Fluctuating Financial Asset Valuations, Destruction of Household Nonfinancial Wealth with Stagnating Total Real Wealth, Unresolved US Balance of Payments Deficits and Fiscal Imbalance Threatening Risk Premium on Treasury Securities, Collapse of United States Dynamism of Income Growth and Employment Creation, United States Industrial Production, World Inflation Waves, World Cyclical Slow Growth and Global Recession Risk
Carlos M. Pelaez
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015
I World Inflation Waves
IA Appendix: Transmission of Unconventional Monetary Policy
IB1 Theory
IB2 Policy
IB3 Evidence
IB4 Unwinding Strategy
IC United States Inflation
IC Long-term US Inflation
ID Current US Inflation
IE Theory and Reality of Economic History, Cyclical Slow Growth Not Secular
II Destruction of Household Nonfinancial Wealth with Stagnating Total Real Wealth
IIA Unresolved US Balance of Payments Deficits and Fiscal Imbalance Threatening Risk Premium on Treasury Securities
IB Collapse of United States Dynamism of Income Growth and Employment Creation
IIB United States Industrial Production
III World Financial Turbulence
IIIA Financial Risks
IIIE Appendix Euro Zone Survival Risk
IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation
IV Global Inflation
V World Economic Slowdown
VA United States
VB Japan
VC China
VD Euro Area
VE Germany
VF France
VG Italy
VH United Kingdom
VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets
VII Economic Indicators
VIII Interest Rates
IX Conclusion
References
Appendixes
Appendix I The Great Inflation
IIIB Appendix on Safe Haven Currencies
IIIC Appendix on Fiscal Compact
IIID Appendix on European Central Bank Large Scale Lender of Last Resort
IIIG Appendix on Deficit Financing of Growth and the Debt Crisis
IIIGA Monetary Policy with Deficit Financing of Economic Growth
IIIGB Adjustment during the Debt Crisis of the 1980s
Table IV-1 shows the simultaneous occurrence of low growth, inflation and unemployment in advanced economies. US GDP fell at 0.7 percent in seasonally adjusted rate (SAAR) in IQ2015 and increased 2.7 percent in IQ2015 relative to IVQ2014 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/dollar-revaluation-squeezing-corporate.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/dollar-devaluation-and-carry-trade.html Table 8 in http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2015/pdf/gdp1q15_2nd.pdf). Japan’s GDP grew at the seasonally adjusted annual rate (SAAR) of 3.9 percent in IQ2015 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/volatility-of-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/interest-rate-policy-and-dollar.html). The UK grew at 0.3 percent in IQ2015 relative to IVQ2014 and GDP increased 2.4 percent in IQ2015 relative to IQ2014 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/dollar-devaluation-and-carry-trade.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/volatility-of-valuations-of-financial.html). The Euro Zone grew at 0.4 percent in IQ2015 and 1.0 percent in IQ2015 relative to IQ2014 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/volatility-of-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/fluctuating-valuations-of-financial.html). These are stagnating or “growth recession” rates, which are positive or about nil growth rates with some contractions that are insufficient to recover employment. The rates of unemployment are quite high: 5.5 percent in the US but 14.9 percent for unemployment/underemployment or job stress of 24.7 million (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/quite-high-equity-valuations-and.html), 3.3 percent for Japan (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/dollar-revaluation-squeezing-corporate.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/dollar-devaluation-and-carry-trade.html), 5.5 percent for the UK with high rates of unemployment for young people (Section VH and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/fluctuating-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/global-portfolio-reallocations-squeeze.html). Twelve-month rates of inflation have been quite high, even when some are moderating at the margin: 0.0 percent in the US, 0.6 percent for Japan, 1.2 percent for China, 0.0 percent for the Euro Zone and 0.1 percent for the UK. Stagflation is still an unknown event but the risk is sufficiently high to be worthy of consideration (see http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/06/risk-aversion-and-stagflation.html). The analysis of stagflation also permits the identification of important policy issues in solving vulnerabilities that have high impact on global financial risks. Six key interrelated vulnerabilities in the world economy have been causing global financial turbulence. (1) Sovereign risk issues in Europe resulting from countries in need of fiscal consolidation and enhancement of their sovereign risk ratings (see Section III and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/volatility-of-financial-asset.html).
(2) The tradeoff of growth and inflation in China now with change in growth strategy to domestic consumption instead of investment, high debt and political developments in a decennial transition. (3) Slow growth by repression of savings with de facto interest rate controls (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/dollar-devaluation-and-carry-trade.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/volatility-of-valuations-of-financial.html), weak hiring with the loss of 10 million full-time jobs (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/volatility-of-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/fluctuating-valuations-of-financial.html) and continuing job stress of 24 to 30 million people in the US and stagnant wages in a fractured job market (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/quite-high-equity-valuations-and.html). (4) The timing, dose, impact and instruments of normalizing monetary and fiscal policies (Section II and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/impatience-with-monetary-policy-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/irrational-exuberance-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/geopolitics-monetary-policy-and.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/weakening-world-economic-growth.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/02/theory-and-reality-of-cyclical-slow.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/09/duration-dumping-and-peaking-valuations.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/02/united-states-unsustainable-fiscal.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/11/united-states-unsustainable-fiscal.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/08/expanding-bank-cash-and-deposits-with.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/02/thirty-one-million-unemployed-or.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/08/united-states-gdp-growth-standstill.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/03/is-there-second-act-of-us-great.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/03/global-financial-risks-and-fed.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/02/policy-inflation-growth-unemployment.html) in advanced and emerging economies. (5) The Tōhoku or Great East Earthquake and Tsunami of Mar 11, 2011 had repercussions throughout the world economy. Japan has share of about 9 percent in world output, role as entry point for business in Asia, key supplier of advanced components and other inputs as well as major role in finance and multiple economic activities (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748704461304576216950927404360.html?mod=WSJ_business_AsiaNewsBucket&mg=reno-wsj); and (6) geopolitical events in the Middle East.
In the effort to increase transparency, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) provides both economic projections of its participants and views on future paths of the policy rate that in the US is the federal funds rate or interest on interbank lending of reserves deposited at Federal Reserve Banks. These policies and views are discussed initially followed with appropriate analysis.
Charles Evans, President of the Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago, proposed an “economic state-contingent policy” or “7/3” approach (Evans 2012 Aug 27):
“I think the best way to provide forward guidance is by tying our policy actions to explicit measures of economic performance. There are many ways of doing this, including setting a target for the level of nominal GDP. But recognizing the difficult nature of that policy approach, I have a more modest proposal: I think the Fed should make it clear that the federal funds rate will not be increased until the unemployment rate falls below 7 percent. Knowing that rates would stay low until significant progress is made in reducing unemployment would reassure markets and the public that the Fed would not prematurely reduce its accommodation.
Based on the work I have seen, I do not expect that such policy would lead to a major problem with inflation. But I recognize that there is a chance that the models and other analysis supporting this approach could be wrong. Accordingly, I believe that the commitment to low rates should be dropped if the outlook for inflation over the medium term rises above 3 percent.
The economic conditionality in this 7/3 threshold policy would clarify our forward policy intentions greatly and provide a more meaningful guide on how long the federal funds rate will remain low. In addition, I would indicate that clear and steady progress toward stronger growth is essential.”
Evans (2012Nov27) modified the “7/3” approach to a “6.5/2.5” approach:
“I have reassessed my previous 7/3 proposal. I now think a threshold of 6-1/2 percent for the unemployment rate and an inflation safeguard of 2-1/2 percent, measured in terms of the outlook for total PCE (Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index) inflation over the next two to three years, would be appropriate.”
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) decided at its meeting on Dec 12, 2012 to implement the “6.5/2.5” approach (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20121212a.htm):
“To support continued progress toward maximum employment and price stability, the Committee expects that a highly accommodative stance of monetary policy will remain appropriate for a considerable time after the asset purchase program ends and the economic recovery strengthens. In particular, the Committee decided to keep the target range for the federal funds rate at 0 to 1/4 percent and currently anticipates that this exceptionally low range for the federal funds rate will be appropriate at least as long as the unemployment rate remains above 6-1/2 percent, inflation between one and two years ahead is projected to be no more than a half percentage point above the Committee’s 2 percent longer-run goal, and longer-term inflation expectations continue to be well anchored.”
Another rising risk is division within the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) on risks and benefits of current policies as expressed in the minutes of the meeting held on Jan 29-30, 2013 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcminutes20130130.pdf 13):
“However, many participants also expressed some concerns about potential costs and risks arising from further asset purchases. Several participants discussed the possible complications that additional purchases could cause for the eventual withdrawal of policy accommodation, a few mentioned the prospect of inflationary risks, and some noted that further asset purchases could foster market behavior that could undermine financial stability. Several participants noted that a very large portfolio of long-duration assets would, under certain circumstances, expose the Federal Reserve to significant capital losses when these holdings were unwound, but others pointed to offsetting factors and one noted that losses would not impede the effective operation of monetary policy.”
Jon Hilsenrath, writing on “Fed maps exit from stimulus,” on May 11, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887324744104578475273101471896.html?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection), analyzes the development of strategy for unwinding quantitative easing and how it can create uncertainty in financial markets. Jon Hilsenrath and Victoria McGrane, writing on “Fed slip over how long to keep cash spigot open,” published on Feb 20, 2013 in the Wall street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887323511804578298121033876536.html), analyze the minutes of the Fed, comments by members of the FOMC and data showing increase in holdings of riskier debt by investors, record issuance of junk bonds, mortgage securities and corporate loans. Jon Hilsenrath, writing on “Jobs upturn isn’t enough to satisfy Fed,” on Mar 8, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887324582804578348293647760204.html), finds that much stronger labor market conditions are required for the Fed to end quantitative easing. Unconventional monetary policy with zero interest rates and quantitative easing is quite difficult to unwind because of the adverse effects of raising interest rates on valuations of risk financial assets and home prices, including the very own valuation of the securities held outright in the Fed balance sheet. Gradual unwinding of 1 percent fed funds rates from Jun 2003 to Jun 2004 by seventeen consecutive increases of 25 percentage points from Jun 2004 to Jun 2006 to reach 5.25 percent caused default of subprime mortgages and adjustable-rate mortgages linked to the overnight fed funds rate. The zero interest rate has penalized liquidity and increased risks by inducing carry trades from zero interest rates to speculative positions in risk financial assets. There is no exit from zero interest rates without provoking another financial crash.
Unconventional monetary policy, or reinvestment of principal in securities and issue of bank reserves to maintain policy interest rates at zero, will remain in perpetuity, or QE→∞, changing to a “growth mandate.” There are two reasons explaining unconventional monetary policy of QE→∞: insufficiency of job creation to reduce unemployment/underemployment at current rates of job creation; and growth of GDP at around 2.0 percent, which is well below 3.0 percent estimated by Lucas (2011May) from 1870 to 2010. Unconventional monetary policy interprets the dual mandate of low inflation and maximum employment as mainly a “growth mandate” of forcing economic growth in the US at a rate that generates full employment. A hurdle to this “growth mandate” is that Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. US economic growth has been at only 2.2 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 23 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IQ2015. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the second estimate of GDP for IQ2015 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2015/pdf/gdp1q15_2nd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,745.9 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,355.6 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,745.9/$14,355.6 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/dollar-revaluation-squeezing-corporate.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/dollar-devaluation-and-carry-trade.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/dollar-revaluation-squeezing-corporate.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/dollar-devaluation-and-carry-trade.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IQ2015 would have accumulated to 23.9 percent. GDP in IQ2015 would be $18,574.8 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2,310.7 billion than actual $16,264.1 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 24.7 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 14.9 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/quite-high-equity-valuations-and.html). US GDP in IQ2015 is 12.4 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,264.1 billion in IQ2015 or 8.5 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.1 percent. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth at average 3.3 percent per year from May 1919 to May 2015. Growth at 3.3 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 99.2392 in Dec 2007 to 126.2585 in May 2015. The actual index NSA in May 2015 is 101.5858, which is 19.5 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.4 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2014. Using trend growth of 2.4 percent per year, the index would increase to 118.3245 in May 2015. The output of manufacturing at 101.5858 in May 2015 is 14.1 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
First, total nonfarm payroll employment seasonally adjusted (SA) increased 280,000 in May 2015 and private payroll employment increased 262,000. The average monthly number of nonfarm jobs created from May 2013 to May 2014 was 207,750 using seasonally adjusted data, while the average number of nonfarm jobs created from May 2014 to May 2015 was 254,833, or increase by 22.7 percent. The average number of private jobs created in the US from May 2013 to May 2014 was 209,083, using seasonally adjusted data, while the average from May 2014 to May 2015 was 246,500, or increase by 17.9 percent. This blog calculates the effective labor force of the US at 163.926 million in May 2014 and 165.801 million in May 2015 (Table I-4), for growth of 1.875 million at average 156,250 per month. The difference between the average increase of 246,500 new private nonfarm jobs per month in the US from May 2014 to May 2015 and the 156,250 average monthly increase in the labor force from May 2014 to May 2015 is 90,250 monthly new jobs net of absorption of new entrants in the labor force. There are 24.677 million in job stress in the US currently. Creation of 90,250 new jobs per month net of absorption of new entrants in the labor force would require 273 months to provide jobs for the unemployed and underemployed (24.677 million divided by 90,250) or 23 years (273 divided by 12). The civilian labor force of the US in May 2015 not seasonally adjusted stood at 155.719 million with 8.370 million unemployed or effectively 16.452 million unemployed in this blog’s calculation by inferring those who are not searching because they believe there is no job for them for effective labor force of 165.801 million. Reduction of one million unemployed at the current rate of job creation without adding more unemployment requires 0.92 years (1 million divided by product of 90,250 by 12, which is 1,083,000). Reduction of the rate of unemployment to 5 percent of the labor force would be equivalent to unemployment of only 8.290 million (0.05 times labor force of 165.801 million). New net job creation would be 0.080 million (8.370 million unemployed minus 8.290 million unemployed at rate of 5 percent) that at the current rate would take 0.07 years (0.080 million divided by 1.083). Under the calculation in this blog, there are 16.452 million unemployed by including those who ceased searching because they believe there is no job for them and effective labor force of 165.801 million. Reduction of the rate of unemployment to 5 percent of the labor force would require creating 8.804 million jobs net of labor force growth that at the current rate would take 7.5 years (16.452 million minus 0.05(165.801 million) = 8.162 million divided by 1.083, using LF PART 66.2% and Total UEM in Table I-4). These calculations assume that there are no more recessions, defying United States economic history with periodic contractions of economic activity when unemployment increases sharply. The number employed in May 2015 was 149.349 million (NSA) or 2.034 million more people with jobs relative to the peak of 147.315 million in Jul 2007 while the civilian noninstitutional population of ages 16 years and over increased from 231.958 million in Jul 2007 to 250.455 million in May 2015 or by 18.497 million. The number employed increased 1.4 percent from Jul 2007 to May 2015 while the noninstitutional civilian population of ages of 16 years and over, or those available for work, increased 8.0 percent. The ratio of employment to population in Jul 2007 was 63.5 percent (147.315 million employment as percent of population of 231.958 million). The same ratio in May 2015 would result in 159.039 million jobs (0.635 multiplied by noninstitutional civilian population of 250.455 million). There are effectively 9.690 million fewer jobs in May 2015 than in Jul 2007, or 159.039 million minus 149.349 million. There is actually not sufficient job creation in merely absorbing new entrants in the labor force because of those dropping from job searches, worsening the stock of unemployed or underemployed in involuntary part-time jobs.
There is current interest in past theories of “secular stagnation.” Alvin H. Hansen (1939, 4, 7; see Hansen 1938, 1941; for an early critique see Simons 1942) argues:
“Not until the problem of full employment of our productive resources from the long-run, secular standpoint was upon us, were we compelled to give serious consideration to those factors and forces in our economy which tend to make business recoveries weak and anaemic (sic) and which tend to prolong and deepen the course of depressions. This is the essence of secular stagnation-sick recoveries which die in their infancy and depressions which feed on them-selves and leave a hard and seemingly immovable core of unemployment. Now the rate of population growth must necessarily play an important role in determining the character of the output; in other words, the com-position of the flow of final goods. Thus a rapidly growing population will demand a much larger per capita volume of new residential building construction than will a stationary population. A stationary population with its larger proportion of old people may perhaps demand more personal services; and the composition of consumer demand will have an important influence on the quantity of capital required. The demand for housing calls for large capital outlays, while the demand for personal services can be met without making large investment expenditures. It is therefore not unlikely that a shift from a rapidly growing population to a stationary or declining one may so alter the composition of the final flow of consumption goods that the ratio of capital to output as a whole will tend to decline.”
The argument that anemic population growth causes “secular stagnation” in the US (Hansen 1938, 1939, 1941) is as misplaced currently as in the late 1930s (for early dissent see Simons 1942). There is currently population growth in the ages of 16 to 24 years but not enough job creation and discouragement of job searches for all ages (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/volatility-of-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/fluctuating-valuations-of-financial.html)
Second, long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. US economic growth has been at only 2.2 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 23 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IQ2015. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the second estimate of GDP for IQ2015 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2015/pdf/gdp1q15_2nd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,745.9 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,355.6 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,745.9/$14,355.6 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/dollar-revaluation-squeezing-corporate.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/dollar-devaluation-and-carry-trade.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/dollar-revaluation-squeezing-corporate.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/dollar-devaluation-and-carry-trade.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IQ2015 would have accumulated to 23.9 percent. GDP in IQ2015 would be $18,574.8 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2,310.7 billion than actual $16,264.1 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 24.7 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 14.9 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/quite-high-equity-valuations-and.html). US GDP in IQ2015 is 12.4 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,264.1 billion in IQ2015 or 8.5 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.1 percent. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth at average 3.3 percent per year from May 1919 to May 2015. Growth at 3.3 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 99.2392 in Dec 2007 to 126.2585 in May 2015. The actual index NSA in May 2015 is 101.5858, which is 19.5 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.4 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2014. Using trend growth of 2.4 percent per year, the index would increase to 118.3245 in May 2015. The output of manufacturing at 101.5858 in May 2015 is 14.1 percent below trend under this alternative calculation. The economy of the US can be summarized in growth of economic activity or GDP as fluctuating from mediocre growth of 2.5 percent on an annual basis in 2010 to 1.6 percent in 2011, 2.3 percent in 2012, 2.2 percent in 2013 and 2.4 percent in 2014. The following calculations show that actual growth is around 2.2 percent per year. The rate of growth of 1.1 percent in the entire cycle from 2007 to 2014 is well below 3 percent per year in trend from 1870 to 2010, which the economy of the US always attained for entire cycles in expansions after events such as wars and recessions (Lucas 2011May). Revisions and enhancements of United States GDP and personal income accounts by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) provide important information on long-term growth and cyclical behavior. Table Summary provides relevant data.
Table Summary, Long-term and Cyclical Growth of GDP, Real Disposable Income and Real Disposable Income per Capita
| GDP | ||
| Long-Term | ||
| 1929-2014 | 3.3 | |
| 1947-2014 | 3.2 | |
| Whole Cycles | ||
| 1980-1989 | 3.5 | |
| 2006-2014 | 1.2 | |
| 2007-2014 | 1.1 | |
| Cyclical Contractions ∆% | ||
| IQ1980 to IIIQ1980, IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 | -4.7 | |
| IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 | -4.2 | |
| Cyclical Expansions Average Annual Equivalent ∆% | ||
| IQ1983 to IVQ1985 IQ1983-IQ1986 IQ1983-IIIQ1986 IQ1983-IVQ1986 IQ1983-IQ1987 IQ1983-IIQ1987 IQ1983-IIIQ1987 IQ1983 to IVQ1987 IQ1983 to IQ1988 IQ1983 to IIQ1988 IQ1983 to IIIQ1988 | 5.9 5.7 5.4 5.2 5.0 5.0 4.9 5.0 4.9 4.9 4.8 | |
| First Four Quarters IQ1983 to IVQ1983 | 7.8 | |
| IIIQ2009 to IQ2015 | 2.2 | |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 | 2.7 | |
| Real Disposable Income | Real Disposable Income per Capita | |
| Long-Term | ||
| 1929-2013 | 3.2 | 2.0 |
| 1947-1999 | 3.7 | 2.3 |
| Whole Cycles | ||
| 1980-1989 | 3.5 | 2.6 |
| 2006-2014 | 1.5 | 0.7 |
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The revisions and enhancements of United States GDP and personal income accounts by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) also provide critical information in assessing the current rhythm of US economic growth. The economy appears to be moving at a pace around 2.2 percent per year. Table Summary GDP provides the data.
1. Average Annual Growth in the Past Twelve Quarters. GDP growth in the four quarters of 2012, the four quarters of 2013, the four quarters of 2014 and IQ2015 accumulated to 7.1 percent. This growth is equivalent to 2.1 percent per year, obtained by dividing GDP in IQ2015 of $16,264.1 billion by GDP in IVQ2011 of $15,190.3 billion and compounding by 4/13: {[($16,264.1/$15,190.3)4/13 -1]100 = 2.1 percent.
2. Average Annual Growth in the Past Four Quarters. GDP growth in the four quarters of IQ2014 to IQ2015 accumulated to 2.7 percent that is equivalent to 2.7 percent in a year. This is obtained by dividing GDP in IQ2015 of $16,264.1 billion by GDP in IQ2014 of $15,831.7 billion and compounding by 4/4: {[($16,264.1/$15,831.7)4/4 -1]100 = 2.7 %}. The US economy grew 2.7 percent in IQ2015 relative to the same quarter a year earlier in IQ2014. Growth was at annual equivalent 4.6 percent in IIQ2014 and 5.0 percent IIIQ2014 and only at 2.2 percent in IVQ2014. GDP fell at annual equivalent 0.7 percent in IQ2015. Another important revelation of the revisions and enhancements is that GDP was flat in IVQ2012, which is in the borderline of contraction, and negative in IQ2014. US GDP fell 0.5 percent in IQ2014. The rate of growth of GDP in the revision of IIIQ2013 is 4.5 percent in seasonally adjusted annual rate (SAAR). Inventory accumulation contributed 1.49 percentage points to this rate of growth. The actual rate without this impulse of unsold inventories would have been 3.0 percent, or 0.74 percent in IIIQ2013, such that annual equivalent growth in 2013 is closer to 2.9 percent {[(1.007)(1.004)(1.0074)(1.010)4/4-1]100 = 2.9%}, compounding the quarterly rates and converting into annual equivalent. Inventory divestment deducted 1.16 percentage points from GDP growth in IQ2014. Without this deduction of inventory divestment, GDP growth would have been minus 0.9 percent in IQ2014, such that the actual growth rates in the four quarters ending in IQ2014 is closer to 2.2 percent {[(1.004)(1.011)(1.009)(0.9977)]4/4 -1]100 = 2.2%}.
