Financial Uncertainty, Mediocre Cyclical United States Economic Growth with GDP Two Trillion Dollars below Trend, Stagnating Real Disposable Income, Financial Repression, United States Commercial Banks, United States Housing, World Cyclical Slow Growth and Global Recession Risk
Carlos M. Pelaez
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014
Executive Summary
I Mediocre Cyclical United States Economic Growth with GDP Two Trillion Dollars Below Trend
IA Mediocre Cyclical United States Economic Growth
IA1 Contracting Real Private Fixed Investment
IA2 Swelling Undistributed Corporate Profits
IB Stagnating Real Disposable Income and Consumption Expenditures
IB1 Stagnating Real Disposable Income and Consumption Expenditures
IB2 Financial Repression
IIA United States Commercial Banks Assets and Liabilities
IIA1 Transmission of Monetary Policy
IIB1 Functions of Banks
IIC United States Commercial Banks Assets and Liabilities
IID Theory and Reality of Economic History, Cyclical Slow Growth Not Secular Stagnation and Monetary Policy Based on Fear of Deflation
IIB United States Housing Collapse
III World Financial Turbulence
IIIA Financial Risks
IIIE Appendix Euro Zone Survival Risk
IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation
IV Global Inflation
V World Economic Slowdown
VA United States
VB Japan
VC China
VD Euro Area
VE Germany
VF France
VG Italy
VH United Kingdom
VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets
VII Economic Indicators
VIII Interest Rates
IX Conclusion
References
Appendixes
Appendix I The Great Inflation
IIIB Appendix on Safe Haven Currencies
IIIC Appendix on Fiscal Compact
IIID Appendix on European Central Bank Large Scale Lender of Last Resort
IIIG Appendix on Deficit Financing of Growth and the Debt Crisis
IIIGA Monetary Policy with Deficit Financing of Economic Growth
IIIGB Adjustment during the Debt Crisis of the 1980s
Executive Summary
Contents of Executive Summary
ESI Increasing Interest Rate Risk, Tapering Quantitative Easing, Duration Dumping, Steepening
Yield Curve and Global Financial and Economic Risk
ESII Mediocre Cyclical United States Economic Growth with GDP Two Trillion Dollars Below Trend
ESIII Contracting Real Private Fixed Investment
ESIV Swelling Undistributed Corporate Profits
ESV Stagnating Real Disposable Income
ESVI Financial Repression
ESVII United States Commercial Banks Assets and Liabilities
ESVIII United States Housing Collapse
ESI Increasing Interest Rate Risk, Tapering Quantitative Easing, Duration Dumping, Steepening Yield Curve and Global Financial and Economic Risk. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) provides an international safety net for prevention and resolution of international financial crises. The IMF’s Financial Sector Assessment Program (FSAP) provides analysis of the economic and financial sectors of countries (see Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), 101-62, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008), 114-23). Relating economic and financial sectors is a challenging task for both theory and measurement. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) provides an international safety net for prevention and resolution of international financial crises. The IMF’s Financial Sector Assessment Program (FSAP) provides analysis of the economic and financial sectors of countries (see Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), 101-62, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008), 114-23). Relating economic and financial sectors is a challenging task for both theory and measurement. The IMF (2013WEOOct) provides surveillance of the world economy with its Global Economic Outlook (WEO) (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2013/02/), of the world financial system with its Global Financial Stability Report (GFSR) (IMF 2013GFSROct) (http://www.imf.org/External/Pubs/FT/GFSR/2013/02/index.htm) and of fiscal affairs with the Fiscal Monitor (IMF 2013FMOct) (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fm/2013/02/fmindex.htm). There appears to be a moment of transition in global economic and financial variables that may prove of difficult analysis and measurement. It is useful to consider a summary of global economic and financial risks, which are analyzed in detail in the comments of this blog in Section VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets, Table VI-4.
Economic risks include the following:
- China’s Economic Growth. China is lowering its growth target to 7.5 percent per year. China’s GDP growth decelerated from 12.1 percent in IQ2010 and 11.2 percent in IIQ2010 to 7.7 percent in IQ2013, 7.5 percent in IIQ2013 and 7.8 percent in IIIQ2013. GDP grew 7.7 percent in IVQ2013 relative to a year earlier and 1.8 percent relative to IIIQ2013, which is equivalent to 7.4 percent per year (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/01/capital-flows-exchange-rates-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/10/twenty-eight-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and_7005.html and earlier at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/01/recovery-without-hiring-world-inflation.html and earlier at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/10/world-inflation-waves-stagnating-united_21.html). There is also concern about indebtedness, move to devaluation and deep policy reforms.
- United States Economic Growth, Labor Markets and Budget/Debt Quagmire. The US is growing slowly with 29.3 million in job stress, fewer 10 million full-time jobs, high youth unemployment, historically low hiring and declining/stagnating real wages. Actual GDP is about two trillion dollars lower than trend GDP.
- Economic Growth and Labor Markets in Advanced Economies. Advanced economies are growing slowly. There is still high unemployment in advanced economies.
- World Inflation Waves. Inflation continues in repetitive waves globally (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/interest-rate-risks-world-inflation.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/02/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html). There is growing concern on capital outflows and currency depreciation of emerging markets.
A list of financial uncertainties includes:
- Euro Area Survival Risk. The resilience of the euro to fiscal and financial doubts on larger member countries is still an unknown risk.
- Foreign Exchange Wars. Exchange rate struggles continue as zero interest rates in advanced economies induce devaluation of their currencies with alternating episodes of revaluation.
- Valuation of Risk Financial Assets. Valuations of risk financial assets have reached extremely high levels in markets with lower volumes.
- Duration Trap of the Zero Bound. The yield of the US 10-year Treasury rose from 2.031 percent on Mar 9, 2012, to 2.294 percent on Mar 16, 2012. Considering a 10-year Treasury with coupon of 2.625 percent and maturity in exactly 10 years, the price would fall from 105.3512 corresponding to yield of 2.031 percent to 102.9428 corresponding to yield of 2.294 percent, for loss in a week of 2.3 percent but far more in a position with leverage of 10:1. Min Zeng, writing on “Treasurys fall, ending brutal quarter,” published on Mar 30, 2012, in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052702303816504577313400029412564.html?mod=WSJ_hps_sections_markets), informs that Treasury bonds maturing in more than 20 years lost 5.52 percent in the first quarter of 2012.
- Credibility and Commitment of Central Bank Policy. There is a credibility issue of the commitment of monetary policy (Sargent and Silber 2012Mar20).
- Carry Trades. Commodity prices driven by zero interest rates have resumed their increasing path with fluctuations caused by intermittent risk aversion
What is truly important is the fixing of the overnight fed funds at 0 to ¼ percent for which there is no end in sight as evident in the FOMC statement for Mar 19, 2014 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20140319a.htm):
“To support continued progress toward maximum employment and price stability, the Committee today reaffirmed its view that a highly accommodative stance of monetary policy remains appropriate. In determining how long to maintain the current 0 to 1/4 percent target range for the federal funds rate, the Committee will assess progress--both realized and expected--toward its objectives of maximum employment and 2 percent inflation. This assessment will take into account a wide range of information, including measures of labor market conditions, indicators of inflation pressures and inflation expectations, and readings on financial developments. The Committee continues to anticipate, based on its assessment of these factors, that it likely will be appropriate to maintain the current target range for the federal funds rate for a considerable time after the asset purchase program ends, especially if projected inflation continues to run below the Committee's 2 percent longer-run goal, and provided that longer-term inflation expectations remain well anchored.” (emphasis added).
How long is “considerable time”? At the press conference following the meeting on Mar 19, 2014, Chair Yellen answered a question of Jon Hilsenrath of the Wall Street Journal explaining “In particular, the Committee has endorsed the view that it anticipates that will be a considerable period after the asset purchase program ends before it will be appropriate to begin to raise rates. And of course on our present path, well, that's not utterly preset. We would be looking at next, next fall. So, I think that's important guidance” (http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20140319.pdf). Many focused on “next fall,” ignoring that the path of increasing rates is not “utterly preset.”
Chart S provides the yield of the two-year Treasury constant maturity from Mar 17, 2014, two days before the guidance of Chair Yellen on Mar 19, 2014, to Mar 27, 2014. Chart SA provides the yield of the ten-year Treasury constant maturity in the same dates. Both yields increased right after the guidance of Chair Yellen. The two-year yield remain at a higher level while the ten-year yield fell. There could be more immediate impact on two-year yields of an increase in the fed funds rates but the effects would spread throughout the term structure of interest rates (Cox, Ingersoll and Ross 1981, 1985, Ingersoll 1987).
Chart S, US, Yield of Two-Year Treasury Constant Maturity, Mar 17 to Mar 27
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/
Chart SA, US, Yield of Ten-Year Treasury Constant Maturity, Mar 17 to Mar 27
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/
Chart VIII-1 of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System provides the rate on the overnight fed funds rate and the yields of the 10-year constant maturity Treasury and the Baa seasoned corporate bond. Table VIII-3 provides the data for selected points in Chart VIII-1. There are two important economic and financial events, illustrating the ease of inducing carry trade with extremely low interest rates and the resulting financial crash and recession of abandoning extremely low interest rates.
- The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) lowered the target of the fed funds rate from 7.03 percent on Jul 3, 2000, to 1.00 percent on Jun 22, 2004, in pursuit of non-existing deflation (Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), 18-28, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 83-85). Central bank commitment to maintain the fed funds rate at 1.00 percent induced adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMS) linked to the fed funds rate. Lowering the interest rate near the zero bound in 2003-2004 caused the illusion of permanent increases in wealth or net worth in the balance sheets of borrowers and also of lending institutions, securitized banking and every financial institution and investor in the world. The discipline of calculating risks and returns was seriously impaired. The objective of monetary policy was to encourage borrowing, consumption and investment. The exaggerated stimulus resulted in a financial crisis of major proportions as the securitization that had worked for a long period was shocked with policy-induced excessive risk, imprudent credit, high leverage and low liquidity by the incentive to finance everything overnight at interest rates close to zero, from adjustable rate mortgages (ARMS) to asset-backed commercial paper of structured investment vehicles (SIV). The consequences of inflating liquidity and net worth of borrowers were a global hunt for yields to protect own investments and money under management from the zero interest rates and unattractive long-term yields of Treasuries and other securities. Monetary policy distorted the calculations of risks and returns by households, business and government by providing central bank cheap money. Short-term zero interest rates encourage financing of everything with short-dated funds, explaining the SIVs created off-balance sheet to issue short-term commercial paper with the objective of purchasing default-prone mortgages that were financed in overnight or short-dated sale and repurchase agreements (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession, 50-1, Regulation of Banks and Finance, 59-60, Globalization and the State Vol. I, 89-92, Globalization and the State Vol. II, 198-9, Government Intervention in Globalization, 62-3, International Financial Architecture, 144-9). ARMS were created to lower monthly mortgage payments by benefitting from lower short-dated reference rates. Financial institutions economized in liquidity that was penalized with near zero interest rates. There was no perception of risk because the monetary authority guaranteed a minimum or floor price of all assets by maintaining low interest rates forever or equivalent to writing an illusory put option on wealth. Subprime mortgages were part of the put on wealth by an illusory put on house prices. The housing subsidy of $221 billion per year created the impression of ever-increasing house prices. The suspension of auctions of 30-year Treasuries was designed to increase demand for mortgage-backed securities, lowering their yield, which was equivalent to lowering the costs of housing finance and refinancing. Fannie and Freddie purchased or guaranteed $1.6 trillion of nonprime mortgages and worked with leverage of 75:1 under Congress-provided charters and lax oversight. The combination of these policies resulted in high risks because of the put option on wealth by near zero interest rates, excessive leverage because of cheap rates, low liquidity by the penalty in the form of low interest rates and unsound credit decisions. The put option on wealth by monetary policy created the illusion that nothing could ever go wrong, causing the credit/dollar crisis and global recession (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession, 157-66, Regulation of Banks, and Finance, 217-27, International Financial Architecture, 15-18, The Global Recession Risk, 221-5, Globalization and the State Vol. II, 197-213, Government Intervention in Globalization, 182-4). The FOMC implemented increments of 25 basis points of the fed funds target from Jun 2004 to Jun 2006, raising the fed funds rate to 5.25 percent on Jul 3, 2006, as shown in Chart VIII-1. The gradual exit from the first round of unconventional monetary policy from 1.00 percent in Jun 2004 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/boarddocs/press/monetary/2004/20040630/default.htm) to 5.25 percent in Jun 2006 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20060629a.htm) caused the financial crisis and global recession.
- On Dec 16, 2008, the policy determining committee of the Fed decided (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20081216b.htm): “The Federal Open Market Committee decided today to establish a target range for the federal funds rate of 0 to 1/4 percent.” Policymakers emphasize frequently that there are tools to exit unconventional monetary policy at the right time. At the confirmation hearing on nomination for Chair of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Vice Chair Yellen (2013Nov14 http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20131114a.htm), states that: “The Federal Reserve is using its monetary policy tools to promote a more robust recovery. A strong recovery will ultimately enable the Fed to reduce its monetary accommodation and reliance on unconventional policy tools such as asset purchases. I believe that supporting the recovery today is the surest path to returning to a more normal approach to monetary policy.” Perception of withdrawal of $2611 billion, or $2.6 trillion, of bank reserves (http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h41/current/h41.htm#h41tab1), would cause Himalayan increase in interest rates that would provoke another recession. There is no painless gradual or sudden exit from zero interest rates because reversal of exposures created on the commitment of zero interest rates forever.
In his classic restatement of the Keynesian demand function in terms of “liquidity preference as behavior toward risk,” James Tobin (http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/economic-sciences/laureates/1981/tobin-bio.html) identifies the risks of low interest rates in terms of portfolio allocation (Tobin 1958, 86):
“The assumption that investors expect on balance no change in the rate of interest has been adopted for the theoretical reasons explained in section 2.6 rather than for reasons of realism. Clearly investors do form expectations of changes in interest rates and differ from each other in their expectations. For the purposes of dynamic theory and of analysis of specific market situations, the theories of sections 2 and 3 are complementary rather than competitive. The formal apparatus of section 3 will serve just as well for a non-zero expected capital gain or loss as for a zero expected value of g. Stickiness of interest rate expectations would mean that the expected value of g is a function of the rate of interest r, going down when r goes down and rising when r goes up. In addition to the rotation of the opportunity locus due to a change in r itself, there would be a further rotation in the same direction due to the accompanying change in the expected capital gain or loss. At low interest rates expectation of capital loss may push the opportunity locus into the negative quadrant, so that the optimal position is clearly no consols, all cash. At the other extreme, expectation of capital gain at high interest rates would increase sharply the slope of the opportunity locus and the frequency of no cash, all consols positions, like that of Figure 3.3. The stickier the investor's expectations, the more sensitive his demand for cash will be to changes in the rate of interest (emphasis added).”
Tobin (1969) provides more elegant, complete analysis of portfolio allocation in a general equilibrium model. The major point is equally clear in a portfolio consisting of only cash balances and a perpetuity or consol. Let g be the capital gain, r the rate of interest on the consol and re the expected rate of interest. The rates are expressed as proportions. The price of the consol is the inverse of the interest rate, (1+re). Thus, g = [(r/re) – 1]. The critical analysis of Tobin is that at extremely low interest rates there is only expectation of interest rate increases, that is, dre>0, such that there is expectation of capital losses on the consol, dg<0. Investors move into positions combining only cash and no consols. Valuations of risk financial assets would collapse in reversal of long positions in carry trades with short exposures in a flight to cash. There is no exit from a central bank created liquidity trap without risks of financial crash and another global recession. The net worth of the economy depends on interest rates. In theory, “income is generally defined as the amount a consumer unit could consume (or believe that it could) while maintaining its wealth intact” (Friedman 1957, 10). Income, Y, is a flow that is obtained by applying a rate of return, r, to a stock of wealth, W, or Y = rW (Friedman 1957). According to a subsequent statement: “The basic idea is simply that individuals live for many years and that therefore the appropriate constraint for consumption is the long-run expected yield from wealth r*W. This yield was named permanent income: Y* = r*W” (Darby 1974, 229), where * denotes permanent. The simplified relation of income and wealth can be restated as:
W = Y/r (1)
Equation (1) shows that as r goes to zero, r→0, W grows without bound, W→∞. Unconventional monetary policy lowers interest rates to increase the present value of cash flows derived from projects of firms, creating the impression of long-term increase in net worth. An attempt to reverse unconventional monetary policy necessarily causes increases in interest rates, creating the opposite perception of declining net worth. As r→∞, W = Y/r →0. There is no exit from unconventional monetary policy without increasing interest rates with resulting pain of financial crisis and adverse effects on production, investment and employment.
Chart VIII-1, Fed Funds Rate and Yields of Ten-year Treasury Constant Maturity and Baa Seasoned Corporate Bond, Jan 2, 2001 to Mar 27, 2014
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/
Table VIII-3, Selected Data Points in Chart VIII-1, % per Year
| Fed Funds Overnight Rate | 10-Year Treasury Constant Maturity | Seasoned Baa Corporate Bond | |
| 1/2/2001 | 6.67 | 4.92 | 7.91 |
| 10/1/2002 | 1.85 | 3.72 | 7.46 |
| 7/3/2003 | 0.96 | 3.67 | 6.39 |
| 6/22/2004 | 1.00 | 4.72 | 6.77 |
| 6/28/2006 | 5.06 | 5.25 | 6.94 |
| 9/17/2008 | 2.80 | 3.41 | 7.25 |
| 10/26/2008 | 0.09 | 2.16 | 8.00 |
| 10/31/2008 | 0.22 | 4.01 | 9.54 |
| 4/6/2009 | 0.14 | 2.95 | 8.63 |
| 4/5/2010 | 0.20 | 4.01 | 6.44 |
| 2/4/2011 | 0.17 | 3.68 | 6.25 |
| 7/25/2012 | 0.15 | 1.43 | 4.73 |
| 5/1/13 | 0.14 | 1.66 | 4.48 |
| 9/5/13 | 0.08 | 2.98 | 5.53 |
| 11/21/2013 | 0.09 | 2.79 | 5.44 |
| 11/26/13 | 0.09 | 2.74 | 5.34 (11/26/13) |
| 12/5/13 | 0.09 | 2.88 | 5.47 |
| 12/11/13 | 0.09 | 2.89 | 5.42 |
| 12/18/13 | 0.09 | 2.94 | 5.36 |
| 12/26/13 | 0.08 | 3.00 | 5.37 |
| 1/1/2014 | 0.08 | 3.00 | 5.34 |
| 1/8/2014 | 0.07 | 2.97 | 5.28 |
| 1/15/2014 | 0.07 | 2.86 | 5.18 |
| 1/22/2014 | 0.07 | 2.79 | 5.11 |
| 1/30/2014 | 0.07 | 2.72 | 5.08 |
| 2/6/2014 | 0.07 | 2.73 | 5.13 |
| 2/13/2014 | 0.06 | 2.73 | 5.12 |
| 2/20/14 | 0.07 | 2.76 | 5.15 |
| 2/27/14 | 0.07 | 2.65 | 5.01 |
| 3/6/14 | 0.08 | 2.74 | 5.11 |
| 3/13/14 | 0.08 | 2.66 | 5.05 |
| 3/20/14 | 0.08 | 2.79 | 5.13 |
| 3/27/14 | 0.08 | 2.69 | 4.95 |
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/
Professionals use a variety of techniques in measuring interest rate risk (Fabozzi, Buestow and Johnson, 2006, Chapter Nine, 183-226):
- Full valuation approach in which securities and portfolios are shocked by 50, 100, 200 and 300 basis points to measure their impact on asset values
- Stress tests requiring more complex analysis and translation of possible events with high impact even if with low probability of occurrence into effects on actual positions and capital
- Value at Risk (VaR) analysis of maximum losses that are likely in a time horizon
- Duration and convexity that are short-hand convenient measurement of changes in prices resulting from changes in yield captured by duration and convexity
- Yield volatility
Analysis of these methods is in Pelaez and Pelaez (International Financial Architecture (2005), 101-162) and Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. (I) (2008a), 78-100). Frederick R. Macaulay (1938) introduced the concept of duration in contrast with maturity for analyzing bonds. Duration is the sensitivity of bond prices to changes in yields. In economic jargon, duration is the yield elasticity of bond price to changes in yield, or the percentage change in price after a percentage change in yield, typically expressed as the change in price resulting from change of 100 basis points in yield. The mathematical formula is the negative of the yield elasticity of the bond price or –[dB/d(1+y)]((1+y)/B), where d is the derivative operator of calculus, B the bond price, y the yield and the elasticity does not have dimension (Hallerbach 2001). The duration trap of unconventional monetary policy is that duration is higher the lower the coupon and higher the lower the yield, other things being constant. Coupons and yields are historically low because of unconventional monetary policy. Duration dumping during a rate increase may trigger the same crossfire selling of high duration positions that magnified the credit crisis. Traders reduced positions because capital losses in one segment, such as mortgage-backed securities, triggered haircuts and margin increases that reduced capital available for positioning in all segments, causing fire sales in multiple segments (Brunnermeier and Pedersen 2009; see Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2008b), 217-24). Financial markets are currently experiencing fear of duration and riskier asset classes resulting from the debate within and outside the Fed on tapering quantitative easing. Table VIII-2 provides the yield curve of Treasury securities on Mar 28, 2014, Dec 31, 2013, May 1, 2013, Mar 28, 2013 and Mar 28, 2006. There is oscillating steepening of the yield curve for longer maturities, which are also the ones with highest duration. The 10-year yield increased from 1.45 percent on Jul 26, 2012 to 3.04 percent on Dec 31, 2013 and 2.73 percent on Mar 28, 2014, as measured by the United States Treasury. Assume that a bond with maturity in 10 years were issued on Dec 31, 2013, at par or price of 100 with coupon of 1.45 percent. The price of that bond would be 86.3778 with instantaneous increase of the yield to 3.04 percent for loss of 13.6 percent and far more with leverage. Assume that the yield of a bond with exactly ten years to maturity and coupon of 2.73 percent as occurred on Mar 28, 2013 would jump instantaneously from yield of 2.73 percent on Mar 28, 2014 to 4.79 percent as occurred on Mar 28, 2006 when the economy was closer to full employment. The price of the hypothetical bond issued with coupon of 2.73 percent would drop from 100 to 83.7828 after an instantaneous increase of the yield to 4.79 percent. The price loss would be 16.2 percent. Losses absorb capital available for positioning, triggering crossfire sales in multiple asset classes (Brunnermeier and Pedersen 2009). What is the path of adjustment of zero interest rates on fed funds and artificially low bond yields? There is no painless exit from unconventional monetary policy. Chris Dieterich, writing on “Bond investors turn to cash,” on Jul 25, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887323971204578625900935618178.html), uses data of the Investment Company Institute (http://www.ici.org/) in showing withdrawals of $43 billion in taxable mutual funds in Jun, which is the largest in history, with flows into cash investments such as $8.5 billion in the week of Jul 17 into money-market funds.
Table VIII-2, United States, Treasury Yields
| 3/28/14 | 12/31/13 | 5/01/13 | 3/28/13 | 3/28/06 | |
| 1 M | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.03 | 0.04 | 4.71 |
| 3 M | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.06 | 0.07 | 4.65 |
| 6 M | 0.06 | 0.10 | 0.08 | 0.11 | 4.83 |
| 1 Y | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.11 | 0.14 | 4.82 |
| 2 Y | 0.45 | 0.38 | 0.20 | 0.25 | 4.81 |
| 3 Y | 0.93 | 0.78 | 0.30 | 0.36 | 4.79 |
| 5 Y | 1.74 | 1.75 | 0.65 | 0.77 | 4.79 |
| 7 Y | 2.31 | 2.45 | 1.07 | 1.24 | 4.79 |
| 10 Y | 2.73 | 3.04 | 1.66 | 1.87 | 4.79 |
| 20 Y | 3.29 | 3.72 | 2.44 | 2.71 | 4.98 |
| 30 Y | 3.55 | 3.96 | 2.83 | 3.10 | 4.80 |
M: Months; Y: Years
Source: United States Treasury
Interest rate risk is increasing in the US with amplifying fluctuations. Chart VI-13 of the Board of Governors provides the conventional mortgage rate for a fixed-rate 30-year mortgage. The rate stood at 5.87 percent on Jan 8, 2004, increasing to 6.79 percent on Jul 6, 2006. The rate bottomed at 3.35 percent on May 2, 2013. Fear of duration risk in longer maturities such as mortgage-backed securities caused continuing increases in the conventional mortgage rate that rose to 4.51 percent on Jul 11, 2013, 4.58 percent on Aug 22, 2013 and 4.40 percent on Mar 27, 2014, which is the last data point in Chart VI-13. Shayndi Raice and Nick Timiraos, writing on “Banks cut as mortgage boom ends,” on Jan 9, 2014, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702303754404579310940019239208), analyze the drop in mortgage applications to a 13-year low, as measured by the Mortgage Bankers Association.
