Risks of Steepening Yield Curve and Peaking Valuations of Risk Financial Assets, Mediocre and Decelerating United States Economic Growth, Stagnating Real Disposable Income, Twenty Eight Million Unemployed or Underemployed, World Economic Slowdown and Global Recession Risk
Carlos M. Pelaez
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013
Executive Summary
I Mediocre and Decelerating United States Economic Growth
IA Mediocre and Decelerating United States Economic Growth
IA1 Contracting Real Private Fixed Investment
IB Stagnating Real Disposable Income and Consumption Expenditures
IB1 Stagnating Real Disposable Income and Consumption Expenditures
IB2 Financial Repression
II Twenty Eight Million Unemployed or Underemployed
IIA1 Summary of the Employment Situation
IIA2 Number of People in Job Stress
IIA3 Long-term and Cyclical Comparison of Employment
IIA4 Job Creation
IIB Stagnating Real Wages
III World Financial Turbulence
IIIA Financial Risks
IIIE Appendix Euro Zone Survival Risk
IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation
IV Global Inflation
V World Economic Slowdown
VA United States
VB Japan
VC China
VD Euro Area
VE Germany
VF France
VG Italy
VH United Kingdom
VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets
VII Economic Indicators
VIII Interest Rates
IX Conclusion
References
Appendixes
Appendix I The Great Inflation
IIIB Appendix on Safe Haven Currencies
IIIC Appendix on Fiscal Compact
IIID Appendix on European Central Bank Large Scale Lender of Last Resort
IIIG Appendix on Deficit Financing of Growth and the Debt Crisis
IIIGA Monetary Policy with Deficit Financing of Economic Growth
IIIGB Adjustment during the Debt Crisis of the 1980s
IV Global Inflation. There is inflation everywhere in the world economy, with slow growth and persistently high unemployment in advanced economies. Table IV-1, updated with every blog comment, provides the latest annual data for GDP, consumer price index (CPI) inflation, producer price index (PPI) inflation and unemployment (UNE) for the advanced economies, China and the highly indebted European countries with sovereign risk issues. The table now includes the Netherlands and Finland that with Germany make up the set of northern countries in the euro zone that hold key votes in the enhancement of the mechanism for solution of sovereign risk issues (Peter Spiegel and Quentin Peel, “Europe: Northern Exposures,” Financial Times, Mar 9, 2011 http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/55eaf350-4a8b-11e0-82ab-00144feab49a.html#axzz1gAlaswcW). Newly available data on inflation is considered below in this section. Data in Table IV-1 for the euro zone and its members are updated from information provided by Eurostat but individual country information is provided in this section as soon as available, following Table IV-1. Data for other countries in Table IV-1 are also updated with reports from their statistical agencies. Economic data for major regions and countries is considered in Section V World Economic Slowdown following with individual country and regional data tables.
Table IV-1, GDP Growth, Inflation and Unemployment in Selected Countries, Percentage Annual Rates
| GDP | CPI | PPI | UNE | |
| US | 1.6 | 1.8 | 2.5 | 7.6 |
| Japan | 0.4 | 0.2 | 1.2 | 3.9 |
| China | 7.5 | 2.7 | -2.7 | |
| UK | 1.4 | 2.9* CPIH 2.7 | 2.0 output | 7.8 |
| Euro Zone | -1.1 | 1.6 | -0.1 | 12.1 |
| Germany | -0.3 | 1.9 | 0.2 | 5.3 |
| France | -0.4 | 1.0 | -0.2 | 10.4 |
| Nether-lands | -1.4 | 3.2 | -1.2 | 6.6 |
| Finland | -2.2 | 2.3 | 0.7 | 8.4 |
| Belgium | -0.6 | 1.5 | 0.8 | 8.6 |
| Portugal | -4.0 | 1.2 | 0.9 | 17.6 |
| Ireland | NA | 0.7 | 0.7 | 13.6 |
| Italy | -2.4 | 1.4 | -1.1 | 12.2 |
| Greece | -5.6 | -0.3 | -0.9 | NA |
| Spain | -2.0 | 2.2 | 0.8 | 26.9 |
Notes: GDP: rate of growth of GDP; CPI: change in consumer price inflation; PPI: producer price inflation; UNE: rate of unemployment; all rates relative to year earlier
*Office for National Statistics http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/cpi/consumer-price-indices/june-2013/index.html **Core
Source: EUROSTAT http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/eurostat/home/; country statistical sources http://www.census.gov/aboutus/stat_int.html
Table IV-1 shows the simultaneous occurrence of low growth, inflation and unemployment in advanced economies. The US grew at 1.4 percent in IIQ2013 relative to IIQ2012 (Table 8 in http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2013/pdf/gdp2q13_adv.pdf Section and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html). Japan’s GDP grew 0.1 percent in IQ2013 relative to IQ2012 and 0.2 percent relative to a year earlier. Japan’s grew at the seasonally adjusted annual rate (SAAR) of 4.1 percent in IQQ2013 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/recovery-without-hiring-seven-million.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/05/word-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html). The UK grew at 0.6 percent in IIQ2013 relative to IQ2013 and GDP increased 1.4 percent in IIQ2013 relative to IIQ2012 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/duration-dumping-steepening-yield-curve.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/twenty-nine-million-unemployed-or.html). The Euro Zone grew at minus 0.3 percent in IQ2013 and minus 1.1 percent in IQ2013 relative to IQ2012 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/twenty-nine-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/twenty-eight-million-unemployed-or.html). These are stagnating or “growth recession” rates, which are positive or about nil growth rates with some contractions that are insufficient to recover employment. The rates of unemployment are quite high: 7.4 percent in the US but 17.4 percent for unemployment/underemployment or job stress of 28.3 million (Section II and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/twenty-nine-million-unemployed-or.html), 3.9 percent for Japan (Section VB and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html), 7.8 percent for the UK with high rates of unemployment for young people (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/recovery-without-hiring-seven-million.html). Twelve-month rates of inflation have been quite high, even when some are moderating at the margin: 1.8 percent in the US, 0.2 percent for Japan, 2.7 percent for China, 1.6 percent for the Euro Zone and 2.9 percent for the UK. Stagflation is still an unknown event but the risk is sufficiently high to be worthy of consideration (see http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/06/risk-aversion-and-stagflation.html). The analysis of stagflation also permits the identification of important policy issues in solving vulnerabilities that have high impact on global financial risks. There are six key interrelated vulnerabilities in the world economy that have been causing global financial turbulence: (1) sovereign risk issues in Europe resulting from countries in need of fiscal consolidation and enhancement of their sovereign risk ratings (see Section III and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/duration-dumping-steepening-yield-curve.html). (2) The tradeoff of growth and inflation in China now with change in growth strategy to domestic consumption instead of investment and political developments in a decennial transition. (3) Slow growth by repression of savings with de facto interest rate controls (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html), weak hiring with the loss of 10 million full-time jobs (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/recovery-without-hiring-tapering.html
and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/recovery-without-hiring-seven-million.html) and continuing job stress of 24 to 30 million people in the US and stagnant wages in a fractured job market (Section II and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/twenty-nine-million-unemployed-or.html); (4) The timing, dose, impact and instruments of normalizing monetary and fiscal policies (see http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/02/united-states-unsustainable-fiscal.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/11/united-states-unsustainable-fiscal.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/08/expanding-bank-cash-and-deposits-with.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/02/thirty-one-million-unemployed-or.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/08/united-states-gdp-growth-standstill.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/03/is-there-second-act-of-us-great.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/03/global-financial-risks-and-fed.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/02/policy-inflation-growth-unemployment.html) in advanced and emerging economies. (5) The Tōhoku or Great East Earthquake and Tsunami of Mar 11, 2011 that had repercussions throughout the world economy because of Japan’s share of about 9 percent in world output, role as entry point for business in Asia, key supplier of advanced components and other inputs as well as major role in finance and multiple economic activities (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748704461304576216950927404360.html?mod=WSJ_business_AsiaNewsBucket&mg=reno-wsj); and (6) geopolitical events in the Middle East.
In the effort to increase transparency, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) provides both economic projections of its participants and views on future paths of the policy rate that in the US is the federal funds rate or interest on interbank lending of reserves deposited at Federal Reserve Banks. These projections and views are discussed initially followed with appropriate analysis.
Charles Evans, President of the Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago, proposed an “economic state-contingent policy” or “7/3” approach (Evans 2012 Aug 27):
“I think the best way to provide forward guidance is by tying our policy actions to explicit measures of economic performance. There are many ways of doing this, including setting a target for the level of nominal GDP. But recognizing the difficult nature of that policy approach, I have a more modest proposal: I think the Fed should make it clear that the federal funds rate will not be increased until the unemployment rate falls below 7 percent. Knowing that rates would stay low until significant progress is made in reducing unemployment would reassure markets and the public that the Fed would not prematurely reduce its accommodation.
Based on the work I have seen, I do not expect that such policy would lead to a major problem with inflation. But I recognize that there is a chance that the models and other analysis supporting this approach could be wrong. Accordingly, I believe that the commitment to low rates should be dropped if the outlook for inflation over the medium term rises above 3 percent.
The economic conditionality in this 7/3 threshold policy would clarify our forward policy intentions greatly and provide a more meaningful guide on how long the federal funds rate will remain low. In addition, I would indicate that clear and steady progress toward stronger growth is essential.”
Evans (2012Nov27) modified the “7/3” approach to a “6.5/2.5” approach:
“I have reassessed my previous 7/3 proposal. I now think a threshold of 6-1/2 percent for the unemployment rate and an inflation safeguard of 2-1/2 percent, measured in terms of the outlook for total PCE (Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index) inflation over the next two to three years, would be appropriate.”
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) decided at its meeting on Dec 12, 2012 to implement the “6.5/2.5” approach (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20121212a.htm):
“To support continued progress toward maximum employment and price stability, the Committee expects that a highly accommodative stance of monetary policy will remain appropriate for a considerable time after the asset purchase program ends and the economic recovery strengthens. In particular, the Committee decided to keep the target range for the federal funds rate at 0 to 1/4 percent and currently anticipates that this exceptionally low range for the federal funds rate will be appropriate at least as long as the unemployment rate remains above 6-1/2 percent, inflation between one and two years ahead is projected to be no more than a half percentage point above the Committee’s 2 percent longer-run goal, and longer-term inflation expectations continue to be well anchored.”
Another rising risk is division within the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) on risks and benefits of current policies as expressed in the minutes of the meeting held on Jan 29-30, 2013 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcminutes20130130.pdf 13):
“However, many participants also expressed some concerns about potential costs and risks arising from further asset purchases. Several participants discussed the possible complications that additional purchases could cause for the eventual withdrawal of policy accommodation, a few mentioned the prospect of inflationary risks, and some noted that further asset purchases could foster market behavior that could undermine financial stability. Several participants noted that a very large portfolio of long-duration assets would, under certain circumstances, expose the Federal Reserve to significant capital losses when these holdings were unwound, but others pointed to offsetting factors and one noted that losses would not impede the effective operation of monetary policy.
Jon Hilsenrath, writing on “Fed maps exit from stimulus,” on May 11, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887324744104578475273101471896.html?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection), analyzes the development of strategy for unwinding quantitative easing and how it can create uncertainty in financial markets. Jon Hilsenrath and Victoria McGrane, writing on “Fed slip over how long to keep cash spigot open,” published on Feb 20, 2013 in the Wall street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887323511804578298121033876536.html), analyze the minutes of the Fed, comments by members of the FOMC and data showing increase in holdings of riskier debt by investors, record issuance of junk bonds, mortgage securities and corporate loans. Jon Hilsenrath, writing on “Jobs upturn isn’t enough to satisfy Fed,” on Mar 8, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887324582804578348293647760204.html), finds that much stronger labor market conditions are required for the Fed to end quantitative easing. Unconventional monetary policy with zero interest rates and quantitative easing is quite difficult to unwind because of the adverse effects of raising interest rates on valuations of risk financial assets and home prices, including the very own valuation of the securities held outright in the Fed balance sheet. Gradual unwinding of 1 percent fed funds rates from Jun 2003 to Jun 2004 by seventeen consecutive increases of 25 percentage points from Jun 2004 to Jun 2006 to reach 5.25 percent caused default of subprime mortgages and adjustable-rate mortgages linked to the overnight fed funds rate. The zero interest rate has penalized liquidity and increased risks by inducing carry trades from zero interest rates to speculative positions in risk financial assets. There is no exit from zero interest rates without provoking another financial crash.
Unconventional monetary policy will remain in perpetuity, or QE→∞, changing to a “growth mandate.” There are two reasons explaining unconventional monetary policy of QE→∞: insufficiency of job creation to reduce unemployment/underemployment at current rates of job creation; and growth of GDP at around 1.8 percent, which is well below 3.0 percent estimated by Lucas (2011May) from 1870 to 2010. Unconventional monetary policy interprets the dual mandate of low inflation and maximum employment as mainly a “growth mandate” of forcing economic growth in the US at a rate that generates full employment. A hurdle to this “growth mandate” is that US economic growth has been at only 2.2 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 15 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2013. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm http://bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2013/pdf/gdp2q13_adv.pdf http://bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi0613.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,738.0 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,356.9 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,738.0/$14,356.9 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.7 percent and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html). Zero interest rates and quantitative easing have not provided the impulse for growth and were not required in past successful cyclical expansions.
First, the average number of nonfarm jobs created in Jan-Jul 2012 was 185,571 while the average number of nonfarm jobs created in Jan-Jul 2013 was 192,429, or increase by 3.7 percent. The average number of private jobs created in the US in Jan-Jul 2012 was 189,000 while the average in Jan-Jul 2013 was 195,571, or increase by 3.5 percent. The US labor force increased from 153.617 million in 2011 to 154.975 million in 2012 by 1.358 million or 113,167 per month. The average increase of nonfarm jobs in the five months from Jan to Jul 2013 was 192,429, which is a rate of job creation inadequate to reduce significantly unemployment and underemployment in the United States because of 113,167 new entrants in the labor force per month with 28.3 million unemployed or underemployed. The difference between the average increase of 192,429 new private nonfarm jobs per month in the US from Jan to Jul 2013 and the 113,167 average monthly increase in the labor force from 2011 to 2012 is 79,262 monthly new jobs net of absorption of new entrants in the labor force. There are 28.3 million in job stress in the US currently. Creation of 79,622 new jobs per month net of absorption of new entrants in the labor force would require 357 months to provide jobs for the unemployed and underemployed (28.315 million divided by 79,262) or 30 years (357 divided by 12). The civilian labor force of the US in Jul 2013 not seasonally adjusted stood at 157.196 million with 12.083 million unemployed or effectively 17.577 million unemployed in this blog’s calculation by inferring those who are not searching because they believe there is no job for them for effective labor force of 162.690 million. Reduction of one million unemployed at the current rate of job creation without adding more unemployment requires 1.1 years (1 million divided by product of 79,262 by 12, which is 951,144). Reduction of the rate of unemployment to 5 percent of the labor force would be equivalent to unemployment of only 7.860 million (0.05 times labor force of 157.196 million) for new net job creation of 4.223 million (12.083 million unemployed minus 7.860 million unemployed at rate of 5 percent) that at the current rate would take 4.4 years (4.223 million divided by 0.951144). Under the calculation in this blog, there are 17.577 million unemployed by including those who ceased searching because they believe there is no job for them and effective labor force of 162.690 million. Reduction of the rate of unemployment to 5 percent of the labor force would require creating 9.586 million jobs net of labor force growth that at the current rate would take 9.9 years (17.577 million minus 0.05(162.690 million) = 9.443 million divided by 0.951144, using LF PART 66.2% and Total UEM in Table I-4). These calculations assume that there are no more recessions, defying United States economic history with periodic contractions of economic activity when unemployment increases sharply. The number employed in the US fell from 147.315 million in Jul 2007 to 145.113 million in Jul 2013, by 2.202 million, or decline of 1.5 percent, while the civilian noninstitutional or economically active population increased from 231.958 million in Jul 2007 to 245.756 million in Jul 2013, by 13.798 million or increase of 5.9 percent, using not seasonally adjusted data. There is actually not sufficient job creation in merely absorbing new entrants in the labor force because of those dropping from job searches, worsening the stock of unemployed or underemployed in involuntary part-time jobs. The United States economy has grown at the average yearly rate of 3 percent per year and 2 percent per year in per capita terms from 1870 to 2010, as measured by Lucas (2011May). An important characteristic of the economic cycle in the US has been rapid growth in the initial phase of expansion after recessions.
Second, revisions and enhancements of United States GDP and personal income accounts by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm http://bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2013/pdf/gdp2q13_adv.pdf http://bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi0613.pdf) provide important information on long-term growth and cyclical behavior. Table Summary provides relevant data.
- Long-term. US GDP grew at the average yearly rate of 3.3 percent from 1929 to 2012 and at 3.2 percent from 1947 to 2012.
- Cycles. The combined contraction of GDP in the two almost consecutive recessions in the early 1980s is 4.6 percent. The contraction of US GDP from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 during the global recession was 4.3 percent. The critical difference in the expansion is growth at average 7.8 percent in annual equivalent in the first four quarters of recovery from IQ1983 to IVQ1983. The average rate of growth of GDP in four cyclical expansions in the postwar period is 7.7 percent. In contrast, the rate of growth in the first four quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 was only 2.7 percent. Average annual equivalent growth in the expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1986 was 5.7 percent. In contrast, average annual equivalent growth in the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2013 was only 2.7 percent. The US appears to have lost its dynamism of income growth and employment creation.
Table Summary, Long-term and Cyclical Growth of GDP, Real Disposable Income and Real Disposable Income per Capita
| GDP | ||
| Long-Term | ||
| 1929-2012 | 3.3 | |
| 1947-2012 | 3.2 | |
| Cyclical Contractions ∆% | ||
| IQ1980 to IIIQ1980, IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 | -4.6 | |
| IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 | -4.3 | |
| Cyclical Expansions Average Annual Equivalent ∆% | ||
| IQ1983 to IQ1986 | 5.7 | |
| First Four Quarters IQ1983 to IVQ1983 | 7.8 | |
| IIIQ2009 to IIQ2013 | 2.2 | |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 | 2.7 | |
| Real Disposable Income | Real Disposable Income per Capita | |
| Long-Term | ||
| 1929-2012 | 3.2 | 2.0 |
| 1947-1999 | 3.7 | 2.3 |
| Whole Cycles | ||
| 1980-1989 | 3.5 | 2.6 |
| 2006-2012 | 1.4 | 0.6 |
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm http://bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2013/pdf/gdp2q13_adv.pdf http://bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi0613.pdf
The revisions and enhancements of United States GDP and personal income accounts by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm http://bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2013/pdf/gdp2q13_adv.pdf http://bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi0613.pdf) also provide critical information in assessing the current rhythm of US economic growth. The economy appears to be moving at a pace from 1.4 to 1.8 percent per year. Table Summary GDP provides the data.
1. Average Annual Growth in the Past Six Quarters. GDP growth in the four quarters of 2012 to IIQ2013 accumulated to 2.7 percent. This growth is equivalent to 1.8 percent per year, obtained by dividing GDP in IIQ2013 of $16,648.7 by GDP in IVQ2011 of $15,242.1 and compounding by 4/6: {[($15,648.7/$15,242.1)4/6 -1]100 = 1.8.
2. Average Annual Growth in the First Two Quarters of 2013. GDP growth in the first two quarters of 2013 accumulated to 0.7 percent that is equivalent to 1.4 percent in a year. This is obtained by dividing GDP in IIQ2013 of $15648.7 by GDP in IVQ2012 to $15,583.9 and compounding by 4/2: {[($15,648.7/$15,539.6)4/2 -1]100 =1.4%}. The US economy grew 1.4 percent in IIQ2013 relative to the same quarter a year earlier in IIQ2012. Another important revelation of the revisions and enhancements is that GDP was flat in IVQ2012.
Table Summary GDP, US, Real GDP and Percentage Change Relative to IVQ2007 and Prior Quarter, Billions Chained 2005 Dollars and ∆%
| Real GDP, Billions Chained 2005 Dollars | ∆% Relative to IVQ2007 | ∆% Relative to Prior Quarter | ∆% | |
| IVQ2007 | 14,996.1 | NA | NA | 1.9 |
| IVQ2011 | 15,242.1 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 2.0 |
| IQ2012 | 15,381.6 | 2.6 | 0.9 | 3.3 |
| IIQ2012 | 15,427.7 | 2.9 | 0.3 | 2.8 |
| IIIQ2012 | 15,534.0 | 3.6 | 0.7 | 3.1 |
| IVQ2012 | 15,539.6 | 3.6 | 0.0 | 2.0 |
| IQ2013 | 15,583.9 | 3.9 | 0.3 | 1.3 |
| IIQ2013 | 15,648.7 | 4.4 | 0.4 | 1.4 |
| Cumulative ∆% IQ2012 to IIQ2013 | 2.7 | 2.6 | ||
| Annual Equivalent ∆% | 1.8 | 1.7 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm http://bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2013/pdf/gdp2q13_adv.pdf
In fact, it is evident to the public that this policy will be abandoned if inflation costs rise. There is concern of the production and employment costs of controlling future inflation. Even if there is no inflation, QE→∞ cannot be abandoned because of the fear of rising interest rates. The economy would operate in an inferior allocation of resources and suboptimal growth path, or interior point of the production possibilities frontier where the optimum of productive efficiency and wellbeing is attained, because of the distortion of risk/return decisions caused by perpetual financial repression. Not even a second-best allocation is feasible with the shocks to efficiency of financial repression in perpetuity.
The statement of the FOMC at the conclusion of its meeting on Dec 12, 2012, revealed policy intentions (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20121212a.htm) practically unchanged in the statement at the conclusion of its meeting on Jan 30, 2013 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20130130a.htm) and at its meeting on Jun 19, 2013 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20130619a.htm):
“Release Date: June 19, 2013
For immediate release
Information received since the Federal Open Market Committee met in May suggests that economic activity has been expanding at a moderate pace. Labor market conditions have shown further improvement in recent months, on balance, but the unemployment rate remains elevated. Household spending and business fixed investment advanced, and the housing sector has strengthened further, but fiscal policy is restraining economic growth. Partly reflecting transitory influences, inflation has been running below the Committee's longer-run objective, but longer-term inflation expectations have remained stable.
Consistent with its statutory mandate, the Committee seeks to foster maximum employment and price stability. The Committee expects that, with appropriate policy accommodation, economic growth will proceed at a moderate pace and the unemployment rate will gradually decline toward levels the Committee judges consistent with its dual mandate. The Committee sees the downside risks to the outlook for the economy and the labor market as having diminished since the fall. The Committee also anticipates that inflation over the medium term likely will run at or below its 2 percent objective.
To support a stronger economic recovery and to help ensure that inflation, over time, is at the rate most consistent with its dual mandate, the Committee decided to continue purchasing additional agency mortgage-backed securities at a pace of $40 billion per month and longer-term Treasury securities at a pace of $45 billion per month. The Committee is maintaining its existing policy of reinvesting principal payments from its holdings of agency debt and agency mortgage-backed securities in agency mortgage-backed securities and of rolling over maturing Treasury securities at auction. Taken together, these actions should maintain downward pressure on longer-term interest rates, support mortgage markets, and help to make broader financial conditions more accommodative.
The Committee will closely monitor incoming information on economic and financial developments in coming months. The Committee will continue its purchases of Treasury and agency mortgage-backed securities, and employ its other policy tools as appropriate, until the outlook for the labor market has improved substantially in a context of price stability. The Committee is prepared to increase or reduce the pace of its purchases to maintain appropriate policy accommodation as the outlook for the labor market or inflation changes. In determining the size, pace, and composition of its asset purchases, the Committee will continue to take appropriate account of the likely efficacy and costs of such purchases as well as the extent of progress toward its economic objectives.
To support continued progress toward maximum employment and price stability, the Committee expects that a highly accommodative stance of monetary policy will remain appropriate for a considerable time after the asset purchase program ends and the economic recovery strengthens. In particular, the Committee decided to keep the target range for the federal funds rate at 0 to 1/4 percent and currently anticipates that this exceptionally low range for the federal funds rate will be appropriate at least as long as the unemployment rate remains above 6-1/2 percent, inflation between one and two years ahead is projected to be no more than a half percentage point above the Committee's 2 percent longer-run goal, and longer-term inflation expectations continue to be well anchored. In determining how long to maintain a highly accommodative stance of monetary policy, the Committee will also consider other information, including additional measures of labor market conditions, indicators of inflation pressures and inflation expectations, and readings on financial developments. When the Committee decides to begin to remove policy accommodation, it will take a balanced approach consistent with its longer-run goals of maximum employment and inflation of 2 percent.
Voting for the FOMC monetary policy action were: Ben S. Bernanke, Chairman; William C. Dudley, Vice Chairman; Elizabeth A. Duke; Charles L. Evans; Jerome H. Powell; Sarah Bloom Raskin; Eric S. Rosengren; Jeremy C. Stein; Daniel K. Tarullo; and Janet L. Yellen. Voting against the action was James Bullard, who believed that the Committee should signal more strongly its willingness to defend its inflation goal in light of recent low inflation readings, and Esther L. George, who was concerned that the continued high level of monetary accommodation increased the risks of future economic and financial imbalances and, over time, could cause an increase in long-term inflation expectations.“
There are several important issues in this statement.
- Mandate. The FOMC pursues a policy of attaining its “dual mandate” of (http://www.federalreserve.gov/aboutthefed/mission.htm):
“Conducting the nation's monetary policy by influencing the monetary and credit conditions in the economy in pursuit of maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates”
- Open-ended Quantitative Easing or QE∞. Earlier programs are continued with an additional open-ended $85 billion of bond purchases per month: “To support a stronger economic recovery and to help ensure that inflation, over time, is at the rate most consistent with its dual mandate, the Committee decided to continue purchasing additional agency mortgage-backed securities at a pace of $40 billion per month and longer-term Treasury securities at a pace of $45 billion per month.”
- Advance Guidance on “6 ¼ 2 ½ “Rule. Policy will be accommodative even after the economy recovers satisfactorily: “To support continued progress toward maximum employment and price stability, the Committee expects that a highly accommodative stance of monetary policy will remain appropriate for a considerable time after the asset purchase program ends and the economic recovery strengthens. In particular, the Committee decided to keep the target range for the federal funds rate at 0 to 1/4 percent and currently anticipates that this exceptionally low range for the federal funds rate will be appropriate at least as long as the unemployment rate remains above 6-1/2 percent, inflation between one and two years ahead is projected to be no more than a half percentage point above the Committee's 2 percent longer-run goal, and longer-term inflation expectations continue to be well anchored.”
- Monitoring and Policy Focus on Jobs. The FOMC reconsiders its policy continuously in accordance with available information: “In determining how long to maintain a highly accommodative stance of monetary policy, the Committee will also consider other information, including additional measures of labor market conditions, indicators of inflation pressures and inflation expectations, and readings on financial developments. When the Committee decides to begin to remove policy accommodation, it will take a balanced approach consistent with its longer-run goals of maximum employment and inflation of 2 percent.”
- Increase or Reduction of Asset Purchases. Market participants focused on slightly different wording about increasing asset purchases: “The Committee is prepared to increase or reduce the pace of its purchases to maintain appropriate policy accommodation as the outlook for the labor market or inflation changes. In determining the size, pace, and composition of its asset purchases, the Committee will continue to take appropriate account of the likely efficacy and costs of such purchases as well as the extent of progress toward its economic objectives.”
