employed increased 17.8 percent, part-time for economic reasons increased 36.8 percent and population increased 13.1 percent. The difference between the 1980s and the current cycle after 2007 is in the high rate of growth after the contraction that maintained trend growth around 3.0 percent for the entire cycle and per capital growth at 2.0 percent. The evident fact is that current weakness in labor markets originates in cyclical slow growth and not in imaginary secular stagnation.
Table EMP, US, Annual Level of Employed, Full-Time Employed, Employed Part-Time for Economic Reasons and Noninstitutional Civilian Population, Millions
| Employed | Full-Time Employed | Part Time Economic Reasons | Noninstitutional Civilian Population | |
| 2000s | ||||
| 2000 | 136.891 | 113.846 | 3.227 | 212.577 |
| 2001 | 136.933 | 113.573 | 3.715 | 215.092 |
| 2002 | 136.485 | 112.700 | 4.213 | 217.570 |
| 2003 | 137.736 | 113.324 | 4.701 | 221.168 |
| 2004 | 139.252 | 114.518 | 4.567 | 223.357 |
| 2005 | 141.730 | 117.016 | 4.350 | 226.082 |
| 2006 | 144.427 | 119.688 | 4.162 | 228.815 |
| 2007 | 146.047 | 121.091 | 4.401 | 231.867 |
| 2008 | 145.362 | 120.030 | 5.875 | 233.788 |
| 2009 | 139.877 | 112.634 | 8.913 | 235.801 |
| 2010 | 139.064 | 111.714 | 8.874 | 237.830 |
| 2011 | 139.869 | 112.556 | 8.560 | 239.618 |
| 2012 | 142.469 | 114.809 | 8.122 | 243.284 |
| 2013 | 143.929 | 116.314 | 7.935 | 245.679 |
| 2014 | 146.305 | 118.718 | 7.213 | 247.947 |
| 2015 | 148.834 | 121.492 | 6.371 | 250.801 |
| 2016 | 151.436 | 123.761 | 5.943 | 253.358 |
| ∆2007-2016 | 5.389 | 2.670 | 1.542 | 21.491 |
| ∆% 2007-2016 | 3.7 | 2.2 | 35.0 | 9.3 |
| 1980s | ||||
| 1979 | 98.824 | 82.654 | 3.577 | 164.863 |
| 1980 | 99.303 | 82.562 | 4.321 | 167.745 |
| 1981 | 100.397 | 83.243 | 4.768 | 170.130 |
| 1982 | 99.526 | 81.421 | 6.170 | 172.271 |
| 1983 | 100.834 | 82.322 | 6.266 | 174.215 |
| 1984 | 105.005 | 86.544 | 5.744 | 176.383 |
| 1985 | 107.150 | 88.534 | 5.590 | 178.206 |
| 1986 | 109.597 | 90.529 | 5.588 | 180.587 |
| 1987 | 112.440 | 92.957 | 5.401 | 182.753 |
| 1988 | 114.968 | 95.214 | 5.206 | 184.613 |
| 1989 | 117.342 | 97.369 | 4.894 | 186.393 |
| ∆1979-1989 | 18.518 | 14.715 | 1.317 | 21.530 |
| ∆% 1979-1989 | 18.7 | 17.8 | 36.8 | 13.1 |
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
The theory of secular stagnation cannot explain sudden collapse of the US economy and labor markets. There are accentuated cyclic factors for both the entire population and the young population of ages 16 to 24 years. Table Summary Total provides the total noninstitutional population (ICP) of the US, full-time employment level (FTE), employment level (EMP), civilian labor force (CLF), civilian labor force participation rate (CLFP), employment/population ratio (EPOP) and unemployment level (UNE). Secular stagnation would spread over long periods instead of immediately. All indicators of the labor market weakened sharply during the contraction and did not recover. Population continued to grow but all other variables collapsed and did not recover. The theory of secular stagnation departs from an aggregate production function in which output grows with the use of labor, capital and technology (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. I (2008a), 11-16). Hansen (1938, 1939) finds secular stagnation in lower growth of an aging population. In the current US economy, Table Summary shows that population is dynamic while the labor market is fractured. There is key explanation in the behavior of the civilian labor force participation rate (CLFP) and the employment population ratio (EPOP) that collapsed during the global recession with inadequate recovery. Abandoning job searches are difficult to capture in labor statistics but likely explain the decline in the participation of the population in the labor force. Allowing for abandoning job searches, the total number of people unemployed or underemployed is 24.2 million or 14.4 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2017/01/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html).
Table Summary Total, US, Total Noninstitutional Civilian Population, Full-time Employment, Employment, Civilian Labor Force, Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate, Employment Population Ratio, Unemployment, NSA, Millions and Percent
| ICP | FTE | EMP | CLF | CLFP | EPOP | UNE | |
| 2006 | 228.8 | 119.7 | 144.4 | 151.4 | 66.2 | 63.1 | 7.0 |
| 2009 | 235.8 | 112.6 | 139.9 | 154.1 | 65.4 | 59.3 | 14.3 |
| 2012 | 243.3 | 114.8 | 142.5 | 155.0 | 63.7 | 58.6 | 12.5 |
| 2013 | 245.7 | 116.3 | 143.9 | 155.4 | 63.2 | 58.6 | 11.5 |
| 2014 | 247.9 | 118.7 | 146.3 | 155.9 | 62.9 | 59.0 | 9.6 |
| 2015 | 250.8 | 121.5 | 148.8 | 157.1 | 62.7 | 59.3 | 8.3 |
| 2016 | 253.5 | 123.8 | 151.4 | 159.2 | 62.8 | 59.7 | 7.8 |
| 12/07 | 233.2 | 121.0 | 146.3 | 153.7 | 65.9 | 62.8 | 7.4 |
| 9/09 | 236.3 | 112.0 | 139.1 | 153.6 | 65.0 | 58.9 | 14.5 |
| 12/16 | 254.7 | 123.6 | 151.8 | 159.0 | 62.4 | 59.6 | 7.2 |
ICP: Total Noninstitutional Civilian Population; FT: Full-time Employment Level, EMP: Total Employment Level; CLF: Civilian Labor Force; CLFP: Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate; EPOP: Employment Population Ratio; UNE: Unemployment
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
The same situation is present in the labor market for young people in ages 16 to 24 years with data in Table Summary Youth. The youth noninstitutional civilian population (ICP) continued to increase during and after the global recession. There is the same disastrous labor market with decline for young people in employment (EMP), civilian labor force (CLF), civilian labor force participation rate (CLFP) and employment population ratio (EPOP). There are only increases for unemployment of young people (UNE) and youth unemployment rate (UNER). If aging were a factor of secular stagnation, growth of population of young people would attract a premium in remuneration in labor markets. The sad fact is that young people are also facing tough labor markets. The application of the theory of secular stagnation to the US economy and labor markets is void of reality in the form of key facts, which are best explained by accentuated cyclic factors analyzed by Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22).
