Twenty Four Million Unemployed or Underemployed, Job Creation, Stagnating Real Wages, United States Commercial Banks Assets and Liabilities, Unresolved US Balance of Payments Deficits and Fiscal Imbalance Threatening Risk Premium on Treasury Securities, World Cyclical Slow Growth and Global Recession Risk
Carlos M. Pelaez
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017
I Twenty Four Million Unemployed or Underemployed
IA1 Summary of the Employment Situation
IA2 Number of People in Job Stress
IA3 Long-term and Cyclical Comparison of Employment
IA4 Job Creation
IB Stagnating Real Wages
IIA United States Commercial Banks Assets and Liabilities
IA Transmission of Monetary Policy
IB Functions of Banking
IC United States Commercial Banks Assets and Liabilities
ID Theory and Reality of Economic History, Cyclical Slow Growth Not Secular Stagnation and Monetary Policy Based on Fear of Deflation
II Unresolved US Balance of Payments Deficits and Fiscal Imbalance Threatening Risk Premium on Treasury Securities
III World Financial Turbulence
IIIA Financial Risks
IIIE Appendix Euro Zone Survival Risk
IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation
IV Global Inflation
V World Economic Slowdown
VA United States
VB Japan
VC China
VD Euro Area
VE Germany
VF France
VG Italy
VH United Kingdom
VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets
VII Economic Indicators
VIII Interest Rates
IX Conclusion
References
Appendixes
Appendix I The Great Inflation
IIIB Appendix on Safe Haven Currencies
IIIC Appendix on Fiscal Compact
IIID Appendix on European Central Bank Large Scale Lender of Last Resort
IIIG Appendix on Deficit Financing of Growth and the Debt Crisis
IIIGA Monetary Policy with Deficit Financing of Economic Growth
IIIGB Adjustment during the Debt Crisis of the 1980s
Executive Summary
Contents of Executive Summary
ESI Financial “Irrational Exuberance,” Increasing Interest Rate and Exchange Rate Risk, Duration Dumping, Competitive Devaluations, Steepening Yield Curve and Global Financial and Economic Risk
ESII Valuations of Risk Financial Assets
ESIII Twenty-three Million Unemployed or Underemployed
ESIV Job Creation
ESV Stagnating Real Wages
ESVI United States Commercial Banks
ESVII Unresolved US Balance of Payments Deficits and Fiscal Imbalance
ESI “Financial “Irrational Exuberance,” Increasing Interest Rate and Exchange Rate Risk, Duration Dumping, Competitive Devaluations, Steepening Yield Curve and Global Financial and Economic Risk. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) provides an international safety net for prevention and resolution of international financial crises. The IMF’s Financial Sector Assessment Program (FSAP) provides analysis of the economic and financial sectors of countries (see Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), 101-62, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008), 114-23). Relating economic and financial sectors is a challenging task for both theory and measurement. The IMF provides surveillance of the world economy with its Global Economic Outlook (WEO) (http://www.imf.org/external/ns/cs.aspx?id=29), of the world financial system with its Global Financial Stability Report (GFSR) (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/gfsr/index.htm) and of fiscal affairs with the Fiscal Monitor (http://www.imf.org/external/ns/cs.aspx?id=262). There appears to be a moment of transition in global economic and financial variables that may prove of difficult analysis and measurement. It is useful to consider a summary of global economic and financial risks, which are analyzed in detail in the comments of this blog in Section VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets, Table VI-4.
Economic risks include the following:
- China’s Economic Growth. The National People’s Congress of China in Mar 2016 is reducing the GDP growth target to the range of 6.5 percent to 7.0 percent in guiding stable market expectations (http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/photo/2016-03/05/c_135157171.htm). President Xi Jinping announced on Nov 3, 2015 that “For China to double 2010 GDP and the per capita income of both urban and rural residents by 2010, annual growth for the 2016-2020 period must be at least 6.5 percent,” as quoted by Xinhuanet (http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2015-11/03/c_134780377.htm). China lowered the growth target to approximately 7.0 percent in 2015, as analyzed by Xiang Bo, writing on “China lowers 2015 economic growth target to around 7 percent,” published on Xinhuanet on Mar 5, 2015 (http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/2015-03/05/c_134039341.htm). China had lowered its growth target to 7.5 percent per year. Lu Hui, writing on “China lowers GDP target to achieve quality economic growth, on Mar 12, 2012, published in Beijing by Xinhuanet (http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/china/2012-03/12/c_131461668.htm), informs that Premier Jiabao wrote in a government work report that the GDP growth target will be lowered to 7.5 percent to enhance the quality and level of development of China over the long term. The Third Plenary Session of the 18th Central Committee of the Communist Party of China adopted unanimously on Nov 15, 2013, a new round of reforms with 300 measures (Xinhuanet, “China details reform decision-making process,” Nov 19, 2013 http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/china/2013-11/19/c_125722517.htm). Growth rates of GDP of China in a quarter relative to the same quarter a year earlier have been declining from 2011 to 2016. China’s GDP grew 1.9 percent in IQ2012, annualizing to 7.8 percent, and 8.1 percent relative to a year earlier. The GDP of China grew at 2.2 percent in IIQ2012, which annualizes to 9.1 percent, and 7.6 percent relative to a year earlier. China grew at 1.8 percent in IIIQ2012, which annualizes at 7.4 percent, and 7.5 percent relative to a year earlier. In IVQ2012, China grew at 1.9 percent, which annualizes at 7.8 percent, and 8.1 percent in IVQ2012 relative to IVQ2011. In IQ2013, China grew at 1.9 percent, which annualizes at 7.8 percent, and 7.9 percent relative to a year earlier. In IIQ2013, China grew at 1.7 percent, which annualizes at 7.0 percent, and 7.6 percent relative to a year earlier. China grew at 2.1 percent in IIIQ2013, which annualizes at 8.7 percent, and increased 7.9 percent relative to a year earlier. China grew at 1.6 percent in IVQ2013, which annualized to 6.6 percent, and 7.7 percent relative to a year earlier. China’s GDP grew 1.7 percent in IQ2014, which annualizes to 7.0 percent, and 7.4 percent relative to a year earlier. China’s GDP grew 1.8 percent in IIQ2014, which annualizes at 7.4 percent, and 7.5 percent relative to a year earlier. China’s GDP grew 1.8 percent in IIIQ2014, which is equivalent to 7.4 percent in a year, and 7.1 percent relative to a year earlier. The GDP of China grew 1.8 percent in IVQ2014, which annualizes at 7.4 percent, and 7.2 percent relative to a year earlier. The GDP of China grew at 1.6 percent in IQ2015, which annualizes at 6.6 percent, and 7.0 percent relative to a year earlier. The GDP of China grew 1.9 percent in IIQ2015, which annualizes at 7.8 percent, and increased 7.0 percent relative to a year earlier. In IIIQ2015, China’s GDP grew at 1.7 percent, which annualizes at 7.0 percent, and increased 6.9 percent relative to a year earlier. The GDP of China grew at 1.6 percent in IVQ2015, which annualizes at 6.6 percent, and increased 6.8 percent relative to a year earlier. The GDP of China grew 1.2 percent in IQ2016, which annualizes at 4.9 percent, and increased 6.7 percent relative to a year earlier. In IIQ2016, the GDP of China increased 1.9 percent, which annualizes to 7.8 percent, and increased 6.7 percent relative to a year earlier. The GDP of China increased at 1.8 percent in IIIQ2016, which annualizes at 7.4 percent, and increased 6.7 percent relative to a year earlier. There is decennial change in leadership in China (http://www.xinhuanet.com/english/special/18cpcnc/index.htm). (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/the-case-for-increase-in-federal-funds.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/unresolved-us-balance-of-payments.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/imf-view-of-world-economy-and-finance.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/uncertainty-of-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/valuation-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/imf-view-of-world-economy-and-finance.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/imf-view-of-economy-and-finance-united.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/01/competitive-currency-conflicts-world.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/10/financial-oscillations-world-inflation.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/financial-irrational-exuberance.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/04/imf-view-world-inflation-waves-squeeze.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/01/capital-flows-exchange-rates-and.html). There is also ongoing political development in China during a decennial political reorganization with new leadership (http://www.xinhuanet.com/english/special/18cpcnc/index.htm). Xinhuanet informs that Premier Wen Jiabao considers the need for macroeconomic stimulus, arguing that “we should continue to implement proactive fiscal policy and a prudent monetary policy, while giving more priority to maintaining growth” (http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/china/2012-05/20/c_131599662.htm). Premier Wen elaborates that “the country should properly handle the relationship between maintaining growth, adjusting economic structures and managing inflationary expectations” (http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/china/2012-05/20/c_131599662.htm). Bob Davis, writing on “At China’s NPC, Proposed Changes,” on Mar 5, 2014, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702304732804579420743344553328?KEYWORDS=%22china%22&mg=reno64-wsj), analyzes the wide ranging policy changes in the annual work report by Prime Minister Li Keqiang to China’s NPC (National People’s Congress of the People’s Republic of China http://www.npc.gov.cn/englishnpc/news/). There are about sixty different fiscal and regulatory measures.
- United States Economic Growth, Labor Markets and Budget/Debt Quagmire. The US is growing slowly with 24.2 million in job stress, fewer 10 million full-time jobs, high youth unemployment, historically low hiring and declining/stagnating real wages. Actual GDP is about two trillion dollars lower than trend GDP.
- Economic Growth and Labor Markets in Advanced Economies. Advanced economies are growing slowly. There is still high unemployment in advanced economies.
- World Inflation Waves. Inflation continues in repetitive waves globally (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/of-course-economic-outlook-is-highly.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/interest-rate-increase-could-well.html). There is growing concern on capital outflows and currency depreciation of emerging markets.
A list of financial uncertainties includes:
- Euro Area Survival Risk. The resilience of the euro to fiscal and financial doubts on larger member countries is still an unknown risk. There are complex economic, financial and political effects of the withdrawal of the UK from the European Union or BREXIT after the referendum on Jun 23, 2016 (https://next.ft.com/eu-referendum for extensive coverage by the Financial Times).
- Competitive Devaluations. Exchange rate struggles continue as zero interest rates and negative interest rates in advanced economies induce devaluation of their currencies with alternating episodes of revaluation. The dollar is revaluing sharply.
- Valuation and Volatility of Risk Financial Assets. Valuations of risk financial assets have reached extremely high levels in markets with oscillating volumes. The President of the European Central Bank (ECB), Mario Draghi, warned on Jun 3, 2015 that (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pressconf/2015/html/is150603.en.html):
“But certainly one lesson is that we should get used to periods of higher volatility. At very low levels of interest rates, asset prices tend to show higher volatility…the Governing Council was unanimous in its assessment that we should look through these developments and maintain a steady monetary policy stance.”
- Duration Trap of the Zero Bound. The yield of the US 10-year Treasury rose from 2.031 percent on Mar 9, 2012, to 2.294 percent on Mar 16, 2012. Considering a 10-year Treasury with coupon of 2.625 percent and maturity in exactly 10 years, the price would fall from 105.3512 corresponding to yield of 2.031 percent to 102.9428 corresponding to yield of 2.294 percent, for loss in a week of 2.3 percent but far more in a position with leverage of 10:1. Min Zeng, writing on “Treasurys fall, ending brutal quarter,” published on Mar 30, 2012, in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052702303816504577313400029412564.html?mod=WSJ_hps_sections_markets), informs that Treasury bonds maturing in more than 20 years lost 5.52 percent in the first quarter of 2012.
- Credibility and Commitment of Central Bank Policy. There is a credibility issue of the commitment of monetary policy (Sargent and Silber 2012Mar20)
- Carry Trades. Commodity prices driven by zero interest rates have resumed their increasing path with fluctuations caused by intermittent risk aversion mixed with reallocations of portfolios of risk financial
There are collateral effects of unconventional monetary policy. Chart VIII-1 of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System provides the rate on the overnight fed funds rate and the yields of the 10-year constant maturity Treasury and the Baa seasoned corporate bond. Table VIII-3 provides the data for selected points in Chart VIII-1. There are two important economic and financial events, illustrating the ease of inducing carry trade with extremely low interest rates and the resulting financial crash and recession of abandoning extremely low interest rates.
- The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) lowered the target of the fed funds rate from 7.03 percent on Jul 3, 2000, to 1.00 percent on Jun 22, 2004, in pursuit of non-existing deflation (Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), 18-28, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 83-85). Central bank commitment to maintain the fed funds rate at 1.00 percent induced adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMS) linked to the fed funds rate. Lowering the interest rate near the zero bound in 2003-2004 caused the illusion of permanent increases in wealth or net worth in the balance sheets of borrowers and also of lending institutions, securitized banking and every financial institution and investor in the world. The discipline of calculating risks and returns was seriously impaired. The objective of monetary policy was to encourage borrowing, consumption and investment. The exaggerated stimulus resulted in a financial crisis of major proportions as the securitization that had worked for a long period was shocked with policy-induced excessive risk, imprudent credit, high leverage and low liquidity by the incentive to finance everything overnight at interest rates close to zero, from adjustable rate mortgages (ARMS) to asset-backed commercial paper of structured investment vehicles (SIV). The consequences of inflating liquidity and net worth of borrowers were a global hunt for yields to protect own investments and money under management from the zero interest rates and unattractive long-term yields of Treasuries and other securities. Monetary policy distorted the calculations of risks and returns by households, business and government by providing central bank cheap money. Short-term zero interest rates encourage financing of everything with short-dated funds, explaining the SIVs created off-balance sheet to issue short-term commercial paper with the objective of purchasing default-prone mortgages that were financed in overnight or short-dated sale and repurchase agreements (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession, 50-1, Regulation of Banks and Finance, 59-60, Globalization and the State Vol. I, 89-92, Globalization and the State Vol. II, 198-9, Government Intervention in Globalization, 62-3, International Financial Architecture, 144-9). ARMS were created to lower monthly mortgage payments by benefitting from lower short-dated reference rates. Financial institutions economized in liquidity that was penalized with near zero interest rates. There was no perception of risk because the monetary authority guaranteed a minimum or floor price of all assets by maintaining low interest rates forever or equivalent to writing an illusory put option on wealth. Subprime mortgages were part of the put on wealth by an illusory put on house prices. The housing subsidy of $221 billion per year created the impression of ever-increasing house prices. The suspension of auctions of 30-year Treasuries was designed to increase demand for mortgage-backed securities, lowering their yield, which was equivalent to lowering the costs of housing finance and refinancing. Fannie and Freddie purchased or guaranteed $1.6 trillion of nonprime mortgages and worked with leverage of 75:1 under Congress-provided charters and lax oversight. The combination of these policies resulted in high risks because of the put option on wealth by near zero interest rates, excessive leverage because of cheap rates, low liquidity by the penalty in the form of low interest rates and unsound credit decisions. The put option on wealth by monetary policy created the illusion that nothing could ever go wrong, causing the credit/dollar crisis and global recession (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession, 157-66, Regulation of Banks, and Finance, 217-27, International Financial Architecture, 15-18, The Global Recession Risk, 221-5, Globalization and the State Vol. II, 197-213, Government Intervention in Globalization, 182-4). The FOMC implemented increments of 25 basis points of the fed funds target from Jun 2004 to Jun 2006, raising the fed funds rate to 5.25 percent on Jul 3, 2006, as shown in Chart VIII-1. The gradual exit from the first round of unconventional monetary policy from 1.00 percent in Jun 2004 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/boarddocs/press/monetary/2004/20040630/default.htm) to 5.25 percent in Jun 2006 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20060629a.htm) caused the financial crisis and global recession.
- On Dec 16, 2008, the policy determining committee of the Fed decided (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20081216b.htm): “The Federal Open Market Committee decided today to establish a target range for the federal funds rate of 0 to 1/4 percent.” Policymakers emphasize frequently that there are tools to exit unconventional monetary policy at the right time. At the confirmation hearing on nomination for Chair of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Vice Chair Yellen (2013Nov14 http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20131114a.htm), states that: “The Federal Reserve is using its monetary policy tools to promote a more robust recovery. A strong recovery will ultimately enable the Fed to reduce its monetary accommodation and reliance on unconventional policy tools such as asset purchases. I believe that supporting the recovery today is the surest path to returning to a more normal approach to monetary policy.” Perception of withdrawal of $2671 billion, or $2.7 trillion, of bank reserves (http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h41/current/h41.htm#h41tab1), would cause Himalayan increase in interest rates that would provoke another recession. There is no painless gradual or sudden exit from zero interest rates because reversal of exposures created on the commitment of zero interest rates forever.
In his classic restatement of the Keynesian demand function in terms of “liquidity preference as behavior toward risk,” James Tobin (http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/economic-sciences/laureates/1981/tobin-bio.html) identifies the risks of low interest rates in terms of portfolio allocation (Tobin 1958, 86):
“The assumption that investors expect on balance no change in the rate of interest has been adopted for the theoretical reasons explained in section 2.6 rather than for reasons of realism. Clearly investors do form expectations of changes in interest rates and differ from each other in their expectations. For the purposes of dynamic theory and of analysis of specific market situations, the theories of sections 2 and 3 are complementary rather than competitive. The formal apparatus of section 3 will serve just as well for a non-zero expected capital gain or loss as for a zero expected value of g. Stickiness of interest rate expectations would mean that the expected value of g is a function of the rate of interest r, going down when r goes down and rising when r goes up. In addition to the rotation of the opportunity locus due to a change in r itself, there would be a further rotation in the same direction due to the accompanying change in the expected capital gain or loss. At low interest rates expectation of capital loss may push the opportunity locus into the negative quadrant, so that the optimal position is clearly no consols, all cash. At the other extreme, expectation of capital gain at high interest rates would increase sharply the slope of the opportunity locus and the frequency of no cash, all consols positions, like that of Figure 3.3. The stickier the investor's expectations, the more sensitive his demand for cash will be to changes in the rate of interest (emphasis added).”
Tobin (1969) provides more elegant, complete analysis of portfolio allocation in a general equilibrium model. The major point is equally clear in a portfolio consisting of only cash balances and a perpetuity or consol. Let g be the capital gain, r the rate of interest on the consol and re the expected rate of interest. The rates are expressed as proportions. The price of the consol is the inverse of the interest rate, (1+re). Thus, g = [(r/re) – 1]. The critical analysis of Tobin is that at extremely low interest rates there is only expectation of interest rate increases, that is, dre>0, such that there is expectation of capital losses on the consol, dg<0. Investors move into positions combining only cash and no consols. Valuations of risk financial assets would collapse in reversal of long positions in carry trades with short exposures in a flight to cash. There is no exit from a central bank created liquidity trap without risks of financial crash and another global recession. The net worth of the economy depends on interest rates. In theory, “income is generally defined as the amount a consumer unit could consume (or believe that it could) while maintaining its wealth intact” (Friedman 1957, 10). Income, Y, is a flow that is obtained by applying a rate of return, r, to a stock of wealth, W, or Y = rW (Friedman 1957). According to a subsequent statement: “The basic idea is simply that individuals live for many years and that therefore the appropriate constraint for consumption is the long-run expected yield from wealth r*W. This yield was named permanent income: Y* = r*W” (Darby 1974, 229), where * denotes permanent. The simplified relation of income and wealth can be restated as:
W = Y/r (1)
Equation (1) shows that as r goes to zero, r→0, W grows without bound, W→∞. Unconventional monetary policy lowers interest rates to increase the present value of cash flows derived from projects of firms, creating the impression of long-term increase in net worth. An attempt to reverse unconventional monetary policy necessarily causes increases in interest rates, creating the opposite perception of declining net worth. As r→∞, W = Y/r →0. There is no exit from unconventional monetary policy without increasing interest rates with resulting pain of financial crisis and adverse effects on production, investment and employment.
Dan Strumpf and Pedro Nicolaci da Costa, writing on “Fed’s Yellen: Stock Valuations ‘Generally are Quite High,’” on May 6, 2015, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/feds-yellen-cites-progress-on-bank-regulation-1430918155?tesla=y ), quote Chair Yellen at open conversation with Christine Lagarde, Managing Director of the IMF, finding “equity-market valuations” as “quite high” with “potential dangers” in bond valuations. The DJIA fell 0.5 percent on May 6, 2015, after the comments and then increased 0.5 percent on May 7, 2015 and 1.5 percent on May 8, 2015.
| Fri May 1 | Mon 4 | Tue 5 | Wed 6 | Thu 7 | Fri 8 |
| DJIA 18024.06 -0.3% 1.0% | 18070.40 0.3% 0.3% | 17928.20 -0.5% -0.8% | 17841.98 -1.0% -0.5% | 17924.06 -0.6% 0.5% | 18191.11 0.9% 1.5% |
There are two approaches in theory considered by Bordo (2012Nov20) and Bordo and Lane (2013). The first approach is in the classical works of Milton Friedman and Anna Jacobson Schwartz (1963a, 1987) and Karl Brunner and Allan H. Meltzer (1973). There is a similar approach in Tobin (1969). Friedman and Schwartz (1963a, 66) trace the effects of expansionary monetary policy into increasing initially financial asset prices: “It seems plausible that both nonbank and bank holders of redundant balances will turn first to securities comparable to those they have sold, say, fixed-interest coupon, low-risk obligations. But as they seek to purchase these they will tend to bid up the prices of those issues. Hence they, and also other holders not involved in the initial central bank open-market transactions, will look farther afield: the banks, to their loans; the nonbank holders, to other categories of securities-higher risk fixed-coupon obligations, equities, real property, and so forth.”
The second approach is by the Austrian School arguing that increases in asset prices can become bubbles if monetary policy allows their financing with bank credit. Professor Michael D. Bordo provides clear thought and empirical evidence on the role of “expansionary monetary policy” in inflating asset prices (Bordo2012Nov20, Bordo and Lane 2013). Bordo and Lane (2013) provide revealing narrative of historical episodes of expansionary monetary policy. Bordo and Lane (2013) conclude that policies of depressing interest rates below the target rate or growth of money above the target influences higher asset prices, using a panel of 18 OECD countries from 1920 to 2011. Bordo (2012Nov20) concludes: “that expansionary money is a significant trigger” and “central banks should follow stable monetary policies…based on well understood and credible monetary rules.” Taylor (2007, 2009) explains the housing boom and financial crisis in terms of expansionary monetary policy. Professor Martin Feldstein (2016), at Harvard University, writing on “A Federal Reserve oblivious to its effects on financial markets,” on Jan 13, 2016, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/a-federal-reserve-oblivious-to-its-effect-on-financial-markets-1452729166), analyzes how unconventional monetary policy drove values of risk financial assets to high levels. Quantitative easing and zero interest rates distorted calculation of risks with resulting vulnerabilities in financial markets.
Another hurdle of exit from zero interest rates is “competitive easing” that Professor Raghuram Rajan, governor of the Reserve Bank of India, characterizes as disguised “competitive devaluation” (http://www.centralbanking.com/central-banking-journal/interview/2358995/raghuram-rajan-on-the-dangers-of-asset-prices-policy-spillovers-and-finance-in-india). The fed has been considering increasing interest rates. The European Central Bank (ECB) announced, on Mar 5, 2015, the beginning on Mar 9, 2015 of its quantitative easing program denominated as Public Sector Purchase Program (PSPP), consisting of “combined monthly purchases of EUR 60 bn [billion] in public and private sector securities” (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/mopo/liq/html/pspp.en.html). Expectation of increasing interest rates in the US together with euro rates close to zero or negative cause revaluation of the dollar (or devaluation of the euro and of most currencies worldwide). US corporations suffer currency translation losses of their foreign transactions and investments (http://www.fasb.org/jsp/FASB/Pronouncement_C/SummaryPage&cid=900000010318) while the US becomes less competitive in world trade (Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. I (2008a), Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c)). The DJIA fell 1.5 percent on Mar 6, 2015 and the dollar revalued 2.2 percent from Mar 5 to Mar 6, 2015. The euro has devalued 51.0 percent relative to the dollar from the high on Jul 15, 2008 to Jan 6, 2017.
| Fri 27 Feb | Mon 3/2 | Tue 3/3 | Wed 3/4 | Thu 3/5 | Fri 3/6 |
| USD/ EUR 1.1197 1.6% 0.0% | 1.1185 0.1% 0.1% | 1.1176 0.2% 0.1% | 1.1081 1.0% 0.9% | 1.1030 1.5% 0.5% | 1.0843 3.2% 1.7% |
Chair Yellen explained the removal of the word “patience” from the advanced guidance at the press conference following the FOMC meeting on Mar 18, 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20150318.pdf):
“In other words, just because we removed the word “patient” from the statement doesn’t mean we are going to be impatient. Moreover, even after the initial increase in the target funds rate, our policy is likely to remain highly accommodative to support continued progress toward our objectives of maximum employment and 2 percent inflation.”
Exchange rate volatility is increasing in response of “impatience” in financial markets with monetary policy guidance and measures:
| Fri Mar 6 | Mon 9 | Tue 10 | Wed 11 | Thu 12 | Fri 13 |
| USD/ EUR 1.0843 3.2% 1.7% | 1.0853 -0.1% -0.1% | 1.0700 1.3% 1.4% | 1.0548 2.7% 1.4% | 1.0637 1.9% -0.8% | 1.0497 3.2% 1.3% |
| Fri Mar 13 | Mon 16 | Tue 17 | Wed 18 | Thu 19 | Fri 20 |
| USD/ EUR 1.0497 3.2% 1.3% | 1.0570 -0.7% -0.7% | 1.0598 -1.0% -0.3% | 1.0864 -3.5% -2.5% | 1.0661 -1.6% 1.9% | 1.0821 -3.1% -1.5% |
| Fri Apr 24 | Mon 27 | Tue 28 | Wed 29 | Thu 30 | May Fri 1 |
| USD/ EUR 1.0874 -0.6% -0.4% | 1.0891 -0.2% -0.2% | 1.0983 -1.0% -0.8% | 1.1130 -2.4% -1.3% | 1.1223 -3.2% -0.8% | 1.1199 -3.0% 0.2% |
In a speech at Brown University on May 22, 2015, Chair Yellen stated (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20150522a.htm):
“For this reason, if the economy continues to improve as I expect, I think it will be appropriate at some point this year to take the initial step to raise the federal funds rate target and begin the process of normalizing monetary policy. To support taking this step, however, I will need to see continued improvement in labor market conditions, and I will need to be reasonably confident that inflation will move back to 2 percent over the medium term. After we begin raising the federal funds rate, I anticipate that the pace of normalization is likely to be gradual. The various headwinds that are still restraining the economy, as I said, will likely take some time to fully abate, and the pace of that improvement is highly uncertain.”
The US dollar appreciated 3.8 percent relative to the euro in the week of May 22, 2015:
| Fri May 15 | Mon 18 | Tue 19 | Wed 20 | Thu 21 | Fri 22 |
| USD/ EUR 1.1449 -2.2% -0.3% | 1.1317 1.2% 1.2% | 1.1150 2.6% 1.5% | 1.1096 3.1% 0.5% | 1.1113 2.9% -0.2% | 1.1015 3.8% 0.9% |
The Managing Director of the International Monetary Fund (IMF), Christine Lagarde, warned on Jun 4, 2015, that: (http://blog-imfdirect.imf.org/2015/06/04/u-s-economy-returning-to-growth-but-pockets-of-vulnerability/):
“The Fed’s first rate increase in almost 9 years is being carefully prepared and telegraphed. Nevertheless, regardless of the timing, higher US policy rates could still result in significant market volatility with financial stability consequences that go well beyond US borders. I weighing these risks, we think there is a case for waiting to raise rates until there are more tangible signs of wage or price inflation than are currently evident. Even after the first rate increase, a gradual rise in the federal fund rates will likely be appropriate.”
The President of the European Central Bank (ECB), Mario Draghi, warned on Jun 3, 2015 that (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pressconf/2015/html/is150603.en.html):
“But certainly one lesson is that we should get used to periods of higher volatility. At very low levels of interest rates, asset prices tend to show higher volatility…the Governing Council was unanimous in its assessment that we should look through these developments and maintain a steady monetary policy stance.”
The Chair of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Janet L. Yellen, stated on Jul 10, 2015 that (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20150710a.htm):
“Based on my outlook, I expect that it will be appropriate at some point later this year to take the first step to raise the federal funds rate and thus begin normalizing monetary policy. But I want to emphasize that the course of the economy and inflation remains highly uncertain, and unanticipated developments could delay or accelerate this first step. I currently anticipate that the appropriate pace of normalization will be gradual, and that monetary policy will need to be highly supportive of economic activity for quite some time. The projections of most of my FOMC colleagues indicate that they have similar expectations for the likely path of the federal funds rate. But, again, both the course of the economy and inflation are uncertain. If progress toward our employment and inflation goals is more rapid than expected, it may be appropriate to remove monetary policy accommodation more quickly. However, if progress toward our goals is slower than anticipated, then the Committee may move more slowly in normalizing policy.”
There is essentially the same view in the Testimony of Chair Yellen in delivering the Semiannual Monetary Policy Report to the Congress on Jul 15, 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20150715a.htm).
At the press conference after the meeting of the FOMC on Sep 17, 2015, Chair Yellen states (http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20150917.pdf 4):
“The outlook abroad appears to have become more uncertain of late, and heightened concerns about growth in China and other emerging market economies have led to notable volatility in financial markets. Developments since our July meeting, including the drop in equity prices, the further appreciation of the dollar, and a widening in risk spreads, have tightened overall financial conditions to some extent. These developments may restrain U.S. economic activity somewhat and are likely to put further downward pressure on inflation in the near term. Given the significant economic and financial interconnections between the United States and the rest of the world, the situation abroad bears close watching.”
Some equity markets fell on Fri Sep 18, 2015:
| Fri Sep 11 | Mon 14 | Tue 15 | Wed 16 | Thu 17 | Fri 18 |
| DJIA 16433.09 2.1% 0.6% | 16370.96 -0.4% -0.4% | 16599.85 1.0% 1.4% | 16739.95 1.9% 0.8% | 16674.74 1.5% -0.4% | 16384.58 -0.3% -1.7% |
| Nikkei 225 18264.22 2.7% -0.2% | 17965.70 -1.6% -1.6% | 18026.48 -1.3% 0.3% | 18171.60 -0.5% 0.8% | 18432.27 0.9% 1.4% | 18070.21 -1.1% -2.0% |
| DAX 10123.56 0.9% -0.9% | 10131.74 0.1% 0.1% | 10188.13 0.6% 0.6% | 10227.21 1.0% 0.4% | 10229.58 1.0% 0.0% | 9916.16 -2.0% -3.1% |
Frank H. Knight (1963, 233), in Risk, uncertainty and profit, distinguishes between measurable risk and unmeasurable uncertainty. Chair Yellen, in a lecture on “Inflation dynamics and monetary policy,” on Sep 24, 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20150924a.htm), states that (emphasis added):
· “The economic outlook, of course, is highly uncertain”
· “Considerable uncertainties also surround the outlook for economic activity”
· “Given the highly uncertain nature of the outlook…”
Is there a “science” or even “art” of central banking under this extreme uncertainty in which policy does not generate higher volatility of money, income, prices and values of financial assets?