Current focus is on tapering quantitative easing by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC). There is sharp distinction between the two measures of unconventional monetary policy: (1) fixing of the overnight rate of fed funds at 0 to ¼ percent; and (2) outright purchase of Treasury and agency securities and mortgage-backed securities for the balance sheet of the Federal Reserve. Market are overreacting to the so-called “paring” of outright purchases of $85 billion of securities per month for the balance sheet of the Fed. What is truly important is the fixing of the overnight fed funds at 0 to ¼ percent for which there is no end in sight as evident in the FOMC statement for Jun 19, 2013 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20130619a.htm):
“To support continued progress toward maximum employment and price stability, the Committee expects that a highly accommodative stance of monetary policy will remain appropriate for a considerable time after the asset purchase program ends and the economic recovery strengthens. In particular, the Committee decided to keep the target range for the federal funds rate at 0 to 1/4 percent and currently anticipates that this exceptionally low range for the federal funds rate will be appropriate at least as long as the unemployment rate remains above 6-1/2 percent, inflation between one and two years ahead is projected to be no more than a half percentage point above the Committee's 2 percent longer-run goal, and longer-term inflation expectations continue to be well anchored. In determining how long to maintain a highly accommodative stance of monetary policy, the Committee will also consider other information, including additional measures of labor market conditions, indicators of inflation pressures and inflation expectations, and readings on financial developments. When the Committee decides to begin to remove policy accommodation, it will take a balanced approach consistent with its longer-run goals of maximum employment and inflation of 2 percent” (emphasis added).
In delivering the biannual report on monetary policy (Board of Governors 2013Jul17), Chairman Bernanke (2013Jul17) advised Congress that:
“Instead, we are providing additional policy accommodation through two distinct yet complementary policy tools. The first tool is expanding the Federal Reserve's portfolio of longer-term Treasury securities and agency mortgage-backed securities (MBS); we are currently purchasing $40 billion per month in agency MBS and $45 billion per month in Treasuries. We are using asset purchases and the resulting expansion of the Federal Reserve's balance sheet primarily to increase the near-term momentum of the economy, with the specific goal of achieving a substantial improvement in the outlook for the labor market in a context of price stability. We have made some progress toward this goal, and, with inflation subdued, we intend to continue our purchases until a substantial improvement in the labor market outlook has been realized. We are relying on near-zero short-term interest rates, together with our forward guidance that rates will continue to be exceptionally low--our second tool--to help maintain a high degree of monetary accommodation for an extended period after asset purchases end, even as the economic recovery strengthens and unemployment declines toward more-normal levels. In appropriate combination, these two tools can provide the high level of policy accommodation needed to promote a stronger economic recovery with price stability.
The Committee's decisions regarding the asset purchase program (and the overall stance of monetary policy) depend on our assessment of the economic outlook and of the cumulative progress toward our objectives. Of course, economic forecasts must be revised when new information arrives and are thus necessarily provisional.”
Friedman (1953) argues there are three lags in effects of monetary policy: (1) between the need for action and recognition of the need; (2) the recognition of the need and taking of actions; and (3) taking of action and actual effects. Friedman (1953) finds that the combination of these lags with insufficient knowledge of the current and future behavior of the economy causes discretionary economic policy to increase instability of the economy or standard deviations of real income σy and prices σp. Policy attempts to circumvent the lags by policy impulses based on forecasts. We are all naïve about forecasting. Data are available with lags and revised to maintain high standards of estimation. Policy simulation models estimate economic relations with structures prevailing before simulations of policy impulses such that parameters change as discovered by Lucas (1977). Economic agents adjust their behavior in ways that cause opposite results from those intended by optimal control policy as discovered by Kydland and Prescott (1977). Advance guidance attempts to circumvent expectations by economic agents that could reverse policy impulses but is of dubious effectiveness. There is strong case for using rules instead of discretionary authorities in monetary policy (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/search?q=rules+versus+authorities).
The key policy is maintaining fed funds rate between 0 and ¼ percent. An increase in fed funds rates could cause flight out of risk financial markets worldwide. There is no exit from this policy without major financial market repercussions. Indefinite financial repression induces carry trades with high leverage, risks and illiquidity.
Unconventional monetary policy drives wide swings in allocations of positions into risk financial assets that generate instability instead of intended pursuit of prosperity without inflation. There is insufficient knowledge and imperfect tools to maintain the gap of actual relative to potential output constantly at zero while restraining inflation in an open interval of (1.99, 2.0). Symmetric targets appear to have been abandoned in favor of a self-imposed single jobs mandate of easing monetary policy even with the economy growing at or close to potential output that is actually a target of growth forecast. The impact on the overall economy and the financial system of errors of policy are magnified by large-scale policy doses of trillions of dollars of quantitative easing and zero interest rates. The US economy has been experiencing financial repression as a result of negative real rates of interest during nearly a decade and programmed in monetary policy statements until 2015 or, for practical purposes, forever. The essential calculus of risk/return in capital budgeting and financial allocations has been distorted. If economic perspectives are doomed until 2015 such as to warrant zero interest rates and open-ended bond-buying by “printing” digital bank reserves (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/12/is-fed-printing-money-what-are.html; see Shultz et al 2012), rational investors and consumers will not invest and consume until just before interest rates are likely to increase. Monetary policy statements on intentions of zero interest rates for another three years or now virtually forever discourage investment and consumption or aggregate demand that can increase economic growth and generate more hiring and opportunities to increase wages and salaries. The doom scenario used to justify monetary policy accentuates adverse expectations on discounted future cash flows of potential economic projects that can revive the economy and create jobs. If it were possible to project the future with the central tendency of the monetary policy scenario and monetary policy tools do exist to reverse this adversity, why the tools have not worked before and even prevented the financial crisis? If there is such thing as “monetary policy science”, why it has such poor record and current inability to reverse production and employment adversity? There is no excuse of arguing that additional fiscal measures are needed because they were deployed simultaneously with similar ineffectiveness.
Table IV-2 provides economic projections of governors of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve and regional presidents of Federal Reserve Banks released at the meeting of Mar 20, 2013. The Fed releases the data with careful explanations (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20130320.pdf). Columns “∆% GDP,” “∆% PCE Inflation” and “∆% Core PCE Inflation” are changes “from the fourth quarter of the previous year to the fourth quarter of the year indicated.” The GDP report for IIQ2013 is analyzed in Section I (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/mediocre-united-states-economic-growth.html) and the PCE inflation data from the report on personal income and outlays in Section IV (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/mediocre-united-states-economic-growth.html). The Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) provides the first estimate of IIQ2013 GDP released on Jul 31 with revisions since 1929 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/gdpnewsrelease.htm See Section I (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/mediocre-united-states-economic-growth.html). PCE inflation is the index of personal consumption expenditures (PCE) of the report of the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) on “Personal Income and Outlays” (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/pinewsrelease.htm), which is analyzed in Section IV (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/mediocre-united-states-economic-growth.html). The report on “Personal Income and Outlays” for Jun was released at 8:30 AM on Aug 2, 2013 with revisions from 1959 to May 2013 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/pinewsrelease.htm). PCE core inflation consists of PCE inflation excluding food and energy. Column “UNEMP %” is the rate of unemployment measured as the average civilian unemployment rate in the fourth quarter of the year. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) provides the Employment Situation Report with the civilian unemployment rate in the first Friday of every month, which is analyzed in this blog. The report for Jul 2013 was released on Aug 2 and analyzed in this blog (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/twenty-nine-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/twenty-eight-million-unemployed-or.html). “Longer term projections represent each participant’s assessment of the rate to which each variable would be expected to converge under appropriate monetary policy and in the absence of further shocks to the economy” (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20121212.pdf).
It is instructive to focus on 2013 as 2014, 2015 and longer term are too far away, and there is not much information even on what will happen in 2013 and beyond. The central tendency should provide reasonable approximation of the view of the majority of members of the FOMC but the second block of numbers provides the range of projections by FOMC participants. The first row for each year shows the projection introduced after the meeting of Mar 20, 2013 and the second row “PR” the projection of the Jun 19, 2013 meeting. There are three major changes in the view.
1. Growth “∆% GDP.” The FOMC has reduced the forecast of GDP growth in 2013 from 2.3 to 2.8 percent at the meeting in Mar 2013 to 2.3 to 2.6 percent at the meeting on Jun 20, 2013. The FOMC increased GDP growth in 2014 from 2.9 to 3.4 percent at the meeting in Mar 2013 to 3.0 to 3.5 percent at the meeting in Jun 2013.
2. Rate of Unemployment “UNEM%.” The FOMC reduced the forecast of the rate of unemployment from 7.3 to 7.5 percent at the meeting on Mar 20, 2013 to 7.2 to 7.3 percent at the meeting on Jun 19, 2013. The projection for 2014 decreased to the range of 6.5 to 6.8 in Jun 2013 from 6.7 to 7.0 in Mar 2013. Projections of the rate of unemployment are moving closer to the desire 6.5 percent or lower with 5.8 to 6.2 percent in 2015 after the meeting on Jun 19, 2013.
3. Inflation “∆% PCE Inflation.” The FOMC changed the forecast of personal consumption expenditures (PCE) inflation from 1.3 to 1.7 percent at the meeting on Mar 20, 2012 to 0.8 to 1.2 percent at the meeting on Jun 19, 2013. There are no projections exceeding 2.0 percent.
4. Core Inflation “∆% Core PCE Inflation.” Core inflation is PCE inflation excluding food and energy. There is again not much of a difference of the projection that changed from 1.5 to 1.6 percent at the meeting on Mar 20, 2013 to 1.2 to 1.3 percent at the meeting on Jun 19, 2013.
Table IV-2, US, Economic Projections of Federal Reserve Board Members and Federal Reserve Bank Presidents in FOMC, Mar 2013 and Jun 19, 2013
| ∆% GDP | UNEM % | ∆% PCE Inflation | ∆% Core PCE Inflation | |
| Central | ||||
| 2013 | 2.3 to 2.6 | 7.2 to 7.3 | 0.8 to 1.2 | 1.2 to 1.3 1.5 to 1.6 |
| 2014 | 3.0 to 3.5 | 6.5 to 6.8 | 1.4 to 2.0 | 1.5 to 1.8 |
| 2015 Mar PR | 2.9 to 3.6 2.9 to 3.7 | 5.8 to 6.2 6.0 to 6.5 | 1.6 to 2.0 1.7 to 2.0 | 1.7 to 2.0 1.8 to 2.1 |
| Longer Run Mar PR | 2.3 to 2.5 2.3 to 2.5 | 5.2 to 6.0 5.2 to 6.0 | 2.0 2.0 | |
| Range | ||||
| 2013 | 2.0 to 2.6 | 6.9 to 7.5 | 0.8 to 1.5 | 1.1 to 1.5 |
| 2014 | 2.2 to 3.6 | 6.2 to 6.9 | 1.4 to 2.0 | 1.5 to 2.1 |
| 2015 Mar PR | 2.3 to 3.8 2.5 to 3.8 | 5.7 to 6.4 5.7 to 6.5 | 1.6 to 2.3 1.6 to 2.6 | 1.7 to 2.3 1.7 to 2.6 |
| Longer Run Mar PR | 2.0 to 3.0 2.0 to 3.0 | 5.0 to 6.0 5.0 to 6.0 | 2.0 2.0 |
Notes: UEM: unemployment; PR: Projection
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, FOMC http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20130619.pdf
Another important decision at the FOMC meeting on Jan 25, 2012, is formal specification of the goal of inflation of 2 percent per year but without specific goal for unemployment (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20120125c.htm):
“Following careful deliberations at its recent meetings, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) has reached broad agreement on the following principles regarding its longer-run goals and monetary policy strategy. The Committee intends to reaffirm these principles and to make adjustments as appropriate at its annual organizational meeting each January.
The FOMC is firmly committed to fulfilling its statutory mandate from the Congress of promoting maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates. The Committee seeks to explain its monetary policy decisions to the public as clearly as possible. Such clarity facilitates well-informed decision making by households and businesses, reduces economic and financial uncertainty, increases the effectiveness of monetary policy, and enhances transparency and accountability, which are essential in a democratic society.
Inflation, employment, and long-term interest rates fluctuate over time in response to economic and financial disturbances. Moreover, monetary policy actions tend to influence economic activity and prices with a lag. Therefore, the Committee's policy decisions reflect its longer-run goals, its medium-term outlook, and its assessments of the balance of risks, including risks to the financial system that could impede the attainment of the Committee's goals.
The inflation rate over the longer run is primarily determined by monetary policy, and hence the Committee has the ability to specify a longer-run goal for inflation. The Committee judges that inflation at the rate of 2 percent, as measured by the annual change in the price index for personal consumption expenditures, is most consistent over the longer run with the Federal Reserve's statutory mandate. Communicating this inflation goal clearly to the public helps keep longer-term inflation expectations firmly anchored, thereby fostering price stability and moderate long-term interest rates and enhancing the Committee's ability to promote maximum employment in the face of significant economic disturbances.
The maximum level of employment is largely determined by nonmonetary factors that affect the structure and dynamics of the labor market. These factors may change over time and may not be directly measurable. Consequently, it would not be appropriate to specify a fixed goal for employment; rather, the Committee's policy decisions must be informed by assessments of the maximum level of employment, recognizing that such assessments are necessarily uncertain and subject to revision. The Committee considers a wide range of indicators in making these assessments. Information about Committee participants' estimates of the longer-run normal rates of output growth and unemployment is published four times per year in the FOMC's Summary of Economic Projections. For example, in the most recent projections, FOMC participants' estimates of the longer-run normal rate of unemployment had a central tendency of 5.2 percent to 6.0 percent, roughly unchanged from last January but substantially higher than the corresponding interval several years earlier.
In setting monetary policy, the Committee seeks to mitigate deviations of inflation from its longer-run goal and deviations of employment from the Committee's assessments of its maximum level. These objectives are generally complementary. However, under circumstances in which the Committee judges that the objectives are not complementary, it follows a balanced approach in promoting them, taking into account the magnitude of the deviations and the potentially different time horizons over which employment and inflation are projected to return to levels judged consistent with its mandate. ”
The probable intention of this specific inflation goal is to “anchor” inflationary expectations. Massive doses of monetary policy of promoting growth to reduce unemployment could conflict with inflation control. Economic agents could incorporate inflationary expectations in their decisions. As a result, the rate of unemployment could remain the same but with much higher rate of inflation (see Kydland and Prescott 1977 and Barro and Gordon 1983; http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/05/slowing-growth-global-inflation-great.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/04/new-economics-of-rose-garden-turned.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/03/is-there-second-act-of-us-great.html See Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 99-116). Strong commitment to maintaining inflation at 2 percent could control expectations of inflation.
The FOMC continues its efforts of increasing transparency that can improve the credibility of its firmness in implementing its dual mandate. Table IV-3 provides the views by participants of the FOMC of the levels at which they expect the fed funds rate in 2013, 2014, 2015 and the in the longer term. Table IV-3 is inferred from a chart provided by the FOMC with the number of participants expecting the target of fed funds rate (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20130320.pdf). There are 18 participants expecting the rate to remain at 0 to ¼ percent in 2013 and one to be higher in the interval below 1.0 percent. The rate would still remain at 0 to ¼ percent in 2014 for 15 participants with three expecting the rate to be in the range of 0.5 to 1.0 percent and one participant expecting rates at 1.0 to 1.5 percent. This table is consistent with the guidance statement of the FOMC that rates will remain at low levels until late in 2014. For 2015, six participants expect rates to be below or at 1.0 percent while nine expect rates from 1.0 to 1.5 percent and four expecting rates in excess of 2.0 percent. In the long term, all 19 participants expect the fed funds rate in the range of 3.0 to 4.5 percent.
Table IV-3, US, Views of Target Federal Funds Rate at Year-End of Federal Reserve Board
Members and Federal Reserve Bank Presidents Participating in FOMC, Jun 19, 2013
| 0 to 0.25 | 0.5 to 1.0 | 1.0 to 1.5 | 1.0 to 2.0 | 2.0 to 3.0 | 3.0 to 4.5 | |
| 2013 | 18 | 1 | ||||
| 2014 | 15 | 3 | 1 | |||
| 2015 | 1 | 5 | 9 | 1 | 3 | |
| Longer Run | 19 |
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, FOMC http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20130619.pdf
Additional information is provided in Table IV-4 with the number of participants expecting increasing interest rates in the years from 2013 to 2015. It is evident from Table IV-4 that the prevailing view of the FOMC is for interest rates to continue at low levels in future years. This view is consistent with the economic projections of low economic growth, relatively high unemployment and subdued inflation provided in Table IV-2. The FOMC states that rates will continue to be low even after return of the economy to potential growth.
Table IV-4, US, Views of Appropriate Year of Increasing Target Federal Funds Rate of Federal
Reserve Board Members and Federal Reserve Bank Presidents Participating in FOMC, June 19, 2013
| Appropriate Year of Increasing Target Fed Funds Rate | Number of Participants |
| 2013 | 1 |
| 2014 | 3 |
| 2015 | 14 |
| 2016 | 1 |
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, FOMC http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20130619.pdf
The revisions and enhancements of United States GDP and personal income accounts by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm http://bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2013/pdf/gdp2q13_adv.pdf http://bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi0613.pdf) also provide critical information in assessing indexes of prices of personal consumption. There are waves of inflation similar to those worldwide (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html) in inflation of personal consumption expenditures (PCE) in Table IV-5. These waves are in part determined by commodity price shocks originating in the carry trade from zero interest rates to positions in risk financial assets, in particular in commodity futures, which increase the prices of food and energy when there is relaxed risk aversion. Return of risk aversion causes collapse in prices. The first wave is in Jan-Apr 2011 when headline PCE inflation increased at the average annual equivalent rate of 3.7 percent and PCE inflation excluding food and energy (PCEX) at 2.1 percent. The drivers of inflation were increases in food prices (PCEF) at the annual equivalent rate of 7.8 percent and of energy prices (PCEE) at 26.4 percent. This behavior will prevail under zero interest rates and relaxed risk aversion because of carry trades from zero interest rates to leveraged positions in commodity futures. The second wave occurred in May-Jun 2011 when risk aversion from the European sovereign risk crisis interrupted the carry trade. PCE prices increased 2.4 percent in annual equivalent and 2.4 percent excluding food and energy. The third wave is captured by the annual equivalent rates in Jul-Sep 2011 of headline PCE inflation of 2.4 percent with subdued PCE inflation excluding food and energy of 2.0 percent while PCE food rose at 6.2 percent and PCE energy increased at 6.2 percent. In the fourth wave in Oct-Dec 2011, increased risk aversion explains the fall of the annual equivalent rate of inflation to 0.8 for headline PCE inflation and 2.0 percent for PCEX excluding food and energy. PCEF of prices of food rose at the annual equivalent rate of 1.2 percent in Oct-Dec 2011 while PCEE of prices of energy fell at the annual equivalent rate of 10.7 percent. In the fifth wave in Jan-Mar 2012, headline PCE in annual equivalent was 2.4 percent and 2.4 percent excluding food and energy (PCEX). Energy prices of personal consumption (PCEE) increased at the annual equivalent rate of 15.8 percent because of the jump of 2.3 percent in Feb 2012 followed by 1.3 percent in Mar 2012. In the sixth wave, renewed risk aversion caused reversal of carry trades with headline PCE inflation at the annual equivalent rate of 0.0 percent in Apr-May 2012 while PCE inflation excluding food and energy increased at the annual equivalent rate of 1.2 percent. In the seventh wave, further shocks of risk aversion resulted in headline PCE annual equivalent inflation at 1.2 percent in Jun-Jul 2012 with core PCE excluding food and energy at 1.8 percent. In the eighth wave, temporarily relaxed risk aversion with zero interest rates resulted in central PCE inflation at 3.7 percent annual equivalent in Aug-Sep 2012 with PCEX excluding food and energy at 0.6 percent while PCEE energy jumped at 67.6 percent annual equivalent. The program of outright monetary transactions (OTM) of the European Central Bank induced relaxed risk aversion (http://www.ecb.int/press/pr/date/2012/html/pr120906_1.en.html). In the ninth wave, prices collapsed with reversal of carry trade positions in a new episode of risk aversion with central PCE at annual equivalent 0.6 percent in Oct 2012 to Jan 2013 and PCEX at 1.8 percent while energy prices fell at minus 16.9 percent. In the tenth wave, central PCE increased at annual equivalent 4.9 percent in Feb 2013, PCEX at 1.2 percent and PCEE at 92.3 percent. In the eleventh wave, renewed risk aversion resulted in decline in annual equivalent of general PCE prices at 2.4 percent in Mar-Apr 2013 while PCEX increased at 0.6 percent and energy prices fell at 34.8 percent. In the twelfth wave, central PCE increased at 1.2 percent annual equivalent in May-Jun 2013 with PCEX increasing at 1.8 percent, food PCEF increasing at 0.6 percent and energy PCEE increasing at 24.4 percent with the jump of 3.5 percent in Jun 2013.
Table IV-5, US, Percentage Change from Prior Month of Prices of Personal Consumption Expenditures, Seasonally Adjusted Monthly ∆%
| PCE | PCEG | PCEG | PCES | PCEX | PCEF | PCEE | |
| 2013 | |||||||
| Jun | 0.4 | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 3.5 |
| May | 0.1 | -0.1 | -0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | -0.2 | 0.2 |
| ∆% AE May | 3.0 | 3.7 | -0.6 | 2.4 | 1.8 | 0.6 | 24.4 |
| Apr | -0.3 | -0.9 | -0.3 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | -4.4 |
| Mar | -0.1 | -0.6 | -0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | -2.6 |
| ∆% AE Mar-Apr | -2.4 | -8.6 | -3.0 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 1.2 | -34.8 |
| Feb | 0.4 | 0.8 | -0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 5.6 |
| ∆% AE Feb | 4.9 | 10.0 | -1.2 | 2.4 | 1.2 | 2.4 | 92.3 |
| Jan | 0.1 | -0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.0 | -1.8 |
| 2012 | |||||||
| Dec | 0.0 | -0.3 | -0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | -0.9 |
| Nov | -0.1 | -0.7 | -0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | -3.5 |
| Oct | 0.2 | 0.1 | -0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| ∆% AE Oct-Jan | 0.6 | -3.3 | -1.2 | 2.4 | 1.8 | 2.1 | -16.9 |
| Sep | 0.3 | 0.6 | -0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | -0.1 | 4.1 |
| Aug | 0.3 | 0.7 | -0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 4.7 |
| ∆% AE Aug-Sep | 3.7 | 8.1 | -2.4 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 67.6 |
| Jul | 0.0 | -0.2 | -0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | -1.2 |
| Jun | 0.2 | 0.0 | -0.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | -0.7 |
| ∆% AE Jun-Jul | 1.2 | -1.2 | -2.4 | 2.4 | 1.8 | 1.2 | -10.8 |
| May | 0.0 | -0.5 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | -2.9 |
| Apr | 0.0 | -0.3 | -0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | -1.9 |
| ∆% AE Apr- May | 0.0 | -4.7 | -0.6 | 2.4 | 1.2 | 0.0 | -25.3 |
| Mar | 0.2 | 0.3 | -0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 1.3 |
| Feb | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 2.3 |
| Jan | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| ∆% AE Jan- Mar | 2.4 | 3.7 | -0.4 | 2.4 | 2.4 | 1.6 | 15.8 |
| 2011 | |||||||
| Dec | 0.1 | -0.1 | -0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | -1.2 |
| Nov | 0.1 | -0.1 | -0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | -0.1 | 0.0 |
| Oct | 0.0 | -0.2 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | -1.6 |
| ∆% AE Oct- Dec | 0.8 | -1.6 | -1.6 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 1.2 | -10.7 |
| Sep | 0.2 | 0.2 | -0.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 1.3 |
| Aug | 0.2 | 0.3 | -0.2 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 0.1 |
| Jul | 0.2 | 0.2 | -0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.1 |
| ∆% AE Jul-Sep | 2.4 | 2.8 | -2.8 | 2.4 | 2.0 | 6.2 | 6.2 |
| Jun | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | -0.7 |
| May | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 1.4 |
| ∆% AE May-Jun | 2.4 | 3.7 | 1.8 | 1.8 | 2.4 | 4.3 | 4.2 |
| Apr | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 1.8 |
| Mar | 0.4 | 0.8 | -0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 3.6 |
| Feb | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 1.7 |
| Jan | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.6 | 0.8 |
| ∆% AE Jan-Apr | 3.7 | 6.8 | 0.9 | 2.1 | 1.5 | 7.8 | 26.4 |
| 2010 | |||||||
| Dec | 0.2 | 0.6 | -0.3 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | 4.1 |
| Nov | 0.2 | 0.2 | -0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.2 | 1.1 |
| Oct | 0.2 | 0.4 | -0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 3.1 |
| Sep | 0.1 | 0.2 | -0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.6 |
| Aug | 0.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 1.0 |
| Jul | 0.1 | 0.1 | -0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 1.2 |
| Jun | 0.1 | -0.1 | -0.4 | 0.1 | 0.1 | -0.1 | -0.5 |
| May | 0.0 | -0.2 | -0.2 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.1 | -1.2 |
| Apr | 0.0 | -0.3 | -0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 | -0.8 |
| Mar | 0.1 | -0.1 | 0.0 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 | -0.5 |
| Feb | 0.0 | -0.2 | -0.3 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | -1.2 |
| Jan | 0.2 | 0.3 | -0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 1.7 |
Notes: percentage changes in price index relative to the same month a year earlier of PCE: personal consumption expenditures; PCEG: PCE goods; PCEG-D: PCE durable goods; PCES: PCE services; PCEX: PCE excluding food and energy; PCEF: PCE food; PCEE: PCE energy goods and services. AE: annual equivalent.
The charts of PCE inflation are also instructive. Chart IV-1 provides the monthly change of headline PCE price index. There is significant volatility in the monthly changes but excluding outliers fluctuations have been in a tight range between 1999 and 2013 around 0.2 percent per month.
Chart IV-1, US, Percentage Change of PCE Price Index from Prior Month, 1999-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
There is much less volatility in the PCE index excluding food and energy shown in Chart IV-2 with monthly percentage changes from 1999 to 2013. With the exception of 2001, there are no negative changes and again changes around 0.2 percent when excluding outliers.
Chart IV-2, US, Percentage Change of PCE Price Index Excluding Food and Energy from Prior Month, 1999-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Fluctuations in the PCE index of food are much wider as shown in Chart IV-3 by monthly percentage changes from 1999 to 2013. There are also multiple negative changes and positive changes even exceeding 1.0 percent in three months.
Chart IV-3, US, Percentage Change of PCE Price Index Food from Prior Month, 1999-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The band of fluctuation of the PCE price index of energy in Chart IV-4 is much wider. An interesting feature is the abundance of negative changes and large percentages.