Table Summary GDP, US, Real GDP and Percentage Change Relative to IVQ2007 and Prior Quarter, Billions Chained 2005 Dollars and ∆%
| Real GDP, Billions Chained 2009 Dollars | ∆% Relative to IVQ2007 | ∆% Relative to Prior Quarter | ∆% | |
| IVQ2007 | 14,991.8 | NA | 0.4 | 1.9 |
| IVQ2011 | 15,190.3 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 1.7 |
| IQ2012 | 15,275.0 | 1.9 | 0.6 | 2.6 |
| IIQ2012 | 15,336.7 | 2.3 | 0.4 | 2.3 |
| IIIQ2012 | 15,431.3 | 2.9 | 0.6 | 2.7 |
| IVQ2012 | 15,433.7 | 2.9 | 0.0 | 1.6 |
| IQ2013 | 15,538.4 | 3.6 | 0.7 | 1.7 |
| IIQ2013 | 15,606.6 | 4.1 | 0.4 | 1.8 |
| IIIQ2013 | 15,779.9 | 5.3 | 1.1 | 2.3 |
| IVQ2013 | 15,916.2 | 6.2 | 0.9 | 3.1 |
| IQ2014 | 15,831.7 | 5.6 | -0.5 | 1.9 |
| IIQ2014 | 16,010.4 | 6.8 | 1.1 | 2.6 |
| IIIQ2014 | 16,205.6 | 8.1 | 1.2 | 2.7 |
| IVQ2014 | 16,294.7 | 8.7 | 0.5 | 2.4 |
| IQ2015 | 16,264.1 | 8.5 | -0.2 | 2.7 |
| Cumulative ∆% IQ2012 to IQ2015 | 7.1 | 7.0 | ||
| Annual Equivalent ∆% | 2.1 | 2.1 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
In fact, it is evident to the public that this policy will be abandoned if inflation costs rise. There is concern of the production and employment costs of controlling future inflation. Even if there is no inflation, QE→∞, or reinvestment of principal in securities and issue of bank reserves to maintain interest rates at zero, cannot be abandoned because of the fear of rising interest rates. The economy would operate in an inferior allocation of resources and suboptimal growth path, or interior point of the production possibilities frontier where the optimum of productive efficiency and wellbeing is attained, because of the distortion of risk/return decisions caused by perpetual financial repression. Not even a second-best allocation is feasible with the shocks to efficiency of financial repression in perpetuity.
The statement of the FOMC at the conclusion of its meeting on Dec 12, 2012, revealed policy intentions (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20121212a.htm) updated in the statement at its meeting on Jun 17, 2015 with maintenance of the current level of the balance sheet (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20150617a.htm):
“Press Release
Release Date: June 17, 2015
For immediate release
Information received since the Federal Open Market Committee met in April suggests that economic activity has been expanding moderately after having changed little during the first quarter. The pace of job gains picked up while the unemployment rate remained steady. On balance, a range of labor market indicators suggests that underutilization of labor resources diminished somewhat. Growth in household spending has been moderate and the housing sector has shown some improvement; however, business fixed investment and net exports stayed soft. Inflation continued to run below the Committee's longer-run objective, partly reflecting earlier declines in energy prices and decreasing prices of non-energy imports; energy prices appear to have stabilized. Market-based measures of inflation compensation remain low; survey-based measures of longer-term inflation expectations have remained stable.
Consistent with its statutory mandate, the Committee seeks to foster maximum employment and price stability. The Committee expects that, with appropriate policy accommodation, economic activity will expand at a moderate pace, with labor market indicators continuing to move toward levels the Committee judges consistent with its dual mandate. The Committee continues to see the risks to the outlook for economic activity and the labor market as nearly balanced. Inflation is anticipated to remain near its recent low level in the near term, but the Committee expects inflation to rise gradually toward 2 percent over the medium term as the labor market improves further and the transitory effects of earlier declines in energy and import prices dissipate. The Committee continues to monitor inflation developments closely.
To support continued progress toward maximum employment and price stability, the Committee today reaffirmed its view that the current 0 to 1/4 percent target range for the federal funds rate remains appropriate. In determining how long to maintain this target range, the Committee will assess progress--both realized and expected--toward its objectives of maximum employment and 2 percent inflation. This assessment will take into account a wide range of information, including measures of labor market conditions, indicators of inflation pressures and inflation expectations, and readings on financial and international developments. The Committee anticipates that it will be appropriate to raise the target range for the federal funds rate when it has seen further improvement in the labor market and is reasonably confident that inflation will move back to its 2 percent objective over the medium term.
The Committee is maintaining its existing policy of reinvesting principal payments from its holdings of agency debt and agency mortgage-backed securities in agency mortgage-backed securities and of rolling over maturing Treasury securities at auction. This policy, by keeping the Committee's holdings of longer-term securities at sizable levels, should help maintain accommodative financial conditions.
When the Committee decides to begin to remove policy accommodation, it will take a balanced approach consistent with its longer-run goals of maximum employment and inflation of 2 percent. The Committee currently anticipates that, even after employment and inflation are near mandate-consistent levels, economic conditions may, for some time, warrant keeping the target federal funds rate below levels the Committee views as normal in the longer run.
Voting for the FOMC monetary policy action were: Janet L. Yellen, Chair; William C. Dudley, Vice Chairman; Lael Brainard; Charles L. Evans; Stanley Fischer; Jeffrey M. Lacker; Dennis P. Lockhart; Jerome H. Powell; Daniel K. Tarullo; and John C. Williams.
There are several important issues in this statement.
- Mandate. The FOMC pursues a policy of attaining its “dual mandate” of (http://www.federalreserve.gov/aboutthefed/mission.htm):
“Conducting the nation's monetary policy by influencing the monetary and credit conditions in the economy in pursuit of maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates”
- Open-ended Quantitative Easing or QE∞ with End of Bond Purchases and Continuing Reinvestment of Principal in Securities. Earlier programs are continued with reinvestment of principal in securities and bank reserves at $2581 billion (http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h41/current/h41.htm#h41tab1): “The Committee is maintaining its existing policy of reinvesting principal payments from its holdings of agency debt and agency mortgage-backed securities in agency mortgage-backed securities and of rolling over maturing Treasury securities at auction. This policy, by keeping the Committee's holdings of longer-term securities at sizable levels, should help maintain accommodative financial conditions.”
- New Advance Guidance. “To support continued progress toward maximum employment and price stability, the Committee today reaffirmed its view that the current 0 to 1/4 percent target range for the federal funds rate remains appropriate. In determining how long to maintain this target range, the Committee will assess progress--both realized and expected--toward its objectives of maximum employment and 2 percent inflation. This assessment will take into account a wide range of information, including measures of labor market conditions, indicators of inflation pressures and inflation expectations, and readings on financial and international developments. The Committee anticipates that it will be appropriate to raise the target range for the federal funds rate when it has seen further improvement in the labor market and is reasonably confident that inflation will move back to its 2 percent objective over the medium term.” (emphasis added).
- Policy Commitment with Maximum Employment. The emphasis of policy is in maintaining full employment: “When the Committee decides to begin to remove policy accommodation, it will take a balanced approach consistent with its longer-run goals of maximum employment and inflation of 2 percent. The Committee currently anticipates that, even after employment and inflation are near mandate-consistent levels, economic conditions may, for some time, warrant keeping the target federal funds rate below levels the Committee views as normal in the longer run.”
Focus is shifting from tapering quantitative easing by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC). There is sharp distinction between the two measures of unconventional monetary policy: (1) fixing of the overnight rate of fed funds at 0 to ¼ percent; and (2) outright purchase of Treasury and agency securities and mortgage-backed securities for the balance sheet of the Federal Reserve. Markets overreacted to the so-called “paring” of outright purchases to $25 billion of securities per month for the balance sheet of the Fed. What is truly important is the fixing of the overnight fed funds at 0 to ¼ percent for which there is no end in sight as evident in the FOMC statement for Jun 17, 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20150617a.htm):
“To support continued progress toward maximum employment and price stability, the Committee today reaffirmed its view that the current 0 to 1/4 percent target range for the federal funds rate remains appropriate. In determining how long to maintain this target range, the Committee will assess progress--both realized and expected--toward its objectives of maximum employment and 2 percent inflation. This assessment will take into account a wide range of information, including measures of labor market conditions, indicators of inflation pressures and inflation expectations, and readings on financial and international developments. The Committee anticipates that it will be appropriate to raise the target range for the federal funds rate when it has seen further improvement in the labor market and is reasonably confident that inflation will move back to its 2 percent objective over the medium term.” (emphasis added). The FOMC added “readings” of “international developments after Jan 28, 2015.
How long is “considerable time”? At the press conference following the meeting on Mar 19, 2014, Chair Yellen answered a question of Jon Hilsenrath of the Wall Street Journal explaining “In particular, the Committee has endorsed the view that it anticipates that will be a considerable period after the asset purchase program ends before it will be appropriate to begin to raise rates. And of course on our present path, well, that's not utterly preset. We would be looking at next, next fall. So, I think that's important guidance” (http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20140319.pdf). Many focused on “next fall,” ignoring that the path of increasing rates is not “utterly preset.”
At the press conference following the meeting on Dec 17, 2014, Chair Yellen answered a question by Jon Hilseranth of the Wall Street Journal explaining “patience” (http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20141217.pdf):
“So I did say that this statement that the committee can be patient should be interpreted as meaning that it is unlikely to begin the normalization process, for at least the next couple of meetings. Now that doesn't point to any preset or predetermined time at which normalization is -- will begin. There are a range of views on the committee, and it will be dependent on how incoming data bears on the progress, the economy is making. First of all, I want to emphasize that no meeting is completely off the table in the sense that if we do see faster progress toward our objectives than we currently expect, then it is possible that the process of normalization would occur sooner than we now anticipated. And of course the converse is also true. So at this point, we think it unlikely that it will be appropriate, that we will see conditions for at least the next couple of meetings that will make it appropriate for us to decide to begin normalization. A number of committee participants have indicated that in their view, conditions could be appropriate by the middle of next year. But there is no preset time.”
Chair Yellen explained the removal of the word “patience” from the advanced guidance at the press conference following the FOMC meeting on Mar 18, 2015(http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20150318.pdf):
“In other words, just because we removed the word “patient” from the statement doesn’t mean we are going to be impatient. Moreover, even after the initial increase in the target funds rate, our policy is likely to remain highly accommodative to support continued progress toward our objectives of maximum employment and 2 percent inflation.”
At a speech on Mar 31, 2014, Chair Yellen analyzed labor market conditions as follows (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20140331a.htm):
“And based on the evidence available, it is clear to me that the U.S. economy is still considerably short of the two goals assigned to the Federal Reserve by the Congress. The first of those goals is maximum sustainable employment, the highest level of employment that can be sustained while maintaining a stable inflation rate. Most of my colleagues on the Federal Open Market Committee and I estimate that the unemployment rate consistent with maximum sustainable employment is now between 5.2 percent and 5.6 percent, well below the 6.7 percent rate in February.
Let me explain what I mean by that word "slack" and why it is so important.
Slack means that there are significantly more people willing and capable of filling a job than there are jobs for them to fill. During a period of little or no slack, there still may be vacant jobs and people who want to work, but a large share of those willing to work lack the skills or are otherwise not well suited for the jobs that are available. With 6.7 percent unemployment, it might seem that there must be a lot of slack in the U.S. economy, but there are reasons why that may not be true.”
Yellen (2014Aug22) provides comprehensive review of the theory and measurement of labor markets. Monetary policy pursues a policy of attaining its “dual mandate” of (http://www.federalreserve.gov/aboutthefed/mission.htm):
“Conducting the nation's monetary policy by influencing the monetary and credit conditions in the economy in pursuit of maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates”
Yellen (2014Aug22) finds that the unemployment rate is not sufficient in determining slack:
“One convenient way to summarize the information contained in a large number of indicators is through the use of so-called factor models. Following this methodology, Federal Reserve Board staff developed a labor market conditions index from 19 labor market indicators, including four I just discussed. This broadly based metric supports the conclusion that the labor market has improved significantly over the past year, but it also suggests that the decline in the unemployment rate over this period somewhat overstates the improvement in overall labor market conditions.”
Yellen (2014Aug22) restates that the FOMC determines monetary policy on newly available information and interpretation of labor markets and inflation and does not follow a preset path:
“But if progress in the labor market continues to be more rapid than anticipated by the Committee or if inflation moves up more rapidly than anticipated, resulting in faster convergence toward our dual objectives, then increases in the federal funds rate target could come sooner than the Committee currently expects and could be more rapid thereafter. Of course, if economic performance turns out to be disappointing and progress toward our goals proceeds more slowly than we expect, then the future path of interest rates likely would be more accommodative than we currently anticipate. As I have noted many times, monetary policy is not on a preset path. The Committee will be closely monitoring incoming information on the labor market and inflation in determining the appropriate stance of monetary policy.”
Yellen (2014Aug22) states that “Historically, slack has accounted for only a small portion of the fluctuations in inflation. Indeed, unusual aspects of the current recovery may have shifted the lead-lag relationship between a tightening labor market and rising inflation pressures in either direction.”
The minutes of the meeting of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) on Sep 16-17, 2014, reveal concern with global economic conditions (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/fomcminutes20140917.htm):
“Most viewed the risks to the outlook for economic activity and the labor market as broadly balanced. However, a number of participants noted that economic growth over the medium term might be slower than they expected if foreign economic growth came in weaker than anticipated, structural productivity continued to increase only slowly, or the recovery in residential construction continued to lag.”
There is similar concern in the minutes of the meeting of the FOMC on Dec 16-17, 2014 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/fomcminutes20141217.htm):
“In their discussion of the foreign economic outlook, participants noted that the implications of the drop in crude oil prices would differ across regions, especially if the price declines affected inflation expectations and financial markets; a few participants said that the effect on overseas employment and output as a whole was likely to be positive. While some participants had lowered their assessments of the prospects for global economic growth, several noted that the likelihood of further responses by policymakers abroad had increased. Several participants indicated that they expected slower economic growth abroad to negatively affect the U.S. economy, principally through lower net exports, but the net effect of lower oil prices on U.S. economic activity was anticipated to be positive.”
Chair Yellen analyzes the view of inflation (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20140416a.htm):
“Inflation, as measured by the price index for personal consumption expenditures, has slowed from an annual rate of about 2-1/2 percent in early 2012 to less than 1 percent in February of this year. This rate is well below the Committee's 2 percent longer-run objective. Many advanced economies are observing a similar softness in inflation.
To some extent, the low rate of inflation seems due to influences that are likely to be temporary, including a deceleration in consumer energy prices and outright declines in core import prices in recent quarters. Longer-run inflation expectations have remained remarkably steady, however. We anticipate that, as the effects of transitory factors subside and as labor market gains continue, inflation will gradually move back toward 2 percent.”
There is a critical phrase in the statement of Sep 19, 2013 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20130918a.htm): “but mortgage rates have risen further.” Did the increase of mortgage rates influence the decision of the FOMC not to taper? Is FOMC “communication” and “guidance” successful? Will the FOMC increase purchases of mortgage-backed securities if mortgage rates increase? A competing event is the high level of valuations of risk financial assets (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/01/peaking-valuations-of-risk-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/01/theory-and-reality-of-secular.html). Matt Jarzemsky, writing on “Dow industrials set record,” on Mar 5, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887324156204578275560657416332.html), analyzes that the DJIA broke the closing high of 14,164.53 set on Oct 9, 2007, and subsequently also broke the intraday high of 14,198.10 reached on Oct 11, 2007. The DJIA closed at 18,015.95 on Fri Jun 19, 2015, which is higher by 27.2 percent than the value of 14,164.53 reached on Oct 9, 2007 and higher by 26.9 percent than the value of 14,198.10 reached on Oct 11, 2007. Values of risk financial assets are approaching or exceeding historical highs.
Perhaps one of the most critical statements on policy is the answer to a question of Peter Barnes by Chair Janet Yellen at the press conference following the meeting on Jun 18, 2014 (page 19 at http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20140618.pdf):
So I don't have a sense--the committee doesn't try to gauge what is the right level of equity prices. But we do certainly monitor a number of different metrics that give us a feeling for where valuations are relative to things like earnings or dividends, and look at where these metrics stand in comparison with previous history to get a sense of whether or not we're moving to valuation levels that are outside of historical norms, and I still don't see that. I still don't see that for equity prices broadly” (emphasis added).
In a speech at the IMF on Jul 2, 2014, Chair Yellen analyzed the link between monetary policy and financial risks (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20140702a.htm):
“Monetary policy has powerful effects on risk taking. Indeed, the accommodative policy stance of recent years has supported the recovery, in part, by providing increased incentives for households and businesses to take on the risk of potentially productive investments. But such risk-taking can go too far, thereby contributing to fragility in the financial system. This possibility does not obviate the need for monetary policy to focus primarily on price stability and full employment--the costs to society in terms of deviations from price stability and full employment that would arise would likely be significant. In the private sector, key vulnerabilities included high levels of leverage, excessive dependence on unstable short-term funding, weak underwriting of loans, deficiencies in risk measurement and risk management, and the use of exotic financial instruments that redistributed risk in nontransparent ways.”
Yellen (2014Jul14) warned again at the Committee on Banking, Housing and Urban Affairs on Jul 15, 2014:
“The Committee recognizes that low interest rates may provide incentives for some investors to “reach for yield,” and those actions could increase vulnerabilities in the financial system to adverse events. While prices of real estate, equities, and corporate bonds have risen appreciably and valuation metrics have increased, they remain generally in line with historical norms. In some sectors, such as lower-rated corporate debt, valuations appear stretched and issuance has been brisk. Accordingly, we are closely monitoring developments in the leveraged loan market and are working to enhance the effectiveness of our supervisory guidance. More broadly, the financial sector has continued to become more resilient, as banks have continued to boost their capital and liquidity positions, and growth in wholesale short-term funding in financial markets has been modest” (emphasis added).
Greenspan (1996) made similar warnings:
“Clearly, sustained low inflation implies less uncertainty about the future, and lower risk premiums imply higher prices of stocks and other earning assets. We can see that in the inverse relationship exhibited by price/earnings ratios and the rate of inflation in the past. But how do we know when irrational exuberance has unduly escalated asset values, which then become subject to unexpected and prolonged contractions as they have in Japan over the past decade? And how do we factor that assessment into monetary policy? We as central bankers need not be concerned if a collapsing financial asset bubble does not threaten to impair the real economy, its production, jobs, and price stability. Indeed, the sharp stock market break of 1987 had few negative consequences for the economy. But we should not underestimate or become complacent about the complexity of the interactions of asset markets and the economy. Thus, evaluating shifts in balance sheets generally, and in asset prices particularly, must be an integral part of the development of monetary policy” (emphasis added).
Bernanke (2010WP) and Yellen (2011AS) reveal the emphasis of monetary policy on the impact of the rise of stock market valuations in stimulating consumption by wealth effects on household confidence. What is the success in evaluating deviations of valuations of risk financial assets from “historical norms”? What are the consequences on economic activity and employment of deviations of valuations of risk financial assets from those “historical norms”? What are the policy tools and their effectiveness in returning valuations of risk financial assets to their “historical norms”?
The key policy is maintaining fed funds rate between 0 and ¼ percent. An increase in fed funds rates could cause flight out of risk financial markets worldwide. There is no exit from this policy without major financial market repercussions. There are high costs and risks of this policy because indefinite financial repression induces carry trades with high leverage, risks and illiquidity.
The Communiqué of the Istanbul meeting of G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors on February 10, 2015, sanctions the need of unconventional monetary policy with warning on collateral effects (http://www.g20.utoronto.ca/2015/150210-finance.html):
“We agree that consistent with central banks' mandates, current economic conditions require accommodative monetary policies in some economies. In this regard, we welcome that central banks take appropriate monetary policy action. The recent policy decision by the ECB aims at fulfilling its price stability mandate, and will further support the recovery in the euro area. We also note that some advanced economies with stronger growth prospects are moving closer to conditions that would allow for policy normalization. In an environment of diverging monetary policy settings and rising financial market volatility, policy settings should be carefully calibrated and clearly communicated to minimize negative spillovers.”
Professor Raguram G Rajan, governor of the Reserve Bank of India, which is India’s central bank, warned about risks in high valuations of asset prices in an interview with Christopher Jeffery of Central Banking Journal on Aug 6, 2014 (http://www.centralbanking.com/central-banking-journal/interview/2358995/raghuram-rajan-on-the-dangers-of-asset-prices-policy-spillovers-and-finance-in-india). Professor Rajan demystifies in the interview “competitive easing” by major central banks as equivalent to competitive devaluation. Rajan (2005) anticipated the risks of the world financial crisis. Professor John B. Taylor (2014Jul15, 2014Jun26) building on advanced research (Taylor (1993, 1998LB, 1999, 1998LB, 1999, 2007JH, 2008Nov, 2009, 2012JMCB, 2014Jan3) finds that a monetary policy rule would function best in promoting an environment of low inflation and strong economic growth with stability of financial markets. There is strong case for using rules instead of discretionary authorities in monetary policy (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/search?q=rules+versus+authorities http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/financial-irrational-exuberance.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/world-inflation-waves-united-states.html).
The key policy is maintaining fed funds rate between 0 and ¼ percent. An increase in fed funds rates could cause flight out of risk financial markets worldwide. There is no exit from this policy without major financial market repercussions. There are high costs and risks of this policy because indefinite financial repression induces carry trades with high leverage, risks and illiquidity.
The FOMC provides guidelines on the process of normalization of monetary policy at the meeting on Sep 17, 2014 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20140917c.htm):
“All FOMC participants but one agreed on the following key elements of the approach they intend to implement when it becomes appropriate to begin normalizing the stance of monetary policy:
- The Committee will determine the timing and pace of policy normalization--meaning steps to raise the federal funds rate and other short-term interest rates to more normal levels and to reduce the Federal Reserve's securities holdings--so as to promote its statutory mandate of maximum employment and price stability.
- When economic conditions and the economic outlook warrant a less accommodative monetary policy, the Committee will raise its target range for the federal funds rate.
- During normalization, the Federal Reserve intends to move the federal funds rate into the target range set by the FOMC primarily by adjusting the interest rate it pays on excess reserve balances.
