Fluctuating Valuations of Risk Financial Assets, Twenty Six Million Unemployed or Underemployed, Stagnating Real Wages, United States International Trade, World Cyclical Slow Growth and Global Recession Risk
Carlos M. Pelaez
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015
I Twenty Six Million Unemployed or Underemployed
IA1 Summary of the Employment Situation
IA2 Number of People in Job Stress
IA3 Long-term and Cyclical Comparison of Employment
IA4 Job Creation
IB Stagnating Real Wages
II United States International Trade
III World Financial Turbulence
IIIA Financial Risks
IIIE Appendix Euro Zone Survival Risk
IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation
IV Global Inflation
V World Economic Slowdown
VA United States
VB Japan
VC China
VD Euro Area
VE Germany
VF France
VG Italy
VH United Kingdom
VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets
VII Economic Indicators
VIII Interest Rates
IX Conclusion
References
Appendixes
Appendix I The Great Inflation
IIIB Appendix on Safe Haven Currencies
IIIC Appendix on Fiscal Compact
IIID Appendix on European Central Bank Large Scale Lender of Last Resort
IIIG Appendix on Deficit Financing of Growth and the Debt Crisis
IIIGA Monetary Policy with Deficit Financing of Economic Growth
IIIGB Adjustment during the Debt Crisis of the 1980s
I Twenty Six Million Unemployed or Underemployed. This section analyzes the employment situation report of the United States of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). There are four subsections: IA1 Summary of the Employment Situation; IA2 Number of People in Job Stress; IA3 Long-term and Cyclical Comparison of Employment; and IA4 Job Creation.
IA1 Summary of the Employment Situation. Table I-1 provides summary statistics of the employment situation report of the BLS. The first four rows provide the data from the establishment report of creation of nonfarm payroll jobs and remuneration of workers (for analysis of the differences in employment between the establishment report and the household survey see Abraham, Haltiwanger, Sandusky and Spletzer 2009). Total nonfarm payroll employment seasonally adjusted (SA) increased 252,000 in Dec 2014 and private payroll employment increased 240,000. The average monthly number of nonfarm jobs created from Dec 2012 to Dec 2013 was 194,250 using seasonally adjusted data, while the average number of nonfarm jobs created from Dec 2013 to Dec 2014 was 246,000, or increase by 26.6 percent. The average number of private jobs created in the US from Dec 2012 to Dec 2013 was 197,083, using seasonally adjusted data, while the average from Dec 2013 to Dec 2014 was 238,417, or increase by 21.0 percent. This blog calculates the effective labor force of the US at 163.345 million in Dec 2013 and 164.856 million in Dec 2014 (Table I-4), for growth of 1.511 million at average 125,917 per month. The difference between the average increase of 238,417 new private nonfarm jobs per month in the US from Dec 2013 to Dec 2014 and the 125,917 average monthly increase in the labor force from Dec 2013 to Dec 2014 is 112,500 monthly new jobs net of absorption of new entrants in the labor force. There are 25.896 million in job stress in the US currently. Creation of 112,500 new jobs per month net of absorption of new entrants in the labor force would require 230 months to provide jobs for the unemployed and underemployed (25.896 million divided by 112.500) or 19 years (230 divided by 12). The civilian labor force of the US in Dec 2014 not seasonally adjusted stood at 155.521 million with 8.331 million unemployed or effectively 16.666 million unemployed in this blog’s calculation by inferring those who are not searching because they believe there is no job for them for effective labor force of 164.856 million. Reduction of one million unemployed at the current rate of job creation without adding more unemployment requires 0.7 years (1 million divided by product of 112,500 by 12, which is 1,350,000). Reduction of the rate of unemployment to 5 percent of the labor force would be equivalent to unemployment of only 7.776 million (0.05 times labor force of 155.521 million). New net job creation would be 0.555 million (8.331 million unemployed minus 7.776 million unemployed at rate of 5 percent) that at the current rate would take 0.4 years (0.555 million divided by 1.350). Under the calculation in this blog, there are 16.666 million unemployed by including those who ceased searching because they believe there is no job for them and effective labor force of 164.856 million. Reduction of the rate of unemployment to 5 percent of the labor force would require creating 8.243 million jobs net of labor force growth that at the current rate would take 6.1 years (16.666 million minus 0.05(164.856 million) = 8.243 million divided by 1.350, using LF PART 66.2% and Total UEM in Table I-4). These calculations assume that there are no more recessions, defying United States economic history with periodic contractions of economic activity when unemployment increases sharply. The number employed in Dec 2014 was 147.190 million (NSA) or 0.125 million fewer people with jobs relative to the peak of 147.315 million in Jul 2007 while the civilian noninstitutional population of ages 16 years and over increased from 231.958 million in Jul 2007 to 249.027 million in Dec 2014 or by 17.069 million. The number employed decreased 0.1 percent from Jul 2007 to Dec 2014 while the noninstitutional civilian population of ages of 16 years and over, or those available for work, increased 7.4 percent. The ratio of employment to population in Jul 2007 was 63.5 percent (147.315 million employment as percent of population of 231.958 million). The same ratio in Dec 2014 would result in 158.132 million jobs (0.635 multiplied by noninstitutional civilian population of 249.027 million). There are effectively 10.942 million fewer jobs in Dec 2014 than in Jul 2007, or 158.132 million minus 147.190 million. There is actually not sufficient job creation in merely absorbing new entrants in the labor force because of those dropping from job searches, worsening the stock of unemployed or underemployed in involuntary part-time jobs.
There is current interest in past theories of “secular stagnation.” Alvin H. Hansen (1939, 4, 7; see Hansen 1938, 1941; for an early critique see Simons 1942) argues:
“Not until the problem of full employment of our productive resources from the long-run, secular standpoint was upon us, were we compelled to give serious consideration to those factors and forces in our economy which tend to make business recoveries weak and anaemic (sic) and which tend to prolong and deepen the course of depressions. This is the essence of secular stagnation-sick recoveries which die in their infancy and depressions which feed on them-selves and leave a hard and seemingly immovable core of unemployment. Now the rate of population growth must necessarily play an important role in determining the character of the output; in other words, the com-position of the flow of final goods. Thus a rapidly growing population will demand a much larger per capita volume of new residential building construction than will a stationary population. A stationary population with its larger proportion of old people may perhaps demand more personal services; and the composition of consumer demand will have an important influence on the quantity of capital required. The demand for housing calls for large capital outlays, while the demand for personal services can be met without making large investment expenditures. It is therefore not unlikely that a shift from a rapidly growing population to a stationary or declining one may so alter the composition of the final flow of consumption goods that the ratio of capital to output as a whole will tend to decline.”
The argument that anemic population growth causes “secular stagnation” in the US (Hansen 1938, 1939, 1941) is as misplaced currently as in the late 1930s (for early dissent see Simons 1942). There is currently population growth in the ages of 16 to 24 years but not enough job creation and discouragement of job searches for all ages (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/global-financial-and-economic-risk.html). The proper explanation is not in secular stagnation but in cyclically slow growth.. Secular stagnation is merely another case of theory without reality with dubious policy proposals. Subsection IA4 Job Creation analyzes the types of jobs created, which are lower paying than earlier. Average hourly earnings in Dec 2014 were $24.57 seasonally adjusted (SA), increasing 1.1 percent not seasonally adjusted (NSA) relative to Dec 2013 and decreasing 0.2 percent relative to Nov 2014 seasonally adjusted. In Nov 2014, average hourly earnings seasonally adjusted were $24.62, increasing 2.6 percent relative to Nov 2013 not seasonally adjusted and increasing 0.2 percent seasonally adjusted relative to Nov 2014. These are nominal changes in workers’ wages. The following row “average hourly earnings in constant dollars” provides hourly wages in constant dollars calculated by the BLS or what is called “real wages” adjusted for inflation. Data are not available for Dec 2014 because the prices indexes of the BLS for Nov 2014 will only be released on Jan 16, 2015 (http://www.bls.gov/cpi/), which will be covered in this blog’s comment on Jan 18, 2015, together with world inflation. The second column provides changes in real wages for Nov 2014. Average hourly earnings adjusted for inflation or in constant dollars increased 1.4 percent in Nov 2014 relative to Nov 2013 but have been decreasing during multiple months. World inflation waves in bouts of risk aversion (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html) mask declining trend of real wages. The fractured labor market of the US is characterized by high levels of unemployment and underemployment together with falling real wages or wages adjusted for inflation (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/financial-risks-twenty-six-million.html). The following section IB Stagnating Real Wages provides more detailed analysis. Average weekly hours of US workers seasonally adjusted remained virtually unchanged around 34.6. Another headline number widely followed is the unemployment rate or number of people unemployed as percent of the labor force. The unemployment rate calculated in the household survey decreased from 5.8 percent in Nov 2014 to 5.6 percent in Dec 2014, seasonally adjusted. This blog provides with every employment situation report the number of people in the US in job stress or unemployed plus underemployed calculated without seasonal adjustment (NSA) at 25.9 million in Dec 2014 and 26.0 million in Nov 2014. The final row in Table I-1 provides the number in job stress as percent of the actual labor force calculated at 15.7 percent in Dec 2014 and 15.7 percent in Dec 2014. Almost one in every five workers in the US is unemployed or underemployed. There is socio-economic stress in the combination of adverse events and cyclical performance:
· Mediocre economic growth below potential and long-term trend, resulting in idle productive resources with GDP two trillion dollars below trend (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html). US GDP grew at the average rate of 3.3 percent per year from 1929 to 2013 with similar performance in whole cycles of contractions and expansions but only at 0.9 percent per year on average from 2007 to 2013. GDP in IIIQ2014 is 12.1 percent lower than what it would have been had it grown at trend of 3.0 percent.
· Private fixed investment stagnating at increase of 2.2 percent in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2014 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html)
· Twenty six million or 15.7 percent of the effective labor force unemployed or underemployed in involuntary part-time jobs with stagnating or declining real wages (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/financial-risks-twenty-six-million.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/rules-discretionary-authorities-and.html)
· Stagnating real disposable income per person or income per person after inflation and taxes (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html)
· Depressed hiring that does not afford an opportunity for reducing unemployment/underemployment and moving to better-paid jobs (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/global-financial-and-economic-risk.html)
- Productivity growth fell from 2.2 percent per year on average from 1947 to 2013 to 1.5 percent per year on average from 2007 to 2013 deteriorating future growth and prosperity (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/financial-risks-twenty-six-million.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/rules-discretionary-authorities-and.html)
- Output of manufacturing in Nov at 18.1 percent below long-term trend since 1919 and at 12.4 percent below trend since 1986 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/10/imf-view-squeeze-of-economic-activity.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html)
- Unsustainable government deficit/debt and balance of payments deficit (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/monetary-policy-world-inflation-waves.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/06/valuation-risks-world-inflation-waves.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/02/theory-and-reality-of-cyclical-slow.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/interest-rate-risks-world-inflation.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/tapering-quantitative-easing-mediocre.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/09/duration-dumping-and-peaking-valuations.html)
- Worldwide waves of inflation (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/10/financial-oscillations-world-inflation.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/monetary-policy-world-inflation-waves.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/world-inflation-waves-united-states.html)
- Deteriorating terms of trade and net revenue margins of production across countries in squeeze of economic activity by carry trades induced by zero interest rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/10/imf-view-squeeze-of-economic-activity.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html)
- Financial repression of interest rates and credit affecting the most people without means and access to sophisticated financial investments with likely adverse effects on income distribution and wealth disparity (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/growth-uncertainties-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/10/world-financial-turbulence-twenty-seven.html)
- 45 million in poverty and 41 million without health insurance with family income adjusted for inflation regressing to 1995 levels (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/financial-volatility-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/09/duration-dumping-and-peaking-valuations.html)
- Net worth of households and nonprofits organizations increasing by 7.5 percent after adjusting for inflation in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2014 when it would have grown over 22.0 percent at trend of 3.1 percent per year in real terms from 1945 to 2013 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/financial-volatility-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/06/financial-indecision-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/global-financial-risks-recovery-without.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/collapse-of-united-states-dynamism-of.html). Financial assets increased $14.3 trillion while nonfinancial assets increased $477.8 billion with likely concentration of wealth in those with access to sophisticated financial investments. Real estate assets adjusted for inflation fell 16.4 percent from 2007 to IIIQ2014
Table I-1, US, Summary of the Employment Situation Report SA
| Dec 2014 | Nov 2014 | |
| New Nonfarm Payroll Jobs | 252,000 | 353,000 |
| New Private Payroll Jobs | 240,000 | 345,000 |
| Average Hourly Earnings | Dec 14 $24.57 SA ∆% Dec 14/ Dec 13 NSA: 1.1 ∆% Dec 14/Nov 14 SA: -0.2 | Nov 14 $24.62 SA ∆% Nov 14/Nov 13 NSA: 2.6 ∆% Nov 14/Oct 13 SA: 0.2 |
| Average Hourly Earnings in Constant Dollars | ∆% Nov 2014/Nov 2013 NSA: 1.4 | |
| Average Weekly Hours | 34.6 SA 34.5 NSA | 34.6 SA 34.9 NSA |
| Unemployment Rate Household Survey % of Labor Force SA | 5.6 | 5.8 |
| Number in Job Stress Unemployed and Underemployed Blog Calculation | 25.9 million NSA | 26.0 million NSA |
| In Job Stress as % Labor Force | 15.7 NSA | 15.7 NSA |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) of the US Department of Labor provides both seasonally adjusted (SA) and not-seasonally adjusted (NSA) or unadjusted data with important uses (Bureau of Labor Statistics 2012Feb3; 2011Feb11):
“Most series published by the Current Employment Statistics program reflect a regularly recurring seasonal movement that can be measured from past experience. By eliminating that part of the change attributable to the normal seasonal variation, it is possible to observe the cyclical and other nonseasonal movements in these series. Seasonally adjusted series are published monthly for selected employment, hours, and earnings estimates.”
Requirements of using best available information and updating seasonality factors affect the comparability over time of United States employment data. In the first month of the year, the BLS revises data for several years by adjusting benchmarks and seasonal factors (page 4 at http://www.bls.gov/news.release/pdf/empsit.pdf ), which is the case of the data for Jan 2014 released on Feb 7, 2014:
“In accordance with annual practice, the establishment survey data released today [Feb 7, 2014] have been benchmarked to reflect comprehensive counts of payroll jobs for March 2013. These counts are derived principally from the Quarterly Census of Employment and Wages (QCEW), which enumerates jobs covered by the UI tax system. The benchmark process results in revisions to not seasonally adjusted data from April 2012 forward. Seasonally adjusted data from January 2009 forward are subject to revision. In addition, data for some series prior to 2009, both seasonally adjusted and unadjusted, incorporate revisions.”
The range of differences in total nonfarm employment in revisions in Table A of the employment situation report for Jan 2014 (page 5 at http://www.bls.gov/news.release/pdf/empsit.pdf) is from minus 1,000 for Mar 2013 to 274,000 for Nov 2013. There are also adjustments of population that affect comparability of labor statistics over time (page 6 at http://www.bls.gov/news.release/pdf/empsit.pdf):
“Effective with data for January 2014, updated population estimates have been used in the household survey. Population estimates for the household survey are developed by the U.S. Census Bureau. Each year, the Census Bureau updates the estimates to reflect new information and assumptions about the growth of the population since the previous decennial census. The change in population reflected in the new estimates results from adjustments for net international migration, updated vital statistics and other information, and some methodological changes in the estimation process.
In accordance with usual practice, BLS will not revise the official household survey estimates for
December 2013 and earlier months. To show the impact of the population adjustments, however, differences in selected December 2013 labor force series based on the old and new population estimates are shown in table B.
The adjustments increased the estimated size of the civilian noninstitutional population in December by 2,000, the civilian labor force by 24,000, employment by 22,000, and unemployment by 2,000. The number of persons not in the labor force was reduced by 22,000. The total unemployment rate, employment-population ratio, and labor force participation rate were unaffected.
Data users are cautioned that these annual population adjustments can affect the comparability of household data series over time. Table C shows the effect of the introduction of new population estimates on the comparison of selected labor force measures between December 2013 and January 2014. Additional information on the population adjustments and their effect on national labor force estimates is available at www.bls.gov/cps/cps14adj.pdf (emphasis added).”
There are also adjustments of benchmarks and seasonality factors for establishment data that affect comparability over time (page 1 at http://www.bls.gov/news.release/pdf/empsit.pdf):
“Establishment survey data have been revised as a result of the annual benchmarking process and the updating of seasonal adjustment factors. Also, household survey data for January 2014 reflect updated population estimates. See the notes beginning on page 4 for more information about these changes.”
All comparisons over time are affected by yearly adjustments of benchmarks and seasonality factors. All data in this blog comment use revised data released by the BLS on Feb 7, 2014 (http://www.bls.gov/).
IA2 Number of People in Job Stress. There are two approaches to calculating the number of people in job stress. The first approach consists of calculating the number of people in job stress unemployed or underemployed with the raw data of the employment situation report as in Table I-2. The data are seasonally adjusted (SA). The first three rows provide the labor force and unemployed in millions and the unemployment rate of unemployed as percent of the labor force. There is increase in the number unemployed from 8.983 million in Oct 2014 to 9.071 million in Nov 2014 and decrease to 8.688 million in Dec 2014. The rate of unemployment increased from 5.7 percent in Oct 2014 to 5.8 percent in Nov 2014 and decreased to 5.6 percent in Dec 2014. An important aspect of unemployment is its persistence for more than 27 weeks with 2.785 million in Dec 2014, corresponding to 32.1 percent of the unemployed. The longer the period of unemployment the lower are the chances of finding another job with many long-term unemployed ceasing to search for a job. Another key characteristic of the current labor market is the high number of people trying to subsist with part-time jobs because they cannot find full-time employment or part-time for economic reasons. The BLS explains as follows: “these individuals were working part time because their hours had been cut back or because they were unable to find full-time work” (http://www.bls.gov/news.release/pdf/empsit.pdf 2). The number of part-time for economic reasons increased from 7.012 million in Oct 2014 to 6.851 million in Nov 2014 and decreased to 6.790 million in Dec 2014. Another important fact is the marginally attached to the labor force. The BLS explains as follows: “these individuals were not in the labor force, wanted and were available for work, and had looked for a job sometime in the prior 12 months. They were not counted as unemployed because they had not searched for work in the 4 weeks preceding the survey” (http://www.bls.gov/news.release/pdf/empsit.pdf 2). The number in job stress unemployed or underemployed of 17.738 million in Dec 2014 is composed of:
· 8.688 million unemployed (of whom 2.785 million, or 32.1 percent, unemployed for 27 weeks or more) compared with 9.071 million unemployed in Nov 2014 (of whom 2.822 million, or 31.1 percent, unemployed for 27 weeks or more),
· 6.790 million employed part-time for economic reasons in Dec 2014 (who suffered reductions in their work hours or could not find full-time employment) compared with 6.851 million in Nov 2014
· 2.260 million who were marginally attached to the labor force in Dec 2014 (who were not in the labor force but wanted and were available for work) compared with 2.109 million in Nov 2014
The final row in Table I-2 provides the number in job stress as percent of the labor force: 11.4 percent in Dec 2014, which is close to 11.5 percent in Nov 2014 and 11.6 percent in Oct 2014.
Table I-2, US, People in Job Stress, Millions and % SA
| 2014 | Dec 2014 | Nov 2014 | Oct 2014 |
| Labor Force Millions | 156.129 | 156.402 | 156.243 |
| Unemployed | 8.688 | 9.071 | 8.983 |
| Unemployment Rate (unemployed as % labor force) | 5.6 | 5.8 | 5.7 |
| Unemployed ≥27 weeks | 2.785 | 2.822 | 2.904 |
| Unemployed ≥27 weeks % | 32.1 | 31.1 | 32.3 |
| Part Time for Economic Reasons | 6.790 | 6.851 | 7.012 |
| Marginally | 2.260 | 2.109 | 2.192 |
| Job Stress | 17,738 | 18.031 | 18.187 |
| In Job Stress as % Labor Force | 11.4 | 11.5 | 11.6 |
Job Stress = Unemployed + Part Time Economic Reasons + Marginally Attached Labor Force
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Table I-3 repeats the data in Table I-2 but including Sep and additional data. What really matters is the number of people with jobs or the total employed, representing the opportunity for exit from unemployment. The final row of Table I-3 provides people employed as percent of the population or employment to population ratio. The number has remained relatively constant around 59 percent, reaching 59.0 in Sep 2014, 59.2 in Oct 2014, 59.2 in Nov 2014 and 59.2 in Dep 2014. The employment to population ratio fell from an annual level of 63.1 percent in 2006 to 58.6 percent in 2012 and 58.6 percent in 2013 with the lowest level at 58.4 percent in 2011.
Table I-3, US, Unemployment and Underemployment, SA, Millions and Percent
| Dec 2014 | Nov 2014 | Oct 2014 | Sep 2014 | |
| Labor Force | 156.129 | 156.402 | 156.243 | 155.845 |
| Participation Rate | 62.7 | 62.9 | 62.8 | 62.7 |
| Unemployed | 8.688 | 9.071 | 8.983 | 9.237 |
| UNE Rate % | 5.6 | 5.8 | 5.7 | 5.9 |
| Part Time Economic Reasons | 6.790 | 6.851 | 7.012 | 7.058 |
| Marginally Attached to Labor Force | 2.260 | 2.109 | 2.192 | 2.226 |
| In Job Stress | 17.738 | 18.031 | 18.187 | 18.521 |
| In Job Stress % Labor Force | 11.4 | 11.5 | 11.6 | 11.9 |
| Employed | 147.442 | 147.331 | 147.260 | 146.607 |
| Employment % Population | 59.2 | 59.2 | 59.2 | 59.0 |
Job Stress = Unemployed + Part Time Economic Reasons + Marginally Attached Labor Force
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The balance of this section considers the second approach. Charts I-1 to I-12 explain the reasons for considering another approach to calculating job stress in the US. Chart I-1 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides the level of employment in the US from 2001 to 2014. There was a big drop of the number of people employed from 147.315 million at the peak in Jul 2007 (NSA) to 136.809 million at the trough in Jan 2010 (NSA) with 10.506 million fewer people employed. Recovery has been anemic compared with the shallow recession of 2001 that was followed by nearly vertical growth in jobs. The number employed in Dec 2014 was 147.190 million (NSA) or 0.125 million fewer people with jobs relative to the peak of 147.315 million in Jul 2007 while the civilian noninstitutional population of ages 16 years and over increased from 231.958 million in Jul 2007 to 249.027 million in Dec 2014 or by 17.069 million. The number employed decreased 0.1 percent from Jul 2007 to Dec 2014 while the noninstitutional civilian population of ages of 16 years and over, or those available for work, increased 7.4 percent. The ratio of employment to population in Jul 2007 was 63.5 percent (147.315 million employment as percent of population of 231.958 million). The same ratio in Dec 2014 would result in 158.132 million jobs (0.635 multiplied by noninstitutional civilian population of 249.027 million). There are effectively 10.942 million fewer jobs in Dec 2014 than in Jul 2007, or 158.132 million minus 147.190 million. There is actually not sufficient job creation in merely absorbing new entrants in the labor force because of those dropping from job searches, worsening the stock of unemployed or underemployed in involuntary part-time jobs.
Chart I-1, US, Employed, Thousands, SA, 2001-2014
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-2 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides 12-month percentage changes of the number of people employed in the US from 2001 to 2014. There was recovery since 2010 but not sufficient to recover lost jobs. Many people in the US who had jobs before the global recession are not working now.
Chart I-2, US, Employed, 12-Month Percentage Change NSA, 2001-2014
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
The foundation of the second approach derives from Chart II-3 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics providing the level of the civilian labor force in the US. The civilian labor force consists of people who are available and willing to work and who have searched for employment recently. The labor force of the US grew 9.4 percent from 142.828 million in Jan 2001 to 156.255 million in Jul 2009 but is 0.5 percent lower at 155.521 million in Dec 2014, all numbers not seasonally adjusted. Chart I-3 shows the flattening of the curve of expansion of the labor force and its decline in 2010 and 2011. The ratio of the labor force of 154.871 million in Jul 2007 to the noninstitutional population of 231.958 million in Jul 2007 was 66.8 percent while the ratio of the labor force of 155.521 million in Dec 2014 to the noninstitutional population of 249.027 million in Dec 2014 was 62.5 percent. The labor force of the US in Dec 2014 corresponding to 66.8 percent of participation in the population would be 166.350 million (0.668 x 249.027. The difference between the measured labor force in Dec 2014 of 155.521 million and the labor force in Dec 2014 with participation rate of 66.8 percent (as in Jul 2007) of 166.350 million is 10.829 million. The level of the labor force in the US has stagnated and is 10.829 million lower than what it would have been had the same participation rate been maintained. Millions of people have abandoned their search for employment because they believe there are no jobs available for them. The key issue is whether the decline in participation of the population in the labor force is the result of people giving up on finding another job.
Chart I-3, US, Civilian Labor Force, Thousands, SA, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-4 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides 12-month percentage changes of the level of the labor force in the US. The rate of growth fell almost instantaneously with the global recession and became negative from 2009 to 2011. The labor force of the US collapsed and did not recover. Growth in the beginning of the summer originates in younger people looking for jobs in the summer after graduation or during school recess.
Chart I-4, US, Civilian Labor Force, Thousands, NSA, 12-month Percentage Change, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-5 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides the labor force participation rate in the US or labor force as percent of the population. The labor force participation rate of the US fell from 66.8 percent in Jan 2001 to 62.5 percent NSA in Dec 2014, all numbers not seasonally adjusted. The annual labor force participation rate for 1979 was 63.7 percent and also 63.7 percent in Nov 1980 during sharp economic contraction. This comparison is further elaborated below. Chart I-5 shows an evident downward trend beginning with the global recession that has continued throughout the recovery beginning in IIIQ2009. The critical issue is whether people left the workforce of the US because they believe there is no longer a job for them.
Chart I-5, Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate, Percent of Population in Labor Force SA, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-6 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides the level of unemployed in the US. The number unemployed rose from the trough of 6.272 million NSA in Oct 2006 to the peak of 16.147 million in Jan 2010, declining to 13.400 million in Jul 2012, 12.696 million in Aug 2012 and 11.741 million in Sep 2012. The level unemployed fell to 11.741 million in Oct 2012, 11.404 million in Nov 2012, 11.844 million in Dec 2012, 13.181 million in Jan 2013, 12.500 million in Feb 2013 and 9.984 million in Dec 2013. The level of unemployment reached 8.331 million in Dec 2014, all numbers not seasonally adjusted.
Chart I-6, US, Unemployed, Thousands, SA, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-7 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides the rate of unemployment in the US or unemployed as percent of the labor force. The rate of unemployment of the US rose from 4.7 percent in Jan 2001 to 6.5 percent in Jun 2003, declining to 4.1 percent in Oct 2006. The rate of unemployment jumped to 10.6 percent in Jan 2010 and declined to 7.6 percent in Dec 2012 but increased to 8.5 percent in Jan 2013 and 8.1 percent in Feb 2013, falling back to 7.3 percent in May 2013 and 7.8 percent in Jun 2013, all numbers not seasonally adjusted. The rate of unemployment not seasonally adjusted stabilized at 7.7 percent in Jul 2013 and fell to 6.5 percent in Dec 2013 and 5.4 percent in Dec 2014.
Chart I-7, US, Unemployment Rate, SA, 2001-2014
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-8 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides 12-month percentage changes of the level of unemployed. There was a jump of 81.8 percent in Apr 2009 with subsequent decline and negative rates since 2010. On an annual basis, the level of unemployed rose 59.8 percent in 2009 and 26.1 percent in 2008 with increase of 3.9 percent in 2010, decline of 7.3 percent in 2011 and decrease of 9.0 percent in 2012. The annual level of unemployment decreased 8.4 percent in 2013 and fell 16.6 percent in Dec 2014 relative to Dec 2013.
Chart I-8, US, Unemployed, 12-month Percentage Change, NSA, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-9 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides the number of people in part-time occupations because of economic reasons, that is, because they cannot find full-time employment. The number underemployed in part-time occupations not seasonally adjusted rose from 3.732 million in Jan 2001 to 5.270 million in Jan 2004, falling to 3.787 million in Apr 2006. The number underemployed seasonally adjusted jumped to 9.114 million in Nov 2009, falling to 8.174 million in Dec 2011 but increasing to 8.291 million in Jan 2012 and 8.193 million in Feb 2012 but then falling to 7.926 million in Dec 2012 and increasing to 8.087 million in Jul 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons seasonally adjusted reached 7.766 million in Dec 2013 and 6.790 million in Dec 2014. Without seasonal adjustment, the number employed part-time for economic reasons reached 9.354 million in Dec 2009, declining to 8.918 million in Jan 2012 and 8.166 million in Dec 2012 but increasing to 8.324 million in Jul 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons NSA stood at 7.990 million in Dec 2013 and 6.879 million in Dec 2014. The longer the period in part-time jobs the lower are the chances of finding another full-time job.
Chart I-9, US, Part-Time for Economic Reasons, Thousands, SA, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-10 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics repeats the behavior of unemployment. The 12-month percentage change of the level of people at work part-time for economic reasons jumped 84.7 percent in Mar 2009 and declined subsequently. The declines have been insufficient to reduce significantly the number of people who cannot shift from part-time to full-time employment. On an annual basis, the number of part-time for economic reasons increased 33.5 percent in 2008 and 51.7 percent in 2009, declining 0.4 percent in 2010, 3.5 percent in 2011 and 5.1 percent in 2012. The annual number of part-time for economic reasons decreased 2.3 percent in 2013. The number of part-time for economic reasons fell 12.8 percent in Dec 2014 relative to a year earlier.
Chart I-10, US, Part-Time for Economic Reasons NSA 12-Month Percentage Change, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-11 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides the same pattern of the number marginally attached to the labor force jumping to significantly higher levels during the global recession and remaining at historically high levels. The number marginally attached to the labor force not seasonally adjusted increased from 1.295 million in Jan 2001 to 1.691 million in Feb 2004. The number of marginally attached to the labor force fell to 1.299 million in Sep 2006 and increased to 2.609 million in Dec 2010 and 2.800 million in Jan 2011. The number marginally attached to the labor force was 2.540 million in Dec 2011, increasing to 2.809 million in Jan 2012, falling to 2.608 million in Feb 2012. The number marginally attached to the labor force fell to 2.352 million in Mar 2012, 2.363 million in Apr 2012, 2.423 million in May 2012, 2.483 million in Jun 2012, 2.529 million in Jul 2012 and 2.561 million in Aug 2012. The number marginally attached to the labor force fell to 2.517 million in Sep 2012, 2.433 million in Oct 2012, 2.505 million in Nov 2012 and 2.427 million in in Dec 2013. The number marginally attached to the labor force reached 2.260 million in Dec 2014.
