Oscillating Valuations of Risk Financial Assets, World Inflation Waves, Recovery without Hiring, Ten Million Fewer Full-time Jobs, Youth and Middle-Age Unemployment, World Cyclical Slow Growth and Global Recession Risk
Carlos M. Pelaez
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016
I World Inflation Waves
IA Appendix: Transmission of Unconventional Monetary Policy
IB1 Theory
IB2 Policy
IB3 Evidence
IB4 Unwinding Strategy
IC United States Inflation
IC Long-term US Inflation
ID Current US Inflation
IE Theory and Reality of Economic History, Cyclical Slow Growth Not Secular Stagnation
II Recovery without Hiring
IA1 Hiring Collapse
IA2 Labor Underutilization
ICA3 Ten Million Fewer Full-time Jobs
IA4 Theory and Reality of Cyclical Slow Growth Not Secular Stagnation: Youth and
Middle-Age Unemployment
III World Financial Turbulence
IIIA Financial Risks
IIIE Appendix Euro Zone Survival Risk
IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation
IV Global Inflation
V World Economic Slowdown
VA United States
VB Japan
VC China
VD Euro Area
VE Germany
VF France
VG Italy
VH United Kingdom
VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets
VII Economic Indicators
VIII Interest Rates
IX Conclusion
References
Appendixes
Appendix I The Great Inflation
IIIB Appendix on Safe Haven Currencies
IIIC Appendix on Fiscal Compact
IIID Appendix on European Central Bank Large Scale Lender of Last Resort
IIIG Appendix on Deficit Financing of Growth and the Debt Crisis
IIIGA Monetary Policy with Deficit Financing of Economic Growth
IIIGB Adjustment during the Debt Crisis of the 1980s
IE Theory and Reality of Economic History, Cyclical Slow Growth Not Secular Stagnation and Monetary Policy Based on Fear of Deflation. Fear of deflation as had occurred during the Great Depression and in Japan was used as an argument for the first round of unconventional monetary policy with 1 percent interest rates from Jun 2003 to Jun 2004 and quantitative easing in the form of withdrawal of supply of 30-year securities by suspension of the auction of 30-year Treasury bonds with the intention of reducing mortgage rates (for fear of deflation see Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), 18-28, and Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 83-95). The financial crisis and global recession were caused by interest rate and housing subsidies and affordability policies that encouraged high leverage and risks, low liquidity and unsound credit (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 157-66, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 217-27, International Financial Architecture (2005), 15-18, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 221-5, Globalization and the State Vol. II (2008b), 197-213, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 182-4). Several past comments of this blog elaborate on these arguments, among which: http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/07/causes-of-2007-creditdollar-crisis.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/professor-mckinnons-bubble-economy.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/world-inflation-quantitative-easing.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/treasury-yields-valuation-of-risk.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/11/quantitative-easing-theory-evidence-and.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/12/is-fed-printing-money-what-are.html
If the forecast of the central bank is of recession and low inflation with controlled inflationary expectations, monetary policy should consist of lowering the short-term policy rate of the central bank, which in the US is the fed funds rate. The intended effect is to lower the real rate of interest (Svensson 2003LT, 146-7). The real rate of interest, r, is defined as the nominal rate, i, adjusted by expectations of inflation, π*, with all variables defined as proportions: (1+r) = (1+i)/(1+π*) (Fisher 1930). If i, the fed funds rate, is lowered by the Fed, the numerator of the right-hand side is lower such that if inflationary expectations, π*, remain unchanged, the left-hand (1+r) decreases, that is, the real rate of interest, r, declines. Expectations of lowering short-term real rates of interest by policy of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) fixing a lower fed funds rate would lower long-term real rates of interest, inducing with a lag investment and consumption, or aggregate demand, that can lift the economy out of recession. Inflation also increases with a lag by higher aggregate demand and inflation expectations (Fisher 1933). This reasoning explains why the FOMC lowered the fed funds rate in Dec 2008 to 0 to 0.25 percent and left it unchanged.
The fear of the Fed is expected deflation or negative π*. In that case, (1+ π*) < 1, and (1+r) would increase because the right-hand side of the equation would be divided by a fraction. A simple numerical example explains the effect of deflation on the real rate of interest. Suppose that the nominal rate of interest or fed funds rate, i, is 0.25 percent, or in proportion 0.25/100 = 0.0025, such that (1+i) = 1.0025. Assume now that economic agents believe that inflation will remain at 1 percent for a long period, which means that π* = 1 percent, or in proportion 1/100 =0.01. The real rate of interest, using the equation, is (1+0.0025)/(1+0.01) = (1+r) = 0.99257, such that r = 0.99257 - 1 = -0.00743, which is a proportion equivalent to –(0.00743)100 = -0.743 percent. That is, Fed policy has created a negative real rate of interest of 0.743 percent with the objective of inducing aggregate demand by higher investment and consumption. This is true if expected inflation, π*, remains at 1 percent. Suppose now that expectations of deflation become generalized such that π* becomes -1 percent, that is, the public believes prices will fall at the rate of 1 percent in the foreseeable future. Then the real rate of interest becomes (1+0.0025) divided by (1-0.01) equal to (1.0025)/(0.99) = (1+r) = 1.01263, or r = (1.01263-1) = 0.01263, which results in positive real rate of interest of (0.01263)100 = 1.263 percent.
Irving Fisher also identified the impact of deflation on debts as an important cause of deepening contraction of income and employment during the Great Depression illustrated by an actual example (Fisher 1933, 346):
“By March, 1933, liquidation had reduced the debts about 20 percent, but had increased the dollar about 75 percent, so that the real debt, that is the debt measured in terms of commodities, was increased about 40 percent [100%-20%)X(100%+75%) =140%]. Unless some counteracting cause comes along to prevent the fall in the price level, such a depression as that of 1929-1933 (namely when the more the debtors pay the more they owe) tends to continue, going deeper, in a vicious spiral, for many years. There is then no tendency of the boat to stop tipping until it has capsized”
The nominal rate of interest must always be nonnegative, that is, i ≥ 0 (Hicks 1937, 154-5):
“If the costs of holding money can be neglected, it will always be profitable to hold money rather than lend it out, if the rate of interest is not greater than zero. Consequently the rate of interest must always be positive. In an extreme case, the shortest short-term rate may perhaps be nearly zero. But if so, the long-term rate must lie above it, for the long rate has to allow for the risk that the short rate may rise during the currency of the loan, and it should be observed that the short rate can only rise, it cannot fall”
The interpretation by Hicks of the General Theory of Keynes is the special case in which at interest rates close to zero liquidity preference is infinitely or perfectly elastic, that is, the public holds infinitely large cash balances at that near zero interest rate because there is no opportunity cost of foregone interest. Increases in the money supply by the central bank would not decrease interest rates below their near zero level, which is called the liquidity trap. The only alternative public policy would consist of fiscal policy that would act similarly to an increase in investment, increasing employment without raising the interest rate. There are negative nominal interest rates fixed by central banks in Europe and Japan.
An influential view on the policy required to steer the economy away from the liquidity trap is provided by Paul Krugman (1998). Suppose the central bank faces an increase in inflation. An important ingredient of the control of inflation is the central bank communicating to the public that it will maintain a sustained effort by all available policy measures and required doses until inflation is subdued and price stability is attained. If the public believes that the central bank will control inflation only until it declines to a more benign level but not sufficiently low level, current expectations will develop that inflation will be higher once the central bank abandons harsh measures. During deflation and recession the central bank has to convince the public that it will maintain zero interest rates and other required measures until the rate of inflation returns convincingly to a level consistent with expansion of the economy and stable prices. Krugman (1998, 161) summarizes the argument as:
“The ineffectuality of monetary policy in a liquidity trap is really the result of a looking-glass version of the standard credibility problem: monetary policy does not work because the public expects that whatever the central bank may do now, given the chance, it will revert to type and stabilize prices near their current level. If the central bank can credibly promise to be irresponsible—that is, convince the market that it will in fact allow prices to rise sufficiently—it can bootstrap the economy out of the trap”
This view is consistent with results of research by Christina Romer that “the rapid rates of growth of real output in the mid- and late 1930s were largely due to conventional aggregate demand stimulus, primarily in the form of monetary expansion. My calculations suggest that in the absence of these stimuli the economy would have remained depressed far longer and far more deeply than it actually did” (Romer 1992, 757-8, cited in Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 210-2). The average growth rate of the money supply in 1933-1937 was 10 percent per year and increased in the early 1940s. Romer calculates that GDP would have been much lower without this monetary expansion. The growth of “the money supply was primarily due to a gold inflow, which was in turn due to the devaluation in 1933 and to capital flight from Europe because of political instability after 1934” (Romer 1992, 759). Gold inflow coincided with the decline in real interest rates in 1933 that remained negative through the latter part of the 1930s, suggesting that they could have caused increases in spending that was sensitive to declines in interest rates. Bernanke finds dollar devaluation against gold to have been important in preventing further deflation in the 1930s (Bernanke 2002):
“There have been times when exchange rate policy has been an effective weapon against deflation. A striking example from US history is Franklin Roosevelt’s 40 percent devaluation of the dollar against gold in 1933-34, enforced by a program of gold purchases and domestic money creation. The devaluation and the rapid increase in money supply it permitted ended the US deflation remarkably quickly. Indeed, consumer price inflation in the United States, year on year, went from -10.3 percent in 1932 to -5.1 percent in 1933 to 3.4 percent in 1934. The economy grew strongly, and by the way, 1934 was one of the best years of the century for the stock market”
Fed policy is seeking what Irving Fisher proposed “that great depressions are curable and preventable through reflation and stabilization” (Fisher 1933, 350).
The President of the Federal Reserve Bank of Chicago argues that (Charles Evans 2010):
“I believe the US economy is best described as being in a bona fide liquidity trap. Highly plausible projections are 1 percent for core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) inflation at the end of 2012 and 8 percent for the unemployment rate. For me, the Fed’s dual mandate misses are too large to shrug off, and there is currently no policy conflict between improving employment and inflation outcomes”
There are two types of monetary policies that could be used in this situation. First, the Fed could announce a price-level target to be attained within a reasonable time frame (Evans 2010):
“For example, if the slope of the price path is 2 percent and inflation has been underunning the path for some time, monetary policy would strive to catch up to the path. Inflation would be higher than 2 percent for a time until the path was reattained”
Optimum monetary policy with interest rates near zero could consist of “bringing the price level back up to a level even higher than would have prevailed had the disturbance never occurred” (Gauti Eggertsson and Michael Woodford 2003, 207). Bernanke (2003JPY) explains as follows:
“Failure by the central bank to meet its target in a given period leads to expectations of (and public demands for) increased effort in subsequent periods—greater quantities of assets purchased on the open market for example. So even if the central bank is reluctant to provide a time frame for meetings its objective, the structure of the price-level objective provides a means for the bank to commit to increasing its anti-deflationary efforts when its earlier efforts prove unsuccessful. As Eggertsson and Woodford show, the expectations that an increasing price level gap will give rise to intensified effort by the central bank should lead the public to believe that ultimately inflation will replace deflation, a belief that supports the central bank’s own objectives by lowering the current real rate of interest”
Second, the Fed could use its balance sheet to increase purchases of long-term securities together with credible commitment to maintain the policy until the dual mandates of maximum employment and price stability are attained. Policy continues with reinvestment of principal in securities.
In the restatement of the liquidity trap and large-scale policies of monetary/fiscal stimulus, Krugman (1998, 162) finds:
“In the traditional open economy IS-LM model developed by Robert Mundell [1963] and Marcus Fleming [1962], and also in large-scale econometric models, monetary expansion unambiguously leads to currency depreciation. But there are two offsetting effects on the current account balance. On one side, the currency depreciation tends to increase net exports; on the other side, the expansion of the domestic economy tends to increase imports. For what it is worth, policy experiments on such models seem to suggest that these effects very nearly cancel each other out.
Krugman (1998) uses a different dynamic model with expectations that leads to similar conclusions.
The central bank could also be pursuing competitive devaluation of the national currency in the belief that it could increase inflation to a higher level and promote domestic growth and employment at the expense of growth and unemployment in the rest of the world. An essay by Chairman Bernanke in 1999 on Japanese monetary policy received attention in the press, stating that (Bernanke 2000, 165):
“Roosevelt’s specific policy actions were, I think, less important than his willingness to be aggressive and experiment—in short, to do whatever it took to get the country moving again. Many of his policies did not work as intended, but in the end FDR deserves great credit for having the courage to abandon failed paradigms and to do what needed to be done”
Quantitative easing has never been proposed by Chairman Bernanke or other economists as certain science without adverse effects. What has not been mentioned in the press is another suggestion to the Bank of Japan (BOJ) by Chairman Bernanke in the same essay that is very relevant to current events and the contentious issue of ongoing devaluation wars (Bernanke 2000, 161):
“Because the BOJ has a legal mandate to pursue price stability, it certainly could make a good argument that, with interest rates at zero, depreciation of the yen is the best available tool for achieving its mandated objective. The economic validity of the beggar-thy-neighbor thesis is doubtful, as depreciation creates trade—by raising home country income—as well as diverting it. Perhaps not all those who cite the beggar-thy-neighbor thesis are aware that it had its origins in the Great Depression, when it was used as an argument against the very devaluations that ultimately proved crucial to world economic recovery. A yen trading at 100 to the dollar is in no one’s interest”
Chairman Bernanke is referring to the argument by Joan Robinson based on the experience of the Great Depression that: “in times of general unemployment a game of beggar-my-neighbour is played between the nations, each one endeavouring to throw a larger share of the burden upon the others” (Robinson 1947, 156). Devaluation is one of the tools used in these policies (Robinson 1947, 157). Banking crises dominated the experience of the United States, but countries that recovered were those devaluing early such that competitive devaluations rescued many countries from a recession as strong as that in the US (see references to Ehsan Choudhri, Levis Kochin and Barry Eichengreen in Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 205-9; for the case of Brazil that devalued early in the Great Depression recovering with an increasing trade balance see Pelaez, 1968, 1968b, 1972; Brazil devalued and abandoned the gold standard during crises in the historical period as shown by Pelaez 1976, Pelaez and Suzigan 1981). Beggar-my-neighbor policies did work for individual countries but the criticism of Joan Robinson was that it was not optimal for the world as a whole.
Chairman Bernanke (2013Mar 25) reinterprets devaluation and recovery from the Great Depression:
“The uncoordinated abandonment of the gold standard in the early 1930s gave rise to the idea of "beggar-thy-neighbor" policies. According to this analysis, as put forth by important contemporary economists like Joan Robinson, exchange rate depreciations helped the economy whose currency had weakened by making the country more competitive internationally. Indeed, the decline in the value of the pound after 1931 was associated with a relatively early recovery from the Depression by the United Kingdom, in part because of some rebound in exports. However, according to this view, the gains to the depreciating country were equaled or exceeded by the losses to its trading partners, which became less internationally competitive--hence, ‘beggar thy neighbor.’ Economists still agree that Smoot-Hawley and the ensuing tariff wars were highly counterproductive and contributed to the depth and length of the global Depression. However, modern research on the Depression, beginning with the seminal 1985 paper by Barry Eichengreen and Jeffrey Sachs, has changed our view of the effects of the abandonment of the gold standard. Although it is true that leaving the gold standard and the resulting currency depreciation conferred a temporary competitive advantage in some cases, modern research shows that the primary benefit of leaving gold was that it freed countries to use appropriately expansionary monetary policies. By 1935 or 1936, when essentially all major countries had left the gold standard and exchange rates were market-determined, the net trade effects of the changes in currency values were certainly small. Yet the global economy as a whole was much stronger than it had been in 1931. The reason was that, in shedding the strait jacket of the gold standard, each country became free to use monetary policy in a way that was more commensurate with achieving full employment at home.”
Nurkse (1944) raised concern on the contraction of trade by competitive devaluations during the 1930s. Haberler (1937) dwelled on the issue of flexible exchange rates. Bordo and James (2001) provide perceptive exegesis of the views of Haberler (1937) and Nurkse (1944) together with the evolution of thought by Haberler. Policy coordination among sovereigns may be quite difficult in practice even if there were sufficient knowledge and sound forecasts. Friedman (1953) provided strong case in favor of a system of flexible exchange rates.
Eichengreen and Sachs (1985) argue theoretically with measurements using a two-sector model that it is possible for series of devaluations to improve the welfare of all countries. There were adverse effects of depreciation on other countries but depreciation by many countries could be beneficial for all. The important counterfactual is if depreciations by many countries would have promoted faster recovery from the Great Depression. Depreciation in the model of Eichengreen and Sachs (1985) affected domestic and foreign economies through real wages, profitability, international competitiveness and world interest rates. Depreciation causes increase in the money supply that lowers world interest rates, promoting growth of world output. Lower world interest rates could compensate contraction of output from the shift of demand away from home goods originating in neighbor’s exchange depreciation. Eichengreen and Sachs (1985, 946) conclude:
“This much, however, is clear. We do not present a blanket endorsement of the competitive devaluations of the 1930s. Though it is indisputable that currency depreciation conferred macroeconomic benefits on the initiating country, because of accompanying policies the depreciations of the 1930s had beggar-thy-neighbor effects. Though it is likely that currency depreciation (had it been even more widely adopted) would have worked to the benefit of the world as a whole, the sporadic and uncoordinated approach taken to exchange-rate policy in the 1930s tended, other things being equal, to reduce the magnitude of the benefits.”
There could major difference in the current world economy. The initiating impulse for depreciation originates in zero interest rates on the fed funds rate. The dollar is the world’s reserve currency. Risk aversion intermittently channels capital flight to the safe haven of the dollar and US Treasury securities. In the absence of risk aversion, zero interest rates induce carry trades of short positions in dollars and US debt (borrowing) together with long leveraged exposures in risk financial assets such as stocks, emerging stocks, commodities and high-yield bonds. Without risk aversion, the dollar depreciates against every currency in the world. The dollar depreciated against the euro by 39.3 percent from USD 1.1423/EUR con Jun 26, 2003 to USD 1.5914/EUR on Jun 14, 2008 during unconventional monetary policy before the global recession (Table VI-1). Unconventional monetary policy causes devaluation of the dollar relative to other currencies, which can increases net exports of the US that increase aggregate economic activity (Yellen 2011AS). The country issuing the world’s reserve currency appropriates the advantage from initiating devaluation that in policy intends to generate net exports that increase domestic output.
The Swiss franc rate relative to the euro (CHF/EUR) appreciated 18.7 percent on Jan 15, 2015. The Swiss franc rate relative to the dollar (CHF/USD) appreciated 17.7 percent. Central banks are taking measures in anticipation of the quantitative easing by the European Central Bank. On Jan 22, 2015, the European Central Bank (ECB) decided to implement an “expanded asset purchase program” with combined asset purchases of €60 billion per month “until at least Sep 2016 (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pr/date/2015/html/pr150122_1.en.html). The DAX index of German equities increased 1.3 percent on Jan 22, 2015 and 2.1 percent on Jan 23, 2015. The euro depreciated from EUR 1.1611/USD (EUR 0.8613/USD) on Wed Jan 21, 2015, to EUR 1.1206/USD (EUR 0.8924/USD) on Fri Jan 23, 2015, or 3.6 percent. Yellen (2011AS, 6) admits that Fed monetary policy results in dollar devaluation with the objective of increasing net exports, which was the policy that Joan Robinson (1947) labeled as “beggar-my-neighbor” remedies for unemployment. Risk aversion erodes devaluation of the dollar.
Pelaez and Pelaez (Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 208-209) summarize the experience of Brazil as follows:
“During 1927–9, Brazil accumulated £30 million of foreign exchange of which £20 million were deposited at its stabilization fund (Pelaez 1968, 43–4). After the decline in coffee prices and the first impact of the Great Depression in Brazil a hot money movement wiped out foreign exchange reserves. In addition, capital inflows stopped entirely. The deterioration of the terms of trade further complicated matters, as the value of exports in foreign currency declined abruptly. Because of this exchange crisis, the service of the foreign debt of Brazil became impossible. In August 1931, the federal government was forced to cancel the payment of principal on certain foreign loans. The balance of trade in 1931 was expected to yield £20 million whereas the service of the foreign debt alone amounted to £22.6 million. Part of the solution given to these problems was typical of the 1930s. In September 1931, the government of Brazil required that all foreign transactions were to be conducted through the Bank of Brazil. This monopoly of foreign exchange was exercised by the Bank of Brazil for the following three years. Export permits were granted only after the exchange derived from sales abroad was officially sold to the Bank, which in turn allocated it in accordance with the needs of the economy. An active black market in foreign exchange developed. Brazil was in the first group of countries that abandoned early the gold standard, in 1931, and suffered comparatively less from the Great Depression. The Brazilian federal government, advised by the BOE, increased taxes and reduced expenditures in 1931 to compensate a decline in custom receipts (Pelaez 1968, 40). Expenditures caused by a revolution in 1932 in the state of Sao Paulo and a drought in the northeast explain the deficit. During 1932–6, the federal government engaged in strong efforts to stabilize the budget. Apart from the deliberate efforts to balance the budget during the 1930s, the recovery in economic activity itself may have induced a large part of the reduction of the deficit (Ibid, 41). Brazil’s experience is similar to that of the United States in that fiscal policy did not promote recovery from the Great Depression.”
Is depreciation of the dollar the best available tool currently for achieving the dual mandate of higher inflation and lower unemployment? Bernanke (2002) finds dollar devaluation against gold to have been important in preventing further deflation in the 1930s (http://www.federalreserve.gov/boarddocs/speeches/2002/20021121/default.htm):
“Although a policy of intervening to affect the exchange value of the dollar is nowhere on the horizon today, it's worth noting that there have been times when exchange rate policy has been an effective weapon against deflation. A striking example from U.S. history is Franklin Roosevelt's 40 percent devaluation of the dollar against gold in 1933-34, enforced by a program of gold purchases and domestic money creation. The devaluation and the rapid increase in money supply it permitted ended the U.S. deflation remarkably quickly. Indeed, consumer price inflation in the United States, year on year, went from -10.3 percent in 1932 to -5.1 percent in 1933 to 3.4 percent in 1934.17 The economy grew strongly, and by the way, 1934 was one of the best years of the century for the stock market. If nothing else, the episode illustrates that monetary actions can have powerful effects on the economy, even when the nominal interest rate is at or near zero, as was the case at the time of Roosevelt's devaluation.”
Should the US devalue following Roosevelt? Alternatively, has monetary policy intended devaluation? Fed policy is seeking, deliberately or as a side effect, what Irving Fisher proposed “that great depressions are curable and preventable through reflation and stabilization” (Fisher, 1933, 350). The Fed has created not only high volatility of assets but also what many countries are regarding as a competitive devaluation similar to those criticized by Nurkse (1944). Yellen (2011AS, 6) admits that Fed monetary policy results in dollar devaluation with the objective of increasing net exports, which was the policy that Joan Robinson (1947) labeled as “beggar-my-neighbor” remedies for unemployment.
Unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates and large-scale purchases of long-term securities for the balance sheet of the central bank is proposed to prevent deflation. The data of CPI inflation of all goods and CPI inflation excluding food and energy for the past six decades does not show even one negative change, as shown in Table CPIEX.
Table CPIEX, Annual Percentage Changes of the CPI All Items Excluding Food and Energy
| Year | Annual ∆% |
| 1958 | 2.4 |
| 1959 | 2.0 |
| 1960 | 1.3 |
| 1961 | 1.3 |
| 1962 | 1.3 |
| 1963 | 1.3 |
| 1964 | 1.6 |
| 1965 | 1.2 |
| 1966 | 2.4 |
| 1967 | 3.6 |
| 1968 | 4.6 |
| 1969 | 5.8 |
| 1970 | 6.3 |
| 1971 | 4.7 |
| 1972 | 3.0 |
| 1973 | 3.6 |
| 1974 | 8.3 |
| 1975 | 9.1 |
| 1976 | 6.5 |
| 1977 | 6.3 |
| 1978 | 7.4 |
| 1979 | 9.8 |
| 1980 | 12.4 |
| 1981 | 10.4 |
| 1982 | 7.4 |
| 1983 | 4.0 |
| 1984 | 5.0 |
| 1985 | 4.3 |
| 1986 | 4.0 |
| 1987 | 4.1 |
| 1988 | 4.4 |
| 1989 | 4.5 |
| 1990 | 5.0 |
| 1991 | 4.9 |
| 1992 | 3.7 |
| 1993 | 3.3 |
| 1994 | 2.8 |
| 1995 | 3.0 |
| 1996 | 2.7 |
| 1997 | 2.4 |
| 1998 | 2.3 |
| 1999 | 2.1 |
| 2000 | 2.4 |
| 2001 | 2.6 |
| 2002 | 2.4 |
| 2003 | 1.4 |
| 2004 | 1.8 |
| 2005 | 2.2 |
| 2006 | 2.5 |
| 2007 | 2.3 |
| 2008 | 2.3 |
| 2009 | 1.7 |
| 2010 | 1.0 |
| 2011 | 1.7 |
| 2012 | 2.1 |
| 2013 | 1.8 |
| 2014 | 1.7 |
| 2015 | 1.8 |
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
The history of producer price inflation in the past five decades does not provide evidence of deflation. The finished core PPI does not register even one single year of decline, as shown in Table PPIEX.
Table PPIEX, Annual Percentage Changes of the PPI Finished Goods Excluding Food
| Year | Annual ∆% |
| 1974 | 11.4 |
| 1975 | 11.4 |
| 1976 | 5.7 |
| 1977 | 6.0 |
| 1978 | 7.5 |
| 1979 | 8.9 |
| 1980 | 11.2 |
| 1981 | 8.6 |
| 1982 | 5.7 |
| 1983 | 3.0 |
| 1984 | 2.4 |
| 1985 | 2.5 |
| 1986 | 2.3 |
| 1987 | 2.4 |
| 1988 | 3.3 |
| 1989 | 4.4 |
| 1990 | 3.7 |
| 1991 | 3.6 |
| 1992 | 2.4 |
| 1993 | 1.2 |
| 1994 | 1.0 |
| 1995 | 2.1 |
| 1996 | 1.4 |
| 1997 | 0.3 |
| 1998 | 0.9 |
| 1999 | 1.7 |
| 2000 | 1.3 |
| 2001 | 1.4 |
| 2002 | 0.1 |
| 2003 | 0.2 |
| 2004 | 1.5 |
| 2005 | 2.4 |
| 2006 | 1.5 |
| 2007 | 1.9 |
| 2008 | 3.4 |
| 2009 | 2.6 |
| 2010 | 1.2 |
| 2011 | 2.4 |
| 2012 | 2.6 |
| 2013 | 1.5 |
| 2014 | 1.9 |
| 2015 | 2.0 |
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
The producer price index of the US from 1947 to 2016 in Chart I-6 shows various periods of more rapid or less rapid inflation but no bumps. The major event is the decline in 2008 when risk aversion because of the global recession caused the collapse of oil prices from $148/barrel to less than $80/barrel with most other commodity prices also collapsing. The event had nothing in common with explanations of deflation but rather with the concentration of risk exposures in commodities after the decline of stock market indexes. Eventually, there was a flight to government securities because of the fears of insolvency of banks caused by statements supporting proposals for withdrawal of toxic assets from bank balance sheets in the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP), as explained by Cochrane and Zingales (2009). The bump in 2008 with decline in 2009 is consistent with the view that zero interest rates with subdued risk aversion induce carry trades into commodity futures.
Chart I-6, US, Producer Price Index, Finished Goods, NSA, 1947-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-7 provides 12-month percentage changes of the producer price index from 1948 to 2016. The distinguishing event in Chart I-7 is the Great Inflation of the 1970s. The shape of the two-hump Bactrian camel of the 1970s resembles the double hump from 2007 to 2016.
Chart I-7, US, Producer Price Index, Finished Goods, 12-Month Percentage Change, NSA, 1948-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Annual percentage changes of the producer price index from 1948 to 2015 are shown in Table I-1A. The producer price index fell 2.8 percent in 1949 following the adjustment to World War II and fell 0.6 percent in 1952 and 1.0 percent in 1953 around the Korean War. There are two other mild decline of 0.3 percent in 1959 and 0.3 percent in 1963. There are only few subsequent and isolated declines of the producer price index of 1.4 percent in 1986, 0.8 percent in 1998, 1.3 percent in 2002 and 2.6 percent in 2009. The decline of 2009 was caused by unwinding of carry trades in 2008 that had lifted oil prices to $140/barrel during deep global recession because of the panic of probable toxic assets in banks that would be removed with the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) (Cochrane and Zingales 2009). Producer prices fell 3.2 percent in 2015 during collapse of commodity prices form high prices induced by zero interest rates. There is no evidence in this history of 65 years of the US producer price index suggesting that there is frequent and persistent deflation shock requiring aggressive unconventional monetary policy. The design of such anti-deflation policy could provoke price and financial instability because of lags in effect of monetary policy, model errors, inaccurate forecasts and misleading analysis of current economic conditions.