Table Summary Youth, US, Youth, Ages 16 to 24 Years, Noninstitutional Civilian Population, Full-time Employment, Employment, Civilian Labor Force, Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate, Employment Population Ratio, Unemployment, NSA, Millions and Percent
| ICP | EMP | CLF | CLFP | EPOP | UNE | UNER | |
| 2006 | 36.9 | 20.0 | 22.4 | 60.6 | 54.2 | 2.4 | 10.5 |
| 2009 | 37.6 | 17.6 | 21.4 | 56.9 | 46.9 | 3.8 | 17.6 |
| 2012 | 38.8 | 17.8 | 21.3 | 54.9 | 46.0 | 3.5 | 16.2 |
| 2013 | 38.8 | 18.1 | 21.4 | 55.0 | 46.5 | 3.3 | 15.5 |
| 2014 | 38.7 | 18.4 | 21.3 | 55.0 | 47.6 | 2.9 | 13.4 |
| 2015 | 38.6 | 18.8 | 21.2 | 55.0 | 48.6 | 2.5 | 11.6 |
| 2016 | 38.4 | 19.0 | 21.2 | 55.2 | 49.4 | 2.2 | 10.4 |
| 12/07 | 37.5 | 19.4 | 21.7 | 57.8 | 51.6 | 2.3 | 10.7 |
| 9/09 | 37.6 | 17.0 | 20.7 | 55.2 | 45.1 | 3.8 | 18.2 |
| 12/16 | 38.3 | 18.3 | 20.7 | 54.0 | 49.1 | 1.9 | 9.0 |
ICP: Youth Noninstitutional Civilian Population; EMP: Youth Employment Level; CLF: Youth Civilian Labor Force; CLFP: Youth Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate; EPOP: Youth Employment Population Ratio; UNE: Unemployment; UNER: Youth Unemployment Rate
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
The United States is experiencing high youth unemployment as in European economies. Table I-10 provides the employment level for ages 16 to 24 years of age estimated by the Bureau of Labor Statistics. On an annual basis, youth employment fell from 20.041 million in 2006 to 17.362 million in 2011 or 2.679 million fewer youth jobs and to 17.834 million in 2012 or 2.207 million fewer jobs. Youth employment fell from 20.041 million in 2006 to 18.057 million in 2013 or 1.984 million fewer jobs. Youth employment fell from 20.041 million in 2006 to 18.442 million in 2014 or 1.599 million. Youth employment fell from 20.041 million in 2006 to 18.756 million in 2015 or 1.285 million. The level of youth jobs fell from 20.129 million in Dec 2006 to 18.347 million in Dec 2014 for 1.782 million fewer youth jobs. The level of youth jobs fell from 20.129 million in Dec 2006 to 18.720 million in Dec 2015 or 1.409 million fewer jobs. Youth jobs fell from 20.129 million in Dec 2006 to 18.830 million in Dec 2016 or 1.299 million. During the seasonal peak months of youth employment in the summer from Jun to Aug, youth employment has fallen by more than two million jobs relative to 21.167 million in Aug 2006 to 18.972 million in Aug 2014 for 2.195 million fewer jobs. Youth employment fell from 21.914 million in Jul 2006 to 20.085 million in Jul 2014 for 1.829 million fewer youth jobs. The number of youth jobs fell from 21.268 million in Jun 2006 million to 19.421 million in Jun 2014 or 1.847 million fewer youth jobs. The number of jobs ages 16 to 24 years fell from 21.167 million in Aug 2006 to 18.636 million in Aug 2013 or by 2.531 million. The number of youth jobs fell from 19.604 million in Sep 2006 to 18.043 million in Sep 2013 or 1.561 million fewer youth jobs. The number of youth jobs fell from 20.129 million in Dec 2006 to 18.106 million in Dec 2013 or 2.023 million fewer jobs. The civilian noninstitutional population ages 16 to 24 years increased from 37.443 million in Jul 2007 to 38.861 million in Jul 2013 or by 1.418 million while the number of jobs for ages 16 to 24 years fell by 2.230 million from 21.914 million in Jul 2006 to 19.684 million in Jul 2013. The civilian noninstitutional population for ages 16 to 24 years increased from 37.455 million in Aug 2007 to 38.841 million in Aug 2013 or by 1.386 million while the number of youth jobs fell by 1.777 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.467 million in Sep 2007 to 38.822 million in Sep 2013 or by 1.355 million while the number of youth jobs fell by 1.455 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.480 million in Oct 2007 to 38.804 million in Oct 2013 or by 1.324 million while the number of youth jobs decreased 1.877 million from Oct 2006 to Oct 2013. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.798 million in Nov 2013 or by 1.722 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.799 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.518 million in Dec 2007 to 38.790 million in Dec 2013 or by 1.272 million while the number of youth jobs fell 2.023 million from Dec 2006 to Dec 2013. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.488 million from 37.282 million in in Jan 2007 to 38.770 million in Jan 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 2.035 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.464 million from 37.302 in Feb 2007 to 38.766 million in Feb 2014 while the number of youth jobs decreased 2.058 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.437 million from 37.324 million in Mar 2007 to 38.761 million in Mar 2014 while jobs for ages 16 to 24 years decreased 1.599 million from 19.538 million in Mar 2007 to 17.939 million in Mar 2014. The civilian noninstitutional population ages 16 to 24 years increased 1.410 million from 37.349 million in Apr 2007 to 38.759 million in Apr 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.347 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.370 million from 37.379 million in May 2007 to 38.749 million in May 2014 while the number of youth jobs decreased 1.128 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.330 million from 37.410 million in Jun 2007 to 38.740 million in Jun 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.847 million from 21.268 million in Jun 2006 to 19.421 million in Jun 2014. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased by 1.292 million from 37.443 million in Jul 2007 to 38.735 million in Jul 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.632 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.445 million in Aug 2007 to 38.706 million in Aug 2014 or 1.251 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.441 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.652 million from 37.027 million in Sep 2006 to 38.679 million in Sep 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.500 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.047 million in Oct 2006 to 38.650 million in Oct 2014 or 1.603 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.072 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.628 million in Nov 2014 or 1.552 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.327 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.100 million in Dec 2006 to 38.606 million in Dec 2014 or 1.506 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.782 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.971 million from 36.761 million in Jan 2006 to 38.732 million in Jan 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.091 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.914 million from 36.791 million in Feb 2006 to 38.705 million in Feb 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 0.960 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.858 million from 36.821 million in Mar 2006 to 38.679 million in Mar 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.215 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.800 million from 36.854 million in Apr 2006 to 38.654 million in Apr 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.165 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1,733 million from 36.897 million in May 2006 to 38.630 million in May 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.060 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.666 million from 36.943 million in Jun 2006 to 38.609 million in Jun 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.479 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.600 million from 36.989 million in Jul 2006 to 38.589 million in Jul 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.581 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.548 million from 37.008 million in Aug 2006 to 38.556 million in Aug 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.590 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1,498 million from 37.027 million in Sep 2006 to 38.525 million in Sep 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.249 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.444 million from 37.047 million in Oct 2006 to 38.491 million in Oct 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.199 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.392 million from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.468 million in Nov 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.418 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.341 million from 37.100 million in Dec 2006 to 38.441 million in Dec 2015 while the level of youth jobs 1.409 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.734 million from 36.761 million in Jan 2006 to 38.495 million in Jan 2016 while the level of youth jobs fell 0.844 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.698 million from 36.791 million in Feb 2006 to 38.489 million in Feb 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 0.726 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1,662 million from 36.821 million in Mar 2006 to 38.483 million in Mar 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 0.711 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.626 million from 36.854 million in Apr 2006 to 38.480 million in Apr 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 0.895 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.571 million from 36.897 million in May 2006 to 38.468 million in May 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 0.894 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.516 million from 36.943 million in Jun 2006 to 38.459 million in Jun 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.301 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.461 million from 36.989 million in Jul 2006 to 38.450 million in Jul 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.458 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.414 million from 37.008 million in Aug 2006 to 38.422 million in Aug 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.291 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.368 million from 37.027 million in Sep 2006 to 38.395 million in Sep 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 0.911 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.320 million from 37.047 million in Oct 2006 to 38.367 million in Oct 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.158 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.283 million from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.359 million in Nov 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.102 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.248 million from 37.100 million in Dec 2006 to 38.348 million in Dec 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.299 million. The hardship does not originate in low growth of population but in underperformance of the economy in the expansion from the business cycle. There are two hardships behind these data. First, young people cannot find employment after finishing high school and college, reducing prospects for achievement in older age. Second, students with more modest means cannot find employment to keep them in college.
Table I-10, US, Employment Level 16-24 Years, Thousands, NSA
| Year | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Annual |
| 2001 | 20529 | 19706 | 19694 | 19675 | 19547 | 20088 |
| 2002 | 20653 | 19466 | 19542 | 19397 | 19394 | 19683 |
| 2003 | 20181 | 18909 | 19139 | 19163 | 19136 | 19351 |
| 2004 | 20660 | 19158 | 19609 | 19615 | 19619 | 19630 |
| 2005 | 20814 | 19503 | 19794 | 19750 | 19733 | 19770 |
| 2006 | 21167 | 19604 | 19853 | 19903 | 20129 | 20041 |
| 2007 | 20413 | 19498 | 19564 | 19660 | 19361 | 19875 |
| 2008 | 20096 | 18818 | 18757 | 18454 | 18378 | 19202 |
| 2009 | 18270 | 16972 | 16671 | 16689 | 16615 | 17601 |
| 2010 | 18061 | 16874 | 16867 | 16946 | 16727 | 17077 |
| 2011 | 18067 | 17238 | 17532 | 17402 | 17234 | 17362 |
| 2012 | 18171 | 17687 | 17842 | 17877 | 17604 | 17834 |
| 2013 | 18636 | 18043 | 17976 | 18104 | 18106 | 18057 |
| 2014 | 18972 | 18104 | 18781 | 18576 | 18347 | 18442 |
| 2015 | 19577 | 18355 | 18654 | 18485 | 18720 | 18756 |
| 2016 | 19876 | 18693 | 18695 | 18801 | 18830 | 18992 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-21 provides US employment level ages 16 to 24 years from 2002 to 2016. Employment level is sharply lower in Sep 2015 relative to the peak in 2007. The following Chart I-21A relates youth employment and youth civilian noninstitutional population.