Chart I-11, US, Marginally Attached to the Labor Force, Thousands, NSA, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-12 provides 12-month percentage changes of the marginally attached to the labor force from 2001 to 2014. There was a jump of 56.1 percent in May 2009 during the global recession followed by declines in percentage changes but insufficient negative changes. On an annual basis, the number of marginally attached to the labor force increased in four consecutive years: 15.7 percent in 2008, 37.9 percent in 2009, 11.7 percent in 2010 and 3.5 percent in 2011. The number marginally attached to the labor force fell 2.2 percent on annual basis in 2012 but increased 2.9 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2012, fell 13.0 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2013, falling 10.7 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2013. The number marginally attached to the labor force increased 4.0 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2013 and fell 4.5 percent in the 12 months ending in Jul 2013 and 8.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2013. The annual number of marginally attached to the labor force fell 6.2 percent in 2013. The number marginally attached to the labor force fell 7.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2013 and 6.9 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2014.
Chart I-12, US, Marginally Attached to the Labor Force 12-Month Percentage Change, NSA, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Table I-4 consists of data and additional calculations using the BLS household survey, illustrating the possibility that the actual rate of unemployment could be 10.1 percent and the number of people in job stress could be around 25.9 million, which is 15.7 percent of the effective labor force. The first column provides for 2006 the yearly average population (POP), labor force (LF), participation rate or labor force as percent of population (PART %), employment (EMP), employment population ratio (EMP/POP %), unemployment (UEM), the unemployment rate as percent of labor force (UEM/LF Rate %) and the number of people not in the labor force (NLF). All data are unadjusted or not-seasonally-adjusted (NSA). The numbers in column 2006 are averages in millions while the monthly numbers for Nov 2013, Oct 2014 and Nov 2014 are in thousands, not seasonally adjusted. The average yearly participation rate of the population in the labor force was in the range of 66.0 percent minimum to 67.1 percent maximum between 2000 and 2006 with the average of 66.4 percent (ftp://ftp.bls.gov/pub/special.requests/lf/aa2006/pdf/cpsaat1.pdf). Table I-4b provides the yearly labor force participation rate from 1979 to 2014. The objective of Table I-4 is to assess how many people could have left the labor force because they do not think they can find another job. Row “LF PART 66.2 %” applies the participation rate of 2006, almost equal to the rates for 2000 to 2006, to the noninstitutional civilian population in Dec 2013, Nov 2014 and Dec 2014 to obtain what would be the labor force of the US if the participation rate had not changed. In fact, the participation rate fell to 62.6 percent by Dec 2013 and was 62.8 percent in Nov 2014 and 62.5 percent in Dec 2014, suggesting that many people simply gave up on finding another job. Row “∆ NLF UEM” calculates the number of people not counted in the labor force because they could have given up on finding another job by subtracting from the labor force with participation rate of 66.2 percent (row “LF PART 66.2%”) the labor force estimated in the household survey (row “LF”). Total unemployed (row “Total UEM”) is obtained by adding unemployed in row “∆NLF UEM” to the unemployed of the household survey in row “UEM.” The row “Total UEM%” is the effective total unemployed “Total UEM” as percent of the effective labor force in row “LF PART 66.2%.” The results are that:
- there are an estimated 9.335 million unemployed in Dec 2014 who are not counted because they left the labor force on their belief they could not find another job (∆NLF UEM), that is, they dropped out of their job searches
- the total number of unemployed is effectively 16.666 million (Total UEM) and not 8.331 million (UEM) of whom many have been unemployed long term
- the rate of unemployment is 10.1 percent (Total UEM%) and not 5.4 percent, not seasonally adjusted, or 5.6 percent seasonally adjusted
- the number of people in job stress is close to 26.0 million by adding the 8.331 million leaving the labor force because they believe they could not find another job.
The row “In Job Stress” in Table I-4 provides the number of people in job stress not seasonally adjusted at 25.896 million in Dec 2014, adding the total number of unemployed (“Total UEM”), plus those involuntarily in part-time jobs because they cannot find anything else (“Part Time Economic Reasons”) and the marginally attached to the labor force (“Marginally attached to LF”). The final row of Table I-4 shows that the number of people in job stress is equivalent to 15.7 percent of the labor force in Dec 2014. The employment population ratio “EMP/POP %” dropped from 62.9 percent on average in 2006 to 58.5 percent in Dec 2013, 59.3 percent in Nov 2014 and 59.1 percent in Dec 2014. The number employed in Dec 2014 was 147.190 million (NSA) or 0.125 million fewer people with jobs relative to the peak of 147.315 million in Jul 2007 while the civilian noninstitutional population of ages 16 years and over increased from 231.958 million in Jul 2007 to 249.027 million in Dec 2014 or by 17.069 million. The number employed decreased 0.1 percent from Jul 2007 to Dec 2014 while the noninstitutional civilian population of ages of 16 years and over, or those available for work, increased 7.4 percent. The ratio of employment to population in Jul 2007 was 63.5 percent (147.315 million employment as percent of population of 231.958 million). The same ratio in Dec 2014 would result in 158.132 million jobs (0.635 multiplied by noninstitutional civilian population of 249.027 million). There are effectively 10.942 million fewer jobs in Dec 2014 than in Jul 2007, or 158.132 million minus 147.190 million. There is actually not sufficient job creation in merely absorbing new entrants in the labor force because of those dropping from job searches, worsening the stock of unemployed or underemployed in involuntary part-time jobs.
The argument that anemic population growth causes “secular stagnation” in the US (Hansen 1938, 1939, 1941) is as misplaced currently as in the late 1930s (for early dissent see Simons 1942). There is currently population growth in the ages of 16 to 24 years but not enough job creation and discouragement of job searches for all ages (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/global-financial-and-economic-risk.html). This is merely another case of theory without reality with dubious policy proposals. The number of hiring relative to the number unemployed measures the chances of becoming employed. The number of hiring in the US economy has declined by 10 million and does not show signs of increasing in an unusual recovery without hiring (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/global-financial-and-economic-risk.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 perc Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2014 would have accumulated to 23.0 percent. GDP in IIIQ2014 would be $18,438.0 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2,232.4 billion than actual $16,205.6 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 25.9 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment of 15.7 percent of the effective labor force (Section I and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/financial-risks-twenty-six-million.html
and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/rules-discretionary-authorities-and.html). US GDP in IIIQ2014 is 12.1 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,205.1 billion in IIIQ2014 or 8.1 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.1 percent. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. The long-term trend is growth at average 3.3 percent per year from Jan 1919 to Nov 2014. Growth at 3.3 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 99.2392 in Dec 2007 to 124.2256 in Nov 2014. The actual index NSA in Nov 2014 is 101.7487, which is 18.1 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.3 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2013, raising the index at trend to 116.1422 in Nov 2014. The output of manufacturing at 101.7487 in Nov 2014 is 12.4 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.ent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions.
Table I-4, US, Population, Labor Force and Unemployment, NSA
| 2006 | Dec 2013 | Nov 2014 | Dec 2014 | |
| POP | 229 | 246,745 | 248,844 | 249,027 |
| LF | 151 | 154,408 | 156,297 | 155,521 |
| PART% | 66.2 | 62.6 | 62.8 | 62.5 |
| EMP | 144 | 144,423 | 147,666 | 147,190 |
| EMP/POP% | 62.9 | 58.5 | 59.3 | 59.1 |
| UEM | 7 | 9,984 | 8,630 | 8,331 |
| UEM/LF Rate% | 4.6 | 6.5 | 5.5 | 5.4 |
| NLF | 77 | 92,338 | 92,547 | 93,506 |
| LF PART 66.2% | 163,345 | 164,735 | 164,856 | |
| ∆NLF UEM | 8,937 | 8,438 | 9,335 | |
| Total UEM | 18,921 | 17,068 | 16,666 | |
| Total UEM% | 11.6 | 10.4 | 10.1 | |
| Part Time Economic Reasons | 7,990 | 6,713 | 6,970 | |
| Marginally Attached to LF | 2,427 | 2,109 | 2,260 | |
| In Job Stress | 29,338 | 25,890 | 25,896 | |
| People in Job Stress as % Labor Force | 18.0 | 15.7 | 15.7 |
Pop: population; LF: labor force; PART: participation; EMP: employed; UEM: unemployed; NLF: not in labor force; ∆NLF UEM: additional unemployed; Total UEM is UEM + ∆NLF UEM; Total UEM% is Total UEM as percent of LF PART 66.2%; In Job Stress = Total UEM + Part Time Economic Reasons + Marginally Attached to LF
Note: the first column for 2006 is in average millions; the remaining columns are in thousands; NSA: not seasonally adjusted
The labor force participation rate of 66.2% in 2006 is applied to current population to obtain LF PART 66.2%; ∆NLF UEM is obtained by subtracting the labor force with participation of 66.2 percent from the household survey labor force LF; Total UEM is household data unemployment plus ∆NLF UEM; and total UEM% is total UEM divided by LF PART 66.2%
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
In the analysis of Hansen (1939, 3) of secular stagnation, economic progress consists of growth of real income per person driven by growth of productivity. The “constituent elements” of economic progress are “(a) inventions, (b) the discovery and development of new territory and new resources, and (c) the growth of population” (Hansen 1939, 3). Secular stagnation originates in decline of population growth and discouragement of inventions. According to Hansen (1939, 2), US population grew by 16 million in the 1920s but grew by one half or about 8 million in the 1930s with forecasts at the time of Hansen’s writing in 1938 of growth of around 5.3 million in the 1940s. Hansen (1939, 2) characterized demography in the US as “a drastic decline in the rate of population growth. Hansen’s plea was to adapt economic policy to stagnation of population in ensuring full employment. In the analysis of Hansen (1939, 8), population caused half of the growth of US GDP per year. Growth of output per person in the US and Europe was caused by “changes in techniques and to the exploitation of new natural resources.” In this analysis, population caused 60 percent of the growth of capital formation in the US. Declining population growth would reduce growth of capital formation. Residential construction provided an important share of growth of capital formation. Hansen (1939, 12) argues that market power of imperfect competition discourages innovation with prolonged use of obsolete capital equipment. Trade unions would oppose labor-savings innovations. The combination of stagnating and aging population with reduced innovation caused secular stagnation. Hansen (1939, 12) concludes that there is role for public investments to compensate for lack of dynamism of private investment but with tough tax/debt issues.
The current application of Hansen’s (1938, 1939, 1941) proposition argues that secular stagnation occurs because full employment equilibrium can be attained only with negative real interest rates between minus 2 and minus 3 percent. Professor Lawrence H. Summers (2013Nov8) finds that “a set of older ideas that went under the phrase secular stagnation are not profoundly important in understanding Japan’s experience in the 1990s and may not be without relevance to America’s experience today” (emphasis added). Summers (2013Nov8) argues there could be an explanation in “that the short-term real interest rate that was consistent with full employment had fallen to -2% or -3% sometime in the middle of the last decade. Then, even with artificial stimulus to demand coming from all this financial imprudence, you wouldn’t see any excess demand. And even with a relative resumption of normal credit conditions, you’d have a lot of difficulty getting back to full employment.” The US economy could be in a situation where negative real rates of interest with fed funds rates close to zero as determined by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) do not move the economy to full employment or full utilization of productive resources. Summers (2013Oct8) finds need of new thinking on “how we manage an economy in which the zero nominal interest rates is a chronic and systemic inhibitor of economy activity holding our economies back to their potential.”
Former US Treasury Secretary Robert Rubin (2014Jan8) finds three major risks in prolonged unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates and quantitative easing: (1) incentive of delaying action by political leaders; (2) “financial moral hazard” in inducing excessive exposures pursuing higher yields of risker credit classes; and (3) major risks in exiting unconventional policy. Rubin (2014Jan8) proposes reduction of deficits by structural reforms that could promote recovery by improving confidence of business attained with sound fiscal discipline.
Professor John B. Taylor (2014Jan01, 2014Jan3) provides clear thought on the lack of relevance of Hansen’s contention of secular stagnation to current economic conditions. The application of secular stagnation argues that the economy of the US has attained full-employment equilibrium since around 2000 only with negative real rates of interest of minus 2 to minus 3 percent. At low levels of inflation, the so-called full-employment equilibrium of negative interest rates of minus 2 to minus 3 percent cannot be attained and the economy stagnates. Taylor (2014Jan01) analyzes multiple contradictions with current reality in this application of the theory of secular stagnation:
- Secular stagnation would predict idle capacity, in particular in residential investment when fed fund rates were fixed at 1 percent from Jun 2003 to Jun 2004. Taylor (2014Jan01) finds unemployment at 4.4 percent with house prices jumping 7 percent from 2002 to 2003 and 14 percent from 2004 to 2005 before dropping from 2006 to 2007. GDP prices doubled from 1.7 percent to 3.4 percent when interest rates were low from 2003 to 2005.
- Taylor (2014Jan01, 2014Jan3) finds another contradiction in the application of secular stagnation based on low interest rates because of savings glut and lack of investment opportunities. Taylor (2009) shows that there was no savings glut. The savings rate of the US in the past decade is significantly lower than in the 1980s.
- Taylor (2014Jan01, 2014Jan3) finds another contradiction in the low ratio of investment to GDP currently and reduced investment and hiring by US business firms.
- Taylor (2014Jan01, 2014Jan3) argues that the financial crisis and global recession were caused by weak implementation of existing regulation and departure from rules-based policies.
- Taylor (2014Jan01, 2014Jan3) argues that the recovery from the global recession was constrained by a change in the regime of regulation and fiscal/monetary policies.
In revealing research, Edward P. Lazear and James R. Spletzer (2012JHJul22) use the wealth of data in the valuable database and resources of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (http://www.bls.gov/data/) in providing clear thought on the nature of the current labor market of the United States. The critical issue of analysis and policy currently is whether unemployment is structural or cyclical. Structural unemployment could occur because of (1) industrial and demographic shifts and (2) mismatches of skills and job vacancies in industries and locations. Consider the aggregate unemployment rate, Y, expressed in terms of share si of a demographic group in an industry i and unemployment rate yi of that demographic group (Lazear and Spletzer 2012JHJul22, 5-6):
Y = ∑isiyi (1)
This equation can be decomposed for analysis as (Lazear and Spletzer 2012JHJul22, 6):
∆Y = ∑i∆siy*i + ∑i∆yis*i (2)
The first term in (2) captures changes in the demographic and industrial composition of the economy ∆si multiplied by the average rate of unemployment y*i , or structural factors. The second term in (2) captures changes in the unemployment rate specific to a group, or ∆yi, multiplied by the average share of the group s*i, or cyclical factors. There are also mismatches in skills and locations relative to available job vacancies. A simple observation by Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22) casts intuitive doubt on structural factors: the rate of unemployment jumped from 4.4 percent in the spring of 2007 to 10 percent in October 2009. By nature, structural factors should be permanent or occur over relative long periods. The revealing result of the exhaustive research of Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22) is:
“The analysis in this paper and in others that we review do not provide any compelling evidence that there have been changes in the structure of the labor market that are capable of explaining the pattern of persistently high unemployment rates. The evidence points to primarily cyclic factors.”
Table I-4b and Chart I-12-b provide the US labor force participation rate or percentage of the labor force in population. It is not likely that simple demographic trends caused the sharp decline during the global recession and failure to recover earlier levels. The civilian labor force participation rate dropped from the peak of 66.9 percent in Jul 2006 to 62.6 percent in Dec 2013 and 62.5 percent in Dec 2014. The civilian labor force participation rate was 63.7 percent on an annual basis in 1979 and 63.4 percent in Dec 1980 and Dec 1981, reaching even 62.9 percent in both Apr and May 1979. The civilian labor force participation rate jumped with the recovery to 64.8 percent on an annual basis in 1985 and 65.9 percent in Jul 1985. Structural factors cannot explain these sudden changes vividly shown visually in the final segment of Chart I-12b. Seniors would like to delay their retiring especially because of the adversities of financial repression on their savings. Labor force statistics are capturing the disillusion of potential workers with their chances in finding a job in what Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22) characterize as accentuated cyclical factors. The argument that anemic population growth causes “secular stagnation” in the US (Hansen 1938, 1939, 1941) is as misplaced currently as in the late 1930s (for early dissent see Simons 1942). There is currently population growth in the ages of 16 to 24 years but not enough job creation and discouragement of job searches for all ages (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/global-financial-and-economic-risk.html). “Secular stagnation” would be a process over many years and not from one year to another. This is merely another case of theory without reality with dubious policy proposals.
Table I-4b, US, Labor Force Participation Rate, Percent of Labor Force in Population, NSA, 1979-2014
| Year | Jan | Feb | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Annual |
| 1979 | 62.9 | 63.0 | 64.5 | 63.8 | 64.0 | 63.8 | 63.8 | 63.7 |
| 1980 | 63.3 | 63.2 | 64.5 | 63.6 | 63.9 | 63.7 | 63.4 | 63.8 |
| 1981 | 63.2 | 63.2 | 64.6 | 63.5 | 64.0 | 63.8 | 63.4 | 63.9 |
| 1982 | 63.0 | 63.2 | 64.9 | 64.0 | 64.1 | 64.1 | 63.8 | 64.0 |
| 1983 | 63.3 | 63.2 | 65.1 | 64.3 | 64.1 | 64.1 | 63.8 | 64.0 |
| 1984 | 63.3 | 63.4 | 65.2 | 64.4 | 64.6 | 64.4 | 64.3 | 64.4 |
| 1985 | 64.0 | 64.0 | 65.4 | 64.9 | 65.1 | 64.9 | 64.6 | 64.8 |
| 1986 | 64.2 | 64.4 | 66.1 | 65.3 | 65.5 | 65.4 | 65.0 | 65.3 |
| 1987 | 64.7 | 64.8 | 66.5 | 65.5 | 65.9 | 65.7 | 65.5 | 65.6 |
| 1988 | 65.1 | 65.2 | 66.8 | 65.9 | 66.1 | 66.2 | 65.9 | 65.9 |
| 1989 | 65.8 | 65.6 | 67.2 | 66.3 | 66.6 | 66.7 | 66.3 | 66.5 |
| 1990 | 66.0 | 66.0 | 67.1 | 66.4 | 66.5 | 66.3 | 66.1 | 66.5 |
| 1991 | 65.5 | 65.7 | 66.6 | 66.1 | 66.1 | 66.0 | 65.8 | 66.2 |
| 1992 | 65.7 | 65.8 | 67.2 | 66.3 | 66.2 | 66.2 | 66.1 | 66.4 |
| 1993 | 65.6 | 65.8 | 67.0 | 66.1 | 66.4 | 66.3 | 66.2 | 66.3 |
| 1994 | 66.0 | 66.2 | 67.2 | 66.5 | 66.8 | 66.7 | 66.5 | 66.6 |
| 1995 | 66.1 | 66.2 | 67.1 | 66.5 | 66.7 | 66.5 | 66.2 | 66.6 |
| 1996 | 65.8 | 66.1 | 67.2 | 66.8 | 67.1 | 67.0 | 66.7 | 66.8 |
| 1997 | 66.4 | 66.5 | 67.6 | 67.0 | 67.1 | 67.1 | 67.0 | 67.1 |
| 1998 | 66.6 | 66.7 | 67.3 | 67.0 | 67.1 | 67.1 | 67.0 | 67.1 |
| 1999 | 66.7 | 66.8 | 67.3 | 66.8 | 67.0 | 67.0 | 67.0 | 67.1 |
| 2000 | 66.8 | 67.0 | 67.2 | 66.7 | 66.9 | 66.9 | 67.0 | 67.1 |
| 2001 | 66.8 | 66.8 | 66.8 | 66.6 | 66.7 | 66.6 | 66.6 | 66.8 |
| 2002 | 66.2 | 66.6 | 66.8 | 66.6 | 66.6 | 66.3 | 66.2 | 66.6 |
| 2003 | 66.1 | 66.2 | 66.3 | 65.9 | 66.1 | 66.1 | 65.8 | 66.2 |
| 2004 | 65.7 | 65.7 | 66.2 | 65.7 | 66.0 | 66.1 | 65.8 | 66.0 |
| 2005 | 65.4 | 65.6 | 66.5 | 66.1 | 66.2 | 66.1 | 65.9 | 66.0 |
| 2006 | 65.5 | 65.7 | 66.5 | 66.1 | 66.4 | 66.4 | 66.3 | 66.2 |
| 2007 | 65.9 | 65.8 | 66.1 | 66.0 | 66.0 | 66.1 | 65.9 | 66.0 |
| 2008 | 65.7 | 65.5 | 66.4 | 65.9 | 66.1 | 65.8 | 65.7 | 66.0 |
| 2009 | 65.4 | 65.5 | 65.6 | 65.0 | 64.9 | 64.9 | 64.4 | 65.4 |
| 2010 | 64.6 | 64.6 | 65.0 | 64.6 | 64.4 | 64.4 | 64.1 | 64.7 |
| 2011 | 63.9 | 63.9 | 64.3 | 64.2 | 64.1 | 63.9 | 63.8 | 64.1 |
| 2012 | 63.4 | 63.6 | 63.7 | 63.6 | 63.8 | 63.5 | 63.4 | 63.7 |
| 2013 | 63.3 | 63.2 | 63.4 | 63.2 | 62.9 | 62.9 | 62.6 | 63.2 |
| 2014 | 62.5 | 62.7 | 63.0 | 62.8 | 63.0 | 62.8 | 62.5 | 62.9 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-12b, US, Labor Force Participation Rate, Percent of Labor Force in Population, NSA, 1979-2014
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Broader perspective is provided by Chart I-12c of the US Bureau of Labor Statistics. The United States civilian noninstitutional population has increased along a consistent trend since 1948 that continued through earlier recessions and the global recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 and the cyclical expansion after IIIQ2009.
Chart I-12c, US, Civilian Noninstitutional Population, Thousands, NSA, 1948-2014
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The labor force of the United States in Chart I-12d has increased along a trend similar to that of the civilian noninstitutional population in Chart I-12c. There is an evident stagnation of the civilian labor force in the final segment of Chart I-12d during the current economic cycle. This stagnation is explained by cyclical factors similar to those analyzed by Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22) that motivated an increasing population to drop out of the labor force instead of structural factors. Large segments of the potential labor force are not observed, constituting unobserved unemployment and of more permanent nature because those afflicted have been seriously discouraged from working by the lack of opportunities.
Chart I-12d, US, Labor Force, Thousands, NSA, 1948-2014
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The rate of labor force participation of the US is in Chart I-12E from 1948 to 2014. There is sudden decline during the global recession after 2007 without recovery explained by cyclic factors (Lazear and Spletzer 2012JHJul22) as many potential workers stopped their job searches disillusioned that there could be an opportunity for them in sharply contracted labor markets.
Chart I-12E, US, Labor Force Participation Rate, Percent of Labor Force in Population, NSA, 1948-2014
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
IA3 Long-term and Cyclical Comparison of Employment. There is initial discussion here of long-term employment trends followed by cyclical comparison. Growth and employment creation have been mediocre in the expansion beginning in Jul IIIQ2009 from the contraction between Dec IVQ2007 and Jun IIQ2009 (http://www.nber.org/cycles.html). A series of charts from the database of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) provides significant insight. Chart I-13 provides the monthly employment level of the US from 1948 to 2014. The number of people employed has trebled. There are multiple contractions throughout the more than six decades but followed by resumption of the strong upward trend. The contraction after 2007 is deeper and followed by a flatter curve of job creation. The United States missed this opportunity of high growth in the initial phase of recovery that historically eliminated unemployment and underemployment created during the contraction. Inferior performance of the US economy and labor markets is the critical current issue of analysis and policy design. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. US economic growth has been at only 2.3 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 21 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2014. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the third estimate of GDP for IIIQ2014 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2014/pdf/gdp3q14_3rd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,745.9 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,355.6 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,745.9/$14,355.6 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1988 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2014 would have accumulated to 23.0 percent. GDP in IIIQ2014 would be $18,438.0 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2,232.4 billion than actual $16,205.6 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 25.9 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment of 15.7 percent of the effective labor force (Section I and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/financial-risks-twenty-six-million.html
and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/rules-discretionary-authorities-and.html). US GDP in IIIQ2014 is 12.1 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,205.1 billion in IIIQ2014 or 8.1 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.1 percent. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. The long-term trend is growth at average 3.3 percent per year from Jan 1919 to Nov 2014. Growth at 3.3 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 99.2392 in Dec 2007 to 124.2256 in Nov 2014. The actual index NSA in Nov 2014 is 101.7487, which is 18.1 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.3 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2013, raising the index at trend to 116.1422 in Nov 2014. The output of manufacturing at 101.7487 in Nov 2014 is 12.4 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Chart I-13, US, Employment Level, Thousands, SA, 1948-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The steep and consistent curve of growth of the US labor force is shown in Chart I-14. The contraction beginning in Dec 2007 flattened the path of the US civilian labor force and is now followed by a flatter curve during the current expansion.
Chart I-14, US, Civilian Labor Force, SA, 1948-2014, Thousands
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-15 for the period from 1948 to 2014. The labor force participation rate is influenced by numerous factors such as the age of the population. There is no comparable episode in the postwar economy to the sharp collapse of the labor force participation rate in Chart I-15 during the contraction and subsequent expansion after 2007. Aging can reduce the labor force participation rate as many people retire but many may have decided to work longer as their wealth and savings have been significantly reduced. There is an important effect of many people just exiting the labor force because they believe there is no job available for them.
Chart I-15, US, Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate, SA, 1948-2014, %
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The number of unemployed in the US jumped seasonally adjusted from 5.8 million in May 1979 to 12.1 million in Dec 1982, by 6.3 million, or 108.6 percent. The jump not seasonally adjusted was from 5.4 million in May 1979 to 12.5 million in Jan 1983, by 7.1 million or 131.5 percent. The number of unemployed seasonally adjusted jumped from 6.7 million in Mar 2007 to 15.4 million in Oct 2009, by 8.7 million, or 129.9 percent. The number of unemployed not seasonally adjusted jumped from 6.5 million in Apr 2007 to 16.1 million in Jan 2010, by 9.6 million or 147.7 percent. These are the two episodes with steepest increase in the level of unemployment in Chart I-16.
Chart I-16, US, Unemployed, SA, 1948-2014, Thousands
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-17 provides the rate of unemployment of the US from 1948 to 2014. The peak of the series is 10.8 percent in both Nov and Dec 1982. The second highest rates are 10.0 percent in Oct 2009 and 9.9 percent in both Nov and Dec 2009. The unadjusted rate of unemployment reached 10.6 percent in Jan 2010.
Chart I-17, US, Unemployment Rate, SA, 1948-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-18 provides the number unemployed for 27 weeks and over from 1948 to 2014. The number unemployed for 27 weeks and over jumped from 510,000 in Dec 1978 to 2.885 million in Jun 1983, by 2.4 million, or 465.7 percent. The number of unemployed 27 weeks or over SA jumped from 1.132 million in May 2007 to 6.623 million in Jun 2010, by 5.491 million, or 485.1 percent.
Chart I-18, US, Unemployed for 27 Weeks or More, SA, 1948-2014, Thousands
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The employment-population ratio in Chart I-19 is an important indicator of wellbeing in labor markets, measuring the number of people with jobs. The US employment-population ratio fell from 63.5 in Dec 2006 to 58.6 in Jul 2011 and stands at 59.1 NSA in Nov 2014. There is no comparable decline followed by stabilization during an expansion in Chart I-19.
Chart I-19, US, Employment-Population Ratio, 1948-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The number employed part-time for economic reasons in Chart I-20 increased in the recessions and declined during the expansions. In the current cycle, the number employed part-time for economic reasons increased sharply and has not returned to normal levels. Lower growth of economic activity in the expansion after IIIQ2009 failed to reduce the number desiring to work full time but finding only part-time occupations.
Chart I-20, US, Part-Time for Economic Reasons, NSA, 1955-2014, Thousands
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Table I-5 provides percentage change of real GDP in the United States in the 1930s, 1980s and 2000s. The recession in 1981-1982 is quite similar on its own to the 2007-2009 recession. In contrast, during the Great Depression in the four years of 1930 to 1933, GDP in constant dollars fell 26.4 percent cumulatively and fell 45.3 percent in current dollars (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 150-2, Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2009b), 205-7 and revisions in http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). Data are available for the 1930s only on a yearly basis. US GDP fell 4.7 percent in the two recessions (1) from IQ1980 to IIIQ1980 and (2) from III1981 to IVQ1981 to IVQ1982 and 4.2 percent cumulatively in the recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. It is instructive to compare the first three years of the expansions in the 1980s and the current expansion. GDP grew at 4.6 percent in 1983, 7.3 percent in 1984, 4.2 percent in 1985, 3.5 percent in 1986 and 3.5 percent in 1987. In contrast, GDP grew 2.5 percent in 2010, 1.6 percent in 2011, 2.3 percent in 2012 and 2.2 percent in 2013. Actual annual equivalent GDP growth in the four quarters of 2012, and seven quarters from IQ2013 to IIIQ2014 is 2.3 percent and 2.4 percent in the four quarters ending in IIIQ2014. GDP grew at 4.2 percent in 1985, 3.5 percent in 1986 and 3.5 percent in 1987 while the forecasts of the central tendency of participants of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) are in the range of 2.6 to 3.0 percent in 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20140917.pdf) with less reliable forecast of 2.5 to 3.0 percent in 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20141217.pdf). Growth of GDP in the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2014 has been at average 2.3 percent in annual equivalent.
Table I-5, US, Percentage Change of GDP in the 1930s, 1980s and 2000s, ∆%
| Year | GDP ∆% | Year | GDP ∆% | Year | GDP ∆% |
| 1930 | -8.5 | 1980 | -0.2 | 2000 | 4.1 |
| 1931 | -6.4 | 1981 | 2.6 | 2001 | 1.0 |
| 1932 | -12.9 | 1982 | -1.9 | 2002 | 1.8 |
| 1933 | -1.3 | 1983 | 4.6 | 2003 | 2.8 |
| 1934 | 10.8 | 1984 | 7.3 | 2004 | 3.8 |
| 1935 | 8.9 | 1985 | 4.2 | 2005 | 3.3 |
| 1936 | 12.9 | 1986 | 3.5 | 2006 | 2.7 |
| 1937 | 5.1 | 1987 | 3.5 | 2007 | 1.8 |
| 1938 | -3.3 | 1988 | 4.2 | 2008 | -0.3 |
| 1930 | 8.0 | 1989 | 3.7 | 2009 | -2.8 |
| 1940 | 8.8 | 1990 | 1.9 | 2010 | 2.5 |
| 1941 | 17.7 | 1991 | -0.1 | 2011 | 1.6 |
| 1942 | 18.9 | 1992 | 3.6 | 2012 | 2.3 |
| 1943 | 17.0 | 1993 | 2.7 | 2013 | 2.2 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Characteristics of the four cyclical contractions are provided in Table I-6 with the first column showing the number of quarters of contraction; the second column the cumulative percentage contraction; and the final column the average quarterly rate of contraction. There were two contractions from IQ1980 to IIIQ1980 and from IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 separated by three quarters of expansion. The drop of output combining the declines in these two contractions is 4.7 percent, which is almost equal to the decline of 4.2 percent in the contraction from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. In contrast, during the Great Depression in the four years of 1930 to 1933, GDP in constant dollars fell 26.4 percent cumulatively and fell 45.3 percent in current dollars (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 150-2, Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2009b), 205-7 and revisions in http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). The comparison of the global recession after 2007 with the Great Depression is entirely misleading.
Table I-6, US, Number of Quarters, GDP Cumulative Percentage Contraction and Average Percentage Annual Equivalent Rate in Cyclical Contractions
| Number of Quarters | Cumulative Percentage Contraction | Average Percentage Rate | |
| IIQ1953 to IIQ1954 | 3 | -2.4 | -0.8 |
| IIIQ1957 to IIQ1958 | 3 | -3.0 | -1.0 |
| IVQ1973 to IQ1975 | 5 | -3.1 | -0.6 |
| IQ1980 to IIIQ1980 | 2 | -2.2 | -1.1 |
| IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 | 4 | -2.5 | -0.64 |
| IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 | 6 | -4.2 | -0.72 |
Sources: Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table I-7 shows the mediocre average annual equivalent growth rate of 2.3 percent of the US economy in the twenty-one quarters of the current cyclical expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2014. In sharp contrast, the average growth rate of GDP was:
- 5.7 percent in the first thirteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1986
- 5.4 percent in the first fifteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986
- 5.2 percent in the first sixteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1986
- 5.0 percent in the first seventeen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1987
- 5.0 percent in the first eighteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIQ1987
- 4.9 percent in the first nineteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987
- 5.0 percent in the first twenty quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1987
- 4.9 percent in the first twenty-first quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1988