Lingling Wei, writing on Oct 23, 2015, on China’s central bank moves to spur economic growth,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/chinas-central-bank-cuts-rates-1445601495), analyzes the reduction by the People’s Bank of China (http://www.pbc.gov.cn/ http://www.pbc.gov.cn/english/130437/index.html) of borrowing and lending rates of banks by 50 basis points and reserve requirements of banks by 50 basis points. Paul Vigna, writing on Oct 23, 2015, on “Stocks rally out of correction territory on latest central bank boost,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://blogs.wsj.com/moneybeat/2015/10/23/stocks-rally-out-of-correction-territory-on-latest-central-bank-boost/), analyzes the rally in financial markets following the statement on Oct 22, 2015, by the President of the European Central Bank (ECB) Mario Draghi of consideration of new quantitative measures in Dec 2015 (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0814riKW25k&rel=0) and the reduction of bank lending/deposit rates and reserve requirements of banks by the People’s Bank of China on Oct 23, 2015. The dollar revalued 2.8 percent from Oct 21 to Oct 23, 2015, following the intended easing of the European Central Bank. The DJIA rose 2.8 percent from Oct 21 to Oct 23 and the DAX index of German equities rose 5.4 percent from Oct 21 to Oct 23, 2015.
| Fri Oct 16 | Mon 19 | Tue 20 | Wed 21 | Thu 22 | Fri 23 |
| USD/ EUR 1.1350 0.1% 0.3% | 1.1327 0.2% 0.2% | 1.1348 0.0% -0.2% | 1.1340 0.1% 0.1% | 1.1110 2.1% 2.0% | 1.1018 2.9% 0.8% |
| DJIA 17215.97 0.8% 0.4% | 17230.54 0.1% 0.1% | 17217.11 0.0% -0.1% | 17168.61 -0.3% -0.3% | 17489.16 1.6% 1.9% | 17646.70 2.5% 0.9% |
| Dow Global 2421.58 0.3% 0.6% | 2414.33 -0.3% -0.3% | 2411.03 -0.4% -0.1% | 2411.27 -0.4% 0.0% | 2434.79 0.5% 1.0% | 2458.13 1.5% 1.0% |
| DJ Asia Pacific 1402.31 1.1% 0.3% | 1398.80 -0.3% -0.3% | 1395.06 -0.5% -0.3% | 1402.68 0.0% 0.5% | 1396.03 -0.4% -0.5% | 1415.50 0.9% 1.4% |
| Nikkei 225 18291.80 -0.8% 1.1% | 18131.23 -0.9% -0.9% | 18207.15 -0.5% 0.4% | 18554.28 1.4% 1.9% | 18435.87 0.8% -0.6% | 18825.30 2.9% 2.1% |
| Shanghai 3391.35 6.5% 1.6% | 3386.70 -0.1% -0.1% | 3425.33 1.0% 1.1% | 3320.68 -2.1% -3.1% | 3368.74 -0.7% 1.4% | 3412.43 0.6% 1.3% |
| DAX 10104.43 0.1% 0.4% | 10164.31 0.6% 0.6% | 10147.68 0.4% -0.2% | 10238.10 1.3% 0.9% | 10491.97 3.8% 2.5% | 10794.54 6.8% 2.9% |
Ben Leubsdorf, writing on “Fed’s Yellen: December is “Live Possibility” for First Rate Increase,” on Nov 4, 2015, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/feds-yellen-december-is-live-possibility-for-first-rate-increase-1446654282) quotes Chair Yellen that a rate increase in “December would be a live possibility.” The remark of Chair Yellen was during a hearing on supervision and regulation before the Committee on Financial Services, US House of Representatives (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20151104a.htm) and a day before the release of the employment situation report for Oct 2015 (Section I). The dollar revalued 2.4 percent during the week. The euro has devalued 51.0 percent relative to the dollar from the high on Jul 15, 2008 to Jan 6, 2016.
| Fri Oct 30 | Mon 2 | Tue 3 | Wed 4 | Thu 5 | Fri 6 |
| USD/ EUR 1.1007 0.1% -0.3% | 1.1016 -0.1% -0.1% | 1.0965 0.4% 0.5% | 1.0867 1.3% 0.9% | 1.0884 1.1% -0.2% | 1.0742 2.4% 1.3% |
The release on Nov 18, 2015 of the minutes of the FOMC (Federal Open Market Committee) meeting held on Oct 28, 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/fomcminutes20151028.htm) states:
“Most participants anticipated that, based on their assessment of the current economic situation and their outlook for economic activity, the labor market, and inflation, these conditions [for interest rate increase] could well be met by the time of the next meeting. Nonetheless, they emphasized that the actual decision would depend on the implications for the medium-term economic outlook of the data received over the upcoming intermeeting period… It was noted that beginning the normalization process relatively soon would make it more likely that the policy trajectory after liftoff could be shallow.”
Markets could have interpreted a symbolic increase in the fed funds rate at the meeting of the FOMC on Dec 15-16, 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/fomccalendars.htm) followed by “shallow” increases, explaining the sharp increase in stock market values and appreciation of the dollar after the release of the minutes on Nov 18, 2015:
| Fri Nov 13 | Mon 16 | Tue 17 | Wed 18 | Thu 19 | Fri 20 |
| USD/ EUR 1.0774 -0.3% 0.4% | 1.0686 0.8% 0.8% | 1.0644 1.2% 0.4% | 1.0660 1.1% -0.2% | 1.0735 0.4% -0.7% | 1.0647 1.2% 0.8% |
| DJIA 17245.24 -3.7% -1.2% | 17483.01 1.4% 1.4% | 17489.50 1.4% 0.0% | 17737.16 2.9% 1.4% | 17732.75 2.8% 0.0% | 17823.81 3.4% 0.5% |
| DAX 10708.40 -2.5% -0.7% | 10713.23 0.0% 0.0% | 10971.04 2.5% 2.4% | 10959.95 2.3% -0.1% | 11085.44 3.5% 1.1% | 11119.83 3.8% 0.3% |
In testimony before The Joint Economic Committee of Congress on Dec 3, 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20151203a.htm), Chair Yellen reiterated that the FOMC (Federal Open Market Committee) “anticipates that even after employment and inflation are near mandate-consistent levels, economic condition may, for some time, warrant keeping the target federal funds rate below the Committee views as normal in the longer run.” Todd Buell and Katy Burne, writing on “Draghi says ECB could step up stimulus efforts if necessary,” on Dec 4, 2015, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/draghi-says-ecb-could-step-up-stimulus-efforts-if-necessary-1449252934), analyze that the President of the European Central Bank (ECB), Mario Draghi, reassured financial markets that the ECB will increase stimulus if required to raise inflation the euro area to targets. The USD depreciated 3.1 percent on Thu Dec 3, 2015 after weaker than expected measures by the European Central Bank. DJIA fell 1.4 percent on Dec 3 and increased 2.1 percent on Dec 4. DAX fell 3.6 percent on Dec 3.
| Fri Nov 27 | Mon 30 | Tue 1 | Wed 2 | Thu 3 | Fri 4 |
| USD/ EUR 1.0594 0.5% 0.2% | 1.0565 0.3% 0.3% | 1.0634 -0.4% -0.7% | 1.0616 -0.2% 0.2% | 1.0941 -3.3% -3.1% | 1.0885 -2.7% 0.5% |
| DJIA 17798.49 -0.1% -0.1% | 17719.92 -0.4% -0.4% | 17888.35 0.5% 1.0% | 17729.68 -0.4% -0.9% | 17477.67 -1.8% -1.4% | 17847.63 0.3% 2.1% |
| DAX 11293.76 1.6% -0.2% | 11382.23 0.8% 0.8% | 11261.24 -0.3% -1.1% | 11190.02 -0.9% -0.6% | 10789.24 -4.5% -3.6% | 10752.10 -4.8% -0.3% |
At the press conference following the meeting of the FOMC on Dec 16, 2015, Chair Yellen states (http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20151216.pdf page 8):
“And we recognize that monetary policy operates with lags. We would like to be able to move in a prudent, and as we've emphasized, gradual manner. It's been a long time since the Federal Reserve has raised interest rates, and I think it's prudent to be able to watch what the impact is on financial conditions and spending in the economy and moving in a timely fashion enables us to do this.”
The implication of this statement is that the state of the art is not accurate in analyzing the effects of monetary policy on financial markets and economic activity. The US dollar appreciated and equities fluctuated:
| Fri Dec 11 | Mon 14 | Tue 15 | Wed 16 | Thu 17 | Fri 18 |
| USD/ EUR 1.0991 -1.0% -0.4% | 1.0993 0.0% 0.0% | 1.0932 0.5% 0.6% | 1.0913 0.7% 0.2% | 1.0827 1.5% 0.8% | 1.0868 1.1% -0.4% |
| DJIA 17265.21 -3.3% -1.8% | 17368.50 0.6% 0.6% | 17524.91 1.5% 0.9% | 17749.09 2.8% 1.3% | 17495.84 1.3% -1.4% | 17128.55 -0.8% -2.1% |
| DAX 10340.06 -3.8% -2.4% | 10139.34 -1.9% -1.9% | 10450.38 -1.1% 3.1% | 10469.26 1.2% 0.2% | 10738.12 3.8% 2.6% | 10608.19 2.6% -1.2% |
On January 29, 2016, the Policy Board of the Bank of Japan introduced a new policy to attain the “price stability target of 2 percent at the earliest possible time” (https://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2016/k160129a.pdf). The new framework consists of three dimensions: quantity, quality and interest rate. The interest rate dimension consists of rates paid to current accounts that financial institutions hold at the Bank of Japan of three tiers zero, positive and minus 0.1 percent. The quantitative dimension consists of increasing the monetary base at the annual rate of 80 trillion yen. The qualitative dimension consists of purchases by the Bank of Japan of Japanese government bonds (JGBs), exchange traded funds (ETFs) and Japan real estate investment trusts (J-REITS). The yen devalued sharply relative to the dollar and world equity markets soared after the new policy announced on Jan 29, 2016:
| Fri 22 | Mon 25 | Tue 26 | Wed 27 | Thu 28 | Fri 29 |
| JPY/ USD 118.77 -1.5% -0.9% | 118.30 0.4% 0.4% | 118.42 0.3% -0.1% | 118.68 0.1% -0.2% | 118.82 0.0% -0.1% | 121.13 -2.0% -1.9% |
| DJIA 16093.51 0.7% 1.3% | 15885.22 -1.3% -1.3% | 16167.23 0.5% 1.8% | 15944.46 -0.9% -1.4% | 16069.64 -0.1% 0.8% | 16466.30 2.3% 2.5% |
| Nikkei 16958.53 -1.1% 5.9% | 17110.91 0.9% 0.9% | 16708.90 -1.5% -2.3% | 17163.92 1.2% 2.7% | 17041.45 0.5% -0.7% | 17518.30 3.3% 2.8% |
| Shanghai 2916.56 0.5% 1.3 | 2938.51 0.8% 0.8% | 2749.79 -5.7% -6.4% | 2735.56 -6.2% -0.5% | 2655.66 -8.9% -2.9% | 2737.60 -6.1% 3.1% |
| DAX 9764.88 2.3% 2.0% | 9736.15 -0.3% -0.3% | 9822.75 0.6% 0.9% | 9880.82 1.2% 0.6% | 9639.59 -1.3% -2.4% | 9798.11 0.3% 1.6% |
In testimony on the Semiannual Monetary Policy Report to the Congress on Feb 10-11, 2016, Chair Yellen (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20160210a.htm) states: “U.S. real gross domestic product is estimated to have increased about 1-3/4 percent in 2015. Over the course of the year, subdued foreign growth and the appreciation of the dollar restrained net exports. In the fourth quarter of last year, growth in the gross domestic product is reported to have slowed more sharply, to an annual rate of just 3/4 percent; again, growth was held back by weak net exports as well as by a negative contribution from inventory investment.”
Jon Hilsenrath, writing on “Yellen Says Fed Should Be Prepared to Use Negative Rates if Needed,” on Feb 11, 2016, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/yellen-reiterates-concerns-about-risks-to-economy-in-senate-testimony-1455203865), analyzes the statement of Chair Yellen in Congress that the FOMC (Federal Open Market Committee) is considering negative interest rates on bank reserves. The Wall Street Journal provides yields of two and ten-year sovereign bonds with negative interest rates on shorter maturities where central banks pay negative interest rates on excess bank reserves:
| Sovereign Yields 2/12/16 | Japan | Germany | USA |
| 2 Year | -0.168 | -0.498 | 0.694 |
| 10 Year | 0.076 | 0.262 | 1.744 |
On Mar 10, 2016, the European Central Bank (ECB) announced (1) reduction of the refinancing rate by 5 basis points to 0.00 percent; decrease the marginal lending rate to 0.25 percent; reduction of the deposit facility rate to 0,40 percent; increase of the monthly purchase of assets to €80 billion; include nonbank corporate bonds in assets eligible for purchases; and new long-term refinancing operations (https://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pr/date/2016/html/pr160310.en.html). The President of the ECB, Mario Draghi, stated in the press conference (https://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pressconf/2016/html/is160310.en.html): “How low can we go? Let me say that rates will stay low, very low, for a long period of time, and well past the horizon of our purchases…We don’t anticipate that it will be necessary to reduce rates further. Of course, new facts can change the situation and the outlook.”
The dollar devalued relative to the euro and open stock markets traded lower after the announcement on Mar 10, 2016, but stocks rebounded on Mar 11:
| Fri 4 | Mon 7 | Tue 8 | Wed 9 | Thu10 | Fri 11 |
| USD/ EUR 1.1006 -0.7% -0.4% | 1.1012 -0.1% -0.1% | 1.1013 -0.1% 0.0% | 1.0999 0.1% 0.1% | 1.1182 -1.6% -1.7% | 1.1151 -1.3% 0.3% |
| DJIA 17006.77 2.2% 0.4% | 17073.95 0.4% 0.4% | 16964.10 -0.3% -0.6% | 17000.36 0.0% 0.2% | 16995.13 -0.1% 0.0% | 17213.31 1.2% 1.3% |
| DAX 9824.17 3.3% 0.7% | 9778.93 -0.5% 0.5% | 9692.82 -1.3% -0.9% | 9723.09 -1.0% 0.3% | 9498.15 -3.3% -2.3% | 9831.13 0.1% 3.5% |
At the press conference after the FOMC meeting on Sep 21, 2016, Chair Yellen states (http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20160921.pdf ): “However, the economic outlook is inherently uncertain.” In the address to the Jackson Hole symposium on Aug 26, 2016, Chair Yellen states: “I believe the case for an increase in in federal funds rate has strengthened in recent months…And, as ever, the economic outlook is uncertain, and so monetary policy is not on a preset course” (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20160826a.htm). In a speech at the World Affairs Council of Philadelphia, on Jun 6, 2016 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20160606a.htm), Chair Yellen finds that “there is considerable uncertainty about the economic outlook.” There are fifteen references to this uncertainty in the text of 18 pages double-spaced. In the Semiannual Monetary Policy Report to the Congress on Jun 21, 2016, Chair Yellen states (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20160621a.htm), “Of course, considerable uncertainty about the economic outlook remains.” Frank H. Knight (1963, 233), in Risk, uncertainty and profit, distinguishes between measurable risk and unmeasurable uncertainty. Is there a “science” or even “art” of central banking under this extreme uncertainty in which policy does not generate higher volatility of money, income, prices and values of financial assets?
Chart VIII-1, Fed Funds Rate and Yields of Ten-year Treasury Constant Maturity and Baa Seasoned Corporate Bond, Jan 2, 2001 to Oct 6, 2016
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/
Chart VIII-1A, Fed Funds Rate and Yields of Ten-year Treasury Constant Maturity, Jan 2, 2001 to Jan 5, 2016
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/
Table VIII-3, Selected Data Points in Chart VIII-1, % per Year
| Fed Funds Overnight Rate | 10-Year Treasury Constant Maturity | Seasoned Baa Corporate Bond | |
| 1/2/2001 | 6.67 | 4.92 | 7.91 |
| 10/1/2002 | 1.85 | 3.72 | 7.46 |
| 7/3/2003 | 0.96 | 3.67 | 6.39 |
| 6/22/2004 | 1.00 | 4.72 | 6.77 |
| 6/28/2006 | 5.06 | 5.25 | 6.94 |
| 9/17/2008 | 2.80 | 3.41 | 7.25 |
| 10/26/2008 | 0.09 | 2.16 | 8.00 |
| 10/31/2008 | 0.22 | 4.01 | 9.54 |
| 4/6/2009 | 0.14 | 2.95 | 8.63 |
| 4/5/2010 | 0.20 | 4.01 | 6.44 |
| 2/4/2011 | 0.17 | 3.68 | 6.25 |
| 7/25/2012 | 0.15 | 1.43 | 4.73 |
| 5/1/13 | 0.14 | 1.66 | 4.48 |
| 9/5/13 | 0.089 | 2.98 | 5.53 |
| 11/21/2013 | 0.09 | 2.79 | 5.44 |
| 11/26/13 | 0.09 | 2.74 | 5.34 (11/26/13) |
| 12/5/13 | 0.09 | 2.88 | 5.47 |
| 12/11/13 | 0.09 | 2.89 | 5.42 |
| 12/18/13 | 0.09 | 2.94 | 5.36 |
| 12/26/13 | 0.08 | 3.00 | 5.37 |
| 1/1/2014 | 0.08 | 3.00 | 5.34 |
| 1/8/2014 | 0.07 | 2.97 | 5.28 |
| 1/15/2014 | 0.07 | 2.86 | 5.18 |
| 1/22/2014 | 0.07 | 2.79 | 5.11 |
| 1/30/2014 | 0.07 | 2.72 | 5.08 |
| 2/6/2014 | 0.07 | 2.73 | 5.13 |
| 2/13/2014 | 0.06 | 2.73 | 5.12 |
| 2/20/14 | 0.07 | 2.76 | 5.15 |
| 2/27/14 | 0.07 | 2.65 | 5.01 |
| 3/6/14 | 0.08 | 2.74 | 5.11 |
| 3/13/14 | 0.08 | 2.66 | 5.05 |
| 3/20/14 | 0.08 | 2.79 | 5.13 |
| 3/27/14 | 0.08 | 2.69 | 4.95 |
| 4/3/14 | 0.08 | 2.80 | 5.04 |
| 4/10/14 | 0.08 | 2.65 | 4.89 |
| 4/17/14 | 0.09 | 2.73 | 4.89 |
| 4/24/14 | 0.10 | 2.70 | 4.84 |
| 5/1/14 | 0.09 | 2.63 | 4.77 |
| 5/8/14 | 0.08 | 2.61 | 4.79 |
| 5/15/14 | 0.09 | 2.50 | 4.72 |
| 5/22/14 | 0.09 | 2.56 | 4.81 |
| 5/29/14 | 0.09 | 2.45 | 4.69 |
| 6/05/14 | 0.09 | 2.59 | 4.83 |
| 6/12/14 | 0.09 | 2.58 | 4.79 |
| 6/19/14 | 0.10 | 2.64 | 4.83 |
| 6/26/14 | 0.10 | 2.53 | 4.71 |
| 7/2/14 | 0.10 | 2.64 | 4.84 |
| 7/10/14 | 0.09 | 2.55 | 4.75 |
| 7/17/14 | 0.09 | 2.47 | 4.69 |
| 7/24/14 | 0.09 | 2.52 | 4.72 |
| 7/31/14 | 0.08 | 2.58 | 4.75 |
| 8/7/14 | 0.09 | 2.43 | 4.71 |
| 8/14/14 | 0.09 | 2.40 | 4.69 |
| 8/21/14 | 0.09 | 2.41 | 4.69 |
| 8/28/14 | 0.09 | 2.34 | 4.57 |
| 9/04/14 | 0.09 | 2.45 | 4.70 |
| 9/11/14 | 0.09 | 2.54 | 4.79 |
| 9/18/14 | 0.09 | 2.63 | 4.91 |
| 9/25/14 | 0.09 | 2.52 | 4.79 |
| 10/02/14 | 0.09 | 2.44 | 4.76 |
| 10/09/14 | 0.08 | 2.34 | 4.68 |
| 10/16/14 | 0.09 | 2.17 | 4.64 |
| 10/23/14 | 0.09 | 2.29 | 4.71 |
| 11/13/14 | 0.09 | 2.35 | 4.82 |
| 11/20/14 | 0.10 | 2.34 | 4.86 |
| 11/26/14 | 0.10 | 2.24 | 4.73 |
| 12/04/14 | 0.12 | 2.25 | 4.78 |
| 12/11/14 | 0.12 | 2.19 | 4.72 |
| 12/18/14 | 0.13 | 2.22 | 4.78 |
| 12/23/14 | 0.13 | 2.26 | 4.79 |
| 12/30/14 | 0.06 | 2.20 | 4.69 |
| 1/8/15 | 0.12 | 2.03 | 4.57 |
| 1/15/15 | 0.12 | 1.77 | 4.42 |
| 1/22/15 | 0.12 | 1.90 | 4.49 |
| 1/29/15 | 0.11 | 1.77 | 4.35 |
| 2/05/15 | 0.12 | 1.83 | 4.43 |
| 2/12/15 | 0.12 | 1.99 | 4.53 |
| 2/19/15 | 0.12 | 2.11 | 4.64 |
| 2/26/15 | 0.11 | 2.03 | 4.47 |
| 3/5/215 | 0.11 | 2.11 | 4.58 |
| 3/12/15 | 0.11 | 2.10 | 4.56 |
| 3/19/15 | 0.12 | 1.98 | 4.48 |
| 3/26/15 | 0.11 | 2.01 | 4.56 |
| 4/03/15 | 0.12 | 1.92 | 4.47 |
| 4/9/15 | 0.12 | 1.97 | 4.50 |
| 4/16/15 | 0.13 | 1.90 | 4.45 |
| 4/23/15 | 0.13 | 1.96 | 4.50 |
| 5/1/15 | 0.08 | 2.05 | 4.65 |
| 5/7/15 | 0.13 | 2.18 | 4.82 |
| 5/14/15 | 0.13 | 2.23 | 4.97 |
| 5/21/15 | 0.12 | 2.19 | 4.94 |
| 5/28/15 | 0.12 | 2.13 | 4.88 |
| 6/04/15 | 0.13 | 2.31 | 5.03 |
| 6/11/15 | 0.13 | 2.39 | 5.10 |
| 6/18/15 | 0.14 | 2.35 | 5.17 |
| 6/25/15 | 0.13 | 2.40 | 5.20 |
| 7/1/15 | 0.13 | 2.43 | 5.26 |
| 7/9/15 | 0.13 | 2.32 | 5.20 |
| 7/16/15 | 0.14 | 2.36 | 5.24 |
| 7/23/15 | 0.13 | 2.28 | 5.13 |
| 7/30/15 | 0.14 | 2.28 | 5.16 |
| 8/06/15 | 0.14 | 2.23 | 5.15 |
| 8/20/15 | 0.15 | 2.09 | 5.13 |
| 8/27/15 | 0.14 | 2.18 | 5.33 |
| 9/03/15 | 0.14 | 2.18 | 5.35 |
| 9/10/15 | 0.14 | 2.23 | 5.35 |
| 9/17/15 | 0.14 | 2.21 | 5.39 |
| 9/25/15 | 0.14 | 2.13 | 5.29 |
| 10/01/15 | 0.13 | 2.05 | 5.36 |
| 10/08/15 | 0.13 | 2.12 | 5.40 |
| 10/15/15 | 0.13 | 2.04 | 5.33 |
| 10/22/15 | 0.12 | 2.04 | 5.30 |
| 10/29/15 | 0.12 | 2.19 | 5.40 |
| 11/05/15 | 0.12 | 2.26 | 5.44 |
| 11/12/15 | 0.12 | 2.32 | 5.51 |
| 11/19/15 | 0.12 | 2.24 | 5.44 |
| 11/25/15 | 0.12 | 2.23 | 5.44 |
| 12/03/15 | 0.13 | 2.33 | 5.51 |
| 12/10/15 | 0.14 | 2.24 | 5.43 |
| 12/17/15 | 0.37 | 2.24 | 5.45 |
| 12/23/15 | 0.36 | 2.27 | 5.53 |
| 12/30/15 | 0.35 | 2.31 | 5.54 |
| 1/07/2016 | 0.36 | 2.16 | 5.44 |
| 01/14/16 | 0.36 | 2.10 | 5.46 |
| 01/20/16 | 0.37 | 2.01 | 5.41 |
| 01/29/16 | 0.38 | 2.00 | 5.48 |
| 02/04/16 | 0.38 | 1.87 | 5.40 |
| 02/11/16 | 0.38 | 1.63 | 5.26 |
| 02/18/16 | 0.38 | 1.75 | 5.37 |
| 02/25/16 | 0.37 | 1.71 | 5.27 |
| 03/03/16 | 0.37 | 1.83 | 5.30 |
| 03/10/16 | 0.36 | 1.93 | 5.23 |
| 03/17/16 | 0.37 | 1.91 | 5.11 |
| 03/24/16 | 0.37 | 1.91 | 4.97 |
| 03/31/16 | 0.25 | 1.78 | 4.90 |
| 04/07/16 | 0.37 | 1.70 | 4.76 |
| 04/14/16 | 0.37 | 1.80 | 4.79 |
| 04/21/16 | 0.37 | 1.88 | 4.79 |
| 04/28/16 | 0.37 | 1.84 | 4.73 |
| 05/05/16 | 0.37 | 1.76 | 4.62 |
| 05/12/16 | 0.37 | 1.75 | 4.66 |
| 05/19/16 | 0.37 | 1.85 | 4.70 |
| 05/26/16 | 0.37 | 1.83 | 4.69 |
| 06/02/16 | 0.37 | 1.81 | 4.64 |
| 06/09/16 | 0.37 | 1.68 | 4.53 |
| 06/16/16 | 0.38 | 1.57 | 4.47 |
| 06/23/16 | 0.39 | 1.74 | 4.60 |
| 06/30/16 | 0.36 | 1.49 | 4.41 |
| 07/07/16 | 0.40 | 1.40 | 4.19 |
| 07/14/16 | 0.40 | 1.53 | 4.23 |
| 07/21/16 | 0.40 | 1.57 | 4.25 |
| 07/28/16 | 0.40 | 1.52 | 4.20 |
| 08/04/16 | 0.40 | 1.51 | 4.27 |
| 08/11/16 | 0.40 | 1.57 | 4.27 |
| 08/18/16 | 0.40 | 1.53 | 4.23 |
| 08/25/16 | 0.40 | 1.58 | 4.21 |
| 09/01/16 | 0.40 | 1.57 | 4.19 |
| 09/08/16 | 0.40 | 1.61 | 4.28 |
| 09/15/16 | 0.40 | 1.71 | 4.43 |
| 09/22/16 | 0.40 | 1.63 | 4.32 |
| 09/29/16 | 0.40 | 1.56 | 4.23 |
| 10/06/16 | 0.40 | 1.75 | 4.36 |
| 10/13/16 | 0.40 | 1.75 | NA* |
| 10/20/16 | 0.41 | 1.76 | NA* |
| 10/27/16 | 0.41 | 1.85 | NA* |
| 11/03/16 | 0.41 | 1.82 | NA* |
| 11/09/16 | 0.41 | 2.07 | NA* |
| 11/17/16 | 0.41 | 2.29 | NA* |
| 11/23/16 | 0.40 | 2.36 | NA* |
| 12/01/16 | 0.40 | 2.45 | NA* |
| 12/08/16 | 0.41 | 2.40 | NA* |
| 12/15/16 | 0.66 | 2.60 | NA* |
| 12/22/16 | 0.66 | 2.55 | NA* |
| 12/29/16 | 0.66 | 2.49 | NA* |
| 01/05/17 | 0.66 | 2.37 | NA* |
*Note: the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System discontinued the publication of the BAA bond yield.
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/
Chart VIII-2 of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System provides the rate of US dollars (USD) per euro (EUR), USD/EUR. The rate appreciated from USD 1.0912/EUR on Dec 30, 2015 to USD 1.0552/EUR on Dec 30, 2016 or 3.3 percent. The euro has devalued 51.0 percent relative to the dollar from the high on Jul 15, 2008 to Jan 6, 2017. US corporations with foreign transactions and net worth experience losses in their balance sheets in converting revenues from depreciated currencies to the dollar. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA fell at $127.9 billion in IVQ2015 with decrease of domestic industries at $149.8 billion, mostly because of decrease of nonfinancial business at $131.7 billion, and increase of profits from operations in the rest of the world at $22.0 billion. Receipts from the rest of the world fell at $19.9 billion. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased at $66.0 billion in IQ2016 with increase of domestic industries at $92.9 billion. Profits from operations from the rest of the world fell at $26.9 billion and payments to the rest of the world increased at $35.6 billion. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA decreased at $12.5 billion in IIQ2016. Profits from domestic industries fell at $50.5 billion and profits from nonfinancial business fell at $56.1 billion. Profits from the rest of the world increased at $38.0 billion. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased at $117.8 billion in IIIQ2016. Profits from domestic industries increased at $116.5 billion and profits from nonfinancial business increased at $66.4 billion. Profits from the rest of the world increased at $1.3 billion. Total corporate profits with IVA and CCA were $2138.8 billion in IIIQ2016 of which $1729.9 billion from domestic industries, or 80.9 percent of the total, and $408.9 billion, or 19.1 percent, from the rest of the world. Nonfinancial corporate profits of $1236.9 billion account for 57.8 percent of the total. Uncertainty originating in fiscal, regulatory and monetary policy causes wide swings in expectations and decisions by the private sector with adverse effects on investment, real economic activity and employment. There is increase in corporate profits from devaluing the dollar with unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates and decrease of corporate profits in revaluing the dollar with attempts at “normalization” or increases in interest rates. Conflicts arise while other central banks differ in their adjustment process. The current account deficit seasonally adjusted increases from 2.3 percent of GDP in IVQ2014 to 2.7 percent in IQ2015. The current account deficit increases to 2.7 percent of GDP in IQ2015 and decreases to 2.5 percent of GDP in IIQ2015. The deficit increases to 2.9 percent of GDP in IIIQ2015, easing to 2.8 percent of GDP in IVQ2015. The net international investment position decreases from minus $7.0 trillion in IVQ2014 to minus $6.8 trillion in IQ2015, decreasing at minus $6.7 trillion in IIQ2015. The net international investment position increases to minus $7.6 trillion in IQ2016 and increases to minus $8.0 trillion in IIQ2016. The BEA explains as follows (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/international/intinv/2016/pdf/intinv216.pdf):
The U.S. net international investment position at the end of the second quarter of 2016 was -$8,042.8 billion (preliminary), according to statistics released today by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA). The net investment position at the end of the first quarter was -$7,582.0 billion (revised). The net investment position decreased $460.8 billion or 6.1 percent in the second quarter, compared with a decrease of 4.1 percent in the first quarter, and an average quarterly decrease of 6.1 percent from the first quarter of 2011 through the fourth quarter of 2015. The $460.8 billion decrease in the net position reflected a $479.9 billion decrease in the net position excluding financial derivatives that was partly offset by a $19.1 billion increase in the net position in financial derivatives.”
The BEA explains further (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/international/intinv/2016/pdf/intinv216.pdf): “U.S. assets increased $404.1 billion to $24,465.9 billion at the end of the second quarter, reflecting increases in both financial derivatives and assets excluding financial derivatives. Financial derivatives with a positive fair value increased $241.4 billion to $3,223.7 billion, mostly in single-currency interest rate contracts. Assets excluding financial derivatives increased $162.7 billion to $21,242.1 billion, reflecting increases in other investment, portfolio investment, and reserve assets that were partly offset by a decrease in direct investment. Increases resulting from financial transactions were partly offset by depreciation of major foreign currencies against the U.S. dollar that lowered the value of U.S. assets in dollar terms.”
Chart VIII-2, Exchange Rate of US Dollars (USD) per Euro (EUR), Dec 30, 2015 to Dec 30, 2016
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/H10/default.htm
Chart VIII-3 of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System provides the yield of the 10-year Treasury constant maturity note from 1.75 percent on Oct 5 2016 to 2.37 percent on Jan 5, 2017. There is turbulence in financial markets originating in a combination of intentions of normalizing or increasing US policy fed funds rate, quantitative easing in Europe and Japan and increasing perception of financial/economic risks.
Chart VIII-3, Yield of Ten-year Constant Maturity Treasury, Oct 5, 2016 to Jan 5, 2017
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/H15/default.htm
Chart S provides the yield of the two-year Treasury constant maturity from Mar 17, 2014, two days before the guidance of Chair Yellen on Mar 19, 2014, to Jan 5, 2017. Chart SA provides the yields of the seven-, ten- and thirty-year Treasury constant maturity in the same dates. Yields increased right after the guidance of Chair Yellen. The two-year yield remain at a higher level than before while the ten-year yield fell and increased again. There could be more immediate impact on two-year yields of an increase in the fed funds rates but the effects would spread throughout the term structure of interest rates (Cox, Ingersoll and Ross 1981, 1985, Ingersoll 1987). Yields converged toward slightly lower earlier levels in the week of Apr 24, 2014 with reallocation of portfolios of risk financial assets away from equities and into bonds and commodities. There is ongoing reshuffling of portfolios to hedge against geopolitical events and world/regional economic performance.
Chart S, US, Yield of Two-Year Treasury Constant Maturity, Mar 17, 2014 to Jan 5, 2017
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/
Chart SA, US, Yield of Seven-Year, Ten-Year and Thirty-Year Treasury Constant Maturity, Mar 17, 2014 to Jan 5, 2017
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/
Chair Yellen states (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20140331a.htm):
“And based on the evidence available, it is clear to me that the U.S. economy is still considerably short of the two goals assigned to the Federal Reserve by the Congress. The first of those goals is maximum sustainable employment, the highest level of employment that can be sustained while maintaining a stable inflation rate. Most of my colleagues on the Federal Open Market Committee and I estimate that the unemployment rate consistent with maximum sustainable employment is now between 5.2 percent and 5.6 percent, well below the 6.7 percent rate in February.
Let me explain what I mean by that word "slack" and why it is so important.
Slack means that there are significantly more people willing and capable of filling a job than there are jobs for them to fill. During a period of little or no slack, there still may be vacant jobs and people who want to work, but a large share of those willing to work lack the skills or are otherwise not well suited for the jobs that are available. With 6.7 percent unemployment, it might seem that there must be a lot of slack in the U.S. economy, but there are reasons why that may not be true.”
Inflation and unemployment in the period 1966 to 1985 is analyzed by Cochrane (2011Jan, 23) by means of a Phillips circuit joining points of inflation and unemployment. Chart VI-1B for Brazil in Pelaez (1986, 94-5) was reprinted in The Economist in the issue of Jan 17-23, 1987 as updated by the author. Cochrane (2011Jan, 23) argues that the Phillips circuit shows the weakness in Phillips curve correlation. The explanation is by a shift in aggregate supply, rise in inflation expectations or loss of anchoring. The case of Brazil in Chart VI-1B cannot be explained without taking into account the increase in the fed funds rate that reached 22.36 percent on Jul 22, 1981 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/data.htm) in the Volcker Fed that precipitated the stress on a foreign debt bloated by financing balance of payments deficits with bank loans in the 1970s. The loans were used in projects, many of state-owned enterprises with low present value in long gestation. The combination of the insolvency of the country because of debt higher than its ability of repayment and the huge government deficit with declining revenue as the economy contracted caused adverse expectations on inflation and the economy. This interpretation is consistent with the case of the 24 emerging market economies analyzed by Reinhart and Rogoff (2010GTD, 4), concluding that “higher debt levels are associated with significantly higher levels of inflation in emerging markets. Median inflation more than doubles (from less than seven percent to 16 percent) as debt rises from the low (0 to 30 percent) range to above 90 percent. Fiscal dominance is a plausible interpretation of this pattern.”