Chart VI-13, US, Conventional Mortgage Rate, Jan 8, 2004 to Mar 27, 2014
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/update/
There is a false impression of the existence of a monetary policy “science,” measurements and forecasting with which to steer the economy into “prosperity without inflation.” Market participants are remembering the Great Bond Crash of 1994 shown in Table VI-7G when monetary policy pursued nonexistent inflation, causing trillions of dollars of losses in fixed income worldwide while increasing the fed funds rate from 3 percent in Jan 1994 to 6 percent in Dec. The exercise in Table VI-7G shows a drop of the price of the 30-year bond by 18.1 percent and of the 10-year bond by 14.1 percent. CPI inflation remained almost the same and there is no valid counterfactual that inflation would have been higher without monetary policy tightening because of the long lag in effect of monetary policy on inflation (see Culbertson 1960, 1961, Friedman 1961, Batini and Nelson 2002, Romer and Romer 2004). The pursuit of nonexistent deflation during the past ten years has resulted in the largest monetary policy accommodation in history that created the 2007 financial market crash and global recession and is currently preventing smoother recovery while creating another financial crash in the future. The issue is not whether there should be a central bank and monetary policy but rather whether policy accommodation in doses from zero interest rates to trillions of dollars in the fed balance sheet endangers economic stability.
Table VI-7G, Fed Funds Rates, Thirty and Ten Year Treasury Yields and Prices, 30-Year Mortgage Rates and 12-month CPI Inflation 1994
| 1994 | FF | 30Y | 30P | 10Y | 10P | MOR | CPI |
| Jan | 3.00 | 6.29 | 100 | 5.75 | 100 | 7.06 | 2.52 |
| Feb | 3.25 | 6.49 | 97.37 | 5.97 | 98.36 | 7.15 | 2.51 |
| Mar | 3.50 | 6.91 | 92.19 | 6.48 | 94.69 | 7.68 | 2.51 |
| Apr | 3.75 | 7.27 | 88.10 | 6.97 | 91.32 | 8.32 | 2.36 |
| May | 4.25 | 7.41 | 86.59 | 7.18 | 88.93 | 8.60 | 2.29 |
| Jun | 4.25 | 7.40 | 86.69 | 7.10 | 90.45 | 8.40 | 2.49 |
| Jul | 4.25 | 7.58 | 84.81 | 7.30 | 89.14 | 8.61 | 2.77 |
| Aug | 4.75 | 7.49 | 85.74 | 7.24 | 89.53 | 8.51 | 2.69 |
| Sep | 4.75 | 7.71 | 83.49 | 7.46 | 88.10 | 8.64 | 2.96 |
| Oct | 4.75 | 7.94 | 81.23 | 7.74 | 86.33 | 8.93 | 2.61 |
| Nov | 5.50 | 8.08 | 79.90 | 7.96 | 84.96 | 9.17 | 2.67 |
| Dec | 6.00 | 7.87 | 81.91 | 7.81 | 85.89 | 9.20 | 2.67 |
Notes: FF: fed funds rate; 30Y: yield of 30-year Treasury; 30P: price of 30-year Treasury assuming coupon equal to 6.29 percent and maturity in exactly 30 years; 10Y: yield of 10-year Treasury; 10P: price of 10-year Treasury assuming coupon equal to 5.75 percent and maturity in exactly 10 years; MOR: 30-year mortgage; CPI: percent change of CPI in 12 months
Sources: yields and mortgage rates http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/data.htm CPI ftp://ftp.bls.gov/pub/special.requests/cpi/cpiai.t
Chart VI-14 provides the overnight fed funds rate, the yield of the 10-year Treasury constant maturity bond, the yield of the 30-year constant maturity bond and the conventional mortgage rate from Jan 1991 to Dec 1996. In Jan 1991, the fed funds rate was 6.91 percent, the 10-year Treasury yield 8.09 percent, the 30-year Treasury yield 8.27 percent and the conventional mortgage rate 9.64 percent. Before monetary policy tightening in Oct 1993, the rates and yields were 2.99 percent for the fed funds, 5.33 percent for the 10-year Treasury, 5.94 for the 30-year Treasury and 6.83 percent for the conventional mortgage rate. After tightening in Nov 1994, the rates and yields were 5.29 percent for the fed funds rate, 7.96 percent for the 10-year Treasury, 8.08 percent for the 30-year Treasury and 9.17 percent for the conventional mortgage rate.
Chart VI-14, US, Overnight Fed Funds Rate, 10-Year Treasury Constant Maturity, 30-Year Treasury Constant Maturity and Conventional Mortgage Rate, Monthly, Jan 1991 to Dec 1996
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/update/
Chart VI-15 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides the all items consumer price index from Jan 1991 to Dec 1996. There does not appear acceleration of consumer prices requiring aggressive tightening.
Chart VI-15, US, Consumer Price Index All Items, Jan 1991 to Dec 1996
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm
Chart IV-16 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides 12-month percentage changes of the all items consumer price index from Jan 1991 to Dec 1996. Inflation collapsed during the recession from Jul 1990 (III) and Mar 1991 (I) and the end of the Kuwait War on Feb 25, 1991 that stabilized world oil markets. CPI inflation remained almost the same and there is no valid counterfactual that inflation would have been higher without monetary policy tightening because of the long lag in effect of monetary policy on inflation (see Culbertson 1960, 1961, Friedman 1961, Batini and Nelson 2002, Romer and Romer 2004). Policy tightening had adverse collateral effects in the form of emerging market crises in Mexico and Argentina and fixed income markets worldwide.
Chart VI-16, US, Consumer Price Index All Items, Twelve-Month Percentage Change, Jan 1991 to Dec 1996
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm
Chinese Yuan/Dollar (CNY/USD) exchange rate that reveal pursuit of exchange rate policies resulting from monetary policy in the US and capital control/exchange rate policy in China. The ultimate intentions are the same: promoting internal economic activity at the expense of the rest of the world. The easy money policy of the US was deliberately or not but effectively to devalue the dollar from USD 1.1423/EUR on Jun 26, 2003 to USD 1.5914/EUR on Jul 14, 2008, or by 39.3 percent. The flight into dollar assets after the global recession caused revaluation to USD 1.192/EUR on Jun 7, 2010, or by 25.1 percent. After the temporary interruption of the sovereign risk issues in Europe from Apr to Jul, 2010, shown in Table VI-4 below, the dollar has devalued again to USD 1.3752/EUR on Mar 28, 2014 or by 15.4 percent {[(1.3752/1.192)-1]100 = 15.4%}. Yellen (2011AS, 6) admits that Fed monetary policy results in dollar devaluation with the objective of increasing net exports, which was the policy that Joan Robinson (1947) labeled as “beggar-my-neighbor” remedies for unemployment. Risk aversion erodes devaluation of the dollar. China fixed the CNY to the dollar for a long period at a highly undervalued level of around CNY 8.2765/USD subsequently revaluing to CNY 6.8211/USD until Jun 7, 2010, or by 17.6 percent. After fixing again the CNY to the dollar, China revalued to CNY 6.2130/USD on Fri Mar 28, 2014, or by an additional 8.9 percent, for cumulative revaluation of 24.9 percent. The final row of Table VI-2 shows: revaluation of 0.4 percent in the week of Mar 7, 2014; devaluation of 0.4 percent in the week of Mar 14, 2014; devaluation of 1.2 percent the week of Mar 21, 2013; and revaluation of 0.2 percent in the week of Mar 28, 2013. There could be reversal of revaluation to devalue the Yuan.
Table VI-2, Dollar/Euro (USD/EUR) Exchange Rate and Chinese Yuan/Dollar (CNY/USD) Exchange Rate
| USD/EUR | 12/26/03 | 7/14/08 | 6/07/10 | 3/28/14 |
| Rate | 1.1423 | 1.5914 | 1.192 | 1.3752 |
| CNY/USD | 01/03 | 07/21 | 7/15 | 3/28/ 2014 |
| Rate | 8.2798 | 8.2765 | 6.8211 | 6.2130 |
| Weekly Rates | 3/7/2014 | 3/14/2014 | 3/21/2014 | 3/28/ 2014 |
| CNY/USD | 6.1260 | 6.1496 | 6.2247 | 6.2130 |
| ∆% from Earlier Week* | 0.4 | -0.4 | -1.2 | 0.2 |
*Negative sign is depreciation; positive sign is appreciation
Source: http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/mdc_currencies.html?mod=mdc_topnav_2_3000
Professor Edward P Lazear (2013Jan7), writing on “Chinese ‘currency manipulation’ is not the problem,” on Jan 7, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887323320404578213203581231448.html), provides clear thought on the role of the yuan in trade between China and the United States and trade between China and Europe. There is conventional wisdom that Chinese exchange rate policy causes the loss of manufacturing jobs in the United States, which is shown by Lazear (2013Jan7) to be erroneous. The fact is that manipulation of the CNY/USD rate by China has only minor effects on US employment. Lazear (2013Jan7) shows that the movement of monthly exports of China to its major trading partners, United States and Europe, since 1995 cannot be explained by the fixing of the CNY/USD rate by China. The period is quite useful because it includes rapid growth before 2007, contraction until 2009 and weak subsequent expansion. Chart VI-1 of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System provides the CNY/USD exchange rate from Jan 3, 1995 to Mar 21, 2014 together with US recession dates in shaded areas. China fixed the CNY/USD rate for a long period as shown in the horizontal segment from 1995 to 2005. There was systematic revaluation of 17.6 percent from CNY 8.2765 on Jul 21, 2005 to CNY 6.8211 on Jul 15, 2008. China fixed the CNY/USD rate until Jun 7, 2010, to avoid adverse effects on its economy from the global recession, which is shown as a horizontal segment from 2009 until mid 2010. China then continued the policy of appreciation of the CNY relative to the USD with oscillations until the beginning of 2012 when the rate began to move sideways followed by a final upward slope of devaluation that is measured in Table VI-2A but virtually disappeared in the rate of CNY 6.3589/USD on Aug 17, 2012 and was nearly unchanged at CNY 6.3558/USD on Aug 24, 2012. China then appreciated 0.2 percent in the week of Dec 21, 2012, to CNY 6.2352/USD for cumulative 1.9 percent revaluation from Oct 28, 2011 and left the rate virtually unchanged at CNY 6.2316/USD on Jan 11, 2013, appreciating to CNY 6.2248/USD on Mar 21, 2014, which is the last data point in Chart VI-1. Revaluation of the CNY relative to the USD by 24.9 percent by Mar 28, 2014 has not reduced the trade surplus of China but reversal of the policy of revaluation could result in international confrontation. The interruption with upward slope in the final segment on the right of Chart VI-I is measured as virtually stability in Table VI-2A followed with decrease or revaluation. Linglin Wei, writing on “China intervenes to lower yuan,” on Feb 26, 2014, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702304071004579406810684766716?KEYWORDS=china+yuan&mg=reno64-wsj), finds from informed sources that the central bank of China conducted the ongoing devaluation of the yuan with the objective of driving out arbitrageurs to widen the band of fluctuation. There is concern if the policy of revaluation is changing to devaluation.
Chart VI-1, Chinese Yuan (CNY) per US Dollar (USD), Business Days, Jan 3, 1995-Mar 21, 2014
Note: US Recessions in Shaded Areas
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/H10/default.htm
Chart VI-1A provides the daily CNY/USD rate from Jan 5, 1981 to Mar 21, 2014. The exchange rate was CNY 1.5418/USD on Jan 5, 1981. There is sharp cumulative depreciation of 107.8 percent to CNY 3.2031 by Jul 2, 1986, continuing to CNY 5.8145/USD on Dec 29, 1993 for cumulative 277.1 percent since Jan 5, 1981. China then devalued sharply to CNY 8.7117/USD on Jan 7, 1994 for 49.8 percent relative to Dec 29, 1993 and cumulative 465.0 percent relative to Jan 5, 1981. China then fixed the rate at CNY 8.2765/USD until Jul 21, 2005 and revalued as analyzed in Chart VI-1. The final data point in Chart VI-1A is CNY 6.2248/USD on Mar 21, 2014. To be sure, China fixed the exchange rate after substantial prior devaluation. It is unlikely that the devaluation could have been effective after many years of fixing the exchange rate with high inflation and multiple changes in the world economy. The argument of Lazear (2013Jan7) is still valid in view of the lack of association between monthly exports of China to the US and Europe since 1995 and the exchange rate of China.
Chart VI-1A, Chinese Yuan (CNY) per US Dollar (USD), Business Days, Jan 5, 1981-Mar 21, 2014
Note: US Recessions in Shaded Areas
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/H10/default.htm
Chart VI-1B provides fine details with the rate of Chinese Yuan (CNY) to the US Dollar (USD) from Oct 28, 2011 to Mar 14, 2014. There have been alternations of revaluation and devaluation. The initial data point is CNY 6.3570 on Oct 28, 2011. There is an episode of devaluation from CNY 6.2790 on Apr 30, 2012 to CNY 6.3879 on Jul 25, 2012, or devaluation of 1.7 percent. Another devaluation is from CNY 6.042/USD on Jan 4, 2014 to CNY 6.2248 on Mar 22, 2014, or devaluation of 3.0 percent.
Chart VI-1B, Chinese Yuan (CNY) per US Dollar (US), Business Days, Oct 28, 2011-Mar 21, 2014
Note: US Recessions in Shaded Areas
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/H10/default.htm
Carry trades induced by zero interest rates increase capital flows into emerging markets that appreciate exchange rates. Portfolio reallocations away from emerging markets depreciate their exchange rates in reversals of capital flows. Chart VI-4A provides the exchange rate of the Mexican peso (MXN) per US dollar from Nov 8, 1993 to Mar 21, 2014. The first data point in Chart VI-4A is MXN 3.1520 on Nov 8, 1993. The rate devalued to 11.9760 on Nov 14, 1995 during emerging market crises in the 1990s and the increase of interest rates in the US in 1994 that stressed world financial markets (Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture 2005, The Global Recession Risk 2007, 147-77). The MXN depreciated sharply to MXN 15.4060/USD on Mar 2, 2009, during the global recession. The rate moved to MXN 11.5050/USD on May 2, 2011, during the sovereign debt crisis in the euro area. The rate depreciated to 11.9760 on May 9, 2013. The final data point in the current flight from emerging markets is MXN 13.2200/USD on Mar 21, 2014.
Chart VI-4A, Mexican Peso (MXN) per US Dollar (USD), Nov 8, 1993 to Mar 21, 2014
Note: US Recessions in Shaded Areas
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/H10/default.htm
There are collateral effects worldwide from unconventional monetary policy. In remarkable anticipation in 2005, Professor Raghuram G. Rajan (2005) warned of low liquidity and high risks of central bank policy rates approaching the zero bound (Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 218-9). Professor Rajan excelled in a distinguished career as an academic economist in finance and was chief economist of the International Monetary Fund (IMF). Shefali Anand and Jon Hilsenrath, writing on Oct 13, 2013, on “India’s central banker lobbies Fed,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702304330904579133530766149484?KEYWORDS=Rajan), interviewed Raghuram G Rajan, who is the current Governor of the Reserve Bank of India, which is India’s central bank (http://www.rbi.org.in/scripts/AboutusDisplay.aspx). In this interview, Rajan argues that central banks should avoid unintended consequences on emerging market economies of inflows and outflows of capital triggered by monetary policy. Professor Rajan, in an interview with Kartik Goyal of Bloomberg (http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2014-01-30/rajan-warns-of-global-policy-breakdown-as-emerging-markets-slide.html), warns of breakdown of global policy coordination. Professor Willem Buiter (2014Feb4), a distinguished economist currently Global Chief Economist at Citigroup (http://www.willembuiter.com/resume.pdf), writing on “The Fed’s bad manners risk offending foreigners,” on Feb 4, 2014, published in the Financial Times (http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/fbb09572-8d8d-11e3-9dbb-00144feab7de.html#axzz2suwrwkFs), concurs with Raghuram Rajan. Buiter (2014Feb4) argues that international policy cooperation in monetary policy is both in the interest of the world and the United States. Portfolio reallocations induced by combination of zero interest rates and risk events stimulate carry trades that generate wide swings in world capital flows. Chart VI-4B provides the rate of the Indian rupee (INR) per US dollar (USD) from Jan 2, 1973 to Mar 21, 2014. The first data point is INR 8.0200 on Jan 2, 1973. The rate depreciated sharply to INR 51.9600 on Mar 3, 2009, during the global recession. The rate appreciated to INR 44.0300/USD on Jul 28, 2011 in the midst of the sovereign debt event in the euro area. The rate overshot to INR 68.8000 on Aug 28, 2013. The final data point if INR 60.9000/USD on Mar 21, 2014.
Chart VI-4B, Indian Rupee (INR) per US Dollar (USD), Jan 2, 1973 to Mar 21, 2014
Note: US Recessions in Shaded Areas
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/H10/default.htm
ChVI-5 provides the exchange rate of JPY (Japan yen) per USD (US dollars). The first data point on the extreme left is JPY 357.7300/USD for Jan 4, 1971. The JPY has appreciated over the long term relative to the USD with fluctuations along an evident long-term appreciation. Before the global recession, the JPY stood at JPY 124.0900/USD on Jun 22, 2007. The use of the JPY as safe haven is evident by sharp appreciation during the global recession to JPY 110.48/USD on Aug 15, 2008, and to JPY 87.8000/USD on Jan 21, 2009. The final data point in Chart VI-5 is JPY 102.3800/USD on Mar 21, 2013 for appreciation of 17.5 percent relative to JPY 124.0900/USD on Jun 22, 2007 before the global recession and expansion characterized by recurring bouts of risk aversion. Takashi Nakamichi and Eleanor Warnock, writing on “Japan lashes out over dollar, euro,” on Dec 29, 2012, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887323530404578207440474874604.html?mod=WSJ_markets_liveupdate&mg=reno64-wsj), analyze the “war of words” launched by Japan’s new Prime Minister Shinzo Abe and his finance minister Taro Aso, arguing of deliberate devaluations of the USD and EUR relative to the JPY, which are hurting Japan’s economic activity. The data in Table VI-6 is obtained from closing dates in New York published by the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_PRO_hps_marketdata).
Chart VI-5, Japanese Yen JPY per US Dollars USD, Monthly, Jan 4, 1971-Mar 21, 2014
Note: US Recessions in Shaded Areas
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/H10/default.htm
The financial crisis and global recession were caused by interest rate and housing subsidies and affordability policies that encouraged high leverage and risks, low liquidity and unsound credit (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 157-66, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 217-27, International Financial Architecture (2005), 15-18, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 221-5, Globalization and the State Vol. II (2008b), 197-213, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 182-4). Several past comments of this blog elaborate on these arguments, among which: http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/07/causes-of-2007-creditdollar-crisis.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/professor-mckinnons-bubble-economy.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/world-inflation-quantitative-easing.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/treasury-yields-valuation-of-risk.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/11/quantitative-easing-theory-evidence-and.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/12/is-fed-printing-money-what-are.html
Zero interest rates in the United States forever tend to depreciate the dollar against every other currency if there is no risk aversion preventing portfolio rebalancing toward risk financial assets, which include the capital markets and exchange rates of emerging-market economies. The objective of unconventional monetary policy as argued by Yellen 2011AS) is to devalue the dollar to increase net exports that increase US economic growth. Increasing net exports and internal economic activity in the US is equivalent to decreasing net exports and internal economic activity in other countries.
Continental territory, rich endowment of natural resources, investment in human capital, teaching and research universities, motivated labor force and entrepreneurial initiative provide Brazil with comparative advantages in multiple economic opportunities. Exchange rate parity is critical in achieving Brazil’s potential but is difficult in a world of zero interest rates. Chart IV-6 of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System provides the rate of Brazilian real (BRL) per US dollar (USD) from BRL 1.2074/USD on Jan 4, 1999 to BRL 2.3215/USD on Mar 21, 2013. The rate reached BRL 3.9450/USD on Oct 10, 2002 appreciating 60.5 percent to BRL 1.5580/USD on Aug 1, 2008. The rate depreciated 68.1 percent to BRL 2.6187/USD on Dec 5, 2008 during worldwide flight from risk. The rate appreciated again by 41.3 percent to BRL 1.5375/USD on Jul 26, 2011. The final data point in Chart VI-6 is BRL 2.3215/USD on Mar 21, 2014 for depreciation of 51.0 percent. The data in Table VI-6 is obtained from closing dates in New York published by the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_PRO_hps_marketdata).
Chart VI-6, Brazilian Real (BRL) per US Dollar (USD) Jan 4, 1999 to Mar 21, 2014
Note: US Recessions in Shaded Areas
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/H10/default.htm
Chart VI-7 of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System provides the history of the BRL beginning with the first data point of BRL 0.8440/USD on Jan 2, 1995. The rate jumped to BRL 2.0700/USD on Jan 29, 1999 after changes in exchange rate policy and then to BRL 2.2000/USD on Mar 3, 1999. The rate depreciated 26.7 percent to BRL 2.7880/USD on Sep 21, 2001 relative to Mar 3, 1999.
Chart VI-7, Brazilian Real (BRL) per US Dollar (USD), Jan 2, 1995 to Mar 21, 2014
Note: US Recessions in Shaded Areas
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/H10/default.htm
The major reason and channel of transmission of unconventional monetary policy is through expectations of inflation. Fisher (1930) provided theoretical and historical relation of interest rates and inflation. Let in be the nominal interest rate, ir the real or inflation-adjusted interest rate and πe the expectation of inflation in the time term of the interest rate, which are all expressed as proportions. The following expression provides the relation of real and nominal interest rates and the expectation of inflation:
(1 + ir) = (1 + in)/(1 + πe) (1)
That is, the real interest rate equals the nominal interest rate discounted by the expectation of inflation in time term of the interest rate. Fisher (1933) analyzed the devastating effect of deflation on debts. Nominal debt contracts remained at original principal interest but net worth and income of debtors contracted during deflation. Real interest rates increase during declining inflation. For example, if the interest rate is 3 percent and prices decline 0.2 percent, equation (1) calculates the real interest rate as:
(1 +0.03)/(1 – 0.02) = 1.03/(0.998) = 1.032
That is, the real rate of interest is (1.032 – 1) 100 or 3.2 percent. If inflation were 2 percent, the real rate of interest would be 0.98 percent, or about 1.0 percent {[(1.03/1.02) -1]100 = 0.98%}.
The yield of the one-year Treasury security was quoted in the Wall Street Journal at 0.114 percent on Fri May 17, 2013 (http://online.wsj.com/mdc/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_topnav_marketdata_main). The expected rate of inflation πe in the next twelve months is not observed. Assume that it would be equal to the rate of inflation in the past twelve months estimated by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BLS) at 1.1 percent (http://www.bls.gov/cpi/). The real rate of interest would be obtained as follows:
(1 + 0.00114)/(1 + 0.011) = (1 + rr) = 0.9902
That is, ir is equal to 1 – 0.9902 or minus 0.98 percent. Investing in a one-year Treasury security results in a loss of 0.98 percent relative to inflation. The objective of unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates is to induce consumption and investment because of the loss to inflation of riskless financial assets. Policy would be truly irresponsible if it intended to increase inflationary expectations or πe. The result could be the same rate of unemployment with higher inflation (Kydland and Prescott 1977).