1. The line “average first four quarters in four expansions” provides the average growth rate of 7.7 percent with 7.8 percent from IIIQ1954 to IIQ1955, 9.2 percent from IIIQ1958 to IIQ1959, 6.1 percent from IIIQ1975 to IIQ1976 and 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983. The United States missed this opportunity of high growth in the initial phase of recovery. BEA data show the US economy in standstill with annual growth of 2.5 percent in 2010 decelerating to 1.6 percent annual growth in 2011, 2.3 percent in 2012 and 2.2 percent in 2013 (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) The expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1986 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.7 percent, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1988 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983. GDP growth in the four quarters of IIIQ2013 to IIIQ2014 accumulated to 2.4 percent that is equivalent to 2.4 percent in a year. This is obtained by dividing GDP in IIIQ2014 of $16,164.1 billion by GDP in IIIQ2013 of $15,779.9 billion and compounding by 4/4: {[($16,164.1/$15,779.9)4/4 -1]100 = 2.4 %}. The US economy grew 2.4 percent in IIIQ2014 relative to the same quarter a year earlier in IIIQ2013. Another important revelation of the revisions and enhancements is that GDP was flat in IVQ2012, which is in the borderline of contraction, and negative in IQ2014. US GDP fell 0.5 percent in IQ2014. The rate of growth of GDP in the revision of IIIQ2013 is 4.5 percent in seasonally adjusted annual rate (SAAR). Inventory accumulation contributed 1.49 percentage points to this rate of growth. The actual rate without this impulse of unsold inventories would have been 3.0 percent, or 0.74 percent in IIIQ2013, such that annual equivalent growth in 2013 is closer to 2.9 percent {[(1.007)(1.004)(1.0074)(1.010)4/4-1]100 = 2.9%}, compounding the quarterly rates and converting into annual equivalent. Inventory divestment deducted 1.16 percentage points from GDP growth in IQ2014. Without this deduction of inventory divestment, GDP growth would have been minus 0.9 percent in IQ2014, such that the actual growth rates in the four quarters ending in IQ2014 is closer to 2.2 percent {[(1.004)(1.011)(1.009)(0.9977)]4/4 -1]100 = 2.2%}.
Table I-7, US, Number of Quarters, Cumulative Growth and Average Annual Equivalent Growth Rate in Cyclical Expansions
| Number | Cumulative Growth ∆% | Average Annual Equivalent Growth Rate | |
| IIIQ 1954 to IQ1957 | 11 | 12.8 | 4.5 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ1954 to IIQ1955 | 4 | 7.8 | |
| IIQ1958 to IIQ1959 | 5 | 10.0 | 7.9 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ1958 to IIQ1959 | 4 | 9.2 | |
| IIQ1975 to IVQ1976 | 8 | 8.3 | 4.1 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ1975 to IIQ1976 | 4 | 6.1 | |
| IQ1983-IQ1986 IQ1983-IIIQ1986 IQ1983-IVQ1986 IQ1983-IQ1987 IQ1983-IIQ1987 IQ1983 to IIIQ1987 IQ1983 to IVQ1987 IQ1983 to IQ1988 | 13 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 | 19.9 21.6 22.3 23.1 24.5 25.6 27.7 28.4 | 5.7 5.4 5.2 5.0 5.0 4.9 5.0 4.9 |
| First Four Quarters IQ1983 to IVQ1983 | 4 | 7.8 | |
| Average First Four Quarters in Four Expansions* | 7.7 | ||
| IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2014 | 21 | 12.6 | 2.3 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 | 2.7 |
*First Four Quarters: 7.8% IIIQ1954-IIQ1955; 9.2% IIIQ1958-IIQ1959; 6.1% IIIQ1975-IQ1976; 7.8% IQ1983-IVQ1983
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
A group of charts from the database of the Bureau of Labor Statistics facilitates the comparison of employment in the 1980s and 2000s. The long-term charts and tables from I-5 to I-7 in the discussion above confirm the view that the comparison of the current expansion should be with that in the 1980s because of similar dimensions. Chart I-21 provides the level of employment in the US between 1979 and 1989. Employment surged after the contraction and grew rapidly during the decade.
Chart I-21, US, Employed, Thousands, 1979-1989
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-22 provides the level of employment in the US from 2001 to 2014. There is actually not sufficient job creation in merely absorbing new entrants in the labor force because of those dropping from job searches, worsening the stock of unemployed or underemployed in involuntary part-time jobs. Recovery has been anemic compared with the shallow recession of 2001 that was followed by nearly vertical growth in jobs. The number employed in Dec 2014 was 147.190 million (NSA) or 0.125 million fewer people with jobs relative to the peak of 147.315 million in Jul 2007 while the civilian noninstitutional population of ages 16 years and over increased from 231.958 million in Jul 2007 to 249.027 million in Dec 2014 or by 17.069 million. The number employed decreased 0.1 percent from Jul 2007 to Dec 2014 while the noninstitutional civilian population of ages of 16 years and over, or those available for work, increased 7.4 percent. The ratio of employment to population in Jul 2007 was 63.5 percent (147.315 million employment as percent of population of 231.958 million). The same ratio in Dec 2014 would result in 158.132 million jobs (0.635 multiplied by noninstitutional civilian population of 249.027 million). There are effectively 10.942 million fewer jobs in Dec 2014 than in Jul 2007, or 158.132 million minus 147.190 million. There is actually not sufficient job creation in merely absorbing new entrants in the labor force because of those dropping from job searches, worsening the stock of unemployed or underemployed in involuntary part-time jobs.
Chart I-22, US, Employed, Thousands, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
There was a steady upward trend in growth of the civilian labor force between 1979 and 1989 as shown in Chart I-23. There were fluctuations but strong long-term dynamism over an entire decade.
Chart I-23, US, Civilian Labor Force, Thousands, 1979-1989
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The civilian labor force in Chart I-24 grew steadily on an upward trend in the 2000s until it contracted together with the economy after 2007. There has not been recovery during the expansion but rather decline and marginal turn of the year 2011 into expansion in 2012 followed by stability and oscillation into 2013-2014. The civilian labor force consists of people who are available and willing to work and who have searched for employment recently. The labor force of the US grew 9.4 percent from 142.828 million in Jan 2001 to 156.255 million in Jul 2009 but is 0.5 percent lower at 155.521 million in Dec 2014, all numbers not seasonally adjusted. Chart I-3 shows the flattening of the curve of expansion of the labor force and its decline in 2010 and 2011. The ratio of the labor force of 154.871 million in Jul 2007 to the noninstitutional population of 231.958 million in Jul 2007 was 66.8 percent while the ratio of the labor force of 155.521 million in Dec 2014 to the noninstitutional population of 249.027 million in Dec 2014 was 62.5 percent. The labor force of the US in Dec 2014 corresponding to 66.8 percent of participation in the population would be 166.350 million (0.668 x 249.027. The difference between the measured labor force in Dec 2014 of 155.521 million and the labor force in Dec 2014 with participation rate of 66.8 percent (as in Jul 2007) of 166.350 million is 10.829 million. The level of the labor force in the US has stagnated and is 10.829 million lower than what it would have been had the same participation rate been maintained. Millions of people have abandoned their search for employment because they believe there are no jobs available for them. The key issue is whether the decline in participation of the population in the labor force is the result of people giving up on finding another job.
Chart I-24, US, Civilian Labor Force, Thousands, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The rate of participation of the labor force in population stagnated during the stagflation and conquest of inflation in the late 1970s and early 1980s, as shown in Chart I-25. Recovery was vigorous during the expansion and lasted through the remainder of the decade.
Chart I-25, US, Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate, 1979-1989, %
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The rate of participation in the labor force declined after the recession of 2001 and stagnated until 2007, as shown in Chart I-26. The rate of participation in the labor force continued to decline both during the contraction after 2007 and the expansion after 2009 with marginal expansion at the turn of the year into 2012 followed by trend of decline and stability.
Chart I-26, US, Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate, 2001-2014, %
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-27 provides the number unemployed during the 1980s. The number unemployed peaked at 12.051 million in Dec 1982 seasonally adjusted and 12.517 in Jan 1983 million not seasonally adjusted, declining to 8.358 million in Dec 1984 seasonally adjusted and 7.978 in Dec 1984 million not seasonally adjusted during the first two years of expansion from the contraction. The number unemployed then fell to 6.667 million in Dec 1989 seasonally adjusted and 6.300 million not seasonally adjusted.
Chart I-27, US, Unemployed Thousands 1979-1989
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-28 provides the number unemployed from 2001 to 2014. Using seasonally adjusted data, the number unemployed rose from 6.727 million in Oct 2006 to 15.352 million in Oct 2009, declining to 13.071 million in Dec 2011 and to 8.688 million in Dec 2014. Using data not seasonally adjusted, the number unemployed rose from 6.272 million in Oct 2006 to 16.147 million in Jan 2010, declining to 11.844 million in Dec 2012, increasing to 13.181 million in Jan 20013 and declining to 9.984 million in Dec 2013. The level of unemployment was 8.331 million in Dec 2014.
Chart I-28, US, Unemployed Thousands 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The rate of unemployment peaked at 10.8 percent in both Nov and Dec 1982 seasonally adjusted, as shown in Chart I-29. The rate of unemployment dropped sharply during the expansion after 1984 and continued to decline during the rest of the decade to 5.4 percent in Dec 1989. Using not seasonally adjusted data, the rate of unemployment peaked at 11.4 percent in Jan 1983, declining to 7.0 percent in Dec 1984 and 5.1 percent in Dec 1989.
Chart I-29, US, Unemployment Rate, 1979-1989, %
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The rate of unemployment in the US seasonally adjusted jumped from 4.4 percent in May 2007 to 10.0 percent in Oct 2009 and 9.9 percent in both Nov and Dec 2009, as shown in Chart I-30. The rate of unemployment fluctuated at around 9.0 percent in 2011, declining to 7.9 percent in Dec 2012 and 6.7 percent in Dec 2013. The rate of unemployed eased to 5.6 percent in Dec 2014.
Chart I-30, US, Unemployment Rate, 2001-2014, %
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The employment population ratio seasonally adjusted fell from around 60.1 in Dec 1979 to 57.1 in both Feb and Mar 1983, as shown in Chart I-31. The employment population ratio seasonally adjusted rose back to 59.9 in Dec 1984 and reached 63.0 later in the decade in Dec 1989. Using not seasonally adjusted data, the employment population ratio dropped from 60.4 percent in Oct 1979 to 56.1 percent in Jan 1983, increasing to 59.8 in Dec 1984 and to 62.9 percent in Dec 1989.
Chart I-31, US, Employment Population Ratio, 1979-1989, %
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The US employment-population ratio seasonally adjusted has fallen from 63.4 in Dec 2006 to 58.6 in Dec 2011, 58.6 in Dec 2012 and 58.6 in Dec 2013, as shown in Chart I-32. The employment-population ratio reached 59.2 in Dec 2014. The employment population-ratio has stagnated during the expansion. Using not seasonally adjusted data, the employment population ratio fell from 63.6 percent in Jul 2006 to 57.6 percent in Jan 2011, 58.5 percent in Dec 2012 and 58.5 percent in Dec 2013. The employment population ratio eased to 59.1 in Dec 2014.
Chart I-32, US, Employment Population Ratio, 2001-2014, %
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The number unemployed 27 weeks or more rose in Chart I-33 rose from 492,000 NSA in Oct 1979 to 2.978 million in Mar 1983. The level unemployed 27 weeks or more NSA fell to 566,000 in Aug 1989.
Chart I-33, US, Number Unemployed for 27 Weeks or More 1979-1989, SA, Thousands
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The number unemployed for 27 weeks or over, seasonally adjusted, increased sharply during the contraction as shown in Chart I-34 from 1.131 million in Nov 2006 to 6.800 million in Apr 2010 seasonally adjusted. The number of unemployed for 27 weeks remained at around 6 million during the expansion compared with somewhat above 1 million before the contraction, falling to 2.785 million in Dec 2014 seasonally adjusted and 2.693 million not seasonally adjusted.
Chart I-34, US, Number Unemployed for 27 Weeks or More, 2001-2014, SA, Thousands
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The number of persons working part-time for economic reasons because they cannot find full-time work peaked during the contraction at 6.857 million SA in Oct 1982, as shown in Chart I-35. The number of persons at work part-time for economic reasons fell sharply during the expansion to 5.797 million in Dec 1984 and continued to fall throughout the decade to 4.817 million in Dec 1989 SA and 4.709 million NSA.
Chart I-35, US, Part-Time for Economic Reasons, 1979-1989, Thousands
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The number of people working part-time because they cannot find full-time employment, not seasonally adjusted, increased sharply during the contraction from 3.787 million in Apr 2006, not seasonally adjusted, to 9.354 million in Dec 2009, as shown in Chart I-36. The number of people working part-time because of failure to find an alternative occupation stagnated at a very high level during the expansion, declining to 6.970 million not seasonally adjusted in Dec 2014.
Chart I-36, US, Part-Time for Economic Reasons, 2001-2014, Thousands
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The number marginally attached to the labor force in Chart I-37 jumped from 1.252 million in Dec 2006 to 2.800 million in Jan 2011, remaining at a high level of 2.540 million in Dec 2011, 2.809 million in Jan 2012 and 2.614 million in Dec 2012. The number marginally attached to the labor force eased to 2.427 million in Dec 2013 and 2.260 million in Dec 2014.
Chart I-37, US, Marginally Attached to the Labor Force, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
IA4 Job Creation. What is striking about the data in Table I-8 is that the numbers of monthly increases in jobs in 1983 and 1984 are several times higher than in 2010 to 2014. The civilian noninstitutional population grew by 42.3 percent from 174.215 million in 1983 to 247.947 million in 2014 and labor force higher by 39.8 percent, growing from 111.550 million in 1983 to 155.922 million in 2014. Total nonfarm payroll employment seasonally adjusted (SA) increased 252,000 in Dec 2014 and private payroll employment increased 240,000. The average monthly number of nonfarm jobs created from Dec 2012 to Dec 2013 was 194,250 using seasonally adjusted data, while the average number of nonfarm jobs created from Dec 2013 to Dec 2014 was 246,000, or increase by 26.6 percent. The average number of private jobs created in the US from Dec 2012 to Dec 2013 was 197,083, using seasonally adjusted data, while the average from Dec 2013 to Dec 2014 was 238,417, or increase by 21.0 percent. This blog calculates the effective labor force of the US at 163.345 million in Dec 2013 and 164.856 million in Dec 2014 (Table I-4), for growth of 1.511 million at average 125,917 per month. The difference between the average increase of 238,417 new private nonfarm jobs per month in the US from Dec 2013 to Dec 2014 and the 125,917 average monthly increase in the labor force from Dec 2013 to Dec 2014 is 112,500 monthly new jobs net of absorption of new entrants in the labor force. There are 25.896 million in job stress in the US currently. Creation of 112,500 new jobs per month net of absorption of new entrants in the labor force would require 230 months to provide jobs for the unemployed and underemployed (25.896 million divided by 112.500) or 19 years (230 divided by 12). The civilian labor force of the US in Dec 2014 not seasonally adjusted stood at 155.521 million with 8.331 million unemployed or effectively 16.666 million unemployed in this blog’s calculation by inferring those who are not searching because they believe there is no job for them for effective labor force of 164.856 million. Reduction of one million unemployed at the current rate of job creation without adding more unemployment requires 0.7 years (1 million divided by product of 112,500 by 12, which is 1,350,000). Reduction of the rate of unemployment to 5 percent of the labor force would be equivalent to unemployment of only 7.776 million (0.05 times labor force of 155.521 million). New net job creation would be 0.555 million (8.331 million unemployed minus 7.776 million unemployed at rate of 5 percent) that at the current rate would take 0.4 years (0.555 million divided by 1.350). Under the calculation in this blog, there are 16.666 million unemployed by including those who ceased searching because they believe there is no job for them and effective labor force of 164.856 million. Reduction of the rate of unemployment to 5 percent of the labor force would require creating 8.243 million jobs net of labor force growth that at the current rate would take 6.1 years (16.666 million minus 0.05(164.856 million) = 8.243 million divided by 1.350, using LF PART 66.2% and Total UEM in Table I-4). These calculations assume that there are no more recessions, defying United States economic history with periodic contractions of economic activity when unemployment increases sharply. The number employed in Dec 2014 was 147.190 million (NSA) or 0.125 million fewer people with jobs relative to the peak of 147.315 million in Jul 2007 while the civilian noninstitutional population of ages 16 years and over increased from 231.958 million in Jul 2007 to 249.027 million in Dec 2014 or by 17.069 million. The number employed decreased 0.1 percent from Jul 2007 to Dec 2014 while the noninstitutional civilian population of ages of 16 years and over, or those available for work, increased 7.4 percent. The ratio of employment to population in Jul 2007 was 63.5 percent (147.315 million employment as percent of population of 231.958 million). The same ratio in Dec 2014 would result in 158.132 million jobs (0.635 multiplied by noninstitutional civilian population of 249.027 million). There are effectively 10.942 million fewer jobs in Dec 2014 than in Jul 2007, or 158.132 million minus 147.190 million. There is actually not sufficient job creation in merely absorbing new entrants in the labor force because of those dropping from job searches, worsening the stock of unemployed or underemployed in involuntary part-time jobs.
There is current interest in past theories of “secular stagnation.” Alvin H. Hansen (1939, 4, 7; see Hansen 1938, 1941; for an early critique see Simons 1942) argues:
“Not until the problem of full employment of our productive resources from the long-run, secular standpoint was upon us, were we compelled to give serious consideration to those factors and forces in our economy which tend to make business recoveries weak and anaemic (sic) and which tend to prolong and deepen the course of depressions. This is the essence of secular stagnation-sick recoveries which die in their infancy and depressions which feed on them-selves and leave a hard and seemingly immovable core of unemployment. Now the rate of population growth must necessarily play an important role in determining the character of the output; in other words, the com-position of the flow of final goods. Thus a rapidly growing population will demand a much larger per capita volume of new residential building construction than will a stationary population. A stationary population with its larger proportion of old people may perhaps demand more personal services; and the composition of consumer demand will have an important influence on the quantity of capital required. The demand for housing calls for large capital outlays, while the demand for personal services can be met without making large investment expenditures. It is therefore not unlikely that a shift from a rapidly growing population to a stationary or declining one may so alter the composition of the final flow of consumption goods that the ratio of capital to output as a whole will tend to decline.”
The argument that anemic population growth causes “secular stagnation” in the US (Hansen 1938, 1939, 1941) is as misplaced currently as in the late 1930s (for early dissent see Simons 1942). There is currently population growth in the ages of 16 to 24 years but not enough job creation and discouragement of job searches for all ages (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/global-financial-and-economic-risk.html). The proper explanation is not in secular stagnation but in cyclically slow growth. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2014 would have accumulated to 23.0 percent. GDP in IIIQ2014 would be $18,438.0 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2,232.4 billion than actual $16,205.6 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 25.9 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment of 15.7 percent of the effective labor force (Section I and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/financial-risks-twenty-six-million.html
and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/rules-discretionary-authorities-and.html). US GDP in IIIQ2014 is 12.1 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,205.1 billion in IIIQ2014 or 8.1 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.1 percent. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. The long-term trend is growth at average 3.3 percent per year from Jan 1919 to Nov 2014. Growth at 3.3 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 99.2392 in Dec 2007 to 124.2256 in Nov 2014. The actual index NSA in Nov 2014 is 101.7487, which is 18.1 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.3 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2013, raising the index at trend to 116.1422 in Nov 2014. The output of manufacturing at 101.7487 in Nov 2014 is 12.4 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Table I-8, US, Monthly Change in Jobs, Number SA
| Month | 1981 | 1982 | 1983 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | Private |
| Jan | 94 | -326 | 224 | 15 | -798 | 18 | 20 |
| Feb | 68 | -5 | -75 | -86 | -701 | -50 | -38 |
| Mar | 105 | -130 | 172 | -80 | -826 | 156 | 113 |
| Apr | 73 | -280 | 276 | -214 | -684 | 251 | 192 |
| May | 10 | -45 | 277 | -182 | -354 | 516 | 94 |
| Jun | 197 | -243 | 379 | -172 | -467 | -122 | 110 |
| Jul | 112 | -342 | 418 | -210 | -327 | -61 | 120 |
| Aug | -36 | -158 | -308 | -259 | -216 | -42 | 117 |
| Sep | -87 | -181 | 1115 | -452 | -227 | -57 | 107 |
| Oct | -99 | -277 | 271 | -474 | -198 | 241 | 199 |
| Nov | -209 | -123 | 353 | -765 | -6 | 137 | 149 |
| Dec | -278 | -14 | 356 | -697 | -283 | 71 | 94 |
| 1984 | 2011 | Private | |||||
| Jan | 446 | 70 | 72 | ||||
| Feb | 481 | 168 | 223 | ||||
| Mar | 275 | 212 | 231 | ||||
| Apr | 363 | 322 | 320 | ||||
| May | 308 | 102 | 166 | ||||
| Jun | 379 | 217 | 186 | ||||
| Jul | 313 | 106 | 219 | ||||
| Aug | 242 | 122 | 125 | ||||
| Sep | 310 | 221 | 268 | ||||
| Oct | 286 | 183 | 177 | ||||
| Nov | 349 | 164 | 191 | ||||
| Dec | 128 | 196 | 222 | ||||
| 1985 | 2012 | Private | |||||
| Jan | 266 | 360 | 364 | ||||
| Feb | 124 | 226 | 228 | ||||
| Mar | 346 | 243 | 246 | ||||
| Apr | 196 | 96 | 102 | ||||
| May | 274 | 110 | 131 | ||||
| Jun | 146 | 88 | 75 | ||||
| Jul | 190 | 160 | 172 | ||||
| Aug | 193 | 150 | 136 | ||||
| Sep | 203 | 161 | 159 | ||||
| Oct | 188 | 225 | 255 | ||||
| Nov | 209 | 203 | 211 | ||||
| Dec | 167 | 214 | 215 | ||||
| 1986 | 2013 | Private | |||||
| Jan | 125 | 197 | 219 | ||||
| Feb | 107 | 280 | 263 | ||||
| Mar | 94 | 141 | 164 | ||||
| Apr | 187 | 203 | 188 | ||||
| May | 127 | 199 | 222 | ||||
| Jun | -94 | 201 | 201 | ||||
| Jul | 318 | 149 | 170 | ||||
| Aug | 114 | 202 | 180 | ||||
| Sep | 347 | 164 | 153 | ||||
| Oct | 186 | 237 | 247 | ||||
| Nov | 186 | 274 | 272 | ||||
| Dec | 205 | 84 | 86 | ||||
| 1987 | 2014 | Private | |||||
| Jan | 172 | 144 | 166 | ||||
| Feb | 232 | 222 | 201 | ||||
| Mar | 249 | 203 | 200 | ||||
| Apr | 338 | 304 | 278 | ||||
| May | 226 | 229 | 228 | ||||
| Jun | 172 | 267 | 260 | ||||
| Jul | 347 | 243 | 239 | ||||
| Aug | 171 | 203 | 200 | ||||
| Sep | 228 | 271 | 249 | ||||
| Oct | 492 | 261 | 255 | ||||
| Nov | 232 | 353 | 345 | ||||
| Dec | 294 | 252 | 240 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Charts numbered from I-38 to I-41 from the database of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provide a comparison of payroll survey data for the contractions and expansions in the 1980s and after 2007. Chart I-38 provides total nonfarm payroll jobs from 2001 to 2013. The sharp decline in total nonfarm jobs during the contraction after 2007 has been followed by initial stagnation and then inadequate growth in 2012 and 2013-2014 while population growth continued.
Chart I-38, US, Total Nonfarm Payroll Jobs SA 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-39 provides total nonfarm jobs SA from 1979 to 1989. Recovery is strong throughout the decade with the economy growing at trend over the entire economic cycle.
Chart I-39, US, Total Nonfarm Payroll Jobs SA 1979-1989
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Most job creation in the US is by the private sector. Chart I-40 shows the sharp destruction of private payroll jobs during the contraction after 2007. There has been growth after 2010 but insufficient to recover higher levels of employment prevailing before the contraction. At current rates, recovery of employment may spread over several years in contrast with past expansions of the business cycle in the US.
Chart I-40, US, Total Private Payroll Jobs SA 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
In contrast, growth of private payroll jobs in the US recovered vigorously during the expansion in 1983 through 1985, as shown in Chart I-41. Rapid growth of creation of private jobs continued throughout the 1980s.
Chart I-41, US, Total Private Payroll Jobs SA 1979-1989
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Types of jobs created, and not only the pace of job creation, may be important. Aspects of growth of payroll jobs from Dec 2013 to Dec 2014, not seasonally adjusted (NSA), are in Table I-9. Total nonfarm employment increased by 2,987,000 (row A, column Change), consisting of growth of total private employment by 2,890,000 (row B, column Change) and increase by 97,000 of government employment (row C, column Change). Monthly average growth of private payroll employment has been 240,833, which is mediocre relative to 24 to 30 million in job stress, while total nonfarm employment has grown on average by only 247,917 per month, which does not significantly reduce job stress with 125,917 new entrants per month in the labor force. These monthly rates of job creation net of the demands of new entrants in the labor force perpetuate unemployment and underemployment. Manufacturing employment increased by 193,000, at the monthly rate of 16,083 while private service providing employment grew by 2,353,000, at the monthly rate of 196,083. An important feature in Table I-9 is that jobs in professional and business services increased by 730,000 with temporary help services increasing by 218,000. This episode of jobless recovery is characterized by part-time jobs and creation of jobs that are inferior to those that have been lost. Monetary and fiscal stimuli fail to increase consumption in a fractured job market. The segment leisure and hospitality added 417,000 jobs in 12 months. An important characteristic is that the loss of government jobs has stabilized in federal government with loss of 10,000 jobs while states added 31,000 jobs and local government added 76,000 jobs. Local government provides the bulk of government jobs, 14.374 million, while federal government provides 2.731 million and states government 5.200 million.
Table I-9, US, Employees in Nonfarm Payrolls Not Seasonally Adjusted, in Thousands
| Dec 2013 | Dec 2014 | Change | |
| A Total Nonfarm | 138,269 | 141,256 | 2,987 |
| B Total Private | 116,061 | 118,951 | 2,890 |
| B1 Goods Producing | 18,703 | 19,240 | 537 |
| B1a Manufacturing | 12,050 | 12,243 | 193 |
| B2 Private service providing | 97,358 | 99,711 | 2,353 |
| B2a Wholesale Trade | 5,805 | 5,913 | 108 |
| B2b Retail Trade | 15,829 | 16,084 | 255 |
| B2c Transportation & Warehousing | 4,700 | 4,851 | 151 |
| B2d Financial Activities | 7,911 | 8,035 | 124 |
| B2e Professional and Business Services | 18,906 | 19,636 | 730 |
| B2e1 Temporary help services | 2,855 | 3,073 | 218 |
| B2f Health Care & Social Assistance | 17,947 | 18,379 | 432 |
| B2g Leisure & Hospitality | 14,095 | 14,512 | 417 |
| C Government | 22,208 | 22,305 | 97 |
| C1 Federal | 2,741 | 2,731 | -10 |
| C2 State | 5,169 | 5,200 | 31 |
| C3 Local | 14,298 | 14,374 | 76 |
Note: A = B+C, B = B1 + B2, C=C1 + C2 + C3
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Greater detail on the types of jobs created is provided in Table I-10 with data for Nov 2014 and Dec 2014. Strong seasonal effects are shown by the significant difference between seasonally adjusted (SA) and not-seasonally-adjusted (NSA) data. The purpose of adjusting for seasonality is to isolate nonseasonal effects. The 252,000 SA total nonfarm jobs created in Dec 2014 relative to Nov 2014 actually correspond to decrease of 65,000 jobs NSA, as shown in row A. Most of this difference in Jan 2014 is due to the necessary benchmark and seasonal adjustments in the beginning of every year. The 240,000 total private payroll jobs SA created in Dec 2014 relative to Nov 2014 actually correspond to increase of 55,000 jobs NSA. The analysis of NSA job creation in the prior Table I-9 does show improvement over the 12 months ending in Dec 2014 that is not clouded by seasonal variations but is inadequate number of jobs created. In fact, the 12-month rate of job creation without seasonal adjustment is stronger indication of marginal improvement in the US job market but that is insufficient in even making a dent in about 30 million people unemployed or underemployed. Benchmark and seasonal adjustments affect comparability of data over time.
Table I-10, US, Employees on Nonfarm Payrolls and Selected Industry Detail, Thousands, SA and NSA
| Nov 2014 SA | Dec 2014 SA | ∆ | Nov 2014 NSA | Dec 2014 NSA | ∆ | |
| A Total Nonfarm | 140,095 | 140,347 | 252 | 141,321 | 141,256 | -65 |
| B Total Private | 118,162 | 118,402 | 240 | 118,896 | 118,951 | 55 |
| B1 Goods Producing | 19,269 | 19,336 | 67 | 19,396 | 19,240 | -156 |
| B1a Constr. | 6,118 | 6,166 | 48 | 6,226 | 6,069 | -157 |
| B Mfg | 12,222 | 12,239 | 17 | 12,239 | 12,243 | 4 |
| B2 Private Service Providing | 98,893 | 99,066 | 173 | 99,500 | 99,711 | 211 |
| B2a Wholesale Trade | 5,898 | 5,908 | 10 | 5,907 | 5,913 | 6 |
| B2b Retail Trade | 15,503 | 15,511 | 8 | 15,915 | 16,084 | 169 |
| B2c Couriers & Mess. | 586.6 | 587.3 | 0.7 | 623 | 720 | 97 |
| B2d Health-care & Social Assistance | 18,259 | 18,303 | 44 | 18,323 | 18,379 | 56 |
| B2De Profess. & Business Services | 19,522 | 19,574 | 52 | 19,664 | 19,636 | -28 |
| B2De1 Temp Help Services | 2,975 | 2,990 | 15 | 3,080 | 3,073 | -7 |
| B2f Leisure & Hospit. | 14,820 | 14,856 | 36 | 14,541 | 14,512 | -29 |
Notes: ∆: Absolute Change; Constr.: Construction; Mess.: Messengers; Temp: Temporary; Hospit.: Hospitality. SA aggregates do not add because of seasonal adjustment.
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-42 of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System shows that output of durable manufacturing accelerated in the 1980s and 1990s with slower growth in the 2000s perhaps because processes matured. Growth was robust after the major drop during the global recession but appears to vacillate in the final segment.
Chart I-42, US, Output of Durable Manufacturing, 1972-2014
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/g17/Current/default.htm
Manufacturing jobs not seasonally adjusted increased 193,000 from Dec 2013 to
Dec 2014 or at the average monthly rate of 16,083. There are effects of the weaker economy and international trade together with the yearly adjustment of labor statistics. Industrial production increased 1.3 percent in Nov 2014 and increased 0.1 percent in Oct 2014 after increasing 0.9 percent in Sep 2014 with all data seasonally adjusted. The Federal Reserve completed its annual revision of industrial production and capacity utilization on Mar 28, 2014 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/g17/revisions/Current/DefaultRev.htm). The report of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System states (http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/g17/Current/default.htm):
“Industrial production increased 1.3 percent in November after edging up in October; output is now reported to have risen at a faster pace over the period from June through October than previously published. In November, manufacturing output increased 1.1 percent, with widespread gains among industries. The rise in factory output was well above its average monthly pace of 0.3 percent over the previous five months and was its largest gain since February. In November, the output of utilities jumped 5.1 percent, as weather that was colder than usual for the month boosted demand for heating. The index for mining decreased 0.1 percent. At 106.7 percent of its 2007 average, total industrial production in November was 5.2 percent above its year-earlier level. Capacity utilization for the industrial sector increased 0.8 percentage point in November to 80.1 percent, a rate equal to its long-run (1972–2013) average.”
In the six months ending in Nov 2014, United States national industrial production accumulated increase of 2.9 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 5.9 percent, which is higher than growth of 5.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2014. Excluding growth of 1.3 percent in Nov 2014, growth in the remaining five months from Jun to Nov 2014 accumulated to 1.6 percent or 3.9 percent annual equivalent. Industrial production declined in one of the past six months. Industrial production expanded at annual equivalent 9.6 percent in the most recent quarter from Sep to Nov 2014 and at 2.4 percent in the prior quarter Jun to Aug 2014. Business equipment accumulated growth of 2.5 percent in the six months from Jun to Nov 2014 at the annual equivalent rate of 5.1 percent, which is lower than growth of 6.5 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2014. The Fed analyzes capacity utilization of total industry in its report (http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/g17/Current/default.htm): “Capacity utilization for the industrial sector increased 0.8 percentage point in November to 80.1 percent, a rate equal to its long-run (1972–2013) average.” United States industry apparently decelerated to a lower growth rate followed by possible acceleration and stronger growth in past months.
Manufacturing decreased 21.9 from the peak in Jun 2007 to the trough in Apr 2009 and increased 19.9 percent from the trough in Apr 2009 to Dec 2013. Manufacturing grew 26.5 percent from the trough in Apr 2009 to Nov 2014. Manufacturing output in Nov 2014 is 1.2 percent below the peak in Jun 2007. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2014 would have accumulated to 23.0 percent. GDP in IIIQ2014 would be $18,438.0 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2,232.4 billion than actual $16,205.6 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 26.0 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment of 15.8 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/financial-risks-twenty-six-million.html
and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/rules-discretionary-authorities-and.html). US GDP in IIIQ2014 is 12.1 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,205.1 billion in IIIQ2014 or 8.1 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.1 percent. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. The long-term trend is growth at average 3.3 percent per year from Jan 1919 to Nov 2014. Growth at 3.3 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 99.2392 in Dec 2007 to 124.2256 in Nov 2014. The actual index NSA in Nov 2014 is 101.7487, which is 18.1 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.3 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2013, raising the index at trend to 116.1422 in Nov 2014. The output of manufacturing at 101.7487 in Nov 2014 is 12.4 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Table I-11 provides national income by industry without capital consumption adjustment (WCCA). “Private industries” or economic activities have share of 87.4 percent in IIIQ2014. Most of US national income is in the form of services. In Dec 2014, there were 141.256 million nonfarm jobs NSA in the US, according to estimates of the establishment survey of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) (http://www.bls.gov/news.release/empsit.nr0.htm Table B-1). Total private jobs of 118.951 million NSA in Dec 2014 accounted for 84.2 percent of total nonfarm jobs of 141.256 million, of which 12.243 million, or 10.3 percent of total private jobs and 8.7 percent of total nonfarm jobs, were in manufacturing. Private service-providing jobs were 99.711 million NSA in Dec 2014, or 70.6 percent of total nonfarm jobs and 83.8 percent of total private-sector jobs. Manufacturing has share of 11.3 percent in US national income in IIIQ2014 and durable goods 6.5 percent, as shown in Table I-11. Most income in the US originates in services. Subsidies and similar measures designed to increase manufacturing jobs will not increase economic growth and employment and may actually reduce growth by diverting resources away from currently employment-creating activities because of the drain of taxation.