Chart I-21, US, Employment Level 16-24 Years, Thousands SA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-21A provides the US civilian noninstitutional population ages 16 to 24 years not seasonally adjusted from 2001 to 2016. The civilian noninstitutional population ages 16 to 24 years increased from 37.443 million in Jul 2007 to 38.861 million in Jul 2013 or by 1.418 million while the number of jobs for ages 16 to 24 years fell by 2.230 million from 21.914 million in Jul 2006 to 19.684 million in Jul 2013. The civilian noninstitutional population for ages 16 to 24 years increased from 37.455 million in Aug 2007 to 38.841 million in Aug 2013 or by 1.386 million while the number of youth jobs fell by 1.777 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.467 million in Sep 2007 to 38.822 million in Sep 2013 or by 1.355 million while the number of youth jobs fell by 1.455 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.480 million in Oct 2007 to 38.804 million in Oct 2013 or by 1.324 million while the number of youth jobs decreased 1.877 million from Oct 2006 to Oct 2013. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.798 million in Nov 2013 or by 1.722 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.799 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.518 million in Dec 2007 to 38.790 million in Dec 2013 or by 1.272 million while the number of youth jobs fell 2.023 million from Dec 2006 to Dec 2013. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.488 million from 37.282 million in in Jan 2007 to 38.770 million in Jan 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 2.035 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.464 million from 37.302 in Feb 2007 to 38.766 million in Feb 2014 while the number of youth jobs decreased 2.058 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.437 million from 37.324 million in Mar 2007 to 38.761 million in Mar 2014 while jobs for ages 16 to 24 years decreased 1.599 million from 19.538 million in Mar 2007 to 17.939 million in Mar 2014. The civilian noninstitutional population ages 16 to 24 years increased 1.410 million from 37.349 million in Apr 2007 to 38.759 million in Apr 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.347 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.370 million from 37.379 million in May 2007 to 38.749 million in May 2014 while the number of youth jobs decreased 1.128 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.330 million from 37.410 million in Jun 2007 to 38.740 million in Jun 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.847 million from 21.268 million in Jun 2006 to 19.421 million in Jun 2014. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased by 1.292 million from 37.443 million in Jul 2007 to 38.735 million in Jul 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.632 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.445 million in Aug 2007 to 38.706 million in Aug 2014 or 1.251 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.441 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.652 million from 37.027 million in Sep 2006 to 38.679 million in Sep 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.500 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.047 million in Oct 2006 to 38.650 million in Oct 2014 or 1.603 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.072 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.628 million in Nov 2014 or 1.552 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.327 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.100 million in Dec 2006 to 38.606 million in Dec 2014 or 1.506 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.782 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.971 million from 36.761 million in Jan 2006 to 38.732 million in Jan 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.091 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.914 million from 36.791 million in Feb 2006 to 38.705 million in Feb 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 0.960 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.858 million from 36.821 million in Mar 2006 to 38.679 million in Mar 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.215 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.800 million from 36.854 million in Apr 2006 to 38.654 million in Apr 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.165 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1,733 million from 36.897 million in May 2006 to 38.630 million in May 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.060 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.666 million from 36.943 million in Jun 2006 to 38.609 million in Jun 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.479 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.600 million from 36.989 million in Jul 2006 to 38.589 million in Jul 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.581 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.548 million from 37.008 million in Aug 2006 to 38.556 million in Aug 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.590 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1,498 million from 37.027 million in Sep 2006 to 38.525 million in Sep 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.249 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.444 million from 37.047 million in Oct 2006 to 38.491 million in Oct 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.199 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.392 million from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.468 million in Nov 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.418 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.341 million from 37.100 million in Dec 2006 to 38.441 million in Dec 2015 while the level of youth jobs 1.409 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.734 million from 36.761 million in Jan 2006 to 38.495 million in Jan 2016 while the level of youth jobs fell 0.844 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.698 million from 36.791 million in Feb 2006 to 38.489 million in Feb 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 0.726 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1,662 million from 36.821 million in Mar 2006 to 38.483 million in Mar 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 0.711 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.626 million from 36.854 million in Apr 2006 to 38.480 million in Apr 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 0.895 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.571 million from 36.897 million in May 2006 to 38.468 million in May 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 0.894 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.516 million from 36.943 million in Jun 2006 to 38.459 million in Jun 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.301 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.461 million from 36.989 million in Jul 2006 to 38.450 million in Jul 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.458 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.414 million from 37.008 million in Aug 2006 to 38.422 million in Aug 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.291 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.368 million from 37.027 million in Sep 2006 to 38.395 million in Sep 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 0.911 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.320 million from 37.047 million in Oct 2006 to 38.367 million in Oct 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.158 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.283 million from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.359 million in Nov 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.102 million. . The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.248 million from 37.100 million in Dec 2006 to 38.348 million in Dec 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.299 million. The hardship does not originate in low growth of population but in underperformance of the economy in the expansion from the business cycle. There are two hardships behind these data. First, young people cannot find employment after finishing high school and college, reducing prospects for achievement in older age. Second, students with more modest means cannot find employment to keep them in college.
Chart I-21A, US, Civilian Noninstitutional Population Ages 16 to 24 Years, Thousands NSA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-21B provides the civilian labor force of the US ages 16 to 24 years NSA from 2001 to 2015. The US civilian labor force ages 16 to 24 years fell from 24.339 million in Jul 2007 to 23.506 million in Jul 2013, by 0.833 million or decline of 3.4 percent, while the civilian noninstitutional population NSA increased from 37.443 million in Jul 2007 to 38.861 million in Jul 2013, by 1.418 million or 3.8 percent. The US civilian labor force ages 16 to 24 fell from 22.801 million in Aug 2007 to 22.089 million in Aug 2013, by 0.712 million or 3.1 percent, while the noninstitutional population for ages 16 to 24 years increased from 37.455 million in Aug 2007 to 38.841 million in Aug 2013, by 1.386 million or 3.7 percent. The US civilian labor force ages 16 to 24 years fell from 21.917 million in Sep 2007 to 21.183 million in Sep 2013, by 0.734 million or 3.3 percent while the civilian noninstitutional youth population increased from 37.467 million in Sep 2007 to 38.822 million in Sep 2013 by 1.355 million or 3.6 percent. The US civilian labor force fell from 21.821 million in Oct 2007 to 21.003 million in Oct 2013, by 0.818 million or 3.7 percent while the noninstitutional youth population increased from 37.480 million in Oct 2007 to 38.804 million in Oct 2013, by 1.324 million or 3.5 percent. The US youth civilian labor force fell from 21.909 million in Nov 2007 to 20.825 million in Nov 2013, by 1.084 million or 4.9 percent while the civilian noninstitutional youth population increased from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.798 million in Nov 2013 or by 1.722 million. The US youth civilian labor force fell from 21.684 million in Dec 2007 to 20.642 million in Dec 2013, by 1.042 million or 4.8 percent, while the civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.518 million in Dec 2007 to 38.790 million in Dec 2013, by 1.272 million or 3.4 percent. The youth civilian labor force of the US fell from 21.770 million in Jan 2007 to 20.423 million in Jan 2014, by 1.347 million or 6.2 percent while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 37.282 million in Jan 2007 to 38.770 million in Jan 2014, by 1.488 million or 4.0 percent. The youth civilian labor force of the US fell 1.255 million from 21.645 million in Feb 2007 to 20.390 million in Feb 2014 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.464 million from 37.302 million in Feb 2007 to 38.766 million in Feb 2014. The youth civilian labor force of the US fell 0.693 million from 21.634 million in Mar 2007 to 20.941 million in Mar 2014 or 3.2 person while the youth noninstitutional civilian population 1.437 million from 37.324 million in Mar 2007 to 38.761 million in Mar 2014 or 3.9 percent. The US youth civilian labor force fell 981 thousand from 21.442 million in Apr 2007 to 20.461 million in Apr 2014 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.349 million in Apr 2007 to 38.759 million in Apr 2014 by 1.410 thousand or 3.8 percent. The youth civilian labor force decreased from 21.659 million in May 2007 to 21.160 million in May 2014 by 499 thousand or 2.3 percent while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.370 million from 37.739 million in May 2007 to 38.749 million in May 2007 or by 2.7 percent. The youth civilian labor force decreased from 24.128 million in Jun 2006 to 22.851 million in Jun 2014 by 1.277 million or 5.3 percent while the civilian noninstitutional population increased from 36.943 million in Jun 2006 to 38.740 million in Jun 2014 by 1.797 million or 4.9 percent. The youth civilian labor force fell from 24.664 million in Jul 2006 to 23.437 million in Jul 2014 while the civilian noninstitutional population increased from 36.989 million in Jul 2006 to 38.735 million in Jul 2014. The youth civilian labor force fell 1.818 million from 23.634 million in Aug 2006 to 21.816 million in Aug 2014 while the civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.008 million in Aug 2006 to 38.706 million in Aug 2914 or 1.698 million. The youth civilian labor force fell 0.942 million from 21.901 million in Sep 2006 to 20.959 million in Sep 2014 while the noninstitutional population increased 1.652 million from 37.027 million in Sep 2006 to 38.679 million in Sep 2014. The youth civilian labor force decreased 0.702 million from 22.105 million in Oct 2006 to 21.403 million in Oct 2014 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.047 million in Oct 2006 to 38.650 million in Oct 2014 or 1.603 million. