Tapering Quantitative Easing, Mediocre and Decelerating US Economic Growth, World Inflation Waves, Unresolved US Balance of Payments Deficits and Fiscal Imbalance, Squeeze of Economic Activity by Carry Trades Induced by Zero Interest Rates, Theory and Reality of Secular Stagnation and Productivity Growth, US Industrial Production, World Economic Slowdown and Global Recession Risk
Carlos M. Pelaez
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013
Executive Summary
I Mediocre and Decelerating United States Economic Growth
IA Mediocre and Decelerating United States Economic Growth
IA1 Contracting Real Private Fixed Investment
IA2 Swelling Undistributed Corporate Profits
II World Inflation Waves
IIA Appendix: Transmission of Unconventional Monetary Policy
IB1 Theory
IB2 Policy
IB3 Evidence
IB4 Unwinding Strategy
IIB United States Inflation
IIC Long-term US Inflation
IID Current US Inflation
IIE Theory and Reality of Economic History and Monetary Policy Based on Fear of Deflation
IIF United States Industrial Production and External and Fiscal Imbalances
IIA Unresolved US Balance of Payments Deficits and Fiscal Imbalance Threatening Risk Premium on Treasury Securities
IIA1 United States Unsustainable Deficit/Debt
IIA2 Unresolved US Balance of Payments Deficits
IIF United States Industrial Production
IV Global Inflation
V World Economic Slowdown
VA United States
VB Japan
VC China
VD Euro Area
VE Germany
VF France
VG Italy
VH United Kingdom
VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets
VII Economic Indicators
VIII Interest Rates
IX Conclusion
References
Appendixes
Appendix I The Great Inflation
IIIB Appendix on Safe Haven Currencies
IIIC Appendix on Fiscal Compact
IIID Appendix on European Central Bank Large Scale Lender of Last Resort
IIIG Appendix on Deficit Financing of Growth and the Debt Crisis
IIIGA Monetary Policy with Deficit Financing of Economic Growth
IIIGB Adjustment during the Debt Crisis of the 1980s
IA Mediocre and Decelerating United States Economic Growth. The US is experiencing the first expansion from a recession after World War II with stressing socioeconomic conditions:
- Mediocre economic growth below potential and long-term trend, resulting in idle productive resources (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html)
- Private fixed investment declining 3.6 percent in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2013 (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html)
- Twenty eight million or 17.2 percent of the effective labor force unemployed or underemployed in involuntary part-time jobs with stagnating or declining real wages (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/11/global-financial-risk-mediocre-united.html)
- Stagnating real disposable income per person or income per person after inflation and taxes (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/11/global-financial-risk-mediocre-united.html)
- Depressed hiring that does not afford an opportunity for reducing unemployment/underemployment and moving to better-paid jobs (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/theory-and-reality-of-secular.html)
- Unsustainable government deficit/debt and balance of payments deficit (Section II and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/09/duration-dumping-and-peaking-valuations.html)
- Worldwide waves of inflation (Section II and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/11/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-world.html)
- Deteriorating terms of trade and net revenue margins in squeeze of economic activity by carry trades induced by zero interest rates (Executive Summary)
- Financial repression of interest rates and credit affecting the most people without means and access to sophisticated financial investments with likely adverse effects on income distribution and wealth disparity (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html)
- 47 million in poverty and 48 million without health insurance with family income adjusted for inflation regressing to 1995 levels (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/09/duration-dumping-and-peaking-valuations.html
- Net worth of households and nonprofits organizations declining by 0.9 percent after adjusting for inflation in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIQ2013 in contrast with growth at 3.0 percent in real terms from 1945 to 2012 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/09/mediocre-and-decelerating-united-states.html)
Valuations of risk financial assets approach historical highs. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. US economic growth has been at only 2.3 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 17 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2013. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the third estimate of GDP for IIIQ2013 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2013/pdf/gdp3q13_3rd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,738.0 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,356.9 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,738.0/$14,356.9 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html). As a result, there are 28.1 million unemployed or underemployed in the United States for an effective unemployment rate of 17.2 percent (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/11/global-financial-risk-mediocre-united.html). The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May).
The economy of the US can be summarized in growth of economic activity or GDP as decelerating from mediocre growth of 2.5 percent on an annual basis in 2010 to 1.8 percent in 2011 to 2.8 percent in 2012. The following calculations show that actual growth is around 2.0 to 2.6 percent per year. This rate is well below 3 percent per year in trend from 1870 to 2010, which the economy of the US always attained for entire cycles in expansions after events such as wars and recessions (Lucas 2011May). Revisions and enhancements of United States GDP and personal income accounts by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) provide important information on long-term growth and cyclical behavior. Table Summary provides relevant data.
- Long-term. US GDP grew at the average yearly rate of 3.3 percent from 1929 to 2012 and at 3.2 percent from 1947 to 2012. There were periodic contractions or recessions in this period but the economy grew at faster rates in the subsequent expansions, maintaining long-term economic growth at trend.
- Cycles. The combined contraction of GDP in the two almost consecutive recessions in the early 1980s is 4.7 percent. The contraction of US GDP from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 during the global recession was 4.3 percent. The critical difference in the expansion is growth at average 7.8 percent in annual equivalent in the first four quarters of recovery from IQ1983 to IVQ1983. The average rate of growth of GDP in four cyclical expansions in the postwar period is 7.7 percent. In contrast, the rate of growth in the first four quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 was only 2.7 percent. Average annual equivalent growth in the expansion from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986 was 5.4 percent and 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986. In contrast, average annual equivalent growth in the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2013 was only 2.3 percent. The US appears to have lost its dynamism of income growth and employment creation.
Table Summary, Long-term and Cyclical Growth of GDP, Real Disposable Income and Real Disposable Income per Capita
| GDP | ||
| Long-Term | ||
| 1929-2012 | 3.3 | |
| 1947-2012 | 3.2 | |
| Cyclical Contractions ∆% | ||
| IQ1980 to IIIQ1980, IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 | -4.7 | |
| IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 | -4.3 | |
| Cyclical Expansions Average Annual Equivalent ∆% | ||
| IQ1983 to IVQ1985 IQ1983-IQ1986 IQ1983-IIIQ1986 IQ1983-IVQ1986 IQ1983-IQ1987 | 5.9 5.7 5.4 5.2 5.0 | |
| First Four Quarters IQ1983 to IVQ1983 | 7.8 | |
| IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2013 | 2.3 | |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 | 2.7 | |
| Real Disposable Income | Real Disposable Income per Capita | |
| Long-Term | ||
| 1929-2012 | 3.2 | 2.0 |
| 1947-1999 | 3.7 | 2.3 |
| Whole Cycles | ||
| 1980-1989 | 3.5 | 2.6 |
| 2006-2012 | 1.4 | 0.6 |
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The revisions and enhancements of United States GDP and personal income accounts by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) also provide critical information in assessing the current rhythm of US economic growth. The economy appears to be moving at a pace from 2.0 to 2.6 percent per year. Table Summary GDP provides the data.
1. Average Annual Growth in the Past Six Quarters. GDP growth in the four quarters of 2012 and the first three quarters of 2013 accumulated to 3.9 percent. This growth is equivalent to 2.2 percent per year, obtained by dividing GDP in IIIQ2013 of $15,839.3 billion by GDP in IVQ2011 of $15,242.1 billion and compounding by 4/7: {[($15,839.3/$15,242.1)4/7 -1]100 = 2.2.
2. Average Annual Growth in the First Three Quarters of 2013. GDP growth in the first three quarters of 2013 accumulated to 1.9 percent that is equivalent to 2.6 percent in a year. This is obtained by dividing GDP in IIIQ2013 of $15,839.3 by GDP in IVQ2012 of $15,539.6 and compounding by 4/3: {[($15,839.3/$15,539.6)4/3 -1]100 = 2.6%}. The US economy grew 2.0 percent in IIIQ2013 relative to the same quarter a year earlier in IIIQ2012. Another important revelation of the revisions and enhancements is that GDP was flat in IVQ2012, which is just at the borderline of contraction. The rate of growth of GDP in the third estimate of IIIQ2013 is 4.1 percent in seasonally adjusted annual rate (SAAR). Inventory accumulation contributed 1.67 percentage points to this rate of growth. The actual rate without this impulse of unsold inventories would have been 2.43 percent, or 0.6 percent in IIIQ2013, such that annual equivalent growth in 2013 is closer to 2.0 percent {[(1.003)(1.006)(1.006)4/3-1]100 = 2.0%}, compounding the quarterly rates and converting into annual equivalent.
Table Summary GDP, US, Real GDP and Percentage Change Relative to IVQ2007 and Prior Quarter, Billions Chained 2005 Dollars and ∆%
| Real GDP, Billions Chained 2009 Dollars | ∆% Relative to IVQ2007 | ∆% Relative to Prior Quarter | ∆% | |
| IVQ2007 | 14,996.1 | NA | NA | 1.9 |
| IVQ2011 | 15,242.1 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 2.0 |
| IQ2012 | 15,381.6 | 2.6 | 0.9 | 3.3 |
| IIQ2012 | 15,427.7 | 2.9 | 0.3 | 2.8 |
| IIIQ2012 | 15,534.0 | 3.6 | 0.7 | 3.1 |
| IVQ2012 | 15,539.6 | 3.6 | 0.0 | 2.0 |
| IQ2013 | 15,583.9 | 3.9 | 0.3 | 1.3 |
| IIQ2013 | 15,679.7 | 4.6 | 0.6 | 1.6 |
| IIIQ2013 | 15,839.3 | 5.6 | 1.0 | 2.0 |
| Cumulative ∆% IQ2012 to IIIQ2013 | 3.9 | 3.9 | ||
| Annual Equivalent ∆% | 2.2 | 2.2 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The objective of this section is analyzing US economic growth in the current cyclical expansion. There is initial discussion of the conventional explanation of the current recovery as being weak because of the depth of the contraction and the financial crisis and brief discussion of the concept of “slow-growth recession.” Analysis that is more complete is in IB Collapse of United States Dynamism of Income Growth and Employment Creation, which is updated with release of more information on the United States economic cycle (IX Conclusion and extended analysis at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/10/collapse-of-united-states-dynamism-of.html). The bulk of the section consists of comparison of the current growth experience of the US with earlier expansions after past deep contractions and consideration of recent performance.
This blog has analyzed systematically the weakness of United States recovery in the current business cycle from IIIQ2009 to the present in comparison with the recovery from the two recessions in the 1980s from IQ1983 to IVQ1986. US economic growth has been at only 2.3 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 17 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2013. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the third estimate of GDP for IIIQ2013 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2013/pdf/gdp3q13_3rd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,738.0 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,356.9 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,738.0/$14,356.9 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html). As a result, there are 28.1 million unemployed or underemployed in the United States for an effective unemployment rate of 17.2 percent (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/11/global-financial-risk-mediocre-united.html). The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May).
The conventional explanation is that the recession from IVQ2007 (Dec) to IIQ2009 (Jun) was so profound that it caused subsequent weak recovery and that historically growth after recessions with financial crises has been weaker. Michael D. Bordo (2012Sep27) and Bordo and Haubrich (2012DR) provide evidence contradicting the conventional explanation: recovery is much stronger on average after profound contractions and much stronger after recessions with financial crises than after recessions without financial crises. Insistence on the conventional explanation prevents finding policies that can accelerate growth, employment and prosperity.
A monumental effort of data gathering, calculation and analysis by Carmen M. Reinhart and Kenneth Rogoff is highly relevant to banking crises, financial crash, debt crises and economic growth (Reinhart 2010CB; Reinhart and Rogoff 2011AF, 2011Jul14, 2011EJ, 2011CEPR, 2010FCDC, 2010GTD, 2009TD, 2009AFC, 2008TDPV; see also Reinhart and Reinhart 2011Feb, 2010AF and Reinhart and Sbrancia 2011). See http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/07/debt-and-financial-risk-aversion-and.html The dataset of Reinhart and Rogoff (2010GTD, 1) is quite unique in breadth of countries and over time periods:
“Our results incorporate data on 44 countries spanning about 200 years. Taken together, the data incorporate over 3,700 annual observations covering a wide range of political systems, institutions, exchange rate and monetary arrangements and historic circumstances. We also employ more recent data on external debt, including debt owed by government and by private entities.”
Reinhart and Rogoff (2010GTD, 2011CEPR) classify the dataset of 2317 observations into 20 advanced economies and 24 emerging market economies. In each of the advanced and emerging categories, the data for countries is divided into buckets according to the ratio of gross central government debt to GDP: below 30, 30 to 60, 60 to 90 and higher than 90 (Reinhart and Rogoff 2010GTD, Table 1, 4). Median and average yearly percentage growth rates of GDP are calculated for each of the buckets for advanced economies. There does not appear to be any relation for debt/GDP ratios below 90. The highest growth rates are for debt/GDP ratios below 30: 3.7 percent for the average and 3.9 for the median. Growth is significantly lower for debt/GDP ratios above 90: 1.7 for the average and 1.9 percent for the median. GDP growth rates for the intermediate buckets are in a range around 3 percent: the highest 3.4 percent average is for the bucket 60 to 90 and 3.1 percent median for 30 to 60. There is even sharper contrast for the United States: 4.0 percent growth for debt/GDP ratio below 30; 3.4 percent growth for debt/GDP ratio of 30 to 60; 3.3 percent growth for debt/GDP ratio of 60 to 90; and minus 1.8 percent, contraction, of GDP for debt/GDP ratio above 90.
For the five countries with systemic financial crises—Iceland, Ireland, UK, Spain and the US—real average debt levels have increased by 75 percent between 2007 and 2009 (Reinhart and Rogoff 2010GTD, Figure 1). The cumulative increase in public debt in the three years after systemic banking crisis in a group of episodes after World War II is 86 percent (Reinhart and Rogoff 2011CEPR, Figure 2, 10).
An important concept is “this time is different syndrome,” which “is rooted in the firmly-held belief that financial crises are something that happens to other people in other countries at other times; crises do not happen here and now to us” (Reinhart and Rogoff 2010FCDC, 9). There is both an arrogance and ignorance in “this time is different” syndrome, as explained by Reinhart and Rogoff (2010FCDC, 34):
“The ignorance, of course, stems from the belief that financial crises happen to other people at other time in other places. Outside a small number of experts, few people fully appreciate the universality of financial crises. The arrogance is of those who believe they have figured out how to do things better and smarter so that the boom can long continue without a crisis.”
There is sober warning by Reinhart and Rogoff (2011CEPR, 42) on the basis of the momentous effort of their scholarly data gathering, calculation and analysis:
“Despite considerable deleveraging by the private financial sector, total debt remains near its historic high in 2008. Total public sector debt during the first quarter of 2010 is 117 percent of GDP. It has only been higher during a one-year sting at 119 percent in 1945. Perhaps soaring US debt levels will not prove to be a drag on growth in the decades to come. However, if history is any guide, that is a risky proposition and over-reliance on US exceptionalism may only be one more example of the “This Time is Different” syndrome.”
As both sides of the Atlantic economy maneuver around defaults, the experience on debt and growth deserves significant emphasis in research and policy. The world economy is slowing with high levels of unemployment in advanced economies. Countries do not grow themselves out of unsustainable debts but rather through de facto defaults by means of financial repression and in some cases through inflation. This time is not different.
Professor Michael D. Bordo (2012Sep27), at Rutgers University, is providing clear thought on the correct comparison of the current business cycles in the United States with those in United States history. There are two issues raised by Professor Bordo: (1) incomplete conclusions by lumping together countries with different institutions, economic policies and financial systems; and (2) the erroneous contention that growth is mediocre after financial crises and deep recessions, which is repeated daily in the media, but that Bordo and Haubrich (2012DR) persuasively demonstrate to be inconsistent with United States experience.
Depriving economic history of institutions is perilous as is illustrated by the economic history of Brazil. Douglass C. North (1994) emphasized the key role of institutions in explaining economic history. Rondo E. Cameron (1961, 1967, 1972) applied institutional analysis to banking history. Friedman and Schwartz (1963) analyzed the relation of money, income and prices in the business cycle and related the monetary policy of an important institution, the Federal Reserve System, to the Great Depression. Bordo, Choudhri and Schwartz (1995) analyze the counterfactual of what would have been economic performance if the Fed had used during the Great Depression the Friedman (1960) monetary policy rule of constant growth of money (for analysis of the Great Depression see Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 198-217). Alan Meltzer (2004, 2010a,b) analyzed the Federal Reserve System over its history. The reader would be intrigued by Figure 5 in Reinhart and Rogoff (2010FCDC, 15) in which Brazil is classified in external default for seven years between 1828 and 1834 but not again until 64 years later in 1989, above the 50 years of incidence for serial default. William R. Summerhill, Jr. (2007SC, 2007IR) has filled this void in scholarly research on nineteenth-century Brazil. There are important conclusions by Summerhill on the exceptional sample of institutional change or actually lack of change, public finance and financial repression in Brazil between 1822 and 1899, combining tools of economics, political science and history. During seven continuous decades, Brazil did not miss a single interest payment with government borrowing without repudiation of debt or default. What is surprising is that Brazil borrowed by means of long-term bonds and, even more surprising, interest rates fell over time. The external debt of Brazil in 1870 was ₤41,275,961 and the domestic debt in the internal market was ₤25,708,711, or 62.3 percent of the total (Summerhill 2007IR, 73).
The experience of Brazil differed from that of Latin America (Summerhill 2007IR). During the six decades when Brazil borrowed without difficulty, Latin American countries becoming independent after 1820 engaged in total defaults, suffering hardship in borrowing abroad. The countries that borrowed again fell again in default during the nineteenth century. Venezuela defaulted in four occasions. Mexico defaulted in 1827, rescheduling its debt eight different times and servicing the debt sporadically. About 44 percent of Latin America’s sovereign debt was in default in 1855 and approximately 86 percent of total government loans defaulted in London originated in Spanish American borrowing countries.
External economies of commitment to secure private rights in sovereign credit would encourage development of private financial institutions, as postulated in classic work by North and Weingast (1989), Summerhill 2007IR, 22). This is how banking institutions critical to the Industrial Revolution were developed in England (Cameron 1967). The obstacle in Brazil found by Summerhill (2007IR) is that sovereign debt credibility combined with financial repression. There was a break in Brazil of the chain of effects from protecting public borrowing, as in North and Weingast (1989), to development of private financial institutions.
Nicia Villela Luz and Carlos Manuel Peláez (1972, 276) find that:
“The lack of interest on historical moments by economists may explain their emphasis on secular trends in their research on the past instead of changes in the historical process. This may be the origin of why they fill gaps in documentation with their extrapolations.”
Vilela Luz (1961) provides classic analysis of industrialization in Brazil. According to Pelaez 1976, 283) following Cameron (1971, 1967):
“The banking law of 1860 placed severe restrictions on two basic modern economic institutions—the corporation and the commercial bank. The growth of the volume of bank credit was one of the most significant factors of financial intermediation and economic growth in the major trading countries of the gold standard group. But Brazil placed strong restrictions on the development of banking and intermediation functions, preventing the channeling of coffee savings into domestic industry at an earlier date.”
Brazil actually abandoned the gold standard during multiple financial crises in the nineteenth century, as it should have to protect domestic economic activity. Pelaez (1975, 447) finds similar experience in the first half of nineteenth-century Brazil:
“Brazil’s experience is particularly interesting in that in the period 1808-1851 there were three types of monetary systems. Between 1808 and 1829, there was only one government-related Bank of Brazil, enjoying a perfect monopoly of banking services. No new banks were established in the 1830s after the liquidation of the Bank of Brazil in 1829. During the coffee boom in the late 1830s and 1840s, a system of banks of issue, patterned after similar institutions in the industrial countries, supplied the financial services required in the first stage of modernization of the export economy.”
Financial crises in the advanced economies transmitted to nineteenth-century Brazil by the arrival of a ship (Pelaez and Suzigan 1981). The explanation of those crises and the economy of Brazil requires knowledge and roles of institutions, economic policies and the financial system chosen by Brazil, in agreement with Bordo (2012Sep27).
The departing theoretical framework of Bordo and Haubrich (2012DR) is the plucking model of Friedman (1964, 1988). Friedman (1988, 1) recalls, “I was led to the model in the course of investigating the direction of influence between money and income. Did the common cyclical fluctuation in money and income reflect primarily the influence of money on income or of income on money?” Friedman (1964, 1988) finds useful for this purpose to analyze the relation between expansions and contractions. Analyzing the business cycle in the United States between 1870 and 1961, Friedman (1964, 15) found that “a large contraction in output tends to be followed on the average by a large business expansion; a mild contraction, by a mild expansion.” The depth of the contraction opens up more room in the movement toward full employment (Friedman 1964, 17):
“Output is viewed as bumping along the ceiling of maximum feasible output except that every now and then it is plucked down by a cyclical contraction. Given institutional rigidities and prices, the contraction takes in considerable measure the form of a decline in output. Since there is no physical limit to the decline short of zero output, the size of the decline in output can vary widely. When subsequent recovery sets in, it tends to return output to the ceiling; it cannot go beyond, so there is an upper limit to output and the amplitude of the expansion tends to be correlated with the amplitude of the contraction.”
Kim and Nelson (1999) test the asymmetric plucking model of Friedman (1964, 1988) relative to a symmetric model using reference cycles of the NBER, finding evidence supporting the Friedman model. Bordo and Haubrich (2012DR) analyze 27 cycles beginning in 1872, using various measures of financial crises while considering different regulatory and monetary regimes. The revealing conclusion of Bordo and Haubrich (2012DR, 2) is that:
“Our analysis of the data shows that steep expansions tend to follow deep contractions, though this depends heavily on when the recovery is measured. In contrast to much conventional wisdom, the stylized fact that deep contractions breed strong recoveries is particularly true when there is a financial crisis. In fact, on average, it is cycles without a financial crisis that show the weakest relation between contraction depth and recovery strength. For many configurations, the evidence for a robust bounce-back is stronger for cycles with financial crises than those without.”
The average rate of growth of real GDP in expansions after recessions with financial crises was 8 percent but only 6.9 percent on average for recessions without financial crises (Bordo 2012Sep27). Real GDP declined 12 percent in the Panic of 1907 and increased 13 percent in the recovery, consistent with the plucking model of Friedman (Bordo 2012Sep27). The comparison of recovery from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 is appropriate even when considering financial crises. There was significant financial turmoil during the 1980s. Bordo and Haubrich (2012DR, 11) identify a financial crisis in the United States starting in 1981. Benston and Kaufman (1997, 139) find that there was failure of 1150 US commercial and savings banks between 1983 and 1990, or about 8 percent of the industry in 1980, which is nearly twice more than between the establishment of the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation in 1934 through 1983. More than 900 savings and loans associations, representing 25 percent of the industry, were closed, merged or placed in conservatorships (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2008b), 74-7). The Financial Institutions Reform, Recovery and Enforcement Act of 1989 (FIRREA) created the Resolution Trust Corporation (RTC) and the Savings Association Insurance Fund (SAIF) that received $150 billion of taxpayer funds to resolve insolvent savings and loans. The GDP of the US in 1989 was $5657.7 billion (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm), such that the partial cost to taxpayers of that bailout was around 2.65 percent of GDP in a year. The US Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) estimates GDP in 2012 at $16,244.6 billion (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm), such that the bailout would be equivalent to cost to taxpayers of about $430.5 billion in current GDP terms. A major difference with the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) for private-sector banks is that most of the costs were recovered with interest gains whereas in the case of savings and loans there was no recovery. Money center banks were under extraordinary pressure from the default of sovereign debt by various emerging nations that represented a large share of their net worth (see Pelaez 1986).
Bordo (2012Sep27) finds two probable explanations for the weak recovery during the current economic cycle: (1) collapse of United States housing; and (2) uncertainty originating in fiscal policy, regulation and structural changes. There are serious doubts if monetary policy is adequate to recover the economy under these conditions.
The concept of growth recession was popular during the stagflation from the late 1960s to the early 1980s. The economy of the US underperformed with several recession episodes in “stop and go” fashion of policy and economic activity while the rate of inflation rose to the highest in a peacetime period (see http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/06/risk-aversion-and-stagflation.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/05/slowing-growth-global-inflation-great.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/05/global-inflation-seigniorage-monetary.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/04/new-economics-of-rose-garden-turned.html Appendix I; see Taylor 1993, 1997, 1999, 1998LB, 2012Mar27, 2012Mar28, 2012FP, 2012JMCB). A growth recession could be defined as a period in which economic growth is insufficient to move the economy toward full employment of humans, equipment and other productive resources. The US is experiencing a dramatic slow growth recession with 28.111 million people in job stress, consisting of an effective number of unemployed of 18.452 million, 7.563 million employed part-time because they cannot find full employment and 2.096 million marginally attached to the labor force for 17.2 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/11/global-financial-risk-mediocre-united.html). The discussion of the growth recession issue in the 1970s by two recognized economists of the twentieth century, James Tobin and Paul A. Samuelson, is worth recalling.
In analysis of the design of monetary policy in 1974, Tobin (1974, 219) finds that the forecast of the President’s Council of Economic Advisers (CEA) was also the target such that monetary policy would have to be designed and implemented to attain that target. The concern was with maintaining full employment as provided in the Employment Law of 1946 (http://www.law.cornell.edu/uscode/15/1021.html http://uscode.house.gov/download/pls/15C21.txt http://www.eric.ed.gov/PDFS/ED164974.pdf) see http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/04/new-economics-of-rose-garden-turned.html), which also created the CEA. Tobin (1974, 219) describes the forecast/target of the CEA for 1974:
“The expected and approved path appears to be quarter-to-quarter rates of growth of real gross national product in 1974 of roughly -0.5, 0.1, and 1 percent, with unemployment rising to about 5.6 percent in the second quarter and remaining there the rest of the year. The rate of price inflation would fall shortly in the second quarter, but rise slightly toward the end of the year.”
Referring to monetary policy design, Tobin (1974, 221) states: “if interest rates remain stable or rise during the current (growth) recession and recovery, this will be a unique episode in business cycle annals.” Subpar economic growth is often called a “growth recession.” The critically important concept is that economic growth is not sufficient to move the economy toward full employment, creating the social and economic adverse outcome of idle capacity and unemployed and underemployed workers, much the same as currently.
Samuelson considers the unexpected incidence of inflation surprises during growth recessions (1974, 76):
“Indeed, if there were in Las Vegas or New York a continuous casino on the money GNP of 1974’s fourth quarter, it would be absurd to think that the best economic forecasters could improve upon the guess posted there. Whatever knowledge and analytical skill they possess would already have been fed into the bidding. It is a manifest contradiction to think that most economists can be expected to do better than their own best performance. I am saying that the best forecasters have been poor in predicting the general price level’s movements and level even a year ahead. By Valentine’s Day 1973 the best forecasters were beginning to talk of the growth recession that we now know did set in at the end of the first quarter. Aside from their end-of-1972 forecasts, the fashionable crowd has little to blame itself for when it comes to their 1973 real GNP projections. But, of course, they did not foresee the upward surge of food and decontrolled industrial prices. This has been a recurring pattern: surprise during the event at the virulence of inflation, wisdom after the event in demonstrating that it did, after all, fit with past patterns of experience.”
Economists are known for their forecasts being second only to those of astrologers. Accurate forecasts are typically realized for the wrong reasons. In contrast with meteorologists, economists do not even agree on what happened. There is not even agreement on what caused the global recession and why the economy has reached a perilous standstill.
There is current interest in past theories of “secular stagnation.” Alvin H. Hansen (1939, 4, 7; see Hansen 1938, 1941; for an early critique see Simons 1942) argues:
“Not until the problem of full employment of our productive resources from the long-run, secular standpoint was upon us, were we compelled to give serious consideration to those factors and forces in our economy which tend to make business recoveries weak and anaemic (sic) and which tend to prolong and deepen the course of depressions. This is the essence of secular stagnation-sick recoveries which die in their infancy and depressions which feed on themselves and leave a hard and seemingly immovable core of unemployment. Now the rate of population growth must necessarily play an important role in determining the character of the output; in other words, the com-position of the flow of final goods. Thus a rapidly growing population will demand a much larger per capita volume of new residential building construction than will a stationary population. A stationary population with its larger proportion of old people may perhaps demand more personal services; and the composition of consumer demand will have an important influence on the quantity of capital required. The demand for housing calls for large capital outlays, while the demand for personal services can be met without making large investment expenditures. It is therefore not unlikely that a shift from a rapidly growing population to a stationary or declining one may so alter the composition of the final flow of consumption goods that the ratio of capital to output as a whole will tend to decline.”
The argument that anemic population growth causes “secular stagnation” in the US (Hansen 1938, 1939, 1941) is as misplaced currently as in the late 1930s (for early dissent see Simons 1942). Youth workers would obtain employment at a premium in an economy with declining population. In fact, there is currently population growth in the ages of 16 to 24 years but not enough job creation and discouragement of job searches for all ages. This is merely another case of theory without reality with dubious policy proposals. Inferior performance of the US economy and labor markets is the critical current issue of analysis and policy design.
In revealing research, Edward P. Lazear and James R. Spletzer (2012JHJul22) use the wealth of data in the valuable database and resources of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (http://www.bls.gov/data/) in providing clear thought on the nature of the current labor market of the United States. The critical issue of analysis and policy currently is whether unemployment is structural or cyclical. Structural unemployment could occur because of (1) industrial and demographic shifts and (2) mismatches of skills and job vacancies in industries and locations. Consider the aggregate unemployment rate, Y, expressed in terms of share si of a demographic group in an industry i and unemployment rate yi of that demographic group (Lazear and Spletzer 2012JHJul22, 5-6):
Y = ∑isiyi (1)
This equation can be decomposed for analysis as (Lazear and Spletzer 2012JHJul22, 6):
∆Y = ∑i∆siy*i + ∑i∆yis*i (2)
The first term in (2) captures changes in the demographic and industrial composition of the economy ∆si multiplied by the average rate of unemployment y*i , or structural factors. The second term in (2) captures changes in the unemployment rate specific to a group, or ∆yi, multiplied by the average share of the group s*i, or cyclical factors. There are also mismatches in skills and locations relative to available job vacancies. A simple observation by Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22) casts intuitive doubt on structural factors: the rate of unemployment jumped from 4.4 percent in the spring of 2007 to 10 percent in October 2009. By nature, structural factors should be permanent or occur over relative long periods. The revealing result of the exhaustive research of Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22) is:
“The analysis in this paper and in others that we review do not provide any compelling evidence that there have been changes in the structure of the labor market that are capable of explaining the pattern of persistently high unemployment rates. The evidence points to primarily cyclic factors.”