Current focus is on tapering quantitative easing by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC). There is sharp distinction between the two measures of unconventional monetary policy: (1) fixing of the overnight rate of fed funds at 0 to ¼ percent; and (2) outright purchase of Treasury and agency securities and mortgage-backed securities for the balance sheet of the Federal Reserve. Market are overreacting to the so-called “paring” of outright purchases of $55 billion of securities per month for the balance sheet of the Fed
(http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20140319a.htm):
“The Committee currently judges that there is sufficient underlying strength in the broader economy to support ongoing improvement in labor market conditions. In light of the cumulative progress toward maximum employment and the improvement in the outlook for labor market conditions since the inception of the current asset purchase program, the Committee decided to make a further measured reduction in the pace of its asset purchases. Beginning in April, the Committee will add to its holdings of agency mortgage-backed securities at a pace of $25 billion per month rather than $30 billion per month, and will add to its holdings of longer-term Treasury securities at a pace of $30 billion per month rather than $35 billion per month. The Committee is maintaining its existing policy of reinvesting principal payments from its holdings of agency debt and agency mortgage-backed securities in agency mortgage-backed securities and of rolling over maturing Treasury securities at auction. The Committee's sizable and still-increasing holdings of longer-term securities should maintain downward pressure on longer-term interest rates, support mortgage markets, and help to make broader financial conditions more accommodative, which in turn should promote a stronger economic recovery and help to ensure that inflation, over time, is at the rate most consistent with the Committee's dual mandate.”
What is truly important is the fixing of the overnight fed funds at 0 to ¼ percent for which there is no end in sight as evident in the FOMC statement for Mar 19, 2014 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20140319a.htm):
“To support continued progress toward maximum employment and price stability, the Committee today reaffirmed its view that a highly accommodative stance of monetary policy remains appropriate. In determining how long to maintain the current 0 to 1/4 percent target range for the federal funds rate, the Committee will assess progress--both realized and expected--toward its objectives of maximum employment and 2 percent inflation. This assessment will take into account a wide range of information, including measures of labor market conditions, indicators of inflation pressures and inflation expectations, and readings on financial developments. The Committee continues to anticipate, based on its assessment of these factors, that it likely will be appropriate to maintain the current target range for the federal funds rate for a considerable time after the asset purchase program ends, especially if projected inflation continues to run below the Committee's 2 percent longer-run goal, and provided that longer-term inflation expectations remain well anchored.” (emphasis added).
How long is “considerable time”? At the press conference following the meeting on Mar 19, 2014, Chair Yellen answered a question of Jon Hilsenrath of the Wall Street Journal explaining “In particular, the Committee has endorsed the view that it anticipates that will be a considerable period after the asset purchase program ends before it will be appropriate to begin to raise rates. And of course on our present path, well, that's not utterly preset. We would be looking at next, next fall. So, I think that's important guidance” (http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20140319.pdf). Many focused on “next fall,” ignoring that the path of increasing rates is not “utterly preset.”
There is a critical phrase in the statement of Sep 19, 2013 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20130918a.htm): “but mortgage rates have risen further.” Did the increase of mortgage rates influence the decision of the FOMC not to taper? Is FOMC “communication” and “guidance” successful? Will the FOMC increase purchases of mortgage-backed securities if mortgage rates increase?
At the confirmation hearing on nomination for Chair of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Vice Chair Yellen (2013Nov14 http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20131114a.htm), states needs and intentions of policy:
“We have made good progress, but we have farther to go to regain the ground lost in the crisis and the recession. Unemployment is down from a peak of 10 percent, but at 7.3 percent in October, it is still too high, reflecting a labor market and economy performing far short of their potential. At the same time, inflation has been running below the Federal Reserve's goal of 2 percent and is expected to continue to do so for some time.
For these reasons, the Federal Reserve is using its monetary policy tools to promote a more robust recovery. A strong recovery will ultimately enable the Fed to reduce its monetary accommodation and reliance on unconventional policy tools such as asset purchases. I believe that supporting the recovery today is the surest path to returning to a more normal approach to monetary policy.”
In testimony on the Semiannual Monetary Policy Report to the Congress before the Committee on Financial Services, US House of Representatives, on Feb 11, 2014, Chair Janet Yellen states (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20140211a.htm):
“Turning to monetary policy, let me emphasize that I expect a great deal of continuity in the FOMC's approach to monetary policy. I served on the Committee as we formulated our current policy strategy and I strongly support that strategy, which is designed to fulfill the Federal Reserve's statutory mandate of maximum employment and price stability. If incoming information broadly supports the Committee's expectation of ongoing improvement in labor market conditions and inflation moving back toward its longer-run objective, the Committee will likely reduce the pace of asset purchases in further measured steps at future meetings. That said, purchases are not on a preset course, and the Committee's decisions about their pace will remain contingent on its outlook for the labor market and inflation as well as its assessment of the likely efficacy and costs of such purchases. In December of last year and again this January, the Committee said that its current expectation--based on its assessment of a broad range of measures of labor market conditions, indicators of inflation pressures and inflation expectations, and readings on financial developments--is that it likely will be appropriate to maintain the current target range for the federal funds rate well past the time that the unemployment rate declines below 6-1/2 percent, especially if projected inflation continues to run below the 2 percent goal. I am committed to achieving both parts of our dual mandate: helping the economy return to full employment and returning inflation to 2 percent while ensuring that it does not run persistently above or below that level (emphasis added).”
In his classic restatement of the Keynesian demand function in terms of “liquidity preference as behavior toward risk,” James Tobin (http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/economic-sciences/laureates/1981/tobin-bio.html) identifies the risks of low interest rates in terms of portfolio allocation (Tobin 1958, 86):
“The assumption that investors expect on balance no change in the rate of interest has been adopted for the theoretical reasons explained in section 2.6 rather than for reasons of realism. Clearly investors do form expectations of changes in interest rates and differfrom each other in their expectations. For the purposes of dynamic theory and of analysis of specific market situations, the theories of sections 2 and 3 are complementary rather than competitive. The formal apparatus of section 3 will serve just as well for a non-zero expected capital gain or loss as for a zero expected value of g. Stickiness of interest rate expectations would mean that the expected value of g is a function of the rate of interest r, going down when r goes down and rising when r goes up. In addition to the rotation of the opportunity locus due to a change in r itself, there would be a further rotation in the same direction due to the accompanying change in the expected capital gain or loss. At low interest rates expectation of capital loss may push the opportunity locus into the negative quadrant, so that the optimal position is clearly no consols, all cash. At the other extreme, expectation of capital gain at high interest rates would increase sharply the slope of the opportunity locus and the frequency of no cash, all consols positions, like that of Figure 3.3. The stickier the investor's expectations, the more sensitive his demand for cash will be to changes in the rate of interest (emphasis added).”
Tobin (1969) provides more elegant, complete analysis of portfolio allocation in a general equilibrium model. The major point is equally clear in a portfolio consisting of only cash balances and a perpetuity or consol. Let g be the capital gain, r the rate of interest on the consol and re the expected rate of interest. The rates are expressed as proportions. The price of the consol is the inverse of the interest rate, (1+re). Thus, g = [(r/re) – 1]. The critical analysis of Tobin is that at extremely low interest rates there is only expectation of interest rate increases, that is, dre>0, such that there is expectation of capital losses on the consol, dg<0. Investors move into positions combining only cash and no consols. Valuations of risk financial assets would collapse in reversal of long positions in carry trades with short exposures in a flight to cash. There is no exit from a central bank created liquidity trap without risks of financial crash and another global recession. The net worth of the economy depends on interest rates. In theory, “income is generally defined as the amount a consumer unit could consume (or believe that it could) while maintaining its wealth intact” (Friedman 1957, 10). Income, Y, is a flow that is obtained by applying a rate of return, r, to a stock of wealth, W, or Y = rW (Ibid). According to a subsequent statement: “The basic idea is simply that individuals live for many years and that therefore the appropriate constraint for consumption is the long-run expected yield from wealth r*W. This yield was named permanent income: Y* = r*W” (Darby 1974, 229), where * denotes permanent. The simplified relation of income and wealth can be restated as:
W = Y/r (10
Equation (1) shows that as r goes to zero, r→0, W grows without bound, W→∞. Unconventional monetary policy lowers interest rates to increase the present value of cash flows derived from projects of firms, creating the impression of long-term increase in net worth. An attempt to reverse unconventional monetary policy necessarily causes increases in interest rates, creating the opposite perception of declining net worth. As r→∞, W = Y/r →0. There is no exit from unconventional monetary policy without increasing interest rates with resulting pain of financial crisis and adverse effects on production, investment and employment.
The argument that anemic population growth causes “secular stagnation” in the US (Hansen 1938, 1939, 1941) is as misplaced currently as in the late 1930s (for early dissent see Simons 1942). There is currently population growth in the ages of 16 to 24 years but not enough job creation and discouragement of job searches for all ages (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/01/capital-flows-exchange-rates-and.htm and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/theory-and-reality-of-secular.html). This is merely another case of theory without reality with dubious policy proposals. The current reality is cyclical slow growth.
In delivering the biannual report on monetary policy (Board of Governors 2013Jul17), Chairman Bernanke (2013Jul17) advised Congress that:
“Instead, we are providing additional policy accommodation through two distinct yet complementary policy tools. The first tool is expanding the Federal Reserve's portfolio of longer-term Treasury securities and agency mortgage-backed securities (MBS); we are currently purchasing $40 billion per month in agency MBS and $45 billion per month in Treasuries. We are using asset purchases and the resulting expansion of the Federal Reserve's balance sheet primarily to increase the near-term momentum of the economy, with the specific goal of achieving a substantial improvement in the outlook for the labor market in a context of price stability. We have made some progress toward this goal, and, with inflation subdued, we intend to continue our purchases until a substantial improvement in the labor market outlook has been realized. We are relying on near-zero short-term interest rates, together with our forward guidance that rates will continue to be exceptionally low--our second tool--to help maintain a high degree of monetary accommodation for an extended period after asset purchases end, even as the economic recovery strengthens and unemployment declines toward more-normal levels. In appropriate combination, these two tools can provide the high level of policy accommodation needed to promote a stronger economic recovery with price stability.
The Committee's decisions regarding the asset purchase program (and the overall stance of monetary policy) depend on our assessment of the economic outlook and of the cumulative progress toward our objectives. Of course, economic forecasts must be revised when new information arrives and are thus necessarily provisional.”
Friedman (1953) argues there are three lags in effects of monetary policy: (1) between the need for action and recognition of the need; (2) the recognition of the need and taking of actions; and (3) taking of action and actual effects. Friedman (1953) finds that the combination of these lags with insufficient knowledge of the current and future behavior of the economy causes discretionary economic policy to increase instability of the economy or standard deviations of real income σy and prices σp. Policy attempts to circumvent the lags by policy impulses based on forecasts. We are all naïve about forecasting. Data are available with lags and revised to maintain high standards of estimation. Policy simulation models estimate economic relations with structures prevailing before simulations of policy impulses such that parameters change as discovered by Lucas (1977). Economic agents adjust their behavior in ways that cause opposite results from those intended by optimal control policy as discovered by Kydland and Prescott (1977). Advance guidance attempts to circumvent expectations by economic agents that could reverse policy impulses but is of dubious effectiveness. There is strong case for using rules instead of discretionary authorities in monetary policy (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/search?q=rules+versus+authorities). Jon Hilsenrath, writing on “New view into Fed’s response to crisis,” on Feb 21, 2014, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702303775504579396803024281322?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection), analyzes 1865 pages of transcripts of eight formal and six emergency policy meetings at the Fed in 2008 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/fomchistorical2008.htm). If there were an infallible science of central banking, models and forecasts would provide accurate information to policymakers on the future course of the economy in advance. Such forewarning is essential to central bank science because of the long lag between the actual impulse of monetary policy and the actual full effects on income and prices many months and even years ahead (Romer and Romer 2004, Friedman 1961, 1953, Culbertson 1960, 1961, Batini and Nelson 2002). The transcripts of the Fed meetings in 2008 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/fomchistorical2008.htm) analyzed by Jon Hilsenrath demonstrate that Fed policymakers frequently did not understand the current state of the US economy in 2008 and much less the direction of income and prices. The conclusion of Friedman (1953) is that monetary impulses increase financial and economic instability because of lags in anticipating needs of policy, taking policy decisions and effects of decisions. This is a fortiori true when untested unconventional monetary policy in gargantuan doses shocks the economy and financial markets.
The key policy is maintaining fed funds rate between 0 and ¼ percent. An increase in fed funds rates could cause flight out of risk financial markets worldwide. There is no exit from this policy without major financial market repercussions. Indefinite financial repression induces carry trades with high leverage, risks and illiquidity. A competing event is the high level of valuations of risk financial assets (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/01/peaking-valuation-of-risk-financial.html). Matt Jarzemsky, writing on “Dow industrials set record,” on Mar 5, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887324156204578275560657416332.html), analyzes that the DJIA broke the closing high of 14,164.53 set on Oct 9, 2007, and subsequently also broke the intraday high of 14,198.10 reached on Oct 11, 2007. The DJIA closed at 16,323.06 on Fri Mar 28, 2014, which is higher by 15.2 percent than the value of 14,164.53 reached on Oct 9, 2007 and higher by 15.0 percent than the value of 14,198.10 reached on Oct 11, 2007. Values of risk financial are approaching or exceeding historical highs.
Jon Hilsenrath, writing on “Jobs upturn isn’t enough to satisfy Fed,” on Mar 8, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887324582804578348293647760204.html), finds that much stronger labor market conditions are required for the Fed to end quantitative easing. Unconventional monetary policy with zero interest rates and quantitative easing is quite difficult to unwind because of the adverse effects of raising interest rates on valuations of risk financial assets and home prices, including the very own valuation of the securities held outright in the Fed balance sheet. Gradual unwinding of 1 percent fed funds rates from Jun 2003 to Jun 2004 by seventeen consecutive increases of 25 percentage points from Jun 2004 to Jun 2006 to reach 5.25 percent caused default of subprime mortgages and adjustable-rate mortgages linked to the overnight fed funds rate. The zero interest rate has penalized liquidity and increased risks by inducing carry trades from zero interest rates to speculative positions in risk financial assets. There is no exit from zero interest rates without provoking another financial crash.
The carry trade from zero interest rates to leveraged positions in risk financial assets had proved strongest for commodity exposures but US equities have regained leadership. The DJIA has increased 68.3 percent since the trough of the sovereign debt crisis in Europe on Jul 2, 2010 to Mar 28, 2014; S&P 500 has gained 81.7 percent and DAX 73.8 percent. Before the current round of risk aversion, almost all assets in the column “∆% Trough to 3/28/14” had double digit gains relative to the trough around Jul 2, 2010 followed by negative performance but now some valuations of equity indexes show varying behavior. China’s Shanghai Composite is 14.3 percent below the trough. Japan’s Nikkei Average is 66.5 percent above the trough. DJ Asia Pacific TSM is 23.2 percent above the trough. Dow Global is 45.9 percent above the trough. STOXX 50 of 50 blue-chip European equities (http://www.stoxx.com/indices/index_information.html?symbol=sx5E) is 27.0 percent above the trough. NYSE Financial Index is 48.2 percent above the trough. DJ UBS Commodities is 8.7 percent above the trough. DAX index of German equities (http://www.bloomberg.com/quote/DAX:IND) is 73.8 percent above the trough. Japan’s Nikkei Average is 66.5 percent above the trough on Aug 31, 2010 and 29.0 percent above the peak on Apr 5, 2010. The Nikkei Average closed at 14,696.03 on Fri Mar 28, 2014 (http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_PRO_hps_marketdata), which is 43.3 percent higher than 10,254.43 on Mar 11, 2011, on the date of the Tōhoku or Great East Japan Earthquake/tsunami. Global risk aversion erased the earlier gains of the Nikkei. The dollar depreciated by 15.4 percent relative to the euro and even higher before the new bout of sovereign risk issues in Europe. The column “∆% week to 3/28/14” in Table VI-4 shows decrease of 0.3 percent in the week for China’s Shanghai Composite. DJ Asia Pacific increased 2.6 percent. NYSE Financial decreased 0.6 percent in the week. DJ UBS Commodities increased 1.4 percent. Dow Global increased 1.4 percent in the week of Mar 28, 2014. The DJIA increased 0.1 percent and S&P 500 decreased 0.5 percent. DAX of Germany increased 5.5 percent. STOXX 50 increased 2.0 percent. The USD appreciated 0.3 percent. There are still high uncertainties on European sovereign risks and banking soundness, US and world growth slowdown and China’s growth tradeoffs. Sovereign problems in the “periphery” of Europe and fears of slower growth in Asia and the US cause risk aversion with trading caution instead of more aggressive risk exposures. There is a fundamental change in Table VI-4 from the relatively upward trend with oscillations since the sovereign risk event of Apr-Jul 2010. Performance is best assessed in the column “∆% Peak to 3/28/14” that provides the percentage change from the peak in Apr 2010 before the sovereign risk event to Mar 28, 2014. Most risk financial assets had gained not only relative to the trough as shown in column “∆% Trough to 3/28/14” but also relative to the peak in column “∆% Peak to 3/28/14.” There are now several equity indexes above the peak in Table VI-4: DJIA 45.7 percent, S&P 500 52.6 percent, DAX 55.7 percent, Dow Global 19.1 percent, DJ Asia Pacific 7.9 percent, NYSE Financial Index (http://www.nyse.com/about/listed/nykid.shtml) 18.1 percent, Nikkei Average 29.0 percent and STOXX 50 7.5 percent. There is only one equity index below the peak: Shanghai Composite by 35.5 percent. DJ UBS Commodities Index is now 7.1 percent below the peak. The US dollar strengthened 9.1 percent relative to the peak. The factors of risk aversion have adversely affected the performance of risk financial assets. The performance relative to the peak in Apr 2010 is more important than the performance relative to the trough around early Jul 2010 because improvement could signal that conditions have returned to normal levels before European sovereign doubts in Apr 2010.
Alexandra Scaggs, writing on “Tepid profits, roaring stocks,” on May 16, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887323398204578487460105747412.html), analyzes stabilization of earnings growth: 70 percent of 458 reporting companies in the S&P 500 stock index reported earnings above forecasts but sales fell 0.2 percent relative to forecasts of increase of 0.5 percent. Paul Vigna, writing on “Earnings are a margin story but for how long,” on May 17, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://blogs.wsj.com/moneybeat/2013/05/17/earnings-are-a-margin-story-but-for-how-long/), analyzes that corporate profits increase with stagnating sales while companies manage costs tightly. More than 90 percent of S&P components reported moderate increase of earnings of 3.7 percent in IQ2013 relative to IQ2012 with decline of sales of 0.2 percent. Earnings and sales have been in declining trend. In IVQ2009, growth of earnings reached 104 percent and sales jumped 13 percent. Net margins reached 8.92 percent in IQ2013, which is almost the same at 8.95 percent in IIIQ2006. Operating margins are 9.58 percent. There is concern by market participants that reversion of margins to the mean could exert pressure on earnings unless there is more accelerated growth of sales. Vigna (op. cit.) finds sales growth limited by weak economic growth. Kate Linebaugh, writing on “Falling revenue dings stocks,” on Oct 20, 2012, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10000872396390444592704578066933466076070.html?mod=WSJPRO_hpp_LEFTTopStories), identifies a key financial vulnerability: falling revenues across markets for United States reporting companies. Global economic slowdown is reducing corporate sales and squeezing corporate strategies. Linebaugh quotes data from Thomson Reuters that 100 companies of the S&P 500 index have reported declining revenue only 1 percent higher in Jun-Sep 2012 relative to Jun-Sep 2011 but about 60 percent of the companies are reporting lower sales than expected by analysts with expectation that revenue for the S&P 500 will be lower in Jun-Sep 2012 for the entities represented in the index. Results of US companies are likely repeated worldwide. Future company cash flows derive from investment projects. In IQ1980, gross private domestic investment in the US was $951.6 billion of 2009 dollars, growing to $1,174.4 billion in IIQ1987 or 23.4 percent. Real gross private domestic investment in the US increased 1.5 percent from $2,605.2 billion of 2009 dollars in IVQ2007 to $2,643.3 billion in IVQ2013. As shown in Table IAI-2, real private fixed investment fell 2.9 percent from $2,586.3 billion of 2009 dollars in IVQ2007 to $2,511.2 billion in IVQ2013. Growth of real private investment in Table IA1-2 is mediocre for all but four quarters from IIQ2011 to IQ2012 (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/financial-risks-slow-cyclical-united.html). The investment decision of United States corporations has been fractured in the current economic cycle in preference of cash. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA fell $26.6 billion in IQ2013 after increasing $34.9 billion in IVQ2012 and $13.9 billion in IIIQ2012. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA rebounded with $66.8 billion in IIQ2013 and $39.2 billion in IIIQ2013. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased $47.1 billion in IVQ2013. Profits after tax with IVA and CCA fell $1.7 billion in IQ2013 after increasing $40.8 billion in IVQ2012 and $4.5 billion in IIIQ2012. In IIQ2013, profits after tax with IVA and CCA increased $56.9 billion and $39.5 billion in IIIQ2013. In IVQ2013, profits after tax with IVA and CCA increased $33.8 billion. Anticipation of higher taxes in the “fiscal cliff” episode caused increase of $120.9 billion in net dividends in IVQ2012 followed with adjustment in the form of decrease of net dividends by $103.8 billion in IQ2013, rebounding with $273.5 billion in IIQ2013. Net dividends fell at $179.0 billion in IIIQ2013 and increased at $90.5 billion in IVQ2013. There is similar decrease of $80.1 billion in undistributed profits with IVA and CCA in IVQ2012 followed by increase of $102.1 billion in IQ2013 and decline of $216.6 billion in IIQ2013. Undistributed profits with IVA and CCA rose at $218.6 billion in IIIQ2013 and fell at $56.7 billion in IVQ2013. Undistributed profits of US corporations swelled 375.4 percent from $107.7 billion IQ2007 to $512.0 billion in IVQ2013 and changed signs from minus $55.9 billion in billion in IVQ2007 (Section IA2). In IQ2013, corporate profits with inventory valuation and capital consumption adjustment fell $26.6 billion relative to IVQ2012, from $2047.2 billion to $2020.6 billion at the quarterly rate of minus 1.3 percent. In IIQ2013, corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased $66.8 billion from $2020.6 billion in IQ2013 to $2087.4 billion at the quarterly rate of 3.3 percent. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased $39.2 billion from $2087.4 billion in IIQ2013 to $2126.6 billion in IIIQ2013 at the annual rate of 1.9 percent. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased at $47.1 billion in IVQ2013 from $2126.6 billion in IIIQ2013 to $2173.7 billion in IVQ2013 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2014/pdf/gdp4q13_3rd.pdf).
Uncertainty originating in fiscal, regulatory and monetary policy causes wide swings in expectations and decisions by the private sector with adverse effects on investment, real economic activity and employment. The investment decision of US business is fractured. The basic valuation equation that is also used in capital budgeting postulates that the value of stocks or of an investment project is given by:
Where Rτ is expected revenue in the time horizon from τ =1 to T; Cτ denotes costs; and ρ is an appropriate rate of discount. In words, the value today of a stock or investment project is the net revenue, or revenue less costs, in the investment period from τ =1 to T discounted to the present by an appropriate rate of discount. In the current weak economy, revenues have been increasing more slowly than anticipated in investment plans. An increase in interest rates would affect discount rates used in calculations of present value, resulting in frustration of investment decisions. If V represents value of the stock or investment project, as ρ → ∞, meaning that interest rates increase without bound, then V → 0, or
declines. Equally, decline in expected revenue from the stock or project, Rτ, causes decline in valuation. An intriguing issue is the difference in performance of valuations of risk financial assets and economic growth and employment. Paul A. Samuelson (http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/economics/laureates/1970/samuelson-bio.html) popularized the view of the elusive relation between stock markets and economic activity in an often-quoted phrase “the stock market has predicted nine of the last five recessions.” In the presence of zero interest rates forever, valuations of risk financial assets are likely to differ from the performance of the overall economy. The interrelations of financial and economic variables prove difficult to analyze and measure.