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.111 million from 22.145 million in Nov 2006 to 21.034 million in Nov 2014 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.628 million in Nov 2014 or 1.552 million. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.472 million from 22.136 million in Dec 2006 to 20.664 million in Dec 2014 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.100 million in Dec 2006 to 38.606 million in Dec 2014 or 1.506 million. The youth civilian labor force decreased 0.831 million from 21.368 million in Jan 2006 to 20.555 million in Jan 2015 while the youth noninstitutional population increased from 36.761 million in Jan 2006 to 38.732 million in Jan 2015 or 1.971 million. The youth civilian labor force decreased 0.864 million from 21.615 million in Feb 2006 to 20.751 million in Feb 2015 while the youth noninstitutional population increased 1.914 million from 36.791 million in Feb 2006 to 38.705 million in Feb 2015. The youth civilian labor force decreased 0.907 million from 21.507 million in Mar 2006 to 20.600 million in Mar 2015 while the civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.858 million from 36.821 million in Mar 2006 to 38.679 million in Mar 2015. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.082 million from 21.498 million in Apr 2006 to 20.416 million in Apr 2015 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.800 million from 36.854 million in Apr 2006 to 38.654 million in Apr 2015. The youth civilian labor force decreased 0.681 million from 22.023 million in May 2006 to 21.342 million in May 2015 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1,733 million from 36.897 million in May 2006 to 38.630 million in May 2015. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.202 million from 24.128 million in Jun 2006 to 22.926 million in Jun 2015 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.666 million from 36.943 million in Jun 2006 to 38.609 million in Jun 2015. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.502 million from 24.664 million in Jul 2007 to 23.162 million in Jul 2015 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.600 million from 36.989 million in Jul 2006 to 38.589 million in Jul 2015. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.667 million from 23.634 million in Aug 2006 to 21.967 million in Aug 2015 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.548 million from 37.008 in Aug 2006 to 38.556 million in Aug 2015. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.290 million from 21.901 million in Sep 2006 to 20.611 in Sep 2015 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.498 million from 37.027 million in Sep 2006 to 38.525 million in Sep 2015. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.228 million from 22.105 million in Oct 2006 to 20.877 million in Oct 2015 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.444 million from 37.047 million in Oct 2006 to 38.491 million in Oct 2015. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.513 million from 22.145 million in Nov 2006 to 20.632 million in Nov 2015 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.392 million from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.468 million in Nov 2015. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.301 million from 22.136 million in Dec 2006 to 20.835 million in Dec 2015 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.341 million from 37.100 million in Dec 2006 to 38.441 million in Dec 2015. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.004 million from 21.368 million in Jan 2006 to 20.364 million in Jan 2016 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.734 million from 36.761 million in Jan 2006 to 38.495 million in Jan 2016. The youth civilian labor force decreased 0.930 million from 21.615 million in Feb 2006 to 20.685 million in Feb 2016 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.698 million from 36.791 million in Feb 2006 to 38.489 million in Feb 2016. The youth civilian labor force decreased 0.767 million from 21.507 million in Mar 2006 to 20.740 million in Mar 2016 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.662 million from 36.821 million in Mar 2006 to 38.483 million in Mar 2016. The youth civilian labor force decreased 0.950 million from 21.498 million in Apr 2006 to 20.548 million in Apr 2016 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.626 million from 36.854 million in Apr 2006 to 38.480 million in Apr 2016. The youth civilian labor force decreased 0.921 million from 22.023 million in May 2006 to 21.102 million in May 2016 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.571 million from 36.897 million in May 2006 to 38.468 million in May 2016. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.373 million from 24.128 million in Jun 2006 to 22.755 million in Jun 2016 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.516 million from 36.943 million in Jun 2006 to 38.459 million in Jun 2016. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.560 million from 24.664 million in Jul 2006 to 23.104 million in Jul 2016 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1,461 million from 36.989 million in Jul 2006 to 38.450 million in Jul 2016. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.536 million from 23.634 million in Aug 2006 to 22.098 million in Aug 2016 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.414 million from 37.008 million in Aug 2006 to 38.422 million in Aug 2016. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.082 million from 21.901 million in Sep 2006 to 20.891 million in Sep 2016 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.368 million from 37.027 million in Sep 2006 to 38.395 million in Sep 2016. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.315 million from 22.105 million in Oct 2006 to 20.790 million in Oct 2016 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.320 million from 37.047 million in Oct 2006 to 38.367 million in Oct 2016. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.410 million from 22.145 million in Nov 2006 to 20.735 million in Nov 2016 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.283 million from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.359 million in Nov 2016. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.447 million from 22.136 million in Dec 2006 to 20.689 million in Dec 2016 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.248 million from 37.100 million in Dec 2006 to 38.348 million in Dec 2016. Youth in the US abandoned their participation in the labor force because of the frustration that there are no jobs available for them.
Chart I-21B, US, Civilian Labor Force Ages 16 to 24 Years, Thousands NSA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-21C provides the ratio of labor force to noninstitutional population or labor force participation of ages 16 to 24 years not seasonally adjusted. The US labor force participation rates for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 66.7 in Jul 2006 to 60.5 in Jul 2013 because of the frustration of young people who believe there may not be jobs available for them. The US labor force participation rate of young people fell from 63.9 in Aug 2006 to 56.9 in Aug 2013. The US labor force participation rate of young people fell from 59.1 percent in Sep 2006 to 54.6 percent in Sep 2013. The US labor force participation rate of young people fell from 59.7 percent in Oct 2006 to 54.1 in Oct 2013. The US labor force participation rate of young people fell from 59.7 percent in Nov 2006 to 53.7 percent in Nov 2013. The US labor force participation rate fell from 57.8 in Dec 2007 to 53.2 in Dec 2013. The youth labor force participation rate fell from 58.4 in Jan 2007 to 52.7 in Jan 2014. The US youth labor force participation rate fell from 58.0 percent in Feb 2007 to 52.6 percent in Feb 2013. The labor force participation rate of ages 16 to 24 years fell from 58.0 in Mar 2007 to 54.0 in Mar 2014. The labor force participation rate of ages 16 to 24 years fell from 57.4 in Apr 2007 to 52.8 in Apr 2014. The labor force participation rate of ages 16 to 24 years fell from 57.9 in May 2007 to 54.6 in May 2014. The labor force participation rate of ages 16 to 24 years fell from 65.3 in Jun 2006 to 59.0 in Jun 2014. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 years fell from 66.7 in Jul 2006 to 60.5 in Jul 2014. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 years fell from 63.9 in Aug 2006 to 56.4 in Aug 2014. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 years fell from 59.1 in Sep 2006 to 54.2 in Sep 2014. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 years fell from 59.7 in Oct 2006 to 55.4 in Oct 2014. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 years fell from 59.7 in Nov 2006 to 54.5 in Nov 2014. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 59.7 in Dec 2006 to 53.5 in Dec 2014. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 58.1 in Jan 2006 to 53.1 in Jan 2015. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 58.8 in Feb 2006 to 53.6 in Feb 2015. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 64 fell from 58.4 in Mar 2006 to 53.3 in Mar 2015. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 64 fell from 58.7 in Apr 2005 to 52.8 in Apr 2006. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 64 fell from 59.7 in May 2006 to 55.2 in May 2015. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 64 fell from 65.3 in Jun 2006 to 59.4 in Jun 2015. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 66.7 in Jul 2006 to 60.0 in Jul 2014. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 63.9 in Aug 2006 to 57.0 in Aug 2015. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 59.1 in Sep 2006 to 53.5 in Sep 2015. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 59.7 in Oct 2006 to 54.2 in Oct 2015. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 59.7 in Nov 2006 to 53.6 in Nov 2015. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 59.7 in Dec 2006 to 54.2 in Dec 2015. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 58.1 in Jan 2006 to 52.9 in Jan 2016. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 58.8 in Feb 2006 to 53.7 in Feb 2016. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 58.4 in Mar 2006 to 53.9 in Mar 2016. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 58.3 in Apr 2006 to 53.4 in Apr 2016. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 59.7 in May 2006 to 54.9 in May 2016. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 65.3 in Jun 2006 to 59.2 in Jun 2016. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 66.7 in Jul 2006 to 60.1 in Jul 2016. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 63.9 in Aug 2006 to 57.5 in Aug 2016. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 59.1 in Sep 2006 to 54.2 in Sep 2016. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 59.7 in Oct 2006 to 54.2 in Oct 2016. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 59.7 in Nov 2006 to 54.1 in Nov 2016. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 59.7 in Dec 2006 to 54.0 in Dec 2016. Many young people abandoned searches for employment, dropping from the labor force.