The reading of the Phillips circuits of the 1970s by Cochrane (2011Jan, 25) is doubtful about the output gap and inflation expectations:
“So, inflation is caused by ‘tightness’ and deflation by ‘slack’ in the economy. This is not just a cause and forecasting variable, it is the cause, because given ‘slack’ we apparently do not have to worry about inflation from other sources, notwithstanding the weak correlation of [Phillips circuits]. These statements [by the Fed] do mention ‘stable inflation expectations. How does the Fed know expectations are ‘stable’ and would not come unglued once people look at deficit numbers? As I read Fed statements, almost all confidence in ‘stable’ or ‘anchored’ expectations comes from the fact that we have experienced a long period of low inflation (adaptive expectations). All these analyses ignore the stagflation experience in the 1970s, in which inflation was high even with ‘slack’ markets and little ‘demand, and ‘expectations’ moved quickly. They ignore the experience of hyperinflations and currency collapses, which happen in economies well below potential.”
Yellen (2014Aug22) states that “Historically, slack has accounted for only a small portion of the fluctuations in inflation. Indeed, unusual aspects of the current recovery may have shifted the lead-lag relationship between a tightening labor market and rising inflation pressures in either direction.”
Chart VI-1B provides the tortuous Phillips Circuit of Brazil from 1963 to 1987. There were no reliable consumer price index and unemployment data in Brazil for that period. Chart VI-1B used the more reliable indicator of inflation, the wholesale price index, and idle capacity of manufacturing as a proxy of unemployment in large urban centers.
ChVI1-B, Brazil, Phillips Circuit, 1963-1987
Source:
©Carlos Manuel Pelaez, O Cruzado e o Austral: Análise das Reformas Monetárias do Brasil e da Argentina. São Paulo: Editora Atlas, 1986, pages 94-5. Reprinted in: Brazil. Tomorrow’s Italy, The Economist, 17-23 January 1987, page 25.
The minutes of the meeting of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) on Sep 16-17, 2014, reveal concern with global economic conditions (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/fomcminutes20140917.htm):
“Most viewed the risks to the outlook for economic activity and the labor market as broadly balanced. However, a number of participants noted that economic growth over the medium term might be slower than they expected if foreign economic growth came in weaker than anticipated, structural productivity continued to increase only slowly, or the recovery in residential construction continued to lag.”
There is similar concern in the minutes of the meeting of the FOMC on Dec 16-17, 2014 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/fomcminutes20141217.htm):
“In their discussion of the foreign economic outlook, participants noted that the implications of the drop in crude oil prices would differ across regions, especially if the price declines affected inflation expectations and financial markets; a few participants said that the effect on overseas employment and output as a whole was likely to be positive. While some participants had lowered their assessments of the prospects for global economic growth, several noted that the likelihood of further responses by policymakers abroad had increased. Several participants indicated that they expected slower economic growth abroad to negatively affect the U.S. economy, principally through lower net exports, but the net effect of lower oil prices on U.S. economic activity was anticipated to be positive.”
There is concern at the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) with the world economy and financial markets (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20160127a.htm): “The Committee is closely monitoring global economic and financial developments and is assessing their implications for the labor market and inflation, and for the balance of risks to the outlook” (emphasis added). This concern should include the effects on dollar revaluation of competitive easing by other central banks such as quantitative and qualitative easing with negative nominal interest rates.”
It is quite difficult to measure inflationary expectations because they tend to break abruptly from past inflation. There could still be an influence of past and current inflation in the calculation of future inflation by economic agents. Table VIII-1 provides inflation of the CPI. In the three months from Sep 2016 to Nov 2016, CPI inflation for all items seasonally adjusted was 3.7 percent in annual equivalent, obtained by calculating accumulated inflation from Sep 2016 to Nov 2016 and compounding for a full year. In the 12 months ending in Nov 2016, CPI inflation of all items not seasonally adjusted was 1.7 percent. Inflation in Nov 2016 seasonally adjusted was 0.2 percent relative to Oct 2016, or 2.4 percent annual equivalent (http://www.bls.gov/cpi/). The second row provides the same measurements for the CPI of all items excluding food and energy: 2.1 percent in 12 months, 1.6 percent in annual equivalent Sep 2016-Nov 2016 and 0.2 percent in Nov 2016 or 2.4 percent in annual equivalent. The Wall Street Journal provides the yield curve of US Treasury securities (http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/mdc_bonds.html?mod=mdc_topnav_2_3000). The shortest term is 0.509 percent for one month, 0.520 percent for three months, 0.615 percent for six months, 0.849 percent for one year, 1.214 percent for two years, 1.484 percent for three years, 1.926 percent for five years, 2.231 percent for seven years, 2.420 percent for ten years and 3.010 percent for 30 years. The Irving Fisher (1930) definition of real interest rates is approximately the difference between nominal interest rates, which are those estimated by the Wall Street Journal, and the rate of inflation expected in the term of the security, which could behave as in Table VIII-1. Inflation in Jan 2016 is low in 12 months because of the unwinding of carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures prices but could ignite again with subdued risk aversion. Real interest rates in the US have been negative during substantial periods in the past decade while monetary policy pursues a policy of attaining its “dual mandate” of (http://www.federalreserve.gov/aboutthefed/mission.htm):
“Conducting the nation's monetary policy by influencing the monetary and credit conditions in the economy in pursuit of maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates”
Negative real rates of interest distort calculations of risk and returns from capital budgeting by firms, through lending by financial intermediaries to decisions on savings, housing and purchases of households. Inflation on near zero interest rates misallocates resources away from their most productive uses and creates uncertainty of the future path of adjustment to higher interest rates that inhibit sound decisions.
Table I-3, US, Consumer Price Index Percentage Changes 12 months NSA and Annual Equivalent ∆%
| % RI | ∆% 12 Months Nov 2016/Nov | ∆% Annual Equivalent Sep 2016 to Nov 2016 SA | ∆% Nov 2016/Oct 2016 SA | |
| CPI All Items | 100.000 | 1.7 | 3.7 | 0.2 |
| CPI ex Food and Energy | 79.193 | 2.1 | 1.6 | 0.2 |
% RI: Percent Relative Importance
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/cpi/
Professionals use a variety of techniques in measuring interest rate risk (Fabozzi, Buestow and Johnson, 2006, Chapter Nine, 183-226):
- Full valuation approach in which securities and portfolios are shocked by 50, 100, 200 and 300 basis points to measure their impact on asset values
- Stress tests requiring more complex analysis and translation of possible events with high impact even if with low probability of occurrence into effects on actual positions and capital
- Value at Risk (VaR) analysis of maximum losses that are likely in a time horizon
- Duration and convexity that are short-hand convenient measurement of changes in prices resulting from changes in yield captured by duration and convexity
- Yield volatility
Analysis of these methods is in Pelaez and Pelaez (International Financial Architecture (2005), 101-162) and Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. (I) (2008a), 78-100). Frederick R. Macaulay (1938) introduced the concept of duration in contrast with maturity for analyzing bonds. Duration is the sensitivity of bond prices to changes in yields. In economic jargon, duration is the yield elasticity of bond price to changes in yield, or the percentage change in price after a percentage change in yield, typically expressed as the change in price resulting from change of 100 basis points in yield. The mathematical formula is the negative of the yield elasticity of the bond price or –[dB/d(1+y)]((1+y)/B), where d is the derivative operator of calculus, B the bond price, y the yield and the elasticity does not have dimension (Hallerbach 2001). The duration trap of unconventional monetary policy is that duration is higher the lower the coupon and higher the lower the yield, other things being constant. Coupons and yields are historically low because of unconventional monetary policy. Duration dumping during a rate increase may trigger the same crossfire selling of high duration positions that magnified the credit crisis. Traders reduced positions because capital losses in one segment, such as mortgage-backed securities, triggered haircuts and margin increases that reduced capital available for positioning in all segments, causing fire sales in multiple segments (Brunnermeier and Pedersen 2009; see Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2008b), 217-24). Financial markets are currently experiencing fear of duration and riskier asset classes resulting from the debate within and outside the Fed on increasing interest rates. Table VIII-2 provides the yield curve of Treasury securities on Jan 6, 2017, Dec 31, 2013, May 1, 2013, Jan 6, 2016 and Jan 6, 2006. There is oscillating steepening of the yield curve for longer maturities, which are also the ones with highest duration. The 10-year yield increased from 1.45 percent on Jul 26, 2012 to 3.04 percent on Dec 31, 2013 and 2.42 percent on Jan 6, 2017, as measured by the United States Treasury. Assume that a bond with maturity in 10 years were issued on Dec 31, 2013, at par or price of 100 with coupon of 1.45 percent. The price of that bond would be 86.3778 with instantaneous increase of the yield to 3.04 percent for loss of 13.6 percent and far more with leverage. Assume that the yield of a bond with exactly ten years to maturity and coupon of 2.42 percent would jump instantaneously from yield of 2.42 percent on Jan 6, 2017 to 4.43 percent as occurred on Jan 6 2006 when the economy was closer to full employment. The price of the hypothetical bond issued with coupon of 2.42 percent would drop from 100 to 83.9027 after an instantaneous increase of the yield to 4.43 percent. The price loss would be 16.1 percent. Losses absorb capital available for positioning, triggering crossfire sales in multiple asset classes (Brunnermeier and Pedersen 2009). What is the path of adjustment of zero interest rates on fed funds and artificially low bond yields? There is no painless exit from unconventional monetary policy. Chris Dieterich, writing on “Bond investors turn to cash,” on Jul 25, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887323971204578625900935618178.html), uses data of the Investment Company Institute (http://www.ici.org/) in showing withdrawals of $43 billion in taxable mutual funds in Jun, which is the largest in history, with flows into cash investments such as $8.5 billion in the week of Jul 17 into money-market funds.
Table VIII-2, United States, Treasury Yields
| 01/06/17 | 12/31/13 | 5/01/13 | 01/06/16 | 01/06/06 | |
| 1 M | 0.50 | 0.00 | 0.03 | 0.21 | 4.15 |
| 3 M | 0.53 | 0.01 | 0.06 | 0.21 | 4.29 |
| 6 M | 0.61 | 0.07 | 0.08 | 0.47 | 4.42 |
| 1 Y | 0.85 | 0.25 | 0.11 | 0.67 | 4.42 |
| 2 Y | 1.22 | 0.56 | 0.20 | 0.99 | 4.41 |
| 3 Y | 1.50 | 0.91 | 0.30 | 1.26 | 4.36 |
| 5 Y | 1.92 | 1.43 | 0.65 | 1.65 | 4.36 |
| 7 Y | 2.23 | 1.80 | 1.07 | 1.98 | 4.38 |
| 10 Y | 2.42 | 3.04 | 1.66 | 2.18 | 4.43 |
| 20 Y | 2.73 | 3.72 | 2.44 | 2.59 | 4.68 |
| 30 Y | 3.00 | 3.96 | 2.83 | 2.94 | NA |
M: Months; Y: Years
Source: United States Treasury
There is a false impression of the existence of a monetary policy “science,” measurements and forecasting with which to steer the economy into “prosperity without inflation.” Market participants are remembering the Great Bond Crash of 1994 shown in Table VI-7G when monetary policy pursued nonexistent inflation, causing trillions of dollars of losses in fixed income worldwide while increasing the fed funds rate from 3 percent in Jan 1994 to 6 percent in Dec. The exercise in Table VI-7G shows a drop of the price of the 30-year bond by 18.1 percent and of the 10-year bond by 14.1 percent. CPI inflation remained almost the same and there is no valid counterfactual that inflation would have been higher without monetary policy tightening because of the long lag in effect of monetary policy on inflation (see Culbertson 1960, 1961, Friedman 1961, Batini and Nelson 2002, Romer and Romer 2004). The pursuit of nonexistent deflation during the past ten years has resulted in the largest monetary policy accommodation in history that created the 2007 financial market crash and global recession and is currently preventing smoother recovery while creating another financial crash in the future. The issue is not whether there should be a central bank and monetary policy but rather whether policy accommodation in doses from zero interest rates to trillions of dollars in the fed balance sheet endangers economic stability.
Table VI-7G, Fed Funds Rates, Thirty and Ten Year Treasury Yields and Prices, 30-Year Mortgage Rates and 12-month CPI Inflation 1994
| 1994 | FF | 30Y | 30P | 10Y | 10P | MOR | CPI |
| Jan | 3.00 | 6.29 | 100 | 5.75 | 100 | 7.06 | 2.52 |
| Feb | 3.25 | 6.49 | 97.37 | 5.97 | 98.36 | 7.15 | 2.51 |
| Mar | 3.50 | 6.91 | 92.19 | 6.48 | 94.69 | 7.68 | 2.51 |
| Apr | 3.75 | 7.27 | 88.10 | 6.97 | 91.32 | 8.32 | 2.36 |
| May | 4.25 | 7.41 | 86.59 | 7.18 | 88.93 | 8.60 | 2.29 |
| Jun | 4.25 | 7.40 | 86.69 | 7.10 | 90.45 | 8.40 | 2.49 |
| Jul | 4.25 | 7.58 | 84.81 | 7.30 | 89.14 | 8.61 | 2.77 |
| Aug | 4.75 | 7.49 | 85.74 | 7.24 | 89.53 | 8.51 | 2.69 |
| Sep | 4.75 | 7.71 | 83.49 | 7.46 | 88.10 | 8.64 | 2.96 |
| Oct | 4.75 | 7.94 | 81.23 | 7.74 | 86.33 | 8.93 | 2.61 |
| Nov | 5.50 | 8.08 | 79.90 | 7.96 | 84.96 | 9.17 | 2.67 |
| Dec | 6.00 | 7.87 | 81.91 | 7.81 | 85.89 | 9.20 | 2.67 |
Notes: FF: fed funds rate; 30Y: yield of 30-year Treasury; 30P: price of 30-year Treasury assuming coupon equal to 6.29 percent and maturity in exactly 30 years; 10Y: yield of 10-year Treasury; 10P: price of 10-year Treasury assuming coupon equal to 5.75 percent and maturity in exactly 10 years; MOR: 30-year mortgage; CPI: percent change of CPI in 12 months
Sources: yields and mortgage rates http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/data.htm CPI ftp://ftp.bls.gov/pub/special.requests/cpi/cpiai.t
Chart VI-14 provides the overnight fed funds rate, the yield of the 10-year Treasury constant maturity bond, the yield of the 30-year constant maturity bond and the conventional mortgage rate from Jan 1991 to Dec 1996. In Jan 1991, the fed funds rate was 6.91 percent, the 10-year Treasury yield 8.09 percent, the 30-year Treasury yield 8.27 percent and the conventional mortgage rate 9.64 percent. Before monetary policy tightening in Oct 1993, the rates and yields were 2.99 percent for the fed funds, 5.33 percent for the 10-year Treasury, 5.94 for the 30-year Treasury and 6.83 percent for the conventional mortgage rate. After tightening in Nov 1994, the rates and yields were 5.29 percent for the fed funds rate, 7.96 percent for the 10-year Treasury, 8.08 percent for the 30-year Treasury and 9.17 percent for the conventional mortgage rate.
Chart VI-14, US, Overnight Fed Funds Rate, 10-Year Treasury Constant Maturity, 30-Year Treasury Constant Maturity and Conventional Mortgage Rate, Monthly, Jan 1991 to Dec 1996
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/update/
Chart VI-15 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides the all items consumer price index from Jan 1991 to Dec 1996. There does not appear acceleration of consumer prices requiring aggressive tightening.
Chart VI-15, US, Consumer Price Index All Items, Jan 1991 to Dec 1996
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm
Chart IV-16 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides 12-month percentage changes of the all items consumer price index from Jan 1991 to Dec 1996. Inflation collapsed during the recession from Jul 1990 (III) and Mar 1991 (I) and the end of the Kuwait War on Feb 25, 1991 that stabilized world oil markets. CPI inflation remained almost the same and there is no valid counterfactual that inflation would have been higher without monetary policy tightening because of the long lag in effect of monetary policy on inflation (see Culbertson 1960, 1961, Friedman 1961, Batini and Nelson 2002, Romer and Romer 2004). Policy tightening had adverse collateral effects in the form of emerging market crises in Mexico and Argentina and fixed income markets worldwide.
Chart VI-16, US, Consumer Price Index All Items, Twelve-Month Percentage Change, Jan 1991 to Dec 1996
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm
Table VI-2 provides the Euro/Dollar (EUR/USD) exchange rate and Chinese Yuan/Dollar (CNY/USD) exchange rate that reveal pursuit of exchange rate policies resulting from monetary policy in the US and capital control/exchange rate policy in China. The ultimate intentions are the same: promoting internal economic activity at the expense of the rest of the world. The easy money policy of the US was deliberately or not but effectively to devalue the dollar from USD 1.1423/EUR on Jun 26, 2003 to USD 1.5914/EUR on Jul 14, 2008, or by 39.3 percent. The flight into dollar assets after the global recession caused revaluation to USD 1.192/EUR on Jun 7, 2010, or by 25.1 percent. After the temporary interruption of the sovereign risk issues in Europe from Apr to Jul, 2010, shown in Table VI-4 below, the dollar has revalued to USD 1.0533 EUR on Jan 6, 2017 or by 11.6 percent {[(1.0533/1.192)-1]100 = -11.6%}. Yellen (2011AS, 6) admits that Fed monetary policy results in dollar devaluation with the objective of increasing net exports, which was the policy that Joan Robinson (1947) labeled as “beggar-my-neighbor” remedies for unemployment. Risk aversion erodes devaluation of the dollar. China fixed the CNY to the dollar for a long period at a highly undervalued level of around CNY 8.2765/USD subsequently revaluing to CNY 6.8211/USD until Jun 7, 2010, or by 17.6 percent. After fixing again the CNY to the dollar, China devalued to CNY 6.9185/USD on Fri Jan 6, 2017, or by 1.4 percent, for cumulative revaluation of 16.4 percent. The final row of Table VI-2 shows: devaluation of 0.7 percent in the week of Dec 16, 2016; revaluation of 0.2 percent in the week of Dec 23, 2016; change of 0.0 percent in the week of Dec 30, 2016; and revaluation of 0.4 percent in the week of Jan 6. There could be reversal of revaluation to devalue the Yuan.
Table VI-2, Dollar/Euro (USD/EUR) Exchange Rate and Chinese Yuan/Dollar (CNY/USD) Exchange Rate
| USD/EUR | 12/26/03 | 7/14/08 | 6/07/10 | 01/06/17 |
| Rate | 1.1423 | 1.5914 | 1.192 | 1.0533 |
| CNY/USD | 01/03 | 07/21 | 7/15 | 01/06/17 |
| Rate | 8.2765 | 8.2765 | 6.8211 | 6.9185 |
| Weekly Rates | 12/16/2016 | 12/23/2016 | 12/30/2016 | 01/06/17 |
| CNY/USD | 6.9593 | 6.9463 | 6.9448 | 6.9185 |
| ∆% from Earlier Week* | -0.7 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.4 |
*Negative sign is depreciation; positive sign is appreciation
Source: http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/mdc_currencies.html?mod=mdc_topnav_2_3000
Professor Edward P Lazear (2013Jan7), writing on “Chinese ‘currency manipulation’ is not the problem,” on Jan 7, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887323320404578213203581231448.html), provides clear thought on the role of the yuan in trade between China and the United States and trade between China and Europe. There is conventional wisdom that Chinese exchange rate policy causes the loss of manufacturing jobs in the United States, which is shown by Lazear (2013Jan7) to be erroneous. The fact is that manipulation of the CNY/USD rate by China has only minor effects on US employment. Lazear (2013Jan7) shows that the movement of monthly exports of China to its major trading partners, United States and Europe, since 1995 cannot be explained by the fixing of the CNY/USD rate by China. The period is quite useful because it includes rapid growth before 2007, contraction until 2009 and weak subsequent expansion. Chart VI-1 of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System provides the CNY/USD exchange rate from Jan 3, 1995 to Dec 30, 2016 together with US recession dates in shaded areas. China fixed the CNY/USD rate for a long period as shown in the horizontal segment from 1995 to 2005. There was systematic revaluation of 17.6 percent from CNY 8.2765 on Jul 21, 2005 to CNY 6.8211 on Jul 15, 2008. China fixed the CNY/USD rate until Jun 7, 2010, to avoid adverse effects on its economy from the global recession, which is shown as a horizontal segment from 2009 until mid 2010. China then continued the policy of appreciation of the CNY relative to the USD with oscillations until the beginning of 2012 when the rate began to move sideways followed by a final upward slope of devaluation that is measured in Table VI-2A but virtually disappeared in the rate of CNY 6.3589/USD on Aug 17, 2012 and was nearly unchanged at CNY 6.3558/USD on Aug 24, 2012. China then appreciated 0.2 percent in the week of Dec 21, 2012, to CNY 6.2352/USD for cumulative 1.9 percent revaluation from Oct 28, 2011 and left the rate virtually unchanged at CNY 6.2316/USD on Jan 11, 2013, appreciating to CNY 6.9430/USD on Dec 30, 2016, which is the last data point in Chart VI-1. Revaluation of the CNY relative to the USD of 16.1 percent by Dec 30, 2016 has not reduced the trade surplus of China but reversal of the policy of revaluation could result in international confrontation. The interruption with upward slope in the final segment on the right of Chart VI-I is measured as virtually stability in Table VI-2A followed with decrease or revaluation and subsequent increase or devaluation. The final segment shows decline or revaluation with another upward move or devaluation. Linglin Wei, writing on “China intervenes to lower yuan,” on Feb 26, 2014, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702304071004579406810684766716?KEYWORDS=china+yuan&mg=reno64-wsj), finds from informed sources that the central bank of China conducted the ongoing devaluation of the yuan with the objective of driving out arbitrageurs to widen the band of fluctuation. There is concern if the policy of revaluation is changing to devaluation.
Chart VI-1, Chinese Yuan (CNY) per US Dollar (USD), Business Days, Jan 3, 1995-Dec 30, 2016
Note: US Recessions in Shaded Areas
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/H10/default.htm
Chart VI-1A provides the daily CNY/USD rate from Jan 5, 1981 to Dec 30, 2016. The exchange rate was CNY 1.5418/USD on Jan 5, 1981. There is sharp cumulative depreciation of 107.8 percent to CNY 3.2031 by Jul 2, 1986, continuing to CNY 5.8145/USD on Dec 29, 1993 for cumulative 277.1 percent since Jan 5, 1981. China then devalued sharply to CNY 8.7117/USD on Jan 7, 1994 for 49.8 percent relative to Dec 29, 1993 and cumulative 465.0 percent relative to Jan 5, 1981. China then fixed the rate at CNY 8.2765/USD until Jul 21, 2005 and revalued as analyzed in Chart VI-1. The final data point in Chart VI-1A is CNY 6.9430/USD on Dec 30, 2016. To be sure, China fixed the exchange rate after substantial prior devaluation. It is unlikely that the devaluation could have been effective after many years of fixing the exchange rate with high inflation and multiple changes in the world economy. The argument of Lazear (2013Jan7) is still valid in view of the lack of association between monthly exports of China to the US and Europe since 1995 and the exchange rate of China.
Chart VI-1A, Chinese Yuan (CNY) per US Dollar (USD), Business Days, Jan 5, 1981-Dec 30 2016
Note: US Recessions in Shaded Areas
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/H10/default.htm
Chart VI-1B provides finer details with the rate of Chinese Yuan (CNY) to the US Dollar (USD) from Oct 28, 2011 to Dec 30, 2016. There have been alternations of revaluation and devaluation. The initial data point is CNY 6.5370 on Oct 28, 2011. There is an episode of devaluation from CNY 6.2790 on Apr 30, 2012 to CNY 6.3879 on Jul 25, 2012, or devaluation of 1.4 percent. Another devaluation is from CNY 6.0402/USD on Jan 21, 2014 to CNY 6.9430/USD on Dec 30, 2016, or devaluation of 14.9 percent. The United States Treasury estimates US government debt held by private investors at $11,184 billion in Sep 2016. China’s holding of US Treasury securities represent 10.0 percent of US government marketable interest-bearing debt held by private investors (http://www.fms.treas.gov/bulletin/index.html). Min Zeng, writing on “China plays a big role as US Treasury yields fall,” on Jul 16, 2014, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/articles/china-plays-a-big-role-as-u-s-treasury-yields-fall-1405545034?tesla=y&mg=reno64-wsj), finds that acceleration in purchases of US Treasury securities by China has been an important factor in the decline of Treasury yields in 2014. Japan decreased its holdings from $1149.2 billion in Oct 2015 to $1131.9 billion in Oct 2016 or 1.5 percent. The combined holdings of China and Japan in Oct 2016 add to $2247.6 billion, which is equivalent to 20.1 percent of US government marketable interest-bearing securities held by investors of $11,184 billion in Jun 2016 (http://www.fms.treas.gov/bulletin/index.html). Total foreign holdings of Treasury securities decreased from $6047.2 billion in Oct 2015 to $6038.9 billion in Oct 2016, or 0.1 percent. The US continues to finance its fiscal and balance of payments deficits with foreign savings (see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007)). A point of saturation of holdings of US Treasury debt may be reached as foreign holders evaluate the threat of reduction of principal by dollar devaluation and reduction of prices by increases in yield, including possibly risk premium. Shultz et al (2012) find that the Fed financed three-quarters of the US deficit in fiscal year 2011, with foreign governments financing significant part of the remainder of the US deficit while the Fed owns one in six dollars of US national debt. Concentrations of debt in few holders are perilous because of sudden exodus in fear of devaluation and yield increases and the limit of refinancing old debt and placing new debt. In their classic work on “unpleasant monetarist arithmetic,” Sargent and Wallace (1981, 2) consider a regime of domination of monetary policy by fiscal policy (emphasis added):
“Imagine that fiscal policy dominates monetary policy. The fiscal authority independently sets its budgets, announcing all current and future deficits and surpluses and thus determining the amount of revenue that must be raised through bond sales and seignorage. Under this second coordination scheme, the monetary authority faces the constraints imposed by the demand for government bonds, for it must try to finance with seignorage any discrepancy between the revenue demanded by the fiscal authority and the amount of bonds that can be sold to the public. Suppose that the demand for government bonds implies an interest rate on bonds greater than the economy’s rate of growth. Then if the fiscal authority runs deficits, the monetary authority is unable to control either the growth rate of the monetary base or inflation forever. If the principal and interest due on these additional bonds are raised by selling still more bonds, so as to continue to hold down the growth of base money, then, because the interest rate on bonds is greater than the economy’s growth rate, the real stock of bonds will growth faster than the size of the economy. This cannot go on forever, since the demand for bonds places an upper limit on the stock of bonds relative to the size of the economy. Once that limit is reached, the principal and interest due on the bonds already sold to fight inflation must be financed, at least in part, by seignorage, requiring the creation of additional base money.”
Chart VI-1B, Chinese Yuan (CNY) per US Dollar (US), Business Days, Oct 28, 2011-Dec 30, 2016
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/H10/default.htm
There are major ongoing and unresolved realignments of exchange rates in the international financial system as countries and regions seek parities that can optimize their productive structures. Seeking exchange rate parity or exchange rate optimizing internal economic activities is complex in a world of unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates and even negative nominal interest rates of government obligations such as negative yields for the two-year government bond of Germany. Regulation, trade and devaluation conflicts should have been expected from a global recession (Pelaez and Pelaez (2007), The Global Recession Risk, Pelaez and Pelaez, Government Intervention in Globalization: Regulation, Trade and Devaluation Wars (2008a)): “There are significant grounds for concern on the basis of this experience. International economic cooperation and the international financial framework can collapse during extreme events. It is unlikely that there will be a repetition of the disaster of the Great Depression. However, a milder contraction can trigger regulatory, trade and exchange wars” (Pelaez and Pelaez, Government Intervention in Globalization: Regulation, Trade and Devaluation Wars (2008c), 181). Chart VI-2 of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System provides the key exchange rate of US dollars (USD) per euro (EUR) from Jan 4, 1999 to Dec 30, 2016. US recession dates are in shaded areas. The rate on Jan 4, 1999 was USD 1.1812/EUR, declining to USD 0.8279/EUR on Oct 25, 2000, or appreciation of the USD by 29.9 percent. The rate depreciated 21.9 percent to USD 1.0098/EUR on Jul 22, 2002. There was sharp devaluation of the USD of 34.9 percent to USD 1.3625/EUR on Dec 27, 2004 largely because of the 1 percent interest rate between Jun 2003 and Jun 2004 together with a form of quantitative easing by suspension of auctions of the 30-year Treasury, which was equivalent to withdrawing supply from markets. Another depreciation of 17.5 percent took the rate to USD 1.6010/EUR on Apr 22, 2008, already inside the shaded area of the global recession. The flight to the USD and obligations of the US Treasury appreciated the dollar by 22.3 percent to USD 1.2446/EUR on Oct 27, 2008. In the return of the carry trade after stress tests showed sound US bank balance sheets, the rate depreciated 21.2 percent to USD 1.5085/EUR on Nov 25, 2009. The sovereign debt crisis of Europe in the spring of 2010 caused sharp appreciation of 20.7 percent to USD 1.1959/EUR on Jun 6, 2010. Renewed risk appetite depreciated the rate 24.4 percent to USD 1.4875/EUR on May 3, 2011. The rate appreciated 11.8 percent to USD 1.0552/EUR on Dec 30, 2016, which is the last point in Chart VI-2. The data in Table VI-6 is obtained from closing dates in New York published by the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_PRO_hps_marketdata).
Chart VI-2, US Dollars (USD) per Euro (EUR), Jan 4, 1999 to Dec 30, 2016
Note: US Recessions in Shaded Areas
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/H10/default.htm
Chart VI-3 provides three indexes of the US Dollars (USD) from Jan 4, 1995 to Dec 30, 2016.
Chart VI-3A provides the overnight fed funds rate and yields of the three-month constant maturity Treasury bill, the ten-year constant maturity Treasury note and Moody’s Baa bond from Jan 4, 1995 to Jul 7, 2016. Chart VI-3B provides the overnight fed funds rate and yields of the three-month constant maturity Treasury bill and the ten-year constant maturity Treasury from Jan 5, 2001 to Jan 5, 2017. The first phase from 1995 to 2001 shows sharp trend of appreciation of the USD while interest rates remained at relatively high levels. The dollar revalued partly because of the emerging market crises that provoked inflows of financial investment into the US and partly because of a deliberate strong dollar policy. DeLong and Eichengreen (2001, 4-5) argue:
“That context was an economic and political strategy that emphasized private investment as the engine for U.S. economic growth. Both components of this term, "private" and "investment," had implications for the administration’s international economic strategy. From the point of view of investment, it was important that international events not pressure on the Federal Reserve to raise interest rates, since this would have curtailed capital formation and vitiated the effects of the administration’s signature achievement: deficit reduction. A strong dollar -- or rather a dollar that was not expected to weaken -- was a key component of a policy which aimed at keeping the Fed comfortable with low interest rates. In addition, it was important to create a demand for the goods and services generated by this additional productive capacity. To the extent that this demand resided abroad, administration officials saw it as important that the process of increasing international integration, of both trade and finance, move forward for the interest of economic development in emerging markets and therefore in support of U.S. economic growth.”
The process of integration consisted of restructuring “international financial architecture” (Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture: G7, IMF, BIS, Debtors and Creditors (2005)). Policy concerns subsequently shifted to the external imbalances, or current account deficits, and internal imbalances, or government deficits (Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk: Dollar Devaluation and the World Economy (2007)). Fed policy consisted of lowering the policy rate or fed funds rate, which is close to the marginal cost of funding of banks, toward zero during the past decade. Near zero interest rates induce carry trades of selling dollar debt (borrowing), shorting the USD and investing in risk financial assets. Without risk aversion, near zero interest rates cause devaluation of the dollar. Chart VI-3 shows the weakening USD between the recession of 2001 and the contraction after IVQ2007. There was a flight to dollar assets and especially obligations of the US government after Sep 2008. Cochrane and Zingales (2009) show that flight was coincident with proposals of TARP (Troubled Asset Relief Program) to withdraw “toxic assets” in US banks (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a) and Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b)). There are shocks to globalization in the form of regulation, trade and devaluation wars and breakdown of international cooperation (Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State: Vol. I (2008a), Globalization and the State: Vol. II (2008b) and Government Intervention in Globalization: Regulation, Trade and Devaluation Wars (2008c)). As evident in Chart VI-3A, there is no exit from near zero interest rates without a financial crisis and economic contraction, verified by the increase of interest rates from 1 percent in Jun 2004 to 5.25 percent in Jun 2006. The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) lowered the target of the fed funds rate from 7.03 percent on Jul 3, 2000, to 1.00 percent on Jun 22, 2004, in pursuit of non-existing deflation (Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), 18-28, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 83-85). The FOMC implemented increments of 25 basis points of the fed funds target from Jun 2004 to Jun 2006, raising the fed funds rate to 5.25 percent on Jul 3, 2006, as shown in Chart VI-3A. The gradual exit from the first round of unconventional monetary policy from 1.00 percent in Jun 2004 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/boarddocs/press/monetary/2004/20040630/default.htm) to 5.25 percent in Jun 2006 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20060629a.htm) caused the financial crisis and global recession. There are conflicts on exchange rate movements among central banks.