Chart IV-4, US, Percentage Change of PCE Price Index Energy from Prior Month, 1999-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table IV-6 provides 12-month rates of PCE inflation from Jan 2012 to Jun 2013, annual inflation rates from 2000 to 2012 and average yearly rates of PCE inflation for various periods since 1929. Headline 12-month PCE inflation decreased from 2.5 percent in in the 12 months ending in Jan 2012 to 1.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2013. PCE inflation excluding food and energy (PCEX), used as indicator in monetary policy, decreased from 2.0 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2012 to 1.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2013, which is still below or at the tolerable maximum of 2.0-2.5 percent in monetary policy. The unintended effect of shocks of commodity prices from zero interest rates captured by PCE food prices (PCEF) and energy (PCEE) in the absence of risk aversion should be weighed in design and implementation of monetary policy. Annual PCE inflation in the second part of Table IV-6 shows significant fluctuations. Headline PCE inflation rose during the period of 1 percent interest rates from Jun 2003 to Jun 2005, reaching 2.9 percent in 2005. PCEE rose at very high two-digit rates after 2003. Headline PCE inflation increased 3.3 percent in 2008 while PCEE energy increased 14.3 percent in carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity derivatives during deep global recession. Flight away from risk financial assets to US government obligations fueled by proposals of TARP in Congress (Cochrane and Zingales 2009) caused decline of PCEE of 19.0 percent in 2009 and minus 0.1 percent in headline PCEE. There is no deflation in the US economy. Headline PCEE inflation increased at the average rate of 2.9 percent from 1929 to 2012, as shown in Table IV-6 using the revisions by the BEA. PCEE inflation was 6.8 percent on average during the Great Inflation episode from 1960 to 1981. PCE inflation was 3.2 percent on average from 1947 to 2012 and 3.2 percent on average for PCEX. The long-term charts of PCEE and PCEX show almost identical behavior.
Table IV-6, US, Percentage Change in 12 Months of Prices of Personal Consumption Expenditures ∆%
| PCE | PCEG | PCEG | PCES | PCEX | PCEF | PCEE | |
| 2013 | |||||||
| Jun | 1.3 | 0.0 | -1.8 | 2.0 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 3.2 |
| May | 1.1 | -0.7 | -1.9 | 2.0 | 1.2 | 1.0 | -1.0 |
| Apr | 0.9 | -1.1 | -1.8 | 2.0 | 1.2 | 1.2 | -4.1 |
| Mar | 1.2 | -0.5 | -1.7 | 2.1 | 1.4 | 1.1 | -1.6 |
| Feb | 1.5 | 0.4 | -1.7 | 2.1 | 1.5 | 1.2 | 2.4 |
| Jan | 1.4 | 0.0 | -1.6 | 2.1 | 1.5 | 1.1 | -0.8 |
| 2012 | |||||||
| Dec | 1.5 | 0.4 | -1.6 | 2.1 | 1.6 | 1.3 | 1.1 |
| Nov | 1.6 | 0.5 | -1.5 | 2.1 | 1.7 | 1.3 | 0.8 |
| Oct | 1.8 | 1.3 | -1.6 | 2.1 | 1.8 | 1.0 | 4.4 |
| Sep | 1.7 | 1.0 | -1.5 | 2.0 | 1.7 | 0.9 | 2.7 |
| Aug | 1.6 | 0.6 | -1.7 | 2.1 | 1.7 | 1.5 | -0.2 |
| Jul | 1.5 | 0.2 | -1.6 | 2.2 | 1.9 | 2.0 | -4.6 |
| Jun | 1.6 | 0.5 | -1.4 | 2.2 | 1.9 | 2.4 | -3.3 |
| May | 1.6 | 0.7 | -1.1 | 2.1 | 1.9 | 2.4 | -3.3 |
| Apr | 2.0 | 1.6 | -1.2 | 2.1 | 1.9 | 2.9 | 1.5 |
| Mar | 2.3 | 2.5 | -0.6 | 2.0 | 2.0 | 3.3 | 4.9 |
| Feb | 2.4 | 2.9 | -0.6 | 2.2 | 2.0 | 3.9 | 7.3 |
| Jan | 2.5 | 3.0 | -0.4 | 2.2 | 2.0 | 4.7 | 6.8 |
| Annual ∆% | |||||||
| 2012 | 1.8 | 1.3 | -1.2 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 2.3 | 1.4 |
| 2011 | 2.4 | 3.6 | -1.0 | 1.8 | 1.4 | 4.0 | 15.8 |
| 2010 | 1.7 | 1.6 | -1.4 | 1.7 | 1.3 | 0.3 | 10.1 |
| 2009 | -0.1 | -2.3 | -1.7 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 1.2 | -19.0 |
| 2008 | 3.1 | 3.0 | -1.9 | 3.1 | 2.1 | 5.6 | 14.3 |
| 2007 | 2.5 | 1.1 | -2.0 | 3.2 | 2.2 | 3.9 | 6.0 |
| 2006 | 2.7 | 1.4 | -1.6 | 3.4 | 2.2 | 3.1 | 11.3 |
| 2005 | 2.9 | 2.0 | -1.0 | 3.3 | 2.2 | 1.7 | 17.3 |
| 2004 | 2.4 | 1.4 | -1.9 | 3.0 | 1.9 | 3.1 | 11.3 |
| 2003 | 2.0 | -0.1 | -3.6 | 3.1 | 1.5 | 1.9 | 12.6 |
| 2002 | 1.3 | -0.9 | -2.5 | 2.6 | 1.7 | 1.5 | -5.8 |
| 2001 | 1.9 | -0.1 | -2.0 | 3.1 | 1.8 | 2.9 | 2.5 |
| 2000 | 2.5 | 2.0 | -1.8 | 2.8 | 1.7 | 2.3 | 18.3 |
| Average ∆% | |||||||
| 2000-2012 | 2.0 | 1.0 | -19.8* | 2.6 | 1.8 | 2.5 | 6.0 |
| 1929-2012 | 2.9 | 3.4 | 1.4 | 3.3 | 2.9 | 2.9 | 3.4 |
| 1947-2012 | 3.2 | 2.4 | 1.2 | 3.9 | 3.2 | 3.1 | 4.3 |
| 1960-1981 | 6.8 | 6.4 | 4.9 | 7.2 | 6.3 | 7.3 | 11.1 |
*Percentage change from 2000 to 2012.
Notes: percentage changes in price index relative to the same month a year earlier of PCE: personal consumption expenditures; PCEG: PCE goods; PCEG-D: PCE durable goods; PCES: PCE services; PCEX: PCE excluding food and energy; PCEF: PCE food; PCEE: PCE energy goods and services
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The headline PCE index is shown in Chart IV-5 from 1999 to 2013. There is an evident upward trend with the carry-trade bump in 2008-2009 during the global recession.
Chart IV-5, US, Price Index of Personal Consumption Expenditures 1999-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The consumer price index in Chart IV-6 mirrors the behavior of the PCE price index in Chart IV-5. There is the same upward trend with the carry-trade bump in 2008 during the global recession.
Chart IV-6, US, Consumer Price Index, NSA, 1999-2013
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm
Chart IV-6 provides the PCE price index excluding food and energy. There is milder upward trend with fewer oscillations.
Chart IV-7, US, Price Index of Personal Consumption Expenditures Excluding Food and Energy 1999-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The core consumer price index, excluding food and energy, is shown in Chart IV-8. There is also an upward trend but with fluctuations.
Chart IV-8, US, Consumer Price Index Excluding Food and Energy, NSA, 1999-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm
The PCE price index of food is shown in Chart IV-9. There is a more pronounced upward trend and sharper fluctuations.
Chart IV-9, US, Price Index of Personal Consumption Expenditures Food 1999-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
There is similar behavior in the consumer price index of food in Chart IV-10. There is an upward trend from 1999 to 2011 with a major bump in 2009 when commodity futures positions were unwound. Zero interest rates with bouts of risk aversion dominate the trend into 2011. Risk aversion softens the trend toward the end of 2011 and in 2012-2013.
Chart IV-10, US, Consumer Price Index, Food, NSA, 1999-2013
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The most pronounced trend of PCE price indexes is that of energy in Chart IV-11. It is impossible to explain the hump in 2008 in the middle of the global recession without the carry trade from zero interest rates to leveraged positions in commodity futures. Risk aversion after Sep 2008 caused flight to the safe haven of government obligations. The return of risk appetite with zero interest rates caused a first wave of carry trades with another upward trend interrupted by the first European sovereign risk crisis in Apr-Jul 2010. Zero interest rates with risk appetite caused another sharp upward trend of commodity prices interrupted by risk aversion from the second sovereign crisis. In the absence of risk aversion, carry trades from zero interest rates to positions in risk financial assets will continue to cause distortions such as commodity price trends and fluctuations.
Chart IV-11, US, Price Index of Personal Consumption Expenditures Energy Goods and Services 1999-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IV-12 provides the consumer price index of energy commodities. Unconventional monetary policy of zero or near zero interest rates causes upward trends in commodity prices reflected in (1) increase from 2003 to 2007; (2) sharp increase during the global contraction in 2008; (3) collapse from 2008 into 2009 as positions in commodity futures were unwound in a flight to government obligations; (4) new upward trend after 2010; and (5) episodes of decline during risk aversion shocks such as the more recent segment during the worsening European debt crisis in Nov and Dec of 2011 and with new strength of commodity prices in the beginning of 2012 followed by softness in another episode of risk aversion and increases during risk appetite.
Chart IV-12, US, Consumer Price Index, Energy, NSA, 1999-2013
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm
Chart IV-13 of the US Energy Information Administration provides prices of the crude oil futures contract. Unconventional monetary policy of very low interest rates and quantitative easing with suspension of the 30-year bond to lower mortgage rates caused a sharp upward trend of oil prices. There is no explanation for the jump of oil prices to $149/barrel in 2008 during a sharp global recession other than carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures. Prices collapsed in the flight to government obligations. Risk appetite with zero interest rates resulted in another upward trend of commodity prices after 2009 with fluctuations during periods of risk aversion. All price indexes are affected by unconventional monetary policy.
Chart IV-13, US, Crude Oil Futures Contract
Source: US Energy Information Administration
http://www.eia.gov/dnav/pet/hist/LeafHandler.ashx?n=PET&s=RCLC1&f=D
Table IV-14 provides the annual PCE price index from the revised and enhanced dataset of the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA). The annual PCEE index increased at the average rate of 3.2 percent from 1929 to 2012. There is no support for fear of deflation.
Chart IV-14, US, Price Index of Personal Consumption Expenditures, Annual, 1929-2012
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IV-15 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) provides the consumer price index from 1914 to 2012. There is long-term inflation and no evidence in support of fear of deflation.
Chart IV-15, US, Consumer Price Index, Annual, 1914-2012
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IV-16 provides the BEA annual index of PCE prices excluding food and energy. The average rate of increase from 1929 to 2012 is 3.2 percent.
Chart IV-16, US, Price Index of Personal Consumption Expenditures Excluding Food and Energy, Annual, 1929-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IV-17 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) provides the annual consumer price index excluding food and energy from 1957 to 2012. There is long-term, fluctuating inflation.
Chart IV-17, US, Consumer Price Index Excluding Food and Energy, Annual, 1957-2012
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
There are waves of inflation of producer prices in France as everywhere in the world economy (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html), as shown in Table IV-7. There was a first wave of sharply increasing inflation in the first four months of 2011 originating in the surge of commodity prices driven by carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures risk positions. Producer price inflation in the first four months of 2011 was at the annual equivalent rate of 10.4 percent. In the second wave, producer prices fell 0.2 percent in May and another 0.1 percent in Jun for annual equivalent inflation in May-Jun 2011 of minus 1.8 percent. In the third wave from Jul to Sep 2011, annual equivalent producer price inflation was 3.7 percent. In the fourth wave Oct-Dec 2011, annual equivalent producer price inflation was 2.8 percent. In the fifth wave Jan-Mar 2012, average annual inflation rose to 6.2 percent during carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures. In the sixth wave in Apr-Jun 2012, annual equivalent inflation fell at the rate of 5.1 percent during unwinding of carry trades because of increasing risk aversion. In the seventh wave, carry trades returned under more relaxed risk aversion with producer price inflation in France at 8.7 percent in annual equivalent in Jul-Oct 2012. In the eighth wave, return of risk aversion caused unwinding carry trade and annual equivalent inflation of minus 4.1 percent in Nov-Dec 2012. In the ninth wave, inflation returned with annual equivalent 3.7 percent in Jan-Mar 2013. In the tenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 10.3 percent in Apr-Jun 2013. The bottom part of Table IV-7 shows producer price inflation at 3.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2005 and again at 4.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2007. Producer prices fell in 2009 during the global contraction and decline of commodity prices but returned at 4.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2010.
Table IV-7, France, Producer Price Index for the French Market, ∆%
| Month | 12 Months | |
| Jun 2013 | -0.2 | 0.2 |
| May | -1.2 | -0.2 |
| Apr | -1.3 | 0.2 |
| AE ∆% Apr-Jun | -10.3 | |
| Mar | 0.0 | 1.6 |
| Feb | 0.5 | 2.0 |
| Jan | 0.4 | 2.1 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Mar | 3.7 | |
| Dec 2012 | -0.5 | 2.2 |
| Nov | -0.2 | 2.4 |
| AE ∆% Nov-Dec | -4.1 | |
| Oct | 0.5 | 3.0 |
| Sep | 0.3 | 3.0 |
| Aug | 1.4 | 3.0 |
| Jul | 0.6 | 1.6 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Oct | 8.7 | |
| Jun | -0.6 | 1.6 |
| May | -0.8 | 2.1 |
| Apr | 0.1 | 2.8 |
| AE ∆% Apr-Jun | -5.1 | |
| Mar | 0.5 | 3.6 |
| Feb | 0.5 | 4.0 |
| Jan | 0.5 | 4.2 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Mar | 6.2 | |
| Dec 2011 | -0.2 | 4.5 |
| Nov | 0.4 | 5.2 |
| Oct | 0.5 | 5.3 |
| AE ∆% Oct-Dec | 2.8 | |
| Sep | 0.3 | 5.4 |
| Aug | 0.0 | 5.6 |
| Jul | 0.6 | 5.7 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Sep | 3.7 | |
| Jun | -0.1 | 5.4 |
| May | -0.2 | 5.7 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun | -1.8 | |
| Apr | 1.0 | 6.0 |
| Mar | 0.8 | 5.7 |
| Feb | 0.7 | 5.2 |
| Jan | 0.8 | 4.6 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr | 10.4 | |
| Dec 2010 | 4.3 | |
| Dec 2009 | -2.9 | |
| Dec 2008 | 0.8 | |
| Dec 2007 | 4.6 | |
| Dec 2006 | 2.6 | |
| Dec 2005 | 3.2 |
Source: Institut National de la Statistique et des Études Économiques
http://www.insee.fr/en/themes/info-rapide.asp?id=25&date=20130731
Chart IV-18 of the Institut National de la Statistique et des Études Économiques of France provides the producer price index for the internal market in France from Jan 1999 to Jun 2013. The index also captures the low price environment of the early 2000s that was used as an argument of fear of deflation. For fear of deflation, see Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), 18-28, and Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 83-95. During the first round of unconventional monetary policy of low interest rates and withdrawal of duration in bond markets by suspension of auctions of the 30-year Treasury bond, inflation accelerated from 2004 to 2007. When policy interest rates were moved toward zero in 2008, carry trades during a global recession caused sharp increases in commodity prices and price indexes worldwide. Inflation collapsed in the risk panic from the latter part of 2008 into the first part of 2009. Carry trades induced by zero interest rates have caused a trend of inflation with oscillations during period of risk aversion (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html).
Chart IV-18, France, Producer Prices for the Internal Market, Jan 1999-May 2013, 2010=100
Source: Institut National de la Statistique et des Études Économiques
http://www.insee.fr/en/themes/info-rapide.asp?id=25&date=20130731
France’s producer price index for the domestic market is shown in Table IV-8 for Jun 2013. The segment of prices of coke and refined petroleum decreased 0.3 percent in Jun 2013 and decreased 0.2 percent in 12 months. Manufacturing prices, with the highest weight in the index, increased 0.2 percent in Jun and increased 0.7 percent in 12 months. Mining prices decreased 1.7 percent in Jun and decreased 1.8 percent in 12 months. Waves of inflation originating in carry trades from unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html) tend to deteriorate sales prices of productive activities relative to prices of inputs and commodities with adverse impact on operational margins and thus on production, investment and hiring.
Table IV-8, France, Producer Price Index for the Domestic Market, %
| Jun 2013 | Weight | Month ∆% | 12 Months ∆% |
| Total | 1000 | -0.3 | -0.1 |
| Mining | 226 | -1.7 | -1.8 |
| Mfg | 774 | 0.2 | 0.7 |
| Food Products, Beverages, Tobacco | 196 | 0.3 | 3.4 |
| Coke and Refined Petroleum | 49 | -0.3 | -0.2 |
| Electrical, Electronic | 53 | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| Transport | 80 | 0.5 | -0.2 |
| Other Mfg | 396 | 0.1 | -0.5 |
Source: Institut National de la Statistique et des Études Économiques http://www.insee.fr/en/themes/info-rapide.asp?id=25&date=20130731
Chart IV-21 of the Institut National de la Statistique et des Études Économiques of France provides the behavior of the producer price index of France for the various segments: import prices, foreign markets, domestic market and all markets. All the components rose to the peak in 2008 driven by carry trades from zero interest rates of unconventional monetary policy that was of such an impulse as to drive increases in commodity prices during the global recession. Prices collapsed with the flight out of financial risk assets such as commodity positions to government obligations. Commodity price increases returned with zero interest rates and subdued risk aversion. The shock of confidence of the current European sovereign risk moderated exposures to financial risk that influenced the flatter curve of France’s producer prices followed by another mild trend of increase and moderation in Dec 2011 and then renewed inflation in the first quarter of 2012 with a new pause in Apr 2012, decline in May-Jun 2012, the jump in Jul-Oct 2012 and the decline in Nov-Dec 2012 followed by increase in Jan-Feb 2013. Prices stabilized in Mar 2013 and collapsed in Apr-Jun 2013.
Chart IV-19, France, Producer Price Index (PPI)
Source: Institut National de la Statistique et des Études Économiques http://www.insee.fr/en/themes/info-rapide.asp?id=25&date=20130731
Italy’s producer price inflation in Table IV-9 also has the same waves in 2011 and into 2012-2013 observed for many countries (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html). The annual equivalent producer price inflation in the first wave Jan-Apr 2011 was 10.7 percent, which was driven by increases in commodity prices resulting from the carry trades from zero interest rates to risk financial assets, in particular leveraged positions in commodities. In the second wave, producer price inflation was 1.8 percent in annual equivalent rate in May-Jun 2011. In the third wave, annual equivalent inflation was 4.9 percent in Jul-Sep 2011. With the return of risk aversion in the fourth wave coinciding with the worsening sovereign debt crisis in Europe, annual equivalent inflation was 2.0 percent in Oct-Dec 2011. Inflation accelerated in the fifth wave in Jan and Feb 2012 to annual equivalent 8.1 percent. In the sixth wave, annual equivalent inflation in Mar-Apr was at 6.8 percent. In the seventh wave, risk aversion originating in world economic slowdown and financial turbulence softened carry trades with annual equivalent inflation falling to minus 0.6 percent in May-Jun 2012. In the eighth wave, more aggressive carry trades into commodity futures exposures resulted in increase of inflation at annual equivalent 9.4 percent in Jul-Aug 2012. In the ninth wave, risk aversion caused unwinding carry trades with annual equivalent inflation of minus 5.2 percent in Sep 2012-Jan 2013. Inflation returned in the tenth wave at 1.2 percent annual equivalent in Feb-Mar 2013. In the eleventh wave, industrial prices fell at annual equivalent 3.5 percent in Apr-May 2013. In the twelfth wave, inflation returned at annual equivalent 4.9 percent in Jun 2013.
Table IV-9, Italy, Industrial Prices, Internal Market
| Month ∆% | 12-Month ∆% | |
| Jun 2013 | 0.4 | -0.7 |
| AE ∆% Jun | 4.9 | |
| May | -0.1 | -1.1 |
| Apr | -0.5 | -1.1 |
| AE ∆% Apr-May | -3.5 | |
| Mar | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Feb | 0.2 | 0.5 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Mar | 1.2 | |
| Jan | -0.6 | 0.7 |
| Dec 2012 | -0.3 | 2.4 |
| Nov | -0.3 | 2.8 |
| Oct | -0.7 | 3.5 |
| Sep | -0.3 | 4.2 |
| AE ∆% Sep-Jan | -5.2 | |
| Aug | 1.1 | 4.5 |
| Jul | 0.4 | 3.8 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Aug | 9.4 | |
| Jun | 0.0 | 4.2 |
| May | -0.1 | 4.4 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun | -0.6 | |
| Apr | 0.6 | 4.6 |
| Mar | 0.5 | 4.8 |
| AE ∆% Mar-Apr | 6.8 | |
| Feb | 0.5 | 5.2 |
| Jan | 0.8 | 5.2 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Feb | 8.1 | |
| Dec 2011 | 0.1 | 5.5 |
| Nov | 0.4 | 6.0 |
| Oct | 0.0 | 6.1 |
| AE ∆% Oct-Dec | 2.0 | |
| Sep | 0.0 | 5.3 |
| Aug | 0.4 | 5.4 |
| Jul | 0.8 | 5.2 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Sep | 4.9 | |
| Jun | 0.2 | 4.6 |
| May | 0.1 | 4.6 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun | 1.8 | |
| Apr | 0.9 | 5.1 |
| Mar | 0.9 | 5.0 |
| Feb | 0.4 | 4.5 |
| Jan | 1.2 | 5.3 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr | 10.7 | |
| Year | ||
| 2012 | 4.2 | |
| 2011 | 5.1 | |
| 2010 | 3.1 | |
| 2009 | -5.4 | |
| 2008 | 5.8 | |
| 2007 | 3.3 | |
| 2006 | 5.3 | |
| 2005 | 4.0 | |
| 2004 | 2.8 | |
| 2003 | 1.6 | |
| 2002 | 0.1 | |
| 2001 | 2.0 |
Source: Istituto Nazionale di Statistica http://www.istat.it/it/archivio/97037
Chart IV-20 of the Istituto Nazionale di Statistica provides 12-month percentage changes of the producer price index of Italy. Rates of change in 12 months stabilized from Jul to Nov 2011 and then fell to 3.5 percent in Jan 2012 with increases of 0.7 percent in the month of Jan 2013 and 0.5 percent in Feb 2013 followed by stability in Mar 2013. Inflation turned negative in Apr-May 2013 with marginal increase in Jun 2013.
Chart IV-20, Italy, Producer Price Index 12-Month Percentage Changes
Source: Istituto Nazionale di Statistica
Monthly and 12-month inflation of the producer price index of Italy and individual components is in Table IV-10. Energy prices increased 1.3 percent in Jun 2013 and fell 3.7 percent in 12 months. Producer-price inflation is low for most components in the month of Jun 2013 with the exception of 0.2 percent for consumer goods and 1.3 percent for energy. There is higher inflation in 12 months of 1.9 percent for nondurable goods than 0.1 percent for durable goods.
Table IV-10, Italy, Industrial Prices, Internal Market, ∆%
| Jun 2013/ | Jun 2013/ | |
| Total | 0.4 | -0.7 |
| Consumer Goods | 0.2 | 1.6 |
| Durable Goods | 0.0 | 0.1 |
| Nondurable | 0.2 | 1.9 |
| Capital Goods | 0.0 | 0.6 |
| Intermediate | -0.3 | -0.4 |
| Energy | 1.3 | -3.7 |
| Total Excluding Energy | 0.0 | 0.5 |
Source: Istituto Nazionale di Statistica http://www.istat.it/it/archivio/97037
The first wave of commodity price increases in the first four months of Jan-Apr 2011 also influenced the surge of consumer price inflation in Italy shown in Table IV-13. Annual equivalent inflation in the first four months of 2011 was 4.9 percent. The crisis of confidence or risk aversion resulted in reversal of carry trades on commodity positions. Consumer price inflation in Italy was subdued in the second wave in Jun and May 2011 at 0.1 percent for annual equivalent 1.2 percent. In the third wave in Jul-Sep 2011, annual equivalent inflation increased to 2.4 percent. In the fourth wave, annual equivalent inflation in Oct-Nov 2011 jumped again at 3.0 percent. Inflation returned in the fifth wave from Dec 2011 to Jan 2012 at annual equivalent 4.3 percent. In the sixth wave, annual equivalent inflation rose to 5.7 percent in Feb-Apr 2012. In the seventh wave, annual equivalent inflation was 1.2 percent in May-Jun 2012. In the eighth wave, annual equivalent inflation increased to 3.0 percent in Jul-Aug 2012. In the ninth wave, inflation collapsed to zero in Sep-Oct 2012 and was minus 0.8 percent in annual equivalent in Sep-Nov 2012. In the tenth wave, annual equivalent inflation in Dec 2012 to Jul 2013 was 1.5 percent. There are worldwide shocks to economies by intermittent waves of inflation originating in combination of zero interest rates and quantitative easing with alternation of risk appetite and risk aversion (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html).
Table IV-11, Italy, Consumer Price Index
| Month | 12 Months | |
| Jul 2013 | 0.0 | 1.1 |
| Jun | 0.3 | 1.2 |
| May | 0.0 | 1.1 |
| Apr | 0.0 | 1.1 |
| Mar | 0.2 | 1.6 |
| Feb | 0.1 | 1.9 |
| Jan | 0.2 | 2.2 |
| Dec 2012 | 0.2 | 2.3 |
| AE ∆% Dec 2012-Jun 2013 | 1.5 | |
| Nov 2012 | -0.2 | 2.5 |
| Oct | 0.0 | 2.6 |
| Sep | 0.0 | 3.2 |
| AE ∆% Sep-Nov | -0.8 | |
| Aug | 0.4 | 3.2 |
| Jul | 0.1 | 3.1 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Aug | 3.0 | |
| June | 0.2 | 3.3 |
| May | 0.0 | 3.2 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun | 1.2 | |
| Apr | 0.5 | 3.3 |
| Mar | 0.5 | 3.3 |
| Feb | 0.4 | 3.3 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Apr | 5.7 | |
| Jan | 0.3 | 3.2 |
| Dec 2011 | 0.4 | 3.3 |
| AE ∆% Dec-Jan | 4.3 | |
| Nov | -0.1 | 3.3 |
| Oct | 0.6 | 3.4 |
| AE ∆% Oct-Nov | 3.0 | |
| Sep | 0.0 | 3.0 |
| Aug | 0.3 | 2.8 |
| Jul | 0.3 | 2.7 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Sep | 2.4 | |
| Jun | 0.1 | 2.7 |
| May | 0.1 | 2.6 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun | 1.2 | |
| Apr | 0.5 | 2.6 |
| Mar | 0.4 | 2.5 |
| Feb | 0.3 | 2.4 |
| Jan | 0.4 | 2.1 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr | 4.9 | |
| Dec 2010 | 0.4 | 1.9 |
| Annual | ||
| 2012 | 3.0 | |
| 2011 | 2.8 | |
| 2010 | 1.5 | |
| 2009 | 0.8 | |
| 2008 | 3.3 | |
| 2007 | 1.8 | |
| 2006 | 2.1 |
Source: Istituto Nazionale di Statistica
http://www.istat.it/it/archivio/97022
Consumer price inflation in Italy by segments in the estimate by ISTAT for Jul 2013 is provided in Table IV-12. Total consumer price inflation in Jul 2013 was 0.0 percent and 1.1 percent in 12 months. Inflation of goods was minus 0.2 percent in Jul 2013 and 1.1 percent in 12 months. Prices of durable goods decreased 0.1 percent in Jul and decreased 0.7 percent in 12 months, as typical in most countries. Prices of energy increased 0.3 percent in Jun and decreased 0.5 percent in 12 months. Food prices increased 0.6 percent in Jul and increased 0.2 percent in 12 months. Prices of services increased 0.4 percent in Jul and rose 1.3 percent in 12 months. Transport prices, also influenced by commodity prices, increased 1.2 percent in Jul and increased 2.8 percent in 12 months. Carry trades from zero interest rates to positions in commodity futures cause increases in commodity prices. Waves of inflation originate in periods when there is no risk aversion and commodity prices decline during periods of risk aversion (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html).