Chart I-21C, US, Labor Force Participation Rate Ages 16 to 24 Years, NSA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
An important measure of the job market is the number of people with jobs relative to population available for work (civilian noninstitutional population) or employment/population ratio. Chart I-21D provides the employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years. The US employment/population ratio NSA for ages 16 to 24 years collapsed from 59.2 in Jul 2006 to 50.7 in Jul 2013. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years dropped from 57.2 in Aug 2006 to 48.0 in Aug 2013. The employment population ratio for ages to 16 to 24 years declined from 52.9 in Sep 2006 to 46.5 in Sep 2013. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 53.6 in Oct 2006 to 46.3 in Oct 2013. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 53.7 in Nov 2007 to 46.7 in Nov 2013. The US employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 51.6 in Dec 2007 to 46.7 in Dec 2013. The US employment population ratio fell from 52.1 in Jan 2007 to 44.8 in Jan 2014. The US employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 52.0 in Feb 2007 to 44.8 in Feb 2014. The US employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 52.3 in Mar 2007 to 46.3 in Mar 2014. The US employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 51.9 in Apr 2007 to 46.5 in Apr 2014. The US employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 52.1 in May 2007 to 47.3 in May 2014. The US employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 57.6 in Jun 2006 to 50.1 in Jun 2014. The US employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 59.2 in Jul 2006 to 50.1 in Jul 2014. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 57.2 in Aug 2006 to 49.0 in Aug 2014. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 52.9 in Sep 2006 to 46.8 in Sep 2014. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 53.6 in Oct 2006 to 48.6 in Oct 2014. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 53.7 in Nov 2006 to 48.1 in Nov 2014. The employment population ration for ages 16 to 24 fell from 54.3 in Dec 2006 to 47.5 in Dec 2014. The employment population ration for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 51.7 in Jan 2006 to 46.2 in Jan 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 52.1 in Feb 2006 to 47.1 in Feb 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 52.4 in Mar 2006 to 46.7 in Mar 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 52.7 in Apr 2006 to 47.2 in Apr 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 53.6 in May 206 to 48.4 in May 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 57.6 in Jun 2006 to 51.3 in Jun 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 59.2 in Jul 2006 to 52.7 in Jul 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 57.2 in Aug 2006 to 50.8 in Aug 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 52.9 in Sep 2006 to 47.6 in Sep 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 53.6 in Oct 2006 to 48.5 in Oct 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 53.7 in Nov 2006 to 48.1 in Nov 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 54.3 in Dec 2006 to 48.7 in Dec 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 51.7 in Jan 2006 to 47.2 in Jan 2016. The employment population ration for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 52.1 in Feb 2006 to 48.0 in Feb 2016. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 52.4 in Mar 2006 to 48.3 in Mar 2016. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 52.7 in Apr 2006 to 48.1 in Apr 2016. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 53.6 in May 2006 to 49.1 in May 2016. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 57.6 in Jun 2006 to 51.9 in Jun 2016. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 59.2 in Jul 2006 to 53.2 in Jul 2016. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 57.2 in Aug 2006 to 51.7 in Aug 2016. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 52.9 in Sep 2006 to 48.7 in Sep 2016. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 53.6 in Oct 2006 to 48.7 in Oct 2016. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 53.7 in Nov 2006 to 49.0 in Nov 2016. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 54.3 in Dec 2006 to 49.1 in Dec 2016. Chart I-21D shows vertical drop during the global recession without recovery.
Chart I-21D, US, Employment Population Ratio Ages 16 to 24 Years, Thousands NSA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Table I-11 provides US unemployment level ages 16 to 24 years. The number unemployed ages 16 to 24 years increased from 2342 thousand in 2007 to 3634 thousand in 2011 or by 1.292 million and 3451 thousand in 2012 or by 1.109 million. The unemployment level ages 16 to 24 years increased from 2342 in 2007 to 3324 thousand in 2013 or by 0.982 million. The unemployment level ages 16 to 24 years increased from 2342 thousand in 2007 to 2853 thousand in 2014 or by 0.511 million. The unemployment level for ages 16 to 24 increased from 2342 thousand in 2007 to 2467 thousand in 2015, decreasing to 2.211 million in 2016. The unemployment level ages 16 to 24 years decreased from 2.007 million in Dec 2006 to 1.859 million in Dec 2016 or decrease by 0.148 million. This situation may persist for many years.
Table I-11, US, Unemployment Level 16-24 Years, NSA, Thousands
| Year | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Annual |
| 2001 | 2775 | 2585 | 2461 | 2301 | 2424 | 2470 | 2412 | 2371 |
| 2002 | 3167 | 3034 | 2688 | 2506 | 2468 | 2570 | 2374 | 2683 |
| 2003 | 3542 | 3200 | 2724 | 2698 | 2522 | 2522 | 2248 | 2746 |
| 2004 | 3191 | 3018 | 2585 | 2493 | 2572 | 2448 | 2294 | 2638 |
| 2005 | 3010 | 2688 | 2519 | 2339 | 2285 | 2369 | 2055 | 2521 |
| 2006 | 2860 | 2750 | 2467 | 2297 | 2252 | 2242 | 2007 | 2353 |
| 2007 | 2883 | 2622 | 2388 | 2419 | 2258 | 2250 | 2323 | 2342 |
| 2008 | 3450 | 3408 | 2990 | 2904 | 2842 | 2833 | 2928 | 2830 |
| 2009 | 4653 | 4387 | 4004 | 3774 | 3789 | 3699 | 3532 | 3760 |
| 2010 | 4481 | 4374 | 3903 | 3604 | 3731 | 3561 | 3352 | 3857 |
| 2011 | 4248 | 4110 | 3820 | 3541 | 3386 | 3287 | 3161 | 3634 |
| 2012 | 4180 | 4011 | 3672 | 3174 | 3285 | 3102 | 3153 | 3451 |
| 2013 | 4198 | 3821 | 3453 | 3139 | 3028 | 2721 | 2536 | 3324 |
| 2014 | 3429 | 3353 | 2844 | 2854 | 2622 | 2458 | 2317 | 2853 |
| 2015 | 3138 | 2829 | 2390 | 2256 | 2223 | 2147 | 2114 | 2467 |
| 2016 | 2789 | 2648 | 2221 | 2126 | 2094 | 1934 | 1859 | 2211 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-22 provides the unemployment level for ages 16 to 24 from 2001 to 2016. The level rose sharply from 2007 to 2010 with tepid improvement into 2012 and deterioration into 2013-2014 with recent marginal improvement in 2015-16 alternating with deterioration.