The theory of secular stagnation cannot explain sudden collapse of the US economy and labor markets. There are accentuated cyclic factors for both the entire population and the young population of ages 16 to 24 years. Table Summary provides the total noninstitutional population (ICP) of the US, full-time employment level (FTE), employment (EMP), civilian labor force (CLF), civilian labor force participation rate (CLFP), employment/population ratio (EPOP) and unemployment level (UNE). Secular stagnation would not be secular but immediate. All indicators of the labor market weakened sharply during the contraction and did not recover. Population continued to grow but all other variables collapsed and did not recover. The theory of secular stagnation departs from an aggregate production function in which output grows with the use of labor, capital and technology (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. I (2008a), 11-6). Hansen (1938, 1939) finds secular stagnation in lower growth of an aging population. In the current US economy, Table Summary shows that population is dynamic while the labor market is fractured. There is key explanation in the behavior of the civilian labor force participation rate (CLFP) and the employment population ratio (EPOP) that collapsed during the global recession with inadequate recovery. Abandoning job searches are difficult to capture in labor statistics but likely explain the decline in the participation of the population in the labor force. Allowing for abandoning job searches, the total number of people unemployed or underemployed is 28.1 million or 17.2 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html).
Table Summary Total, US, Total Noninstitutional Civilian Population, Full-time Employment, Employment, Civilian Labor Force, Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate, Employment Population Ratio, Unemployment, NSA, Millions and Percent
| ICP | FTE | EMP | CLF | CLFP | EPOP | UNE | |
| 2006 | 288.8 | 119.7 | 144.4 | 151.4 | 66.2 | 63.1 | 7.0 |
| 2009 | 235.8 | 112.6 | 139.9 | 154.1 | 65.4 | 59.3 | 14.3 |
| 2012 | 243.3 | 114.8 | 142.5 | 155.0 | 63.7 | 58.6 | 12.5 |
| 12/07 | 233.2 | 121.0 | 146.3 | 153.7 | 65.9 | 62.8 | 7.4 |
| 9/09 | 236.3 | 112.0 | 139.1 | 153.6 | 65.0 | 58.9 | 14.5 |
| 11/13 | 246.6 | 116.9 | 144.8 | 155.0 | 62.9 | 58.7 | 10.3 |
ICP: Total Noninstitutional Civilian Population; FT: Full-time Employment Level, EMP: Total Employment Level; CLF: Civilian Labor Force; CLFP: Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate; EPOP: Employment Population Ratio; UNE: Unemployment
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
The same situation is present in the labor market for young people in ages 16 to 24 years with data in Table Summary Youth. The youth noninstitutional civilian population (ICP) continued to increase during and after the global recession. There is the same disastrous labor market with decline for young people in employment (EMP), civilian labor force (CLF), civilian labor force participation rate (CLFP) and employment population ratio (EPOP). There are only increases for unemployment of young people (UNE) and youth unemployment rate (UNER). If aging were a factor of secular stagnation, growth of population of young people would attract a premium in remuneration in labor markets. The sad fact is that young people are also facing tough labor markets. The application of the theory of secular stagnation to the US economy and labor markets is void of reality in the form of key facts.
Table Summary Youth, US, Youth, Ages 16 to 24 Years, Noninstitutional Civilian Population, Full-time Employment, Employment, Civilian Labor Force, Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate, Employment Population Ratio, Unemployment, NSA, Millions and Percent
| ICP | EMP | CLF | CLFP | EPOP | UNE | UNER | |
| 2006 | 36.9 | 20.0 | 22.4 | 60.6 | 54.2 | 2.4 | 10.5 |
| 2009 | 37.6 | 17.6 | 21.4 | 56.9 | 46.9 | 3.8 | 17.6 |
| 2012 | 38.8 | 17.8 | 21.3 | 54.9 | 46.0 | 3.5 | 16.2 |
| 12/07 | 37.5 | 19.4 | 21.7 | 57.8 | 51.6 | 2.3 | 10.7 |
| 9/09 | 37.6 | 17.0 | 20.7 | 55.2 | 45.1 | 3.8 | 18.2 |
| 11/13 | 38.8 | 18.1 | 20.8 | 53.7 | 46.7 | 2.7 | 13.1 |
ICP: Youth Noninstitutional Civilian Population; EMP: Youth Employment Level; CLF: Youth Civilian Labor Force; CLFP: Youth Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate; EPOP: Youth Employment Population Ratio; UNE: Unemployment; UNER: Youth Unemployment Rate
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/home.htm
Historical parallels are instructive but have all the limitations of empirical research in economics. The more instructive comparisons are not with the Great Depression of the 1930s but rather with the recessions in the 1950s, 1970s and 1980s. The growth rates and job creation in the expansion of the economy away from recession are subpar in the current expansion compared to others in the past. Four recessions are initially considered, following the reference dates of the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) (http://www.nber.org/cycles/cyclesmain.html ): IIQ1953-IIQ1954, IIIQ1957-IIQ1958, IIIQ1973-IQ1975 and IQ1980-IIIQ1980. The data for the earlier contractions illustrate that the growth rate and job creation in the current expansion are inferior. The sharp contractions of the 1950s and 1970s are considered in Table I-1, showing the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) quarter-to-quarter, seasonally adjusted (SA), yearly-equivalent growth rates of GDP. The recovery from the recession of 1953 consisted of four consecutive quarters of high percentage growth rates from IIIQ1954 to IIIQ1955: 4.6, 8.0, 11.9 and 6.7. The recession of 1957 was followed by four consecutive high percentage growth rates from IIIQ1958 to IIQ1959: 9.6, 9.7, 7.7 and 10.1. The recession of 1973-1975 was followed by high percentage growth rates from IIQ1975 to IQ1976: 3.1, 6.8, 5.5 and 9.3. The disaster of the Great Inflation and Unemployment of the 1970s, which made stagflation notorious, is even better in growth rates during the expansion phase in comparison with the current slow-growth recession.
Table I-1, US, Seasonally Adjusted Quarterly Percentage Growth Rates in Annual Equivalent of GDP in Cyclical Recessions and Following Four Quarter Expansions ∆%
| IQ | IIQ | IIIQ | IV | |
| R IIQ1953-IIQ1954 | ||||
| 1953 | -2.2 | -5.9 | ||
| 1954 | -1.9 | |||
| E IIIQ1954-IIQ1955 | ||||
| 1954 | 4.6 | 8.0 | ||
| 1955 | 11.9 | 6.7 | ||
| R IIIQ1957-IIQ1958 | ||||
| 1957 | -4.1 | |||
| 1958 | -10.0 | |||
| E IIIQ1958-IIQ1959 | ||||
| 1958 | 9.6 | 9.7 | ||
| 1959 | 7.7 | 10.1 | ||
| R IVQ1969-IV1970 | ||||
| 1969 | -1.7 | |||
| 1970 | -0.7 | |||
| E IIQ1970-IQ1971 | ||||
| 1970 | 0.7 | 3.6 | -4.1 | |
| 1971 | 11.2 | |||
| R IVQ1973-IQ1975 | ||||
| 1973 | 3.8 | |||
| 1974 | -3.3 | 1.0 | -3.8 | -1.6 |
| 1975 | -4.7 | |||
| E IIQ1975-IQ1976 | ||||
| 1975 | 3.1 | 6.8 | 5.5 | |
| 1976 | 9.3 | |||
| R IQ1980-IIIQ1980 | ||||
| 1980 | 1.3 | -7.9 | -0.6 | |
| R IQ1981-IVQ1982 | ||||
| 1981 | 8.5 | -2.9 | 4.7 | -4.6 |
| 1982 | -6.5 | 2.2 | -1.4 | 0.4 |
| E IQ1983-IVQ1983 | ||||
| 1983 | 5.3 | 9.4 | 8.1 | 8.5 |
| R IVQ2007-IIQ2009 | ||||
| 2008 | -2.7 | 2.0 | -2.0 | -8.3 |
| 2009 | -5.4 | -0.4 | ||
| E IIIQ2009-IIQ2010 | ||||
| 2009 | 1.3 | 3.9 | ||
| 2010 | 1.6 | 3.9 |
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm Reference Cycles National Bureau of Economic Research http://www.nber.org/cycles/cyclesmain.html
The NBER dates another recession in 1980 that lasted about half a year. If the two recessions from IQ1980s to IIIQ1980 and IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 are combined, the impact of lost GDP of 4.7 percent is more comparable to the latest revised 4.3 percent drop of the recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. The recession in 1981-1982 is quite similar on its own to the 2007-2009 recession. In contrast, during the Great Depression in the four years of 1930 to 1933, GDP in constant dollars fell 26.4 percent cumulatively and fell 45.3 percent in current dollars (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 150-2, Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2009b), 205-7 and revisions in http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). Table I-2 provides the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) quarterly growth rates of GDP in SA yearly equivalents for the recessions of 1981 to 1982 and 2007 to 2009, using the latest major revision published on July 31, 2013 and the third estimate for IIIQ2013 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2013/pdf/gdp3q13_3rd.pdf), which are available in the dataset of the US Bureau of Economic Analysis (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). There were four quarters of contraction in 1981-1982 ranging in rate from -1.4 percent to -6.5 percent and five quarters of contraction in 2007-2009 ranging in rate from -0.4 percent to -8.3 percent. The striking difference is that in the first sixteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, shown in Table I-2 in relief, GDP grew at the high quarterly percentage growth rates of 5.3, 9.4, 8.1, 8.5, 8.2, 7.2, 4.0, 3.2, 4.0, 3.7, 6.4, 3.0, 3.8, 1.9, 4.1 and 2.1. In contrast, the percentage growth rates in the first sixteen quarters of expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2013 shown in relief in Table I-2 were mediocre: 1.3, 3.9, 1.6, 3.9, 2.8, 2.8, -1.3, 3.2, 1.4, 4.9, 3.7, 1.2, 2.8, 0.1, 1.1, 2.5 and 4.1. Inventory accumulation contributed 2.73 percentage points to the rate of growth of 4.9 percent in IVQ2011, which is the only relatively high rate from IQ2011 to IIIQ2012, 0.60 percentage points to the rate of 2.8 percent in IIIQ2012 and 1.67 percentage points to the rate of 4.1 percent in IIIQ2013. Economic growth and employment creation decelerated rapidly during 2012 and in 2013 while much stronger growth would be required in movement to full employment.
Table I-2, US, Quarterly Growth Rates of GDP, % Annual Equivalent SA
| Q | 1981 | 1982 | 1983 | 1984 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 |
| I | 8.5 | -6.5 | 5.3 | 8.2 | -2.7 | -5.4 | 1.6 |
| II | -2.9 | 2.2 | 9.4 | 7.2 | 2.0 | -0.4 | 3.9 |
| III | 4.7 | -1.4 | 8.1 | 4.0 | -2.0 | 1.3 | 2.8 |
| IV | -4.6 | 0.4 | 8.5 | 3.2 | -8.3 | 3.9 | 2.8 |
| 1985 | 2011 | ||||||
| I | 4.0 | -1.3 | |||||
| II | 3.7 | 3.2 | |||||
| III | 6.4 | 1.4 | |||||
| IV | 3.0 | 4.9 | |||||
| 1986 | 2012 | ||||||
| I | 3.8 | 3.7 | |||||
| II | 1.9 | 1.2 | |||||
| III | 4.1 | 2.8 | |||||
| IV | 2.1 | 0.1 | |||||
| 1987 | 2013 | ||||||
| I | 2.8 | 1.1 | |||||
| II | 4.6 | 2.5 | |||||
| III | 3.7 | 4.1 | |||||
| IV | 6.8 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-1 of the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) provides strong growth of real GDP in the US between 1929 and 1999 at the yearly average rate of 3.5 percent. There is an evident acceleration of the rate of GDP growth in the 1990s as shown by a much sharper slope of the growth curve. Cobet and Wilson (2002) define labor productivity as the value of manufacturing output produced per unit of labor input used (see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 137-44). Between 1950 and 2000, labor productivity in the US grew less rapidly than in Germany and Japan. The major part of the increase in productivity in Germany and Japan occurred between 1950 and 1973 while the rate of productivity growth in the US was relatively subdued in several periods. While Germany and Japan reached their highest growth rates of productivity before 1973, the US accelerated its rate of productivity growth in the second half of the 1990s. Between 1950 and 2000, the rate of productivity growth in the US of 2.9 percent per year was much lower than 6.3 percent in Japan and 4.7 percent in Germany. Between 1995 and 2000, the rate of productivity growth of the US of 4.6 percent exceeded that of Japan of 3.9 percent and the rate of Germany of 2.6 percent.
Chart I-1, US, Real GDP 1929-1999
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-2 provides the growth of real quarterly GDP in the US between 1947 and 2012. The drop of output in the recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 has been followed by anemic recovery compared with return to trend at 3.0 percent from 1870 to 2010 after events such as wars and recessions (Lucas 2011May) and a standstill that can lead to growth recession, or low rates of economic growth, but perhaps even another contraction or conventional recession. The average rate of growth from 1947 to 2012 is 3.2 percent. The average growth rate from 2000 to 2012 is only 1.7 percent with 2.8 percent annual equivalent from the end of the recession in IVQ2001 to the end of the expansion in IVQ2007.
Chart I-2, US, Real GDP, Quarterly, 1947-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-3 provides real GDP percentage change on the quarter a year earlier for 1983-1984. The objective is simply to compare expansion in two recoveries from sharp contractions as shown in Table I-2. Growth rates in the early phase of the recovery in 1983 and 1984 were very high, which is the opportunity to reduce unemployment that has characterized cyclical expansion in the postwar US economy.
Chart I-3, Real GDP Percentage Change on Quarter a Year Earlier 1983-1986
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
In contrast, growth rates in the comparable first sixteen quarters of expansion from 2009 to 2013 in Chart I-4 have been mediocre. As a result, growth has not provided the exit from unemployment and underemployment as in other cyclical expansions in the postwar period. Growth rates did not rise in V shape as in earlier expansions and then declined close to the standstill of growth recessions.
Chart I-4, US, Real GDP Percentage Change on Quarter a Year Earlier 2009-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table I-3 provides percentage change of real GDP in the United States in the 1930s, 1980s and 2000s. The recession in 1981-1982 is quite similar on its own to the 2007-2009 recession. In contrast, during the Great Depression in the four years of 1930 to 1933, GDP in constant dollars fell 26.4 percent cumulatively and fell 45.3 percent in current dollars (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 150-2, Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2009b), 205-7 and revisions in http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). Data are available for the 1930s only on a yearly basis. US GDP fell 4.7 percent in the two recessions (1) from IQ1980 to IIIQ1980 and (2) from III1981 to IVQ1981 to IVQ1982 and 4.3 percent cumulatively in the recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. It is instructive to compare the first three years of the expansions in the 1980s and the current expansion. GDP grew at 4.6 percent in 1983, 7.3 percent in 1984 and 4.2 percent in 1985 while GDP grew, 2.5 percent in 2010, 1.8 percent in 2011 and 2.8 percent in 2012. Actual annual equivalent GDP growth in the four quarters of 2012 and first two quarters of 2013 is 2.2 percent and 2.6 percent in the first three quarters of 2013 but only 2.0 percent discounting contribution of 1.67 percentage points of inventory accumulation to growth in IIIQ2013. GDP grew at 4.2 percent in 1985 and 3.5 percent in 1986 while the forecasts of the central tendency of participants of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) are in the range of 2.2 to 2.3 percent in 2013 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20131218.pdf) with less reliable forecast of 2.8 to 3.2 percent in 2014 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20131218.pdf). Growth of GDP in the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2013 has been at average 2.3 percent in annual equivalent.
Table I-3, US, Percentage Change of GDP in the 1930s, 1980s and 2000s, ∆%
| Year | GDP ∆% | Year | GDP ∆% | Year | GDP ∆% |
| 1930 | -8.5 | 1980 | -0.2 | 2000 | 4.1 |
| 1931 | -6.4 | 1981 | 2.6 | 2001 | 1.0 |
| 1932 | -12.9 | 1982 | -1.9 | 2002 | 1.8 |
| 1933 | -1.3 | 1983 | 4.6 | 2003 | 2.8 |
| 1934 | 10.8 | 1984 | 7.3 | 2004 | 3.8 |
| 1935 | 8.9 | 1985 | 4.2 | 2005 | 3.4 |
| 1936 | 12.9 | 1986 | 3.5 | 2006 | 2.7 |
| 1937 | 5.1 | 1987 | 3.5 | 2007 | 1.8 |
| 1938 | -3.3 | 1988 | 4.2 | 2008 | -0.3 |
| 1930 | 8.0 | 1989 | 3.7 | 2009 | -2.8 |
| 1940 | 8.8 | 1990 | 1.9 | 2010 | 2.5 |
| 1941 | 17.7 | 1991 | -0.1 | 2011 | 1.8 |
| 1942 | 18.9 | 1992 | 3.6 | 2012 | 2.8 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-5 provides percentage change of GDP in the US during the 1930s. There is vast literature analyzing the Great Depression (Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009), 198-217). Cole and Ohanian (1999) find that US real per capita output was lower by 11 percent in 1939 than in 1929 while the typical expansion of real per capita output in the US during a decade is 31 percent. Private hours worked in the US were 25 percent lower in 1939 relative to 1929.
Chart I-5, US, Percentage Change of GDP in the 1930s
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
In contrast, Chart I-6 shows rapid recovery from the recessions in the 1980s. High growth rates in the initial quarters of expansion eliminated the unemployment and underemployment created during the contraction. The economy then returned to grow at the trend of expansion, interrupted by another contraction in 1991.
Chart I-6, US, Percentage Change of GDP in the 1980s
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-7 provides the rates of growth during the 2000s. Growth rates in the initial sixteen quarters of expansion have been relatively lower than during recessions after World War II. As a result, unemployment and underemployment continue at the rate of 17.2 percent of the US labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/11/global-financial-risk-mediocre-united.html) with weak hiring (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/theory-and-reality-of-secular.html).
Chart I-7, US, Percentage Change of GDP in the 2000s
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Characteristics of the four cyclical contractions are provided in Table I-4 with the first column showing the number of quarters of contraction; the second column the cumulative percentage contraction; and the final column the average quarterly rate of contraction. There were two contractions from IQ1980 to IIIQ1980 and from IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 separated by three quarters of expansion. The drop of output combining the declines in these two contractions is 4.7 percent, which is almost equal to the decline of 4.3 percent in the contraction from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. In contrast, during the Great Depression in the four years of 1930 to 1933, GDP in constant dollars fell 26.4 percent cumulatively and fell 45.3 percent in current dollars (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 150-2, Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2009b), 205-7 and revisions in http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). The comparison of the global recession after 2007 with the Great Depression is entirely misleading.
Table I-4, US, Number of Quarters, GDP Cumulative Percentage Contraction and Average Percentage Annual Equivalent Rate in Cyclical Contractions
| Number of Quarters | Cumulative Percentage Contraction | Average Percentage Rate | |
| IIQ1953 to IIQ1954 | 3 | -2.4 | -0.8 |
| IIIQ1957 to IIQ1958 | 3 | -3.0 | -1.0 |
| IVQ1973 to IQ1975 | 5 | -3.1 | -0.6 |
| IQ1980 to IIIQ1980 | 2 | -2.2 | -1.1 |
| IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 | 4 | -2.5 | -0.64 |
| IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 | 6 | -4.3 | -0.72 |
Sources: Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm Reference Cycles National Bureau of Economic Research http://www.nber.org/cycles/cyclesmain.html
Table I-5 shows the extraordinary contrast between the mediocre average annual equivalent growth rate of 2.3 percent of the US economy in the seventeen quarters of the current cyclical expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2013 and the average of 5.7 percent in the first thirteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1986, 5.3 percent in the first fifteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent in the first sixteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1986 and 5.0 percent in the first seventeen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1987. The line “average first four quarters in four expansions” provides the average growth rate of 7.7 percent with 7.8 percent from IIIQ1954 to IIQ1955, 9.2 percent from IIIQ1958 to IIQ1959, 6.1 percent from IIIQ1975 to IIQ1976 and 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983. The United States missed this opportunity of high growth in the initial phase of recovery. BEA data show the US economy in standstill with annual growth of 2.4 percent in 2010 decelerating to 1.8 percent annual growth in 2011 and 2.8 percent in 2012 (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.7 percent, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983. GDP growth in the first three quarters of 2013 accumulated to 1.9 percent that is equivalent to 2.6 percent in a year. This is obtained by dividing GDP in IIIQ2013 of $15,839.3 by GDP in IVQ2012 of $15,539.6 and compounding by 4/3: {[($15,839.3/$15,539.6)4/3 -1]100 = 2.6%}. The US economy grew 2.0 percent in IIIQ2013 relative to the same quarter a year earlier in IIIQ2012. Another important revelation of the revisions and enhancements is that GDP was flat in IVQ2012, which is just at the borderline of contraction. The rate of growth of GDP in the third estimate of IIIQ2013 is 4.1 percent in seasonally adjusted annual rate (SAAR). Inventory accumulation contributed 1.67 percentage points to this rate of growth. The actual rate without this impulse of unsold inventories would have been 2.43 percent, or 0.6 percent in IIIQ2013, such that annual equivalent growth in 2013 is closer to 2.0 percent {[(1.003)(1.006)(1.006)4/3-1]100 = 2.0%}, compounding the quarterly rates and converting into annual equivalent.
Table I-5, US, Number of Quarters, Cumulative Growth and Average Annual Equivalent Growth Rate in Cyclical Expansions
| Number | Cumulative Growth ∆% | Average Annual Equivalent Growth Rate | |
| IIIQ 1954 to IQ1957 | 11 | 12.8 | 4.5 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ1954 to IIQ1955 | 4 | 7.8 | |
| IIQ1958 to IIQ1959 | 5 | 10.0 | 7.9 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ1958 to IIQ1959 | 4 | 9.2 | |
| IIQ1975 to IVQ1976 | 8 | 8.3 | 4.1 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ1975 to IIQ1976 | 4 | 6.1 | |
| IQ1983-IQ1986 IQ1983-IIIQ1986 IQ1983-IVQ1986 IQ1983-IQ1987 | 13 15 16 17 | 19.9 21.6 22.3 23.1 | 5.7 5.4 5.2 5.0 |
| First Four Quarters IQ1983 to IVQ1983 | 4 | 7.8 | |
| Average First Four Quarters in Four Expansions* | 7.7 | ||
| IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2013 | 17 | 10.3 | 2.3 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 | 2.7 |
*First Four Quarters: 7.8% IIIQ1954-IIQ1955; 9.2% IIIQ1958-IIQ1959; 6.1% IIIQ1975-IIQ1976; 7.8% IQ1983-IVQ1983
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm Reference Cycles National Bureau of Economic Research http://www.nber.org/cycles/cyclesmain.html
Chart I-8 shows US real quarterly GDP growth from 1980 to 1989. The economy contracted during the recession and then expanded vigorously throughout the 1980s, rapidly eliminating the unemployment caused by the contraction.
Chart I-8, US, Real GDP, 1980-1989
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-9 shows the entirely different situation of real quarterly GDP in the US between 2007 and 2012. The economy has underperformed during the first sixteen quarters of expansion for the first time in the comparable contractions since the 1950s. The US economy is now in a perilous standstill.
Chart I-9, US, Real GDP, 2007-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
As shown in Tables I-4 and I-5 above the loss of real GDP in the US during the contraction was 4.3 percent but the gain in the cyclical expansion has been only 10.2 percent (first to the last row in Table I-5), using all latest revisions. As a result, the level of real GDP in IIIQ2013 with the second estimate and revisions is only higher by 5.6 percent than the level of real GDP in IVQ2007. Growth at trend of 3.0 percent in the entire cycle as in past cyclical expansions would result in GDP higher by 19.4 percent in IIIQ2013 relative to IVQ2007. Trend GDP would be $17,905.3 billion, which is higher than actual GDP in IIIQ2013 of $15,839.3 billion, for underperformance of $2,066.0 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of economic activity than what would be required to provide for full employment, explaining unemployment/underemployment of 28.1 million or 17.2 percent of the labor force. Table I-6 provides in the second column real GDP in billions of chained 2009 dollars. The third column provides the percentage change of the quarter relative to IVQ2007; the fourth column provides the percentage change relative to the prior quarter; and the final fifth column provides the percentage change relative to the same quarter a year earlier. The contraction actually concentrated in two quarters: decline of 2.2 percent in IVQ2008 relative to the prior quarter and decline of 1.4 percent in IQ2009 relative to IVQ2008. The combined fall of GDP in IVQ2008 and IQ2009 was 3.6 percent {[(1-0.022) x (1-0.014) -1]100 = -3.6%}, or {[(IQ2009 $14,372.1)/(IIIQ2008 $14,895.1) – 1]100 = -3.5%} except for rounding. Those two quarters coincided with the worst effects of the financial crisis. GDP fell 0.1 percent in IIQ2009 but grew 0.3 percent in IIIQ2009, which is the beginning of recovery in the cyclical dates of the NBER. Most of the recovery occurred in five successive quarters from IVQ2009 to IVQ2010 of growth of 1.0 percent in IVQ2009, 0.4 percent in IQ2010, 0.9 percent in IIQ2010 and equal growth at 0.7 percent in IIIQ2010 and 0.7 percent in IVQ2010 for cumulative growth in those five quarters of 3.8 percent, obtained by accumulating the quarterly rates {[(1.01 x 1.004 x 1.009 x 1.007 x 1.007) – 1]100 = 3.8%} or {[(IVQ2010 $14,942.4)/(IIIQ2009 $14,402.5) – 1]100 = 3.7%} with minor rounding difference. The economy then stalled during the first half of 2011 with decline of 0.3 percent in IQ2011 and growth of 0.8 percent in IIQ2011 for combined annual equivalent rate of 1.0 percent {(0.997 x 1.008)2}. The economy grew 0.3 percent in IIIQ2011 for annual equivalent growth of 1.1 percent in the first three quarters {[(0.997 x 1.008 x 1.003)4/3 -1]100 = 1.1%}. Growth picked up in IVQ2011 with 1.2 percent relative to IIIQ2011. Growth in a quarter relative to a year earlier in Table I-6 slows from over 2.7 percent during three consecutive quarters from IIQ2010 to IVQ2010 to 2.0 percent in IQ2011, 1.9 percent in IIQ2011, 1.5 percent in IIIQ2011 and 2.0 percent in IVQ2011. As shown below, growth of 1.2 percent in IVQ2011 was partly driven by inventory accumulation. In IQ2012, GDP grew 0.9 percent relative to IVQ2011 and 3.3 percent relative to IQ2011, decelerating to 0.3 percent in IIQ2012 and 2.8 percent relative to IIQ2011 and 0.7 percent in IIIQ2012 and 3.1 percent relative to IIIQ2011 largely because of inventory accumulation and national defense expenditures. Growth was 0.0 percent in IVQ2012 with 2.0 percent relative to a year earlier but mostly because of deduction of 2.00 percentage points of inventory divestment and 1.22 percentage points of reduction of one-time national defense expenditures. Growth was 0.3 percent in IQ2013 and 1.3 percent relative to IQ2012 in large part because of burning savings to consume caused by financial repression of zero interest rates. There is similar growth of 0.6 percent in IIQ2013 and 1.6 percent relative to a year earlier. In IIIQ2013, GDP grew 1.0 percent relative to the prior quarter and 2.0 percent relative to the same quarter a year earlier with inventory accumulation contributing 1.67 percentage points to growth at 4.1 percent SAAR in IIIQ2013. Rates of a quarter relative to the prior quarter capture better deceleration of the economy than rates on a quarter relative to the same quarter a year earlier. The critical question for which there is not yet definitive solution is whether what lies ahead is continuing growth recession with the economy crawling and unemployment/underemployment at extremely high levels or another contraction or conventional recession. Forecasts of various sources continued to maintain high growth in 2011 without taking into consideration the continuous slowing of the economy in late 2010 and the first half of 2011. The sovereign debt crisis in the euro area is one of the common sources of doubts on the rate and direction of economic growth in the US but there is weak internal demand in the US with almost no investment and spikes of consumption driven by burning saving because of financial repression forever in the form of zero interest rates.
Table I-6, US, Real GDP and Percentage Change Relative to IVQ2007 and Prior Quarter, Billions Chained 2005 Dollars and ∆%
| Real GDP, Billions Chained 2009 Dollars | ∆% Relative to IVQ2007 | ∆% Relative to Prior Quarter | ∆% | |
| IVQ2007 | 14,996.1 | NA | NA | 1.9 |
| IQ2008 | 14,895.4 | -0.7 | -0.7 | 1.1 |
| IIQ2008 | 14,969.2 | -0.2 | 0.5 | 0.9 |
| IIIQ2008 | 14,895.1 | -0.7 | -0.5 | -0.3 |
| IVQ2008 | 14,574.6 | -2.8 | -2.2 | -2.8 |
| IQ2009 | 14,372.1 | -4.2 | -1.4 | -3.5 |
| IIQ2009 | 14,356.9 | -4.3 | -0.1 | -4.1 |
| IIIQ2009 | 14,402.5 | -4.0 | 0.3 | -3.3 |
| IV2009 | 14,540.2 | -3.0 | 1.0 | -0.2 |
| IQ2010 | 14,597.7 | -2.7 | 0.4 | 1.6 |
| IIQ2010 | 14,738.0 | -1.7 | 0.9 | 2.7 |
| IIIQ2010 | 14,839.3 | -1.0 | 0.7 | 3.0 |
| IVQ2010 | 14,942.4 | -0.4 | 0.7 | 2.8 |
| IQ2011 | 14,894.0 | -0.7 | -0.3 | 2.0 |
| IIQ2011 | 15,011.3 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 1.9 |
| IIIQ2011 | 15,062.1 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 1.5 |
| IVQ2011 | 15,242.1 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 2.0 |
| IQ2012 | 15,381.6 | 2.6 | 0.9 | 3.3 |
| IIQ2012 | 15,427.7 | 2.9 | 0.3 | 2.8 |
| IIIQ2012 | 15,534.0 | 3.6 | 0.7 | 3.1 |
| IVQ2012 | 15,539.6 | 3.6 | 0.0 | 2.0 |
| IQ2013 | 15,583.9 | 3.9 | 0.3 | 1.3 |
| IIQ2013 | 15,679.7 | 4.6 | 0.6 | 1.6 |
| IIIQ2013 | 15,839.3 | 5.6 | 1.0 | 2.0 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-10 provides the percentage change of real GDP from the same quarter a year earlier from 1980 to 1989. There were two contractions almost in succession in 1980 and from 1981 to 1983. The expansion was marked by initial high rates of growth as in other recession in the postwar US period during which employment lost in the contraction was recovered. Growth rates continued to be high after the initial phase of expansion.