- During normalization, the Federal Reserve intends to use an overnight reverse repurchase agreement facility and other supplementary tools as needed to help control the federal funds rate. The Committee will use an overnight reverse repurchase agreement facility only to the extent necessary and will phase it out when it is no longer needed to help control the federal funds rate.
- The Committee intends to reduce the Federal Reserve's securities holdings in a gradual and predictable manner primarily by ceasing to reinvest repayments of principal on securities held in the SOMA.
- The Committee expects to cease or commence phasing out reinvestments after it begins increasing the target range for the federal funds rate; the timing will depend on how economic and financial conditions and the economic outlook evolve.
- The Committee currently does not anticipate selling agency mortgage-backed securities as part of the normalization process, although limited sales might be warranted in the longer run to reduce or eliminate residual holdings. The timing and pace of any sales would be communicated to the public in advance.
- The Committee intends that the Federal Reserve will, in the longer run, hold no more securities than necessary to implement monetary policy efficiently and effectively, and that it will hold primarily Treasury securities, thereby minimizing the effect of Federal Reserve holdings on the allocation of credit across sectors of the economy.
- The Committee is prepared to adjust the details of its approach to policy normalization in light of economic and financial developments.”
In the Semiannual Monetary Policy Report to Congress on Feb 24, 2015, Chair Yellen analyzes the timing of interest rate increases (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20150224a.htm):
“The FOMC's assessment that it can be patient in beginning to normalize policy means that the Committee considers it unlikely that economic conditions will warrant an increase in the target range for the federal funds rate for at least the next couple of FOMC meetings. If economic conditions continue to improve, as the Committee anticipates, the Committee will at some point begin considering an increase in the target range for the federal funds rate on a meeting-by-meeting basis. Before then, the Committee will change its forward guidance. However, it is important to emphasize that a modification of the forward guidance should not be read as indicating that the Committee will necessarily increase the target range in a couple of meetings. Instead the modification should be understood as reflecting the Committee's judgment that conditions have improved to the point where it will soon be the case that a change in the target range could be warranted at any meeting. Provided that labor market conditions continue to improve and further improvement is expected, the Committee anticipates that it will be appropriate to raise the target range for the federal funds rate when, on the basis of incoming data, the Committee is reasonably confident that inflation will move back over the medium term toward our 2 percent objective.”
In testimony on the Semiannual Monetary Policy Report to the Congress before the Committee on Financial Services, US House of Representatives, on Feb 11, 2014, Chair Janet Yellen states (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20140211a.htm):
“Turning to monetary policy, let me emphasize that I expect a great deal of continuity in the FOMC's approach to monetary policy. I served on the Committee as we formulated our current policy strategy and I strongly support that strategy, which is designed to fulfill the Federal Reserve's statutory mandate of maximum employment and price stability. If incoming information broadly supports the Committee's expectation of ongoing improvement in labor market conditions and inflation moving back toward its longer-run objective, the Committee will likely reduce the pace of asset purchases in further measured steps at future meetings. That said, purchases are not on a preset course, and the Committee's decisions about their pace will remain contingent on its outlook for the labor market and inflation as well as its assessment of the likely efficacy and costs of such purchases. In December of last year and again this January, the Committee said that its current expectation--based on its assessment of a broad range of measures of labor market conditions, indicators of inflation pressures and inflation expectations, and readings on financial developments--is that it likely will be appropriate to maintain the current target range for the federal funds rate well past the time that the unemployment rate declines below 6-1/2 percent, especially if projected inflation continues to run below the 2 percent goal. I am committed to achieving both parts of our dual mandate: helping the economy return to full employment and returning inflation to 2 percent while ensuring that it does not run persistently above or below that level (emphasis added).”
At the confirmation hearing on nomination for Chair of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Vice Chair Yellen (2013Nov14 http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20131114a.htm), states needs and intentions of policy:
“We have made good progress, but we have farther to go to regain the ground lost in the crisis and the recession. Unemployment is down from a peak of 10 percent, but at 7.3 percent in October, it is still too high, reflecting a labor market and economy performing far short of their potential. At the same time, inflation has been running below the Federal Reserve's goal of 2 percent and is expected to continue to do so for some time.
For these reasons, the Federal Reserve is using its monetary policy tools to promote a more robust recovery. A strong recovery will ultimately enable the Fed to reduce its monetary accommodation and reliance on unconventional policy tools such as asset purchases. I believe that supporting the recovery today is the surest path to returning to a more normal approach to monetary policy.”
In testimony before the Committee on the Budget of the US Senate on May 8, 2004, Chair Yellen provides analysis of the current economic situation and outlook (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20140507a.htm):
“The economy has continued to recover from the steep recession of 2008 and 2009. Real gross domestic product (GDP) growth stepped up to an average annual rate of about 3-1/4 percent over the second half of last year, a faster pace than in the first half and during the preceding two years. Although real GDP growth is currently estimated to have paused in the first quarter of this year, I see that pause as mostly reflecting transitory factors, including the effects of the unusually cold and snowy winter weather. With the harsh winter behind us, many recent indicators suggest that a rebound in spending and production is already under way, putting the overall economy on track for solid growth in the current quarter. One cautionary note, though, is that readings on housing activity--a sector that has been recovering since 2011--have remained disappointing so far this year and will bear watching.
Conditions in the labor market have continued to improve. The unemployment rate was 6.3 percent in April, about 1-1/4 percentage points below where it was a year ago. Moreover, gains in payroll employment averaged nearly 200,000 jobs per month over the past year. During the economic recovery so far, payroll employment has increased by about 8-1/2 million jobs since its low point, and the unemployment rate has declined about 3-3/4 percentage points since its peak.
While conditions in the labor market have improved appreciably, they are still far from satisfactory. Even with recent declines in the unemployment rate, it continues to be elevated. Moreover, both the share of the labor force that has been unemployed for more than six months and the number of individuals who work part time but would prefer a full-time job are at historically high levels. In addition, most measures of labor compensation have been rising slowly--another signal that a substantial amount of slack remains in the labor market.
Inflation has been quite low even as the economy has continued to expand. Some of the factors contributing to the softness in inflation over the past year, such as the declines seen in non-oil import prices, will probably be transitory. Importantly, measures of longer-run inflation expectations have remained stable. That said, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) recognizes that inflation persistently below 2 percent--the rate that the Committee judges to be most consistent with its dual mandate--could pose risks to economic performance, and we are monitoring inflation developments closely.
Looking ahead, I expect that economic activity will expand at a somewhat faster pace this year than it did last year, that the unemployment rate will continue to decline gradually, and that inflation will begin to move up toward 2 percent. A faster rate of economic growth this year should be supported by reduced restraint from changes in fiscal policy, gains in household net worth from increases in home prices and equity values, a firming in foreign economic growth, and further improvements in household and business confidence as the economy continues to strengthen. Moreover, U.S. financial conditions remain supportive of growth in economic activity and employment.”
In his classic restatement of the Keynesian demand function in terms of “liquidity preference as behavior toward risk,” James Tobin (http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/economic-sciences/laureates/1981/tobin-bio.html) identifies the risks of low interest rates in terms of portfolio allocation (Tobin 1958, 86):
“The assumption that investors expect on balance no change in the rate of interest has been adopted for the theoretical reasons explained in section 2.6 rather than for reasons of realism. Clearly investors do form expectations of changes in interest rates and differ from each other in their expectations. For the purposes of dynamic theory and of analysis of specific market situations, the theories of sections 2 and 3 are complementary rather than competitive. The formal apparatus of section 3 will serve just as well for a non-zero expected capital gain or loss as for a zero expected value of g. Stickiness of interest rate expectations would mean that the expected value of g is a function of the rate of interest r, going down when r goes down and rising when r goes up. In addition to the rotation of the opportunity locus due to a change in r itself, there would be a further rotation in the same direction due to the accompanying change in the expected capital gain or loss. At low interest rates expectation of capital loss may push the opportunity locus into the negative quadrant, so that the optimal position is clearly no consols, all cash. At the other extreme, expectation of capital gain at high interest rates would increase sharply the slope of the opportunity locus and the frequency of no cash, all consols positions, like that of Figure 3.3. The stickier the investor's expectations, the more sensitive his demand for cash will be to changes in the rate of interest (emphasis added).”
Tobin (1969) provides more elegant, complete analysis of portfolio allocation in a general equilibrium model. The major point is equally clear in a portfolio consisting of only cash balances and a perpetuity or consol. Let g be the capital gain, r the rate of interest on the consol and re the expected rate of interest. The rates are expressed as proportions. The price of the consol is the inverse of the interest rate, (1+re). Thus, g = [(r/re) – 1]. The critical analysis of Tobin is that at extremely low interest rates there is only expectation of interest rate increases, that is, dre>0, such that there is expectation of capital losses on the consol, dg<0. Investors move into positions combining only cash and no consols. Valuations of risk financial assets would collapse in reversal of long positions in carry trades with short exposures in a flight to cash. There is no exit from a central bank created liquidity trap without risks of financial crash and another global recession. The net worth of the economy depends on interest rates. In theory, “income is generally defined as the amount a consumer unit could consume (or believe that it could) while maintaining its wealth intact” (Friedman 1957, 10). Income, Y, is a flow that is obtained by applying a rate of return, r, to a stock of wealth, W, or Y = rW (Ibid). According to a subsequent statement: “The basic idea is simply that individuals live for many years and that therefore the appropriate constraint for consumption is the long-run expected yield from wealth r*W. This yield was named permanent income: Y* = r*W” (Darby 1974, 229), where * denotes permanent. The simplified relation of income and wealth can be restated as:
W = Y/r (10
Equation (1) shows that as r goes to zero, r→0, W grows without bound, W→∞. Unconventional monetary policy lowers interest rates to increase the present value of cash flows derived from projects of firms, creating the impression of long-term increase in net worth. An attempt to reverse unconventional monetary policy necessarily causes increases in interest rates, creating the opposite perception of declining net worth. As r→∞, W = Y/r →0. There is no exit from unconventional monetary policy without increasing interest rates with resulting pain of financial crisis and adverse effects on production, investment and employment.
In delivering the biannual report on monetary policy (Board of Governors 2013Jul17), Chairman Bernanke (2013Jul17) advised Congress that:
“Instead, we are providing additional policy accommodation through two distinct yet complementary policy tools. The first tool is expanding the Federal Reserve's portfolio of longer-term Treasury securities and agency mortgage-backed securities (MBS); we are currently purchasing $40 billion per month in agency MBS and $45 billion per month in Treasuries. We are using asset purchases and the resulting expansion of the Federal Reserve's balance sheet primarily to increase the near-term momentum of the economy, with the specific goal of achieving a substantial improvement in the outlook for the labor market in a context of price stability. We have made some progress toward this goal, and, with inflation subdued, we intend to continue our purchases until a substantial improvement in the labor market outlook has been realized. We are relying on near-zero short-term interest rates, together with our forward guidance that rates will continue to be exceptionally low--our second tool--to help maintain a high degree of monetary accommodation for an extended period after asset purchases end, even as the economic recovery strengthens and unemployment declines toward more-normal levels. In appropriate combination, these two tools can provide the high level of policy accommodation needed to promote a stronger economic recovery with price stability.
The Committee's decisions regarding the asset purchase program (and the overall stance of monetary policy) depend on our assessment of the economic outlook and of the cumulative progress toward our objectives. Of course, economic forecasts must be revised when new information arrives and are thus necessarily provisional.”
Friedman (1953) argues there are three lags in effects of monetary policy: (1) between the need for action and recognition of the need; (2) the recognition of the need and taking of actions; and (3) taking of action and actual effects. Friedman (1953) finds that the combination of these lags with insufficient knowledge of the current and future behavior of the economy causes discretionary economic policy to increase instability of the economy or standard deviations of real income σy and prices σp. Policy attempts to circumvent the lags by policy impulses based on forecasts. We are all naïve about forecasting. Data are available with lags and revised to maintain high standards of estimation. Policy simulation models estimate economic relations with structures prevailing before simulations of policy impulses such that parameters change as discovered by Lucas (1977). Economic agents adjust their behavior in ways that cause opposite results from those intended by optimal control policy as discovered by Kydland and Prescott (1977). Advance guidance attempts to circumvent expectations by economic agents that could reverse policy impulses but is of dubious effectiveness. There is strong case for using rules instead of discretionary authorities in monetary policy (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/search?q=rules+versus+authorities http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/financial-irrational-exuberance.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/world-inflation-waves-united-states.html).
The key policy is maintaining the fed funds rate between 0 and ¼ percent. An increase in fed funds rates could cause flight out of risk financial markets worldwide. There is no exit from this policy without major financial market repercussions. Indefinite financial repression induces carry trades with high leverage, risks and illiquidity.
Unconventional monetary policy drives wide swings in allocations of positions into risk financial assets that generate instability instead of intended pursuit of prosperity without inflation. There is insufficient knowledge and imperfect tools to maintain the gap of actual relative to potential output constantly at zero while restraining inflation in an open interval of (1.99, 2.0). Symmetric targets appear to have been abandoned in favor of a self-imposed single jobs mandate of easing monetary policy even with the economy growing at or close to potential output that is actually a target of growth forecast. The impact on the overall economy and the financial system of errors of policy are magnified by large-scale policy doses of trillions of dollars of quantitative easing and zero interest rates. The US economy has been experiencing financial repression as a result of negative real rates of interest during nearly a decade and programmed in monetary policy statements until 2015 or, for practical purposes, forever. The essential calculus of risk/return in capital budgeting and financial allocations has been distorted. If economic perspectives are doomed until 2015 such as to warrant zero interest rates and open-ended bond-buying by “printing” digital bank reserves (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/12/is-fed-printing-money-what-are.html; see Shultz et al 2012), rational investors and consumers will not invest and consume until just before interest rates are likely to increase. Monetary policy statements on intentions of zero interest rates for another three years or now virtually forever discourage investment and consumption or aggregate demand that can increase economic growth and generate more hiring and opportunities to increase wages and salaries. The doom scenario used to justify monetary policy accentuates adverse expectations on discounted future cash flows of potential economic projects that can revive the economy and create jobs. If it were possible to project the future with the central tendency of the monetary policy scenario and monetary policy tools do exist to reverse this adversity, why the tools have not worked before and even prevented the financial crisis? If there is such thing as “monetary policy science”, why it has such poor record and current inability to reverse production and employment adversity? There is no excuse of arguing that additional fiscal measures are needed because they were deployed simultaneously with similar ineffectiveness. Jon Hilsenrath, writing on “New view into Fed’s response to crisis,” on Feb 21, 2014, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702303775504579396803024281322?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection), analyzes 1865 pages of transcripts of eight formal and six emergency policy meetings at the Fed in 2008 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/fomchistorical2008.htm). If there were an infallible science of central banking, models and forecasts would provide accurate information to policymakers on the future course of the economy in advance. Such forewarning is essential to central bank science because of the long lag between the actual impulse of monetary policy and the actual full effects on income and prices many months and even years ahead (Romer and Romer 2004, Friedman 1961, 1953, Culbertson 1960, 1961, Batini and Nelson 2002). The transcripts of the Fed meetings in 2008 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/fomchistorical2008.htm) analyzed by Jon Hilsenrath demonstrate that Fed policymakers frequently did not understand the current state of the US economy in 2008 and much less the direction of income and prices. The conclusion of Friedman (1953) is that monetary impulses increase financial and economic instability because of lags in anticipating needs of policy, taking policy decisions and effects of decisions. This is a fortiori true when untested unconventional monetary policy in gargantuan doses shocks the economy and financial markets.
In remarkable anticipation in 2005, Professor Raghuram G. Rajan (2005) warned of low liquidity and high risks of central bank policy rates approaching the zero bound (Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 218-9). Professor Rajan excelled in a distinguished career as an academic economist in finance and was chief economist of the International Monetary Fund (IMF). Shefali Anand and Jon Hilsenrath, writing on Oct 13, 2013, on “India’s central banker lobbies Fed,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702304330904579133530766149484?KEYWORDS=Rajan), interviewed Raghuram G Rajan, who is the current Governor of the Reserve Bank of India, which is India’s central bank (http://www.rbi.org.in/scripts/AboutusDisplay.aspx). In this interview, Rajan argues that central banks should avoid unintended consequences on emerging market economies of inflows and outflows of capital triggered by monetary policy. Portfolio reallocations induced by combination of zero interest rates and risk events stimulate carry trades that generate wide swings in world capital flows. Professor Rajan, in an interview with Kartik Goyal of Bloomberg (http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2014-01-30/rajan-warns-of-global-policy-breakdown-as-emerging-markets-slide.html), warns of breakdown of global policy coordination. Professor Raguram G Rajan, governor of the Reserve Bank of India, which is India’s central bank, warned about risks in high valuations of asset prices in an interview with Christopher Jeffery of Central Banking Journal on Aug 6, 2014 (http://www.centralbanking.com/central-banking-journal/interview/2358995/raghuram-rajan-on-the-dangers-of-asset-prices-policy-spillovers-and-finance-in-india). Professor Rajan demystifies in the interview “competitive easing” by major central banks as equivalent to competitive devaluation.
The Swiss National Bank (SNB) announced on Jan 15, 2015, the termination of its peg of the exchange rate of the Swiss franc to the euro (http://www.snb.ch/en/mmr/speeches/id/ref_20150115_tjn/source/ref_20150115_tjn.en.pdf):
“The Swiss National Bank (SNB) has decided to discontinue the minimum exchange rate of
CHF 1.20 per euro with immediate effect and to cease foreign currency purchases associated with enforcing it.”
The SNB also lowered interest rates to nominal negative percentages (http://www.snb.ch/en/mmr/speeches/id/ref_20150115_tjn/source/ref_20150115_tjn.en.pdf):
“At the same time as discontinuing the minimum exchange rate, the SNB will be lowering the interest rate for balances held on sight deposit accounts to –0.75% from 22 January. The exemption thresholds remain unchanged. Further lowering the interest rate makes Swiss-franc investments considerably less attractive and will mitigate the effects of the decision to discontinue the minimum exchange rate. The target range for the three-month Libor is being lowered by 0.5 percentage points to between –1.25% and –0.25%.”
The Swiss franc rate relative to the euro (CHF/EUR) appreciated 18.7 percent on Jan 15, 2015. The Swiss franc rate relative to the dollar (CHF/USD) appreciated 17.7 percent. Central banks are taking measures in anticipation of the quantitative easing by the European Central Bank.
On Jan 22, 2015, the European Central Bank (ECB) decided to implement an “expanded asset purchase program” with combined asset purchases of €60 billion per month “until at least Sep 2016 (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pr/date/2015/html/pr150122_1.en.html). The objective of the program is that (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pr/date/2015/html/pr150122_1.en.html):
“Asset purchases provide monetary stimulus to the economy in a context where key ECB interest rates are at their lower bound. They further ease monetary and financial conditions, making access to finance cheaper for firms and households. This tends to support investment and consumption, and ultimately contributes to a return of inflation rates towards 2%.”
The President of the ECB, Mario Draghi, explains the coordination of asset purchases with NCBs (National Central Banks) of the euro area and risk sharing (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pressconf/2015/html/is150122.en.html):
“In March 2015 the Eurosystem will start to purchase euro-denominated investment-grade securities issued by euro area governments and agencies and European institutions in the secondary market. The purchases of securities issued by euro area governments and agencies will be based on the Eurosystem NCBs’ shares in the ECB’s capital key. Some additional eligibility criteria will be applied in the case of countries under an EU/IMF adjustment programme. As regards the additional asset purchases, the Governing Council retains control over all the design features of the programme and the ECB will coordinate the purchases, thereby safeguarding the singleness of the Eurosystem’s monetary policy. The Eurosystem will make use of decentralised implementation to mobilise its resources. With regard to the sharing of hypothetical losses, the Governing Council decided that purchases of securities of European institutions (which will be 12% of the additional asset purchases, and which will be purchased by NCBs) will be subject to loss sharing. The rest of the NCBs’ additional asset purchases will not be subject to loss sharing. The ECB will hold 8% of the additional asset purchases. This implies that 20% of the additional asset purchases will be subject to a regime of risk sharing.”
The President of the ECB, Mario Draghi, rejected the possibility of seigniorage in the new asset purchase program, or central bank financing of fiscal expansion (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pressconf/2015/html/is150122.en.html):
“As I just said, it would be a big mistake if countries were to consider that the presence of this programme might be an incentive to fiscal expansion. They would undermine the confidence, so it’s not directed to monetary financing at all. Actually, it’s been designed as to avoid any monetary financing.”
The President of the ECB, Mario Draghi, does not find effects of monetary policy in inflating asset prices (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pressconf/2015/html/is150122.en.html):
“On the first question, we monitor closely any potential instance of risk to financial stability. So we're very alert to that risk. So far we don't see bubbles. There may be some local episodes of certain specific markets where prices are going up fast. But to have a bubble, besides having that, one should also identify, detect an increase, dramatic increase in leverage or in bank credit, and we don't see that now. However, we, as I said, we are alert. If bubbles are of a local nature, they should be addressed by local instruments, namely macro-prudential instruments rather than by monetary policy.”
The DAX index of German equities increased 1.3 percent on Jan 22, 2015 and 2.1 percent on Jan 23, 2015. The euro depreciated from EUR 1.1611/USD (EUR 0.8613/USD) on Wed Jan 21, 2015, to EUR 1.1206/USD (EUR 0.8924/USD) on Fri Jan 23, 2015, or 3.6 percent. Yellen (2011AS, 6) admits that Fed monetary policy results in dollar devaluation with the objective of increasing net exports, which was the policy that Joan Robinson (1947) labeled as “beggar-my-neighbor” remedies for unemployment. Risk aversion erodes devaluation of the dollar.
Dan Strumpf and Pedro Nicolaci da Costa, writing on “Fed’s Yellen: Stock Valuations ‘Generally are Quite High,’” on May 6, 2015, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/feds-yellen-cites-progress-on-bank-regulation-1430918155?tesla=y ), quote Chair Yellen at open conversation with Christine Lagarde, Managing Director of the IMF, finding “equity-market valuations” as “quite high” with “potential dangers” in bond valuations. The DJIA fell 0.5 percent on May 6, 2015, after the comments and then increased 0.5 percent on May 7, 2015 and 1.5 percent on May 8, 2015.
| Fri May 1 | Mon 4 | Tue 5 | Wed 6 | Thu 7 | Fri 8 |
| DJIA 18024.06 -0.3% 1.0% | 18070.40 0.3% 0.3% | 17928.20 -0.5% -0.8% | 17841.98 -1.0% -0.5% | 17924.06 -0.6% 0.5% | 18191.11 0.9% 1.5% |
There are two approaches in theory considered by Bordo (2012Nov20) and Bordo and Lane (2013). The first approach is in the classical works of Milton Friedman and Anna Jacobson Schwartz (1963a, 1987) and Karl Brunner and Allan H. Meltzer (1973). There is a similar approach in Tobin (1969). Friedman and Schwartz (1963a, 66) trace the effects of expansionary monetary policy into increasing initially financial asset prices: “It seems plausible that both nonbank and bank holders of redundant balances will turn first to securities comparable to those they have sold, say, fixed-interest coupon, low-risk obligations. But as they seek to purchase these they will tend to bid up the prices of those issues. Hence they, and also other holders not involved in the initial central bank open-market transactions, will look farther afield: the banks, to their loans; the nonbank holders, to other categories of securities-higher risk fixed-coupon obligations, equities, real property, and so forth.”