Table IV-12, Italy, Consumer Price Index and Segments, Month and 12-Month ∆%
| Jul 2013 | Weights | Month ∆% | 12-Month ∆% |
| General Index | 1,000,000 | 0.0 | 1.1 |
| I Goods | 559,402 | -0.2 | 1.1 |
| Food | 168,499 | -0.8 | 3.0 |
| Energy | 94,758 | 0.6 | 0.2 |
| Durable | 89,934 | -0.1 | -0.7 |
| Nondurable | 71,031 | 0.1 | 1.4 |
| II Services | 440,598 | 0.4 | 1.3 |
| Housing | 71,158 | 0.1 | 2.0 |
| Communications | 20,227 | -0.2 | -4.1 |
| Transport | 81,266 | 1.2 | 2.8 |
Source: Istituto Nazionale di Statistica http://www.istat.it/it/archivio/97022
Chart IV-21 of the Istituto Nazionale di Statistica shows moderation in 12-month percentage changes of the consumer price index of Italy with marginal increase followed by decline to 2.5 percent in Nov 2012, 2.3 percent in Dec 2012, 2.2 percent in Jan 2013, 1.9 percent in Feb 2013 and 1.6 percent in Mar 2013. Consumer prices increased 1.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Apr-May 2013 and 1.2 percent in Jun 2013. In Jul 2013, consumer prices increased 1.1 percent in 12 months.
Chart, IV-21, Italy, Consumer Price Index, 12-Month Percentage Changes
Source: Istituto Nazionale di Statistica
V World Economic Slowdown. Table V-1 is constructed with the database of the IMF (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2013/01/weodata/index.aspx) to show GDP in dollars in 2012 and the growth rate of real GDP of the world and selected regional countries from 2013 to 2016. The IMF provides an update of the macroeconomic forecast of the world (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2013/update/02/). The data illustrate the concept often repeated of “two-speed recovery” of the world economy from the global recession that affected the US economy from IVQ2007 (Dec) to IIQ2009 (Jun) (http://www.nber.org/cycles.html). A new fact is slowing growth in emerging and developing economies. The IMF has lowered its forecast of the world economy to 3.1 percent in 2013 but accelerating to 3.8 percent in 2014 with the unmodified earlier forecasts of 4.4 percent in 2015 and 4.5 percent in 2016. Slow-speed recovery occurs in the “major advanced economies” of the G7 that account for $33,932 billion of world output of $71,707 billion, or 47.3 percent, but are projected to grow at much lower rates than world output, 1.2 percent in 2013 and 2.1 percent in 2014 and 2.1 on average from 2013 to 2016 in contrast with 3.9 percent for the world as a whole. While the world would grow 16.8 percent in the four years from 2013 to 2016, the G7 as a whole would grow 8.6 percent. The difference in dollars of 2012 is rather high: growing by 16.8 percent would add $12.0 trillion of output to the world economy, or roughly, two times the output of the economy of Japan of $5,964 but growing by 8.6 percent would add $6.2 trillion of output to the world, or about the output of Japan in 2012. The “two speed” concept is in reference to the growth of the 150 countries labeled as emerging and developing economies (EMDE) with joint output in 2012 of $27,290 billion, or 38.1 percent of world output. The EMDEs would grow cumulatively 24.5 percent or at the average yearly rate of 5.6 percent, contributing $6.7 trillion from 2013 to 2016 or the equivalent of somewhat less than the GDP of $8,227 billion of China in 2012. The final four countries in Table 1 often referred as BRIC (Brazil, Russia, India, China), are large, rapidly growing emerging economies. Their combined output in 2012 adds to $14,470 billion, or 20.2 percent of world output, which is equivalent to 42.6 percent of the combined output of the major advanced economies of the G7.
The IMF explains the major factors of the change in forecast (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2013/update/02/):
“Global growth is projected to remain subdued at slightly above 3 percent in 2013, the same as in 2012. This is less than forecast in the April 2013 World Economic Outlook (WEO), driven to a large extent by appreciably weaker domestic demand and slower growth in several key emerging market economies, as well as a more protracted recession in the euro area. Downside risks to global growth prospects still dominate: while old risks remain, new risks have emerged, including the possibility of a longer growth slowdown in emerging market economies, especially given risks of lower potential growth, slowing credit, and possibly tighter financial conditions if the anticipated unwinding of monetary policy stimulus in the United States leads to sustained capital flow reversals. Stronger global growth will require additional policy action. Specifically, major advanced economies should maintain a supportive macroeconomic policy mix, combined with credible plans for reaching medium-term debt sustainability and reforms to restore balance sheets and credit channels. Many emerging market and developing economies face a tradeoff between macroeconomic policies to support weak activity and those to contain capital outflows. Macroprudential and structural reforms can help make this tradeoff less stark.”
Table V-1, IMF World Economic Outlook Database Projections of Real GDP Growth
| GDP USD 2012 | Real GDP ∆% | Real GDP ∆% | Real GDP ∆% | Real GDP ∆% | |
| World | 71,707 | 3.1 | 3.8 | 4.4 | 4.5 |
| G7 | 33,932 | 1.2 | 2.1 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Canada | 1,819 | 1.7 | 2.2 | 2.5 | 2.4 |
| France | 2,609 | -0.2 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 1.7 |
| DE | 3,401 | 0.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 |
| Italy | 2,014 | -1.8 | 0.7 | 1.2 | 1.4 |
| Japan | 5,964 | 2.0 | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.2 |
| UK | 2,441 | 0.9 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 1.9 |
| US | 15,685 | 1.7 | 2.7 | 3.6 | 3.4 |
| Euro Area | 12,198 | -0.3 | 1.1 | 1.4 | 1.6 |
| DE | 3,401 | 0.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.3 |
| France | 2,609 | -0.2 | 0.8 | 1.5 | 1.7 |
| Italy | 2,014 | -1.8 | 0.7 | 1.2 | 1.4 |
| POT | 213 | -2.3 | 0.6 | 1.5 | 1.8 |
| Ireland | 210 | 1.1 | 2.2 | 2.7 | 2.7 |
| Greece | 249 | -4.2 | 0.6 | 2.9 | 3.7 |
| Spain | 1,352 | -1.6 | 0.7 | 1.4 | 1.5 |
| EMDE | 27,290 | 5.0 | 5.4 | 6.0 | 6.1 |
| Brazil | 2,396 | 2.5 | 3.2 | 4.1 | 4.2 |
| Russia | 2,022 | 2.5 | 3.3 | 3.7 | 3.6 |
| India | 1,825 | 5.6 | 6.3 | 6.6 | 6.9 |
| China | 8,227 | 7.8 | 7.7 | 8.5 | 8.5 |
Notes; DE: Germany; EMDE: Emerging and Developing Economies (150 countries); POT: Portugal
Source: IMF World Economic Outlook databank http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2013/01/weodata/index.aspx http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2013/update/02/
Continuing high rates of unemployment in advanced economies constitute another characteristic of the database of the WEO (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2013/01/weodata/index.aspx). Table I-2 is constructed with the WEO database to provide rates of unemployment from 2012 to 2016 for major countries and regions. In fact, unemployment rates for 2012 in Table I-2 are high for all countries: unusually high for countries with high rates most of the time and unusually high for countries with low rates most of the time. The rates of unemployment are particularly high for the countries with sovereign debt difficulties in Europe: 15.7 percent for Portugal (POT), 14.7 percent for Ireland, 24.2 percent for Greece, 25.0 percent for Spain and 10.6 percent for Italy, which is lower but still high. The G7 rate of unemployment is 7.4 percent. Unemployment rates are not likely to decrease substantially if slow growth persists in advanced economies.
Table V-2, IMF World Economic Outlook Database Projections of Unemployment Rate as Percent of Labor Force
| % Labor Force 2012 | % Labor Force 2013 | % Labor Force 2014 | % Labor Force 2015 | % Labor Force 2016 | |
| World | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| G7 | 7.4 | 7.4 | 7.3 | 7.0 | 6.6 |
| Canada | 7.3 | 7.3 | 7.2 | 7.1 | 7.0 |
| France | 10.2 | 11.2 | 11.6 | 11.4 | 10.9 |
| DE | 5.5 | 5.6 | 5.7 | 5.6 | 5.6 |
| Italy | 10.6 | 12.0 | 12.4 | 12.0 | 11.2 |
| Japan | 4.4 | 4.1 | 4.1 | 4.1 | 4.1 |
| UK | 8.0 | 7.8 | 7.8 | 7.4 | 6.9 |
| US | 8.1 | 7.7 | 7.5 | 6.9 | 6.3 |
| Euro Area | 11.4 | 12.3 | 12.3 | 11.9 | 11.4 |
| DE | 5.5 | 5.6 | 5.7 | 5.6 | 5.6 |
| France | 10.2 | 11.2 | 11.6 | 11.4 | 10.9 |
| Italy | 10.6 | 12.0 | 12.4 | 12.0 | 11.2 |
| POT | 15.7 | 18.3 | 18.5 | 18.1 | 17.5 |
| Ireland | 14.7 | 14.2 | 13.8 | 12.9 | 11.9 |
| Greece | 24.2 | 27.0 | 26.1 | 24.0 | 21.0 |
| Spain | 25.0 | 27.0 | 26.5 | 25.6 | 24.7 |
| EMDE | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Brazil | 5.5 | 6.0 | 6.5 | 6.5 | 6.5 |
| Russia | 6.0 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 | 5.5 |
| India | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| China | 4.1 | 4.1 | 4.1 | 4.1 | 4.1 |
Notes; DE: Germany; EMDE: Emerging and Developing Economies (150 countries)
Source: IMF World Economic Outlook databank http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2013/01/weodata/index.aspx
Table V-3 provides the latest available estimates of GDP for the regions and countries followed in this blog from IQ2012 to IQ2013 available now for all countries. Growth is weak throughout most of the world. Japan’s GDP increased 1.2 percent in IQ2012 and 3.4 percent relative to a year earlier but part of the jump could be the low level a year earlier because of the Tōhoku or Great East Earthquake and Tsunami of Mar 11, 2011. Japan is experiencing difficulties with the overvalued yen because of worldwide capital flight originating in zero interest rates with risk aversion in an environment of softer growth of world trade. Japan’s GDP fell 0.2 percent in IIQ2012 at the seasonally adjusted annual rate (SAAR) of minus 0.6 percent, which is much lower than 4.8 percent in IQ2012. Growth of 3.9 percent in IIQ2012 in Japan relative to IIQ2011 has effects of the low level of output because of Tōhoku or Great East Earthquake and Tsunami of Mar 11, 2011. Japan’s GDP contracted 0.9 percent in IIIQ2012 at the SAAR of minus 3.6 percent and increased 0.2 percent relative to a year earlier. Japan’s GDP grew 0.3 percent in IVQ2012 at the SAAR of 1.2 percent and increased 0.4 percent relative to a year earlier. Japan grew 1.0 percent in IQ2013 at the SAAR of 4.1 percent and 0.4 percent relative to a year earlier. China grew at 2.1 percent in IIQ2012, which annualizes to 8.7 percent and 7.6 percent relative to a year earlier. China grew at 2.0 percent in IIIQ2012, which annualizes at 8.2 percent and 7.4 percent relative to a year earlier. In IVQ2012, China grew at 1.9 percent, which annualizes at 7.8 percent, and 7.9 percent in IVQ2012 relative to IVQ2011. In IQ2013, China grew at 1.6 percent, which annualizes at 6.6 percent and 7.7 percent relative to a year earlier. In IIQ2013, China grew at 1.7 percent, which annualizes at 7.0 percent and 7.5 percent relative to a year earlier. There is decennial change in leadership in China (http://www.xinhuanet.com/english/special/18cpcnc/index.htm). Growth rates of GDP of China in a quarter relative to the same quarter a year earlier have been declining from 2011 to 2013. GDP fell 0.1 percent in the euro area in IQ2012 and decreased 0.1 in IQ2012 relative to a year earlier. Euro area GDP contracted 0.2 percent IIQ2012 and fell 0.5 percent relative to a year earlier. In IIIQ2012, euro area GDP fell 0.1 percent and declined 0.7 percent relative to a year earlier. In IVQ2012, euro area GDP fell 0.6 percent relative to the prior quarter and fell 0.9 percent relative to a year earlier. In IQ2013, the GDP of the euro area fell 0.3 percent and decreased 1.1 percent relative to a year earlier. Germany’s GDP increased 0.6 percent in IQ2012 and 1.8 percent relative to a year earlier. In IIQ2012, Germany’s GDP increased 0.2 percent and 0.5 percent relative to a year earlier but 1.0 percent relative to a year earlier when adjusted for calendar (CA) effects. In IIIQ2012, Germany’s GDP increased 0.2 percent and 0.4 percent relative to a year earlier. Germany’s GDP contracted 0.7 percent in IVQ2012 and increased 0.0 percent relative to a year earlier. In IQ2013, Germany’s GDP increased 0.1 percent and fell 1.4 percent relative to a year earlier. Growth of US GDP in IQ2012 was 0.9 percent, at SAAR of 3.7 percent and higher by 3.3 percent relative to IQ2011. US GDP increased 0.3 percent in IIQ2012, 1.2 percent at SAAR and 2.8 percent relative to a year earlier. In IIIQ2012, GDP grew 0.7 percent, 2.8 percent at SAAR and 3.1 percent relative to IIIQ2011. In IVQ2012, GDP grew 0.0 percent, 0.1 percent at SAAR and 2.0 percent relative to IVQ2011. In IQ2013, US GDP grew at 1.1 percent SAAR, 0.3 percent relative to the prior quarter and 1.3 percent relative to the same quarter in 2013. In IIQ2013, US GDP grew at 1.7 percent in SAAR, 0.4 percent relative to the prior quarter and 1.4 percent relative to IIQ2012 (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html) with weak hiring (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/recovery-without-hiring-tapering.htm and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/recovery-without-hiring-seven-million.html). In IQ2012, UK GDP changed 0.0 percent, increasing 0.6 percent relative to a year earlier. UK GDP fell 0.5 percent in IIQ2012 and changed 0.0 percent relative to a year earlier. UK GDP increased 0.7 percent in IIIQ2012 and increased 0.1 percent relative to a year earlier. UK GDP fell 0.2 percent in IVQ2012 relative to IIIQ2012 and changed 0.0 percent relative to a year earlier. UK GDP increased 0.3 percent in IQ2013 and 0.3 percent relative to a year earlier. UK GDP increased 0.6 percent in IIQ2013 and 1.4 percent relative to a year earlier. Italy has experienced decline of GDP in seven consecutive quarters from IIIQ2011 to IQ2013. Italy’s GDP fell 1.0 percent in IQ2012 and declined 1.7 percent relative to IQ2011. Italy’s GDP fell 0.6 percent in IIQ2012 and declined 2.5 percent relative to a year earlier. In IIIQ2012, Italy’s GDP fell 0.3 percent and declined 2.6 percent relative to a year earlier. The GDP of Italy contracted 0.9 percent in IVQ2012 and fell 2.8 percent relative to a year earlier. In IQ2013, Italy’s GDP contracted 0.6 percent and fell 2.3 percent relative to a year earlier. France’s GDP changed 0.0 percent in IQ2012 and increased 0.3 percent relative to a year earlier. France’s GDP decreased 0.2 percent in IIQ2012 and increased 0.1 percent relative to a year earlier. In IIIQ2012, France’s GDP increased 0.1 percent and increased 0.0 percent relative to a year earlier. France’s GDP fell 0.2 percent in IVQ2012 and declined 0.3 percent relative to a year earlier. In IQ2013, France GDP fell 0.2 percent and declined 0.4 percent relative to a year earlier.
Table V-3, Percentage Changes of GDP Quarter on Prior Quarter and on Same Quarter Year Earlier, ∆%
| IQ2012/IVQ2011 | IQ2012/IQ2011 | |
| United States | QOQ: 0.9 SAAR: 3.7 | 3.3 |
| Japan | QOQ: 1.2 SAAR: 4.8 | 3.4 |
| China | 1.5 | 8.1 |
| Euro Area | -0.1 | -0.1 |
| Germany | 0.6 | 1.8 |
| France | 0.0 | 0.3 |
| Italy | -1.0 | -1.7 |
| United Kingdom | 0.0 | 0.6 |
| IIQ2012/IQ2012 | IIQ2012/IIQ2011 | |
| United States | QOQ: 0.3 SAAR: 1.2 | 2.8 |
| Japan | QOQ: -0.2 | 3.9 |
| China | 2.1 | 7.6 |
| Euro Area | -0.2 | -0.5 |
| Germany | 0.2 | 0.5 1.0 CA |
| France | -0.2 | 0.1 |
| Italy | -0.6 | -2.5 |
| United Kingdom | -0.5 | 0.0 |
| IIIQ2012/ IIQ2012 | IIIQ2012/ IIIQ2011 | |
| United States | QOQ: 0.7 | 3.1 |
| Japan | QOQ: –0.9 | 0.2 |
| China | 2.0 | 7.4 |
| Euro Area | -0.1 | -0.7 |
| Germany | 0.2 | 0.4 |
| France | 0.1 | 0.0 |
| Italy | -0.3 | -2.6 |
| United Kingdom | 0.7 | 0.1 |
| IVQ2012/IIIQ2012 | IVQ2012/IVQ2011 | |
| United States | QOQ: 0.0 | 2.0 |
| Japan | QOQ: 0.3 SAAR: 1.2 | 0.4 |
| China | 1.9 | 7.9 |
| Euro Area | -0.6 | -0.9 |
| Germany | -0.7 | 0.0 |
| France | -0.2 | -0.3 |
| Italy | -0.9 | -2.8 |
| United Kingdom | -0.2 | 0.0 |
| IQ2013/IVQ2012 | IQ2013/IQ2012 | |
| United States | QOQ: 0.3 | 1.3 |
| Japan | QOQ: 1.0 SAAR: 4.1 | 0.4 |
| China | 1.6 | 7.7 |
| Euro Area | -0.3 | -1.1 |
| Germany | 0.1 | -1.4 |
| France | -0.2 | -0.4 |
| Italy | -0.6 | -2.4 |
| UK | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| IIQ2013/IQ2013 | IIQ2013/IIQ2012 | |
| United States | QOQ: 0.4 SAAR: 1.7 | 1.4 |
| China | 1.7 | 7.5 |
| UK | 0.6 | 1.4 |
QOQ: Quarter relative to prior quarter; SAAR: seasonally adjusted annual rate
Source: Country Statistical Agencies http://www.bea.gov/national/index.htm#gdp
There is evidence of deceleration of growth of world trade and even contraction in recent data. Table V-4 provides two types of data: growth of exports and imports in the latest available months and in the past 12 months; and contributions of net trade (exports less imports) to growth of real GDP. Japan provides the most worrisome data (Section VB and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/paring-quantitative-easing-policy-and_4699.html and earlier at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/05/united-states-commercial-banks-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/04/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/03/united-states-commercial-banks-assets.html and earlier at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/02/world-inflation-waves-united-states.html and earlier at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/02/thirty-one-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/12/mediocre-and-decelerating-united-states_24.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/11/contraction-of-united-states-real_25.html and for GDP Section VB and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/02/recovery-without-hiring-united-states.html and earlier at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/12/recovery-without-hiring-forecast-growth.html). In Jun 2013, Japan’s exports grew 7.4 percent in 12 months while imports increased 11.8 percent. The second part of Table V-4 shows that net trade deducted 1.1 percentage points from Japan’s growth of GDP in IIQ2012, deducted 2.8 percentage points from GDP growth in IIIQ2012 and deducted 0.6 percentage points from GDP growth in IVQ2012. In Jun 2013, China exports decreased 3.1 percent relative to a year earlier and imports fell 0.7 percent. Germany’s exports decreased 2.4 percent in the month of May 2013 and decreased 4.8 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2013 while imports increased 1.7 percent in the month of May and decreased 2.6 percent in the 12 months ending in May. Net trade contributed 0.4 percentage points to growth of GDP in IQ2012, contributed 1.3 percentage points in IIQ2012, contributed 1.4 percentage points in IIIQ2012, contributed 0.7 percentage points in IVQ2012 and contributed 1.0 percentage points in 2012. Net trade deducted 0.1 percentage points from Germany’s GDP growth. Net trade deducted 0.7 percentage points from UK value added in IQ2012, deducted 0.7 percentage points in IIQ2012, added 0.4 percentage points in IIIQ2012 and subtracted 0.3 percentage points in IVQ2012. In IQ2013, net trade added 0.6 percentage points to UK’s growth of value added. France’s exports decreased 4.3 percent in May 2013 while imports decreased 0.2 percent and net trade added 0.1 percentage points to GDP growth in IIQ2012, adding 0.1 percentage points in IIIQ2012 and 0.1 percentage points in IVQ2012. Net trade deducted 0.2 percentage points from France’s GDP growth in IQ2013. US exports decreased 1.2 percent in Apr 2013 and goods exports increased 0.8 percent in Jan-Apr 2013 relative to a year earlier but net trade added 0.38 percentage points to GDP growth in IIIQ2012 and added 0.33 percentage points in IVQ2012. In IQ2013, net trade deducted 0.09 percentage points from US GDP growth. US imports increased 2.4 percent in Apr 2013 and goods imports decreased 1.9 percent in Jan-Apr 2013 relative to a year earlier. Industrial production increased 0.3 percent in Jun 2013 after changing 0.0 percent in May 2013 and falling 0.3 percent in Apr 2013, as shown in Table II-1, with all data seasonally adjusted. The report of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System states (http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/g17/Current/default.htm):
“Industrial production increased 0.3 percent in June after having been unchanged in May. For the second quarter as a whole, industrial production moved up at an annual rate of 0.6 percent. In June, manufacturing production rose 0.3 percent following an increase of 0.2 percent in May. The output at mines advanced 0.8 percent in June, while the output of utilities decreased 0.1 percent. At 99.1 percent of its 2007 average, total industrial production was 2.0 percent above its year-earlier level.”
In the six months ending in Jun 2013, United States national industrial production accumulated increase of 0.9 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 1.8 percent, which is lower than growth of 2.0 percent in 12 months. Excluding growth of 0.7 in Feb 2013, growth in the remaining five months from Jan 2012 to Jun 2013 accumulated to 0.2 percent or 0.5 percent annual equivalent. Industrial production stagnated in two of the past six months and fell in one. Business equipment accumulated growth of 0.9 percent in the six months from Dec 2012 to May 2013 at the annual equivalent rate of 1.8 percent, which is much lower than growth of 2.2 percent in 12 months. The Fed analyzes capacity utilization of total industry in its report (http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/g17/Current/default.htm): “The rate of capacity utilization for total industry edged up 0.1 percentage point to 77.8 percent, a rate that was 0.1 percentage point above its level of a year earlier but 2.4 percentage points below its long-run (1972–2012) average.” United States industry is apparently decelerating.
Manufacturing increased 0.3 percent in Jun 2013 after increasing 0.2 percent in May 2013 and decreasing 0.3 percent in Apr 2013 seasonally adjusted, increasing 1.7 percent not seasonally adjusted in 12 months ending in Jun 2013, as shown in Table II-2. Manufacturing grew cumulatively 0.5 percent in the six months ending in Jun 2013 or at the annual equivalent rate of 1.0 percent. Excluding the increase of 0.7 percent in Feb 2012, manufacturing accumulated growth of minus 0.2 percent from Jan 2013 to Jun 2013 or at the annual equivalent rate of minus 0.5 percent. Manufacturing output fell by 21.9 from the peak in Jun 2007 to the trough in Apr 2009 and increased by 16.8 percent from the trough in Apr 2009 to Dec 2012. Manufacturing grew 21.8 percent from the trough in Apr 2009 to Jun 2013. Manufacturing output in Jun 2013 is 4.8 percent below the peak in Jun 2007.Data do suggest that world trade slowdown is accompanying world economic slowdown.
Table V-4, Growth of Trade and Contributions of Net Trade to GDP Growth, ∆% and % Points
| Exports | Exports 12 M ∆% | Imports | Imports 12 M ∆% | |
| USA | -0.3 May | 0.9 Jan-May | 1.9 May | -1.7 Jan-May |
| Japan | Jun 2013 7.4 May 2013 10.1 Apr 2013 3.8 Mar 2013 1.1 Feb 2013 -2.9 Jan 2013 6.4 Dec -5.8 Nov -4.1 Oct -6.5 Sep -10.3 Aug -5.8 Jul -8.1 | Jun 2013 11.8 May 2013 10.0 Apr 2013 9.4 Mar 2013 5.5 Feb 2013 7.3 Jan 2013 7.3 Dec 1.9 Nov 0.8 Oct -1.6 Sep 4.1 Aug -5.4 Jul 2.1 | ||
| China | -3.1 Jun 1.0 May 14.7 Apr 10.0 Mar 21.8 Feb | -0.7 Jun -0.3 May 16.8 Apr 14.1 Mar -15.2 Feb | ||
| Euro Area | -0.1 12-M May | 2.5 Jan-May | -5.7 12-M May | -3.9 Jan-May |
| Germany | -2.4 May CSA | -4.8 May | 1.7 May CSA | -2.6 May |
| France May | -4.3 | -4.4 | -0.2 | -2.2 |
| Italy Apr | 0.0 | 4.4 | -0.9 | -2.6 |
| UK | -1.3 Apr | 0.3 Feb-Apr 13 /Feb-Apr 12 | -2.7 Apr | -0.9 Feb-Apr 13/Feb-Apr 12 |
| Net Trade % Points GDP Growth | % Points | |||
| USA | IQ2013 -0.09 IVQ2012 +0.33 IIIQ2012 +0.38 IIQ2012 +0.23 IQ2012 +0.06 | |||
| Japan | -1.1 IIQ2012 -2.8 IIIQ2012 -0.6 IVQ2012 | |||
| Germany | 0.4 IQ2012 1.3 IIQ2012 1.4 IIIQ2012 0.7 IVQ2012 1.0 2012 IQ2013 -0.1 | |||
| France | 0.1 IIQ2012 0.1 IIIQ2012 0.1 IVQ2012 -0.2 IQ2013 | |||
| UK | -0.7 IQ2012 -0.7 IIQ2012 +0.4 IIIQ2012 -0.3 IVQ2012 0.6 IQ2013 |
Sources: Country Statistical Agencies http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/ http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The geographical breakdown of exports and imports of Japan with selected regions and countries is provided in Table V-5 for Jun 2013. The share of Asia in Japan’s trade is more than one-half for 54.9 percent of exports and 44.3 percent of imports. Within Asia, exports to China are 17.8 percent of total exports and imports from China 21.3 percent of total imports. While exports to China increased 4.8 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2013, imports from China increased 14.3 percent. The largest export market for Japan in Jun 2013 is the US with share of 18.7 percent of total exports, which is almost equal to that of China, and share of imports from the US of 9.4 percent in total imports. Western Europe has share of 9.5 percent in Japan’s exports and of 10.6 percent in imports. Rates of growth of exports of Japan in May 2013 are relatively high for several countries and regions with growth of 14.6 percent for exports to the US, 9.6 for exports to Mexico, 10.4 percent for exports to Brazil and 21.5 percent for exports to Australia. Comparisons relative to 2011 may have some bias because of the effects of the Tōhoku or Great East Earthquake and Tsunami of Mar 11, 2011. Deceleration of growth in China and the US and threat of recession in Europe can reduce world trade and economic activity. Growth rates of imports in the 12 months ending in Jun 2013 are positive for all trading partners. Imports from Asia increased 10.0 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2013 while imports from China increased 14.3 percent. Data are in millions of yen, which may have effects of recent depreciation of the yen relative to the United States dollar (USD).