Chart I-10, Percentage Change of Real Gross Domestic Product from Quarter a Year Earlier 1980-1989
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The experience of recovery after 2009 is not as complete as during the 1980s. Chart I-11 shows the much lower rates of growth in the early phase of the current expansion and sharp decline from an early peak. The US missed the initial high growth rates in cyclical expansions that eliminate unemployment and underemployment.
Chart I-11, Percentage Change of Real Gross Domestic Product from Quarter a Year Earlier 2007-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-12 provides growth rates from a quarter relative to the prior quarter during the 1980s. There is the same strong initial growth followed by a long period of sustained growth.
Chart I-12, Percentage Change of Real Gross Domestic Product from Prior Quarter 1980-1989
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-13 provides growth rates in a quarter relative to the prior quarter from 2007 to 2013. Growth in the current expansion after IIIQ2009 has not been as strong as in other postwar cyclical expansions.
Chart I-13, Percentage Change of Real Gross Domestic Product from Prior Quarter 2007-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The revised estimates and earlier estimates from IQ2008 to IQ2012 in seasonally adjusted annual equivalent rates are shown in Table I-7. The strongest revision is for IVQ2008 for which the contraction of GDP is revised from minus 6.8 percent to minus 8.9 percent and minus 8.3 percent. IQ2009 is also revised from contraction of minus 4.9 percent to minus 6.7 percent but then lowered to contraction of 5.3 percent and 5.4 percent. There is only minor revision in IIIQ2008 of the contraction of minus 4.0 percent to minus 3.7 percent and minus 2.0 percent. Growth of 5.0 percent in IV2009 is revised to 3.8 percent and then increased to 4.0 percent but lowered to 3.9 percent. Growth in IQ2010 is lowered from 3.9 percent to 2.3 percent and 1.6 percent. Growth in IIQ2010 is upwardly revised to 3.8 percent but then lowered to 2.2 percent. The final revision increased growth in IIQ2010 to 3.9 percent. Revisions lowered growth of 1.9 percent in IQ2011 to minus 1.3 percent. The revisions lowered growth of 1.8 percent in IQ2013 to 1.1 percent but increased growth of 2.0 percent in IQ2012 to 3.7 percent. The revisions do not alter the conclusion that the current expansion is much weaker than historical sharp contractions since the 1950s and is now changing into slow growth recession with higher risks of contraction and continuing underperformance.
Table I-7, US, Quarterly Growth Rates of GDP, % Annual Equivalent SA, Revised and Earlier Estimates
| Quarters | Revised Estimate Jul 31, 2013 | Revised Estimate Jul 27, 2012 | Revised Estimate Jul 29, 2011 | Earlier Estimate |
| 2008 | ||||
| I | -2.7 | -1.8 | -0.7 | |
| II | 2.0 | 1.3 | 0.6 | |
| III | -2.0 | -3.7 | -4.0 | |
| IV | -8.3 | -8.9 | -6.8 | |
| 2009 | ||||
| I | -5.4 | -5.3 | -6.7 | -4.9 |
| II | -0.4 | -0.3 | -0.7 | -0.7 |
| III | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.7 | 1.6 |
| IV | 3.9 | 4.0 | 3.8 | 5.0 |
| 2010 | ||||
| I | 1.6 | 2.3 | 3.9 | 3.7 |
| II | 3.9 | 2.2 | 3.8 | 1.7 |
| III | 2.8 | 2.6 | 2.5 | 2.6 |
| IV | 2.8 | 2.4 | 2.3 | 3.1 |
| 2011 | ||||
| I | -1.3 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 1.9 |
| II | 3.2 | 2.5 | ||
| III | 1.4 | 1.3 | ||
| IV | 4.9 | 4.1 | ||
| 2012 | ||||
| I | 3.7 | 2.0 | ||
| II | 1.2 | 1.3 | ||
| III | 2.8 | 3.1 | ||
| IV | 0.1 | 0.4 | ||
| 2013 | ||||
| I | 1.1 | 1.8 | ||
| II | 2.5 | |||
| III | 4.1 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Aggregate demand, personal consumption expenditures (PCE) and gross private domestic investment (GDI) were much stronger during the expansion phase in IQ1983 to IVQ1986 than in IIIQ2009 to IIQ2013, as shown in Table I-8. GDI provided the impulse of growth in 1983 and 1984, which has not been the case from 2009 to 2013. The investment decision in the US economy has been frustrated in the current cyclical expansion. Growth of GDP in IIIQ2013 at seasonally adjusted annual rate of 4.1 percent consisted of positive contribution of 1.36 percentage points of personal consumption expenditures (PCE) plus positive contribution of 2.56 percentage points of gross private domestic investment (GDI) of which 1.67 percentage points of inventory investment (∆PI), contribution of net exports (trade or exports less imports) of 0.14 percentage points and 0.08 percentage points of government consumption expenditures and gross investment (GOV) partly because of one-time reduction of national defense expenditures of 0.02 percentage points. The economy of the United States has lost the dynamic growth impulse of earlier cyclical expansions with mediocre growth resulting from consumption forced by one-time effects of financial repression, national defense expenditures and inventory accumulation.
Table I-8, US, Contributions to the Rate of Growth of GDP in Percentage Points
| GDP | PCE | GDI | ∆ PI | Trade | GOV | |
| 2013 | ||||||
| I | 1.1 | 1.54 | 0.71 | 0.93 | -0.28 | -0.82 |
| II | 2.5 | 1.24 | 1.38 | 0.41 | -0.07 | -0.07 |
| III | 4.1 | 1.36 | 2.56 | 1.67 | 0.14 | 0.08 |
| 2012 | ||||||
| I | 3.7 | 1.98 | 1.57 | 0.36 | 0.44 | -0.28 |
| II | 1.2 | 1.28 | -0.23 | -0.91 | 0.10 | 0.05 |
| III | 2.8 | 1.15 | 0.99 | 0.60 | -0.03 | 0.67 |
| IV | 0.1 | 1.13 | -0.36 | -2.00 | 0.68 | -1.31 |
| 2011 | ||||||
| I | -1.3 | 1.42 | -1.11 | -1.06 | 0.01 | -1.61 |
| II | 3.2 | 1.03 | 1.88 | 0.72 | 0.53 | -0.25 |
| III | 1.4 | 1.42 | 0.36 | -1.60 | 0.10 | -0.52 |
| IV | 4.9 | 1.65 | 4.13 | 2.73 | -0.60 | -0.31 |
| 2010 | ||||||
| I | 1.6 | 1.42 | 1.77 | 1.66 | -0.96 | -0.63 |
| II | 3.9 | 2.21 | 2.86 | 1.09 | -1.77 | 0.61 |
| III | 2.8 | 1.87 | 1.86 | 1.90 | -0.88 | -0.07 |
| IV | 2.8 | 2.86 | -0.51 | -1.64 | 1.32 | -0.87 |
| 2009 | ||||||
| I | -5.4 | -0.83 | -7.02 | -2.26 | 2.25 | 0.15 |
| II | -0.4 | -1.13 | -3.25 | -1.12 | 2.40 | 1.56 |
| III | 1.3 | 1.73 | -0.40 | -0.38 | -0.53 | 0.48 |
| IV | 3.9 | 0.05 | 4.05 | 4.40 | -0.05 | -0.17 |
| 1982 | ||||||
| I | -6.5 | 1.61 | -7.60 | -5.34 | -0.49 | -0.05 |
| II | 2.2 | 0.89 | -0.06 | 2.26 | 0.81 | 0.56 |
| III | -1.4 | 1.88 | -0.62 | 1.11 | -3.22 | 0.53 |
| IV | 0.4 | 4.51 | -5.37 | -5.33 | -0.10 | 1.35 |
| 1983 | ||||||
| I | 5.3 | 2.45 | 2.36 | 0.92 | -0.29 | 0.82 |
| II | 9.4 | 5.06 | 5.96 | 3.43 | -2.46 | 0.89 |
| III | 8.1 | 4.50 | 4.40 | 0.57 | -2.25 | 1.42 |
| IV | 8.5 | 4.06 | 6.94 | 3.01 | -1.13 | -1.36 |
| 1984 | ||||||
| I | 8.2 | 2.26 | 7.23 | 4.94 | -2.31 | 1.01 |
| II | 7.2 | 3.64 | 2.57 | -0.29 | -0.87 | 1.87 |
| III | 4.0 | 1.95 | 1.69 | 0.21 | -0.35 | 0.70 |
| IV | 3.2 | 3.29 | -1.08 | -2.44 | -0.56 | 1.58 |
| 1985 | ||||||
| I | 4.0 | 4.23 | -2.14 | -2.86 | 0.94 | 1.01 |
| II | 3.7 | 2.35 | 1.34 | 0.35 | -1.90 | 1.93 |
| III | 6.4 | 4.82 | -0.43 | -0.15 | -0.01 | 1.98 |
| IV | 3.0 | 0.62 | 2.80 | 1.40 | -0.66 | 0.27 |
| 1986 | ||||||
| I | 3.8 | 2.10 | 0.04 | -0.17 | 0.92 | 0.70 |
| II | 1.9 | 2.77 | -1.30 | -1.30 | -1.33 | 1.70 |
| III | 4.1 | 4.55 | -1.97 | -1.62 | -0.45 | 1.95 |
| IV | 2.1 | 1.62 | 0.24 | -0.29 | 0.71 | -0.48 |
Note: PCE: personal consumption expenditures; GDI: gross private domestic investment; ∆ PI: change in private inventories; Trade: net exports of goods and services; GOV: government consumption expenditures and gross investment; – is negative and no sign positive
GDP: percent change at annual rate; percentage points at annual rates
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (pages 1-2 http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2013/pdf/gdp3q13_3rd.pdf) explains growth of GDP in IIIQ2013 as follows:
“Real gross domestic product -- the output of goods and services produced by labor and property located in the United States -- increased at an annual rate of 4.1 percent in the third quarter of 2013 (that is, from the second quarter to the third quarter), according to the "third" estimate released by the Bureau of Economic Analysis. In the second quarter, real GDP increased 2.5 percent.
The GDP estimate released today is based on more complete source data than were available for the "second" estimate issued on December 5, 2013. In the second estimate, the increase in real GDP was 3.6 percent (see "Revisions" on page 3). With this third estimate for the third quarter, increases in personal consumption expenditures (PCE) and in nonresidential fixed investment were larger than previously estimated.
The increase in real GDP in the third quarter primarily reflected positive contributions from private inventory investment, PCE, nonresidential fixed investment, exports, residential fixed investment, and state and local government spending that were partly offset by a negative contribution from federal government spending. Imports, which are a subtraction in the calculation of GDP,increased.
The acceleration in real GDP growth in the third quarter primarily reflected an acceleration in private inventory investment, a deceleration in imports, and accelerations in state and local government spending and in PCE that were partly offset by a deceleration in exports. “
There are positive contributions to growth in IIIQ2013 shown in Table I-9:
- Personal consumption expenditures (PCE) growing at 2.0 percent with consumption of durable goods growing at 7.9 percent
- Residential fixed investment (RFI) growing at 10.3 percent
- Nonresidential fixed investment growing at 3.9 percent
- Private inventory investment contributing 1.67 percentage points
- Growth of exports at 3.9 percent, which is higher than imports at 2.4 percent
There were negative contributions in IIIQ2013:
- Federal government expenditures declining at 1.5 percent partly because of decrease of national defense expenditures at 0.5 percent that deducted 0.02 percentage points from GDP growth
- Growth of imports, which are deduction to growth, at 2.4 percent
The BEA explains acceleration in real GDP growth in IIIQ2013 by:
- Acceleration of inventory investment contributing 1.67 percentage points in IIIQ2013 that is higher than 0.41 percentage points in IIQ2013
- Growth of state and local expenditures at 1.7 percent in IIIQ2013 compared with 0.4 percent in IIQ2013
- Growth of imports at 2.4 percent in IIIQ2013 compared with growth at 6.9 percent in IIQ2013
An important aspect of growth in the US is the decline in growth of real disposable personal income, or what is left after taxes and inflation, which increased at the rate of 1.8 percent in IIIQ2013 compared with a year earlier. The effects of financial repression, or zero interest, are vividly shown in the decline of the savings rate, or personal saving as percent of disposable income from 6.6 percent in IVQ2012 to 4.9 percent in IIIQ2013. Anticipation of income in IVQ2012 to avoid higher taxes in 2013 caused increases in income and savings while higher payroll taxes in 2013 restricted income growth and savings in IQ2013. Zero interest rates induce risky investments with high leverage and can contract balance sheets of families, business and financial institutions when interest rates inevitably increase in the future. There is a tradeoff of weaker economy in the future when interest rates increase by meager growth in the present with forced consumption by zero interest rates.
Table I-9, US, Percentage Seasonally Adjusted Annual Equivalent Quarterly Rates of Increase, %
| IIIQ 2012 | IVQ 2012 | IQ 2013 | IIQ 2013 | IIIQ 2012 | |
| GDP | 2.8 | 0.1 | 1.1 | 2.5 | 4.1 |
| PCE | 1.7 | 1.7 | 2.3 | 1.8 | 2.0 |
| Durable Goods | 8.3 | 10.5 | 5.8 | 6.2 | 7.9 |
| NRFI | 0.3 | 9.8 | -4.6 | 4.7 | 4.8 |
| RFI | 14.1 | 19.8 | 12.5 | 14.2 | 10.3 |
| Exports | 0.4 | 1.1 | -1.3 | 8.0 | 3.9 |
| Imports | 0.5 | -3.1 | 0.6 | 6.9 | 2.4 |
| GOV | 3.5 | -6.5 | -4.2 | -0.4 | 0.4 |
| Federal GOV | 8.9 | -13.9 | -8.4 | -1.6 | -1.5 |
| National Defense | 12.5 | -21.6 | -11.2 | -0.6 | -0.5 |
| Cont to GDP Growth % Points | 0.60 | -1.22 | -0.57 | -0.03 | -0.02 |
| State/Local GOV | -0.2 | -1.0 | -1.3 | 0.4 | 1.7 |
| ∆ PI (PP) | 0.60 | -2.00 | 0.93 | 0.41 | 1.67 |
| Final Sales of Domestic Product | 2.2 | 2.2 | 0.2 | 2.1 | 2.5 |
| Gross Domestic Purchases | 2.7 | -0.5 | 1.4 | 2.5 | 3.9 |
| Prices Gross | 1.4 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 0.2 | 1.8 |
| Prices of GDP | 2.3 | 1.1 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 2.0 |
| Prices of GDP Excluding Food and Energy | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.6 | 0.9 | 1.9 |
| Prices of PCE | 1.7 | 1.6 | 1.1 | -0.1 | 1.9 |
| Prices of PCE Excluding Food and Energy | 1.4 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 0.6 | 1.4 |
| Prices of Market Based PCE | 1.6 | 1.4 | 1.3 | -0.3 | 2.0 |
| Prices of Market Based PCE Excluding Food and Energy | 1.3 | 0.9 | 1.6 | 0.5 | 1.4 |
| Real Disposable Personal Income* | 1.3 | 3.6 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 1.8 |
| Personal Savings As % Disposable Income | 4.9 | 6.6 | 4.1 | 4.7 | 4.9 |
Note: PCE: personal consumption expenditures; NRFI: nonresidential fixed investment; RFI: residential fixed investment; GOV: government consumption expenditures and gross investment; ∆ PI: change in
private inventories; GDP - ∆ PI: final sales of domestic product; PP: percentage points; Personal savings rate: savings as percent of disposable income
*Percent change from quarter one year ago
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Percentage shares of GDP are shown in Table I-10. PCE is equivalent to 68.2 percent of GDP and is under pressure with stagnant real disposable income, high levels of unemployment and underemployment and higher savings rates than before the global recession, temporarily interrupted by financial repression in the form of zero interest rates. Gross private domestic investment is also growing slowly even with about two trillion dollars in cash holdings by companies. In a slowing world economy, it may prove more difficult to grow exports faster than imports to generate higher growth. Bouts of risk aversion revalue the dollar relative to most currencies in the world as investors increase their holdings of dollar-denominated assets
Table I-10, US, Percentage Shares of GDP, %
| IIIQ2013 | |
| GDP | 100.0 |
| PCE | 68.2 |
| Goods | 23.1 |
| Durable | 7.5 |
| Nondurable | 15.6 |
| Services | 45.1 |
| Gross Private Domestic Investment | 16.2 |
| Fixed Investment | 15.3 |
| NRFI | 12.2 |
| Structures | 2.8 |
| Equipment & Software | 5.5 |
| Intellectual Property | 3.9 |
| RFI | 3.1 |
| Change in Private | 0.9 |
| Net Exports of Goods and Services | -3.0 |
| Exports | 13.4 |
| Goods | 9.3 |
| Services | 4.1 |
| Imports | 16.4 |
| Goods | 13.6 |
| Services | 2.7 |
| Government | 18.6 |
| Federal | 7.4 |
| National Defense | 4.6 |
| Nondefense | 2.8 |
| State and Local | 11.2 |
PCE: personal consumption expenditures; NRFI: nonresidential fixed investment; RFI: residential fixed investment
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table I-11 shows percentage point (PP) contributions to the annual levels of GDP growth in the earlier recessions 1958-1959, 1975-1976, 1982-1983 and 2009, 2010, 2011 and 2012. The data incorporate the new revisions released by the BEA on Jul 31, 2013. The most striking contrast is in the rates of growth of annual GDP in the expansion phases of 6.9 percent in 1959, 5.4 percent in 1976, and 4.6 percent in 1983 followed by 7.3 percent in 1984 and 4.2 percent in 1985. In contrast, GDP grew 2.5 percent in 2010 after six consecutive quarters of growth, 1.8 percent in 2011 after ten consecutive quarters of expansion and 2.8 percent in 2012 after 14 quarters of expansion. Annual levels also show much stronger growth of PCEs in the expansions after the earlier contractions than in the expansion after the global recession of 2007. Gross domestic investment was much stronger in the earlier expansions than in 2010, 2011 and 2012.
Table I-11, US, Percentage Point Contributions to the Annual Growth Rate of GDP
| GDP | PCE | GDI | ∆ PI | Trade | GOV | |
| 1958 | -0.7 | 0.52 | -1.16 | -0.17 | -0.87 | 0.77 |
| 1959 | 6.9 | 3.49 | 2.82 | 0.83 | 0.00 | 0.59 |
| 1975 | -0.2 | 1.36 | -2.90 | -1.23 | 0.86 | 0.49 |
| 1976 | 5.4 | 3.41 | 2.91 | 1.37 | -1.05 | 0.12 |
| 1982 | -1.9 | 0.86 | -2.55 | -1.30 | -0.59 | 0.38 |
| 1983 | 4.6 | 3.54 | 1.60 | 0.28 | -1.32 | 0.81 |
| 1984 | 7.3 | 3.32 | 4.73 | 1.90 | -1.54 | 0.76 |
| 1985 | 4.2 | 3.25 | -0.01 | -1.03 | -0.39 | 1.38 |
| 2009 | -2.8 | -1.06 | -3.52 | -0.76 | 1.14 | 0.64 |
| 2010 | 2.5 | 1.34 | 1.66 | 1.45 | -0.51 | 0.02 |
| 2011 | 1.8 | 1.74 | 0.69 | -0.16 | 0.10 | -0.68 |
| 2012 | 2.8 | 1.52 | 1.36 | 0.20 | 0.10 | -0.20 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysishttp://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table I-12 provides more detail of the contributions to growth of GDP from 2009 to 2012 using annual-level data. PCEs contributed 1.34 PPs to GDP growth in 2010 of which 0.77 percentage points (PP) in goods and 0.57 PP in services. Gross private domestic investment (GPDI) deducted 3.52 PPs of GDP growth in 2009 of which -2.77 PPs by fixed investment and -0.76 PPs of inventory change (∆PI) and added 1.66 PPs of GPDI in 2010 of which minus 0.21 PPs of fixed investment and 1.45 PPs of inventory accumulation (∆PI). Trade, or exports of goods and services net of imports, contributed 1.14 PPs in 2009 of which exports deducted 1.10 PPs and imports added 2.24 PPs. In 2010, trade deducted 0.51 PPs with exports contributing 1.28 PPs and imports deducting 1.79 PPs likely benefitting from dollar revaluation. In 2009, government added 0.64 PP of which 0.44 PPs by the federal government and 0.20 PPs by state and local government; in 2010, government added 0.02 PPs of which 0.37 PPs by the federal government with state and local government deducting 0.35 PPs. The final two columns of Table I-12 provide the estimates for 2011 and 2012. PCE contributed 1.74 PPs in 2011 after 1.34 PPs in 2010. The contribution of PCE fell to 1.52 points in 2012. The breakdown into goods and services is similar but with contributions in 2012 of 0.77 PPs of goods and 0.74 PPs of services. Gross private domestic investment contributed 1.66 PPs in 2010 with 1.45 PPs of change of private inventories but the contribution of gross private domestic investment was only 0.69 PPs in 2011. The contribution of GPDI in 2012 increased to 1.36 PPs with fixed investment increasing its contribution to 1.17 PPs and residential investment contributing 0.32 PPs for the first time since 2009. Net exports of goods and services contributed marginally in 2011 with 0.10 PPs and 0.10 PPs in 2012. The contribution of exports fell from 1.28 PPs in 2010 and 0.89 PPs in 2011 to only 0.48 PPs in 2012. Government deducted 0.68 PPs in 2011 and 0.20 PPs in 2012. The expansion since IIIQ2009 has been characterized by weak contributions of aggregate demand, which is the sum of personal consumption expenditures plus gross private domestic investment. The US did not recover strongly from the global recessions as typical in past cyclical expansions. Recoveries tend to be more sluggish as expansions mature. At the margin in IVQ2011, the acceleration of expansion was driven by inventory accumulation instead of aggregate demand of consumption and investment. Growth of PCE was partly the result of burning savings because of financial repression, which may not be sustainable in the future while creating multiple distortions of resource allocation and growth restraint.
Table I-12, US, Contributions to Growth of Gross Domestic Product in Percentage Points
| 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | |
| GDP Growth ∆% | -2.8 | 2.5 | 1.8 | 2.8 |
| Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) | -1.06 | 1.34 | 1.74 | 1.52 |
| Goods | -0.68 | 0.77 | 0.76 | 0.77 |
| Durable | -0.41 | 0.43 | 0.46 | 0.56 |
| Nondurable | -0.27 | 0.34 | 0.30 | 0.22 |
| Services | -0.38 | 0.57 | 0.98 | 0.74 |
| Gross Private Domestic Investment (GPDI) | -3.52 | 1.66 | 0.69 | 1.36 |
| Fixed Investment | -2.77 | 0.21 | 0.85 | 1.17 |
| Nonresidential | -2.04 | 0.28 | 0.84 | 0.85 |
| Structures | -0.70 | -0.49 | 0.05 | 0.31 |
| Equipment, software | -1.29 | 0.70 | 0.62 | 0.41 |
| Intellectual Property | -0.05 | 0.07 | 0.17 | 0.13 |
| Residential | -0.73 | -0.07 | 0.01 | 0.32 |
| Change Private Inventories | -0.76 | 1.45 | -0.16 | 0.20 |
| Net Exports of Goods and Services | 1.14 | -0.51 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Exports | -1.10 | 1.28 | 0.89 | 0.48 |
| Goods | -1.02 | 1.08 | 0.63 | 0.36 |
| Services | -0.08 | 0.20 | 0.27 | 0.12 |
| Imports | 2.24 | -1.79 | -0.79 | -0.38 |
| Goods | 2.15 | -1.72 | -0.70 | -0.30 |
| Services | 0.08 | -0.07 | -0.09 | -0.07 |
| Government Consumption Expenditures and Gross Investment | 0.64 | 0.02 | -0.68 | -0.20 |
| Federal | 0.44 | 0.37 | -0.23 | -0.12 |
| National Defense | 0.27 | 0.18 | -0.13 | -0.17 |
| Nondefense | 0.17 | 0.19 | -0.10 | 0.05 |
| State and Local | 0.20 | -0.35 | -0.46 | -0.08 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Manufacturing jobs increased 27,000 in Nov 2013 relative to Oct 2013, seasonally adjusted (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/11/global-financial-risk-mediocre-united.html). Manufacturing jobs not seasonally adjusted increased 83,000 from Nov 2012 to Nov 2013 or at the average monthly rate of 6,917. There are effects of the weaker economy and international trade together with the yearly adjustment of labor statistics. Industrial production increased 1.1 percent in Nov 2013 after increasing 0.1 percent in Oct 2013 and increasing 0.5 percent in Se 2013, as shown in Table I-1, with all data seasonally adjusted. The report of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System states (http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/g17/Current/default.htm):
“Industrial production increased 1.1 percent in November after having edged up 0.1 percent in October; output was previously reported to have declined 0.1 percent in October. The gain in November was the largest since November 2012, when production rose 1.3 percent. Manufacturing output increased 0.6 percent in November for its fourth consecutive monthly gain. Production at mines advanced 1.7 percent to more than reverse a decline of 1.5 percent in October. The index for utilities was up 3.9 percent in November, as colder-than-average temperatures boosted demand for heating. At 101.3 percent of its 2007 average, total industrial production was 3.2 percent above its year-earlier level. In November, industrial production surpassed for the first time its pre-recession peak of December 2007 and was 21 percent above its trough of June 2009. Capacity utilization for the industrial sector increased 0.8 percentage point in November to 79.0 percent, a rate 1.2 percentage points below its long-run (1972-2012) average.”
In the six months ending in Nov 2013, United States national industrial production accumulated increase of 2.2 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 4.5 percent, which is higher than growth of 3.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2013. Excluding growth of 1.1 percent in Nov 2013, growth in the remaining five months from Jun 2012 to Oct 2013 accumulated to 1.1 percent or 2.2 percent annual equivalent. Industrial production fell in one of the past six months. Business equipment accumulated growth of 1.4 percent in the six months from Jun to Nov 2013 at the annual equivalent rate of 2.8 percent, which is higher than growth of 2.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Nov 2013. The Fed analyzes capacity utilization of total industry in its report (http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/g17/Current/default.htm): “Capacity utilization for the industrial sector increased 0.8 percentage point in November to 79.0 percent, a rate 1.2 percentage points below its long-run (1972-2012) average.” United States industry apparently decelerated to a lower growth rate with possible acceleration in Nov 2013.
Manufacturing increased 0.3 percent in Oct 2013 after increasing 0.1 percent in Sep 2013 and increasing 0.7 percent in Aug 2013 seasonally adjusted, increasing 3.4 percent not seasonally adjusted in 12 months ending in Oct 2013, as shown in Table I-2 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/11/risks-of-unwinding-monetary-policy.html). Manufacturing increased 0.6 percent in No 2013 after increasing 0.5 percent in Oct 2013 and increasing 0.1 percent in Sep 2013 seasonally adjusted, increasing 3.0 percent not seasonally adjusted in 12 months ending in Nov 2013, as shown in Table I-2. Manufacturing grew cumulatively 1.7 percent in the six months ending in Nov 2013 or at the annual equivalent rate of 3.4 percent. Excluding the increase of 0.6 percent in Nov 2013, manufacturing accumulated growth of 1.1 percent from Jun 2013 to Oct 2013 or at the annual equivalent rate of 2.2 percent. Table I-2 provides a longer perspective of manufacturing in the US. There has been evident deceleration of manufacturing growth in the US from 2010 and the first three months of 2011 into more recent months as shown by 12 months rates of growth. Growth rates appeared to be increasing again closer to 5 percent in Apr-Jun 2012 but deteriorated. The rates of decline of manufacturing in 2009 are quite high with a drop of 18.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Apr 2009. Manufacturing recovered from this decline and led the recovery from the recession. Rates of growth appeared to be returning to the levels at 3 percent or higher in the annual rates before the recession but the pace of manufacturing fell steadily in the past six months with some weakness at the margin. Manufacturing fell by 21.9 from the peak in Jun 2007 to the trough in Apr 2009 and increase by 16.8 percent from the trough in Apr 2009 to Dec 2012. Manufacturing grew 20.5 percent from the trough in Apr 2009 to Nov 2013. Manufacturing output in Nov 2013 is 5.9 percent below the peak in Jun 2007.
Table I-13 provides national income by industry without capital consumption adjustment (WCCA). “Private industries” or economic activities have share of 86.8 percent in IIIQ2013. Most of US national income is in the form of services. In Nov 2013, there were 137.942 million nonfarm jobs NSA in the US, according to estimates of the establishment survey of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) (http://www.bls.gov/news.release/empsit.nr0.htm Table B-1). Total private jobs of 115.622 million NSA in Nov 2013 accounted for 83.8 percent of total nonfarm jobs of 137.942 million, of which 12.022 million, or 10.4 percent of total private jobs and 8.7 percent of total nonfarm jobs, were in manufacturing. Private service-producing jobs were 96.761 million NSA in Nov 2013, or 70.1 percent of total nonfarm jobs and 83.7 percent of total private-sector jobs. Manufacturing has share of 10.8 percent in US national income in IIQ2013, as shown in Table I-13. Most income in the US originates in services. Subsidies and similar measures designed to increase manufacturing jobs will not increase economic growth and employment and may actually reduce growth by diverting resources away from currently employment-creating activities because of the drain of taxation.