Table I-11, US, National Income without Capital Consumption Adjustment by Industry, Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rates, Billions of Dollars, % of Total
| SAAR | % Total | SAAR IIIQ2014 | % Total | |
| National Income WCCA | 15,222.0 | 100.0 | 15,472.0 | 100.0 |
| Domestic Industries | 15,008.6 | 98.6 | 15,242.2 | 98.5 |
| Private Industries | 13,287.8 | 87.3 | 13,516.5 | 87.4 |
| Agriculture | 179.0 | 1.2 | 167.3 | 1.1 |
| Mining | 261.4 | 1.7 | 274.4 | 1.8 |
| Utilities | 215.6 | 1.4 | 221.7 | 1.4 |
| Construction | 670.3 | 4.4 | 680.4 | 4.4 |
| Manufacturing | 1712.8 | 11.3 | 1741.7 | 11.3 |
| Durable Goods | 975.4 | 6.4 | 1,000.7 | 6.5 |
| Nondurable Goods | 737.4 | 4.8 | 740.9 | 4.8 |
| Wholesale Trade | 917.7 | 6.0 | 936.9 | 6.1 |
| Retail Trade | 1048.0 | 6.9 | 1054.2 | 6.8 |
| Transportation & WH | 478.1 | 3.1 | 480.3 | 3.1 |
| Information | 580.3 | 3.8 | 576.5 | 3.7 |
| Finance, Insurance, RE | 2642.8 | 17.4 | 2787.2 | 18.0 |
| Professional & Business Services | 2064.5 | 13.6 | 2060.0 | 13.3 |
| Education, Health Care | 1484.3 | 9.8 | 1494.1 | 9.7 |
| Arts, Entertainment | 605.0 | 4.0 | 610.6 | 3.9 |
| Other Services | 428.0 | 2.8 | 431.3 | 2.8 |
| Government | 1720.8 | 11.3 | 1725.6 | 11.2 |
| Rest of the World | 213.5 | 1.4 | 229.9 | 1.5 |
Notes: SSAR: Seasonally-Adjusted Annual Rate; WCCA: Without Capital Consumption Adjustment by Industry; WH: Warehousing; RE, includes rental and leasing: Real Estate; Art, Entertainment includes recreation, accommodation and food services; BS: business services
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The NBER dates recessions in the US from peaks to troughs as: IQ80 to IIIQ80, IIIQ81 to IV82 and IVQ07 to IIQ09 (http://www.nber.org/cycles/cyclesmain.html). Table I-12 provides total annual level nonfarm employment in the US for the 1980s and the 2000s, which is different from 12-month comparisons. Nonfarm jobs rose by 4.859 million from 1982 to 1984, or 5.4 percent, and continued rapid growth in the rest of the decade. In contrast, nonfarm jobs are down by 7.661 million in 2010 relative to 2007 and fell by 958,000 in 2010 relative to 2009 even after six quarters of GDP growth. Monetary and fiscal stimuli have failed in increasing growth to rates required for mitigating job stress. The initial growth impulse reflects a flatter growth curve in the current expansion. Nonfarm jobs declined from 137.936 million in 2007 to 136.368 million in 2013, by 1.568 million or 1.1 percent. Nonfarm jobs increased from 137.936 million in 2007 to 138.907 million in 2014, by 0.971 million or 0.7 percent. The US noninstitutional population or in condition to work increased from 231.867 million in 2007 to 247.947 million in 2014, by 16.080 million or 6.9 percent. The ratio of nonfarm jobs of 137.936 million in 2007 to the noninstitutional population of 231.867 was 59.5. Nonfarm jobs in 2014 corresponding to the ratio of 59.5 of nonfarm jobs/noninstitutional population would be 147.528 million (0.595x247.947). The difference between actual nonfarm jobs of 138.907 million in 2014 and nonfarm jobs of 147.528 million that are equivalent to 59.5 percent of the noninstitutional population as in 2007 is 8.621 million. The proper explanation for this loss of work opportunities is not in secular stagnation but in cyclically slow growth. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2014 would have accumulated to 23.0 percent. GDP in IIIQ2014 would be $18,438.0 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2,232.4 billion than actual $16,205.6 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 25.9 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment of 15.7 percent of the effective labor force (Section I and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/financial-risks-twenty-six-million.html
and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/rules-discretionary-authorities-and.html). US GDP in IIIQ2014 is 12.1 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,205.1 billion in IIIQ2014 or 8.1 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.1 percent. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. The long-term trend is growth at average 3.3 percent per year from Jan 1919 to Nov 2014. Growth at 3.3 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 99.2392 in Dec 2007 to 124.2256 in Nov 2014. The actual index NSA in Nov 2014 is 101.7487, which is 18.1 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.3 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2013, raising the index at trend to 116.1422 in Nov 2014. The output of manufacturing at 101.7487 in Nov 2014 is 12.4 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Table I-12, US, Total Nonfarm Employment in Thousands
| Year | Total Nonfarm | Year | Total Nonfarm |
| 1980 | 90,533 | 2000 | 132,019 |
| 1981 | 91,297 | 2001 | 132,074 |
| 1982 | 89,689 | 2002 | 130,628 |
| 1983 | 90,295 | 2003 | 130,318 |
| 1984 | 94,548 | 2004 | 131,749 |
| 1985 | 97,532 | 2005 | 134,005 |
| 1986 | 99,500 | 2006 | 136,398 |
| 1987 | 102,116 | 2007 | 137,936 |
| 1988 | 105,378 | 2008 | 137,170 |
| 1989 | 108,051 | 2009 | 131,233 |
| 1990 | 109,527 | 2010 | 130,275 |
| 1991 | 108,427 | 2011 | 131,842 |
| 1992 | 108,802 | 2012 | 134,104 |
| 1993 | 110,935 | 2013 | 136,368 |
| 1994 | 114,398 | 2014 | 138,907 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/
Chart I-43 provides annual nonfarm jobs in the US not seasonally adjusted from 2000 to 2013. Cyclically slow growth in the expansion since IIIQ2009 has not been sufficient to recover nonfarm jobs. Because of population growth, there are 8.621 million fewer nonfarm jobs in the US in 2014 than in 2007.
Chart I-43, US, Annual Nonfarm Jobs, NSA, Thousands, 2000-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/
Chart I-44 provides annual nonfarm jobs in the US not seasonally adjusted from 1980 to 1993. Much more rapid cyclical growth as in other expansions historically allowed steady and rapid growth of nonfarm job opportunities even with similarly dynamic population growth.
Chart I-44, US, Annual Nonfarm Jobs, NSA, Thousands, 1980-1994
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov
The highest average yearly percentage of unemployed to the labor force since 1940 was 14.6 percent in 1940 followed by 9.9 percent in 1941, 8.5 percent in 1975, 9.7 percent in 1982 and 9.6 percent in 1983 (ftp://ftp.bls.gov/pub/special.requests/lf/aa2006/pdf/cpsaat1.pdf). The rate of unemployment remained at high levels in the 1930s, rising from 3.2 percent in 1929 to 22.9 percent in 1932 in one estimate and 23.6 percent in another with real wages increasing by 16.4 percent (Margo 1993, 43; see Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 214-5). There are alternative estimates of 17.2 percent or 9.5 percent for 1940 with real wages increasing by 44 percent. Employment declined sharply during the 1930s. The number of hours worked remained in 1939 at 29 percent below the level of 1929 (Cole and Ohanian 1999). Private hours worked fell in 1939 to 25 percent of the level in 1929. The policy of encouraging collusion through the National Industrial Recovery Act (NIRA), to maintain high prices, together with the National Labor Relations Act (NLRA), to maintain high wages, prevented the US economy from recovering employment levels until Roosevelt abandoned these policies toward the end of the 1930s (for review of the literature analyzing the Great Depression see Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 198-217).
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) makes yearly revisions of its establishment survey (Harris 2011BA):
“With the release of data for January 2011, the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) introduced its annual revision of national estimates of employment, hours, and earnings from the Current Employment Statistics (CES) monthly survey of nonfarm establishments. Each year, the CES survey realigns its sample-based estimates to incorporate universe counts of employment—a process known as benchmarking. Comprehensive counts of employment, or benchmarks, are derived primarily from unemployment insurance (UI) tax reports that nearly all employers are required to file with State Workforce Agencies.”
The number of not seasonally adjusted total private jobs in the US in Dec 2010 is 108.464 million, declining to 106.079 million in Jan 2011, or by 2.385 million, because of the adjustment of a different benchmark and not actual job losses. The not seasonally adjusted number of total private jobs in Dec 1984 is 80.250 million, declining to 78.704 million in Jan 1985, or by 1.546 million for the similar adjustment. Table I-13 attempts to measure job losses and gains in the recessions and expansions of 1981-1985 and 2007-2011. The final ten rows provide job creation from May 1983 to May 1984 and from May 2010 to May 2011, that is, at equivalent stages of the recovery from two comparable strong recessions. The row “Change ∆%” for May 1983 to May 1984 shows an increase of total nonfarm jobs by 4.9 percent and of 5.9 percent for total private jobs. The row “Change ∆%” for May 2010 to May 2011 shows an increase of total nonfarm jobs by 0.7 percent and of 1.7 percent for total private jobs. The last two rows of Table 7 provide a calculation of the number of jobs that would have been created from May 2010 to May 2011 if the rate of job creation had been the same as from May 1983 to May 1984. If total nonfarm jobs had grown between May 2010 and May 2011 by 4.9 percent, as between May 1983 and May 1984, 6.409 million jobs would have been created in the past 12 months for a difference of 5.457 million more total nonfarm jobs relative to 0.952 million jobs actually created. If total private jobs had grown between May 2010 and May 2011 by 5.9 percent as between May 1983 and May 1984, 6.337 million private jobs would have been created for a difference of 4.539 million more total private jobs relative to 1.798 million jobs actually created.
Table I-13, US, Total Nonfarm and Total Private Jobs Destroyed and Subsequently Created in Two Recessions IIIQ1981-IVQ1982 and IVQ2007-IIQ2009, Thousands and Percent
| Total Nonfarm Jobs | Total Private Jobs | |
| 06/1981 # | 92,288 | 75,969 |
| 11/1982 # | 89,482 | 73,260 |
| Change # | -2,806 | -2,709 |
| Change ∆% | -3.0 | -3.6 |
| 12/1982 # | 89,383 | 73,185 |
| 05/1984 # | 94,471 | 78,049 |
| Change # | 5,088 | 4,864 |
| Change ∆% | 5.7 | 6.6 |
| 11/2007 # | 139,090 | 116,291 |
| 05/2009 # | 131,626 | 108,601 |
| Change % | -7,464 | -7,690 |
| Change ∆% | -5.4 | -6.6 |
| 12/2009 # | 130,178 | 107,338 |
| 05/2011 # | 131,753 | 108,494 |
| Change # | 1,575 | 1,156 |
| Change ∆% | 1.2 | 1.1 |
| 05/1983 # | 90,005 | 73,667 |
| 05/1984 # | 94,471 | 78,049 |
| Change # | 4,466 | 4,382 |
| Change ∆% | 4.9 | 5.9 |
| 05/2010 # | 130,801 | 107,405 |
| 05/2011 # | 131,753 | 109,203 |
| Change # | 952 | 1,798 |
| Change ∆% | 0.7 | 1.7 |
| Change # by ∆% as in 05/1984 to 05/1985 | 6,409* | 6,337** |
| Difference in Jobs that Would Have Been Created | 5,457 = | 4,539 = |
*[(130,801x1.049)-130,801] = 6,409 thousand
**[(107,405)x1.059 – 107,405] = 6,337 thousand
Source: http://www.bls.gov/data/
IB Stagnating Real Wages. The wage bill is the product of average weekly hours times the earnings per hour. Table IB-1 provides the estimates by the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) of earnings per hour seasonally adjusted, increasing from $24.17/hour in Dec 2013 to $24.57/hour in Dec 2014, or by 1.7 percent. There has been disappointment about the pace of wage increases because of rising food and energy costs that inhibit consumption and thus sales and similar concern about growth of consumption that accounts for about 68.2 percent of GDP (Table I-10 at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html). Growth of consumption by decreasing savings by means of controlling interest rates in what is called financial repression may not be lasting and sound for personal finances (See Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008c), 81-6, Pelaez (1975), http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/growth-uncertainties-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/geopolitical-and-financial-risks.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/fluctuating-financial-valuations.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/06/financial-indecision-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/06/financial-instability-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/financial-uncertainty-mediocre-cyclical.html
http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/02/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/collapse-of-united-states-dynamism-of.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/11/global-financial-risk-mediocre-united.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/09/mediocre-and-decelerating-united-states.html
http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/09/increasing-interest-rate-risk.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/08/risks-of-steepening-yield-curve-and.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html
http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/mediocre-united-states-economic-growth.html
http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/04/mediocre-and-decelerating-united-states.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/03/mediocre-gdp-growth-at-16-to-20-percent.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/12/mediocre-and-decelerating-united-states_24.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/12/mediocre-and-decelerating-united-states.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/09/historically-sharper-recoveries-from.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/09/collapse-of-united-states-dynamism-of.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/07/recovery-without-jobs-stagnating-real.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/mediocre-recovery-without-jobs.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/04/mediocre-growth-with-high-unemployment.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/04/mediocre-economic-growth-falling-real.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/03/mediocre-economic-growth-flattening.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/01/mediocre-economic-growth-financial.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/12/slow-growth-falling-real-disposable.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/11/us-growth-standstill-falling-real.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/10/slow-growth-driven-by-reducing-savings.html). Average hourly earnings seasonally adjusted decreased 0.2 percent from $24.62 in Nov 2014 to $24.57 in Dec 2014. Average private weekly earnings increased $21.09 from $829.03 in Dec 2013 to $850.12 in Dec 2014 or 2.5 percent and decreased from $851.85 in Nov 2014 to $850.12 in Dec 2014 or 0.72percent. The inflation-adjusted wage bill can only be calculated for Nov, which is the most recent month for which there are estimates of the consumer price index. Earnings per hour (not-seasonally-adjusted (NSA)) rose from $24.11 in Nov 2013 to $24.74 in Nov 2014 or by 2.6 percent (http://www.bls.gov/data/; see Table IB-3 below). Data NSA are more suitable for comparison over a year. Average weekly hours NSA were 34.4 in Nov 2013 and 34.9 in Nov 2014 (http://www.bls.gov/data/; see Table IB-2 below). The wage bill increased 4.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2014:
{[(wage bill in Nov 2014)/(wage bill in Nov 2013)]-1}100 =
{[($24.74x34.9)/($24.11x34.4)]-1]}100
= {[($863.43)/($829.38)]-1}100 = 4.1%
CPI inflation was 1.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2014 (http://www.bls.gov/cpi/) for an inflation-adjusted wage-bill change of 2.8 percent :{[(1.041/1.013)-1]100 = 2.8 %} (see Table IB-5 below for Nov 2014 with minor rounding difference). The wage bill for Dec 2014 before inflation adjustment increased 0.8 percent relative to the wage bill for Dec 2013:
{[(wage bill in Dec 2014)/(wage bill in Dec 2013)]-1}100 =
{[($24.56x34.6)/($24.30x34.7)]-1]}100
= {[$849.78)/($843.21]-1}100 = 0.8%
Average hourly earnings increased 1.1 percent from Dec 2013 to Dec 2014 {[($24.56/$24.30) – 1]100 = 1.1%} while hours worked decreased 1.5 percent {[(34.6/34.7) – 1]100 = 0.3%}. The increase of the wage bill is the product of the increase of hourly earnings of 1.1 percent and decrease of hours worked of 0.3 percent {[(1.011x0.997) -1]100 = 0.8%}.
Energy and food price increases are similar to a “silent tax” that is highly regressive, harming the most those with lowest incomes. There are concerns that the wage bill would deteriorate in purchasing power because of renewed raw materials shocks in the form of increases in prices of commodities such as the 31.1 percent steady increase in the DJ-UBS Commodity Index from Jul 2, 2010 to Sep 2, 2011. The charts of four commodity price indexes by Bloomberg show steady increase since Jul 2, 2010 that was interrupted briefly only in Nov 2010 with the sovereign issues in Europe triggered by Ireland; in Mar 2011 by the earthquake and tsunami in Japan; and in the beginning of May 2011 by the decline in oil prices and sovereign risk difficulties in Europe (http://www.bloomberg.com/markets/commodities/futures/). Renewed risk aversion because of the sovereign risks in Europe had reduced the rate of increase of the DJ UBS commodity index to 10.2 percent on May 2, 2014, relative to Jul 2, 2010 (see Table VI-4) but there has been a shift in investor preferences into equities. Inflation has been rising in waves with carry trades driven by zero interest rates to commodity futures during periods of risk appetite with interruptions during risk aversion (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html). Inflation-adjusted wages fall sharply during carry trades from zero interest rates to long positions in commodity futures during periods of risk appetite.
Table IB-1, US, Earnings per Hour and Average Weekly Hours SA
| Earnings per Hour | Dec 2013 | Oct 2014 | Nov 2014 | Dec 2014 |
| Total Private | $24.17 | $24.56 | $24.62 | $24.57 |
| Goods Producing | $25.44 | $25.84 | $25.87 | $25.81 |
| Service Providing | $23.87 | $24.26 | $24.33 | $24.28 |
| Average Weekly Earnings | ||||
| Total Private | $829.03 | $847.32 | $851.85 | $850.12 |
| Goods Producing | $1,027.78 | $1,049.10 | $1,052.91 | $1,050.47 |
| Service Providing | $790.10 | $810.28 | $812.62 | $810.95 |
| Average Weekly Hours | ||||
| Total Private | 34.3 | 34.5 | 34.6 | 34.6 |
| Goods Producing | 40.4 | 40.6 | 40.7 | 40.7 |
| Service Providing | 33.1 | 33.4 | 33.4 | 33.4 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Average weekly hours in Table IB-2 fell from 34.9 in Dec 2007 at the beginning of the contraction to 33.8 in Jun 2009, which was the last month of the contraction. Average weekly hours rose to 34.4 in Dec 2011 and oscillated to 34.9 in Dec 2012 and 34.7 in Dec 2013. Average weekly hours of all employees decreased to 34.6 in Dec 2014.
Table IB-2, US, Average Weekly Hours of All Employees, NSA 2006-2014
| Year | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Annual |
| 2006 | 34.2 | 34.6 | 34.3 | 34.6 | 34.9 | 34.6 | 34.5 | 34.9 | 34.4 | 34.6 | |||
| 2007 | 34.1 | 34.1 | 34.3 | 34.7 | 34.4 | 34.7 | 34.9 | 34.7 | 35.0 | 34.5 | 34.5 | 34.9 | 34.6 |
| 2008 | 34.1 | 34.2 | 34.7 | 34.4 | 34.4 | 34.9 | 34.5 | 34.6 | 34.4 | 34.4 | 34.6 | 34.1 | 34.4 |
| 2009 | 33.8 | 34.2 | 33.9 | 33.6 | 33.7 | 33.8 | 33.8 | 34.3 | 33.7 | 33.8 | 34.2 | 33.9 | 33.9 |
| 2010 | 33.7 | 33.6 | 33.8 | 34.0 | 34.4 | 34.1 | 34.2 | 34.7 | 34.1 | 34.3 | 34.2 | 34.2 | 34.1 |
| 2011 | 34.2 | 34.0 | 34.1 | 34.2 | 34.6 | 34.4 | 34.4 | 34.4 | 34.4 | 34.8 | 34.3 | 34.4 | 34.4 |
| 2012 | 34.5 | 34.2 | 34.2 | 34.6 | 34.2 | 34.4 | 34.8 | 34.5 | 34.9 | 34.3 | 34.3 | 34.9 | 34.5 |
| 2013 | 34.0 | 34.2 | 34.3 | 34.3 | 34.3 | 34.9 | 34.3 | 34.5 | 34.9 | 34.4 | 34.4 | 34.7 | 34.4 |
| 2014 | 34.0 | 34.4 | 34.7 | 34.4 | 34.4 | 34.9 | 34.5 | 34.6 | 34.5 | 34.5 | 34.9 | 34.6 | 34.5 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart IB-1 provides average weekly hours monthly from Mar 2006 to May 2014. Average weekly hours remained relatively stable in the period before the contraction and fell sharply during the contraction as business could not support lower production with the same labor input. Average weekly hours rose rapidly during the expansion but have stabilized at a level below that prevailing before the contraction.
Chart IB-1, US, Average Weekly Hours of All Employees, SA 2006-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Calculations of inflation-adjusted average hourly earnings using BLS data are in Table IB-3. The final column of Table IB-3 (“12-Month Real ∆%”) provides inflation-adjusted average hourly earnings of all employees in the US. Average hourly earnings rose above inflation throughout the first nine months of 2007 just before the global recession that began in the final quarter of 2007 when average hourly earnings began to lose to inflation. In contrast, average hourly earnings of all US workers have risen less than inflation in four months in 2010 and in all but the first month in 2011 and the loss accelerated at 1.8 percent in Sep 2011, declining to a real loss of 1.1 percent in Feb 2012 and 0.6 percent in Mar 2012. There was a gain of 0.5 percent in Apr 2012 in inflation-adjusted average hourly earnings but another fall of 0.6 percent in May 2012 followed by increases of 0.3 percent in Jun and 1.0 percent in Jul 2012. Real hourly earnings stagnated in the 12 months ending in Aug 2012 with increase of only 0.1 percent, and increased 0.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep 2012. Real hourly earnings fell 1.3 percent in Oct 2012 and gained 1.0 percent in Dec 2012 but declined 0.3 percent in Jan 2013 and stagnated at change of 0.1 percent in Feb 2013. Real hourly earnings increased 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Mar 2013 and 0.2 percent in Apr 2013, increasing 0.6 percent in May 2013. In Jun 2013, real hourly earnings increased 1.0 percent relative to Jun 2012. Real hourly earnings fell 0.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Jul 2013 and increased 0.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2013. Real hourly earnings increased 1.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2013 and 1.0 percent in Nov 2013. Real hourly earnings increased 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2013. Real hourly earnings increased 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2014 and 1.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Feb 2014. Real hourly earnings increased 1.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Mar 2014. Real hourly earnings fell 0.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Apr 2014. Real hourly earnings stagnated at 0.0 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2014. Real hourly earnings fell 0.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2014. Real hourly earnings changed 0.0 percent in the 12 months ending in Jul 2014 and increased 0.5 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2014. Real hourly earnings fell 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep 2014 and increased 0.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2014. Real hourly earnings increased 1.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2014. Real hourly earnings are oscillating in part because of world inflation waves caused by carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html) and in part because of the collapse of hiring (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/global-financial-and-economic-risk.html) originating in weak economic growth (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html).
Table IB-3, US, Average Hourly Earnings Nominal and Inflation Adjusted, Dollars and % NSA
| AHE ALL | 12 Month- | ∆% 12 Month CPI | 12-Month | |
| 2007 | ||||
| Jan* | $20.69* | 4.2* | 2.1 | 2.1* |
| Feb* | $20.77* | 4.1* | 2.4 | 1.7* |
| Mar | $20.80 | 3.6 | 2.8 | 0.8 |
| Apr | $21.03 | 3.3 | 2.6 | 0.7 |
| May | $20.82 | 3.8 | 2.7 | 1.1 |
| Jun | $20.81 | 3.8 | 2.7 | 1.1 |
| Jul | $20.97 | 3.4 | 2.4 | 1.0 |
| Aug | $20.83 | 3.5 | 2.0 | 1.5 |
| Sep | $21.17 | 4.0 | 2.8 | 1.2 |
| Oct | $21.05 | 2.6 | 3.5 | -0.9 |
| Nov | $21.12 | 3.3 | 4.3 | -1.0 |
| Dec | $21.35 | 3.6 | 4.1 | -0.5 |
| 2010 | ||||
| Jan | $22.53 | 2.0 | 2.6 | -0.6 |
| Feb | $22.59 | 1.4 | 2.1 | -0.7 |
| Mar | $22.49 | 1.1 | 2.3 | -1.2 |
| Apr | $22.54 | 1.8 | 2.2 | -0.4 |
| May | $22.61 | 2.5 | 2.0 | 0.5 |
| Jun | $22.35 | 1.7 | 1.1 | 0.6 |
| Jul | $22.42 | 1.8 | 1.2 | 0.6 |
| Aug | $22.55 | 1.7 | 1.1 | 0.6 |
| Sep | $22.61 | 1.8 | 1.1 | 0.7 |
| Oct | $22.70 | 1.9 | 1.2 | 0.7 |
| Nov | $22.70 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 0.0 |
| Dec | $22.77 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 0.2 |
| 2011 | ||||
| Jan | $23.17 | 2.8 | 1.6 | 1.2 |
| Feb | $23.00 | 1.8 | 2.1 | -0.3 |
| Mar | $22.91 | 1.9 | 2.7 | -0.8 |
| Apr | $22.97 | 1.9 | 3.2 | -1.3 |
| May | $23.07 | 2.0 | 3.6 | -1.5 |
| Jun | $22.82 | 2.1 | 3.6 | -1.4 |
| Jul | $22.95 | 2.4 | 3.6 | -1.2 |
| Aug | $22.86 | 1.4 | 3.8 | -2.3 |
| Sep | $23.06 | 2.0 | 3.9 | -1.8 |
| Oct | $23.31 | 2.7 | 3.5 | -0.8 |
| Nov | $23.16 | 2.0 | 3.4 | -1.4 |
| Dec | $23.22 | 2.0 | 3.0 | -1.0 |
| 2012 | ||||
| Jan | $23.57 | 1.7 | 2.9 | -1.2 |
| Feb | $23.41 | 1.8 | 2.9 | -1.1 |
| Mar | $23.40 | 2.1 | 2.7 | -0.6 |
| Apr | $23.62 | 2.8 | 2.3 | 0.5 |
| May | $23.33 | 1.1 | 1.7 | -0.6 |
| Jun | $23.28 | 2.0 | 1.7 | 0.3 |
| Jul | $23.49 | 2.4 | 1.4 | 1.0 |
| Aug | $23.27 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 0.1 |
| Sep | $23.68 | 2.7 | 2.0 | 0.7 |
| Oct | $23.52 | 0.9 | 2.2 | -1.3 |
| Nov | $23.59 | 1.9 | 1.8 | 0.1 |
| Dec | $23.85 | 2.7 | 1.7 | 1.0 |
| 2013 | ||||
| Jan | $23.88 | 1.3 | 1.6 | -0.3 |
| Feb | $23.91 | 2.1 | 2.0 | 0.1 |
| Mar | $23.84 | 1.9 | 1.5 | 0.4 |
| Apr | $23.92 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 0.2 |
| May | $23.80 | 2.0 | 1.4 | 0.6 |
| Jun | $23.93 | 2.8 | 1.8 | 1.0 |
| Jul | $23.81 | 1.4 | 2.0 | -0.6 |
| Aug | $23.79 | 2.2 | 1.5 | 0.7 |
| Sep | $24.16 | 2.0 | 1.2 | 0.8 |
| Oct | $24.04 | 2.2 | 1.0 | 1.2 |
| Nov | $24.11 | 2.2 | 1.2 | 1.0 |
| Dec | $24.30 | 1.9 | 1.5 | 0.4 |
| 2014 | ||||
| Jan | $24.35 | 2.0 | 1.6 | 0.4 |
| Feb | $24.58 | 2.8 | 1.1 | 1.7 |
| Mar | $24.48 | 2.7 | 1.5 | 1.2 |
| Apr | $24.38 | 1.9 | 2.0 | -0.1 |
| May | $24.29 | 2.1 | 2.1 | 0.0 |
| Jun | $24.40 | 2.0 | 2.1 | -0.1 |
| Jul | $24.29 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 0.0 |
| Aug | $24.31 | 2.2 | 1.7 | 0.5 |
| Sep | $24.48 | 1.3 | 1.7 | -0.4 |
| Oct | $24.51 | 2.0 | 1.7 | 0.3 |
| Nov | $24.74 | 2.6 | 1.3 | 1.3 |
| Dec | $24.56 | 1.1 |
Note: AHE ALL: average hourly earnings of all employees; CPI: consumer price index; Real: adjusted by CPI inflation; NA: not available
*AHE of production and nonsupervisory employees because of unavailability of data for all employees for Jan-Feb 2006
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Calculations of inflation-adjusted average hourly earnings using BLS data are in Table IB-3. The final column of Table IB-3 (“12-Month Real ∆%”) provides inflation-adjusted average hourly earnings of all employees in the US. Average hourly earnings rose above inflation throughout the first nine months of 2007 just before the global recession that began in the final quarter of 2007 when average hourly earnings began to lose to inflation. In contrast, average hourly earnings of all US workers have risen less than inflation in four months in 2010 and in all but the first month in 2011 and the loss accelerated at 1.8 percent in Sep 2011, declining to a real loss of 1.1 percent in Feb 2012 and 0.6 percent in Mar 2012. There was a gain of 0.6 percent in Apr 2012 in inflation-adjusted average hourly earnings but another fall of 0.6 percent in May 2012 followed by increases of 0.3 percent in Jun and 0.9 percent in Jul 2012. Real hourly earnings stagnated in the 12 months ending in Aug 2012 with increase of only 0.1 percent, and increased 0.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep 2012. Real hourly earnings fell 1.2 percent in Oct 2012 and gained 1.0 percent in Dec 2012 but declined 0.3 percent in Jan 2013 and stagnated at change of 0.2 percent in Feb 2013. Real hourly earnings increased 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Mar 2013 and 0.2 percent in Apr 2013, increasing 0.7 percent in May 2013. In Jun 2013, real hourly earnings increased 1.1 percent relative to Jun 2012. Real hourly earnings fell 0.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Jul 2013 and increased 0.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2013. Real hourly earnings increased 1.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2013 and 0.9 percent in Nov 2013. Real hourly earnings increased 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2013. Real hourly earnings increased 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2014 and 1.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Feb 2014. Real hourly earnings increased 1.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Mar 2014. Real hourly earnings fell 0.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Apr 2014. Real hourly earnings fell 0.1 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2014. Real hourly earnings fell 0.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2014. Real hourly earnings increased 0.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Jul 2014 and increased 0.5 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2014. Real hourly earnings fell 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep 2014 and increased 0.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2014. Real hourly earnings increased 1.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2014. Real hourly earnings are oscillating in part because of world inflation waves caused by carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html) and in part because of the collapse of hiring (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/global-financial-and-economic-risk.html) originating in weak economic growth (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html).
Table IB-4, US, Average Hourly Earnings of All Employees NSA in Constant Dollars of 1982-1984
| Year | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
| 2006 | 9.91 | 9.88 | 9.97 | 9.87 | 10.03 | 10.16 | 10.14 | 10.21 |
| 2007 | 10.01 | 9.99 | 10.07 | 10.02 | 10.15 | 10.07 | 10.05 | 10.16 |
| 2008 | 9.90 | 9.83 | 9.76 | 9.82 | 9.93 | 10.05 | 10.36 | 10.46 |
| 2009 | 10.31 | 10.19 | 10.23 | 10.28 | 10.29 | 10.31 | 10.38 | 10.37 |
| 2010 | 10.36 | 10.25 | 10.28 | 10.33 | 10.35 | 10.38 | 10.37 | 10.39 |
| 2011 | 10.21 | 10.11 | 10.16 | 10.09 | 10.16 | 10.29 | 10.24 | 10.29 |
| 2012 | 10.15 | 10.14 | 10.25 | 10.10 | 10.23 | 10.17 | 10.25 | 10.39 |
| ∆%12M | -0.6 | 0.3 | 0.9 | 0.1 | 0.7 | -1.2 | 0.1 | 1.0 |
| 2013 | 10.22 | 10.25 | 10.19 | 10.17 | 10.32 | 10.29 | 10.34 | 10.43 |
| ∆%12M | 0.7 | 1.1 | -0.6 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 0.9 | 0.4 |
| 2014 | 10.21 | 10.24 | 10.20 | 10.22 | 10.28 | 10.32 | 10.48 | |
| ∆%12M | -0.1 | -0.1 | 0.1 | 0.5 | -0.4 | 0.3 | 1.4 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart IB-2 of the US Bureau of Labor Statistics plots average hourly earnings of all US employees in constant 1982-1984 dollars with evident decline from annual earnings of $10.34 in 2009 and $10.35 in 2010 to $10.24 in 2011 and $10.24 again in 2012 or loss of 1.1 percent (data in http://www.bls.gov/data/). Annual real hourly earnings increased 0.5 percent in 2013 relative to 2012. The economic welfare or wellbeing of United States workers deteriorated in a recovery without hiring (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/global-financial-and-economic-risk.html), stagnating/declining real wages and 25.9 million unemployed or underemployed (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/financial-risks-twenty-six-million.html) because of mediocre economic growth (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html).
Chart IB-2, US, Average Hourly Earnings of All Employees in Constant Dollars of 1982-1984, SA 2006-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/
Chart IB-3 provides 12-month percentage changes of average hourly earnings of all employees in constant dollars of 1982-1984, that is, adjusted for inflation. There was sharp contraction of inflation-adjusted average hourly earnings of US employees during parts of 2007 and 2008. Rates of change in 12 months became positive in parts of 2009 and 2010 but then became negative again in 2011 and into 2012 with temporary increase in Apr 2012 that was reversed in May with another gain in Jun and Jul 2012 followed by stagnation in Aug 2012. There was marginal gain in Sep 2012 with sharp decline in Oct 2012, stagnation in Nov 2012, increase in Dec 2012 and renewed decrease in Jan 2013 with near stagnation in Feb 2013 followed by mild increase in Mar-Apr 2013. Hourly earnings adjusted for inflation increased in Jun 2013 and fell in Jul 2013, increasing in Aug-Dec 2013 and Jan-Mar 2014. Average hourly earnings decreased in Apr-May 2014 and rebounded mildly in Jun-Jul 2014, increasing in Aug 2014 and decreasing in Sep 2014. Average hourly earnings increased in Oct-Nov 2014.
Chart IB-3, Average Hourly Earnings of All Employees NSA 12-Month Percent Change, 1982-1984 Dollars, NSA 2007-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/
Average weekly earnings of all US employees in the US in constant dollars of 1982-1984 from the dataset of the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) are provided in Table IB-5. Average weekly earnings fell 3.2 percent after adjusting for inflation in the 12 months ending in Aug 2011, decreased 0.9 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep 2011 and increased 0.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2011. Average weekly earnings fell 1.0 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2011 and 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2011. Average weekly earnings declined 0.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2012 and 0.5 percent in the 12 months ending in Feb 2012. Average weekly earnings in constant dollars were virtually flat in Mar 2012 relative to Mar 2011, decreasing 0.2 percent. Average weekly earnings in constant dollars increased 1.7 percent in Apr 2012 relative to Apr 2011 but fell 1.7 percent in May 2012 relative to May 2011, increasing 0.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2012 and 2.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Jul 2012. Real weekly earnings increased 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2012 and 2.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep 2012. Real weekly earnings fell 2.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2012 and increased 0.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2012 and 2.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2012. Real weekly earnings fell 1.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2013 and virtually stagnated with gain of 0.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Feb 2013, increasing 0.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Mar 2013. Real weekly earnings fell 0.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Apr 2013 and increased 0.9 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2013. Average weekly earnings increased 2.5 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2013 and fell 2.0 percent in the 12 months ending in Jul 2013. Real weekly earnings increased 0.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2013, 0.8 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep 2013 and 1.5 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2013. Average weekly earnings increased 1.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2013 and fell 0.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2013. Average weekly earnings increased 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2014 and 2.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Feb 2014. Average weekly earnings increased 2.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Mar 2014 and 0.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Apr 2014. Average weekly earnings in constant dollars increased 0.2 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2014 and fell 0.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2014. Real average weekly earnings increased 0.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Jul 2014 and 0.8 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2014.