At the press conference after the FOMC meeting on Sep 21, 2016, Chair Yellen states (http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20160921.pdf ): “However, the economic outlook is inherently uncertain.” In the address to the Jackson Hole symposium on Aug 26, 2016, Chair Yellen states: “I believe the case for an increase in in federal funds rate has strengthened in recent months…And, as ever, the economic outlook is uncertain, and so monetary policy is not on a preset course” (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20160826a.htm). In a speech at the World Affairs Council of Philadelphia, on Jun 6, 2016 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20160606a.htm), Chair Yellen finds that “there is considerable uncertainty about the economic outlook.” There are fifteen references to this uncertainty in the text of 18 pages double-spaced. In the Semiannual Monetary Policy Report to the Congress on Jun 21, 2016, Chair Yellen states (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20160621a.htm), “Of course, considerable uncertainty about the economic outlook remains.” Frank H. Knight (1963, 233), in Risk, uncertainty and profit, distinguishes between measurable risk and unmeasurable uncertainty. Is there a “science” or even “art” of central banking under this extreme uncertainty in which policy does not generate higher volatility of money, income, prices and values of financial assets?
Chart VI-3, US Dollar Currency Indexes, Jan 4, 1995-Dec 30, 2016
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/H10/default.htm
Chart VI-3A, US, Overnight Fed Funds Rate, Yield of Three-Month Treasury Constant Maturity, Yield of Ten-Year Treasury Constant Maturity and Yield of Moody’s Baa Bond, Jan 4, 1995 to Jul 7, 2016
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/
Chart VI-3B, US, Overnight Fed Funds Rate, Yield of Three-Month Treasury Constant Maturity and Yield of Ten-Year Treasury Constant Maturity, Jan 5, 2001 to Jan 5, 2017
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/
The major reason and channel of transmission of unconventional monetary policy is through expectations of inflation. Fisher (1930) provided theoretical and historical relation of interest rates and inflation. Let in be the nominal interest rate, ir the real or inflation-adjusted interest rate and πe the expectation of inflation in the time term of the interest rate, which are all expressed as proportions. The following expression provides the relation of real and nominal interest rates and the expectation of inflation:
(1 + ir) = (1 + in)/(1 + πe) (1)
That is, the real interest rate equals the nominal interest rate discounted by the expectation of inflation in time term of the interest rate. Fisher (1933) analyzed the devastating effect of deflation on debts. Nominal debt contracts remained at original principal interest but net worth and income of debtors contracted during deflation. Real interest rates increase during declining inflation. For example, if the interest rate is 3 percent and prices decline 0.2 percent, equation (1) calculates the real interest rate as:
(1 +0.03)/(1 – 0.02) = 1.03/(0.998) = 1.032
That is, the real rate of interest is (1.032 – 1)100 or 3.2 percent. If inflation were 2 percent, the real rate of interest would be 0.98 percent, or about 1.0 percent {[(1.03/1.02) -1]100 = 0.98%}.
The yield of the one-year Treasury security was quoted in the Wall Street Journal at 0.114 percent on Fri May 17, 2013 (http://online.wsj.com/mdc/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_topnav_marketdata_main). The expected rate of inflation πe in the next twelve months is not observed. Assume that it would be equal to the rate of inflation in the past twelve months estimated by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BLS) at 1.1 percent (http://www.bls.gov/cpi/). The real rate of interest would be obtained as follows:
(1 + 0.00114)/(1 + 0.011) = (1 + rr) = 0.9902
That is, ir is equal to 1 – 0.9902 or minus 0.98 percent. Investing in a one-year Treasury security results in a loss of 0.98 percent relative to inflation. The objective of unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates is to induce consumption and investment because of the loss to inflation of riskless financial assets. Policy would be truly irresponsible if it intended to increase inflationary expectations or πe. The result could be the same rate of unemployment with higher inflation (Kydland and Prescott 1977).
At the press conference after the FOMC meeting on Sep 21, 2016, Chair Yellen states (http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20160921.pdf ): “However, the economic outlook is inherently uncertain.” In the address to the Jackson Hole symposium on Aug 26, 2016, Chair Yellen states: “I believe the case for an increase in in federal funds rate has strengthened in recent months…And, as ever, the economic outlook is uncertain, and so monetary policy is not on a preset course” (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20160826a.htm). In a speech at the World Affairs Council of Philadelphia, on Jun 6, 2016 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20160606a.htm), Chair Yellen finds that “there is considerable uncertainty about the economic outlook.” There are fifteen references to this uncertainty in the text of 18 pages double-spaced. In the Semiannual Monetary Policy Report to the Congress on Jun 21, 2016, Chair Yellen states (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20160621a.htm), “Of course, considerable uncertainty about the economic outlook remains.” Frank H. Knight (1963, 233), in Risk, uncertainty and profit, distinguishes between measurable risk and unmeasurable uncertainty. Is there a “science” or even “art” of central banking under this extreme uncertainty in which policy does not generate higher volatility of money, income, prices and values of financial assets?
The carry trade from zero interest rates to leveraged positions in risk financial assets had proved strongest for commodity exposures but US equities have regained leadership. There are complex economic, financial and political effects of the withdrawal of the UK from the European Union or BREXIT after the referendum on Jun 23, 2016 (https://next.ft.com/eu-referendum for extensive coverage by the Financial Times). The DJIA has increased 106.1 percent since the trough of the sovereign debt crisis in Europe on Jul 16, 2010 to Jan 6, 2017; S&P 500 has gained 122.7 percent and DAX 104.6 percent. Before the current round of risk aversion, almost all assets in the column “∆% Trough to 01/06/17” had double digit gains relative to the trough around Jul 2, 2010 followed by negative performance but now some valuations of equity indexes show varying behavior. China’s Shanghai Composite is 32.4 percent above the trough. Japan’s Nikkei Average is 120.5 percent above the trough. DJ Asia Pacific TSM is 27.2 percent above the trough. Dow Global is 51.7 percent above the trough. STOXX 50 of 50 blue-chip European equities (http://www.stoxx.com/indices/index_information.html?symbol=sx5E) is 32.8 percent above the trough. NYSE Financial Index is 67.1 percent above the trough. DAX index of German equities (http://www.bloomberg.com/quote/DAX:IND) is 104.6 percent above the trough. Japan’s Nikkei Average is 120.5 percent above the trough on Aug 31, 2010 and 70.8 percent above the peak on Apr 5, 2010. The Nikkei Average closed at 19,454.33 on Jan 6, 2017 (http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_PRO_hps_marketdata), which is 89.7 percent higher than 10,254.43 on Mar 11, 2011, on the date of the Tōhoku or Great East Japan Earthquake/tsunami. Global risk aversion erased the earlier gains of the Nikkei. The dollar appreciated 11.6 percent relative to the euro. The dollar devalued before the new bout of sovereign risk issues in Europe. The column “∆% week to 01/06/17” in Table VI-4 shows
increase of 1.6 percent in the week for China’s Shanghai Composite. The Nikkei increased 1.8 percent. DJ Asia Pacific increased 2.4 percent. NYSE Financial increased 2.1 percent in the week. Dow Global increased 2.0 percent in the week of Jan 6, 2017. The DJIA increased 1.0 percent and S&P 500 increased 1.7 percent. DAX of Germany increased 1.0 percent. STOXX 50 increased 1.3 percent. The USD depreciated 0.1 percent. There are still high uncertainties on European sovereign risks and banking soundness, US and world growth slowdown and China’s growth tradeoffs. Sovereign problems in the “periphery” of Europe and fears of slower growth in Asia and the US cause risk aversion with trading caution instead of more aggressive risk exposures. There is a fundamental change in Table VI-4 from the relatively upward trend with oscillations since the sovereign risk event of Apr-Jul 2010. Performance is best assessed in the column “∆% Peak to 01/06/17” that provides the percentage change from the peak in Apr 2010 before the sovereign risk event to Jan 6, 2017. Most risk financial assets had gained not only relative to the trough as shown in column “∆% Trough to 01/06/17” but also relative to the peak in column “∆% Peak to 01/06/17.” There are now several equity indexes above the peak in Table VI-4: DJIA 78.2 percent, S&P 500 87.1 percent, DAX 83.2 percent, NYSE Financial Index (http://www.nyse.com/about/listed/nykid.shtml) 33.1 percent, Dow Global 23.7 percent, and Nikkei Average 70.8 percent. Shanghai Composite is 0.3 percent below the peak; STOXX 50 is 12.5 percent above the peak; and DJ Asia Pacific TSM is 11.4 percent above the peak. The Shanghai Composite increased 59.8 percent from March 12, 2014, to Jan 6, 2017. The US dollar strengthened 30.4 percent relative to the peak. The factors of risk aversion have adversely affected the performance of risk financial assets. The performance relative to the peak in Apr 2010 is more important than the performance relative to the trough around early Jul 2010 because improvement could signal that conditions have returned to normal levels before European sovereign doubts in Apr 2010. Sharp and continuing strengthening of the dollar is affecting balance sheets of US corporations with foreign operations (http://www.fasb.org/jsp/FASB/Pronouncement_C/SummaryPage&cid=900000010318). The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) is following “financial and international developments” as part of the process of framing interest rate policy (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20150128a.htm). Kate Linebaugh, writing on “Corporate profits set to shrink for fourth consecutive quarter,” on Jul 17, 2016, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/corporate-profits-set-to-shrink-for-fourth-consecutive-quarter-1468799278), quotes forecasts of Thomson Reuters of 4.7 decline of adjusted earnings per share in the S&P 500 index in IIQ2016 relative to a year earlier. That would be the fourth consecutive quarterly decline. Theo Francis and Kate Linebaugh, writing on “US corporate profits on pace for third straight decline,” on Apr 28, 2016, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/u-s-corporate-profits-on-pace-for-third-straight-decline-1461872242), analyze three consecutive quarters of decline of corporate earnings and revenue in companies in S&P 500. They quote Thomson Reuters on expected decline of earnings of 6.1 percent in IQ2016 based on 55 percent of reporting companies. Weakness of economic activity shows in decline of revenues in IQ2016 of 1.4 percent, increasing 1.7 percent excluding energy, and contraction of profits of 0.5 percent. Justin Lahart, writing on “S&P 500 Earnings: far worse than advertised,” on Feb 24, 2016, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/s-p-500-earnings-far-worse-than-advertised-1456344483), analyzes S&P 500 earnings in 2015. Under data provided by companies, earnings increased 0.4 percent in 2015 relative to 2014 but under GAAP (Generally Accepted Accounting Principles), earnings fell 12.7 percent, which is the worst decrease since 2008. Theo Francis e Kate Linebaugh, writing on Oct 25, 2015, on “US Companies Warn of Slowing Economy, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/u-s-companies-warn-of-slowing-economy-1445818298) analyze the first contraction of earnings and revenue of big US companies. Production, sales and employment are slowing in a large variety of companies with some contracting. Corporate profits also suffer from revaluation of the dollar that constrains translation of foreign profits into dollar balance sheets. Francis and Linebaugh quote Thomson Reuters that analysts expect decline of earnings per share of 2.8 percent in IIIQ2015 relative to IIIQ2014 based on reports by one third of companies in the S&P 500. Sales would decline 4.0% in a third quarter for the first joint decline of earnings per share and revenue in the same quarter since IIIQ2009. Dollar revaluation also constrains corporate results.
Inyoung Hwang, writing on “Fed optimism spurs record bets against stock volatility,” on Aug 21, 2014, published in Bloomberg.com (http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2014-08-21/fed-optimism-spurs-record-bets-against-stock-voalitlity.html), informs that the S&P 500 is trading at 16.6 times estimated earnings, which is higher than the five-year average of 14.3 Tom Lauricella, writing on Mar 31, 2014, on “Stock investors see hints of a stronger quarter,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702304157204579473513864900656?mod=WSJ_smq0314_LeadStory&mg=reno64-wsj), finds views of stronger earnings among many money managers with positive factors for equity markets in continuing low interest rates and US economic growth. There is important information in the Quarterly Markets review of the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/public/page/quarterly-markets-review-03312014.html) for IQ2014. Alexandra Scaggs, writing on “Tepid profits, roaring stocks,” on May 16, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887323398204578487460105747412.html), analyzes stabilization of earnings growth: 70 percent of 458 reporting companies in the S&P 500 stock index reported earnings above forecasts but sales fell 0.2 percent relative to forecasts of increase of 0.5 percent. Paul Vigna, writing on “Earnings are a margin story but for how long,” on May 17, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://blogs.wsj.com/moneybeat/2013/05/17/earnings-are-a-margin-story-but-for-how-long/), analyzes that corporate profits increase with stagnating sales while companies manage costs tightly. More than 90 percent of S&P components reported moderate increase of earnings of 3.7 percent in IQ2013 relative to IQ2012 with decline of sales of 0.2 percent. Earnings and sales have been in declining trend. In IVQ2009, growth of earnings reached 104 percent and sales jumped 13 percent. Net margins reached 8.92 percent in IQ2013, which is almost the same at 8.95 percent in IIIQ2006. Operating margins are 9.58 percent. There is concern by market participants that reversion of margins to the mean could exert pressure on earnings unless there is more accelerated growth of sales. Vigna (op. cit.) finds sales growth limited by weak economic growth. Kate Linebaugh, writing on “Falling revenue dings stocks,” on Oct 20, 2012, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10000872396390444592704578066933466076070.html?mod=WSJPRO_hpp_LEFTTopStories), identifies a key financial vulnerability: falling revenues across markets for United States reporting companies. Global economic slowdown is reducing corporate sales and squeezing corporate strategies. Linebaugh quotes data from Thomson Reuters that 100 companies of the S&P 500 index have reported declining revenue only 1 percent higher in Jun-Sep 2012 relative to Jun-Sep 2011 but about 60 percent of the companies are reporting lower sales than expected by analysts with expectation that revenue for the S&P 500 will be lower in Jun-Sep 2012 for the entities represented in the index. Results of US companies are likely repeated worldwide. Future company cash flows derive from investment projects. Future company cash flows derive from investment projects. In IQ1980, real gross private domestic investment in the US was $951.6 billion of chained 2009 dollars, growing to $1,270.0 billion in IQ1990 or 33.5 percent. Real gross private domestic investment in the US increased 7.7 percent from $2605.2 billion in IVQ2007 to $2,804.7 billion in IIIQ2016. As shown in Table IAI-2, real private fixed investment increased 7.5 percent from $2,586.3 billion of chained 2009 dollars in IVQ2007 to $2,779.3 billion in IIIQ2016. Private fixed investment fell relative to IVQ2007 in all quarters preceding IQ2014 and changed 0.0 percent in IIIQ2016, declining 0.3 percent in IIQ2016 and falling 0.2 percent in IQ2016. Growth of real private investment in Table IA1-2 is mediocre for all but four quarters from IIQ2011 to IQ2012. The investment decision of United States corporations is fractured in the current economic cycle in preference of cash. There are three aspects. First, there is fluctuation in corporate profits. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA decreased at $127.9 billion in IVQ2015 and increased at $66.0 billion in IQ2016. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA fell at $12.5 billion in IIQ2016 and increased at $117.8 billion in IIIQ2016. Profits after tax with IVA and CCA fell at $172.7 billion in IVQ2015 and increased at $113.4 billion in IQ2016. Profits after tax with IVA and CCA fell at $28.9 billion in IIQ2016 and increased at $98.3 billion in IIIQ2016. Net dividends fell at $20.8 billion in IVQ2015 and increased at $7.3 billion in IQ2016. Net dividends fell at $9.3 billion in IIQ2016. Net dividends increased at $18.5 billion in IIIQ2016. Undistributed corporate profits with IVA and CCA fell at $152.0 billion in IVQ2015. Undistributed profits with IVA and CCA increased at $106.1 billion in IQ2016. Undistributed corporate profits fell at $19.6 billion in IIQ2016. Undistributed corporate profits increased at $79.8 billion in IIIQ2016. Undistributed corporate profits swelled 238.8 percent from $107.7 billion in IQ2007 to $364.9 billion in IIIQ2016 and changed signs from minus $55.9 billion in current dollars in IVQ2007. Uncertainty originating in fiscal, regulatory and monetary policy causes wide swings in expectations and decisions by the private sector with adverse effects on investment, real economic activity and employment. Second, sharp and continuing strengthening of the dollar is affecting balance sheets of US corporations with foreign operations (http://www.fasb.org/jsp/FASB/Pronouncement_C/SummaryPage&cid=900000010318) and the overall US economy. The bottom part of Table IA1-9 provides the breakdown of corporate profits with IVA and CCA in domestic industries and the rest of the world. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA fell at $127.9 billion in IVQ2015 with decrease of domestic industries at $149.8 billion, mostly because of decrease of nonfinancial business at $131.7 billion, and increase of profits from operations in the rest of the world at $22.0 billion. Receipts from the rest of the world fell at $19.9 billion. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased at $66.0 billion in IQ2016 with increase of domestic industries at $92.9 billion. Profits from operations from the rest of the world fell at $26.9 billion and payments to the rest of the world increased at $35.6 billion. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA decreased at $12.5 billion in IIQ2016. Profits from domestic industries fell at $50.5 billion and profits from nonfinancial business fell at $56.1 billion. Profits from the rest of the world increased at $38.0 billion. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased at $117.8 billion in IIIQ2016. Profits from domestic industries increased at $116.5 billion and profits from nonfinancial business increased at $66.4 billion. Profits from the rest of the world increased at $1.3 billion. Total corporate profits with IVA and CCA were $2138.8 billion in IIIQ2016 of which $1729.9 billion from domestic industries, or 80.9 percent of the total, and $408.9 billion, or 19.1 percent, from the rest of the world. Nonfinancial corporate profits of $1236.9 billion account for 57.8 percent of the total. Third, there is reduction in the use of corporate cash for investment. Vipal Monga, David Benoit and Theo Francis, writing on “Companies send more cash back to shareholders,” published on May 26, 2015 in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/companies-send-more-cash-back-to-shareholders-1432693805?tesla=y), use data of a study by Capital IQ conducted for the Wall Street Journal. This study shows that companies in the S&P 500 reduced investment in plant and equipment to median 29 percent of operating cash flow in 2013 from 33 percent in 2003 while increasing dividends and buybacks to median 36 percent in 2013 from 18 percent in 2003.
The basic valuation equation that is also used in capital budgeting postulates that the value of stocks or of an investment project is given by:
Where Rτ is expected revenue in the time horizon from τ =1 to T; Cτ denotes costs; and ρ is an appropriate rate of discount. In words, the value today of a stock or investment project is the net revenue, or revenue less costs, in the investment period from τ =1 to T discounted to the present by an appropriate rate of discount. In the current weak economy, revenues have been increasing more slowly than anticipated in investment plans. An increase in interest rates would affect discount rates used in calculations of present value, resulting in frustration of investment decisions. If V represents value of the stock or investment project, as ρ → ∞, meaning that interest rates increase without bound, then V → 0, or
declines. Equally, decline in expected revenue from the stock or project, Rτ, causes decline in valuation.
An intriguing issue is the difference in performance of valuations of risk financial assets and economic growth and employment. Paul A. Samuelson (http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/economics/laureates/1970/samuelson-bio.html) popularized the view of the elusive relation between stock markets and economic activity in an often-quoted phrase “the stock market has predicted nine of the last five recessions.” In the presence of zero interest rates forever, valuations of risk financial assets are likely to differ from the performance of the overall economy. The interrelations of financial and economic variables prove difficult to analyze and measure.
Table VI-4, Stock Indexes, Commodities, Dollar and 10-Year Treasury
| Peak | Trough | ∆% to Trough | ∆% Peak to 01/06/ /17 | ∆% Week 01/06/17 | ∆% Trough to 01/06/ 17 | |
| DJIA | 4/26/ | 7/2/10 | -13.6 | 78.2 | 1.0 | 106.1 |
| S&P 500 | 4/23/ | 7/20/ | -16.0 | 87.1 | 1.7 | 122.7 |
| NYSE Finance | 4/15/ | 7/2/10 | -20.3 | 33.1 | 2.1 | 67.1 |
| Dow Global | 4/15/ | 7/2/10 | -18.4 | 23.7 | 2.0 | 51.7 |
| Asia Pacific | 4/15/ | 7/2/10 | -12.5 | 11.4 | 2.4 | 27.2 |
| Japan Nikkei Aver. | 4/05/ | 8/31/ | -22.5 | 70.8 | 1.8 | 120.5 |
| China Shang. | 4/15/ | 7/02 | -24.7 | -0.3 | 1.6 | 32.4 |
| STOXX 50 | 4/15/10 | 7/2/10 | -15.3 | 12.5 | 1.3 | 32.8 |
| DAX | 4/26/ | 5/25/ | -10.5 | 83.2 | 1.0 | 104.6 |
| Dollar | 11/25 2009 | 6/7 | 21.2 | 30.4 | -0.1 | 11.6 |
| DJ UBS Comm. | 1/6/ | 7/2/10 | -14.5 | NA | NA | NA |
| 10-Year T Note | 4/5/ | 4/6/10 | 3.986 | 2.784 | 2.416 |
T: trough; Dollar: positive sign appreciation relative to euro (less dollars paid per euro), negative sign depreciation relative to euro (more dollars paid per euro)
Source: http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_hps_marketdata
ESII Valuations of Risk Financial Assets. There are complex economic, financial and political effects of the withdrawal of the UK from the European Union or BREXIT after the referendum on Jun 23, 2016 (https://next.ft.com/eu-referendum for extensive coverage by the Financial Times).The most important source of financial turbulence is shifting toward fluctuating interest rates. The dollar/euro rate is quoted as number of US dollars USD per one euro EUR, USD 1.0520/EUR in the first row, first column in the block for currencies in Table III-1 for Fri Dec 30, appreciating to USD 1.0477/EUR on Mon Jan 2, 2017, or by 0.4 percent. The dollar appreciated because fewer dollars, 1.0477, were required on Mon Jan 2 to buy one euro than $1.0520 on Fri Dec 30. Table III-1 defines a country’s exchange rate as number of units of domestic currency per unit of foreign currency. USD/EUR would be the definition of the exchange rate of the US and the inverse [1/(USD/EUR)] is the definition in this convention of the rate of exchange of the euro zone, EUR/USD. A convention used throughout this blog is required to maintain consistency in characterizing movements of the exchange rate such as in Table III-1 as appreciation and depreciation. The first row for each of the currencies shows the exchange rate at 5 PM New York time, such as USD 1.0520/EUR on Dec 30. The second row provides the cumulative percentage appreciation or depreciation of the exchange rate from the rate on the last business day of the prior week, in this case Fri Dec 30, to the last business day of the current week, in this case Jan 6, such as depreciation of 0.1 percent to USD 1.0533/EUR by Jan 6. The third row provides the percentage change from the prior business day to the current business day. For example, the USD depreciated (denoted by negative sign) by 0.1 percent from the rate of USD 1.0520/EUR on Fri Dec 30 to the rate of USD 1.0533/EUR on Jan 6 {[(1.0533/1.0520) - 1]100 = 0.1%}. The dollar appreciated (denoted by positive sign) by 0.7 percent from the rate of USD 1.0607 on
Thu Jan 5 to USD 1.0533/EUR on Fri Jan 6 {[(1.0533/1.0607) -1]100 = -0.7%}. Other factors constant, increasing risk aversion causes appreciation of the dollar relative to the euro, with rising uncertainty on European and global sovereign risks increasing dollar-denominated assets with sales of risk financial investments. Funds move away from higher yielding risk assets to the safety of dollar-denominated assets.
There is mixed performance in equity indexes with several indexes in Table III-1 increasing in the week ending on Jan 6, 2017, after wide swings caused by reallocations of investment portfolios worldwide. Stagnating revenues, corporate cash hoarding, effects of currency oscillations on corporate earnings and declining investment are causing reevaluation of discounted net earnings with deteriorating views on the world economy and United States fiscal sustainability but investors have been driving indexes higher. There are complex economic, financial and political effects of the withdrawal of the UK from the European Union or BREXIT after the referendum on Jun 23, 2016 (https://next.ft.com/eu-referendum for extensive coverage by the Financial Times). DJIA increased 0.3 percent on Jan 6, increasing 1.0 percent in the week. Germany’s DAX increased 0.1 percent on Jan 6 and increased 1.0 percent in the week. Dow Global increased 0.1 percent on Jan 6 and increased 2.0 percent in the week. Japan’s Nikkei Average decreased 0.3 percent on Jan 6 and increased 1.8 percent in the week as the yen continues oscillating but relatively weaker and the stock market gains in expectations of success of fiscal stimulus by a new administration and monetary stimulus by a new board of the Bank of Japan. Dow Asia Pacific TSM decreased 0.5 percent on Jan 6 and increased 2.4 percent in the week. Shanghai Composite that decreased 1.0 percent on Mar 8 and decreased 1.7 percent in the week of Mar 8, falling below 2000 at 1974.38 on Mar 12, 2014 but closing at 3154.32 on Jan 6, 2017, for decrease of 0.4 percent and increasing 1.6 percent in the week. The Shanghai Composite increased 59.8 percent from March 12, 2014 to Jan 6, 2017. There is deceleration with oscillations of the world economy that could affect corporate revenue and equity valuations, causing fluctuations in equity markets with increases during favorable risk appetite. The global hunt for yield induced by central bank policy rates of near zero percent motivates wide portfolio reshufflings among classes of risk financial assets.
Commodities were mixed in the week of Jan 6, 2017. Table III-1 shows that WTI increased 0.5 percent in the week of Jan 6 while Brent increased 0.5 percent in the week with turmoil in oil producing regions but oscillating action by OPEC. Gold decreased 0.7 percent on Jan 6 and increased 1.9 percent in the week.
Table III-I, Weekly Financial Risk Assets Jan 2 to Jan 6, 2017
| Fri 30 | Mon 2 | Tue 3 | Wed 4 | Thu 5 | Fri 6 |
| USD/ EUR 1.0520 -0.6% -0.3% | 1.0477 0.4% 0.4% | 1.0406 1.1% 0.7% | 1.0490 0.3% -0.8% | 1.0607 -0.8% -1.1% | 1.0533 -0.1 0.7% |
| JPY/ USD 117.00 0.3% -0.4% | 117.61 -0.5% -0.5% | 117.75 -0.6% -0.1% | 117.25 -0.2% 0.4% | 115.35 1.4% 1.6% | 116.99 0.0% -1.4% |
| CHF/ USD 1.0189 0.8% 0.4% | 1.0238 -0.5% -0.5% | 1.0275 -0.8% -0.4% | 1.0209 -0.2% 0.6% | 1.0097 0.9% 1.1% | 1.0181 0.1% -0.8% |
| CHF/ EUR 1.0718 0.1% 0.1% | 1.0726 -0.1% -0.1% | 1.0692 0.2% 0.3% | 1.0709 0.1% -0.2% | 1.0709 0.1% 0.0% | 1.0723 0.0% -0.1% |
| USD/ AUD 0.7202 1.3885 0.4% -0.2% | 0.7185 1.3918 -0.2% -0.2% | 0.7220 1.3850 0.3% 0.5% | 0.7283 1.3731 1.1% 0.9% | 0.7337 1.3630 1.8% 0.7% | 0.7299 1.3701 1.3% -0.5% |
| 10Y Note 2.447 | 2.445 | 2.447 | 2.452 | 2.374 | 2.416 |
| 2Y Note 1.210 | 1.206 | 1.222 | 1.230 | 1.170 | 1.226 |
| German Bond 2Y -0.79 10Y 0.21 | 2Y -0.79 10Y 0.19 | 2Y -0.78 10Y 0.27 | 2Y -0.78 10Y 0.28 | 2Y -0.73 10Y 0.23 | 2Y -0.73 10Y 0.30 |
| DJIA 19762.60 -0.9% -0.3% | 19762.60 0.0% 0.0% | 19881.76 0.6% 0.6% | 19942.16 0.9% 0.3% | 19899.29 0.7% -0.2% | 19963.80 1.0% 0.3% |
| Dow Global 2531.51 -0.2% 0.1% | 2531.51 0.0% 0.0% | 2541.23 0.4% 0.4% | 2564.01 1.3% 0.9% | 2579.18 1.9% 0.6% | 2582.66 2.0% 0.1% |
| DJ Asia Pacific 1422.73 0.5% 0.3% | 1422.73 0.0% 0.0% | 1420.41 -0.2% -0.2% | 1441.91 1.3% 1.5% | 1463.30 2.9% 1.5% | 1456.53 2.4% -0.5% |
| Nikkei 19114.37 -1.6% -0.2% | 19114.37 0.0% 0.0% | 19114.37 0.0% 0.0% | 19594.16 2.5% 2.5% | 19520.69 2.1% -0.4% | 19454.33 1.8% -0.3% |
| Shanghai 3103.64 -0.2% 0.2% | 3103.64 0.0% 0.0% | 3135.92 1.0% 1.0% | 3158.79 1.8% 0.7% | 3165.41 2.0% 0.2% | 3154.32 1.6% -0.4% |
| DAX 11481.06 0.3% 0.3% | 11598.33 1.0% 1.0% | 11584.24 0.9% -0.1% | 11584.31 0.9% 0.0% | 11584.94 0.9% 0.0% | 11599.01 1.0% 0.1% |
| DJ UBS Comm. NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| WTI $/B 53.72 1.3% -0.1% | 53.72 0.0% 0.0% | 52.33 -2.6% -2.6% | 53.26 -0.9% 1.8% | 53.76 0.1% 0.9% | 53.99 0.5% 0.4% |
| Brent $/B 56.82 3.0% 1.2% | 56.82 0.0% 0.0% | 55.47 -2.4% -2.4% | 56.46 -0.6% 1.8% | 56.89 0.1% 0.8% | 57.10 0.5% 0.4% |
| 44Gold 1150.0 1.6% -0.6% | 1150.0 0.0% 0.0% | 1160.4 0.9% 0.9% | 1163.8 1.2% 0.3% | 1179.70 2.6% 1.4% | 1171.9 1.9% -0.7% |
Note: USD: US dollar; JPY: Japanese Yen; CHF: Swiss
Franc; AUD: Australian dollar; Comm.: commodities; OZ: ounce
Sources: http://www.bloomberg.com/markets/
http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_hps_marketdata
Table VI-6, updated with every blog comment, shows that exchange rate valuations affect a large variety of countries, in fact, almost the entire world, in magnitudes that cause major problems for domestic monetary policy and trade flows. Dollar devaluation/fluctuation is expected to continue because of zero fed funds rate, expectations of rising inflation, large budget deficit of the federal government (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703907004576279321350926848.html?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection) and now near zero interest rates indefinitely but with interruptions caused by risk aversion events. The euro has devalued 51.0 percent relative to the dollar from the high on Jul 15, 2008 to Jan 6, 2017. There are complex economic, financial and political effects of the withdrawal of the UK from the European Union or BREXIT after the referendum on Jun 23, 2016 (https://next.ft.com/eu-referendum for extensive coverage by the Financial Times). The British pound (GBP) devalued 13.0 percent from the trough of ₤1.388 on Jan 2, 2009 to ₤1.2285 on Jan 6, 2017 and devalued 63.3 percent from the high of ₤2.006 on Sep 15, 2008. Such similar event actually occurred in the week of Sep 23, 2011 reversing the devaluation of the dollar in the form of sharp appreciation of the dollar relative to other currencies from all over the world including the offshore Chinese yuan market. The Bank of England reduced the Bank Rate to 0.25 percent on Aug 4, 2016, and announced new measures of quantitative easing (http://www.bankofengland.co.uk/publications/Pages/news/2016/008.aspx).