Table I-13, US, National Income without Capital Consumption Adjustment by Industry, Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rates, Billions of Dollars, % of Total
| SAAR | % Total | SAAR IQ2013 | % Total | |
| National Income WCCA | 14,495.5 | 100.0 | 14,643.3 | 100.0 |
| Domestic Industries | 14,248.7 | 98.3 | 14,380.3 | 98.2 |
| Private Industries | 12,568.6 | 86.7 | 12,705.2 | 86.8 |
| Agriculture | 220.3 | 1.5 | 225.2 | 1.5 |
| Mining | 254.3 | 1.8 | 256.4 | 1.8 |
| Utilities | 216.5 | 1.5 | 221.2 | 1.5 |
| Construction | 629.0 | 4.3 | 639.1 | 4.4 |
| Manufacturing | 1558.9 | 10.8 | 1577.7 | 10.8 |
| Durable Goods | 888.1 | 6.1 | 910.1 | 6.2 |
| Nondurable Goods | 670.1 | 4.6 | 667.6 | 4.6 |
| Wholesale Trade | 874.4 | 6.0 | 884.0 | 6.0 |
| Retail Trade | 995.8 | 6.9 | 1000.2 | 6.8 |
| Transportation & WH | 436.3 | 3.0 | 443.6 | 3.0 |
| Information | 507.2 | 3.5 | 497.5 | 3.4 |
| Finance, Insurance, RE | 2448.1 | 16.9 | 2521.0 | 17.2 |
| Professional, BS | 2004.7 | 13.8 | 2004.0 | 13.7 |
| Education, Health Care | 1438.9 | 9.9 | 1439.2 | 9.8 |
| Arts, Entertainment | 577.1 | 4.0 | 585.2 | 4.0 |
| Other Services | 409.7 | 2.8 | 410.8 | 2.8 |
| Government | 1680.1 | 11.6 | 1675.1 | 11.4 |
| Rest of the World | 246.8 | 1.7 | 262.9 | 1.8 |
Notes: SSAR: Seasonally-Adjusted Annual Rate; WCCA: Without Capital Consumption Adjustment by Industry; WH: Warehousing; RE, includes rental and leasing: Real Estate; Art, Entertainment includes recreation, accommodation and food services; BS: business services
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
IA1. Contracting Real Private Fixed Investment. The United States economy has grown at the average yearly rate of 3 percent per year and 2 percent per year in per capita terms from 1870 to 2010, as measured by Lucas (2011May). An important characteristic of the economic cycle in the US has been rapid growth in the initial phase of expansion after recessions.
Inferior performance of the US economy and labor markets is the critical current issue of analysis and policy design. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. US economic growth has been at only 2.3 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 17 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2013. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the third estimate of GDP for IIIQ2013 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2013/pdf/gdp3q13_3rd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,738.0 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,356.9 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,738.0/$14,356.9 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html). As a result, there are 28.1 million unemployed or underemployed in the United States for an effective unemployment rate of 17.2 percent (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/11/global-financial-risk-mediocre-united.html). The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). Table IA1-1 provides quarterly seasonally adjusted annual rates (SAAR) of growth of private fixed investment for the recessions of the 1980s and the current economic cycle. In the cyclical expansion beginning in IQ1983 (http://www.nber.org/cycles.html), real private fixed investment in the United States grew at the average annual rate of 14.7 percent in the first eight quarters from IQ1983 to IVQ1984. Growth rates fell to an average of 2.2 percent in the following eight quarters from IQ1985 to IVQ1986. There were only two quarters of contraction of private fixed investment from IQ1983 to IVQ1986. There is quite different behavior of private fixed investment in the seventeen quarters of cyclical expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2013. The average annual growth rate in the first eight quarters of expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2011 was 3.3 percent, which is significantly lower than 14.7 percent in the first eight quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1984. There is only strong growth of private fixed investment in the four quarters of expansion from IIQ2011 to IQ2012 at the average annual rate of 10.5 percent. Growth has fallen from the SAAR of 14.8 percent in IIIQ2011 to 2.7 percent in IIIQ2012, recovering to 11.6 percent in IVQ2012 and falling to minus 1.5 percent in IQ2013. The SAAR of fixed investment rose to 6.5 percent in IIQ2013 and fell to 5.9 percent in IIIQ2013. Sudeep Reddy and Scott Thurm, writing on “Investment falls off a cliff,” on Nov 18, 2012, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887324595904578123593211825394.html?mod=WSJPRO_hpp_LEFTTopStories) analyze the decline of private investment in the US and inform that a review by the Wall Street Journal of filing and conference calls finds that 40 of the largest publicly traded corporations in the US have announced intentions to reduce capital expenditures in 2012. The SAAR of real private fixed investment jumped to 11.6 percent in IVQ2012 but declined to minus 1.5 percent in IQ2013, recovering to 6.5 percent in IIQ2013 and falling to 5.9 percent in IIIQ2013.
Table IA1-1, US, Quarterly Growth Rates of Real Private Fixed Investment, % Annual Equivalent SA
| Q | 1981 | 1982 | 1983 | 1984 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 |
| I | 3.8 | -12.2 | 9.4 | 13.1 | -7.1 | -27.4 | 0.8 |
| II | 3.2 | -12.1 | 16.0 | 16.6 | -5.5 | -14.2 | 13.6 |
| III | 0.1 | -9.3 | 24.4 | 8.2 | -12.1 | -0.5 | -0.4 |
| IV | -1.5 | 0.2 | 24.3 | 7.3 | -23.9 | -2.8 | 8.5 |
| 1985 | 2011 | ||||||
| I | 3.7 | -0.5 | |||||
| II | 5.2 | 8.6 | |||||
| III | -1.6 | 14.8 | |||||
| IV | 7.8 | 10.0 | |||||
| 1986 | 2012 | ||||||
| I | 1.1 | 8.6 | |||||
| II | 0.1 | 4.7 | |||||
| III | -1.8 | 2.7 | |||||
| IV | 3.1 | 11.6 | |||||
| 1987 | 2013 | ||||||
| I | -6.7 | -1.5 | |||||
| II | 6.3 | 6.5 | |||||
| III | 7.1 | 5.9 | |||||
| IV | -0.2 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-1 of the US Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) provides seasonally adjusted annual rates of growth of real private fixed investment from 1981 to 1986. Growth rates recovered sharply during the first eight quarters, which was essential in returning the economy to trend growth and eliminating unemployment and underemployment accumulated during the contractions.
Chart IA1-1, US, Real Private Fixed Investment, Seasonally-Adjusted Annual Rates Percent Change from Prior Quarter, 1981-1986
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Weak behavior of real private fixed investment from 2007 to 2013 is shown in Chart IA1-2. Growth rates of real private fixed investment were much lower during the initial phase of expansion in the current economic cycle and have entered sharp trend of decline.
Chart IA1-2, US, Real Private Fixed Investment, Seasonally-Adjusted Annual Rates Percent Change from Prior Quarter, 2007-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table IA1-2 provides real private fixed investment at seasonally adjusted annual rates from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2013 or for the complete economic cycle. The first column provides the quarter, the second column percentage change relative to IVQ2007, the third column the quarter percentage change in the quarter relative to the prior quarter and the final column percentage change in a quarter relative to the same quarter a year earlier. In IQ1980, gross private domestic investment in the US was $951.6 billion of 2009 dollars, growing to $1,143.0 billion in IVQ1986 or 20.1 percent. Real gross private domestic investment in the US increased 0.8 percent from $2,605.2 billion of 2009 dollars in IVQ2007 to $2,627.2 billion in IIIQ2013. As shown in Table IAI-2, real private fixed investment fell 3.6 percent from $2,586.3 billion of 2009 dollars in IVQ2007 to $2,494.0 billion in IIIQ2013. Growth of real private investment in Table IA1-2 is mediocre for all but four quarters from IIQ2011 to IQ2012.
Table IA1-2, US, Real Private Fixed Investment and Percentage Change Relative to IVQ2007 and Prior Quarter, Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars and ∆%
| Real PFI, Billions Chained 2009 Dollars | ∆% Relative to IVQ2007 | ∆% Relative to Prior Quarter | ∆% | |
| IVQ2007 | 2586.3 | NA | -1.2 | -1.4 |
| IQ2008 | 2539.1 | -1.8 | -1.8 | -3.0 |
| IIQ2008 | 2503.4 | -3.2 | -1.4 | -4.6 |
| IIIQ2008 | 2424.1 | -6.3 | -3.2 | -7.1 |
| IV2008 | 2263.8 | -12.5 | -6.6 | -12.5 |
| IQ2009 | 2089.3 | -19.2 | -7.7 | -17.7 |
| IIQ2009 | 2011.0 | -22.2 | -3.7 | -19.7 |
| IIIQ2009 | 2008.4 | -22.3 | -0.1 | -17.1 |
| IVQ2009 | 1994.1 | -22.9 | -0.7 | -11.9 |
| IQ2010 | 1997.9 | -22.8 | 0.2 | -4.4 |
| IIQ2010 | 2062.8 | -20.2 | 3.2 | 2.6 |
| IIIQ2010 | 2060.8 | -20.3 | -0.1 | 2.6 |
| IVQ2010 | 2103.1 | -18.7 | 2.1 | 5.5 |
| IQ2011 | 2100.7 | -18.8 | -0.1 | 5.1 |
| IIQ2011 | 2144.4 | -17.1 | 2.1 | 4.0 |
| IIIQ2011 | 2219.8 | -14.2 | 3.5 | 7.7 |
| IVQ2011 | 2273.4 | -12.1 | 2.4 | 8.1 |
| IQ2012 | 2320.8 | -10.3 | 2.1 | 10.5 |
| IIQ2012 | 2347.9 | -9.2 | 1.2 | 9.5 |
| IIIQ2012 | 2363.5 | -8.6 | 0.7 | 6.5 |
| IVQ2012 | 2429.1 | -6.1 | 2.8 | 6.8 |
| IQ2013 | 2420.0 | -6.4 | -0.4 | 4.3 |
| IIQ2013 | 2458.4 | -4.9 | 1.6 | 4.7 |
| IIIQ2013 | 2,494.0 | -3.6 | 1.4 | 5.5 |
PFI: Private Fixed Investment
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-3 provides real private fixed investment in billions of chained 2009 dollars from IQ2007 to IIIQ2013. Real private fixed investment has not recovered, stabilizing at a level in IIIQ2013 that is 3.6 percent below the level in IVQ2007.
Chart IA1-3, US, Real Private Fixed Investment, Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars, IQ2007 to IIIQ2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-4 provides real gross private domestic investment in chained dollars of 2009 from 1980 to 1986. Real gross private domestic investment climbed 20.1 percent to $1143.0 billion of 2009 dollars in IVQ1986 above the level of $951.6 billion in IQ1980.
Chart IA1-4, US, Real Gross Private Domestic Investment, Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars at Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rate, 1980-1986
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-5 provides real gross private domestic investment in the United States in billions of dollars of 2009 from 2006 to 2013. Gross private domestic investment reached a level of $2627.2 in IIIQ2013, which was 0.8 percent higher than the level of $2605.2 billion in IVQ2007 (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm).
Chart IA1-5, US, Real Gross Private Domestic Investment, Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars at Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rate, 2007-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table IA1-3 provides percentage shares in GDP of gross private domestic investment and its components in IIIQ2013, IIIQ2006 and IIIQ2000. The share of gross private domestic investment in GDP has fallen from 19.8 percent in IIIQ2000 and 19.3 percent in IIIQ2006 to 16.2 percent in IIIQ2013. There are declines in percentage shares in GDP of all components with sharp reduction of residential investment from 4.7 percent in IIIQ2000 and 5.8 percent in IIIQ2006 to 3.1 percent in IIIQ2013. The share of fixed investment in GDP fell from 19.3 percent in IIIQ2000 and 18.7 percent in IIIQ2006 to 15.3 percent in IIIQ2013.
Table IA1-3, Percentage Shares of Gross Private Domestic Investment and Components in Gross Domestic Product, % of GDP, IQ2013
| IIIQ2013 | IIIQ2006 | IIIQ2000 | |
| Gross Private Domestic Investment | 16.2 | 19.3 | 19.8 |
| Fixed Investment | 15.3 | 18.7 | 19.3 |
| Nonresidential | 12.2 | 12.9 | 14.6 |
| Structures | 2.8 | 3.1 | 3.2 |
| Equipment and Software | 5.5 | 6.2 | 7.5 |
| Intellectual | 3.9 | 3.7 | 4.0 |
| Residential | 3.1 | 5.8 | 4.7 |
| Change in Private Inventories | 0.9 | 0.6 | 0.6 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Broader perspective is provided in Chart IA1-6 with the percentage share of gross private domestic investment in GDP in annual data from 1929 to 2012. There was sharp drop during the current economic cycle with almost no recovery in contrast with sharp recovery after the recessions of the 1980s.
Chart IA1-6, US, Percentage Share of Gross Private Domestic Investment in Gross Domestic Product, Annual, 1929-2012
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-7 provides percentage shares of private fixed investment in GDP with annual data from 1929 to 2012. The sharp contraction after the recessions of the 1980s was followed by sustained recovery while the sharp drop in the current economic cycle has not been recovered.
Chart IA1-7, US, Percentage Share of Private Fixed Investment in Gross Domestic Product, Annual, 1929-2012
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-8 provides percentage shares in GDP of nonresidential investment from 1929 to 2012. There is again recovery from sharp contraction in the 1980s but inadequate recovery in the current economic cycle.
Chart IA1-8, US, Percentage Share of Nonresidential Investment in Gross Domestic Product, Annual, 1929-2012
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-9 provides percentage shares of business equipment and software in GDP with annual data from 1929 to 2012. There is again inadequate recovery in the current economic cycle.
Chart IA1-9, US, Percentage Share of Business Equipment and Software in Gross Domestic Product, Annual, 1929-2012
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-10 provides percentage shares of residential investment in GDP with annual data from 1929 to 2012. The salient characteristic of Chart IA1-10 is the vertical increase of the share of residential investment in GDP up to 2006 and subsequent collapse.
Chart IA1-10, US, Percentage Share of Residential Investment in Gross Domestic Product, Annual, 1929-2012
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Finer detail is provided by the quarterly share of residential investment in GDP from 1979 to 2013 in Chart IA1-11. There was protracted growth of that share, accelerating sharply into 2006 followed with nearly vertical drop. The explanation of the sharp contraction of United States housing can probably be found in the origins of the financial crisis and global recession. Let V(T) represent the value of the firm’s equity at time T and B stand for the promised debt of the firm to bondholders and assume that corporate management, elected by equity owners, is acting on the interests of equity owners. Robert C. Merton (1974, 453) states:
“On the maturity date T, the firm must either pay the promised payment of B to the debtholders or else the current equity will be valueless. Clearly, if at time T, V(T) > B, the firm should pay the bondholders because the value of equity will be V(T) – B > 0 whereas if they do not, the value of equity would be zero. If V(T) ≤ B, then the firm will not make the payment and default the firm to the bondholders because otherwise the equity holders would have to pay in additional money and the (formal) value of equity prior to such payments would be (V(T)- B) < 0.”
Pelaez and Pelaez (The Global Recession Risk (2007), 208-9) apply this analysis to the US housing market in 2005-2006 concluding:
“The house market [in 2006] is probably operating with low historical levels of individual equity. There is an application of structural models [Duffie and Singleton 2003] to the individual decisions on whether or not to continue paying a mortgage. The costs of sale would include realtor and legal fees. There could be a point where the expected net sale value of the real estate may be just lower than the value of the mortgage. At that point, there would be an incentive to default. The default vulnerability of securitization is unknown.”
There are multiple important determinants of the interest rate: “aggregate wealth, the distribution of wealth among investors, expected rate of return on physical investment, taxes, government policy and inflation” (Ingersoll 1987, 405). Aggregate wealth is a major driver of interest rates (Ingersoll 1987, 406). Unconventional monetary policy, with zero fed funds rates and flattening of long-term yields by quantitative easing, causes uncontrollable effects on risk taking that can have profound undesirable effects on financial stability. Excessively aggressive and exotic monetary policy is the main culprit and not the inadequacy of financial management and risk controls.
The net worth of the economy depends on interest rates. In theory, “income is generally defined as the amount a consumer unit could consume (or believe that it could) while maintaining its wealth intact” (Friedman 1957, 10). Income, Y, is a flow that is obtained by applying a rate of return, r, to a stock of wealth, W, or Y = rW (Ibid). According to a subsequent restatement: “The basic idea is simply that individuals live for many years and that therefore the appropriate constraint for consumption decisions is the long-run expected yield from wealth r*W. This yield was named permanent income: Y* = r*W” (Darby 1974, 229), where * denotes permanent. The simplified relation of income and wealth can be restated as:
W = Y/r (1)
Equation (1) shows that as r goes to zero, r →0, W grows without bound, W→∞.
Lowering the interest rate near the zero bound in 2003-2004 caused the illusion of permanent increases in wealth or net worth in the balance sheets of borrowers and also of lending institutions, securitized banking and every financial institution and investor in the world. The discipline of calculating risks and returns was seriously impaired. The objective of monetary policy was to encourage borrowing, consumption and investment but the exaggerated stimulus resulted in a financial crisis of major proportions as the securitization that had worked for a long period was shocked with policy-induced excessive risk, imprudent credit, high leverage and low liquidity by the incentive to finance everything overnight at close to zero interest rates, from adjustable rate mortgages (ARMS) to asset-backed commercial paper of structured investment vehicles (SIV).
The consequences of inflating liquidity and net worth of borrowers were a global hunt for yields to protect own investments and money under management from the zero interest rates and unattractive long-term yields of Treasuries and other securities. Monetary policy distorted the calculations of risks and returns by households, business and government by providing central bank cheap money. Short-term zero interest rates encourage financing of everything with short-dated funds, explaining the SIVs created off-balance sheet to issue short-term commercial paper to purchase default-prone mortgages that were financed in overnight or short-dated sale and repurchase agreements (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession, 50-1, Regulation of Banks and Finance, 59-60, Globalization and the State Vol. I, 89-92, Globalization and the State Vol. II, 198-9, Government Intervention in Globalization, 62-3, International Financial Architecture, 144-9). ARMS were created to lower monthly mortgage payments by benefitting from lower short-dated reference rates. Financial institutions economized in liquidity that was penalized with near zero interest rates. There was no perception of risk because the monetary authority guaranteed a minimum or floor price of all assets by maintaining low interest rates forever or equivalent to writing an illusory put option on wealth. Subprime mortgages were part of the put on wealth by an illusory put on house prices. The housing subsidy of $221 billion per year created the impression of ever increasing house prices. The suspension of auctions of 30-year Treasuries was designed to increase demand for mortgage-backed securities, lowering their yield, which was equivalent to lowering the costs of housing finance and refinancing. Fannie and Freddie purchased or guaranteed $1.6 trillion of nonprime mortgages and worked with leverage of 75:1 under Congress-provided charters and lax oversight. The combination of these policies resulted in high risks because of the put option on wealth by near zero interest rates, excessive leverage because of cheap rates, low liquidity because of the penalty in the form of low interest rates and unsound credit decisions because the put option on wealth by monetary policy created the illusion that nothing could ever go wrong, causing the credit/dollar crisis and global recession (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession, 157-66, Regulation of Banks, and Finance, 217-27, International Financial Architecture, 15-18, The Global Recession Risk, 221-5, Globalization and the State Vol. II, 197-213, Government Intervention in Globalization, 182-4).
Chart IA1-11, US, Percentage Share of Residential Investment in Gross Domestic Product, Quarterly, 1979-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-12 provides the share of intellectual property products investment in GDP with annual data from 1929 to 2012. This is an important addition in the revision and enhancement of GDP provided by the Bureau of Economic Analysis. The share rose sharply over time but in the past decade and stabilized at a lower level.
Chart IA1-12, US, Percentage Share of Intellectual Property Products Investment in Gross Domestic Product, Annual, 1929-2012
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-13 provides the percentage share of intellectual property investment in GDP on a quarterly basis from 1979 to 2013. The share stabilized in the 2000s.
Chart IA1-13, US, Percentage Share of Intellectual Property Investment in Gross Domestic Product, Quarterly, 1979-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table IA1-4 provides the seasonally adjusted annual rate of real GDP percentage change and contributions in percentage points in annual equivalent rate of gross domestic investment (GDI), real private fixed investment (PFI), nonresidential investment (NRES), business equipment and software (BES), residential investment (RES), intellectual property products (IPP) and change in inventories (∆INV) for the cyclical expansions from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 and from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2013. GDI provided strong percentage points contributions to GDP growth in the critical first year of expansion in 1983 and also in several quarters in 1984 and 1985 while it has been muted in the cyclical expansion since IIIQ2009 with contributions largely only from IQ2010 to IVQ2011. Gross domestic investment added 2.56 percentage points to GDP growth of 4.1 percent in IIIQ2013 partly because of change of inventories of 1.67 percentage points with PFI adding 0.81 percentage points. Nonresidential investment added 0.58 percentage points and residential investment added 0.31 percentage points to GDP growth of 4.1 percent in IIIQ2013. GDI added 1.38 percentage points to GDP growth of 2.5 percent in IIQ2013 with 0.41 percentage points from inventory change while nonresidential investment added 0.56 percentage points and residential investment 0.40 percentage points. GDI added 0.71 percentage points in IQ2013 mostly because of 0.93 percentage points of inventory investment while private fixed investment deducted 0.23 percentage points. Nonresidential investment deducted 0.57 percentage points. Business equipment and software added 0.09 percentage points and residential investment 0.34 percentage points. Intellectual property products (IPP) added 0.14 percentage points in IQ2013, deducted 0.06 percentage points in IIQ2013 and added 0.22 percentage points in IIIQ2013. Much of the strong performance of GDI in the cyclical expansion after IQ1983 originated in contributions by real private fixed investment (PFI). Nonresidential investment also contributed strongly to growth in the expansion of the 1980s but has been muted in the current expansion. The contribution of business equipment and software collapsed to negative 0.22 percentage points in IIIQ2012 as business scales down investment but rebounded with 0.47 percentage points in IVQ2012, 0.09 percentage points in IQ2013 and 0.18 percentage points in IIQ2013. Business equipment and software contributed 0.2 percentage points in IIIQ2013. Residential investment (RES) was relatively strong in 1983 but was muted in following quarters. Residential investment only contributed significantly to growth of GDP in the four quarters of 2012, IQ2013, IIQ2013 and IIIQ2013.
Table IA1-4, US, Contributions to the Rate of Growth of Real GDP in Percentage Points
| GDP | GDI | PFI | NRES | BES | IPP | RES | ∆INV | |
| 2013 | ||||||||
| I | 1.1 | 0.71 | -0.23 | -0.57 | 0.09 | 0.14 | 0.34 | 0.93 |
| II | 2.5 | 1.38 | 0.96 | 0.56 | 0.18 | -0.06 | 0.40 | 0.41 |
| III | 4.1 | 2.56 | 0.81 | 0.58 | 0.02 | 0.22 | 0.31 | 1.67 |
| 2012 | ||||||||
| I | 3.7 | 1.57 | 1.21 | 0.68 | 0.45 | 0.05 | 0.53 | 0.36 |
| II | 1.2 | -0.23 | 0.68 | 0.53 | 0.29 | 0.07 | 0.15 | -0.91 |
| III | 2.8 | 0.99 | 0.39 | 0.04 | -0.22 | 0.11 | 0.35 | 0.60 |
| IV | 0.1 | -0.36 | 1.63 | 1.13 | 0.47 | 0.21 | 0.50 | -2.00 |
| 2011 | ||||||||
| I | -1.3 | -1.11 | -0.05 | -0.09 | 0.59 | 0.14 | 0.04 | -1.06 |
| II | 3.2 | 1.88 | 1.16 | 1.09 | 0.23 | 0.18 | 0.07 | 0.72 |
| III | 1.4 | 0.36 | 1.96 | 1.81 | 0.99 | 0.20 | 0.15 | -1.60 |
| IV | 4.9 | 4.13 | 1.39 | 1.10 | 0.54 | 0.21 | 0.29 | 2.73 |
| 2010 | ||||||||
| I | 1.6 | 1.77 | 0.11 | 0.46 | 1.25 | -0.07 | -0.35 | 1.66 |
| II | 3.9 | 2.86 | 1.77 | 1.21 | 1.02 | -0.08 | 0.56 | 1.09 |
| III | 2.8 | 1.86 | -0.04 | 0.90 | 0.83 | 0.22 | -0.94 | 1.90 |
| IV | 2.8 | -0.51 | 1.13 | 0.94 | 0.57 | 0.19 | 0.19 | -1.64 |
| 2009 | ||||||||
| I | -5.4 | -7.02 | -4.75 | -3.58 | -2.25 | -0.23 | -1.17 | -2.26 |
| II | -0.4 | -3.25 | -2.13 | -1.46 | -0.60 | 0.16 | -0.66 | -1.12 |
| III | 1.3 | -0.40 | -0.02 | -0.54 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 0.52 | -0.38 |
| IV | 3.9 | 4.05 | -0.36 | -0.37 | 0.36 | 0.25 | 0.01 | 4.40 |
| 1982 | ||||||||
| I | -6.5 | -7.60 | -2.26 | -1.45 | -0.83 | 0.14 | -0.81 | -5.34 |
| II | 2.2 | -0.06 | -2.32 | -1.89 | -1.20 | 0.08 | -0.44 | 2.26 |
| III | -1.4 | -0.62 | -1.73 | -1.71 | -0.55 | 0.06 | -0.02 | 1.11 |
| IV | 0.4 | -5.37 | -0.03 | -1.05 | -0.57 | 0.00 | 1.01 | -5.33 |
| 1983 | ||||||||
| I | 5.3 | 2.36 | 1.44 | -0.92 | -0.27 | 0.16 | 2.36 | 0.92 |
| II | 9.4 | 5.96 | 2.53 | 0.67 | 1.24 | 0.29 | 1.86 | 3.43 |
| III | 8.1 | 4.40 | 3.82 | 2.13 | 1.43 | 0.31 | 1.70 | 0.57 |
| IV | 8.5 | 6.94 | 3.93 | 3.14 | 2.32 | 0.35 | 0.79 | 3.01 |
| 1984 | ||||||||
| I | 8.2 | 7.23 | 2.29 | 1.71 | 0.46 | 0.30 | 0.58 | 4.94 |
| II | 7.2 | 2.57 | 2.86 | 2.52 | 1.36 | 0.29 | 0.34 | -0.29 |
| III | 4.0 | 1.69 | 1.48 | 1.70 | 0.88 | 0.25 | -0.22 | 0.21 |
| IV | 3.2 | -1.08 | 1.36 | 1.34 | 0.86 | 0.29 | 0.02 | -2.44 |
| 1985 | ||||||||
| I | 4.0 | -2.14 | 0.72 | 0.67 | -0.23 | 0.14 | 0.05 | -2.86 |
| II | 3.7 | 1.34 | 0.99 | 0.83 | 0.64 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.35 |
| III | 6.4 | -0.43 | -0.28 | -0.62 | -0.38 | 0.13 | 0.34 | -0.15 |
| IV | 3.0 | 2.80 | 1.40 | 1.00 | 0.53 | 0.26 | 0.40 | 1.40 |
| 1986 | ||||||||
| I | 3.8 | 0.04 | 0.21 | -0.55 | -0.28 | 0.17 | 0.76 | -0.17 |
| II | 1.9 | -1.30 | 0.00 | -1.12 | 0.34 | 0.15 | 1.12 | -1.30 |
| III | 4.1 | -1.97 | -0.34 | -0.63 | -0.17 | 0.10 | 0.28 | -1.62 |
| IV | 2.1 | 0.24 | 0.53 | 0.48 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.05 | -0.29 |
GDP: Gross Domestic Product; GDI: Gross Domestic Investment; PFI: Private Fixed Investment; NRES: Nonresidential; BES: Business Equipment and Software; IPP: Intellectual Property Products; RES: Residential; ∆INV: Change in Private Inventories.
GDI = PFI + ∆INV, may not add exactly because of errors of rounding.
GDP: Seasonally adjusted annual equivalent rate of growth in a quarter; components: percentage points at annual rate.
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
IA2 Swelling Undistributed Corporate Profits. Table IA1-5 provides value added of corporate business, dividends and corporate profits in billions of current dollars at seasonally adjusted annual rates (SAAR) in IVQ2007 and IIIQ2013 together with percentage changes. The last three rows of Table IA1-5 provide gross value added of nonfinancial corporate business, consumption of fixed capital and net value added in billions of chained 2009 dollars at SAARs. Deductions from gross value added of corporate profits down the rows of Table IA1-5 end with undistributed corporate profits. Profits after taxes with inventory valuation adjustment (IVA) and capital consumption adjustment (CCA) increased by 103.6 percent in nominal terms from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2013 while net dividends increased 11.7 percent and undistributed corporate profits swelled 382.4 percent from $107.7 billion in IQ2007 to $519.5 billion in IIQ2013 and changed signs from minus $55.9 billion in current dollars in IVQ2007. The investment decision of United States corporations has been fractured in the current economic cycle in preference of cash. Gross value added of nonfinancial corporate business adjusted for inflation increased 5.4 percent from IVQ2007 to IIQ2013, which is much lower than nominal increase of 16.6 percent in the same period for gross value added of total corporate business.