Table V-5, Japan, Value and 12-Month Percentage Changes of Exports and Imports by Regions and Countries, ∆% and Millions of Yens
| Jun 2013 | Exports | 12 months ∆% | Imports Millions Yen | 12 months ∆% |
| Total | 6,061,431 | 7.4 | 6,242,207 | 11.8 |
| Asia | 3,330,000 | 7.4 | 2,762,718 | 10.0 |
| China | 1,080,621 | 4.8 | 1,327,321 | 14.3 |
| USA | 1,133,856 | 14.6 | 589,179 | 18.8 |
| Canada | 76,204 | 12.1 | 91,279 | 5.6 |
| Brazil | 45,894 | 10.4 | 86,816 | 17.3 |
| Mexico | 81,492 | 9.5 | 34,500 | 23.5 |
| Western Europe | 575,348 | 8.4 | 664,680 | 16.1 |
| Germany | 164,936 | 17.3 | 167,493 | 15.1 |
| France | 45,672 | 7.2 | 107,293 | 15.2 |
| UK | 85,134 | 9.2 | 53,281 | 22.5 |
| Middle East | 209,370 | 12.2 | 1,115,449 | 8.0 |
| Australia | 150,485 | 21.5 | 416,161 | 29.2 |
Source: Japan, Ministry of Finance http://www.customs.go.jp/toukei/info/index_e.htm
World trade projections of the IMF are in Table V-6. There is increasing growth of the volume of world trade of goods and services from revised 3.1 percent in 2013 and 5.4 percent in 2014 to 6.1 percent in 2015 and 5.7 percent in 2018. World trade would be slower for advanced economies while emerging and developing economies (EMDE) experience faster growth. World economic slowdown would more challenging with lower growth of world trade.
Table V-6, IMF, Projections of World Trade, ∆%
| 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | Average ∆% 2013-2018 | |
| World Trade Volume (Goods and Services) | 3.1 | 5.4 | 6.1 | 5.7 |
| Oil Price USD/Barrel | 102.60 | 97.58 | NA | NA |
| Commodity Price Index | 181.84 | 174.06 | NA | NA |
| Commodity Industrial Inputs Price | 170.04 | 164.66 | NA | NA |
| Imports Goods & Services | ||||
| G7 | 1.4 | 4.3 | 4.7 | 4.3 |
| EMDE | 6.0 | 7.3 | 7.9 | 7.5 |
| Exports Goods & Services | ||||
| G7 | 2.4 | 4.7 | 4.9 | 4.5 |
| EMDE | 4.3 | 6.3 | 7.6 | 7.1 |
Notes: Commodity Price Index includes Fuel and Non-fuel Prices; Commodity Industrial Inputs Price includes agricultural raw materials and metal prices; Oil price is average of WTI, Brent and Dubai
Source: International Monetary Fund World Economic Outlook databank http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2013/01/weodata/index.aspx http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2013/update/02/
The JP Morgan Global All-Industry Output Index of the JP Morgan Manufacturing and Services PMI™, produced by JP Morgan and Markit in association with ISM and IFPSM, with high association with world GDP, decreased to 51.4 in Jun from 52.9 in May, indicating expansion at a moderate rate (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/6c45a62f0c5a427c8ecdcf4ffffb6688). This index has remained above the contraction territory of 50.0 during 47 consecutive months but the reading in Jun is the slowest in a year. The employment index increased from 50.3 in May to 51.7 in Jun with input prices rising at higher rate and new orders and output increasing at slower rates (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/6c45a62f0c5a427c8ecdcf4ffffb6688). David Hensley, Director of Global Economic Coordination at JP Morgan, finds that the index fell below trend in Jun with services slowing especially in the US (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/6c45a62f0c5a427c8ecdcf4ffffb6688). The JP Morgan Global Manufacturing PMI™, produced by JP Morgan and Markit in association with ISM and IFPSM, was unchanged at 50.6 in Jun from 50.6 in May, which is the sixth consecutive reading above 50 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/3104066a480f4276bbcefe12f0387391). New export business fell sharply in Jun for the US and China while total new orders increased from 51.3 in May to 51.5 in Jun. The HSBC Brazil Composite Output Index, compiled by Markit, decreased marginally from 51.2 in May to 51.1 in Jun, indicating moderate increase in private sector activity (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/d6238894628a42bcb1c8ab6ce970cee0). The HSBC Brazil Services Business Activity index, compiled by Markit, was unchanged from 51.0 in May to 51.0 in Jun (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/d6238894628a42bcb1c8ab6ce970cee0). Andre Loes, Chief Economist, Brazil, at HSBC, finds that the survey data suggest weakness in growth in IIQ2013 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/d6238894628a42bcb1c8ab6ce970cee0). The HSBC Brazil Purchasing Managers’ IndexTM (PMI™) was unchanged from 50.4 in May, which was the weakest reading in seven months, to 50.4 in Jun (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/84c2905cbe394285bcc24f85a426ca6d). Andre Loes, Chief Economist, Brazil at HSBC, finds that companies are facing the fastest rate of growth of input prices since Mar 2011 with the quarterly average of the index of 50.5 at the slowest reading since IIIQ2012 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/84c2905cbe394285bcc24f85a426ca6d).
VA United States. The Markit Flash US Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index™ (PMI™) seasonally adjusted increased to 53.2 in Jul from 51.9 in Jun, for the highest reading in four months (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/60b7d12f272b42cc9ac764e0cd386ab6).New export orders registered 47.5 in Jun down from 49.8 in Apr, indicating contraction at a faster rate while output fell from 56.6 in Mar to 53.6 in Apr. Chris Williams, Chief Economist at Markit, finds that the survey data are consistent with growth at only 2.4 percent annual rhythm in IIQ2013 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/60b7d12f272b42cc9ac764e0cd386ab6). The Markit US Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index™ (PMI™) decreased to 51.9 in Jun from 52.3 in May (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/61c3e275eedf42b5abc0566f4adf015e). The index of new exports orders rose from 46.3 in Jun to 52.3 in Jul while total new orders increased from 53.4 in Jun to 55.1 in Jul. Chris Williamson, Chief Economist at Markit, finds that the improvement in the index in Jul could support GDP growth in IIIQ2013 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/61c3e275eedf42b5abc0566f4adf015e). The purchasing managers’ index (PMI) of the Institute for Supply Management (ISM) Report on Business® increased 1.9 percentage points from 49.0 in May to 50.9 in Jun, which indicates growth in change of direction from contraction (http://www.ism.ws/ISMReport/MfgROB.cfm?navItemNumber=12942). The index of new orders increased 3.1 percentage points from 48.8 in May to 51.9 in Jun. The index of exports increased 3.5 percentage points from 51.0 in May to 54.5 in Jun, advancing in expansion territory. The Non-Manufacturing ISM Report on Business® PMI decreased 1.5 percentage points from 53.7 in May to 52.2 in Jun, indicating growth of business activity/production during 47 consecutive months, while the index of new orders decreased 5.2 percentage points from 56.0 in May to 50.8 in Jun (http://www.ism.ws/ISMReport/NonMfgROB.cfm?navItemNumber=12943). Table USA provides the country economic indicators for the US.
Table USA, US Economic Indicators
| Consumer Price Index | Jun 12 months NSA ∆%: 1.8; ex food and energy ∆%: 1.6 Jun month SA ∆%: 0.5; ex food and energy ∆%: 0.2 |
| Producer Price Index | Jun 12-month NSA ∆%: 2.5; ex food and energy ∆% 1.7 |
| PCE Inflation | Jun 12-month NSA ∆%: headline 1.3; ex food and energy ∆% 1.2 |
| Employment Situation | Household Survey: Jul Unemployment Rate SA 7.4% |
| Nonfarm Hiring | Nonfarm Hiring fell from 63.8 million in 2006 to 52.0 million in 2012 or by 11.8 million |
| GDP Growth | BEA Revised National Income Accounts IIQ2012/IIQ2011 2.8 IIIQ2012/IIIQ2011 3.1 IVQ2012/IVQ2011 2.0 IQ2013/IQ2012 1.3 IIQ2013/IIQ2012 1.4 IQ2012 SAAR 3.7 IIQ2012 SAAR 1.2 IIIQ2012 SAAR 2.8 IVQ2012 SAAR 0.1 IQ2013 SAAR 1.1 IIQ2013 SAAR 1.7 |
| Real Private Fixed Investment | SAAR IIQ2013 6.3 ∆% IVQ2007 to IIQ2013: minus 5.0% Blog 8/4/13 |
| Personal Income and Consumption | Jun month ∆% SA Real Disposable Personal Income (RDPI) SA ∆% minus 0.1 |
| Quarterly Services Report | IQ13/IQ12 SA ∆%: Financial & Insurance 1.8 |
| Employment Cost Index | Compensation Private IQ2013 SA ∆%: 0.3 |
| Industrial Production | Jun month SA ∆%: 0.3 Manufacturing Jun SA ∆% 0.3 Jun 12 months SA ∆% 1.8, NSA 1.7 |
| Productivity and Costs | Nonfarm Business Productivity IQ2013∆% SAAE 0.5; IQ2013/IQ2012 ∆% 0.9; Unit Labor Costs SAAE IQ2013 ∆% -4.3; IQ2013/IQ2012 ∆%: 1.1 Blog 6/9/2013 |
| New York Fed Manufacturing Index | General Business Conditions From Jun 7.84 to Jul 9.46 |
| Philadelphia Fed Business Outlook Index | General Index from Jun 12.5 to Jul 19.8 |
| Manufacturing Shipments and Orders | New Orders SA May ∆% 2.1 Ex Transport 0.6 Jan-May NSA New Orders 0.9 Ex transport 0.4 |
| Durable Goods | Jun New Orders SA ∆%: 4.2; ex transport ∆%: 0.0 |
| Sales of New Motor Vehicles | Jan-Jun 2013 7,829,141; Jan-Jun 2012 7,272,160. Jun 13 SAAR 15.96 million, May 13 SAAR 15.31 million, Jun 2012 SAAR 14.38 million Blog 7/7/13 |
| Sales of Merchant Wholesalers | Jan-May 2013/Jan-May 2012 NSA ∆%: Total 2.4; Durable Goods: 2.6; Nondurable |
| Sales and Inventories of Manufacturers, Retailers and Merchant Wholesalers | May 13/May 12 NSA ∆%: Sales Total Business 3.3; Manufacturers 1.3 |
| Sales for Retail and Food Services | Jan-Jun 2013/Jan-Jun 2012 ∆%: Retail and Food Services 3.7; Retail ∆% 3.7 |
| Value of Construction Put in Place | May SAAR month SA ∆%: 0.5 May 12-month NSA: 5.4 Jan-May 2013 ∆% 6.2 |
| Case-Shiller Home Prices | May 2013/May 2012 ∆% NSA: 10 Cities 11.8; 20 Cities: 12.2 |
| FHFA House Price Index Purchases Only | May SA ∆% 0.7; |
| New House Sales | Jun 2013 month SAAR ∆%: 8.3 |
| Housing Starts and Permits | Jun Starts month SA ∆%: minus 9.9 ; Permits ∆%: minus 7.5 |
| Trade Balance | Balance May SA -$45,027 million versus Apr -$40,149 million |
| Export and Import Prices | Jun 12-month NSA ∆%: Imports 0.2; Exports -0.8 |
| Consumer Credit | May ∆% annual rate: 8.3 |
| Net Foreign Purchases of Long-term Treasury Securities | Apr Net Foreign Purchases of Long-term US Securities: minus $37.3 billion |
| Treasury Budget | Fiscal Year 2013/2012 ∆% Jun: Receipts 14.4; Outlays -4.8; Individual Income Taxes 18.0 Deficit Fiscal Year 2012 $1,087 billion Blog 7/14/2013 |
| CBO Budget and Economic Outlook | 2012 Deficit $1089 B 7.0% GDP Debt 11,280 B 72.5% GDP 2013 Deficit $845 B, Debt 12,229 B 76.3% GDP Blog 8/26/12 11/18/12 2/10/13 |
| Commercial Banks Assets and Liabilities | Jun 2013 SAAR ∆%: Securities -8.2 Loans 2.2 Cash Assets 44.8 Deposits 5.9 Blog 7/28/13 |
| Flow of Funds | IQ2013 ∆ since 2007 Assets +$2612.8 MM Real estate -$2733.8 MM Financial +4799.7 MM Net Worth +$3487.4 MM Blog 6/16/13 |
| Current Account Balance of Payments | IQ2013 -83,219 MM %GDP 2.7 Blog 6/16/13 |
Links to blog comments in Table USA:
7/28/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/duration-dumping-steepening-yield-curve.html
7/21/2013 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html
7/14/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/recovery-without-hiring-tapering.html
7/7/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/twenty-nine-million-unemployed-or.html
6/16/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/recovery-without-hiring-seven-million.html
6/9/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/twenty-eight-million-unemployed-or.html
5/5/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/05/twenty-nine-million-unemployed-or.html
2/10/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/02/united-states-unsustainable-fiscal.html
11/18/12 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/11/united-states-unsustainable-fiscal.html
Table VA-1 shows the euphoria of prices during the housing boom and the subsequent decline. House prices rose 94.1 percent in the 10-city composite of the Case-Shiller home price index and 78.0 percent in the 20-city composite between May 2000 and May 2005. Prices rose around 100 percent from May 2000 to May 2006, increasing 113.2 percent for the 10-city composite and 95.7 percent for the 20-city composite. House prices rose 38.9 percent between May 2003 and May 2005 for the 10-city composite and 33.7 percent for the 20-city composite propelled by low fed funds rates of 1.0 percent between Jun 2003 and Jun 2004. Fed funds rates increased by 0.25 basis points at every meeting of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) until Jun 2006, reaching 5.25 percent. Simultaneously, the suspension of auctions of the 30-year Treasury bond caused decline of yields of mortgage-backed securities with intended decrease in mortgage rates. Similarly, between May 2003 and May 2006, the 10-city index gained 52.5 percent and the 20-city index increased 47.0 percent. House prices have fallen from May 2006 to May 2013 by 24.9 percent for the 10-city composite and 24.2 percent for the 20-city composite. Measuring house prices is quite difficult because of the lack of homogeneity that is typical of standardized commodities. In the 12 months ending in May 2013, house prices increased 11.8 percent in the 10-city composite and increased 12.2 percent in the 20-city composite. Table VA-1 also shows that house prices increased 60.1 percent between May 2000 and May 2013 for the 10-city composite and increased 48.4 percent for the 20-city composite. House prices are close to the lowest level since peaks during the boom before the financial crisis and global recession. The 10-city composite fell 25.0 percent from the peak in Jun 2006 to May 2013 and the 20-city composite fell 24.4 percent from the peak in Jul 2006 to May 2013. The final part of Table VA-1 provides average annual percentage rates of growth of the house price indexes of Standard & Poor’s Case-Shiller. The average annual growth rate between Dec 1987 and Dec 2012 for the 10-city composite was 3.3 percent. Data for the 20-city composite are available only beginning in Jan 2000. House prices accelerated in the 1990s with the average rate of the 10-city composite of 5.0 percent between Dec 1992 and Dec 2000 while the average rate for the period Dec 1987 to Dec 2000 was 3.8 percent. Although the global recession affecting the US between IVQ2007 (Dec) and IIQ2009 (Jun) caused decline of house prices of slightly above 30 percent, the average annual growth rate of the 10-city composite between Dec 2000 and Dec 2012 was 2.8 percent while the rate of the 20-city composite was 2.3 percent.
Table VA-1, US, Percentage Changes of Standard & Poor’s Case-Shiller Home Price Indices, Not Seasonally Adjusted, ∆%
| 10-City Composite | 20-City Composite | |
| ∆% May 2000 to May 2003 | 39.8 | 33.1 |
| ∆% May 2000 to May 2005 | 94.1 | 78.0 |
| ∆% May 2003 to May 2005 | 38.9 | 33.7 |
| ∆% May 2000 to May 2006 | 113.2 | 95.7 |
| ∆% May 2003 to May 2006 | 52.5 | 47.0 |
| ∆% May 2005 to May 2013 | -17.5 | -16.6 |
| ∆% May 2006 to May 2013 | -24.9 | -24.2 |
| ∆% May 2009 to May 2013 | 12.2 | 11.5 |
| ∆% May 2010 to May 2013 | 6.5 | 6.6 |
| ∆% May 2011 to May 2013 | 10.7 | 11.6 |
| ∆% May 2012 to May 2013 | 11.8 | 12.2 |
| ∆% May 2000 to May 2013 | 60.1 | 48.4 |
| ∆% Peak Jun 2006 May 2013 | -25.0 | |
| ∆% Peak Jul 2006 May 2013 | -24.4 | |
| Average ∆% Dec 1987-Dec 2012 | 3.3 | NA |
| Average ∆% Dec 1987-Dec 2000 | 3.8 | NA |
| Average ∆% Dec 1992-Dec 2000 | 5.0 | NA |
| Average ∆% Dec 2000-Dec 2012 | 2.8 | 2.3 |
Source: http://us.spindices.com/index-family/real-estate/sp-case-shiller
Monthly house prices increased sharply from Feb to May 2013 for both the 10- and 20-city composites. In May 2013, the seasonally adjusted 10-city composite increased 1.1 percent and the 20-city 1.0 percent while the 10-city not seasonally adjusted increased 2.5 percent and the 20-city 2.4 percent. With the exception of Feb through Apr 2012, house prices seasonally adjusted declined in every month for both the 10-city and 20-city Case-Shiller composites from Dec 2010 to Jan 2012, as shown in Table VA-2. The most important seasonal factor in house prices is school changes for wealthier homeowners with more expensive houses. Without seasonal adjustment, house prices fell from Dec 2010 throughout Mar 2011 and then increased in every month from Apr to Aug 2011 but fell in every month from Sep 2011 to Feb 2012. The not seasonally adjusted index registers decline in Mar 2012 of 0.1 percent for the 10-city composite and is flat for the 20-city composite. House prices seasonally adjusted increased 0.5 percent in Mar and Apr 2012 for both the 10-city and 20-city indexes. Not seasonally adjusted house prices increased 1.4 percent in Apr 2012. Declining house prices cause multiple adverse effects of which two are quite evident. (1) There is a disincentive to buy houses in continuing price declines. (2) More mortgages could be losing fair market value relative to mortgage debt. Another possibility is a wealth effect that consumers restrain purchases because of the decline of their net worth in houses.
Table VA-2, US, Monthly Percentage Change of S&P Case-Shiller Home Price Indices, Seasonally Adjusted and Not Seasonally Adjusted, ∆%
| 10-City Composite SA | 10-City Composite NSA | 20-City Composite SA | 20-City Composite NSA | |
| May 2013 | 1.1 | 2.5 | 1.0 | 2.4 |
| Apr | 1.8 | 2.6 | 1.7 | 2.6 |
| Mar | 2.0 | 1.4 | 1.9 | 1.4 |
| Feb | 1.3 | 0.3 | 1.2 | 0.3 |
| Jan | 0.9 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.1 |
| Dec 2012 | 0.9 | 0.2 | 0.9 | 0.2 |
| Nov | 0.5 | -0.2 | 0.7 | -0.1 |
| Oct | 0.6 | -0.2 | 0.7 | -0.1 |
| Sep | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.3 |
| Aug | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 0.9 |
| Jul | 0.2 | 1.5 | 0.3 | 1.6 |
| Jun | 0.9 | 2.1 | 1.0 | 2.3 |
| May | 0.9 | 2.2 | 1.0 | 2.4 |
| Apr | 0.5 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 1.4 |
| Mar | 0.5 | -0.1 | 0.5 | 0.0 |
| Feb | 0.0 | -0.9 | 0.1 | -0.8 |
| Jan | -0.2 | -1.1 | -0.1 | -1.0 |
| Dec 2011 | -0.5 | -1.2 | -0.4 | -1.2 |
| Nov | -0.6 | -1.4 | -0.6 | -1.3 |
| Oct | -0.6 | -1.3 | -0.6 | -1.3 |
| Sep | -0.4 | -0.6 | -0.5 | -0.7 |
| Aug | -0.3 | 0.1 | -0.3 | 0.1 |
| Jul | -0.3 | 0.9 | -0.3 | 1.0 |
| Jun | -0.1 | 1.0 | -0.1 | 1.2 |
| May | -0.2 | 1.0 | -0.3 | 1.0 |
| Apr | -0.1 | 0.6 | -0.1 | 0.6 |
| Mar | -0.3 | -1.0 | -0.5 | -1.0 |
| Feb | -0.3 | -1.3 | -0.3 | -1.2 |
| Jan | -0.2 | -1.1 | -0.2 | -1.1 |
| Dec 2010 | -0.2 | -0.9 | -0.2 | -1.0 |
Source:
http://us.spindices.com/index-family/real-estate/sp-case-shiller
VB Japan. Table VB-BOJF provides the forecasts of economic activity and inflation in Japan by the majority of members of the Policy Board of the Bank of Japan, which is part of their Outlook for Economic Activity and Prices (http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2013/k130711a.pdf). For fiscal 2013, the forecast is of growth of GDP between 2.5 and 3.0 percent, with the all items CPI less fresh food of 0.5 to 0.8 percent. The critical difference is forecast of the CPI excluding fresh food of 2.7 to 3.6 percent in 2014 and 1.6 to 2.9 percent in 2015. The new monetary policy of the Bank of Japan aims to increase inflation to 2 percent. These forecasts are biannual in Apr and Oct. The Cabinet Office, Ministry of Finance and Bank of Japan released on Jan 22, 2013, a “Joint Statement of the Government and the Bank of Japan on Overcoming Deflation and Achieving Sustainable Economic Growth” (http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2013/k130122c.pdf) with the important change of increasing the inflation target of monetary policy from 1 percent to 2 percent:
“The Bank of Japan conducts monetary policy based on the principle that the policy shall be aimed at achieving price stability, thereby contributing to the sound development of the national economy, and is responsible for maintaining financial system stability. The Bank aims to achieve price stability on a sustainable basis, given that there are various factors that affect prices in the short run.
The Bank recognizes that the inflation rate consistent with price stability on a sustainable basis will rise as efforts by a wide range of entities toward strengthening competitiveness and growth potential of Japan's economy make progress. Based on this recognition, the Bank sets the price stability target at 2 percent in terms of the year-on-year rate of change in the consumer price index.
Under the price stability target specified above, the Bank will pursue monetary easing and aim to achieve this target at the earliest possible time. Taking into consideration that it will take considerable time before the effects of monetary policy permeate the economy, the Bank will ascertain whether there is any significant risk to the sustainability of economic growth, including from the accumulation of financial imbalances.”
The Bank of Japan also provided explicit analysis of its view on price stability in a “Background note regarding the Bank’s thinking on price stability” (http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2013/data/rel130123a1.pdf http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2013/rel130123a.htm/). The Bank of Japan also amended “Principal terms and conditions for the Asset Purchase Program” (http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2013/rel130122a.pdf): “Asset purchases and loan provision shall be conducted up to the maximum outstanding amounts by the end of 2013. From January 2014, the Bank shall purchase financial assets and provide loans every month, the amount of which shall be determined pursuant to the relevant rules of the Bank.”
Financial markets in Japan and worldwide were shocked by new bold measures of “quantitative and qualitative monetary easing” by the Bank of Japan (http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2013/k130404a.pdf). The objective of policy is to “achieve the price stability target of 2 percent in terms of the year-on-year rate of change in the consumer price index (CPI) at the earliest possible time, with a time horizon of about two years” (http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2013/k130404a.pdf). The main elements of the new policy are as follows:
- Monetary Base Control. Most central banks in the world pursue interest rates instead of monetary aggregates, injecting bank reserves to lower interest rates to desired levels. The Bank of Japan (BOJ) has shifted back to monetary aggregates, conducting money market operations with the objective of increasing base money, or monetary liabilities of the government, at the annual rate of 60 to 70 trillion yen. The BOJ estimates base money outstanding at “138 trillion yen at end-2012) and plans to increase it to “200 trillion yen at end-2012 and 270 trillion yen at end 2014” (http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2013/k130404a.pdf).
- Maturity Extension of Purchases of Japanese Government Bonds. Purchases of bonds will be extended even up to bonds with maturity of 40 years with the guideline of extending the average maturity of BOJ bond purchases from three to seven years. The BOJ estimates the current average maturity of Japanese government bonds (JGB) at around seven years. The BOJ plans to purchase about 7.5 trillion yen per month (http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2013/rel130404d.pdf). Takashi Nakamichi, Tatsuo Ito and Phred Dvorak, wiring on “Bank of Japan mounts bid for revival,” on Apr 4, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887323646604578401633067110420.html ), find that the limit of maturities of three years on purchases of JGBs was designed to avoid views that the BOJ would finance uncontrolled government deficits.
- Seigniorage. The BOJ is pursuing coordination with the government that will take measures to establish “sustainable fiscal structure with a view to ensuring the credibility of fiscal management” (http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2013/k130404a.pdf).
- Diversification of Asset Purchases. The BOJ will engage in transactions of exchange traded funds (ETF) and real estate investment trusts (REITS) and not solely on purchases of JGBs. Purchases of ETFs will be at an annual rate of increase of one trillion yen and purchases of REITS at 30 billion yen.