Real weekly earnings decreased 1.5 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep 2014 and increased 0.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2014. Average weekly earnings increased 2.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2014. Table I-5 confirms the trend of deterioration of purchasing power of average weekly earnings in 2011 and into 2013 with oscillations according to carry trades causing world inflation waves (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html). On an annual basis, average weekly earnings in constant 1982-1984 dollars increased from $349.34 in 2007 to $354.16 in 2013, by 1.4 percent or at the average rate of 0.2 percent per year (data in http://www.bls.gov/data/). Annual average weekly earnings in constant dollars of $353.11 in 2010 were virtually unchanged at $353.00 in 2012. Those who still work bring back home a paycheck that buys fewer high-quality goods than a year earlier. The fractured US job market does not provide an opportunity for advancement as in past booms following recessions because of poor job creation with 25.9 million unemployed or underemployed (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/financial-risks-twenty-six-million.html) in a recovery without hiring (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/global-financial-and-economic-risk.html) because of mediocre economic growth (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html).
Table IB-5, US, Average Weekly Earnings of All Employees in Constant Dollars of 1982-1984, NSA 2007-2014
| Year | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov |
| 2006 | 341.73 | 347.80 | 341.42 | 346.02 | 354.71 | 348.95 |
| 2007 | 346.58 | 351.35 | 347.64 | 355.39 | 347.58 | 346.68 |
| 2008 | 343.08 | 336.75 | 339.86 | 341.51 | 345.63 | 358.50 |
| 2009 | 344.28 | 345.61 | 352.48 | 346.72 | 348.35 | 355.07 |
| 2010 | 349.66 | 351.71 | 358.43 | 352.96 | 356.00 | 354.81 |
| 2011 | 347.78 | 349.45 | 347.12 | 349.62 | 358.27 | 351.14 |
| 2012 | 348.98 | 356.80 | 348.48 | 357.13 | 348.76 | 351.46 |
| ∆%12M | 0.3 | 2.1 | 0.4 | 2.1 | -2.7 | 0.1 |
| 2013 | 357.66 | 349.61 | 350.94 | 360.10 | 354.10 | 355.85 |
| ∆%12M | 2.5 | -2.0 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 1.2 |
| 2014 | 357.28 | 351.74 | 353.64 | 354.81 | 356.14 | 365.63 |
| ∆%12M | -0.1 | 0.6 | 0.8 | -1.5 | 0.6 | 2.7 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/
Chart IB-4 provides average weekly earnings of all employees in constant dollars of 1982-1984. The same pattern emerges of sharp decline during the contraction, followed by recovery in the expansion and continuing fall with oscillations caused by carry trades from zero interest rates into commodity futures from 2010 to 2011 and into 2012-2014.
Chart IB-4, US, Average Weekly Earnings of All Employees in Constant Dollars of 1982-1984, SA 2006-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/
Chart IB-5 provides 12-month percentage changes of average weekly earnings of all employees in the US in constant dollars of 1982-1984. There is the same pattern of contraction during the global recession in 2008 and then again trend of deterioration in the recovery without hiring and inflation waves. (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/10/financial-oscillations-world-inflation.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/monetary-policy-world-inflation-waves.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/world-inflation-waves-united-states.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/06/valuation-risks-world-inflation-waves.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/05/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/04/imf-view-world-inflation-waves-squeeze.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/interest-rate-risks-world-inflation.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/01/world-inflation-waves-interest-rate.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/tapering-quantitative-easing-mediocre.html
http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/11/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-world.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/10/world-inflation-waves-regional-economic.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/08/duration-dumping-and-peaking-valuations.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html
http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/paring-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/05/word-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/04/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/04/recovery-without-hiring-ten-million.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/04/mediocre-and-decelerating-united-states.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/02/world-inflation-waves-united-states.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/12/recovery-without-hiring-forecast-growth.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/11/united-states-unsustainable-fiscal.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/09/recovery-without-hiring-world-inflation.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012_09_01_archive.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/07/world-inflation-waves-financial.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/destruction-of-three-trillion-dollars.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/05/world-inflation-waves-monetary-policy.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/recovery-without-hiring-continuance-of.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/04/fractured-labor-market-with-hiring.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/03/global-financial-and-economic-risk.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/02/world-inflation-waves-united-states.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/01/world-inflation-waves-united-states.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/01/recovery-without-hiring-united-states.html
http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/09/recovery-without-hiring-world-inflation.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012_09_01_archive.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/07/world-inflation-waves-financial.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/05/world-inflation-waves-monetary-policy.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/recovery-without-hiring-continuance-of.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/04/fractured-labor-market-with-hiring.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/03/global-financial-and-economic-risk.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/02/world-inflation-waves-united-states.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/01/world-inflation-waves-united-states.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/01/recovery-without-hiring-united-states.html).
Chart IB-5, US, Average Weekly Earnings of All Employees NSA in Constant Dollars of 1982-1984 12-Month Percent Change, NSA 2007-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/
IIA United States International Trade. Table IIA-1 provides the trade balance of the US and monthly growth of exports and imports seasonally adjusted with the latest release and revisions (http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/). Because of heavy dependence on imported oil, fluctuations in the US trade account originate largely in fluctuations of commodity futures prices caused by carry trades from zero interest rates into commodity futures exposures in a process similar to world inflation waves (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html). The Census Bureau revised data for 2014, 2013 and 2012. Exports decreased 1.2 percent from Sep to Nov 2014 while imports decreased 1.5 percent. The trade deficit decreased from $43.603 million in Sep 2014 to $39.001 million in Nov 2014. The US trade balance improved from deficits of $39,083 million in Oct 2013 and $42,263 million in Sep 2013 to deficit of $35,972 million in Nov 2013 but higher deficit of $37,393 million in Dec 2013. The trade deficit increased to $39,181 million in Jan 2014 and deficit of $42,230 million in Feb 2014. The trade deficit increased to $43,124 million in Mar 2014 and $45,914 million in Apr 2014. The deficit improved to $43,562 million in May 2014 and $40,695 million in Jul 2014. The trade deficit improved to $40.031 million in Aug 2014, deteriorating to $43.603 million in Sep 2014 and $42.249 million in Oct 2014. The trade deficit improved to $39.001 million in Nov 2014. Exports increased 1.8 percent from Dec 2013 to Nov 2014 while imports increased 2.2 percent. The trade balance deteriorated from cumulative deficit of $494,658 million in Jan-Dec 2010 to deficit of $548,625 million in Jan-Dec 2011 and improved to marginally lower deficit of $537,605 million in Jan-Dec 2012. The trade deficit improved to $476,392 million in Jan-Dec 2013.
Table IIA-1, US, Trade Balance of Goods and Services Seasonally Adjusted Millions of Dollars and ∆%
| Trade Balance | Exports | Month ∆% | Imports | Month ∆% | |
| Nov 2014 | -39,001 | 196,357 | -1.0 | 235,359 | -2.2 |
| Oct | -42,249 | 198,321 | 1.6 | 240,570 | 0.7 |
| Sep | -43,603 | 195,232 | -1.8 | 238,835 | 0.0 |
| Aug | -40,031 | 198,736 | 0.4 | 238,767 | 0.0 |
| Jul | -40,695 | 198,031 | 1.2 | 238,726 | 0.5 |
| Jun | -41,745 | 195,698 | -0.4 | 237,443 | -1.1 |
| May | -43,562 | 196,559 | 1.2 | 240,121 | 0.0 |
| Apr | -45,914 | 194,318 | 0.2 | 240,233 | 1.3 |
| Mar | -43,124 | 193,940 | 3.3 | 237,064 | 3.1 |
| Feb | -42,230 | 187,773 | -2.4 | 230,003 | -0.7 |
| Jan | -39,181 | 192,475 | -0.2 | 231,655 | 0.6 |
| Dec 2013 | -37,393 | 192,799 | -1.1 | 230,193 | -0.3 |
| Nov | -35,972 | 194,922 | 0.5 | 230,894 | -0.9 |
| Oct | -39,083 | 193,971 | 2.0 | 233,053 | 0.2 |
| Sep | -42,263 | 190,249 | -0.2 | 232,512 | 1.0 |
| Aug | -39,515 | 190,606 | 0.4 | 230,121 | 0.3 |
| Jul | -39,419 | 189,902 | -0.2 | 229,321 | 1.1 |
| Jun | -36,552 | 190,366 | 1.7 | 226,918 | -2.2 |
| May | -44,831 | 187,206 | -0.3 | 232,037 | 1.7 |
| Apr | -40,417 | 187,763 | 0.5 | 228,180 | 1.9 |
| Mar | -36,973 | 186,903 | -0.6 | 223,876 | -2.6 |
| Feb | -41,770 | 188,030 | 0.3 | 229,800 | 0.1 |
| Jan | -42,205 | 187,478 | -1.2 | 229,683 | 1.0 |
| Jan-Dec 2013 | -476,392 | 2,280,194 | 2,756,586 | ||
| Dec 2012 | -37,634 | 189,765 | 1.9 | 227,399 | -2.4 |
| Nov | -46,604 | 186,286 | 1.5 | 232,891 | 3.1 |
| Oct | -42,358 | 183,512 | -2.7 | 225,870 | -1.3 |
| Sep | -40,150 | 188,696 | 3.2 | 228,846 | 0.6 |
| Aug | -44,536 | 182,845 | -0.5 | 227,380 | -0.1 |
| Jul | -43,834 | 183,673 | -0.9 | 227,507 | -0.4 |
| Jun | -43,078 | 185,330 | 0.6 | 228,408 | -1.3 |
| May | -47,184 | 184,306 | -0.1 | 231,490 | -0.4 |
| Apr | -47,773 | 184,543 | -0.9 | 232,317 | -1.6 |
| Mar | -49,850 | 186,257 | 2.5 | 236,107 | 4.9 |
| Feb | -43,338 | 181,720 | 1.2 | 225,058 | -2.5 |
| Jan | -51,266 | 179,606 | 0.2 | 230,873 | 0.2 |
| Jan-Dec 2012 | -537,605 | 2,216,540 | 2,754,145 | ||
| Jan-Dec | -548,625 | 2,127,021 | 2,675,646 | ||
| Jan-Dec | -494,658 | 1,853,606 | 2,348,263 |
Note: Trade Balance of Goods = Exports of Goods less Imports of Goods. Trade balance may not add exactly because of errors of rounding and seasonality. Source: US Census Bureau, Foreign Trade Division
http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
Table IIA-1B provides US exports, imports and the trade balance of goods. The US has not shown a trade surplus in trade of goods since 1976. The deficit of trade in goods deteriorated sharply during the boom years from 2000 to 2007. The deficit improved during the contraction in 2009 but deteriorated in the expansion after 2009. The deficit could deteriorate sharply with growth at full employment.
Table IIA-1B, US, International Trade Balance of Goods, Exports and Imports of Goods, Millions of Dollars, Census Basis
| Balance | ∆% | Exports | ∆% | Imports | ∆% | |
| 1960 | 4,608 | (X) | 19,626 | (X) | 15,018 | (X) |
| 1961 | 5,476 | 18.8 | 20,190 | 2.9 | 14,714 | -2.0 |
| 1962 | 4,583 | -16.3 | 20,973 | 3.9 | 16,390 | 11.4 |
| 1963 | 5,289 | 15.4 | 22,427 | 6.9 | 17,138 | 4.6 |
| 1964 | 7,006 | 32.5 | 25,690 | 14.5 | 18,684 | 9.0 |
| 1965 | 5,333 | -23.9 | 26,699 | 3.9 | 21,366 | 14.4 |
| 1966 | 3,837 | -28.1 | 29,379 | 10.0 | 25,542 | 19.5 |
| 1967 | 4,122 | 7.4 | 30,934 | 5.3 | 26,812 | 5.0 |
| 1968 | 837 | -79.7 | 34,063 | 10.1 | 33,226 | 23.9 |
| 1969 | 1,289 | 54.0 | 37,332 | 9.6 | 36,043 | 8.5 |
| 1970 | 3,224 | 150.1 | 43,176 | 15.7 | 39,952 | 10.8 |
| 1971 | -1,476 | -145.8 | 44,087 | 2.1 | 45,563 | 14.0 |
| 1972 | -5,729 | 288.1 | 49,854 | 13.1 | 55,583 | 22.0 |
| 1973 | 2,389 | -141.7 | 71,865 | 44.2 | 69,476 | 25.0 |
| 1974 | -3,884 | -262.6 | 99,437 | 38.4 | 103,321 | 48.7 |
| 1975 | 9,551 | -345.9 | 108,856 | 9.5 | 99,305 | -3.9 |
| 1976 | -7,820 | -181.9 | 116,794 | 7.3 | 124,614 | 25.5 |
| 1977 | -28,352 | 262.6 | 123,182 | 5.5 | 151,534 | 21.6 |
| 1978 | -30,205 | 6.5 | 145,847 | 18.4 | 176,052 | 16.2 |
| 1979 | -23,922 | -20.8 | 186,363 | 27.8 | 210,285 | 19.4 |
| 1980 | -19,696 | -17.7 | 225,566 | 21.0 | 245,262 | 16.6 |
| 1981 | -22,267 | 13.1 | 238,715 | 5.8 | 260,982 | 6.4 |
| 1982 | -27,510 | 23.5 | 216,442 | -9.3 | 243,952 | -6.5 |
| 1983 | -52,409 | 90.5 | 205,639 | -5.0 | 258,048 | 5.8 |
| 1984 | -106,702 | 103.6 | 223,976 | 8.9 | 330,678 | 28.1 |
| 1985 | -117,711 | 10.3 | 218,815 | -2.3 | 336,526 | 1.8 |
| 1986 | -138,279 | 17.5 | 227,159 | 3.8 | 365,438 | 8.6 |
| 1987 | -152,119 | 10.0 | 254,122 | 11.9 | 406,241 | 11.2 |
| 1988 | -118,526 | -22.1 | 322,426 | 26.9 | 440,952 | 8.5 |
| 1989 | -109,399 | -7.7 | 363,812 | 12.8 | 473,211 | 7.3 |
| 1990 | -101,719 | -7.0 | 393,592 | 8.2 | 495,311 | 4.7 |
| 1991 | -66,723 | -34.4 | 421,730 | 7.1 | 488,453 | -1.4 |
| 1992 | -84,501 | 26.6 | 448,164 | 6.3 | 532,665 | 9.1 |
| 1993 | -115,568 | 36.8 | 465,091 | 3.8 | 580,659 | 9.0 |
| 1994 | -150,630 | 30.3 | 512,626 | 10.2 | 663,256 | 14.2 |
| 1995 | -158,801 | 5.4 | 584,742 | 14.1 | 743,543 | 12.1 |
| 1996 | -170,214 | 7.2 | 625,075 | 6.9 | 795,289 | 7.0 |
| 1997 | -180,522 | 6.1 | 689,182 | 10.3 | 869,704 | 9.4 |
| 1998 | -229,758 | 27.3 | 682,138 | -1.0 | 911,896 | 4.9 |
| 1999 | -328,821 | 43.1 | 695,797 | 2.0 | 1,024,618 | 12.4 |
| 2000 | -436,104 | 32.6 | 781,918 | 12.4 | 1,218,022 | 18.9 |
| 2001 | -411,899 | -5.6 | 729,100 | -6.8 | 1,140,999 | -6.3 |
| 2002 | -468,263 | 13.7 | 693,103 | -4.9 | 1,161,366 | 1.8 |
| 2003 | -532,350 | 13.7 | 724,771 | 4.6 | 1,257,121 | 8.2 |
| 2004 | -654,830 | 23.0 | 814,875 | 12.4 | 1,469,704 | 16.9 |
| 2005 | -772,373 | 18.0 | 901,082 | 10.6 | 1,673,455 | 13.9 |
| 2006 | -827,971 | 7.2 | 1,025,967 | 13.9 | 1,853,938 | 10.8 |
| 2007 | -808,763 | -2.3 | 1,148,199 | 11.9 | 1,956,962 | 5.6 |
| 2008 | -816,199 | 0.9 | 1,287,442 | 12.1 | 2,103,641 | 7.5 |
| 2009 | -503,582 | -38.3 | 1,056,043 | -18.0 | 1,559,625 | -25.9 |
| 2010 | -635,362 | 26.2 | 1,278,495 | 21.1 | 1,913,857 | 22.7 |
| 2011 | -725,447 | 14.2 | 1,482,508 | 16.0 | 2,207,954 | 15.4 |
| 2012 | -730,599 | 0.7 | 1,545,703 | 4.3 | 2,276,302 | 3.1 |
| 2013 | -688,728 | -5.7 | 1,579,593 | 2.2 | 2,268,321 | -0.4 |
Source: US Census Bureau, Foreign Trade Division
http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
Chart IIA-1 of the US Census Bureau of the Department of Commerce shows that the trade deficit (gap between exports and imports) fell during the economic contraction after 2007 but has grown again during the expansion. The low average rate of growth of GDP of 2.2 percent during the expansion beginning since IIIQ2009 does not deteriorate further the trade balance. Higher rates of growth may cause sharper deterioration.
Chart IIA-1, US, International Trade Balance, Exports and Imports of Goods and Services USD Billions
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/briefrm/esbr/www/esbr042.html
Table IIA-2B provides the US international trade balance, exports and imports of goods and services on an annual basis from 1992 to 2013. The trade balance deteriorated sharply over the long term. The US has a large deficit in goods or exports less imports of goods but it has a surplus in services that helps to reduce the trade account deficit or exports less imports of goods and services. The current account deficit of the US not seasonally adjusted increased from $87 billion in IVQ2013 to $119 billion in IIIQ2014 (http://www.bea.gov/international/index.htm). The current account deficit seasonally adjusted at annual rate increased from 2.0 percent of GDP in IIQ2013 to 2.4 percent of GDP in IQ2014, decreasing to 2.3 percent of GDP in IIQ2014 and 2.3 percent of GDP in IIIQ2014 (http://www.bea.gov/international/index.htm http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). The ratio of the current account deficit to GDP has stabilized around 3 percent of GDP compared with much higher percentages before the recession (see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008b), 183-94, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 167-71). The last row of Table IIA-2B shows marginal improvement of the trade deficit from $548,625 million in 2011 to lower $537,605 million in 2012 with exports growing 4.2 percent and imports 2.9 percent. The trade balance improved further to deficit of $476,392 million in 2013 with growth of exports of 2.9 percent while imports stagnated. Growth and commodity shocks under alternating inflation waves (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html) have deteriorated the trade deficit from the low of $383,774 million in 2009.
Table IIA-2B, US, International Trade Balance of Goods and Services, Exports and Imports of Goods and Services, SA, Millions of Dollars, Balance of Payments Basis
| Balance | Exports | ∆% | Imports | ∆% | |
| 1960 | 3,508 | 25,940 | NA | 22,432 | NA |
| 1961 | 4,195 | 26,403 | 1.8 | 22,208 | -1.0 |
| 1962 | 3,370 | 27,722 | 5.0 | 24,352 | 9.7 |
| 1963 | 4,210 | 29,620 | 6.8 | 25,410 | 4.3 |
| 1964 | 6,022 | 33,341 | 12.6 | 27,319 | 7.5 |
| 1965 | 4,664 | 35,285 | 5.8 | 30,621 | 12.1 |
| 1966 | 2,939 | 38,926 | 10.3 | 35,987 | 17.5 |
| 1967 | 2,604 | 41,333 | 6.2 | 38,729 | 7.6 |
| 1968 | 250 | 45,543 | 10.2 | 45,293 | 16.9 |
| 1969 | 91 | 49,220 | 8.1 | 49,129 | 8.5 |
| 1970 | 2,254 | 56,640 | 15.1 | 54,386 | 10.7 |
| 1971 | -1,302 | 59,677 | 5.4 | 60,979 | 12.1 |
| 1972 | -5,443 | 67,222 | 12.6 | 72,665 | 19.2 |
| 1973 | 1,900 | 91,242 | 35.7 | 89,342 | 23.0 |
| 1974 | -4,293 | 120,897 | 32.5 | 125,190 | 40.1 |
| 1975 | 12,404 | 132,585 | 9.7 | 120,181 | -4.0 |
| 1976 | -6,082 | 142,716 | 7.6 | 148,798 | 23.8 |
| 1977 | -27,246 | 152,301 | 6.7 | 179,547 | 20.7 |
| 1978 | -29,763 | 178,428 | 17.2 | 208,191 | 16.0 |
| 1979 | -24,565 | 224,131 | 25.6 | 248,696 | 19.5 |
| 1980 | -19,407 | 271,834 | 21.3 | 291,241 | 17.1 |
| 1981 | -16,172 | 294,398 | 8.3 | 310,570 | 6.6 |
| 1982 | -24,156 | 275,236 | -6.5 | 299,391 | -3.6 |
| 1983 | -57,767 | 266,106 | -3.3 | 323,874 | 8.2 |
| 1984 | -109,072 | 291,094 | 9.4 | 400,166 | 23.6 |
| 1985 | -121,880 | 289,070 | -0.7 | 410,950 | 2.7 |
| 1986 | -138,538 | 310,033 | 7.3 | 448,572 | 9.2 |
| 1987 | -151,684 | 348,869 | 12.5 | 500,552 | 11.6 |
| 1988 | -114,566 | 431,149 | 23.6 | 545,715 | 9.0 |
| 1989 | -93,141 | 487,003 | 13.0 | 580,144 | 6.3 |
| 1990 | -80,864 | 535,233 | 9.9 | 616,097 | 6.2 |
| 1991 | -31,135 | 578,344 | 8.1 | 609,479 | -1.1 |
| 1992 | -39,212 | 616,882 | 6.7 | 656,094 | 7.6 |
| 1993 | -70,311 | 642,863 | 4.2 | 713,174 | 8.7 |
| 1994 | -98,493 | 703,254 | 9.4 | 801,747 | 12.4 |
| 1995 | -96,384 | 794,387 | 13.0 | 890,771 | 11.1 |
| 1996 | -104,065 | 851,602 | 7.2 | 955,667 | 7.3 |
| 1997 | -108,273 | 934,453 | 9.7 | 1,042,726 | 9.1 |
| 1998 | -166,140 | 933,174 | -0.1 | 1,099,314 | 5.4 |
| 1999 | -258,617 | 969,867 | 3.9 | 1,228,485 | 11.8 |
| 2000 | -372,517 | 1,075,321 | 10.9 | 1,447,837 | 17.9 |
| 2001 | -361,511 | 1,005,654 | -6.5 | 1,367,165 | -5.6 |
| 2002 | -418,955 | 978,706 | -2.7 | 1,397,660 | 2.2 |
| 2003 | -493,890 | 1,020,418 | 4.3 | 1,514,308 | 8.3 |
| 2004 | -609,883 | 1,161,549 | 13.8 | 1,771,433 | 17.0 |
| 2005 | -714,245 | 1,286,022 | 10.7 | 2,000,267 | 12.9 |
| 2006 | -761,716 | 1,457,642 | 13.3 | 2,219,358 | 11.0 |
| 2007 | -705,375 | 1,653,548 | 13.4 | 2,358,922 | 6.3 |
| 2008 | -708,726 | 1,841,612 | 11.4 | 2,550,339 | 8.1 |
| 2009 | -383,774 | 1,583,053 | -14.0 | 1,966,827 | -22.9 |
| 2010 | -494,658 | 1,853,606 | 17.1 | 2,348,263 | 19.4 |
| 2011 | -548,625 | 2,127,021 | 14.8 | 2,675,646 | 13.9 |
| 2012 | -537,605 | 2,216,540 | 4.2 | 2,754,145 | 2.9 |
| 2013 | -476,392 | 2,280,194 | 2.9 | 2,756,586 | 0.1 |
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/briefrm/esbr/www/esbr042.html
Chart IIA-2 of the US Census Bureau provides the US trade account in goods and services SA from Jan 1992 to Oct 2014. There is long-term trend of deterioration of the US trade deficit shown vividly by Chart IIA-2. The global recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 reversed the trend of deterioration. Deterioration resumed together with incomplete recovery and was influenced significantly by the carry trade from zero interest rates to commodity futures exposures (these arguments are elaborated in Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 157-66, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 217-27, International Financial Architecture (2005), 15-18, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 221-5, Globalization and the State Vol. II (2008b), 197-213, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 182-4 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/07/causes-of-2007-creditdollar-crisis.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/professor-mckinnons-bubble-economy.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/world-inflation-quantitative-easing.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/treasury-yields-valuation-of-risk.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/11/quantitative-easing-theory-evidence-and.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/12/is-fed-printing-money-what-are.html). Earlier research focused on the long-term external imbalance of the US in the form of trade and current account deficits (Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), Globalization and the State Vol. II (2008b) 183-94, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 167-71). US external imbalances have not been fully resolved and tend to widen together with improving world economic activity and commodity price shocks.
Chart IIA-2, US, Balance of Trade SA, Monthly, Millions of Dollars, Jan 1992-Nov 2014
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
Chart IIA-3 of the US Census Bureau provides US exports SA from Jan 1992 to Sep 2014. There was sharp acceleration from 2003 to 2007 during worldwide economic boom and increasing inflation. Exports fell sharply during the financial crisis and global recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. Growth picked up again together with world trade and inflation but stalled in the final segment with less rapid global growth and inflation.
Chart IIA-3, US, Exports SA, Monthly, Millions of Dollars Jan 1992-Nov 2014
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
Chart IIA-4 of the US Census Bureau provides US imports SA from Jan 1992 to Sep 2014. Growth was stronger between 2003 and 2007 with worldwide economic boom and inflation. There was sharp drop during the financial crisis and global recession. There is stalling import levels in the final segment resulting from weaker world economic growth and diminishing inflation because of risk aversion and portfolio reallocations from commodity exposures to equities.
Chart IIA-4, US, Imports SA, Monthly, Millions of Dollars Jan 1992-Oct 2014
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
There is deterioration of the US trade balance in goods in Table IIA-3 from deficit of $54,765 million in Nov 2013 to deficit of $58,729 million in Nov 2014. The nonpetroleum deficit increased by $7,595 million while the petroleum deficit shrank by $4,307 million. Total exports of goods changed 0.0 percent in Nov 2014 relative to a year earlier while total imports increased 1.8 percent. Nonpetroleum exports increased 1.5 percent from Nov 2013 to Nov 2014 while nonpetroleum imports increased 5.9 percent. Petroleum imports fell 20.0 percent.
Table IIA-3, US, International Trade in Goods Balance, Exports and Imports $ Millions and ∆% SA
| Nov 2014 | Nov 2013 | ∆% | |
| Total Balance | -58,729 | -54,765 | |
| Petroleum | -11,437 | -15,744 | |
| Non Petroleum | -45,697 | -38,102 | |
| Total Exports | 136,730 | 136,752 | 0.0 |
| Petroleum | 11,629 | 13,091 | -11.2 |
| Non Petroleum | 124,160 | 122,307 | 1.5 |
| Total Imports | 195,009 | 191,517 | 1.8 |
| Petroleum | 23,065 | 28,835 | -20.0 |
| Non Petroleum | 169,857 | 160,409 | 5.9 |
Details may not add because of rounding and seasonal adjustment
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
US exports and imports of goods not seasonally adjusted in Jan-Nov 2014 and Jan-Nov 2013 are in Table IIA-4. The rate of growth of exports was 2.9 percent and 3.0 percent for imports. The US has partial hedge of commodity price increases in exports of agricultural commodities that increased 5.0 percent and of mineral fuels that increased 8.7 percent both because prices of raw materials and commodities increase and fall recurrently as a result of shocks of risk aversion and portfolio reallocations. The US exports an insignificant but growing amount of crude oil, increasing 7.8 percent in cumulative Jan-Nov 2014 relative to a year earlier. US exports and imports consist mostly of manufactured products, with less rapidly increasing prices. US manufactured exports increased 0.9 percent while manufactured imports rose 4.8 percent. Significant part of the US trade imbalance originates in imports of mineral fuels decreasing 8.6 percent and petroleum decreasing 9.8 percent with wide oscillations in oil prices. The limited hedge in exports of agricultural commodities and mineral fuels compared with substantial imports of mineral fuels and crude oil results in waves of deterioration of the terms of trade of the US, or export prices relative to import prices, originating in commodity price increases caused by carry trades from zero interest rates. These waves are similar to those in worldwide inflation (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html). There is current reversal because of the sharp decline of commodity prices.
Table IIA-4, US, Exports and Imports of Goods, Not Seasonally Adjusted Millions of Dollars and %, Census Basis
| Jan-Nov 2014 $ Millions | Jan-Nov 2014 $ Millions | ∆% | |
| Exports | 1,489,634 | 1,447,637 | 2.9 |
| Manufactured | 1,095,796 | 1,086,332 | 0.9 |
| Agricultural | 136,533 | 130,059 | 5.0 |
| Mineral Fuels | 143,573 | 132,109 | 8.7 |
| Petroleum | 118,477 | 109,902 | 7.8 |
| Imports | 2,149,013 | 2,085,856 | 3.0 |
| Manufactured | 1,763,884 | 1,682,752 | 4.8 |
| Agricultural | 102,302 | 95,988 | 6.6 |
| Mineral Fuels | 320,670 | 350,684 | -8.6 |
| Petroleum | 302,950 | 335,957 | -9.8 |
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
The current account of the US balance of payments is provided in Table IIA2-1 for IIIQ2013 and IIIQ2014. The US has a large deficit in goods or exports less imports of goods but it has a surplus in services that helps to reduce the trade account deficit or exports less imports of goods and services. The current account deficit of the US not seasonally adjusted increased from $118.7 billion in IIIQ2013 to $118.8 billion in IIIQ2014. The current account deficit seasonally adjusted at annual rate fell from 2.5 percent of GDP in IIIQ2013 to 2.4 percent of GDP in IIQ2014, decreasing to 2.3 percent of GDP in IIIQ2014. The ratio of the current account deficit to GDP has stabilized below 3 percent of GDP compared with much higher percentages before the recession but is combined now with much higher imbalance in the Treasury budget (see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008b), 183-94, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 167-71).
Table IIA2-1, US, Balance of Payments, Millions of Dollars NSA
| IIIQ2013 | IIIQ2014 | Difference | |
| Goods Balance | -196,941 | -202,280 | -5,339 |
| X Goods | 392,164 | 407,722 | 4.0 ∆% |
| M Goods | -589,104 | -610,002 | 3.5 ∆% |
| Services Balance | 59,727 | 61,050 | 1,323 |
| X Services | 179,815 | 185,191 | 3.0 ∆% |
| M Services | -120,088 | -124,141 | 3.4 ∆% |
| Balance Goods and Services | -137,214 | -141,230 | -4,016 |
| Exports of Goods and Services and Income Receipts | 798,444 | 829,937 | |
| Imports of Goods and Services and Income Payments | -917,148 | -948,689 | |
| Current Account Balance | -118,705 | -118,752 | -4.7 |
| % GDP | IIIQ2013 | IIIQ2014 | IIQ2014 |
| 2.5 | 2.3 | 2.4 |
X: exports; M: imports
Balance on Current Account = Exports of Goods and Services – Imports of Goods and Services and Income Payments
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/international/index.htm#bop
In their classic work on “unpleasant monetarist arithmetic,” Sargent and Wallace (1981, 2) consider a regime of domination of monetary policy by fiscal policy (emphasis added):
“Imagine that fiscal policy dominates monetary policy. The fiscal authority independently sets its budgets, announcing all current and future deficits and surpluses and thus determining the amount of revenue that must be raised through bond sales and seignorage. Under this second coordination scheme, the monetary authority faces the constraints imposed by the demand for government bonds, for it must try to finance with seignorage any discrepancy between the revenue demanded by the fiscal authority and the amount of bonds that can be sold to the public. Suppose that the demand for government bonds implies an interest rate on bonds greater than the economy’s rate of growth. Then if the fiscal authority runs deficits, the monetary authority is unable to control either the growth rate of the monetary base or inflation forever. If the principal and interest due on these additional bonds are raised by selling still more bonds, so as to continue to hold down the growth of base money, then, because the interest rate on bonds is greater than the economy’s growth rate, the real stock of bonds will growth faster than the size of the economy. This cannot go on forever, since the demand for bonds places an upper limit on the stock of bonds relative to the size of the economy. Once that limit is reached, the principal and interest due on the bonds already sold to fight inflation must be financed, at least in part, by seignorage, requiring the creation of additional base money.”
The alternative fiscal scenario of the CBO (2012NovCDR, 2013Sep17) resembles an economic world in which eventually the placement of debt reaches a limit of what is proportionately desired of US debt in investment portfolios. This unpleasant environment is occurring in various European countries.
The current real value of government debt plus monetary liabilities depends on the expected discounted values of future primary surpluses or difference between tax revenue and government expenditure excluding interest payments (Cochrane 2011Jan, 27, equation (16)). There is a point when adverse expectations about the capacity of the government to generate primary surpluses to honor its obligations can result in increases in interest rates on government debt.
First, Unpleasant Monetarist Arithmetic. Fiscal policy is described by Sargent and Wallace (1981, 3, equation 1) as a time sequence of D(t), t = 1, 2,…t, …, where D is real government expenditures, excluding interest on government debt, less real tax receipts. D(t) is the real deficit excluding real interest payments measured in real time t goods. Monetary policy is described by a time sequence of H(t), t=1,2,…t, …, with H(t) being the stock of base money at time t. In order to simplify analysis, all government debt is considered as being only for one time period, in the form of a one-period bond B(t), issued at time t-1 and maturing at time t. Denote by R(t-1) the real rate of interest on the one-period bond B(t) between t-1 and t. The measurement of B(t-1) is in terms of t-1 goods and [1+R(t-1)] “is measured in time t goods per unit of time t-1 goods” (Sargent and Wallace 1981, 3). Thus, B(t-1)[1+R(t-1)] brings B(t-1) to maturing time t. B(t) represents borrowing by the government from the private sector from t to t+1 in terms of time t goods. The price level at t is denoted by p(t). The budget constraint of Sargent and Wallace (1981, 3, equation 1) is:
D(t) = {[H(t) – H(t-1)]/p(t)} + {B(t) – B(t-1)[1 + R(t-1)]} (1)
Equation (1) states that the government finances its real deficits into two portions. The first portion, {[H(t) – H(t-1)]/p(t)}, is seigniorage, or “printing money.” The second part,
{B(t) – B(t-1)[1 + R(t-1)]}, is borrowing from the public by issue of interest-bearing securities. Denote population at time t by N(t) and growing by assumption at the constant rate of n, such that:
N(t+1) = (1+n)N(t), n>-1 (2)
The per capita form of the budget constraint is obtained by dividing (1) by N(t) and rearranging:
B(t)/N(t) = {[1+R(t-1)]/(1+n)}x[B(t-1)/N(t-1)]+[D(t)/N(t)] – {[H(t)-H(t-1)]/[N(t)p(t)]} (3)
On the basis of the assumptions of equal constant rate of growth of population and real income, n, constant real rate of return on government securities exceeding growth of economic activity and quantity theory equation of demand for base money, Sargent and Wallace (1981) find that “tighter current monetary policy implies higher future inflation” under fiscal policy dominance of monetary policy. That is, the monetary authority does not permanently influence inflation, lowering inflation now with tighter policy but experiencing higher inflation in the future.
Second, Unpleasant Fiscal Arithmetic. The tool of analysis of Cochrane (2011Jan, 27, equation (16)) is the government debt valuation equation:
(Mt + Bt)/Pt = Et∫(1/Rt, t+τ)st+τdτ (4)
Equation (4) expresses the monetary, Mt, and debt, Bt, liabilities of the government, divided by the price level, Pt, in terms of the expected value discounted by the ex-post rate on government debt, Rt, t+τ, of the future primary surpluses st+τ, which are equal to Tt+τ – Gt+τ or difference between taxes, T, and government expenditures, G. Cochrane (2010A) provides the link to a web appendix demonstrating that it is possible to discount by the ex post Rt, t+τ. The second equation of Cochrane (2011Jan, 5) is:
MtV(it, ·) = PtYt (5)
Conventional analysis of monetary policy contends that fiscal authorities simply adjust primary surpluses, s, to sanction the price level determined by the monetary authority through equation (5), which deprives the debt valuation equation (4) of any role in price level determination. The simple explanation is (Cochrane 2011Jan, 5):
“We are here to think about what happens when [4] exerts more force on the price level. This change may happen by force, when debt, deficits and distorting taxes become large so the Treasury is unable or refuses to follow. Then [4] determines the price level; monetary policy must follow the fiscal lead and ‘passively’ adjust M to satisfy [5]. This change may also happen by choice; monetary policies may be deliberately passive, in which case there is nothing for the Treasury to follow and [4] determines the price level.”
An intuitive interpretation by Cochrane (2011Jan 4) is that when the current real value of government debt exceeds expected future surpluses, economic agents unload government debt to purchase private assets and goods, resulting in inflation. If the risk premium on government debt declines, government debt becomes more valuable, causing a deflationary effect. If the risk premium on government debt increases, government debt becomes less valuable, causing an inflationary effect.
There are multiple conclusions by Cochrane (2011Jan) on the debt/dollar crisis and Global recession, among which the following three:
(1) The flight to quality that magnified the recession was not from goods into money but from private-sector securities into government debt because of the risk premium on private-sector securities; monetary policy consisted of providing liquidity in private-sector markets suffering stress
(2) Increases in liquidity by open-market operations with short-term securities have no impact; quantitative easing can affect the timing but not the rate of inflation; and purchase of private debt can reverse part of the flight to quality
(3) The debt valuation equation has a similar role as the expectation shifting the Phillips curve such that a fiscal inflation can generate stagflation effects similar to those occurring from a loss of anchoring expectations.
This analysis suggests that there may be a point of saturation of demand for United States financial liabilities without an increase in interest rates on Treasury securities. A risk premium may develop on US debt. Such premium is not apparent currently because of distressed conditions in the world economy and international financial system. Risk premiums are observed in the spread of bonds of highly indebted countries in Europe relative to bonds of the government of Germany.
The issue of global imbalances centered on the possibility of a disorderly correction (Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), Globalization and the State Vol. II (2008b) 183-94, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 167-71). Such a correction has not occurred historically but there is no argument proving that it could not occur. The need for a correction would originate in unsustainable large and growing United States current account deficits (CAD) and net international investment position (NIIP) or excess of financial liabilities of the US held by foreigners net relative to financial liabilities of foreigners held by US residents. The IMF estimated that the US could maintain a CAD of two to three percent of GDP without major problems (Rajan 2004). The threat of disorderly correction is summarized by Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 15):