Table IA1-5, US, Value Added of Corporate Business, Corporate Profits and Dividends, IVQ2007-IQ2013
| IVQ2007 | IIIQ2013 | ∆% | |
| Current Billions of Dollars Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rates (SAAR) | |||
| Gross Value Added of Corporate Business | 8,165.9 | 9,521.0 | 16.6 |
| Consumption of Fixed Capital | 1,216.5 | 1,429.5 | 17.5 |
| Net Value Added | 6,949.4 | 8,091.5 | 16.4 |
| Compensation of Employees | 4,945.8 | 5,414.3 | 9.5 |
| Taxes on Production and Imports Less Subsidies | 688.5 | 759.1 | 10.3 |
| Net Operating Surplus | 1,315.1 | 1,918.1 | 45.9 |
| Net Interest and Misc | 204.2 | 118.1 | -42.2 |
| Business Current Transfer Payment Net | 68.9 | 93.2 | 35.3 |
| Corporate Profits with IVA and CCA Adjustments | 1,042.0 | 1,706.8 | 63.8 |
| Taxes on Corporate Income | 408.8 | 417.8 | 2.2 |
| Profits after Tax with IVA and CCA Adjustment | 633.2 | 1,289.0 | 103.6 |
| Net Dividends | 689.1 | 769.4 | 11.7 |
| Undistributed Profits with IVA and CCA Adjustment | -55.9 | 519.5 | NA ∆% 382.4 relative to 107.7 in IQ2007 |
| Billions of Chained USD 2009 SAAR | |||
| Gross Value Added of Nonfinancial Corporate Business | 7,519.3 | 7,924.2 | 5.4 |
| Consumption of Fixed Capital | 1,066.0 | 1,173.1 | 10.0 |
| Net Value Added | 6,453.4 | 6,751.1 | 4.6 |
IVA: Inventory Valuation Adjustment; CCA: Capital Consumption Adjustment
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table IA1-6 provides comparable United States value added of corporate business, corporate profits and dividends from IQ1980 to IVQ1986. There is significant difference both in nominal and inflation-adjusted data. Between IQ1980 and IVQ1986, profits after tax with IVA and CCA increased 66.6 percent with dividends growing 118.6 percent and undistributed profits increasing 15.5 percent. There was much higher inflation in the 1980s than in the current cycle. For example, the consumer price index for all items not seasonally adjusted increased 37.9 percent between Mar 1980 and Dec 1986 but only 11.5 percent between Dec 2007 and Sep 2013 (http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm). The comparison is still valid in terms of inflation-adjusted data: gross value added of nonfinancial corporate business adjusted for inflation increased 25.5 percent between IQ1980 and IVQ1986 but only 5.4 percent between IVQ2007 and IIIQ2013 while net value added adjusted for inflation increased 24.3 percent between IQ1980 and IVQ1986 but only 4.6 percent between IVQ2007 and IIIQ2013.
Table IA1-6, US, Value Added of Corporate Business, Corporate Profits and Dividends, IQ1980-IVQ1985
| IQ1980 | IVQ1986 | ∆% | |
| Current Billions of Dollars Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rates (SAAR) | |||
| Gross Value Added of Corporate Business | 1,654.1 | 2,756.0 | 66.6 |
| Consumption of Fixed Capital | 200.5 | 357.7 | 78.4 |
| Net Value Added | 1,453.6 | 2,398.4 | 65.0 |
| Compensation of Employees | 1,072.9 | 1,765.1 | 64.5 |
| Taxes on Production and Imports Less Subsidies | 121.5 | 224.5 | 84.8 |
| Net Operating Surplus | 259.2 | 408.7 | 57.7 |
| Net Interest and Misc. | 50.4 | 106.0 | 110.3 |
| Business Current Transfer Payment Net | 11.5 | 26.3 | 128.7 |
| Corporate Profits with IVA and CCA Adjustments | 197.2 | 276.4 | 40.2 |
| Taxes on Corporate Income | 97.0 | 118.5 | 22.2 |
| Profits after Tax with IVA and CCA Adjustment | 100.2 | 158.0 | 57.7 |
| Net Dividends | 40.9 | 89.4 | 118.6 |
| Undistributed Profits with IVA and CCA Adjustment | 59.3 | 68.5 | 15.5 |
| Billions of Chained USD 2009 SAAR | |||
| Gross Value Added of Nonfinancial Corporate Business | 2,952.3 | 3,704.6 | 25.5 |
| Consumption of Fixed Capital | 315.6 | 428.0 | 35.6 |
| Net Value Added | 2,636.7 | 3,276.6 | 24.3 |
IVA: Inventory Valuation Adjustment; CCA: Capital Consumption Adjustment
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-12 of the US Bureau of Economic Analysis provides quarterly corporate profits after tax and undistributed profits with IVA and CCA from 1979 to 2013. There is tightness between the series of quarterly corporate profits and undistributed profits in the 1980s with significant gap developing from 1988 and to the present with the closest approximation peaking in IVQ2005 and surrounding quarters. These gaps widened during all recessions including in 1991 and 2001 and recovered in expansions with exceptionally weak performance in the current expansion.
Chart IA1-14, US, Corporate Profits after Tax and Undistributed Profits with Inventory Valuation Adjustment and Capital Consumption Adjustment, Quarterly, 1979-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table IA1-7 provides price, costs and profit per unit of gross value added of nonfinancial domestic corporate income for IVQ2007 and IIIQ2013 in the upper block and for IQ1980 and IVQ1986 in the lower block. Compensation of employees or labor costs per unit of gross value added of nonfinancial domestic corporate income hardly changed from 0.577 in IVQ2007 to 0.600 in IIIQ2013 in a fractured labor market but increased from 0.340 in IQ1980 to 0.436 in IVQ1986 in a more vibrant labor market. Unit nonlabor costs increased mildly from 0.270 per unit of gross value added in IVQ2007 to 0.296 in IIIQ2013 but increased from 0.124 in IQ1980 to 0.181 in IVQ1986 in an economy closer to full employment of resources. Profits after tax with IVA and CCA per unit of gross value added of nonfinancial domestic corporate income increased from 0.076 in IVQ2007 to 0.123 in IIIQ2013 and from 0.029 in IQ1980 to 0.037 in IVQ1986.
Table IA1-7, US, Price, Costs and Profit per Unit of Gross Value Added of Nonfinancial Domestic Corporate Income
| IVQ2007 | IIIQ2013 | |
| Price per Unit of Real Gross Value Added of Nonfinancial Corporate Business | 0.961 | 1.052 |
| Compensation of Employees (Unit Labor Cost) | 0.577 | 0.600 |
| Unit Nonlabor Cost | 0.270 | 0.296 |
| Consumption of Fixed Capital | 0.140 | 0.157 |
| Taxes on Production and Imports less Subsidies plus Business Current Transfer Payments (net) | 0.093 | 0.099 |
| Net Interest and Misc. Payments | 0.037 | 0.040 |
| Corporate Profits with IVA and CCA Adjustment (Unit Profits from Current Production) | 0.114 | 0.157 |
| Taxes on Corporate Income | 0.038 | 0.033 |
| Profits after Tax with IVA and CCA Adjustment | 0.076 | 0.123 |
| IQ1980 | IVQ1986 | |
| Price per Unit of Real Gross Value Added of Nonfinancial Corporate Business | 0.518 | 0.678 |
| Compensation of Employees (Unit Labor Cost) | 0.340 | 0.436 |
| Unit Nonlabor Cost | 0.124 | 0.181 |
| Consumption of Fixed Capital | 0.064 | 0.087 |
| Taxes on Production and Imports less Subsidies plus Business Current Transfer Payments (net) | 0.042 | 0.064 |
| Net Interest and Misc. Payments | 0.018 | 0.030 |
| Corporate Profits with IVA and CCA Adjustment (Unit Profits from Current Production) | 0.055 | 0.060 |
| Taxes on Corporate Income | 0.026 | 0.023 |
| Profits after Tax with IVA and CCA Adjustment | 0.029 | 0.037 |
IVA: Inventory Valuation Adjustment; CCA: Capital Consumption Adjustment
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-13 provides quarterly profits after tax with IVA and CCA per unit of gross value added of nonfinancial domestic corporate income from 1980 to 2013. In an environment of idle labor and other productive resources nonfinancial corporate income increased after tax profits with IVA and CCA per unit of gross value added at a faster pace in the weak economy from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2013 than in the vibrant expansion of the cyclical contractions of the 1980s. Part of the profits was distributed as dividends and significant part was retained as undistributed profits in the current economic cycle with frustrated investment decision.
Chart IA1-15, US, Profits after Tax with Inventory Valuation Adjustment and Capital Consumption Adjustment per Unit of Gross Value Added of Nonfinancial Domestic Corporate Income, 1980-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table IA1-8 provides seasonally adjusted annual rates of change of corporate profits from IVQ2012 to IIIQ2013. US corporate profits with inventory valuation adjustment (IVA) and capital consumption adjustment (CCA) fell 1.3 percent in IQ2013 and 0.1 percent after taxes. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA rebounded at 3.3 percent in IIQ2013 and at 3.5 percent after taxes. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased at 1.9 percent in IIIQ2013 and 2.4 percent after taxes. Net dividends jumped 16.2 percent in IVQ2012 in generalized anticipation of income because of fear of the so-called “fiscal cliff,” or increases in taxes in 2013, and fell 12.0 percent in IQ2013 in adjustment to normal levels. Net dividends jumped at 35.8 percent in IIQ2013 and fell at 17.3 percent in IIIQ2013. Undistributed profits fell 9.7 percent in IVQ2012 in anticipation of tax increases and adjusted by increasing 13.7 percent in IQ2013. Undistributed profits fell at 25.5 percent in IIQ2013 and increased at 34.6 percent in IIIQ2013.
Table IA1-8, Quarterly Seasonally Adjusted Annual Equivalent Percentage Rates of Change of Corporate Profits, ∆%
| IVQ2012 | IQ2013 | IIQ2013 | IIIQ2013 | |
| Corporate Profits with IVA and CCA | 1.7 | -1.3 | 3.3 | 1.9 |
| Corporate Income Taxes | -1.3 | -5.8 | 2.4 | -0.1 |
| After Tax Profits with IVA and CCA | 2.6 | -0.1 | 3.5 | 2.4 |
| Net Dividends | 16.2 | -12.0 | 35.8 | -17.3 |
| Und Profits with IVA and CCA | -9.7 | 13.7 | -25.5 | 34.6 |
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table IA1-9 provides change from prior quarter of the level of seasonally adjusted annual rates of US corporate profits. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA fell $26.6 billion in IQ2013 after increasing $34.9 billion in IVQ2012 and $13.9 billion in IIIQ2012. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA rebounded with $66.8 billion in IIQ2013 and $39.2 billion in IIIQ2013. Profits after tax with IVA and CCA fell $1.7 billion in IQ2013 after increasing $40.8 billion in IVQ2012 and $4.5 billion in IIIQ2012. In IIQ2013, profits after tax with IVA and CCA increased $56.9 billion and $39.5 billion in IIIQ2013. Anticipation of higher taxes in the “fiscal cliff” episode caused increase of $120.9 billion in net dividends in IVQ2012 followed with adjustment in the form of decrease of net dividends by $103.8 billion in IQ2013, rebounding with $273.5 billion in IIQ2013. Net dividends fell at $179.0 billion in IIIQ2013. There is similar decrease of $80.1 billion in undistributed profits with IVA and CCA in IVQ2012 followed by increase of $102.1 billion in IQ2013 and decline of $216.6 billion in IIQ2013. Undistributed profits with IVA and CCA rose at $218.6 billion in IIIQ2013. Undistributed profits of US corporations swelled 382.4 percent from $107.7 billion IQ2007 to $519.5 billion in IIIQ2013 and changed signs from minus $55.9 billion in billion in IVQ2007 (Section IA2). In IQ2013, corporate profits with inventory valuation and capital consumption adjustment fell $26.6 billion relative to IVQ2012, from $2047.2 billion to $2020.6 billion at the quarterly rate of minus 1.3 percent. In IIQ2013, corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased $66.8 billion from $2020.6 billion in IQ2013 to $2087.4 billion at the quarterly rate of 3.3 percent. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased $39.2 billion from $2087.4 billion in IIQ2013 to $2126.6 billion in IIIQ2013 at the annual rate of 1.9 percent (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2013/pdf/gdp3q13_3rd.pdf). Uncertainty originating in fiscal, regulatory and monetary policy causes wide swings in expectations and decisions by the private sector with adverse effects on investment, real economic activity and employment.
Table IA1-9, Change from Prior Quarter of Level of Seasonally Adjusted Annual Equivalent Rates of Corporate Profits, Billions of Dollars
| IVQ2012 | IQ2013 | IIQ2013 | IIIQ2013 | |
| Corporate Profits with IVA and CCA | 34.9 | -26.6 | 66.8 | 39.2 |
| Corporate Income Taxes | -5.9 | -25.0 | 10.0 | -0.4 |
| After Tax Profits with IVA and CCA | 40.8 | -1.7 | 56.9 | 39.5 |
| Net Dividends | 120.9 | -103.8 | 273.5 | -179.0 |
| Und Profits with IVA and CCA | -80.1 | 102.1 | -216.6 | 218.6 |
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
II World Inflation Waves. This section provides analysis and data on world inflation waves. IA Appendix: Transmission of Unconventional Monetary Policy provides more technical analysis. Section IB United States Inflation analyzes inflation in the United States in two subsections: IC Long-term US Inflation and ID Current US Inflation. There is similar lack of reality in economic history as in monetary policy based on fear of deflation as analyzed in Subsection IE Theory and Reality of Economic History and Monetary Policy Based on Fear of Deflation.
The critical fact of current world financial markets is the combination of “unconventional” monetary policy with intermittent shocks of financial risk aversion. There are two interrelated unconventional monetary policies. First, unconventional monetary policy consists primarily of reducing short-term policy interest rates toward the “zero bound” such as fixing the fed funds rate at 0 to ¼ percent by decision of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) since Dec 16, 2008 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20081216b.htm). Fixing policy rates at zero is the strongest measure of monetary policy with collateral effects of inducing carry trades from zero interest rates to exposures in risk financial assets such as commodities, exchange rates, stocks and higher yielding fixed income. Second, unconventional monetary policy also includes a battery of measures in also reducing long-term interest rates of government securities and asset-backed securities such as mortgage-backed securities.
When inflation is low, the central bank lowers interest rates to stimulate aggregate demand in the economy, which consists of consumption and investment. When inflation is subdued and unemployment high, monetary policy would lower interest rates to stimulate aggregate demand, reducing unemployment. When interest rates decline to zero, unconventional monetary policy would consist of policies such as large-scale purchases of long-term securities to lower their yields. Long-term asset-backed securities finance a major portion of credit in the economy. Loans for purchasing houses, automobiles and other consumer products are bundled in securities that in turn are sold to investors. Corporations borrow funds for investment by issuing corporate bonds. Loans to small businesses are also financed by bundling them in long-term bonds. Securities markets bridge the needs of higher returns by savers obtaining funds from investors that are channeled to consumers and business for consumption and investment. Lowering the yields of these long-term bonds could lower costs of financing purchases of consumer durables and investment by business. The essential mechanism of transmission from lower interest rates to increases in aggregate demand is portfolio rebalancing. Withdrawal of bonds in a specific maturity segment or directly in a bond category such as currently mortgage-backed securities causes reductions in yields that are equivalent to increases in the prices of the bonds. There can be secondary increases in purchases of those bonds in private portfolios in pursuit of their increasing prices. Lower yields translate into lower costs of buying homes and consumer durables such as automobiles and also lower costs of investment for business. There are two additional intended routes of transmission.
1. Unconventional monetary policy or its expectation can increase stock market valuations (Bernanke 2010WP). Increases in equities traded in stock markets can augment perceptions of the wealth of consumers, inducing increases in consumption.
2. Unconventional monetary policy causes devaluation of the dollar relative to other currencies, which can cause increases in net exports of the US that increase aggregate economic activity (Yellen 2011AS).
Monetary policy can lower short-term interest rates quite effectively. Lowering long-term yields is somewhat more difficult. The critical issue is that monetary policy cannot ensure that increasing credit at low interest cost increases consumption and investment. There is a large variety of possible allocation of funds at low interest rates from consumption and investment to multiple risk financial assets. Monetary policy does not control how investors will allocate asset categories. A critical financial practice is to borrow at low short-term interest rates to invest in high-risk, leveraged financial assets. Investors may increase in their portfolios asset categories such as equities, emerging market equities, high-yield bonds, currencies, commodity futures and options and multiple other risk financial assets including structured products. If there is risk appetite, the carry trade from zero interest rates to risk financial assets will consist of short positions at short-term interest rates (or borrowing) and short dollar assets with simultaneous long positions in high-risk, leveraged financial assets such as equities, commodities and high-yield bonds. Low interest rates may induce increases in valuations of risk financial assets that may fluctuate in accordance with perceptions of risk aversion by investors and the public. During periods of muted risk aversion, carry trades from zero interest rates to exposures in risk financial assets cause temporary waves of inflation that may intensify instead of preventing financial instability. During periods of risk aversion such as fears of disruption of world financial markets and the global economy resulting from events such as collapse of the European Monetary Union, carry trades are unwound with sharp deterioration of valuations of risk financial assets. More technical discussion is in IA Appendix: Transmission of Unconventional Monetary Policy.
Symmetric inflation targets are temporarily of secondary priority in favor of a self-imposed single jobs mandate of easing monetary policy even with the economy growing at or close to potential output. Monetary easing by unconventional measures, including zero interest rates and outright purchases of securities for the portfolio of the central bank, is now open ended in perpetuity, or QE→∞, as provided in the statement of the meeting of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) on Sep 13, 2012 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20120913a.htm):
“To support a stronger economic recovery and to help ensure that inflation, over time, is at the rate most consistent with its dual mandate, the Committee agreed today to increase policy accommodation by purchasing additional agency mortgage-backed securities at a pace of $40 billion per month. The Committee also will continue through the end of the year its program to extend the average maturity of its holdings of securities as announced in June, and it is maintaining its existing policy of reinvesting principal payments from its holdings of agency debt and agency mortgage-backed securities in agency mortgage-backed securities. These actions, which together will increase the Committee’s holdings of longer-term securities by about $85 billion each month through the end of the year, should put downward pressure on longer-term interest rates, support mortgage markets, and help to make broader financial conditions more accommodative.
To support continued progress toward maximum employment and price stability, the Committee expects that a highly accommodative stance of monetary policy will remain appropriate for a considerable time after the economic recovery strengthens.”
Charles Evans, President of the Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago, proposed an “economic state-contingent policy” or “7/3” approach (Evans 2012 Aug 27):
“I think the best way to provide forward guidance is by tying our policy actions to explicit measures of economic performance. There are many ways of doing this, including setting a target for the level of nominal GDP. But recognizing the difficult nature of that policy approach, I have a more modest proposal: I think the Fed should make it clear that the federal funds rate will not be increased until the unemployment rate falls below 7 percent. Knowing that rates would stay low until significant progress is made in reducing unemployment would reassure markets and the public that the Fed would not prematurely reduce its accommodation.
Based on the work I have seen, I do not expect that such policy would lead to a major problem with inflation. But I recognize that there is a chance that the models and other analysis supporting this approach could be wrong. Accordingly, I believe that the commitment to low rates should be dropped if the outlook for inflation over the medium term rises above 3 percent.
The economic conditionality in this 7/3 threshold policy would clarify our forward policy intentions greatly and provide a more meaningful guide on how long the federal funds rate will remain low. In addition, I would indicate that clear and steady progress toward stronger growth is essential.”
Evans (2012Nov27) modified the “7/3” approach to a “6.5/2.5” approach:
“I have reassessed my previous 7/3 proposal. I now think a threshold of 6-1/2 percent for the unemployment rate and an inflation safeguard of 2-1/2 percent, measured in terms of the outlook for total PCE (Personal Consumption Expenditures Price Index) inflation over the next two to three years, would be appropriate.”
The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) decided at its meeting on Dec 12, 2012 to implement the “6.5/2.5” approach (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20121212a.htm):
“To support continued progress toward maximum employment and price stability, the Committee expects that a highly accommodative stance of monetary policy will remain appropriate for a considerable time after the asset purchase program ends and the economic recovery strengthens. In particular, the Committee decided to keep the target range for the federal funds rate at 0 to 1/4 percent and currently anticipates that this exceptionally low range for the federal funds rate will be appropriate at least as long as the unemployment rate remains above 6-1/2 percent, inflation between one and two years ahead is projected to be no more than a half percentage point above the Committee’s 2 percent longer-run goal, and longer-term inflation expectations continue to be well anchored.”
Unconventional monetary policy will remain in perpetuity, or QE→∞, changing to a “growth mandate.” There are two reasons explaining unconventional monetary policy of QE→∞: insufficiency of job creation to reduce unemployment/underemployment at current rates of job creation; and growth of GDP at around 1.8 percent, which is well below 3.0 percent estimated by Lucas (2011May) from 1870 to 2010. Unconventional monetary policy interprets the dual mandate of low inflation and maximum employment as mainly a “growth mandate” of forcing economic growth in the US at a rate that generates full employment. A hurdle to this “growth mandate” is that US economic growth has been at only 2.3 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 17 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2013. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the third estimate of GDP for IIIQ2013 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2013/pdf/gdp3q13_3rd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,738.0 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,356.9 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,738.0/$14,356.9 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html). As a result, there are 28.1 million unemployed or underemployed in the United States for an effective unemployment rate of 17.2 percent (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/11/global-financial-risk-mediocre-united.html). The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May).
First, total nonfarm payroll employment seasonally adjusted (SA) increased 203,000 in Nov 2013 and private payroll employment rose 196,000. The average number of nonfarm jobs created in Jan-Nov 2012 was 179,455 while the average number of nonfarm jobs created in Jan-Nov 2013 was 188,455, or increase by 5.0 percent. The average number of private jobs created in the US in Jan-Nov 2012 was 185,909 while the average in Jan-Nov 2013 was 190,091, or increase by 2.2 percent. The US labor force increased from 153.617 million in 2011 to 154.975 million in 2012 by 1.358 million or 113,167 per month. The average increase of nonfarm jobs in the ten months from Jan to Nov 2013 was 188,455, which is a rate of job creation inadequate to reduce significantly unemployment and underemployment in the United States because of 113,167 new entrants in the labor force per month with 28.1 million unemployed or underemployed. The difference between the average increase of 188,455 new private nonfarm jobs per month in the US from Jan to Nov 2013 and the 113,167 average monthly increase in the labor force from 2011 to 2012 is 75,288 monthly new jobs net of absorption of new entrants in the labor force. There are 28.1 million in job stress in the US currently. Creation of 75,288 new jobs per month net of absorption of new entrants in the labor force would require 373 months to provide jobs for the unemployed and underemployed (28.111 million divided by 75,288) or 31 years (373 divided by 12). The civilian labor force of the US in Nov 2013 not seasonally adjusted stood at 155.046 million with 10.271 million unemployed or effectively 18.452 million unemployed in this blog’s calculation by inferring those who are not searching because they believe there is no job for them for effective labor force of 163.227 million. Reduction of one million unemployed at the current rate of job creation without adding more unemployment requires 1.1 years (1 million divided by product of 75,288 by 12, which is 903,456). Reduction of the rate of unemployment to 5 percent of the labor force would be equivalent to unemployment of only 7.752 million (0.05 times labor force of 155.046 million) for new net job creation of 2.499 million (10.271 million unemployed minus 7.772 million unemployed at rate of 5 percent) that at the current rate would take 2.8 years (2.499 million divided by 0.903456). Under the calculation in this blog, there are 18.452 million unemployed by including those who ceased searching because they believe there is no job for them and effective labor force of 163.227 million. Reduction of the rate of unemployment to 5 percent of the labor force would require creating 10.164 million jobs net of labor force growth that at the current rate would take 11.4 years (18.452 million minus 0.05(163.227 million) = 10.291 million divided by 0.903456, using LF PART 66.2% and Total UEM in Table I-4). These calculations assume that there are no more recessions, defying United States economic history with periodic contractions of economic activity when unemployment increases sharply. The number employed in Nov 2013 was 144.775 million (NSA) or 2.540 million fewer people with jobs relative to the peak of 147.315 million in Jul 2007 while the civilian noninstitutional population increased from 231.958 million in Jul 2007 to 246.567 million in Nov 2013 or by 14.609 million. The number employed fell 1.7 percent from Jul 2007 to Nov 2013 while population increased 6.3 percent. There is actually not sufficient job creation in merely absorbing new entrants in the labor force because of those dropping from job searches, worsening the stock of unemployed or underemployed in involuntary part-time jobs.
There is current interest in past theories of “secular stagnation.” Alvin H. Hansen (1939, 4, 7; see Hansen 1938, 1941; for an early critique see Simons 1942) argues:
“Not until the problem of full employment of our productive resources from the long-run, secular standpoint was upon us, were we compelled to give serious consideration to those factors and forces in our economy which tend to make business recoveries weak and anaemic (sic) and which tend to prolong and deepen the course of depressions. This is the essence of secular stagnation-sick recoveries which die in their infancy and depressions which feed on themselves and leave a hard and seemingly immovable core of unemployment. Now the rate of population growth must necessarily play an important role in determining the character of the output; in other words, the composition of the flow of final goods. Thus a rapidly growing population will demand a much larger per capita volume of new residential building construction than will a stationary population. A stationary population with its larger proportion of old people may perhaps demand more personal services; and the composition of consumer demand will have an important influence on the quantity of capital required. The demand for housing calls for large capital outlays, while the demand for personal services can be met without making large investment expenditures. It is therefore not unlikely that a shift from a rapidly growing population to a stationary or declining one may so alter the composition of the final flow of consumption goods that the ratio of capital to output as a whole will tend to decline.”
The argument that anemic population growth causes “secular stagnation” in the US (Hansen 1938, 1939, 1941) is as misplaced currently as in the late 1930s (for early dissent see Simons 1942). There is currently population growth in the ages of 16 to 24 years but not enough job creation and discouragement of job searches for all ages (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/theory-and-reality-of-secular.html). This is merely another case of theory without reality with dubious policy proposals.
Inferior performance of the US economy and labor markets is the critical current issue of analysis and policy design.
Second, there are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the third estimate of GDP for IIIQ2013 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2013/pdf/gdp3q13_3rd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,738.0 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,356.9 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,738.0/$14,356.9 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html). As a result, there are 28.1 million unemployed or underemployed in the United States for an effective unemployment rate of 17.2 percent (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/11/global-financial-risk-mediocre-united.html). The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May).
The economy of the US can be summarized in growth of economic activity or GDP as decelerating from mediocre growth of 2.5 percent on an annual basis in 2010 to 1.8 percent in 2011 to 2.8 percent in 2012. The following calculations show that actual growth is around 2.0 to 2.6 percent per year. This rate is well below 3 percent per year in trend from 1870 to 2010, which the economy of the US always attained for entire cycles in expansions after events such as wars and recessions (Lucas 2011May). Revisions and enhancements of United States GDP and personal income accounts by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) provide important information on long-term growth and cyclical behavior. Table Summary provides relevant data.
- Long-term. US GDP grew at the average yearly rate of 3.3 percent from 1929 to 2012 and at 3.2 percent from 1947 to 2012. There were periodic contractions or recessions in this period but the economy grew at faster rates in the subsequent expansions, maintaining long-term economic growth at trend.
- Cycles. The combined contraction of GDP in the two almost consecutive recessions in the early 1980s is 4.7 percent. The contraction of US GDP from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 during the global recession was 4.3 percent. The critical difference in the expansion is growth at average 7.8 percent in annual equivalent in the first four quarters of recovery from IQ1983 to IVQ1983. The average rate of growth of GDP in four cyclical expansions in the postwar period is 7.7 percent. In contrast, the rate of growth in the first four quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 was only 2.7 percent. Average annual equivalent growth in the expansion from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986 was 5.4 percent and 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986. In contrast, average annual equivalent growth in the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2013 was only 2.3 percent. The US appears to have lost its dynamism of income growth and employment creation.
Table Summary, Long-term and Cyclical Growth of GDP, Real Disposable Income and Real Disposable Income per Capita
| GDP | ||
| Long-Term | ||
| 1929-2012 | 3.3 | |
| 1947-2012 | 3.2 | |
| Cyclical Contractions ∆% | ||
| IQ1980 to IIIQ1980, IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 | -4.7 | |
| IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 | -4.3 | |
| Cyclical Expansions Average Annual Equivalent ∆% | ||
| IQ1983 to IVQ1985 IQ1983-IQ1986 IQ1983-IIIQ1986 IQ1983-IVQ1986 IQ1983-IQ1987 | 5.9 5.7 5.4 5.2 5.0 | |
| First Four Quarters IQ1983 to IVQ1983 | 7.8 | |
| IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2013 | 2.3 | |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 | 2.7 | |
| Real Disposable Income | Real Disposable Income per Capita | |
| Long-Term | ||
| 1929-2012 | 3.2 | 2.0 |
| 1947-1999 | 3.7 | 2.3 |
| Whole Cycles | ||
| 1980-1989 | 3.5 | 2.6 |
| 2006-2012 | 1.4 | 0.6 |
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The revisions and enhancements of United States GDP and personal income accounts by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) also provide critical information in assessing the current rhythm of US economic growth. The economy appears to be moving at a pace from 2.0 to 2.6 percent per year. Table Summary GDP provides the data.
3. Average Annual Growth in the Past Six Quarters. GDP growth in the four quarters of 2012 and the first three quarters of 2013 accumulated to 3.9 percent. This growth is equivalent to 2.2 percent per year, obtained by dividing GDP in IIIQ2013 of $15,839.3 billion by GDP in IVQ2011 of $15,242.1 billion and compounding by 4/7: {[($15,839.3/$15,242.1)4/7 -1]100 = 2.2.
4. Average Annual Growth in the First Three Quarters of 2013. GDP growth in the first three quarters of 2013 accumulated to 1.9 percent that is equivalent to 2.6 percent in a year. This is obtained by dividing GDP in IIIQ2013 of $15,839.3 by GDP in IVQ2012 of $15,539.6 and compounding by 4/3: {[($15,839.3/$15,539.6)4/3 -1]100 = 2.6%}. The US economy grew 2.0 percent in IIIQ2013 relative to the same quarter a year earlier in IIIQ2012. Another important revelation of the revisions and enhancements is that GDP was flat in IVQ2012, which is just at the borderline of contraction. The rate of growth of GDP in the third estimate of IIIQ2013 is 4.1 percent in seasonally adjusted annual rate (SAAR). Inventory accumulation contributed 1.67 percentage points to this rate of growth. The actual rate without this impulse of unsold inventories would have been 2.43 percent, or 0.6 percent in IIIQ2013, such that annual equivalent growth in 2013 is closer to 2.0 percent {[(1.003)(1.006)(1.006)4/3-1]100 = 2.0%}, compounding the quarterly rates and converting into annual equivalent.