The second approach is by the Austrian School arguing that increases in asset prices can become bubbles if monetary policy allows their financing with bank credit. Professor Michael D. Bordo provides clear thought and empirical evidence on the role of “expansionary monetary policy” in inflating asset prices (Bordo2012Nov20, Bordo and Lane 2013). Bordo and Lane (2013) provide revealing narrative of historical episodes of expansionary monetary policy. Bordo and Lane (2013) conclude that policies of depressing interest rates below the target rate or growth of money above the target influences higher asset prices, using a panel of 18 OECD countries from 1920 to 2011. Bordo (2012Nov20) concludes: “that expansionary money is a significant trigger” and “central banks should follow stable monetary policies…based on well understood and credible monetary rules.” Taylor (2007, 2009) explains the housing boom and financial crisis in terms of expansionary monetary policy.
Another hurdle of exit from zero interest rates is “competitive easing” that Professor Raghuram Rajan, governor of the Reserve Bank of India, characterizes as disguised “competitive devaluation” (http://www.centralbanking.com/central-banking-journal/interview/2358995/raghuram-rajan-on-the-dangers-of-asset-prices-policy-spillovers-and-finance-in-india). The fed has been considering increasing interest rates. The European Central Bank (ECB) announced, on Mar 5, 2015, the beginning on Mar 9, 2015 of its quantitative easing program denominated as Public Sector Purchase Program (PSPP), consisting of “combined monthly purchases of EUR 60 bn [billion] in public and private sector securities” (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/mopo/liq/html/pspp.en.html). Expectation of increasing interest rates in the US together with euro rates close to zero or negative cause revaluation of the dollar (or devaluation of the euro and of most currencies worldwide). US corporations suffer currency translation losses of their foreign transactions and investments (http://www.fasb.org/jsp/FASB/Pronouncement_C/SummaryPage&cid=900000010318) while the US becomes less competitive in world trade (Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. I (2008a), Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c)). The DJIA fell 1.5 percent on Mar 6, 2015 and the dollar revalued 2.2 percent from Mar 5 to Mar 6, 2015. The euro has devalued 40.1 percent relative to the dollar from the high on Jul 15, 2008 to Jun 19, 2015.
| Fri 27 Feb | Mon 3/2 | Tue 3/3 | Wed 3/4 | Thu 3/5 | Fri 3/6 |
| USD/ EUR 1.1197 1.6% 0.0% | 1.1185 0.1% 0.1% | 1.1176 0.2% 0.1% | 1.1081 1.0% 0.9% | 1.1030 1.5% 0.5% | 1.0843 3.2% 1.7% |
Chair Yellen explained the removal of the word “patience” from the advanced guidance at the press conference following the FOMC meeting on Mar 18, 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20150318.pdf):
“In other words, just because we removed the word “patient” from the statement doesn’t mean we are going to be impatient. Moreover, even after the initial increase in the target funds rate, our policy is likely to remain highly accommodative to support continued progress toward our objectives of maximum employment and 2 percent inflation.”
Exchange rate volatility is increasing in response of “impatience” in financial markets with monetary policy guidance and measures:
| Fri Mar 6 | Mon 9 | Tue 10 | Wed 11 | Thu 12 | Fri 13 |
| USD/ EUR 1.0843 3.2% 1.7% | 1.0853 -0.1% -0.1% | 1.0700 1.3% 1.4% | 1.0548 2.7% 1.4% | 1.0637 1.9% -0.8% | 1.0497 3.2% 1.3% |
| Fri Mar 13 | Mon 16 | Tue 17 | Wed 18 | Thu 19 | Fri 20 |
| USD/ EUR 1.0497 3.2% 1.3% | 1.0570 -0.7% -0.7% | 1.0598 -1.0% -0.3% | 1.0864 -3.5% -2.5% | 1.0661 -1.6% 1.9% | 1.0821 -3.1% -1.5% |
| Fri Apr 24 | Mon 27 | Tue 28 | Wed 29 | Thu 30 | May Fri 1 |
| USD/ EUR 1.0874 -0.6% -0.4% | 1.0891 -0.2% -0.2% | 1.0983 -1.0% -0.8% | 1.1130 -2.4% -1.3% | 1.1223 -3.2% -0.8% | 1.1199 -3.0% 0.2% |
In a speech at Brown University on May 22, 2015, Chair Yellen stated (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20150522a.htm):
“For this reason, if the economy continues to improve as I expect, I think it will be appropriate at some point this year to take the initial step to raise the federal funds rate target and begin the process of normalizing monetary policy. To support taking this step, however, I will need to see continued improvement in labor market conditions, and I will need to be reasonably confident that inflation will move back to 2 percent over the medium term. After we begin raising the federal funds rate, I anticipate that the pace of normalization is likely to be gradual. The various headwinds that are still restraining the economy, as I said, will likely take some time to fully abate, and the pace of that improvement is highly uncertain.”
The US dollar appreciated 3.8 percent relative to the euro in the week of May 22, 2015:
| Fri May 15 | Mon 18 | Tue 19 | Wed 20 | Thu 21 | Fri 22 |
| USD/ EUR 1.1449 -2.2% -0.3% | 1.1317 1.2% 1.2% | 1.1150 2.6% 1.5% | 1.1096 3.1% 0.5% | 1.1113 2.9% -0.2% | 1.1015 3.8% 0.9% |
The Managing Director of the International Monetary Fund (IMF), Christine Lagarde, warned on Jun 4, 2015, that: (http://blog-imfdirect.imf.org/2015/06/04/u-s-economy-returning-to-growth-but-pockets-of-vulnerability/):
“The Fed’s first rate increase in almost 9 years is being carefully prepared and telegraphed. Nevertheless, regardless of the timing, higher US policy rates could still result in significant market volatility with financial stability consequences that go well beyond US borders. I weighing these risks, we think there is a case for waiting to raise rates until there are more tangible signs of wage or price inflation than are currently evident. Even after the first rate increase, a gradual rise in the federal fund rates will likely be appropriate.”
The President of the European Central Bank (ECB), Mario Draghi, warned on Jun 3, 2015 that (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pressconf/2015/html/is150603.en.html):
“But certainly one lesson is that we should get used to periods of higher volatility. At very low levels of interest rates, asset prices tend to show higher volatility…the Governing Council was unanimous in its assessment that we should look through these developments and maintain a steady monetary policy stance.”
Professor Ronald I. McKinnon (2013Oct27), writing on “Tapering without tears—how to end QE3,” on Oct 27, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702304799404579153693500945608?KEYWORDS=Ronald+I+McKinnon), finds that the major central banks of the world have fallen into a “near-zero-interest-rate trap.” World economic conditions are weak such that exit from the zero interest rate trap could have adverse effects on production, investment and employment. The maintenance of interest rates near zero creates long-term near stagnation. The proposal of Professor McKinnon is credible, coordinated increase of policy interest rates toward 2 percent. Professor John B. Taylor at Stanford University, writing on “Economic failures cause political polarization,” on Oct 28, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702303442004579121010753999086?KEYWORDS=John+B+Taylor), analyzes that excessive risks induced by near zero interest rates in 2003-2004 caused the financial crash. Monetary policy continued in similar paths during and after the global recession with resulting political polarization worldwide.
Table IV-2 provides economic projections of governors of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve and regional presidents of Federal Reserve Banks released at the meeting of Jun 17, 2015. The Fed releases the data with careful explanations (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20141217.pdf). Columns “∆% GDP,” “∆% PCE Inflation” and “∆% Core PCE Inflation” are changes “from the fourth quarter of the previous year to the fourth quarter of the year indicated.” The GDP report for IQ2015 is analyzed in Section I (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/dollar-revaluation-squeezing-corporate.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/dollar-devaluation-and-carry-trade.html) and the PCE inflation data from the report on personal income and outlays in Section IV (and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/dollar-devaluation-and-carry-trade.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/volatility-of-valuations-of-financial.html). The Bureau of Economic Analysis provides the estimate of IQ2015 GDP (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/dollar-revaluation-squeezing-corporate.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/dollar-devaluation-and-carry-trade.html). PCE inflation is the index of personal consumption expenditures (PCE) of the report of the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) on “Personal Income and Outlays” (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/pinewsrelease.htm), which is analyzed in Section IV (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/dollar-devaluation-and-carry-trade.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/volatility-of-valuations-of-financial.html). The report on “Personal Income and Outlays” was released on Jun 1, 2015 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html). PCE core inflation consists of PCE inflation excluding food and energy. Column “UNEMP %” is the rate of unemployment measured as the average civilian unemployment rate in the fourth quarter of the year. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) provides the Employment Situation Report with the civilian unemployment rate in the first Friday of every month, which is analyzed in this blog. The report for May was released on Jun 5, 2015 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/quite-high-equity-valuations-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/volatility-of-valuations-of-financial.html). “The longer-run projections are the rates of growth, unemployment, and inflation to which a policymaker expects the economy to converge over time—maybe in five or six years—in the absence of further shocks and under appropriate monetary policy” (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20131218.pdf).
It is instructive to focus on 2015 and 2016 because 2017 and longer term are too far away. There is not much information even on what will happen in 2016-2017 and beyond. The central tendency should provide reasonable approximation of the view of the majority of members of the FOMC but the second block of numbers provides the range of projections by FOMC participants. The first row for each year shows the projection introduced after the meeting of Jun 17, 2015 and the second row “PR” the projection of the Mar 18, 2014 meeting. The projections for 2014 are those released in the Sep 2014 and Dec 2014 meetings. There are three changes in the view.
1. Growth “∆% GDP.” The FOMC lowers the forecast of GDP growth in 2015. The FOMC projects GDP growth in 2015 from 2.3 to 2.7 percent at the meeting in Mar 2015 to 1.8 to 2.0 percent at the meeting in Jun 2015.
2. Rate of Unemployment “UNEM%.” The FOMC increased the forecast of the rate of unemployment for 2015 from 5.0 to 5.2 percent at the meeting on Mar 18, 2014 to 5.2 to 5.3 percent at the meeting on Jun 17, 2015. The projection for 2016 did not change to the range of 4.9 to 5.1 in Jun 2015 from 4.9 to 5.1 in Jun 2015. Projections of the rate of unemployment are moving closer to around 5 percent or lower with 4.9 to 5.1 percent in 2017 after the meeting on Jun 17, 2015.
3. Inflation “∆% PCE Inflation.” The FOMC lowered the forecast prices of personal consumption expenditures (PCE) inflation for 2015 to 0.6 to 0.8 percent at the meeting on Jun 17, 2015. There are no projections exceeding 2.0 percent in the central tendency but some in the range reach 2.4 percent in 2016. The longer run projection is at 2.0 percent.
4. Core Inflation “∆% Core PCE Inflation.” Core inflation is PCE inflation excluding food and energy. There is milder inflation in the projection for 2015, changing to 1.3 to 1.4 at the meeting on Jun 17, 2015. In 2016, there is minor change in the projection from 1.5 to 1.9 percent at the meeting on Mar 18, 2015 to 1.6 to 1.9 percent on Jun 17, 2015. The rate of change of the core PCE is below 2.0 percent in the central tendency with 2.4 percent at the top of the range in 2016.
Table IV-2, US, Economic Projections of Federal Reserve Board Members and Federal Reserve Bank Presidents in FOMC, Mar 18, 2014 and Jun 17, 20014
| ∆% GDP | UNEM % | ∆% PCE Inflation | ∆% Core PCE Inflation | |
| Central | ||||
| 2014 | 2.3 to 2.4 | 5.8 | 1.2 to 1.3 | 1.5 to 1.6 |
| 2015 Mar PR | 1.8 to 2.0 2.3 to 2.7 | 5.2 to 5.3 5.0 to 5.2 | 0.6 to 0.8 0.6 to 0.8 | 1.3 to 1.4 1.3 to 1.4 |
| 2016 Mar PR | 2.4 to 2.7 2.3 to 2.7 | 4.9 to 5.1 4.9 to 5.1 | 1.6 to 1.9 1.7 to 1.9 | 1.6 to 1.9 1.5 to 1.9 |
| 2017 Mar PR | 2.1 to 2.5 2.0 to 2.4 | 4.9 to 5.1 4.8 to 5.1 | 1.9 to 2.0 1.9 to 2.0 | 1.9 to 2.0 1.8 to 2.0 |
| Longer Run Mar PR | 2.0 to 2.3 2.0 to 2.3 | 5.0 to 5.2 5.0 to 5.2 | 2.0 2.0 | |
| Range | ||||
| 2014 | 2.3 to 2.5 | 5.7 to 5.8 | 1.2 to 1.6 | 1.5 to 1.6 |
| 2015 Mar PR | 1.7 to 2.3 2.1 to 3.1 | 5.0 to 5.3 4.8 to 5.3 | 0.6 to 1.0 0.6 to 1.5 | 1.2 to 1.6 1.2 to 1.6 |
| 2016 Mar PR | 2.3 to 3.0 2.2 to 3.0 | 4.6 to 5.2 4.5 to 5.2 | 1.5 to 2.4 1.6 to 2.4 | 1.5 to 2.4 1.5 to 2.4 |
| 2017 Mar PR | 2.0 to 2.5 1.8 to 2.5 | 4.8 to 5.5 4.8 to 5.5 | 1.7 to 2.2 1.7 to 2.2 | 1.7 to 2.2 1.7 to 2.2 |
| Longer Run Mar PR | 1.8 to 2.5 1.8 to 2.5 | 5.0 to 5.8 4.9 to 5.8 | 2.0 2.0 |
Notes: UEM: unemployment; PR: Projection
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, FOMC
http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20140917.pdf
http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20141217.pdf
http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20150318.pdf
http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20150617.pdf
Another important decision at the FOMC meeting on Jan 25, 2012, is formal specification of the goal of inflation of 2 percent per year but without specific goal for unemployment (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20120125c.htm):
“Following careful deliberations at its recent meetings, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) has reached broad agreement on the following principles regarding its longer-run goals and monetary policy strategy. The Committee intends to reaffirm these principles and to make adjustments as appropriate at its annual organizational meeting each January.
The FOMC is firmly committed to fulfilling its statutory mandate from the Congress of promoting maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates. The Committee seeks to explain its monetary policy decisions to the public as clearly as possible. Such clarity facilitates well-informed decision making by households and businesses, reduces economic and financial uncertainty, increases the effectiveness of monetary policy, and enhances transparency and accountability, which are essential in a democratic society.
Inflation, employment, and long-term interest rates fluctuate over time in response to economic and financial disturbances. Moreover, monetary policy actions tend to influence economic activity and prices with a lag. Therefore, the Committee's policy decisions reflect its longer-run goals, its medium-term outlook, and its assessments of the balance of risks, including risks to the financial system that could impede the attainment of the Committee's goals.
The inflation rate over the longer run is primarily determined by monetary policy, and hence the Committee has the ability to specify a longer-run goal for inflation. The Committee judges that inflation at the rate of 2 percent, as measured by the annual change in the price index for personal consumption expenditures, is most consistent over the longer run with the Federal Reserve's statutory mandate. Communicating this inflation goal clearly to the public helps keep longer-term inflation expectations firmly anchored, thereby fostering price stability and moderate long-term interest rates and enhancing the Committee's ability to promote maximum employment in the face of significant economic disturbances.
The maximum level of employment is largely determined by nonmonetary factors that affect the structure and dynamics of the labor market. These factors may change over time and may not be directly measurable. Consequently, it would not be appropriate to specify a fixed goal for employment; rather, the Committee's policy decisions must be informed by assessments of the maximum level of employment, recognizing that such assessments are necessarily uncertain and subject to revision. The Committee considers a wide range of indicators in making these assessments. Information about Committee participants' estimates of the longer-run normal rates of output growth and unemployment is published four times per year in the FOMC's Summary of Economic Projections. For example, in the most recent projections, FOMC participants' estimates of the longer-run normal rate of unemployment had a central tendency of 5.2 percent to 6.0 percent, roughly unchanged from last January but substantially higher than the corresponding interval several years earlier.
In setting monetary policy, the Committee seeks to mitigate deviations of inflation from its longer-run goal and deviations of employment from the Committee's assessments of its maximum level. These objectives are generally complementary. However, under circumstances in which the Committee judges that the objectives are not complementary, it follows a balanced approach in promoting them, taking into account the magnitude of the deviations and the potentially different time horizons over which employment and inflation are projected to return to levels judged consistent with its mandate. ”
The probable intention of this specific inflation goal is to “anchor” inflationary expectations. Massive doses of monetary policy of promoting growth to reduce unemployment could conflict with inflation control. Economic agents could incorporate inflationary expectations in their decisions. As a result, the rate of unemployment could remain the same but with much higher rate of inflation (see Kydland and Prescott 1977 and Barro and Gordon 1983; http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/05/slowing-growth-global-inflation-great.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/04/new-economics-of-rose-garden-turned.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/03/is-there-second-act-of-us-great.html See Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 99-116). Strong commitment to maintaining inflation at 2 percent could control expectations of inflation.
The FOMC continues its efforts of increasing transparency that can improve the credibility of its firmness in implementing its dual mandate. Table IV-3 provides the views by participants of the FOMC of the levels at which they expect the fed funds rate in 2015, 2016, 2017 and the in the longer term. Table IV-3 is inferred from a chart provided by the FOMC with the number of participants expecting the target of fed funds rate (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20150617.pdf). The rate would still remain at 0 to ¼ percent in 2015 for 2 participants. This table is consistent with the guidance statement of the FOMC that rates will remain at low levels. For 2015, 15 participants expect the rate to remain between 0.5 and 1.0 percent and 2 between 0 to 0.25 percent. For 2016, 2 participants expect the rate between 0.5 and 1 percent, 5 participant between 1 and 1.5 percent, 9 between 1 and 2 percent, 5 between 2.0 and 3.0 percent and none above 3 percent. In the long term, all 17 participants expect the fed funds rate in the range of 3.0 to 4.5 percent.
Table IV-3, US, Views of Target Federal Funds Rate at Year-End of Federal Reserve Board
Members and Federal Reserve Bank Presidents Participating in FOMC, Jun 17, 2014
| 0 to 0.25 | 0.5 to 1.0 | 1.0 to 1.5 | 1.0 to 2.0 | 2.0 to 3.0 | 3.0 to 4.5 | |
| 2015 | 2 | 15 | ||||
| 2016 | 2 | 5 | 9 | 5 | ||
| 2017 | 1 | 8 | 8 | |||
| Longer Run | 17 |
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, FOMC
http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20150617.pdf
Additional information is provided in Table IV-4 with the number of participants expecting increasing interest rates in the years from 2015 to 2016. It is evident from Table IV-4 that the prevailing view of the FOMC is for interest rates to continue at low levels until 2015 but with some increase. This view is consistent with the economic projections of low economic growth, relatively high unemployment and subdued inflation provided in Table IV-2. The FOMC states that rates will continue to be low even after return of the economy to potential growth.
Table IV-4, US, Views of Appropriate Year of Increasing Target Federal Funds Rate of Federal Reserve Board Members and Federal Reserve Bank Presidents Participating in FOMC, Dec 17, 2014
| Appropriate Year of Increasing Target Fed Funds Rate | Number of Participants |
| 2015 | 15 |
| 2016 | 2 |
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, FOMC
http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20150617.pdf
There are two categories of responses in the Empire State Manufacturing Survey of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York (http://www.newyorkfed.org/survey/empire/empiresurvey_overview.html): current conditions and expectations for the next six months. There are responses in the survey for two types of prices: prices received or inputs of production and prices paid or sales prices of products. Table IV-5 provides indexes for the two categories and within them for the two types of prices from Jan 2011 to Jun 2015. The index of current prices paid or costs of inputs moved from 16.13 in Dec 2012 to 9.62 in Jun 2015 while the index of current prices received or sales prices decreased from 1.08 in Dec 2012 to 0.96 in Jun 2015. The farther the index is from the area of no change at zero, the faster the rate of change. Prices paid or costs of inputs at 9.62 in Jun 2015 are expanding at faster pace than prices received or of sales of products at 0.96. The index of future prices paid or expectations of costs of inputs in the next six months fell from 51.61 in Dec 2012 to 24.04 in Jun 2015 while the index of future prices received or expectation of sales prices in the next six months decreased from 25.81 in Dec 2012 to 5.77 in Jun 2015. Priced paid or of inputs are expected to increase at a faster pace in the next six months than prices received or prices of sales products. Prices of sales of finished products are less dynamic than prices of costs of inputs during waves of increases. Prices of costs of costs of inputs fall less rapidly than prices of sales of finished products during waves of price decreases. As a result, margins of prices of sales less costs of inputs oscillate with typical deterioration against producers, forcing companies to manage tightly costs and labor inputs. Instability of sales/costs margins discourages investment and hiring.