Table VI-6, Exchange Rates
| Peak | Trough | ∆% P/T | Jan 6, 2017 | ∆% T Jan 6, 2017 | ∆% P Jan 6, 2017 | |
| EUR USD | 7/15 | 6/7 2010 | 01/06/17 2017 | |||
| 1Rate | 1.59 | 1.192 | 1.0533 | |||
| ∆% | -33.4 | -13.2 | -51.0 | |||
| JPY USD | 8/18 | 9/15 | 01/06/17 2017 | |||
| Rate | 110.19 | 83.07 | 116.99 | |||
| ∆% | 24.6 | -40.8 | -6.2 | |||
| CHF USD | 11/21 2008 | 12/8 2009 | 01/06/17 2017 | |||
| Rate | 1.225 | 1.025 | 1.0181 | |||
| ∆% | 16.3 | 0.7 | 16.9 | |||
| USD GBP | 7/15 | 1/2/ 2009 | 01/06/17 2017 | |||
| Rate | 2.006 | 1.388 | 1.2285 | |||
| ∆% | -44.5 | -13.0 | -63.3 | |||
| USD AUD | 7/15 2008 | 10/27 2008 | 01/06/17 2017 | |||
| Rate | 1.0215 | 1.6639 | 0.7299 | |||
| ∆% | -62.9 | 17.7 | -34.1 | |||
| ZAR USD | 10/22 2008 | 8/15 | 01/06/17 2017 | |||
| Rate | 11.578 | 7.238 | 13.7600 | |||
| ∆% | 37.5 | -90.1 | -18.8 | |||
| SGD USD | 3/3 | 8/9 | 01/06/17 2017 | |||
| Rate | 1.553 | 1.348 | 1.4389 | |||
| ∆% | 13.2 | -6.7 | 7.3 | |||
| HKD USD | 8/15 2008 | 12/14 2009 | 01/06/17 2017 | |||
| Rate | 7.813 | 7.752 | 7.7556 | |||
| ∆% | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.7 | |||
| BRL USD | 12/5 2008 | 4/30 2010 | 01/06/17 2017 | |||
| Rate | 2.43 | 1.737 | 3.2242 | |||
| ∆% | 28.5 | -85.6 | -32.7 | |||
| CZK USD | 2/13 2009 | 8/6 2010 | 01/06/17 2017 | |||
| Rate | 22.19 | 18.693 | 25.654 | |||
| ∆% | 15.7 | -37.2 | -15.6 | |||
| SEK USD | 3/4 2009 | 8/9 2010 | 01/06/17 2017 | |||
| Rate | 9.313 | 7.108 | 9.0595 | |||
| ∆% | 23.7 | -27.5 | 2.7 | |||
| CNY USD | 7/20 2005 | 7/15 | 01/06/17 2017 | |||
| Rate | 8.2765 | 6.8211 | 6.9185 | -1.4 | 16.4 | |
| ∆% | 17.6 |
Symbols: USD: US dollar; EUR: euro; JPY: Japanese yen; CHF: Swiss franc; GBP: UK pound; AUD: Australian dollar; ZAR: South African rand; SGD: Singapore dollar; HKD: Hong Kong dollar; BRL: Brazil real; CZK: Czech koruna; SEK: Swedish krona; CNY: Chinese yuan; P: peak; T: trough
Note: percentages calculated with currencies expressed in units of domestic currency per dollar; negative sign means devaluation and no sign appreciation
Source:
http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/mdc_currencies.html?mod=mdc_topnav_2_3000
ESIII Twenty-four Million Unemployed or Underemployed. The balance of this section considers the second approach. Charts I-1 to I-12 explain the reasons for considering another approach to calculating job stress in the US. Chart I-1 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides the level of employment in the US from 2001 to 2016. There was a big drop of the number of people employed from 147.315 million at the peak in Jul 2007 (NSA) to 136.809 million at the trough in Jan 2010 (NSA) with 10.506 million fewer people employed. Recovery has been anemic compared with the shallow recession of 2001 that was followed by nearly vertical growth in jobs. The number employed in Dec 2016 was 151.798 million (NSA) or 4.483 million more people with jobs relative to the peak of 147.315 million in Jul 2007 while the civilian noninstitutional population of ages 16 years and over increased from 231.958 million in Jul 2007 to 254.742 million in Dec 2016 or by 22.784 million. The number employed increased 3.0 percent from Jul 2007 to Dec 2016 while the noninstitutional civilian population of ages of 16 years and over, or those available for work, increased 9.8 percent. The ratio of employment to population in Jul 2007 was 63.5 percent (147.315 million employment as percent of population of 231.958 million). The same ratio in Dec 2016 would result in 161.761 million jobs (0.635 multiplied by noninstitutional civilian population of 254.742 million). There are effectively 9.963 million fewer jobs in Dec 2016 than in Jul 2007, or 161.761 million minus 151.798 million. There is actually not sufficient job creation in merely absorbing new entrants in the labor force because of those dropping from job searches, worsening the stock of unemployed or underemployed in involuntary part-time jobs.
Chart I-1, US, Employed, Thousands, SA, 2001-2016
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-2 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides 12-month percentage changes of the number of people employed in the US from 2001 to 2016. There was recovery since 2010 but not sufficient to recover lost jobs. Many people in the US who had jobs before the global recession are not working now and many who entered the labor force cannot find employment.
Chart I-2, US, Employed, 12-Month Percentage Change NSA, 2001-2016
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
The foundation of the second approach derives from Chart I-3 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics providing the level of the civilian labor force in the US. The civilian labor force consists of people who are available and willing to work and who have searched for employment recently. The labor force of the US NSA grew 9.4 percent from 142.828 million in Jan 2001 to 156.255 million in Jul 2009. The civilian labor force is 1.7 percent higher at 158.968 million in Dec 2016 than in Jul 2009, all numbers not seasonally adjusted. Chart I-3 shows the flattening of the curve of expansion of the labor force and its decline in 2010 and 2011. The ratio of the labor force of 154.871 million in Jul 2007 to the noninstitutional population of 231.958 million in Jul 2007 was 66.8 percent while the ratio of the labor force of 158.968 million in Dec 2016 to the noninstitutional population of 254.742 million in Dec 2016 was 62.4 percent. The labor force of the US in Dec 2016 corresponding to 66.8 percent of participation in the population would be 170.168 million (0.668 x 254.742). The difference between the measured labor force in Dec 2016 of 158.968 million and the labor force in Dec 2016 with participation rate of 66.8 percent (as in Jul 2007) of 170.168 million is 11.200 million. The level of the labor force in the US has stagnated and is 11.200 million lower than what it would have been had the same participation rate been maintained. Millions of people have abandoned their search for employment because they believe there are no jobs available for them. The key issue is whether the decline in participation of the population in the labor force is the result of people giving up on finding another job.
Chart I-3, US, Civilian Labor Force, Thousands, SA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-4 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides 12-month percentage changes of the level of the labor force in the US. The rate of growth fell almost instantaneously with the global recession and became negative from 2009 to 2011. The labor force of the US collapsed and did not recover. Growth in the beginning of the summer originates in younger people looking for jobs in the summer after graduation or during school recess.
Chart I-4, US, Civilian Labor Force, Thousands, NSA, 12-month Percentage Change, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-5 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides the labor force participation rate in the US or labor force as percent of the population. The labor force participation rate of the US fell from 66.8 percent in Jan 2001 to 62.4 percent NSA in Dec 2016, all numbers not seasonally adjusted. The annual labor force participation rate for 1979 was 63.7 percent and also 63.7 percent in Nov 1980 during sharp economic contraction. This comparison is further elaborated below. Chart I-5 shows an evident downward trend beginning with the global recession that has continued throughout the recovery beginning in IIIQ2009. The critical issue is whether people left the workforce of the US because they believe there is no longer a job for them.
Chart I-5, Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate, Percent of Population in Labor Force SA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-6 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides the level of unemployed in the US. The number unemployed rose from the trough of 6.272 million NSA in Oct 2006 to the peak of 16.147 million in Jan 2010, declining to 13.400 million in Jul 2012, 12.696 million in Aug 2012 and 11.741 million in Sep 2012. The level unemployed fell to 11.741 million in Oct 2012, 11.404 million in Nov 2012, 11.844 million in Dec 2012, 13.181 million in Jan 2013, 12.500 million in Feb 2013 and 9.984 million in Dec 2013. The level of unemployment reached 7.170 million in Dec 2016, all numbers not seasonally adjusted.
Chart I-6, US, Unemployed, Thousands, SA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-7 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides the rate of unemployment in the US or unemployed as percent of the labor force. The rate of unemployment of the US rose from 4.7 percent in Jan 2001 to 6.5 percent in Jun 2003, declining to 4.1 percent in Oct 2006. The rate of unemployment jumped to 10.6 percent in Jan 2010 and declined to 7.6 percent in Dec 2012 but increased to 8.5 percent in Jan 2013 and 8.1 percent in Feb 2013, falling back to 7.3 percent in May 2013 and 7.8 percent in Jun 2013, all numbers not seasonally adjusted. The rate of unemployment not seasonally adjusted stabilized at 7.7 percent in Jul 2013 and fell to 6.5 percent in Dec 2013 and 5.4 percent in Dec 2014. The rate of unemployment NSA decreased to 4.8 percent in Dec 2015 and 4.5 percent in Dec 2016.
Chart I-7, US, Unemployment Rate, SA, 2001-2016
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-8 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides 12-month percentage changes of the level of unemployed. There was a jump of 81.8 percent in Apr 2009 with subsequent decline and negative rates since 2010. On an annual basis, the level of unemployed rose 59.8 percent in 2009 and 26.1 percent in 2008 with increase of 3.9 percent in 2010, decline of 7.3 percent in 2011 and decrease of 9.0 percent in 2012. The annual level of unemployment decreased 8.4 percent in 2013 and fell 16.1 percent in 2014. The annual level of unemployment fell 13.7 percent in 2015. The level of unemployment decreased 4.9 percent in Dec 2016 relative to a year earlier.
Chart I-8, US, Unemployed, 12-month Percentage Change, NSA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-9 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides the number of people in part-time occupations because of economic reasons, that is, because they cannot find full-time employment. The number underemployed in part-time occupations not seasonally adjusted rose from 3.732 million in Jan 2001 to 5.270 million in Jan 2004, falling to 3.787 million in Apr 2006. The number underemployed seasonally adjusted jumped to 9.114 million in Nov 2009, falling to 8.171 million in Dec 2011 but increasing to 8.267 million in Jan 2012 and 8.214 million in Feb 2012 but then falling to 7.922 million in Dec 2012 and increasing to 8.093 million in Jul 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons seasonally adjusted reached 5.669 million in Nov 2016. Without seasonal adjustment, the number employed part-time for economic reasons reached 9.354 million in Dec 2009, declining to 8.918 million in Jan 2012 and 8.166 million in Dec 2012 but increasing to 8.324 million in Jul 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons NSA stood at 7.990 million in Dec 2013, 6.970 million in Dec 2014 and 6.179 million in Dec 2015. The number employed part-time for economic reasons NSA stood at 5.707 million in Dec 2016. The longer the period in part-time jobs the lower are the chances of finding another full-time job.
Chart I-9, US, Part-Time for Economic Reasons, Thousands, SA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-10 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics repeats the behavior of unemployment. The 12-month percentage change of the level of people at work part-time for economic reasons jumped 84.7 percent in Mar 2009 and declined subsequently. The declines have been insufficient to reduce significantly the number of people who cannot shift from part-time to full-time employment. On an annual basis, the number of part-time for economic reasons increased 33.5 percent in 2008 and 51.7 percent in 2009, declining 0.4 percent in 2010, 3.5 percent in 2011 and 5.1 percent in 2012. The annual number of part-time for economic reasons decreased 2.3 percent in 2013 and fell 9.1 percent in 2014. The annual number of part-time for economic reasons fell 11.7 percent in 2015. The number of part-time for economic reasons decreased 7.6 percent in Dec 2016 relative to a year earlier.
Chart I-10, US, Part-Time for Economic Reasons NSA 12-Month Percentage Change, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-11 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides the same pattern of the number marginally attached to the labor force jumping to significantly higher levels during the global recession and remaining at historically high levels. The number marginally attached to the labor force not seasonally adjusted increased from 1.295 million in Jan 2001 to 1.691 million in Feb 2004. The number of marginally attached to the labor force fell to 1.299 million in Sep 2006 and increased to 2.609 million in Dec 2010 and 2.800 million in Jan 2011. The number marginally attached to the labor force was 2.540 million in Dec 2011, increasing to 2.809 million in Jan 2012, falling to 2.608 million in Feb 2012. The number marginally attached to the labor force fell to 2.352 million in Mar 2012, 2.363 million in Apr 2012, 2.423 million in May 2012, 2.483 million in Jun 2012, 2.529 million in Jul 2012 and 2.561 million in Aug 2012. The number marginally attached to the labor force fell to 2.517 million in Sep 2012, 2.433 million in Oct 2012, 2.505 million in Nov 2012 and 2.427 million in in Dec 2013. The number marginally attached to the labor force reached 2.260 million in Dec 2014 and 1.833 million in Dec 2015. The number marginally attached to the labor force stood at 1.684 million in Dec 2016.
Chart I-11, US, Marginally Attached to the Labor Force, Thousands, NSA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-12 provides 12-month percentage changes of the marginally attached to the labor force from 2001 to 2016. There was a jump of 56.1 percent in May 2009 during the global recession followed by declines in percentage changes but insufficient negative changes. On an annual basis, the number of marginally attached to the labor force increased in four consecutive years: 15.7 percent in 2008, 37.9 percent in 2009, 11.7 percent in 2010 and 3.5 percent in 2011. The number marginally attached to the labor force fell 2.2 percent on annual basis in 2012 but increased 2.9 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2012, fell 13.0 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2013, falling 10.7 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2013. The number marginally attached to the labor force increased 4.0 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2013 and fell 4.5 percent in the 12 months ending in Jul 2013 and 8.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2013. The annual number of marginally attached to the labor force fell 6.2 percent in 2013 and fell 6.5 percent in 2014. The annual number of marginally attached to the labor force fell 11.4 percent in 2015. The number marginally attached to the labor force fell 7.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2013 and fell 6.9 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2014. The number marginally attached to the labor force fell 18.9 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2015 and decreased 8.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2016.
Chart I-12, US, Marginally Attached to the Labor Force 12-Month Percentage Change, NSA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Table I-4 consists of data and additional calculations using the BLS household survey, illustrating the possibility that the actual rate of unemployment could be 10.0 percent and the number of people in job stress could be around 24.3 million, which is 14.4 percent of the effective labor force. The first column provides for 2006 the yearly average population (POP), labor force (LF), participation rate or labor force as percent of population (PART %), employment (EMP), employment population ratio (EMP/POP %), unemployment (UEM), the unemployment rate as percent of labor force (UEM/LF Rate %) and the number of people not in the labor force (NLF). All data are unadjusted or not-seasonally-adjusted (NSA). The numbers in column 2006 are averages in millions while the monthly numbers for Dec 2015, Nov 2016 and Dec 2016 are in thousands, not seasonally adjusted. The average yearly participation rate of the population in the labor force was in the range of 66.0 percent minimum to 67.1 percent maximum between 2000 and 2006 with the average of 66.4 percent (http://www.bls.gov/data/). Table I-4b provides the yearly labor force participation rate from 1979 to 2016. The objective of Table I-4 is to assess how many people could have left the labor force because they do not think they can find another job. Row “LF PART 66.2 %” applies the participation rate of 2006, almost equal to the rates for 2000 to 2006, to the noninstitutional civilian population in Dec 2015, Nov 2016 and Dec 2016 to obtain what would be the labor force of the US if the participation rate had not changed. In fact, the participation rate fell to 62.4 percent by Dec 2015 and was 62.6 percent in Nov 2016 and 62.4 percent in Dec 2016, suggesting that many people simply gave up on finding another job. Row “∆ NLF UEM” calculates the number of people not counted in the labor force because they could have given up on finding another job by subtracting from the labor force with participation rate of 66.2 percent (row “LF PART 66.2%”) the labor force estimated in the household survey (row “LF”). Total unemployed (row “Total UEM”) is obtained by adding unemployed in row “∆NLF UEM” to the unemployed of the household survey in row “UEM.” The row “Total UEM%” is the effective total unemployed “Total UEM” as percent of the effective labor force in row “LF PART 66.2%.” The results are that:
- there are an estimated 9.671 million unemployed in Dec 2016 who are not counted because they left the labor force on their belief they could not find another job (∆NLF UEM), that is, they dropped out of their job searches
- the total number of unemployed is effectively 16.841 million (Total UEM) and not 7.170 million (UEM) of whom many have been unemployed long term
- the rate of unemployment is 10.0 percent (Total UEM%) and not 4.5 percent, not seasonally adjusted, or 4.7 percent seasonally adjusted
- the number of people in job stress is close to 24.2 million by adding the 9.054 million leaving the labor force because they believe they could not find another job, corresponding to 14.4 percent of the effective labor force.
The row “In Job Stress” in Table I-4 provides the number of people in job stress not seasonally adjusted at 23.373 million in Oct 2016, adding the total number of unemployed (“Total UEM”), plus those involuntarily in part-time jobs because they cannot find anything else (“Part Time Economic Reasons”) and the marginally attached to the labor force (“Marginally attached to LF”). The final row of Table I-4 shows that the number of people in job stress is equivalent to 14.4 percent of the labor force in Nov 2016. The employment population ratio “EMP/POP %” dropped from 62.9 percent on average in 2006 to 59.4 percent in Dec 2015, 59.9 percent in Nov 2016 and 59.6 percent in Dec 2016. The number employed in Dec 2016 was 151.798 million (NSA) or 4.483 million more people with jobs relative to the peak of 147.315 million in Jul 2007 while the civilian noninstitutional population of ages 16 years and over increased from 231.958 million in Jul 2007 to 254.742 million in Dec 2016 or by 22.784 million. The number employed increased 3.0 percent from Jul 2007 to Dec 2016 while the noninstitutional civilian population of ages of 16 years and over, or those available for work, increased 9.8 percent. The ratio of employment to population in Jul 2007 was 63.5 percent (147.315 million employment as percent of population of 231.958 million). The same ratio in Dec 2016 would result in 161.761 million jobs (0.635 multiplied by noninstitutional civilian population of 254.742 million). There are effectively 9.963 million fewer jobs in Dec 2016 than in Jul 2007, or 161.761 million minus 151.798 million. There is actually not sufficient job creation in merely absorbing new entrants in the labor force because of those dropping from job searches, worsening the stock of unemployed or underemployed in involuntary part-time jobs.
The argument that anemic population growth causes “secular stagnation” in the US (Hansen 1938, 1939, 1941) is as misplaced currently as in the late 1930s (for early dissent see Simons 1942). There is currently population growth in the ages of 16 to 24 years but not enough job creation and discouragement of job searches for all ages (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-values-of-risk-financial-assets.html). This is merely another case of theory without reality with dubious policy proposals. The number of hiring relative to the number unemployed measures the chances of becoming employed. The number of hiring in the US economy has declined by 10 million and does not show signs of increasing in an unusual recovery without hiring. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. US economic growth has been at only 2.1 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 29 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2016. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the third estimate of GDP for IIIQ2016 (https://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2016/pdf/gdp3q16_3rd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,745.9 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,355.6 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,745.9/$14,355.6 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1989, 4.5 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1989. 4.5 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1990 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2016 would have accumulated to 29.5 percent. GDP in IIIQ2016 would be $19,414.4 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2687.4 billion than actual $16,727.0 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 24.2 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 14.4 percent of the effective labor force (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). US GDP in IIIQ2016 is 13.8 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,727.0 billion in IIIQ2016 or 11.6 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.3 percent. Professor John H. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. Cochrane (2016May02) measures GDP growth in the US at average 3.5 percent per year from 1950 to 2000 and only at 1.76 percent per year from 2000 to 2015 with only at 2.0 percent annual equivalent in the current expansion. Cochrane (2016May02) proposes drastic changes in regulation and legal obstacles to private economic activity. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth of manufacturing at average 3.1 percent per year from Nov 1919 to Nov 2016. Growth at 3.1 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 108.2316 in Dec 2007 to 142.1081 in Nov 2016. The actual index NSA in Nov 2016 is 103.0759, which is 27.5 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.1 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2015. Using trend growth of 2.1 percent per year, the index would increase to 130.3109 in Nov 2016. The output of manufacturing at 103.0759 in Nov 2016 is 20.9 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Table I-4, US, Population, Labor Force and Unemployment, NSA
| 2006 | Dec 2015 | Nov 2016 | Dec 2016 | |
| POP | 229 | 251,936 | 254,540 | 254,742 |
| LF | 151 | 157,245 | 159,451 | 158,968 |
| PART% | 66.2 | 62.4 | 62.6 | 62.4 |
| EMP | 144 | 149,703 | 152,385 | 151,798 |
| EMP/POP% | 62.9 | 59.4 | 59.9 | 59.6 |
| UEM | 7 | 7,542 | 7,066 | 7,170 |
| UEM/LF Rate% | 4.6 | 4.8 | 4.4 | 4.5 |
| NLF | 77 | 94,691 | 95,089 | 95,774 |
| LF PART 66.2% | 166,782 | 168,505 | 168,639 | |
| ∆NLF UEM | 9,537 | 9,054 | 9,671 | |
| Total UEM | 17,079 | 16,120 | 16,841 | |
| Total UEM% | 10.2 | 9.6 | 10.0 | |
| Part Time Economic Reasons | 6,179 | 5,518 | 5,707 | |
| Marginally Attached to LF | 1,833 | 1,932 | 1,684 | |
| In Job Stress | 25,091 | 23,570 | 24,232 | |
| People in Job Stress as % Labor Force | 15.0 | 14.0 | 14.4 |
Pop: population; LF: labor force; PART: participation; EMP: employed; UEM: unemployed; NLF: not in labor force; ∆NLF UEM: additional unemployed; Total UEM is UEM + ∆NLF UEM; Total UEM% is Total UEM as percent of LF PART 66.2%; In Job Stress = Total UEM + Part Time Economic Reasons + Marginally Attached to LF
Note: the first column for 2006 is in average millions; the remaining columns are in thousands; NSA: not seasonally adjusted
The labor force participation rate of 66.2% in 2006 is applied to current population to obtain LF PART 66.2%; ∆NLF UEM is obtained by subtracting the labor force with participation of 66.2 percent from the household survey labor force LF; Total UEM is household data unemployment plus ∆NLF UEM; and total UEM% is total UEM divided by LF PART 66.2%
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
In the analysis of Hansen (1939, 3) of secular stagnation, economic progress consists of growth of real income per person driven by growth of productivity. The “constituent elements” of economic progress are “(a) inventions, (b) the discovery and development of new territory and new resources, and (c) the growth of population” (Hansen 1939, 3). Secular stagnation originates in decline of population growth and discouragement of inventions. According to Hansen (1939, 2), US population grew by 16 million in the 1920s but grew by one half or about 8 million in the 1930s with forecasts at the time of Hansen’s writing in 1938 of growth of around 5.3 million in the 1940s. Hansen (1939, 2) characterized demography in the US as “a drastic decline in the rate of population growth. Hansen’s plea was to adapt economic policy to stagnation of population in ensuring full employment. In the analysis of Hansen (1939, 8), population caused half of the growth of US GDP per year. Growth of output per person in the US and Europe was caused by “changes in techniques and to the exploitation of new natural resources.” In this analysis, population caused 60 percent of the growth of capital formation in the US. Declining population growth would reduce growth of capital formation. Residential construction provided an important share of growth of capital formation. Hansen (1939, 12) argues that market power of imperfect competition discourages innovation with prolonged use of obsolete capital equipment. Trade unions would oppose labor-savings innovations. The combination of stagnating and aging population with reduced innovation caused secular stagnation. Hansen (1939, 12) concludes that there is role for public investments to compensate for lack of dynamism of private investment but with tough tax/debt issues.
The current application of Hansen’s (1938, 1939, 1941) proposition argues that secular stagnation occurs because full employment equilibrium can be attained only with negative real interest rates between minus 2 and minus 3 percent. Professor Lawrence H. Summers (2013Nov8) finds that “a set of older ideas that went under the phrase secular stagnation are not profoundly important in understanding Japan’s experience in the 1990s and may not be without relevance to America’s experience today” (emphasis added). Summers (2013Nov8) argues there could be an explanation in “that the short-term real interest rate that was consistent with full employment had fallen to -2% or -3% sometime in the middle of the last decade. Then, even with artificial stimulus to demand coming from all this financial imprudence, you wouldn’t see any excess demand. And even with a relative resumption of normal credit conditions, you’d have a lot of difficulty getting back to full employment.” The US economy could be in a situation where negative real rates of interest with fed funds rates close to zero as determined by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) do not move the economy to full employment or full utilization of productive resources. Summers (2013Oct8) finds need of new thinking on “how we manage an economy in which the zero nominal interest rates is a chronic and systemic inhibitor of economy activity holding our economies back to their potential.”
Former US Treasury Secretary Robert Rubin (2014Jan8) finds three major risks in prolonged unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates and quantitative easing: (1) incentive of delaying action by political leaders; (2) “financial moral hazard” in inducing excessive exposures pursuing higher yields of risker credit classes; and (3) major risks in exiting unconventional policy. Rubin (2014Jan8) proposes reduction of deficits by structural reforms that could promote recovery by improving confidence of business attained with sound fiscal discipline.
Professor John B. Taylor (2014Jan01, 2014Jan3) provides clear thought on the lack of relevance of Hansen’s contention of secular stagnation to current economic conditions. The application of secular stagnation argues that the economy of the US has attained full-employment equilibrium since around 2000 only with negative real rates of interest of minus 2 to minus 3 percent. At low levels of inflation, the so-called full-employment equilibrium of negative interest rates of minus 2 to minus 3 percent cannot be attained and the economy stagnates. Taylor (2014Jan01) analyzes multiple contradictions with current reality in this application of the theory of secular stagnation:
- Secular stagnation would predict idle capacity, in particular in residential investment when fed fund rates were fixed at 1 percent from Jun 2003 to Jun 2004. Taylor (2014Jan01) finds unemployment at 4.4 percent with house prices jumping 7 percent from 2002 to 2003 and 14 percent from 2004 to 2005 before dropping from 2006 to 2007. GDP prices doubled from 1.7 percent to 3.4 percent when interest rates were low from 2003 to 2005.
- Taylor (2014Jan01, 2014Jan3) finds another contradiction in the application of secular stagnation based on low interest rates because of savings glut and lack of investment opportunities. Taylor (2009) shows that there was no savings glut. The savings rate of the US in the past decade is significantly lower than in the 1980s.
- Taylor (2014Jan01, 2014Jan3) finds another contradiction in the low ratio of investment to GDP currently and reduced investment and hiring by US business firms.
- Taylor (2014Jan01, 2014Jan3) argues that the financial crisis and global recession were caused by weak implementation of existing regulation and departure from rules-based policies.
- Taylor (2014Jan01, 2014Jan3) argues that the recovery from the global recession was constrained by a change in the regime of regulation and fiscal/monetary policies.
In revealing research, Edward P. Lazear and James R. Spletzer (2012JHJul22) use the wealth of data in the valuable database and resources of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (http://www.bls.gov/data/) in providing clear thought on the nature of the current labor market of the United States. The critical issue of analysis and policy currently is whether unemployment is structural or cyclical. Structural unemployment could occur because of (1) industrial and demographic shifts and (2) mismatches of skills and job vacancies in industries and locations. Consider the aggregate unemployment rate, Y, expressed in terms of share si of a demographic group in an industry i and unemployment rate yi of that demographic group (Lazear and Spletzer 2012JHJul22, 5-6):
Y = ∑isiyi (1)
This equation can be decomposed for analysis as (Lazear and Spletzer 2012JHJul22, 6):
∆Y = ∑i∆siy*i + ∑i∆yis*i (2)
The first term in (2) captures changes in the demographic and industrial composition of the economy ∆si multiplied by the average rate of unemployment y*i , or structural factors. The second term in (2) captures changes in the unemployment rate specific to a group, or ∆yi, multiplied by the average share of the group s*i, or cyclical factors. There are also mismatches in skills and locations relative to available job vacancies. A simple observation by Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22) casts intuitive doubt on structural factors: the rate of unemployment jumped from 4.4 percent in the spring of 2007 to 10 percent in October 2009. By nature, structural factors should be permanent or occur over relative long periods. The revealing result of the exhaustive research of Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22) is:
“The analysis in this paper and in others that we review do not provide any compelling evidence that there have been changes in the structure of the labor market that are capable of explaining the pattern of persistently high unemployment rates. The evidence points to primarily cyclic factors.”
Table I-4b and Chart I-12-b provide the US labor force participation rate or percentage of the labor force in population. It is not likely that simple demographic trends caused the sharp decline during the global recession and failure to recover earlier levels. The civilian labor force participation rate dropped from the peak of 66.9 percent in Jul 2006 to 62.6 percent in Dec 2013, 62.5 percent in Dec 2014, 62.4 percent in Dec 2015 and 62.4 in Dec 2016. The civilian labor force participation rate was 62.4 percent in Dec 2016. The civilian labor force participation rate was 63.7 percent on an annual basis in 1979 and 63.4 percent in Dec 1980 and Dec 1981, reaching even 62.9 percent in both Apr and May 1979. The civilian labor force participation rate jumped with the recovery to 64.8 percent on an annual basis in 1985 and 65.9 percent in Jul 1985. Structural factors cannot explain these sudden changes vividly shown visually in the final segment of Chart I-12b. Seniors would like to delay their retiring especially because of the adversities of financial repression on their savings. Labor force statistics are capturing the disillusion of potential workers with their chances in finding a job in what Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22) characterize as accentuated cyclical factors. The argument that anemic population growth causes “secular stagnation” in the US (Hansen 1938, 1939, 1941) is as misplaced currently as in the late 1930s (for early dissent see Simons 1942). There is currently population growth in the ages of 16 to 24 years but not enough job creation and discouragement of job searches for all ages (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-values-of-risk-financial-assets.html). “Secular stagnation” would be a process over many years and not from one year to another. This is merely another case of theory without reality with dubious policy proposals.
Table I-4b, US, Labor Force Participation Rate, Percent of Labor Force in Population, NSA, 1979-2016
| Year | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Annual |
| 1979 | 62.9 | 62.9 | 64.5 | 64.9 | 64.5 | 63.8 | 64.0 | 63.8 | 63.8 | 63.7 |
| 1980 | 63.2 | 63.5 | 64.6 | 65.1 | 64.5 | 63.6 | 63.9 | 63.7 | 63.4 | 63.8 |
| 1981 | 63.6 | 63.9 | 64.6 | 65.0 | 64.6 | 63.5 | 64.0 | 63.8 | 63.4 | 63.9 |
| 1982 | 63.3 | 63.9 | 64.8 | 65.3 | 64.9 | 64.0 | 64.1 | 64.1 | 63.8 | 64.0 |
| 1983 | 63.2 | 63.4 | 65.1 | 65.4 | 65.1 | 64.3 | 64.1 | 64.1 | 63.8 | 64.0 |
| 1984 | 63.7 | 64.3 | 65.5 | 65.9 | 65.2 | 64.4 | 64.6 | 64.4 | 64.3 | 64.4 |
| 1985 | 64.3 | 64.6 | 65.5 | 65.9 | 65.4 | 64.9 | 65.1 | 64.9 | 64.6 | 64.8 |
| 1986 | 64.6 | 65.0 | 66.3 | 66.6 | 66.1 | 65.3 | 65.5 | 65.4 | 65.0 | 65.3 |
| 1987 | 64.9 | 65.6 | 66.3 | 66.8 | 66.5 | 65.5 | 65.9 | 65.7 | 65.5 | 65.6 |
| 1988 | 65.3 | 65.5 | 66.7 | 67.1 | 66.8 | 65.9 | 66.1 | 66.2 | 65.9 | 65.9 |
| 1989 | 65.9 | 66.2 | 67.4 | 67.7 | 67.2 | 66.3 | 66.6 | 66.7 | 66.3 | 66.5 |
| 1990 | 66.1 | 66.5 | 67.4 | 67.7 | 67.1 | 66.4 | 66.5 | 66.3 | 66.1 | 66.5 |
| 1991 | 66.0 | 66.0 | 67.2 | 67.3 | 66.6 | 66.1 | 66.1 | 66.0 | 65.8 | 66.2 |
| 1992 | 66.0 | 66.4 | 67.6 | 67.9 | 67.2 | 66.3 | 66.2 | 66.2 | 66.1 | 66.4 |
| 1993 | 65.6 | 66.3 | 67.3 | 67.5 | 67.0 | 66.1 | 66.4 | 66.3 | 66.2 | 66.3 |
| 1994 | 66.0 | 66.5 | 67.2 | 67.5 | 67.2 | 66.5 | 66.8 | 66.7 | 66.5 | 66.6 |
| 1995 | 66.4 | 66.4 | 67.2 | 67.7 | 67.1 | 66.5 | 66.7 | 66.5 | 66.2 | 66.6 |
| 1996 | 66.2 | 66.7 | 67.4 | 67.9 | 67.2 | 66.8 | 67.1 | 67.0 | 66.7 | 66.8 |
| 1997 | 66.7 | 67.0 | 67.8 | 68.1 | 67.6 | 67.0 | 67.1 | 67.1 | 67.0 | 67.1 |
| 1998 | 66.6 | 67.0 | 67.7 | 67.9 | 67.3 | 67.0 | 67.1 | 67.1 | 67.0 | 67.1 |
| 1999 | 66.7 | 67.0 | 67.7 | 67.9 | 67.3 | 66.8 | 67.0 | 67.0 | 67.0 | 67.1 |
| 2000 | 67.0 | 67.0 | 67.7 | 67.6 | 67.2 | 66.7 | 66.9 | 66.9 | 67.0 | 67.1 |
| 2001 | 66.7 | 66.6 | 67.2 | 67.4 | 66.8 | 66.6 | 66.7 | 66.6 | 66.6 | 66.8 |
| 2002 | 66.4 | 66.5 | 67.1 | 67.2 | 66.8 | 66.6 | 66.6 | 66.3 | 66.2 | 66.6 |
| 2003 | 66.2 | 66.2 | 67.0 | 66.8 | 66.3 | 65.9 | 66.1 | 66.1 | 65.8 | 66.2 |
| 2004 | 65.7 | 65.8 | 66.5 | 66.8 | 66.2 | 65.7 | 66.0 | 66.1 | 65.8 | 66.0 |
| 2005 | 65.8 | 66.0 | 66.5 | 66.8 | 66.5 | 66.1 | 66.2 | 66.1 | 65.9 | 66.0 |
| 2006 | 65.8 | 66.0 | 66.7 | 66.9 | 66.5 | 66.1 | 66.4 | 66.4 | 66.3 | 66.2 |
| 2007 | 65.7 | 65.8 | 66.6 | 66.8 | 66.1 | 66.0 | 66.0 | 66.1 | 65.9 | 66.0 |
| 2008 | 65.7 | 66.0 | 66.6 | 66.8 | 66.4 | 65.9 | 66.1 | 65.8 | 65.7 | 66.0 |
| 2009 | 65.4 | 65.5 | 66.2 | 66.2 | 65.6 | 65.0 | 64.9 | 64.9 | 64.4 | 65.4 |
| 2010 | 64.9 | 64.8 | 65.1 | 65.3 | 65.0 | 64.6 | 64.4 | 64.4 | 64.1 | 64.7 |
| 2011 | 63.9 | 64.1 | 64.5 | 64.6 | 64.3 | 64.2 | 64.1 | 63.9 | 63.8 | 64.1 |
| 2012 | 63.4 | 63.8 | 64.3 | 64.3 | 63.7 | 63.6 | 63.8 | 63.5 | 63.4 | 63.7 |
| 2013 | 63.1 | 63.5 | 64.0 | 64.0 | 63.4 | 63.2 | 62.9 | 62.9 | 62.6 | 63.2 |
| 2014 | 62.6 | 62.9 | 63.4 | 63.5 | 63.0 | 62.8 | 63.0 | 62.8 | 62.5 | 62.9 |
| 2015 | 62.6 | 63.0 | 63.1 | 63.2 | 62.7 | 62.3 | 62.5 | 62.5 | 62.4 | 62.7 |
| 2016 | 62.7 | 62.7 | 63.2 | 63.4 | 62.9 | 62.8 | 62.8 | 62.6 | 62.4 | 62.8 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-12b, US, Labor Force Participation Rate, Percent of Labor Force in Population, NSA, 1979-2016
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Broader perspective is in Chart I-12c of the US Bureau of Labor Statistics. The United States civilian noninstitutional population has increased along a consistent trend since 1948 that continued through earlier recessions and the global recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 and the cyclical expansion after IIIQ2009.