Table I-1A, US, Annual PPI Inflation ∆% 1948-2015
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
| Year | Annual ∆% |
| 1948 | 8.0 |
| 1949 | -2.8 |
| 1950 | 1.8 |
| 1951 | 9.2 |
| 1952 | -0.6 |
| 1953 | -1.0 |
| 1954 | 0.3 |
| 1955 | 0.3 |
| 1956 | 2.6 |
| 1957 | 3.8 |
| 1958 | 2.2 |
| 1959 | -0.3 |
| 1960 | 0.9 |
| 1961 | 0.0 |
| 1962 | 0.3 |
| 1963 | -0.3 |
| 1964 | 0.3 |
| 1965 | 1.8 |
| 1966 | 3.2 |
| 1967 | 1.1 |
| 1968 | 2.8 |
| 1969 | 3.8 |
| 1970 | 3.4 |
| 1971 | 3.1 |
| 1972 | 3.2 |
| 1973 | 9.1 |
| 1974 | 15.4 |
| 1975 | 10.6 |
| 1976 | 4.5 |
| 1977 | 6.4 |
| 1978 | 7.9 |
| 1979 | 11.2 |
| 1980 | 13.4 |
| 1981 | 9.2 |
| 1982 | 4.1 |
| 1983 | 1.6 |
| 1984 | 2.1 |
| 1985 | 1.0 |
| 1986 | -1.4 |
| 1987 | 2.1 |
| 1988 | 2.5 |
| 1989 | 5.2 |
| 1990 | 4.9 |
| 1991 | 2.1 |
| 1992 | 1.2 |
| 1993 | 1.2 |
| 1994 | 0.6 |
| 1995 | 1.9 |
| 1996 | 2.7 |
| 1997 | 0.4 |
| 1998 | -0.8 |
| 1999 | 1.8 |
| 2000 | 3.8 |
| 2001 | 2.0 |
| 2002 | -1.3 |
| 2003 | 3.2 |
| 2004 | 3.6 |
| 2005 | 4.8 |
| 2006 | 3.0 |
| 2007 | 3.9 |
| 2008 | 6.3 |
| 2009 | -2.6 |
| 2010 | 4.2 |
| 2011 | 6.1 |
| 2012 | 1.9 |
| 2013 | 1.2 |
| 2014 | 1.9 |
| 2015 | -3.2 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-12 provides the consumer price index NSA from 1917 to 2016. The dominating characteristic is the increase in slope during the Great Inflation from the middle of the 1960s through the 1970s. There is long-term inflation in the US and no evidence of deflation risks.
Chart I-12, US, Consumer Price Index, NSA, 1917-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm
Chart I-13 provides 12-month percentage changes of the consumer price index from 1917 to 2016. The only episode of deflation after 1950 is in 2009, which is explained by the reversal of speculative commodity futures carry trades that were induced by interest rates driven to zero in a shock of monetary policy in 2008. The only persistent case of deflation is from 1930 to 1933, which has little if any relevance to the contemporary United States economy. There are actually three waves of inflation in the second half of the 1960s, in the mid-1970s and again in the late 1970s. Inflation rates then stabilized in a range with only two episodes above 5 percent.
Chart I-13, US, Consumer Price Index, All Items, 12- Month Percentage Change 1917-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm
Table I-2 provides annual percentage changes of United States consumer price inflation from 1914 to 2015. There have been only cases of annual declines of the CPI after wars:
- World War I minus 10.5 percent in 1921 and minus 6.1 percent in 1922 following cumulative increases of 83.5 percent in four years from 1917 to 1920 at the average of 16.4 percent per year
- World War II: minus 1.2 percent in 1949 following cumulative 33.9 percent in three years from 1946 to 1948 at average 10.2 percent per year
- Minus 0.4 percent in 1955 two years after the end of the Korean War
- Minus 0.4 percent in 2009.
- The decline of 0.4 percent in 2009 followed increase of 3.8 percent in 2008 and is explained by the reversal of speculative carry trades into commodity futures that were created in 2008 as monetary policy rates were driven to zero. The reversal occurred after misleading statement on toxic assets in banks in the proposal for TARP (Cochrane and Zingales 2009).
There were declines of 1.7 percent in both 1927 and 1928 during the episode of revival of rules of the gold standard. The only persistent deflationary period since 1914 was during the Great Depression in the years from 1930 to 1933 and again in 1938-1939. Consumer prices increased only 0.1 percent in 2015 because of the collapse of commodity prices from artificially high levels induced by zero interest rates. Fear of deflation on the basis of that experience does not justify unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates that has failed to stop deflation in Japan. Financial repression causes far more adverse effects on allocation of resources by distorting the calculus of risk/returns than alleged employment-creating effects or there would not be current recovery without jobs and hiring after zero interest rates since Dec 2008 and intended now forever in a self-imposed forecast growth and employment mandate of monetary policy. Unconventional monetary policy drives wide swings in allocations of positions into risk financial assets that generate instability instead of intended pursuit of prosperity without inflation. There is insufficient knowledge and imperfect tools to maintain the gap of actual relative to potential output constantly at zero while restraining inflation in an open interval of (1.99, 2.0). Symmetric targets appear to have been abandoned in favor of a self-imposed single jobs mandate of easing monetary policy even with the economy growing at or close to potential output that is actually a target of growth forecast. The impact on the overall economy and the financial system of errors of policy are magnified by large-scale policy doses of trillions of dollars of quantitative easing and zero interest rates. The US economy has been experiencing financial repression as a result of negative real rates of interest during nearly a decade and programmed in monetary policy statements until 2015 or, for practical purposes, forever. The essential calculus of risk/return in capital budgeting and financial allocations has been distorted. If economic perspectives are doomed until 2015 such as to warrant zero interest rates and open-ended bond-buying by “printing” digital bank reserves (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/12/is-fed-printing-money-what-are.html; see Shultz et al 2012), rational investors and consumers will not invest and consume until just before interest rates are likely to increase. Monetary policy statements on intentions of zero interest rates for another three years or now virtually forever discourage investment and consumption or aggregate demand that can increase economic growth and generate more hiring and opportunities to increase wages and salaries. The doom scenario used to justify monetary policy accentuates adverse expectations on discounted future cash flows of potential economic projects that can revive the economy and create jobs. If it were possible to project the future with the central tendency of the monetary policy scenario and monetary policy tools do exist to reverse this adversity, why the tools have not worked before and even prevented the financial crisis? If there is such thing as “monetary policy science”, why it has such poor record and current inability to reverse production and employment adversity? There is no excuse of arguing that additional fiscal measures are needed because they were deployed simultaneously with similar ineffectiveness. Jon Hilsenrath, writing on “New view into Fed’s response to crisis,” on Feb 21, 2014, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702303775504579396803024281322?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection), analyzes 1865 pages of transcripts of eight formal and six emergency policy meetings at the Fed in 2008 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/fomchistorical2008.htm). If there were an infallible science of central banking, models and forecasts would provide accurate information to policymakers on the future course of the economy in advance. Such forewarning is essential to central bank science because of the long lag between the actual impulse of monetary policy and the actual full effects on income and prices many months and even years ahead (Romer and Romer 2004, Friedman 1961, 1953, Culbertson 1960, 1961, Batini and Nelson 2002). Jon Hilsenrath, writing on “New view into Fed’s response to crisis,” on Feb 21, 2014, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702303775504579396803024281322?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection), analyzed 1865 pages of transcripts of eight formal and six emergency policy meetings at the Fed in 2008 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/fomchistorical2008.htm). Jon Hilsenrath demonstrates that Fed policymakers frequently did not understand the current state of the US economy in 2008 and much less the direction of income and prices. The conclusion of Friedman (1953) that monetary impulses increase financial and economic instability because of lags in anticipating needs of policy, taking policy decisions and effects of decisions. This a fortiori true when untested unconventional monetary policy in gargantuan doses shocks the economy and financial markets.
Table I-2, US, Annual CPI Inflation ∆% 1914-2015
| Year | Annual ∆% |
| 1914 | 1.0 |
| 1915 | 1.0 |
| 1916 | 7.9 |
| 1917 | 17.4 |
| 1918 | 18.0 |
| 1919 | 14.6 |
| 1920 | 15.6 |
| 1921 | -10.5 |
| 1922 | -6.1 |
| 1923 | 1.8 |
| 1924 | 0.0 |
| 1925 | 2.3 |
| 1926 | 1.1 |
| 1927 | -1.7 |
| 1928 | -1.7 |
| 1929 | 0.0 |
| 1930 | -2.3 |
| 1931 | -9.0 |
| 1932 | -9.9 |
| 1933 | -5.1 |
| 1934 | 3.1 |
| 1935 | 2.2 |
| 1936 | 1.5 |
| 1937 | 3.6 |
| 1938 | -2.1 |
| 1939 | -1.4 |
| 1940 | 0.7 |
| 1941 | 5.0 |
| 1942 | 10.9 |
| 1943 | 6.1 |
| 1944 | 1.7 |
| 1945 | 2.3 |
| 1946 | 8.3 |
| 1947 | 14.4 |
| 1948 | 8.1 |
| 1949 | -1.2 |
| 1950 | 1.3 |
| 1951 | 7.9 |
| 1952 | 1.9 |
| 1953 | 0.8 |
| 1954 | 0.7 |
| 1955 | -0.4 |
| 1956 | 1.5 |
| 1957 | 3.3 |
| 1958 | 2.8 |
| 1959 | 0.7 |
| 1960 | 1.7 |
| 1961 | 1.0 |
| 1962 | 1.0 |
| 1963 | 1.3 |
| 1964 | 1.3 |
| 1965 | 1.6 |
| 1966 | 2.9 |
| 1967 | 3.1 |
| 1968 | 4.2 |
| 1969 | 5.5 |
| 1970 | 5.7 |
| 1971 | 4.4 |
| 1972 | 3.2 |
| 1973 | 6.2 |
| 1974 | 11.0 |
| 1975 | 9.1 |
| 1976 | 5.8 |
| 1977 | 6.5 |
| 1978 | 7.6 |
| 1979 | 11.3 |
| 1980 | 13.5 |
| 1981 | 10.3 |
| 1982 | 6.2 |
| 1983 | 3.2 |
| 1984 | 4.3 |
| 1985 | 3.6 |
| 1986 | 1.9 |
| 1987 | 3.6 |
| 1988 | 4.1 |
| 1989 | 4.8 |
| 1990 | 5.4 |
| 1991 | 4.2 |
| 1992 | 3.0 |
| 1993 | 3.0 |
| 1994 | 2.6 |
| 1995 | 2.8 |
| 1996 | 3.0 |
| 1997 | 2.3 |
| 1998 | 1.6 |
| 1999 | 2.2 |
| 2000 | 3.4 |
| 2001 | 2.8 |
| 2002 | 1.6 |
| 2003 | 2.3 |
| 2004 | 2.7 |
| 2005 | 3.4 |
| 2006 | 3.2 |
| 2007 | 2.8 |
| 2008 | 3.8 |
| 2009 | -0.4 |
| 2010 | 1.6 |
| 2011 | 3.2 |
| 2012 | 2.1 |
| 2013 | 1.5 |
| 2014 | 1.6 |
| 2015 | 0.1 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm
Friedman (1969) finds that the optimal rule for the quantity of money is deflation at a rate that results in a zero nominal interest rate (see Ireland 2003 and Cole and Kocherlakota 1998). Atkeson and Kehoe (2004) argue that central bankers are not inclined to implement policies that could result in deflation because of the interpretation of the Great Depression as closely related to deflation. They use panel data on inflation and growth of real output for 17 countries over more than 100 years. The time-series data for each individual country are broken into five-year events with deflation measured as average negative inflation and depression as average negative growth rate of real output. Atkeson and Kehoe (2004) find that the Great Depression from 1929 to 1934 is the only case of association between deflation and depression without any evidence whatsoever of such relation in any other period. Their conclusion is (Atkeson and Kehoe 2004, 99): “Our finding thus suggests that policymakers’ fear of anticipated policy-induced deflation that would result from following, say, the Friedman rule is greatly overblown.” Their conclusion on the experience of Japan is (Atkeson and Kehoe 2004, 99):
“Since 1960, Japan’s average growth rates have basically fallen monotonically, and since 1970, its average inflation rates have too. Attributing this 40-year slowdown to monetary forces is a stretch. More reasonable, we think, is that much of the slowdown is the natural pattern for a country that was far behind the world leaders and had begun to catch up.”
In the sample of Atkeson and Kehoe (2004), there are only eight five-year periods besides the Great Depression with both inflation and depression. Deflation and depression is shown in 65 cases with 21 of depression without deflation. There is no depression in 65 of 73 five-year periods and there is no deflation in 29 episodes of depression. There is a remarkable result of no depression in 90 percent of deflation episodes. Excluding the Great Depression, there is virtually no relation of deflation and depression. Atkeson and Kehoe (2004, 102) find that the average growth rate of Japan of 1.41 percent in the 1990s is “dismal” when compared with 3.20 percent in the United States but is not “dismal” when compared with 1.61 percent for Italy and 1.84 percent for France, which are also catch-up countries in modern economic growth (see Atkeson and Kehoe 1998). The conclusion of Atkeson and Kehoe (2004), without use of controls, is that there is no association of deflation and depression in their dataset.
Benhabib and Spiegel (2009) use a dataset similar to that of Atkeson and Kehoe (2004) but allowing for nonlinearity and inflation volatility. They conclude that in cases of low and negative inflation an increase of average inflation of 1 percent is associated with an increase of 0.31 percent of average annual growth. The analysis of Benhabib and Spiegel (2009) leads to the significantly different conclusion that inflation and economic performance are strongly associated for low and negative inflation. There is no claim of causality by Atkeson and Kehoe (2004) and Benhabib and Spiegel (2009).
Delfim Netto (1959) partly reprinted in Pelaez (1973) conducted two classical nonparametric tests (Mann 1945, Wallis and Moore 1941; see Kendall and Stuart 1968) with coffee-price data in the period of free markets from 1857 to 1906 with the following conclusions (Pelaez, 1976a, 280):
“First, the null hypothesis of no trend was accepted with high confidence; secondly, the null hypothesis of no oscillation was rejected also with high confidence. Consequently, in the nineteenth century international prices of coffee fluctuated but without long-run trend. This statistical fact refutes the extreme argument of structural weakness of the coffee trade.”
In his classic work on the theory of international trade, Jacob Viner (1937, 563) analyzed the “index of total gains from trade,” or “amount of gain per unit of trade,” denoted as T:
T= (∆Pe/∆Pi)∆Q
Where ∆Pe is the change in export prices, ∆Pi is the change in import prices and ∆Q is the change in export volume. Dorrance (1948, 52) restates “Viner’s index of total gain from trade” as:
“What should be done is to calculate an index of the value (quantity multiplied by price) of exports and the price of imports for any country whose foreign accounts are to be analysed. Then the export value index should be divided by the import price index. The result would be an index which would reflect, for the country concerned, changes in the volume of imports obtainable from its export income (i.e. changes in its "real" export income, measured in import terms). The present writer would suggest that this index be referred to as the ‘income terms of trade’ index to differentiate it from the other indexes at present used by economists.”
What really matters for an export activity especially during modernization is the purchasing value of goods that it exports in terms of prices of imports. For a primary producing country, the purchasing power of exports in acquiring new technology from the country providing imports is the critical measurement. The barter terms of trade of Brazil improved from 1857 to 1906 because international coffee prices oscillated without trend (Delfim Netto 1959) while import prices from the United Kingdom declined at the rate of 0.5 percent per year (Imlah 1958). The accurate measurement of the opportunity afforded by the coffee exporting economy was incomparably greater when considering the purchasing power in British prices of the value of coffee exports, or Dorrance’s (1948) income terms of trade.
The conventional theory that the terms of trade of Brazil deteriorated over the long term is without reality (Pelaez 1976a, 280-281):
“Moreover, physical exports of coffee by Brazil increased at the high average rate of 3.5 per cent per year. Brazil's exchange receipts from coffee-exporting in sterling increased at the average rate of 3.5 per cent per year and receipts in domestic currency at 4.5 per cent per year. Great Britain supplied nearly all the imports of the coffee economy. In the period of the free coffee market, British export prices declined at the rate of 0.5 per cent per year. Thus, the income terms of trade of the coffee economy improved at the relatively satisfactory average rate of 4.0 per cent per year. This is only a lower bound of the rate of improvement of the terms of trade. While the quality of coffee remained relatively constant, the quality of manufactured products improved significantly during the fifty-year period considered. The trade data and the non-parametric tests refute conclusively the long-run hypothesis. The valid historical fact is that the tropical export economy of Brazil experienced an opportunity of absorbing rapidly increasing quantities of manufactures from the "workshop" countries. Therefore, the coffee trade constituted a golden opportunity for modernization in nineteenth-century Brazil.”
Imlah (1958) provides decline of British export prices at 0.5 percent in the nineteenth century and there were no lost decades, depressions or unconventional monetary policies in the highly dynamic economy of England that drove the world’s growth impulse. Inflation in the United Kingdom between 1857 and 1906 is measured by the composite price index of O’Donoghue and Goulding (2004) at minus 7.0 percent or average rate of decline of 0.2 percent per year.
Simon Kuznets (1971) analyzes modern economic growth in his Lecture in Memory of Alfred Nobel:
“The major breakthroughs in the advance of human knowledge, those that constituted dominant sources of sustained growth over long periods and spread to a substantial part of the world, may be termed epochal innovations. And the changing course of economic history can perhaps be subdivided into economic epochs, each identified by the epochal innovation with the distinctive characteristics of growth that it generated. Without considering the feasibility of identifying and dating such economic epochs, we may proceed on the working assumption that modern economic growth represents such a distinct epoch - growth dating back to the late eighteenth century and limited (except in significant partial effects) to economically developed countries. These countries, so classified because they have managed to take adequate advantage of the potential of modern technology, include most of Europe, the overseas offshoots of Western Europe, and Japan—barely one quarter of world population.”
Cameron (1961) analyzes the mechanism by which the Industrial Revolution in Great Britain spread throughout Europe and Cameron (1967) analyzes the financing by banks of the Industrial Revolution in Great Britain. O’Donoghue and Goulding (2004) provide consumer price inflation in England since 1750 and MacFarlane and Mortimer-Lee (1994) analyze inflation in England over 300 years. Lucas (2004) estimates world population and production since the year 1000 with sustained growth of per capita incomes beginning to accelerate for the first time in English-speaking countries and in particular in the Industrial Revolution in Great Britain. The conventional theory is unequal distribution of the gains from trade and technical progress between the industrialized countries and developing economies (Singer 1950, 478):
“Dismissing, then, changes in productivity as a governing factor in changing terms of trade, the following explanation presents itself: the fruits of technical progress may be distributed either to producers (in the form of rising incomes) or to consumers (in the form of lower prices). In the case of manufactured commodities produced in more developed countries, the former method, i.e., distribution to producers through higher incomes, was much more important relatively to the second method, while the second method prevailed more in the case of food and raw material production in the underdeveloped countries. Generalizing, we may say -that technical progress in manufacturing industries showed in a rise in incomes while technical progress in the production of food and raw materials in underdeveloped countries showed in a fall in prices”
Temin (1997, 79) uses a Ricardian trade model to discriminate between two views on the Industrial Revolution with an older view arguing broad-based increases in productivity and a new view concentration of productivity gains in cotton manufactures and iron:
“Productivity advances in British manufacturing should have lowered their prices relative to imports. They did. Albert Imlah [1958] correctly recognized this ‘severe deterioration’ in the net barter terms of trade as a signal of British success, not distress. It is no surprise that the price of cotton manufactures fell rapidly in response to productivity growth. But even the price of woolen manufactures, which were declining as a share of British exports, fell almost as rapidly as the price of exports as a whole. It follows, therefore, that the traditional ‘old-hat’ view of the Industrial Revolution is more accurate than the new, restricted image. Other British manufactures were not inefficient and stagnant, or at least, they were not all so backward. The spirit that motivated cotton manufactures extended also to activities as varied as hardware and haberdashery, arms, and apparel.”
Phyllis Deane (1968, 96) estimates growth of United Kingdom gross national product (GNP) at around 2 percent per year for several decades in the nineteenth century. The facts that the terms of trade of Great Britain deteriorated during the period of epochal innovation and high rates of economic growth while the income terms of trade of the coffee economy of nineteenth-century Brazil improved at the average yearly rate of 4.0 percent from 1857 to 1906 disprove the hypothesis of weakness of trade as an explanation of relatively lower income and wealth. As Temin (1997) concludes, Britain did pass on lower prices and higher quality the benefits of technical innovation. Explanation of late modernization must focus on laborious historical research on institutions and economic regimes together with economic theory, data gathering and measurement instead of grand generalizations of weakness of trade and alleged neocolonial dependence (Stein and Stein 1970, 134-5):
“Great Britain, technologically and industrially advanced, became as important to the Latin American economy as to the cotton-exporting southern United States. [After Independence in the nineteenth century] Latin America fell back upon traditional export activities, utilizing the cheapest available factor of production, the land, and the dependent labor force.”
Summerhill (2015) contributes momentous solid facts and analysis with an ideal method combining economic theory, econometrics, international comparisons, data reconstruction and exhaustive archival research. Summerhill (2015) finds that Brazil committed to service of sovereign foreign and internal debt. Contrary to conventional wisdom, Brazil generated primary fiscal surpluses during most of the Empire until 1889 (Summerhill 2015, 37-8, Figure 2.1). Econometric tests by Summerhill (2015, 19-44) show that Brazil’s sovereign debt was sustainable. Sovereign credibility in the North-Weingast (1989) sense spread to financial development that provided the capital for modernization in England and parts of Europe (see Cameron 1961, 1967). Summerhill (2015, 3, 194-6, Figure 7.1) finds that “Brazil’s annual cost of capital in London fell from a peak of 13.9 percent in 1829 to only 5.12 percent in 1889. Average rates on secured loans in the private sector in Rio, however, remained well above 12 percent through 1850.” Financial development would have financed diversification of economic activities, increasing productivity and wages and ensuring economic growth. Brazil restricted creation of limited liability enterprises (Summerhill 2015, 151-82) that prevented raising capital with issue of stocks and corporate bonds. Cameron (1961) analyzed how the industrial revolution in England spread to France and then to the rest of Europe. The Société Générale de Crédit Mobilier of Émile and Isaac Péreire provided the “mobilization of credit” for the new economic activities (Cameron 1961). Summerhill (2015, 151-9) provides facts and analysis demonstrating that regulation prevented the creation of a similar vehicle for financing modernization by Irineu Evangelista de Souza, the legendary Visconde de Mauá. Regulation also prevented the use of negotiable bearing notes of the Caisse Générale of Jacques Lafitte (Cameron 1961, 118-9). The government also restricted establishment and independent operation of banks (Summerhill 2015, 183-214). Summerhill (2005, 198-9) measures concentration in banking that provided economic rents or a social loss. The facts and analysis of Summerhill (2015) provide convincing evidence in support of the economic theory of regulation, which postulates that regulated entities capture the process of regulation to promote their self-interest. There appears to be a case that excessively centralized government can result in regulation favoring private instead of public interests with adverse effects on economic activity. The contribution of Summerhill (2015) explains why Brazil did not benefit from trade as an engine of growth—as did regions of recent settlement in the vision of nineteenth-century trade and development of Ragnar Nurkse (1959)—partly because of restrictions on financing and incorporation.
The experience of the United Kingdom with deflation and economic growth is relevant and rich. Table IE-1 uses yearly percentage changes of the composite index of prices of the United Kingdom of O’Donoghue and Goulding (2004). There are 73 declines of inflation in the 145 years from 1751 to 1896. Prices declined in 50.3 percent of 145 years. Some price declines were quite sharp and many occurred over several years. Table IE-1 also provides yearly percentage changes of the UK composite price index of O’Donoghue and Goulding (2004) from 1929 to 1934. Deflation was much sharper in continuous years in earlier periods than during the Great Depression. The United Kingdom could not have led the world in modern economic growth if there were meaningful causality from deflation to depression.
Table IE-1, United Kingdom, Negative Percentage Changes of Composite Price Index, 1751-1896, 1929-1934, Yearly ∆%
| Year | ∆% | Year | ∆% | Year | ∆% | Year | ∆% |
| 1751 | -2.7 | 1797 | -10.0 | 1834 | -7.8 | 1877 | -0.7 |
| 1753 | -2.7 | 1798 | -2.2 | 1841 | -2.3 | 1878 | -2.2 |
| 1755 | -6.0 | 1802 | -23.0 | 1842 | -7.6 | 1879 | -4.4 |
| 1758 | -0.3 | 1803 | -5.9 | 1843 | -11.3 | 1881 | -1.1 |
| 1759 | -7.9 | 1806 | -4.4 | 1844 | -0.1 | 1883 | -0.5 |
| 1760 | -4.5 | 1807 | -1.9 | 1848 | -12.1 | 1884 | -2.7 |
| 1761 | -4.5 | 1811 | -2.9 | 1849 | -6.3 | 1885 | -3.0 |
| 1768 | -1.1 | 1814 | -12.7 | 1850 | -6.4 | 1886 | -1.6 |
| 1769 | -8.2 | 1815 | -10.7 | 1851 | -3.0 | 1887 | -0.5 |
| 1770 | -0.4 | 1816 | -8.4 | 1857 | -5.6 | 1893 | -0.7 |
| 1773 | -0.3 | 1819 | -2.5 | 1858 | -8.4 | 1894 | -2.0 |
| 1775 | -5.6 | 1820 | -9.3 | 1859 | -1.8 | 1895 | -1.0 |
| 1776 | -2.2 | 1821 | -12.0 | 1862 | -2.6 | 1896 | -0.3 |
| 1777 | -0.4 | 1822 | -13.5 | 1863 | -3.6 | 1929 | -0.9 |
| 1779 | -8.5 | 1826 | -5.5 | 1864 | -0.9 | 1930 | -2.8 |
| 1780 | -3.4 | 1827 | -6.5 | 1868 | -1.7 | 1931 | -4.3 |
| 1785 | -4.0 | 1828 | -2.9 | 1869 | -5.0 | 1932 | -2.6 |
| 1787 | -0.6 | 1830 | -6.1 | 1874 | -3.3 | 1933 | -2.1 |
| 1789 | -1.3 | 1832 | -7.4 | 1875 | -1.9 | 1934 | 0.0 |
| 1791 | -0.1 | 1833 | -6.1 | 1876 | -0.3 |
Source:
O’Donoghue, Jim and Louise Goulding, 2004. Consumer Price Inflation since 1750. UK Office for National Statistics Economic Trends 604, Mar 2004, 38-46.
There is current interest in past theories of “secular stagnation.” Alvin H. Hansen (1939, 4, 7; see Hansen 1938, 1941; for an early critique see Simons 1942) argues:
“Not until the problem of full employment of our productive resources from the long-run, secular standpoint was upon us, were we compelled to give serious consideration to those factors and forces in our economy which tend to make business recoveries weak and anaemic (sic) and which tend to prolong and deepen the course of depressions. This is the essence of secular stagnation-sick recoveries which die in their infancy and depressions which feed on themselves and leave a hard and seemingly immovable core of unemployment. Now the rate of population growth must necessarily play an important role in determining the character of the output; in other words, the composition of the flow of final goods. Thus a rapidly growing population will demand a much larger per capita volume of new residential building construction than will a stationary population. A stationary population with its larger proportion of old people may perhaps demand more personal services; and the composition of consumer demand will have an important influence on the quantity of capital required. The demand for housing calls for large capital outlays, while the demand for personal services can be met without making large investment expenditures. It is therefore not unlikely that a shift from a rapidly growing population to a stationary or declining one may so alter the composition of the final flow of consumption goods that the ratio of capital to output as a whole will tend to decline.”
In the analysis of Hansen (1939, 3) of secular stagnation, economic progress consists of growth of real income per person driven by growth of productivity. The “constituent elements” of economic progress are “(a) inventions, (b) the discovery and development of new territory and new resources, and (c) the growth of population” (Hansen 1939, 3). Secular stagnation originates in decline of population growth and discouragement of inventions. According to Hansen (1939, 2), US population grew by 16 million in the 1920s but grew by one half or about 8 million in the 1930s with forecasts at the time of Hansen’s writing in 1938 of growth of around 5.3 million in the 1940s. Hansen (1939, 2) characterized demography in the US as “a drastic decline in the rate of population growth. Hansen’s plea was to adapt economic policy to stagnation of population in ensuring full employment. In the analysis of Hansen (1939, 8), population caused half of the growth of US GDP per year. Growth of output per person in the US and Europe was caused by “changes in techniques and to the exploitation of new natural resources.” In this analysis, population caused 60 percent of the growth of capital formation in the US. Declining population growth would reduce growth of capital formation. Residential construction provided an important share of growth of capital formation. Hansen (1939, 12) argues that market power of imperfect competition discourages innovation with prolonged use of obsolete capital equipment. Trade unions would oppose labor-savings innovations. The combination of stagnating and aging population with reduced innovation caused secular stagnation. Hansen (1939, 12) concludes that there is role for public investments to compensate for lack of dynamism of private investment but with tough tax/debt issues.