“It is possible that foreigners may be unwilling to increase their positions in US financial assets at prevailing interest rates. An exit out of the dollar could cause major devaluation of the dollar. The depreciation of the dollar would cause inflation in the US, leading to increases in American interest rates. There would be an increase in mortgage rates followed by deterioration of real estate values. The IMF has simulated that such an adjustment would cause a decline in the rate of growth of US GDP to 0.5 percent over several years. The decline of demand in the US by four percentage points over several years would result in a world recession because the weakness in Europe and Japan could not compensate for the collapse of American demand. The probability of occurrence of an abrupt adjustment is unknown. However, the adverse effects are quite high, at least hypothetically, to warrant concern.”
The United States could be moving toward a situation typical of heavily indebted countries, requiring fiscal adjustment and increases in productivity to become more competitive internationally. The CAD and NIIP of the United States are not observed in full deterioration because the economy is well below trend. There are two complications in the current environment relative to the concern with disorderly correction in the first half of the past decade. In the release of Jun 14, 2013, the Bureau of Economic Analysis (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/international/transactions/2013/pdf/trans113.pdf) informs of revisions of US data on US international transactions since 1999:
“The statistics of the U.S. international transactions accounts released today have been revised for the first quarter of 1999 to the fourth quarter of 2012 to incorporate newly available and revised source data, updated seasonal adjustments, changes in definitions and classifications, and improved estimating methodologies.”
The BEA introduced new concepts and methods (http://www.bea.gov/international/concepts_methods.htm) in comprehensive restructuring on Jun 18, 2014 (http://www.bea.gov/international/modern.htm):
“BEA introduced a new presentation of the International Transactions Accounts on June 18, 2014 and will introduce a new presentation of the International Investment Position on June 30, 2014. These new presentations reflect a comprehensive restructuring of the international accounts that enhances the quality and usefulness of the accounts for customers and bring the accounts into closer alignment with international guidelines.”
Table IIA2-3 provides data on the US fiscal and balance of payments imbalances incorporating all revisions and methods. In 2007, the federal deficit of the US was $161 billion corresponding to 1.1 percent of GDP while the Congressional Budget Office estimates the federal deficit in 2012 at $1087 billion or 6.8 percent of GDP. The estimate of the deficit for 2013 is $680 billion or 4.1 percent of GDP. The combined record federal deficits of the US from 2009 to 2012 are $5090 billion or 31.6 percent of the estimate of GDP for fiscal year 2012 implicit in the CBO (CBO 2013Sep11) estimate of debt/GDP. The deficits from 2009 to 2012 exceed one trillion dollars per year, adding to $5.090 trillion in four years, using the fiscal year deficit of $1087 billion for fiscal year 2012, which is the worst fiscal performance since World War II. Federal debt in 2007 was $5035 billion, less than the combined deficits from 2009 to 2012 of $5090 billion. Federal debt in 2012 was 70.1 percent of GDP (CBO 2013Sep11) and 72.1 percent of GDP in 2013 (http://www.cbo.gov/). This situation may worsen in the future (CBO 2013Sep17):
“Between 2009 and 2012, the federal government recorded the largest budget deficits relative to the size of the economy since 1946, causing federal debt to soar. Federal debt held by the public is now about 73 percent of the economy’s annual output, or gross domestic product (GDP). That percentage is higher than at any point in U.S. history except a brief period around World War II, and it is twice the percentage at the end of 2007. If current laws generally remained in place, federal debt held by the public would decline slightly relative to GDP over the next several years, CBO projects. After that, however, growing deficits would ultimately push debt back above its current high level. CBO projects that federal debt held by the public would reach 100 percent of GDP in 2038, 25 years from now, even without accounting for the harmful effects that growing debt would have on the economy. Moreover, debt would be on an upward path relative to the size of the economy, a trend that could not be sustained indefinitely.
The gap between federal spending and revenues would widen steadily after 2015 under the assumptions of the extended baseline, CBO projects. By 2038, the deficit would be 6½ percent of GDP, larger than in any year between 1947 and 2008, and federal debt held by the public would reach 100 percent of GDP, more than in any year except 1945 and 1946. With such large deficits, federal debt would be growing faster than GDP, a path that would ultimately be unsustainable.
Incorporating the economic effects of the federal policies that underlie the extended baseline worsens the long-term budget outlook. The increase in debt relative to the size of the economy, combined with an increase in marginal tax rates (the rates that would apply to an additional dollar of income), would reduce output and raise interest rates relative to the benchmark economic projections that CBO used in producing the extended baseline. Those economic differences would lead to lower federal revenues and higher interest payments. With those effects included, debt under the extended baseline would rise to 108 percent of GDP in 2038.”
Table IIA2-3, US, Current Account, NIIP, Fiscal Balance, Nominal GDP, Federal Debt and Direct Investment, Dollar Billions and %
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | |
| Goods & | -705 | -709 | -384 | -495 | -549 | -538 | -476 |
| Primary Income | 101 | 146 | 124 | 178 | 221 | 203 | 200 |
| Secondary Income | -114 | -124 | -121 | -127 | -132 | -126 | -124 |
| Current Account | -719 | -687 | -381 | -444 | -459 | -461 | -400 |
| NGDP | 14478 | 14719 | 14419 | 14964 | 15518 | 16163 | 16768 |
| Current Account % GDP | -5.0 | -4.7 | -2.6 | -3.0 | -3.0 | -2.9 | -2.4 |
| NIIP | -1279 | -3995 | -2628 | -2512 | -4455 | -4578 | -5383 |
| US Owned Assets Abroad | 20705 | 19423 | 19426 | 21768 | 22209 | 22520 | 23710 |
| Foreign Owned Assets in US | 21984 | 23418 | 22054 | 24280 | 26664 | 27098 | 29093 |
| NIIP % GDP | -8.8 | -27.1 | -18.2 | -16.8 | -28.7 | -28.3 | -32.1 |
| Exports | 2569 | 2751 | 2286 | 2631 | 2988 | 3085 | 3179 |
| NIIP % | -50 | -145 | -115 | -95 | -149 | -148 | -169 |
| DIA MV | 5858 | 3707 | 4945 | 5486 | 5215 | 5938 | 7080 |
| DIUS MV | 4134 | 3091 | 3619 | 4099 | 4199 | 4671 | 5791 |
| Fiscal Balance | -161 | -459 | -1413 | -1294 | -1300 | -1087 | -680 |
| Fiscal Balance % GDP | -1.1 | -3.1 | -9.8 | -8.7 | -8.4 | -6.8 | -4.1 |
| Federal Debt | 5035 | 5803 | 7545 | 9019 | 10128 | 11281 | 11983 |
| Federal Debt % GDP | 35.1 | 39.3 | 52.3 | 61.0 | 65.8 | 70.1 | 72.0 |
| Federal Outlays | 2729 | 2983 | 3518 | 3457 | 3603 | 3537 | 3455 |
| ∆% | 2.8 | 9.3 | 17.9 | -1.7 | 4.2 | -1.8 | -2.3 |
| % GDP | 19.0 | 20.2 | 24.4 | 23.4 | 23.4 | 22.0 | 20.8 |
| Federal Revenue | 2568 | 2524 | 2105 | 2163 | 2304 | 2450 | 2775 |
| ∆% | 6.7 | -1.7 | -16.6 | 2.7 | 6.5 | 6.3 | 13.3 |
| % GDP | 17.9 | 17.1 | 14.6 | 14.6 | 15.0 | 15.2 | 16.7 |
Sources:
Notes: NGDP: nominal GDP or in current dollars; NIIP: Net International Investment Position; DIA MV: US Direct Investment Abroad at Market Value; DIUS MV: Direct Investment in the US at Market Value. There are minor discrepancies in the decimal point of percentages of GDP between the balance of payments data and federal debt, outlays, revenue and deficits in which the original number of the CBO source is maintained. See Bureau of Economic Analysis, US International Economic Accounts: Concepts and Methods. 2014. Washington, DC: BEA, Department of Commerce, Jun 2014 http://www.bea.gov/international/concepts_methods.htm These discrepancies do not alter conclusions. Budget http://www.cbo.gov/ Balance of Payments and NIIP http://www.bea.gov/international/index.htm#bop Gross Domestic Product, Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table IIA2-3 provides quarterly estimates NSA of the external imbalance of the United States. The current account deficit seasonally adjusted falls from 2.4 percent of GDP in IIIQ2013 to 2.0 percent in IVQ2013. The current account deficit increases to 2.4 percent of GDP in IQ2014 and decreases to 2.3 percent of GDP in IIQ2014. The deficit stabilizes at 2.3 percent of GDP in IIIQ2014. The net international investment position increases from $5.0 trillion in IIIQ2013 to $5.4 trillion in IVQ2013, increasing to $5.5 trillion in IQ2014. The net international investment position eases to $5.5 trillion in IIQ2014 and increases to $6.2 trillion in IIIQ2014.
Table IIA2-3, US, Current Account, NIIP, Fiscal Balance, Nominal GDP, Federal Debt and Direct Investment, Dollar Billions and % NSA
| IIIQ2013 | IVQ2013 | IQ2014 | IIQ2014 | IIIQ2014 | |
| Goods & | -137 | -111 | -100 | -139 | -141 |
| Primary Income | 51 | 53 | 52 | 56 | 58 |
| Secondary Income | -33 | -29 | -31 | -21 | -36 |
| Current Account | -119 | -87 | -77 | -103 | -119 |
| Current Account % GDP | -2.4 | -2.0 | -2.4 | -2.3 | -2.3 |
| NIIP | -4995 | -5383 | -5512 | -5475 | -6158 |
| US Owned Assets Abroad | 22954 | 23710 | 24020 | 24977 | 24615 |
| Foreign Owned Assets in US | -27949 | -29093 | -29532 | -30452 | -30772 |
| DIA MV | 6690 | 7080 | 7117 | 7489 | 7235 |
| DIA MV Equity | 5699 | 6070 | 6135 | 6429 | 6170 |
| DIUS MV | 5342 | 5791 | 5689 | 5999 | 6044 |
| DIUS MV Equity | 4041 | 4462 | 4387 | 4624 | 4669 |
Notes: NIIP: Net International Investment Position; DIA MV: US Direct Investment Abroad at Market Value; DIUS MV: Direct Investment in the US at Market Value. See Bureau of Economic Analysis, US International Economic Accounts: Concepts and Methods. 2014. Washington, DC: BEA, Department of Commerce, Jun 2014 http://www.bea.gov/international/concepts_methods.htm
Chart VI-10 of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System provides the overnight Fed funds rate on business days from Jul 1, 1954 at 1.13 percent through Jan 10, 1979, at 9.91 percent per year, to Jan 8, 2015, at 0.12 percent per year. US recessions are in shaded areas according to the reference dates of the NBER (http://www.nber.org/cycles.html). In the Fed effort to control the “Great Inflation” of the 1930s (see http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/05/slowing-growth-global-inflation-great.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/04/new-economics-of-rose-garden-turned.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/03/is-there-second-act-of-us-great.html and Appendix I The Great Inflation; see Taylor 1993, 1997, 1998LB, 1999, 2012FP, 2012Mar27, 2012Mar28, 2012JMCB and http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/rules-versus-discretionary-authorities.html), the fed funds rate increased from 8.34 percent on Jan 3, 1979 to a high in Chart VI-10 of 22.36 percent per year on Jul 22, 1981 with collateral adverse effects in the form of impaired savings and loans associations in the United States, emerging market debt and money-center banks (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 72-7; Pelaez 1986, 1987). Another episode in Chart VI-10 is the increase in the fed funds rate from 3.15 percent on Jan 3, 1994, to 6.56 percent on Dec 21, 1994, which also had collateral effects in impairing emerging market debt in Mexico and Argentina and bank balance sheets in a world bust of fixed income markets during pursuit by central banks of non-existing inflation (Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), 113-5). Another interesting policy impulse is the reduction of the fed funds rate from 7.03 percent on Jul 3, 2000, to 1.00 percent on Jun 22, 2004, in pursuit of equally non-existing deflation (Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), 18-28, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 83-85), followed by increments of 25 basis points from Jun 2004 to Jun 2006, raising the fed funds rate to 5.25 percent on Jul 3, 2006 in Chart VI-10. Central bank commitment to maintain the fed funds rate at 1.00 percent induced adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMS) linked to the fed funds rate. Lowering the interest rate near the zero bound in 2003-2004 caused the illusion of permanent increases in wealth or net worth in the balance sheets of borrowers and also of lending institutions, securitized banking and every financial institution and investor in the world. The discipline of calculating risks and returns was seriously impaired. The objective of monetary policy was to encourage borrowing, consumption and investment but the exaggerated stimulus resulted in a financial crisis of major proportions as the securitization that had worked for a long period was shocked with policy-induced excessive risk, imprudent credit, high leverage and low liquidity by the incentive to finance everything overnight at interest rates close to zero, from adjustable rate mortgages (ARMS) to asset-backed commercial paper of structured investment vehicles (SIV).
The consequences of inflating liquidity and net worth of borrowers were a global hunt for yields to protect own investments and money under management from the zero interest rates and unattractive long-term yields of Treasuries and other securities. Monetary policy distorted the calculations of risks and returns by households, business and government by providing central bank cheap money. Short-term zero interest rates encourage financing of everything with short-dated funds, explaining the SIVs created off-balance sheet to issue short-term commercial paper with the objective of purchasing default-prone mortgages that were financed in overnight or short-dated sale and repurchase agreements (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession, 50-1, Regulation of Banks and Finance, 59-60, Globalization and the State Vol. I, 89-92, Globalization and the State Vol. II, 198-9, Government Intervention in Globalization, 62-3, International Financial Architecture, 144-9). ARMS were created to lower monthly mortgage payments by benefitting from lower short-dated reference rates. Financial institutions economized in liquidity that was penalized with near zero interest rates. There was no perception of risk because the monetary authority guaranteed a minimum or floor price of all assets by maintaining low interest rates forever or equivalent to writing an illusory put option on wealth. Subprime mortgages were part of the put on wealth by an illusory put on house prices. The housing subsidy of $221 billion per year created the impression of ever-increasing house prices. The suspension of auctions of 30-year Treasuries was designed to increase demand for mortgage-backed securities, lowering their yield, which was equivalent to lowering the costs of housing finance and refinancing. Fannie and Freddie purchased or guaranteed $1.6 trillion of nonprime mortgages and worked with leverage of 75:1 under Congress-provided charters and lax oversight. The combination of these policies resulted in high risks because of the put option on wealth by near zero interest rates, excessive leverage because of cheap rates, low liquidity because of the penalty in the form of low interest rates and unsound credit decisions because the put option on wealth by monetary policy created the illusion that nothing could ever go wrong, causing the credit/dollar crisis and global recession (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession, 157-66, Regulation of Banks, and Finance, 217-27, International Financial Architecture, 15-18, The Global Recession Risk, 221-5, Globalization and the State Vol. II, 197-213, Government Intervention in Globalization, 182-4). A final episode in Chart VI-10 is the reduction of the fed funds rate from 5.41 percent on Aug 9, 2007, to 2.97 percent on October 7, 2008, to 0.12 percent on Dec 5, 2008 and close to zero throughout a long period with the final point at 0.12 percent on Jan 8, 2015. Evidently, this behavior of policy would not have occurred had there been theory, measurements and forecasts to avoid these violent oscillations that are clearly detrimental to economic growth and prosperity without inflation. Current policy consists of forecast mandate of maintaining policy accommodation until the forecast of the rate of unemployment reaches 6.5 percent and the rate of personal consumption expenditures excluding food and energy reaches 2.5 percent (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20121212a.htm). The FOMC dropped the numbers but affirmed guidance (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20140319a.htm): “With the unemployment rate nearing 6-1/2 percent, the Committee has updated its forward guidance. The change in the Committee's guidance does not indicate any change in the Committee's policy intentions as set forth in its recent statements.” It is a forecast mandate because of the lags in effect of monetary policy impulses on income and prices (Romer and Romer 2004). The intention is to reduce unemployment close to the “natural rate” (Friedman 1968, Phelps 1968) of around 5 percent and inflation at or below 2.0 percent. If forecasts were reasonably accurate, there would not be policy errors. A commonly analyzed risk of zero interest rates is the occurrence of unintended inflation that could precipitate an increase in interest rates similar to the Himalayan rise of the fed funds rate from 9.91 percent on Jan 10, 1979, at the beginning in Chart VI-10, to 22.36 percent on Jul 22, 1981. There is a less commonly analyzed risk of the development of a risk premium on Treasury securities because of the unsustainable Treasury deficit/debt of the United States (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html
and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/02/theory-and-reality-of-cyclical-slow.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/02/united-states-unsustainable-fiscal.html). There is not a fiscal cliff or debt limit issue ahead but rather free fall into a fiscal abyss. The combination of the fiscal abyss with zero interest rates could trigger the risk premium on Treasury debt or Himalayan hike in interest rates.
Chart VI-10, US, Fed Funds Rate, Business Days, Jul 1, 1954 to Jan 8, 2015, Percent per Year
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/update/
Chart VI-14 provides the overnight fed funds rate, the yield of the 10-year Treasury constant maturity bond, the yield of the 30-year constant maturity bond and the conventional mortgage rate from Jan 1991 to Dec 1996. In Jan 1991, the fed funds rate was 6.91 percent, the 10-year Treasury yield 8.09 percent, the 30-year Treasury yield 8.27 percent and the conventional mortgage rate 9.64 percent. Before monetary policy tightening in Oct 1993, the rates and yields were 2.99 percent for the fed funds, 5.33 percent for the 10-year Treasury, 5.94 for the 30-year Treasury and 6.83 percent for the conventional mortgage rate. After tightening in Nov 1994, the rates and yields were 5.29 percent for the fed funds rate, 7.96 percent for the 10-year Treasury, 8.08 percent for the 30-year Treasury and 9.17 percent for the conventional mortgage rate.
Chart VI-14, US, Overnight Fed Funds Rate, 10-Year Treasury Constant Maturity, 30-Year Treasury Constant Maturity and Conventional Mortgage Rate, Monthly, Jan 1991 to Dec 1996
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/update/
Chart VI-15 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides the all items consumer price index from Jan 1991 to Dec 1996. There does not appear acceleration of consumer prices requiring aggressive tightening.
Chart VI-15, US, Consumer Price Index All Items, Jan 1991 to Dec 1996
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm
Chart IV-16 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides 12-month percentage changes of the all items consumer price index from Jan 1991 to Dec 1996. Inflation collapsed during the recession from Jul 1990 (III) and Mar 1991 (I) and the end of the Kuwait War on Feb 25, 1991 that stabilized world oil markets. CPI inflation remained almost the same and there is no valid counterfactual that inflation would have been higher without monetary policy tightening because of the long lag in effect of monetary policy on inflation (see Culbertson 1960, 1961, Friedman 1961, Batini and Nelson 2002, Romer and Romer 2004). Policy tightening had adverse collateral effects in the form of emerging market crises in Mexico and Argentina and fixed income markets worldwide.
Chart VI-16, US, Consumer Price Index All Items, Twelve-Month Percentage Change, Jan 1991 to Dec 1996
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm
The Congressional Budget Office (CBO 2014BEOFeb4) estimates potential GDP, potential labor force and potential labor productivity provided in Table IB-3. The CBO estimates average rate of growth of potential GDP from 1950 to 2012 at 3.3 percent per year. The projected path is significantly lower at 2.1 percent per year from 2013 to 2024. The legacy of the economic cycle expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2014 at 2.3 percent on average is in contrast with 4.9 percent on average in the expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1988 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html). Subpar economic growth may perpetuate unemployment and underemployment estimated at 25.9 million or 15.7 percent of the effective labor force in Dec 2014 (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/financial-risks-twenty-six-million.html) with much lower hiring than in the period before the current cycle (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/global-financial-and-economic-risk.html).
Table IB-3, US, Congressional Budget Office History and Projections of Potential GDP of US Overall Economy, ∆%
| Potential GDP | Potential Labor Force | Potential Labor Productivity* | |
| Average Annual ∆% | |||
| 1950-1973 | 3.9 | 1.6 | 2.3 |
| 1974-1981 | 3.2 | 2.5 | 0.8 |
| 1982-1990 | 3.2 | 1.6 | 1.6 |
| 1991-2001 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 1.9 |
| 2002-2012 | 2.2 | 0.8 | 1.4 |
| 2007-2012 | 1.7 | 0.6 | 1.1 |
| Total 1950-2012 | 3.3 | 1.5 | 1.8 |
| Projected Average Annual ∆% | |||
| 2013-2018 | 2.1 | 0.6 | 1.5 |
| 2019-2024 | 2.1 | 0.5 | 1.6 |
| 2013-2024 | 2.1 | 0.5 | 1.6 |
*Ratio of potential GDP to potential labor force
Source: CBO (2014BEOFeb4), CBO, Key assumptions in projecting potential GDP—February 2014 baseline. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb 4, 2014.
Chart IB-1 of the Congressional Budget Office (CBO 2013BEOFeb5) provides actual and potential GDP of the United States from 2000 to 2011 and projected to 2024. Lucas (2011May) estimates trend of United States real GDP of 3.0 percent from 1870 to 2010 and 2.2 percent for per capita GDP. The United States successfully returned to trend growth of GDP by higher rates of growth during cyclical expansion as analyzed by Bordo (2012Sep27, 2012Oct21) and Bordo and Haubrich (2012DR). Growth in expansions following deeper contractions and financial crises was much higher in agreement with the plucking model of Friedman (1964, 1988). The unusual weakness of growth at 2.3 percent on average from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2014 during the current economic expansion in contrast with 4.9 percent on average in the cyclical expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1988 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html) cannot be explained by the contraction of 4.3 percent of GDP from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 and the financial crisis. Weakness of growth in the expansion is perpetuating unemployment and underemployment of 25.9 million or 15.7 percent of the labor force as estimated for Dec 2014 (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/financial-risks-twenty-six-million.html). There is no exit from unemployment/underemployment and stagnating real wages because of the collapse of hiring (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/global-financial-and-economic-risk.html). The US economy and labor markets collapsed without recovery. Abrupt collapse of economic conditions can be explained only with cyclic factors (Lazear and Spletzer 2012Jul22) and not by secular stagnation (Hansen 1938, 1939, 1941 with early dissent by Simons 1942).
Chart IB-1, US, Congressional Budget Office, Actual and Projections of Potential GDP, 2000-2024, Trillions of Dollars
Source: Congressional Budget Office, CBO (2013BEOFeb5). The last year in common in both projections is 2017. The revision lowers potential output in 2017 by 7.3 percent relative to the projection in 2007.
Chart IB-2 provides differences in the projections of potential output by the CBO in 2007 and more recently on Feb 4, 2014, which the CBO explains in CBO (2014Feb28).
Chart IB-2, Congressional Budget Office, Revisions of Potential GDP
Source: Congressional Budget Office, 2014Feb 28. Revisions to CBO’s Projection of Potential Output since 2007. Washington, DC, CBO, Feb 28, 2014.
Chart IB-3 provides actual and projected potential GDP from 2000 to 2024. The gap between actual and potential GDP disappears at the end of 2017 (CBO2014Feb4). GDP increases in the projection at 2.5 percent per year.
Chart IB-3, Congressional Budget Office, GDP and Potential GDP
Source: CBO (2013BEOFeb5), CBO, Key assumptions in projecting potential GDP—February 2014 baseline. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb 4, 2014.
Chart IIA2-3 of the Bureau of Economic Analysis of the Department of Commerce shows on the lower negative panel the sharp increase in the deficit in goods and the deficits in goods and services from 1960 to 2012. The upper panel shows the increase in the surplus in services that was insufficient to contain the increase of the deficit in goods and services. The adjustment during the global recession has been in the form of contraction of economic activity that reduced demand for goods.
Chart IIA2-3, US, Balance of Goods, Balance on Services and Balance on Goods and Services, 1960-2013, Millions of Dollars
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_ita.cfm
Chart IIA2-4 of the Bureau of Economic Analysis shows exports and imports of goods and services from 1960 to 2012. Exports of goods and services in the upper positive panel have been quite dynamic but have not compensated for the sharp increase in imports of goods. The US economy apparently has become less competitive in goods than in services.
Chart IIA2-4, US, Exports and Imports of Goods and Services, 1960-2013, Millions of Dollars
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_ita.cfm
Chart IIA2-5 of the Bureau of Economic Analysis shows the US balance on current account from 1960 to 2012. The sharp devaluation of the dollar resulting from unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates and elimination of auctions of 30-year Treasury bonds did not adjust the US balance of payments. Adjustment only occurred after the contraction of economic activity during the global recession.
Chart IIA2-5, US, Balance on Current Account, 1960-2013, Millions of Dollars
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_ita.cfm
Chart IIA2-6 of the Bureau of Economic Analysis provides real GDP in the US from 1960 to 2012. The contraction of economic activity during the global recession was a major factor in the reduction of the current account deficit as percent of GDP.
Chart IIA2-6, US, Real GDP, 1960-2013, Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IIA-7 provides the US current account deficit on a quarterly basis from 1980 to IQ1983. The deficit is at a lower level because of growth below potential not only in the US but worldwide. The combination of high government debt and deficit with external imbalance restricts potential prosperity in the US.
Chart IIA-7, US, Balance on Current Account, Quarterly, 1980-2013
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Risk aversion channels funds toward US long-term and short-term securities that finance the US balance of payments and fiscal deficits benefitting from risk flight to US dollar denominated assets. There are now temporary interruptions because of fear of rising interest rates that erode prices of US government securities because of mixed signals on monetary policy and exit from the Fed balance sheet of four trillion dollars of securities held outright. Net foreign purchases of US long-term securities (row C in Table VA-9) decreased from $164.3 billion in Sep 2014 to minus $1.4 billion in Oct 2014. Foreign (residents) purchases minus sales of US long-term securities (row A in Table VA-9) in Sep 2014 of $94.2 billion decreased to minus $15.0 billion in Oct 2014. Net US (residents) purchases of long-term foreign securities (row B in Table VA-9) decreased from $70.1 billion in Sep 2014 to $13.6 billion in Oct 2014. In Oct 2014,
C = A + B = -$15.0 billion + $13.6 billion = -$1.4 billion
There are minor rounding errors. There is weakening demand in Table VA-9 in Jun in A1 private purchases by residents overseas of US long-term securities of minus $15.4 billion of which deterioration in A11 Treasury securities of $3.1 billion, deterioration in A12 of $2.2 billion in agency securities, deterioration of $6/3 billion of corporate bonds and deterioration of minus $27.1 billion in equities. Worldwide risk aversion causes flight into US Treasury obligations with significant oscillations. Official purchases of securities in row A2 decreased $0.5 billion with decrease of Treasury securities of $2.5 billion in Oct 2014. Official purchases of agency securities decreased $1.6 billion in Oct. Row D shows increase in Oct 2014 of $13.6 billion in purchases of short-term dollar denominated obligations. Foreign private holdings of US Treasury bills increased $12.3 billion (row D11) with foreign official holdings increasing $11.7 billion while the category “other” increased $1.8 billion. Foreign private holdings of US Treasury bills increased $12.3 billion in what could be arbitrage of duration exposures. Risk aversion of default losses in foreign securities dominates decisions to accept zero interest rates in Treasury securities with no perception of principal losses. In the case of long-term securities, investors prefer to sacrifice inflation and possible duration risk to avoid principal losses with significant oscillations in risk perceptions.
Table VA-9, Net Cross-Borders Flows of US Long-Term Securities, Billion Dollars, NSA
| Oct 2013 12 Months | Oct 2014 12 Months | Sep 2014 | Oct 2014 | |
| A Foreign Purchases less Sales of | 249.6 | 164.3 | 94.2 | -15.0 |
| A1 Private | 154.9 | 79.1 | 79.7 | -15.4 |
| A11 Treasury | 81.7 | 131.7 | 44.2 | 3.1 |
| A12 Agency | 33.0 | 9.5 | 11.7 | 2.2 |
| A13 Corporate Bonds | 10.7 | -22.9 | 19.4 | 6.3 |
| A14 Equities | 29.6 | -39.3 | 4.4 | -27.1 |
| A2 Official | 94.8 | 85.3 | 14.6 | 0.5 |
| A21 Treasury | -2.0 | 68.0 | 3.9 | -2.5 |
| A22 Agency | 79.3 | 17.4 | 9.3 | 1.6 |
| A23 Corporate Bonds | 18.0 | 8.0 | 1.3 | 1.6 |
| A24 Equities | -0.5 | -8.1 | 0.0 | -0.2 |
| B Net US Purchases of LT Foreign Securities | -193.7 | -31.4 | 70.1 | 13.6 |
| B1 Foreign Bonds | -31.6 | 69.1 | 40.1 | 27.6 |
| B2 Foreign Equities | -162.1 | -100.5 | 29.9 | -14.0 |
| C Net Foreign Purchases of US LT Securities | 56.0 | 132.9 | 164.3 | -1.4 |
| D Increase in Foreign Holdings of Dollar Denominated Short-term | -46.0 | 24.3 | -22.0 | 25.8 |
| D1 US Treasury Bills | -42.4 | 8.3 | -16.2 | 24.0 |
| D11 Private | -41.7 | -49.8 | -3.0 | 12.3 |
| D12 Official | 0.8 | -41.5 | -13.1 | 11.7 |
| D2 Other | -3.5 | 16.1 | -6.0 | 1.8 |
C = A + B;
A = A1 + A2
A1 = A11 + A12 + A13 + A14
A2 = A21 + A22 + A23 + A24
B = B1 + B2
D = D1 + D2
Sources: United States Treasury
http://www.treasury.gov/resource-center/data-chart-center/tic/Pages/ticpress.aspx
http://www.treasury.gov/press-center/press-releases/Pages/jl2609.aspx
Table VA-10 provides major foreign holders of US Treasury securities. China is the largest holder with $1252.7 billion in Oct 2014, decreasing 4.0 percent from $1304.5 billion in Oct 2013 while decreasing $13.6 billion from Sep 2014 or 1.1 percent. The United States Treasury estimates US government debt held by private investors at $9670 billion in Jun 2014. China’s holding of US Treasury securities represent 12.9 percent of US government marketable interest-bearing debt held by private investors (http://www.fms.treas.gov/bulletin/index.html). Min Zeng, writing on “China plays a big role as US Treasury yields fall,” on Jul 16, 2004, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/articles/china-plays-a-big-role-as-u-s-treasury-yields-fall-1405545034?tesla=y&mg=reno64-wsj), finds that acceleration in purchases of US Treasury securities by China has been an important factor in the decline of Treasury yields in 2014. Japan increased its holdings from $1174.4 billion in Oct 2013 to $1222.4 billion in Oct 2014 or 4.1 percent. The combined holdings of China and Japan in Oct 2014 add to $2475 billion, which is equivalent to 25.6 percent of US government marketable interest-bearing securities held by investors of $9670 billion in Jun 2014 (http://www.fms.treas.gov/bulletin/index.html). Total foreign holdings of Treasury securities rose from $5655.1 billion in Oct 2013 to $6058.9 billion in Oct 2014, or 7.1 percent. The US continues to finance its fiscal and balance of payments deficits with foreign savings (see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007)). A point of saturation of holdings of US Treasury debt may be reached as foreign holders evaluate the threat of reduction of principal by dollar devaluation and reduction of prices by increases in yield, including possibly risk premium. Shultz et al (2012) find that the Fed financed three-quarters of the US deficit in fiscal year 2011, with foreign governments financing significant part of the remainder of the US deficit while the Fed owns one in six dollars of US national debt. Concentrations of debt in few holders are perilous because of sudden exodus in fear of devaluation and yield increases and the limit of refinancing old debt and placing new debt. In their classic work on “unpleasant monetarist arithmetic,” Sargent and Wallace (1981, 2) consider a regime of domination of monetary policy by fiscal policy (emphasis added):
“Imagine that fiscal policy dominates monetary policy. The fiscal authority independently sets its budgets, announcing all current and future deficits and surpluses and thus determining the amount of revenue that must be raised through bond sales and seignorage. Under this second coordination scheme, the monetary authority faces the constraints imposed by the demand for government bonds, for it must try to finance with seignorage any discrepancy between the revenue demanded by the fiscal authority and the amount of bonds that can be sold to the public. Suppose that the demand for government bonds implies an interest rate on bonds greater than the economy’s rate of growth. Then if the fiscal authority runs deficits, the monetary authority is unable to control either the growth rate of the monetary base or inflation forever. If the principal and interest due on these additional bonds are raised by selling still more bonds, so as to continue to hold down the growth of base money, then, because the interest rate on bonds is greater than the economy’s growth rate, the real stock of bonds will growth faster than the size of the economy. This cannot go on forever, since the demand for bonds places an upper limit on the stock of bonds relative to the size of the economy. Once that limit is reached, the principal and interest due on the bonds already sold to fight inflation must be financed, at least in part, by seignorage, requiring the creation of additional base money.”
Table VA-10, US, Major Foreign Holders of Treasury Securities $ Billions at End of Period
| Oct 2014 | Sep 2014 | Oct 2013 | |
| Total | 6058.9 | 6066.4 | 5655.1 |
| China | 1252.7 | 1266.3 | 1304.5 |
| Japan | 1222.4 | 1221.8 | 1174.4 |
| Belgium | 348.1 | 353.9 | 180.3 |
| Caribbean Banking Centers | 324.9 | 315.0 | 291.9 |
| Oil Exporters | 281.8 | 279.4 | 236.8 |
| Brazil | 261.7 | 262.3 | 246.7 |
| Switzerland | 184.3 | 186.2 | 174.3 |
| Taiwan | 172.9 | 173.4 | 184.5 |
| United Kingdom | 171.3 | 167.9 | 158.5 |
| Luxembourg | 162.5 | 156.1 | 133.3 |
| Hong Kong | 161.0 | 159.0 | 137.3 |
| Ireland | 123.9 | 110.6 | 110.9 |
| Russia | 108.9 | 117.7 | 149.9 |
| Foreign Official Holdings | 4124.1 | 4139.9 | 4052.3 |
| A. Treasury Bills | 337.1 | 325.4 | 378.6 |
| B. Treasury Bonds and Notes | 3787.0 | 3814.5 | 3673.7 |
Source: United States Treasury
http://www.treasury.gov/resource-center/data-chart-center/tic/Pages/ticpress.aspx
http://www.treasury.gov/resource-center/data-chart-center/tic/Pages/index.aspx
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015.