Chart I-12c, US, Civilian Noninstitutional Population, Thousands, NSA, 1948-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The labor force of the United States in Chart I-12d has increased along a trend similar to that of the civilian noninstitutional population in Chart I-12c. There is an evident stagnation of the civilian labor force in the final segment of Chart I-12d during the current economic cycle. This stagnation is explained by cyclical factors similar to those analyzed by Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22) that motivated an increasing population to drop out of the labor force instead of structural factors. Large segments of the potential labor force are not observed, constituting unobserved unemployment and of more permanent nature because those afflicted have been seriously discouraged from working by the lack of opportunities.
Chart I-12d, US, Labor Force, Thousands, NSA, 1948-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The rate of labor force participation in the US is in Chart I-12E from 1948 to 2016. There is sudden decline during the global recession after 2007 without recovery explained by cyclical factors (Lazear and Spletzer2012JHJul22) as may many potential workers stopped their searches disillusioned that there could be an opportunity for them in sharply contracted markets.
Chart I-12E, US, Labor Force Participation Rate, Percent of Labor Force in Population, NSA, 1948-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
ESIV Job Creation. What is striking about the data in Table I-8 is that the numbers of monthly increases in jobs in 1983 and 1984 are several times higher than in 2010 to 2015. The civilian noninstitutional population grew by 44.0 percent from 174.215 million in 1983 to 250.801 million in 2015 and labor force higher by 40.9 percent, growing from 111.550 million in 1983 to 157.130 million in 2015. Total nonfarm payroll employment seasonally adjusted (SA) increased 156,000 in Dec 2016 and private payroll employment increased 144,000. The average monthly number of nonfarm jobs created from Dec 2014 to Dec 2015 was 228,667 using seasonally adjusted data, while the average number of nonfarm jobs created from Dec 2015 to Dec 2016 was 179,750, or decrease by 21.4 percent. The average number of private jobs created in the US from Dec 2014 to Dec 2015 was 220,917, using seasonally adjusted data, while the average from Dec 2015 to Dec 2016 was 164,500, or decrease by 25.5 percent. This blog calculates the effective labor force of the US at 168,639 million in Dec 2016 and 166,782 million in Dec 2015 (Table I-4), for growth of 1.857 million at average 154,750 per month. The difference between the average increase of 164,500 new private nonfarm jobs per month in the US from Dec 2015 to Dec 2016 and the 154,750 average monthly increase in the labor force from Dec 2015 to Dec 2016 is 9,750 monthly new jobs net of absorption of new entrants in the labor force. There are 24.232 million in job stress in the US currently. Creation of 9,750 new jobs per month net of absorption of new entrants in the labor force would require 2,485 months to provide jobs for the unemployed and underemployed (24.232 million divided by 9,750) or 207 years (2,485 divided by 12). The civilian labor force of the US in Dec 2016 not seasonally adjusted stood at 158.968 million with 7.170 million unemployed or effectively 16.841 million unemployed in this blog’s calculation by inferring those who are not searching because they believe there is no job for them for effective labor force of 168.639 million. Reduction of one million unemployed at the current rate of job creation without adding more unemployment requires 8.5 years (1 million divided by product of 9,750 by 12, which is 117,000). Reduction of the rate of unemployment to 5 percent of the labor force would be equivalent to unemployment of only 7.948 million (0.05 times labor force of 158.968 million). New net job creation would be minus 0.778 million (7.170 million unemployed minus 7.948 million unemployed at rate of 5 percent) that at the current rate would take 0.0 years (0.778 million divided by 117,000). Under the calculation in this blog, there are 16.841 million unemployed by including those who ceased searching because they believe there is no job for them and effective labor force of 168.639 million. Reduction of the rate of unemployment to 5 percent of the labor force would require creating 7.695 million jobs net of labor force growth that at the current rate would take 76.1 years (16.841 million minus 0.05(158.639 million) = 8.909 million divided by 117,000 using LF PART 66.2% and Total UEM in Table I-4). These calculations assume that there are no more recessions, defying United States economic history with periodic contractions of economic activity when unemployment increases sharply. The number employed in Dec 2016 was 151.798 million (NSA) or 4.483 million more people with jobs relative to the peak of 147.315 million in Jul 2007 while the civilian noninstitutional population of ages 16 years and over increased from 231.958 million in Jul 2007 to 254.742 million in Dec 2016 or by 22.784 million. The number employed increased 3.0 percent from Jul 2007 to Dec 2016 while the noninstitutional civilian population of ages of 16 years and over, or those available for work, increased 9.8 percent. The ratio of employment to population in Jul 2007 was 63.5 percent (147.315 million employment as percent of population of 231.958 million). The same ratio in Dec 2016 would result in 161.761 million jobs (0.635 multiplied by noninstitutional civilian population of 254.742 million). There are effectively 9.963 million fewer jobs in Dec 2016 than in Jul 2007, or 161.761 million minus 151.798 million. There is actually not sufficient job creation in merely absorbing new entrants in the labor force because of those dropping from job searches, worsening the stock of unemployed or underemployed in involuntary part-time jobs.
There is current interest in past theories of “secular stagnation.” Alvin H. Hansen (1939, 4, 7; see Hansen 1938, 1941; for an early critique see Simons 1942) argues:
“Not until the problem of full employment of our productive resources from the long-run, secular standpoint was upon us, were we compelled to give serious consideration to those factors and forces in our economy which tend to make business recoveries weak and anaemic (sic) and which tend to prolong and deepen the course of depressions. This is the essence of secular stagnation-sick recoveries which die in their infancy and depressions which feed on them-selves and leave a hard and seemingly immovable core of unemployment. Now the rate of population growth must necessarily play an important role in determining the character of the output; in other words, the com-position of the flow of final goods. Thus a rapidly growing population will demand a much larger per capita volume of new residential building construction than will a stationary population. A stationary population with its larger proportion of old people may perhaps demand more personal services; and the composition of consumer demand will have an important influence on the quantity of capital required. The demand for housing calls for large capital outlays, while the demand for personal services can be met without making large investment expenditures. It is therefore not unlikely that a shift from a rapidly growing population to a stationary or declining one may so alter the composition of the final flow of consumption goods that the ratio of capital to output as a whole will tend to decline.”
The argument that anemic population growth causes “secular stagnation” in the US (Hansen 1938, 1939, 1941) is as misplaced currently as in the late 1930s (for early dissent see Simons 1942). There is currently population growth in the ages of 16 to 24 years but not enough job creation and discouragement of job searches for all ages (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/11/dollar-revaluation-and-valuations-of.html). The proper explanation is not in secular stagnation but in cyclically slow growth. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2016 would have accumulated to 29.5 percent. GDP in IIIQ2016 would be $19,414.4 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2687.4 billion than actual $16,727.0 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 24.2 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 14.4 percent of the effective labor force (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). US GDP in IIIQ2016 is 13.8 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,727.0 billion in IIIQ2016 or 11.6 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.3 percent. Professor John H. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. Cochrane (2016May02) measures GDP growth in the US at average 3.5 percent per year from 1950 to 2000 and only at 1.76 percent per year from 2000 to 2015 with only at 2.0 percent annual equivalent in the current expansion. Cochrane (2016May02) proposes drastic changes in regulation and legal obstacles to private economic activity. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth of manufacturing at average 3.1 percent per year from Nov 1919 to Nov 2016. Growth at 3.1 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 108.2316 in Dec 2007 to 142.1081 in Nov 2016. The actual index NSA in Nov 2016 is 103.0759, which is 27.5 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.1 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2015. Using trend growth of 2.1 percent per year, the index would increase to 130.3109 in Nov 2016. The output of manufacturing at 103.0759 in Nov 2016 is 20.9 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Table I-8, US, Monthly Change in Jobs, Number SA
| Month | 1981 | 1982 | 1983 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | Private |
| Jan | 94 | -326 | 224 | 19 | -791 | 28 | 19 |
| Feb | 68 | -5 | -75 | -86 | -703 | -69 | -54 |
| Mar | 105 | -130 | 172 | -78 | -823 | 163 | 121 |
| Apr | 73 | -280 | 276 | -210 | -686 | 243 | 192 |
| May | 10 | -45 | 277 | -185 | -351 | 522 | 95 |
| Jun | 197 | -243 | 379 | -165 | -470 | -133 | 123 |
| Jul | 112 | -342 | 418 | -209 | -329 | -70 | 101 |
| Aug | -36 | -158 | -308 | -266 | -212 | -34 | 115 |
| Sep | -87 | -181 | 1115 | -452 | -219 | -52 | 121 |
| Oct | -99 | -277 | 271 | -473 | -200 | 257 | 207 |
| Nov | -209 | -123 | 353 | -769 | -7 | 123 | 133 |
| Dec | -278 | -14 | 356 | -695 | -279 | 88 | 109 |
| 1984 | 2011 | Private | |||||
| Jan | 446 | 42 | 50 | ||||
| Feb | 481 | 188 | 231 | ||||
| Mar | 275 | 225 | 248 | ||||
| Apr | 363 | 346 | 354 | ||||
| May | 308 | 73 | 128 | ||||
| Jun | 379 | 235 | 200 | ||||
| Jul | 313 | 70 | 185 | ||||
| Aug | 242 | 107 | 139 | ||||
| Sep | 310 | 246 | 280 | ||||
| Oct | 286 | 202 | 187 | ||||
| Nov | 349 | 146 | 173 | ||||
| Dec | 128 | 207 | 224 | ||||
| 1985 | 2012 | Private | |||||
| Jan | 266 | 338 | 347 | ||||
| Feb | 124 | 257 | 261 | ||||
| Mar | 346 | 239 | 237 | ||||
| Apr | 196 | 75 | 90 | ||||
| May | 274 | 115 | 130 | ||||
| Jun | 146 | 87 | 72 | ||||
| Jul | 190 | 143 | 160 | ||||
| Aug | 193 | 190 | 174 | ||||
| Sep | 203 | 181 | 180 | ||||
| Oct | 188 | 132 | 164 | ||||
| Nov | 209 | 149 | 171 | ||||
| Dec | 167 | 243 | 233 | ||||
| 1986 | 2013 | Private | |||||
| Jan | 125 | 190 | 203 | ||||
| Feb | 107 | 311 | 297 | ||||
| Mar | 94 | 135 | 150 | ||||
| Apr | 187 | 192 | 193 | ||||
| May | 127 | 218 | 225 | ||||
| Jun | -94 | 146 | 173 | ||||
| Jul | 318 | 140 | 162 | ||||
| Aug | 114 | 269 | 242 | ||||
| Sep | 347 | 185 | 179 | ||||
| Oct | 186 | 189 | 203 | ||||
| Nov | 186 | 291 | 280 | ||||
| Dec | 205 | 45 | 71 | ||||
| 1987 | 2014 | Private | |||||
| Jan | 172 | 187 | 197 | ||||
| Feb | 232 | 168 | 158 | ||||
| Mar | 249 | 272 | 261 | ||||
| Apr | 338 | 310 | 282 | ||||
| May | 226 | 213 | 215 | ||||
| Jun | 172 | 306 | 267 | ||||
| Jul | 347 | 232 | 244 | ||||
| Aug | 171 | 218 | 231 | ||||
| Sep | 228 | 286 | 237 | ||||
| Oct | 492 | 200 | 190 | ||||
| Nov | 232 | 331 | 324 | ||||
| Dec | 294 | 292 | 279 | ||||
| 1988 | 2015 | Private | |||||
| Jan | 94 | 221 | 214 | ||||
| Feb | 453 | 265 | 252 | ||||
| Mar | 276 | 84 | 90 | ||||
| Apr | 245 | 251 | 241 | ||||
| May | 229 | 273 | 256 | ||||
| Jun | 363 | 228 | 226 | ||||
| Jul | 222 | 277 | 245 | ||||
| Aug | 124 | 150 | 123 | ||||
| Sep | 339 | 149 | 162 | ||||
| Oct | 268 | 295 | 304 | ||||
| Nov | 339 | 280 | 279 | ||||
| Dec | 290 | 271 | 259 | ||||
| 1989 | 2016 | Private | |||||
| Jan | 262 | 168 | 155 | ||||
| Feb | 258 | 233 | 222 | ||||
| Mar | 193 | 186 | 167 | ||||
| Apr | 173 | 144 | 147 | ||||
| May | 118 | 24 | -1 | ||||
| Jun | 116 | 271 | 238 | ||||
| Jul | 40 | 252 | 221 | ||||
| Aug | 49 | 176 | 132 | ||||
| Sep | 250 | 208 | 205 | ||||
| Oct | 111 | 135 | 146 | ||||
| Nov | 277 | 204 | 198 | ||||
| Dec | 96 | 156 | 144 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The NBER dates recessions in the US from peaks to troughs as: IQ80 to IIIQ80, IIIQ81 to IV82 and IVQ07 to IIQ09 (http://www.nber.org/cycles/cyclesmain.html). Table I-12 provides total annual level nonfarm employment in the US for the 1980s and the 2000s, which is different from 12-month comparisons. Nonfarm jobs rose by 4.859 million from 1982 to 1984, or 5.4 percent, and continued rapid growth in the rest of the decade. In contrast, nonfarm jobs are down by 7.638 million in 2010 relative to 2007 and fell by 952,000 in 2010 relative to 2009 even after six quarters of GDP growth. Monetary and fiscal stimuli have failed in increasing growth to rates required for mitigating job stress. The initial growth impulse reflects a flatter growth curve in the current expansion. Nonfarm jobs declined from 137.999 million in 2007 to 136.381 million in 2013, by 1.618 million or 1.2 percent. Nonfarm jobs increased from 137.999 million in 2007 to 141,865 million in 2015, by 3.866 million or 2.8 percent. The US noninstitutional population or in condition to work increased from 231.867 million in 2007 to 250,801 million in 2015, by 18.934 million or 8.2 percent. The ratio of nonfarm jobs of 137.999 million in 2007 to the noninstitutional population of 231.867 was 59.5. Nonfarm jobs in 2015 corresponding to the ratio of 59.5 of nonfarm jobs/noninstitutional population would be 149.227 million (0.595x250.801). The difference between actual nonfarm jobs of 141.865 million in 2015 and nonfarm jobs of 149.227 million that are equivalent to 59.5 percent of the noninstitutional population as in 2007 is 7.362 million fewer jobs. The proper explanation for this loss of work opportunities is not in secular stagnation but in cyclically slow growth. The NBER dates recessions in the US from peaks to troughs as: IQ80 to IIIQ80, IIIQ81 to IV82 and IVQ07 to IIQ09 (http://www.nber.org/cycles/cyclesmain.html). Table I-12 provides total annual level nonfarm employment in the US for the 1980s and the 2000s, which is different from 12-month comparisons. Nonfarm jobs rose by 4.859 million from 1982 to 1984, or 5.4 percent, and continued rapid growth in the rest of the decade. In contrast, nonfarm jobs are down by 7.638 million in 2010 relative to 2007 and fell by 952,000 in 2010 relative to 2009 even after six quarters of GDP growth. Monetary and fiscal stimuli have failed in increasing growth to rates required for mitigating job stress. The initial growth impulse reflects a flatter growth curve in the current expansion. Nonfarm jobs declined from 137.999 million in 2007 to 136.381 million in 2013, by 1.618 million or 1.2 percent. Nonfarm jobs increased from 137.999 million in 2007 to 141,865 million in 2015, by 3.866 million or 2.8 percent. The US noninstitutional population or in condition to work increased from 231.867 million in 2007 to 250,801 million in 2015, by 18.934 million or 8.2 percent. The ratio of nonfarm jobs of 137.999 million in 2007 to the noninstitutional population of 231.867 was 59.5. Nonfarm jobs in 2015 corresponding to the ratio of 59.5 of nonfarm jobs/noninstitutional population would be 149.227 million (0.595x250.801). The difference between actual nonfarm jobs of 141.865 million in 2015 and nonfarm jobs of 149.227 million that are equivalent to 59.5 percent of the noninstitutional population as in 2007 is 7.362 million fewer jobs. The proper explanation for this loss of work opportunities is not in secular stagnation but in cyclically slow growth. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2016 would have accumulated to 29.5 percent. GDP in IIIQ2016 would be $19,414.4 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2687.4 billion than actual $16,727.0 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 24.2 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 14.4 percent of the effective labor force (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html). US GDP in IIIQ2016 is 13.8 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,727.0 billion in IIIQ2016 or 11.6 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.3 percent. Professor John H. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. Cochrane (2016May02) measures GDP growth in the US at average 3.5 percent per year from 1950 to 2000 and only at 1.76 percent per year from 2000 to 2015 with only at 2.0 percent annual equivalent in the current expansion. Cochrane (2016May02) proposes drastic changes in regulation and legal obstacles to private economic activity. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth of manufacturing at average 3.1 percent per year from Nov 1919 to Nov 2016. Growth at 3.1 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 108.2316 in Dec 2007 to 142.1081 in Nov 2016. The actual index NSA in Nov 2016 is 103.0759, which is 27.5 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.1 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2015. Using trend growth of 2.1 percent per year, the index would increase to 130.3109 in Nov 2016. The output of manufacturing at 103.0759 in Nov 2016 is 20.9 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Table I-12, US, Total Nonfarm Employment in Thousands
| Year | Total Nonfarm | Year | Total Nonfarm |
| 1980 | 90,533 | 2000 | 132,024 |
| 1981 | 91,297 | 2001 | 132,087 |
| 1982 | 89,689 | 2002 | 130,649 |
| 1983 | 90,295 | 2003 | 130,347 |
| 1984 | 94,548 | 2004 | 131,787 |
| 1985 | 97,532 | 2005 | 134,051 |
| 1986 | 99,500 | 2006 | 136,453 |
| 1987 | 102,116 | 2007 | 137,999 |
| 1988 | 105,378 | 2008 | 137,242 |
| 1989 | 108,051 | 2009 | 131,313 |
| 1990 | 109,527 | 2010 | 130,361 |
| 1991 | 108,427 | 2011 | 131,932 |
| 1992 | 108,802 | 2012 | 134,175 |
| 1993 | 110,935 | 2013 | 136,381 |
| 1994 | 114,398 | 2014 | 139,958 |
| 1995 | 117,407 | 2015 | 141,865 |
| 1996 | 119,836 | 2016 | 144,319 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/
Chart I-43 provides annual nonfarm jobs from 2000 to 2016. Cyclically slow growth in the expansion since IIIQ2009 has not been sufficient to recover nonfarm jobs. Because of population growth, there are 7.362 million fewer nonfarm jobs in the US in 2015 than in 2007.
Chart I-43, US, Annual Nonfarm Jobs, NSA, Thousands, 2000-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/
Chart I-44 provides annual nonfarm jobs in the US from 1980 to 1995. Much more rapid cyclical growth as in other expansions historically allowed steady and rapid growth of nonfarm job opportunities even with similarly dynamic population growth.
Chart I-44, US, Annual Nonfarm Jobs, NSA, Thousands, 1980-1996
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov
ESV Stagnating Real Wages. Calculations of inflation-adjusted average hourly earnings by the BLS are in Table IB-4. Average hourly earnings rose above inflation throughout the first nine months of 2007 just before the global recession that began in the final quarter of 2007 when average hourly earnings began to lose to inflation. In contrast, average hourly earnings of all US workers have risen less than inflation in five months in 2010 and in all but the first month in 2011 and the loss accelerated at 1.8 percent in Sep 2011, declining to a real loss of 1.1 percent in Feb 2012 and 0.5 percent in Mar 2012. There was a gain of 0.6 percent in Apr 2012 in inflation-adjusted average hourly earnings but another fall of 0.6 percent in May 2012 followed by increases of 0.3 percent in Jun and 1.0 percent in Jul 2012. Real hourly earnings stagnated in the 12 months ending in Aug 2012 with increase of only 0.1 percent, and increased 0.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep 2012. Real hourly earnings fell 1.2 percent in Oct 2012 and gained 1.0 percent in Dec 2012 but declined 0.2 percent in Jan 2013 and stagnated at change of 0.2 percent in Feb 2013. Real hourly earnings increased 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Mar 2013 and 0.2 percent in Apr 2013, increasing 0.7 percent in May 2013. In Jun 2013, real hourly earnings increased 1.1 percent relative to Jun 2012. Real hourly earnings fell 0.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Jul 2013 and increased 0.8 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2013. Real hourly earnings increased 1.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2013 and 1.0 percent in Nov 2013. Real hourly earnings increased 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2013. Real hourly earnings increased 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2014 and 1.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Feb 2014. Real hourly earnings increased 1.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Mar 2014. Real hourly changed 0.0 percent in the 12 months ending in Apr 2014. Real hourly changed 0.0 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2014. Real hourly earnings changed 0.0 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2014. Real hourly earnings increased 0.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Jul 2014 and increased 0.5 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2014. Real hourly earnings fell 0.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep 2014 and increased 0.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2014. Real hourly earnings increased 1.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2014 and 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2014. Real hourly earnings increased 2.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2015 and increased 2.0 percent in the 12 months ending in Feb 2015. Real hourly earnings increased 2.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Mar 2015 and increased 2.5 percent in the 12 months ending in Apr 2015. Real hourly earnings increased 2.4 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2015 and 1.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2015. Real hourly earnings increased 2.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Jul 2015 and increased 2.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2015. Real hourly earnings increased 2.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep 2015. Real hourly earnings increased 2.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2015 and increased 1.9 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2015. Average hourly earnings increased 1.8 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2015 and increased 1.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2016. Real hourly earnings increased 0.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Feb 2016 and increased 0.8 percent in the 12 months ending in Mar 2016. Real hourly earnings increased 1.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Apr 2016 and increased 2.1 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2016. Real hourly earnings increased 1.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2016 and increased 1.9 percent in the 12 months ending in Jul 2016. Real hourly earnings increased 0.9 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2016 and increased 1.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep 2016. Real hourly earnings increased 1.8 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2016 and increased 0.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2016. Real hourly earnings are oscillating in part because of world inflation waves caused by carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/of-course-economic-outlook-is-highly.html) and in part because of the collapse of hiring (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-values-of-risk-financial-assets.html) originating in weak economic growth (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html). The BLS is revising the data from 2006 to 2009 (http://www.bls.gov/ces/#notices) now available in the release for Jan 2016 and subsequent releases.
Table IB-4, US, Average Hourly Earnings of All Employees NSA in Constant Dollars of 1982-1984
| Year | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
| 2006 | 9.88 | 9.97 | 9.87 | 10.03 | 10.16 | 10.14 | 10.21 |
| 2007 | 9.97 | 10.05 | 10.00 | 10.13 | 10.06 | 10.02 | 10.15 |
| 2008 | 9.82 | 9.75 | 9.81 | 9.91 | 10.03 | 10.34 | 10.45 |
| 2009 | 10.18 | 10.22 | 10.27 | 10.28 | 10.30 | 10.38 | 10.36 |
| 2010 | 10.25 | 10.28 | 10.33 | 10.35 | 10.38 | 10.37 | 10.38 |
| 2011 | 10.11 | 10.15 | 10.09 | 10.16 | 10.29 | 10.23 | 10.29 |
| 2012 | 10.14 | 10.25 | 10.10 | 10.23 | 10.17 | 10.25 | 10.39 |
| ∆%12M | 0.3 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 0.7 | -1.2 | 0.2 | 1.0 |
| 2013 | 10.25 | 10.19 | 10.18 | 10.32 | 10.30 | 10.35 | 10.43 |
| ∆%12M | 1.1 | -0.6 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 0.4 |
| 2014 | 10.25 | 10.20 | 10.23 | 10.29 | 10.33 | 10.50 | 10.47 |
| ∆%12M | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.5 | -0.3 | 0.3 | 1.4 | 0.4 |
| 2015 | 10.38 | 10.41 | 10.51 | 10.54 | 10.58 | 10.70 | 10.66 |
| ∆%12M | 1.3 | 2.1 | 2.7 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 1.9 | 1.8 |
| 2016 | 10.55 | 10.61 | 10.60 | 10.66 | 10.77 | 10.71 | |
| ∆%12M | 1.6 | 1.9 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 1.8 | 0.1 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart IB-2 of the US Bureau of Labor Statistics plots average hourly earnings of all US employees in constant 1982-1984 dollars with evident decline from annual earnings of $10.34 in 2009 and $10.35 in 2010 to $10.24 in 2011 and $10.24 again in 2012 or loss of 1.1 percent (data in http://www.bls.gov/data/). Annual real hourly earnings increased 0.5 percent in 2013 relative to 2012 and increased 0.5 percent in 2014 relative to 2013. Annual real hourly earnings increased 2.1 percent in 2015 relative to 2014. Annual real hourly earnings increased 4.7 percent from 2007 to 2015 at the rate of 0.6 percent per year. Annual real hourly earnings increased 2.1 percent from 2009 to 2015 at the rate of 0.4 percent per year. Real hourly earnings of US workers are crawling in a fractured labor market. The economic welfare or wellbeing of United States workers deteriorated in a recovery without hiring (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-values-of-risk-financial-assets.html), stagnating/declining real wages and 24.2 million unemployed or underemployed (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html) because of mediocre economic growth (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html). The BLS is revising the data from 2006 to 2009 (http://www.bls.gov/ces/#notices) now available for the release of Jan 2016 and subsequent releases.
Chart IB-2, US, Average Hourly Earnings of All Employees in Constant Dollars of 1982-1984, SA 2006-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/
Chart IB-3 provides 12-month percentage changes of average hourly earnings of all employees in constant dollars of 1982-1984, that is, adjusted for inflation. There was sharp contraction of inflation-adjusted average hourly earnings of US employees during parts of 2007 and 2008. Rates of change in 12 months became positive in parts of 2009 and 2010 but then became negative again in 2011 and into 2012 with temporary increase in Apr 2012 that was reversed in May with another gain in Jun and Jul 2012 followed by stagnation in Aug 2012. There was marginal gain in Sep 2012 with sharp decline in Oct 2012, stagnation in Nov 2012, increase in Dec 2012 and renewed decrease in Jan 2013 with near stagnation in Feb 2013 followed by mild increase in Mar-Apr 2013. Hourly earnings adjusted for inflation increased in Jun 2013 and fell in Jul 2013, increasing in Aug-Dec 2013 and Jan-Mar 2014. Average hourly earnings stagnated in Apr-May 2014 and rebounded mildly in Jul 2014, increasing in Aug 2014 and Sep 2014. Average hourly earnings adjusted for inflation increased in Oct-Dec 2014, Jan-Dec 2015 and Jan-Nov 2016.
Chart IB-3, Average Hourly Earnings of All Employees NSA 12-Month Percent Change, 1982-1984 Dollars, NSA 2007-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/
Average weekly earnings of all US employees in the US in constant dollars of 1982-1984 from the dataset of the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) are in Table IB-5. Average weekly earnings fell 3.2 percent after adjusting for inflation in the 12 months ending in Aug 2011, decreased 0.9 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep 2011 and increased 0.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2011. Average weekly earnings fell 1.0 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2011 and fell 0.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2011. Average weekly earnings declined 0.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2012 and fell 0.5 percent in the 12 months ending in Feb 2012. Average weekly earnings in constant dollars were virtually flat in Mar 2012 relative to Mar 2011, decreasing 0.2 percent. Average weekly earnings in constant dollars increased 1.7 percent in Apr 2012 relative to Apr 2011 but fell 1.7 percent in May 2012 relative to May 2011, increasing 0.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2012 and 1.8 percent in the 12 months ending in Jul 2012. Real weekly earnings increased 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2012 and 2.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep 2012. Real weekly earnings fell 2.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2012 and increased 0.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2012 and 2.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2012. Real weekly earnings fell 1.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2013 and virtually stagnated with gain of 0.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Feb 2013, increasing 0.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Mar 2013. Real weekly earnings fell 0.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Apr 2013 and increased 1.0 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2013. Average weekly earnings increased 2.5 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2013 and fell 1.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Jul 2013. Real weekly earnings increased 0.8 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2013, 0.9 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep 2013 and 1.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2013. Average weekly earnings increased 1.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2013 and increased 0.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2013. Average weekly earnings increased 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2014 and 2.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Feb 2014. Average weekly earnings increased 2.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Mar 2014 and 0.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Apr 2014. Average weekly earnings in constant dollars increased 0.3 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2014 and changed 0.0 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2014. Real average weekly earnings increased 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Jul 2014 and 0.8 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2014. Real weekly earnings decreased 1.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep 2014 and increased 0.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2014. Average weekly earnings increased 2.9 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2014 and increased 0.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2014. Average weekly earnings increased 2.9 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2015 and increased 2.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Feb 2015. Average weekly earnings adjusted for inflation increased 2.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Mar 2015 and increased 2.5 percent in the 12 months ending in Apr 2015. Average weekly earnings adjusted for inflation increased 2.4 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2015 and increased 0.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2015. Average weekly earnings increased 2.0 percent in the 12 months ending in Jul 2015 and 4.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2015. Average weekly earnings adjusted for inflation increased 1.8 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep 2015 and increased 2.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2015. Average weekly earnings adjusted for inflation increased 1.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2015 and increased 1.5 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2015. Average weekly earnings increased 1.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2016. Average weekly earnings contracted 0.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Feb 2015 and contracted 0.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Mar 2016. Average weekly earnings increased 1.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Apr 2016 and increased 2.7 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2016. Average weekly earnings increased 1.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2016 and increased 1.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Jul 2016. Average weekly earnings decreased 1.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2016 and increased 1.5 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep 2016. Average weekly earnings increased 2.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2016 and decreased 1.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2016. Table I-5 confirms the trend of deterioration of purchasing power of average weekly earnings in 2011 and into 2013 with oscillations according to carry trades causing world inflation waves (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/oscillating-valuations-of-risk.html). On an annual basis, average weekly earnings in constant 1982-1984 dollars increased from $347.19 in 2007 to $354.30 in 2013, by 2.0 percent or at the average rate of 0.3 percent per year (data in http://www.bls.gov/data/). Annual average weekly earnings in constant dollars of $352.96 in 2010 fell 0.4 percent to $351.68 in 2012. Annual average weekly earnings increased from $347.19 in 2007 to $356.94 in 2014 or by 2.8 at the average rate of 0.4 percent. Annual average weekly earnings in constant increased from $347.19 in 2007 to $364.78 in 2015 by 5.1 percent at the average rate of 0.6 percent per year. Those who still work bring back home a paycheck that buys fewer high-quality goods than a year earlier. The fractured US job market does not provide an opportunity for advancement as in past booms following recessions because of poor job creation with 24.2 million unemployed or underemployed (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-yields-and-dollar-revaluation.html) in a recovery without hiring (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/rising-values-of-risk-financial-assets.html) because of mediocre economic growth (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html). The BLS is revising the data from 2006 to 2009 (http://www.bls.gov/ces/#notices) available in the release for Jan 2016 and subsequent releases.