Table VI-4, Stock Indexes, Commodities, Dollar and 10-Year Treasury
| Peak | Trough | ∆% to Trough | ∆% Peak to 3/28/ /14 | ∆% Week 3/28/14 | ∆% Trough to 3/28/ 14 | |
| DJIA | 4/26/ | 7/2/10 | -13.6 | 45.7 | 0.1 | 68.3 |
| S&P 500 | 4/23/ | 7/20/ | -16.0 | 52.6 | -0.5 | 81.7 |
| NYSE Finance | 4/15/ | 7/2/10 | -20.3 | 18.1 | -0.6 | 48.2 |
| Dow Global | 4/15/ | 7/2/10 | -18.4 | 19.1 | 1.4 | 45.9 |
| Asia Pacific | 4/15/ | 7/2/10 | -12.5 | 7.9 | 2.6 | 23.2 |
| Japan Nikkei Aver. | 4/05/ | 8/31/ | -22.5 | 29.0 | 3.3 | 66.5 |
| China Shang. | 4/15/ | 7/02 | -24.7 | -35.5 | -0.3 | -14.3 |
| STOXX 50 | 4/15/10 | 7/2/10 | -15.3 | 7.5 | 2.0 | 27.0 |
| DAX | 4/26/ | 5/25/ | -10.5 | 55.7 | 5.5 | 73.8 |
| Dollar | 11/25 2009 | 6/7 | 21.2 | 9.1 | 0.3 | -15.4 |
| DJ UBS Comm. | 1/6/ | 7/2/10 | -14.5 | -7.1 | 1.4 | 8.7 |
| 10-Year T Note | 4/5/ | 4/6/10 | 3.986 | 2.784 | 2.721 |
T: trough; Dollar: positive sign appreciation relative to euro (less dollars paid per euro), negative sign depreciation relative to euro (more dollars paid per euro)
Source: http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_hps_marketdata
ESII Mediocre Cyclical United States Economic Growth with GDP Two Trillion Dollars below Trend. Valuations of risk financial assets approach historical highs. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. US economic growth has been at only 2.4 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 18 quarters from IVQ2009 to IVQ2013. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the second estimate of GDP for IVQ2013 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2014/pdf/gdp4q13_2nd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,738.0 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,356.9 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,738.0/$14,356.9 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/financial-risks-slow-cyclical-united.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/financial-risks-slow-cyclical-united.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth under trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IV2013 would have accumulated to 20.3 percent. GDP in IVQ2013 would be $18,040.3 billion if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2,098.0 billion than actual $15,942.3 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than under trend, explaining the 29.1 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment of 17.8 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/rules-discretionary-authorities-and.html). US GDP grew from $14,996.1 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $15,942.3 billion in IVQ2013 or 6.3 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.0 percent. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. The economy of the US can be summarized in growth of economic activity or GDP as decelerating from mediocre growth of 2.5 percent on an annual basis in 2010 to 1.8 percent in 2011, 2.8 percent in 2012 and 1.9 percent in 2013. The following calculations show that actual growth is around 2.2 to 2.5 percent per year. The rate of growth of 1.0 percent in the entire cycle from 2007 to 2013 is well below 3 percent per year in trend from 1870 to 2010, which the economy of the US always attained for entire cycles in expansions after events such as wars and recessions (Lucas 2011May). Revisions and enhancements of United States GDP and personal income accounts by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) provide important information on long-term growth and cyclical behavior. Table Summary provides relevant data.
- Long-term. US GDP grew at the average yearly rate of 3.3 percent from 1929 to 2013 and at 3.2 percent from 1947 to 2013. There were periodic contractions or recessions in this period but the economy grew at faster rates in the subsequent expansions, maintaining long-term economic growth at trend.
- Whole Cycles. Long-term growth was around 3.0 percent per year during entire cycles including contractions and expansions. The average growth rate of GDP was 3.2 percent per year in the entire cycle from 1980 to 1989 but only 1.0 percent in the entire cycle from 2007 to 2013.
- Cycles. The combined contraction of GDP in the two almost consecutive recessions in the early 1980s is 4.7 percent. The contraction of US GDP from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 during the global recession was 4.3 percent. The critical difference in the expansion is growth at average 7.8 percent in annual equivalent in the first four quarters of recovery from IQ1983 to IVQ1983. The average rate of growth of GDP in four cyclical expansions in the postwar period is 7.7 percent. In contrast, the rate of growth in the first four quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 was only 2.7 percent. Average annual equivalent growth in the expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was 5.9 percent and 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987. In contrast, average annual equivalent growth in the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IVQ2013 was only 2.4 percent. The US appears to have lost its dynamism of income growth and employment creation.
Table Summary, Long-term and Cyclical Growth of GDP, Real Disposable Income and Real Disposable Income per Capita
| GDP | ||
| Long-Term | ||
| 1929-2013 | 3.3 | |
| 1947-2013 | 3.2 | |
| Whole Cycles | ||
| 1980-1989 | 3.2 | |
| 2006-2013 | 1.1 | |
| 2007-2013 | 1.0 | |
| Cyclical Contractions ∆% | ||
| IQ1980 to IIIQ1980, IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 | -4.7 | |
| IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 | -4.3 | |
| Cyclical Expansions Average Annual Equivalent ∆% | ||
| IQ1983 to IVQ1985 IQ1983-IQ1986 IQ1983-IIIQ1986 IQ1983-IVQ1986 IQ1983-IQ1987 IQ1983-IIQ1987 | 5.9 5.7 5.4 5.2 5.0 5.0 | |
| First Four Quarters IQ1983 to IVQ1983 | 7.8 | |
| IIIQ2009 to IVQ2013 | 2.4 | |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 | 2.7 | |
| Real Disposable Income | Real Disposable Income per Capita | |
| Long-Term | ||
| 1929-2013 | 3.2 | 2.0 |
| 1947-1999 | 3.7 | 2.3 |
| Whole Cycles | ||
| 1980-1989 | 3.5 | 2.6 |
| 2006-2013 | 1.3 | 0.5 |
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The revisions and enhancements of United States GDP and personal income accounts by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) also provide critical information in assessing the current rhythm of US economic growth. The economy appears to be moving at a pace from 2.3 to 2.6 percent per year. Table Summary GDP provides the data.
1. Average Annual Growth in the Past Eight Quarters. GDP growth in the four quarters of 2012 and the four quarters of 2013 accumulated to 4.6 percent. This growth is equivalent to 2.2 percent per year, obtained by dividing GDP in IVQ2013 of $15,942.3 billion by GDP in IVQ2011 of $15,242.1 billion and compounding by 4/8: {[($15,942.3/$15,242.1)4/8 -1]100 = 2.3 percent.
2. Average Annual Growth in the Four Quarters of 2013. GDP growth in the four quarters of 2013 accumulated to 2.6 percent that is equivalent to 2.6 percent in a year. This is obtained by dividing GDP in IVQ2013 of $15,942.3 billion by GDP in IVQ2012 of $15,539.6 billion and compounding by 4/4: {[($15,942.3/$15,539.6)4/4 -1]100 = 2.6%}. The US economy grew 2.6 percent in IVQ2013 relative to the same quarter a year earlier in IVQ2012. Another important revelation of the revisions and enhancements is that GDP was flat in IVQ2012, which is just at the borderline of contraction. The rate of growth of GDP in the third estimate of IIIQ2013 is 4.1 percent in seasonally adjusted annual rate (SAAR). Inventory accumulation contributed 1.67 percentage points to this rate of growth. The actual rate without this impulse of unsold inventories would have been 2.43 percent, or 0.6 percent in IIIQ2013, such that annual equivalent growth in 2013 is closer to 2.1 percent {[(1.003)(1.006)(1.006)(1.007)4/4-1]100 = 2.2%}, compounding the quarterly rates and converting into annual equivalent.
Table Summary GDP, US, Real GDP and Percentage Change Relative to IVQ2007 and Prior Quarter, Billions Chained 2005 Dollars and ∆%
| Real GDP, Billions Chained 2009 Dollars | ∆% Relative to IVQ2007 | ∆% Relative to Prior Quarter | ∆% | |
| IVQ2007 | 14,996.1 | NA | NA | 1.9 |
| IVQ2011 | 15,242.1 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 2.0 |
| IQ2012 | 15,381.6 | 2.6 | 0.9 | 3.3 |
| IIQ2012 | 15,427.7 | 2.9 | 0.3 | 2.8 |
| IIIQ2012 | 15,534.0 | 3.6 | 0.7 | 3.1 |
| IVQ2012 | 15,539.6 | 3.6 | 0.0 | 2.0 |
| IQ2013 | 15,583.9 | 3.9 | 0.3 | 1.3 |
| IIQ2013 | 15,679.7 | 4.6 | 0.6 | 1.6 |
| IIIQ2013 | 15,839.3 | 5.6 | 1.0 | 2.0 |
| IVQ2013 | 15,942.3 | 6.3 | 0.7 | 2.6 |
| Cumulative ∆% IQ2012 to IVQ2013 | 4.6 | 4.6 | ||
| Annual Equivalent ∆% | 2.3 | 2.3 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The NBER dates another recession in 1980 that lasted about half a year. If the two recessions from IQ1980s to IIIQ1980 and IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 are combined, the impact of lost GDP of 4.7 percent is more comparable to the latest revised 4.3 percent drop of the recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. The recession in 1981-1982 is quite similar on its own to the 2007-2009 recession. In contrast, during the Great Depression in the four years of 1930 to 1933, GDP in constant dollars fell 26.4 percent cumulatively and fell 45.3 percent in current dollars (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 150-2, Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2009b), 205-7 and revisions in http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). Table I-2 provides the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) quarterly growth rates of GDP in SA yearly equivalents for the recessions of 1981 to 1982 and 2007 to 2009, using the latest major revision published on July 31, 2013 and the third estimate for IVQ2013 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2014/pdf/gdp4q13_3rd.pdf), which are available in the dataset of the US Bureau of Economic Analysis (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). There were four quarters of contraction in 1981-1982 ranging in rate from -1.4 percent to -6.5 percent and five quarters of contraction in 2007-2009 ranging in rate from -0.4 percent to -8.3 percent. The striking difference is that in the first eighteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, shown in Table I-2 in relief, GDP grew at the high quarterly percentage growth rates of 5.3, 9.4, 8.1, 8.5, 8.2, 7.2, 4.0, 3.2, 4.0, 3.7, 6.4, 3.0, 3.8, 1.9, 4.1, 2.1, 2.8 and 4.6. In contrast, the percentage growth rates in the first eighteen quarters of expansion from IIIQ2009 to IVQ2013 shown in relief in Table I-2 were mediocre: 1.3, 3.9, 1.6, 3.9, 2.8, 2.8, -1.3, 3.2, 1.4, 4.9, 3.7, 1.2, 2.8, 0.1, 1.1, 2.5, 4.1 and 2.6. Inventory accumulation contributed 2.73 percentage points to the rate of growth of 4.9 percent in IVQ2011, which is the only relatively high rate from IQ2011 to IIIQ2012, 0.60 percentage points to the rate of 2.8 percent in IIIQ2012 and 1.67 percentage points to the rate of 4.1 percent in IIIQ2013. Economic growth and employment creation continued at slow rhythm during 2012 and in 2013 while much stronger growth would be required in movement to full employment. The cycle is now long by historical standards and growth rates are typically weaker in the final periods of cyclical expansions.
Table I-2, US, Quarterly Growth Rates of GDP, % Annual Equivalent SA
| Q | 1981 | 1982 | 1983 | 1984 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 |
| I | 8.5 | -6.5 | 5.3 | 8.2 | -2.7 | -5.4 | 1.6 |
| II | -2.9 | 2.2 | 9.4 | 7.2 | 2.0 | -0.4 | 3.9 |
| III | 4.7 | -1.4 | 8.1 | 4.0 | -2.0 | 1.3 | 2.8 |
| IV | -4.6 | 0.4 | 8.5 | 3.2 | -8.3 | 3.9 | 2.8 |
| 1985 | 2011 | ||||||
| I | 4.0 | -1.3 | |||||
| II | 3.7 | 3.2 | |||||
| III | 6.4 | 1.4 | |||||
| IV | 3.0 | 4.9 | |||||
| 1986 | 2012 | ||||||
| I | 3.8 | 3.7 | |||||
| II | 1.9 | 1.2 | |||||
| III | 4.1 | 2.8 | |||||
| IV | 2.1 | 0.1 | |||||
| 1987 | 2013 | ||||||
| I | 2.8 | 1.1 | |||||
| II | 4.6 | 2.5 | |||||
| III | 3.7 | 4.1 | |||||
| IV | 6.8 | 2.6 | |||||
| 1988 | 2014 | ||||||
| I | 2.3 | ||||||
| II | 5.4 | ||||||
| III | 2.3 | ||||||
| IV | 5.4 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-1 of the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) provides strong growth of real GDP in the US between 1929 and 1999 at the yearly average rate of 3.5 percent. There is an evident acceleration of the rate of GDP growth in the 1990s as shown by a much sharper slope of the growth curve. Cobet and Wilson (2002) define labor productivity as the value of manufacturing output produced per unit of labor input used (see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 137-44). Between 1950 and 2000, labor productivity in the US grew less rapidly than in Germany and Japan. The major part of the increase in productivity in Germany and Japan occurred between 1950 and 1973 while the rate of productivity growth in the US was relatively subdued in several periods. While Germany and Japan reached their highest growth rates of productivity before 1973, the US accelerated its rate of productivity growth in the second half of the 1990s. Between 1950 and 2000, the rate of productivity growth in the US of 2.9 percent per year was much lower than 6.3 percent in Japan and 4.7 percent in Germany. Between 1995 and 2000, the rate of productivity growth of the US of 4.6 percent exceeded that of Japan of 3.9 percent and the rate of Germany of 2.6 percent.
Chart I-1, US, Real GDP 1929-1999
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-1A provides real GDP annually from 1929 to 2013. Growth after the global recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 has not been sufficiently high to compensate for the contraction as it had occurred in past economic cycles. GDP is about two trillion lower than trend GDP, explaining 30.3 million unemployed or underemployed. There is dramatic decline of productivity growth in the whole cycle from 2.2 percent per year on average from 1947 to 2013 to 1.6 percent per year on average from 2007 to 2013. There is profound drop in the average rate of output growth from 3.4 percent on average from 1947 to 2013 to 1.0 percent from 2007 to 2013. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth on trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IV2013 would have accumulated to 20.3 percent. GDP in IVQ2013 would be $18,040.3 billion if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2,107.4 billion than actual $15,932.9 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than on trend, explaining the 29.1 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment of 17.8 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/rules-discretionary-authorities-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/02/financial-instability-rules.html).
Chart I-1A, US, Real GDP 1929-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-2 provides the growth of real quarterly GDP in the US between 1947 and 2013. The drop of output in the recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 has been followed by anemic recovery compared with return to trend at 3.0 percent from 1870 to 2010 after events such as wars and recessions (Lucas 2011May) and a standstill that can lead to growth recession, or low rates of economic growth. The expansion is relatively long compared to earlier expansion and there could be even another contraction or conventional recession in the future. The average rate of growth from 1947 to 2013 is 3.2 percent. The average growth rate from IV2007 to IVQ2013 is only 1.0 percent with 2.8 percent annual equivalent from the end of the recession in IVQ2001 to the end of the expansion in IVQ2007.
Chart I-2, US, Real GDP, Quarterly, 1947-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-3 provides real GDP percentage change on the quarter a year earlier for 1983-1984. The objective is simply to compare expansion in two recoveries from sharp contractions as shown in Table I-2. Growth rates in the early phase of the recovery in 1983 and 1984 were very high, which is the opportunity to reduce unemployment that has characterized cyclical expansion in the postwar US economy.
Chart I-3, Real GDP Percentage Change on Quarter a Year Earlier 1983-1987
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
In contrast, growth rates in the comparable first eighteen quarters of expansion from 2009 to 2013 in Chart I-4 have been mediocre. As a result, growth has not provided the exit from unemployment and underemployment as in other cyclical expansions in the postwar period. Growth rates did not rise in V shape as in earlier expansions and then declined close to the standstill of growth recessions.
Chart I-4, US, Real GDP Percentage Change on Quarter a Year Earlier 2009-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table I-3 provides percentage change of real GDP in the United States in the 1930s, 1980s and 2000s. The recession in 1981-1982 is quite similar on its own to the 2007-2009 recession. In contrast, during the Great Depression in the four years of 1930 to 1933, GDP in constant dollars fell 26.4 percent cumulatively and fell 45.3 percent in current dollars (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 150-2, Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2009b), 205-7 and revisions in http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). Data are available for the 1930s only on a yearly basis. US GDP fell 4.7 percent in the two recessions (1) from IQ1980 to IIIQ1980 and (2) from III1981 to IVQ1981 to IVQ1982 and 4.3 percent cumulatively in the recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. It is instructive to compare the first three years of the expansions in the 1980s and the current expansion. GDP grew at 4.6 percent in 1983, 7.3 percent in 1984, 4.2 percent in 1985 and 3.5 percent in 1986 while GDP grew, 2.5 percent in 2010, 1.8 percent in 2011, 2.8 percent in 2012 and 1.9 percent in 2013. Actual annual equivalent GDP growth in the four quarters of 2012 and first four quarters of 2013 is 2.3 percent and 2.6 percent in the four quarters of 2013 but only 2.2 percent discounting contribution of 1.67 percentage points of inventory accumulation to growth in IIIQ2013. GDP grew at 4.2 percent in 1985 and 3.5 percent in 1986 while the forecasts of the central tendency of participants of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) are in the range of 2.8 to 3.0 percent in 2014 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20140319b.htm) with less reliable forecast of 3.0 to 3.2 percent in 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20140319b.htm). Growth of GDP in the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IVQ2013 has been at average 2.4 percent in annual equivalent.
Table I-3, US, Percentage Change of GDP in the 1930s, 1980s and 2000s, ∆%
| Year | GDP ∆% | Year | GDP ∆% | Year | GDP ∆% |
| 1930 | -8.5 | 1980 | -0.2 | 2000 | 4.1 |
| 1931 | -6.4 | 1981 | 2.6 | 2001 | 1.0 |
| 1932 | -12.9 | 1982 | -1.9 | 2002 | 1.8 |
| 1933 | -1.3 | 1983 | 4.6 | 2003 | 2.8 |
| 1934 | 10.8 | 1984 | 7.3 | 2004 | 3.8 |
| 1935 | 8.9 | 1985 | 4.2 | 2005 | 3.4 |
| 1936 | 12.9 | 1986 | 3.5 | 2006 | 2.7 |
| 1937 | 5.1 | 1987 | 3.5 | 2007 | 1.8 |
| 1938 | -3.3 | 1988 | 4.2 | 2008 | -0.3 |
| 1930 | 8.0 | 1989 | 3.7 | 2009 | -2.8 |
| 1940 | 8.8 | 1990 | 1.9 | 2010 | 2.5 |
| 1941 | 17.7 | 1991 | -0.1 | 2011 | 1.8 |
| 1942 | 18.9 | 1992 | 3.6 | 2012 | 2.8 |
| 1943 | 17.0 | 1993 | 2.7 | 2013 | 1.9 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-5 provides percentage change of GDP in the US during the 1930s. There is vast literature analyzing the Great Depression (Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009), 198-217). Cole and Ohanian (1999) find that US real per capita output was lower by 11 percent in 1939 than in 1929 while the typical expansion of real per capita output in the US during a decade is 31 percent. Private hours worked in the US were 25 percent lower in 1939 relative to 1929.
Chart I-5, US, Percentage Change of GDP in the 1930s
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
In contrast, Chart I-6 shows rapid recovery from the recessions in the 1980s. High growth rates in the initial quarters of expansion eliminated the unemployment and underemployment created during the contraction. The economy then returned to grow at the trend of expansion, interrupted by another contraction in 1991.
Chart I-6, US, Percentage Change of GDP in the 1980s
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-7 provides the rates of growth during the 2000s. Growth rates in the initial eighteen quarters of expansion have been relatively lower than during recessions after World War II. As a result, unemployment and underemployment continue at the rate of 17.8 percent of the US labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/rules-discretionary-authorities-and.html) with weak hiring (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/global-financial-risks-recovery-without.html).
Chart I-7, US, Percentage Change of GDP in the 2000s
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Characteristics of the four cyclical contractions are provided in Table I-4 with the first column showing the number of quarters of contraction; the second column the cumulative percentage contraction; and the final column the average quarterly rate of contraction. There were two contractions from IQ1980 to IIIQ1980 and from IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 separated by three quarters of expansion. The drop of output combining the declines in these two contractions is 4.7 percent, which is almost equal to the decline of 4.3 percent in the contraction from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. In contrast, during the Great Depression in the four years of 1930 to 1933, GDP in constant dollars fell 26.4 percent cumulatively and fell 45.3 percent in current dollars (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 150-2, Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2009b), 205-7 and revisions in http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). The comparison of the global recession after 2007 with the Great Depression is entirely misleading.
Table I-4, US, Number of Quarters, GDP Cumulative Percentage Contraction and Average Percentage Annual Equivalent Rate in Cyclical Contractions
| Number of Quarters | Cumulative Percentage Contraction | Average Percentage Rate | |
| IIQ1953 to IIQ1954 | 3 | -2.4 | -0.8 |
| IIIQ1957 to IIQ1958 | 3 | -3.0 | -1.0 |
| IVQ1973 to IQ1975 | 5 | -3.1 | -0.6 |
| IQ1980 to IIIQ1980 | 2 | -2.2 | -1.1 |
| IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 | 4 | -2.5 | -0.64 |
| IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 | 6 | -4.3 | -0.72 |
Sources: Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table I-5 shows the mediocre average annual equivalent growth rate of 2.3 percent of the US economy in the eighteen quarters of the current cyclical expansion from IIIQ2009 to IVQ2013. In sharp contrast, the average growth rate of GDP was: 5.7 percent in the first thirteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1986, 5.4 percent in the first fifteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent in the first sixteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent in the first seventeen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1987 and 5.0 percent in the eighteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIQ1987. The line “average first four quarters in four expansions” provides the average growth rate of 7.7 percent with 7.8 percent from IIIQ1954 to IIQ1955, 9.2 percent from IIIQ1958 to IIQ1959, 6.1 percent from IIIQ1975 to IIQ1976 and 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983. The United States missed this opportunity of high growth in the initial phase of recovery. BEA data show the US economy in standstill with annual growth of 2.4 percent in 2010 decelerating to 1.8 percent annual growth in 2011, 2.8 percent in 2012 and 1.9 percent in 2013 (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) The expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1986 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.7 percent, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983. GDP growth in the four quarters of 2012 and 2013 accumulated to 4.6 percent that is equivalent to 2.4 percent in a year. This is obtained by dividing GDP in IVQ2013 of $15,942.3 billion by GDP in IVQ2011 of $15,242.1 billion and compounding by 4/8: {[($15,942.3/$15,242.1)4/8 -1]100 = 2.3%}. The US economy grew 2.6 percent in IVQ2013 relative to the same quarter a year earlier in IVQ2012. Another important revelation of the revisions and enhancements is that GDP was flat in IVQ2012, which is just at the borderline of contraction. The rate of growth of GDP in the third estimate of IIIQ2013 is 4.1 percent in seasonally adjusted annual rate (SAAR). Inventory accumulation contributed 1.67 percentage points to this rate of growth. The actual rate without this impulse of unsold inventories would have been 2.43 percent, or 0.6 percent in IIIQ2013, such that annual equivalent growth in 2013 is closer to 2.1 percent {[(1.003)(1.006)(1.006)(1.007)4/4-1]100 = 2.2%}, compounding the quarterly rates and converting into annual equivalent.
Table I-5, US, Number of Quarters, Cumulative Growth and Average Annual Equivalent Growth Rate in Cyclical Expansions
| Number | Cumulative Growth ∆% | Average Annual Equivalent Growth Rate | |
| IIIQ 1954 to IQ1957 | 11 | 12.8 | 4.5 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ1954 to IIQ1955 | 4 | 7.8 | |
| IIQ1958 to IIQ1959 | 5 | 10.0 | 7.9 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ1958 to IIQ1959 | 4 | 9.2 | |
| IIQ1975 to IVQ1976 | 8 | 8.3 | 4.1 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ1975 to IIQ1976 | 4 | 6.1 | |
| IQ1983-IQ1986 IQ1983-IIIQ1986 IQ1983-IVQ1986 IQ1983-IQ1987 IQ1983-IIQ1987 | 13 15 16 17 18 | 19.9 21.6 22.3 23.1 24.5 | 5.7 5.4 5.2 5.0 5.0 |
| First Four Quarters IQ1983 to IVQ1983 | 4 | 7.8 | |
| Average First Four Quarters in Four Expansions* | 7.7 | ||
| IIIQ2009 to IVQ2013 | 18 | 11.0 | 2.4 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 | 2.7 |
*First Four Quarters: 7.8% IIIQ1954-IIQ1955; 9.2% IIIQ1958-IIQ1959; 6.1% IIIQ1975-IIQ1976; 7.8% IQ1983-IVQ1983
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-8 shows US real quarterly GDP growth from 1980 to 1989. The economy contracted during the recession and then expanded vigorously throughout the 1980s, rapidly eliminating the unemployment caused by the contraction.
Chart I-8, US, Real GDP, 1980-1989
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-9 shows the entirely different situation of real quarterly GDP in the US between 2007 and 2013. The economy has underperformed during the first sixteen quarters of expansion for the first time in the comparable contractions since the 1950s. The US economy is now in a perilous standstill.