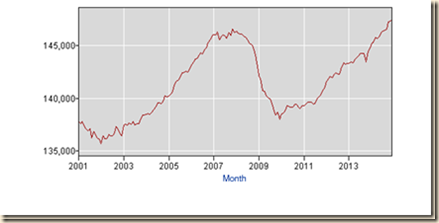
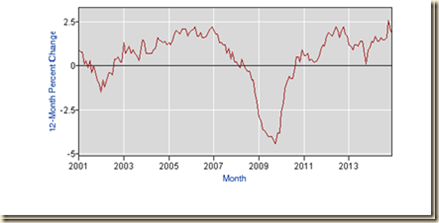

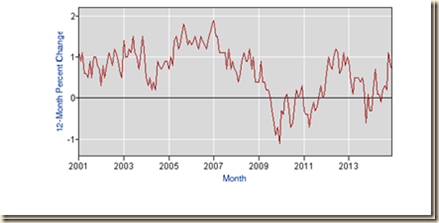
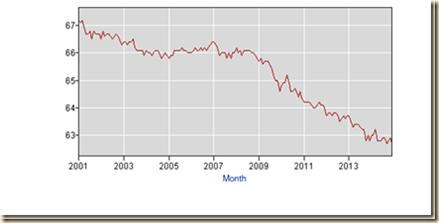
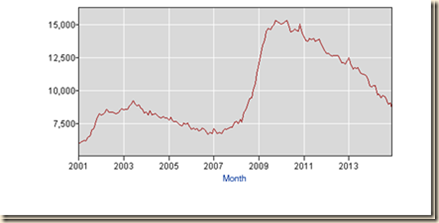