Table SE1 provides contributions to growth of GDP in the 1930s. These data were not available until much more recently. Residential investment (RSI) contributed 1.03 percentage points to growth of GDP of 8.0 percent in 1939, which is a high percentage of the contribution of gross private domestic investment of 2.39 percentage points. Residential investment contributed 0.42 percentage points to GDP growth of 8.8 percent in 1940 with gross private domestic investment contributing 3.99 percentage points.
Table SE1, US, Contributions to Growth of GDP
| GDP ∆% | PCE PP | GDI PP | NRI PP | RSI PP | Net Trade PP | GOVT | |
| 1930 | -8.5 | -3.96 | -5.18 | -1.84 | -1.50 | -0.31 | 0.94 |
| 1931 | -6.4 | -2.37 | -4.28 | -3.32 | -0.40 | -0.22 | 0.48 |
| 1932 | -12.9 | -7.00 | -5.28 | -2.78 | -1.02 | -0.20 | -0.42 |
| 1933 | -1.3 | -1.79 | 1.16 | -0.44 | -0.24 | -0.11 | -0.52 |
| 1934 | 10.8 | 5.71 | 2.83 | 1.31 | 0.38 | 0.33 | 1.91 |
| 1935 | 8.9 | 4.69 | 4.54 | 1.41 | 0.56 | -0.83 | 0.50 |
| 1936 | 12.9 | 7.68 | 2.58 | 2.10 | 0.47 | 0.24 | 2.44 |
| 1937 | 5.1 | 2.72 | 2.57 | 1.42 | 0.17 | 0.45 | -0.64 |
| 1938 | -3.3 | -1.15 | -4.13 | -2.13 | 0.01 | 0.88 | 1.09 |
| 1939 | 8.0 | 4.11 | 2.39 | 0.71 | 1.03 | 0.07 | 1.41 |
| 1940 | 8.8 | 3.72 | 3.99 | 1.60 | 0.42 | 0.52 | 0.57 |
GDP ∆%: Annual Growth of GDP; PCE PP: Percentage Points Contributed by Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE); GDI PP: Percentage Points Contributed by Gross Private Domestic Investment (GDI); NRI PP: Percentage Points Contributed by Nonresidential Investment (NRI); RSI: Percentage Points Contributed by Residential Investment; Net Trade PP: Percentage Points Contributed by Net Exports less Imports of Goods and Services; GOVT PP: Percentage Points Contributed by Government Consumption and Gross Investment
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table ES2 provides percentage shares of GDP in 1929, 1939, 1940, 2006 and 2015. The share of residential investment was 3.9 percent in 1929, 3.4 percent in 1939 and 6.0 percent in 2006 at the peak of the real estate boom. The share of residential investment in GDP has not been very high historically.
Table ES2, Percentage Shares in GDP
| 1929 | 1939 | 1940 | 2006 | 2015 | |
| GDP | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| PCE | 74.0 | 71.9 | 69.2 | 67.1 | 68.4 |
| GDI | 16.4 | 10.9 | 14.2 | 19.3 | 16.8 |
| NRI | 11.1 | 7.3 | 8.3 | 12.8 | 12.8 |
| RSI | 3.9 | 3.4 | 3.5 | 6.0 | 3.4 |
| Net Trade | 0.4 | 0.9 | 1.4 | -5.6 | -3.0 |
| GOVT | 9.2 | 16.3 | 15.2 | 19.1 | 17.8 |
PCE: Personal Consumption Expenditures; GDI: Gross Domestic Investment; NRI: Nonresidential Investment; RSI: Residential Investment; Net Trade: Net Exports less Imports of Goods and Services; GOVT: Government Consumption and Gross Investment
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis
PCE: Personal Consumption Expenditures; GDI: Gross Private Domestic Investment; NRI: Nonresidential Investment; RSI: Residential Investment; Net Trade: Net Exports less Imports of Goods and Services; GOVT: Government Consumption and Gross Investment
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
An interpretation of the New Deal is that fiscal stimulus must be massive in recovering growth and employment and that it should not be withdrawn prematurely to avoid a sharp second contraction as it occurred in 1937 (Christina Romer 2009). Proposals for another higher dose of stimulus explain the current weakness by insufficient fiscal expansion and warn that failure to spend more can cause another contraction as in 1937. According to a different interpretation, private hours worked declined by 25 percent by 1939 compared with the level in 1929, suggesting that the economy fell to a lower path of expansion than in 1929 (works by Harold Cole and Lee Ohanian (1999) (cited in Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance, 215-7). Major real variables of output and employment were below trend by 1939: -26.8 percent for GNP, -25.4 percent for consumption, -51 percent for investment and -25.6 percent for hours worked. Surprisingly, total factor productivity increased by 3.1 percent and real wages by 21.8 percent (Cole and Ohanian 1999). The policies of the Roosevelt administration encouraged increasing unionization to maintain high wages with lower hours worked and high prices by lax enforcement of antitrust law to encourage cartels or collusive agreements among producers. The encouragement by the government of labor bargaining by unions and higher prices by collusion depressed output and employment throughout the 1930s until Roosevelt abandoned the policies during World War II after which the economy recovered full employment (Cole and Ohanian 1999). The fortunate ones who worked during the New Deal received higher real wages at the expense of many who never worked again. In a way, the administration behaved like the father of the unionized workers and the uncle of the collusive rich, neglecting the majority in the middle. Inflation-adjusted GDP increased by 10.8 percent in 1934, 8.9 percent in 1935, 12.9 percent in 1936 but only 5.1 percent in 1937, contracting by -3.3 percent in 1938 (US Bureau of Economic Analysis cited in Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession, 151, Globalization and the State, Vol. II, 206). The competing explanation is that the economy did not decline from 1937 to 1938 because of lower government spending in 1937 but rather because of the expansion of unions promoted by the New Deal and increases in tax rates (Thomas Cooley and Lee Ohanian 2010). Government spending adjusted for inflation fell only 0.7 percent in 1936 and 1937 and could not explain the decline of GDP by 3.4 percent in 1938. In 1936, the administration imposed a tax on retained profits not distributed to shareholders according to a sliding scale of 7 percent for retaining 1 percent of total net income up to 27 percent for retaining 70 percent of total net income, increasing costs of investment that were mostly financed in that period with retained earnings (Cooley and Ohanian 2010). The tax rate on dividends jumped from 10.1 percent in 1929 to 15.9 percent in 1932 and doubled by 1936. A recent study finds that “tax rates on dividends rose dramatically during the 1930s and imply significant declines in investment and equity values and nontrivial declines in GDP and hours of work” (Ellen McGrattan 2010), explaining a significant part of the decline of 26 percent in business fixed investment in 1937-1938. The National Labor Relations Act of 1935 caused an increase in union membership from 12 percent in 1934 to 25 percent in 1938. The alternative lesson from the 1930s is that capital income taxes and higher unionization caused increases in business costs that perpetuated job losses of the recession with current risks of repeating the 1930s (Cooley and Ohanian 1999).
In the analysis of Hansen (1939, 3) of secular stagnation, economic progress consists of growth of real income per person driven by growth of productivity. The “constituent elements” of economic progress are “(a) inventions, (b) the discovery and development of new territory and new resources, and (c) the growth of population” (Hansen 1939, 3). Secular stagnation originates in decline of population growth and discouragement of inventions. According to Hansen (1939, 2), US population grew by 16 million in the 1920s but grew by one half or about 8 million in the 1930s with forecasts at the time of Hansen’s writing in 1938 of growth of around 5.3 million in the 1940s. Hansen (1939, 2) characterized demography in the US as “a drastic decline in the rate of population growth. Hansen’s plea was to adapt economic policy to stagnation of population in ensuring full employment. In the analysis of Hansen (1939, 8), population caused half of the growth of US GDP per year. Growth of output per person in the US and Europe was caused by “changes in techniques and to the exploitation of new natural resources.” In this analysis, population caused 60 percent of the growth of capital formation in the US. Declining population growth would reduce growth of capital formation. Residential construction provided an important share of growth of capital formation. Hansen (1939, 12) argues that market power of imperfect competition discourages innovation with prolonged use of obsolete capital equipment. Trade unions would oppose labor-savings innovations. The combination of stagnating and aging population with reduced innovation caused secular stagnation. Hansen (1939, 12) concludes that there is role for public investments to compensate for lack of dynamism of private investment but with tough tax/debt issues.
The current application of Hansen’s (1938, 1939, 1941) proposition argues that secular stagnation occurs because full employment equilibrium can be attained only with negative real interest rates between minus 2 and minus 3 percent. Professor Lawrence H. Summers (2013Nov8) finds that “a set of older ideas that went under the phrase secular stagnation are not profoundly important in understanding Japan’s experience in the 1990s and may not be without relevance to America’s experience today” (emphasis added). Summers (2013Nov8) argues there could be an explanation in “that the short-term real interest rate that was consistent with full employment had fallen to -2% or -3% sometime in the middle of the last decade. Then, even with artificial stimulus to demand coming from all this financial imprudence, you wouldn’t see any excess demand. And even with a relative resumption of normal credit conditions, you’d have a lot of difficulty getting back to full employment.” The US economy could be in a situation where negative real rates of interest with fed funds rates close to zero as determined by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) do not move the economy to full employment or full utilization of productive resources. Summers (2013Oct8) finds need of new thinking on “how we manage an economy in which the zero nominal interest rates is a chronic and systemic inhibitor of economy activity holding our economies back to their potential.”
Former US Treasury Secretary Robert Rubin (2014Jan8) finds three major risks in prolonged unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates and quantitative easing: (1) incentive of delaying action by political leaders; (2) “financial moral hazard” in inducing excessive exposures pursuing higher yields of risker credit classes; and (3) major risks in exiting unconventional policy. Rubin (2014Jan8) proposes reduction of deficits by structural reforms that could promote recovery by improving confidence of business attained with sound fiscal discipline.
Professor John B. Taylor (2014Jan01, 2014Jan3) provides clear thought on the lack of relevance of Hansen’s contention of secular stagnation to current economic conditions. The application of secular stagnation argues that the economy of the US has attained full-employment equilibrium since around 2000 only with negative real rates of interest of minus 2 to minus 3 percent. At low levels of inflation, the so-called full-employment equilibrium of negative interest rates of minus 2 to minus 3 percent cannot be attained and the economy stagnates. Taylor (2014Jan01) analyzes multiple contradictions with current reality in this application of the theory of secular stagnation:
- Secular stagnation would predict idle capacity, in particular in residential investment when fed fund rates were fixed at 1 percent from Jun 2003 to Jun 2004. Taylor (2014Jan01) finds unemployment at 4.4 percent with house prices jumping 7 percent from 2002 to 2003 and 14 percent from 2004 to 2005 before dropping from 2006 to 2007. GDP prices doubled from 1.7 percent to 3.4 percent when interest rates were low from 2003 to 2005.
- Taylor (2014Jan01, 2014Jan3) finds another contradiction in the application of secular stagnation based on low interest rates because of savings glut and lack of investment opportunities. Taylor (2009) shows that there was no savings glut. The savings rate of the US in the past decade is significantly lower than in the 1980s.
- Taylor (2014Jan01, 2014Jan3) finds another contradiction in the low ratio of investment to GDP currently and reduced investment and hiring by US business firms.
- Taylor (2014Jan01, 2014Jan3) argues that the financial crisis and global recession were caused by weak implementation of existing regulation and departure from rules-based policies.
- Taylor (2014Jan01, 2014Jan3) argues that the recovery from the global recession was constrained by a change in the regime of regulation and fiscal/monetary policies.
In revealing research, Edward P. Lazear and James R. Spletzer (2012JHJul22) use the wealth of data in the valuable database and resources of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (http://www.bls.gov/data/) in providing clear thought on the nature of the current labor market of the United States. The critical issue of analysis and policy currently is whether unemployment is structural or cyclical. Structural unemployment could occur because of (1) industrial and demographic shifts and (2) mismatches of skills and job vacancies in industries and locations. Consider the aggregate unemployment rate, Y, expressed in terms of share si of a demographic group in an industry i and unemployment rate yi of that demographic group (Lazear and Spletzer 2012JHJul22, 5-6):
Y = ∑isiyi (1)
This equation can be decomposed for analysis as (Lazear and Spletzer 2012JHJul22, 6):
∆Y = ∑i∆siy*i + ∑i∆yis*i (2)
The first term in (2) captures changes in the demographic and industrial composition of the economy ∆si multiplied by the average rate of unemployment y*i , or structural factors. The second term in (2) captures changes in the unemployment rate specific to a group, or ∆yi, multiplied by the average share of the group s*i, or cyclical factors. There are also mismatches in skills and locations relative to available job vacancies. A simple observation by Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22) casts intuitive doubt on structural factors: the rate of unemployment jumped from 4.4 percent in the spring of 2007 to 10 percent in October 2009. By nature, structural factors should be permanent or occur over relative long periods. The revealing result of the exhaustive research of Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22) is:
“The analysis in this paper and in others that we review do not provide any compelling evidence that there have been changes in the structure of the labor market that are capable of explaining the pattern of persistently high unemployment rates. The evidence points to primarily cyclic factors.”
Table I-4b and Chart I-12-b provide the US labor force participation rate or percentage of the labor force in population. It is not likely that simple demographic trends caused the sharp decline during the global recession and failure to recover earlier levels. The civilian labor force participation rate dropped from the peak of 66.9 percent in Jul 2006 to 62.6 percent in Dec 2013, 62.5 percent in Dec 2014 and 62.4 percent in Dec 2015. The civilian labor force participation rate was 63.2 percent in Jun 2016. The civilian labor force participation rate was 63.7 percent on an annual basis in 1979 and 63.4 percent in Dec 1980 and Dec 1981, reaching even 62.9 percent in both Apr and May 1979. The civilian labor force participation rate jumped with the recovery to 64.8 percent on an annual basis in 1985 and 65.9 percent in Jul 1985. Structural factors cannot explain these sudden changes vividly shown visually in the final segment of Chart I-12b. Seniors would like to delay their retiring especially because of the adversities of financial repression on their savings. Labor force statistics are capturing the disillusion of potential workers with their chances in finding a job in what Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22) characterize as accentuated cyclical factors. The argument that anemic population growth causes “secular stagnation” in the US (Hansen 1938, 1939, 1941) is as misplaced currently as in the late 1930s (for early dissent see Simons 1942). There is currently population growth in the ages of 16 to 24 years but not enough job creation and discouragement of job searches for all ages (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/considerable-uncertainty-about-economic.html). “Secular stagnation” would be a process over many years and not from one year to another. This is merely another case of theory without reality with dubious policy proposals.
Table I-4b, US, Labor Force Participation Rate, Percent of Labor Force in Population, NSA, 1979-2016
| Year | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Annual |
| 1979 | 62.9 | 63.0 | 63.2 | 62.9 | 62.9 | 64.5 | 63.8 | 64.0 | 63.8 | 63.8 | 63.7 |
| 1980 | 63.3 | 63.2 | 63.2 | 63.2 | 63.5 | 64.6 | 63.6 | 63.9 | 63.7 | 63.4 | 63.8 |
| 1981 | 63.2 | 63.2 | 63.5 | 63.6 | 63.9 | 64.6 | 63.5 | 64.0 | 63.8 | 63.4 | 63.9 |
| 1982 | 63.0 | 63.2 | 63.4 | 63.3 | 63.9 | 64.8 | 64.0 | 64.1 | 64.1 | 63.8 | 64.0 |
| 1983 | 63.3 | 63.2 | 63.3 | 63.2 | 63.4 | 65.1 | 64.3 | 64.1 | 64.1 | 63.8 | 64.0 |
| 1984 | 63.3 | 63.4 | 63.6 | 63.7 | 64.3 | 65.5 | 64.4 | 64.6 | 64.4 | 64.3 | 64.4 |
| 1985 | 64.0 | 64.0 | 64.4 | 64.3 | 64.6 | 65.5 | 64.9 | 65.1 | 64.9 | 64.6 | 64.8 |
| 1986 | 64.2 | 64.4 | 64.6 | 64.6 | 65.0 | 66.3 | 65.3 | 65.5 | 65.4 | 65.0 | 65.3 |
| 1987 | 64.7 | 64.8 | 65.0 | 64.9 | 65.6 | 66.3 | 65.5 | 65.9 | 65.7 | 65.5 | 65.6 |
| 1988 | 65.1 | 65.2 | 65.2 | 65.3 | 65.5 | 66.7 | 65.9 | 66.1 | 66.2 | 65.9 | 65.9 |
| 1989 | 65.8 | 65.6 | 65.7 | 65.9 | 66.2 | 67.4 | 66.3 | 66.6 | 66.7 | 66.3 | 66.5 |
| 1990 | 66.0 | 66.0 | 66.2 | 66.1 | 66.5 | 67.4 | 66.4 | 66.5 | 66.3 | 66.1 | 66.5 |
| 1991 | 65.5 | 65.7 | 65.9 | 66.0 | 66.0 | 67.2 | 66.1 | 66.1 | 66.0 | 65.8 | 66.2 |
| 1992 | 65.7 | 65.8 | 66.0 | 66.0 | 66.4 | 67.6 | 66.3 | 66.2 | 66.2 | 66.1 | 66.4 |
| 1993 | 65.6 | 65.8 | 65.8 | 65.6 | 66.3 | 67.3 | 66.1 | 66.4 | 66.3 | 66.2 | 66.3 |
| 1994 | 66.0 | 66.2 | 66.1 | 66.0 | 66.5 | 67.2 | 66.5 | 66.8 | 66.7 | 66.5 | 66.6 |
| 1995 | 66.1 | 66.2 | 66.4 | 66.4 | 66.4 | 67.2 | 66.5 | 66.7 | 66.5 | 66.2 | 66.6 |
| 1996 | 65.8 | 66.1 | 66.4 | 66.2 | 66.7 | 67.4 | 66.8 | 67.1 | 67.0 | 66.7 | 66.8 |
| 1997 | 66.4 | 66.5 | 66.9 | 66.7 | 67.0 | 67.8 | 67.0 | 67.1 | 67.1 | 67.0 | 67.1 |
| 1998 | 66.6 | 66.7 | 67.0 | 66.6 | 67.0 | 67.7 | 67.0 | 67.1 | 67.1 | 67.0 | 67.1 |
| 1999 | 66.7 | 66.8 | 66.9 | 66.7 | 67.0 | 67.7 | 66.8 | 67.0 | 67.0 | 67.0 | 67.1 |
| 2000 | 66.8 | 67.0 | 67.1 | 67.0 | 67.0 | 67.7 | 66.7 | 66.9 | 66.9 | 67.0 | 67.1 |
| 2001 | 66.8 | 66.8 | 67.0 | 66.7 | 66.6 | 67.2 | 66.6 | 66.7 | 66.6 | 66.6 | 66.8 |
| 2002 | 66.2 | 66.6 | 66.6 | 66.4 | 66.5 | 67.1 | 66.6 | 66.6 | 66.3 | 66.2 | 66.6 |
| 2003 | 66.1 | 66.2 | 66.2 | 66.2 | 66.2 | 67.0 | 65.9 | 66.1 | 66.1 | 65.8 | 66.2 |
| 2004 | 65.7 | 65.7 | 65.8 | 65.7 | 65.8 | 66.5 | 65.7 | 66.0 | 66.1 | 65.8 | 66.0 |
| 2005 | 65.4 | 65.6 | 65.6 | 65.8 | 66.0 | 66.5 | 66.1 | 66.2 | 66.1 | 65.9 | 66.0 |
| 2006 | 65.5 | 65.7 | 65.8 | 65.8 | 66.0 | 66.7 | 66.1 | 66.4 | 66.4 | 66.3 | 66.2 |
| 2007 | 65.9 | 65.8 | 65.9 | 65.7 | 65.8 | 66.6 | 66.0 | 66.0 | 66.1 | 65.9 | 66.0 |
| 2008 | 65.7 | 65.5 | 65.7 | 65.7 | 66.0 | 66.6 | 65.9 | 66.1 | 65.8 | 65.7 | 66.0 |
| 2009 | 65.4 | 65.5 | 65.4 | 65.4 | 65.5 | 66.2 | 65.0 | 64.9 | 64.9 | 64.4 | 65.4 |
| 2010 | 64.6 | 64.6 | 64.8 | 64.9 | 64.8 | 65.1 | 64.6 | 64.4 | 64.4 | 64.1 | 64.7 |
| 2011 | 63.9 | 63.9 | 64.0 | 63.9 | 64.1 | 64.5 | 64.2 | 64.1 | 63.9 | 63.8 | 64.1 |
| 2012 | 63.4 | 63.6 | 63.6 | 63.4 | 63.8 | 64.3 | 63.6 | 63.8 | 63.5 | 63.4 | 63.7 |
| 2013 | 63.3 | 63.2 | 63.1 | 63.1 | 63.5 | 64.0 | 63.2 | 62.9 | 62.9 | 62.6 | 63.2 |
| 2014 | 62.5 | 62.7 | 62.9 | 62.6 | 62.9 | 63.4 | 62.8 | 63.0 | 62.8 | 62.5 | 62.9 |
| 2015 | 62.5 | 62.5 | 62.5 | 62.6 | 63.0 | 63.1 | 62.3 | 62.5 | 62.5 | 62.4 | 62.7 |
| 2016 | 62.3 | 62.7 | 62.8 | 62.7 | 62.7 | 63.2 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-12b, US, Labor Force Participation Rate, Percent of Labor Force in Population, NSA, 1979-2016
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Broader perspective is in Chart I-12c of the US Bureau of Labor Statistics. The United States civilian noninstitutional population has increased along a consistent trend since 1948 that continued through earlier recessions and the global recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 and the cyclical expansion after IIIQ2009.
Chart I-12c, US, Civilian Noninstitutional Population, Thousands, NSA, 1948-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The labor force of the United States in Chart I-12d has increased along a trend similar to that of the civilian noninstitutional population in Chart I-12c. There is an evident stagnation of the civilian labor force in the final segment of Chart I-12d during the current economic cycle. This stagnation is explained by cyclical factors similar to those analyzed by Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22) that motivated an increasing population to drop out of the labor force instead of structural factors. Large segments of the potential labor force are not observed, constituting unobserved unemployment and of more permanent nature because those afflicted have been seriously discouraged from working by the lack of opportunities.
Chart I-12d, US, Labor Force, Thousands, NSA, 1948-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The rate of labor force participation in the US is in Chart I-12E from 1948 to 2016. There is sudden decline during the global recession after 2007 without recovery explained by cyclical factors (Lazear and Spletzer2012JHJul22) as may many potential workers stopped their searches disillusioned that there could be an opportunity for them in sharply contracted markets.
Chart I-12E, US, Labor Force Participation Rate, Percent of Labor Force in Population, NSA, 1948-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-20 provides the level of full-time jobs from 2001 to 2016. The magnitude of the stress in US labor markets is magnified by the increase in the civilian noninstitutional population of the United States from 231.958 million in Jul 2007 to 253.397 million in Jun 2016 or by 21.439 million (http://www.bls.gov/data/). The number with full-time jobs in Jun 2016 is 124.903 million, which is higher by 1.684 million relative to the peak of 123.219 million in Jul 2007. The ratio of full-time jobs of 123.219 million in Jul 2007 to civilian noninstitutional population of 231.958 million was 53.1 percent. If that ratio had remained the same, there would be 134.554 million full-time jobs with population of 253.397 million in Jun 2016 (0.531 x 253.397) or 9.651 million fewer full-time jobs relative to actual 124.903 million. There appear to be around 10 million fewer full-time jobs in the US than before the global recession while population increased around 20 million. Mediocre GDP growth is the main culprit of the fractured US labor market.
There is current interest in past theories of “secular stagnation.” Alvin H. Hansen (1939, 4, 7; see Hansen 1938, 1941; for an early critique see Simons 1942) argues:
“Not until the problem of full employment of our productive resources from the long-run, secular standpoint was upon us, were we compelled to give serious consideration to those factors and forces in our economy which tend to make business recoveries weak and anaemic (sic) and which tend to prolong and deepen the course of depressions. This is the essence of secular stagnation-sick recoveries which die in their infancy and depressions which feed on them-selves and leave a hard and seemingly immovable core of unemployment. Now the rate of population growth must necessarily play an important role in determining the character of the output; in other words, the com-position of the flow of final goods. Thus a rapidly growing population will demand a much larger per capita volume of new residential building construction than will a stationary population. A stationary population with its larger proportion of old people may perhaps demand more personal services; and the composition of consumer demand will have an important influence on the quantity of capital required. The demand for housing calls for large capital outlays, while the demand for personal services can be met without making large investment expenditures. It is therefore not unlikely that a shift from a rapidly growing population to a stationary or declining one may so alter the composition of the final flow of consumption goods that the ratio of capital to output as a whole will tend to decline.”
The argument that anemic population growth causes “secular stagnation” in the US (Hansen 1938, 1939, 1941) is as misplaced currently as in the late 1930s (for early dissent see Simons 1942). This is merely another case of theory without reality with dubious policy proposals.
Inferior performance of the US economy and labor markets, during cyclical slow growth not secular stagnation, is the critical current issue of analysis and policy design.
Chart I-20, US, Full-time Employed, Thousands, NSA, 2001-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-20A provides the noninstitutional civilian population of the United States from 2001 to 2016. There is clear trend of increase of the population while the number of full-time jobs collapsed after 2008 without sufficient recovery as shown in the preceding Chart I-20.
Chart I-20A, US, Noninstitutional Civilian Population, Thousands, 2001-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-20B provides number of full-time jobs in the US from 1968 to 2016. There were multiple recessions followed by expansions without contraction of full-time jobs and without recovery as during the period after 2008. The problem is specific of the current cycle and not secular.
Chart I-20B, US, Full-time Employed, Thousands, NSA, 1968-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-20C provides the noninstitutional civilian population of the United States from 1968 to 2016. Population expanded at a relatively constant rate of increase with the assurance of creation of full-time jobs that has been broken since 2008.
Chart I-20C, US, Noninstitutional Civilian Population, Thousands, 1968-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Table EMP provides the comparison between the labor market in the current whole cycle from 2007 to 2015 and the whole cycle from 1979 to 1989. In the entire cycle from 2007 to 2015, the number employed increased 2.787 million, full-time employed increased 0.401 million, part-time for economic reasons increased 1.970 million and population increased 18.934 million. The number employed increased 1.9 percent, full-time employed increased 0.3 percent, part-time for economic reasons increased 44.8 percent and population increased 8.2 percent. There is sharp contrast with the contractions of the 1980s and with most economic history of the United States. In the whole cycle from 1979 to 1989, the number employed increased 18.518 million, full-time employed increased 14.715 million, part-time for economic reasons increased 1.317 million and population increased 21.530 million. In the entire cycle from 1979 to 1989, the number employed increased 18.7 percent, full-time employed increased 17.8 percent, part-time for economic reasons increased 36.8 percent and population increased 13.1 percent. The difference between the 1980s and the current cycle after 2007 is in the high rate of growth after the contraction that maintained trend growth around 3.0 percent for the entire cycle and per capital growth at 2.0 percent. The evident fact is that current weakness in labor markets originates in cyclical slow growth and not in imaginary secular stagnation.