Table Summary GDP, US, Real GDP and Percentage Change Relative to IVQ2007 and Prior Quarter, Billions Chained 2005 Dollars and ∆%
| Real GDP, Billions Chained 2009 Dollars | ∆% Relative to IVQ2007 | ∆% Relative to Prior Quarter | ∆% | |
| IVQ2007 | 14,996.1 | NA | NA | 1.9 |
| IVQ2011 | 15,242.1 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 2.0 |
| IQ2012 | 15,381.6 | 2.6 | 0.9 | 3.3 |
| IIQ2012 | 15,427.7 | 2.9 | 0.3 | 2.8 |
| IIIQ2012 | 15,534.0 | 3.6 | 0.7 | 3.1 |
| IVQ2012 | 15,539.6 | 3.6 | 0.0 | 2.0 |
| IQ2013 | 15,583.9 | 3.9 | 0.3 | 1.3 |
| IIQ2013 | 15,679.7 | 4.6 | 0.6 | 1.6 |
| IIIQ2013 | 15,839.3 | 5.6 | 1.0 | 2.0 |
| Cumulative ∆% IQ2012 to IIIQ2013 | 3.9 | 3.9 | ||
| Annual Equivalent ∆% | 2.2 | 2.2 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
In fact, it is evident to the public that this policy will be abandoned if inflation costs rise. There is concern of the production and employment costs of controlling future inflation. Even if there is no inflation, QE→∞ cannot be abandoned because of the fear of rising interest rates. The economy would operate in an inferior allocation of resources and suboptimal growth path, or interior point of the production possibilities frontier where the optimum of productive efficiency and wellbeing is attained, because of the distortion of risk/return decisions caused by perpetual financial repression. Not even a second-best allocation is feasible with the shocks to efficiency of financial repression in perpetuity.
Current focus is on tapering quantitative easing by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC). There is sharp distinction between the two measures of unconventional monetary policy: (1) fixing of the overnight rate of fed funds at 0 to ¼ percent; and (2) outright purchase of Treasury and agency securities and mortgage-backed securities for the balance sheet of the Federal Reserve. Market are overreacting to the so-called “paring” of outright purchases to $75 billion of securities per month for the balance sheet of the Fed. What is truly important is the fixing of the overnight fed funds at 0 to ¼ percent for which there is no end in sight as evident in the FOMC statement for Dec 18, 2013 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20131218a.htm):
“To support continued progress toward maximum employment and price stability, the Committee today reaffirmed its view that a highly accommodative stance of monetary policy will remain appropriate for a considerable time after the asset purchase program ends and the economic recovery strengthens. The Committee also reaffirmed its expectation that the current exceptionally low target range for the federal funds rate of 0 to 1/4 percent will be appropriate at least as long as the unemployment rate remains above 6-1/2 percent, inflation between one and two years ahead is projected to be no more than a half percentage point above the Committee's 2 percent longer-run goal, and longer-term inflation expectations continue to be well anchored” (emphasis added).
There is a critical phrase in the statement of Sep 19, 2013 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20130918a.htm): “but mortgage rates have risen further.” Did the increase of mortgage rates influence the decision of the FOMC not to taper? Is FOMC “communication” and “guidance” successful?
In delivering the biannual report on monetary policy (Board of Governors 2013Jul17), Chairman Bernanke (2013Jul17) advised Congress that:
“Instead, we are providing additional policy accommodation through two distinct yet complementary policy tools. The first tool is expanding the Federal Reserve's portfolio of longer-term Treasury securities and agency mortgage-backed securities (MBS); we are currently purchasing $40 billion per month in agency MBS and $45 billion per month in Treasuries. We are using asset purchases and the resulting expansion of the Federal Reserve's balance sheet primarily to increase the near-term momentum of the economy, with the specific goal of achieving a substantial improvement in the outlook for the labor market in a context of price stability. We have made some progress toward this goal, and, with inflation subdued, we intend to continue our purchases until a substantial improvement in the labor market outlook has been realized. We are relying on near-zero short-term interest rates, together with our forward guidance that rates will continue to be exceptionally low--our second tool--to help maintain a high degree of monetary accommodation for an extended period after asset purchases end, even as the economic recovery strengthens and unemployment declines toward more-normal levels. In appropriate combination, these two tools can provide the high level of policy accommodation needed to promote a stronger economic recovery with price stability.
The Committee's decisions regarding the asset purchase program (and the overall stance of monetary policy) depend on our assessment of the economic outlook and of the cumulative progress toward our objectives. Of course, economic forecasts must be revised when new information arrives and are thus necessarily provisional.”
Friedman (1953) argues there are three lags in effects of monetary policy: (1) between the need for action and recognition of the need; (2) the recognition of the need and taking of actions; and (3) taking of action and actual effects. Friedman (1953) finds that the combination of these lags with insufficient knowledge of the current and future behavior of the economy causes discretionary economic policy to increase instability of the economy or standard deviations of real income σy and prices σp. Policy attempts to circumvent the lags by policy impulses based on forecasts. We are all naïve about forecasting. Data are available with lags and revised to maintain high standards of estimation. Policy simulation models estimate economic relations with structures prevailing before simulations of policy impulses such that parameters change as discovered by Lucas (1977). Economic agents adjust their behavior in ways that cause opposite results from those intended by optimal control policy as discovered by Kydland and Prescott (1977). Advance guidance attempts to circumvent expectations by economic agents that could reverse policy impulses but is of dubious effectiveness. There is strong case for using rules instead of discretionary authorities in monetary policy (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/search?q=rules+versus+authorities).
The key policy is maintaining fed funds rate between 0 and ¼ percent. An increase in fed funds rates could cause flight out of risk financial markets worldwide. There is no exit from this policy without major financial market repercussions. Indefinite financial repression induces carry trades with high leverage, risks and illiquidity.
Unconventional monetary policy drives wide swings in allocations of positions into risk financial assets that generate instability instead of intended pursuit of prosperity without inflation. There is insufficient knowledge and imperfect tools to maintain the gap of actual relative to potential output constantly at zero while restraining inflation in an open interval of (1.99, 2.0). Symmetric targets appear to have been abandoned in favor of a self-imposed single jobs mandate of easing monetary policy even with the economy growing at or close to potential output that is actually a target of growth forecast. The impact on the overall economy and the financial system of errors of policy are magnified by large-scale policy doses of trillions of dollars of quantitative easing and zero interest rates. The US economy has been experiencing financial repression as a result of negative real rates of interest during nearly a decade and programmed in monetary policy statements until 2015 or, for practical purposes, forever. The essential calculus of risk/return in capital budgeting and financial allocations has been distorted. If economic perspectives are doomed until 2015 such as to warrant zero interest rates and open-ended bond-buying by “printing” digital bank reserves (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/12/is-fed-printing-money-what-are.html; see Shultz et al 2012), rational investors and consumers will not invest and consume until just before interest rates are likely to increase. Monetary policy statements on intentions of zero interest rates for another three years or now virtually forever discourage investment and consumption or aggregate demand that can increase economic growth and generate more hiring and opportunities to increase wages and salaries. The doom scenario used to justify monetary policy accentuates adverse expectations on discounted future cash flows of potential economic projects that can revive the economy and create jobs. If it were possible to project the future with the central tendency of the monetary policy scenario and monetary policy tools do exist to reverse this adversity, why the tools have not worked before and even prevented the financial crisis? If there is such thing as “monetary policy science”, why it has such poor record and current inability to reverse production and employment adversity? There is no excuse of arguing that additional fiscal measures are needed because they were deployed simultaneously with similar ineffectiveness.
In remarkable anticipation in 2005, Professor Raghuram G. Rajan (2005) warned of low liquidity and high risks of central bank policy rates approaching the zero bound (Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 218-9). Professor Rajan excelled in a distinguished career as an academic economist in finance and was chief economist of the International Monetary Fund (IMF). Shefali Anand and Jon Hilsenrath, writing on Oct 13, 2013, on “India’s central banker lobbies Fed,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702304330904579133530766149484?KEYWORDS=Rajan), interviewed Raghuram G Rajan, who is the current Governor of the Reserve Bank of India, which is India’s central bank (http://www.rbi.org.in/scripts/AboutusDisplay.aspx). In this interview, Rajan argues that central banks should avoid unintended consequences on emerging market economies of inflows and outflows of capital triggered by monetary policy. Portfolio reallocations induced by combination of zero interest rates and risk events stimulate carry trades that generate wide swings in world capital flows.
Professor Ronald I. McKinnon (2013Oct27), writing on “Tapering without tears—how to end QE3,” on Oct 27, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702304799404579153693500945608?KEYWORDS=Ronald+I+McKinnon), finds that the major central banks of the world have fallen into a “near-zero-interest-rate trap.” World economic conditions are weak such that exist from the zero interest rate trap could have adverse effects on production, investment and employment. The maintenance of interest rates near zero creates long-term near stagnation. The proposal of Professor McKinnon is credible, coordinated increase of policy interest rates toward 2 percent. Professor John B. Taylor at Stanford University, writing on “Economic failures cause political polarization,” on Oct 28, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702303442004579121010753999086?KEYWORDS=John+B+Taylor), analyzes that excessive risks induced by near zero interest rates in 2003-2004 caused the financial crash. Monetary policy continued in similar paths during and after the global recession with resulting political polarization worldwide.
Carry trades induced by zero interest rates increase the volatility of inflation σp and real income σy. World inflation waves originating in carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures and options deteriorate the sales prices of producing and investing companies net of costs of inputs and real income of consumers. The main objective of monetary policy is providing for financial stability. Unconventional monetary policy creates economic instability with higher volatilities of prices and real income as well as financial instability with major oscillations of risk financial assets. Carry trades induced by zero interest rates cause alternating improvements and deteriorations of net margins of sales prices less costs of raw materials and real income of consumers, disrupting decisions on production, investment and consumption.
At the confirmation hearing on nomination for Chair of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Vice Chair Yellen (2013Nov14 http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20131114a.htm), states needs and intentions of policy:
“We have made good progress, but we have farther to go to regain the ground lost in the crisis and the recession. Unemployment is down from a peak of 10 percent, but at 7.3 percent in October, it is still too high, reflecting a labor market and economy performing far short of their potential. At the same time, inflation has been running below the Federal Reserve's goal of 2 percent and is expected to continue to do so for some time.
For these reasons, the Federal Reserve is using its monetary policy tools to promote a more robust recovery. A strong recovery will ultimately enable the Fed to reduce its monetary accommodation and reliance on unconventional policy tools such as asset purchases. I believe that supporting the recovery today is the surest path to returning to a more normal approach to monetary policy.”
In his classic restatement of the Keynesian demand function in terms of “liquidity preference as behavior toward risk,” James Tobin (http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/economic-sciences/laureates/1981/tobin-bio.html) identifies the risks of low interest rates in terms of portfolio allocation (Tobin 1958, 86):
“The assumption that investors expect on balance no change in the rate of interest has been adopted for the theoretical reasons explained in section 2.6 rather than for reasons of realism. Clearly investors do form expectations of changes in interest rates and differfrom each other in their expectations. For the purposes of dynamic theory and of analysis of specific market situations, the theories of sections 2 and 3 are complementary rather than competitive. The formal apparatus of section 3 will serve just as well for a non-zero expected capital gain or loss as for a zero expected value of g. Stickiness of interest rate expectations would mean that the expected value of g is a function of the rate of interest r, going down when r goes down and rising when r goes up. In addition to the rotation of the opportunity locus due to a change in r itself, there would be a further rotation in the same direction due to the accompanying change in the expected capital gain or loss. At low interest rates expectation of capital loss may push the opportunity locus into the negative quadrant, so that the optimal position is clearly no consols, all cash. At the other extreme, expectation of capital gain at high interest rates would increase sharply the slope of the opportunity locus and the frequency of no cash, all consols positions, like that of Figure 3.3. The stickier the investor's expectations, the more sensitive his demand for cash will be to changes in the rate of interest (emphasis added).”
Tobin (1969) provides more elegant, complete analysis of portfolio allocation in a general equilibrium model. The major point is equally clear in a portfolio consisting of only cash balances and a perpetuity or consol. Let g be the capital gain, r the rate of interest on the consol and re the expected rate of interest. The rates are expressed as proportions. The price of the consol is the inverse of the interest rate, (1+re). Thus, g = [(r/re) – 1]. The critical analysis of Tobin is that at extremely low interest rates there is only expectation of interest rate increases, that is, dre>0, such that there is expectation of capital losses on the consol, dg<0. Investors move into positions combining only cash and no consols. Valuations of risk financial assets would collapse in reversal of long positions in carry trades with short exposures in a flight to cash. There is no exit from a central bank created liquidity trap without risks of financial crash and another global recession. The net worth of the economy depends on interest rates. In theory, “income is generally defined as the amount a consumer unit could consume (or believe that it could) while maintaining its wealth intact” (Friedman 1957, 10). Income, Y, is a flow that is obtained by applying a rate of return, r, to a stock of wealth, W, or Y = rW (Ibid). According to a subsequent statement: “The basic idea is simply that individuals live for many years and that therefore the appropriate constraint for consumption is the long-run expected yield from wealth r*W. This yield was named permanent income: Y* = r*W” (Darby 1974, 229), where * denotes permanent. The simplified relation of income and wealth can be restated as:
W = Y/r (10
Equation (1) shows that as r goes to zero, r→0, W grows without bound, W→∞. Unconventional monetary policy lowers interest rates to increase the present value of cash flows derived from projects of firms, creating the impression of long-term increase in net worth. An attempt to reverse unconventional monetary policy necessarily causes increases in interest rates, creating the opposite perception of declining net worth. As r→∞, W = Y/r →0. There is no exit from unconventional monetary policy without increasing interest rates with resulting pain of financial crisis and adverse effects on production, investment and employment.
Table IA-1 provides annual equivalent rates of inflation for producer price indexes followed in this blog of countries and regions that account for close to three quarters of world output. The behavior of the US producer price index in 2011 and into 2012-2013 shows neatly multiple waves. (1) In Jan-Apr 2011, without risk aversion, US producer prices rose at the annual equivalent rate of 10.0 percent. (2) After risk aversion, producer prices increased in the US at the annual equivalent rate of 1.8 percent in May-Jun 2011. (3) From Jul to Sep 2011, under alternating episodes of risk aversion, producer prices increased at the annual equivalent rate of 4.9 percent. (4) Under the pressure of risk aversion because of the European debt crisis, US producer prices increased at the annual equivalent rate of 0.6 percent in Oct-Nov 2011. (5) From Dec 2011 to Jan 2012, US producer were flat at the annual equivalent rate of 0.0 percent. (6) Inflation of producer prices returned with 2.4 percent annual equivalent in Feb-Mar 2012. (7) With return of risk aversion from the European debt crisis, producer prices fell at the annual equivalent rate of 4.7 percent in Apr-May 2012. (8) New positions in commodity futures even with continuing risk aversion caused annual equivalent inflation of 3.0 percent in Jun-Jul 2012. (9) Relaxed risk aversion because of announcement of sovereign bond buying by the European Central Bank induced carry trades that resulted in annual equivalent producer price inflation in the US of 12.7 percent in Aug-Sep 2012. (10) Renewed risk aversion caused unwinding of carry trades of zero interest rates to commodity futures exposures with annual equivalent inflation of minus 3.2 percent in Oct-Dec 2012. (10) In Jan-Feb 2013, producer prices rose at the annual equivalent rate of 5.5 percent with more relaxed risk aversion at the margin. (11) Return of risk aversion resulted in annual equivalent inflation of minus 7.5 percent in Mar-Apr 2013 with worldwide portfolio reallocation toward equities and high-yield bonds and away from commodity exposures. (12) Inflation of producer prices returned at 5.2 percent in annual equivalent in May-Aug 2013. (13) Continuing reallocation of investment portfolios away from commodities into equities is causing downward pressure on prices. In Sep-Nov 2013, the US producer price index fell at the annual equivalent rate of 1.6 percent. Resolution of the European debt crisis if there is not an unfavorable growth event with political development in China would result in jumps of valuations of risk financial assets. Increases in commodity prices would cause the same high producer price inflation experienced in Jan-Apr 2011 and Aug-Sep 2012. An episode of exploding commodity prices could ignite inflationary expectations that would result in an inflation phenomenon of costly resolution. There are nine producer-price indexes in Table IA-1 for seven countries (two for the UK) and one region (euro area) showing very similar behavior. Zero interest rates without risk aversion cause increases in commodity prices that in turn increase input prices at a faster pace than output prices. Producer price inflation rose at very high rates during the first part of 2011 for the US, Japan, China, Euro Area, Germany, France, Italy and the UK when risk aversion was contained. With the increase in risk aversion in May and Jun 2011, inflation moderated because carry trades were unwound. Producer price inflation returned after Jul 2011, with alternating bouts of risk aversion. In the final months of the year producer price inflation collapsed because of the disincentive to exposures in commodity futures resulting from fears of resolution of the European debt crisis. There is renewed worldwide inflation in the early part of 2012 with subsequent collapse because of another round of sharp risk aversion and relative portfolio reallocation away from commodities and into equities and high-yield bonds. Sharp worldwide jump in producer prices occurred recently because of the combination of zero interest rates forever or QE→∞ with temporarily relaxed risk aversion. Producer prices were moderating or falling in the final months of 2012 because of renewed risk aversion that causes unwinding of carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures exposures. In the first months of 2013, new carry trades caused higher worldwide inflation. Lower inflation recently originates in portfolio reallocations away from commodity exposures into equities. Unconventional monetary policy fails in stimulating the overall real economy, merely introducing undesirable instability because monetary authorities cannot control allocation of floods of money at zero interest rates to carry trades into risk financial assets. The economy is constrained in a suboptimal allocation of resources that is perpetuated along a continuum of short-term periods. The result is long-term or dynamic inefficiency in the form of a trajectory of economic activity that is lower than what would be attained with rules instead of discretionary authorities in monetary policy (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/rules-versus-discretionary-authorities.html).
Table IA-1, Annual Equivalent Rates of Producer Price Indexes
| INDEX 2011-2013 | AE ∆% |
| US Producer Price Index | |
| AE ∆% Sep-Nov 2013 | -1.6 |
| AE ∆% May-Aug 2013 | 5.2 |
| AE ∆% Mar-Apr 2013 | -7.5 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Feb 2013 | 5.5 |
| AE ∆% Oct-Dec 2012 | -3.2 |
| AE ∆% Aug-Sep 2012 | 12.7 |
| AE ∆% Jun-Jul 2012 | 3.0 |
| AE ∆% Apr-May 2012 | -4.7 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Mar 2012 | 2.4 |
| AE ∆% Dec 2011-Jan-2012 | 0.0 |
| AE ∆% Oct-Nov 2011 | 0.6 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Sep 2011 | 4.9 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun 2011 | 1.8 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr 2011 | 10.0 |
| Japan Corporate Goods Price Index | |
| AE ∆% Nov 2013 | 1.2 |
| AE ∆% Oct 2013 | -1.2 |
| AE ∆% Dec 2012-Sep 2013 | 3.3 |
| AE ∆% Oct-Nov 2012 | -3.0 |
| AE ∆% Aug-Sep 2012 | 2.4 |
| AE ∆% May-Jul 2012 | -5.5 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Apr 2012 | 2.0 |
| AE ∆% Dec 2011-Jan 2012 | -0.6 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Nov 2011 | -2.1 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun 2011 | -1.2 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr 2011 | 5.8 |
| China Producer Price Index | |
| AE ∆% Oct-Nov 2013 | 0.0 |
| AE ∆% Aug-Sep 2013 | 1.8 |
| AE ∆% Mar-Jul 2013 | -4.9 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Feb 2013 | 2.4 |
| AE ∆% Nov-Dec 2012 | -1.2 |
| AE ∆% Oct 2012 | 2.4 |
| AE ∆% May-Sep 2012 | -5.8 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Apr 2012 | 2.4 |
| AE ∆% Dec 2011-Jan 2012 | -2.4 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Nov 2011 | -3.1 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Jun 2011 | 6.4 |
| Euro Zone Industrial Producer Prices | |
| AE ∆% Oct 2013 | -5.8 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Sep 2013 | 1.6 |
| AE ∆% Mar-Jun 2013 | -3.5 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Feb 2013 | 2.4 |
| AE ∆% Nov-Dec 2012 | -2.4 |
| AE ∆% Sep-Oct 2012 | 0.6 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Aug 2012 | 6.8 |
| AE ∆% Apr-Jun 2012 | -2.4 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Mar 2012 | 7.9 |
| AE ∆% Oct-Dec 2011 | 0.4 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Sep 2011 | 2.4 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun 2011 | -0.6 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr 2011 | 11.3 |
| Germany Producer Price Index | |
| AE ∆% Oct-Nov | -1.8 NSA –1.8 SA |
| AE ∆% Sep | 3.7 NSA 0.0 SA |
| AE ∆% May-Aug 2013 | -1.8 NSA –0.6 SA |
| AE ∆% Feb-Apr 2013 | -2.4 NSA –3.2 SA |
| AE ∆% Jan 2013 | 7.4 NSA 1.2 SA |
| AE ∆% Oct-Dec 2012 | -0.8 NSA 1.2 SA |
| AE ∆% Aug-Sep 2012 | 4.3 NSA 3.0 SA |
| AE ∆% May-Jul 2012 | -2.8 NSA –0.4 SA |
| AE ∆% Feb-Apr 2012 | 4.9 NSA 2.0 SA |
| AE ∆% Dec 2011-Jan 2012 | 0.0 NSA –0.6 SA |
| AE ∆% Oct-Nov 2011 | 0.6 NSA 1.8 SA |
| AE ∆% Jul-Sep 2011 | 2.4 NSA 3.2 SA |
| AE ∆% May-Jun 2011 | 0.6 NSA 3.7 SA |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr 2011 | 10.4 NSA 6.2 SA |
| France Producer Price Index for the French Market | |
| AE ∆% Oct 2013 | -2.4 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Sep 2013 | 4.9 |
| AE ∆% Apr-Jun 2013 | -11.0 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Mar 2013 | 4.9 |
| AE ∆% Nov-Dec 2012 | -4.1 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Oct 2012 | 7.4 |
| AE ∆% Apr-Jun 2012 | -4.3 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Mar 2012 | 6.2 |
| AE ∆% Oct-Dec 2011 | 2.8 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Sep 2011 | 3.7 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun 2011 | -1.8 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr 2011 | 10.4 |
| Italy Producer Price Index | |
| AE ∆% Oct 2013 | -14.5 |
| AE ∆% Jun-Sep 2013 | 0.3 |
| AE ∆% Apr-May 2013 | -3.5 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Mar 2013 | 1.2 |
| AE ∆% Sep 2012-Jan 2013 | -5.2 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Aug 2012 | 9.4 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun 2012 | -0.6 |
| AE ∆% Mar-Apr 2012 | 6.8 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Feb 2012 | 8.1 |
| AE ∆% Oct-Dec 2011 | 2.0 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Sep 2011 | 4.9 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun 2011 | 1.8 |
| AE ∆% Jan-April 2011 | 10.7 |
| UK Output Prices | |
| AE ∆% Sep-Nov 2013 | 2.0 |
| AE ∆% Jun-Aug 2013 | 2.0 |
| AE ∆% Apr-May 2013 | -0.6 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Mar 2013 | 4.9 |
| AE ∆% Nov-Dec 2012 | -2.4 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Oct 2012 | 4.1 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun 2012 | -3.5 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Apr 2012 | 5.3 |
| AE ∆% Nov 2011-Jan-2012 | 1.2 |
| AE ∆% May-Oct 2011 | 1.6 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr 2011 | 10.0 |
| UK Input Prices | |
| AE ∆% Aug-Nov 2013 | -8.6 |
| AE ∆% Jul 2013 | 18.2 |
| AE ∆% Mar-Jun 2013 | -9.5 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Feb 2013 | 24.6 |
| AE ∆% Sep-Dec 2012 | 3.0 |
| AE ∆% Aug 2012 | 23.9 |
| AE ∆% Apr-Jul 2012 | -16.1 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Mar 2012 | 14.9 |
| AE ∆% Nov-Dec 2011 | 0.0 |
| AE ∆% May-Oct 2011 | -1.3 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr 2011 | 30.6 |
| AE ∆% Oct-Dec 2010 | 31.8 |
AE: Annual Equivalent
Sources: http://www.bls.gov/cpi/ http://www.boj.or.jp/en/
http://www.stats.gov.cn/enGliSH/
http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/statistics/search_database
https://www.destatis.de/EN/Homepage.html
http://www.insee.fr/en/default.asp
http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/index.html
Similar world inflation waves are in the behavior of consumer price indexes of six countries and the euro zone in Table IA-2. US consumer price inflation shows similar waves. (1) Under risk appetite in Jan-Apr 2011, consumer prices increased at the annual equivalent rate of 4.6 percent. (2) Risk aversion caused the collapse of inflation to annual equivalent 3.0 percent in May-Jun 2011. (3) Risk appetite drove the rate of consumer price inflation in the US to 3.3 percent in Jul-Sep 2011. (4) Gloomier views of carry trades caused the collapse of inflation in Oct-Nov 2011 to annual equivalent 0.6 percent. (5) Consumer price inflation resuscitated with increased risk appetite at annual equivalent of 1.2 percent in Dec 2011 to Jan 2012. (6) Consumer price inflation returned at 2.4 percent annual equivalent in Feb-Apr 2012. (7) Under renewed risk aversion, annual equivalent consumer price inflation in the US was 0.0 percent in May-Jul 2012. (8) Inflation jumped to annual equivalent 4.9 percent in Aug-Oct 2012. (9) Unwinding of carry trades caused negative annual equivalent inflation of 0.8 percent in Nov 2012-Jan 2013 but some countries experienced higher inflation in Dec 2012 and Jan 2013. (10) Inflation jumped again with annual equivalent inflation of 8.7 percent in Feb 2013 in a mood of relaxed risk aversion. (11) Inflation fell at 3.5 percent annual equivalent in Mar-Apr 2013. (12) Inflation rose at 2.7 percent in annual equivalent in May-Sep 2013. (3) Inflation fell at the annual equivalent rate of 0.6 percent in Oct-Nov 2013. Inflationary expectations can be triggered in one of these episodes of accelerating inflation because of commodity carry trades induced by unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates in perpetuity or QE→∞ in almost continuous time. Alternating episodes of increase and decrease of inflation introduce uncertainty in household planning that frustrates consumption and home buying. Announcement of purchases of impaired sovereign bonds by the European Central Bank relaxed risk aversion that induced carry trades into commodity exposures, increasing prices of food, raw materials and energy. There is similar behavior in all the other consumer price indexes in Table IA-2. China’s CPI increased at annual equivalent 8.3 percent in Jan-Mar 2011, 2.0 percent in Apr-Jun, 2.9 percent in Jul-Nov and resuscitated at 5.8 percent annual equivalent in Dec 2011 to Mar 2012, declining to minus 3.9 percent in Apr-Jun 2012 but resuscitating at 4.1 percent in Jul-Sep 2012, declining to minus 1.2 percent in Oct 2012 and 0.0 percent in Oct-Nov 2012. High inflation in China at annual equivalent 5.5 percent in Nov-Dec 2012 is attributed to inclement winter weather that caused increases in food prices. Continuing pressure of food prices caused annual equivalent inflation of 12.2 percent in China in Dec 2012 to Feb 2013. Inflation in China fell at annual equivalent 10.3 percent in Mar 2013 and increased at annual equivalent 2.4 percent in Apr 2013. Adjustment to lower food prices caused annual equivalent inflation of minus 7.0 percent in May 2013 and minus 3.5 percent in annual equivalent in May-Jun 2013. Inflation in China returned at annual equivalent 4.6 percent in Jul-Oct 2013, falling at 1.2 percent in annual equivalent in Nov 2013. The euro zone harmonized index of consumer prices (HICP) increased at annual equivalent 5.2 percent in Jan-Apr 2011, minus 2.4 percent in May-Jul 2011, 4.3 percent in Aug-Dec 2011, minus 3.0 percent in Dec 2011-Jan 2012 and then 9.6 percent in Feb-Apr 2012, falling to minus 2.8 percent annual equivalent in May-Jul 2012 but resuscitating at 5.3 percent in Aug-Oct 2012. The recent shock of risk aversion forced minus 2.4 percent annual equivalent in Nov 2012. As in several European countries, annual equivalent inflation jumped to 4.9 percent in the euro area in Dec 2012. The HICP price index fell at annual equivalent 11.4 percent in Jan 2013 and increased at 10.0 percent in Feb-Mar 2013. As in most countries and regions, euro zone inflation fell at the annual equivalent rate of 1.2 percent in Apr 2013. Prices in the euro zone rose at 1.2 percent in May-Jun 2013. Inflation in the euro zone fell at annual equivalent 5.8 percent in Jul 2013. Inflation returned in the euro zone at annual equivalent 3.7 percent in Aug-Sep 2013. Euro zone inflation fell at the annual equivalent rate of 2.4 percent in Oct-Nov 2013. The price indexes of the largest members of the euro zone, Germany, France and Italy, and the euro zone as a whole, exhibit the same inflation waves. The United Kingdom CPI increased at annual equivalent 6.5 percent in Jan-Apr 2011, falling to only 0.4 percent in May-Jul 2011 and then increasing at 4.6 percent in Aug-Nov 2011. UK consumer prices fell at 0.6 percent annual equivalent in Dec 2011 to Jan 2012 but increased at 6.2 percent annual equivalent from Feb to Apr 2012. In May-Jun 2012, with renewed risk aversion, UK consumer prices fell at the annual equivalent rate of minus 3.0 percent. Inflation returned in the UK at average annual equivalent of 4.5 percent in Jul-Dec 2012 with inflation in Oct 2012 caused mostly by increases of university tuition fees. Inflation returned at 4.5 percent annual equivalent in Jul-Dec 2012 and was higher in annual equivalent inflation of producer prices in the UK in Jul-Oct 2012 at 4.1 percent for output prices and 23.9 percent for input prices in Aug 2012 (see Table IA-1). Consumer prices in the UK fell at annual equivalent 5.8 percent in Jan 2013. Inflation returned in the UK with annual equivalent 4.3 percent in Feb-May 2013 and fell at 1.2 percent in Jun-Jul 2013. UK annual equivalent inflation returned at 3.0 percent in Aug-Nov 2013.