Chart I-9, US, Real GDP, 2007-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
As shown in Tables I-4 and I-5 above the loss of real GDP in the US during the contraction was 4.3 percent but the gain in the cyclical expansion has been only 11.0 percent (first to the last row in Table I-5), using all latest revisions. As a result, the level of real GDP in IVQ2013 with the second estimate and revisions is only higher by 6.3 percent than the level of real GDP in IVQ2007. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. US GDP grew from $14,996.1 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $15,942.3 billion in IVQ2013 or 6.3 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.0 percent. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth under trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IV2013 would have accumulated to 20.3 percent. GDP in IVQ2013 would be $18,040.3 billion if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2,098.0 billion higher than actual $15,942.3 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than under trend, explaining the 29.1 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment of 17.8 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/rules-discretionary-authorities-and.html). The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The contraction actually concentrated in two quarters: decline of 2.2 percent in IVQ2008 relative to the prior quarter and decline of 1.4 percent in IQ2009 relative to IVQ2008. The combined fall of GDP in IVQ2008 and IQ2009 was 3.6 percent {[(1-0.022) x (1-0.014) -1]100 = -3.6%}, or {[(IQ2009 $14,372.1)/(IIIQ2008 $14,895.1) – 1]100 = -3.5%} except for rounding. Those two quarters coincided with the worst effects of the financial crisis. GDP fell 0.1 percent in IIQ2009 but grew 0.3 percent in IIIQ2009, which is the beginning of recovery in the cyclical dates of the NBER. Most of the recovery occurred in five successive quarters from IVQ2009 to IVQ2010 of growth of 1.0 percent in IVQ2009, 0.4 percent in IQ2010, 0.9 percent in IIQ2010 and equal growth at 0.7 percent in IIIQ2010 and 0.7 percent in IVQ2010 for cumulative growth in those five quarters of 3.8 percent, obtained by accumulating the quarterly rates {[(1.01 x 1.004 x 1.009 x 1.007 x 1.007) – 1]100 = 3.8%} or {[(IVQ2010 $14,942.4)/(IIIQ2009 $14,402.5) – 1]100 = 3.7%} with minor rounding difference. The economy then stalled during the first half of 2011 with decline of 0.3 percent in IQ2011 and growth of 0.8 percent in IIQ2011 for combined annual equivalent rate of 1.0 percent {(0.997 x 1.008)2}. The economy grew 0.3 percent in IIIQ2011 for annual equivalent growth of 1.1 percent in the first three quarters {[(0.997 x 1.008 x 1.003)4/3 -1]100 = 1.1%}. Growth picked up in IVQ2011 with 1.2 percent relative to IIIQ2011. Growth in a quarter relative to a year earlier in Table I-6 slows from over 2.7 percent during three consecutive quarters from IIQ2010 to IVQ2010 to 2.0 percent in IQ2011, 1.9 percent in IIQ2011, 1.5 percent in IIIQ2011 and 2.0 percent in IVQ2011. As shown below, growth of 1.2 percent in IVQ2011 was partly driven by inventory accumulation. In IQ2012, GDP grew 0.9 percent relative to IVQ2011 and 3.3 percent relative to IQ2011, decelerating to 0.3 percent in IIQ2012 and 2.8 percent relative to IIQ2011 and 0.7 percent in IIIQ2012 and 3.1 percent relative to IIIQ2011 largely because of inventory accumulation and national defense expenditures. Growth was 0.0 percent in IVQ2012 with 2.0 percent relative to a year earlier but mostly because of deduction of 2.00 percentage points of inventory divestment and 1.22 percentage points of reduction of one-time national defense expenditures. Growth was 0.3 percent in IQ2013 and 1.3 percent relative to IQ2012 in large part because of burning savings to consume caused by financial repression of zero interest rates. There is similar growth of 0.6 percent in IIQ2013 and 1.6 percent relative to a year earlier. In IIIQ2013, GDP grew 1.0 percent relative to the prior quarter and 2.0 percent relative to the same quarter a year earlier with inventory accumulation contributing 1.67 percentage points to growth at 4.1 percent SAAR in IIIQ2013. GDP increased 0.7 percent in IVQ2013 and 2.6 percent relative to a year earlier. Rates of a quarter relative to the prior quarter capture better deceleration of the economy than rates on a quarter relative to the same quarter a year earlier. The critical question for which there is not yet definitive solution is whether what lies ahead is continuing growth recession with the economy crawling and unemployment/underemployment at extremely high levels or another contraction or conventional recession. Forecasts of various sources continued to maintain high growth in 2011 without taking into consideration the continuous slowing of the economy in late 2010 and the first half of 2011. The sovereign debt crisis in the euro area and growth in China are common sources of doubts on the rate and direction of economic growth in the US. There is weak internal demand in the US with almost no investment and spikes of consumption driven by burning saving because of financial repression forever in the form of zero interest rates.
Table I-6, US, Real GDP and Percentage Change Relative to IVQ2007 and Prior Quarter, Billions Chained 2009 Dollars and ∆%
| Real GDP, Billions Chained 2009 Dollars | ∆% Relative to IVQ2007 | ∆% Relative to Prior Quarter | ∆% | |
| IVQ2007 | 14,996.1 | NA | NA | 1.9 |
| IQ2008 | 14,895.4 | -0.7 | -0.7 | 1.1 |
| IIQ2008 | 14,969.2 | -0.2 | 0.5 | 0.9 |
| IIIQ2008 | 14,895.1 | -0.7 | -0.5 | -0.3 |
| IVQ2008 | 14,574.6 | -2.8 | -2.2 | -2.8 |
| IQ2009 | 14,372.1 | -4.2 | -1.4 | -3.5 |
| IIQ2009 | 14,356.9 | -4.3 | -0.1 | -4.1 |
| IIIQ2009 | 14,402.5 | -4.0 | 0.3 | -3.3 |
| IV2009 | 14,540.2 | -3.0 | 1.0 | -0.2 |
| IQ2010 | 14,597.7 | -2.7 | 0.4 | 1.6 |
| IIQ2010 | 14,738.0 | -1.7 | 0.9 | 2.7 |
| IIIQ2010 | 14,839.3 | -1.0 | 0.7 | 3.0 |
| IVQ2010 | 14,942.4 | -0.4 | 0.7 | 2.8 |
| IQ2011 | 14,894.0 | -0.7 | -0.3 | 2.0 |
| IIQ2011 | 15,011.3 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 1.9 |
| IIIQ2011 | 15,062.1 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 1.5 |
| IVQ2011 | 15,242.1 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 2.0 |
| IQ2012 | 15,381.6 | 2.6 | 0.9 | 3.3 |
| IIQ2012 | 15,427.7 | 2.9 | 0.3 | 2.8 |
| IIIQ2012 | 15,534.0 | 3.6 | 0.7 | 3.1 |
| IVQ2012 | 15,539.6 | 3.6 | 0.0 | 2.0 |
| IQ2013 | 15,583.9 | 3.9 | 0.3 | 1.3 |
| IIQ2013 | 15,679.7 | 4.6 | 0.6 | 1.6 |
| IIIQ2013 | 15,839.3 | 5.6 | 1.0 | 2.0 |
| IVQ2013 | 15,942.3 | 6.3 | 0.7 | 2.6 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
ESIII Contracting Real Private Fixed Investment. The United States economy has grown at the average yearly rate of 3 percent per year and 2 percent per year in per capita terms from 1870 to 2010, as measured by Lucas (2011May). An important characteristic of the economic cycle in the US has been rapid growth in the initial phase of expansion after recessions. US economic growth has been at only 2.4 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 18 quarters from IVQ2009 to IVQ2013. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the second estimate of GDP for IVQ2013 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2014/pdf/gdp4q13_2nd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,738.0 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,356.9 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,738.0/$14,356.9 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/financial-risks-slow-cyclical-united.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/financial-risks-slow-cyclical-united.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth under trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IV2013 would have accumulated to 20.3 percent. GDP in IVQ2013 would be $18,040.3 billion if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2,098.0 billion than actual $15,942.3 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than under trend, explaining the 29.1 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment of 17.8 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/rules-discretionary-authorities-and.html). US GDP grew from $14,996.1 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $15,942.3 billion in IVQ2013 or 6.3 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.0 percent. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation.
Inferior performance of the US economy and labor markets is the critical current issue of analysis and policy design. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. Table IA1-1 provides quarterly seasonally adjusted annual rates (SAAR) of growth of private fixed investment for the recessions of the 1980s and the current economic cycle. In the cyclical expansion beginning in IQ1983 (http://www.nber.org/cycles.html), real private fixed investment in the United States grew at the average annual rate of 14.7 percent in the first eight quarters from IQ1983 to IVQ1984. Growth rates fell to an average of 2.2 percent in the following eight quarters from IQ1985 to IVQ1986. There were only two quarters of contraction of private fixed investment from IQ1983 to IVQ1986. There is quite different behavior of private fixed investment in the eighteen quarters of cyclical expansion from IIIQ2009 to IVQ2013. The average annual growth rate in the first eight quarters of expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2011 was 3.3 percent, which is significantly lower than 14.7 percent in the first eight quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1984. There is only strong growth of private fixed investment in the four quarters of expansion from IIQ2011 to IQ2012 at the average annual rate of 10.5 percent. Growth has fallen from the SAAR of 14.8 percent in IIIQ2011 to 2.7 percent in IIIQ2012, recovering to 11.6 percent in IVQ2012 and falling to minus 1.5 percent in IQ2013. The SAAR of fixed investment rose to 6.5 percent in IIQ2013 and fell to 5.9 percent in IIIQ2013. The SAAR of fixed investment fell to 2.8 percent in IVQ2013. Sudeep Reddy and Scott Thurm, writing on “Investment falls off a cliff,” on Nov 18, 2012, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887324595904578123593211825394.html?mod=WSJPRO_hpp_LEFTTopStories) analyze the decline of private investment in the US and inform that a review by the Wall Street Journal of filing and conference calls finds that 40 of the largest publicly traded corporations in the US have announced intentions to reduce capital expenditures in 2012.
Table IA1-1, US, Quarterly Growth Rates of Real Private Fixed Investment, % Annual Equivalent SA
| Q | 1981 | 1982 | 1983 | 1984 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 |
| I | 3.8 | -12.2 | 9.4 | 13.1 | -7.1 | -27.4 | 0.8 |
| II | 3.2 | -12.1 | 16.0 | 16.6 | -5.5 | -14.2 | 13.6 |
| III | 0.1 | -9.3 | 24.4 | 8.2 | -12.1 | -0.5 | -0.4 |
| IV | -1.5 | 0.2 | 24.3 | 7.3 | -23.9 | -2.8 | 8.5 |
| 1985 | 2011 | ||||||
| I | 3.7 | -0.5 | |||||
| II | 5.2 | 8.6 | |||||
| III | -1.6 | 14.8 | |||||
| IV | 7.8 | 10.0 | |||||
| 1986 | 2012 | ||||||
| I | 1.1 | 8.6 | |||||
| II | 0.1 | 4.7 | |||||
| III | -1.8 | 2.7 | |||||
| IV | 3.1 | 11.6 | |||||
| 1987 | 2013 | ||||||
| I | -6.7 | -1.5 | |||||
| II | 6.3 | 6.5 | |||||
| III | 7.1 | 5.9 | |||||
| IV | -0.2 | 2.8 | |||||
| 1988 | |||||||
| I | 0.2 | ||||||
| II | 8.1 | ||||||
| III | 1.9 | ||||||
| IV | 4.8 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-1 of the US Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) provides seasonally adjusted annual rates of growth of real private fixed investment from 1981 to 1987. Growth rates recovered sharply during the first eight quarters, which was essential in returning the economy to trend growth and eliminating unemployment and underemployment accumulated during the contractions.
Chart IA1-1, US, Real Private Fixed Investment, Seasonally-Adjusted Annual Rates Percent Change from Prior Quarter, 1981-1987
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Weak behavior of real private fixed investment from 2007 to 2013 is shown in Chart IA1-2. Growth rates of real private fixed investment were much lower during the initial phase of expansion in the current economic cycle and have entered sharp trend of decline.
Chart IA1-2, US, Real Private Fixed Investment, Seasonally-Adjusted Annual Rates Percent Change from Prior Quarter, 2007-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table IA1-2 provides real private fixed investment at seasonally adjusted annual rates from IVQ2007 to IVQ2013 or for the complete economic cycle. The first column provides the quarter, the second column percentage change relative to IVQ2007, the third column the quarter percentage change in the quarter relative to the prior quarter and the final column percentage change in a quarter relative to the same quarter a year earlier. In IQ1980, gross private domestic investment in the US was $951.6 billion of 2009 dollars, growing to $1,174.4 billion in IIQ1987 or 23.4 percent. Real gross private domestic investment in the US increased 1.5 percent from $2,605.2 billion of 2009 dollars in IVQ2007 to $2,643.3 billion in IVQ2013. As shown in Table IAI-2, real private fixed investment fell 2.9 percent from $2,586.3 billion of 2009 dollars in IVQ2007 to $2,511.2 billion in IVQ2013. Growth of real private investment in Table IA1-2 is mediocre for all but four quarters from IIQ2011 to IQ2012.
Table IA1-2, US, Real Private Fixed Investment and Percentage Change Relative to IVQ2007 and Prior Quarter, Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars and ∆%
| Real PFI, Billions Chained 2009 Dollars | ∆% Relative to IVQ2007 | ∆% Relative to Prior Quarter | ∆% | |
| IVQ2007 | 2586.3 | NA | -1.2 | -1.4 |
| IQ2008 | 2539.1 | -1.8 | -1.8 | -3.0 |
| IIQ2008 | 2503.4 | -3.2 | -1.4 | -4.6 |
| IIIQ2008 | 2424.1 | -6.3 | -3.2 | -7.1 |
| IV2008 | 2263.8 | -12.5 | -6.6 | -12.5 |
| IQ2009 | 2089.3 | -19.2 | -7.7 | -17.7 |
| IIQ2009 | 2011.0 | -22.2 | -3.7 | -19.7 |
| IIIQ2009 | 2008.4 | -22.3 | -0.1 | -17.1 |
| IVQ2009 | 1994.1 | -22.9 | -0.7 | -11.9 |
| IQ2010 | 1997.9 | -22.8 | 0.2 | -4.4 |
| IIQ2010 | 2062.8 | -20.2 | 3.2 | 2.6 |
| IIIQ2010 | 2060.8 | -20.3 | -0.1 | 2.6 |
| IVQ2010 | 2103.1 | -18.7 | 2.1 | 5.5 |
| IQ2011 | 2100.7 | -18.8 | -0.1 | 5.1 |
| IIQ2011 | 2144.4 | -17.1 | 2.1 | 4.0 |
| IIIQ2011 | 2219.8 | -14.2 | 3.5 | 7.7 |
| IVQ2011 | 2273.4 | -12.1 | 2.4 | 8.1 |
| IQ2012 | 2320.8 | -10.3 | 2.1 | 10.5 |
| IIQ2012 | 2347.9 | -9.2 | 1.2 | 9.5 |
| IIIQ2012 | 2363.5 | -8.6 | 0.7 | 6.5 |
| IVQ2012 | 2429.1 | -6.1 | 2.8 | 6.8 |
| IQ2013 | 2420.0 | -6.4 | -0.4 | 4.3 |
| IIQ2013 | 2458.4 | -4.9 | 1.6 | 4.7 |
| IIIQ2013 | 2,494.0 | -3.6 | 1.4 | 5.5 |
| IVQ2013 | 2,511.2 | -2.9 | 0.7 | 3.4 |
PFI: Private Fixed Investment
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
ESIV Swelling Undistributed Corporate Profits. Table IA1-5 provides value added of corporate business, dividends and corporate profits in billions of current dollars at seasonally adjusted annual rates (SAAR) in IVQ2007 and IVQ2013 together with percentage changes. The last three rows of Table IA1-5 provide gross value added of nonfinancial corporate business, consumption of fixed capital and net value added in billions of chained 2009 dollars at SAARs. Deductions from gross value added of corporate profits down the rows of Table IA1-5 end with undistributed corporate profits. Profits after taxes with inventory valuation adjustment (IVA) and capital consumption adjustment (CCA) increased by 105.3 percent in nominal terms from IVQ2007 to IVQ2013 while net dividends increased 14.3 percent and undistributed corporate profits swelled 375.4 percent from $107.7 billion in IQ2007 to $512.0 billion in IVQ2013 and changed signs from minus $55.9 billion in current dollars in IVQ2007. The investment decision of United States corporations has been fractured in the current economic cycle in preference of cash. Gross value added of nonfinancial corporate business adjusted for inflation increased 6.5 percent from IVQ2007 to IVQ2013, which is much lower than nominal increase of 17.9 percent in the same period for gross value added of total corporate business.
Table IA1-5, US, Value Added of Corporate Business, Corporate Profits and Dividends, IVQ2007-IQ2013
| IVQ2007 | IVQ2013 | ∆% | |
| Current Billions of Dollars Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rates (SAAR) | |||
| Gross Value Added of Corporate Business | 8,165.9 | 9,627.9 | 17.9 |
| Consumption of Fixed Capital | 1,216.5 | 1,444.8 | 18.8 |
| Net Value Added | 6,949.4 | 8,183.1 | 17.8 |
| Compensation of Employees | 4,945.8 | 5,462.7 | 10.5 |
| Taxes on Production and Imports Less Subsidies | 688.5 | 765.3 | 11.2 |
| Net Operating Surplus | 1,315.1 | 1,955.1 | 48.7 |
| Net Interest and Misc | 204.2 | 121.6 | -40.5 |
| Business Current Transfer Payment Net | 68.9 | 102.5 | 48.8 |
| Corporate Profits with IVA and CCA Adjustments | 1,042.0 | 1,730.9 | 66.1 |
| Taxes on Corporate Income | 408.8 | 431.1 | 3.2 |
| Profits after Tax with IVA and CCA Adjustment | 633.2 | 1,299.8 | 105.3 |
| Net Dividends | 689.1 | 787.8 | 14.3 |
| Undistributed Profits with IVA and CCA Adjustment | -55.9 | 512.0 | NA ∆% 375.4 relative to 107.7 in IQ2007 |
| Billions of Chained USD 2009 SAAR | |||
| Gross Value Added of Nonfinancial Corporate Business | 7,519.3 | 8,004.5 | 6.5 |
| Consumption of Fixed Capital | 1,066.0 | 1,182.0 | 10.9 |
| Net Value Added | 6,453.4 | 6,822.5 | 5.7 |
IVA: Inventory Valuation Adjustment; CCA: Capital Consumption Adjustment
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table IA1-6 provides comparable United States value added of corporate business, corporate profits and dividends from IQ1980 to IIQ1987. There is significant difference both in nominal and inflation-adjusted data. Between IQ1980 and IIQ1987, profits after tax with IVA and CCA increased 81.2 percent with dividends growing 125.9 percent and undistributed profits increasing 50.6 percent. There was much higher inflation in the 1980s than in the current cycle. For example, the consumer price index for all items not seasonally adjusted increased 41.7 percent between Mar 1980 and Jun 1987 but only 11.0 percent between Dec 2007 and Dec 2013 (http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm). The comparison is still valid in terms of inflation-adjusted data: gross value added of nonfinancial corporate business adjusted for inflation increased 29.3 percent between IQ1980 and IIQ1987 but only 6.5 percent between IVQ2007 and IVQ2013 while net value added adjusted for inflation increased 28.2 percent between IQ1980 and IIQ1987 but only 5.7 percent between IVQ2007 and IVQ2013.
Table IA1-6, US, Value Added of Corporate Business, Corporate Profits and Dividends, IQ1980-IVQ1985
| IQ1980 | IIQ1987 | ∆% | |
| Current Billions of Dollars Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rates (SAAR) | |||
| Gross Value Added of Corporate Business | 1,654.1 | 2,872.8 | 73.7 |
| Consumption of Fixed Capital | 200.5 | 367.8 | 83.4 |
| Net Value Added | 1,453.6 | 2,504.9 | 72.3 |
| Compensation of Employees | 1,072.9 | 1,825.8 | 70.2 |
| Taxes on Production and Imports Less Subsidies | 121.5 | 231.4 | 90.5 |
| Net Operating Surplus | 259.2 | 447.8 | 72.8 |
| Net Interest and Misc. | 50.4 | 107.7 | 113.7 |
| Business Current Transfer Payment Net | 11.5 | 25.7 | 123.5 |
| Corporate Profits with IVA and CCA Adjustments | 197.2 | 314.4 | 59.4 |
| Taxes on Corporate Income | 97.0 | 132.8 | 36.9 |
| Profits after Tax with IVA and CCA Adjustment | 100.2 | 181.6 | 81.2 |
| Net Dividends | 40.9 | 92.4 | 125.9 |
| Undistributed Profits with IVA and CCA Adjustment | 59.3 | 89.3 | 50.6 |
| Billions of Chained USD 2009 SAAR | |||
| Gross Value Added of Nonfinancial Corporate Business | 2,952.3 | 3,817.0 | 29.3 |
| Consumption of Fixed Capital | 315.6 | 436.8 | 38.4 |
| Net Value Added | 2,636.7 | 3,380.2 | 28.2 |
IVA: Inventory Valuation Adjustment; CCA: Capital Consumption Adjustment
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-12 of the US Bureau of Economic Analysis provides quarterly corporate profits after tax and undistributed profits with IVA and CCA from 1979 to 2013. There is tightness between the series of quarterly corporate profits and undistributed profits in the 1980s with significant gap developing from 1988 and to the present with the closest approximation peaking in IVQ2005 and surrounding quarters. These gaps widened during all recessions including in 1991 and 2001 and recovered in expansions with exceptionally weak performance in the current expansion.
Chart IA1-14, US, Corporate Profits after Tax and Undistributed Profits with Inventory Valuation Adjustment and Capital Consumption Adjustment, Quarterly, 1979-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table IA1-7 provides price, costs and profit per unit of gross value added of nonfinancial domestic corporate income for IVQ2007 and IVQ2013 in the upper block and for IQ1980 and IIQ1987 in the lower block. Compensation of employees or labor costs per unit of gross value added of nonfinancial domestic corporate income hardly changed from 0.577 in IVQ2007 to 0.599 in IVQ2013 in a fractured labor market but increased from 0.340 in IQ1980 to 0.436 in IIQ1987 in a more vibrant labor market. Unit nonlabor costs increased mildly from 0.270 per unit of gross value added in IVQ2007 to 0.297 in IVQ2013 but increased from 0.124 in IQ1980 to 0.181 in IIQ1987 in an economy closer to full employment of resources. Profits after tax with IVA and CCA per unit of gross value added of nonfinancial domestic corporate income increased from 0.076 in IVQ2007 to 0.123 in IVQ2013 and from 0.029 in IQ1980 to 0.042 in IIQ1987.
Table IA1-7, US, Price, Costs and Profit per Unit of Gross Value Added of Nonfinancial Domestic Corporate Income
| IVQ2007 | IVQ2013 | |
| Price per Unit of Real Gross Value Added of Nonfinancial Corporate Business | 0.961 | 1.053 |
| Compensation of Employees (Unit Labor Cost) | 0.577 | 0.599 |
| Unit Nonlabor Cost | 0.270 | 0.297 |
| Consumption of Fixed Capital | 0.140 | 0.157 |
| Taxes on Production and Imports less Subsidies plus Business Current Transfer Payments (net) | 0.093 | 0.099 |
| Net Interest and Misc. Payments | 0.037 | 0.041 |
| Corporate Profits with IVA and CCA Adjustment (Unit Profits from Current Production) | 0.114 | 0.157 |
| Taxes on Corporate Income | 0.038 | 0.034 |
| Profits after Tax with IVA and CCA Adjustment | 0.076 | 0.123 |
| IQ1980 | IIQ1987 | |
| Price per Unit of Real Gross Value Added of Nonfinancial Corporate Business | 0.518 | 0.685 |
| Compensation of Employees (Unit Labor Cost) | 0.340 | 0.436 |
| Unit Nonlabor Cost | 0.124 | 0.181 |
| Consumption of Fixed Capital | 0.064 | 0.087 |
| Taxes on Production and Imports less Subsidies plus Business Current Transfer Payments (net) | 0.042 | 0.064 |
| Net Interest and Misc. Payments | 0.018 | 0.030 |
| Corporate Profits with IVA and CCA Adjustment (Unit Profits from Current Production) | 0.055 | 0.067 |
| Taxes on Corporate Income | 0.026 | 0.025 |
| Profits after Tax with IVA and CCA Adjustment | 0.029 | 0.042 |
IVA: Inventory Valuation Adjustment; CCA: Capital Consumption Adjustment
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-13 provides quarterly profits after tax with IVA and CCA per unit of gross value added of nonfinancial domestic corporate income from 1980 to 2013. In an environment of idle labor and other productive resources nonfinancial corporate income increased after tax profits with IVA and CCA per unit of gross value added at a faster pace in the weak economy from IVQ2007 to IVQ2013 than in the vibrant expansion of the cyclical contractions of the 1980s. Part of the profits was distributed as dividends and significant part was retained as undistributed profits in the current economic cycle with frustrated investment decision.