Table EMP, US, Annual Level of Employed, Full-Time Employed, Employed Part-Time for Economic Reasons and Noninstitutional Civilian Population, Millions
| Employed | Full-Time Employed | Part Time Economic Reasons | Noninstitutional Civilian Population | |
| 2000s | ||||
| 2000 | 136.891 | 113.846 | 3.227 | 212.577 |
| 2001 | 136.933 | 113.573 | 3.715 | 215.092 |
| 2002 | 136.485 | 112.700 | 4.213 | 217.570 |
| 2003 | 137.736 | 113.324 | 4.701 | 221.168 |
| 2004 | 139.252 | 114.518 | 4.567 | 223.357 |
| 2005 | 141.730 | 117.016 | 4.350 | 226.082 |
| 2006 | 144.427 | 119.688 | 4.162 | 228.815 |
| 2007 | 146.047 | 121.091 | 4.401 | 231.867 |
| 2008 | 145.362 | 120.030 | 5.875 | 233.788 |
| 2009 | 139.877 | 112.634 | 8.913 | 235.801 |
| 2010 | 139.064 | 111.714 | 8.874 | 237.830 |
| 2011 | 139.869 | 112.556 | 8.560 | 239.618 |
| 2012 | 142.469 | 114.809 | 8.122 | 243.284 |
| 2013 | 143.929 | 116.314 | 7.935 | 245.679 |
| 2014 | 146.305 | 118.718 | 7.213 | 247.947 |
| 2015 | 148.834 | 121.492 | 6.371 | 250.801 |
| ∆2007-2015 | 2.787 | 0.401 | 1.970 | 18.934 |
| ∆% 2007-2015 | 1.9 | 0.3 | 44.8 | 8.2 |
| 1980s | ||||
| 1979 | 98.824 | 82.654 | 3.577 | 164.863 |
| 1980 | 99.303 | 82.562 | 4.321 | 167.745 |
| 1981 | 100.397 | 83.243 | 4.768 | 170.130 |
| 1982 | 99.526 | 81.421 | 6.170 | 172.271 |
| 1983 | 100.834 | 82.322 | 6.266 | 174.215 |
| 1984 | 105.005 | 86.544 | 5.744 | 176.383 |
| 1985 | 107.150 | 88.534 | 5.590 | 178.206 |
| 1986 | 109.597 | 90.529 | 5.588 | 180.587 |
| 1987 | 112.440 | 92.957 | 5.401 | 182.753 |
| 1988 | 114.968 | 95.214 | 5.206 | 184.613 |
| 1989 | 117.342 | 97.369 | 4.894 | 186.393 |
| ∆1979-1989 | 18.518 | 14.715 | 1.317 | 21.530 |
| ∆% 1979-1989 | 18.7 | 17.8 | 36.8 | 13.1 |
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
The theory of secular stagnation cannot explain sudden collapse of the US economy and labor markets. There are accentuated cyclic factors for both the entire population and the young population of ages 16 to 24 years. Table Summary Total provides the total noninstitutional population (ICP) of the US, full-time employment level (FTE), employment level (EMP), civilian labor force (CLF), civilian labor force participation rate (CLFP), employment/population ratio (EPOP) and unemployment level (UNE). Secular stagnation would spread over long periods instead of immediately. All indicators of the labor market weakened sharply during the contraction and did not recover. Population continued to grow but all other variables collapsed and did not recover. The theory of secular stagnation departs from an aggregate production function in which output grows with the use of labor, capital and technology (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. I (2008a), 11-16). Hansen (1938, 1939) finds secular stagnation in lower growth of an aging population. In the current US economy, Table Summary shows that population is dynamic while the labor market is fractured. There is key explanation in the behavior of the civilian labor force participation rate (CLFP) and the employment population ratio (EPOP) that collapsed during the global recession with inadequate recovery. Abandoning job searches are difficult to capture in labor statistics but likely explain the decline in the participation of the population in the labor force. Allowing for abandoning job searches, the total number of people unemployed or underemployed is 23.7 million or 14.1 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/fluctuating-valuations-of-risk.html).
Table Summary Total, US, Total Noninstitutional Civilian Population, Full-time Employment, Employment, Civilian Labor Force, Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate, Employment Population Ratio, Unemployment, NSA, Millions and Percent
| ICP | FTE | EMP | CLF | CLFP | EPOP | UNE | |
| 2006 | 228.8 | 119.7 | 144.4 | 151.4 | 66.2 | 63.1 | 7.0 |
| 2009 | 235.8 | 112.6 | 139.9 | 154.1 | 65.4 | 59.3 | 14.3 |
| 2012 | 243.3 | 114.8 | 142.5 | 155.0 | 63.7 | 58.6 | 12.5 |
| 2013 | 245.7 | 116.3 | 143.9 | 155.4 | 63.2 | 58.6 | 11.5 |
| 2014 | 247.9 | 118.7 | 146.3 | 155.9 | 62.9 | 59.0 | 9.6 |
| 2015 | 250.8 | 121.5 | 148.8 | 157.1 | 62.7 | 59.3 | 8.3 |
| 12/07 | 233.2 | 121.0 | 146.3 | 153.7 | 65.9 | 62.8 | 7.4 |
| 9/09 | 236.3 | 112.0 | 139.1 | 153.6 | 65.0 | 58.9 | 14.5 |
| 6/16 | 253.4 | 124.9 | 152.0 | 160.1 | 63.2 | 60.0 | 8.1 |
ICP: Total Noninstitutional Civilian Population; FT: Full-time Employment Level, EMP: Total Employment Level; CLF: Civilian Labor Force; CLFP: Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate; EPOP: Employment Population Ratio; UNE: Unemployment
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
The same situation is present in the labor market for young people in ages 16 to 24 years with data in Table Summary Youth. The youth noninstitutional civilian population (ICP) continued to increase during and after the global recession. There is the same disastrous labor market with decline for young people in employment (EMP), civilian labor force (CLF), civilian labor force participation rate (CLFP) and employment population ratio (EPOP). There are only increases for unemployment of young people (UNE) and youth unemployment rate (UNER). If aging were a factor of secular stagnation, growth of population of young people would attract a premium in remuneration in labor markets. The sad fact is that young people are also facing tough labor markets. The application of the theory of secular stagnation to the US economy and labor markets is void of reality in the form of key facts, which are best explained by accentuated cyclic factors analyzed by Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22).
Table Summary Youth, US, Youth, Ages 16 to 24 Years, Noninstitutional Civilian Population, Full-time Employment, Employment, Civilian Labor Force, Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate, Employment Population Ratio, Unemployment, NSA, Millions and Percent
| ICP | EMP | CLF | CLFP | EPOP | UNE | UNER | |
| 2006 | 36.9 | 20.0 | 22.4 | 60.6 | 54.2 | 2.4 | 10.5 |
| 2009 | 37.6 | 17.6 | 21.4 | 56.9 | 46.9 | 3.8 | 17.6 |
| 2012 | 38.8 | 17.8 | 21.3 | 54.9 | 46.0 | 3.5 | 16.2 |
| 2013 | 38.8 | 18.1 | 21.4 | 55.0 | 46.5 | 3.3 | 15.5 |
| 2014 | 38.7 | 18.4 | 21.3 | 55.0 | 47.6 | 2.9 | 13.4 |
| 2015 | 38.6 | 18.8 | 21.2 | 55.0 | 48.6 | 2.5 | 11.6 |
| 12/07 | 37.5 | 19.4 | 21.7 | 57.8 | 51.6 | 2.3 | 10.7 |
| 9/09 | 37.6 | 17.0 | 20.7 | 55.2 | 45.1 | 3.8 | 18.2 |
| 6/16 | 38.5 | 20.0 | 22.8 | 59.2 | 51.9 | 2.8 | 12.3 |
ICP: Youth Noninstitutional Civilian Population; EMP: Youth Employment Level; CLF: Youth Civilian Labor Force; CLFP: Youth Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate; EPOP: Youth Employment Population Ratio; UNE: Unemployment; UNER: Youth Unemployment Rate
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
The eminent economist and historian Professor Rondo E. Cameron (1989, 3) searches for the answer of “why are some nations rich and others poor?” by analyzing economic history since Paleolithic times. Cameron (1989, 4) argues that:
“Policymakers and their staffs of experts, faced with the responsibility of proposing and implementing policies for development, frequently shrug off the potential contributions of historical analysis to the solution of their problems with the observation that the contemporary situation is unique and therefore history is irrelevant to their concerns. Such an attitude contains a double fallacy. In the first place, those who are ignorant of the past are not qualified to generalize about it. Second, it implicitly denies the uniformity of nature, including human behavior and the behavior of social institutions—an assumption on which all scientific inquiry is founded. Such attitudes reveal how easy it is, without historical perspective, to mistake the symptoms of a problem for its causes.”
Scholars detached from practical issues of economic policy are more likely to discover sound knowledge (Cohen and Nagel 1934). There is troublesome sacrifice of rigorous scientific objectivity in cutting the economic past by a procrustean bed fitting favored current economic policies.
Nicholas Georgescu-Rogen (1960, 1) reprinted in Pelaez (1973) argues that “the agrarian economy has to this day remained a reality without theory.” The economic history of Latin America shares with the relation of deflation and unconventional monetary policy and secular stagnation when the event is cyclical slow growth a more frustrating intellectual misfortune: theory without reality. MacFarlane and Mortimer-Lee (1994, 159) quote in a different context a phrase by Thomas Henry Huxley in the President’s Address to the British Association for the Advancement of Science on Sep 14, 1870 that is appropriate to these issues: “The great tragedy of science—the slaying of a beautiful hypothesis by an ugly fact.” There may be current relevance in another quote from Thomas Henry Huxley: “The deepest sin against the human mind is to believe things without evidence.”
I Recovery without Hiring. Professor Edward P. Lazear (2012Jan19) at Stanford University finds that recovery of hiring in the US to peaks attained in 2007 requires an increase of hiring by 30 percent while hiring levels increased by only 4 percent from Jan 2009 to Jan 2012. The high level of unemployment with low level of hiring reduces the statistical probability that the unemployed will find a job. According to Lazear (2012Jan19), the probability of finding a new job in early 2012 is about one third of the probability of finding a job in 2007. Improvements in labor markets have not increased the probability of finding a new job. Lazear (2012Jan19) quotes an essay coauthored with James R. Spletzer in the American Economic Review (Lazear and Spletzer 2012Mar, 2012May) on the concept of churn. A dynamic labor market occurs when a similar amount of workers is hired as those who are separated. This replacement of separated workers is called churn, which explains about two-thirds of total hiring. Typically, wage increases received in a new job are higher by 8 percent. Lazear (2012Jan19) argues that churn has declined 35 percent from the level before the recession in IVQ2007. Because of the collapse of churn, there are no opportunities in escaping falling real wages by moving to another job. As this blog argues, there are meager chances of escaping unemployment because of the collapse of hiring and those employed cannot escape falling real wages by moving to another job (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/fluctuating-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/financial-turbulence-twenty-four.html). Lazear and Spletzer (2012Mar, 1) argue that reductions of churn reduce the operational effectiveness of labor markets. Churn is part of the allocation of resources or in this case labor to occupations of higher marginal returns. The decline in churn can harm static and dynamic economic efficiency. Losses from decline of churn during recessions can affect an economy over the long-term by preventing optimal growth trajectories because resources are not used in the occupations where they provide highest marginal returns. Lazear and Spletzer (2012Mar 7-8) conclude that: “under a number of assumptions, we estimate that the loss in output during the recession [of 2007 to 2009] and its aftermath resulting from reduced churn equaled $208 billion. On an annual basis, this amounts to about .4% of GDP for a period of 3½ years.”
There are two additional facts discussed below: (1) there are about ten million fewer full-time jobs currently than before the recession of 2008 and 2009; and (2) the extremely high and rigid rate of youth unemployment is denying an early start to young people ages 16 to 24 years while unemployment of ages 45 years or over has swelled. There are four subsections. IA1 Hiring Collapse provides the data and analysis on the weakness of hiring in the United States economy. IA2 Labor Underutilization provides the measures of labor underutilization of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). Statistics on the decline of full-time employment are in IA3 Ten Million Fewer Full-time Jobs. IA4 Theory and Reality of Cyclical Slow Growth Not Secular Stagnation: Youth and Middle-Age Unemployment provides the data on high unemployment of ages 16 to 24 years and of ages 45 years or over.
IA1 Hiring Collapse. An important characteristic of the current fractured labor market of the US is the closing of the avenue for exiting unemployment and underemployment normally available through dynamic hiring. Another avenue that is closed is the opportunity for advancement in moving to new jobs that pay better salaries and benefits again because of the collapse of hiring in the United States. Those who are unemployed or underemployed cannot find a new job even accepting lower wages and no benefits. The employed cannot escape declining inflation-adjusted earnings because there is no hiring. The objective of this section is to analyze hiring and labor underutilization in the United States.
Blanchard and Katz (1997, 53 consider an appropriate measure of job stress:
“The right measure of the state of the labor market is the exit rate from unemployment, defined as the number of hires divided by the number unemployed, rather than the unemployment rate itself. What matters to the unemployed is not how many of them there are, but how many of them there are in relation to the number of hires by firms.”
The natural rate of unemployment and the similar NAIRU are quite difficult to estimate in practice (Ibid; see Ball and Mankiw 2002).
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) created the Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey (JOLTS) with the purpose that (http://www.bls.gov/jlt/jltover.htm#purpose):
“These data serve as demand-side indicators of labor shortages at the national level. Prior to JOLTS, there was no economic indicator of the unmet demand for labor with which to assess the presence or extent of labor shortages in the United States. The availability of unfilled jobs—the jobs opening rate—is an important measure of tightness of job markets, parallel to existing measures of unemployment.”
The BLS collects data from about 16,000 US business establishments in nonagricultural industries through the 50 states and DC. The data are released monthly and constitute an important complement to other data provided by the BLS (see also Lazear and Spletzer 2012Mar, 6-7).
There is socio-economic stress in the combination of adverse events and cyclical performance:
- Mediocre economic growth below potential and long-term trend, resulting in idle productive resources with GDP two trillion dollars below trend (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/financial-asset-values-rebound-from.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/appropriate-for-fed-to-increase.html). US GDP grew at the average rate of 3.2 percent per year from 1929 to 2015, with similar performance in whole cycles of contractions and expansions, but only at 1.2 percent per year on average from 2007 to 2015. GDP in IQ2016 is 13.7 percent lower than what it would have been had it grown at trend of 3.0 percent
- Private fixed investment stagnating at increase of 6.7 percent in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IQ2016 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/financial-asset-values-rebound-from.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/appropriate-for-fed-to-increase.html)
- Twenty four million or 14.1 percent of the effective labor force unemployed or underemployed in involuntary part-time jobs with stagnating or declining real wages (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/fluctuating-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/financial-turbulence-twenty-four.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/proceeding-cautiously-in-monetary.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets-in.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/weakening-equities-with-exchange-rate.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/liftoff-of-fed-funds-rate-followed-by.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/live-possibility-of-interest-rates.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/labor-market-uncertainty-and-interest.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-policy-dependent-on-what.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/turbulence-of-financial-asset.html)
- Stagnating real disposable income per person or income per person after inflation and taxes (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/financial-asset-values-rebound-from.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/financial-turbulence-twenty-four.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/proceeding-cautiously-in-monetary.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets-in.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/dollar-revaluation-and-decreasing.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/dollar-revaluation-constraining.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/dollar-revaluation-constraining.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/live-possibility-of-interest-rates.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/labor-market-uncertainty-and-interest.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-policy-dependent-on-what.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/international-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/dollar-devaluation-and-carry-trade.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/volatility-of-valuations-of-financial.html)
- Depressed hiring that does not afford an opportunity for reducing unemployment/underemployment and moving to better-paid jobs (Section II and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/considerable-uncertainty-about-economic.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/recovery-without-hiring-ten-million.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/proceeding-cautiously-in-reducing.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/contraction-of-united-states-corporate.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/subdued-foreign-growth-and-dollar.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/unconventional-monetary-policy-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/liftoff-of-interest-rates-with-volatile_17.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/interest-rate-policy-conundrum-recovery.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/impact-of-monetary-policy-on-exchange.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-policy-dependent-on-what_13.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/exchange-rate-and-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/oscillating-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/volatility-of-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/volatility-of-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/fluctuating-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/dollar-revaluation-recovery-without.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/global-exchange-rate-struggle-recovery.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/02/g20-monetary-policy-recovery-without.html)
- Productivity growth fell from 2.2 percent per year on average from 1947 to 2015 and average 2.3 percent per year from 1947 to 2007 to 1.2 percent per year on average from 2007 to 2015, deteriorating future growth and prosperity (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/considerable-uncertainty-about-economic.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/closely-monitoring-global-economic-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/liftoff-of-fed-funds-rate-followed-by.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/live-possibility-of-interest-rates.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-policy-dependent-on-what.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/exchange-rate-and-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/quite-high-equity-valuations-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/global-competitive-devaluation-rules.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/02/job-creation-and-monetary-policy-twenty.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/financial-risks-twenty-six-million.html)
- Output of manufacturing in May 2016 at 26.9 percent below long-term trend since 1919 and at 20.0 percent below trend since 1986 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/fomc-projections-world-inflation-waves.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/most-fomc-participants-judged-that-if.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/contracting-united-states-industrial.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/monetary-policy-and-competitive.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/unconventional-monetary-policy-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/liftoff-of-interest-rates-with-monetary.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/interest-rate-liftoff-followed-by.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/interest-rate-policy-quagmire-world.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-increase-on-hold-because.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/exchange-rate-and-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/fluctuating-financial-asset-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/fluctuating-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/global-portfolio-reallocations-squeeze.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/impatience-with-monetary-policy-of.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/02/world-financial-turbulence-squeeze-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/01/exchange-rate-conflicts-squeeze-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/10/imf-view-squeeze-of-economic-activity.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html)
- Unsustainable government deficit/debt and balance of payments deficit (Section II and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/proceeding-cautiously-in-reducing.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/weakening-equities-and-dollar.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/monetary-policy-designed-on-measurable.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/fluctuating-financial-asset-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/impatience-with-monetary-policy-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/irrational-exuberance-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/monetary-policy-world-inflation-waves.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/06/valuation-risks-world-inflation-waves.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/02/theory-and-reality-of-cyclical-slow.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/interest-rate-risks-world-inflation.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/tapering-quantitative-easing-mediocre.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/09/duration-dumping-and-peaking-valuations.html)
- Worldwide waves of inflation (Section I and earlier) http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/fomc-projections-world-inflation-waves.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/most-fomc-participants-judged-that-if.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/contracting-united-states-industrial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/monetary-policy-and-competitive.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/uncertainty-of-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/liftoff-of-interest-rates-with-monetary.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/interest-rate-liftoff-followed-by.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/interest-rate-policy-quagmire-world.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-increase-on-hold-because.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/global-decline-of-values-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/fluctuating-financial-asset-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/interest-rate-policy-and-dollar.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/global-portfolio-reallocations-squeeze.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/dollar-revaluation-and-financial-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/irrational-exuberance-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/01/competitive-currency-conflicts-world.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/10/financial-oscillations-world-inflation.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/monetary-policy-world-inflation-waves.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/world-inflation-waves-united-states.html)
- Deteriorating terms of trade and net revenue margins of production across countries in squeeze of economic activity by carry trades induced by zero interest rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/fomc-projections-world-inflation-waves.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/most-fomc-participants-judged-that-if.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/imf-view-of-world-economy-and-finance.html and earlier) (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/monetary-policy-and-competitive.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/uncertainty-of-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/liftoff-of-interest-rates-with-monetary.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/interest-rate-liftoff-followed-by.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/interest-rate-policy-quagmire-world.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-increase-on-hold-because.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/global-decline-of-values-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/fluctuating-financial-asset-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/global-portfolio-reallocations-squeeze.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/impatience-with-monetary-policy-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/02/world-financial-turbulence-squeeze-of.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/01/exchange-rate-conflicts-squeeze-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/10/imf-view-squeeze-of-economic-activity.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html)
- Financial repression of interest rates and credit affecting the most people without means and access to sophisticated financial investments with likely adverse effects on income distribution and wealth disparity (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/financial-asset-values-rebound-from.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/financial-turbulence-twenty-four.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/twenty-four-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/04/proceeding-cautiously-in-monetary.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/closely-monitoring-global-economic-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/12/dollar-revaluation-and-decreasing.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/dollar-revaluation-constraining.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/11/live-possibility-of-interest-rates.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/labor-market-uncertainty-and-interest.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/interest-rate-policy-dependent-on-what.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/08/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/international-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/dollar-devaluation-and-carry-trade.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/volatility-of-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/global-competitive-devaluation-rules.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/02/job-creation-and-monetary-policy-twenty.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/growth-uncertainties-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/10/world-financial-turbulence-twenty-seven.html)
- 47 million in poverty and 33 million without health insurance with family income adjusted for inflation regressing to 1996 levels (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/10/interest-rate-policy-uncertainty-imf.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/financial-volatility-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/09/duration-dumping-and-peaking-valuations.html)
- Net worth of households and nonprofits organizations increasing by 16.7 percent after adjusting for inflation in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IQ2016 when it would have grown over 28.6 percent at trend of 3.1 percent per year in real terms from IVQ1945 to IQ2016 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/of-course-considerable-uncertainty.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/monetary-policy-and-fluctuations-of_13.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/weakening-equities-and-dollar.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/09/monetary-policy-designed-on-measurable.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/fluctuating-financial-asset-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/dollar-revaluation-and-financial-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/financial-volatility-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/06/financial-indecision-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/global-financial-risks-recovery-without.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/collapse-of-united-states-dynamism-of.html). Financial assets increased $18.3 trillion while nonfinancial assets increased $3.4 trillion with likely concentration of wealth in those with access to sophisticated financial investments. Real estate assets adjusted for inflation fell 2.7 percent.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) revised on Mar 17, 2016 “With the release of January 2016 data on March 17, job openings, hires, and separations data have been revised from December 2000 forward to incorporate annual updates to the Current Employment Statistics employment estimates and the Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey (JOLTS) seasonal adjustment factors. In addition, all data series are now available on a seasonally adjusted basis. Tables showing the revisions from 2000 through 2015 can be found using this link:http://www.bls.gov/jlt/revisiontables.htm.” (http://www.bls.gov/jlt/). Hiring in the nonfarm sector (HNF) has declined from 63.491 million in 2006 to 61.680 million in 2015 or by 1.811 million while hiring in the private sector (HP) has declined from 59.206 million in 2006 to 57.557 million in 2015 or by 1.649 million, as shown in Table I-1. The ratio of nonfarm hiring to employment (RNF) has fallen from 47.1 in 2005 to 43.5 in 2015 and in the private sector (RHP) from 52.8 in 2005 to 48.0 in 2015. Hiring has not recovered as in previous cyclical expansions because of the low rate of economic growth in the current cyclical expansion. The civilian noninstitutional population or those in condition to work increased from 228.815 million in 2006 to 250.801 million in 2015 or by 21.986 million. Hiring has not recovered prerecession levels while needs of hiring multiplied because of growth of population by more than 21 million. Private hiring of 59.206 million in 2006 was equivalent to 25.9 percent of the civilian noninstitutional population of 228.815, or those in condition of working, falling to 57.557 million in 2015 or 22.9 percent of the civilian noninstitutional population of 250.801 million in 2015. The percentage of hiring in civilian noninstitutional population of 25.9 percent in 2006 would correspond to 64.957 million of hiring in 2015, which would be 7.400 million higher than actual 57.557 million in 2015. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. US economic growth has been at only 2.1 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 27 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IQ2016. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the third estimate of GDP for IQ2016 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2016/pdf/gdp1q16_3rd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,745.9 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,355.6 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,745.9/$14,355.6 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/financial-asset-values-rebound-from.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/appropriate-for-fed-to-increase.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1989 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/financial-asset-values-rebound-from.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/appropriate-for-fed-to-increase.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IQ2016 would have accumulated to 27.6 percent. GDP in IQ2016 would be $19,129.5 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2614.9 billion than actual $16,514.6 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 23.7 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 14.1 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/fluctuating-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/financial-turbulence-twenty-four.html). US GDP in IQ2016 is 13.7 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,514.6 billion in IQ2016 or 10.2 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.2 percent. Professor John H. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. Cochrane (2016May02) measures GDP growth in the US at average 3.5 percent per year from 1950 to 2000 and only at 1.76 percent per year from 2000 to 2015 with only at 2.0 percent annual equivalent in the current expansion. Cochrane (2016May02) proposes drastic changes in regulation and legal obstacles to private economic activity. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth of manufacturing at average 3.2 percent per year from May 1919 to May 2016. Growth at 3.2 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 108.2316 in Dec 2007 to 141.0886 in May 2016. The actual index NSA in May 2016 is 103.0898, which is 26.9 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.1 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2015. Using trend growth of 2.1 percent per year, the index would increase to 128.9038 in May 2016. The output of manufacturing at 103.0898 in May 2016 is 20.0 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Table I-1, US, Annual Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF) and Total Private Hiring (HP) in the US in Thousands and Percentage of Total Employment
| HNF | Rate RNF | HP | Rate HP | |
| 2001 | 62,727 | 47.5 | 58,616 | 52.8 |
| 2002 | 58,416 | 44.7 | 54,592 | 50.0 |
| 2003 | 56,919 | 43.7 | 53,529 | 49.2 |
| 2004 | 60,236 | 45.7 | 56,567 | 51.3 |
| 2005 | 63,089 | 47.1 | 59,298 | 52.8 |
| 2006 | 63,491 | 46.5 | 59,206 | 51.7 |
| 2007 | 62,239 | 45.1 | 57,816 | 49.9 |
| 2008 | 54,764 | 39.9 | 51,260 | 44.7 |
| 2009 | 46,190 | 35.2 | 42,882 | 39.4 |
| 2010 | 48,659 | 37.3 | 44,831 | 41.6 |
| 2011 | 50,253 | 38.1 | 47,166 | 42.9 |
| 2012 | 52,354 | 39.0 | 48,914 | 43.6 |
| 2013 | 54,318 | 39.8 | 50,879 | 44.4 |
| 2014 | 58,632 | 42.2 | 54,980 | 47.0 |
| 2015 | 61,680 | 43.5 | 57,557 | 48.0 |
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-1 shows the annual level of total nonfarm hiring (HNF) that collapsed during the global recession after 2007 in contrast with milder decline in the shallow recession of 2001. Nonfarm hiring has not recovered, remaining at a depressed level. The civilian noninstitutional population or those in condition to work increased from 228.815 million in 2006 to 250.801 million in 2015 or by 21.986 million. Hiring has not recovered precession levels while needs of hiring multiplied because of growth of population by more than 21 million.
Chart I-1, US, Level Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF), Annual, 2001-2015
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-2 shows the ratio or rate of nonfarm hiring to employment (RNF) that also fell much more in the recession of 2007 to 2009 than in the shallow recession of 2001. Recovery is weak in the current environment of cyclical slow growth.
Chart I-2, US, Rate Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF), Annual, 2001-2015
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Yearly percentage changes of total nonfarm hiring (HNF) are provided in Table I-2. There were much milder declines in 2002 of 6.9 percent and 2.6 percent in 2003 followed by strong rebounds of 5.8 percent in 2004 and 4.7 percent in 2005. In contrast, the contractions of nonfarm hiring in the recession after 2007 were much sharper in percentage points: 2.0 in 2007, 12.0 in 2008 and 15.7 percent in 2009. On a yearly basis, nonfarm hiring grew 5.3 percent in 2010 relative to 2009, 3.3 percent in 2011, 4.2 percent in 2012 and 3.8 percent in 2013. Nonfarm hiring grew 7.9 percent in 2014 and increased 5.2 percent in 2015. The relatively large length of 27 quarters of the current expansion reduces the likelihood of significant recovery of hiring levels in the United States because lower rates of growth and hiring in the final phase of expansions.
Table I-2, US, Annual Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF), Annual Percentage Change, 2002-2015
| Year | Annual ∆% |
| 2002 | -6.9 |
| 2003 | -2.6 |
| 2004 | 5.8 |
| 2005 | 4.7 |
| 2006 | 0.6 |
| 2007 | -2.0 |
| 2008 | -12.0 |
| 2009 | -15.7 |
| 2010 | 5.3 |
| 2011 | 3.3 |
| 2012 | 4.2 |
| 2013 | 3.8 |
| 2014 | 7.9 |
| 2015 | 5.2 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Total private hiring (HP) 12-month percentage changes of annual data are in Chart I-3. There has been sharp contraction of total private hiring in the US and only milder recovery from 2010 to 2015.
Chart I-3, US, Total Nonfarm Hiring Level, Annual, ∆%, 2001-2015
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Total private hiring (HP) annual data are in Chart I-5. There has been sharp contraction of total private hiring in the US and only milder recovery from 2010 to 2015.
Chart I-5, US, Total Private Hiring, Annual, 2001-2015
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-5A plots the rate of total private hiring relative to employment (RHP). The rate collapsed during the global recession after 2007 with insufficient recovery.
Chart I-5A, US, Rate Total Private Hiring, Annual, 2001-2015
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Total nonfarm hiring (HNF), total private hiring (HP) and their respective rates are in Table I-3 for the month of May in the years from 2001 to 2016. Hiring numbers are in thousands. There is recovery in HNF from 4187 thousand (or 4.2 million) in May 2009 to 4815 thousand in May 2010, 4617 thousand in May 2011, 4979 thousand in May 2012, 5134 thousand in May 2013, 5397 thousand in May 2014, 5756 thousand in May 2015 and 5595 thousand in May 2016 for cumulative gain of 33.6 percent at average rate of 4.2 percent per year. HP rose from 3908 thousand in May 2009 to 4060 thousand in May 2010, 4347 thousand in May 2011, 4675 thousand in May 2012, 4829 thousand in May 2013, 5064 thousand in May 2014, 5391 in May 2015 and 5225 thousand in May 2016 for cumulative gain of 33.7 percent at the average yearly rate of 4.2 percent. HNF has decreased from 5931 thousand in May 2006 to 5595 thousand in May 2016 or by 5.7 percent. HP has decreased from 5546 thousand in May 2006 to 5225 thousand in May 2016 or by 5.8 percent. The civilian noninstitutional population of the US, or those in condition of working, rose from 228.428 million in May 2006 to 253.174 million in May 2016, by 24.746 million or 10.8 percent. There is often ignored ugly fact that hiring decreased by around 5.8 percent while population available for working increased around 10.8 percent. Private hiring of 59.206 million in 2006 was equivalent to 25.9 percent of the civilian noninstitutional population of 228.815, or those in condition of working, falling to 57.557 million in 2015 or 22.9 percent of the civilian noninstitutional population of 250.801 million in 2015. The percentage of hiring in civilian noninstitutional population of 25.9 percent in 2006 would correspond to 64.957 million of hiring in 2015, which would be 7.400 million higher than actual 57.557 million in 2015. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. Cyclical slow growth over the entire business cycle from IVQ2007 to the present in comparison with earlier cycles and long-term trend (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/financial-asset-values-rebound-from.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/appropriate-for-fed-to-increase.html) explains the fact that there are many million fewer hires in the US than before the global recession. The labor market continues to be fractured, failing to provide an opportunity to exit from unemployment/underemployment or to find an opportunity for advancement away from declining inflation-adjusted earnings.