Table IV-5, US, FRBNY Empire State Manufacturing Survey, Diffusion Indexes, Prices Paid and Prices Received, SA
| Current Prices Paid | Current Prices Received | Six Months Prices Paid | Six Months Prices Received | |
| Jan-11 | 35.79 | 15.79 | 60 | 42.11 |
| Feb-11 | 45.78 | 16.87 | 55.42 | 27.71 |
| Mar-11 | 53.25 | 20.78 | 71.43 | 36.36 |
| Apr-11 | 57.69 | 26.92 | 56.41 | 38.46 |
| May-11 | 69.89 | 27.96 | 68.82 | 35.48 |
| Jun-11 | 56.12 | 11.22 | 55.1 | 19.39 |
| Jul-11 | 43.33 | 5.56 | 51.11 | 30 |
| Aug-11 | 28.26 | 2.17 | 42.39 | 15.22 |
| Sep-11 | 32.61 | 8.7 | 53.26 | 22.83 |
| Oct-11 | 22.47 | 4.49 | 40.45 | 17.98 |
| Nov-11 | 18.29 | 6.1 | 36.59 | 25.61 |
| Dec-11 | 24.42 | 3.49 | 56.98 | 36.05 |
| Jan-12 | 26.37 | 23.08 | 53.85 | 30.77 |
| Feb-12 | 25.88 | 15.29 | 62.35 | 34.12 |
| Mar-12 | 50.62 | 13.58 | 66.67 | 32.1 |
| Apr-12 | 45.78 | 19.28 | 50.6 | 22.89 |
| May-12 | 37.35 | 12.05 | 57.83 | 22.89 |
| Jun-12 | 19.59 | 1.03 | 34.02 | 17.53 |
| Jul-12 | 7.41 | 3.7 | 35.8 | 16.05 |
| Aug-12 | 16.47 | 2.35 | 31.76 | 14.12 |
| Sep-12 | 19.15 | 5.32 | 40.43 | 23.4 |
| Oct-12 | 17.2 | 4.3 | 44.09 | 24.73 |
| Nov-12 | 14.61 | 5.62 | 39.33 | 15.73 |
| Dec-12 | 16.13 | 1.08 | 51.61 | 25.81 |
| Jan-13 | 22.58 | 10.75 | 38.71 | 21.51 |
| Feb-13 | 26.26 | 8.08 | 44.44 | 13.13 |
| Mar-13 | 25.81 | 2.15 | 50.54 | 23.66 |
| Apr-13 | 28.41 | 5.68 | 44.32 | 14.77 |
| May-13 | 20.45 | 4.55 | 29.55 | 14.77 |
| Jun-13 | 20.97 | 11.29 | 45.16 | 17.74 |
| Jul-13 | 17.39 | 1.09 | 28.26 | 11.96 |
| Aug-13 | 20.48 | 3.61 | 40.96 | 19.28 |
| Sep-13 | 21.51 | 8.6 | 39.78 | 24.73 |
| Oct-13 | 21.69 | 2.41 | 45.78 | 25.3 |
| Nov-13 | 17.11 | -3.95 | 42.11 | 17.11 |
| Dec-13 | 15.66 | 3.61 | 48.19 | 27.71 |
| Jan-14 | 36.59 | 13.41 | 45.12 | 23.17 |
| Feb-14 | 25 | 15 | 40 | 23.75 |
| Mar-14 | 21.18 | 2.35 | 43.53 | 25.88 |
| Apr-14 | 22.45 | 10.2 | 33.67 | 14.29 |
| May-14 | 19.78 | 6.59 | 31.87 | 14.29 |
| Jun-14 | 17.2 | 4.3 | 36.56 | 16.13 |
| Jul-14 | 25 | 6.82 | 37.5 | 18.18 |
| Aug-14 | 27.27 | 7.95 | 42.05 | 21.59 |
| Sep-14 | 23.91 | 17.39 | 43.48 | 32.61 |
| Oct-14 | 11.36 | 6.82 | 42.05 | 26.14 |
| Nov-14 | 10.64 | 0 | 41.49 | 25.53 |
| Dec-14 | 10.42 | 6.25 | 40.63 | 32.29 |
| Jan-15 | 12.63 | 12.63 | 33.68 | 15.79 |
| Feb-15 | 14.61 | 3.37 | 26.97 | 5.62 |
| Mar-15 | 12.37 | 8.25 | 31.96 | 12.37 |
| Apr-15 | 19.15 | 4.26 | 38.3 | 13.83 |
| May-15 | 9.38 | 1.04 | 26.04 | 7.29 |
| Jun-15 | 9.62 | 0.96 | 24.04 | 5.77 |
http://www.newyorkfed.org/survey/empire/empiresurvey_overview.html
Price indexes of the Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia Outlook Survey are in Table IV-5A. As inflation waves throughout the world (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/interest-rate-policy-and-dollar.html), indexes of both current and expectations of future prices paid and received were quite high until May 2011. Prices paid, or inputs, were more dynamic, reflecting carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures. All indexes softened after May 2011 with even decline of prices received in Aug 2011 during the first round of risk aversion. Current and future price indexes have increased again but not back to the intensity in the beginning of 2011 because of risk aversion frustrating carry trades even induced by zero interest rates. The index of prices paid or prices of inputs moved from 20.8 in Dec 2012 to 17.2 in Jun 2015. The index of current prices received was minus 2.4 in Apr 2013, indicating decrease of prices received. The index of current prices received decreased from 9.2 in Dec 2012 to minus 4.8 in Jun 2015. The farther the index is from the area of no change at zero, the faster the rate of change. The index of current prices paid or costs of inputs at 17.2 in May 2015 indicates faster expansion than the index of current prices received or sales prices of production at 4.8. Prices paid indicate faster expansion than prices received during most of the history of the index. The index of future prices paid increased to 46.3 in Jun 2015 from 40.6 in Dec 2012 while the index of future prices received decreased from 21.9 in Dec 2012 to 12.8 in Jun 2015. Expectations are incorporating faster increases in prices of inputs or costs of production, 46.3 in Jun 2015, than of sales prices of produced goods, 12.8 in Jun 2015, forcing companies to manage tightly costs and labor inputs. Volatility of margins of sales/costs discourages investment and hiring.
Table IV-5A, US, Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia Business Outlook Survey, Current and Future Prices Paid and Prices Received, SA
| Current Prices Paid | Current Prices Received | Future Prices Paid | Future Prices Received | |
| 10-Dec | 42.8 | 5.3 | 56.0 | 24.2 |
| 11-Jan | 48.1 | 12.3 | 58.3 | 34.8 |
| 11-Feb | 61.1 | 13.4 | 67.7 | 31.5 |
| 11-Mar | 59 | 17.6 | 62.4 | 33.4 |
| 11-Apr | 52.1 | 23.6 | 56.2 | 35.7 |
| 11-May | 49.8 | 20.6 | 54.9 | 28.6 |
| 11-Jun | 37.4 | 7.2 | 41.4 | 6.9 |
| 11-Jul | 34.4 | 5.5 | 49.3 | 17.5 |
| 11-Aug | 23.6 | -3.9 | 43.5 | 22.8 |
| 11-Sep | 30.7 | 6.3 | 38.3 | 20.6 |
| 11-Oct | 23 | 1.7 | 41.5 | 27.9 |
| 11-Nov | 22.2 | 5.3 | 33.3 | 26.3 |
| 11-Dec | 25.1 | 5.8 | 42 | 21.1 |
| 12-Jan | 25.8 | 8.6 | 46.9 | 22.2 |
| 12-Feb | 32.7 | 9.9 | 50.5 | 26.3 |
| 12-Mar | 16.6 | 6.5 | 38.7 | 24.3 |
| 12-Apr | 19.9 | 10 | 36.7 | 23.7 |
| 12-May | 8.9 | 0.9 | 39.9 | 9.6 |
| 12-Jun | 3.4 | -4.5 | 34.5 | 16.9 |
| 12-Jul | 9 | 3.5 | 29.1 | 21.4 |
| 12-Aug | 17 | 6.1 | 36.8 | 23.9 |
| 12-Sep | 14 | 2.6 | 39 | 24.9 |
| 12-Oct | 18 | 5.2 | 44.1 | 15.4 |
| 12-Nov | 22.8 | 5.1 | 44.6 | 10.6 |
| 12-Dec | 20.8 | 9.2 | 40.6 | 21.9 |
| 13-Jan | 12.3 | -0.5 | 33.2 | 22.3 |
| 13-Feb | 11.9 | -0.7 | 33.9 | 22.5 |
| 13-Mar | 11.4 | 0.6 | 34.3 | 19.3 |
| 13-Apr | 7.6 | -2.4 | 31.1 | 14.7 |
| 13-May | 11.9 | 0.5 | 34.3 | 19.8 |
| 13-Jun | 20.8 | 13.6 | 33.1 | 24 |
| 13-Jul | 20.3 | 6 | 42.7 | 26.9 |
| 13-Aug | 19.6 | 12 | 36.9 | 23 |
| 13-Sep | 23.8 | 11.6 | 39 | 27.9 |
| 13-Oct | 18.5 | 10.2 | 41.2 | 35 |
| 13-Nov | 24.4 | 7.6 | 39.4 | 36 |
| 13-Dec | 16.9 | 8.5 | 37.9 | 28.8 |
| 14-Jan | 18.8 | 6.3 | 34.3 | 14.2 |
| 14-Feb | 14.8 | 7.9 | 27.2 | 18.1 |
| 14-Mar | 18.3 | 6.4 | 31.8 | 18.8 |
| 14-Apr | 14.5 | 9.6 | 38.3 | 18.6 |
| 14-May | 26.5 | 18 | 36.9 | 29.6 |
| 14-Jun | 32 | 13.1 | 45.1 | 30.1 |
| 14-Jul | 32.3 | 14.7 | 40.1 | 25 |
| 14-Aug | 24.1 | 5.1 | 47.5 | 27.7 |
| 14-Sep | 24.4 | 8 | 41.9 | 26.6 |
| 14-Oct | 24.9 | 18.2 | 30.5 | 23 |
| 14-Nov | 15.8 | 10 | 30.5 | 18.7 |
| 14-Dec | 14.4 | 9.8 | 22.3 | 20.6 |
| 15-Jan | 9.8 | -0.2 | 26 | 20.7 |
| 15-Feb | 4.7 | -0.2 | 32.2 | 19.3 |
| 15-Mar | -3 | -6.4 | 27.5 | 7.4 |
| 15-Apr | -7.5 | -4.1 | 19.9 | 10.7 |
| 15-May | -14.2 | -5.4 | 20.9 | 19.4 |
| 15-Jun | 17.2 | 4.8 | 46.3 | 12.8 |
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia
http://www.philadelphiafed.org/index.cfm
Chart IV-1 of the Business Outlook Survey of the Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia Outlook Survey provides the diffusion index of current prices paid or prices of inputs from 2006 to 2015. Recession dates are in shaded areas. In the middle of deep global contraction after IVQ2007, input prices continued to increase in speculative carry trades from central bank policy rates falling toward zero into commodities futures. The index peaked above 70 in the second half of 2008. Inflation of inputs moderated significantly during the shock of risk aversion in late 2008, even falling briefly into contraction territory below zero during several months in 2009 in the flight away from risk financial assets into US government securities (Cochrane and Zingales 2009) that unwound carry trades. Return of risk appetite induced carry trade with significant increase until return of risk aversion in the first round of the European sovereign debt crisis in Apr 2010. Carry trades returned during risk appetite in expectation that the European sovereign debt crisis was resolved. The various inflation waves originating in carry trades induced by zero interest rates with alternating episodes of risk aversion are mirrored in the prices of inputs after 2011, in particular after Aug 2012 with the announcement of the Outright Monetary Transactions Program of the European Central Bank (http://www.ecb.int/press/pr/date/2012/html/pr120906_1.en.html). Subsequent risk aversion and flows of capital away from commodities into stocks and high-yield bonds caused sharp decline in the index of prices paid followed by another recent rebound with marginal decline and new increase. The index falls, rebounds and falls again in the final segment but there are no episodes of contraction after 2009 with exception of minus 3.0 in Mar 2015, minus 7.5 in Apr 2015 and minus 14.2 in May 2015.
Chart IV-1, Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia Business Outlook Survey Current Prices Paid Diffusion Index SA
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia
http://www.philadelphiafed.org/index.cfm
Chart IV-2 of the Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia Outlook Survey provides the diffusion index of current prices received from 2006 to 2015. The significant difference between the index of current prices paid in Chart IV-1 and the index of current prices received in Chart IV-2 is that increases in prices paid are significantly sharper than increases in prices received. There were several periods of negative readings of prices received from 2010 to 2015. There were only three contraction of prices paid: 3.0 Mar 2015 with sharper contraction of 6.4 of prices received; minus 7.5 for prices paid in Apr 2015 with minus 4.1 for prices received; and minus 14.2 for prices paid in May 2015 with minus 5.4 for prices received. Prices received relative to prices paid deteriorate most of the time largely because of the carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures. Profit margins of business are compressed intermittently by fluctuations of commodity prices induced by unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates, frustrating production, investment and hiring decisions of business, which is precisely the opposite outcome pursued by unconventional monetary policy.
Chart IV-2, Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia Business Outlook Survey Current Prices Received Diffusion Index SA
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia
http://www.philadelphiafed.org/index.cfm
The harmonized index of consumer prices of the euro area in Table IV-6 has similar inflation waves as in most countries (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/interest-rate-policy-and-dollar.html and earlier). In the first wave, consumer prices in the euro area increased at the annual equivalent rate of 4.9 percent in Jan-Apr 2011. In the second wave, risk aversion caused unwinding of commodity carry trades with inflation decreasing at the annual equivalent rate of minus 2.4 percent in May-Jul 2011. In the third wave, improved risk appetite resulted in annual equivalent inflation in Aug-Nov 2011 at 4.0 percent. In the fourth wave, return of risk aversion caused decline of consumer prices at the annual equivalent rate of minus 3.0 percent in Dec 2011 to Jan 2012. In the fifth wave, improved attitudes toward risk aversion resulted in higher consumer price inflation at the high annual equivalent rate of 9.6 percent in Feb-Apr 2012. In the sixth wave, annual equivalent inflation fell to minus 2.8 percent in May-Jul 2012. In the seventh wave, increasing risk appetite caused new carry trade exposures that resulted in annual equivalent inflation of 6.8 percent in Aug-Sep 2012 and 5.3 percent in Aug-Oct 2012. In the eighth wave, annual-equivalent inflation was minus 2.4 percent in Nov 2012. In the ninth wave, annual equivalent inflation was 4.9 percent in Dec 2012. In the tenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 11.4 percent in Jan 2013. In the eleventh wave, annual equivalent inflation was 10.0 percent in Feb-Mar 2013. In the twelfth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 1.2 percent in Apr 2013. In the thirteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation rose to 1.2 percent in May-Jun 2013. In the fourteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 5.8 percent in Jul 2013. In the fifteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was 3.7 percent in Aug-Sep 2013. In the sixteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 2.4 percent in Oct-Nov 2013. In the eighteenth wave, annual inflation returned at 4.9 percent in Dec 2013. In the nineteenth wave, inflation fell at annual equivalent 12.4 percent in Jan 2014. In the twentieth wave, annual equivalent inflation was at 5.7 percent in Feb-Apr 2014. In the twenty-first wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 1.2 percent in May 2014. Inflation volatility around the world is confusing the information required in investment and consumption decisions. In the twenty-second wave, annual equivalent inflation was 1.2 percent in Jun 2014. In the twenty-third wave, annual equivalent inflation was at minus 8.1 percent in Jul 2014. In the twenty-fourth wave, annual equivalent inflation was 3.0 percent in Aug-Sep 2014. In the twenty-fifth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 5.6 percent in Oct 2014-Jan 2015. In the twenty-sixth wave, annual equivalent inflation was 6.5 percent in Feb-May 2015. The bottom part of Table IV-6 provides annual inflation in the euro area from 1999 to 2014. HICP inflation was 3.3 percent in 2008 mostly because of carry trades from interest rates falling to zero into commodity futures. Exposures in commodity futures were reversed in the flight to US government obligations with resulting inflation of 0.3 percent in 2009. Reallocations of portfolios of financial investors according to risk aversion caused high volatility of inflation in 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014 and 2015.
Table IV-6, Euro Area Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices Month and 12 Months ∆%
| Month ∆% | 12 Months ∆% | |
| May 2015 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| Apr | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| Mar | 1.1 | -0.1 |
| Feb | 0.6 | -0.3 |
| AE ∆% Feb-May | 6.5 | |
| Jan | -1.5 | -0.6 |
| Dec 2014 | -0.1 | -0.2 |
| Nov | -0.2 | 0.3 |
| Oct | -0.1 | 0.4 |
| AE ∆% Oct-Jan | -5.6 | |
| Sep | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| Aug | 0.1 | 0.4 |
| AE ∆% Aug-Sep | 3.0 | |
| Jul | -0.7 | 0.4 |
| AE ∆% Jul | -8.1 | |
| Jun | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| AE ∆% Jun | 1.2 | |
| May | -0.1 | 0.5 |
| AE ∆% May | -1.2 | |
| Apr | 0.2 | 0.7 |
| Mar | 0.9 | 0.5 |
| Feb | 0.3 | 0.7 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Apr | 5.7 | |
| Jan | -1.1 | 0.8 |
| AE ∆% Jan | -12.4 | |
| Dec 2013 | 0.4 | 0.8 |
| AE ∆% Dec | 4.9 | |
| Nov | -0.1 | 0.8 |
| Oct | -0.1 | 0.7 |
| AE ∆% Oct-Nov | -2.4 | |
| Sep | 0.5 | 1.1 |
| Aug | 0.1 | 1.3 |
| AE ∆% Aug- Sep | 3.7 | |
| Jul 2013 | -0.5 | 1.6 |
| AE ∆% Jul | -5.8 | |
| Jun | 0.1 | 1.6 |
| May | 0.1 | 1.4 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun | 1.2 | |
| Apr | -0.1 | 1.2 |
| AE ∆% Apr | -1.2 | |
| Mar | 1.2 | 1.7 |
| Feb | 0.4 | 1.8 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Mar | 10.0 | |
| Jan | -1.0 | 2.0 |
| AE ∆% Jan | -11.4 | |
| Dec 2012 | 0.4 | 2.2 |
| AE ∆% Dec | 4.9 | |
| Nov | -0.2 | 2.2 |
| AE ∆% Nov | -2.4 | |
| Oct | 0.2 | 2.5 |
| Sep | 0.7 | 2.6 |
| Aug | 0.4 | 2.6 |
| AE ∆% Aug-Oct | 5.3 | |
| Jul 2012 | -0.5 | 2.4 |
| Jun | -0.1 | 2.4 |
| May | -0.1 | 2.4 |
| AE ∆% May-Jul | -2.8 | |
| Apr | 0.5 | 2.6 |
| Mar | 1.3 | 2.7 |
| Feb | 0.5 | 2.7 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Apr | 9.6 | |
| Jan | -0.8 | 2.7 |
| Dec 2011 | 0.3 | 2.8 |
| AE ∆% Dec-Jan | -3.0 | |
| Nov | 0.1 | 3.0 |
| Oct | 0.3 | 3.0 |
| Sep | 0.7 | 3.0 |
| Aug | 0.2 | 2.6 |
| AE ∆% Aug-Nov | 4.0 | |
| Jul | -0.6 | 2.6 |
| Jun | 0.0 | 2.7 |
| May | 0.0 | 2.7 |
| AE ∆% May-Jul | -2.4 | |
| Apr | 0.6 | 2.8 |
| Mar | 1.3 | 2.7 |
| Feb | 0.4 | 2.4 |
| Jan | -0.7 | 2.3 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr | 4.9 | |
| Dec 2010 | 0.6 | 2.2 |
| Annual ∆% | ||
| 2014 | 0.4 | |
| 2013 | 1.3 | |
| 2012 | 2.5 | |
| 2011 | 2.7 | |
| 2010 | 1.6 | |
| 2009 | 0.3 | |
| 2008 | 3.3 | |
| 2007 | 2.2 | |
| 2006 | 2.2 | |
| 2005 | 2.2 | |
| 2004 | 2.2 | |
| 2003 | 2.1 | |
| 2002 | 2.3 | |
| 2001 | 2.4 | |
| 2000 | 2.2 | |
| 1999 | 1.2 |
AE: annual equivalent Source: EUROSTAT
http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/data/database
Table IV-7 provides weights and inflation of selected components of the HICP of the euro area. Inflation of all items excluding energy increased 1.0 percent in May 2015 relative to May 2014. Prices of non-energy industrial goods increased 0.2 percent in May 2015 relative to a year earlier. Inflation of services was 1.3 percent in May 2015 relative to a year earlier.
Table IV-7, Euro Area, HICP Inflation and Selected Components, ∆%
| Weight 2015 | May 15 2014/ May 14 | Apr 2015/Apr 2014 | ∆% Mar 2015/Mar 2014 | |
| All Items | 1000.0 | 0.3 | 0.0 | -0.1 |
| All Items ex Energy | 893.9 | 1.0 | 0.7 | 0.6 |
| All Items ex Energy, Food, Alcohol & Tobacco | 697.3 | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| All Items ex Energy & Unprocessed Food | 819.4 | 0.9 | 0.7 | 0.6 |
| All Items ex Energy & Seasonal Food | 855.5 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
| All Items ex Tobacco | 976.3 | 0.3 | -0.1 | -0.1 |
| Energy | 106.1 | -4.8 | -5.8 | -6.0 |
| Food, Alcohol & Tobacco | 196.6 | 1.2 | 1.0 | 0.6 |
| Non-energy Industrial Goods | 262.6 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.0 |
| Services | 434.7 | 1.3 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
AE: annual equivalent
Source: EUROSTAT
http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/data/database
The index of producer prices for industrial products of Germany changed 0.0 percent in May 2015, not seasonally adjusted (NSA), changed 0.0 percent calendar and seasonally adjusted (CSA) in May 2015 and decreased 1.3 percent not seasonally adjusted (NSA) in the 12 months ending in May 2015, as shown in Table IV-8. The producer price index of Germany has similar waves of inflation as in many other countries (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/interest-rate-policy-and-dollar.html). In the first wave from Jan to Apr 2011, the annual equivalent rate of producer price inflation was 10.4 percent NSA and 5.9 percent CSA, propelled by carry trades from zero interest rates to exposures in commodity futures in a mood of risk appetite. In the second wave in May and Jun 2011, the annual equivalent rate of producer price inflation was only 0.6 percent NSA because of the collapse of the carry trade in fear of risks of European sovereign debt but 3.7 percent CSA. In the third wave from Jul to Sep 2011, annual-equivalent producer price inflation in Germany was 2.4 percent NSA and 3.2 percent CSA with fluctuations in commodity prices resulting from perceptions of the sovereign risk crisis in Europe. In the fourth wave from Oct to Nov 2011, annual equivalent inflation was 0.6 percent NSA and 1.8 percent CSA. In the fifth wave from Dec 2011 to Jan 2012, annual equivalent inflation was at 0.0 percent NSA and minus 0.6 percent CSA in return of risk aversion. In the sixth wave, annual equivalent inflation increased to 6.2 percent in Feb-Mar 2012 NSA and 4.9 percent in Feb-Apr and 2.0 percent CSA. In the seventh wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 2.8 percent in May-Jul 2012 NSA and -0.4 percent CSA. In the eighth wave, annual equivalent inflation was 4.3 percent in Aug-Sep 2012 NSA and 2.4 percent CSA. In the ninth wave, renewed risk aversion resulted in annual equivalent inflation NSA of minus 0.8 percent in Oct-Dec 2012 and 0.8 percent CSA. In the tenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was 7.4 percent NSA and 2.4 percent CSA in Jan 2013. In the eleventh wave, annual equivalent inflation NSA was minus 2.4 percent in Feb-Apr 2013 and minus 2.0 percent CSA. In the twelfth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 1.8 percent in May-Aug 2013 and minus 1.2 percent CSA. In the thirteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was 3.7 percent NSA and 0.0 CSA in Sep 2013. In the fourteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 1.8 percent in Oct-Nov 2013 NSA and minus 1.2 percent CSA. In the fifteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was 1.2 NSA in Dec 2013 and 2.4 percent SA. In the sixteenth wave, annual equivalent was minus 1.2 percent in Jan-Sep 2014 NSA and minus 1.3 percent CSA. In the seventeenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 4.4 percent NSA and minus 3.3 percent CSA in Oct 2014-Jan 2015. In the eighteenth-wave, annual equivalent inflation was 0.9 percent in Feb-May 2015 and 0.3 percent CSA.