Table IB-5, US, Average Weekly Earnings of All Employees in Constant Dollars of 1982-1984, NSA 2007-2016
| Year | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov |
| 2006 | 340.92 | 345.81 | 340.60 | 344.02 | 352.68 | 347.94 |
| 2007 | 343.92 | 349.84 | 345.14 | 352.69 | 344.91 | 343.85 |
| 2008 | 341.61 | 334.32 | 338.41 | 338.90 | 342.99 | 355.78 |
| 2009 | 343.10 | 345.45 | 352.16 | 346.57 | 348.20 | 354.92 |
| 2010 | 349.50 | 351.55 | 358.43 | 352.80 | 356.00 | 354.66 |
| 2011 | 346.61 | 349.30 | 346.97 | 349.47 | 358.11 | 350.99 |
| 2012 | 348.83 | 355.63 | 348.33 | 356.98 | 348.76 | 351.46 |
| ∆%12M | 0.6 | 1.8 | 0.4 | 2.1 | -2.6 | 0.1 |
| 2013 | 357.66 | 350.63 | 351.08 | 360.25 | 354.24 | 356.00 |
| ∆%12M | 2.5 | -1.4 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.6 | 1.3 |
| 2014 | 357.58 | 352.03 | 353.93 | 355.10 | 356.29 | 366.36 |
| ∆%12M | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.8 | -1.4 | 0.6 | 2.9 |
| 2015 | 358.25 | 359.09 | 368.95 | 361.39 | 364.96 | 372.29 |
| ∆%12M | 0.2 | 2.0 | 4.2 | 1.8 | 2.4 | 1.6 |
| 2016 | 362.82 | 364.97 | 364.50 | 366.76 | 374.88 | 367.51 |
| ∆%12M | 1.3 | 1.6 | -1.2 | 1.5 | 2.7 | -1.3 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/
Chart IB-4 provides average weekly earnings of all employees in constant dollars of 1982-1984. The same pattern emerges of sharp decline during the contraction, followed by recovery in the expansion and continuing fall with oscillations caused by carry trades from zero interest rates into commodity futures from 2010 to 2011 and into 2012-2016. The increase in the final segment is mostly because of collapse of commodity prices in reversals of carry trade exposures. The BLS is revising the data from 2006 to 2009 (http://www.bls.gov/ces/#notices) available for the release of Jan 2016 and subsequent releases.
Chart IB-4, US, Average Weekly Earnings of All Employees in Constant Dollars of 1982-1984, SA 2006-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/
Chart IB-5 provides 12-month percentage changes of average weekly earnings of all employees in the US in constant dollars of 1982-1984. The BLS is revising the data from 2006 to 2009 (http://www.bls.gov/ces/#notices) available for the release of Jan 2016 and subsequent releases. There is the same pattern of contraction during the global recession in 2008 and then again weakness in the recovery without hiring and inflation waves. (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/12/of-course-economic-outlook-is-highly.html).
Chart IB-5, US, Average Weekly Earnings of All Employees NSA in Constant Dollars of 1982-1984 12-Month Percent Change, NSA 2007-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/
ESVI United States Commercial Banks. Selected assets and liabilities of US commercial banks, not seasonally adjusted, in billions of dollars, from Report H.8 of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System are in Table I-1. Data are not seasonally adjusted to permit comparison between Nov 2015 and Nov 2016. Total assets of US commercial banks grew 2.7 percent from $15,634.9 billion in Nov 2015 to $15,061.8 billion in Nov 2016. The Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) estimates US GDP in 2015 at $18,036.6 billion (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). Thus, total assets of US commercial banks are equivalent to over 80 percent of US GDP. Bank credit grew 8.0 percent from $11,507.5 billion in Oct 2015 to $12,432.5 billion in Oct 2016. Securities in bank credit increased 8.2 percent from $3094 billion in Nov 2015 to $3347 billion in Nov 2016. A large part of securities in banking credit consists of US Treasury and agency securities, increasing 10.5 percent from $2208 billion in Nov 2015 to $2440 billion in Nov 2016. Credit to the government that issues or backs Treasury and agency securities of $2440 billion in Nov 2016 is about 19.5 percent of total bank credit of US commercial banks of $12,492.7 billion. Mortgage-backed securities, providing financing of home loans, increased 8.3 percent, from $1559 billion in Nov 2015 to $1688 billion in Nov 2016. Loans and leases are relatively dynamic, growing 7.2 percent from $8529 billion in Nov 2015 to $9146 billion in Nov 2016. A dynamic class is commercial and industrial loans, growing 8.1 percent from $1941 billion in Nov 2015 and providing $2099 billion or 22.9 percent of total loans and leases of $9146 billion in Nov 2016. Real estate loans increased 6.9 percent, providing $4115 billion in Nov 2016 or 45.0 percent of total loans and leases. Consumer loans increased 8.0 percent, providing $1355 billion in Nov 2016 or 14.8 percent of total loans. Cash assets are measured to “include vault cash, cash items in process of collection, balances due from depository institutions and balances due from Federal Reserve Banks” (https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h8/current/default.htm). Cash assets in US commercial banks decreased 16.9 percent from $2710 billion in Nov 2015 to $2252 billion in Nov 2016 but a single year of the series masks exploding cash in banks because of unconventional monetary policy, which is discussed below. Bank deposits increased 4.1 percent from $10,981 billion in Nov 2015 to $11,429 billion in Nov 2016. The difference between bank deposits and total loans and leases in banks decreased from $2452 billion in Nov 2015 to $2283 billion in Nov 2016 or by $169 billion. Securities in bank credit increased $253 billion from $3094 billion in Nov 2015 to $3347 billion in Nov 2016 and Treasury and agency securities increased $232 billion from $2208 billion in Nov 2015 to $2440 billion in Nov 2016. Loans and leases increased $617 billion from $8529 billion in Nov 2015 to $9146 billion in Nov 2016. Banks expanded both lending and investment in lower risk securities partly because of the weak economy and credit disappointments during the global recession that has resulted in an environment of fewer sound lending opportunities. Investing in securities with high duration, or price elasticity of yields, is riskier because of the increase in yields that can cause loss of principal as investors shift away from bond funds into money market funds invested in short-term assets. Lower interest rates resulting from monetary policy may not necessarily encourage higher borrowing in the current loss of dynamism of the US economy. Real disposable income per capita in IIIQ2016 is higher by only 9,2 percent than in IVQ2007 (Table IB-2 IX Conclusion and extended analysis in IB Collapse of United States Dynamism of Income Growth and Employment Creation), which is significantly lower than 18.9 percent higher if the economy had performed in long-term growth of per capita income in the United States at 2 percent per year from 1870 to 2010 (Lucas 2011May). In contrast, real disposable income per capita grew cumulatively 26.6 percent in the cycle from IQ1980 to IQ1990 that was close to trend growth of 23.1 percent.
Table I-1, US, Assets and Liabilities of Commercial Banks, NSA, Billions of Dollars
| Nov 2015 | Nov 2016 | ∆% | |
| Total Assets | 15,634.9 | 16,061.8 | 2.7 |
| Bank Credit | 11,622.8 | 12,492.7 | 7.5 |
| Securities in Bank Credit | 3094 | 3347 | 8.2 |
| Treasury & Agency Securities | 2208 | 2440 | 10.5 |
| Mortgage-Backed Securities | 1559 | 1688 | 8.3 |
| Loans & Leases | 8529 | 9146 | 7.2 |
| Real Estate Loans | 3850 | 4115 | 6.9 |
| Commercial Real Estate Loans | 1762 | 1954 | 10.9 |
| Consumer Loans | 1255 | 1355 | 8.0 |
| Commercial & Industrial Loans | 1941 | 2099 | 8.1 |
| Other Loans & Leases | 1483 | 1578 | 6.4 |
| Cash Assets* | 2710 | 2252 | -16.9 |
| Total Liabilities | 13,942 | 14,314 | 2.7 |
| Deposits | 10,981 | 11,429 | 4.1 |
| Residual (Assets less Liabilities) | 1693 | 1748 | NA |
Note: balancing item of residual assets less liabilities not included
*”Includes vault cash, cash items in process of collection, balances due from depository institutions and balances due from Federal Reserve Banks.”
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h8/current/default.htm
Table I-2, US, Selected Assets and Liabilities of Commercial Banks, at Break Adjusted, Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rate, ∆%
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | Oct 2016 | Nov 2016 | |
| Total Assets | 5.2 | 2.6 | 7.1 | 7.4 | 3.5 | -3.4 | 1.8 |
| Bank Credit | 1.6 | 4.1 | 1.3 | 6.9 | 7.3 | 7.4 | 2.5 |
| Securities in Bank Credit | 1.9 | 7.6 | -1.5 | 7.1 | 5.9 | 10.5 | 0.8 |
| Treasury & Agency Securities | 3.2 | 8.4 | -5.2 | 11.8 | 8.8 | 16.8 | 3.8 |
| Other Securities | -0.9 | 5.8 | 6.8 | -2.3 | -0.6 | -5.8 | -7.1 |
| Loans & Leases | 1.5 | 2.9 | 2.3 | 6.8 | 7.8 | 6.3 | 3.2 |
| Real Estate Loans | -3.7 | -1.1 | -1.0 | 2.5 | 5.1 | 7.7 | 3.8 |
| Commercial Real Estate Loans | -6.3 | -1.2 | 4.5 | 6.8 | 10.0 | 9.7 | 7.9 |
| Consumer Loans | -1.7 | 0.5 | 3.2 | 5.3 | 5.9 | 7.0 | 6.0 |
| Commercial & Industrial Loans | 8.6 | 11.6 | 6.9 | 12.0 | 10.6 | 9.1 | 2.9 |
| Other Loans & Leases | 18.6 | 8.1 | 6.0 | 14.6 | 13.3 | -1.7 | -0.2 |
| Cash Assets | 48.1 | -2.3 | 54.5 | 12.2 | -7.9 | -59.6 | -4.1 |
| Total Liabilities | 5.5 | 2.4 | 8.2 | 7.6 | 3.3 | -5.1 | 2.6 |
| Deposits | 6.7 | 7.2 | 6.5 | 6.4 | 5.0 | 0.3 | 4.9 |
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h8/current/default.htm
Chart I-16 and Chart I-16A are quite revealing in analyzing the state of bank credit in the US economy. The upper curves are (1) deposits and (2) loans and leases in bank credit. Historically since 1973, the level and rate of change of deposits and loans and leases in bank credit were almost identical. The lower two curves are Treasury and agency securities in bank credit and cash assets with treasury and agency securities moving closely with cash assets until the 1990s when Treasury and agency securities exceeded cash assets. There is convergence in the final segment after cash assets exceeded treasury and agency securities. The shaded area of the recession from IV2007 to IIQ2009 shows a break in the level and rate of movement of the series. Deposits continued to expand rapidly through the recession and the following expansion period. Loans and leases fell and barely recovered the level of trend before the recession while deposits moved nearly vertically well above the level before the recession. While Treasury and agency securities in bank credit continued to expand at a higher rate, reaching a level well above that before the recession, cash assets jumped as the counterpart of excess reserves in banks that financed quantitative easing or massive outright purchases of securities for the balance sheet of the Fed. Unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates and outright purchases of securities caused sharp increases of deposits, cash assets and Treasury and agency securities in bank credit but not in loans and leases. There is much discussion about the almost impossible task of evaluating monetary policy in terms of costs and benefits. Before the financial crisis, Chairman Greenspan (2004) analyzes monetary policy and its limitations (see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 13-4, 212-13) that do not differ from those of private financial institutions:
“The Federal Reserve’s experiences over the past two decades make it clear that uncertainty is not just a pervasive feature of the monetary policy landscape; it is the defining characteristic of that landscape. The term “uncertainty” is meant here to encompass both “Knightian uncertainty,” in which the probability distribution of outcomes is unknown, and “risk,” in which uncertainty of outcomes is delimited by a known probability distribution. In practice, one is never quite sure what type of uncertainty one is dealing with in real time, and it may be best to think of a continuum ranging from well-defined risks to the truly unknown.
As a consequence, the conduct of monetary policy in the United States has come to involve, at its core, crucial elements of risk management. This conceptual framework emphasizes understanding as much as possible the many sources of risk and uncertainty that policymakers face, quantifying those risks when possible, and assessing the costs associated with each of the risks. In essence, the risk management approach to monetary policymaking is an application of Bayesian decision making.
This framework also entails devising, in light of those risks, a strategy for policy directed at maximizing the probabilities of achieving over time our goals of price stability and the maximum sustainable economic growth that we associate with it. In designing strategies to meet our policy objectives, we have drawn on the work of analysts, both inside and outside the Fed, who over the past half century have devoted much effort to improving our understanding of the economy and its monetary transmission mechanism. A critical result has been the identification of a relatively small set of key relationships that, taken together, provide a useful approximation of our economy’s dynamics. Such an approximation underlies the statistical models that we at the Federal Reserve employ to assess the likely influence of our policy decisions.
However, despite extensive efforts to capture and quantify what we perceive as the key macroeconomic relationships, our knowledge about many of the important linkages is far from complete and, in all likelihood, will always remain so. Every model, no matter how detailed or how well designed, conceptually and empirically, is a vastly simplified representation of the world that we experience with all its intricacies on a day-to-day basis.
Given our inevitably incomplete knowledge about key structural aspects of an ever-changing economy and the sometimes asymmetric costs or benefits of particular outcomes, a central bank needs to consider not only the most likely future path for the economy but also the distribution of possible outcomes about that path. The decision makers then need to reach a judgment about the probabilities, costs, and benefits of the various possible outcomes under alternative choices for policy.”
Risk management tools are as likely to fail in private financial institutions as in central banks because of the difficulty of modeling risk during uncertainty. There is no such thing as riskless financial management. “Whale” trades at official institutions causing wide swings of financial and economic variables do not receive the same attention as those in large private banking institutions such as the teapot storm over JP Morgan Chase.
The post of this blog on Nov 8, 2009 is currently relevant (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2009/11/how-big-bank-carlos-manuel-pelaezs.html):
Sunday, November 8, 2009
How Big a Bank
Carlos Manuel Peláez's Latest Blog Posts
How Big a Bank
5:56 PM PST, November 8, 2009
Agendas of financial regulation in parliaments, international official institutions and monetary authorities include limits on the size of banks or how big a bank should be. These proposals imply that regulators would decide the total value of assets held by banks. Assets would have to be weighted by risk, which is the best practice applied in the Basel capital accords. Regulators would decide not only the total value of assets but also the structure or percentage share of assets by risk class and credit rating such as how much in consumer credit, real estate lending, securities holding, corporate lending and so on. If the regulators decide on the total value of assets and their risk, they effectively micro manage bank decisions on risk and return. Managers would only implement regulatory criteria with little decision power on how best to reward shareholder capital. Regulators would mandate maximum assets and their risk distribution by leverage, credit and liquidity regulation. There are two concerns on the regulation of how big a bank should be. First, there is the issue of best practice in bank management and its consequences for financing prosperity. Banking is characterized by declining costs because of bulky fixed investments required for initiation of lines of business (Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance, 82-9, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession, 63-9). There has been a new industrial/technological revolution in the past three decades centered on information technology (IT). Banking is highly intensive in the creation, processing, transmission and decision use of information. The first transaction of a $100 million IT facility costs $100 million but the hundred millionth costs only one dollar. Competitive banking requires a large volume of transactions to reach the minimum cost of operations. At the time of the call report for the implementation of Basel II in 2006, 11 banking organizations had total assets of $4.6 trillion, equivalent to 44 percent of total US banking assets of $10.5 trillion, and about $978 billion in foreign assets, equivalent to 96 percent of US foreign banking assets of $1 trillion (Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State: Vol. II, 147). Concentration likely increased during the credit/dollar crisis and its reversal by regulation could cause another confidence shock. The regulation of how big a bank should be would disrupt investment in the best practice of using technology and delivery of products at lowest cost by US banking organizations. It would also undermine the competitiveness of US banks in international business, violating the essential principle of the Basel capital accords of maintaining fair competitive international banking. Second, the regulation of how big a bank should be is based on an inadequate interpretation of the credit crisis/global recession. The panic of confidence in financial markets is commonly attributed to the failure of Lehman Bros. in September 2008. Cochrane and Zingales have shown that the crisis of confidence originated in the proposal of the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) of $700 billion two weeks after the failure of Lehman Bros. TARP was proposed in negative terms of: withdraw "toxic" assets from bank balance sheets of banks or there would be an economic catastrophe similar to the Great Depression. Counterparty risk perception rose sharply because of fear of banking panics, paralyzing sale and repurchase transactions and causing illiquidity of multiple market segments. The "toxin" was introduced by zero interest rates in 2003-4 that induced high leverage and risk, low liquidity and imprudent credit together with the purchase or guarantee of $1.6 trillion of nonprime mortgages by Fannie and Freddie on the good faith and credit of the US. Regulatory micro management of the volume and structure of risk of banks and financial markets will weaken banks, reducing the volume of credit required for steering the world economy from currently low levels of activity. It will also restructure markets with arbitrary concession of monopolistic power to less efficient banks, creating vulnerabilities to new crises. There is need for less intrusive regulation that induces a sustainable path of prosperity, using effectively the staff, expertise and resources of existing regulatory agencies.
Chart I-16, US, Deposits, Loans and Leases in Bank Credit, Cash Assets and Treasury and Agency Securities in Bank Credit, US Commercial Banks, Not Seasonally Adjusted, Monthly, 1973-2016, Billions of Dollars
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h8/current/default.htm
Chart I-16A, Deposits, Loans and Leases in Bank Credit, Cash Assets and Treasury and Agency Securities in Bank Credit, US Commercial Banks, Not Seasonally Adjusted, Monthly, 1995-2016, Billions of Dollars
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
https://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h8/current/default.htm
ESVII Unresolved US Balance of Payments Deficits and Fiscal Imbalance. Table IIA1-1 of the CBO (https://www.cbo.gov/about/products/budget-economic-data#6) shows the significant worsening of United States fiscal affairs from 2007-2008 to 2009-2012 with marginal improvement in 2013-2015 but with much higher debt relative to GDP. The deficit of $1.1 trillion in fiscal year 2012 was the fourth consecutive federal deficit exceeding one trillion dollars. All four deficits are the highest in share of GDP since 1946 (https://www.cbo.gov/about/products/budget-economic-data#6).
Table IAI-1, US, Budget Fiscal Year Totals, Billions of Dollars and % GDP
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | |
| Receipts | 2568 | 2524 | 2105 | 2163 | 2303 |
| Outlays | 2729 | 2983 | 3518 | 3457 | 3603 |
| Deficit | -161 | -459 | 1413 | 1294 | 1300 |
| % GDP | -1.1 | -3.1 | -9.8 | -8.7 | -8.5 |
| 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |
| Receipts | 2450 | 2775 | 3021 | 3250 |
| Outlays | 3537 | 3455 | 3506 | 3688 |
| Deficit | 1087 | 680 | -485 | -438 |
| % GDP | -6.8 | -4.1 | -2.8 | -2.5 |
Source: CBO, An update to the budget and economic outlook: 2016 to 2026. Washington, DC, Aug 23, 2016.
The US is facing a major fiscal challenge. Table IIA1-5 provides federal revenues, expenditures, deficit and debt as percent of GDP and the yearly change in GDP in the more than eight decades from 1930 to 2015. The most recent period of debt exceeding 90 percent of GDP based on yearly observations in Table IIA1-5 is between 1944 and 1948. The data in Table IIA-15 use the earlier GDP estimates of the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) until 1972 for the ratios to GDP of revenue, expenditures, deficit and debt and the revised CBO (https://www.cbo.gov/about/products/budget-economic-data#6) after 1973 that incorporate the new BEA GDP estimates (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). The percentage change of GDP is based on the new BEA estimates for all years. The debt/GDP ratio actually rose to 106.2 percent of GDP in 1945 and to 108.7 percent of GDP in 1946. GDP fell revised 11.6 percent in 1946, which is only matched in Table I-5 by the decline of revised 12.9 percent in 1932. Part of the decline is explained by the bloated US economy during World War II, growing at revised 17.7 percent in 1941, 18.9 percent in 1942 and 17.0 percent in 1943. Expenditures as a share of GDP rose to their highest in the series: 43.6 percent in 1943, 43.6 percent in 1944 and 41.9 percent in 1945. The repetition of 43.6 percent in 1943 and 1944 is in the original source of Table IIA1-5. During the Truman administration from Apr 1945 to Jan 1953, the federal debt held by the public fell systematically from the peak of 108.7 percent of GDP in 1946 to 61.6 percent of GDP in 1952. During the Eisenhower administration from Jan 1953 to Jan 1961, the federal debt held by the public fell from 58.6 percent of GDP in 1953 to 45.6 percent of GDP in 1960. The Truman and Eisenhower debt reductions were facilitated by diverse factors such as low interest rates, lower expenditure/GDP ratios that could be attained again after lowering war outlays and less rigid structure of mandatory expenditures than currently. There is no subsequent jump of debt as the one from revised 39.3 percent of GDP in 2008 to 65.9 percent of GDP in 2011, 70.4 percent in 2012, 72.6 percent in 2013 and 74.4 percent in 2014.The debt/GDP ratio eased slightly to 73.6 percent in 2015.
Table IIA1-5, United States Central Government Revenue, Expenditure, Deficit, Debt and GDP Growth 1930-2011
| Rev | Exp | Deficit | Debt | GDP | |
| 1930 | 4.2 | 3.4 | 0.8 | -8.5 | |
| 1931 | 3.7 | 4.3 | -0.6 | -6.4 | |
| 1932 | 2.8 | 6.9 | -4.0 | -12.9 | |
| 1933 | 3.5 | 8.0 | -4.5 | -1.3 | |
| 1934 | 4.8 | 10.7 | -5.9 | 10.8 | |
| 1935 | 5.2 | 9.2 | -4.0 | 8.9 | |
| 1936 | 5.0 | 10.5 | -5.5 | 12.9 | |
| 1937 | 6.1 | 8.6 | -2.5 | 5.1 | |
| 1938 | 7.6 | 7.7 | -0.1 | -3.3 | |
| 1939 | 7.1 | 10.3 | -3.2 | 8.0 | |
| 1940s | |||||
| 1940 | 6.8 | 9.8 | -3.0 | 44.2 | 8.8 |
| 1941 | 7.6 | 12.0 | -4.3 | 42.3 | 17.7 |
| 1942 | 10.1 | 24.3 | -14.2 | 47.0 | 18.9 |
| 1943 | 13.3 | 43.6 | -30.3 | 70.9 | 17.0 |
| 1944 | 20.9 | 43.6 | -22.7 | 88.3 | 8.0 |
| 1945 | 20.4 | 41.9 | -21.5 | 106.2 | -1.0 |
| 1946 | 17.7 | 24.8 | -7.2 | 108.7 | -11.6 |
| 1947 | 16.5 | 14.8 | 1.7 | 96.2 | -1.1 |
| 1948 | 16.2 | 11.6 | 4.6 | 84.3 | 4.1 |
| 1949 | 14.5 | 14.3 | 0.2 | 79.0 | -0.5 |
| 1950s | |||||
| 1950 | 14.4 | 15.6 | -1.1 | 80.2 | 8.7 |
| 1951 | 16.1 | 14.2 | 1.9 | 66.9 | 8.1 |
| 1952 | 19.0 | 19.4 | -0.4 | 61.6 | 4.1 |
| 1953 | 18.7 | 20.4 | -1.7 | 58.6 | 4.7 |
| 1954 | 18.5 | 18.8 | -0.3 | 59.5 | -0.6 |
| 1955 | 16.5 | 17.3 | -0.8 | 57.2 | 7.1 |
| 1956 | 17.5 | 16.5 | 0.9 | 52.0 | 2.1 |
| 1957 | 17.7 | 17.0 | 0.8 | 48.6 | 2.1 |
| 1958 | 17.3 | 17.9 | -0.6 | 49.2 | -0.7 |
| 1959 | 16.2 | 18.8 | -2.6 | 47.9 | 6.9 |
| 1960s | |||||
| 1960 | 17.8 | 17.8 | 0.1 | 45.6 | 2.6 |
| 1961 | 17.8 | 18.4 | -0.6 | 45.0 | 2.6 |
| 1962 | 17.6 | 18.8 | -1.3 | 43.7 | 6.1 |
| 1963 | 17.8 | 18.6 | -0.8 | 42.4 | 4.4 |
| 1964 | 17.6 | 18.5 | -0.9 | 40.0 | 5.8 |
| 1965 | 16.4 | 16.6 | -0.2 | 36.7 | 6.5 |
| 1966 | 16.7 | 17.2 | -0.5 | 33.7 | 6.6 |
| 1967 | 17.8 | 18.8 | -1.0 | 31.8 | 2.7 |
| 1968 | 17.0 | 19.8 | -2.8 | 32.2 | 4.9 |
| 1969 | 19.0 | 18.7 | 0.3 | 28.3 | 3.1 |
| 1970s | |||||
| 1970 | 18.4 | 18.7 | -0.3 | 27.0 | 0.2 |
| 1971 | 16.7 | 18.8 | -2.1 | 27.1 | 3.3 |
| 1972 | 17.0 | 18.9 | -1.9 | 26.4 | 5.2 |
| 1973 | 17.0 | 18.1 | -1.1 | 25.1 | 5.6 |
| 1974 | 17.7 | 18.1 | -0.4 | 23.1 | -0.5 |
| 1975 | 17.3 | 20.6 | -3.3 | 24.5 | -0.2 |
| 1976 | 16.6 | 20.8 | -4.1 | 26.7 | 5.4 |
| 1977 | 17.5 | 20.2 | -2.6 | 27.1 | 4.6 |
| 1978 | 17.5 | 20.1 | -2.6 | 26.6 | 5.6 |
| 1979 | 18.0 | 19.6 | -1.6 | 24.9 | 3.2 |
| 1980s | |||||
| 1980 | 18.5 | 21.1 | -2.6 | 25.5 | -0.2 |
| 1981 | 19.1 | 21.6 | -2.5 | 25.2 | 2.6 |
| 1982 | 18.6 | 22.5 | -3.9 | 27.9 | -1.9 |
| 1983 | 17.0 | 22.8 | -5.9 | 32.1 | 4.6 |
| 1984 | 16.9 | 21.5 | -4.7 | 33.1 | 7.3 |
| 1985 | 17.2 | 22.2 | -5.0 | 35.3 | 4.2 |
| 1986 | 17.0 | 21.8 | -4.9 | 38.4 | 3.5 |
| 1987 | 17.9 | 21.0 | -3.1 | 39.5 | 3.5 |
| 1988 | 17.6 | 20.6 | -3.0 | 39.8 | 4.2 |
| 1989 | 17.8 | 20.5 | -2.7 | 39.3 | 3.7 |
| 1990s | |||||
| 1990 | 17.4 | 21.2 | -3.7 | 40.8 | 1.9 |
| 1991 | 17.3 | 21.7 | -4.4 | 44.0 | -0.1 |
| 1992 | 17.0 | 21.5 | -4.5 | 46.6 | 3.6 |
| 1993 | 17.0 | 20.7 | -3.8 | 47.8 | 2.7 |
| 1994 | 17.5 | 20.3 | -2.8 | 47.7 | 4.0 |
| 1995 | 17.8 | 20.0 | -2.2 | 47.5 | 2.7 |
| 1996 | 18.2 | 19.6 | -1.3 | 46.8 | 3.8 |
| 1997 | 18.6 | 18.9 | -0.3 | 44.5 | 4.5 |
| 1998 | 19.2 | 18.5 | 0.8 | 41.6 | 4.5 |
| 1999 | 19.2 | 17.9 | 1.3 | 38.2 | 4.7 |
| 2000s | |||||
| 2000 | 20.0 | 17.6 | 2.3 | 33.6 | 4.1 |
| 2001 | 18.8 | 17.6 | 1.2 | 31.4 | 1.0 |
| 2002 | 17.0 | 18.5 | -1.5 | 32.6 | 1.8 |
| 2003 | 15.7 | 19.1 | -3.3 | 34.5 | 2.8 |
| 2004 | 15.6 | 19.0 | -3.4 | 35.5 | 3.8 |
| 2005 | 16.7 | 19.2 | -2.5 | 35.6 | 3.3 |
| 2006 | 17.6 | 19.4 | -1.8 | 35.3 | 2.7 |
| 2007 | 17.9 | 19.1 | -1.1 | 35.2 | 1.8 |
| 2008 | 17.1 | 20.2 | -3.1 | 39.3 | -0.3 |
| 2009 | 14.6 | 24.4 | -9.8 | 52.3 | -2.8 |
| 2010s | |||||
| 2010 | 14.6 | 23.4 | -8.7 | 60.9 | 2.5 |
| 2011 | 15.0 | 23.4 | -8.5 | 65.9 | 1.6 |
| 2012 | 15.3 | 22.1 | -6.8 | 70.4 | 2.2 |
| 2013 | 16.8 | 20.9 | -4.1 | 72.6 | 1.7 |
| 2014 | 17.6 | 20.4 | -2.8 | 74.4 | 2.4 |
| 2015 | 18.2 | 20.7 | -2.5 | 73.6 | 2.6 |
Sources: CBO, An update to the budget and economic outlook: 2016 to 2026. Washington, DC, Aug 23, 2016.
https://www.cbo.gov/about/products/budget-economic-data#6
https://www.cbo.gov/about/products/budget_economic_data#3 https://www.cbo.gov/about/products/budget_economic_data#2 Office of Management and Budget. 2011. Historical Tables. Budget of the US Government Fiscal Year 2011. Washington, DC: OMB. CBO (2012JanBEO). CBO (2012Jan31). CBO (2012AugBEO). CBO (2013BEOFeb5). CBO2013HBDFeb5), CBO (2013Aug12). CBO, Historical Budget Data—February 2014, Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb. CBO, Historical budget data—April 2014 release. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Apr 14, 2014. Congressional Budget Office, August 2014 baseline: an update to the budget and economic outlook: 2014 to 2024. Washington, DC, CBO, Aug 27, 2014. CBO, Historical Budget Data, January 2015 Baseline from Budget and economic outlook: 2015 to 2025. Washington, DC, CBO, Jan 26.
Table IIA1-7 provides the latest exercise by the CBO (CBO, An update to the budget and economic outlook: 2016 to 2026. Washington, DC, Aug 23, 2016.
https://www.cbo.gov/about/products/budget-economic-data#6) of projecting the fiscal accounts of the US. Table IIA1-7 extends data back to 1995 with the projections of the CBO from 2016 to 2026, using the new estimates of the Bureau of Economic Analysis of US GDP (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). Budget analysis in the US uses a ten-year horizon. The significant event in the data before 2011 is the budget surpluses from 1998 to 2001, from 0.8 percent of GDP in 1998 to 2.3 percent of GDP in 2000 and 1.2 percent of GDP in 2001. Debt held by the public fell from 47.5 percent of GDP in 1995 to 31.4 percent of GDP in 2001. The deb/GDP ratio would rise in the projection from actual 73.6 percent in 2015 to 85.5 percent in 2026.
Table IIA1-7, US, CBO Baseline Budget Outlook 2016-2026
| Out | Out | Deficit | Deficit | Debt | Debt | |
| 1995 | 1,516 | 20.0 | -164 | -2.2 | 3,604 | 47.5 |
| 1996 | 1,560 | 19.6 | -107 | -1.3 | 3,734 | 46.8 |
| 1997 | 1,601 | 18.9 | -22 | -0.3 | 3,772 | 44.5 |
| 1998 | 1,652 | 18.5 | +69 | +0.8 | 3,721 | 41.6 |
| 1999 | 1,702 | 17.9 | +126 | +1.3 | 3,632 | 38.2 |
| 2000 | 1,789 | 17.6 | +236 | +2.3 | 3,410 | 33.6 |
| 2001 | 1,863 | 17.6 | +128 | +1.2 | 3,320 | 31.4 |
| 2002 | 2,011 | 18.5 | -158 | -1.5 | 3,540 | 32.6 |
| 2003 | 2,159 | 19.1 | -378 | -3.3 | 3,913 | 34.5 |
| 2004 | 2,293 | 19.0 | -413 | -3.4 | 4,295 | 35.5 |
| 2005 | 2,472 | 19.2 | -318 | -2.5 | 4,592 | 35.6 |
| 2006 | 2,655 | 19.4 | -248 | -1.8 | 4,829 | 35.3 |
| 2007 | 2,729 | 19.1 | -161 | -1.1 | 5,035 | 35.2 |
| 2008 | 2,983 | 20.2 | -459 | -3.1 | 5,803 | 39.3 |
| 2009 | 3,518 | 24.4 | -1,413 | -9.8 | 7,545 | 52.3 |
| 2010 | 3,457 | 23.4 | -1,294 | -8.7 | 9,019 | 60.9 |
| 2011 | 3,603 | 23.4 | -1,300 | -8.5 | 10,128 | 65.9 |
| 2012 | 3,537 | 22.1 | -1,087 | -6.8 | 11,281 | 70.4 |
| 2013 | 3,455 | 20.9 | -680 | -4.1 | 11,983 | 72.6 |
| 2014 | 3,506 | 20.4 | -485 | -2.8 | 12,780 | 74.4 |
| 2015 | 3,688 | 20.7 | -438 | -2.5 | 13,117 | 73.6 |
| 2016 | 3,866 | 21.1 | -590 | -3.2 | 14,073 | 76.6 |
| 2017 | 4,015 | 21.0 | -594 | -3.1 | 14,743 | 77.2 |
| 2018 | 4,120 | 20.7 | -520 | -2.6 | 15,325 | 77.0 |
| 2019 | 4,370 | 21.2 | -625 | -3.0 | 16,001 | 77.5 |
| 2020 | 4,614 | 21.6 | -714 | -3.3 | 16,758 | 78.4 |
| 2021 | 4,853 | 21.9 | -806 | -3.6 | 17,597 | 79.3 |
| 2022 | 5,166 | 22.4 | -954 | -4.1 | 18,584 | 80.5 |
| 2023 | 5,373 | 22.4 | -988 | -4.1 | 19,608 | 81.7 |
| 2024 | 5,574 | 22.3 | -1,000 | -4.0 | 20,649 | 82.7 |
| 2025 | 5,908 | 22.7 | -1,128 | -4.3 | 21,824 | 84.0 |
| 2026 | 6,235 | 23.1 | -1,243 | -4.6 | 23,118 | 85.5 |
| 2017 to 2021 | 21,973 | 21.3 | -3,258 | -3.2 | NA | NA |
| 2017 | 50,229 | 22.0 | -8,571 | -3.8 | NA | NA |
Note: Out = outlays
Sources: CBO (2011AugBEO); Office of Management and Budget. 2011. Historical Tables. Budget of the US Government Fiscal Year 2011. Washington, DC: OMB; CBO. 2011JanBEO. Budget and Economic Outlook. Washington, DC, Jan. CBO. 2012AugBEO. Budget and Economic Outlook. Washington, DC, Aug 22. CBO. 2012Jan31. Historical budget data. Washington, DC, Jan 31. CBO. 2012NovCDR. Choices for deficit reduction. Washington, DC. Nov. CBO. 2013HBDFeb5. Historical budget data—February 2013 baseline projections. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb 5. CBO. 2013HBDFeb5. Historical budget data—February 2013 baseline projections. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb 5. CBO (2013Sep11). CBO, Historical Budget Data—February 2014, Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb. CBO, The Budget and Economic Outlook 2014 to 2024. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb 2014. CBO, Historical budget data—April 2014 release. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Apr 14, 2014. CBO, Updated Budget Projections: 2014 to 2024. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Apr 14, 2014.