Table I-3, US, Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF) and Total Private Hiring (HP) in the US in
Thousands and in Percentage of Total Employment Not Seasonally Adjusted
| HNF | Rate RNF | HP | Rate HP | |
| 2001 May | 5841 | 4.4 | 5462 | 4.9 |
| 2002 May | 5334 | 4.1 | 4978 | 4.6 |
| 2003 May | 4999 | 3.8 | 4710 | 4.3 |
| 2004 May | 5356 | 4.0 | 5068 | 4.6 |
| 2005 May | 5729 | 4.3 | 5406 | 4.8 |
| 2006 May | 5931 | 4.3 | 5546 | 4.8 |
| 2007 May | 5758 | 4.2 | 5353 | 4.6 |
| 2008 May | 5058 | 3.7 | 4730 | 4.1 |
| 2009 May | 4187 | 3.2 | 3908 | 3.6 |
| 2010 May | 4815 | 3.7 | 4060 | 3.8 |
| 2011 May | 4617 | 3.5 | 4347 | 4.0 |
| 2012 May | 4979 | 3.7 | 4675 | 4.2 |
| 2013 May | 5134 | 3.8 | 4829 | 4.2 |
| 2014 May | 5397 | 3.9 | 5064 | 4.3 |
| 2015 May | 5756 | 4.0 | 5391 | 4.5 |
| 2016 May | 5595 | 3.9 | 5225 | 4.3 |
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-6 provides total nonfarm hiring on a monthly basis from 2001 to 2016. Nonfarm hiring rebounded in early 2010 but then fell and stabilized at a lower level than the early peak not-seasonally adjusted (NSA) of 4815 in May 2010 until it surpassed it with 5006 in Jun 2011 but declined to 3092 in Dec 2012. Nonfarm hiring fell to 2997 in Dec 2011 from 3814 in Nov 2011 and to revised 3629 in Feb 2012, increasing to 4197 in Mar 2012, 3092 in Dec 2012 and 4238 in Jan 2013 and declining to 3690 in Feb 2013. Nonfarm hires not seasonally adjusted increased to 4257 in Nov 2013 and 3223 in Dec 2013. Nonfarm hires reached 3730 in Dec 2014, 3919 in Dec 2015 and 5595 in May 2016. Chart I-6 provides seasonally adjusted (SA) monthly data. The number of seasonally-adjusted hires in Oct 2011 was 4239 thousand, increasing to revised 4470 thousand in Feb 2012, or 5.4 percent, moving to 4345 in Dec 2012 for cumulative increase of 2.6 percent from 4234 in Dec 2011 and 4488 in Dec 2013 for increase of 3.3 percent relative to 4345 in Dec 2012. The number of hires not seasonally adjusted was 5006 in Jun 2011, falling to 2997 in Dec 2011 but increasing to 4110 in Jan 2012 and declining to 3092 in Dec 2012. The number of nonfarm hiring not seasonally adjusted fell by 40.1 percent from 5006 in Jun 2011 to 2997 in Dec 2011 and fell 40.1 percent from 5162 in Jun 2012 to 3092 in Dec 2012 in a yearly-repeated seasonal pattern. The number of nonfarm hires not seasonally adjusted fell from 5114 in Jun 2013 to 3223 in Dec 2013, or decline of 37.0 percent, showing strong seasonality. The number of nonfarm hires not seasonally adjusted fell from 5570 in Jun 2014 to 3730 in Dec 2014 or 33.0 percent. The level of nonfarm hires fell from 5918 in Jun 2015 to 3919 in Dec 2015 or 33.8 percent.
Chart I-6, US, Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF), 2001-2016 Month SA
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Similar behavior occurs in the rate of nonfarm hiring in Chart I-7. Recovery in early 2010 was followed by decline and stabilization at a lower level but with stability in monthly SA estimates of 3.2 in Aug 2011 to 3.2 in Jan 2012, increasing to 3.3 in May 2012 and stabilizing to 3.3 in Jun 2012. The rate stabilized at 3.2 in Jul 2012, increasing to 3.3 in Aug 2012 but falling to 3.2 in Dec 2012 and 3.3 in Dec 2013. The rate not seasonally adjusted fell from 3.8 in Jun 2011 to 2.2 in Dec 2011, climbing to 3.8 in Jun 2012 but falling to 2.3 in Dec 2012. The rate of nonfarm hires not seasonally adjusted fell from 3.7 in Jun 2013 to 2.3 in Dec 2013. The NSA rate of nonfarm hiring fell from 4.0 in Jun 2014 to 2.6 in Dec 2014. The NSA rate fell from 4.1 in Jun 2015 to 2.7 in Dec 2015. Rates of nonfarm hiring NSA were in the range of 2.7 (Dec) to 4.4 (Jun) in 2006. The rate of nonfarm hiring SA stood at 3.5 in May 2016 and at 3.9 NSA.
Chart I-7, US, Rate Total Nonfarm Hiring, Month SA 2001-2016
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
There is only milder improvement in total private hiring shown in Chart I-8. Hiring private (HP) rose in 2010 with stability and renewed increase in 2011 followed by almost stationary series in 2012. The number of private hiring seasonally adjusted fell from 4043 thousand in Sep 2011 to 3933 in Dec 2011 or by 2.7 percent, decreasing to 4015 in Jan 2012 or decline by 0.7 percent relative to the level in Sep 2011. Private hiring fell to 3961 in Sep 2012 or lower by 2.0 percent relative to Sep 2011, moving to 4049 in Dec 2012 for increase of 0.8 percent relative to 4015 in Jan 2012. The number of private hiring not seasonally adjusted fell from 4626 in Jun 2011 to 2817 in Dec 2011 or by 39.1 percent, reaching 3855 in Jan 2012 or decline of 16.7 percent relative to Jun 2011 and moving to 2911 in Dec 2012 or 38.8 percent lower relative to 4757 in Jun 2012. Hires not seasonally adjusted fell from 4761 in Jun 2013 to 3059 in Dec 2013. The level of private hiring NSA fell from 5151 in Jun 2014 to 3532 in Dec 2014 or 31.4 percent. The level of private hiring fell from 5475 in Jun 2015 to 3697 in Dec 2015 or 32.5 percent. Companies reduce hiring in the latter part of the year that explains the high seasonality in year-end employment data. For example, NSA private hiring fell from 5614 in Jun 2006 to 3579 in Dec 2006 or by 36.2 percent. Private hiring NSA data are useful in showing the huge declines from the period before the global recession. HP has decreased from 5546 thousand in May 2006 to 5225 thousand in May 2016 or by 5.8 percent. The civilian noninstitutional population of the US, or those in condition of working, rose from 228.428 million in May 2006 to 253.174 million in May 2016, by 24.746 million or 10.8 percent. There is often ignored ugly fact that hiring decreased by around 5.8 percent while population available for working increased around 10.8 percent. Private hiring of 59.206 million in 2006 was equivalent to 25.9 percent of the civilian noninstitutional population of 228.815, or those in condition of working, falling to 57.557 million in 2015 or 22.9 percent of the civilian noninstitutional population of 250.801 million in 2015. The percentage of hiring in civilian noninstitutional population of 25.9 percent in 2006 would correspond to 64.957 million of hiring in 2015, which would be 7.400 million higher than actual 57.557 million in 2015. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. Cyclical slow growth over the entire business cycle from IVQ2007 to the present in comparison with earlier cycles and long-term trend (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/financial-asset-values-rebound-from.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/appropriate-for-fed-to-increase.html) explains the fact that there are many million fewer hires in the US than before the global recession. The labor market continues to be fractured, failing to provide an opportunity to exit from unemployment/underemployment or to find an opportunity for advancement away from declining inflation-adjusted earnings.
Chart I-8, US, Total Private Hiring Month SA 2001-2016
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-9 shows similar behavior in the rate of private hiring. The rate in 2011 in monthly SA data did not rise significantly above the peak in 2010. The rate seasonally adjusted fell from 3.7 in Sep 2011 to 3.5 in Dec 2011 and reached 3.6 in Dec 2012 and 3.6 in Dec 2013. The rate not seasonally adjusted (NSA) fell from 3.7 in Sep 2011 to 2.5 in Dec 2011, increasing to 3.8 in Oct 2012 but falling to 2.6 in Dec 2012 and 3.4 in Mar 2013. The NSA rate of private hiring fell from 4.8 in Jul 2006 to 3.4 in Aug 2009 but recovery was insufficient to only 3.9 in Aug 2012, 2.6 in Dec 2012 and 2.6 in Dec 2013. The NSA rate increased to 3.0 in Dec 2015 and 4.3 in May 2016.
Chart I-9, US, Rate Total Private Hiring Month SA 2001-2016
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
The JOLTS report of the Bureau of Labor Statistics also provides total nonfarm job openings (TNF JOB), TNF JOB rate and TNF LD (layoffs and discharges) shown in Table I-4 for the month of Apr from 2001 to 2016. The final column provides annual TNF LD for the years from 2001 to 2015. Nonfarm job openings (TNF JOB) increased from a peak of 4564 in May 2007 to 5499 in May 2016 or by 20.5 percent while the rate increased from 3.2 to 3.7. This was mediocre performance because the civilian noninstitutional population of the US, or those in condition of working, rose from 228.428 million in May 2007 to 253.174 million in May 2016, by 24.746 million or 10.8 percent. Nonfarm layoffs and discharges (TNF LD) rose from 1523 in May 2007 to 1905 in May 2009 or by 25.1 percent. The annual data show layoffs and discharges rising from 20.9 million in 2006 to 26.6 million in 2009 or by 27.3 percent. Business pruned payroll jobs to survive the global recession but there has not been hiring because of the low rate of GDP growth. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions.
Table I-4, US, Total Nonfarm Job Openings and Total Nonfarm Layoffs and Discharges, Thousands NSA
| TNF JOB | TNF JOB | TNF LD | TNF LD | |
| May 2001 | 4515 | 3.3 | 1637 | 24271 |
| May 2002 | 3575 | 2.6 | 1609 | 22719 |
| May 2003 | 3205 | 2.4 | 1607 | 23420 |
| May 2004 | 3643 | 2.7 | 1517 | 22584 |
| May 2005 | 3879 | 2.8 | 1577 | 22151 |
| May 2006 | 4388 | 3.1 | 1627 | 20856 |
| May 2007 | 4564 | 3.2 | 1523 | 21997 |
| May 2008 | 3974 | 2.8 | 1623 | 23969 |
| May 2009 | 2427 | 1.8 | 1905 | 26557 |
| May 2010 | 2893 | 2.2 | 1584 | 21703 |
| May 2011 | 3110 | 2.3 | 1583 | 20756 |
| May 2012 | 3705 | 2.7 | 1725 | 20952 |
| May 2013 | 3880 | 2.8 | 1630 | 19903 |
| May 2014 | 4610 | 3.2 | 1567 | 20420 |
| May 2015 | 5390 | 3.7 | 1624 | 20942 |
| May 2016 | 5499 | 3.7 | 1563 |
Notes: TNF JOB: Total Nonfarm Job Openings; LD: Layoffs and Discharges
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-10 shows monthly job openings rising from the trough in 2009 to a high in the beginning of 2010. Job openings then stabilized into 2011 but have surpassed the peak of 3220 seasonally adjusted in Apr 2010 with 3576 seasonally adjusted in Dec 2012, which is higher by 11.1 percent relative to Apr 2010 but higher by 0.6 percent relative to 3556 in Nov 2012 and lower by 7.2 percent than 3852 in Mar 2012. Nonfarm job openings increased from 3576 in Dec 2012 to 3742 in Dec 2013 or by 4.6 percent and to 4815 in Dec 2014 or 28.7 percent relative to 2013. The high of job openings not seasonally adjusted was 3408 in Apr 2010 that was surpassed by 3647 in Jul 2011, increasing to 3905 in Oct 2012 but declining to 3218 in Dec 2012 and increasing to 3369 in Dec 2013. The level of job opening NSA increased to 4844 in Dec 2015. The level of job opening NSA increased to 5499 in May 2016. The level of job openings not seasonally adjusted fell to 3218 in Dec 2012 or by 17.3 percent relative to 3891 in Apr 2012. There is here again the strong seasonality of year-end labor data. Job openings fell from 4199 in Apr 2013 to 3369 in Dec 2013 and from 4829 in Apr 2014 to 44033 in Dec 2014, showing strong seasonal effects. The level of nonfarm job openings decreased from 5862 in Apr 2015 to 4844 in Dec 2015 or by 17.4 percent. Nonfarm job openings (TNF JOB) increased from a peak of 4564 in May 2007 to 5499 in May 2016 or by 20.5 percent while the rate increased from 3.2 to 3.7. This was mediocre performance because the civilian noninstitutional population of the US, or those in condition of working, rose from 228.428 million in May 2007 to 253.174 million in May 2016, by 24.746 million or 10.8 percent. Nonfarm layoffs and discharges (TNF LD) rose from 1523 in May 2007 to 1905 in May 2009 or by 25.1 percent. The annual data show layoffs and discharges rising from 20.9 million in 2006 to 26.6 million in 2009 or by 27.3 percent. Business pruned payroll jobs to survive the global recession but there has not been hiring because of the low rate of GDP growth. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. US economic growth has been at only 2.1 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 27 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IQ2016. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the third estimate of GDP for IQ2016 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2016/pdf/gdp1q16_3rd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,745.9 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,355.6 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,745.9/$14,355.6 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/financial-asset-values-rebound-from.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/appropriate-for-fed-to-increase.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1989 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/financial-asset-values-rebound-from.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/appropriate-for-fed-to-increase.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IQ2016 would have accumulated to 27.6 percent. GDP in IQ2016 would be $19,129.5 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2614.9 billion than actual $16,514.6 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 23.7 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 14.1 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/fluctuating-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/financial-turbulence-twenty-four.html). US GDP in IQ2016 is 13.7 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,514.6 billion in IQ2016 or 10.2 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.2 percent. Professor John H. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. Cochrane (2016May02) measures GDP growth in the US at average 3.5 percent per year from 1950 to 2000 and only at 1.76 percent per year from 2000 to 2015 with only at 2.0 percent annual equivalent in the current expansion. Cochrane (2016May02) proposes drastic changes in regulation and legal obstacles to private economic activity. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth of manufacturing at average 3.2 percent per year from May 1919 to May 2016. Growth at 3.2 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 108.2316 in Dec 2007 to 141.0886 in May 2016. The actual index NSA in May 2016 is 103.0898, which is 26.9 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.1 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2015. Using trend growth of 2.1 percent per year, the index would increase to 128.9038 in May 2016. The output of manufacturing at 103.0898 in May 2016 is 20.0 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Chart I-10, US Job Openings, Thousands NSA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The rate of job openings in Chart I-11 shows similar behavior. The rate seasonally adjusted increased from 2.2 in Jan 2011 to 2.5 in Dec 2011, 2.6 in Dec 2012, 2.7 in Dec 2013 and 3.3 in Dec 2014. The rate seasonally adjusted stood at 3.6 in Dec 2015 and 3.7 in May 2016. The rate not seasonally adjusted rose from the high of 2.6 in Apr 2010 to 3.0 in Apr 2013, easing to 2.4 in Dec 2013. The rate of job openings NSA fell from 3.3 in Jul 2007 to 1.6 in Nov-Dec 2009, recovering to 3.3 in Dec 2015. The rate of job opening NSA stood at 3.7 in May 2016.
Chart I-11, US, Rate of Job Openings, NSA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Total separations are shown in Chart I-12. Separations are lower in 2012-16 than before the global recession but hiring has not recovered.
Chart I-12, US, Total Nonfarm Separations, Month Thousands SA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-13 provides annual total separations. Separations fell sharply during the global recession but hiring has not recovered relative to population growth.
Chart I-13, US, Total Separations, Annual, Thousands, 2001-2015
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Table I-5 provides total nonfarm total separations from 2001 to 2015. Separations fell from 61.3 million in 2006 to 47.6 million in 2010 or by 13.6 million and 48.2 million in 2011 or by 13.1 million. Total separations increased from 48.2 million in 2011 to 52.0 million in 2013 or by 3.7 million and to 55.6 million in 2014 or by 7.4 million relative to 2011. Total separations increased to 58.943 million in 2015 or by 10.7 million relative to 2011.
Table I-5, US, Total Nonfarm Total Separations, Thousands, 2001-2015
| Year | Annual Thousands |
| 2001 | 64560 |
| 2002 | 58942 |
| 2003 | 56961 |
| 2004 | 58224 |
| 2005 | 60633 |
| 2006 | 61284 |
| 2007 | 60984 |
| 2008 | 58209 |
| 2009 | 51358 |
| 2010 | 47649 |
| 2011 | 48214 |
| 2012 | 50143 |
| 2013 | 51951 |
| 2014 | 55625 |
| 2015 | 58943 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Monthly data of layoffs and discharges reach a peak in early 2009, as shown in Chart I-14. Layoffs and discharges dropped sharply with the recovery of the economy in 2010 and 2011 once employers reduced their job count to what was required for cost reductions and loss of business. Weak rates of growth of GDP (Table I-5 provides total nonfarm total separations from 2001 to 2015. Separations fell from 61.3 million in 2006 to 47.6 million in 2010 or by 13.6 million and 48.2 million in 2011 or by 13.1 million. Total separations increased from 48.2 million in 2011 to 52.0 million in 2013 or by 3.7 million and to 55.6 million in 2014 or by 7.4 million relative to 2011. Total separations increased to 58.943 million in 2015 or by 10.7 million relative to 2011.) frustrated employment recovery. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth.
Chart I-14, US, Total Nonfarm Layoffs and Discharges, Monthly Thousands SA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Layoffs and discharges in Chart I-15 rose sharply to a peak in 2009. There was pronounced drop into 2010 and 2011 with mild increase into 2012 and renewed decline into 2013. There is mild increase into 2014-2015.
Chart I-15, US, Total Nonfarm Layoffs and Discharges, Annual, 2001-2015
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Annual layoff and discharges are in Table I-6. Layoffs and discharges increased sharply from 20.856 million in 2006 to 26.557 million in 2009 or 27.3 percent. Layoff and discharges fell to 19.903 million in 2013 or 25.1 percent relative to 2009 and increased to 20.420 million in 2014 or 2.6 percent relative to 2013. Layoffs and discharges increased to 20.942 million in 2015 or 2.6 percent relative to 2014.
Table I-6, US, Total Nonfarm Layoffs and Discharges, Thousands, 2001-2015
| Year | Annual Thousands |
| 2001 | 24271 |
| 2002 | 22719 |
| 2003 | 23420 |
| 2004 | 22584 |
| 2005 | 22151 |
| 2006 | 20856 |
| 2007 | 21997 |
| 2008 | 23969 |
| 2009 | 26557 |
| 2010 | 21703 |
| 2011 | 20756 |
| 2012 | 20952 |
| 2013 | 19903 |
| 2014 | 20420 |
| 2015 | 20942 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
IA2 Labor Underutilization. The Bureau of Labor Statistics also provides alternative measures of labor underutilization shown in Table I-7. The most comprehensive measure is U6 that consists of total unemployed plus total employed part time for economic reasons plus all marginally attached workers as percent of the labor force. U6 not seasonally adjusted has risen from 8.2 percent in 2006 to 9.9 percent in Jun 2016.
Table I-7, US, Alternative Measures of Labor Underutilization NSA %
| U1 | U2 | U3 | U4 | U5 | U6 | |
| 2016 | ||||||
| Jun | 1.9 | 2.3 | 5.1 | 5.4 | 6.1 | 9.9 |
| May | 2.0 | 2.1 | 4.5 | 4.9 | 5.6 | 9.4 |
| Apr | 2.2 | 2.3 | 4.7 | 5.0 | 5.7 | 9.3 |
| Mar | 2.3 | 2.6 | 5.1 | 5.5 | 6.1 | 9.9 |
| Feb | 2.2 | 2.7 | 5.2 | 5.6 | 6.3 | 10.1 |
| Jan | 2.1 | 2.7 | 5.3 | 5.7 | 6.5 | 10.5 |
| 2015 | ||||||
| Dec | 2.1 | 2.4 | 4.8 | 5.2 | 5.9 | 9.8 |
| Nov | 2.1 | 2.3 | 4.8 | 5.2 | 5.8 | 9.6 |
| Oct | 2.1 | 2.3 | 4.8 | 5.2 | 6.0 | 9.5 |
| Sep | 2.0 | 2.2 | 4.9 | 5.3 | 6.0 | 9.6 |
| Aug | 2.1 | 2.5 | 5.2 | 5.6 | 6.3 | 10.3 |
| Jul | 2.0 | 2.7 | 5.6 | 6.0 | 6.7 | 10.7 |
| Jun | 2.1 | 2.5 | 5.5 | 5.8 | 6.6 | 10.8 |
| May | 2.4 | 2.5 | 5.3 | 5.6 | 6.4 | 10.4 |
| Apr | 2.4 | 2.5 | 5.1 | 5.5 | 6.4 | 10.4 |
| Mar | 2.6 | 2.9 | 5.6 | 6.0 | 6.8 | 11.0 |
| Feb | 2.7 | 3.0 | 5.8 | 6.3 | 7.1 | 11.4 |
| Jan | 2.7 | 3.1 | 6.1 | 6.5 | 7.4 | 12.0 |
| 2014 | ||||||
| Dec | 2.5 | 2.8 | 5.4 | 5.8 | 6.7 | 11.1 |
| Nov | 2.7 | 2.7 | 5.5 | 5.9 | 6.8 | 11.0 |
| Oct | 2.7 | 2.6 | 5.5 | 6.0 | 6.8 | 11.1 |
| Sep | 2.7 | 2.7 | 5.7 | 6.2 | 7.1 | 11.3 |
| Aug | 2.8 | 3.0 | 6.3 | 6.7 | 7.5 | 12.0 |
| Jul | 2.8 | 3.1 | 6.5 | 7.0 | 7.8 | 12.6 |
| Jun | 2.8 | 3.0 | 6.3 | 6.7 | 7.5 | 12.4 |
| May | 3.1 | 3.0 | 6.1 | 6.5 | 7.3 | 11.7 |
| Apr | 3.3 | 3.2 | 5.9 | 6.3 | 7.2 | 11.8 |
| Mar | 3.7 | 3.7 | 6.8 | 7.2 | 8.1 | 12.8 |
| Feb | 3.6 | 3.9 | 7.0 | 7.5 | 8.4 | 13.1 |
| Jan | 3.5 | 4.0 | 7.0 | 7.5 | 8.6 | 13.5 |
| 2013 | ||||||
| Dec | 3.5 | 3.5 | 6.5 | 7.0 | 7.9 | 13.0 |
| Nov | 3.7 | 3.5 | 6.6 | 7.1 | 7.9 | 12.7 |
| Oct | 3.7 | 3.6 | 7.0 | 7.4 | 8.3 | 13.2 |
| Sep | 3.7 | 3.5 | 7.0 | 7.5 | 8.4 | 13.1 |
| Aug | 3.7 | 3.8 | 7.3 | 7.9 | 8.7 | 13.6 |
| Jul | 3.7 | 3.8 | 7.7 | 8.3 | 9.1 | 14.3 |
| Jun | 3.9 | 3.8 | 7.8 | 8.4 | 9.3 | 14.6 |
| May | 4.1 | 3.7 | 7.3 | 7.7 | 8.5 | 13.4 |
| Apr | 4.3 | 3.9 | 7.1 | 7.6 | 8.5 | 13.4 |
| Mar | 4.3 | 4.3 | 7.6 | 8.1 | 9.0 | 13.9 |
| Feb | 4.3 | 4.6 | 8.1 | 8.6 | 9.6 | 14.9 |
| Jan | 4.3 | 4.9 | 8.5 | 9.0 | 9.9 | 15.4 |
| 2012 | ||||||
| Dec | 4.2 | 4.3 | 7.6 | 8.3 | 9.2 | 14.4 |
| Nov | 4.2 | 3.9 | 7.4 | 7.9 | 8.8 | 13.9 |
| Oct | 4.3 | 3.9 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 9.0 | 13.9 |
| Sep | 4.2 | 4.0 | 7.6 | 8.0 | 9.0 | 14.2 |
| Aug | 4.3 | 4.4 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 9.7 | 14.6 |
| Jul | 4.3 | 4.6 | 8.6 | 9.1 | 10.0 | 15.2 |
| Jun | 4.5 | 4.4 | 8.4 | 8.9 | 9.9 | 15.1 |
| May | 4.7 | 4.3 | 7.9 | 8.4 | 9.3 | 14.3 |
| Apr | 4.8 | 4.3 | 7.7 | 8.3 | 9.1 | 14.1 |
| Mar | 4.9 | 4.8 | 8.4 | 8.9 | 9.7 | 14.8 |
| Feb | 4.9 | 5.1 | 8.7 | 9.3 | 10.2 | 15.6 |
| Jan | 4.9 | 5.4 | 8.8 | 9.4 | 10.5 | 16.2 |
| 2011 | ||||||
| Dec | 4.8 | 5.0 | 8.3 | 8.8 | 9.8 | 15.2 |
| Nov | 4.9 | 4.7 | 8.2 | 8.9 | 9.7 | 15.0 |
| Oct | 5.0 | 4.8 | 8.5 | 9.1 | 10.0 | 15.3 |
| Sep | 5.2 | 5.0 | 8.8 | 9.4 | 10.2 | 15.7 |
| Aug | 5.2 | 5.1 | 9.1 | 9.6 | 10.6 | 16.1 |
| Jul | 5.2 | 5.2 | 9.3 | 10.0 | 10.9 | 16.3 |
| Jun | 5.1 | 5.1 | 9.3 | 9.9 | 10.9 | 16.4 |
| May | 5.5 | 5.1 | 8.7 | 9.2 | 10.0 | 15.4 |
| Apr | 5.5 | 5.2 | 8.7 | 9.2 | 10.1 | 15.5 |
| Mar | 5.7 | 5.8 | 9.2 | 9.7 | 10.6 | 16.2 |
| Feb | 5.6 | 6.0 | 9.5 | 10.1 | 11.1 | 16.7 |
| Jan | 5.6 | 6.2 | 9.8 | 10.4 | 11.4 | 17.3 |
| Dec 2010 | 5.4 | 5.9 | 9.1 | 9.9 | 10.7 | 16.6 |
| Annual | ||||||
| 2015 | 2.3 | 2.6 | 5.3 | 5.7 | 6.4 | 10.4 |
| 2014 | 3.0 | 3.1 | 6.2 | 6.6 | 7.5 | 12.0 |
| 2013 | 3.9 | 3.9 | 7.4 | 7.9 | 8.8 | 13.8 |
| 2012 | 4.5 | 4.4 | 8.1 | 8.6 | 9.5 | 14.7 |
| 2011 | 5.3 | 5.3 | 8.9 | 9.5 | 10.4 | 15.9 |
| 2010 | 5.7 | 6.0 | 9.6 | 10.3 | 11.1 | 16.7 |
| 2009 | 4.7 | 5.9 | 9.3 | 9.7 | 10.5 | 16.2 |
| 2008 | 2.1 | 3.1 | 5.8 | 6.1 | 6.8 | 10.5 |
| 2007 | 1.5 | 2.3 | 4.6 | 4.9 | 5.5 | 8.3 |
| 2006 | 1.5 | 2.2 | 4.6 | 4.9 | 5.5 | 8.2 |
| 2005 | 1.8 | 2.5 | 5.1 | 5.4 | 6.1 | 8.9 |
| 2004 | 2.1 | 2.8 | 5.5 | 5.8 | 6.5 | 9.6 |
| 2003 | 2.3 | 3.3 | 6.0 | 6.3 | 7.0 | 10.1 |
| 2002 | 2.0 | 3.2 | 5.8 | 6.0 | 6.7 | 9.6 |
| 2001 | 1.2 | 2.4 | 4.7 | 4.9 | 5.6 | 8.1 |
| 2000 | 0.9 | 1.8 | 4.0 | 4.2 | 4.8 | 7.0 |
Note: LF: labor force; U1, persons unemployed 15 weeks % LF; U2, job losers and persons who completed temporary jobs %LF; U3, total unemployed % LF; U4, total unemployed plus discouraged workers, plus all other marginally attached workers; % LF plus discouraged workers; U5, total unemployed, plus discouraged workers, plus all other marginally attached workers % LF plus all marginally attached workers; U6, total unemployed, plus all marginally attached workers, plus total employed part time for economic reasons % LF plus all marginally attached workers
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Monthly seasonally adjusted measures of labor underutilization are provided in Table I-8. U6 climbed from 16.1 percent in Aug 2011 to 16.4 percent in Sep 2011 and then fell to 14.5 percent in Mar 2012, reaching 9.6 percent in Jun 2016. Unemployment is an incomplete measure of the stress in US job markets. A different calculation in this blog is provided by using the participation rate in the labor force before the global recession. This calculation shows 23.7 million in job stress of unemployment/underemployment in Jun 2016, not seasonally adjusted, corresponding to 14.1 percent of the labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/fluctuating-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/financial-turbulence-twenty-four.html).