Table IV-8, Germany, Index of Producer Prices for Industrial Products ∆%
| 12 Months ∆% NSA | Month ∆% NSA | Month ∆% Calendar and SA | |
| May 2015 | -1.3 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Apr | -1.5 | 0.1 | 0.0 |
| Mar | -1.7 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Feb | -2.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 |
| AE ∆% Feb-May | 0.9 | 0.3 | |
| Jan | -2.2 | -0.6 | -0.4 |
| Dec 2014 | -1.7 | -0.7 | -0.5 |
| Nov | -0.9 | 0.0 | -0.1 |
| Oct | -1.0 | -0.2 | -0.1 |
| AE ∆% Oct-Jan | -4.4 | -3.3 | |
| Sep | -1.0 | 0.0 | -0.3 |
| Aug | -0.8 | -0.1 | -0.1 |
| Jul | -0.8 | -0.1 | -0.1 |
| Jun | -0.7 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| May | -0.8 | -0.2 | -0.1 |
| Apr | -0.9 | -0.1 | -0.1 |
| Mar | -0.9 | -0.3 | -0.1 |
| Feb | -0.9 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Jan | -1.1 | -0.1 | -0.2 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Sep | -1.2 | -1.3 | |
| Dec 2013 | -0.5 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| AE ∆% Dec | 1.2 | 2.4 | |
| Nov | -0.8 | -0.1 | -0.1 |
| Oct | -0.7 | -0.2 | -0.1 |
| AE ∆% Oct-Nov | -1.8 | -1.2 | |
| Sep | -0.5 | 0.3 | 0.0 |
| AE ∆% Sep | 3.7 | 0.0 | |
| Aug | -0.5 | -0.1 | -0.2 |
| Jul | 0.0 | -0.1 | -0.1 |
| Jun | 0.1 | -0.1 | 0.0 |
| May | -0.2 | -0.3 | -0.1 |
| AE ∆% May-Aug | -1.8 | -1.2 | |
| Apr | -0.2 | -0.1 | -0.1 |
| Mar | 0.1 | -0.3 | -0.2 |
| Feb | 0.9 | -0.2 | -0.2 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Apr | -2.4 | -2.0 | |
| Jan | 1.5 | 0.6 | 0.2 |
| AE ∆% Jan | 7.4 | 2.4 | |
| Dec 2012 | 1.4 | -0.3 | 0.0 |
| Nov | 1.2 | 0.0 | 0.1 |
| Oct | 1.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| AE ∆% Oct-Dec | -0.8 | 0.8 | |
| Sep | 1.2 | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| Aug | 1.1 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| AE ∆% Aug-Sep | 4.3 | 2.4 | |
| Jul | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Jun | 1.1 | -0.4 | -0.1 |
| May | 1.6 | -0.3 | 0.0 |
| AE ∆% May-Jul | -2.8 | -0.4 | |
| Apr | 1.9 | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| Mar | 2.6 | 0.6 | 0.3 |
| Feb | 2.6 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Apr | 4.9 | 2.0 | |
| Jan | 2.9 | 0.5 | 0.0 |
| Dec 2011 | 3.5 | -0.5 | -0.1 |
| AE ∆% Dec-Jan | 0.0 | -0.6 | |
| Nov | 4.6 | -0.1 | 0.1 |
| Oct | 4.9 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| AE ∆% Oct-Nov | 0.6 | 1.8 | |
| Sep | 5.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Aug | 5.2 | -0.2 | 0.1 |
| Jul | 5.3 | 0.6 | 0.5 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Sep | 2.4 | 3.2 | |
| Jun | 5.1 | 0.1 | 0.3 |
| May | 5.6 | 0.0 | 0.3 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun | 0.6 | 3.7 | |
| Apr | 6.1 | 0.9 | 0.5 |
| Mar | 6.2 | 0.6 | 0.3 |
| Feb | 6.1 | 0.7 | 0.5 |
| Jan | 5.3 | 1.1 | 0.6 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr | 10.4 | 5.9 |
Source:
Federal Statistical Agency of Germany (Statistiche Bundesamt Deutschland)
https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
Chart IV-3 of the Federal Statistical Agency of Germany Statistiche Bundesamt Deutschland provides the producer price index of Germany from 2007 to 2015. Producer price inflation peaked in 2008 with the rise of commodity prices induced by the carry trade from zero interest rates to commodity futures during a global contraction. Prices then declined with the flight away from risk financial assets to government obligations after the financial panic in Sep 2008. With zero interest rates and no risk aversion, the carry trade pushed commodity futures prices upwardly resulting in new rising trend of the producer price index. The right-hand side of the chart shows moderation and even decline in prices because of risk aversion and portfolio reallocations across financial risk assets frustrating carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures.
Chart IV-3, Germany, Index of Producer Prices for Industrial Products, 2010=100
Source: Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
Chart IV-4 provides the index of producer finished goods in the US from 2007 to 2015. Chart IV-4 of the US mirrors behavior in Chart IV-3 of Germany. Carry trades from zero interest rates to exposures in commodity futures and risk financial assets have synchronized worldwide inflation during periods of risk appetite and disinflation during periods of risk aversion and portfolio reallocations.
Chart IV-4, US, Producer Price Index, Finished Goods, NSA, 2007-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart IV-5 of the Federal Statistical Agency of Germany Statistiche Bundesamt Deutschland provides the unadjusted producer price index, trend and trend ends. There is a clear upward trend of prices after the end of risk aversion with zero interest rates in 2009. Oscillations of the actual curve relative to trend originate in carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures. The final segment shows declining trend in reallocation of carry trades toward stocks and high-yield bonds and away from commodities.
Chart IV-5, Germany, Index of Producer Prices for Industrial Products, Non-adjusted Value and Trend, 2010=100
Source: Statistiche Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
The estimate of consumer price inflation in Germany in Table IV-9 is 0.7 percent in 12 months ending in May 2015, 0.1 percent NSA (not seasonally adjusted) in May 2015 relative to Apr 2015 and 0.1 percent CSA (calendar and seasonally adjusted) in May 2015 relative to Apr 2015. There are waves of consumer price inflation in Germany similar to those worldwide (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/interest-rate-policy-and-dollar.html). In the first wave, annual equivalent inflation was 3.0 percent in Feb-Apr 2011 NSA and 2.4 percent CSA during risk appetite in carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures. In the second wave, annual equivalent consumer price inflation collapsed to 0.6 percent NSA and 3.0 percent CSA in May-Jun 2011 because of risk aversion caused by the European sovereign debt event. In the third wave, annual equivalent consumer price inflation was 1.7 percent NSA and 1.9 percent CSA in Jul-Nov 2011 because of relaxed risk aversion. In the fourth wave, annual equivalent inflation was 0.6 percent NSA and 1.8 percent CSA in Dec 2011 to Jan 2012. In the fifth wave, annual equivalent inflation rose to 4.5 percent NSA and 2.4 percent CSA in Feb-Apr 2012 during another energy-commodity carry trade shock. In the sixth wave, annual equivalent inflation in May-Jun 2012 is minus 1.2 percent NSA and 0.6 percent CSA. In the seventh wave, annual equivalent inflation NSA is 4.9 percent in Jul-Aug 2012 and 3.0 percent CSA. In the eighth wave in Sep-Dec 2012, annual equivalent inflation is 1.5 percent NSA and 1.5 percent CSA. In the ninth wave, annual equivalent inflation fell to minus 5.8 percent NSA in Jan 2013 and 1.2 percent CSA. In the eleventh wave, annual equivalent inflation rose to 6.8 percent NSA in Feb-Mar 2013 and 1.2 percent CSA. In the twelfth wave, annual equivalent inflation in Apr fell to minus 5.8 percent NSA and 0.0 percent CSA in reversal of carry trades into commodity futures. In the thirteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation returned at 4.1 percent in May-Jul 2013 NSA and 2.4 percent CSA. In the fourteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was nil NSA and 0.6 percent CSA in Aug-Sep 2013. In the fifteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 2.4 percent NSA in Oct 2013 and 1.2 percent CSA. In the sixteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was 3.7 percent NSA and 1.8 percent CSA in Nov-Dec 2013. In the seventeenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 7.0 percent NSA in Jan 2014 and 2.4 percent CSA. In the eighteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation returned at 4.9 percent in Feb-Mar 2014 and 0.0 percent CSA. In the nineteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 1.8 percent NSA and 0.0 CSA in Apr-May 2014. In the twentieth wave, annual equivalent inflation was 3.7 percent in Jun-Jul NSA and 1.2 percent CSA. In the twenty-first wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 0.7 percent NSA and 0.0 percent CSA in Aug-Dec 2014. In the twenty-second wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 11.4 percent NSA in Jan 2015 and minus 2.4 percent CSA. In the twenty-third wave, annual equivalent inflation was 4.6 percent NSA and 2.4 percent SA in Feb-May 2015. Under unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates and quantitative easing, inflation becomes highly volatile during alternative shocks of risk aversion and risk appetite, preventing sound investment and consumption decisions.
Table IV-9, Germany, Consumer Price Index ∆%
| 12-Month ∆% | Month ∆% NSA | Month ∆% CSA | |
| May 2015 | 0.7 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Apr | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.2 |
| Mar | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.2 |
| Feb | 0.1 | 0.9 | 0.3 |
| AE ∆% Feb-May | 4.6 | 2.4 | |
| Jan | -0.3 | -1.0 | -0.2 |
| AE ∆% Jan | -11.4 | -2.4 | |
| Dec 2014 | 0.2 | 0.0 | -0.1 |
| Nov | 0.6 | 0.0 | -0.1 |
| Oct | 0.8 | -0.3 | 0.0 |
| Sep | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.1 |
| Aug | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.1 |
| AE ∆% Aug-Dec | -0.7 | 0.0 | |
| Jul | 0.8 | 0.3 | 0.0 |
| Jun | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| AE ∆% Jun-Jul | 3.7 | 1.2 | |
| May | 0.9 | -0.1 | -0.1 |
| Apr | 1.3 | -0.2 | 0.1 |
| AE ∆% Apr-May | -1.8 | 0.0 | |
| Mar | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.0 |
| Feb | 1.2 | 0.5 | 0.0 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Mar | 4.9 | 0.0 | |
| Jan | 1.3 | -0.6 | 0.2 |
| AE ∆% Jan | -7.0 | 2.4 | |
| Dec 2013 | 1.4 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
| Nov | 1.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| AE ∆% Nov-Dec | 3.7 | 1.8 | |
| Oct | 1.2 | -0.2 | 0.1 |
| AE ∆% Oct | -2.4 | 1.2 | |
| Sep | 1.4 | 0.0 | 0.1 |
| Aug | 1.5 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| AE ∆% Aug-Sep | 0.0 | 0.6 | |
| Jul | 1.9 | 0.5 | 0.2 |
| Jun | 1.8 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| May | 1.5 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| AE ∆% May-Jul | 4.1 | 2.4 | |
| Apr | 1.2 | -0.5 | 0.0 |
| AE ∆% Apr | -5.8 | 0.0 | |
| Mar | 1.4 | 0.5 | 0.1 |
| Feb | 1.5 | 0.6 | 0.1 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Mar | 6.8 | 1.2 | |
| Jan | 1.7 | -0.5 | 0.1 |
| AE ∆% Jan | -5.8 | 1.2 | |
| Dec 2012 | 2.0 | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| Nov | 1.9 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Oct | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 |
| Sep | 2.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| AE ∆% Sep-Dec | 1.5 | 1.5 | |
| Aug | 2.2 | 0.4 | 0.3 |
| Jul | 1.9 | 0.4 | 0.2 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Aug | 4.9 | 3.0 | |
| Jun | 1.7 | -0.2 | 0.0 |
| May | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.1 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun | -1.2 | 0.6 | |
| Apr | 2.0 | -0.2 | 0.2 |
| Mar | 2.2 | 0.6 | 0.2 |
| Feb | 2.2 | 0.7 | 0.2 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Apr | 4.5 | 2.4 | |
| Jan | 2.1 | -0.1 | 0.3 |
| Dec 2011 | 2.0 | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| AE ∆% Dec-Jan | 0.6 | 1.8 | |
| Nov | 2.4 | 0.2 | 0.2 |
| Oct | 2.3 | 0.0 | 0.1 |
| Sep | 2.4 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| Aug | 2.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Jul | 2.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Nov | 1.7 | 1.9 | |
| Jun | 2.1 | 0.1 | 0.3 |
| May | 2.0 | 0.0 | 0.2 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun | 0.6 | 3.0 | |
| Apr | 1.9 | 0.0 | 0.2 |
| Mar | 2.0 | 0.6 | 0.2 |
| Feb | 1.9 | 0.6 | 0.2 |
| Jan | 1.7 | -0.2 | 0.2 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Apr | 3.0 | 2.4 | |
| Dec 2010 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 0.2 |
| Nov | 1.5 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Oct | 1.3 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Sep | 1.2 | -0.1 | 0.1 |
| Aug | 1.0 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Annual Average ∆% | |||
| 2014 | 0.9 | ||
| 2013 | 1.5 | ||
| 2012 | 2.0 | ||
| 2011 | 2.1 | ||
| 2010 | 1.1 | ||
| 2009 | 0.4 | ||
| 2008 | 2.6 | ||
| Dec 2009 | 0.8 | ||
| Dec 2008 | 1.1 | ||
| Dec 2007 | 3.2 | ||
| Dec 2006 | 1.4 | ||
| Dec 2005 | 1.4 | ||
| Dec 2004 | 2.2 | ||
| Dec 2003 | 1.1 | ||
| Dec 2002 | 1.1 | ||
| Dec 2001 | 1.6 |
AE: Annual Equivalent
Source: Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
Chart IV-6 of the Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland, or federal statistical office of Germany, provides the unadjusted consumer price index of Germany from 2006 to 2014. There is evident acceleration in the form of sharper slope in the first months of 2011 and then a flattening in subsequent months with renewed strength in Dec 2011, decline in Jan 2012 and another upward spike from Feb to Apr 2012, new drop in May-Jun 2012 and increases in Jul and Aug 2012 relaxed in Sep-Nov 2012. Inflation returned in Dec 2012 and fell in Jan 2013, rebounding in Feb-Mar 2013. Inflation fell in Apr 2013 and rebounded in May 2013. Reversals of commodity exposures caused the decline in Apr 2013 followed by increases in May-Jul 2013. Inflation stabilized in Aug-Sep 2013 and fell in Oct 2013. Inflation increased in Nov-Dec 2013 and fell in Jan 2014. Consumer prices increased again in Feb-Mar 2014 and fell in Apr-May 2014. If risk aversion declines, new carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures could again result in higher inflation. Inflation increased in Jun-Jul 2014 and was unchanged in Aug-Sep 2014, decreasing in Oct 2014. Inflation was nil in Nov-Dec 2014, fell sharply in Jan 2015 and rebounded in Feb-Mar 2015, stabilizing in Apr-May 2015.
Chart IV-6, Germany, Consumer Price Index, Unadjusted, 2010=100
Source: Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
Chart IV-6A provides the consumer price index NSA of the US from 2006 to 2015. The salient similarity is the hump in 2008 caused by commodity carry trades driven by the movement to zero interest rates. Inflation communicated worldwide through carry trade from zero interest rates to exposures in commodity futures, creating instability in financial and economic decisions.
Chart IV-6A, US, Consumer Price Index, All Items, NSA, 2007-2015
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm4
Chart IV-7, of the Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland, or Federal Statistical Agency of Germany, provides the unadjusted consumer price index and trend of Germany from 2010 to 2014. Chart IV-10 captures inflation waves with alternation of periods of positive and negative slopes resulting from zero interest rates with shocks of risk appetite and risk aversion. For example, the negative slope of decline of inflation by 0.2 percent in Jun 2012 and 0.0 percent in May 2012 follows an upward slope of price increases in Feb-Apr 2012 after decline of inflation by 0.1 percent in Jan 2012. The is another positive slope caused by inflation of 0.4 percent in Jul 2012, which is followed by 0.4 percent in Aug 2012 and flattening segment, as inflation remains almost unchanged with 0.1 percent in Sep and 0.0 percent in Oct 2012, increasing 0.1 percent in Nov 2012 and increasing 0.3 percent in Dec 2012. Inflation fell 0.5 percent in Jan 2013 and jumped 0.6 percent in Feb 2013 and 0.5 percent in Mar 2013. Another declining segment indicates the decline of 0.5 percent in Apr 2013 followed by the increases in May-Jul 2013. Inflation was nil in Aug-Sep 2013 and fell in Oct 2013. Inflation increased in Nov-Dec 2013 and fell in Jan 2014. Inflation returned in Feb-Mar 2014 and fell in Apr-May 2014. Inflation returned in Jun-Jul 2014 and prices did not change in Aug-Sep 2014. Prices fell in Oct 2014 and did not change in Nov-Dec 2014. Prices fell sharply in Jan 2015, rebounded in Feb-Mar 2015 and stabilizing in Apr 2015. The index increased marginally in May 2015. The waves occur around an upward trend of prices, disproving the proposition of fear of deflation.
Chart IV-7, Germany, Consumer Price Index, Unadjusted and Trend, 2010=100
Source: Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
Table IV-10 provides 12-month and monthly consumer price inflation in Germany in May 2015. Services increased 0.1 percent in May 2015 and increased 1.5 percent in 12 months. Excluding heating oil and motor fuels, consumer prices changed 0.0 percent in May and increased 1.2 percent in 12 months.
Table IV-10, Germany, Consumer Price Index ∆%
| May 2015 | Weight | 12- Month ∆% | Month ∆% |
| Total | 1,000.00 | 0.7 | 0.1 |
| Excluding heating oil and motor fuels | 950.52 | 1.2 | 0.0 |
| Excluding household energy | 931.81 | 1.0 | 0.1 |
| Excluding Energy | 893.44 | 1.3 | 0.0 |
| Total Goods | 479.77 | -0.3 | 0.1 |
| Nondurable Consumer Goods | 307.89 | -0.6 | 0.4 |
| Energy | 106.56 | -5.0 | 1.0 |
| Services | 520.23 | 1.5 | 0.1 |
| Energy Components | |||
| Motor Fuels | 38.37 | -6.3 | 2.3 |
| Household Energy | 68.19 | -4.3 | 0.3 |
| Heating Oil | 11.11 | -16.7 | 3.7 |
| Food | 90.52 | 1.4 | 0.0 |
Source: Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/EN/PressServices/Press/pr/2015/06/PE15_220_611.html
The first wave of commodity price increases in the first four months of Jan-Apr 2011 also influenced the surge of consumer price inflation in Italy shown in Table IV-11. Annual equivalent inflation in the first four months of 2011 from Jan to Apr was 4.9 percent. The crisis of confidence or risk aversion resulted in reversal of carry trades on commodity positions. Consumer price inflation in Italy was subdued in the second wave in Jun and May 2011 at 0.1 percent for annual equivalent 1.2 percent. In the third wave in Jul-Sep 2011, annual equivalent inflation increased to 2.4 percent. In the fourth wave, annual equivalent inflation in Oct-Nov 2011 jumped again at 3.0 percent. Inflation returned in the fifth wave from Dec 2011 to Jan 2012 at annual equivalent 4.3 percent. In the sixth wave, annual equivalent inflation rose to 5.7 percent in Feb-Apr 2012. In the seventh wave, annual equivalent inflation was 1.2 percent in May-Jun 2012. In the eighth wave, annual equivalent inflation increased to 3.0 percent in Jul-Aug 2012. In the ninth wave, inflation collapsed to zero in Sep-Oct 2012 and was minus 0.8 percent in annual equivalent in Sep-Nov 2012. In the tenth wave, annual equivalent inflation in Dec 2012 to Aug 2013 was 2.0 percent. In the twelfth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 3.2 percent in Sep-Nov 2013 during reallocations of investment portfolios away from commodity futures. In the thirteenth wave, inflation returned in annual equivalent 2.4 percent in Dec 2013-Jan 2014. In the fourteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation fell at 1.2 percent in Feb 2014. In the fifteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was 1.8 percent in Mar-Apr 2014. In the sixteen wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 1.2 percent in May 2014. In the seventeenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was 1.2 percent in Jun 2014. In the eighteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 1.2 percent in Jul 2014. In the nineteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was 2.4 percent in Aug 2014. In the twentieth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 4.7 percent in Sep 2014. In the twenty-first wave, annual equivalent inflation returned at 1.2 percent in Oct 2014. In the twenty-second wave, annual equivalent inflation fell at 2.4 percent in Nov 2014-Jan 2015. In the twenty-third wave, annual equivalent rose to 2.4 percent in Feb-
May 2015. There are worldwide shocks to economies by intermittent waves of inflation originating in combination of zero interest rates and quantitative easing with alternation of risk appetite and risk aversion (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/interest-rate-policy-and-dollar.html).