Congressional Budget Office, August 2014 baseline: an update to the budget and economic outlook: 2014 to 2024. Washington, DC, CBO, Aug 27, 2014. CBO, The budget and economic outlook: 2015 to 2025. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Jan 26, 2015. CBO. 2015. An update to the budget and economic outlook: 2015 to 2025. Washington, DC, CBO, Aug 25. CBO, Updated budget projections: 2016 to 2026. Washington, DC, Mar 2016. CBO, An update to the budget and economic outlook: 2016 to 2026. Washington, DC, Aug 23, 2016.
https://www.cbo.gov/about/products/budget-economic-data#6 https://www.cbo.gov/about/products/budget_economic_data#3 https://www.cbo.gov/about/products/budget_economic_data#2
Table IIA1-8 provides baseline CBO projections of federal revenues, outlays, deficit and debt as percent of GDP. The adjustment depends on increasing revenues from 15.0 percent of GDP in 2011 and 18.2 percent in 2015 to 18.5 percent of GDP in 2026, which is above the average of 17.4 percent of GDP from 1966 to 2015. Outlays fall from 23.4 percent of GDP in 2011 and 20.7 percent of GDP in 2015 to 23.1 percent of GDP in 2026, which is much higher than 20.2 percent on average from 1966 to 2015. The last row of Table IIA1-8 provides the CBO estimates of averages for 1966 to 2015 of 17.4 percent for revenues/GDP, 20.2 percent for outlays/GDP and 39.0 percent for debt/GDP. The debt/GDP ratio increases to 85.5 percent of GDP in 2026. The United States faces tough adjustment of its fiscal accounts. There is an additional source of pressure on financing the current account deficit of the balance of payments.
Table IIA1-8, US, Baseline CBO Projections of Federal Government Revenues, Outlays, Deficit and Debt as Percent of GDP
| Revenues | Outlays | Deficit | Debt | |
| 2011 | 15.0 | 23.4 | -8.5 | 65.9 |
| 2012 | 15.3 | 22.1 | -6.8 | 70.4 |
| 2013 | 16.8 | 20.9 | -4.1 | 72.6 |
| 2014 | 17.6 | 20.4 | -2.8 | 74.4 |
| 2015 | 18.2 | 20.7 | -2.5 | 73.6 |
| 2016 | 17.8 | 21.1 | -3.2 | 76.6 |
| 2017 | 17.9 | 21.0 | -3.1 | 77.2 |
| 2018 | 18.1 | 20.7 | -2.6 | 77.0 |
| 2019 | 18.1 | 21.2 | -3.0 | 77.5 |
| 2020 | 18.2 | 21.6 | -3.3 | 78.4 |
| 2021 | 18.2 | 21.9 | -3.6 | 79.3 |
| 2022 | 18.3 | 22.4 | -4.1 | 80.5 |
| 2023 | 18.3 | 22.4 | -4.1 | 81.7 |
| 2024 | 18.3 | 22.3 | -4.0 | 82.7 |
| 2025 | 18.4 | 22.7 | -4.3 | 84.0 |
| 2026 | 18.5 | 23.1 | -4.6 | 85.5 |
| Total 2017-2021 | 18.1 | 21.3 | -3.2 | NA |
| Total 2017-2026 | 18.3 | 22.0 | -3.8 | NA |
| Average | 17.4 | 20.2 | -2.8 | 39.0 |
Source: CBO (2012AugBEO). CBO (2012NovCDR). CBO (2013BEOFeb5). CBO 2013HBDFeb5), CBO (2013Sep11), CBO (2013Aug12Av). Kim Kowaleski and Amber Marcellino. CBO, Historical Budget Data—February 2014, Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb. CBO, The Budget and Economic Outlook 2014 to 2024. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb 2014. CBO, Historical budget data—April 2014 release. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Apr 14, 2014. CBO, Updated Budget Projections: 2014 to 2024. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Apr 14, 2014. CBO, The budget and economic outlook: 2015 to 2025. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Jan 26, 2015. CBO. 2015. An update to the budget and economic outlook: 2015 to 2025. Washington, DC, CBO, Aug 25. CBO, Updated budget projections: 2016 to 2026. Washington, DC, Mar 2016. CBO, An update to the budget and economic outlook: 2016 to 2026. Washington, DC, Aug 23, 2016.
https://www.cbo.gov/about/products/budget-economic-data#6 https://www.cbo.gov/about/products/budget_economic_data#3 https://www.cbo.gov/about/products/budget_economic_data#2
The current account of the US balance of payments is in Table VI-3A for IIIQ2015 and IIIQ2016. The Bureau of Economic Analysis analyzes as follows (https://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/international/transactions/2016/pdf/trans316.pdf):
“The U.S. current account deficit decreased to $113.0 billion (preliminary) in the third quarter of 2016 from $118.3 billion (revised) in the second quarter of 2016, according to statistics released by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA). The deficit decreased to 2.4 percent of current-dollar gross domestic product (GDP) from 2.6 percent in the second quarter.
The $5.3 billion decrease in the current account deficit reflected a $9.0 billion decrease in the deficit on goods that was partly offset by changes in the balances on secondary income, primary income, and services.”
The US has a large deficit in goods or exports less imports of goods but it has a surplus in services that helps to reduce the trade account deficit or exports less imports of goods and services. The current account deficit of the US not seasonally adjusted decreased from $137.2 billion in IIIQ2015 to $133.2 billion in IIQ2016. The current account deficit seasonally adjusted at annual rate increased from 2.7 percent of GDP in IIIQ2015 to 2.6 percent of GDP in IIQ2016, decreasing to 2.4 percent of GDP in IIIQ2016. The ratio of the current account deficit to GDP has stabilized below 3 percent of GDP compared with much higher percentages before the recession but is combined now with much higher imbalance in the Treasury budget (see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008b), 183-94, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 167-71).
Table VI-3A, US, Balance of Payments, Millions of Dollars NSA
| IIIQ2015 | IIIQ2016 | Difference | |
| Goods Balance | -207,992 | -201,707 | 6,285 |
| X Goods | 373,337 | 365,767 | -2.0 ∆% |
| M Goods | -581,329 | -567,474 | -2.4 ∆% |
| Services Balance | 68,913 | 66,231 | -2,682 |
| X Services | 194,854 | 196,008 | 0.6 ∆% |
| M Services | -125,941 | -129,777 | 3.0 ∆% |
| Balance Goods and Services | -139,079 | -135,476 | 3,603 |
| Exports of Goods and Services and Income Receipts | 798,193 | 799,083 | |
| Imports of Goods and Services and Income Payments | -935,400 | -932,272 | |
| Current Account Balance | -137,207 | -133,188 | -4,019 |
| % GDP | IIIQ2015 | IIIQ2016 | IIQ2016 |
| 2.7 | 2.4 | 2.6 |
X: exports; M: imports
Balance on Current Account = Exports of Goods and Services – Imports of Goods and Services and Income Payments
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/international/index.htm#bop
In their classic work on “unpleasant monetarist arithmetic,” Sargent and Wallace (1981, 2) consider a regime of domination of monetary policy by fiscal policy (emphasis added):
“Imagine that fiscal policy dominates monetary policy. The fiscal authority independently sets its budgets, announcing all current and future deficits and surpluses and thus determining the amount of revenue that must be raised through bond sales and seignorage. Under this second coordination scheme, the monetary authority faces the constraints imposed by the demand for government bonds, for it must try to finance with seignorage any discrepancy between the revenue demanded by the fiscal authority and the amount of bonds that can be sold to the public. Suppose that the demand for government bonds implies an interest rate on bonds greater than the economy’s rate of growth. Then if the fiscal authority runs deficits, the monetary authority is unable to control either the growth rate of the monetary base or inflation forever. If the principal and interest due on these additional bonds are raised by selling still more bonds, so as to continue to hold down the growth of base money, then, because the interest rate on bonds is greater than the economy’s growth rate, the real stock of bonds will growth faster than the size of the economy. This cannot go on forever, since the demand for bonds places an upper limit on the stock of bonds relative to the size of the economy. Once that limit is reached, the principal and interest due on the bonds already sold to fight inflation must be financed, at least in part, by seignorage, requiring the creation of additional base money.”
The alternative fiscal scenario of the CBO (2012NovCDR, 2013Sep17) resembles an economic world in which eventually the placement of debt reaches a limit of what is proportionately desired of US debt in investment portfolios. This unpleasant environment is occurring in various European countries.
The current real value of government debt plus monetary liabilities depends on the expected discounted values of future primary surpluses or difference between tax revenue and government expenditure excluding interest payments (Cochrane 2011Jan, 27, equation (16)). There is a point when adverse expectations about the capacity of the government to generate primary surpluses to honor its obligations can result in increases in interest rates on government debt.
First, Unpleasant Monetarist Arithmetic. Fiscal policy is described by Sargent and Wallace (1981, 3, equation 1) as a time sequence of D(t), t = 1, 2,…t, …, where D is real government expenditures, excluding interest on government debt, less real tax receipts. D(t) is the real deficit excluding real interest payments measured in real time t goods. Monetary policy is described by a time sequence of H(t), t=1,2,…t, …, with H(t) being the stock of base money at time t. In order to simplify analysis, all government debt is considered as being only for one time period, in the form of a one-period bond B(t), issued at time t-1 and maturing at time t. Denote by R(t-1) the real rate of interest on the one-period bond B(t) between t-1 and t. The measurement of B(t-1) is in terms of t-1 goods and [1+R(t-1)] “is measured in time t goods per unit of time t-1 goods” (Sargent and Wallace 1981, 3). Thus, B(t-1)[1+R(t-1)] brings B(t-1) to maturing time t. B(t) represents borrowing by the government from the private sector from t to t+1 in terms of time t goods. The price level at t is denoted by p(t). The budget constraint of Sargent and Wallace (1981, 3, equation 1) is:
D(t) = {[H(t) – H(t-1)]/p(t)} + {B(t) – B(t-1)[1 + R(t-1)]} (1)
Equation (1) states that the government finances its real deficits into two portions. The first portion, {[H(t) – H(t-1)]/p(t)}, is seigniorage, or “printing money.” The second part,
{B(t) – B(t-1)[1 + R(t-1)]}, is borrowing from the public by issue of interest-bearing securities. Denote population at time t by N(t) and growing by assumption at the constant rate of n, such that:
N(t+1) = (1+n)N(t), n>-1 (2)
The per capita form of the budget constraint is obtained by dividing (1) by N(t) and rearranging:
B(t)/N(t) = {[1+R(t-1)]/(1+n)}x[B(t-1)/N(t-1)]+[D(t)/N(t)] – {[H(t)-H(t-1)]/[N(t)p(t)]} (3)
On the basis of the assumptions of equal constant rate of growth of population and real income, n, constant real rate of return on government securities exceeding growth of economic activity and quantity theory equation of demand for base money, Sargent and Wallace (1981) find that “tighter current monetary policy implies higher future inflation” under fiscal policy dominance of monetary policy. That is, the monetary authority does not permanently influence inflation, lowering inflation now with tighter policy but experiencing higher inflation in the future.
Second, Unpleasant Fiscal Arithmetic. The tool of analysis of Cochrane (2011Jan, 27, equation (16)) is the government debt valuation equation:
(Mt + Bt)/Pt = Et∫(1/Rt, t+τ)st+τdτ (4)
Equation (4) expresses the monetary, Mt, and debt, Bt, liabilities of the government, divided by the price level, Pt, in terms of the expected value discounted by the ex-post rate on government debt, Rt, t+τ, of the future primary surpluses st+τ, which are equal to Tt+τ – Gt+τ or difference between taxes, T, and government expenditures, G. Cochrane (2010A) provides the link to a web appendix demonstrating that it is possible to discount by the ex post Rt, t+τ. The second equation of Cochrane (2011Jan, 5) is:
MtV(it, ·) = PtYt (5)
Conventional analysis of monetary policy contends that fiscal authorities simply adjust primary surpluses, s, to sanction the price level determined by the monetary authority through equation (5), which deprives the debt valuation equation (4) of any role in price level determination. The simple explanation is (Cochrane 2011Jan, 5):
“We are here to think about what happens when [4] exerts more force on the price level. This change may happen by force, when debt, deficits and distorting taxes become large so the Treasury is unable or refuses to follow. Then [4] determines the price level; monetary policy must follow the fiscal lead and ‘passively’ adjust M to satisfy [5]. This change may also happen by choice; monetary policies may be deliberately passive, in which case there is nothing for the Treasury to follow and [4] determines the price level.”
An intuitive interpretation by Cochrane (2011Jan 4) is that when the current real value of government debt exceeds expected future surpluses, economic agents unload government debt to purchase private assets and goods, resulting in inflation. If the risk premium on government debt declines, government debt becomes more valuable, causing a deflationary effect. If the risk premium on government debt increases, government debt becomes less valuable, causing an inflationary effect.
There are multiple conclusions by Cochrane (2011Jan) on the debt/dollar crisis and Global recession, among which the following three:
(1) The flight to quality that magnified the recession was not from goods into money but from private-sector securities into government debt because of the risk premium on private-sector securities; monetary policy consisted of providing liquidity in private-sector markets suffering stress
(2) Increases in liquidity by open-market operations with short-term securities have no impact; quantitative easing can affect the timing but not the rate of inflation; and purchase of private debt can reverse part of the flight to quality
(3) The debt valuation equation has a similar role as the expectation shifting the Phillips curve such that a fiscal inflation can generate stagflation effects similar to those occurring from a loss of anchoring expectations.
This analysis suggests that there may be a point of saturation of demand for United States financial liabilities without an increase in interest rates on Treasury securities. A risk premium may develop on US debt. Such premium is not apparent currently because of distressed conditions in the world economy and international financial system. Risk premiums are observed in the spread of bonds of highly indebted countries in Europe relative to bonds of the government of Germany.
The issue of global imbalances centered on the possibility of a disorderly correction (Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), Globalization and the State Vol. II (2008b) 183-94, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 167-71). Such a correction has not occurred historically but there is no argument proving that it could not occur. The need for a correction would originate in unsustainable large and growing United States current account deficits (CAD) and net international investment position (NIIP) or excess of financial liabilities of the US held by foreigners net relative to financial liabilities of foreigners held by US residents. The IMF estimated that the US could maintain a CAD of two to three percent of GDP without major problems (Rajan 2004). The threat of disorderly correction is summarized by Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 15):
“It is possible that foreigners may be unwilling to increase their positions in US financial assets at prevailing interest rates. An exit out of the dollar could cause major devaluation of the dollar. The depreciation of the dollar would cause inflation in the US, leading to increases in American interest rates. There would be an increase in mortgage rates followed by deterioration of real estate values. The IMF has simulated that such an adjustment would cause a decline in the rate of growth of US GDP to 0.5 percent over several years. The decline of demand in the US by four percentage points over several years would result in a world recession because the weakness in Europe and Japan could not compensate for the collapse of American demand. The probability of occurrence of an abrupt adjustment is unknown. However, the adverse effects are quite high, at least hypothetically, to warrant concern.”
The United States could be moving toward a situation typical of heavily indebted countries, requiring fiscal adjustment and increases in productivity to become more competitive internationally. The CAD and NIIP of the United States are not observed in full deterioration because the economy is well below trend. There are two complications in the current environment relative to the concern with disorderly correction in the first half of the past decade. In the release of Jun 14, 2013, the Bureau of Economic Analysis (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/international/transactions/2013/pdf/trans113.pdf) informs of revisions of US data on US international transactions since 1999:
“The statistics of the U.S. international transactions accounts released today have been revised for the first quarter of 1999 to the fourth quarter of 2012 to incorporate newly available and revised source data, updated seasonal adjustments, changes in definitions and classifications, and improved estimating methodologies.”
The BEA introduced new concepts and methods (http://www.bea.gov/international/concepts_methods.htm) in comprehensive restructuring on Jun 18, 2014 (http://www.bea.gov/international/modern.htm):
“BEA introduced a new presentation of the International Transactions Accounts on June 18, 2014 and will introduce a new presentation of the International Investment Position on June 30, 2014. These new presentations reflect a comprehensive restructuring of the international accounts that enhances the quality and usefulness of the accounts for customers and bring the accounts into closer alignment with international guidelines.”
Table IIA2-3 provides data on the US fiscal and balance of payments imbalances incorporating all revisions and methods. In 2007, the federal deficit of the US was $161 billion corresponding to 1.1 percent of GDP while the Congressional Budget Office estimates the federal deficit in 2012 at $1087 billion or 6.8 percent of GDP. The estimate of the deficit for 2013 is $680 billion or 4.1 percent of GDP. The combined record federal deficits of the US from 2009 to 2012 are $5094 billion or 31.6 percent of the estimate of GDP for fiscal year 2012 implicit in the CBO (CBO 2013Sep11) estimate of debt/GDP. The deficits from 2009 to 2012 exceed one trillion dollars per year, adding to $5.094 trillion in four years, using the fiscal year deficit of $1087 billion for fiscal year 2012, which is the worst fiscal performance since World War II. Federal debt in 2007 was $5035 billion, slightly less than the combined deficits from 2009 to 2012 of $5094 billion. Federal debt in 2012 was 70.4 percent of GDP (CBO 2015Jan26) and 72.6 percent of GDP in 2013 (http://www.cbo.gov/). This situation may worsen in the future (CBO 2013Sep17):
“Between 2009 and 2012, the federal government recorded the largest budget deficits relative to the size of the economy since 1946, causing federal debt to soar. Federal debt held by the public is now about 73 percent of the economy’s annual output, or gross domestic product (GDP). That percentage is higher than at any point in U.S. history except a brief period around World War II, and it is twice the percentage at the end of 2007. If current laws generally remained in place, federal debt held by the public would decline slightly relative to GDP over the next several years, CBO projects. After that, however, growing deficits would ultimately push debt back above its current high level. CBO projects that federal debt held by the public would reach 100 percent of GDP in 2038, 25 years from now, even without accounting for the harmful effects that growing debt would have on the economy. Moreover, debt would be on an upward path relative to the size of the economy, a trend that could not be sustained indefinitely.
The gap between federal spending and revenues would widen steadily after 2015 under the assumptions of the extended baseline, CBO projects. By 2038, the deficit would be 6½ percent of GDP, larger than in any year between 1947 and 2008, and federal debt held by the public would reach 100 percent of GDP, more than in any year except 1945 and 1946. With such large deficits, federal debt would be growing faster than GDP, a path that would ultimately be unsustainable.
Incorporating the economic effects of the federal policies that underlie the extended baseline worsens the long-term budget outlook. The increase in debt relative to the size of the economy, combined with an increase in marginal tax rates (the rates that would apply to an additional dollar of income), would reduce output and raise interest rates relative to the benchmark economic projections that CBO used in producing the extended baseline. Those economic differences would lead to lower federal revenues and higher interest payments. With those effects included, debt under the extended baseline would rise to 108 percent of GDP in 2038.”
The most recent CBO long-term budget on Jul 12, 2016, projects US federal debt at 141.1 percent of GDP in 2046 (Congressional Budget Office, The 2016 long-term budget outlook. Washington, DC, Jul 12 https://www.cbo.gov/publication/51580).
Table VI-3B, US, Current Account, NIIP, Fiscal Balance, Nominal GDP, Federal Debt and Direct Investment, Dollar Billions and %
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | |
| Goods & | -705 | -709 | -384 | -495 | -549 |
| Primary Income | 101 | 146 | 124 | 178 | 221 |
| Secondary Income | -114 | -128 | -124 | -125 | -133 |
| Current Account | -719 | -691 | -384 | -442 | -460 |
| NGDP | 14478 | 14719 | 14419 | 14964 | 15518 |
| Current Account % GDP | -5.0 | -4.7 | -2.7 | -3.0 | -3.0 |
| NIIP | -1279 | -3995 | -2628 | -2512 | -4455 |
| US Owned Assets Abroad | 20705 | 19423 | 19426 | 21767 | 22209 |
| Foreign Owned Assets in US | 21984 | 23418 | 22054 | 24279 | 26664 |
| NIIP % GDP | -8.8 | -27.1 | -18.2 | -16.8 | -28.7 |
| Exports | 2569 | 2751 | 2286 | 2631 | 2988 |
| NIIP % | -50 | -145 | -115 | -95 | -149 |
| DIA MV | 5858 | 3707 | 4945 | 5486 | 5215 |
| DIUS MV | 4134 | 3091 | 3619 | 4099 | 4199 |
| Fiscal Balance | -161 | -459 | -1413 | -1294 | -1300 |
| Fiscal Balance % GDP | -1.1 | -3.1 | -9.8 | -8.7 | -8.5 |
| Federal Debt | 5035 | 5803 | 7545 | 9019 | 10128 |
| Federal Debt % GDP | 35.2 | 39.3 | 52.3 | 60.9 | 65.9 |
| Federal Outlays | 2729 | 2983 | 3518 | 3457 | 3603 |
| ∆% | 2.8 | 9.3 | 17.9 | -1.7 | 4.2 |
| % GDP | 19.1 | 20.2 | 24.4 | 23.4 | 23.4 |
| Federal Revenue | 2568 | 2524 | 2105 | 2163 | 2303 |
| ∆% | 6.7 | -1.7 | -16.6 | 2.7 | 6.5 |
| % GDP | 17.9 | 17.1 | 14.6 | 14.6 | 15.0 |
| 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |
| Goods & | -538 | -462 | -490 | -500 |
| Primary Income | 216 | 219 | 224 | 182 |
| Secondary Income | -126 | -124 | -126 | -145 |
| Current Account | -447 | -366 | -392 | -463 |
| NGDP | 16155 | 16692 | 17393 | 18037 |
| Current Account % GDP | -2.8 | -2.2 | -2.3 | -2.6 |
| NIIP | -4518 | -5373 | -7046 | -7281 |
| US Owned Assets Abroad | 22562 | 24145 | 24718 | 23341 |
| Foreign Owned Assets in US | 27080 | 29517 | 31764 | 30621 |
| NIIP % GDP | -28.0 | -32.2 | -40.5 | -40.4 |
| Exports | 3097 | 3215 | 3339 | 3173 |
| NIIP % | -146 | -167 | -211 | -229 |
| DIA MV | 5969 | 7121 | 7133 | 6978 |
| DIUS MV | 4662 | 5815 | 6350 | 6544 |
| Fiscal Balance | -1087 | -680 | -485 | -438 |
| Fiscal Balance % GDP | -6.8 | -4.1 | -2.8 | -2.5 |
| Federal Debt | 11281 | 11983 | 12780 | 13117 |
| Federal Debt % GDP | 70.4 | 72.6 | 74.4 | 73.6 |
| Federal Outlays | 3537 | 3455 | 3506 | 3688 |
| ∆% | -1.8 | -2.3 | 1.5 | 5.2 |
| % GDP | 22.1 | 20.9 | 20.4 | 20.7 |
| Federal Revenue | 2450 | 2775 | 3022 | 3250 |
| ∆% | 6.4 | 13.3 | 8.9 | 7.6 |
| % GDP | 15.3 | 16.8 | 17.6 | 18.2 |
Sources:
Notes: NGDP: nominal GDP or in current dollars; NIIP: Net International Investment Position; DIA MV: US Direct Investment Abroad at Market Value; DIUS MV: Direct Investment in the US at Market Value. There are minor discrepancies in the decimal point of percentages of GDP between the balance of payments data and federal debt, outlays, revenue and deficits in which the original number of the CBO source is maintained. See Bureau of Economic Analysis, US International Economic Accounts: Concepts and Methods. 2014. Washington, DC: BEA, Department of Commerce, Jun 2014 http://www.bea.gov/international/concepts_methods.htm These discrepancies do not alter conclusions. Budget http://www.cbo.gov/
https://www.cbo.gov/about/products/budget-economic-data#6
https://www.cbo.gov/about/products/budget_economic_data#3 https://www.cbo.gov/about/products/budget_economic_data#2 Balance of Payments and NIIP http://www.bea.gov/international/index.htm#bop Gross Domestic Product, Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table VI-3C provides quarterly estimates NSA of the external imbalance of the United States. The current account deficit seasonally adjusted decreases from 2.7 percent of GDP in IIIQ2015 to 2.5 percent in IVQ2015. The current account deficit increases to 2.9 percent of GDP in IQ2016. The deficit decreases to 2.6 percent in IIQ2016 and decreases to 2.4 percent in IIIQ2016. The net international investment position increases from minus $7.2 trillion in IIIQ2015 to minus $7.3 trillion in IVQ2015, increasing at minus $7.6 trillion in IQ2016. The net international investment position increases to minus $8.0 trillion in IIQ2016 and decreases to minus $7.8 trillion in IIIQ2016. The BEA explains as follows (https://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/international/intinv/2016/pdf/intinv316.pdf):
“The U.S. net international investment position increased to −$7,781.1 billion (preliminary) at the end of the third quarter of 2016 from −$8,026.9 billion (revised) at the end of the second quarter, according to statistics released today by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA). The $245.8 billion increase in the net investment position reflected a $346.2 billion increase in U.S. assets and a $100.5 billion increase in U.S. liabilities. The net investment position increased 3.1 percent in the third quarter, compared with a decrease of 5.9 percent in the second quarter and an average quarterly decrease of 6.0 percent from the first quarter of 2011 through the first quarter of 2016.”
The BEA explains further (https://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/international/intinv/2016/pdf/intinv316.pdf): “U.S. assets increased $346.2 billion to $24,861.2 billion at the end of the third quarter, reflecting an increase in assets excluding financial derivatives that was partly offset by a decrease in financial derivatives. Assets excluding financial derivatives increased $794.9 billion to $22,086.1 billion, mostly reflecting increases in portfolio investment and direct investment assets due to increases in foreign equity prices. Financial derivatives decreased $448.7 billion to $2,775.1 billion, mostly in single-currency interest rate contracts and in foreign exchange contracts. U.S. liabilities increased $100.5 billion to $32,642.3 billion at the end of the third quarter, reflecting an increase in liabilities excluding financial derivatives that was partly offset by a decrease in financial derivatives. Liabilities excluding financial derivatives increased $546.3 billion to $29,922.5 billion, reflecting increases in portfolio investment and direct investment liabilities due to financial transactions and increases in U.S. equity prices. Financial derivatives decreased $445.8 billion to $2,719.9 billion, mostly in single-currency interest rate contracts and in foreign exchange contracts.”
Table VI-3C, US, Current Account, NIIP, Fiscal Balance, Nominal GDP, Federal Debt and Direct Investment, Dollar Billions and % NSA
| IIIQ2015 | IVQ2015 | IQ2016 | IIQ2016 | IIIQ2016 | |
| Goods & | -139 | -127 | -103 | -134 | -135 |
| Primary Income | 43 | 48 | 34 | 42 | 44 |
| Secondary Income | -41 | -36 | -41 | -36 | -42 |
| Current Account | -137 | -114 | -110 | -127 | -133 |
| Current Account % GDP | -2.7 | -2.5 | -2.9 | -2.6 | -2.4 |
| NIIP | -7240 | -7281 | -7582 | -8027 | -7781 |
| US Owned Assets Abroad | 23478 | 23341 | 24062 | 24515 | 24861 |
| Foreign Owned Assets in US | -30718 | -30621 | -31644 | -32542 | -32642 |
| DIA MV | 6785 | 6978 | 6993 | 6964 | 7384 |
| DIA MV Equity | 5640 | 5811 | 5838 | 5797 | 6161 |
| DIUS MV | 6260 | 6544 | 6665 | 6955 | 7194 |
| DIUS MV Equity | 4682 | 4979 | 5070 | 5272 | 5498 |
Notes: NIIP: Net International Investment Position; DIA MV: US Direct Investment Abroad at Market Value; DIUS MV: Direct Investment in the US at Market Value. See Bureau of Economic Analysis, US International Economic Accounts: Concepts and Methods. 2014. Washington, DC: BEA, Department of Commerce, Jun 2014 http://www.bea.gov/international/concepts_methods.htm
Chart VI-3C of the US Bureau of Economic Analysis provides the quarterly US net international investment position (NIIP) NSA in billion dollars. The NIIP deteriorated in 2008, improving in 2009-2011 followed by deterioration after 2012.
Chart VI-3C, US Net International Investment Positon, NSA, Billion US Dollars
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/international/intinv/intinvnewsrelease.htm
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016, 2017.

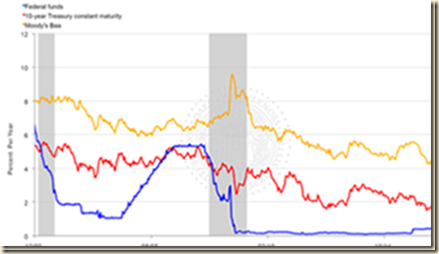



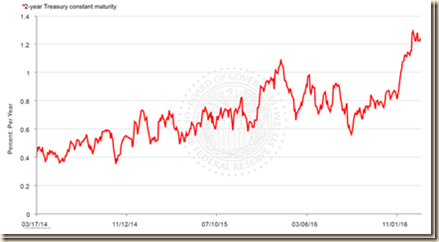

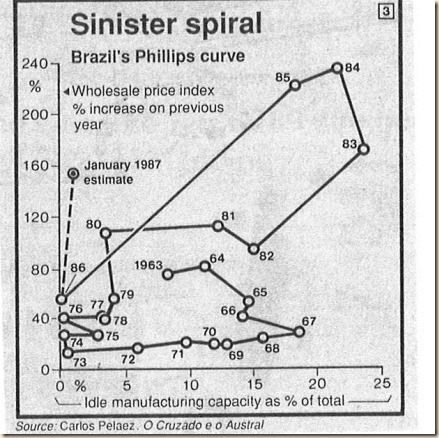



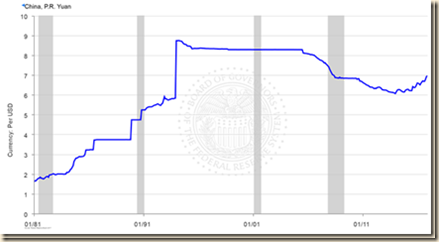

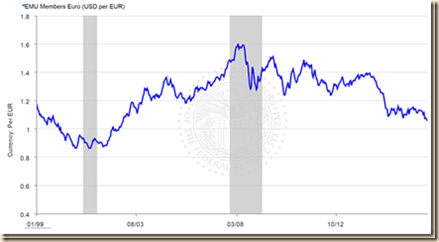

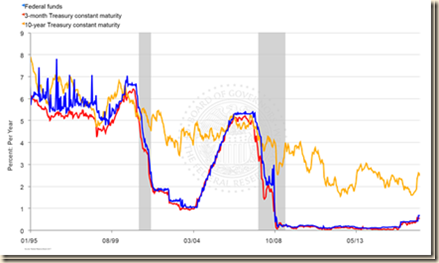

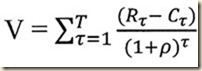







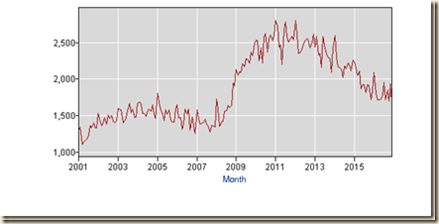






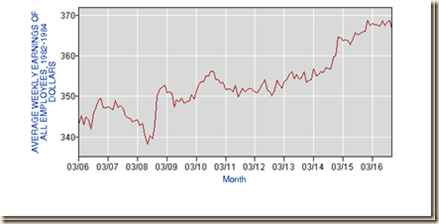
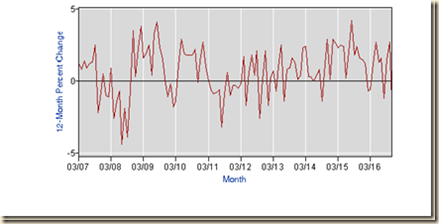
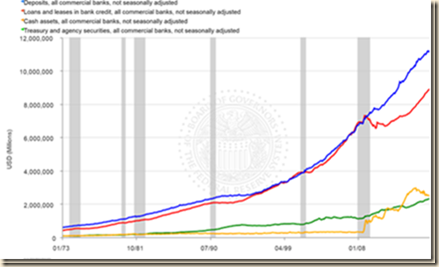


No comments:
Post a Comment