Chart I-22, US, Unemployment Level 16-24 Years, Thousands SA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Table I-12 provides the rate of unemployment of young peoples in ages 16 to 24 years. The annual rate jumped from 10.5 percent in 2007 to 18.4 percent in 2010, 17.3 percent in 2011 and 16.2 percent in 2012. The rate of youth unemployment fell marginally to 15.5 percent in 2013, declining to 13.4 percent in Dec 2014. During the seasonal peak in Jul, the rate of youth unemployed was 18.1 percent in Jul 2011, 17.1 percent in Jul 2012 and 16.3 percent in Jul 2013 compared with 10.8 percent in Jul 2007. The rate of youth unemployment rose from 11.2 percent in Jul 2006 to 16.3 percent in Jul 2013 and likely higher if adding those who ceased searching for a job in frustration none may be available. The rate of youth unemployment rose from 10.8 in Jul 2007 to 14.3 in Jul 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 9.1 percent in Dec 2006 to 12.3 percent in Dec 2013. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.9 percent in Jan 2007 to 14.9 percent in Jan and Feb 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 9.7 percent in Mar 2007 to 14.3 percent in Mar 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 9.7 percent in Apr 2007 to 11.9 percent in Apr 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.2 percent in May 2007 to 13.4 percent in May 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 12.0 percent in Jun 2007 to 15.0 percent in Jun 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.8 in Jul 2007 to 14.3 in Jul 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.5 in Aug 2007 to 13.0 in Aug 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 11.0 in Sep 2007 to 13.6 in Sep 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.3 in Oct 2007 to 12.2 in Oct 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.3 in Nov 2007 to 11.7 in Nov 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.7 in Dec 2007 to 11.2 in Dec 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.9 in Jan 2007 to 12.9 in Jan 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.3 percent in Feb 2007 to 12.2 percent in Feb 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 9.7 in Mar 2007 to 12.3 in Mar 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 9.7 in Apr 2007 to 10.7 in Apr 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.2 in May 2007 to 12.3 in May 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 11.9 in Jun 2006 to 13.7 in Jun 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.8 in Jul 2007 to 12.2 in Jul 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.5 in Aug 2007 to 10.9 in Aug 2015. The rate of youth unemployment decreased from 11.0 in Sep 2007 to 10.9 in Sep 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.3 in Oct 2007 to 10.6 in Oct 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.3 in Nov 2007 to 10.4 in Nov 2015. The rate of youth unemployment decreased from 10.7 in Dec 2007 to 10.1 in Dec 2015. The rate of youth unemployment decreased from 10.9 in Jan 2007 to 10.8 in Jan 2016. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.3 in Feb 2007 to 10.8 in Feb 2016. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 9.7 in Mar 2007 to 10.4 in Mar 2016. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 9.7 in Apr 2007 to 9.9 in Apr 2016. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.2 in May 2007 to 10.6 in May 2016. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 12.0 in Jun 2007 to 12.3 in Jun 2016. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.8 in Jul 2007 to 11.5 in Jul 2016. The rate of youth unemplopyment fell from 10.5 in Aug 2007 to 10.1 in Aug 2016. The rate of youth unemployment fell from 11.0 in Sep 2007 to 10.2 in Sep 2016. The rate of youth unemployment fell from 10.3 in Oct 2007 to 10.1 in Oct 2016. The rate of youth unemployment fell from 10.3 in Nov 2007 to 9.3 in Nov 2016. The rate of youth unemployment fell from 10.7 in Dec 2007 to 9.0 in Dec 2016. The actual rate is higher because of the difficulty in counting those dropping from the labor force because they believe there are no jobs available for them.
Table I-12, US, Unemployment Rate 16-24 Years, Thousands, NSA
| Year | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Annual |
| 2001 | 10.3 | 10.3 | 10.2 | 9.6 | 10.0 | 11.6 | 10.5 | 10.7 | 10.5 | 11.0 | 11.2 | 11.0 | 10.6 |
| 2002 | 12.9 | 12.5 | 12.9 | 11.6 | 11.6 | 13.2 | 12.4 | 11.5 | 11.4 | 11.2 | 11.7 | 10.9 | 12.0 |
| 2003 | 12.7 | 12.7 | 12.2 | 12.0 | 13.0 | 14.8 | 13.3 | 11.9 | 12.5 | 11.6 | 11.6 | 10.5 | 12.4 |
| 2004 | 12.8 | 12.3 | 12.1 | 11.1 | 12.2 | 13.4 | 12.3 | 11.1 | 11.5 | 11.6 | 11.1 | 10.5 | 11.8 |
| 2005 | 12.4 | 13.0 | 11.7 | 11.2 | 11.9 | 12.6 | 11.0 | 10.8 | 10.7 | 10.3 | 10.7 | 9.4 | 11.3 |
| 2006 | 11.1 | 11.3 | 10.3 | 9.7 | 10.2 | 11.9 | 11.2 | 10.4 | 10.5 | 10.2 | 10.1 | 9.1 | 10.5 |
| 2007 | 10.9 | 10.3 | 9.7 | 9.7 | 10.2 | 12.0 | 10.8 | 10.5 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.3 | 10.7 | 10.5 |
| 2008 | 12.3 | 11.8 | 11.1 | 10.3 | 13.3 | 14.4 | 14.0 | 13.0 | 13.4 | 13.2 | 13.3 | 13.7 | 12.8 |
| 2009 | 15.8 | 16.4 | 16.1 | 15.8 | 18.0 | 19.9 | 18.5 | 18.0 | 18.2 | 18.5 | 18.1 | 17.5 | 17.6 |
| 2010 | 19.8 | 19.2 | 18.4 | 18.5 | 18.4 | 20.0 | 19.1 | 17.8 | 17.6 | 18.1 | 17.4 | 16.7 | 18.4 |
| 2011 | 18.9 | 18.2 | 17.2 | 16.5 | 17.5 | 18.9 | 18.1 | 17.5 | 17.0 | 16.2 | 15.9 | 15.5 | 17.3 |
| 2012 | 16.8 | 17.0 | 16.0 | 15.4 | 16.3 | 18.1 | 17.1 | 16.8 | 15.2 | 15.5 | 14.8 | 15.2 | 16.2 |
| 2013 | 17.6 | 16.7 | 15.9 | 15.1 | 16.4 | 18.0 | 16.3 | 15.6 | 14.8 | 14.4 | 13.1 | 12.3 | 15.5 |
| 2014 | 14.9 | 14.9 | 14.3 | 11.9 | 13.4 | 15.0 | 14.3 | 13.0 | 13.6 | 12.2 | 11.7 | 11.2 | 13.4 |
| 2015 | 12.9 | 12.2 | 12.3 | 10.7 | 12.3 | 13.7 | 12.2 | 10.9 | 10.9 | 10.6 | 10.4 | 10.1 | 11.6 |
| 2016 | 10.8 | 10.8 | 10.4 | 9.9 | 10.6 | 12.3 | 11.5 | 10.1 | 10.2 | 10.1 | 9.3 | 9.0 | 10.4 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-23 provides the BLS estimate of the not-seasonally-adjusted rate of youth unemployment for ages 16 to 24 years from 2001 to 2016. The rate of youth unemployment increased sharply during the global recession of 2008 and 2009 but has failed to drop to earlier lower levels because of low growth of GDP. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E. Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent.