Table IV-11, Italy, Consumer Price Index
| Month | 12 Months | |
| May 2015 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| Apr | 0.2 | -0.1 |
| Mar | 0.1 | -0.1 |
| Feb | 0.4 | -0.1 |
| AE ∆% Feb-May | 2.4 | |
| Jan | -0.4 | -0.6 |
| Dec 2014 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Nov | -0.2 | 0.2 |
| AE ∆% Nov-Jan | -2.4 | |
| Oct | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| AE ∆% Oct | 1.2 | |
| Sep | -0.4 | -0.2 |
| AE ∆% Sep | -4.7 | |
| Aug | 0.2 | -0.1 |
| AE ∆% Aug | 2.4 | |
| Jul | -0.1 | 0.1 |
| AE ∆% Jul | -1.2 | |
| Jun | 0.1 | 0.3 |
| AE ∆% Jun | 1.2 | |
| May | -0.1 | 0.5 |
| AE ∆% May | -1.2 | |
| Apr | 0.2 | 0.6 |
| Mar | 0.1 | 0.4 |
| AE ∆% Mar-Apr | 1.8 | |
| Feb | -0.1 | 0.5 |
| AE ∆% Feb | -1.2 | |
| Jan | 0.2 | 0.7 |
| Dec 2013 | 0.2 | 0.7 |
| AE ∆% Dec 2013-Jan 2014 | 2.4 | |
| Nov | -0.3 | 0.7 |
| Oct | -0.2 | 0.8 |
| Sep | -0.3 | 0.9 |
| AE ∆% Sep-Nov | -3.2 | |
| Aug | 0.4 | 1.2 |
| Jul | 0.1 | 1.2 |
| Jun | 0.3 | 1.2 |
| May | 0.0 | 1.1 |
| Apr | 0.0 | 1.1 |
| Mar | 0.2 | 1.6 |
| Feb | 0.1 | 1.9 |
| Jan | 0.2 | 2.2 |
| Dec 2012 | 0.2 | 2.3 |
| AE ∆% Dec 2012-Aug 2013 | 2.0 | |
| Nov | -0.2 | 2.5 |
| Oct | 0.0 | 2.6 |
| Sep | 0.0 | 3.2 |
| AE ∆% Sep-Nov | -0.8 | |
| Aug | 0.4 | 3.2 |
| Jul | 0.1 | 3.1 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Aug | 3.0 | |
| June | 0.2 | 3.3 |
| May | 0.0 | 3.2 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun | 1.2 | |
| Apr | 0.5 | 3.3 |
| Mar | 0.5 | 3.3 |
| Feb | 0.4 | 3.3 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Apr | 5.7 | |
| Jan | 0.3 | 3.2 |
| Dec 2011 | 0.4 | 3.3 |
| AE ∆% Dec-Jan | 4.3 | |
| Nov | -0.1 | 3.3 |
| Oct | 0.6 | 3.4 |
| AE ∆% Oct-Nov | 3.0 | |
| Sep | 0.0 | 3.0 |
| Aug | 0.3 | 2.8 |
| Jul | 0.3 | 2.7 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Sep | 2.4 | |
| Jun | 0.1 | 2.7 |
| May | 0.1 | 2.6 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun | 1.2 | |
| Apr | 0.5 | 2.6 |
| Mar | 0.4 | 2.5 |
| Feb | 0.3 | 2.4 |
| Jan | 0.4 | 2.1 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr | 4.9 | |
| Dec 2010 | 0.4 | 1.9 |
| Annual | ||
| 2014 | 0.2 | |
| 2013 | 1.2 | |
| 2012 | 3.0 | |
| 2011 | 2.8 | |
| 2010 | 1.5 | |
| 2009 | 0.8 | |
| 2008 | 3.3 | |
| 2007 | 1.8 | |
| 2006 | 2.1 |
Source: Istituto Nazionale di Statistica
http://www.istat.it/it/archivio/162199
Chart IV-12 of the Istituto Nazionale di Statistica shows moderation in 12-month percentage changes of the consumer price index of Italy with marginal increase followed by decline to 2.5 percent in Nov 2012, 2.3 percent in Dec 2012, 2.2 percent in Jan 2013, 1.9 percent in Feb 2013 and 1.6 percent in Mar 2013. Consumer prices increased 1.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Apr-May 2013 and 1.2 percent in Jun-Jul 2013. In Aug 2013, consumer prices increased 1.2 percent in 12 months. Consumer prices increased 0.9 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep 2013 and 0.8 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2013. Consumer price inflation increased 0.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2013 and 0.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2013. Consumer prices increased 0.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2014 and 0.5 percent in the 12 months ending in Feb 2014. Consumer prices increased 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Mar 2014 and 0.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Apr 2014. Consumer prices increased 0.5 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2014 and 0.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2014. Consumer prices increased 0.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Jul 2014 and fell 0.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2014. Consumer prices fell 0.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep 2014 and increased 0.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2014. Consumer prices increased 0.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2014 and changed 0.0 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2014. Consumer prices fell 0.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2015 and decreased 0.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Feb 2015. Consumer prices fell 0.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Mar 2015 and decreased 0.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Apr 2015. Consumer prices increased 0.1 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2015.
Chart IV-8, Italy, Consumer Price Index 12-Month Percentage Changes
Source: Istituto Nazionale di Statistica
onsumer price inflation in Italy by segments in the estimate by ISTAT for May 2015 is provided in Table IV-12. Total consumer price inflation in May 2015 was 0.1 percent and 0.1 percent in 12 months. Inflation of goods was 0.2 percent in May 2015 and minus 0.3 percent in 12 months. Prices of durable goods decreased 0.1 percent in May and decreased 0.4 percent in 12 months, as typical in most countries. Prices of energy increased 0.8 percent in May and decreased 5.8 percent in 12 months. Food prices increased 0.1 percent in May and increased 1.0 percent in 12 months. Prices of services increased 0.1 percent in May and rose 0.7 percent in 12 months. Transport prices, also influenced by commodity prices, decreased 0.3 percent in May and increased 0.8 percent in 12 months. Carry trades from zero interest rates to positions in commodity futures cause increases in commodity prices. Waves of inflation originate in periods when there is no risk aversion and commodity prices decline during periods of risk aversion and portfolio reallocations (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/interest-rate-policy-and-dollar.html).
Table IV-12, Italy, Consumer Price Index and Segments, Month and 12-Month ∆%
| May 2015 | Weights | Month ∆% | 12-Month ∆% |
| General Index All Items | 1,000,000 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| I Goods | 535,475 | 0.2 | -0.3 |
| Food | 176,032 | 0.1 | 1.0 |
| Energy | 93,467 | 0.8 | -5.8 |
| Durable | 73,312 | -0.1 | -0.4 |
| Nondurable | 70,570 | 0.1 | 0.9 |
| II Services | 464,525 | 0.1 | 0.7 |
| Housing | 80,193 | 0.0 | -0.1 |
| Communications | 21,410 | -0.2 | 0.8 |
| Transport | 79,231 | -0.3 | 0.8 |
Source: Istituto Nazionale di Statistica
http://www.istat.it/it/archivio/162199
Inflation in the UK is somewhat higher than in many advanced economies, deserving more detailed analysis. Table IV-13 provides 12-month percentage changes of UK output prices for all manufactured products, excluding food, beverage and petroleum and excluding duty. The UK Office for National Statistics introduced rebasing for 2010=100 of the producer price index with important revisions (http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/ppi2/producer-price-index/producer-price-index-rebasing--2010-100-/index.html). The 12-month rates rose significantly in 2011 in all three categories, reaching 5.3 percent for all manufactured products in Sep 2011 but declining to 4.9 percent in Oct 2011, 4.6 percent in Nov 2011 and down to 1.3 percent in Jul 2012. Inflation of all manufactured products increased marginally to 1.7 percent in Aug 2012, 1.8 percent in Sep 2012, 1.9 percent in Oct 2012, 1.7 percent in Feb 2013, 1.5 percent in Mar 2013 and 1.0 percent in Apr 2013. Output prices increased 1.2 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2013, 1.7 percent in Jun 2013 and 1.8 percent in Jul 2013. Output price inflation was 1.5 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2013 and 1.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep 2013. Output price inflation was 0.8 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2013 and 0.8 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2013. Prices of output increased 1.0 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2013 and 0.9 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2014. Output prices increased 0.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Feb 2014 and 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Mar 2014. Output prices increased 0.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Apr 2014 and 0.5 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2014 down to minus 0.1 percent in Jul 2014. Output prices fell 0.3 percent in Aug 2014 and fell 0.5 percent in Sep 2014. Output prices fell 0.7 percent in Oct 2014 and fell 0.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2014. Output prices fell 1.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2014 and fell 1.8 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2015. Output prices fell 1.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Feb 2015 and declined 1.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Mar 2015. Output prices fell 1.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Apr 2015 and fell 1.6 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2015. Output price inflation is highly sensitive to commodity prices as shown by the increase by 6.7 percent in 2008 when oil prices rose over $140/barrel even in the midst of a global recession driven by the carry trade from zero interest rates to oil futures. The mirage episode of false deflation in 2001 and 2002 is also captured by output prices for the UK, which originated in decline of commodity prices (see Barsky and Killian 2004) but was used as an argument for unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates and quantitative easing during the past decade. Arguments for symmetric up and down inflation targets are based on fear of deflation (Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), 18-28, Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 83-95).
Table IV-13, UK Output Prices 12 Months ∆% NSA
| All Manufactured Products | Excluding Food, Beverage, Tobacco and | All Excluding Duty | |
| May 2015 | -1.6 | 0.1 | -1.3 |
| Apr | -1.7 | 0.1 | -1.4 |
| Mar | -1.7 | 0.1 | -1.5 |
| Feb | -1.7 | 0.3 | -1.4 |
| Jan | -1.8 | 0.5 | -1.4 |
| Dec 2014 | -1.1 | 0.8 | -0.8 |
| Nov | -0.6 | 0.9 | -0.5 |
| Oct | -0.7 | 0.6 | -0.5 |
| Sep | -0.5 | 0.8 | -0.2 |
| Aug | -0.3 | 0.9 | -0.1 |
| Jul | -0.1 | 0.8 | 0.1 |
| Jun | 0.3 | 1.0 | 0.3 |
| May | 0.5 | 1.0 | 0.6 |
| Apr | 0.6 | 1.0 | 0.6 |
| Mar | 0.4 | 1.1 | 0.6 |
| Feb | 0.6 | 1.1 | 0.6 |
| Jan | 0.9 | 1.2 | 1.0 |
| Dec 2013 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.1 |
| Nov | 0.8 | 0.7 | 1.0 |
| Oct | 0.8 | 0.8 | 1.1 |
| Sep | 1.2 | 0.8 | 1.4 |
| Aug | 1.5 | 0.9 | 1.7 |
| Jul | 1.8 | 0.9 | 2.0 |
| Jun | 1.7 | 0.9 | 2.0 |
| May | 1.2 | 0.8 | 1.5 |
| Apr | 1.0 | 0.8 | 1.4 |
| Mar | 1.5 | 0.9 | 1.5 |
| Feb | 1.7 | 0.7 | 1.7 |
| Jan | 1.6 | 0.8 | 1.6 |
| Dec 2012 | 1.4 | 0.4 | 1.4 |
| Nov | 1.5 | 0.7 | 1.6 |
| Oct | 1.9 | 0.6 | 1.7 |
| Sep | 1.8 | 0.5 | 1.5 |
| Aug | 1.7 | 0.5 | 1.5 |
| Jul | 1.3 | 0.8 | 1.1 |
| Jun | 1.4 | 1.0 | 1.2 |
| May | 2.0 | 1.3 | 1.9 |
| Apr | 2.3 | 1.4 | 2.1 |
| Mar | 2.9 | 2.0 | 2.9 |
| Feb | 3.4 | 2.3 | 3.3 |
| Jan | 3.5 | 2.2 | 3.4 |
| Dec 2011 | 4.0 | 2.6 | 3.9 |
| Nov | 4.6 | 2.6 | 4.4 |
| Oct | 4.9 | 2.9 | 4.7 |
| Sep | 5.3 | 3.1 | 5.2 |
| Aug | 5.2 | 3.2 | 5.0 |
| Jul | 5.2 | 2.8 | 5.0 |
| Jun | 5.0 | 2.8 | 4.9 |
| May | 4.8 | 3.0 | 4.6 |
| Apr | 4.9 | 3.0 | 4.8 |
| Mar | 4.7 | 2.5 | 4.4 |
| Feb | 4.4 | 2.5 | 4.2 |
| Jan | 4.0 | 2.4 | 3.7 |
| Dec 2010 | 3.4 | 2.0 | 2.9 |
| Year ∆% | |||
| 2014 | 0.0 | 0.9 | 0.2 |
| 2013 | 1.3 | 0.9 | 1.5 |
| 2012 | 2.1 | 1.1 | 1.9 |
| 2011 | 4.8 | 2.8 | 4.6 |
| 2010 | 2.7 | 1.5 | 2.1 |
| 2009 | 0.5 | 1.4 | -0.1 |
| 2008 | 6.7 | 3.6 | 6.8 |
| 2007 | 2.3 | 1.4 | 2.0 |
| 2006 | 2.1 | 1.5 | 2.0 |
| 2005 | 1.9 | 0.9 | 1.8 |
| 2004 | 1.1 | -0.1 | 0.7 |
| 2003 | 0.6 | 0.0 | 0.6 |
| 2002 | -0.1 | -0.3 | -0.1 |
| 2001 | -0.2 | -0.7 | -0.3 |
| 2000 | 1.4 | -0.4 | 0.8 |
| 1999 | 0.5 | -1.1 | -0.2 |
| 1998 | 0.1 | -0.9 | -1.0 |
| 1997 | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
Source: UK Office for National Statistics
http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/ppi2/producer-price-index/may-2015/index.html
Monthly and annual equivalent rates of change of output prices are shown in Table IV-14. There are waves of inflation similar to those in other countries (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/interest-rate-policy-and-dollar.html). In the first wave, annual equivalent inflation was 10.0 percent in Jan-Apr 2011 with relaxed risk aversion in commodity markets. In the second wave, intermittent risk aversion resulted in annual equivalent inflation of 1.6 percent in May-Oct 2011. In the third wave, alternation of risk aversion resulted in annual equivalent inflation of 1.2 percent in Nov 2011 to Jan 2012. In the fourth wave, the energy commodity shock processed through carry trades caused the jump of annual equivalent inflation to 5.3 percent in Feb-Apr 2012. A fifth wave occurred in May-Jun 2012 with decline of output inflation at 3.5 percent annual equivalent in an environment of risk aversion that caused decline of commodity prices. A sixth wave under commodity shocks induced by carry trades from zero interest rates resulted in annual equivalent inflation of 3.7 percent in Jul-Sep 2012 and 3.0 percent in Jul-Oct 2012. In the seventh wave, annual equivalent inflation in Nov-Dec 2012 fell to minus 2.4 percent. In the eighth wave, annual equivalent inflation returned at 4.9 percent in Jan-Mar 2013. In the ninth wave, risk aversion returned with annual equivalent inflation of minus 0.6 percent in Apr-May 2013. In the tenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was 2.0 percent in Jun-Aug 2013. In the eleventh wave, annual equivalent inflation was -1.5 percent in Sep-Dec 2013. In the twelfth wave, annual equivalent inflation returned at 2.0 percent in Jan-Mar 2014. In the thirteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 0.7 percent in Apr-Aug 2014. In the fourteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 4.7 percent in Sep-Oct 2015. In the fifteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 4.3 percent in Nov 2014-Jan 2015. In the sixteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was 1.5 percent in Feb-May 2015.
Table IV-14, UK Output Prices Month ∆% NSA
| All Manufactured Products | Excluding Food, Beverage and | All Excluding Duty | |
| May 2015 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Apr | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 |
| Mar | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.2 |
| Feb | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.1 |
| ∆% AE Feb-May | 1.5 | 0.0 | 1.2 |
| Jan | -0.5 | 0.2 | -0.3 |
| Dec 2014 | -0.5 | 0.0 | -0.5 |
| Nov | -0.1 | 0.2 | -0.1 |
| ∆% AE Nov-Jan | -4.3 | 1.6 | -3.5 |
| Oct | -0.6 | -0.2 | -0.5 |
| Sep | -0.2 | -0.1 | -0.1 |
| ∆% AE Sep-Oct | -4.7 | -1.8 | -3.5 |
| Aug | -0.1 | 0.1 | -0.1 |
| Jul | -0.1 | -0.1 | 0.0 |
| Jun | -0.1 | 0.0 | -0.2 |
| May | -0.1 | 0.0 | -0.1 |
| Apr | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| ∆% AE Apr-Aug | -0.7 | 0.0 | -1.0 |
| Mar | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| Feb | 0.1 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Jan | 0.3 | 0.5 | 0.3 |
| ∆% AE Jan-Mar | 2.0 | 3.7 | 2.8 |
| Dec 2013 | 0.0 | 0.1 | -0.1 |
| Nov | -0.2 | -0.1 | -0.1 |
| Oct | -0.3 | 0.0 | -0.2 |
| Sep | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| ∆% AE Sep-Dec | -1.5 | 0.0 | -1.2 |
| Aug | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 |
| Jul | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Jun | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 |
| ∆% AE Jun-Aug | 2.0 | 0.4 | 1.6 |
| May | 0.0 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| Apr | -0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 |
| ∆% AE Apr-May | -0.6 | 0.6 | 0.0 |
| Mar | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Feb | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.5 |
| Jan | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.4 |
| ∆% AE Jan-Mar | 4.9 | 3.2 | 4.9 |
| Dec 2012 | -0.2 | -0.2 | -0.2 |
| Nov | -0.2 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| ∆% AE Nov-Dec | -2.4 | -1.2 | -1.2 |
| Oct | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.1 |
| Sep | 0.3 | 0.1 | 0.3 |
| Aug | 0.4 | 0.0 | 0.4 |
| Jul | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| ∆% AE Jul-Oct | 3.0 | 0.6 | 3.0 |
| Jun | -0.4 | -0.1 | -0.4 |
| May | -0.2 | 0.0 | -0.1 |
| ∆% AE May-Jun | -3.5 | -0.6 | -3.0 |
| Apr | 0.4 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Mar | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| Feb | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.4 |
| ∆% AE Feb-Apr | 5.3 | 2.4 | 4.1 |
| Jan | 0.2 | -0.1 | 0.2 |
| Dec 2011 | -0.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 |
| Nov | 0.2 | -0.1 | 0.1 |
| ∆% AE Nov-Jan | 1.2 | -0.4 | 1.2 |
| Oct | 0.0 | -0.1 | -0.1 |
| Sep | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.3 |
| Aug | 0.0 | 0.3 | 0.0 |
| Jul | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Jun | 0.2 | 0.2 | 0.3 |
| May | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 |
| ∆% AE May-Oct | 1.6 | 1.8 | 1.8 |
| Apr | 1.0 | 0.8 | 0.9 |
| Mar | 1.0 | 0.4 | 0.9 |
| Feb | 0.5 | 0.2 | 0.5 |
| Jan | 0.7 | 0.3 | 0.7 |
| Jan-Apr | 10.0 | 5.2 | 9.4 |
| Dec 2010 | 0.5 | 0.1 | 0.4 |
Source: UK Office for National Statistics
http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/ppi2/producer-price-index/may-2015/index.html
Input prices in the UK have been more dynamic than output prices until the current event of risk aversion and portfolio reallocations, as shown by Table IV-15, but with sharp oscillations because of the commodity and raw material content. The UK Office for National Statistics introduced rebasing for 2010=100 of the producer price index with important revisions (http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/ppi2/producer-price-index/producer-price-index-rebasing--2010-100-/index.html). The 12-month rates of increase of input prices, even excluding food, tobacco, beverages and petroleum, are very high, reaching 16.9 percent in Sep 2011 for materials and fuels purchased and 10.6 percent excluding food, beverages and petroleum. Inflation in 12 months of materials and fuels purchased moderated to 5.7 percent in Mar 2012 and 3.2 percent excluding food, tobacco, beverages and petroleum with the rates falling further in Apr 2012 to 1.5 percent for materials and fuels purchased and 1.1 percent excluding food, tobacco, beverages and petroleum. Input-price inflation collapsed in the 12 months ending in Jul 2012 to minus 2.5 percent for materials and fuels purchased and minus 2.5 percent excluding food, beverages and tobacco. Inflation returned at 0.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2012 but minus 2.6 percent excluding food, tobacco, beverages and petroleum. Inflation of input prices in Sep 2012 was minus 1.2 percent and minus 3.1 percent excluding food, beverages and petroleum. In Nov 2012, inflation of input prices of all manufacturing and materials purchased was minus 0.2 percent in 12 months and minus 1.6 percent in 12 months excluding food, tobacco, beverages and petroleum. Inflation of materials and fuels purchased in 12 months was 0.4 percent in Dec 2012 and minus 1.2 percent excluding tobacco, beverages and petroleum. Inflation of inputs returned with 1.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2013 and minus 0.2 percent excluding various items, increasing to 2.0 percent in Feb 2013 and 1.0 percent excluding various items. In Mar 2013, inflation of all manufacturing materials and fuels increased 0.9 percent in 12 months and 1.6 percent excluding various items. Prices of all manufacturing materials and fuels increased 0.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Apr 2013 and increased 0.9 percent excluding food and other items. Prices of all manufacturing increased 1.4 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2013 and 0.4 percent excluding various items. In Jul 2013, prices of manufactured products increased 4.7 percent in 12 months and 2.1 percent excluding food, tobacco, beverages and petroleum. In Aug 2013, prices of manufactured products increased 1.8 percent in 12 months and 1.4 percent excluding items. Inflation of input prices in the 12 months ending in Sep 2013 was 1.0 percent and 0.4 percent excluding items. Inflation collapsed in Oct 2013, with 0.0 percent for all manufacturing materials and fuels and minus 0.2 percent excluding various items. In Nov 2013, inflation of all manufacturing materials and fuels purchased fell 0.9 percent in 12 months and excluding items 1.0 percent. In Dec 2013, input prices for all manufacturing fell 0.9 percent in 12 months and fell 1.4 percent with exclusions. Inflation of all manufacturing fell 2.9 percent in the 12 months ending in Jan 2014 and 2.8 percent with exclusions. Inflation of input prices fell 5.8 percent in the 12 months ending in Feb 2014 and 5.1 percent with exclusions. Inflation of input prices fell 6.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Mar 2014 and 5.4 percent excluding items. In Apr 2014, inflation of input prices fell 5.3 percent in 12 months and 5.0 with exclusions. Inflation of input prices fell 12.0 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2015 and fell 3.4 percent with exclusions. There is comparable experience with 22.1 percent inflation of materials and fuels purchased in 2008 and 16.9 percent excluding food, beverages and petroleum followed in 2009 by decline of 5.7 percent for materials and fuels purchased and decrease of 1.3 percent for the index excluding items. UK input and output inflation is sensitive to commodity price increases driven by carry trades from zero interest rates. The mirage of false deflation is also observed in input prices in 1997-9 and then again from 2001 to 2003.