Chart IA1-15, US, Profits after Tax with Inventory Valuation Adjustment and Capital Consumption Adjustment per Unit of Gross Value Added of Nonfinancial Domestic Corporate Income, 1980-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table IA1-8 provides percentage changes of corporate profits in 2012 and 2013 and seasonally adjusted annual rates of change of corporate profits from IQ2013 to IVQ2013. US corporate profits with inventory valuation adjustment (IVA) and capital consumption adjustment (CCA) fell 1.3 percent in IQ2013 and 0.1 percent after taxes. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA rebounded at 3.3 percent in IIQ2013 and at 3.5 percent after taxes. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased at 1.9 percent in IIIQ2013 and 2.4 percent after taxes. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased at 2.2 percent in IVQ2013 and 2.0 percent after taxes. Net dividends jumped 16.2 percent in IVQ2012 in generalized anticipation of income because of fear of the so-called “fiscal cliff,” or increases in taxes in 2013, and fell 12.0 percent in IQ2013 in adjustment to normal levels. Net dividends jumped at 35.8 percent in IIQ2013 and fell at 17.3 percent in IIIQ2013. Net dividends rebounded at 10.5 percent in IVQ2013. Undistributed profits fell 9.7 percent in IVQ2012 in anticipation of tax increases and adjusted by increasing 13.7 percent in IQ2013. Undistributed profits fell at 25.5 percent in IIQ2013 and increased at 34.6 percent in IIIQ2013. Undistributed profits fell at 6.7 percent in IVQ2013.
Table IA1-8, Quarterly Seasonally Adjusted Annual Equivalent Percentage Rates of Change of Corporate Profits, ∆%
| 2012 | 2013 | IQ 2013 | IIQ 2013 | IIIQ 2013 | IVQ | |
| Corporate Profits with IVA and CCA | 7.0 | 4.6 | -1.3 | 3.3 | 1.9 | 2.2 |
| Corporate Income Taxes | 16.2 | -3.7 | -5.8 | 2.4 | -0.1 | 3.2 |
| After Tax Profits with IVA and CCA | 4.7 | 6.9 | -0.1 | 3.5 | 2.4 | 2.0 |
| Net Dividends | 9.8 | 17.1 | -12.0 | 35.8 | -17.3 | 10.5 |
| Und Profits with IVA and CCA | 0.3 | -2.9 | 13.7 | -25.5 | 34.6 | -6.7 |
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table IA1-9 provides change from prior quarter of the level of seasonally adjusted annual rates of US corporate profits. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA fell $26.6 billion in IQ2013 after increasing $34.9 billion in IVQ2012 and $13.9 billion in IIIQ2012. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA rebounded with $66.8 billion in IIQ2013 and $39.2 billion in IIIQ2013. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased $47.1 billion in IVQ2013. Profits after tax with IVA and CCA fell $1.7 billion in IQ2013 after increasing $40.8 billion in IVQ2012 and $4.5 billion in IIIQ2012. In IIQ2013, profits after tax with IVA and CCA increased $56.9 billion and $39.5 billion in IIIQ2013. In IVQ2013, profits after tax with IVA and CCA increased $33.8 billion. Anticipation of higher taxes in the “fiscal cliff” episode caused increase of $120.9 billion in net dividends in IVQ2012 followed with adjustment in the form of decrease of net dividends by $103.8 billion in IQ2013, rebounding with $273.5 billion in IIQ2013. Net dividends fell at $179.0 billion in IIIQ2013 and increased at $90.5 billion in IVQ2013. There is similar decrease of $80.1 billion in undistributed profits with IVA and CCA in IVQ2012 followed by increase of $102.1 billion in IQ2013 and decline of $216.6 billion in IIQ2013. Undistributed profits with IVA and CCA rose at $218.6 billion in IIIQ2013 and fell at $56.7 billion in IVQ2013. Undistributed profits of US corporations swelled 375.4 percent from $107.7 billion IQ2007 to $512.0 billion in IVQ2013 and changed signs from minus $55.9 billion in billion in IVQ2007 (Section IA2). In IQ2013, corporate profits with inventory valuation and capital consumption adjustment fell $26.6 billion relative to IVQ2012, from $2047.2 billion to $2020.6 billion at the quarterly rate of minus 1.3 percent. In IIQ2013, corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased $66.8 billion from $2020.6 billion in IQ2013 to $2087.4 billion at the quarterly rate of 3.3 percent. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased $39.2 billion from $2087.4 billion in IIQ2013 to $2126.6 billion in IIIQ2013 at the annual rate of 1.9 percent. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased at $47.1 billion in IVQ2013 from $2126.6 billion in IIIQ2013 to $2173.7 billion in IVQ2013 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2014/pdf/gdp4q13_3rd.pdf). Uncertainty originating in fiscal, regulatory and monetary policy causes wide swings in expectations and decisions by the private sector with adverse effects on investment, real economic activity and employment.
Table IA1-9, Change from Prior Quarter of Level of Seasonally Adjusted Annual Equivalent Rates of Corporate Profits, Billions of Dollars
| 2012 | 2013 | IQ 2013 | IIQ 2013 | IIIQ 2013 | IVQ | |
| Corporate Profits with IVA and CCA | 131.8 | 92.6 | -26.6 | 66.8 | 39.2 | 47.1 |
| Corporate Income Taxes | 60.6 | -15.9 | -25.0 | 10.0 | -0.4 | 13.3 |
| After Tax Profits with IVA and CCA | 71.2 | 108.5 | -1.7 | 56.9 | 39.5 | 33.8 |
| Net Dividends | 68.7 | 131.7 | -103.8 | 273.5 | -179.0 | 90.5 |
| Und Profits with IVA and CCA | 2.4 | -23.1 | 102.1 | -216.6 | 218.6 | -56.7 |
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
ESV Stagnating Real Disposable Income. The Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) provides a wealth of revisions and enhancements of US personal income and outlays since 1929 (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). Table IB-4 provides growth rates of real disposable income and real disposable income per capita in the long-term and selected periods. Real disposable income consists of after-tax income adjusted for inflation. Real disposable income per capita is income per person after taxes and inflation. There is remarkable long-term trend of real disposable income of 3.2 percent per year on average from 1929 to 2013 and 2.0 percent in real disposable income per capita. Real disposable income increased at the average yearly rate of 3.7 percent from 1947 to 1999 and real disposable income per capita at 2.3 percent. These rates of increase broadly accompany rates of growth of GDP. Institutional arrangements in the United States provided the environment for growth of output and income after taxes, inflation and population growth. There is significant break of growth by much lower 2.3 percent for real disposable income on average from 1999 to 2013 and 1.4 percent in real disposable per capita income. Real disposable income grew at 3.5 percent from 1980 to 1989 and real disposable per capita income at 2.6 percent. In contrast, real disposable income grew at only 1.3 percent on average from 2006 to 2013 and real disposable income at 0.5 percent. The United States has interrupted its long-term and cyclical dynamism of output, income and employment growth. Recovery of this dynamism could prove to be a major challenge. Cyclical uncommonly slow growth explains weakness in the current whole cycle instead of the allegation of secular stagnation.
Table IB-4, Average Annual Growth Rates of Real Disposable Income (RDPI) and Real Disposable Income per Capita (RDPIPC), Percent per Year
| RDPI Average ∆% | |
| 1929-2013 | 3.2 |
| 1947-1999 | 3.7 |
| 1999-2013 | 2.3 |
| 1999-2006 | 3.2 |
| 1980-1989 | 3.5 |
| 2006-2013 | 1.3 |
| RDPIPC Average ∆% | |
| 1929-2013 | 2.0 |
| 1947-1999 | 2.3 |
| 1999-2013 | 1.4 |
| 1999-2006 | 2.2 |
| 1980-1989 | 2.6 |
| 2006-2013 | 0.5 |
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IB-3 provides personal income in the US between 1980 and 1989. These data are not adjusted for inflation that was still high in the 1980s in the exit from the Great Inflation of the 1960s and 1970s. Personal income grew steadily during the 1980s after recovery from two recessions from Jan IQ1980 to Jul IIIQ1980 and from Jul IIIQ1981 to Nov IVQ1982.
Chart IB-3, US, Personal Income, Billion Dollars, Quarterly Seasonally Adjusted at Annual Rates, 1980-1989
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
A different evolution of personal income is shown in Chart IB-4. Personal income also fell during the recession from Dec IVQ2007 to Jun IIQ2009 (http://www.nber.org/cycles.html). Growth of personal income during the expansion has been tepid even with the new revisions. In IVQ2012, nominal disposable personal income grew at the SAAR of 10.7 percent and real disposable personal income at 9.0 percent (Table 6 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2014/pdf/pi0214.pdf) The BEA explains as follows: “Personal income in November and December was boosted by accelerated and special dividend payments to persons and by accelerated bonus payments and other irregular pay in private wages and salaries in anticipation of changes in individual income tax rates. Personal income in December was also boosted by lump-sum social security benefit payments” (page 2 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi1212.pdf pages 1-2 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi0113.pdf). The Bureau of Economic Analysis explains as (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi0213.pdf 2-3): “The January estimate of employee contributions for government social insurance reflected the expiration of the “payroll tax holiday,” that increased the social security contribution rate for employees and self-employed workers by 2.0 percentage points, or $114.1 billion at an annual rate. For additional information, see FAQ on “How did the expiration of the payroll tax holiday affect personal income for January 2013?” at www.bea.gov. The January estimate of employee contributions for government social insurance also reflected an increase in the monthly premiums paid by participants in the supplementary medical insurance program, in the hospital insurance provisions of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, and in the social security taxable wage base.”
The increase was provided in the “fiscal cliff” law H.R. 8 American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 (http://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/BILLS-112hr8eas/pdf/BILLS-112hr8eas.pdf).
In IQ2013, personal income fell at the SAAR of minus 4.1 percent; real personal income excluding current transfer receipts at minus 7.2 percent; and real disposable personal income at minus 7.9 percent (Table 6 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2014/pdf/pi0214.pdf). The BEA explains as follows (page 3 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi0313.pdf):
“The February and January changes in disposable personal income (DPI) mainly reflected the effect of special factors in January, such as the expiration of the “payroll tax holiday” and the acceleration of bonuses and personal dividends to November and to December in anticipation of changes in individual tax rates.”
In IIQ2013, personal income grew at 4.7 percent, real personal income excluding current transfer receipts at 5.6 percent and real disposable income at 4.1 percent (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2014/pdf/pi0214.pdf). In IIIQ2013, personal income grew at 4.0 percent, real personal income excluding current transfers at 1.9 percent and real disposable income at 3.0 percent (Table 6 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2014/pdf/pi0214.pdf). In IVQ2013, personal income grew at 2.2 percent and real disposable income at 0.8 percent (Table 6 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2014/pdf/pi0214.pdf).
Chart IB-4, US, Personal Income, Current Billions of Dollars, Quarterly Seasonally Adjusted at Annual Rates, 2007-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Real or inflation-adjusted disposable personal income is provided in Chart IB-5 from 1980 to 1989. Real disposable income after allowing for taxes and inflation grew steadily at high rates during the entire decade.
Chart IB-5, US, Real Disposable Income, Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars, Quarterly Seasonally Adjusted at Annual Rates 1980-1989
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
In IQ2013, personal income fell at the SAAR of minus 4.1 percent; real personal income excluding current transfer receipts at minus 7.2 percent; and real disposable personal income at minus 7.9 percent (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2014/pdf/pi0214.pdf). The BEA explains as follows (page 3 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi0313.pdf):
“The February and January changes in disposable personal income (DPI) mainly reflected the effect of special factors in January, such as the expiration of the “payroll tax holiday” and the acceleration of bonuses and personal dividends to November and to December in anticipation of changes in individual tax rates.”
This is the explanation for the decline in IQ2013 in Chart IB-6. In IIQ2013, personal income increased at 4.7 percent, real disposable income excluding current transfer receipts at 5.6 percent and real disposable income at 4.1 percent. In IIIQ2013, personal income increased at 4.0 percent, real personal income excluding current transfer receipts at 1.9 percent and real disposable income at 3.0 percent (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2014/pdf/pi0214.pdf). In IVQ2013, personal income increased at 2.2 percent, real personal income excluding current transfers at 1.5 percent and real disposable personal income at 0.8 percent (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2014/pdf/pi0214.pdf).
Chart IB-6, US, Real Disposable Income, Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars, Quarterly Seasonally Adjusted at Annual Rates, 2007-2013
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IB-7 provides percentage quarterly changes in real disposable income from the preceding period at seasonally adjusted annual rates from 1980 to 1989. Rates of changes were high during the decade with few negative changes.
Chart IB-7, US, Real Disposable Income Percentage Change from Preceding Period at Quarterly Seasonally-Adjusted Annual Rates, 1980-1989
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IB-8 provides percentage quarterly changes in real disposable income from the preceding period at seasonally adjusted annual rates from 2007 to 2013. There has been a period of positive rates followed by decline of rates and then negative and low rates in 2011. Recovery in 2012 has not reproduced the dynamism of the brief early phase of expansion. In IVQ2012, nominal disposable personal income grew at the SAAR of 10.7 percent and real disposable personal income at 9.0 percent (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2014/pdf/pi0214.pdf), which the BEA explains as: “Personal income in November and December was boosted by accelerated and special dividend payments to persons and by accelerated bonus payments and other irregular pay in private wages and salaries in anticipation of changes in individual income tax rates. Personal income in December was also boosted by lump-sum social security benefit payments” (page 2 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi1212.pdf). The BEA explains as follows (page 3 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi0313.pdf):
“The February and January changes in disposable personal income (DPI) mainly reflected the effect of special factors in January, such as the expiration of the “payroll tax holiday” and the acceleration of bonuses and personal dividends to November and to December in anticipation of changes in individual tax rates.”
Personal income fell at 4.1 percent in IQ2013, nominal disposable personal income fell at 7.0 percent while real disposable income fell at 7.2 percent. In IIQ2013, personal income increased at 4.7 percent, real personal income excluding current transfer receipts at 5.6 percent and real disposable income at 4.1 percent. In IIIQ2013, personal income increased at 4.0 percent, real personal income excluding current transfer receipts at 1.9 percent and real disposable income at 3.0 percent. In IVQ2013, nominal personal income increased at 2.2 percent, nominal disposable income at 1.8 percent, real personal income excluding current transfers at 1.5 percent and real disposable income at 0.8 percent.
Chart, IB-8, US, Real Disposable Income, Percentage Change from Preceding Period at Seasonally-Adjusted Annual Rates, 2007-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) estimates US personal income in Feb 2014 at the seasonally adjusted annual rate of $14,398.8 billion, as shown in Table IB-3 above (see Table 1 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2014/pdf/pi0214.pdf). The major portion of personal income is compensation of employees of $9,019.5 billion, or 62.6 percent of the total. Wages and salaries are $7,272.7 billion, of which $6,068.4 billion by private industries and supplements to wages and salaries of $1,746.8 billion (employer contributions to pension and insurance funds are $1,206.8 billion and contributions to social insurance are $540.4 billion). In Jun 1987 (at the comparable end of the 18th quarter of cyclical expansion), US personal income was $3,929.2 billion at SAAR (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). Compensation of employees was $2,707.8 billion, or 68.9 percent of the total. Wages and salaries were $2,241.4 billion of which $1819.7 billion by private industries. Supplements to wages and salaries were $466.4 billion with employer contributions to pension and insurance funds of $301.0 billion and $165.3 billion to government social insurance. Chart IB-9 provides US wages and salaries by private industries in the 1980s. Growth was robust after the interruption of the recessions.
Chart IB-9, US, Wages and Salaries, Private Industries, Quarterly, Seasonally Adjusted at Annual Rates Billions of Dollars, 1980-1989
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IB-10 shows US wages and salaries of private industries from 2007 to 2013. There is a drop during the contraction followed by initial recovery in 2010 and then the current much weaker relative performance in 2011, 2012 and 2013.
Chart IB-10, US, Wage and Salary Disbursement, Private Industries, Quarterly, Seasonally Adjusted at Annual Rates, Billions of Dollars 2007-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IB-11 provides finer detail with monthly wages and salaries of private industries from 2007 to 2013. Anticipations of income in late 2012 to avoid tax increases in 2013 cloud comparisons.
Chart IB-11, US, Wages and Salaries, Private Industries, Monthly, Seasonally Adjusted at Annual Rates, Billions of Dollars 2007-2014
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IB-12 provides monthly real disposable personal income per capita from 1980 to 1989. This is the ultimate measure of wellbeing in receiving income by obtaining the value per inhabitant. The measure cannot adjust for the distribution of income. Real disposable personal income per capita grew rapidly during the expansion after 1983 and continued growing during the rest of the decade.
Chart IB-12, US, Real Disposable Per Capita Income, Monthly, Seasonally Adjusted at Annual Rates, Chained 2009 Dollars 1980-1989
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IB-13 provides monthly real disposable personal income per capita from 2007 to 2013. There was initial recovery from the drop during the global recession followed by stagnation. Real per capita disposable income increased 1.2 percent from $36,584 in chained dollars of 2009 in Oct 2012 to $37,035 in Nov 2012 and 3.1 percent to $38,175 in Dec 2012 for cumulative increase of 4.3 percent from Oct 2012 to Dec 2012. Real per capita disposable income fell 5.2 percent from $38,175 in Dec 2012 to $36,195 in Jan 2013, increasing marginally 0.9 percent to $36,503 in Feb 2013 for cumulative change of minus 0.2 percent from Oct 2012 (data at http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). This increase is shown in a jump in the final segment in Chart II-13 with Nov-Dec 2012, decline in Jan 2013 and recovery in Feb 2013. Real per capita disposable income increased 0.4 percent from $36,503 in Feb 2013 in chained dollars of 2009 to $36,633 in Mar 2013 for cumulative increase of 0.1 percent relative to Oct 2012. Real per capita disposable income increased to $36,794 in May 2013 for gain of 0.2 percent relative to $36,715 in Apr 2013 and 0.6 percent from Oct 2012. Real disposable per capita income eased to $36,743 in Jun 2013 for decrease of 0.1 percent relative to May 2013 and increase of 0.4 percent relative to Oct 2012. Real disposable income per capita increased 0.2 percent from $36,743 in Jun 2013 to $36,801 in Jul 2013 and 0.6 percent relative to $36,580 in Oct 2013. Real per capita disposable income increased to $36,966 in Aug 2013 or 0.4 percent higher than in Jul 2013 and 1.0 percent above Oct 2012. Real per capita disposable income increased 0.3 percent from $36,966 in Aug 2013 to $37,076 in Sep 2013 and increased 1.3 percent relative to $36,584 in Oct 2012. Real per capita disposable income decreased 0.3 percent from $37,076 in Sep 2013 to $36,976 in Oct 2013 and increased 1.1 percent relative to $36,584 in Oct 2012. Real per capita disposable income increased 0.1 percent from $36,976 in Oct 2013 to $36,995 in Nov 2013 and increased 1.1 percent relative to $36,584 in Oct 2012. Real per capita income fell 0.3 percent in Dec 2013 to $36,875 and increased 0.8 percent from $36,584 in Oct 2012. Real disposable income per capita fell 0.3 percent from $36,995 in Nov 2013 to $36,875 in Dec 2013 and increased 0.8 percent from $36,584 in Oct 2012. Real disposable income fell 3.4 percent from $38,175 in Dec 2012 to $36,875 in Dec 2013, largely because of anticipations of income in late 2012. BEA explains as: “Personal income in November and December was boosted by accelerated and special dividend payments to persons and by accelerated bonus payments and other irregular pay in private wages and salaries in anticipation of changes in individual income tax rates. Personal income in December was also boosted by lump-sum social security benefit payments” (page 2 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi1212.pdf pages 1-2 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi0113.pdf). The Bureau of Economic Analysis explains as (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi0213.pdf 2-3): “The January estimate of employee contributions for government social insurance reflected the expiration of the “payroll tax holiday,” that increased the social security contribution rate for employees and self-employed workers by 2.0 percentage points, or $114.1 billion at an annual rate. For additional information, see FAQ on “How did the expiration of the payroll tax holiday affect personal income for January 2013?” at www.bea.gov. The January estimate of employee contributions for government social insurance also reflected an increase in the monthly premiums paid by participants in the supplementary medical insurance program, in the hospital insurance provisions of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, and in the social security taxable wage base.”
The increase was provided in the “fiscal cliff” law H.R. 8 American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 (http://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/BILLS-112hr8eas/pdf/BILLS-112hr8eas.pdf).
The BEA explains as follows (page 3 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi0313.pdf):
“The February and January changes in disposable personal income (DPI) mainly reflected the effect of special factors in January, such as the expiration of the “payroll tax holiday” and the acceleration of bonuses and personal dividends to November and to December in anticipation of changes in individual tax rates.”
Real disposable per capita income increased 0.2 from $36,875 in Dec 2013 to $36,933 in Jan 2014 and an additional 0.2 percent to $37,010 in Feb 2014. Real disposable income increased 1.2 percent from $36,584 in Oct 2012 to $37,010 in Feb 2014.
Chart IB-13, US, Real Disposable Per Capita Income, Monthly, Seasonally Adjusted at Annual Rates, Chained 2009 Dollars 2007-2014
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
ESVI Financial Repression. McKinnon (1973) and Shaw (1974) argue that legal restrictions on financial institutions can be detrimental to economic development. “Financial repression” is the term used in the economic literature for these restrictions (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008b), 81-6; for historical analysis see Pelaez 1975). Excessive official regulation frustrates financial development required for growth (Haber 2011). Emphasis on disclosure can reduce bank fragility and corruption, empowering investors to enforce sound governance (Barth, Caprio and Levine 2006). Interest rate ceilings on deposits and loans have been commonly used. The Banking Act of 1933 imposed prohibition of payment of interest on demand deposits and ceilings on interest rates on time deposits. These measures were justified by arguments that the banking panic of the 1930s was caused by competitive rates on bank deposits that led banks to engage in high-risk loans (Friedman, 1970, 18; see Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 74-5). The objective of policy was to prevent unsound loans in banks. Savings and loan institutions complained of unfair competition from commercial banks that led to continuing controls with the objective of directing savings toward residential construction. Friedman (1970, 15) argues that controls were passive during periods when rates implied on demand deposit were zero or lower and when Regulation Q ceilings on time deposits were above market rates on time deposits. The Great Inflation or stagflation of the 1960s and 1970s changed the relevance of Regulation Q.
Most regulatory actions trigger compensatory measures by the private sector that result in outcomes that are different from those intended by regulation (Kydland and Prescott 1977). Banks offered services to their customers and loans at rates lower than market rates to compensate for the prohibition to pay interest on demand deposits (Friedman 1970, 24). The prohibition of interest on demand deposits was eventually lifted in recent times. In the second half of the 1960s, already in the beginning of the Great Inflation (DeLong 1997), market rates rose above the ceilings of Regulation Q because of higher inflation. Nobody desires savings allocated to time or savings deposits that pay less than expected inflation. This is a fact currently with zero interest rates and consumer price inflation of 1.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Feb 2013 (http://www.bls.gov/cpi/) but rising during waves of carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures exposures (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/interest-rate-risks-world-inflation.html). Funding problems motivated compensatory measures by banks. Money-center banks developed the large certificate of deposit (CD) to accommodate increasing volumes of loan demand by customers. As Friedman (1970, 25) finds:
“Large negotiable CD’s were particularly hard hit by the interest rate ceiling because they are deposits of financially sophisticated individuals and institutions who have many alternatives. As already noted, they declined from a peak of $24 billion in mid-December, 1968, to less than $12 billion in early October, 1969.”