Chart I-23, US, Unemployment Rate 16-24 Years, Percent, NSA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-24 provides longer perspective with the rate of youth unemployment in ages 16 to 24 years from 1948 to 2016. The rate of youth unemployment rose to 20 percent during the contractions of the early 1980s and also during the contraction of the global recession in 2008 and 2009. The data illustrate again the argument in this blog that the contractions of the early 1980s are the valid framework for comparison with the global recession of 2008 and 2009 instead of misleading comparisons with the 1930s. During the initial phase of recovery, the rate of youth unemployment 16 to 24 years NSA fell from 18.9 percent in Jun 1983 to 14.5 percent in Jun 1984. In contrast, the rate of youth unemployment 16 to 24 years was nearly the same during the expansion after IIIQ2009: 17.5 percent in Dec 2009, 16.7 percent in Dec 2010, 15.5 percent in Dec 2011, 15.2 percent in Dec 2012, 17.6 percent in Jan 2013, 16.7 percent in Feb 2013, 15.9 percent in Mar 2013, 15.1 percent in Apr 2013. The rate of youth unemployment was 16.4 percent in May 2013, 18.0 percent in Jun 2013, 16.3 percent in Jul 2013 and 15.6 percent in Aug 2013. In Sep 2006, the rate of youth unemployment was 10.5 percent, increasing to 14.8 percent in Sep 2013. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.3 in Oct 2007, increasing to 14.4 percent in Oct 2013. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.3 percent in Nov 2007, increasing to 13.1 percent in Nov 2013. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.7 percent in Dec 2013, increasing to 12.3 percent in Dec 2013. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.9 percent in Jan 2007, increasing to 14.9 percent in Jan 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.3 percent in Feb 2007, increasing to 14.9 percent in Feb 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 9.7 percent in Mar 2007, increasing to 14.3 percent in Mar 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 9.7 percent in Apr 2007, increasing to 11.9 percent in Apr 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.2 percent in May 2007, increasing to 13.4 percent in May 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 12.0 percent in Jun 2007, increasing to 15.0 percent in Jun 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.8 percent in Jul 2007, increasing to 14.3 percent in Jul 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.5 percent in Aug 2007, increasing to 13.0 percent in Aug 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 11.0 percent in Sep 2007, increasing to 13.6 percent in Sep 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.3 in Oct 2007 to 12.2 in Oct 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.3 percent in Nov 2007 to 11.7 percent in Nov 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.7 in Dec 2007 to 11.2 in Dec 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 9.7 in Mar 2007 to 12.3 in Mar 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 9.7 in Apr 2007 to 10.7 in Apr 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.2 in May 2007 to 12.3 in May 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 12.0 in Jun 2007 to 13.7 in Jun 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.8 in Jul 2007 to 12.2 in Jul 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.5 in Aug 2007 to 10.9 in Aug 2015. The rate of youth unemployment decreased from 11.0 in Sep 2007 to 10.9 in Sep 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.3 in Oct 2007 to 10.6 in Oct 2015, decreasing to 10.4 in Nov 2015. The rate of youth unemployment decreased to 10.1 in Dec 2015. The rate of youth unemployment stood at 10.8 in Jan 2016, 10.8 in Feb 2016, 10.4 in Mar 2016 and 9.9 in Apr 2016. The rate of youth unemployment increased to 10.6 in May 2016 and 12.3 in Jun 2016. The rate of youth unemployment fell to 11.5 in Jul 2016, decreasing to 10.1 in Aug 2016. The rate of youth unemployment increased to 10.2 in Sep 2016, decreasing to 10.1 in Oct 2016 and 9.3 in Nov 2016. The rate of youth unemployment decreased to 90.0 in Dec 2016. The actual rate is higher because of the difficulty in counting those dropping from the labor force because they believe there are no jobs available for them. The difference originates in the vigorous seasonally adjusted annual equivalent average rate of GDP growth of 5.9 percent during the recovery from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 and 4.5 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1989 compared with 2.1 percent on average during the first 28 quarters of expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2016. US economic growth has been at only 2.1 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 29 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2016. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the third estimate of GDP for IIIQ2016 (https://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2016/pdf/gdp3q16_3rd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,745.9 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,355.6 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,745.9/$14,355.6 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1989, 4.5 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1989. 4.5 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1990 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2016 would have accumulated to 29.5 percent. GDP in IIIQ2016 would be $19,414.4 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2687.4 billion than actual $16,727.0 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 24.2 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 14.4 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2017/01/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). US GDP in IIIQ2016 is 13.8 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,727.0 billion in IIIQ2016 or 11.6 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.3 percent. Professor John H. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. Cochrane (2016May02) measures GDP growth in the US at average 3.5 percent per year from 1950 to 2000 and only at 1.76 percent per year from 2000 to 2015 with only at 2.0 percent annual equivalent in the current expansion. Cochrane (2016May02) proposes drastic changes in regulation and legal obstacles to private economic activity. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth of manufacturing at average 3.1 percent per year from Nov 1919 to Nov 2016. Growth at 3.1 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 108.2316 in Dec 2007 to 142.1081 in Nov 2016. The actual index NSA in Nov 2016 is 103.0759, which is 27.5 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.1 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2015. Using trend growth of 2.1 percent per year, the index would increase to 130.3109 in Nov 2016. The output of manufacturing at 103.0759 in Nov 2016 is 20.9 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Chart I-24, US, Unemployment Rate 16-24 Years, Percent NSA, 1948-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
It is more difficult to move to other jobs after a certain age because of fewer available opportunities for mature individuals than for new entrants into the labor force. Middle-aged unemployed are less likely to find another job. Table I-13 provides the unemployment level ages 45 years and over. The number unemployed ages 45 years and over rose from 1.607 million in Oct 2006 to 4.576 million in Oct 2010 or by 184.8 percent. The number of unemployed ages 45 years and over declined to 3.800 million in Oct 2012 that is still higher by 136.5 percent than in Oct 2006. The number unemployed age 45 and over increased from 1.704 million in Nov 2006 to 3.861 million in Nov 2012, or 126.6 percent. The number unemployed age 45 and over is still higher by 98.5 percent at 3.383 million in Nov 2013 than 1.704 million in Nov 2006. The number unemployed age 45 and over jumped from 1.794 million in Dec 2006 to 4.762 million in Dec 2010 or 165.4 percent. At 3.927 million in Dec 2012, mature unemployment is higher by 2.133 million or 118.9 percent higher than 1.794 million in Dec 2006. The level of unemployment of those aged 45 year or more of 3.632 million in Oct 2013 is higher by 2.025 million than 1.607 million in Oct 2006 or higher by 126.0 percent. The number of unemployed 45 years and over increased from 1.794 million in Dec 2006 to 3.378 million in Nov 2013 or 88.3 percent. The annual number of unemployed 45 years and over increased from 1.848 million in 2006 to 3.719 million in 2013 or 101.2 percent. The number of unemployed 45 years and over increased from 2.126 million in Jan 2006 to 4.394 million in Jan 2013, by 2.618 million or 106.7 percent. The number of unemployed 45 years and over rose from 2.126 million in Jan 2006 to 3.508 million in Jan 2014, by 1.382 million or 65.0 percent. The level of unemployed 45 years or older increased 2.051 million or 99.8 percent from 2.056 million in Feb 2006 to 4.107 million in Feb 2013 and at 3.490 million in Feb 2014 is higher by 69.7 percent than in Feb 2006. The number of unemployed 45 years and over increased 2.048 million or 108.9 percent from 1.881 million in Mar 2006 to 3.929 million in Mar 2013 and at 3.394 million in Mar 2014 is higher by 80.4 percent than in Mar 2006. The number of unemployed 45 years and over increased 1.846 million or 100.2 percent from 1.843 million in Apr 2006 to 3.689 million in Apr 2013 and at 3.006 million in Apr 2014 is higher by 1.163 million or 63.1 percent. The number of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 102.1 percent from 1.784 million in May 2006 to 3.605 million in May 2014 and at 2.913 million in May 2014 is higher by 63.3 percent than in May 2007.