Table IA-2, Annual Equivalent Rates of Consumer Price Indexes
| Index 2011-2013 | AE ∆% |
| US Consumer Price Index | |
| AE ∆% Oct-Nov 2013 | -0.6 |
| AE ∆% May-Sep 2013 | 2.7 |
| AE ∆% Mar-Apr 2013 | -3.5 |
| AE ∆% Feb 2013 | 8.7 |
| AE ∆% Nov 2012-Jan 2013 | -0.8 |
| AE ∆% Aug-Oct 2012 | 4.9 |
| AE ∆% May-Jul 2012 | 0.0 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Apr 2012 | 2.4 |
| AE ∆% Dec 2011-Jan 2012 | 1.2 |
| AE ∆% Oct-Nov 2011 | 0.6 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Sep 2011 | 3.3 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun 2011 | 3.0 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr 2011 | 4.6 |
| China Consumer Price Index | |
| AE ∆% Nov 2013 | -1.2 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Oct 2013 | 4.6 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun 2013 | -3.5 |
| AE ∆% Apr 2013 | 2.4 |
| AE ∆% Mar 2013 | -10.3 |
| AE ∆% Dec 2012-Feb 2013 | 12.2 |
| AE ∆% Oct-Nov 2012 | 0.0 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Sep 2012 | 4.1 |
| AE ∆% Apr-Jun 2012 | -3.9 |
| AE ∆% Dec 2011-Mar 2012 | 5.8 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Nov 2011 | 2.9 |
| AE ∆% Apr-Jun 2011 | 2.0 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Mar 2011 | 8.3 |
| Euro Zone Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices | |
| AE ∆% Oct-Nov | -2.4 |
| AE ∆% Aug-Sep 2013 | 3.7 |
| AE ∆% Jul 2013 | -5.8 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun 2013 | 1.2 |
| AE ∆% Apr 2013 | -1.2 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Mar 2013 | 10.0 |
| AE ∆% Jan 2013 | -11.4 |
| AE ∆% Dec 2012 | 4.9 |
| AE ∆% Nov 2012 | -2.4 |
| AE ∆% Aug-Oct 2012 | 5.3 |
| AE ∆% May-Jul 2012 | -2.8 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Apr 2012 | 9.6 |
| AE ∆% Dec 2011-Jan 2012 | -3.0 |
| AE ∆% Aug-Nov 2011 | 4.3 |
| AE ∆% May-Jul 2011 | -2.4 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr 2011 | 5.2 |
| Germany Consumer Price Index | |
| AE ∆% Nov 2013 | 2.4 NSA 2.4 SA |
| AE ∆% Oct 2013 | -2.4 NSA 0.0 SA |
| AE ∆% Aug-Sep 2013 | 0.0 NSA 0.0 SA |
| AE ∆% May-Jul 2013 | 4.1 NSA 3.7 SA |
| AE ∆% Apr 2013 | -5.8 NSA 0.0 SA |
| AE ∆% Feb-Mar 2013 | 6.8 NSA 1.2 SA |
| AE ∆% Jan 2013 | -5.8 NSA 0.0 SA |
| AE ∆% Sep-Dec 2012 | 1.5 NSA 1.8 SA |
| AE ∆% Jul-Aug 2012 | 4.9 NSA 3.0 SA |
| AE ∆% May-Jun 2012 | -1.2 NSA 0.6 SA |
| AE ∆% Feb-Apr 2012 | 4.5 NSA 2.4 SA |
| AE ∆% Dec 2011-Jan 2012 | 0.6 NSA 1.8 SA |
| AE ∆% Jul-Nov 2011 | 1.7 NSA 1.9 SA |
| AE ∆% May-Jun 2011 | 0.6 NSA 3.0 SA |
| AE ∆% Feb-Apr 2011 | 3.0 NSA 2.4 SA |
| France Consumer Price Index | |
| AE ∆% Sep-Nov 2013 | -1.2 |
| AE ∆% Aug 2013 | 6.2 |
| AE ∆% Jul 2013 | -3.5 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun 2013 | 1.8 |
| AE ∆% Apr 2013 | -1.2 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Mar 2013 | 6.8 |
| AE ∆% Nov 2012-Jan 2013 | -1.6 |
| AE ∆% Aug-Oct 2012 | 2.4 |
| AE ∆% May-Jul 2012 | -2.0 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Apr 2012 | 5.3 |
| AE ∆% Dec 2011-Jan 2012 | 0.0 |
| AE ∆% Aug-Nov 2011 | 2.7 |
| AE ∆% May-Jul 2011 | -0.8 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr 2011 | 4.3 |
| Italy Consumer Price Index | |
| AE ∆% Sep-Nov 2013 | -3.2 |
| AE ∆% Dec 2012-Aug 2013 | 2.0 |
| AE ∆% Sep-Nov 2012 | -0.8 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Aug 2012 | 3.0 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun 2012 | 1.2 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Apr 2012 | 5.7 |
| AE ∆% Dec 2011-Jan 2012 | 4.3 |
| AE ∆% Oct-Nov 2011 | 3.0 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Sep 2011 | 2.4 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun 2011 | 1.2 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr 2011 | 4.9 |
| UK Consumer Price Index | |
| AE ∆% Aug-Nov 2013 | 3.0 |
| AE ∆% Jun-Jul 2013 | -1.2 |
| AE ∆% Feb-May 2013 | 4.3 |
| AE ∆% Jan 2013 | -5.8 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Dec 2012 | 4.5 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun 2012 | -3.0 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Apr 2012 | 6.2 |
| AE ∆% Dec 2011-Jan 2012 | -0.6 |
| AE ∆% Aug-Nov 2011 | 4.6 |
| AE ∆% May-Jul 2011 | 0.4 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr 2011 | 6.5 |
AE: Annual Equivalent
Sources: http://www.bls.gov/cpi/
http://www.stats.gov.cn/enGliSH/
http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/statistics/search_database
https://www.destatis.de/EN/Homepage.html
http://www.insee.fr/en/default.asp
IA Appendix: Transmission of Unconventional Monetary Policy. Janet L. Yellen, Vice Chair of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, provides analysis of the policy of purchasing large amounts of long-term securities for the Fed’s balance sheet. The new analysis provides three channels of transmission of quantitative easing to the ultimate objectives of increasing growth and employment and increasing inflation to “levels of 2 percent or a bit less that most Committee participants judge to be consistent, over the long run, with the FOMC’s dual mandate” (Yellen 2011AS, 4, 7):
“There are several distinct channels through which these purchases tend to influence aggregate demand, including a reduced cost of credit to consumers and businesses, a rise in asset prices that boost household wealth and spending, and a moderate change in the foreign exchange value of the dollar that provides support to net exports.”
The new analysis by Yellen (2011AS) is considered below in four separate subsections: IA1 Theory; IA2 Policy; IA3 Evidence; and IA4 Unwinding Strategy.
IA1 Theory. The transmission mechanism of quantitative easing can be analyzed in three different forms. (1) Portfolio choice theory. General equilibrium value theory was proposed by Hicks (1935) in analyzing the balance sheets of individuals and institutions with assets in the capital segment consisting of money, debts, stocks and productive equipment. Net worth or wealth would be comparable to income in value theory. Expected yield and risk would be the constraint comparable to income in value theory. Markowitz (1952) considers a portfolio of individual securities with mean μp and variance σp. The Markowitz (1952, 82) rule states that “investors would (or should” want to choose a portfolio of combinations of (μp, σp) that are efficient, which are those with minimum variance or risk for given expected return μp or more and maximum expected μp for given variance or risk or less. The more complete model of Tobin (1958) consists of portfolio choice of monetary assets by maximizing a utility function subject to a budget constraint. Tobin (1961, 28) proposes general equilibrium analysis of the capital account to derive choices of capital assets in balance sheets of economic units with the determination of yields in markets for capital assets with the constraint of net worth. A general equilibrium model of choice of portfolios was developed simultaneously by various authors (Hicks 1962; Treynor 1962; Sharpe 1964; Lintner 1965; Mossin 1966). If shocks such as by quantitative easing displace investors from the efficient frontier, there would be reallocations of portfolios among assets until another efficient point is reached. Investors would bid up the prices or lower the returns (interest plus capital gains) of long-term assets targeted by quantitative easing, causing the desired effect of lowering long-term costs of investment and consumption.
(2) General Equilibrium Theory. Bernanke and Reinhart (2004, 88) argue that “the possibility monetary policy works through portfolio substitution effects, even in normal times, has a long intellectual history, having been espoused by both Keynesians (James Tobin 1969) and monetarists (Karl Brunner and Allan Meltzer 1973).” Andres et al. (2004) explain the Tobin (1969) contribution by optimizing agents in a general-equilibrium model. Both Tobin (1969) and Brunner and Meltzer (1973) consider capital assets to be gross instead of perfect substitutes with positive partial derivatives of own rates of return and negative partial derivatives of cross rates in the vector of asset returns (interest plus principal gain or loss) as argument in portfolio balancing equations (see Pelaez and Suzigan 1978, 113-23). Tobin (1969, 26) explains portfolio substitution after monetary policy:
“When the supply of any asset is increased, the structure of rates of return, on this and other assets, must change in a way that induces the public to hold the new supply. When the asset’s own rate can rise, a large part of the necessary adjustment can occur in this way. But if the rate is fixed, the whole adjustment must take place through reductions in other rates or increases in prices of other assets. This is the secret of the special role of money; it is a secret that would be shared by any other asset with a fixed interest rate.”
Andrés et al. (2004, 682) find that in their multiple-channels model “base money expansion now matters for the deviations of long rates from the expected path of short rates. Monetary policy operates by both the expectations channel (the path of current and expected future short rates) and this additional channel. As in Tobin’s framework, interest rates spreads (specifically, the deviations from the pure expectations theory of the term structure) are an endogenous function of the relative quantities of assets supplied.”
The interrelation among yields of default-free securities is measured by the term structure of interest rates. This schedule of interest rates along time incorporates expectations of investors. (Cox, Ingersoll and Ross 1985). The expectations hypothesis postulates that the expectations of investors about the level of future spot rates influence the level of current long-term rates. The normal channel of transmission of monetary policy in a recession is to lower the target of the fed funds rate that will lower future spot rates through the term structure and also the yields of long-term securities. The expectations hypothesis is consistent with term premiums (Cox, Ingersoll and Ross 1981, 774-7) such as liquidity to compensate for risk or uncertainty about future events that can cause changes in prices or yields of long-term securities (Hicks 1935; see Cox, Ingersoll and Ross 1981, 784; Chung et al. 2011, 22).
(3) Preferred Habitat. Another approach is by the preferred-habitat models proposed by Culbertson (1957, 1963) and Modigliani and Sutch (1966). This approach is formalized by Vayanos and Vila (2009). The model considers investors or “clientele” who do not abandon their segment of operations unless there are extremely high potential returns and arbitrageurs who take positions to profit from discrepancies. Pension funds matching benefit liabilities would operate in segments above 15 years; life insurance companies operate around 15 years or more; and asset managers and bank treasury managers are active in maturities of less than 10 years (Ibid, 1). Hedge funds, proprietary trading desks and bank maturity transformation activities are examples of potential arbitrageurs. The role of arbitrageurs is to incorporate “information about current and future short rates into bond prices” (Ibid, 12). Suppose monetary policy raises the short-term rate above a certain level. Clientele would not trade on this information, but arbitrageurs would engage in carry trade, shorting bonds and investing at the short-term rate, in a “roll-up” trade, resulting in decline of bond prices or equivalently increases in yields. This is a situation of an upward-sloping yield curve. If the short-term rate were lowered, arbitrageurs would engage in carry trade borrowing at the short-term rate and going long bonds, resulting in an increase in bond prices or equivalently decline in yields, or “roll-down” trade. The carry trade is the mechanism by which bond yields adjust to changes in current and expected short-term interest rates. The risk premiums of bonds are positively associated with the slope of the term structure (Ibid, 13). Fama and Bliss (1987, 689) find with data for 1964-85 that “1-year expected returns for US Treasury maturities to 5 years, measured net of the interest rate on a 1-year bond, vary through time. Expected term premiums are mostly positive during good times but mostly negative during recessions.” Vayanos and Vila (2009) develop a model with two-factors, the short-term rate and demand or quantity. The term structure moves because of shocks of short-term rates and demand. An important finding is that demand or quantity shocks are largest for intermediate and long maturities while short-rate shocks are largest for short-term maturities.
IA2 Policy. A simplified analysis could consider the portfolio balance equations Aij = f(r, x) where Aij is the demand for i = 1,2,∙∙∙n assets from j = 1,2, ∙∙∙m sectors, r the 1xn vector of rates of return, ri, of n assets and x a vector of other relevant variables. Tobin (1969) and Brunner and Meltzer (1973) assume imperfect substitution among capital assets such that the own first derivatives of Aij are positive, demand for an asset increases if its rate of return (interest plus capital gains) is higher; and cross first derivatives are negative, demand for an asset decreases if the rate of return of alternative assets increases. Theoretical purity would require the estimation of the complete model with all rates of return. In practice, it may be impossible to observe all rates of return such as in the critique of Roll (1976). Policy proposals by the Fed have been focused on the likely impact of withdrawals of stocks of securities in specific segments, that is, of effects of one or several specific rates of return among the n possible rates. There have been at least seven approaches on the role of monetary policy in purchasing long-term securities that have increased the classes of rates of return targeted by the Fed:
(1) Suspension of Auctions of 30-year Treasury Bonds. Auctions of 30-year Treasury bonds were suspended between 2001 and 2005. This was Treasury policy not Fed policy. The effects were similar to those of quantitative easing: withdrawal of supply from the segment of 30-year bonds would result in higher prices or lower yields for close-substitute mortgage-backed securities with resulting lower mortgage rates. The objective was to encourage refinancing of house loans that would increase family income and consumption by freeing income from reducing monthly mortgage payments.
(2) Purchase of Long-term Securities by the Fed. Between Nov 2008 and Mar 2009 the Fed announced the intention of purchasing $1750 billion of long-term securities: $600 billion of agency mortgage-backed securities and agency debt announced on Nov 25 and $850 billion of agency mortgaged-backed securities and agency debt plus $300 billion of Treasury securities announced on Mar 18, 2009 (Yellen 2011AS, 5-6). The objective of buying mortgage-backed securities was to lower mortgage rates that would “support the housing sector” (Bernanke 2009SL). The FOMC statement on Dec 16, 2008 informs that: “over the next few quarters the Federal Reserve will purchase large quantities of agency debt and mortgage-backed securities to provide support to the mortgage and housing markets, and its stands ready to expand its purchases of agency debt and mortgage-backed securities as conditions warrant” (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20081216b.htm). The Mar 18, 2009, statement of the FOMC explained that: “to provide greater support to mortgage lending and housing markets, the Committee decided today to increase the size of the Federal Reserve’s balance sheet further by purchasing up to an additional $750 billion of agency mortgage-backed securities, bringing its total purchases of these securities up to $1.25 trillion this year, and to increase its purchase of agency debt this year by up to $100 billion to a total of up to $200 billion. Moreover, to help improve conditions in private credit markets, the Committee decided to purchase up to $300 billion of longer-term Treasury securities over the next six months” (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20090318a.htm). Policy changed to increase prices or reduce yields of mortgage-backed securities and Treasury securities with the objective of supporting housing markets and private credit markets by lowering costs of housing and long-term private credit.
(3) Portfolio Reinvestment. On Aug 10, 2010, the FOMC statement explains the reinvestment policy: “to help support the economic recovery in a context of price stability, the Committee will keep constant the Federal Reserve’s holdings of securities at their current level by reinvesting principal payments from agency debt and agency mortgage-backed securities in long-term Treasury securities. The Committee will continue to roll over the Federal Reserve’s holdings of Treasury securities as they mature” (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20100810a.htm). The objective of policy appears to be supporting conditions in housing and mortgage markets with slow transfer of the portfolio to Treasury securities that would support private-sector markets.
(4) Increasing Portfolio. As widely anticipated, the FOMC decided on Dec 3, 2010: “to promote a stronger pace of economic recovery and to help ensure that inflation, over time, is at levels consistent with its mandate, the Committee decided today to expand its holdings of securities. The Committee will maintain its existing policy of reinvesting principal payments from its securities holdings. In addition, the Committee intends to purchase a further $600 billion of longer-term Treasury securities by the end of the second quarter of 2011, a pace of about $75 billion per month” (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20101103a.htm). The emphasis appears to shift from housing markets and private-sector credit markets to the general economy, employment and preventing deflation.
(5) Increasing Stock Market Valuations. Chairman Bernanke (2010WP) explained on Nov 4 the objectives of purchasing an additional $600 billion of long-term Treasury securities and reinvesting maturing principal and interest in the Fed portfolio. Long-term interest rates fell and stock prices rose when investors anticipated the new round of quantitative easing. Growth would be promoted by easier lending such as for refinancing of home mortgages and more investment by lower corporate bond yields. Consumers would experience higher confidence as their wealth in stocks rose, increasing outlays. Income and profits would rise and, in a “virtuous circle,” support higher economic growth. Bernanke (2000) analyzes the role of stock markets in central bank policy (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 99-100). Fed policy in 1929 increased interest rates to avert a gold outflow and failed to prevent the deepening of the banking crisis without which the Great Depression may not have occurred. In the crisis of Oct 19, 1987, Fed policy supported stock and futures markets by persuading banks to extend credit to brokerages. Collapse of stock markets would slow consumer spending.
(6) Devaluing the Dollar. Yellen (2011AS, 6) broadens the effects of quantitative easing by adding dollar devaluation: “there are several distinct channels through which these purchases tend to influence aggregate demand, including a reduced cost of credit to consumers and businesses, a rise in asset prices that boosts household wealth and spending, and a moderate change in the foreign exchange value of the dollar that provides support to net exports.”
(7) Let’s Twist Again Monetary Policy. The term “operation twist” grew out of the dance “twist” popularized by successful musical performer Chubby Chekker (http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=aWaJ0s0-E1o). Meulendyke (1998, 39) describes the coordination of policy by Treasury and the FOMC in the beginning of the Kennedy administration in 1961 (see Modigliani and Sutch 1966, 1967; http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/09/imf-view-of-world-economy-and-finance.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/09/collapse-of-household-income-and-wealth.html):
“In 1961, several developments led the FOMC to abandon its “bills only” restrictions. The new Kennedy administration was concerned about gold outflows and balance of payments deficits and, at the same time, it wanted to encourage a rapid recovery from the recent recession. Higher rates seemed desirable to limit the gold outflows and help the balance of payments, while lower rates were wanted to speed up economic growth.
To deal with these problems simultaneously, the Treasury and the FOMC attempted to encourage lower long-term rates without pushing down short-term rates. The policy was referred to in internal Federal Reserve documents as “operation nudge” and elsewhere as “operation twist.” For a few months, the Treasury engaged in maturity exchanges with trust accounts and concentrated its cash offerings in shorter maturities.
The Federal Reserve participated with some reluctance and skepticism, but it did not see any great danger in experimenting with the new procedure.
It attempted to flatten the yield curve by purchasing Treasury notes and bonds while selling short-term Treasury securities. The domestic portfolio grew by $1.7 billion over the course of 1961. Note and bond holdings increased by a substantial $8.8 billion, while certificate of indebtedness holdings fell by almost $7.4 billion (Table 2). The extent to which these actions changed the yield curve or modified investment decisions is a source of dispute, although the predominant view is that the impact on yields was minimal. The Federal Reserve continued to buy coupon issues thereafter, but its efforts were not very aggressive. Reference to the efforts disappeared once short-term rates rose in 1963. The Treasury did not press for continued Fed purchases of long-term debt. Indeed, in the second half of the decade, the Treasury faced an unwanted shortening of its portfolio. Bonds could not carry a coupon with a rate above 4 1/4 percent, and market rates persistently exceeded that level. Notes—which were not subject to interest rate restrictions—had a maximum maturity of five years; it was extended to seven years in 1967.”
As widely anticipated by markets, perhaps intentionally, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) decided at its meeting on Sep 21 that it was again “twisting time” (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20110921a.htm):
“Information received since the Federal Open Market Committee met in August indicates that economic growth remains slow. Recent indicators point to continuing weakness in overall labor market conditions, and the unemployment rate remains elevated. Household spending has been increasing at only a modest pace in recent months despite some recovery in sales of motor vehicles as supply-chain disruptions eased. Investment in nonresidential structures is still weak, and the housing sector remains depressed. However, business investment in equipment and software continues to expand. Inflation appears to have moderated since earlier in the year as prices of energy and some commodities have declined from their peaks. Longer-term inflation expectations have remained stable.
Consistent with its statutory mandate, the Committee seeks to foster maximum employment and price stability. The Committee continues to expect some pickup in the pace of recovery over coming quarters but anticipates that the unemployment rate will decline only gradually toward levels that the Committee judges to be consistent with its dual mandate. Moreover, there are significant downside risks to the economic outlook, including strains in global financial markets. The Committee also anticipates that inflation will settle, over coming quarters, at levels at or below those consistent with the Committee's dual mandate as the effects of past energy and other commodity price increases dissipate further. However, the Committee will continue to pay close attention to the evolution of inflation and inflation expectations.
To support a stronger economic recovery and to help ensure that inflation, over time, is at levels consistent with the dual mandate, the Committee decided today to extend the average maturity of its holdings of securities. The Committee intends to purchase, by the end of June 2012, $400 billion of Treasury securities with remaining maturities of 6 years to 30 years and to sell an equal amount of Treasury securities with remaining maturities of 3 years or less. This program should put downward pressure on longer-term interest rates and help make broader financial conditions more accommodative. The Committee will regularly review the size and composition of its securities holdings and is prepared to adjust those holdings as appropriate.
To help support conditions in mortgage markets, the Committee will now reinvest principal payments from its holdings of agency debt and agency mortgage-backed securities in agency mortgage-backed securities. In addition, the Committee will maintain its existing policy of rolling over maturing Treasury securities at auction.
The Committee also decided to keep the target range for the federal funds rate at 0 to 1/4 percent and currently anticipates that economic conditions--including low rates of resource utilization and a subdued outlook for inflation over the medium run--are likely to warrant exceptionally low levels for the federal funds rate at least through mid-2013.
The Committee discussed the range of policy tools available to promote a stronger economic recovery in a context of price stability. It will continue to assess the economic outlook in light of incoming information and is prepared to employ its tools as appropriate.”
The FOMC decided at its meeting on Jun 20, 2012, to continue “Let’s Twist Again” monetary policy until the end of 2012 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20120620a.htm http://www.newyorkfed.org/markets/opolicy/operating_policy_120620.html):
“The Committee also decided to continue through the end of the year its program to extend the average maturity of its holdings of securities. Specifically, the Committee intends to purchase Treasury securities with remaining maturities of 6 years to 30 years at the current pace and to sell or redeem an equal amount of Treasury securities with remaining maturities of approximately 3 years or less. This continuation of the maturity extension program should put downward pressure on longer-term interest rates and help to make broader financial conditions more accommodative. The Committee is maintaining its existing policy of reinvesting principal payments from its holdings of agency debt and agency mortgage-backed securities in agency mortgage-backed securities. The Committee is prepared to take further action as appropriate to promote a stronger economic recovery and sustained improvement in labor market conditions in a context of price stability.”
IA3 Evidence. There are multiple empirical studies on the effectiveness of quantitative easing that have been covered in past posts such as (Andrés et al. 2004, D’Amico and King 2010, Doh 2010, Gagnon et al. 2010, Hamilton and Wu 2010). On the basis of simulations of quantitative easing with the FRB/US econometric model, Chung et al (2011, 28-9) find that:
”Lower long-term interest rates, coupled with higher stock market valuations and a lower foreign exchange value of the dollar, provide a considerable stimulus to real activity over time. Phase 1 of the program by itself is estimated to boost the level of real GDP almost 2 percent above baseline by early 2012, while the full program raises the level of real GDP almost 3 percent by the second half of 2012. This boost to real output in turn helps to keep labor market conditions noticeably better than they would have been without large scale asset purchases. In particular, the model simulations suggest that private payroll employment is currently 1.8 million higher, and the unemployment rate ¾ percentage point lower, that would otherwise be the case. These benefits are predicted to grow further over time; by 2012, the incremental contribution of the full program is estimated to be 3 million jobs, with an additional 700,000 jobs provided by the most recent phase of the program alone.”
An additional conclusion of these simulations is that quantitative easing may have prevented actual deflation. Empirical research is continuing.
IA4 Unwinding Strategy. Fed Vice-Chair Yellen (2011AS) considers four concerns on quantitative easing discussed below in turn. First, Excessive Inflation. Yellen (2011AS, 9-12) considers concerns that quantitative easing could result in excessive inflation because fast increases in aggregate demand from quantitative easing could raise the rate of inflation, posing another problem of adjustment with tighter monetary policy or higher interest rates. The Fed estimates significant slack of resources in the economy as measured by the difference of four percentage points between the high current rate of unemployment above 9 percent and the NAIRU (non-accelerating rate of unemployment) of 5.75 percent (Ibid, 2). Thus, faster economic growth resulting from quantitative easing would not likely result in upward trend of costs as resources are bid up competitively. The Fed monitors frequently slack indicators and is committed to maintaining inflation at a “level of 2 percent or a bit less than that” (Ibid, 13), say, in the narrow open interval (1.9, 2.1).
Second, Inflation and Bank Reserves. On Jan 12, 2012, the line “Reserve Bank credit” in the Fed balance sheet stood at $2450.6 billion, or $2.5 trillion, with the portfolio of long-term securities of $2175.7 billion, or $2.2 trillion, composed of $987.6 billion of notes and bonds, $49.7 billion of inflation-adjusted notes and bonds, $146.3 billion of Federal agency debt securities, and $992.1 billion of mortgage-backed securities; reserves balances with Federal Reserve Banks stood at $1095.5 billion, or $1.1 trillion (http://federalreserve.gov/releases/h41/current/h41.htm#h41tab1). The concern addressed by Yellen (2011AS, 12-4) is that this high level of reserves could eventually result in demand growth that could accelerate inflation. Reserves would be excessively high relative to the levels before the recession. Reserves of depository institutions at the Federal Reserve Banks rose from $45.6 billion in Aug 2008 to $1084.8 billion in Aug 2010, not seasonally adjusted, multiplying by 23.8 times, or to $1038.2 billion in Nov 2010, multiplying by 22.8 times. The monetary base consists of the monetary liabilities of the government, composed largely of currency held by the public plus reserves of depository institutions at the Federal Reserve Banks. The monetary base not seasonally adjusted, or issue of money by the government, rose from $841.1 billion in Aug 2008 to $1991.1 billion or by 136.7 percent and to $1968.1 billion in Nov 2010 or by 133.9 percent (http://federalreserve.gov/releases/h3/hist/h3hist1.pdf). Policy can be viewed as creating government monetary liabilities that ended mostly in reserves of banks deposited at the Fed to purchase $2.1 trillion of long-term securities or assets, which in nontechnical language would be “printing money” (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/12/is-fed-printing-money-what-are.html). The marketable debt of the US government in Treasury securities held by the public stood at $8.7 trillion on Nov 30, 2010 (http://www.treasurydirect.gov/govt/reports/pd/mspd/2010/opds112010.pdf). The current holdings of long-term securities by the Fed of $2.1 trillion, in the process of converting fully into Treasury securities, are equivalent to 24 percent of US government debt held by the public, and would represent 29.9 percent with the new round of quantitative easing if all the portfolio of the Fed, as intended, were in Treasury securities. Debt in Treasury securities held by the public on Dec 31, 2009, stood at $7.2 trillion (http://www.treasurydirect.gov/govt/reports/pd/mspd/2009/opds122009.pdf), growing on Nov 30, 2010, to $1.5 trillion or by 20.8 percent. In spite of this growth of bank reserves, “the 12-month change in core PCE [personal consumption expenditures] prices dropped from about 2 ½ percent in mid-2008 to around 1 ½ percent in 2009 and declined further to less than 1 percent by late 2010” (Yellen 2011AS, 3). The PCE price index, excluding food and energy, is around 0.8 percent in the past 12 months, which could be, in the Fed’s view, too close for comfort to negative inflation or deflation. Yellen (2011AS, 12) agrees “that an accommodative monetary policy left in place too long can cause inflation to rise to undesirable levels” that would be true whether policy was constrained or not by “the zero bound on interest rates.” The FOMC is monitoring and reviewing the “asset purchase program regularly in light of incoming information” and will “adjust the program as needed to meet its objectives” (Ibid, 12). That is, the FOMC would withdraw the stimulus once the economy is closer to full capacity to maintain inflation around 2 percent. In testimony at the Senate Committee on the Budget, Chairman Bernanke stated that “the Federal Reserve has all the tools its needs to ensure that it will be able to smoothly and effectively exit from this program at the appropriate time” (http://federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/bernanke20110107a.htm). The large quantity of reserves would not be an obstacle in attaining the 2 percent inflation level. Yellen (2011A, 13-4) enumerates Fed tools that would be deployed to withdraw reserves as desired: (1) increasing the interest rate paid on reserves deposited at the Fed currently at 0.25 percent per year; (2) withdrawing reserves with reverse sale and repurchase agreement in addition to those with primary dealers by using mortgage-backed securities; (3) offering a Term Deposit Facility similar to term certificates of deposit for member institutions; and (4) sale or redemption of all or parts of the portfolio of long-term securities. The Fed would be able to increase interest rates and withdraw reserves as required to attain its mandates of maximum employment and price stability.