Table VB-BOJF, Bank of Japan, Forecasts of the Majority of Members of the Policy Board, % Year on Year
| Fiscal Year | Real GDP | CPI All Items Less Fresh Food | Excluding Effects of Consumption Tax Hikes |
| 2013 | |||
| Jul 2013 | +2.5 to +3.0 [+2.8] | +0.5 to +0.8 [+0.6] | |
| Apr 2013 | +2.4 to +3.0 [+2.9] | +0.4 to +0.8 [+0.7] | |
| 2014 | |||
| Jul 2013 | +0.8 to +1.5 [+1.3] | +2.7 to +3.6 [+3.3] | +0.7 to +1.6 [+1.3] |
| Apr 2013 | +1.0 to +1.5 [+1.4] | +2.7 to +3.6 [+3.4] | +0.7 to +1.6 [+1.4] |
| 2015 | |||
| Jul 2013 | +1.3 to +1.9 [+1.5] | +1.6 to +2.9 [+2.6] | +0.9 to +2.2 [+1.9] |
| Apr 2013 | +1.4 to +1.9 [+1.6] | +1.6 to +2.9 [+2.6] | +0.9 to +2.2 [+1.9] |
Figures in brackets are the median of forecasts of Policy Board members
Source: Policy Board, Bank of Japan
http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2013/k130711a.pdf
Private-sector activity in Japan expanded with the Markit Composite Output PMI™ Index decreasing from the high of the series at 54.1 in May to 52.3 in Jun (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/c5f4daed191042f198cf2cdb41e04285). Paul Smith, economist at Markit and author of the report, finds that the survey data suggest continuing growth of the economy of Japan with accelerating performance of the economy of Japan in IIQ2013 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/c5f4daed191042f198cf2cdb41e04285). The Markit Business Activity Index of Services decreased from the record high of 54.8 in May to 52.1 in Jun (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/c5f4daed191042f198cf2cdb41e04285). Paul Smith, Senior Economist at Markit and author of the report, finds continuing optimism in services and manufacturing companies in Japan with positive outlook for the economy (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/c5f4daed191042f198cf2cdb41e04285). Markit/JMMA Purchasing Managers’ Index™ (PMI™), seasonally adjusted, increased from 51.5 in Apr to 52.3 in Jun, which is the highest reading in 28 months, indicating solid growth (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/07f08c5d1667427d93cb8bfd767d581d). New orders grew at rapid pace with higher strength in domestic demand while export orders increased for a fourth consecutive month but at slower pace. Paul Smith, Senior Economist at Markit and author of the report, finds manufacturing expanding at an annual rate of 5 percent in IIQ2013 that should contribute to GDP growth (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/07f08c5d1667427d93cb8bfd767d581d).Table JPY provides the country data table for Japan.
Table JPY, Japan, Economic Indicators
| Historical GDP and CPI | 1981-2010 Real GDP Growth and CPI Inflation 1981-2010 |
| Corporate Goods Prices | Jun ∆% +0.1 |
| Consumer Price Index | Jun NSA ∆% 0.0; Jun 12 months NSA ∆% 0.2 |
| Real GDP Growth | IQ2013 ∆%: 1.0 on IVQ2012; IQ2013 SAAR 4.1; |
| Employment Report | Jun Unemployed 2.60 million Change in unemployed since last year: minus 280 thousand |
| All Industry Indices | May month SA ∆% 1.1 Blog 7/21/13 |
| Industrial Production | Jun SA month ∆%: -3.3 |
| Machine Orders | Total May ∆% 12.0 Private ∆%: 12.4 May ∆% Excluding Volatile Orders 10.5 |
| Tertiary Index | May month SA ∆% 1.2 |
| Wholesale and Retail Sales | May 12 months: |
| Family Income and Expenditure Survey | Jun 12-month ∆% total nominal consumption -0.1, real -0.4 Blog 8/4/13 |
| Trade Balance | Exports Jun 12 months ∆%: 7.4 Imports Jun 12 months ∆% 11.8 Blog 7/28/13 |
Links to blog comments in Table JPY:
7/28/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/duration-dumping-steepening-yield-curve.html
7/21/2013 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html
7/14/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/recovery-without-hiring-tapering.html
6/30/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html
6/16/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/recovery-without-hiring-seven-million.html
8/9/11 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/08/turbulence-in-world-financial-markets.html
In Jun 2013, industrial production in Japan decreased 3.3 percent and decreased 4.8 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2013, as shown in Table VB-1, interrupting four consecutive monthly increases from Feb through May 2013. Japan’s industrial production was strengthening with growth of 1.4 percent in Dec 2012, 0.9 percent in Feb 2013, 0.1 percent in Mar 2013, 0.9 percent in Apr 2013 and 1.9 percent in May 2013. Growth in 12 months had improved from minus 10.1 percent in Feb 2013 to minus 1.1 percent in May 2013. Industrial production fell 21.9 percent in 2009 after falling 3.4 percent in 2008 but recovered by 15.6 percent in 2010. The annual average in calendar year 2011 fell 2.8 percent largely because of the Tōhoku or Great East Earthquake and Tsunami of Mar 11, 2011.
Table VB-1, Japan, Industrial Production ∆%
| ∆% Month SA | ∆% 12 Months NSA | |
| Jun 2013 | -3.3 | -4.8 |
| May | 1.9 | -1.1 |
| Apr | 0.9 | -3.4 |
| Mar | 0.1 | -7.2 |
| Feb | 0.9 | -10.1 |
| Jan | -0.6 | -6.0 |
| Dec 2012 | 1.4 | -7.6 |
| Nov | -1.0 | -5.5 |
| Oct | 0.3 | -4.7 |
| Sep | -2.2 | -7.6 |
| Aug | -1.4 | -4.1 |
| Jul | -0.5 | 0.1 |
| Jun | -0.8 | -0.6 |
| May | -1.8 | 7.6 |
| Apr | -0.5 | 15.1 |
| Mar | 0.2 | 16.6 |
| Calendar Year | ||
| 2012 | 0.6 | |
| 2011 | -2.8 | |
| 2010 | 15.6 |
Source: http://www.meti.go.jp/english/statistics/tyo/iip/index.html
The employment report for Japan in Jun 2013 is in Table VB-2. The rate of unemployment seasonally adjusted decreased to 4.2 percent in Sep 2012 from 4.3 percent in Jul 2012 and remained at 4.2 percent in Oct 2012, declining to 4.1 percent in Nov 2012, increasing to 4.2 percent in Dec 2012, stabilizing at 4.2 percent in Jan 2013 and increasing to 4.3 percent in Feb 2013. The seasonally adjusted rate of unemployment fell to 4.1 percent in Apr and May 2013. The rate of unemployment not seasonally adjusted stood at 4.2 percent in Apr 2013 and 0.3 percentage points lower from a year earlier. The rate of unemployment fell to 3.9 percent in Jun 2013 seasonally and not seasonally adjusted. The employment rate stood at 57.1 percent in Jun 2013 and increased 0.3 percentage points from a year earlier.
Table VB-2, Japan, Employment Report Apr 2013
| Jun 2013 Unemployed | 2.60 million |
| Change since last year | -280 thousand; ∆% –9.7 |
| Unemployment rate | 3.9% SA -0.2; NSA 3.9%, -0.5 from earlier year |
| Population ≥ 15 years | 110.90 million |
| Change since last year | ∆% -0.1 |
| Labor Force | 66.93 million |
| Change since last year | ∆% 0.0 |
| Employed | 63.33 million |
| Change since last year | ∆% 0.5 |
| Labor force participation rate | 59.4 |
| Change since last year | 0.0 |
| Employment rate | 57.1% |
| Change since last year | 0.3 |
Source: Japan, Statistics Bureau, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications
http://www.stat.go.jp/english/data/roudou/results/month/index.htm
Chart VB-1 of Japan’s Statistics Bureau at the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications provides the unemployment rate of Japan from 2010 to 2013. The sharp decline in Sep 2011 was the best reading in 2011 but the rate increased in the final quarter of the year, declining in Feb 2012 and stabilizing in Mar 2012 but increasing to 4.6 percent in Apr 2012 and declining again to 4.4 percent in May 2012 and 4.3 percent in both Jun and Jul 2012 with further decline to 4.2 percent in Aug, Sep and Oct 2012, 4.1 percent in Nov 2012, 4.2 percent in Dec 2012, 4.2 percent in Jan 2013, 4.3 percent in Feb 2013 and 4.1 percent in Mar-May 2013. The rate of unemployment fell to 3.9 percent in Jun 2013.
Chart VB-1, Japan, Unemployment Rate
Source: Japan, Statistics Bureau, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications
http://www.stat.go.jp/english/data/roudou/results/month/index.htm
During the “lost decade” of the 1990s from 1991 to 2002 (Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 82-3), Japan’s GDP grew at the average yearly rate of 1.0 percent, the CPI at 0.1 percent and the implicit deflator at minus 0.8 percent. Japan’s growth rate from the mid 1970s to 1992 was 4 percent (Ito 2004). Table VB-3 provides Japan’s rates of unemployment, participation in labor force and employment for 1968, 1975, 1980 and 1985 and yearly from 1990 to 2012. The rate of unemployment jumped from 2.1 percent in 1991 to 5.4 percent in 2002, which was a year of global economic weakness. The participation rate dropped from 64.0 percent in 1992 to 61.2 percent in 2002 and the employment rate fell from 62.4 percent in 1992 to 57.9 percent in 2002. The rate of unemployment rose from 3.9 percent in 2007 to 5.1 percent in 2010, falling to 4.6 percent in 2011 and 4.3 percent in 2012, while the participation rate fell from 60.4 percent to 59.6 percent, falling to 59.3 percent in 2011 and 59.1 in 2012, and the employment rate fell from 58.1 percent to 56.6 percent in 2010 and 56.5 percent in 2011 and 2012. The global recession adversely affected labor markets in advanced economies.
Table VB-3, Japan, Rates of Unemployment, Participation in Labor Force and Employment, %
| Participation | Employment Rate | Unemployment Rate | |
| 1953 | 70.0 | 68.6 | 1.9 |
| 1960 | 69.2 | 68.0 | 1.7 |
| 1965 | 85.7 | 64.9 | 1.2 |
| 1970 | 65.9 | 65.1 | 1.2 |
| 1975 | 63.0 | 61.9 | 1.9 |
| 1980 | 63.3 | 62.0 | 2.0 |
| 1985 | 63.0 | 61.4 | 2.6 |
| 1990 | 63.3 | 61.9 | 2.1 |
| 1991 | 63.8 | 62.4 | 2.1 |
| 1992 | 64.0 | 62.6 | 2.2 |
| 1993 | 63.8 | 62.2 | 2.5 |
| 1994 | 63.6 | 61.8 | 2.9 |
| 1995 | 63.4 | 61.4 | 3.2 |
| 1996 | 63.5 | 61.4 | 3.4 |
| 1997 | 63.7 | 61.5 | 3.4 |
| 1998 | 63.3 | 60.7 | 4.1 |
| 1999 | 62.9 | 59.9 | 4.7 |
| 2000 | 62.4 | 59.5 | 4.7 |
| 2001 | 62.0 | 58.9 | 5.0 |
| 2002 | 61.2 | 57.9 | 5.4 |
| 2003 | 60.8 | 57.6 | 5.3 |
| 2004 | 60.4 | 57.6 | 4.7 |
| 2005 | 60.4 | 57.7 | 4.4 |
| 2006 | 60.4 | 57.9 | 4.1 |
| 2007 | 60.4 | 58.1 | 3.9 |
| 2008 | 60.2 | 57.8 | 4.0 |
| 2009 | 59.9 | 56.9 | 5.1 |
| 2010 | 59.6 | 56.6 | 5.1 |
| 2011 | 59.3 | 56.5 | 4.6 |
| 2012 | 59.1 | 56.5 | 4.3 |
Source: Japan, Statistics Bureau, Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications
http://www.stat.go.jp/english/data/roudou/results/month/index.htm
The survey of household income and consumption of Japan in Table VB-4 is showing noticeable improvement in recent months relative to earlier months, which can be appreciated in the chart in the link in parentheses but followed by decline in Nov 2011, renewed strength in Dec 2011, another decline in Jan 2012 and increase in Feb and Mar 2012 with stabilization in Apr and May 2012 but sharp decline into Jun 2012 with recovery in Jul and Aug 2012, interrupted in Sep-Oct 2012 and new increases in Nov 2012, Jan 2013, Feb 2013, Mar 2013 and Apr 2013 (http://www.stat.go.jp/english/data/kakei/156.htm). Total consumption decreased 1.6 percent in real terms in May 2013 and decreased 1.9 percent in nominal terms relative to a year earlier. Real consumption fell 0.4 percent in Jun 2013 and nominal consumption declined 0.1 percent. There are several segments of decreasing real consumption: housing falling 16.9 percent in nominal terms and 16.5 percent in real terms, transportation/communications falling 7.9 percent in nominal terms and 7.1 percent in real terms and education decreasing 6.6 percent in nominal terms and 7.1 percent in real terms. Fuel, light and water charges increased 1.8 percent in nominal terms and decreased 3.7 percent in real terms. Real household income increased 2.0 percent; real disposable income increased 1.4 percent; and real consumption expenditures increased 0.9 percent.
Table VB-4, Japan, Family Income and Expenditure Survey 12-months ∆% Relative to a Year Earlier
| Jun 2013 | Nominal | Real |
| Households of Two or More Persons | ||
| Total Consumption | -0.1 | -0.4 |
| Excluding Housing, Vehicles & Remittance | 2.5* | |
| Food | 3.7 | 4.6 |
| Housing | -16.9 | -16.5 |
| Fuel, Light & Water Charges | 1.8 | -3.7 |
| Furniture & Household Utensils | 1.4 | 3.9 |
| Clothing & Footwear | 8.3 | 8.1 |
| Medical Care | 7.2 | 7.8 |
| Transport and Communications | -7.9 | -9.5 |
| Education | -6.6 | -7.1 |
| Culture & Recreation | 6.4 | 7.7 |
| Other Consumption Expenditures | 0.7 | 0.4* |
| Workers’ Households | ||
| Income | 2.3 | 2.0 |
| Disposable Income | 1.7 | 1.4 |
| Consumption Expenditures | 1.2 | 0.9 |
*Real: nominal deflated by CPI excluding imputed rent
Source: Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, Statistics Bureau, Director General for Policy Planning and Statistical Research and Training Institute
http://www.stat.go.jp/english/data/kakei/156.htm
Chart VB-2 of the Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communication provides year-on-year change of real consumption expenditures. There is marginal improvement in the final segment.
Chart VB-2, Japan, Real Percentage Change of Consumption Year-on-Year
Source: Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, Statistics Bureau, Director General for Policy Planning and Statistical Research and Training Institute
http://www.stat.go.jp/english/data/kakei/156.htm
Percentage changes in 12 months of nominal and real consumption expenditures in Japan are provided in Table VB-5. Real consumption expenditures decreased 0.5 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2013 and 0.1 percent in nominal terms. Declines in May and Jun 2013 interrupted growth from Jan to Apr 2013. There was sharp decline in nominal consumption of 8.8 percent in Mar 2011 and 8.2 percent in real consumption because of the Tōhoku or Great East Earthquake and Tsunami of Mar 11, 2011. Dec was the first month in 2011 with increases in 12 months in both nominal and real consumption expenditures followed by Feb 2012 through Aug 2012. Nominal and real consumption fell in both Sep and Oct 2012 and increased in Nov 2012. Real consumption fell 0.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2012 and nominal consumption fell 0.8 percent. Real consumption expenditures increased 2.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2013 and 2.1 percent in nominal terms. Nominal consumption increased 0.8 percent in Feb 2013 and nominal consumption increased 0.1 percent. Real consumption increased 5.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Mar 2013 and nominal consumption 4.1 percent. Consumption was an important driver of GDP growth in Japan in IQ2012. Real GDP grew at the seasonally adjusted annual rate (SAAR) of 4.8 percent in IQ2012 with private consumption contributing 2.0 percentage points for the highest contribution to growth (Table VB-2 at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/recovery-without-hiring-seven-million.html). There was deceleration in IIQ2012 with growth of GDP at SAAR of minus 0.6 percent and contribution of 0.5 percentage points of personal consumption. In IIIQ2012, Japan’s GDP contracted at the SAAR of 3.6 percent and personal consumption deducted 1.0 percentage points. Japan’s GDP grew at the SAAR of 1.2 percent in IVQ2012 with personal consumption contributing 1.1 percentage points. Japan’s GDP growth in IQ2013 was at 4.1 percent SAAR with highest contribution of 2.2 percentage points by personal consumption expenditures.
Table VB-5, Japan, Family Income and Expenditure Survey 12-months ∆% Relative to a Year Earlier
| Nominal Consumption Expenditures | Real Consumption Expenditures | |
| Jun 2013 | -0.1 | -0.4 |
| May | -1.9 | -1.6 |
| Apr | 0.8 | 1.5 |
| Mar | 4.1 | 5.2 |
| Feb | 0.1 | 0.8 |
| Jan | 2.1 | 2.4 |
| Dec 2012 | -0.8 | -0.7 |
| Nov | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Oct | -0.5 | -0.1 |
| Sep | -1.2 | -0.9 |
| Aug | 1.4 | 1.8 |
| Jul | 1.2 | 1.7 |
| Jun | 1.5 | 1.6 |
| May | 4.3 | 4.0 |
| Apr | 3.2 | 2.6 |
| Mar | 4.1 | 3.4 |
| Feb | 2.7 | 2.3 |
| Jan | -2.1 | -2.3 |
| Dec 2011 | 0.3 | 0.5 |
| Nov | -3.8 | -3.2 |
| Oct | -0.6 | -0.4 |
| Sep | -1.9 | -1.9 |
| Aug | -3.9 | -4.1 |
| Jul | -1.8 | -2.1 |
| Jun | -3.9 | -3.5 |
| May | -1.6 | -1.2 |
| Apr | -2.5 | -2.0 |
| Mar | -8.8 | -8.2 |
| Feb | -0.1 | 0.5 |
| Jan | -0.9 | -0.3 |
| Dec 2010 | -3.2 | -3.3 |
| Dec 2009 | 0.3 | 2.1 |
Source:
Source: Ministry of Internal Affairs and Communications, Statistics Bureau, Director General for Policy Planning and Statistical Research and Training Institute
http://www.stat.go.jp/english/data/kakei/156.htm
Japan is experiencing weak internal demand as in most advanced economies, interrupted by strong growth in IQ2012 but renewed weakening at the end of IIQ2012, beginning of IIIQ2012 with recovery in IVQ2012 and IQ2013. Table VB-6 provides Japan’s wholesale and retail sales. There is strong performance in May with growth of 0.8 percent for retail sales followed by 1.6 percent in Jun 2013. Retail sales are recovering from deep drops in Mar and Apr 2011 following the Tōhoku or Great East Earthquake and Tsunami of Mar 11, 2011. Retail sales have been increasing in 12-month percentage changes from Dec 2011 through May 2012 but fell again by 1.3 percent in Jul 2012, increasing 1.3 percent in Aug 2012 and 0.4 percent in Sep 2012 but declining 1.2 percent in Oct 2012, rebounding by 0.9 percent in Nov 2012 and only 0.2 percent in Dec 2012 but contracting 1.1 percent in Jan 2013 and 2.2 percent in Feb 2013. In May 2013, retail sales increased 0.8 percent relative to a year earlier and 1.6 percent in Jun 2013.
Table VB-6, Japan, Wholesale and Retail Sales 12 Month ∆%
| Total | Wholesale | Retail | |
| Jun 2013 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 1.6 |
| May | 0.6 | 0.5 | 0.8 |
| Apr | -0.1 | -0.1 | -0.2 |
| Mar | -1.3 | -1.8 | -0.3 |
| Feb | -1.6 | -1.3 | -2.2 |
| Jan | -0.3 | 0.1 | -1.1 |
| Dec 2012 | -1.7 | -2.5 | 0.2 |
| Nov | -0.9 | -1.6 | 0.9 |
| Oct | -1.6 | -1.8 | -1.2 |
| Sep | -3.6 | -5.1 | 0.4 |
| Aug | -2.7 | -4.4 | 1.3 |
| Jul | -3.1 | -4.0 | -1.3 |
| Jun | -2.6 | -3.6 | -0.2 |
| May | 2.7 | 2.6 | 3.0 |
| Apr | 1.8 | 0.4 | 5.0 |
| Mar | 3.2 | 0.9 | 9.3 |
| Feb | -0.1 | -1.3 | 3.1 |
| Jan | -2.1 | -3.8 | 1.6 |
| Dec 2011 | -0.8 | -2.0 | 2.5 |
| Nov | -2.3 | -2.4 | -2.2 |
| Oct | 1.1 | 0.8 | 1.9 |
| Sep | 0.3 | 0.8 | -1.1 |
| Aug | 3.1 | 5.2 | -2.6 |
| Jul | 2.3 | 3.0 | 0.6 |
| Jun | 3.1 | 3.8 | 1.2 |
| May | 1.3 | 2.3 | -1.3 |
| Apr | -2.6 | -1.7 | -4.8 |
| Mar | -1.3 | 1.2 | -8.3 |
| Feb | 5.3 | 7.2 | 0.1 |
| Jan | 3.3 | 4.6 | 0.1 |
| Dec 2010 | 3.5 | 5.7 | -2.1 |
| Calendar Year | |||
| 2012 | -0.9 | -2.0 | 1.8 |
| 2011 | 1.0 | 1.9 | -1.0 |
| 2010 | 2.4 | 2.3 | 2.6 |
| 2009 | -20.5 | -25.6 | -2.3 |
| 2008 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 0.3 |
Source: http://www.meti.go.jp/english/statistics/index.html
VC China. China estimates an index of nonmanufacturing purchasing managers on the basis of a sample of 1200 nonmanufacturing enterprises across the country (http://www.stats.gov.cn/english/pressrelease/t20121009_402841094.htm). Table CIPMNM provides this index and components. The index fell from 58.0 in Mar to 55.2 in May but climbed to 56.7 in Jun, which is lower than 58.0 in Mar and 57.3 in Feb but higher than in any other of the months in 2012. In Jul 2012 the index fell marginally to 55.6 and then to 56.3 in Aug and 53.7 in Sep but rebounded to 55.5 in Oct and 55.6 in Nov 2012. Improvement continued with 56.1 in Dec 2012 and 56.2 in Jan 2013, declining marginally to 54.5 in Feb 2013 and 55.6 in Mar 2013. The index fell to 54.5 in Apr 2013, 54.3 in May 2013 and 53.9 in Jun 2013.
Table CIPMNM, China, Nonmanufacturing Index of Purchasing Managers, %, Seasonally Adjusted
| Total Index | New Orders | Interm. | Subs Prices | Exp | |
| Jun 2013 | 53.9 | 50.3 | 55.0 | 50.6 | 61.8 |
| May | 54.3 | 50.1 | 54.4 | 50.7 | 62.9 |
| Apr | 54.5 | 50.9 | 51.1 | 47.6 | 62.5 |
| Mar | 55.6 | 52.0 | 55.3 | 50.0 | 62.4 |
| Feb | 54.5 | 51.8 | 56.2 | 51.1 | 62.7 |
| Jan | 56.2 | 53.7 | 58.2 | 50.9 | 61.4 |
| Dec 2012 | 56.1 | 54.3 | 53.8 | 50.0 | 64.6 |
| Nov | 55.6 | 53.2 | 52.5 | 48.4 | 64.6 |
| Oct | 55.5 | 51.6 | 58.1 | 50.5 | 63.4 |
| Sep | 53.7 | 51.8 | 57.5 | 51.3 | 60.9 |
| Aug | 56.3 | 52.7 | 57.6 | 51.2 | 63.2 |
| Jul | 55.6 | 53.2 | 49.7 | 48.7 | 63.9 |
| Jun | 56.7 | 53.7 | 52.1 | 48.6 | 65.5 |
| May | 55.2 | 52.5 | 53.6 | 48.5 | 65.4 |
| Apr | 56.1 | 52.7 | 57.9 | 50.3 | 66.1 |
| Mar | 58.0 | 53.5 | 60.2 | 52.0 | 66.6 |
| Feb | 57.3 | 52.7 | 59.0 | 51.2 | 63.8 |
| Jan | 55.7 | 52.2 | 58.2 | 51.1 | 65.3 |
Notes: Interm.: Intermediate; Subs: Subscription; Exp: Business Expectations
Source: National Bureau of Statistics of China
http://www.stats.gov.cn/english/
Chart CIPMNM provides China’s nonmanufacturing purchasing managers’ index. There was slowing of the general index in Apr 2012 after the increase in Jan-Mar 2012 and further decline to 55.2 in May 2012 but increase to 56.7 in Jun 2012 with marginal decline to 55.6 in Jul 2012 and 56.3 in Aug 2012 and sharper drop to 53.7 in Sep 2012, rebounding to 55.5 in Oct 2012, 55.6 in Nov 2012, 56.1 in Dec 2012 and 55.6 in Mar 2013. The index fell again to 54.5 in Apr 2013, 54.3 in May 2013 and 53.9 in Jun 2013.
Chart CIPMNM, China, Nonmanufacturing Index of Purchasing Managers, Seasonally Adjusted
Source: National Bureau of Statistics of China
http://www.stats.gov.cn/english/
Table CIPMMFG provides the index of purchasing managers of manufacturing seasonally adjusted of the National Bureau of Statistics of China. The general index (IPM) rose from 50.5 in Jan 2012 to 53.3 in Apr and declined to 50.1 in Jul and to the contraction zone at 49.2 in Aug and 49.8 in Sep, climbing above 50.0 to 50.2 in Oct, 50.6 in Nov-Dec 2012, 50.9 in Mar 2013 and 50.6 in Apr 2013. The index increased to 50.8 in May 2013, falling to 50.1 in Jun 2013. The index of new orders (NOI) fell from 54.5 in Apr 2012 to 49.0 in Jul and 48.7 in Aug, climbing above 50.0, 51.2 in Nov 2012-Dec 2012, 52.3 in Mar 2013 and 51.7 in Apr 2013. The index of new orders increased to 51.8 in May 2013, falling to 50.4 in Jun 2013. The index of employment also fell from 51.0 in Apr to 49.1 in Aug and further down to 48.7 in Nov 2012, 49.9 in Dec 2012, 49.8 in Mar 2013 and 49.0 in Apr 2013. The index of employment fell to 48.8 in May 2013 and 48.7 in Jun 2013.
Table CIPMMFG, China, Manufacturing Index of Purchasing Managers, %, Seasonally Adjusted
| IPM | PI | NOI | INV | EMP | SDEL | |
| Jun 2013 | 50.1 | 52.0 | 50.4 | 47.4 | 48.7 | 50.3 |
| May | 50.8 | 53.3 | 51.8 | 47.6 | 48.8 | 50.8 |
| Apr | 50.6 | 52.6 | 51.7 | 47.5 | 49.0 | 50.8 |
| Mar | 50.9 | 52.7 | 52.3 | 47.5 | 49.8 | 51.1 |
| Feb | 50.1 | 51.2 | 50.1 | 49.5 | 47.6 | 48.3 |
| Jan | 50.4 | 51.3 | 51.6 | 50.1 | 47.8 | 50.0 |
| Dec 2012 | 50.6 | 52.0 | 51.2 | 47.3 | 49.0 | 48.8 |
| Nov | 50.6 | 52.5 | 51.2 | 47.9 | 48.7 | 49.9 |
| Oct | 50.2 | 52.1 | 50.4 | 47.3 | 49.2 | 50.1 |
| Sep | 49.8 | 51.3 | 49.8 | 47.0 | 48.9 | 49.5 |
| Aug | 49.2 | 50.9 | 48.7 | 45.1 | 49.1 | 50.0 |
| Jul | 50.1 | 51.8 | 49.0 | 48.5 | 49.5 | 49.0 |
| Jun | 50.2 | 52.0 | 49.2 | 48.2 | 49.7 | 49.1 |
| May | 50.4 | 52.9 | 49.8 | 45.1 | 50.5 | 49.0 |
| Apr | 53.3 | 57.2 | 54.5 | 48.5 | 51.0 | 49.6 |
| Mar | 53.1 | 55.2 | 55.1 | 49.5 | 51.0 | 48.9 |
| Feb | 51.0 | 53.8 | 51.0 | 48.8 | 49.5 | 50.3 |
| Jan | 50.5 | 53.6 | 50.4 | 49.7 | 47.1 | 49.7 |
IPM: Index of Purchasing Managers; PI: Production Index; NOI: New Orders Index; EMP: Employed Person Index; SDEL: Supplier Delivery Time Index
Source: National Bureau of Statistics of China
http://www.stats.gov.cn/english/
China estimates the manufacturing index of purchasing managers on the basis of a sample of 820 enterprises (http://www.stats.gov.cn/english/pressrelease/t20121009_402841094.htm). Chart CIPMMFG provides the manufacturing index of purchasing managers. There is deceleration from 51.2 in Sep 2011 to marginal contraction at 49.0 in Nov 2011. Manufacturing activity recovered to 53.3 in Apr 2012 but then declined to 50.4 in May 2012 and 50.1 in Jun 2012, which is the lowest in a year with exception of contraction at 49.0 in Nov 2011. The index then fell to contraction at 49.2 in Aug 2012 and improved to 49.8 in Sep with movement to 50.2 in Oct 2012, 50.6 in Nov 2012, 50.9 in Mar 2013 and 50.6 in Apr 2013 above the neutral zone of 50.0. The index increased to 50.8 in May 2013 and fell to 50.1 in Jun 2013.