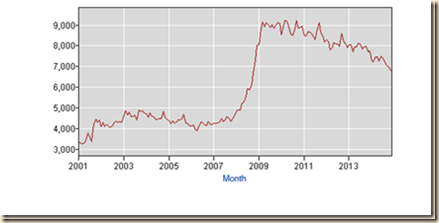


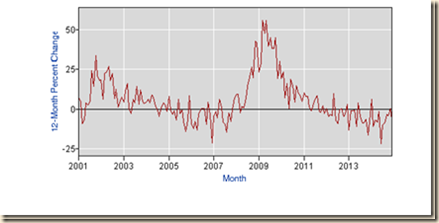

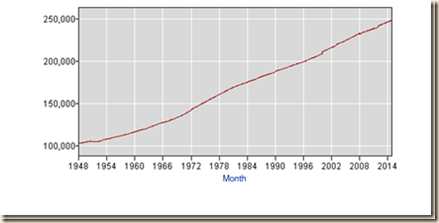





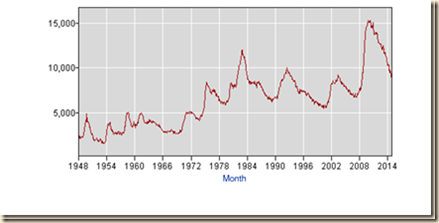





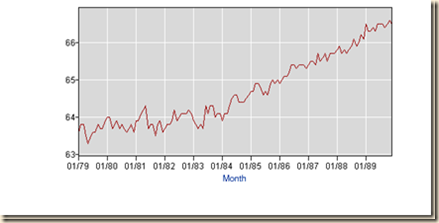

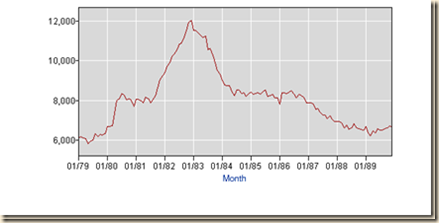



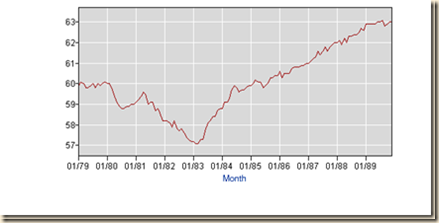
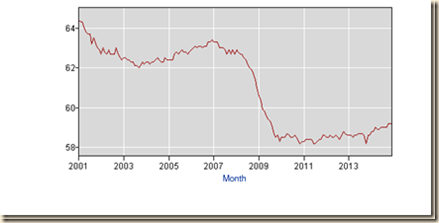
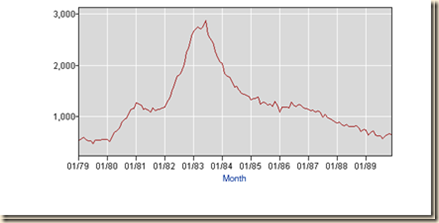





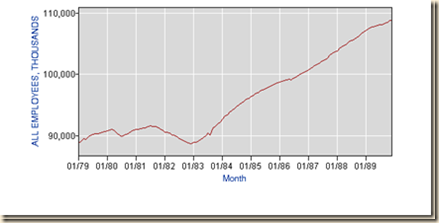




![clip_image047[1] clip_image047[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhZJ20KFCtmZpmLQhJsXC9U4PqXNh2CAScjf-JfiPsedi8SjewaX-JorcPtEP_flCwhKXP_ZCGB2JFehRoymYARc0XSdgNDlg9L1lbD9q86U_jJlSG7Cb9NiH_Fcr38QKADmEdW-soBHSrc/?imgmax=800)




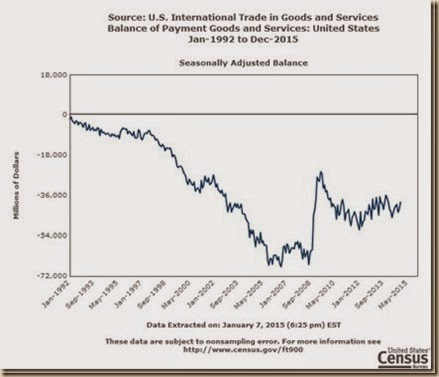

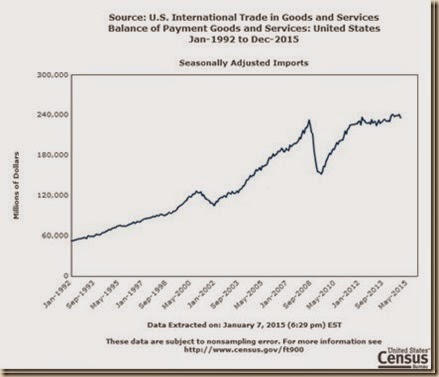
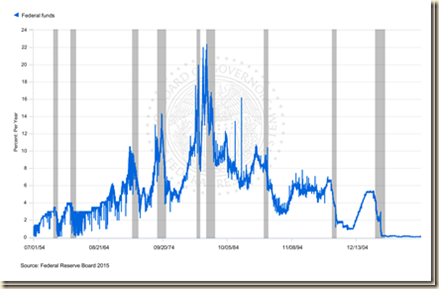

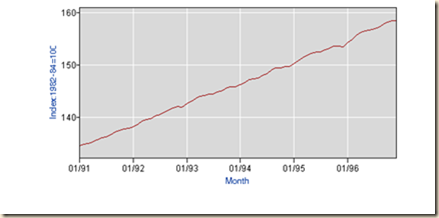





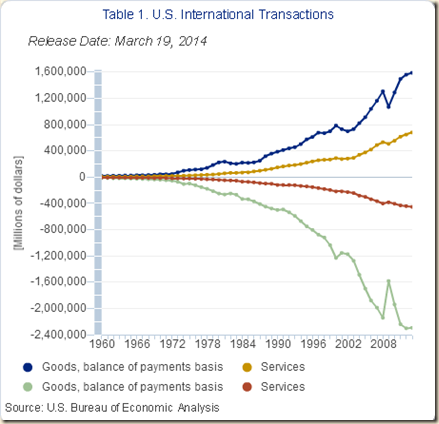



No comments:
Post a Comment