Table IV-15, UK, Input Prices 12-Month ∆% NSA
| All Manufacturing Materials and Fuels Purchased | Excluding Food, Tobacco, Beverages and Petroleum | |
| May 2015 | -12.0 | -3.4 |
| Apr | -11.0 | -3.7 |
| Mar | -13.1 | -4.4 |
| Feb | -13.5 | -4.0 |
| Jan | -14.1 | -3.2 |
| Dec 2014 | -11.6 | -2.3 |
| Nov | -8.3 | -1.7 |
| Oct | -8.1 | -2.4 |
| Sep | -7.4 | -2.7 |
| Aug | -7.5 | -4.0 |
| Jul | -7.5 | -5.2 |
| Jun | -4.6 | -3.5 |
| May | -3.9 | -3.9 |
| Apr | -5.3 | -5.0 |
| Mar | -6.3 | -5.4 |
| Feb | -5.8 | -5.1 |
| Jan | -2.9 | -2.8 |
| Dec 2013 | -0.9 | -1.4 |
| Nov | -0.9 | -1.0 |
| Oct | 0.0 | -0.2 |
| Sep | 1.0 | 0.4 |
| Aug | 1.8 | 1.4 |
| Jul | 4.7 | 2.1 |
| Jun | 3.0 | 0.0 |
| May | 1.4 | 0.4 |
| Apr | 0.3 | 0.9 |
| Mar | 0.9 | 1.6 |
| Feb | 2.0 | 1.0 |
| Jan | 1.6 | -0.2 |
| Dec 2012 | 0.4 | -1.2 |
| Nov | -0.2 | -1.6 |
| Oct | -0.2 | -2.1 |
| Sep | -1.2 | -3.1 |
| Aug | 0.7 | -2.6 |
| Jul | -2.5 | -2.5 |
| Jun | -1.7 | -1.0 |
| May | 0.3 | -0.5 |
| Apr | 1.5 | 1.1 |
| Mar | 5.7 | 3.2 |
| Feb | 7.5 | 4.4 |
| Jan | 6.4 | 3.9 |
| Dec 2011 | 8.6 | 5.0 |
| Nov | 12.8 | 7.6 |
| Oct | 13.4 | 8.1 |
| Sep | 16.9 | 10.6 |
| Aug | 15.6 | 10.9 |
| Jul | 17.6 | 10.7 |
| Jun | 16.4 | 10.3 |
| May | 15.3 | 9.3 |
| Apr | 16.9 | 10.2 |
| Mar | 13.5 | 7.8 |
| Feb | 13.9 | 9.2 |
| Jan | 13.2 | 9.6 |
| Dec 2010 | 12.1 | 8.9 |
| Year ∆% | ||
| 2014 | -6.6 | -3.7 |
| 2013 | 1.2 | 0.4 |
| 2012 | 1.3 | -0.2 |
| 2011 | 14.5 | 9.1 |
| 2010 | 8.0 | 4.7 |
| 2009 | -5.7 | -1.3 |
| 2008 | 22.1 | 16.9 |
| 2007 | 2.9 | 2.5 |
| 2006 | 9.8 | 7.2 |
| 2005 | 10.9 | 7.0 |
| 2004 | 3.4 | 1.7 |
| 2003 | 1.1 | -0.7 |
| 2002 | -4.5 | -4.9 |
| 2001 | -1.1 | -1.2 |
| 2000 | 7.3 | 3.8 |
| 1999 | -1.3 | -3.6 |
| 1998 | -8.9 | -4.6 |
| 1997 | -8.3 | -6.4 |
Source: UK Office for National Statistics
http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/ppi2/producer-price-index/may-2015/index.html
Table IV-12 provides monthly percentage changes of UK input prices for materials and fuels purchased and excluding food, tobacco, beverages and petroleum. There are strong waves of inflation of input prices in the UK similar to those worldwide (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/interest-rate-policy-and-dollar.html). In the first wave, input prices rose at the high annual equivalent rate of 30.6 percent in Jan-Apr 2011, driven by carry trades from unconventional monetary policy into commodity exposures. Inflation of input prices was at 31.8 percent annual equivalent in Oct-Dec 2010. In the second wave, alternating risk aversion caused annual equivalent inflation of minus 1.3 percent in May-Oct 2011. In the third wave, renewed risk aversion resulted in annual equivalent inflation of 0.0 percent in Nov-Dec 2011. In the fourth wave, annual equivalent inflation of input prices in the UK surged at 14.9 percent in Jan-Mar 2012 under relaxed risk aversion. In the fifth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 16.1 percent in Apr-Jul 2012 because of collapse of commodity prices during increasing risk aversion. In the sixth wave, annual equivalent inflation of materials and fuels purchased jumped to 23.9 percent in Aug 2012. In the seventh wave, annual equivalent inflation moderated to 3.0 percent in Sep-Dec 2012. In the eighth wave, annual equivalent inflation in Jan-Feb 2013 jumped to 24.6 percent. In the eighth wave, annual equivalent inflation of materials and fuels purchased was minus 9.5 percent in Mar-Jun 2013. In the ninth wave, annual equivalent inflation returned at 18.2 percent in annual equivalent in Jul 2013. In the tenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 8.4 percent in Aug-Nov 2013. In the eleventh wave, annual equivalent inflation of manufacturing materials and fuels was 3.7 percent in Dec 2013. In the twelfth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 7.8 percent in Jan-Apr 2014. In the thirteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation returned at 2.4 percent in May 2014. In the fifteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation fell at 12.3 percent in Jun-Nov 2014. In the sixteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation fell at 34.4 percent in Dec 2014-Jan 2014. In the seventeenth wave, annual equivalent inflation increased at 7.0 percent in Feb-Apr 2015. In the eighteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation decreased at 10.3 percent in May 2015.
Table IV-16, UK Input Prices Month ∆%
| All Manufacturing Materials and Fuels Purchased NSA | Excluding Food, Tobacco, Beverages and Petroleum SA | |
| May 2015 | -0.9 | 0.2 |
| ∆% May | -10.3 | 2.4 |
| Apr | 1.4 | 0.2 |
| Mar | 0.1 | -0.6 |
| Feb | 0.2 | -1.5 |
| ∆% Feb-Apr | 7.0 | -7.4 |
| Jan | -3.6 | -1.1 |
| Dec 2014 | -3.3 | -0.9 |
| ∆% Dec-Jan | -34.4 | -11.4 |
| Nov | -0.8 | 0.0 |
| Oct | -1.2 | -0.1 |
| Sep | -0.8 | 0.3 |
| Aug | -1.0 | 0.4 |
| Jul | -1.7 | -0.2 |
| Jun | -1.0 | -0.2 |
| ∆% Jun-Nov | -12.3 | 0.4 |
| May | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| ∆% May | 2.4 | 0.0 |
| Apr | -0.9 | -0.3 |
| Mar | -0.4 | -0.4 |
| Feb | -0.5 | -0.7 |
| Jan | -0.9 | -0.7 |
| ∆% Jan-Apr | -7.8 | -6.1 |
| Dec 2013 | 0.3 | -0.5 |
| ∆% Dec | 3.7 | -5.8 |
| Nov | -0.6 | -0.5 |
| Oct | -0.4 | -0.3 |
| Sep | -0.9 | -0.9 |
| Aug | -1.0 | -0.5 |
| ∆% Aug-Nov | -8.4 | -6.4 |
| Jul | 1.4 | 1.1 |
| ∆% Jul | 18.2 | 14.0 |
| Jun | -0.3 | -0.3 |
| May | -1.3 | -1.1 |
| Apr | -1.9 | -0.8 |
| Mar | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| ∆% Mar-Jun | -9.5 | -6.1 |
| Feb | 2.5 | 1.5 |
| Jan | 1.2 | 0.6 |
| ∆% Jan-Feb | 24.6 | 13.3 |
| Dec 2012 | 0.3 | 0.0 |
| Nov | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| Oct | 0.5 | 0.4 |
| Sep | -0.1 | 0.2 |
| ∆% Sep-Dec | 3.0 | 2.7 |
| Aug | 1.8 | 0.0 |
| ∆% Aug | 23.9 | 0.0 |
| Jul | -0.3 | -0.7 |
| Jun | -1.8 | 0.2 |
| May | -2.4 | -0.6 |
| Apr | -1.3 | -0.1 |
| ∆% Apr-Jul | -16.1 | -3.5 |
| Mar | 1.3 | -0.5 |
| Feb | 2.2 | 0.4 |
| Jan | 0.0 | -0.4 |
| ∆% AE Jan-Mar | 14.9 | -2.0 |
| Dec 2011 | -0.3 | -0.7 |
| Nov | 0.3 | -0.1 |
| ∆% AE Nov-Dec | 0.0 | -4.7 |
| Oct | -0.5 | -0.6 |
| Sep | 1.8 | 0.5 |
| Aug | -1.5 | 0.3 |
| Jul | 0.5 | 0.7 |
| Jun | 0.2 | 0.8 |
| May | -1.1 | 0.6 |
| ∆% AE May-Oct | -1.3 | 4.7 |
| Apr | 2.8 | 2.1 |
| Mar | 3.0 | 0.6 |
| Feb | 1.1 | 0.1 |
| Jan | 2.1 | 0.7 |
| ∆% AE Jan-Apr | 30.6 | 11.0 |
| Dec 2010 | 3.5 | 1.7 |
| Nov | 0.9 | 0.4 |
| Oct | 2.5 | 1.7 |
| ∆% AE Oct-Dec | 31.8 | 16.3 |
Source: UK Office for National Statistics
http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/ppi2/producer-price-index/may-2015/index.html
The UK Office for National Statistics also provides contributions in percentage points to the monthly and 12-month rates of inflation of manufactured products, shown in Table IV-17. There are contributions to 12-month percentage changes of 0.09 percentage points by tobacco and alcohol, 0.08 percentage points by computer, electrical and optical and 0.19 percentage points by other manufactured products. There are diversified sources of contributions to 12 months output price inflation such as 0.06 percentage points by clothing, textile and leather and deduction of 0.13 percentage points by transport equipment. Petroleum deducted 1.23 percentage points. In general, contributions by products rich in commodities are the drivers of price changes. There were diversified contributions in percentage points to monthly inflation: 0.16 percentage points added by petroleum and 0.04 percentage points deducted by food products.
Table IV-17, UK, Contributions to Month and 12-Month Change in Prices of All Manufactured Products, Percentage Points, NSA
| May 2015 | 12 Months | 12 Months ∆% | Month % Points | Month ∆% |
| Total % | -1.6 | 0.1 | ||
| Food Products | -0.55 | -3.4 | -0.04 | -0.3 |
| Tobacco & Alcohol | 0.09 | 1.0 | 0.00 | 0.0 |
| Clothing, Textile & Leather | 0.06 | 0.4 | -0.04 | -0.4 |
| Paper and Printing | -0.02 | -0.5 | 0.00 | 0.0 |
| Petroleum | -1.23 | -14.3 | 0.16 | 2.0 |
| Chemicals & Pharmaceutical | -0.15 | -1.9 | 0.01 | 0.1 |
| Metal, Machinery & Equipment | 0.05 | 0.6 | 0.01 | 0.0 |
| Computer, Electrical & Optical | 0.08 | 0.7 | -0.01 | -0.1 |
| Transport Equipment | -0.13 | -1.1 | 0.01 | 0.1 |
| Other Manufactured Products | 0.19 | 1.3 | 0.01 | 0.1 |
Source: UK Office for National Statistics
http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/ppi2/producer-price-index/may-2015/index.html
The UK Office for National Statistics also provides contributions in percentage points to the monthly and 12-month rates of inflation of input prices in May 2015, shown in Table IV-18. Crude oil is a large factor with deduction of 8.46 percentage points from the 12-month rate and contribution of 0.36 percentage points to the monthly rate in Apr 2015. Price changes also transfer to the domestic economy through the prices of imported inputs: imported metals deducted 0.43 percentage points from the 12-month rate and deducted 0.12 percentage points from the May rate. Domestic food materials deducted 1.96 percentage points from the 12-month rate and deducted 0.96 percentage points from the May rate. Exposures and reversals of commodity exposures in carry trades during risk aversion are a major source of price and financial instability.
Table IV-18, UK, Contributions to Month and 12-Month Change in Prices of Inputs, Percentage Points NSA
| May 2015 | 12 Months | 12 Months ∆% | Month % Points | Month ∆% |
| Total | -12.0 | -0.9 | ||
| Fuel | -0.25 | -2.4 | -0.05 | -0.4 |
| Crude Oil | -8.46 | -37.2 | 0.36 | 2.4 |
| Domestic Food Materials | -1.96 | -14.0 | -0.96 | -6.9 |
| Imported Food Materials | -0.43 | -6.3 | -0.14 | -2.0 |
| Other Domestic Produced Materials | 0.16 | 5.7 | 0.04 | 1.2 |
| Imported Metals | -0.43 | -6.4 | -0.12 | -1.6 |
| Imported Chemicals | -0.72 | -5.6 | -0.01 | -0.1 |
| Imported Parts and Equipment | 0.28 | 1.8 | 0.10 | 0.6 |
| Other Imported Materials | -0.22 | -2.8 | -0.13 | -1.5 |
Source: UK Office for National Statistics
http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/ppi2/producer-price-index/may-2015/index.html
Consumer price inflation in the UK is shown in Table IV-19. The CPI index increased 0.2 percent in Apr 2015 and fell 0.1 percent in 12 months. The same inflation waves (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/interest-rate-policy-and-dollar.html) are present in UK CPI inflation. In the first wave in Jan-Apr 2011, annual equivalent inflation was at a high 6.5 percent. In the second wave in May-Jul 2011, annual equivalent inflation fell to only 0.4 percent. In the third wave in Aug-Nov 2011, annual equivalent inflation returned at 4.6 percent. In the fourth wave in Dec 2011 to Jan 2012, annual equivalent inflation was minus 0.6 percent because of decline of 0.5 percent in Jan 2012. In the fifth wave, annual equivalent inflation increased to 6.2 percent in Feb-Apr 2012. In the seventh wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 3.0 percent in May-Jun 2012. In the eighth wave, annual equivalent inflation in Jul-Dec 2012 was 4.5 percent and 6.2 percent in Oct 2012 with the rate in Oct caused mostly by increases in university tuition payments. In the ninth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 5.8 percent in Jan 2013. In the tenth wave, annual equivalent inflation jumped to 4.3 percent in Feb-May 2013. In the eleventh wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 1.2 percent in Jun-Jul 2013. In the twelfth wave, annual equivalent inflation was 3.4 percent in Aug-Dec 2013. In the thirteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 7.0 percent in Jan 2014. In the fourteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation returned at 4.5 percent in Feb-Apr 2014. In the fifteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 1.2 percent in May 2014. In the sixteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was 2.4 percent in Jun 2014. In the seventeenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 3.5 percent in Jul 2014. In the eighteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was 2.0 percent in Aug-Oct 2014. In the eighteenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was minus 4.7 percent in Nov 2014-Jan 2015. In the seventeenth wave, annual equivalent inflation was 2.7 percent in Feb-May 2015.
Table IV-19, UK, Consumer Price Index All Items, Month and 12-Month ∆%
| Month ∆% | 12 Months ∆% | |
| May 2015 | 0.2 | 0.1 |
| Apr | 0.2 | -0.1 |
| Mar | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| Feb | 0.3 | 0.0 |
| AE ∆% Feb-May | 2.7 | |
| Jan | -0.9 | 0.3 |
| Dec 2014 | 0.0 | 0.5 |
| Nov | -0.3 | 1.0 |
| AE ∆% Nov-Jan | -4.7 | |
| Oct | 0.1 | 1.3 |
| Sep | 0.0 | 1.2 |
| Aug | 0.4 | 1.5 |
| AE ∆% Aug-Oct | 2.0 | |
| Jul | -0.3 | 1.6 |
| AE ∆% Jul | -3.5 | |
| Jun | 0.2 | 1.9 |
| AE ∆% Jun | 2.4 | |
| May | -0.1 | 1.5 |
| AE ∆% May | -1.2 | |
| Apr | 0.4 | 1.8 |
| Mar | 0.2 | 1.6 |
| Feb | 0.5 | 1.7 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Apr | 4.5 | |
| Jan | -0.6 | 1.9 |
| AE ∆% Jan | -7.0 | |
| Dec 2013 | 0.4 | 2.0 |
| Nov | 0.1 | 2.1 |
| Oct | 0.1 | 2.2 |
| Sep | 0.4 | 2.7 |
| Aug | 0.4 | 2.7 |
| AE ∆% Aug-Dec | 3.4 | |
| Jul | 0.0 | 2.8 |
| Jun | -0.2 | 2.9 |
| AE ∆% Jun-Jul | -1.2 | |
| May | 0.2 | 2.7 |
| Apr | 0.2 | 2.4 |
| Mar | 0.3 | 2.8 |
| Feb | 0.7 | 2.8 |
| AE ∆% Feb-May | 4.3 | |
| Jan 2013 | -0.5 | 2.7 |
| AE ∆% Jan | -5.8 | |
| Dec 2012 | 0.5 | 2.7 |
| Nov | 0.2 | 2.7 |
| Oct | 0.5 | 2.7 |
| Sep | 0.4 | 2.2 |
| Aug | 0.5 | 2.5 |
| Jul | 0.1 | 2.6 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Dec | 4.5 | |
| Jun | -0.4 | 2.4 |
| May | -0.1 | 2.8 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun | -3.0 | |
| Apr | 0.6 | 3.0 |
| Mar | 0.3 | 3.5 |
| Feb | 0.6 | 3.4 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Apr | 6.2 | |
| Jan | -0.5 | 3.6 |
| Dec 2011 | 0.4 | 4.2 |
| AE ∆% Dec-Jan | -0.6 | |
| Nov | 0.2 | 4.8 |
| Oct | 0.1 | 5.0 |
| Sep | 0.6 | 5.2 |
| Aug | 0.6 | 4.5 |
| AE ∆% Aug-Nov | 4.6 | |
| Jul | 0.0 | 4.4 |
| Jun | -0.1 | 4.2 |
| May | 0.2 | 4.5 |
| May-Jul | 0.4 | |
| Apr | 1.0 | 4.5 |
| Mar | 0.3 | 4.0 |
| Feb | 0.7 | 4.4 |
| Jan | 0.1 | 4.0 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr | 6.5 | |
| Dec 2010 | 1.0 | 3.7 |
| Nov | 0.4 | 3.3 |
| Oct | 0.3 | 3.2 |
| Sep | 0.0 | 3.1 |
| Aug | 0.5 | 3.1 |
| Jul | -0.2 | 3.1 |
| Jun | 0.1 | 3.2 |
| May | 0.2 | 3.4 |
| Apr | 0.6 | 3.7 |
| Mar | 0.6 | 3.4 |
| Feb | 0.4 | 3.0 |
| Jan | -0.2 | 3.5 |
Source: UK Office for National Statistics
http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/cpi/consumer-price-indices/may-2015/index.html
Inflation has been unusually high in the UK since 2006, as shown in Table IV-20. There were no rates of inflation close to 2.0 percent in the period from 1997 to 2004. Inflation exceeded 2 percent from 2005 to 2013, reaching 3.6 percent in 2008, 3.3 percent in 2010, 4.5 percent in 2011 and 2.8 percent in 2012. Annual inflation in 2013 was 2.6 percent, declining to 1.5 percent in 2014.
Table IV-20, UK, Consumer Price Index, Annual ∆%
| Annual ∆% | |
| 1998 | 1.6 |
| 1999 | 1.3 |
| 2000 | 0.8 |
| 2001 | 1.2 |
| 2002 | 1.3 |
| 2003 | 1.4 |
| 2004 | 1.3 |
| 2005 | 2.1 |
| 2006 | 2.3 |
| 2007 | 2.3 |
| 2008 | 3.6 |
| 2009 | 2.2 |
| 2010 | 3.3 |
| 2011 | 4.5 |
| 2012 | 2.8 |
| 2013 | 2.6 |
| 2014 | 1.5 |
Source: UK Office for National Statistics
http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/cpi/consumer-price-indices/may-2015/index.html
Table IV-21 provides the analysis of inflation in May 2015 by the UK Office for National Statistics. In the rate of 0.2 percent for May 2015, clothing and footwear added 0.04 percentage points, furniture and household goods added 0.03 percentage points and transport added 0.09 percentage points. Contributions of percentage points to the 12-month rate of consumer price inflation of 0.1 percent are in the second column in Table IV-21. Food and nonalcoholic beverages deducted 0.20 percentage points, alcohol and tobacco added 0.09 percentage points, housing and household services added 0.06 percentage points while transport deducted 0.23 percentage points.
Table IV-21, UK, Consumer Price Index Month and Twelve-month Percentage Point Contributions to Change by Components
| May 2015 | Percentage Point Contribution 12 Months May | Percentage Point Contribution May |
| CPI All Items ∆% | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Food & Non-Alcoholic Beverages | -0.20 | -0.01 |
| Alcohol & Tobacco | 0.09 | 0.03 |
| Clothing & Footwear | 0.03 | 0.04 |
| Housing & Household Services | 0.06 | 0.00 |
| Furniture & Household Goods | -0.02 | 0.03 |
| Health | 0.06 | 0.01 |
| Transport | -0.23 | 0.09 |
| Communication | 0.04 | -0.01 |
| Recreation & Culture | -0.14 | -0.02 |
| Education | 0.22 | 0.00 |
| Restaurants & Hotels | 0.23 | 0.02 |
| Miscellaneous Goods & Services | -0.01 | -0.02 |
| Rounding Effects | -0.03 | 0.04 |
Note: there are rounding effects in contributions
http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/cpi/consumer-price-indices/may-2015/index.html
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015.

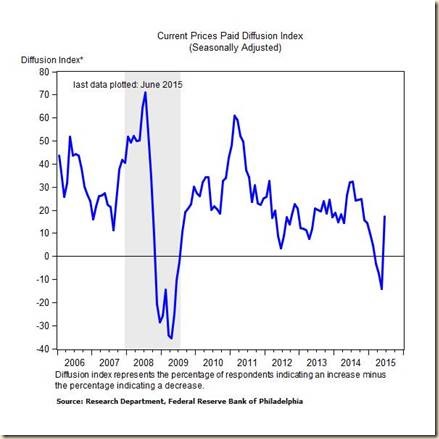

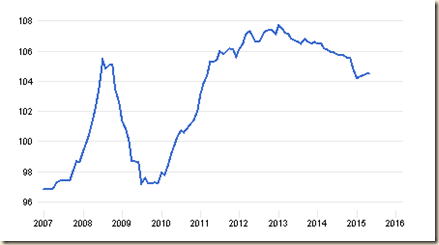






No comments:
Post a Comment