Chart CIPMMFG, China, Manufacturing Index of Purchasing Managers, Seasonally Adjusted
Source: National Bureau of Statistics of China
http://www.stats.gov.cn/english/
Cumulative growth of China’s GDP in IIQ2013 relative to the same period in 2012 was 7.6 percent, as shown in Table VC-GDP. Secondary industry accounts for 47.2 percent of GDP of which industry alone for 41.0 percent in IQ2013 and construction with the remaining 6.2 percent in the first three quarters of 2012. Tertiary industry accounts for 45.3 percent of cumulative GDP in IIQ2013 and primary industry for 7.5 percent. China’s growth strategy consisted of rapid increases in productivity in industry to absorb population from agriculture where incomes are lower (Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 56-80). The bottom block of Table VC-1 provides quarter-on-quarter growth rates of GDP and their annual equivalent. China’s GDP growth decelerated significantly from annual equivalent 10.4 percent in IIQ2011 to 7.4 percent in IVQ2011 and 6.2 percent in IQ2012, rebounding to 8.7 percent in IIQ2012, 8.2 percent in IIIQ2012 and 7.8 percent in IVQ2012. Annual equivalent growth in IQ2013 fell to 6.6 percent and to 7.0 percent in IIQ2013.
Table VC-GDP, China, Quarterly Growth of GDP, Current CNY 100 Million and Inflation Adjusted ∆%
| Cumulative GDP IIQ2013 | Value Current CNY 100 Million | 2013 Year-on-Year Constant Prices ∆% |
| GDP | 248009 | 7.6 |
| Primary Industry | 18622 | 3.0 |
| Farming | 18622 | 3.0 |
| Secondary Industry | 117037 | 7.6 |
| Industry | 101601 | 7.3 |
| Construction | 15436 | 9.6 |
| Tertiary Industry | 112350 | 8.3 |
| Transport, Storage, Post | 12995 | 6.8 |
| Wholesale, Retail Trades | 23291 | 10.2 |
| Hotel & Catering Services | 4824 | 4.7 |
| Financial Intermediation | 16036 | 10.8 |
| Real Estate | 16127 | 7.5 |
| Other | 39077 | 7.4 |
| Growth in Quarter Relative to Prior Quarter | ∆% on Prior Quarter | ∆% Annual Equivalent |
| 2013 | ||
| IIQ2013 | 1.7 | 7.0 |
| IQ2013 | 1.6 | 6.6 |
| 2012 | ||
| IVQ2012 | 1.9 | 7.8 |
| IIIQ2012 | 2.0 | 8.2 |
| IIQ2012 | 2.1 | 8.7 |
| IQ2012 | 1.5 | 6.2 |
| 2011 | ||
| IVQ2011 | 1.8 | 7.4 |
| IIIQ2011 | 2.2 | 9.1 |
| IIQ2011 | 2.5 | 10.4 |
| IQ2011 | 2.3 | 9.5 |
Source: National Bureau of Statistics of China
http://www.stats.gov.cn/english/
Growth of China’s GDP in IIQ2013 relative to the same period in 2012 was 7.5 percent, as shown in Table VC-GDPA. Secondary industry accounts for 47.2 percent of GDP of which industry alone for 41.0 percent in cumulative IIQ2013 and construction with the remaining 7.5 percent in the first two quarters of 2013. Tertiary industry accounts for 45.3 percent of GDP in the cumulative to IIQ2013 and primary industry for 7.5 percent. China’s growth strategy consisted of rapid increases in productivity in industry to absorb population from agriculture where incomes are lower (Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 56-80). GDP growth decelerated from 12.1 percent in IQ2010 and 11.2 percent in IIQ2010 to 7.7 percent in IQ2013 and 7.5 percent in IIQ2013.
Table VC-GDPA, China, Growth Rate of GDP, ∆% Relative to a Year Earlier and ∆% Relative to Prior Quarter
| IQ 2013 | IIQ 2013 | |||||||
| GDP | 7.7 | 7.5 | ||||||
| Primary Industry | 3.4 | 3.0 | ||||||
| Secondary Industry | 7.8 | 7.6 | ||||||
| Tertiary Industry | 8.3 | 8.3 | ||||||
| GDP ∆% Relative to a Prior Quarter | 1.6 | 1.7 | ||||||
| IQ 2011 | IIQ 2011 | IIIQ 2011 | IVQ 2011 | IQ 2012 | IIQ 2012 | IIIQ 2012 | IVQ 2012 | |
| GDP | 9.7 | 9.5 | 9.1 | 8.9 | 8.1 | 7.6 | 7.4 | 7.9 |
| Primary Industry | 3.5 | 3.2 | 3.8 | 4.5 | 3.8 | 4.3 | 4.2 | 4.5 |
| Secondary Industry | 11.1 | 11.0 | 10.8 | 10.6 | 9.1 | 8.3 | 8.1 | 8.1 |
| Tertiary Industry | 9.1 | 9.2 | 9.0 | 8.9 | 7.5 | 7.7 | 7.9 | 8.1 |
| GDP ∆% Relative to a Prior Quarter | 2.3 | 2.4 | 2.3 | 1.8 | 1.6 | 1.9 | 2.1 | 2.0 |
| IQ 2010 | IIQ 2010 | IIIQ 2010 | IVQ 2010 | |||||
| GDP | 12.1 | 11.2 | 10.7 | 12.1 | ||||
| Primary Industry | 3.8 | 3.6 | 4.0 | 3.8 | ||||
| Secondary Industry | 14.5 | 13.3 | 12.6 | 14.5 | ||||
| Tertiary Industry | 10.5 | 9.9 | 9.7 | 10.5 |
Source: National Bureau of Statistics of China http://www.stats.gov.cn/english/
Chart VC-GDP of the National Bureau of Statistics of China provides annual value and growth rates of GDP. China’s GDP growth in 2012 is still high at 7.8 percent but at the lowest rhythm in five years
Chart VC-GDP, China, Gross Domestic Product, Million Yuan and ∆%, 2008-2012
Source: National Bureau of Statistics of China http://www.stats.gov.cn/english/
The HSBC Flash China Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index™ (PMI™) compiled by Markit (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/69676b0fae3d429b89c74bcf671abde4) is moving at slower pace. The overall Flash HSBC China Manufacturing PMI™ decreased from 48.2 in Jun to 47.7 in Jul, which is moderately below the contraction frontier of 50.0, while the Flash HSBC China Manufacturing Output Index decreased from 48.6 in Jun to 48.2 in Jul, moving into moderate contraction territory. Hongbin Qu, Chief Economist, China and Co-Head of Asian Economic Research at HSBC, finds that weakness in the index suggests need for further stimulus to support growth (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/69676b0fae3d429b89c74bcf671abde4). The HSBC China Services PMI™, compiled by Markit, shows marginal weakness in business activity in China with the HSBC Composite Output, combining manufacturing and services, decreasing from 50.9 in May to 49.8 in Jun with the first output reduction in ten months (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/cae4f011435d4230b6cfb98dcde4e488). Hongbin Qu, Chief Economist, China and Co-Head of Asian Economic Research at HSBC, finds that combined manufacturing and services data suggest downward effects on growth from both manufacturing and services (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/cae4f011435d4230b6cfb98dcde4e488). The HSBC Business Activity index increased from 51.2 in May to 51.3 in Jun (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/cae4f011435d4230b6cfb98dcde4e488). Hongbin Ku, Chief Economist, China & Co-Head of Asian Economic Research at HSBC, finds slowing services (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/cae4f011435d4230b6cfb98dcde4e488). The HSBC Purchasing Managers’ Index™ (PMI™), compiled by Markit, decreased to 48.2 in Jun from 49.2 in May, indicating moderate contraction in manufacturing for the second consecutive month after six prior consecutive months of improvement (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/43d33bc53a2142e8b5c3dde180f3b9d4). New export orders decreased for the third consecutive month at the fastest rate since Sep 2012. Hongbin Qu, Chief Economist, China and Co-Head of Asian Economic Research at HSBC, finds weakening manufacturing because of declining orders and increasing inventories with weak lending because of the credit squeeze (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/43d33bc53a2142e8b5c3dde180f3b9d4). Table CNY provides the country data table for China.
Table CNY, China, Economic Indicators
| Price Indexes for Industry | Jun 12-month ∆%: minus 2.7 Jun month ∆%: -0.6 |
| Consumer Price Index | Jun month ∆%: 0.0 Jun 12 months ∆%: 2.7 |
| Value Added of Industry | Jun month ∆%: 0.68 Jan-Jun 2013/Jan-Jun 2012 ∆%: 9.3 |
| GDP Growth Rate | Year IIQ2013 ∆%: 7.5 |
| Investment in Fixed Assets | Jun month ∆%: 1.51 Total Jan-Jun 2013 ∆%: 20.1 Real estate development: 20.3 |
| Retail Sales | Jun month ∆%: 1.26 Jan-Jun ∆%: 12.7 |
| Trade Balance | Jun balance $27.13 billion Cumulative Jun: $108.55 billion |
Links to blog comments in Table CNY:
7/21/2013 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html
7/14/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/recovery-without-hiring-tapering.html
VD Euro Area. Table VD-EUR provides yearly growth rates of the combined GDP of the members of the European Monetary Union (EMU) or euro area since 1996. Growth was very strong at 3.2 percent in 2006 and 3.0 percent in 2007. The global recession had strong impact with growth of only 0.4 percent in 2008 and decline of 4.4 percent in 2009. Recovery was at lower growth rates of 2.0 percent in 2010 and 1.5 percent in 2011. EUROSTAT forecasts growth of GDP of the euro area of minus 0.6 percent in 2012 and minus 0.4 percent in 2013 but 1.2 percent in 2014.
Table VD-EUR, Euro Area, Yearly Percentage Change of Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices, Unemployment and GDP ∆%
| Year | HICP ∆% | Unemployment | GDP ∆% |
| 1999 | 1.2 | 9.6 | 2.9 |
| 2000 | 2.2 | 8.7 | 3.8 |
| 2001 | 2.4 | 8.1 | 2.0 |
| 2002 | 2.3 | 8.5 | 0.9 |
| 2003 | 2.1 | 9.0 | 0.7 |
| 2004 | 2.2 | 9.3 | 2.2 |
| 2005 | 2.2 | 9.2 | 1.7 |
| 2006 | 2.2 | 8.5 | 3.2 |
| 2007 | 2.1 | 7.6 | 3.0 |
| 2008 | 3.3 | 7.6 | 0.4 |
| 2009 | 0.3 | 9.6 | -4.4 |
| 2010 | 1.6 | 10.1 | 2.0 |
| 2011 | 2.7 | 10.2 | 1.5 |
| 2012* | 2.5 | 11.4 | -0.6 |
| 2013* | -0.4 | ||
| 2014* | 1.2 |
*EUROSTAT forecast Source: EUROSTAT http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/eurostat/home/
http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/statistics/search_database
The GDP of the euro area in 2011 in current US dollars in the dataset of the World Economic Outlook (WEO) of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) is $13,114.4 billion (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/02/weodata/index.aspx). The sum of the GDP of France is $2778.1 billion with the GDP of Germany of $3607.4 billion, Italy of $2198.7 billion and Spain $1479.6 billion is $10,063.8 billion or 76.7 percent of total euro area GDP. The four largest economies account for slightly more than three quarters of economic activity of the euro area. Table VD-EUR1 is constructed with the dataset of EUROSTAT, providing growth rates of the euro area as a whole and of the largest four economies of Germany, France, Italy and Spain annually from 1996 to 2011 with the estimate of 2012 and forecasts for 2013 and 2014 by EUROSTAT. The impact of the global recession on the overall euro area economy and on the four largest economies was quite strong. There was sharp contraction in 2009 and growth rates have not rebounded to earlier growth with exception of Germany in 2010 and 2011.
Table VD-EUR1, Euro Area, Real GDP Growth Rate, ∆%
| Euro Area | Germany | France | Italy | Spain | |
| 2014* | 1.2 | 1.8 | 1.1 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| 2013* | -0.4 | 0.4 | -0.1 | -1.3 | -1.5 |
| 2012 | -0.6 | 0.7 | 0.0* | -2.4 | -1.4* |
| 2011 | 1.5 | 3.0 | 2.0 | 0.4 | 0.4 |
| 2010 | 2.0 | 4.2 | 1.7 | 1.7 | -0.3 |
| 2009 | -4.4 | -5.1 | -3.1 | -5.5 | -3.7 |
| 2008 | 0.4 | 1.1 | -0.1 | -1.2 | 0.9 |
| 2007 | 3.0 | 3.3 | 2.3 | 1.7 | 3.5 |
| 2006 | 3.2 | 3.7 | 2.5 | 2.2 | 4.1 |
| 2005 | 1.7 | 0.7 | 1.8 | 0.9 | 3.6 |
| 2004 | 2.2 | 1.2 | 2.5 | 1.7 | 3.3 |
| 2003 | 0.7 | -0.4 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 3.1 |
| 2002 | 0.9 | 0.0 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 2.7 |
| 2001 | 2.0 | 1.5 | 1.8 | 1.9 | 3.7 |
| 2000 | 3.8 | 3.1 | 3.7 | 3.7 | 5.0 |
| 1999 | 2.9 | 1.9 | 3.3 | 1.5 | 4.7 |
| 1998 | 2.8 | 1.9 | 3.4 | 1.4 | 4.5 |
| 1997 | 2.6 | 1.7 | 2.2 | 1.9 | 3.9 |
| 1996 | 1.5 | 0.8 | 1.1 | 1.1 | 2.5 |
Source: EUROSTAT http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/eurostat/home/
The Flash Eurozone PMI Composite Output Index of the Markit Flash Eurozone PMI®, combining activity in manufacturing and services, increased from 48.7 in Jun to 50.4 in Jul, interrupting seventeen consecutive contractions with the highest reading in eighteen months. The respondents indicated the highest growth of output since Jun 2011. Chris Williamson, Chief Economist at Markit, finds that the Markit Flash Eurozone PMI index suggests that the euro area could move out of contraction in IIIQ2013 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/b9f7cd408c63428ca6cab343f4dbed5d). The Markit Eurozone PMI® Composite Output Index, combining services and manufacturing activity with close association with GDP, increased from 47.7 in May to 48.7 in Jun with aggregate output declining during 17 consecutive months (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/609476644add42bcb8c486547e55cf4d). Chris Williamson, Chief Economist at Markit, finds that the data are consistent GDP falling in IIQ2012 at 0.2 percent (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/609476644add42bcb8c486547e55cf4d). The Markit Eurozone Services Business Activity Index increased from 47.2 in May to 48.3 in Jun, indicating contraction (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/609476644add42bcb8c486547e55cf4d). The Markit Eurozone Manufacturing PMI® increased marginally to 48.8 in Jun from 48.3 in May, which indicates contraction for the twenty-third consecutive month since Aug 2011 but at the highest reading in 16 months (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/2bc1f71d2a9f427183cd528a3ed7832a). New orders fell at the slowest rate since Jun 2011 with marginal decline in export orders and lower rate of decline internal orders. Chris Williamson, Chief Economist at Markit, finds the survey data consistent with growth in IIIQ2013 if the trend of improvement continues (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/2bc1f71d2a9f427183cd528a3ed7832a). Table EUR provides the data table for the euro area.
Table EUR, Euro Area Economic Indicators
| GDP | IQ2013 ∆% -0.3; IQ2013/IQ2012 ∆% -1.1 Blog 7/7/13 |
| Unemployment | Jun 2013: 12.1% unemployment rate May 2013: 19.266 million unemployed Blog 8/4/13 |
| HICP | Jun month ∆%: 0.1 12 months Apr ∆%: 1.6 |
| Producer Prices | Euro Zone industrial producer prices May ∆%: -0.3 |
| Industrial Production | May month ∆%: -0.3; May 12 months ∆%: -1.3 |
| Retail Sales | May month ∆%: 1.0 |
| Confidence and Economic Sentiment Indicator | Sentiment 92.5 Jul 2013 Consumer minus 17.4 Jul 2013 Blog 8/4/13 |
| Trade | Jan-May 2013/Jan-May 2012 Exports ∆%: 2.5 May 2013 12-month Exports ∆% -0.1 Imports ∆% -5.7 |
Links to blog comments in Table EUR:
7/21/2013 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html
7/14/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/recovery-without-hiring-tapering.html
7/7/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/twenty-nine-million-unemployed-or.html
6/23/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/paring-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html
EUROSTAT estimates the rate of unemployment in the euro area at 12.1 percent in Jun 2013, as shown in Table VD-1. The number of unemployed in Jun 2013 was 19.266 million, which was 1.129 million higher than 18.137 million in Jun 2012. The rate of unemployment jumped from 11.4 percent in Jun 2012 to 12.1 percent in Jun 2013.
Table VD-1, Euro Area, Unemployment Rate and Number of Unemployed, % and Millions, SA
| Unemployment Rate % | Number Unemployed | |
| Jun 2013 | 12.1 | 19.266 |
| May | 12.1 | 19.290 |
| Apr | 12.1 | 19.240 |
| Mar | 12.1 | 19.163 |
| Feb | 12.0 | 19.137 |
| Jan | 12.0 | 19.098 |
| Dec 2012 | 11.9 | 18.855 |
| Nov | 11.8 | 18.794 |
| Oct | 11.7 | 18.692 |
| Sep | 11.6 | 18.480 |
| Aug | 11.5 | 18.303 |
| Jul | 11.5 | 18.231 |
| Jun | 11.4 | 18.137 |
| May | 11.3 | 17.890 |
| Apr | 11.2 | 17.746 |
| Mar | 11.0 | 17.466 |
| Feb | 10.9 | 17.239 |
| Jan | 10.8 | 17.033 |
| Dec 2011 | 10.7 | 16.922 |
| Nov | 10.6 | 16.814 |
| Oct | 10.4 | 16.523 |
| Sep | 10.3 | 16.342 |
| Aug | 10.2 | 16.088 |
| Jul | 10.1 | 15.943 |
| Jun | 10.0 | 15.728 |
| May | 9.9 | 15.667 |
| Apr | 9.9 | 15.518 |
| Mar | 9.9 | 15.585 |
| Feb | 9.9 | 15.607 |
| Jan | 10.0 | 15.689 |
| Dec 2010 | 10.1 | 15.804 |
Source: EUROSTAT
http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/eurostat/home/
http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/statistics/search_database
Table VD-2 shows the disparity in rates of unemployment in the euro area with 12.1 percent for the region as a whole and 19.266 million unemployed but 5.4 percent in Germany and 2.297 million unemployed. At the other extreme is Spain with rate of unemployment of 26.3 percent and 5.959 million unemployed. The rate of unemployment of the European Union in Jun 2013 is 10.9 percent with 26.424 million unemployed.
Table VD-2, Unemployed and Unemployment Rate in Countries and Regions, Millions and %
| Jun 2013 | Unemployment Rate % | Unemployed Millions |
| Euro Zone | 12.1 | 19.266 |
| Germany | 5.4 | 2.297 |
| France | 11.0 | 3.246 |
| Netherlands | 6.8 | 0.613 |
| Finland | 8.0 | 0.215 |
| Portugal | 17.4 | 0.923 |
| Ireland | 13.5 | 0.289 |
| Italy | 12.1 | 3.089 |
| Greece | NA | NA |
| Spain | 26.3 | 5.959 |
| Belgium | 8.7 | 0.429 |
| European Union | 10.9 | 26.424 |
Source: EUROSTAT http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/eurostat/home/
http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/statistics/search_database
Chart VD-1 of EUROSTAT illustrates the wide difference in rates of unemployment in countries and regions.
Chart VD-1, Unemployment Rate in Various Countries and Regions
Source: EUROSTAT
http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/eurostat/home/
The Economic Sentiment Indicator of the European Economic Commission, Economic and Financial Affairs, provides correlation with the economic cycle since 1990, capturing all three recessions in the period and even the threat of recession from 1994 to 1995. The latest chart of this index accessible in the link in parenthesis shows trend of decline in 2011 and 2012 that has punctured the historical average of 100 and resumed downward trend in 2012 followed by recovery but at a relatively low level (http://ec.europa.eu/economy_finance/db_indicators/surveys/index_en.htm). This deterioration is shown in Table VD-3 with the index increasing from 87.3 in Aug 2012 to 92.5 in Jul 2013. There is stagnating trend with the index still above the minimum value of 70.0 reached in Mar 2009 but still below the average of 100.
Table VD-3, Euro Area, Indicators of Confidence and Economic Sentiment SA
| ESI | IND | SERV | CON | RET | CONS | |
| Historical Average | 100.0 | -7.0 | 9.5 | -13.3 | -9.3 | -18.0 |
| Maximum | 118.1 | 7.9 | 35.3 | 2.4 | 5.2 | 6.0 |
| Minimum | 70.0 | -38.1 | -26.1 | -34.3 | -24.9 | -46.2 |
| Jul 2013 | 92.5 | -10.6 | -7.8 | -17.4 | -13.7 | -32.6 |
| Jun | 91.3 | -11.2 | -9.6 | -18.8 | -14.6 | -31.5 |
| May | 89.5 | -13.0 | -9.3 | -21.8 | -16.7 | -33.0 |
| Apr | 88.6 | -13.7 | -11.1 | -22.2 | -18.4 | -31.1 |
| Mar | 90.1 | -12.2 | -7.1 | -23.5 | -17.1 | -29.9 |
| Feb | 90.5 | -11.1 | -8.5 | -23.6 | -16.1 | -29.2 |
| Jan | 89.7 | -13.3 | -7.9 | -23.9 | -15.5 | -28.1 |
| Dec 2012 | 88.0 | -13.8 | -9.8 | -26.3 | -15.9 | -33.0 |
| Nov | 86.9 | -14.7 | -11.5 | -26.7 | -14.8 | -33.8 |
| Oct | 85.4 | -17.8 | -12.0 | -25.5 | -17.3 | -31.3 |
| Sep | 86.0 | -15.5 | -12.5 | -25.7 | -18.4 | -30.0 |
| Aug | 87.3 | -14.8 | -10.5 | -24.4 | -17.1 | -31.2 |
ESI: Economic Sentiment Index; IND: Industry; SERV: Services; CON: Consumer; RET: Retail Trade; CONS: Construction
Source: European Commission Services
http://ec.europa.eu/economy_finance/db_indicators/surveys/index_en.htm
VE Germany. Table VE-DE provides yearly growth rates of the German economy from 1992 to 2012, price adjusted chain-linked and price and calendar-adjusted chain-linked. Germany’s GDP fell 5.1 percent in 2009 after growing below trend at 1.1 percent in 2008. Recovery has been robust in contrast with other advanced economies. The German economy grew at 4.2 percent in 2010, 3.0 percent in 2011 and 0.7 percent in 2012.
The Federal Statistical Agency of Germany analyzes the fall and recovery of the German economy (http://www.destatis.de/jetspeed/portal/cms/Sites/destatis/Internet/EN/Content/Statistics/VolkswirtschaftlicheGesamtrechnungen/Inlandsprodukt/Aktuell,templateId=renderPrint.psml):
“The German economy again grew strongly in 2011. The price-adjusted gross domestic product (GDP) increased by 3.0% compared with the previous year. Accordingly, the catching-up process of the German economy continued during the second year after the economic crisis. In the course of 2011, the price-adjusted GDP again exceeded its pre-crisis level. The economic recovery occurred mainly in the first half of 2011. In 2009, Germany experienced the most serious post-war recession, when GDP suffered a historic decline of 5.1%. The year 2010 was characterised by a rapid economic recovery (+3.7%).”
Table VE-DE, Germany, GDP Year ∆%
| Price Adjusted Chain-Linked | Price- and Calendar-Adjusted Chain Linked | |
| 2012 | 0.7 | 0.9 |
| 2011 | 3.0 | 3.1 |
| 2010 | 4.2 | 4.0 |
| 2009 | -5.1 | -5.1 |
| 2008 | 1.1 | 0.8 |
| 2007 | 3.3 | 3.4 |
| 2006 | 3.7 | 3.9 |
| 2005 | 0.7 | 0.8 |
| 2004 | 1.2 | 0.7 |
| 2003 | -0.4 | -0.4 |
| 2002 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 2001 | 1.5 | 1.6 |
| 2000 | 3.1 | 3.3 |
| 1999 | 1.9 | 1.8 |
| 1998 | 1.9 | 1.7 |
| 1997 | 1.7 | 1.8 |
| 1996 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| 1995 | 1.7 | 1.8 |
| 1994 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| 1993 | -1.0 | -1.0 |
| 1992 | 1.9 | 1.5 |
Source: Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland (Destatis) https://www.destatis.de/EN/PressServices/Press/pr/2013/02/PE13_066_811.html;jsessionid=59DE7E440F9F7393B12C16FDA63BEB66.cae1
The Flash Germany Composite Output Index of the Markit Flash Germany PMI®, combining manufacturing and services, increased from 50.4 in Jun to 52.8 in Jul, for the highest reading in five months with stronger improvement in services at 52.4 in Jul while manufacturing moved into expansion at 50.3 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/813702faa006423d91c19091988c8c89). New export orders for manufacturing decreased for the fifth consecutive month with internal activities compensating for the weakness in markets in China and the euro area. Tim Moore, Senior Economist at Markit, finds improvement in manufacturing and services in the beginning of IIIQ2013 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/813702faa006423d91c19091988c8c89). The Markit Germany Composite Output Index of the Markit Germany Services PMI®, combining manufacturing and services with close association with Germany’s GDP, increased from 50.2 in May to 50.4 in Jun (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/fff41c347a20425bb0c0e63f4a8fe8f6). Tim Moore, Senior Economist at Markit and author of the report, finds risks of standstill in the economy of Germany with minor increases in output and concerned outlook (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/fff41c347a20425bb0c0e63f4a8fe8f6). The Germany Services Business Activity Index increased from 49.7 in May to 50.4 in Jun (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/fff41c347a20425bb0c0e63f4a8fe8f6). The Markit/BME Germany Purchasing Managers’ Index® (PMI®), showing close association with Germany’s manufacturing conditions, decreased from 49.4 in May to 48.6 in Jun, in very moderate contraction territory below 50.0 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/1923f6df3e784218afce4dde78ee6c2f). New export orders fell at the fastest rate in 2013 with declines in Asia and Europe. Tim Moore, Senior Economist at Markit and author of the report, finds restrain from weakness in markets, especially in exports, even with reduction of sales prices at the fastest rate in more than three years (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/1923f6df3e784218afce4dde78ee6c2f).Table DE provides the country data table for Germany.