Table I-8, US, Alternative Measures of Labor Underutilization SA %
| U1 | U2 | U3 | U4 | U5 | U6 | |
| Jun 2016 | 2.0 | 2.4 | 4.9 | 5.2 | 6.0 | 9.6 |
| May | 1.9 | 2.3 | 4.7 | 5.0 | 5.7 | 9.7 |
| Apr | 2.1 | 2.4 | 5.0 | 5.3 | 6.0 | 9.7 |
| Mar | 2.1 | 2.4 | 5.0 | 5.3 | 6.0 | 9.8 |
| Feb | 2.1 | 2.4 | 4.9 | 5.3 | 6.0 | 9.7 |
| Jan | 2.0 | 2.3 | 4.9 | 5.3 | 6.2 | 9.9 |
| Dec 2015 | 2.1 | 2.4 | 5.0 | 5.4 | 6.1 | 9.9 |
| Nov | 2.1 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 5.4 | 6.1 | 9.9 |
| Oct | 2.1 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 5.4 | 6.2 | 9.8 |
| Sep | 2.1 | 2.5 | 5.1 | 5.4 | 6.2 | 10.0 |
| Aug | 2.2 | 2.6 | 5.1 | 5.5 | 6.2 | 10.3 |
| Jul | 2.1 | 2.6 | 5.3 | 5.7 | 6.4 | 10.4 |
| Jun | 2.2 | 2.6 | 5.3 | 5.7 | 6.4 | 10.5 |
| May | 2.4 | 2.7 | 5.5 | 5.8 | 6.6 | 10.7 |
| Apr | 2.3 | 2.6 | 5.4 | 5.9 | 6.7 | 10.8 |
| Mar | 2.4 | 2.7 | 5.5 | 5.9 | 6.7 | 10.9 |
| Feb | 2.5 | 2.7 | 5.5 | 6.0 | 6.8 | 11.0 |
| Jan | 2.6 | 2.7 | 5.7 | 6.1 | 7.0 | 11.3 |
| Dec 2014 | 2.6 | 2.8 | 5.6 | 6.0 | 6.9 | 11.2 |
| Nov | 2.7 | 2.9 | 5.8 | 6.2 | 7.0 | 11.4 |
| Oct | 2.8 | 2.8 | 5.7 | 6.2 | 7.1 | 11.5 |
| Sep | 2.8 | 2.9 | 6.0 | 6.4 | 7.3 | 11.8 |
| Aug | 2.9 | 3.1 | 6.2 | 6.6 | 7.4 | 12.0 |
| July | 3.0 | 3.1 | 6.2 | 6.6 | 7.5 | 12.2 |
| Jun | 3.0 | 3.1 | 6.1 | 6.5 | 7.3 | 12.0 |
| May | 3.1 | 3.2 | 6.2 | 6.7 | 7.5 | 12.1 |
| Apr | 3.2 | 3.3 | 6.2 | 6.7 | 7.5 | 12.3 |
| Mar | 3.4 | 3.5 | 6.7 | 7.1 | 7.9 | 12.6 |
| Feb | 3.4 | 3.5 | 6.7 | 7.1 | 8.0 | 12.6 |
| Jan | 3.4 | 3.5 | 6.6 | 7.1 | 8.1 | 12.7 |
| Dec 2013 | 3.6 | 3.5 | 6.7 | 7.3 | 8.1 | 13.1 |
| Nov | 3.7 | 3.7 | 6.9 | 7.4 | 8.2 | 13.1 |
| Oct | 3.8 | 4.0 | 7.2 | 7.7 | 8.6 | 13.7 |
| Sep | 3.8 | 3.8 | 7.3 | 7.8 | 8.6 | 13.7 |
| Aug | 3.9 | 3.8 | 7.3 | 7.8 | 8.6 | 13.6 |
| Jul | 3.9 | 3.8 | 7.3 | 7.9 | 8.7 | 13.8 |
| Jun | 4.0 | 3.9 | 7.5 | 8.1 | 9.1 | 14.2 |
| May | 4.1 | 3.9 | 7.5 | 7.9 | 8.8 | 13.8 |
| Apr | 4.1 | 4.1 | 7.6 | 8.1 | 8.9 | 14.0 |
| Mar | 4.1 | 4.1 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 8.9 | 13.8 |
| Feb | 4.1 | 4.1 | 7.7 | 8.2 | 9.2 | 14.3 |
| Jan | 4.2 | 4.3 | 8.0 | 8.4 | 9.4 | 14.5 |
| Dec 2012 | 4.3 | 4.2 | 7.9 | 8.5 | 9.4 | 14.4 |
| Nov | 4.2 | 4.2 | 7.7 | 8.3 | 9.2 | 14.4 |
| Oct | 4.4 | 4.2 | 7.8 | 8.3 | 9.2 | 14.4 |
| Sep | 4.4 | 4.2 | 7.8 | 8.3 | 9.3 | 14.8 |
| Aug | 4.5 | 4.4 | 8.1 | 8.6 | 9.6 | 14.6 |
| Jul | 4.5 | 4.6 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 9.6 | 14.8 |
| Jun | 4.7 | 4.6 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 9.6 | 14.8 |
| May | 4.6 | 4.5 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 9.6 | 14.8 |
| Apr | 4.6 | 4.4 | 8.2 | 8.8 | 9.6 | 14.6 |
| Mar | 4.6 | 4.5 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 9.6 | 14.5 |
| Feb | 4.7 | 4.6 | 8.3 | 8.9 | 9.8 | 15.0 |
| Jan | 4.8 | 4.7 | 8.3 | 8.9 | 9.9 | 15.2 |
| Dec 2011 | 4.9 | 4.9 | 8.5 | 9.1 | 10.0 | 15.2 |
| Nov | 5.0 | 5.0 | 8.6 | 9.3 | 10.1 | 15.5 |
| Oct | 5.1 | 5.1 | 8.8 | 9.4 | 10.3 | 15.8 |
| Sep | 5.4 | 5.2 | 9.0 | 9.7 | 10.5 | 16.4 |
| Aug | 5.4 | 5.2 | 9.0 | 9.6 | 10.5 | 16.1 |
| Jul | 5.3 | 5.3 | 9.0 | 9.6 | 10.6 | 15.9 |
| Jun | 5.3 | 5.3 | 9.1 | 9.7 | 10.7 | 16.1 |
| May | 5.3 | 5.4 | 9.0 | 9.5 | 10.3 | 15.8 |
| Apr | 5.2 | 5.4 | 9.1 | 9.7 | 10.5 | 16.1 |
| Mar | 5.3 | 5.4 | 9.0 | 9.5 | 10.4 | 15.9 |
| Feb | 5.3 | 5.5 | 9.0 | 9.6 | 10.6 | 16.0 |
| Jan | 5.5 | 5.5 | 9.1 | 9.7 | 10.8 | 16.2 |
Note: LF: labor force; U1, persons unemployed 15 weeks % LF; U2, job losers and persons who completed temporary jobs %LF; U3, total unemployed % LF; U4, total unemployed plus discouraged workers, plus all other marginally attached workers; % LF plus discouraged workers; U5, total unemployed, plus discouraged workers, plus all other marginally attached workers % LF plus all marginally attached workers; U6, total unemployed, plus all marginally attached workers, plus total employed part time for economic reasons % LF plus all marginally attached workers
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-16 provides U6 on a monthly basis from 2001 to 2016. There was a steep climb from 2007 into 2009 and then this measure of unemployment and underemployment stabilized at that high level but declined into 2012. The low of U6 SA was 8.0 percent in Mar 2007 and the peak was 17.1 percent in Apr 2010. The low NSA was 7.6 percent in Oct 2006 and the peak was 18.0 percent in Jan 2010.
Chart I-16, US, U6, total unemployed, plus all marginally attached workers, plus total employed Part-Time for Economic Reasons, Month, SA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-17 provides the number employed part-time for economic reasons or who cannot find full-time employment. There are sharp declines at the end of 2009, 2010 and 2011 but an increase in 2012 followed by relative stability in 2013-2016.
Chart I-17, US, Working Part-time for Economic Reasons
Thousands, Month SA 2001-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
ICA3 Ten Million Fewer Full-time Jobs. There is strong seasonality in US labor markets around the end of the year.
- Seasonally adjusted part-time for economic reasons. The number employed part-time for economic reasons because they could not find full-time employment fell from 9.166 million in Sep 2011 to 7.793 million in Mar 2012, seasonally adjusted, or decline of 1.373 million in six months, as shown in Table I-9. The number employed part-time for economic reasons rebounded to 8.667 million in Sep 2012 for increase of 669,000 in one month from Aug to Sep 2012. The number employed part-time for economic reasons declined to 8.229 million in Oct 2012 or by 438,000 again in one month, further declining to 8.150 million in Nov 2012 for another major one-month decline of 79,000 and 7.922 million in Dec 2012 or fewer 228,000 in just one month. The number employed part-time for economic reasons increased to 8.030 million in Jan 2013 or 108,000 more than in Dec 2012 and to 8.089 million in Feb 2013, declining to 7.901 million in May 2013 but increasing to 8.104 million in Jun 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 7.837 million in Aug 2013 for decline of 256,000 in one month from 8.093 million in Jul 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons increased 171,000 from 7.837 million in Aug 2013 to 8.008 million in Sep 2013. The number part-time for economic reasons rose to 8.028 million in Oct 2013, falling by 320,000 to 7.708 million in Nov 2013. The number part-time for economic reasons increased to 7.763 million in Dec 2013, decreasing to 7.250 million in Jan 2014. The number employed part-time for economic reasons fell from 7.250 million in Jan 2014 to 7.230 million in Feb 2014. The number employed part-time for economic reasons increased to 7.428 million in Mar 2014 and 7.452 million in Apr 2014. The number employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 7.219 million in May 2014, increasing to 7.473 million in Jun 2014. The level employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 7.440 million in Jul 2014 and 7.213 million in Aug 2014. The level employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 7.124 million in Sep 2014, 7.065 million in Oct 2014 and 6.844 million in Nov 2014. The level employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 6.786 million in Dec 2014, increasing to 6.784 million in Jan 2015. The level employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 6.630 million in Feb 2015, increasing to 6.673 million in Mar 2015. The level of employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 6.549 million in Apr 2015, increasing to 6.600 million in May 2015. The level employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 6.465 million in Jun 2015 and 6.300 million in Jul 2015. The level employed part-time for economic reasons increased to 6.481 million in Aug 2015, declining to 6.034 million in Sep 2015. The level employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 5.761 million in Oct 2015, increasing to 6.085 million in Nov 2015. The level of part-time for economic reasons fell to 6.022 million in Dec 2015, decreasing to 5.998 million in Jan 2016. The level employed part-time for economic reasons did not change to 5.988 in Feb 2016 and increased to 6.123 million in Mar 2016. The level employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 5.962 million in Apr 2016 and increased to 6.430 million in May 2016. The level of part-time for economic reasons fell to 5.843 million in Jun 2016. There is an increase of 231,000 in part-time for economic reasons from Aug 2012 to Oct 2012 and of 152,000 from Aug 2012 to Nov 2012.
- Seasonally adjusted full-time. The number employed full-time increased from 112.923 million in Oct 2011 to 115.023 million in Mar 2012 or 2.100 million but then fell to 114.224 million in May 2012 or 0.799 million fewer full-time employed than in Mar 2012. The number employed full-time increased from 114.750 million in Aug 2012 to 115.558 million in Oct 2012 or increase of 0.808 million full-time jobs in two months and further to 115.759 million in Jan 2013 or increase of 1.009 million more full-time jobs in five months from Aug 2012 to Jan 2013. The number of full time jobs decreased slightly to 115.689 million in Feb 2013, increasing to 116.211 million in May 2013 and 116.120 million in Jun 2013. Then number of full-time jobs increased to 116.156 million in Jul 2013, 116.475 million in Aug 2013 and 116.907 million in Sep 2013. The number of full-time jobs fell to 116.345 million in Oct 2013 and increased to 117.044 in Nov 2013. The level of full-time jobs increased to 117.307 million in Dec 2013, increasing to 117.568 million in Jan 2014 and 117.765 million in Feb 2014. The level of employment full-time increased to 117.950 million in Mar 2014 and 118.466 million in Apr 2014. The level of full-time employment reached 118.746 million in May 2014, decreasing to 118.233 million in Jun 2014. The level of full-time jobs increased to 118.454 million in Jul 2014 and 118.778 million in Aug 2014. The level of full-time jobs increased to 119.364 million in Sep 2014, 119.745 million in Oct 2014 and 119.641 million in Nov 2014. The level of full-time jobs increased to 119.999 million in Dec 2014 and 120.662 million in Jan 2015. The level of full-time jobs increased to 120.788 million in Feb 2015 and 120.976 million in Mar 2015. The level of full-time jobs decreased to 120.799 million in Apr 2015, increasing to 121.415 million in May 2015 and decreasing to 121.056 million in Jun 2015. The level of full-time jobs increased to 121.641 million in Jul 2015 and increased to 122.045 million in Aug 2015, decreasing to 121.873 million in Sep 2015. The level of full-time jobs increased to 122.054 million in Oct 2015 and increased to 122.099 million in Nov 2015. The level of full-time jobs increased to 122.603 million in Dec 2015 and 123.141 million in Jan 2016. The level of full-time jobs increased to 123.206 million in Feb 2016 and increased to 123.447 million in Mar 2016. The level of full-time jobs decreased to 123.194 million in Apr 2016 and 123.135 million in May 2016. The level of full-time jobs increased to 123.586 million in Jun 2016. Adjustments of benchmark and seasonality-factors at the turn of every year could affect comparability of labor market indicators (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets-in.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/02/job-creation-and-monetary-policy-twenty.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/02/financial-instability-rules.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/02/thirty-one-million-unemployed-or.html).
- Not seasonally adjusted part-time for economic reasons. The number of employed part-time for economic reasons actually increased without seasonal adjustment from 8.271 million in Nov 2011 to 8.428 million in Dec 2011 or by 157,000 and then to 8.918 million in Jan 2012 or by an additional 490,000 for cumulative increase from Nov 2011 to Jan 2012 of 647,000. The level of employed part-time for economic reasons then fell from 8.918 million in Jan 2012 to 7.867 million in Mar 2012 or by 1.051 million and to 7.694 million in Apr 2012 or 1.224 million fewer relative to Jan 2012. In Aug 2012, the number employed part-time for economic reasons reached 7.842 million NSA or 148,000 more than in Apr 2012. The number employed part-time for economic reasons increased from 7.842 million in Aug 2012 to 8.110 million in Sep 2012 or by 3.4 percent. The number part-time for economic reasons fell from 8.110 million in Sep 2012 to 7.870 million in Oct 2012 or by 240.000 in one month. The number employed part-time for economic reasons NSA increased to 8.628 million in Jan 2013 or 758,000 more than in Oct 2012. The number employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 8.298 million in Feb 2013, which is lower by 330,000 relative to 8.628 million in Jan 2013 but higher by 428,000 relative to 7.870 million in Oct 2012. The number employed part time for economic reasons fell to 7.734 million in Mar 2013 or 564,000 fewer than in Feb 2013 and fell to 7.709 million in Apr 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons reached 7.618 million in May 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons jumped from 7.618 million in May 2013 to 8.440 million in Jun 2013 or 822,000 in one month. The number employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 8.324 million in Jul 2013 and 7.690 million in Aug 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons NSA fell to 7.522 million in Sep 2013, increasing to 7.700 million in Oct 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 7.563 million in Nov 2013 and increased to 7.990 million in Dec 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 7.771 million in Jan 2014 and 7.397 million in Feb 2014. The level of part-time for economic reasons increased to 7.455 million in Mar 2014 and fell to 7.243 million in Apr 2014. The number of part-time for economic reasons fell to 6.960 million in May 2014, increasing to 7.805 million in Jun 2014. The level of part-time for economic reasons fell to 7.665 million in Jul 2014 and 7.083 million in Aug 2014. The level of part-time for economic reasons fell to 6.711 million in Sep 2014 and increased to 6.787 million in Oct 2014. The level of part-time for economic reasons reached 6.713 million in Nov 2014 and 6.970 million in Dec 2014, increasing to 7.269 million in Jan 2015. The level of part-time for economic reasons fell to 6.772 million in Feb 2015 and 6.672 million in Mar 2015, falling to 6.356 million in Apr 2015. The level of part-time for economic reasons increased to 6.363 million in May 2015 and to 6.776 million in Jun 2015, decreasing to 6.511 million in Jul 2015. The level of part-time for economic reasons fell to 6.361 million in Aug 2015 and 5.693 million in Sep 2015. The level of part-time for economic reasons fell to 5.536 million in Oct 2015, increasing to 5.967 million in Nov 2015. The level of part-time for economic reasons increased to 6.179 million in Dec 2015, increasing to 6.406 million in Jan 2016. The level of part-time for economic reasons decreased to 6.106 million in Feb 2016 and increased to 6.138 million in Mar 2016. The level of part-time for economic reasons decreased to 5.771 million in Apr 2016 and increased to 6.238 million in May 2016. The level of part-time for economic reasons decreased to 6.119 million in Jun 2016.
- Not seasonally adjusted full-time. The number employed full time without seasonal adjustment fell from 113.138 million in Nov 2011 to 113.050 million in Dec 2011 or by 88,000 and fell further to 111.879 in Jan 2012 for cumulative decrease of 1.259 million. The number employed full-time not seasonally adjusted fell from 113.138 million in Nov 2011 to 112.587 million in Feb 2012 or by 551.000 but increased to 116.214 million in Aug 2012 or 3.076 million more full-time jobs than in Nov 2011. The number employed full-time not seasonally adjusted decreased from 116.214 million in Aug 2012 to 115.678 million in Sep 2012 for loss of 536,000 full-time jobs and rose to 116.045 million in Oct 2012 or by 367,000 full-time jobs in one month relative to Sep 2012. The number employed full-time NSA fell from 116.045 million in Oct 2012 to 115.515 million in Nov 2012 or decline of 530.000 in one month. The number employed full-time fell from 115.515 in Nov 2012 to 115.079 million in Dec 2012 or decline by 436,000 in one month. The number employed full time fell from 115.079 million in Dec 2012 to 113.868 million in Jan 2013 or decline of 1.211 million in one month. The number of full time jobs increased to 114.191 in Feb 2012 or by 323,000 in one month and increased to 114.796 million in Mar 2013 for cumulative increase from Jan by 928,000 full-time jobs but decrease of 283,000 from Dec 2012. The number employed full time reached 117.400 million in Jun 2013 and increased to 117.688 in Jul 2013 or by 288,000. The number employed full-time reached 117.868 million in Aug 2013 for increase of 180,000 in one month relative to Jul 2013. The number employed full-time fell to 117.308 million in Sep 2013 or by 560,000. The number employed full-time fell to 116.798 million in Oct 2013 or decline of 510.000 in one month. The number employed full-time rose to 116.875 million in Nov 2013, falling to 116.661 million in Dec 2013. The number employed full-time fell to 115.744 million in Jan 2014 but increased to 116.323 million in Feb 2014. The level of full-time jobs increased to 116.985 in Mar 2014 and 118.073 million in Apr 2014. The number of full-time jobs increased to 119.179 million in May 2014, increasing to 119.472 million in Jun 2014. The level of full-time jobs increased to 119.900 million in Jul 2014. Comparisons over long periods require use of NSA data. The number with full-time jobs fell from a high of 123.219 million in Jul 2007 to 108.777 million in Jan 2010 or by 14.442 million. The number with full-time jobs in Jun 2016 is 124.903 million, which is higher by 1.684 million relative to the peak of 123.219 million in Jul 2007.
- Loss of full-time jobs. The magnitude of the stress in US labor markets is magnified by the increase in the civilian noninstitutional population of the United States from 231.958 million in Jul 2007 to 253.397 million in Jun 2016 or by 21.439 million (http://www.bls.gov/data/). The number with full-time jobs in Jun 2016 is 124.903 million, which is higher by 1.684 million relative to the peak of 123.219 million in Jul 2007. The ratio of full-time jobs of 123.219 million in Jul 2007 to civilian noninstitutional population of 231.958 million was 53.1 percent. If that ratio had remained the same, there would be 134.554 million full-time jobs with population of 253.397 million in Jun 2016 (0.531 x 253.397) or 9.651 million fewer full-time jobs relative to actual 124.903 million. There appear to be around 10 million fewer full-time jobs in the US than before the global recession while population increased around 20 million. Mediocre GDP growth is the main culprit of the fractured US labor market. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. US economic growth has been at only 2.1 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 27 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IQ2016. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the third estimate of GDP for IQ2016 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2016/pdf/gdp1q16_3rd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,745.9 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,355.6 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,745.9/$14,355.6 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/financial-asset-values-rebound-from.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/appropriate-for-fed-to-increase.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1989 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/financial-asset-values-rebound-from.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/appropriate-for-fed-to-increase.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IQ2016 would have accumulated to 27.6 percent. GDP in IQ2016 would be $19,129.5 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2614.9 billion than actual $16,514.6 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 23.7 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 14.1 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/fluctuating-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/financial-turbulence-twenty-four.html). US GDP in IQ2016 is 13.7 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,514.6 billion in IQ2016 or 10.2 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.2 percent. Professor John H. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. Cochrane (2016May02) measures GDP growth in the US at average 3.5 percent per year from 1950 to 2000 and only at 1.76 percent per year from 2000 to 2015 with only at 2.0 percent annual equivalent in the current expansion. Cochrane (2016May02) proposes drastic changes in regulation and legal obstacles to private economic activity. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth of manufacturing at average 3.2 percent per year from May 1919 to May 2016. Growth at 3.2 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 108.2316 in Dec 2007 to 141.0886 in May 2016. The actual index NSA in May 2016 is 103.0898, which is 26.9 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.1 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2015. Using trend growth of 2.1 percent per year, the index would increase to 128.9038 in May 2016. The output of manufacturing at 103.0898 in May 2016 is 20.0 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Table I-9, US, Employed Part-time for Economic Reasons, Thousands, and Full-time, Millions
| Part-time Thousands | Full-time Millions | |
| Seasonally Adjusted | ||
| Jun 2016 | 5,843 | 123.586 |
| May 2016 | 6,430 | 123.135 |
| Apr 2016 | 5,962 | 123.194 |
| Mar 2016 | 6,123 | 123.447 |
| Feb 2016 | 5,988 | 123.206 |
| Jan 2016 | 5,988 | 123.141 |
| Dec 2015 | 6,022 | 122.603 |
| Nov 2015 | 6,085 | 122.099 |
| Oct 2015 | 5,761 | 122.054 |
| Sep 2015 | 6,034 | 121.873 |
| Aug 2015 | 6,481 | 122.045 |
| Jul 2015 | 6,300 | 121.641 |
| Jun 2015 | 6,465 | 121.056 |
| May 2015 | 6,600 | 121.415 |
| Apr 2015 | 6,549 | 120.799 |
| Mar 2015 | 6,673 | 120.976 |
| Feb 2015 | 6,630 | 120.788 |
| Jan 2015 | 6,784 | 120.662 |
| Dec 2014 | 6,786 | 119.999 |
| Nov 2014 | 6,844 | 119.641 |
| Oct 2014 | 7,065 | 119.745 |
| Sep 2014 | 7,124 | 119.364 |
| Aug 2014 | 7,213 | 118.778 |
| Jul 2014 | 7,440 | 118.454 |
| Jun 2014 | 7,473 | 118.233 |
| May 2014 | 7,219 | 118.746 |
| Apr 2014 | 7,452 | 118.466 |
| Mar 2014 | 7,428 | 117.950 |
| Feb 2014 | 7,230 | 117.765 |
| Jan 2014 | 7,250 | 117.568 |
| Dec 2013 | 7,763 | 117.307 |
| Nov 2013 | 7,708 | 117.044 |
| Oct 2013 | 8,028 | 116.345 |
| Sep 2013 | 8,008 | 116.907 |
| Aug 2013 | 7,837 | 116.475 |
| Jul 2013 | 8,093 | 116.156 |
| Jun 2013 | 8,104 | 116.120 |
| May 2013 | 7,901 | 116.211 |
| Apr 2013 | 7,924 | 116.017 |
| Mar 2013 | 7,682 | 115.789 |
| Feb 2013 | 8,089 | 115.689 |
| Jan 2013 | 8,030 | 115.759 |
| Dec 2012 | 7,922 | 115.774 |
| Nov 2012 | 8,150 | 115.656 |
| Oct 2012 | 8,229 | 115.558 |
| Sep 2012 | 8,667 | 115.254 |
| Aug 2012 | 7,998 | 114.750 |
| Jul 2012 | 8,092 | 114.575 |
| Jun 2012 | 8,081 | 114.742 |
| May 2012 | 8,123 | 114.224 |
| Apr 2012 | 7,907 | 114.358 |
| Mar 2012 | 7,793 | 115.023 |
| Feb 2012 | 8,214 | 114.151 |
| Jan 2012 | 8,267 | 113.767 |
| Dec 2011 | 8,171 | 113.774 |
| Nov 2011 | 8,447 | 113.213 |
| Oct 2011 | 8,657 | 112.923 |
| Sep 2011 | 9,166 | 112.544 |
| Aug 2011 | 8,788 | 112.723 |
| Jul 2011 | 8,281 | 112.193 |
| Not Seasonally Adjusted | ||
| Jun 2016 | 6,119 | 124.903 |
| May 2016 | 6,238 | 123.548 |
| Apr 2016 | 5,771 | 122.742 |
| Mar 2016 | 6,138 | 122.522 |
| Feb 2016 | 6,106 | 121.757 |
| Jan 2016 | 6,406 | 121.411 |
| Dec 2015 | 6,179 | 122.013 |
| Nov 2015 | 5,967 | 121.897 |
| Oct 2015 | 5,536 | 122.466 |
| Sep 2015 | 5,693 | 122.303 |
| Aug 2015 | 6,361 | 123.420 |
| Jul 2015 | 6,511 | 123.142 |
| Jun 2015 | 6,776 | 122.268 |
| May 2015 | 6,363 | 121.863 |
| Apr 2015 | 6,356 | 120.402 |
| Mar 2015 | 6,672 | 119.981 |
| Feb 2015 | 6,772 | 119.313 |
| Jan 2015 | 7,269 | 118.840 |
| Dec 2014 | 6,970 | 119.394 |
| Nov 2014 | 6,713 | 119.441 |
| Oct 2014 | 6,787 | 120.176 |
| Sep 2014 | 6,711 | 119.791 |
| Aug 2014 | 7,083 | 120.110 |
| Jul 2014 | 7,665 | 119.900 |
| Jun 2014 | 7,805 | 119.472 |
| May 2014 | 6,960 | 119.179 |
| Apr 2014 | 7,243 | 118.073 |
| Mar 2014 | 7,455 | 116.985 |
| Feb 2014 | 7,397 | 116.323 |
| Jan 2014 | 7,771 | 115.774 |
| Dec 2013 | 7,990 | 116.661 |
| Nov 2013 | 7,563 | 116.875 |
| Oct 2013 | 7,700 | 116.798 |
| Sep 2013 | 7,522 | 117.308 |
| Aug 2013 | 7,690 | 117.868 |
| Jul 2013 | 8,324 | 117.688 |
| Jun 2013 | 8,440 | 117.400 |
| May 2013 | 7,618 | 116.643 |
| Apr 2013 | 7,709 | 115.674 |
| Mar 2013 | 7,734 | 114.796 |
| Feb 2013 | 8,298 | 114.191 |
| Jan 2013 | 8,628 | 113.868 |
| Dec 2012 | 8,166 | 115.079 |
| Nov 2012 | 7,994 | 115.515 |
| Oct 2012 | 7,870 | 116.045 |
| Sep 2012 | 8,110 | 115.678 |
| Aug 2012 | 7,842 | 116.214 |
| Jul 2012 | 8,316 | 116.131 |
| Jun 2012 | 8,394 | 116.024 |
| May 2012 | 7,837 | 114.634 |
| Apr 2012 | 7,694 | 113.999 |
| Mar 2012 | 7,867 | 113.916 |
| Feb 2012 | 8,455 | 112.587 |
| Jan 2012 | 8,918 | 111.879 |
| Dec 2011 | 8,428 | 113.050 |
| Nov 2011 | 8,271 | 113.138 |
| Oct 2011 | 8,258 | 113.456 |
| Sep 2011 | 8,541 | 112.980 |
| Aug 2011 | 8,604 | 114.286 |
| Jul 2011 | 8,514 | 113.759 |
| Jun 2011 | 8,738 | 113.255 |
| May 2011 | 8,270 | 112.618 |
| Apr 2011 | 8,425 | 111.844 |
| Mar 2011 | 8,737 | 111.186 |
| Feb 2011 | 8,749 | 110.731 |
| Jan 2011 | 9,187 | 110.373 |
| Dec 2010 | 9,205 | 111.207 |
| Nov 2010 | 8,670 | 111.348 |
| Oct 2010 | 8,408 | 112.342 |
| Sep 2010 | 8,628 | 112.385 |
| Aug 2010 | 8,628 | 113.508 |
| Jul 2010 | 8,737 | 113.974 |
| Jun 2010 | 8,867 | 113.856 |
| May 2010 | 8,513 | 112.809 |
| Apr 2010 | 8,921 | 111.391 |
| Mar 2010 | 9,343 | 109.877 |
| Feb 2010 | 9,282 | 109.100 |
| Jan 2010 | 9,290 | 108.777 (low) |
| Dec 2009 | 9,354 (high) | 109.875 |
| Nov 2009 | 8,894 | 111.274 |
| Oct 2009 | 8,474 | 111.599 |
| Sep 2009 | 8,255 | 111.991 |
| Aug 2009 | 8,835 | 113.863 |
| Jul 2009 | 9,103 | 114.184 |
| Jun 2009 | 9,301 | 114.014 |
| May 2009 | 8,785 | 113.083 |
| Apr 2009 | 8,648 | 112.746 |
| Mar 2009 | 9,305 | 112.215 |
| Feb 2009 | 9,170 | 112.947 |
| Jan 2009 | 8,829 | 113.815 |
| Dec 2008 | 8,250 | 116.422 |
| Nov 2008 | 7,135 | 118.432 |
| Oct 2008 | 6,267 | 120.020 |
| Sep 2008 | 5,701 | 120.213 |
| Aug 2008 | 5,736 | 121.556 |
| Jul 2008 | 6,054 | 122.378 |
| Jun 2008 | 5,697 | 121.845 |
| May 2008 | 5,096 | 120.809 |
| Apr 2008 | 5,071 | 120.027 |
| Mar 2008 | 5,038 | 119.875 |
| Feb 2008 | 5,114 | 119.452 |
| Jan 2008 | 5,340 | 119.332 |
| Dec 2007 | 4,750 | 121.042 |
| Nov 2007 | 4,374 | 121.846 |
| Oct 2007 | 4,028 | 122.006 |
| Sep 2007 | 4,137 | 121.728 |
| Aug 2007 | 4,494 | 122.870 |
| Jul 2007 | 4,516 | 123.219 (high) |
| Jun 2007 | 4,469 | 122.150 |
| May 2007 | 4,315 | 120.846 |
| Apr 2007 | 4,205 | 119.609 |
| Mar 2007 | 4,384 | 119.640 |
| Feb 2007 | 4,417 | 119.041 |
| Jan 2007 | 4,726 | 119.094 |
| Dec 2006 | 4,281 | 120.371 |
| Nov 2006 | 4,054 | 120.507 |
| Oct 2006 | 4,010 | 121.199 |
| Sep 2006 | 3,735 (low) | 120.780 |
| Aug 2006 | 4,104 | 121.979 |
| Jul 2006 | 4,450 | 121.951 |
| Jun 2006 | 4,456 | 121.070 |
| May 2006 | 3,968 | 118.925 |
| Apr 2006 | 3,787 | 118.559 |
| Mar 2006 | 4,097 | 117.693 |
| Feb 2006 | 4,403 | 116.823 |
| Jan 2006 | 4,597 | 116.395 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
People lose their marketable job skills after prolonged unemployment and face increasing difficulty in finding another job. Chart I-18 shows the sharp rise in unemployed over 27 weeks and stabilization at an extremely high level.