Third, Financial Imbalances. Fed policy intends to lower costs to business and households with the objective of stimulating investment and consumption generating higher growth and employment. Yellen (2011A, 14-7) considers a possible consequence of excessively reducing interest rates: “a reasonable fear is that this process could go too far, encouraging potential borrowers to employ excessive leverage to take advantage of low financing costs and leading investors to accept less compensation for bearing risks as they seek to enhance their rates of return in an environment of very low yields. This concern deserves to be taken seriously, and the Federal Reserve is carefully monitoring financial indicators for signs of potential threats to financial stability.” Regulation and supervision would be the “first line of defense” against imbalances threatening financial stability but the Fed would also use monetary policy to check imbalances (Yellen 2011AS, 17).
Fourth, Adverse Effects on Foreign Economies. The issue is whether the now recognized dollar devaluation would promote higher growth and employment in the US at the expense of lower growth and employment in other countries.
IB United States Inflation. There are two subsections. IC Long-term US inflation analyzes data on inflation over the long run. ID Current US inflation analyzes current inflation in the United States.
IC Long-term US Inflation. Key percentage average yearly rates of the US economy on growth and inflation are provided in Table I-1 updated with release of new data. The choice of dates prevents the measurement of long-term potential economic growth because of two recessions from IQ2001 (Mar) to IVQ2001 (Nov) with decline of GDP of 0.3 percent and the drop in GDP of 4.3 percent in the recession from IVQ2007 (Dec) to IIQ2009 (June) (http://www.nber.org/cycles.html) followed with unusually low economic growth for an expansion phase after recession (Section I and earlierhttp://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html). US economic growth has been at only 2.3 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 17 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2013. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the third estimate of GDP for IIIQ2013 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2013/pdf/gdp3q13_3rd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,738.0 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,356.9 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,738.0/$14,356.9 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html). As a result, there are 28.1 million unemployed or underemployed in the United States for an effective unemployment rate of 17.2 percent (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/11/global-financial-risk-mediocre-united.html). The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). In the period from 1929 to 2012 the average growth rate of GDP was 3.3 percent and 3.2 percent between 1947 to 2012, which is almost the same as 3.0 percent from 1870 to 2010 measured by Lucas (2011May), as shown in Table I-1. From 1929 to 2012, nominal GDP grew at the average rate of 6.3 percent and 6.6 percent from 1947 to 2012. The implicit deflator increased at the average rate of 2.9 percent from 1929 to 2012 and at 3.3 percent from 1947 to 2012. Between 2000 and 2012, real GDP grew at the average rate of 1.7 percent per year, nominal GDP at 3.9 percent and the implicit deflator at 2.1 percent. The annual average rate of CPI increase was 3.2 percent from 1913 to 2012 and 3.7 percent from 1947 to 2012. Between 2000 and 2012, the average rate of CPI inflation was 2.4 percent per year and 2.0 percent excluding food and energy. From 2000 to 2013, the average rate of CPI inflation was 2.3 percent and 2.0 percent excluding food and energy. The average annual rate of PPI inflation was 3.1 percent from 1947 to 2012. PPI inflation increased at 2.8 percent per year on average from 2000 to 2012, 2.6 percent on average from 2000 to 2013 and at 1.8 percent excluding food and energy from 2000 to 2012 and 1.7 percent from 2000 to 2013. Producer price inflation of finished energy goods increased at average 5.4 percent between 2000 and 2012 and 5.0 percent between 2000 and 2013. There is also inflation in international trade. Import prices increased at 2.8 percent per year between 2000 and 2012 and 2.4 percent between 2000 and 2013. The commodity price shock is revealed by inflation of import prices of petroleum increasing at 10.8 percent per year between 2000 and 2012 and at 9.7 percent between 2000 and 2013. Import prices excluding petroleum increased at the average rate of 1.3 percent from 2000 to 2012 and at 1.1 percent from 2000 to 2013. The average percentage rates of increase of import prices excluding fuels are at 1.9 percent for 2002 to 2012 and 1.6 percent for 2002 to 2013. Export prices rose at the average rate of 2.4 percent between 2000 and 2012 and at 2.1 percent from 2000 to 2013. What spared the US of sharper decade-long deterioration of the terms of trade, (export prices)/(import prices), was its diversification and competitiveness in agriculture. Agricultural export prices grew at the average yearly rate of 7.0 percent from 2000 to 2012 and at 5.9 percent from 2000 to 2013. US nonagricultural export prices rose at 2.0 percent per year from 2000 to 2012 and at 1.8 percent from 2000 to 2013. The share of petroleum imports in US trade far exceeds that of agricultural exports. Unconventional monetary policy inducing carry trades in commodities has deteriorated US terms of trade, prices of exports relative to prices of imports, tending to restrict growth of US aggregate real income. These dynamic inflation rates are not similar to those for the economy of Japan where inflation was negative in seven of the 10 years in the 2000s. There is no reality of the proposition of need of unconventional monetary policy in the US because of deflation panic.
Table I-1, US, Average Growth Rates of Real and Nominal GDP, Consumer Price Index, Producer Price Index and Import and Export Prices, Percent per Year
| Real GDP | 2000-2012: 1.7% 1929-2012: 3.3% 1947-2012: 3.2% |
| Nominal GDP | 2000-2012: 3.9% 1929-2012: 6.3% 1947-2012: 6.6% |
| Implicit Price Deflator | 2000-2012: 2.1% 1929-2012: 2.9% 1947-2012: 3.3% |
| CPI | 2000-2012: 2.4% Annual 1913-2012: 3.2% 1947-2012: 3.7% |
| CPI ex Food and Energy | 2000-2012: 2.0% |
| PPI | 2000-2012: 2.8% Annual 1947-2012: 3.1% |
| PPI ex Food and Energy | 2000-2012: 1.8% |
| PPI Finished Energy Goods | 2000-2012: 5.4% 2000-2013: 5.0% |
| Import Prices | 2000-2012: 2.8% |
| Import Prices of Petroleum and Petroleum Products | 2000-2012: 10.8% |
| Import Prices Excluding Petroleum | 2000-2012: 1.3% |
| Import Prices Excluding Fuels | 2002-2012: 1.9% |
| Export Prices | 2000-2012: 2.4% |
| Agricultural Export Prices | 2000-2012: 7.0% |
| Nonagricultural Export Prices | 2000-2012: 2.0% |
Note: rates for price indexes in the row beginning with “CPI” and ending in the row “Nonagricultural Export Prices” are for Nov 2000 to Nov 2012 and for Nov 2000 to Nov 2013 using not seasonally adjusted indexes. Import prices excluding fuels are not available before Dec 2001.
Sources: http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm http://www.bls.gov/ppi/ http://www.bls.gov/cpi/ http://www.bls.gov/mxp/home.htm
Unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates and large-scale purchases of long-term securities for the balance sheet of the central bank is proposed to prevent deflation. The data of CPI inflation of all goods and CPI inflation excluding food and energy for the past six decades show only one negative change by 0.4 percent in the CPI all goods annual index in 2009. There is no other year of negative annual yearly change in the CPI excluding food and energy measuring annual inflation (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/08/world-financial-turbulence-global.html). Zero interest rates and quantitative easing are designed to lower costs of borrowing for investment and consumption, increase stock market valuations and devalue the dollar. In practice, the carry trade is from zero interest rates to a large variety of risk financial assets including commodities. Resulting commodity price inflation squeezes family budgets and deteriorates the terms of trade with negative effects on aggregate demand and employment. Excessive valuations of risk financial assets eventually result in crashes of financial markets with possible adverse effects on economic activity and employment.
The history of producer price inflation in the past five decades does not provide evidence of deflation. The finished core PPI does not register even one single year of decline. The headline PPI experienced only six isolated cases of decline since the 1960s (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/08/world-financial-turbulence-global.html):
-0.3 percent in 1963,
-1.4 percent in 1986,
-0.8 percent in 1998,
-1.3 percent in 2002
-2.6 percent in 2009.
Deflation should show persistent cases of decline of prices and not isolated events. Fear of deflation in the US has caused a distraction of monetary policy. Symmetric inflation targets around 2 percent in the presence of multiple lags in effect of monetary policy and imperfect knowledge and forecasting are mostly unfeasible and likely to cause price and financial instability instead of desired price and financial stability.
Chart I-1 provides US nominal GDP from 1929 to 2012. The chart disguises the decline of nominal GDP during the 1930s from $104.6 billion in 1929 to $57.2 billion in 1933 or by 45.3 percent (data from the US Bureau of Economic Analysis at http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). The level of nominal GDP reached $102.9 billion in 1940 and exceeded the $104.6 billion of 1929 only with $129.4 billion in 1941. The only major visible bump in the chart occurred in the recession of IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 with revised cumulative decline of real GDP of 4.3 percent. US nominal GDP fell from $14,720.3 billion in 2008 to $14,417.9 billion in 2009 or by 2.1 percent but rose to $14,958.3 billion in 2010 or by 3.7 percent, to $15,533.8 billion in 2011 for an additional 3.8 percent for cumulative increase of 7.7 percent relative to 2009 and to $16,244.6 billion in 2012 for an additional 4.6 percent and cumulative increase of 12.7 percent relative to 2009. US nominal GDP increased from $14,480.3 in 2007 to $16,244.6 billion in 2012 or by 12.2 percent (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). Tendency for deflation would be reflected in persistent bumps. In contrast, during the Great Depression in the four years of 1929 to 1933, GDP in constant dollars fell 26.3 percent cumulatively and fell 45.3 percent in current dollars (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 150-2, Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2009b), 205-7). The comparison of the global recession after 2007 with the Great Depression is entirely misleading (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/risks-of-zero-interest-rates-mediocre.html).
Chart I-1, US, Nominal GDP 1929-2012
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-2 provides US real GDP from 1929 to 2012. The chart also disguises the Great Depression of the 1930s. In the four years of 1929 to 1933, GDP in constant dollars fell 26.3 percent cumulatively and fell 45.3 percent in current dollars (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 150-2, Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2009b), 205-7; data from the US Bureau of Economic Analysis at http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). Persistent deflation threatening real economic activity would also be reflected in the series of long-term growth of real GDP. There is no such behavior in Chart I-2 except for periodic recessions in the US economy that have occurred throughout history.
Chart I-2, US, Real GDP 1929-2012
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Deflation would also be in evidence in long-term series of prices in the form of bumps. The GDP implicit deflator series in Chart I-3 from 1929 to 2012 shows sharp dynamic behavior over time. There is decline of the implicit price deflator of GDP by 25.8 percent from 1929 to 1933 (data from the US Bureau of Economic Analysis at http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). In contrast, the implicit price deflator of GDP of the US increased from 97.335 (2009 =100) in 2007 to 100.00 in 2009 or by 2.7 percent and increased to 105.002 in 2012 or by 5.0 percent relative to 2009 and 7.9 percent relative to 2007. The implicit price deflator of US GDP increased in every quarter from IVQ2007 to IVQ2012 with only one decline from 100.064 in IQ2009 to 99.897 in IIQ2009 or by 0.2 percent (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). Wars are characterized by rapidly rising prices followed by declines when peace is restored. The US economy is not plagued by deflation but by long-run inflation.
Chart I-3, US, GDP Implicit Price Deflator 1929-2012
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-4 provides percent change from preceding quarter in prices of GDP at seasonally adjusted annual rates (SAAR) from 1980 to 2012. There is one case of negative change by 0.6 percent in IIQ2009 that was adjustment from 2.8 percent in IIIQ2008 following 2.3 percent in IQ2008 and 1.8 percent IIQ2008 caused by carry trades from policy interest rates being moved to zero into commodity futures. These positions were reversed because of the fear of toxic assets in banks in the proposal of TARP in late 2008 (Cochrane and Zingales 2009). There has not been actual deflation or risk of deflation threatening depression in the US that would justify unconventional monetary policy.
Chart I-4, Percent Change from Preceding Period in Prices for GDP Seasonally Adjusted at Annual Rates 1980-2013
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-5 provides percent change from preceding year in prices of GDP from 1929 to 2012. There are four consecutive years of declines of prices of GDP during the Great Depression: 3.8 percent in 1930, 9.9 percent in 1931, 11.4 percent in 1932 and 2.7 percent in 1933. There were two consecutive declines of 1.8 percent in 1938 and 1.2 percent in 1939. Prices of GDP fell 0.1 percent in 1949 after increasing 12.6 percent in 1946, 11.2 percent in 1947 and 5.6 percent in 1948, which is similar to experience with wars in other countries. There are no other negative changes of annual prices of GDP in 72 years from 1939 to 2012.
Chart I-5, Percent Change from Preceding Year in Prices for Gross Domestic Product 1930-2012
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The producer price index of the US from 1947 to 2013 in Chart I-6 shows various periods of more rapid or less rapid inflation but no bumps. The major event is the decline in 2008 when risk aversion because of the global recession caused the collapse of oil prices from $148/barrel to less than $80/barrel with most other commodity prices also collapsing. The event had nothing in common with explanations of deflation but rather with the concentration of risk exposures in commodities after the decline of stock market indexes. Eventually, there was a flight to government securities because of the fears of insolvency of banks caused by statements supporting proposals for withdrawal of toxic assets from bank balance sheets in the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP), as explained by Cochrane and Zingales (2009). The bump in 2008 with decline in 2009 is consistent with the view that zero interest rates with subdued risk aversion induce carry trades into commodity futures.
Chart I-6, US, Producer Price Index, Finished Goods, NSA, 1947-2013
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-7 provides 12-month percentage changes of the producer price index from 1948 to 2013. The distinguishing event in Chart I-7 is the Great Inflation of the 1970s. The shape of the two-hump Bactrian camel of the 1970s resembles the double hump from 2007 to 2013.
Chart I-7, US, Producer Price Index, Finished Goods, 12-Month Percentage Change, NSA, 1948-2013
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Annual percentage changes of the producer price index from 1948 to 2012 are shown in Table I-1A. The producer price index fell 2.8 percent in 1949 following the adjustment to World War II and fell 0.6 percent in 1952 and 1.0 percent in 1953 around the Korean War. There are two other mild decline of 0.3 percent in 1959 and 0.3 percent in 1963. There are only few subsequent and isolated declines of the producer price index of 1.4 percent in 1986, 0.8 percent in 1998, 1.3 percent in 2002 and 2.6 percent in 2009. The decline of 2009 was caused by unwinding of carry trades in 2008 that had lifted oil prices to $140/barrel during deep global recession because of the panic of probable toxic assets in banks that would be removed with the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) (Cochrane and Zingales 2009). There is no evidence in this history of 65 years of the US producer price index suggesting that there is frequent and persistent deflation shock requiring aggressive unconventional monetary policy. The design of such anti-deflation policy could provoke price and financial instability because of lags in effect of monetary policy, model errors, inaccurate forecasts and misleading analysis of current economic conditions.
Table I-1A, US, Annual PPI Inflation ∆% 1948-2012
| Year | Annual ∆% |
| 1948 | 8.0 |
| 1949 | -2.8 |
| 1950 | 1.8 |
| 1951 | 9.2 |
| 1952 | -0.6 |
| 1953 | -1.0 |
| 1954 | 0.3 |
| 1955 | 0.3 |
| 1956 | 2.6 |
| 1957 | 3.8 |
| 1958 | 2.2 |
| 1959 | -0.3 |
| 1960 | 0.9 |
| 1961 | 0.0 |
| 1962 | 0.3 |
| 1963 | -0.3 |
| 1964 | 0.3 |
| 1965 | 1.8 |
| 1966 | 3.2 |
| 1967 | 1.1 |
| 1968 | 2.8 |
| 1969 | 3.8 |
| 1970 | 3.4 |
| 1971 | 3.1 |
| 1972 | 3.2 |
| 1973 | 9.1 |
| 1974 | 15.4 |
| 1975 | 10.6 |
| 1976 | 4.5 |
| 1977 | 6.4 |
| 1978 | 7.9 |
| 1979 | 11.2 |
| 1980 | 13.4 |
| 1981 | 9.2 |
| 1982 | 4.1 |
| 1983 | 1.6 |
| 1984 | 2.1 |
| 1985 | 1.0 |
| 1986 | -1.4 |
| 1987 | 2.1 |
| 1988 | 2.5 |
| 1989 | 5.2 |
| 1990 | 4.9 |
| 1991 | 2.1 |
| 1992 | 1.2 |
| 1993 | 1.2 |
| 1994 | 0.6 |
| 1995 | 1.9 |
| 1996 | 2.7 |
| 1997 | 0.4 |
| 1998 | -0.8 |
| 1999 | 1.8 |
| 2000 | 3.8 |
| 2001 | 2.0 |
| 2002 | -1.3 |
| 2003 | 3.2 |
| 2004 | 3.6 |
| 2005 | 4.8 |
| 2006 | 3.0 |
| 2007 | 3.9 |
| 2008 | 6.3 |
| 2009 | -2.6 |
| 2010 | 4.2 |
| 2011 | 6.0 |
| 2012 | 1.9 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The producer price index excluding food and energy from 1973 to 2013, the first historical date of availability in the dataset of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS), shows similarly dynamic behavior as the overall index, as shown in Chart I-8. There is no evidence of persistent deflation in the US PPI.
Chart I-8, US Producer Price Index, Finished Goods Excluding Food and Energy, NSA, 1973-2013
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-9 provides 12-month percentage rates of change of the finished goods index excluding food and energy. The dominating characteristic is the Great Inflation of the 1970s. The double hump illustrates how inflation may appear to be subdued and then returns with strength.
Chart I-9, US Producer Price Index, Finished Goods Excluding Food and Energy, 12-Month Percentage Change, NSA, 1974-2013
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The producer price index of energy goods from 1974 to 2013 is provided in Chart I-10. The first jump occurred during the Great Inflation of the 1970s analyzed in various comments of this blog (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/rules-versus-discretionary-authorities.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/05/slowing-growth-global-inflation-great.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/04/new-economics-of-rose-garden-turned.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/03/is-there-second-act-of-us-great.html) and in Appendix I. There is relative stability of producer prices after 1986 with another jump and decline in the late 1990s into the early 2000s. The episode of commodity price increases during a global recession in 2008 could only have occurred with interest rates dropping toward zero, which stimulated the carry trade from zero interest rates to leveraged positions in commodity futures. Commodity futures exposures were dropped in the flight to government securities after Sep 2008. Commodity future exposures were created again when risk aversion diminished around Mar 2010 after the finding that US bank balance sheets did not have the toxic assets that were mentioned in proposing TARP in Congress (see Cochrane and Zingales 2009). Fluctuations in commodity prices and other risk financial assets originate in carry trade when risk aversion ameliorates. There are also fluctuations originating in shifts in preference for asset classes such as between commodities and equities.
Chart I-10, US, Producer Price Index, Finished Energy Goods, NSA, 1974-2013
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-11 shows 12-month percentage changes of the producer price index of finished energy goods from 1975 to 2013. This index is only available after 1974 and captures only one of the humps of energy prices during the Great Inflation. Fluctuations in energy prices have occurred throughout history in the US but without provoking deflation. Two cases are the decline of oil prices in 2001 to 2002 that has been analyzed by Barsky and Kilian (2004) and the collapse of oil prices from over $140/barrel with shock of risk aversion to the carry trade in Sep 2008.
Chart I-11, US, Producer Price Index, Finished Energy Goods, 12-Month Percentage Change, NSA, 1974-2013
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-12 provides the consumer price index NSA from 1914 to 2013. The dominating characteristic is the increase in slope during the Great Inflation from the middle of the 1960s through the 1970s. There is long-term inflation in the US and no evidence of deflation risks.
Chart I-12, US, Consumer Price Index, NSA, 1914-2013
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm
Chart I-13 provides 12-month percentage changes of the consumer price index from 1914 to 2013. The only episode of deflation after 1950 is in 2009, which is explained by the reversal of speculative commodity futures carry trades that were induced by interest rates driven to zero in a shock of monetary policy in 2008. The only persistent case of deflation is from 1930 to 1933, which has little if any relevance to the contemporary United States economy. There are actually three waves of inflation in the second half of the 1960s, in the mid-1970s and again in the late 1970s. Inflation rates then stabilized in a range with only two episodes above 5 percent.
Chart I-13, US, Consumer Price Index, All Items, 12- Month Percentage Change 1914-2013
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm
Table I-2 provides annual percentage changes of United States consumer price inflation from 1914 to 2013. There have been only cases of annual declines of the CPI after wars: (1) World War I minus 10.5 percent in 1921 and minus 6.1 percent in 1922 following cumulative increases of 83.5 percent in four years from 1917 to 1920 at the average of 16.4 percent per year; (2) World War II: minus 1.2 percent in 1949 following cumulative 33.9 percent in three years from 1946 to 1948 at average 10.2 percent per year (3) minus 0.4 percent in 1955 two years after the end of the Korean War; and (4) minus 0.4 percent in 2009. The decline of 0.4 percent in 2009 followed increase of 3.8 percent in 2008 and is explained by the reversal of speculative carry trades into commodity futures that were created in 2008 as monetary policy rates were driven to zero. The reversal occurred after misleading statement on toxic assets in banks in the proposal for TARP (Cochrane and Zingales 2009). There were declines of 1.7 percent in both 1927 and 1928 during the episode of revival of rules of the gold standard. The only persistent deflationary period since 1914 was during the Great Depression in the years from 1930 to 1933 and again in 1938-1939. Fear of deflation on the basis of that experience does not justify unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates that has failed to stop deflation in Japan. Financial repression causes far more adverse effects on allocation of resources by distorting the calculus of risk/returns than alleged employment-creating effects or there would not be current recovery without jobs and hiring after zero interest rates since Dec 2008 and intended now forever in a self-imposed forecast growth and employment mandate of monetary policy.
Table I-2, US, Annual CPI Inflation ∆% 1914-2012
| Year | Annual ∆% |
| 1914 | 1.0 |
| 1915 | 1.0 |
| 1916 | 7.9 |
| 1917 | 17.4 |
| 1918 | 18.0 |
| 1919 | 14.6 |
| 1920 | 15.6 |
| 1921 | -10.5 |
| 1922 | -6.1 |
| 1923 | 1.8 |
| 1924 | 0.0 |
| 1925 | 2.3 |
| 1926 | 1.1 |
| 1927 | -1.7 |
| 1928 | -1.7 |
| 1929 | 0.0 |
| 1930 | -2.3 |
| 1931 | -9.0 |
| 1932 | -9.9 |
| 1933 | -5.1 |
| 1934 | 3.1 |
| 1935 | 2.2 |
| 1936 | 1.5 |
| 1937 | 3.6 |
| 1938 | -2.1 |
| 1939 | -1.4 |
| 1940 | 0.7 |
| 1941 | 5.0 |
| 1942 | 10.9 |
| 1943 | 6.1 |
| 1944 | 1.7 |
| 1945 | 2.3 |
| 1946 | 8.3 |
| 1947 | 14.4 |
| 1948 | 8.1 |
| 1949 | -1.2 |
| 1950 | 1.3 |
| 1951 | 7.9 |
| 1952 | 1.9 |
| 1953 | 0.8 |
| 1954 | 0.7 |
| 1955 | -0.4 |
| 1956 | 1.5 |
| 1957 | 3.3 |
| 1958 | 2.8 |
| 1959 | 0.7 |
| 1960 | 1.7 |
| 1961 | 1.0 |
| 1962 | 1.0 |
| 1963 | 1.3 |
| 1964 | 1.3 |
| 1965 | 1.6 |
| 1966 | 2.9 |
| 1967 | 3.1 |
| 1968 | 4.2 |
| 1969 | 5.5 |
| 1970 | 5.7 |
| 1971 | 4.4 |
| 1972 | 3.2 |
| 1973 | 6.2 |
| 1974 | 11.0 |
| 1975 | 9.1 |
| 1976 | 5.8 |
| 1977 | 6.5 |
| 1978 | 7.6 |
| 1979 | 11.3 |
| 1980 | 13.5 |
| 1981 | 10.3 |
| 1982 | 6.2 |
| 1983 | 3.2 |
| 1984 | 4.3 |
| 1985 | 3.6 |
| 1986 | 1.9 |
| 1987 | 3.6 |
| 1988 | 4.1 |
| 1989 | 4.8 |
| 1990 | 5.4 |
| 1991 | 4.2 |
| 1992 | 3.0 |
| 1993 | 3.0 |
| 1994 | 2.6 |
| 1995 | 2.8 |
| 1996 | 3.0 |
| 1997 | 2.3 |
| 1998 | 1.6 |
| 1999 | 2.2 |
| 2000 | 3.4 |
| 2001 | 2.8 |
| 2002 | 1.6 |
| 2003 | 2.3 |
| 2004 | 2.7 |
| 2005 | 3.4 |
| 2006 | 3.2 |
| 2007 | 2.8 |
| 2008 | 3.8 |
| 2009 | -0.4 |
| 2010 | 1.6 |
| 2011 | 3.2 |
| 2012 | 2.1 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm
Chart I-14 provides the consumer price index excluding food and energy from 1957 to 2013. There is long-term inflation in the US without episodes of persistent deflation.
Chart I-14, US, Consumer Price Index Excluding Food and Energy, NSA, 1957-2013
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm
Chart I-15 provides 12-month percentage changes of the consumer price index excluding food and energy from 1958 to 2013. There are three waves of inflation in the 1970s during the Great Inflation. There is no episode of deflation.
Chart I-15, US, Consumer Price Index Excluding Food and Energy, 12-Month Percentage Change, NSA, 1958-2013
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm
The consumer price index of housing is provided in Chart I-16. There was also acceleration during the Great Inflation of the 1970s. The index flattens after the global recession in IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. Housing prices collapsed under the weight of construction of several times more housing than needed. Surplus housing originated in subsidies and artificially low interest rates in the shock of unconventional monetary policy in 2003 to 2004 in fear of deflation.
Chart I-16, US, Consumer Price Index Housing, NSA, 1967-2013
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm
Chart I-17 provides 12-month percentage changes of the housing CPI. The Great Inflation also had extremely high rates of housing inflation. Housing is considered as potential hedge of inflation.
Chart I-17, US, Consumer Price Index, Housing, 12- Month Percentage Change, NSA, 1968-2013
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013


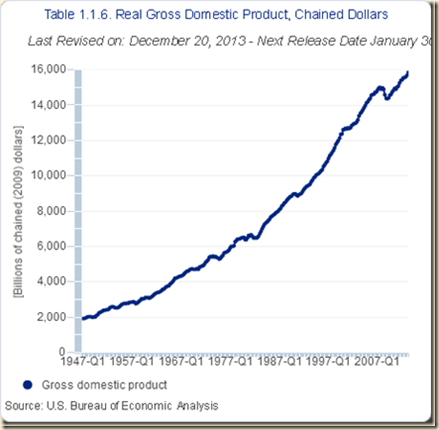







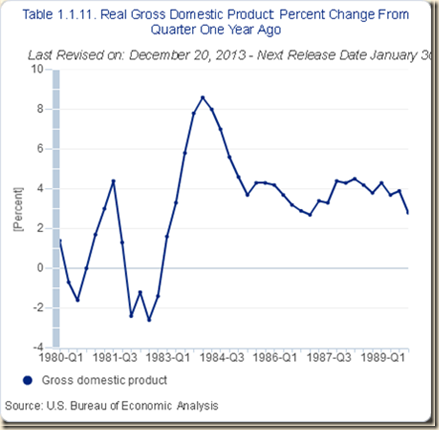




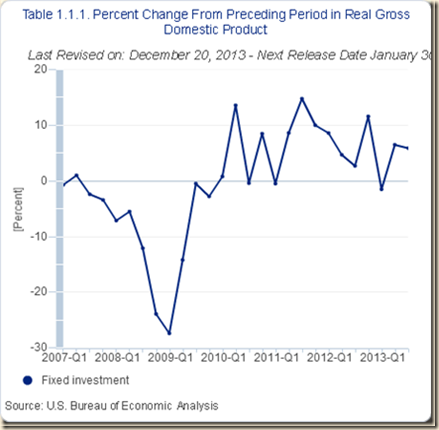


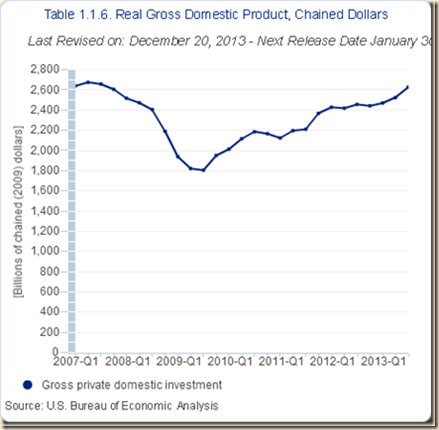



![clip_image009[1] clip_image009[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj_BzzcbmEFNd-J8VZjfwDf85UMV-W1xliz-x1SdyyRsje9aGLwYX4jBxwpbFAyO0AH7FKDI-vRwB2LksuPsvmTxSrsKR6ecZvgvucGRbImhMRFMkUmzIOWZRgOjg7EELlxYPt_u2JGPSQY/?imgmax=800)





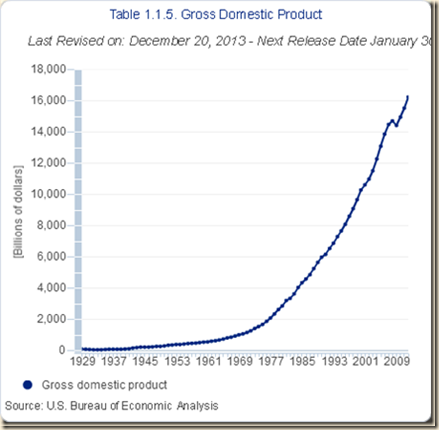









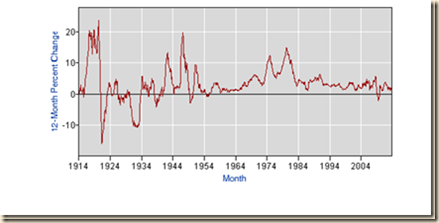
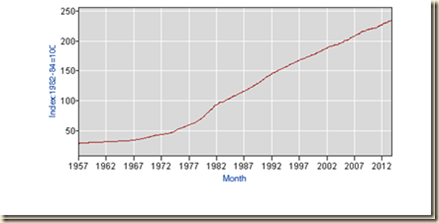



No comments:
Post a Comment