Table DE, Germany, Economic Indicators
| GDP | IQ2013 0.1 ∆%; I/Q2013/IQ2012 ∆% -1.4 2012/2011: 0.7% GDP ∆% 1992-2012 Blog 8/26/12 5/27/12 11/25/12 2/24/13 5/19/13 5/26/13 |
| Consumer Price Index | Jun month NSA ∆%: 0.1 |
| Producer Price Index | Jun month ∆%: 0.0 CSA, 0.3 |
| Industrial Production | MFG Apr month CSA ∆%: minus 0.7 |
| Machine Orders | MFG May month ∆%: -1.3 |
| Retail Sales | Jun Month ∆% -1.5 12-Month ∆% -2.9 Blog 8/4/13 |
| Employment Report | Unemployment Rate SA Jun 5.4% |
| Trade Balance | Exports May 12-month NSA ∆%: minus 4.8 Blog 7/14/13 |
Links to blog comments in Table DE:
7/21/2013 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html
7/14/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/recovery-without-hiring-tapering.html
7/7/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/twenty-nine-million-unemployed-or.html
http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/twenty-nine-million-unemployed-or.html
5/26/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/05/united-states-commercial-banks-assets.html
Germany’s labor market continues to show strength not found in most of the advanced economies, as shown in Table VE-1. The number unemployed, not seasonally adjusted, increased from 2.22 million in Jun 2012 to 2.32 million in Jun 2013, or 4.5 percent, while the unemployment rate increased from 5.3 percent in Jun 2012 to 5.5 percent in Jun 2013. The number of persons in employment, not seasonally adjusted, increased from 39.84 million in Jun 2012 to 40.20 million in Jun 2013, or 0.9 percent, while the employment rate increased from 63.2 percent in Jun 2012 to 63.9 percent in Jun 2013. The number unemployed, seasonally adjusted, stabilized from 2.30 million in May 2013 to 2.30 million in Jun 2013, while the unemployment rate stabilized from 5.4 percent in May 2013 to 5.4 percent in Jun 2013. The number of persons in employment, seasonally adjusted, increased from 40.22 million in May 2013 to 40.25 million in Jun 2013, or 0.1 percent.
Table VE-1, Germany, Unemployment Labor Force Survey
| Jun 2013 | May 2013 | Jun 2012 | |
| NSA | |||
| Number | 2.32 ∆% Jun 2013 /May 2013: 3.1 ∆% Jun 2013/Jun 2012: +4.5 | 2.25 | 2.22 |
| % Rate Unemployed | 5.5 | 5.3 | 5.3 |
| Persons in Employment Millions | 40.20 ∆% Jun 2013/May 2013: -0.1 ∆% Jun 2013/Jun 2012: 0.9 | 40.25 | 39.84 |
| Employment Rate | 63.9 | 64.0 | 63.2 |
| SA | |||
| Number | 2.30 ∆% Jun 2013/May 2013: 0.0 ∆% Jun 2013/Jun 2012: –0.4 | 2.30 | 2.31 |
| % Rate Unemployed | 5.4 | 5.4 | 5.5 |
| Persons in Employment Millions | 40.25 ∆% Jun 2013/May 2013: 0.1 ∆% Jun 2013/Jun 2012: 0.7 | 40.22 | 39.96 |
NSA: not seasonally adjusted; SA: seasonally adjusted
Source: Statistisches Bundesamt https://www.destatis.de/EN/PressServices/Press/pr/2013/07/PE13_256_132.html
The unemployment rate in Germany as percent of the labor force in Table VE-2 stood at 6.5 percent in Sep, Oct and Nov 2012, increasing to 6.7 percent in Dec 2012, 7.4 percent in Jan 2013, 7.3 in Feb 2013 and 7.1 percent in Apr 2013. The unemployment rate fell to 6.8 percent in May 2013 and 6.6 percent in Jun 2013 and rose to 6.8 percent in Jul 2013. The rate is much lower than 11.1 percent in 2005 and 9.6 percent in 2006.
Table VE-2, Germany, Unemployment Rate in Percent of Labor Force
| Percent of Labor Force | |
| Jul 2013 | 6.8 |
| Jun | 6.6 |
| May | 6.8 |
| Apr | 7.1 |
| Feb | 7.3 |
| Jan | 7.4 |
| Dec 2012 | 6.7 |
| Nov | 6.5 |
| Oct | 6.5 |
| Sep | 6.5 |
| Aug | 6.8 |
| Jul | 6.8 |
| Jun | 6.6 |
| May | 6.7 |
| Apr | 7.0 |
| Mar | 7.2 |
| Feb | 7.4 |
| Jan | 7.3 |
| Dec 2011 | 6.6 |
| Nov | 6.4 |
| Oct | 6.5 |
| Sep | 6.6 |
| Aug | 7.0 |
| Jul | 7.0 |
| Jun | 6.9 |
| May | 7.0 |
| Apr | 7.3 |
| Mar | 7.6 |
| Feb | 7.9 |
| Jan | 7.9 |
| Dec 2010 | 7.1 |
| Dec 2009 | 7.8 |
| Dec 2008 | 7.4 |
| Dec 2007 | 8.1 |
| Dec 2006 | 9.6 |
| Dec 2005 | 11.1 |
Source: Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
Chart VE-1 of Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland, or Federal Statistical Office of Germany, shows the long-term decline of the rate of unemployment in Germany from more than 12 percent in early 2005 to 6.6 percent in Dec 2011, 6.6 percent in Jun 2012, 6.8 percent in Jul and Aug 2012 and 6.5 percent from Sep to Nov 2012, increasing to 6.7 percent in Dec 2012, 6.8 percent in Apr 2013 and 6.6 percent in May 2013. The unemployment rate rose slightly to 6.8 percent in Jun 2013.
Chart VE-1, Germany, Unemployment Rate, Unadjusted, Percent
Source: Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
Retail sales in Germany adjusted for inflation are provided in Table VE-3. There have been sharp fluctuations in monthly and 12 months percentage changes. In Jun 2013, retail sales fell 1.5 percent and 2.9 percent in 12 months. Retail sales increased 0.8 percent in May 2013 and increased 0.7 percent in 12 months. Retail sales rebounded in Jan 2013 with monthly increase of 2.9 percent and 3.3 percent in 12 months.
Table VE-3, Retail Sales in Germany Adjusted for Inflation
| 12-Month ∆% NSA | Month ∆% SA and Calendar Adjusted | |
| Jun 2013 | -2.9 | -1.5 |
| May | 0.8 | 0.7 |
| Apr | 3.4 | 0.3 |
| Mar | -2.3 | -0.2 |
| Feb | -2.6 | -0.5 |
| Jan | 2.9 | 3.3 |
| Dec 2012 | -3.3 | -2.1 |
| Nov | 0.5 | 1.1 |
| Oct | 1.6 | -0.7 |
| Sep | -3.2 | 0.0 |
| Aug | -0.2 | 0.1 |
| Jul | -0.8 | -1.1 |
| Jun | 4.8 | 0.4 |
| May | -0.5 | 0.2 |
| Apr | -4.5 | -0.3 |
| Mar | 4.3 | 0.7 |
| Feb | 2.6 | 0.8 |
| Jan | 2.0 | -1.7 |
| Dec 2011 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
| Nov | 0.9 | -0.6 |
| Oct | -0.4 | 0.3 |
| Sep | 1.2 | 0.2 |
| Aug | 3.4 | -0.5 |
| Jul | -2.4 | 0.5 |
| Jun | -2.0 | 2.0 |
| May | 4.5 | -1.6 |
| Apr | 4.8 | 1.0 |
| Mar | -2.9 | -2.7 |
| Feb | 3.0 | 1.2 |
| Jan | 3.3 | 0.9 |
| Dec 2010 | -0.2 | 0.3 |
| Dec 2009 | -2.2 | |
| Dec 2008 | 3.4 | |
| Dec 2007 | -6.2 | |
| Dec 2006 | 1.3 |
Source: Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland (Destatis)
https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
Chart VE-2 of the Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland, Federal Statistical Office of Germany, shows retail sales at constant prices from 2009 to 2013. There appear to be fluctuations without trend.
Chart VE-2, Germany, Turnover in Retail Trade at Constant Prices 2005=100
Source: Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland (Destatis), Federal Statistical Office of Germany
https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
Chart VE-3 of the Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland, Federal Statistical Office of Germany, shows retail sales at current prices from 2005 to 2013. There are also sharp fluctuations but without trend.
Chart VE-3, Germany, Turnover in Retail Sales at Current Prices, Original Values, 2005=100
Source: Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland (Destatis), Federal Statistical Office of Germany
https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
VF France. Table VF-FR provides growth rates of GDP of France with the estimates of Institut National de la Statistique et des Études Économiques (INSEE). The long-term rate of GDP growth of France from IVQ1949 to IVQ2012 is quite high at 3.2 percent. France’s growth rates were quite high in the four decades of the 1950s, 1960, 1970s and 1980s with an average growth rate of 4.0 percent compounding the average rates in the decades and discounting to one decade. The growth impulse diminished with 1.9 percent in the 1990s and 1.7 percent from 2000 to 2007. The average growth rate from 2000 to 2012, using fourth quarter data, is 1.0 percent because of the sharp impact of the global recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. The growth rate from 2000 to 2012 is 1.0 percent. Cobet and Wilson (2002) provide estimates of output per hour and unit labor costs in national currency and US dollars for the US, Japan and Germany from 1950 to 2000 (see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 137-44). The average yearly rate of productivity change from 1950 to 2000 was 2.9 percent in the US, 6.3 percent for Japan and 4.7 percent for Germany while unit labor costs in USD increased at 2.6 percent in the US, 4.7 percent in Japan and 4.3 percent in Germany. From 1995 to 2000, output per hour increased at the average yearly rate of 4.6 percent in the US, 3.9 percent in Japan and 2.6 percent in Germany while unit labor costs in US fell at minus 0.7 percent in the US, 4.3 percent in Japan and 7.5 percent in Germany. There was increase in productivity growth in the G7 in Japan and France in the second half of the 1990s but significantly lower than the acceleration of 1.3 percentage points per year in the US. Lucas (2011May) compares growth of the G7 economies (US, UK, Japan, Germany, France, Italy and Canada) and Spain, finding that catch-up growth with earlier rates for the US and UK stalled in the 1970s.
Table VF-FR, France, Average Growth Rates of GDP Fourth Quarter, 1949-2012
| Period | Average ∆% |
| 1949-2012 | 3.2 |
| 2000-2012 | 1.0 |
| 2000-2011 | 1.1 |
| 2000-2007 | 1.7 |
| 1990-1999 | 1.9 |
| 1980-1989 | 2.5 |
| 1970-1979 | 3.8 |
| 1960-1969 | 5.7 |
| 1950-1959 | 4.2 |
Source: Institut National de la Statistique et des Études Économiques http://www.insee.fr/en/themes/info-rapide.asp?id=28&date=20130626
The Markit Flash France Composite Output Index increased from 47.4 in Jun to 48.8 in Jul for the highest reading in seventeen months (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/ff874f59bf1442d3a8c96ef0a33d8ac0). Jack Kennedy, Senior Economist at Markit and author of the report, finds that the data suggest improvement with manufacturing suggestin increase in output while decline of services slowed (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/ff874f59bf1442d3a8c96ef0a33d8ac0). The Markit France Composite Output Index, combining services and manufacturing with close association with French GDP, increased from 44.6 in May to 47.2 in Jun, indicating contraction of private sector activity at the slowest rate of deterioration in 2013 and the highest reading in ten months (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/a1f570072f9a426a9ec90e289936095c). Jack Kennedy, Senior Economist at Markit and author of the France Services PMI®, finds that composite data for manufacturing and services indicate movement toward stability away from sharper contraction in IQ2013 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/a1f570072f9a426a9ec90e289936095c). The Markit France Services Activity index increased from 44.3 in May to 47.2 in Jun for the highest reading in ten months (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/a1f570072f9a426a9ec90e289936095c). The Markit France Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index® increased to 48.4 in Jun from 46.4 in May, for the highest reading in sixteen consecutive months below the neutral level of 50.0 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/4951772002d4429881c48fda4cafcae5). Jack Kennedy, Senior Economist at Markit and author of the France Manufacturing PMI®, finds slower decline in manufacturing but that the current period of 16 consecutive months of deterioration is the longest since beginning of the survey in 1998 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/4951772002d4429881c48fda4cafcae5). Table FR provides the country data table for France.
Table FR, France, Economic Indicators
| CPI | Jun month ∆% 0.2 |
| PPI | Jun month ∆%: -0.2 Blog 8/4/13 |
| GDP Growth | IQ2013/IQ2012 ∆%: -0.4 |
| Industrial Production | May ∆%: |
| Consumer Spending | Manufactured Goods |
| Employment | Unemployment Rate: 10.4% |
| Trade Balance | May Exports ∆%: month -4.3, 12 months -4.4 May Imports ∆%: month -0.2, 12 months -2.2 Blog 7/7/13 |
| Confidence Indicators | Historical averages 100 Jul Mfg Business Climate 95 Blog 7/28/13 |
Links to blog comments in Table FR:
7/28/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/duration-dumping-steepening-yield-curve.html
7/14/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/recovery-without-hiring-tapering.html
7/7/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/twenty-nine-million-unemployed-or.html
6/30/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html
6/16/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/recovery-without-hiring-seven-million.html
6/9/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/twenty-eight-million-unemployed-or.html
5/19/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/05/word-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html
VG Italy. Table VG-IT provides percentage changes in a quarter relative to the same quarter a year earlier of Italy’s expenditure components in chained volume measures. GDP has been declining at sharper rates from minus 0.5 percent in IVQ2011 to minus 2.8 percent in IVQ2012 and minus 2.4 percent in IQ2013. The aggregate demand components of consumption and gross fixed capital formation (GFCF) have been declining at faster rates.
Table VG-IT, Italy, GDP and Expenditure Components, Chained Volume Measures, Quarter ∆% on Same Quarter Year Earlier
| GDP | Imports | Consumption | GFCF | Exports | |
| 2013 | |||||
| IQ | -2.4 | -5.2 | -2.7 | -7.5 | -0.2 |
| 2012 | |||||
| IVQ | -2.8 | -6.7 | -4.2 | -7.8 | 1.8 |
| IIIQ | -2.6 | -8.1 | -4.3 | -8.2 | 2.5 |
| IIQ | -2.5 | -7.5 | -3.9 | -8.3 | 2.5 |
| IQ | -1.7 | -8.9 | -3.3 | -7.6 | 2.1 |
| 2011 | |||||
| IVQ | -0.5 | -6.9 | -1.8 | -3.3 | 3.1 |
| IIIQ | 0.3 | 0.1 | -0.7 | -2.1 | 5.6 |
| IIQ | 0.9 | 3.1 | 0.6 | -0.6 | 7.0 |
| IQ | 1.3 | 8.8 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 10.9 |
| 2010 | |||||
| IVQ | 2.0 | 15.3 | 1.1 | 0.8 | 13.2 |
| IIIQ | 1.8 | 13.2 | 1.3 | 2.4 | 12.0 |
| IIQ | 1.9 | 13.5 | 0.8 | 1.1 | 12.0 |
| IQ | 1.1 | 7.2 | 0.8 | -2.0 | 7.3 |
| 2009 | |||||
| IVQ | -3.4 | -6.4 | 0.2 | -7.8 | -9.3 |
| IIIQ | -4.9 | -12.2 | -0.8 | -12.6 | -16.4 |
| IIQ | -6.6 | -17.9 | -1.5 | -13.6 | -21.4 |
| IQ | -7.0 | -17.2 | -1.7 | -12.6 | -22.8 |
| 2008 | |||||
| IVQ | -3.0 | -8.2 | -0.9 | -8.3 | -10.3 |
| IIIQ | -1.9 | -5.0 | -0.8 | -4.5 | -3.9 |
| IIQ | -0.2 | -0.1 | -0.3 | -1.5 | 0.4 |
| IQ | 0.5 | 1.7 | 0.1 | -1.0 | 2.9 |
GFCF: Gross Fixed Capital Formation
Source: Istituto Nazionale di Statistica http://www.istat.it/it/archivio/92338
The Markit/ADACI Business Activity Index decreased from 46.5 in May to 45.8 in Jun, indicating contraction of output of Italy’s services sector for 25 consecutive months of decline since Jun 2011 with contraction sharp relative to the history of the index (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/5bd5c06b053d42a3a8c527b6d68f4a9b). Phil Smith, economist at Markit and author of the Italy Services PMI®, finds acceleration of contraction in May and Jun (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/5bd5c06b053d42a3a8c527b6d68f4a9b). The Markit/ADACI Purchasing Managers’ Index® (PMI®), increased from 47.3 in May to 49.1 in Jun for 23 consecutive months of contraction of Italy’s manufacturing below 50.0 with the Jun at the highest in five months, indicating only marginal deterioration of overall business while output increased for the first time in 23 months (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/675369f0f11f4232a9cd0a1dc5c63c8f). Phil Smith, economist at Markit and author of the Italian Manufacturing PMI®, finds that manufacturing has been improving by obtaining foreign orders with internal demand still weak (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/675369f0f11f4232a9cd0a1dc5c63c8f). Table IT provides the country data table for Italy.
Table IT, Italy, Economic Indicators
| Consumer Price Index | Jul month ∆%: 0.0 |
| Producer Price Index | Jun month ∆%: 0.4 Blog 8/4/13 |
| GDP Growth | IQ2013/IVQ2012 SA ∆%: minus 0.6 |
| Labor Report | Apr 2013 Participation rate 63.8% Employment ratio 56.0% Unemployment rate 12.0% Blog 6/2/13 |
| Industrial Production | May month ∆%: 0.1 |
| Retail Sales | Apr month ∆%: -0.1 Apr 12-month ∆%: -2.9 Blog 6/30/13 |
| Business Confidence | Mfg Jul 91.7, Mar 89.0 Construction Jul 76.5, Mar 79.4 Blog 8/4/13 |
| Trade Balance | Balance May SA €3155 million versus Apr €2683 |
Links to blog comments in Table IT:
7/21/2013 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html
7/14/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/recovery-without-hiring-tapering.html
6/16/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/recovery-without-hiring-seven-million.html
6/2/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/06/mediocre-united-states-economic-growth.html
3/17/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/03/recovery-without-hiring-ten-million.html
Italy’s index of business confidence in manufacturing and construction is provided in Table VG-1. There has been stabilization of manufacturing confidence below the historical average of 100 from 89.0 in Mar 2013 to 91.7 in Jul 2013. Order books deteriorated to minus 43 in May 2013 but improved to minus 39 in Jun 2013 and minus 37 in Jul 2013. There is oscillation in construction with the index moving from 79.4 in Mar 2013 to 81.1 in May 2013, falling to 76.5 in Jun 2013.
Table VG-1, Italy, Index of Business Confidence in Manufacturing and Construction 2005=100
| Jul 2013 | Jun 2013 | May 2013 | Apr 2013 | Mar 2013 | |
| Mfg Confidence | 91.7 | 90.5 | 88.0 | 88.2 | 89.0 |
| Order Books | -37 | -39 | -43 | -45 | -43 |
| Stocks Finished Products | 0 | 1 | 1 | -1 | 0 |
| Production | 0 | -2 | -2 | -4 | -3 |
| Construction Confidence | 76.5 | 71.1 | 81.1 | 77.7 | 79.4 |
| Order Books | -52 | -56 | -49 | -52 | -53 |
| Employment | -20 | -27 | -13 | -17 | -13 |
Mfg: manufacturing
Source: Istituto Nazionale di Statistica
http://www.istat.it/it/archivio/96736
VH United Kingdom. Annual data in Table VH-UK show the strong impact of the global recession in the UK with decline of GDP of 5.2 percent in 2009 after dropping 0.8 percent in 2008. Recovery of 1.7 percent in 2010 is relatively low compared to annual growth rates in 2007 and earlier years. Growth was only 1.1 percent in 2011 and 0.2 percent in 2012.
Table VH-UK, UK, Gross Domestic Product, ∆%
| ∆% on Prior Year | |
| 1998 | 3.6 |
| 1999 | 2.9 |
| 2000 | 4.4 |
| 2001 | 2.2 |
| 2002 | 2.3 |
| 2003 | 3.9 |
| 2004 | 3.2 |
| 2005 | 3.2 |
| 2006 | 2.8 |
| 2007 | 3.4 |
| 2008 | -0.8 |
| 2009 | -5.2 |
| 2010 | 1.7 |
| 2011 | 1.1 |
| 2012 | 0.2 |
Source: UK Office for National Statistics http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/naa2/quarterly-national-accounts/q1-2013/index.html
The Business Activity Index of the Markit/CIPS UK Services PMI® increased from 54.9 in May to 56.9 in Jun, indicating increase in activity in every month since the beginning of 2013 and at the fastest rate since 27 months (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/d8b5be871614424e84c8dcd2e5573427). Chris Williamson, Chief Economist at Markit, finds continuing improvement in the UK’s economy that depending on Jun could result in growth of GDP of 0.5 percent in IIQ2013 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/d8b5be871614424e84c8dcd2e5573427). The Markit/CIPS UK Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index® (PMI®) increased from 51.5 in May to 52.5 in Jun, which is the highest rate of improvement in 25 months (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/c853fab910d9425083c5eee0326d3fe3). Rob Dobson, Senior Economist at Markit that compiles the Markit/CIPS Manufacturing PMI®, finds manufacturing improving at the highest rates since the beginning of 2011 with improving domestic demand and supporting foreign orders, suggesting growth of output of manufacturing by 0.5 percent in IIQ2013 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/Survey/PressRelease.mvc/c853fab910d9425083c5eee0326d3fe3). Table UK provides the economic indicators for the United Kingdom.
Table UK, UK Economic Indicators
| CPI | Jun month ∆%: -0.2 |
| Output/Input Prices | Output Prices: Jun 12-month NSA ∆%: 2.0; excluding food, petroleum ∆%: 1.0 |
| GDP Growth | IIQ2013 prior quarter ∆% 0.6; year earlier same quarter ∆%: 1.4 |
| Industrial Production | May 2013/May 2012 ∆%: Production Industries minus 2.3; Manufacturing minus 2.9 |
| Retail Sales | Jun month ∆%: 0.2 |
| Labor Market | Mar-May Unemployment Rate: 7.8%; Claimant Count 4.4%; Earnings Growth 1.7% |
| Trade Balance | Balance Apr minus ₤2579 million |
Links to blog comments in Table UK:
7/28/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/duration-dumping-steepening-yield-curve.html
7/21/2013 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/tapering-quantitative-easing-policy-and.html
7/14/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/07/recovery-without-hiring-tapering.html
5/26/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/05/united-states-commercial-banks-assets.html
4/28/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/04/mediocre-and-decelerating-united-states_28.html
03/31/13 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/04/mediocre-and-decelerating-united-states.html
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013

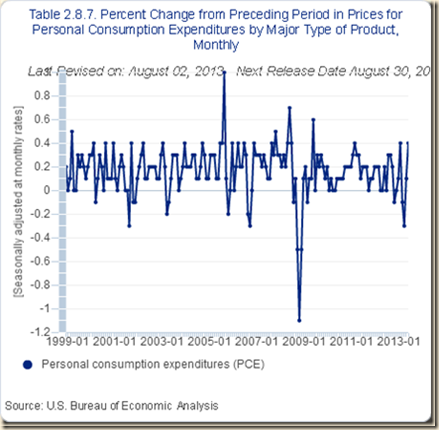


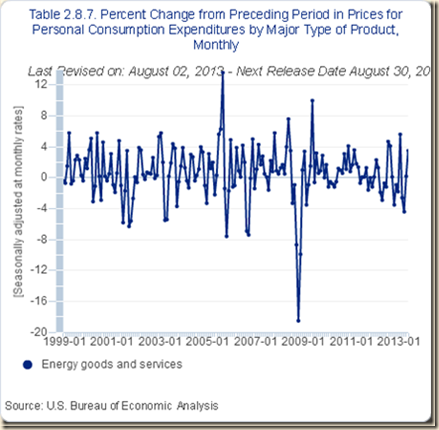
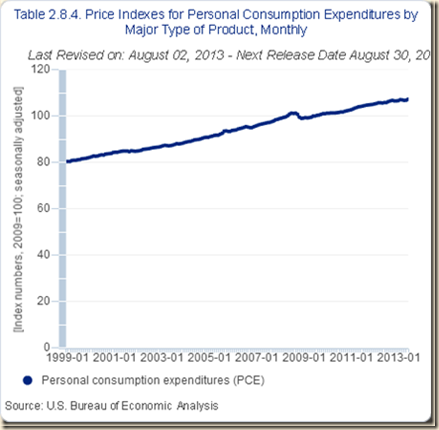


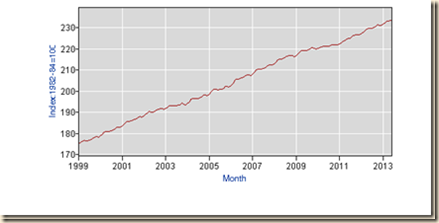






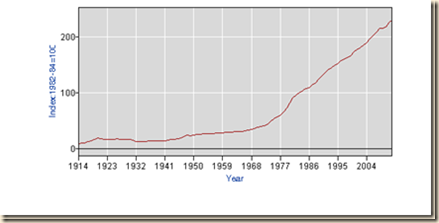








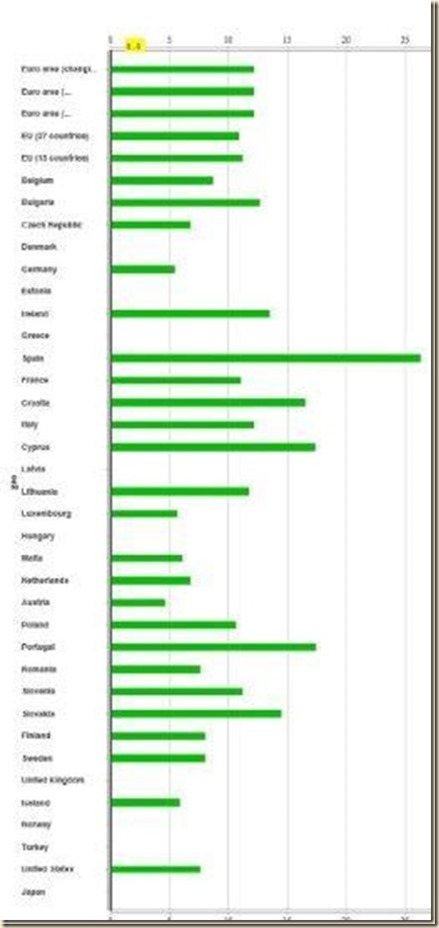
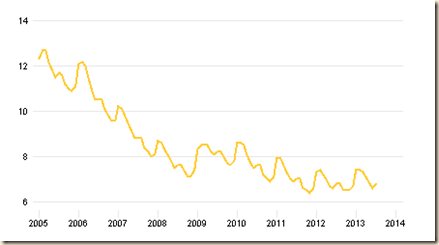


No comments:
Post a Comment