Banks created different liabilities to compensate for the decline in CDs. As Friedman (1970, 25; 1969) explains:
“The most important single replacement was almost surely ‘liabilities of US banks to foreign branches.’ Prevented from paying a market interest rate on liabilities of home offices in the United States (except to foreign official institutions that are exempt from Regulation Q), the major US banks discovered that they could do so by using the Euro-dollar market. Their European branches could accept time deposits, either on book account or as negotiable CD’s at whatever rate was required to attract them and match them on the asset side of their balance sheet with ‘due from head office.’ The head office could substitute the liability ‘due to foreign branches’ for the liability ‘due on CDs.”
Friedman (1970, 26-7) predicted the future:
“The banks have been forced into costly structural readjustments, the European banking system has been given an unnecessary competitive advantage, and London has been artificially strengthened as a financial center at the expense of New York.”
In short, Depression regulation exported the US financial system to London and offshore centers. What is vividly relevant currently from this experience is the argument by Friedman (1970, 27) that the controls affected the most people with lower incomes and wealth who were forced into accepting controlled-rates on their savings that were lower than those that would be obtained under freer markets. As Friedman (1970, 27) argues:
“These are the people who have the fewest alternative ways to invest their limited assets and are least sophisticated about the alternatives.”
Chart IB-14 of the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) provides quarterly savings as percent of disposable income or the US savings rate from 1980 to 2013. There was a long-term downward sloping trend from 12 percent in the early 1980s to 2.0 percent in Jul 2005. The savings rate then rose during the contraction and in the expansion. In 2011 and into 2012 the savings rate declined as consumption is financed with savings in part because of the disincentive or frustration of receiving a few pennies for every $10,000 of deposits in a bank. The savings rate increased in the final segment of Chart IB-14 in 2012 followed by another decline because of the pain of the opportunity cost of zero remuneration for hard-earned savings. Swelling realization of income in Oct-Dec 2012 in anticipation of tax increases in Jan 2012 caused the jump of the savings rate to 8.7 percent in Dec 2012. The BEA explains as: Personal income in November and December was boosted by accelerated and special dividend payments to persons and by accelerated bonus payments and other irregular pay in private wages and salaries in anticipation of changes in individual income tax rates. Personal income in December was also boosted by lump-sum social security benefit payments” (page 2 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi1212.pdf). The savings rate then collapsed to 3.6 percent in Jan 2013 in part because of the decline of 5.1 percent in real disposable personal income and to 4.2 percent with increase of real disposable income by 0.9 percent in Feb 2013. The savings rate increased to 4.3 percent in Mar 2013 with increase of real disposable income by 0.4 percent and at 4.6 percent in Apr 2013 with increase of real disposable income by 0.3 percent. The savings rate rose to 4.8 percent in May 2013 with increase of real disposable income by 0.3 percent. The savings rate fell to 4.6 percent in Jun 2013 with decline of real disposable personal income by 0.1 percent. The savings rate increased to 4.7 percent in Jul 2013 with increase of real disposable income by 0.2 percent. In Aug 2013, real disposable income increased 0.5 percent and the savings rate increased to 4.9 percent. In Sep 2013, the savings rate increased to 5.1 percent with increase of real disposable income of 0.4 percent. The savings rate fell to 4.6 percent in Oct 2013 with decrease of real disposable income by 0.2 percent. The savings rate fell to 4.3 percent in Nov 2013 with increase of real disposable income of 0.1 percent. In Dec 2013, the savings rate fell to 4.1 percent with decrease of real disposable income by 0.3 percent. The decline of personal income was caused by increasing contributions to government social insurance (page 1 http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi0113.pdf http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi0213.pdf). The savings rate increased at 4.2 percent in Jan 2014 with increase of real disposable income by 0.2 percent. The savings rate increased to 4.3 percent in Feb 2014 with increase of real disposable income by 0.3 percent. The objective of monetary policy is to reduce borrowing rates to induce consumption but it has collateral disincentive of reducing savings and misallocating resources away from their best uses. The zero interest rate of monetary policy is a tax on saving. This tax is highly regressive, meaning that it affects the most people with lower income or wealth and retirees. The long-term decline of savings rates in the US has created a dependence on foreign savings to finance the deficits in the federal budget and the balance of payments (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/interest-rate-risks-world-inflation.html).
Chart IB-14, US, Personal Savings as a Percentage of Disposable Personal Income, Quarterly, 1980-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IB-15 of the US Bureau of Economic Analysis provides personal savings as percent of personal disposable income, or savings ratio, from Jan 2007 to Feb 2014. The uncertainties caused by the global recession resulted in sharp increase in the savings ratio that peaked at 8.0 percent in May 2008 (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). The second peak occurred at 8.1 percent in May 2009. There was another rising trend until 5.9 percent in Jun 2010 and then steady downward trend until 4.8 percent in Nov 2011. This was followed by an upward trend with 5.6 percent in Jun 2012 but decline to 4.9 percent in Aug 2012 followed by jump to 8.7 percent in Dec 2012. Swelling realization of income in Oct-Dec 2012 in anticipation of tax increases in Jan 2013 caused the jump of the savings rate to 8.7 percent in Dec 2012. The BEA explains as: Personal income in November and December was boosted by accelerated and special dividend payments to persons and by accelerated bonus payments and other irregular pay in private wages and salaries in anticipation of changes in individual income tax rates. Personal income in December was also boosted by lump-sum social security benefit payments” (page 2 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi1212.pdf). There was a reverse effect in Jan 2013 with decline of the savings rate to 3.6 percent. Real disposable personal income fell 5.1 percent and real disposable per capita income fell from $38,175 in Dec 2012 to $36,195 in Jan 2013 or by 5.2 percent, which is explained by the Bureau of Economic Analysis as follows (page 3 http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi0213.pdf):
“Contributions for government social insurance -- a subtraction in calculating personal income --increased $6.4 billion in February, compared with an increase of $126.8 billion in January. The
January estimate reflected increases in both employer and employee contributions for government social insurance. The January estimate of employee contributions for government social insurance reflected the expiration of the “payroll tax holiday,” that increased the social security contribution rate for employees and self-employed workers by 2.0 percentage points, or $114.1 billion at an annual rate. For additional information, see FAQ on “How did the expiration of the payroll tax holiday affect personal income for January 2013?” at www.bea.gov. The January estimate of employee contributions for government social insurance also reflected an increase in the monthly premiums paid by participants in the supplementary medical insurance program, in the hospital insurance provisions of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, and in the social security taxable wage base; together, these changes added $12.9 billion to January. Employer contributions were boosted $5.9 billion in January, which reflected increases in the social security taxable wage base (from $110,100 to $113,700), in the tax rates paid by employers to state unemployment insurance, and in employer contributions for the federal unemployment tax and for pension guaranty. The total contribution of special factors to the January change in contributions for government social insurance was $132.9 billion.”
The savings rate then collapsed to 3.6 percent in Jan 2013 in part because of the decline of 5.1 percent in real disposable personal income and to 4.2 percent with increase of real disposable income by 0.9 percent in Feb 2013. The savings rate increased to 4.3 percent in Mar 2013 with increase of real disposable income by 0.4 percent and at 4.6 percent in Apr 2013 with increase of real disposable income by 0.3 percent. The savings rate rose to 4.8 percent in May 2013 with increase of real disposable income by 0.3 percent. The savings rate fell to 4.6 percent in Jun 2013 with decline of real disposable personal income by 0.1 percent. The savings rate increased to 4.7 percent in Jul 2013 with increase of real disposable income by 0.2 percent. In Aug 2013, real disposable income increased 0.5 percent and the savings rate increased to 4.9 percent. In Sep 2013, the savings rate increased to 5.1 percent with increase of real disposable income of 0.4 percent. The savings rate fell to 4.6 percent in Oct 2013 with decrease of real disposable income by 0.2 percent. The savings rate fell to 4.3 percent in Nov 2013 with increase of real disposable income of 0.1 percent. In Dec 2013, the savings rate fell to 4.1 percent with decrease of real disposable income by 0.3 percent. The decline of personal income was caused by increasing contributions to government social insurance (page 1 http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi0113.pdf http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi0213.pdf). The savings rate increased at 4.2 percent in Jan 2014 with increase of real disposable income by 0.2 percent. The savings rate increased to 4.3 percent in Feb 2014 with increase of real disposable income by 0.3 percent.Permanent manipulation of the entire spectrum of interest rates with monetary policy measures distorts the compass of resource allocation with inferior outcomes of future growth, employment and prosperity and dubious redistribution of income and wealth worsening the most the personal welfare of people without vast capital and financial relations to manage their savings.
Chart IB-15, US, Personal Savings as a Percentage of Disposable Income, Monthly 2007-2014
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
ESVII United States Commercial Banks Assets and Liabilities. Modern banking theory analyzes three important functions provided by banks: monitoring of borrowers, provision of liquidity services and transformation of illiquid assets into immediately liquid assets (Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 51-60). These functions require valuation of alternative investment projects that may be distorted by zero interest rates of monetary policy and artificially low long-term interest rates. The QE∞ trap frustrates essential banking functions.
- Monitoring. Banks monitor projects to ensure that funds are allocated to their intended projects (Diamond 1984, 1996). Banks issue deposits, which are secondary assets, to acquire loans, which are primary assets. Monitoring reduces costs of participating in business projects. Acting as delegated monitor, banks obtain information on the borrower, allowing less costly participation through the issue of unmonitored deposits. Monitoring of borrowers provides enhanced less costly participation by investors through the issue of deposits. There is significant reduction of monitoring costs by delegating to a bank. If there are many potential investors, monitoring by the bank of a credit name is less costly than the sum of individual monitoring of the same credit name by all potential investors. Banks permit borrowers to reach many investors for their projects while affording investors less costly participation in the returns of projects of bank borrowers.
- Transformation of Illiquid Loans into Liquid Deposits. Diamond and Dybvig (1986) analyze bank services through bank balance sheets.
i. Assets. Banks provide loans to borrowers. The evaluation of borrowers prevents “adverse selection,” which consists of banks choosing unsound projects and failing to finance sound projects. Monitoring of loans prevents “moral hazard,” which consists of borrowers using the funds of the loan for purposes other than the project for which they were lent, as for example, using borrowed bank funds for speculative real estate instead of for the intended industrial project. Relationship banking improves the information on borrowers and the monitoring function.
ii. Liabilities. Banks provide numerous services to their clients such as holding deposits, clearing transactions, currency inventory and payments for goods, services and obligations.
iii. Assets and Liabilities: Transformation Function. The transformation function operates through both sides of the balance sheet: banks convert illiquid loans in the asset side into liquid deposits in the liability side. There is rich theory of banking (Diamond and Rajan 2000, 2001a,b). Securitized banking provides the same transformation function by bundling mortgage and other consumer loans into securities that are then sold to investors who finance them in short-dated sale and repurchase agreements (Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2008b), 61-6).
Banking was important in facilitating economic growth in historical periods (Cameron 1961, 1967, 1972; Cameron et al. 1992). Banking is also important currently because small- and medium-size business may have no other form of financing than banks in contrast with many options for larger and more mature companies that have access to capital markets. Personal consumptions expenditures have share of 68.2 percent of GDP in IVQ2013 (Table I-10 in Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/financial-risks-slow-cyclical-united.html). Most consumers rely on their banks for real estate loans, credit cards and personal consumer loans. Thus, it should be expected that success of monetary policy in stimulating the economy would be processed through bank balance sheets.
Selected assets and liabilities of US commercial banks, not seasonally adjusted, in billions of dollars, from Report H.8 of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System are in Table I-1. Data are not seasonally adjusted to permit comparison between Feb 2013 and Feb 2014. Total assets of US commercial banks grew 7.2 percent from $13,275.3 billion in Feb 2013 to $14,226.3 billion in Feb 2014. US GDP in 2013 is estimated at $16,799.7 billion (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). Thus, total assets of US commercial banks are equivalent to around 85 percent of US GDP. Bank credit grew 2.0 percent from $9991.1 billion in Feb 2013 to $10,187.4 billion in Feb 2014. Securities in bank credit increased 0.5 percent from $2720.7 billion in Feb 2013 to $2734.5billion in Feb 2014. A large part of securities in banking credit consists of US Treasury and agency securities, falling 1.5 percent from $1856.9 billion in Feb 2013 to $1828.9 billion in Feb 2014. Credit to the government that issues or backs Treasury and agency securities of $1828.9 billion in Feb 2014 is about 18.0 percent of total bank credit of US commercial banks of $10,187.4 billion. Mortgage-backed securities, providing financing of home loans, fell 0.4 percent, from $1337.2 billion in Feb 2013 to $1331.4 billion in Feb 2014. Loans and leases are relatively more dynamic, growing 2.5 percent from $7270.4 billion in Feb 2013 to $7453.0 billion in Feb 2014. The only dynamic class is commercial and industrial loans, growing 9.2 percent from Feb 2013 to Feb 2014 and providing $1651.3billion or 22.2 percent of total loans and leases of $7453.5 billion in Feb 2014. Real estate loans decreased 0.5 percent, providing $3529.6 billion in Feb 2014 or 47.4 percent of total loans and leases. Consumer loans increased 2.3 percent, providing $1146.9 billion in Feb 2014 or 15.4 percent of total loans. Cash assets are measured to “include vault cash, cash items in process of collection, balances due from depository institutions and balances due from Federal Reserve Banks” (http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h8/current/default.htm). Cash assets in US commercial banks increased 46.6 percent from $1853.9 billion in Feb 2013 to $2717.4 billion in Feb 2014 but a single year of the series masks exploding cash in banks because of unconventional monetary policy, which is discussed below. Bank deposits increased 7.0 percent from $9261.3 billion in Feb 2013 to $9913.8 billion in Feb 2014. The difference between bank deposits and total loans and leases in banks increased from $1990.9 billion in Feb 2013 to $2460.8 billion in Feb 2014 or by $469.9 billion. Securities in bank credit increased by $13.8 billion from $2720.7 billion in Feb 2013 to $2734.5 billion in Feb 2014 and Treasury and agency securities decreased by $28.0 billion from $1856.9 billion in Feb 2013 to $1828.9 billion in Feb 2014. Loans and leases increased $182.6 billion from $7270.4 billion in Feb 2013 to $7453.0 billion in Feb 2014. Banks expanded both lending and investment in lower risk securities partly because of the weak economy and credit disappointments during the global recession that has resulted in an environment of fewer sound lending opportunities. Investing in securities with high duration, or price elasticity of yields, is riskier because of the increase in yields that can cause loss of principal as investors shift away from bond funds into money market funds invested in short-term assets. Lower interest rates resulting from monetary policy may not necessarily encourage higher borrowing in the current loss of dynamism of the US economy with real disposable income per capita in IVQ2013 higher by only 3.1 percent than in IVQ2007 (Table IB-2 IX Conclusion and extended analysis in IB Collapse of United States Dynamism of Income Growth and Employment Creation) in contrast with 13.2 percent higher if the economy had performed in long-term growth of per capita income in the United States at 2 percent per year from 1870 to 2010 (Lucas 2011May). In contrast, growth of real disposable income per capita grew cumulatively 16.6 percent in the cycle from IQ1980 to IIQ1987 that was close to trend growth of 16.6 percent.
Table I-1, US, Assets and Liabilities of Commercial Banks, NSA, Billions of Dollars
| Feb 2013 | Feb 2014 | ∆% | |
| Total Assets | 13,275.3 | 14,226.3 | 7.2 |
| Bank Credit | 9991.1 | 10,187.4 | 2.0 |
| Securities in Bank Credit | 2720.7 | 2734.5 | 0.5 |
| Treasury & Agency Securities | 1856.9 | 1828.9 | -1.5 |
| Mortgage-Backed Securities | 1337.2 | 1331.4 | -0.4 |
| Loans & Leases | 7270.4 | 7453.0 | 2.5 |
| Real Estate Loans | 3549.1 | 3529.6 | -0.5 |
| Commercial Real Estate Loans | 1429.6 | 1507.4 | 5.4 |
| Consumer Loans | 1121.3 | 1146.9 | 2.3 |
| Commercial & Industrial Loans | 1512.3 | 1651.3 | 9.2 |
| Other Loans & Leases | 1087.7 | 1125.1 | 3.4 |
| Cash Assets* | 1853.9 | 2717.4 | 46.6 |
| Total Liabilities | 11,765.8 | 12,684.7 | 7.8 |
| Deposits | 9261.3 | 9913.8 | 7.0 |
| Residual (Assets less Liabilities) | 1509.5 | 1541.6 | NA |
Note: balancing item of residual assets less liabilities not included
*”Includes vault cash, cash items in process of collection, balances due from depository institutions and balances due from Federal Reserve Banks.”
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
Benchmarked to Sep 2013
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h8/20140321/
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h8/20140321/
Seasonally adjusted annual equivalent rates (SAAR) of change of selected assets and liabilities of US commercial banks from the report H.8 of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System are in Table I-2 annually from 2009 to 2013 and for Jan 2014 and Feb 2014. The global recession had strong impact on bank assets as shown by declines of total assets of 6.0 percent in 2009 and 2.6 percent in 2010. Loans and leases fell 10.2 percent in 2009 and 5.7 percent in 2010. Commercial and industrial loans fell 18.4 percent in 2009 and 8.9 percent in 2010. Unconventional monetary policy caused an increase of cash assets of banks of 159.2 percent in 2008, 49.5 percent in 2009 and 47.7 percent in 2011 followed by decline by 2.2 percent in 2012. Cash assets of banks increased 55.2 percent in 2013. Cash assets of banks increased at the SAAR of 22.5 percent in Aug 2012 but contraction by 49.6 percent in Sep 2012 and 6.3 percent in Oct 2012. Cash assets of banks increased at 56.0 percent in Nov 2012, minus 7.8 percent in Dec 2012, 38.8 percent in Jan 2013, 66.2 percent in Feb 2013, 66.0 percent in Mar 2013 and 14.5 percent in Apr 2013. Cash assets of banks increased at the SAAR of 63.2 percent in May 2013, 42.4 percent in Jun 2013, 28.6 percent in Jul 2013, 71.5 percent in Aug 2013, 57.5 percent in Sep 2013 and 50.2 percent in Oct 2013. Cash assets of banks increased at the rate of 29.0 percent in Nov 2013 and fell at 1.5 percent in Dec 2013. Cash assets of banks increased at 20.1 percent in Jan 2014 and at 21.7 percent in Feb 2014. Acquisitions of securities for the portfolio of the central bank injected reserves in depository institutions that banks held as cash and reserves at the central bank because of the lack of sound lending opportunities and the adverse expectations in the private sector on doing business. The truly dynamic investment of banks has been in securities in bank credit: growing at the SAAR of 15.4 percent in Jul 2012, 2.6 percent in Aug 2012, 5.3 percent in Sep 2012, 4.7 percent in Oct 2012, 1.7 percent in Nov 2012 and 20.5 percent in Dec 2012. There were declines of securities in bank credit at 1.1 percent in Jan 2013, 3.2 percent in Feb 2013 and 2.7 percent in Mar 2013 but growth of 1.5 percent in Apr 2013. Securities in bank credit fell at the SAAR of 2.6 percent in May 2013 and 5.7 percent in Jun 2013. Securities in bank credit fell at the SAAR of 11.9 percent in Jul 2013 and at 8.3 percent in Aug 2013. Securities in bank credit fell at the SAAR of 6.8 percent in Sep 2013 and increased at 3.0 percent in Oct 2013. Securities in bank credit increased at 5.2 percent in Nov 2013 and at 10.5 percent in Dec 2013. Securities in bank credit increased at 3.2 percent in Jan 2014 and at 5.7 percent in Feb 2014. Fear of loss of principal in securities with high duration or price elasticity of yield is shifting investments away from bonds into cash and other assets with less price risk. Positions marked to market in balance sheets experience sharp declines. Throughout the crisis banks allocated increasing part of their assets to the safety of Treasury and agency securities, or credit to the US government and government-backed credit: with growth of 13.5 percent in 2009 and 15.2 percent in 2010 and at the rate of 16.3 percent in Jul 2012, declining to the rate of 3.4 percent in Aug 2012, 2.1 percent in Sep 2012 and 0.7 percent in Oct 2012. Treasury and agency securities in bank credit fell at the rate of 0.8 percent in Nov 2012, increasing at 17.2 percent in Dec 2012. Treasury and agency securities in bank credit fell at 5.9 percent in Jan 2013, 3.1 percent in Feb 2013, 7.0 percent in Mar 2013 and 5.4 percent in Apr 2013 and 8.3 percent in May 2013. Treasury and agency securities in US commercial banks fell at the SAAR of 6.8 percent in Jun 2013, 19.7 percent in Jul 2013 and 15.7 percent in Aug 2013. Treasury and agency securities fell at the SAAR of 5.6 percent in Sep 2013 and increased at 1.3 percent in Oct 2013. Treasury and agency securities increased at 5.6 percent in Nov 2013 and at 8.9 percent in Dec 2013. Treasury and agency securities increased at 4.0 percent in Jan 2014 and at 7.7 percent in Feb 2014. Increases in yield result in capital losses that may explain less interest in holding securities with higher duration. Deposits grew at the rate of 10.5 percent in Jul 2012, with the rate declining as for most assets of commercial banks to the rate of 6.2 percent in Aug 2012 but increasing to 7.2 percent in Sep 2012, 8.4 percent in Oct 2012, 5.7 percent in Nov 2012, 18.7 percent in Dec 2012, 2.7 percent in Jan 2013. Deposits grew at the rate of 4.4 percent in Feb 2013, 7.7 percent in Mar 2013, 3.5 percent in Apr 2013 and 2.4 percent in May 2013. Deposits increased at the SAAR of 6.3 percent in Jun 2013, 8.0 percent in Jul 2013 and 3.5 percent in Aug 2013. Deposits grew at the rate of 7.2 percent in Sep 2013 and at 9.0 percent in Oct 2013. Deposits grew at 9.1 percent in Nov 2013 and at 8.7 percent in Dec 2013. Deposits increased at 8.7 percent in Jan 2014 and at 9.5 percent in Feb 2014. The credit intermediation function of banks is broken because of adverse expectations on future business and cannot be fixed by monetary and fiscal policy. Incentives to business and consumers are more likely to be effective in this environment in recovering willingness to assume risk on the part of the private sector, which is the driver of growth and job creation.
Table I-2, US, Selected Assets and Liabilities of Commercial Banks, at Break Adjusted, Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rate, ∆%
| 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | Jan 2014 | Feb 2014 | |
| Total Assets | -6.0 | -2.6 | 5.3 | 2.6 | 7.2 | 7.2 | 10.1 |
| Bank Credit | -6.7 | -2.6 | 1.8 | 4.0 | 1.1 | 3.5 | 8.0 |
| Securities in Bank Credit | 6.2 | 6.9 | 1.8 | 7.5 | -1.9 | 3.2 | 5.7 |
| Treasury & Agency Securities | 13.5 | 15.2 | 3.0 | 8.6 | -5.6 | 4.0 | 7.7 |
| Other Securities | -4.3 | -7.2 | -0.7 | 5.2 | 6.5 | -1.6 | 1.4 |
| Loans & Leases | -10.2 | -5.7 | 1.7 | 2.8 | 2.2 | 3.6 | 8.9 |
| Real Estate Loans | -5.7 | -5.6 | -3.7 | -1.1 | -1.0 | 0.7 | 2.5 |
| Commercial Real Estate Loans | -4.7 | -8.9 | -6.3 | -1.2 | 4.4 | 5.4 | 6.4 |
| Consumer Loans | -3.2 | -6.8 | -1.2 | 1.2 | 3.5 | 0.2 | 2.7 |
| Commercial & Industrial Loans | -18.4 | -8.9 | 8.6 | 11.4 | 7.7 | 6.5 | 26.4 |
| Other Loans & Leases | -23.0 | 0.4 | 20.1 | 6.9 | 4.4 | 12.0 | 9.9 |
| Cash Assets | 49.5 | -7.8 | 47.7 | -2.2 | 55.2 | 20.1 | 21.7 |
| Total Liabilities | -7.1 | -3.3 | 5.5 | 2.3 | 8.1 | 8.8 | 8.5 |
| Deposits | 5.2 | 2.4 | 6.7 | 7.1 | 6.4 | 8.7 | 9.5 |
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h8/current/default.htm
Chart I-16 is quite revealing in analyzing the state of bank credit in the US economy. The upper curves are (1) deposits and (2) loans and leases in bank credit. Historically since 1973, the level and rate of change of deposits and loans and leases in bank credit were almost identical. The lower two curves are Treasury and agency securities in bank credit and cash assets with treasury and agency securities moving closely with cash assets until the 1990s when Treasury and agency securities exceeded cash assets. The shaded area of the recession from IV2007 to IIQ2009 shows a break in the level and rate of movement of the series. Deposits continued to expand rapidly through the recession and the following expansion period. Loans and leases fell and barely recovered the level before the recession while deposits moved nearly vertically well above the level before the recession. While Treasury and agency securities in bank credit continued to expand at a higher rate, reaching a level well above that before the recession, cash assets jumped as the counterpart of excess reserves in banks that financed quantitative easing or massive outright purchases of securities for the balance sheet of the Fed. Unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates and outright purchases of securities caused sharp increases of deposits, cash assets and Treasury and agency securities in bank credit but not in loans and leases. There is much discussion about the almost impossible task of evaluating monetary policy in terms of costs and benefits. Before the financial crisis, Chairman Greenspan (2004) analyzes monetary policy and its limitations (see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 13-4, 212-13) that do not differ from those of private financial institutions:
“The Federal Reserve’s experiences over the past two decades make it clear that uncertainty is not just a pervasive feature of the monetary policy landscape; it is the defining characteristic of that landscape. The term “uncertainty” is meant here to encompass both “Knightian uncertainty,” in which the probability distribution of outcomes is unknown, and “risk,” in which uncertainty of outcomes is delimited by a known probability distribution. In practice, one is never quite sure what type of uncertainty one is dealing with in real time, and it may be best to think of a continuum ranging from well-defined risks to the truly unknown.