The number of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 102.1 percent from 1.805 million in Jun 2007 to 3.648 million in Jun 2013 and at 2.832 million in Jun 2014 is higher by 56.9 percent than in Jun 2007. The number of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 81.5 percent from 2.053 million in Jul 2007 to 3.727 million in Jul 2013 and at 3.083 million in Jul 2014 is higher by 50.2 percent than in Jul 2007. The level unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 84.4 percent from 1.956 million in Aug 2007 to 3.607 million in Aug 2013 and at 3.037 million in Aug 2014 is 55.2 percent higher than in Aug 2007. The level unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 90.7 percent from 1.854 million in Sep 2007 to 3.535 million in Sep 2013 and at 2.640 million in Sep 2014 is 42.4 percent higher than in Sep 2007. The level unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 1.747 million from 1.885 million in Oct 2007 to 3.632 million in Oct 2013 and at 2.606 million in Oct 2014 is 38.2 percent higher than in Oct 2007. The level unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 1.458 million from 1.925 million in Nov 2007 to 3.383 million in Nov 2013 and at 2.829 million in Nov 2014 is 47.0 percent higher than in Nov 2007. The level of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 1.258 million from Dec 2007 to Dec 2013 and at 2.667 million in Dec 2014 is 25.8 higher than in Dec 2007. The level unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 1.353 million from Jan 2007 to Jan 2015 and at 3.077 million in Jan 2015 is 42.8 percent higher than in Jan 2007. The level unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 1.352 million from 2.138 million in Feb 2007 to 3.490 million in Feb 2014 and at 2.991 million in Feb 2015 is 39.9 percent higher than in Feb 2007. The level of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 1.363 million from 2.031 million in Mar 2007 to 3.394 million in Mar 2014 and at 2.724 million in Mar 2015 is 34.1 percent higher than in Mar 2007. The level of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased from 1.871 million in Apr 2007 to 3.006 million in Apr 2014 and at 2.579 million in Apr 2015 is 37.8 higher than in Apr 2007. The level of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased from 1.803 million in May 2007 to 2.913 million in Jun 2014 and at 2.457 million in May 2015 is 36.3 percent higher than in May 2007. The level of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased from 1.805 million in Jun 2007 to 2.832 million in Jun 2014 and at 2.359 million in Jun 2015 is 30.7 percent higher than in Jun 2007. The level of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased from 2.053 million in Jul 2007 to 3.083 million in Jul 2014 and at 2.666 million in Jul 2015 is 30.0 percent higher than in Jul 2007. The level of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased from 1.956 million in Aug 2007 to 3.037 million in Aug 2014 and at 2.693 million in Aug 2015 is 37.7 higher than in Aug 2007. The level of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased from 1.854 million in Sep 2007 to 2.640 million in Sep 2015 and at 2.388 million in Sep 2015 is 28.8 percent higher than in Sep 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 years and over increased from 1.885 million in Oct 2007 to 2.606 million in Oct 2014 and at 2.290 million in Oct 2015 is 21.5 percent higher than in Oct 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 years and over increased from 1.925 million in Nov 2007 to 2.829 million in Nov 2014 and at 2.349 million in Nov 2015 is 22.0 percent higher than in Nov 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 years and over increased from 2.120 million in Dec 2007 to 2.667 million in Dec 2014 and at 2.317 million in Dec 2015 is 9.3 percent higher than in Dec 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 and over increased from 2.155 million in Jan 2007 to 3.077 million in Jan 2015 and at 2.736 million in Jan 2016 is 27.0 percent higher than in Jan 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 and over increased from 2.138 million in Feb 2007 to 2.991 million in Feb 2015 and at 2.744 million in Feb 2016 is 28.3 percent higher than in Feb 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 and over increased from 2.031 million in Mar 2007 to 2.724 million in Mar 2015 and at 2.747 million in Mar 2016 is 35.3 percent higher than in Mar 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 and over increased from 1.871 million in Apr 2007 to 2.579 million in Apr 2015 and at 2.410 million in Apr 2016 is 28.8 percent higher than in Apr 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 and over increased from 1.803 million in May 2007 to 2.457 million in May 2015 and at 2.190 million in May 2016 is 21.5 percent higher than in May 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 and over increased from 1.805 million in Jun 2007 to 2.359 million in Jun 2015 and at 2.345 million in Jun 2016 is 29.9 percent higher than in Jun 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 and over increased from 2.053 million in Jul 2007 to 2.666 million in Jul 2015 and at 2.619 million in Jul 2016 is 27.6 percent higher than in Jul 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 and over increased from 1.956 million in Aug 2007 to 2.693 million in Aug 2015 and at 2.565 million in Aug 2016 is 31.1 percent higher than in Aug 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 and over increased from 1.854 million in Sep 2007 to 2.388 million in Sep 2015 and at 2.414 million in Sep 2016 is 30.2 percent higher than in Sep 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 and over increased from 1.885 million in Oct 2007 to 2.290 million in Oct 2015 and at 2.337 million in Oct 2016 is 24.0 percent higher than in Oct 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 and over increased from 1.925 million in Nov 2007 to 2.349 million in Nov 2015 and at 2.355 million in Nov 2016 is 22.3 percent higher than in Nov 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 and over increased from 2.120 million in Dec 2007 to 2.317 million in Dec 2015 and at 2.360 million in Dec 2016 is 11.3 percent higher than in Dec 2007. The actual number unemployed is likely much higher because many are not accounted who abandoned job searches in frustration there may not be a job for them. Recent improvements may be illusory. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. US economic growth has been at only 2.1 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 29 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2016. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the third estimate of GDP for IIIQ2016 (https://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2016/pdf/gdp3q16_3rd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,745.9 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,355.6 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,745.9/$14,355.6 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1989, 4.5 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1989. 4.5 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1990 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2016 would have accumulated to 29.5 percent. GDP in IIIQ2016 would be $19,414.4 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2687.4 billion than actual $16,727.0 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 24.2 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 14.4 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2017/01/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). US GDP in IIIQ2016 is 13.8 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,727.0 billion in IIIQ2016 or 11.6 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.3 percent. Professor John H. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. Cochrane (2016May02) measures GDP growth in the US at average 3.5 percent per year from 1950 to 2000 and only at 1.76 percent per year from 2000 to 2015 with only at 2.0 percent annual equivalent in the current expansion. Cochrane (2016May02) proposes drastic changes in regulation and legal obstacles to private economic activity. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth of manufacturing at average 3.1 percent per year from Nov 1919 to Nov 2016. Growth at 3.1 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 108.2316 in Dec 2007 to 142.1081 in Nov 2016. The actual index NSA in Nov 2016 is 103.0759, which is 27.5 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.1 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2015. Using trend growth of 2.1 percent per year, the index would increase to 130.3109 in Nov 2016. The output of manufacturing at 103.0759 in Nov 2016 is 20.9 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Table I-13, US, Unemployment Level 45 Years and Over, Thousands NSA
| Year | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Annual |
| 2000 | 1074 | 1163 | 1253 | 1339 | 1254 | 1202 | 1242 | 1217 | 1249 |
| 2001 | 1259 | 1371 | 1539 | 1640 | 1586 | 1722 | 1786 | 1901 | 1576 |
| 2002 | 1999 | 2190 | 2173 | 2114 | 1966 | 1945 | 2013 | 2210 | 2114 |
| 2003 | 2112 | 2212 | 2281 | 2301 | 2157 | 2032 | 2132 | 2130 | 2253 |
| 2004 | 2025 | 2182 | 2116 | 2082 | 1951 | 1931 | 2053 | 2086 | 2149 |
| 2005 | 1844 | 1868 | 2119 | 1895 | 1992 | 1875 | 1920 | 1963 | 2009 |
| 2006 | 1784 | 1813 | 1985 | 1869 | 1710 | 1607 | 1704 | 1794 | 1848 |
| 2007 | 1803 | 1805 | 2053 | 1956 | 1854 | 1885 | 1925 | 2120 | 1966 |
| 2008 | 2095 | 2211 | 2492 | 2695 | 2595 | 2728 | 3078 | 3485 | 2540 |
| 2009 | 4175 | 4505 | 4757 | 4683 | 4560 | 4492 | 4655 | 4960 | 4500 |
| 2010 | 4565 | 4564 | 4821 | 5128 | 4640 | 4576 | 4909 | 4762 | 4879 |
| 2011 | 4356 | 4559 | 4772 | 4592 | 4426 | 4375 | 4195 | 4182 | 4537 |
| 2012 | 4083 | 4084 | 4405 | 4179 | 3899 | 3800 | 3861 | 3927 | 4133 |
| 2013 | 3605 | 3648 | 3727 | 3607 | 3535 | 3632 | 3383 | 3378 | 3719 |
| 2014 | 2913 | 2832 | 3083 | 3037 | 2640 | 2606 | 2829 | 2667 | 3000 |
| 2015 | 2457 | 2359 | 2666 | 2693 | 2388 | 2290 | 2349 | 2317 | 2574 |
| 2016 | 2190 | 2345 | 2619 | 2565 | 2414 | 2337 | 2355 | 2360 | 2485 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-25 provides the level unemployed ages 45 years and over. There was an increase in the recessions of the 1980s, 1991 and 2001 followed by declines to earlier levels. The current expansion of the economy after IIIQ2009 has not been sufficiently vigorous to reduce significantly middle-age unemployment. Recent improvements could be illusory because many abandoned job searches in frustration that there may not be jobs for them and are not counted as unemployed.
Chart I-25, US, Unemployment Level Ages 45 Years and Over, Thousands, NSA, 1976-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017.

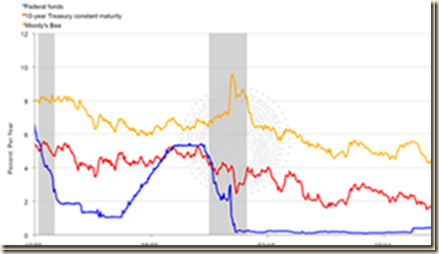





















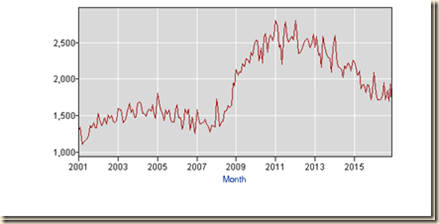

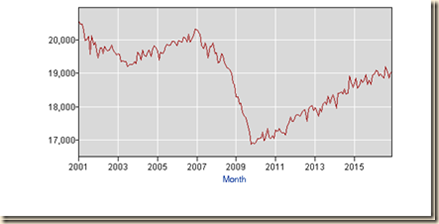



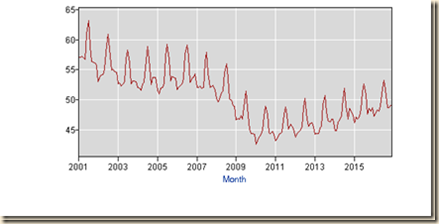



No comments:
Post a Comment