Chart I-18, US, Number Unemployed for 27 Weeks or Over, Thousands SA Month 2001-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Another segment of U6 consists of people marginally attached to the labor force who continue to seek employment but less frequently on the frustration there may not be a job for them. Chart I-19 shows the sharp rise in people marginally attached to the labor force after 2007 and subsequent stabilization.
Chart I-19, US, Marginally Attached to the Labor Force, NSA Month, Thousands, 2001-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-20 provides the level of full-time jobs from 2001 to 2016. The magnitude of the stress in US labor markets is magnified by the increase in the civilian noninstitutional population of the United States from 231.958 million in Jul 2007 to 253.397 million in Jun 2016 or by 21.439 million (http://www.bls.gov/data/). The number with full-time jobs in Jun 2016 is 124.903 million, which is higher by 1.684 million relative to the peak of 123.219 million in Jul 2007. The ratio of full-time jobs of 123.219 million in Jul 2007 to civilian noninstitutional population of 231.958 million was 53.1 percent. If that ratio had remained the same, there would be 134.554 million full-time jobs with population of 253.397 million in Jun 2016 (0.531 x 253.397) or 9.651 million fewer full-time jobs relative to actual 124.903 million. There appear to be around 10 million fewer full-time jobs in the US than before the global recession while population increased around 20 million. Mediocre GDP growth is the main culprit of the fractured US labor market.
There is current interest in past theories of “secular stagnation.” Alvin H. Hansen (1939, 4, 7; see Hansen 1938, 1941; for an early critique see Simons 1942) argues:
“Not until the problem of full employment of our productive resources from the long-run, secular standpoint was upon us, were we compelled to give serious consideration to those factors and forces in our economy which tend to make business recoveries weak and anaemic (sic) and which tend to prolong and deepen the course of depressions. This is the essence of secular stagnation-sick recoveries which die in their infancy and depressions which feed on them-selves and leave a hard and seemingly immovable core of unemployment. Now the rate of population growth must necessarily play an important role in determining the character of the output; in other words, the com-position of the flow of final goods. Thus a rapidly growing population will demand a much larger per capita volume of new residential building construction than will a stationary population. A stationary population with its larger proportion of old people may perhaps demand more personal services; and the composition of consumer demand will have an important influence on the quantity of capital required. The demand for housing calls for large capital outlays, while the demand for personal services can be met without making large investment expenditures. It is therefore not unlikely that a shift from a rapidly growing population to a stationary or declining one may so alter the composition of the final flow of consumption goods that the ratio of capital to output as a whole will tend to decline.”
The argument that anemic population growth causes “secular stagnation” in the US (Hansen 1938, 1939, 1941) is as misplaced currently as in the late 1930s (for early dissent see Simons 1942). This is merely another case of theory without reality with dubious policy proposals.
Inferior performance of the US economy and labor markets, during cyclical slow growth not secular stagnation, is the critical current issue of analysis and policy design.
Chart I-20, US, Full-time Employed, Thousands, NSA, 2001-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-20A provides the noninstitutional civilian population of the United States from 2001 to 2016. There is clear trend of increase of the population while the number of full-time jobs collapsed after 2008 without sufficient recovery as shown in the preceding Chart I-20.
Chart I-20A, US, Noninstitutional Civilian Population, Thousands, 2001-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-20B provides number of full-time jobs in the US from 1968 to 2016. There were multiple recessions followed by expansions without contraction of full-time jobs and without recovery as during the period after 2008. The problem is specific of the current cycle and not secular.
Chart I-20B, US, Full-time Employed, Thousands, NSA, 1968-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-20C provides the noninstitutional civilian population of the United States from 1968 to 2016. Population expanded at a relatively constant rate of increase with the assurance of creation of full-time jobs that has been broken since 2008.
Chart I-20C, US, Noninstitutional Civilian Population, Thousands, 1968-2016
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
IA4 Theory and Reality of Secular Stagnation: Youth and Middle-Age Unemployment. Three tables support the argument that the proper comparison of the business cycle is between the recessions of the 1980s and the global recession after IVQ2007 and not as argued erroneously with the Great Depression of the 1930s. Table I-5 provides percentage change of real GDP in the United States in the 1930s, 1980s and 2000s. The recession in 1981-1982 is quite similar on its own to the 2007-2009 recession. In contrast, during the Great Depression in the four years of 1930 to 1933, GDP in constant dollars fell 26.4 percent cumulatively and fell 45.3 percent in current dollars (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 150-2, Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2009b), 205-7 and revisions in http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). Data are available for the 1930s only on a yearly basis. US GDP fell 4.7 percent in the two recessions (1) from IQ1980 to IIIQ1980 and (2) from III1981 to IVQ1982 and 4.2 percent cumulatively in the recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. It is instructive to compare the first years of the expansions in the 1980s and the current expansion. GDP grew at 4.6 percent in 1983, 7.3 percent in 1984, 4.2 percent in 1985, 3.5 percent in 1986, 3.5 percent in 1987, 4.2 percent in 1988 and 3.7 percent in 1989. In contrast, GDP grew 2.5 percent in 2010, 1.6 percent in 2011, 2.2 percent in 2012, 1.5 percent in 2013, 2.4 percent in 2014 and 2.4 percent in 2015. Actual annual equivalent GDP growth in the four quarters of 2012, twelve quarters from IQ2013 to IVQ2015 and IQ2016 is 2.0 percent and 2.0 percent in the four quarters ending in IQ2016. GDP grew at 4.2 percent in 1985, 3.5 percent in 1986, 3.5 percent in 1987, 4.2 percent in 1988 and 3.7 percent in 1989. The forecasts of the central tendency of participants of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) are in the range of 1.9 to 2.0 percent in 2016 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20160615.pdf) with less reliable forecast of 1.9 to 2.2 percent in 2017 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20160615.pdf). Growth of GDP in the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IQ2016 has been at average 2.1 percent in annual equivalent.
Table I-5, US, Percentage Change of GDP in the 1930s, 1980s and 2000s, ∆%
| Year | GDP ∆% | Year | GDP ∆% | Year | GDP ∆% |
| 1930 | -8.5 | 1980 | -0.2 | 2000 | 4.1 |
| 1931 | -6.4 | 1981 | 2.6 | 2001 | 1.0 |
| 1932 | -12.9 | 1982 | -1.9 | 2002 | 1.8 |
| 1933 | -1.3 | 1983 | 4.6 | 2003 | 2.8 |
| 1934 | 10.8 | 1984 | 7.3 | 2004 | 3.8 |
| 1935 | 8.9 | 1985 | 4.2 | 2005 | 3.3 |
| 1936 | 12.9 | 1986 | 3.5 | 2006 | 2.7 |
| 1937 | 5.1 | 1987 | 3.5 | 2007 | 1.8 |
| 1938 | -3.3 | 1988 | 4.2 | 2008 | -0.3 |
| 1939 | 8.0 | 1989 | 3.7 | 2009 | -2.8 |
| 1940 | 8.8 | 1990 | 1.9 | 2010 | 2.5 |
| 1941 | 17.7 | 1991 | -0.1 | 2011 | 1.6 |
| 1942 | 18.9 | 1992 | 3.6 | 2012 | 2.2 |
| 1943 | 17.0 | 1993 | 2.7 | 2013 | 1.5 |
| 1944 | 8.0 | 1994 | 4.0 | 2014 | 2.4 |
| 1945 | -1.0 | 1995 | 2.7 | 2015 | 2.4 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Characteristics of the four cyclical contractions are in Table I-6 with the first column showing the number of quarters of contraction; the second column the cumulative percentage contraction; and the final column the average quarterly rate of contraction. There were two contractions from IQ1980 to IIIQ1980 and from IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 separated by three quarters of expansion. The drop of output combining the declines in these two contractions is 4.7 percent, which is almost equal to the decline of 4.2 percent in the contraction from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. In contrast, during the Great Depression in the four years of 1930 to 1933, GDP in constant dollars fell 26.4 percent cumulatively and fell 45.3 percent in current dollars (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 150-2, Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2009b), 205-7 and revisions in http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). The comparison of the global recession after 2007 with the Great Depression is entirely misleading.
Table I-6, US, Number of Quarters, GDP Cumulative Percentage Contraction and Average Percentage Annual Equivalent Rate in Cyclical Contractions
| Number of Quarters | Cumulative Percentage Contraction | Average Percentage Rate | |
| IIQ1953 to IIQ1954 | 3 | -2.4 | -0.8 |
| IIIQ1957 to IIQ1958 | 3 | -3.0 | -1.0 |
| IVQ1973 to IQ1975 | 5 | -3.1 | -0.6 |
| IQ1980 to IIIQ1980 | 2 | -2.2 | -1.1 |
| IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 | 4 | -2.5 | -0.64 |
| IVQ2007 to IIQ27009 | 6 | -4.2 | -0.72 |
Sources: Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table I-7 shows the mediocre average annual equivalent growth rate of 2.1 percent of the US economy in the twenty-seven quarters of the current cyclical expansion from IIIQ2009 to IQ2016. In sharp contrast, the average growth rate of GDP was:
- 5.7 percent in the first thirteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1986
- 5.4 percent in the first fifteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986
- 5.2 percent in the first sixteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1986
- 5.0 percent in the first seventeen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1987
- 5.0 percent in the first eighteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIQ1987
- 4.9 percent in the first nineteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987
- 5.0 percent in the first twenty quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1987
- 4.9 percent in the first twenty-first quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1988
- 4.9 percent in the first twenty-two quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIQ1988
- 4.8 percent in the first twenty-three quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988
- 4.8 percent in the first twenty-four quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1988
- 4.8 percent in the first twenty-five quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1989
- 4.7 percent in the first twenty-six quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIQ1989
- 4.7 percent in the first twenty-seven quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIIQ1989
The line “average first four quarters in four expansions” provides the average growth rate of 7.7 percent with 7.8 percent from IIIQ1954 to IIQ1955, 9.2 percent from IIIQ1958 to IIQ1959, 6.1 percent from IIIQ1975 to IIQ1976 and 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983. The United States missed this opportunity of high growth in the initial phase of recovery. BEA data show the US economy in standstill with annual growth of 2.5 percent in 2010 decelerating to 1.6 percent annual growth in 2011, 2.2 percent in 2012, 1.5 percent in 2013, 2.4 percent in 2014 and 2.4 percent in 2015 (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) The expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1986 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.7 percent, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1988, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988. 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1989 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983. GDP grew 2.7 percent in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010. GDP growth in the four quarters of 2012, the four quarters of 2013, the four quarters of 2014, the four quarters of Q2015 and IQ2016 accumulated to 8.7 percent. This growth is equivalent to 2.0 percent per year, obtained by dividing GDP in IQ2016 of $16,514.6 billion by GDP in IVQ2011 of $15,190.3 billion and compounding by 4/17: {[($16,514.6/$15,190.3)4/17 -1]100 = 2.0 percent}.
Table I-7 shows that GDP grew 15.0 percent in the first twenty-seven quarters of expansion from IIIQ2009 to IQ2016 at the annual equivalent rate of 2.1 percent.
Table I-5, US, Number of Quarters, Cumulative Growth and Average Annual Equivalent Growth Rate in Cyclical Expansions
| Number | Cumulative Growth ∆% | Average Annual Equivalent Growth Rate | |
| IIIQ 1954 to IQ1957 | 11 | 12.8 | 4.5 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ1954 to IIQ1955 | 4 | 7.8 | |
| IIQ1958 to IIQ1959 | 5 | 10.0 | 7.9 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ1958 to IIQ1959 | 4 | 9.2 | |
| IIQ1975 to IVQ1976 | 8 | 8.3 | 4.1 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ1975 to IIQ1976 | 4 | 6.1 | |
| IQ1983-IQ1986 IQ1983-IIIQ1986 IQ1983-IVQ1986 IQ1983-IQ1987 IQ1983-IIQ1987 IQ1983 to IIIQ1987 IQ1983 to IVQ1987 IQ1983 to IQ1988 IQ1983 to IIQ1988 IQ1983 to IIIQ1988 IQ1983 to IVQ1988 IQ1983 to IQ1989 IQ1983 to IIQ1989 IQ1983 to IIIQ1989 | 13 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 | 19.9 21.6 22.3 23.1 24.5 25.6 27.7 28.4 30.1 30.9 32.6 34.0 35.0 36.0 | 5.7 5.4 5.2 5.0 5.0 4.9 5.0 4.9 4.9 4.8 4.8 4.8 4.7 4.7 |
| First Four Quarters IQ1983 to IVQ1983 | 4 | 7.8 | |
| Average First Four Quarters in Four Expansions* | 7.7 | ||
| IIIQ2009 to IQ2016 | 27 | 15.0 | 2.1 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 | 2.7 |
*First Four Quarters: 7.8% IIIQ1954-IIQ1955; 9.2% IIIQ1958-IIQ1959; 6.1% IIIQ1975-IQ1976; 7.8% IQ1983-IVQ1983
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table EMP provides the comparison between the labor market in the current whole cycle from 2007 to 2015 and the whole cycle from 1979 to 1989. In the entire cycle from 2007 to 2015, the number employed increased 2.787 million, full-time employed increased 0.401 million, part-time for economic reasons increased 1.970 million and population increased 18.934 million. The number employed increased 1.9 percent, full-time employed increased 0.3 percent, part-time for economic reasons increased 44.8 percent and population increased 8.2 percent. There is sharp contrast with the contractions of the 1980s and with most economic history of the United States. In the whole cycle from 1979 to 1989, the number employed increased 18.518 million, full-time employed increased 14.715 million, part-time for economic reasons increased 1.317 million and population increased 21.530 million. In the entire cycle from 1979 to 1989, the number employed increased 18.7 percent, full-time employed increased 17.8 percent, part-time for economic reasons increased 36.8 percent and population increased 13.1 percent. The difference between the 1980s and the current cycle after 2007 is in the high rate of growth after the contraction that maintained trend growth around 3.0 percent for the entire cycle and per capital growth at 2.0 percent. The evident fact is that current weakness in labor markets originates in cyclical slow growth and not in imaginary secular stagnation.
Table EMP, US, Annual Level of Employed, Full-Time Employed, Employed Part-Time for Economic Reasons and Noninstitutional Civilian Population, Millions
| Employed | Full-Time Employed | Part Time Economic Reasons | Noninstitutional Civilian Population | |
| 2000s | ||||
| 2000 | 136.891 | 113.846 | 3.227 | 212.577 |
| 2001 | 136.933 | 113.573 | 3.715 | 215.092 |
| 2002 | 136.485 | 112.700 | 4.213 | 217.570 |
| 2003 | 137.736 | 113.324 | 4.701 | 221.168 |
| 2004 | 139.252 | 114.518 | 4.567 | 223.357 |
| 2005 | 141.730 | 117.016 | 4.350 | 226.082 |
| 2006 | 144.427 | 119.688 | 4.162 | 228.815 |
| 2007 | 146.047 | 121.091 | 4.401 | 231.867 |
| 2008 | 145.362 | 120.030 | 5.875 | 233.788 |
| 2009 | 139.877 | 112.634 | 8.913 | 235.801 |
| 2010 | 139.064 | 111.714 | 8.874 | 237.830 |
| 2011 | 139.869 | 112.556 | 8.560 | 239.618 |
| 2012 | 142.469 | 114.809 | 8.122 | 243.284 |
| 2013 | 143.929 | 116.314 | 7.935 | 245.679 |
| 2014 | 146.305 | 118.718 | 7.213 | 247.947 |
| 2015 | 148.834 | 121.492 | 6.371 | 250.801 |
| ∆2007-2015 | 2.787 | 0.401 | 1.970 | 18.934 |
| ∆% 2007-2015 | 1.9 | 0.3 | 44.8 | 8.2 |
| 1980s | ||||
| 1979 | 98.824 | 82.654 | 3.577 | 164.863 |
| 1980 | 99.303 | 82.562 | 4.321 | 167.745 |
| 1981 | 100.397 | 83.243 | 4.768 | 170.130 |
| 1982 | 99.526 | 81.421 | 6.170 | 172.271 |
| 1983 | 100.834 | 82.322 | 6.266 | 174.215 |
| 1984 | 105.005 | 86.544 | 5.744 | 176.383 |
| 1985 | 107.150 | 88.534 | 5.590 | 178.206 |
| 1986 | 109.597 | 90.529 | 5.588 | 180.587 |
| 1987 | 112.440 | 92.957 | 5.401 | 182.753 |
| 1988 | 114.968 | 95.214 | 5.206 | 184.613 |
| 1989 | 117.342 | 97.369 | 4.894 | 186.393 |
| ∆1979-1989 | 18.518 | 14.715 | 1.317 | 21.530 |
| ∆% 1979-1989 | 18.7 | 17.8 | 36.8 | 13.1 |
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
The theory of secular stagnation cannot explain sudden collapse of the US economy and labor markets. There are accentuated cyclic factors for both the entire population and the young population of ages 16 to 24 years. Table Summary Total provides the total noninstitutional population (ICP) of the US, full-time employment level (FTE), employment level (EMP), civilian labor force (CLF), civilian labor force participation rate (CLFP), employment/population ratio (EPOP) and unemployment level (UNE). Secular stagnation would spread over long periods instead of immediately. All indicators of the labor market weakened sharply during the contraction and did not recover. Population continued to grow but all other variables collapsed and did not recover. The theory of secular stagnation departs from an aggregate production function in which output grows with the use of labor, capital and technology (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. I (2008a), 11-16). Hansen (1938, 1939) finds secular stagnation in lower growth of an aging population. In the current US economy, Table Summary shows that population is dynamic while the labor market is fractured. There is key explanation in the behavior of the civilian labor force participation rate (CLFP) and the employment population ratio (EPOP) that collapsed during the global recession with inadequate recovery. Abandoning job searches are difficult to capture in labor statistics but likely explain the decline in the participation of the population in the labor force. Allowing for abandoning job searches, the total number of people unemployed or underemployed is 23.7 million or 14.1 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/fluctuating-valuations-of-risk.html).
Table Summary Total, US, Total Noninstitutional Civilian Population, Full-time Employment, Employment, Civilian Labor Force, Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate, Employment Population Ratio, Unemployment, NSA, Millions and Percent
| ICP | FTE | EMP | CLF | CLFP | EPOP | UNE | |
| 2006 | 228.8 | 119.7 | 144.4 | 151.4 | 66.2 | 63.1 | 7.0 |
| 2009 | 235.8 | 112.6 | 139.9 | 154.1 | 65.4 | 59.3 | 14.3 |
| 2012 | 243.3 | 114.8 | 142.5 | 155.0 | 63.7 | 58.6 | 12.5 |
| 2013 | 245.7 | 116.3 | 143.9 | 155.4 | 63.2 | 58.6 | 11.5 |
| 2014 | 247.9 | 118.7 | 146.3 | 155.9 | 62.9 | 59.0 | 9.6 |
| 2015 | 250.8 | 121.5 | 148.8 | 157.1 | 62.7 | 59.3 | 8.3 |
| 12/07 | 233.2 | 121.0 | 146.3 | 153.7 | 65.9 | 62.8 | 7.4 |
| 9/09 | 236.3 | 112.0 | 139.1 | 153.6 | 65.0 | 58.9 | 14.5 |
| 6/16 | 253.4 | 124.9 | 152.0 | 160.1 | 63.2 | 60.0 | 8.1 |
ICP: Total Noninstitutional Civilian Population; FT: Full-time Employment Level, EMP: Total Employment Level; CLF: Civilian Labor Force; CLFP: Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate; EPOP: Employment Population Ratio; UNE: Unemployment
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
The same situation is present in the labor market for young people in ages 16 to 24 years with data in Table Summary Youth. The youth noninstitutional civilian population (ICP) continued to increase during and after the global recession. There is the same disastrous labor market with decline for young people in employment (EMP), civilian labor force (CLF), civilian labor force participation rate (CLFP) and employment population ratio (EPOP). There are only increases for unemployment of young people (UNE) and youth unemployment rate (UNER). If aging were a factor of secular stagnation, growth of population of young people would attract a premium in remuneration in labor markets. The sad fact is that young people are also facing tough labor markets. The application of the theory of secular stagnation to the US economy and labor markets is void of reality in the form of key facts, which are best explained by accentuated cyclic factors analyzed by Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22).
Table Summary Youth, US, Youth, Ages 16 to 24 Years, Noninstitutional Civilian Population, Full-time Employment, Employment, Civilian Labor Force, Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate, Employment Population Ratio, Unemployment, NSA, Millions and Percent
| ICP | EMP | CLF | CLFP | EPOP | UNE | UNER | |
| 2006 | 36.9 | 20.0 | 22.4 | 60.6 | 54.2 | 2.4 | 10.5 |
| 2009 | 37.6 | 17.6 | 21.4 | 56.9 | 46.9 | 3.8 | 17.6 |
| 2012 | 38.8 | 17.8 | 21.3 | 54.9 | 46.0 | 3.5 | 16.2 |
| 2013 | 38.8 | 18.1 | 21.4 | 55.0 | 46.5 | 3.3 | 15.5 |
| 2014 | 38.7 | 18.4 | 21.3 | 55.0 | 47.6 | 2.9 | 13.4 |
| 2015 | 38.6 | 18.8 | 21.2 | 55.0 | 48.6 | 2.5 | 11.6 |
| 12/07 | 37.5 | 19.4 | 21.7 | 57.8 | 51.6 | 2.3 | 10.7 |
| 9/09 | 37.6 | 17.0 | 20.7 | 55.2 | 45.1 | 3.8 | 18.2 |
| 6/16 | 38.5 | 20.0 | 22.8 | 59.2 | 51.9 | 2.8 | 12.3 |
ICP: Youth Noninstitutional Civilian Population; EMP: Youth Employment Level; CLF: Youth Civilian Labor Force; CLFP: Youth Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate; EPOP: Youth Employment Population Ratio; UNE: Unemployment; UNER: Youth Unemployment Rate
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
The United States is experiencing high youth unemployment as in European economies. Table I-10 provides the employment level for ages 16 to 24 years of age estimated by the Bureau of Labor Statistics. On an annual basis, youth employment fell from 20.041 million in 2006 to 17.362 million in 2011 or 2.679 million fewer youth jobs and to 17.834 million in 2012 or 2.207 million fewer jobs. Youth employment fell from 20.041 million in 2006 to 18.057 million in 2013 or 1.984 million fewer jobs. Youth employment fell from 20.041 million in 2006 to 18.442 million in 2014 or 1.599 million. Youth employment fell from 20.041 million in 2006 to 18.756 million in 2015 or 1.285 million. The level of youth jobs fell from 20.129 million in Dec 2006 to 18.347 million in Dec 2014 for 1.782 million fewer youth jobs. The level of youth jobs fell from 20.129 million in Dec 2006 to 18.720 million in Dec 2015 or 1.409 million fewer jobs. Youth jobs fell from 21.268 million in Jun 2006 to 19.967 million in Jun 2016 or 1.301 million. During the seasonal peak months of youth employment in the summer from Jun to Aug, youth employment has fallen by more than two million jobs relative to 21.167 million in Aug 2006 to 18.972 million in Aug 2014 for 2.195 million fewer jobs. Youth employment fell from 21.914 million in Jul 2006 to 20.085 million in Jul 2014 for 1.829 million fewer youth jobs. The number of youth jobs fell from 21.268 million in Jun 2006 million to 19.421 million in Jun 2014 or 1.847 million fewer youth jobs. The number of jobs ages 16 to 24 years fell from 21.167 million in Aug 2006 to 18.636 million in Aug 2013 or by 2.531 million. The number of youth jobs fell from 19.604 million in Sep 2006 to 18.043 million in Sep 2013 or 1.561 million fewer youth jobs. The number of youth jobs fell from 20.129 million in Dec 2006 to 18.106 million in Dec 2013 or 2.023 million fewer jobs. The civilian noninstitutional population ages 16 to 24 years increased from 37.443 million in Jul 2007 to 38.861 million in Jul 2013 or by 1.418 million while the number of jobs for ages 16 to 24 years fell by 2.230 million from 21.914 million in Jul 2006 to 19.684 million in Jul 2013. The civilian noninstitutional population for ages 16 to 24 years increased from 37.455 million in Aug 2007 to 38.841 million in Aug 2013 or by 1.386 million while the number of youth jobs fell by 1.777 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.467 million in Sep 2007 to 38.822 million in Sep 2013 or by 1.355 million while the number of youth jobs fell by 1.455 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.480 million in Oct 2007 to 38.804 million in Oct 2013 or by 1.324 million while the number of youth jobs decreased 1.877 million from Oct 2006 to Oct 2013. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.798 million in Nov 2013 or by 1.722 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.799 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.518 million in Dec 2007 to 38.790 million in Dec 2013 or by 1.272 million while the number of youth jobs fell 2.023 million from Dec 2006 to Dec 2013. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.488 million from 37.282 million in in Jan 2007 to 38.770 million in Jan 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 2.035 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.464 million from 37.302 in Feb 2007 to 38.766 million in Feb 2014 while the number of youth jobs decreased 2.058 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.437 million from 37.324 million in Mar 2007 to 38.761 million in Mar 2014 while jobs for ages 16 to 24 years decreased 1.599 million from 19.538 million in Mar 2007 to 17.939 million in Mar 2014. The civilian noninstitutional population ages 16 to 24 years increased 1.410 million from 37.349 million in Apr 2007 to 38.759 million in Apr 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.347 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.370 million from 37.379 million in May 2007 to 38.749 million in May 2014 while the number of youth jobs decreased 1.128 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.330 million from 37.410 million in Jun 2007 to 38.740 million in Jun 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.847 million from 21.268 million in Jun 2006 to 19.421 million in Jun 2014. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased by 1.292 million from 37.443 million in Jul 2007 to 38.735 million in Jul 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.632 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.445 million in Aug 2007 to 38.706 million in Aug 2014 or 1.251 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.441 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.652 million from 37.027 million in Sep 2006 to 38.679 million in Sep 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.500 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.047 million in Oct 2006 to 38.650 million in Oct 2014 or 1.603 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.072 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.628 million in Nov 2014 or 1.552 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.327 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.100 million in Dec 2006 to 38.606 million in Dec 2014 or 1.506 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.782 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.971 million from 36.761 million in Jan 2006 to 38.732 million in Jan 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.091 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.914 million from 36.791 million in Feb 2006 to 38.705 million in Feb 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 0.960 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.858 million from 36.821 million in Mar 2006 to 38.679 million in Mar 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.215 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.800 million from 36.854 million in Apr 2006 to 38.654 million in Apr 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.165 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1,733 million from 36.897 million in May 2006 to 38.630 million in May 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.060 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.666 million from 36.943 million in Jun 2006 to 38.609 million in Jun 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.479 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.600 million from 36.989 million in Jul 2006 to 38.589 million in Jul 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.581 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.548 million from 37.008 million in Aug 2006 to 38.556 million in Aug 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.590 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1,498 million from 37.027 million in Sep 2006 to 38.525 million in Sep 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.249 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.444 million from 37.047 million in Oct 2006 to 38.491 million in Oct 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.199 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.392 million from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.468 million in Nov 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.418 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.341 million from 37.100 million in Dec 2006 to 38.441 million in Dec 2015 while the level of youth jobs 1.409 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.734 million from 36.761 million in Jan 2006 to 38.495 million in Jan 2016 while the level of youth jobs fell 0.844 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.698 million from 36.791 million in Feb 2006 to 38.489 million in Feb 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 0.726 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1,662 million from 36.821 million in Mar 2006 to 38.483 million in Mar 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 0.711 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.626 million from 36.854 million in Apr 2006 to 38.480 million in Apr 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 0.895 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.571 million from 36.897 million in May 2006 to 38.468 million in May 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 0.894 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.516 million from 36.943 million in Jun 2006 to 38.459 million in Jun 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.301 million. The hardship does not originate in low growth of population but in underperformance of the economy in the expansion from the business cycle. There are two hardships behind these data. First, young people cannot find employment after finishing high school and college, reducing prospects for achievement in older age. Second, students with more modest means cannot find employment to keep them in college.