As a consequence, the conduct of monetary policy in the United States has come to involve, at its core, crucial elements of risk management. This conceptual framework emphasizes understanding as much as possible the many sources of risk and uncertainty that policymakers face, quantifying those risks when possible, and assessing the costs associated with each of the risks. In essence, the risk management approach to monetary policymaking is an application of Bayesian decision making.
This framework also entails devising, in light of those risks, a strategy for policy directed at maximizing the probabilities of achieving over time our goals of price stability and the maximum sustainable economic growth that we associate with it. In designing strategies to meet our policy objectives, we have drawn on the work of analysts, both inside and outside the Fed, who over the past half century have devoted much effort to improving our understanding of the economy and its monetary transmission mechanism. A critical result has been the identification of a relatively small set of key relationships that, taken together, provide a useful approximation of our economy’s dynamics. Such an approximation underlies the statistical models that we at the Federal Reserve employ to assess the likely influence of our policy decisions.
However, despite extensive efforts to capture and quantify what we perceive as the key macroeconomic relationships, our knowledge about many of the important linkages is far from complete and, in all likelihood, will always remain so. Every model, no matter how detailed or how well designed, conceptually and empirically, is a vastly simplified representation of the world that we experience with all its intricacies on a day-to-day basis.
Given our inevitably incomplete knowledge about key structural aspects of an ever-changing economy and the sometimes asymmetric costs or benefits of particular outcomes, a central bank needs to consider not only the most likely future path for the economy but also the distribution of possible outcomes about that path. The decision makers then need to reach a judgment about the probabilities, costs, and benefits of the various possible outcomes under alternative choices for policy.”
Chart I-16, US, Deposits, Treasury and Government Securities in Bank Credit, Loans and Leases in Bank Credit and Cash Assets, US Commercial Banks, Not Seasonally Adjusted, Monthly, 1973-2014, Billions of Dollars
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h8/current/default.htm
Risk management tools are as likely to fail in private financial institutions as in central banks because of the difficulty of modeling risk during uncertainty. There is no such thing as riskless financial management.
ESVIII United States Housing Collapse. Data and other information continue to provide depressed conditions in the US housing market in a longer perspective, with recent improvement at the margin. Table IIB-1 shows sales of new houses in the US at seasonally adjusted annual equivalent rate (SAAR). House sales fell in nineteen of thirty-eight months from Jan 2011 to Feb 2014 but mostly concentrated in Jan-Feb 2011 and May-Aug 2011. In Jan-Apr 2012, house sales increased at the annual equivalent rate of 10.3 percent and at 23.5 percent in May-Sep 2012. There was significant strength in Sep-Dec 2011 with annual equivalent rate of 48.4 percent. Sales of new houses fell 0.5 percent in Dec 2012 and 4.9 percent in Oct 2012 with increase of 9.0 percent in Nov 2012. Sales of new houses rebounded 15.7 percent in Jan 2013 with annual equivalent rate of 69.9 percent from Oct 2012 to Jan 2013 because of the increase of 15.7 percent in Jan 2013. New house sales fell at annual equivalent 17.7 percent in Feb-Mar 2013. New house sales weakened, decreasing at 4.7 percent in annual equivalent from Apr to Dec 2013 with significant volatility illustrated by decline of 17.1 percent in Jul 2013 and increase of 12.2 percent in Oct 2013. House sales fell 1.6 percent in Dec 2013. New house sales increased 3.2 percent in Jan 2014 and fell 3.3 percent in Feb 2014 with annual equivalent rate of minus 0.5 percent in Jan-Feb 2014. Robbie Whelan and Conor Dougherty, writing on “Builders fuel home sale rise,” on Feb 26, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887324338604578327982067761860.html), analyze how builders have provided financial assistance to home buyers, including those short of cash and with weaker credit background, explaining the rise in new home sales and the highest gap between prices of new and existing houses. The 30-year conventional mortgage rate increased from 3.40 on Apr 25, 2013 to 4.58 percent on Aug 22, 2013 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/data.htm), which could also be a factor in recent weakness with improvement after the rate fell to 4.26 in Nov 2013. The conventional mortgage rate rose to 4.48 percent on Dec 26, 2013 and fell to 4.32 percent on Jan 30, 2014. The conventional mortgage rate increased to 4.37 percent on Feb 26, 2014 and 4.40 percent on Mar 27, 2014. The conventional mortgage rate measured in a survey by Freddie Mac (http://www.freddiemac.com/pmms/release.html) is the “contract interest rate on commitments for fixed-rate first mortgages” (http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/data.htm).
Table IIB-1, US, Sales of New Houses at Seasonally-Adjusted (SA) Annual Equivalent Rate, Thousands and %
| SA Annual Rate | ∆% | |
| Feb 2014 | 440 | -3.3 |
| Jan 2014 | 455 | 3.2 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Feb | -0.5 | |
| Dec 2013 | 441 | -1.6 |
| Nov | 448 | -0.9 |
| Oct | 452 | 12.2 |
| Sep | 403 | 3.9 |
| Aug | 388 | 4.0 |
| Jul | 373 | -17.1 |
| Jun | 450 | 4.9 |
| May | 429 | -3.8 |
| Apr | 446 | 0.7 |
| AE ∆% Apr-Dec | -4.7 | |
| Mar | 443 | -0.4 |
| Feb | 445 | -2.8 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Mar | -17.7 | |
| Jan | 458 | 15.7 |
| Dec 2012 | 396 | -0.5 |
| Nov | 398 | 9.0 |
| Oct | 365 | -4.9 |
| AE ∆% Oct-Jan | 69.9 | |
| Sep | 384 | 2.7 |
| Aug | 374 | 1.4 |
| Jul | 369 | 2.5 |
| Jun | 360 | -2.4 |
| May | 369 | 4.8 |
| AE ∆% May-Sep | 23.5 | |
| Apr | 352 | 0.9 |
| Mar | 349 | -4.6 |
| Feb | 366 | 8.3 |
| Jan | 338 | -0.9 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr | 10.3 | |
| Dec 2011 | 341 | 4.0 |
| Nov | 328 | 3.8 |
| Oct | 316 | 3.9 |
| Sep | 304 | 1.7 |
| AE ∆% Sep-Dec | 48.4 | |
| Aug | 299 | -1.7 |
| Jul | 296 | -2.3 |
| Jun | 301 | -1.3 |
| May | 305 | -1.6 |
| AE ∆% May-Aug | -18.9 | |
| Apr | 310 | 3.3 |
| Mar | 300 | 11.1 |
| Feb | 270 | -12.1 |
| Jan | 307 | -5.8 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr | -14.2 | |
| Dec 2010 | 326 | 13.6 |
AE: Annual Equivalent
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/construction/nrs/
The depressed level of residential construction and new house sales in the US is evident in Table IIB-3 providing new house sales not seasonally adjusted in Jan-Feb of various years. Sales of new houses are virtually the same in Jan-Feb 2014 relative to Jan-Feb 2013. Sales of new houses in Jan-Feb 2014 are substantially lower than in any year between 1963 and 2013 with the exception of the years from 2009 to 2012. There are only three increases of 28.3 percent relative to Jan-Dec 2012, 58.1 percent relative to Jan-Dec 2011, 33.3 percent relative to Jan-Feb 2010 and 28.3 percent relative to Jan-Feb 2009. Sales of new houses in Jan-Feb 2014 are lower by 26.1 percent relative to Jan-Feb 2008, 49.3 percent relative to 2007, 61.6 percent relative to 2006 and 66.2 percent relative to 2005. The housing boom peaked in 2005 and 2006 when increases in fed funds rates to 5.25 percent in Jun 2006 from 1.0 percent in Jun 2004 affected subprime mortgages that were programmed for refinancing in two or three years on the expectation that price increases forever would raise home equity. Higher home equity would permit refinancing under feasible mortgages incorporating full payment of principal and interest (Gorton 2009EFM; see other references in http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/07/causes-of-2007-creditdollar-crisis.html). Sales of new houses in Jan-Feb 2013 relative to the same period in 2004 fell 64.4 percent and 56.9 percent relative to the same period in 2003. Similar percentage declines are also observed for 2013 relative to years from 2000 to 2004. Sales of new houses in Jan-Feb 2014 fell 27.7 per cent relative to the same period in 1995. The population of the US was 179.3 million in 1960 and 281.4 million in 2000 (Hobbs and Stoops 2002, 16). Detailed historical census reports are available from the US Census Bureau at (http://www.census.gov/population/www/censusdata/hiscendata.html). The US population reached 308.7 million in 2010 (http://2010.census.gov/2010census/data/). The US population increased by 129.4 million from 1960 to 2010 or 72.2 percent. The final row of Table IIB-3 reveals catastrophic data: sales of new houses in Jan-Feb 2014 of 68 thousand units are lower by 11.7 percent relative to 77 thousand units of houses sold in Jan-Feb 1963, the first year when data become available. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 123.360 million in Dec 1963 to 246.745 million in Dec 2013, or 100.0 percent (http://www.bls.gov/data/). The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) defines the civilian noninstitutional population (http://www.bls.gov/lau/rdscnp16.htm#cnp): “The civilian noninstitutional population consists of persons 16 years of age and older residing in the 50 States and the District of Columbia who are not inmates of institutions (for example, penal and mental facilities and homes for the aged) and who are not on active duty in the Armed Forces.”
Table IIB-3, US, Sales of New Houses Not Seasonally Adjusted, Thousands and %
| Not Seasonally Adjusted Thousands | |
| Jan-Feb 2014 | 68 |
| Jan-Feb 2013 | 68 |
| ∆% Jan-Feb 2014/Jan-Feb 2013 | -0.1* |
| Jan-Feb 2012 | 53 |
| ∆% Jan-Feb 2014/Jan-Feb 2012 | 28.3 |
| Jan-Feb 2011 | 43 |
| ∆% Jan-Feb 2013/Jan-Feb 2011 | 58.1 |
| Jan-Feb 2010 | 51 |
| ∆% Jan-Feb 2014/ | 33.3 |
| Jan-Feb 2009 | 53 |
| ∆% Jan-Feb 2014/ | 28.3 |
| Jan-Feb 2008 | 92 |
| ∆% Jan-Feb 2014/ | -26.1 |
| Jan-Feb 2007 | 134 |
| ∆% Jan-Feb 2013/ | -49.3 |
| Jan-Feb 2006 | 177 |
| ∆% Jan-Feb 2013/Jan-Feb 2006 | -61.6 |
| Jan-Feb 2005 | 201 |
| ∆% Jan-Feb 2013/Jan-Feb 2005 | -66.2 |
| Jan-Feb 2004 | 191 |
| ∆% Jan-Feb 2013/Jan-Feb 2004 | -64.4 |
| Jan-Feb 2003 | 158 |
| ∆% Jan-Feb 2013/ | -56.9 |
| Jan-Feb 2002 | 150 |
| ∆% Jan-Feb 2013/ | -54.7 |
| Jan-Feb 2001 | 157 |
| ∆% Jan-Feb 2013/ | -56.7 |
| Jan-Feb 2000 | 145 |
| ∆% Jan-Feb 2013/ | -53.1 |
| Jan-Feb 1995 | 94 |
| ∆% Jan-Feb 2013/ | -27.7 |
| Jan-Feb 1963 | 77.0 |
| ∆% Jan-Feb 2013/ | -11.7 |
*Computed using unrounded data
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/construction/nrs/
Table IIB-4 provides the entire available annual series of new house sales from 1963 to 2013. The revised level of 306 thousand new houses sold in 2011 is the lowest since 560 thousand in 1963 in the 48 years of available data while the level of 368 thousand in 2012 is only higher than 323 thousand in 2010. The level of sales of new houses of 430 thousand in 2013 is the lowest from 1963 to 2009 with exception of 412 thousand in 1982. The population of the US increased 129.4 million from 179.3 million in 1960 to 308.7 million in 2010, or 72.2 percent. The civilian noninstitutional population of the US increased from 122.416 million in 1963 to 245.679 million in 2013 or 100.7 percent (http://www.bls.gov/data/). The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) defines the civilian noninstitutional population (http://www.bls.gov/lau/rdscnp16.htm#cnp): “The civilian noninstitutional population consists of persons 16 years of age and older residing in the 50 States and the District of Columbia who are not inmates of institutions (for example, penal and mental facilities and homes for the aged) and who are not on active duty in the Armed Forces.”
The civilian noninstitutional population is the universe of the labor force. In fact, there is no year from 1963 to 2013 in Table IIA-4 with sales of new houses below 400 thousand with the exception of the immediately preceding years of 2009, 2010, 2011 and 2012.
Table IIB-4, US, New Houses Sold, NSA Thousands
| 1963 | 560 |
| 1964 | 565 |
| 1965 | 575 |
| 1966 | 461 |
| 1967 | 487 |
| 1968 | 490 |
| 1969 | 448 |
| 1970 | 485 |
| 1971 | 656 |
| 1972 | 718 |
| 1973 | 634 |
| 1974 | 519 |
| 1975 | 549 |
| 1976 | 646 |
| 1977 | 819 |
| 1978 | 817 |
| 1979 | 709 |
| 1980 | 545 |
| 1981 | 436 |
| 1982 | 412 |
| 1983 | 623 |
| 1984 | 639 |
| 1985 | 688 |
| 1986 | 750 |
| 1987 | 671 |
| 1988 | 676 |
| 1989 | 650 |
| 1990 | 534 |
| 1991 | 509 |
| 1992 | 610 |
| 1993 | 666 |
| 1994 | 670 |
| 1995 | 667 |
| 1996 | 757 |
| 1997 | 804 |
| 1998 | 886 |
| 1999 | 880 |
| 2000 | 877 |
| 2001 | 908 |
| 2002 | 973 |
| 2003 | 1,086 |
| 2004 | 1,203 |
| 2005 | 1,283 |
| 2006 | 1,051 |
| 2007 | 776 |
| 2008 | 485 |
| 2009 | 375 |
| 2010 | 323 |
| 2011 | 306 |
| 2012 | 368 |
| 2013 | 430 |
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/construction/nrs/
Chart IIB-1 of the US Bureau of the Census shows the sharp decline of sales of new houses in the US. Sales rose temporarily until about mid 2010 but then declined to a lower plateau followed by increase and stability.
Chart IIB-1, US, New One-Family Houses Sold in the US, SAAR (Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rate)
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/briefrm/esbr/www/esbr051.html
Percentage changes and average rates of growth of new house sales for selected periods are shown in Table IIB-5. The percentage change of new house sales from 1963 to 2013 is minus 23.2 percent. Between 1991 and 2001, sales of new houses rose 78.4 percent at the average yearly rate of 6.0 percent. Between 1995 and 2005 sales of new houses increased 92.4 percent at the yearly rate of 6.8 percent. There are similar rates in all years from 2000 to 2005. The boom in housing construction and sales began in the 1980s and 1990s. The collapse of real estate culminated several decades of housing subsidies and policies to lower mortgage rates and borrowing terms (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009b), 42-8). Sales of new houses sold in 2013 fell 35.5 percent relative to the same period in 1995 and 66.5 percent relative to 2005.
Table IIB-5, US, Percentage Change and Average Yearly Rate of Growth of Sales of New One-Family Houses
| ∆% | Average Yearly % Rate | |
| 1963-2013 | -23.2 | NA |
| 1991-2001 | 78.4 | 6.0 |
| 1995-2005 | 92.4 | 6.8 |
| 2000-2005 | 46.3 | 7.9 |
| 1995-2013 | -35.5 | NA |
| 2000-2013 | -51.0 | NA |
| 2005-2013 | -66.5 | NA |
NA: Not Applicable
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/construction/nrs/
Chart IIB-2 of the US Bureau of the Census provides the entire monthly sample of new houses sold in the US between Jan 1963 and Feb 2014 without seasonal adjustment. The series is almost stationary until the 1990s. There is sharp upward trend from the early 1990s to 2005-2006 after which new single-family houses sold collapse to levels below those in the beginning of the series in the 1960s.
Chart IIB-2, US, New Single-family Houses Sold, NSA, 1963-2014
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/construction/nrs/
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014.

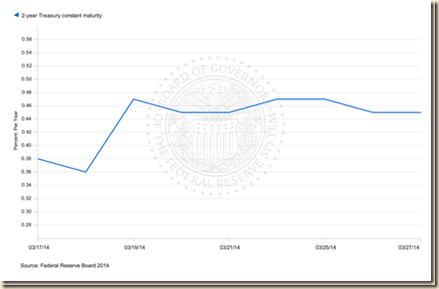



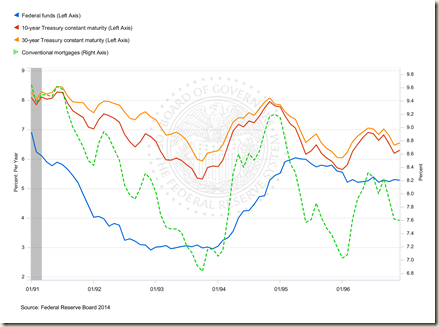

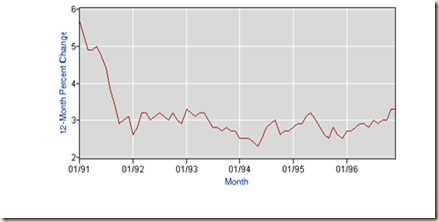


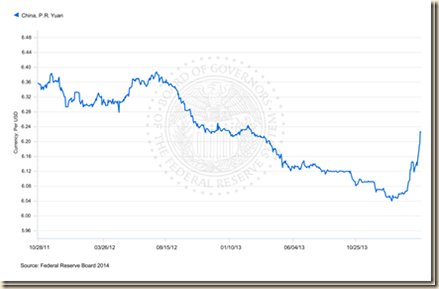



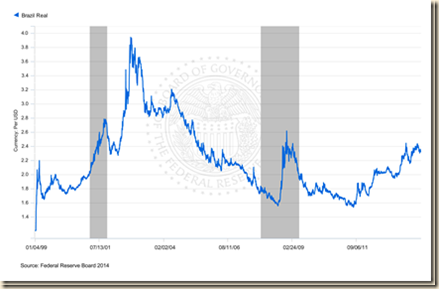









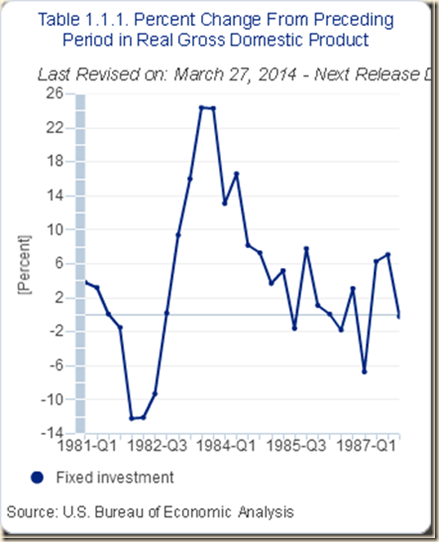


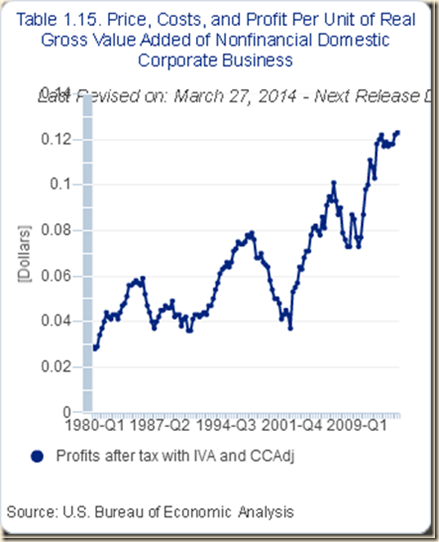



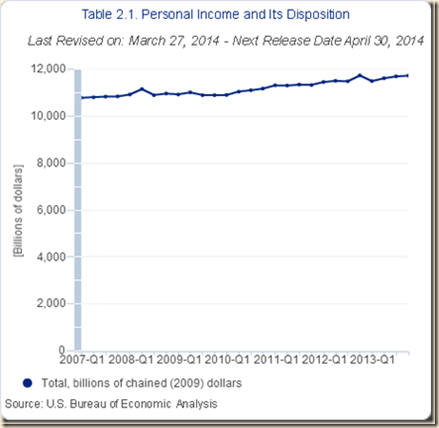
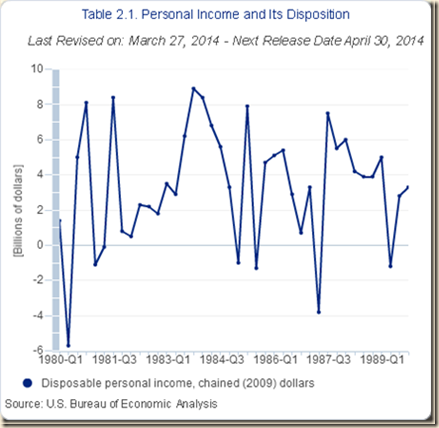

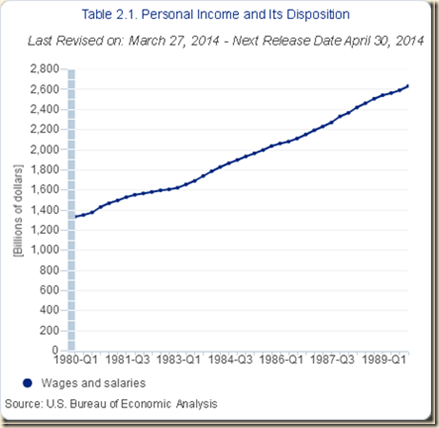

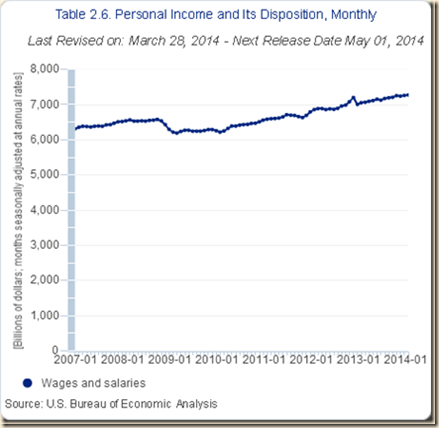



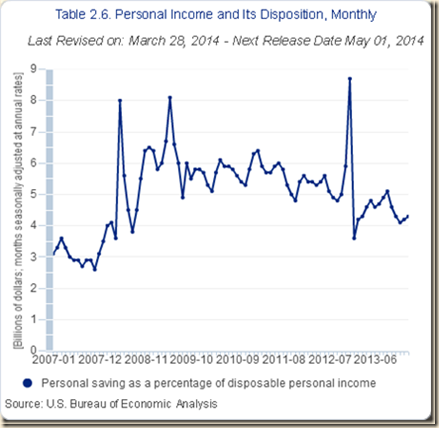


No comments:
Post a Comment