Table I-10, US, Employment Level 16-24 Years, Thousands, NSA
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
| Year | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Dec | Annual |
| 2001 | 19678 | 19745 | 19800 | 19778 | 19648 | 21212 | 19547 | 20088 |
| 2002 | 18653 | 19074 | 19091 | 19108 | 19484 | 20828 | 19394 | 19683 |
| 2003 | 18811 | 18880 | 18709 | 18873 | 19032 | 20432 | 19136 | 19351 |
| 2004 | 18852 | 18841 | 18752 | 19184 | 19237 | 20587 | 19619 | 19630 |
| 2005 | 18858 | 18670 | 18989 | 19071 | 19356 | 20949 | 19733 | 19770 |
| 2006 | 19003 | 19182 | 19291 | 19406 | 19769 | 21268 | 20129 | 20041 |
| 2007 | 19407 | 19415 | 19538 | 19368 | 19457 | 21098 | 19361 | 19875 |
| 2008 | 18724 | 18546 | 18745 | 19161 | 19254 | 20466 | 18378 | 19202 |
| 2009 | 17467 | 17606 | 17564 | 17739 | 17588 | 18726 | 16615 | 17601 |
| 2010 | 16166 | 16412 | 16587 | 16764 | 17039 | 17920 | 16727 | 17077 |
| 2011 | 16512 | 16638 | 16898 | 16970 | 17045 | 18180 | 17234 | 17362 |
| 2012 | 16944 | 17150 | 17301 | 17387 | 17681 | 18907 | 17604 | 17834 |
| 2013 | 17183 | 17257 | 17271 | 17593 | 17704 | 19125 | 18106 | 18057 |
| 2014 | 17372 | 17357 | 17939 | 18021 | 18329 | 19421 | 18347 | 18442 |
| 2015 | 17912 | 18222 | 18076 | 18241 | 18709 | 19789 | 18720 | 18756 |
| 2016 | 18159 | 18456 | 18580 | 18511 | 18875 | 19967 |
Chart I-21, US, Employment Level 16-24 Years, Thousands SA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-21 provides US employment level ages 16 to 24 years from 2002 to 2016. Employment level is sharply lower in Aug 2015 relative to the peak in 2007. The following Chart I-21A relates youth employment and youth civilian noninstitutional population.
Chart I-21, US, Employment Level 16-24 Years, Thousands SA, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-21A provides the US civilian noninstitutional population ages 16 to 24 years not seasonally adjusted from 2001 to 2016. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased by 1.292 million from 37.443 million in Jul 2007 to 38.735 million in Jul 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.632 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.445 million in Aug 2007 to 38.706 million in Aug 2014 or 1.251 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.441 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.652 million from 37.027 million in Sep 2006 to 38.679 million in Sep 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.500 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.047 million in Oct 2006 to 38.650 million in Oct 2014 or 1.603 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.072 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.628 million in Nov 2014 or 1.552 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.327 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.100 million in Dec 2006 to 38.606 million in Dec 2014 or 1.506 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.782 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.971 million from 36.761 million in Jan 2006 to 38.732 million in Jan 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.091 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.914 million from 36.791 million in Feb 2006 to 38.705 million in Feb 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 0.960 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.858 million from 36.821 million in Mar 2006 to 38.679 million in Mar 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.215 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.800 million from 36.854 million in Apr 2006 to 38.654 million in Apr 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.165 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1,733 million from 36.897 million in May 2006 to 38.630 million in May 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.060 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.666 million from 36.943 million in Jun 2006 to 38.609 million in Jun 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.479 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.600 million from 36.989 million in Jul 2006 to 38.589 million in Jul 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.581 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.548 million from 37.008 million in Aug 2006 to 38.556 million in Aug 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.590 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1,498 million from 37.027 million in Sep 2006 to 38.525 million in Sep 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.249 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.444 million from 37.047 million in Oct 2006 to 38.491 million in Oct 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.199 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.392 million from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.468 million in Nov 2015 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.418 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.341 million from 37.100 million in Dec 2006 to 38.441 million in Dec 2015 while the level of youth jobs 1.409 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.734 million from 36.761 million in Jan 2006 to 38.495 million in Jan 2016 while the level of youth jobs fell 0.844 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.698 million from 36.791 million in Feb 2006 to 38.489 million in Feb 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 0.726 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1,662 million from 36.821 million in Mar 2006 to 38.483 million in Mar 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 0.711 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.626 million from 36.854 million in Apr 2006 to 38.480 million in Apr 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 0.895 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.571 million from 36.897 million in May 2006 to 38.468 million in May 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 0.894 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.516 million from 36.943 million in Jun 2006 to 38.459 million in Jun 2016 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.301 million. The hardship does not originate in low growth of population but in underperformance of the economy in the expansion from the business cycle. There are two hardships behind these data. First, young people cannot find employment after finishing high school and college, reducing prospects for achievement in older age. Second, students with more modest means cannot find employment to keep them in college.
Chart I-21A, US, Civilian Noninstitutional Population Ages 16 to 24 Years, Thousands NSA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-21B provides the civilian labor force of the US ages 16 to 24 years NSA from 2001 to 2015. The US civilian labor force ages 16 to 24 years fell from 24.339 million in Jul 2007 to 23.506 million in Jul 2013, by 0.833 million or decline of 3.4 percent, while the civilian noninstitutional population NSA increased from 37.443 million in Jul 2007 to 38.861 million in Jul 2013, by 1.418 million or 3.8 percent. The US civilian labor force ages 16 to 24 fell from 22.801 million in Aug 2007 to 22.089 million in Aug 2013, by 0.712 million or 3.1 percent, while the noninstitutional population for ages 16 to 24 years increased from 37.455 million in Aug 2007 to 38.841 million in Aug 2013, by 1.386 million or 3.7 percent. The US civilian labor force ages 16 to 24 years fell from 21.917 million in Sep 2007 to 21.183 million in Sep 2013, by 0.734 million or 3.3 percent while the civilian noninstitutional youth population increased from 37.467 million in Sep 2007 to 38.822 million in Sep 2013 by 1.355 million or 3.6 percent. The US civilian labor force fell from 21.821 million in Oct 2007 to 21.003 million in Oct 2013, by 0.818 million or 3.7 percent while the noninstitutional youth population increased from 37.480 million in Oct 2007 to 38.804 million in Oct 2013, by 1.324 million or 3.5 percent. The US youth civilian labor force fell from 21.909 million in Nov 2007 to 20.825 million in Nov 2013, by 1.084 million or 4.9 percent while the civilian noninstitutional youth population increased from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.798 million in Nov 2013 or by 1.722 million. The US youth civilian labor force fell from 21.684 million in Dec 2007 to 20.642 million in Dec 2013, by 1.042 million or 4.8 percent, while the civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.518 million in Dec 2007 to 38.790 million in Dec 2013, by 1.272 million or 3.4 percent. The youth civilian labor force of the US fell from 21.770 million in Jan 2007 to 20.423 million in Jan 2014, by 1.347 million or 6.2 percent while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 37.282 million in Jan 2007 to 38.770 million in Jan 2014, by 1.488 million or 4.0 percent. The youth civilian labor force of the US fell 1.255 million from 21.645 million in Feb 2007 to 20.390 million in Feb 2014 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.464 million from 37.302 million in Feb 2007 to 38.766 million in Feb 2014. The youth civilian labor force of the US fell 0.693 million from 21.634 million in Mar 2007 to 20.941 million in Mar 2014 or 3.2 person while the youth noninstitutional civilian population 1.437 million from 37.324 million in Mar 2007 to 38.761 million in Mar 2014 or 3.9 percent. The US youth civilian labor force fell 981 thousand from 21.442 million in Apr 2007 to 20.461 million in Apr 2014 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.349 million in Apr 2007 to 38.759 million in Apr 2014 by 1.410 thousand or 3.8 percent. The youth civilian labor force decreased from 21.659 million in May 2007 to 21.160 million in May 2014 by 499 thousand or 2.3 percent while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.370 million from 37.739 million in May 2007 to 38.749 million in May 2007 or by 2.7 percent. The youth civilian labor force decreased from 24.128 million in Jun 2006 to 22.851 million in Jun 2014 by 1.277 million or 5.3 percent while the civilian noninstitutional population increased from 36.943 million in Jun 2006 to 38.740 million in Jun 2014 by 1.797 million or 4.9 percent. The youth civilian labor force fell from 24.664 million in Jul 2006 to 23.437 million in Jul 2014 while the civilian noninstitutional population increased from 36.989 million in Jul 2006 to 38.735 million in Jul 2014. The youth civilian labor force fell 1.818 million from 23.634 million in Aug 2006 to 21.816 million in Aug 2014 while the civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.008 million in Aug 2006 to 38.706 million in Aug 2914 or 1.698 million. The youth civilian labor force fell 0.942 million from 21.901 million in Sep 2006 to 20.959 million in Sep 2014 while the noninstitutional population increased 1.652 million from 37.027 million in Sep 2006 to 38.679 million in Sep 2014. The youth civilian labor force decreased 0.702 million from 22.105 million in Oct 2006 to 21.403 million in Oct 2014 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.047 million in Oct 2006 to 38.650 million in Oct 2014 or 1.603 million. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.111 million from 22.145 million in Nov 2006 to 21.034 million in Nov 2014 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.628 million in Nov 2014 or 1.552 million. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.472 million from 22.136 million in Dec 2006 to 20.664 million in Dec 2014 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.100 million in Dec 2006 to 38.606 million in Dec 2014 or 1.506 million. The youth civilian labor force decreased 0.831 million from 21.368 million in Jan 2006 to 20.555 million in Jan 2015 while the youth noninstitutional population increased from 36.761 million in Jan 2006 to 38.732 million in Jan 2015 or 1.971 million. The youth civilian labor force decreased 0.864 million from 21.615 million in Feb 2006 to 20.751 million in Feb 2015 while the youth noninstitutional population increased 1.914 million from 36.791 million in Feb 2006 to 38.705 million in Feb 2015. The youth civilian labor force decreased 0.907 million from 21.507 million in Mar 2006 to 20.600 million in Mar 2015 while the civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.858 million from 36.821 million in Mar 2006 to 38.679 million in Mar 2015. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.082 million from 21.498 million in Apr 2006 to 20.416 million in Apr 2015 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.800 million from 36.854 million in Apr 2006 to 38.654 million in Apr 2015. The youth civilian labor force decreased 0.681 million from 22.023 million in May 2006 to 21.342 million in May 2015 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1,733 million from 36.897 million in May 2006 to 38.630 million in May 2015. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.202 million from 24.128 million in Jun 2006 to 22.926 million in Jun 2015 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.666 million from 36.943 million in Jun 2006 to 38.609 million in Jun 2015. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.502 million from 24.664 million in Jul 2007 to 23.162 million in Jul 2015 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.600 million from 36.989 million in Jul 2006 to 38.589 million in Jul 2015. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.667 million from 23.634 million in Aug 2006 to 21.967 million in Aug 2015 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.548 million from 37.008 in Aug 2006 to 38.556 million in Aug 2015. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.290 million from 21.901 million in Sep 2006 to 20.611 in Sep 2015 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.498 million from 37.027 million in Sep 2006 to 38.525 million in Sep 2015. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.228 million from 22.105 million in Oct 2006 to 20.877 million in Oct 2015 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.444 million from 37.047 million in Oct 2006 to 38.491 million in Oct 2015. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.513 million from 22.145 million in Nov 2006 to 20.632 million in Nov 2015 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.392 million from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.468 million in Nov 2015. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.301 million from 22.136 million in Dec 2006 to 20.835 million in Dec 2015 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.341 million from 37.100 million in Dec 2006 to 38.441 million in Dec 2015. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.004 million from 21.368 million in Jan 2006 to 20.364 million in Jan 2016 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.734 million from 36.761 million in Jan 2006 to 38.495 million in Jan 2016. The youth civilian labor force decreased 0.930 million from 21.615 million in Feb 2006 to 20.685 million in Feb 2016 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.698 million from 36.791 million in Feb 2006 to 38.489 million in Feb 2016. The youth civilian labor force decreased 0.767 million from 21.507 million in Mar 2006 to 20.740 million in Mar 2016 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.662 million from 36.821 million in Mar 2006 to 38.483 million in Mar 2016. The youth civilian labor force decreased 0.950 million from 21.498 million in Apr 2006 to 20.548 million in Apr 2016 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.626 million from 36.854 million in Apr 2006 to 38.480 million in Apr 2016. The youth civilian labor force decreased 0.921 million from 22.023 million in May 2006 to 21.102 million in May 2016 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.571 million from 36.897 million in May 2006 to 38.468 million in May 2016. The youth civilian labor force decreased 1.373 million from 24.128 million in Jun 2006 to 22.755 million in Jun 2016 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.516 million from 36.943 million in Jun 2006 to 38.459 million in Jun 2016. Youth in the US abandoned their participation in the labor force because of the frustration that there are no jobs available for them.
Chart I-21B, US, Civilian Labor Force Ages 16 to 24 Years, Thousands NSA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-21C provides the ratio of labor force to noninstitutional population or labor force participation of ages 16 to 24 years not seasonally adjusted. The US labor force participation rates for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 66.7 in Jul 2006 to 60.5 in Jul 2013 because of the frustration of young people who believe there may not be jobs available for them. The US labor force participation rate of young people fell from 63.9 in Aug 2006 to 56.9 in Aug 2013. The US labor force participation rate of young people fell from 59.1 percent in Sep 2006 to 54.6 percent in Sep 2013. The US labor force participation rate of young people fell from 59.7 percent in Oct 2006 to 54.1 in Oct 2013. The US labor force participation rate of young people fell from 59.7 percent in Nov 2006 to 53.7 percent in Nov 2013. The US labor force participation rate fell from 57.8 in Dec 2007 to 53.2 in Dec 2013. The youth labor force participation rate fell from 58.4 in Jan 2007 to 52.7 in Jan 2014. The US youth labor force participation rate fell from 58.0 percent in Feb 2007 to 52.6 percent in Feb 2013. The labor force participation rate of ages 16 to 24 years fell from 58.0 in Mar 2007 to 54.0 in Mar 2014. The labor force participation rate of ages 16 to 24 years fell from 57.4 in Apr 2007 to 52.8 in Apr 2014. The labor force participation rate of ages 16 to 24 years fell from 57.9 in May 2007 to 54.6 in May 2014. The labor force participation rate of ages 16 to 24 years fell from 65.3 in Jun 2006 to 59.0 in Jun 2014. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 years fell from 66.7 in Jul 2006 to 60.5 in Jul 2014. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 years fell from 63.9 in Aug 2006 to 56.4 in Aug 2014. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 years fell from 59.1 in Sep 2006 to 54.2 in Sep 2014. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 years fell from 59.7 in Oct 2006 to 55.4 in Oct 2014. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 years fell from 59.7 in Nov 2006 to 54.5 in Nov 2014. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 59.7 in Dec 2006 to 53.5 in Dec 2014. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 58.1 in Jan 2006 to 53.1 in Jan 2015. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 58.8 in Feb 2006 to 53.6 in Feb 2015. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 64 fell from 58.4 in Mar 2006 to 53.3 in Mar 2015. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 64 fell from 58.7 in Apr 2005 to 52.8 in Apr 2006. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 64 fell from 59.7 in May 2006 to 55.2 in May 2015. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 64 fell from 65.3 in Jun 2006 to 59.4 in Jun 2015. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 66.7 in Jul 2006 to 60.0 in Jul 2014. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 63.9 in Aug 2006 to 57.0 in Aug 2015. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 59.1 in Sep 2006 to 53.5 in Sep 2015. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 59.7 in Oct 2006 to 54.2 in Oct 2015. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 59.7 in Nov 2006 to 53.6 in Nov 2015. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 59.7 in Dec 2006 to 54.2 in Dec 2015. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 58.1 in Jan 2006 to 52.9 in Jan 2016. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 58.8 in Feb 2006 to 53.7 in Feb 2016. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 58.4 in Mar 2006 to 53.9 in Mar 2016. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 58.3 in Apr 2006 to 53.4 in Apr 2016. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 59.7 in May 2006 to 54.9 in May 2016. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 fell from 65.3 in Jun 2006 to 59.2 in Jun 2016. Many young people abandoned searches for employment, dropping from the labor force.
Chart I-21C, US, Labor Force Participation Rate Ages 16 to 24 Years, NSA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
An important measure of the job market is the number of people with jobs relative to population available for work (civilian noninstitutional population) or employment/population ratio. Chart I-21D provides the employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years. The US employment/population ratio NSA for ages 16 to 24 years collapsed from 59.2 in Jul 2006 to 50.7 in Jul 2013. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years dropped from 57.2 in Aug 2006 to 48.0 in Aug 2013. The employment population ratio for ages to 16 to 24 years declined from 52.9 in Sep 2006 to 46.5 in Sep 2013. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 53.6 in Oct 2006 to 46.3 in Oct 2013. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 53.7 in Nov 2007 to 46.7 in Nov 2013. The US employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 51.6 in Dec 2007 to 46.7 in Dec 2013. The US employment population ratio fell from 52.1 in Jan 2007 to 44.8 in Jan 2014. The US employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 52.0 in Feb 2007 to 44.8 in Feb 2014. The US employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 52.3 in Mar 2007 to 46.3 in Mar 2014. The US employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 51.9 in Apr 2007 to 46.5 in Apr 2014. The US employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 52.1 in May 2007 to 47.3 in May 2014. The US employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 57.6 in Jun 2006 to 50.1 in Jun 2014. The US employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 59.2 in Jul 2006 to 50.1 in Jul 2014. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 57.2 in Aug 2006 to 49.0 in Aug 2014. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 52.9 in Sep 2006 to 46.8 in Sep 2014. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 53.6 in Oct 2006 to 48.6 in Oct 2014. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 53.7 in Nov 2006 to 48.1 in Nov 2014. The employment population ration for ages 16 to 24 fell from 54.3 in Dec 2006 to 47.5 in Dec 2014. The employment population ration for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 51.7 in Jan 2006 to 46.2 in Jan 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 52.1 in Feb 2006 to 47.1 in Feb 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 52.4 in Mar 2006 to 46.7 in Mar 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 52.7 in Apr 2006 to 47.2 in Apr 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 53.6 in May 206 to 48.4 in May 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 57.6 in Jun 2006 to 51.3 in Jun 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 59.2 in Jul 2006 to 52.7 in Jul 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 57.2 in Aug 2006 to 50.8 in Aug 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 52.9 in Sep 2006 to 47.6 in Sep 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 53.6 in Oct 2006 to 48.5 in Oct 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 53.7 in Nov 2006 to 48.1 in Nov 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 54.3 in Dec 2006 to 48.7 in Dec 2015. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 51.7 in Jan 2006 to 47.2 in Jan 2016. The employment population ration for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 52.1 in Feb 2006 to 48.0 in Feb 2016. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 52.4 in Mar 2006 to 48.3 in Mar 2016. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 52.7 in Apr 2006 to 48.1 in Apr 2016. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 53.6 in May 2006 to 49.1 in May 2016. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 57.6 in Jun 2006 to 51.9 in Jun 2016. Chart I-21D shows vertical drop during the global recession without recovery.
Chart I-21D, US, Employment Population Ratio Ages 16 to 24 Years, Thousands NSA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Table I-11 provides US unemployment level ages 16 to 24 years. The number unemployed ages 16 to 24 years increased from 2342 thousand in 2007 to 3634 thousand in 2011 or by 1.292 million and 3451 thousand in 2012 or by 1.109 million. The unemployment level ages 16 to 24 years increased from 2342 in 2007 to 3324 thousand in 2013 or by 0.982 million. The unemployment level ages 16 to 24 years increased from 2342 thousand in 2007 to 2853 thousand in 2014 or by 0.511 million. The unemployment level for ages 16 to 24 increased from 2342 thousand in 2007 to 2467 thousand in 2015. The unemployment level ages 16 to 24 years decreased from 2.860 million in Jun 2006 to 2.789 million in Jun 2016 or decrease by 0.071 million. This situation may persist for many years.
Table I-11, US, Unemployment Level 16-24 Years, NSA, Thousands
| Year | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Dec | Annual |
| 2001 | 2250 | 2258 | 2253 | 2095 | 2171 | 2775 | 2412 | 2371 |
| 2002 | 2754 | 2731 | 2822 | 2515 | 2568 | 3167 | 2374 | 2683 |
| 2003 | 2748 | 2740 | 2601 | 2572 | 2838 | 3542 | 2248 | 2746 |
| 2004 | 2767 | 2631 | 2588 | 2387 | 2684 | 3191 | 2294 | 2638 |
| 2005 | 2661 | 2787 | 2520 | 2398 | 2619 | 3010 | 2055 | 2521 |
| 2006 | 2366 | 2433 | 2216 | 2092 | 2254 | 2860 | 2007 | 2353 |
| 2007 | 2363 | 2230 | 2096 | 2074 | 2203 | 2883 | 2323 | 2342 |
| 2008 | 2633 | 2480 | 2347 | 2196 | 2952 | 3450 | 2928 | 2830 |
| 2009 | 3278 | 3457 | 3371 | 3321 | 3851 | 4653 | 3532 | 3760 |
| 2010 | 3983 | 3888 | 3748 | 3803 | 3854 | 4481 | 3352 | 3857 |
| 2011 | 3851 | 3696 | 3520 | 3365 | 3628 | 4248 | 3161 | 3634 |
| 2012 | 3416 | 3507 | 3294 | 3175 | 3438 | 4180 | 3153 | 3451 |
| 2013 | 3674 | 3449 | 3261 | 3129 | 3478 | 4198 | 2536 | 3324 |
| 2014 | 3051 | 3033 | 3002 | 2440 | 2831 | 3429 | 2317 | 2853 |
| 2015 | 2644 | 2529 | 2524 | 2175 | 2633 | 3138 | 2114 | 2467 |
| 2016 | 2205 | 2229 | 2160 | 2037 | 2227 | 2789 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-22 provides the unemployment level for ages 16 to 24 from 2001 to 2016. The level rose sharply from 2007 to 2010 with tepid improvement into 2012 and deterioration into 2013-2014 with recent marginal improvement in 2015-16 alternating with deterioration.
Chart I-22, US, Unemployment Level 16-24 Years, Thousands SA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Table I-12 provides the rate of unemployment of young peoples in ages 16 to 24 years. The annual rate jumped from 10.5 percent in 2007 to 18.4 percent in 2010, 17.3 percent in 2011 and 16.2 percent in 2012. The rate of youth unemployment fell marginally to 15.5 percent in 2013, declining to 13.4 percent in Dec 2014. During the seasonal peak in Jul, the rate of youth unemployed was 18.1 percent in Jul 2011, 17.1 percent in Jul 2012 and 16.3 percent in Jul 2013 compared with 10.8 percent in Jul 2007. The rate of youth unemployment rose from 11.2 percent in Jul 2006 to 16.3 percent in Jul 2013 and likely higher if adding those who ceased searching for a job in frustration none may be available. The rate of youth unemployment rose from 10.8 in Jul 2007 to 14.3 in Jul 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 9.1 percent in Dec 2006 to 12.3 percent in Dec 2013. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.9 percent in Jan 2007 to 14.9 percent in Jan and Feb 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 9.7 percent in Mar 2007 to 14.3 percent in Mar 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 9.7 percent in Apr 2007 to 11.9 percent in Apr 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.2 percent in May 2007 to 13.4 percent in May 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 12.0 percent in Jun 2007 to 15.0 percent in Jun 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.8 in Jul 2007 to 14.3 in Jul 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.5 in Aug 2007 to 13.0 in Aug 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 11.0 in Sep 2007 to 13.6 in Sep 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.3 in Oct 2007 to 12.2 in Oct 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.3 in Nov 2007 to 11.7 in Nov 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.7 in Dec 2007 to 11.2 in Dec 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.9 in Jan 2007 to 12.9 in Jan 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.3 percent in Feb 2007 to 12.2 percent in Feb 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 9.7 in Mar 2007 to 12.3 in Mar 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 9.7 in Apr 2007 to 10.7 in Apr 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.2 in May 2007 to 12.3 in May 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 11.9 in Jun 2006 to 13.7 in Jun 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.8 in Jul 2007 to 12.2 in Jul 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.5 in Aug 2007 to 10.9 in Aug 2015. The rate of youth unemployment decreased from 11.0 in Sep 2007 to 10.9 in Sep 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.3 in Oct 2007 to 10.6 in Oct 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.3 in Nov 2007 to 10.4 in Nov 2015. The rate of youth unemployment decreased from 10.7 in Dec 2007 to 10.1 in Dec 2015. The rate of youth unemployment decreased from 10.9 in Jan 2007 to 10.8 in Jan 2016. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.3 in Feb 2007 to 10.8 in Feb 2016. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 9.7 in Mar 2007 to 10.4 in Mar 2016. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 9.7 in Apr 2007 to 9.9 in Apr 2016. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.2 in May 2007 to 10.6 in May 2016. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 12.0 in Jun 2007 to 12.3 in Jun 2016. The actual rate is higher because of the difficulty in counting those dropping from the labor force because they believe there are no jobs available for them.
Table I-12, US, Unemployment Rate 16-24 Years, Thousands, NSA
| Year | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Annual |
| 2001 | 10.3 | 10.3 | 10.2 | 9.6 | 10.0 | 11.6 | 10.5 | 10.7 | 10.5 | 11.0 | 11.2 | 11.0 | 10.6 |
| 2002 | 12.9 | 12.5 | 12.9 | 11.6 | 11.6 | 13.2 | 12.4 | 11.5 | 11.4 | 11.2 | 11.7 | 10.9 | 12.0 |
| 2003 | 12.7 | 12.7 | 12.2 | 12.0 | 13.0 | 14.8 | 13.3 | 11.9 | 12.5 | 11.6 | 11.6 | 10.5 | 12.4 |
| 2004 | 12.8 | 12.3 | 12.1 | 11.1 | 12.2 | 13.4 | 12.3 | 11.1 | 11.5 | 11.6 | 11.1 | 10.5 | 11.8 |
| 2005 | 12.4 | 13.0 | 11.7 | 11.2 | 11.9 | 12.6 | 11.0 | 10.8 | 10.7 | 10.3 | 10.7 | 9.4 | 11.3 |
| 2006 | 11.1 | 11.3 | 10.3 | 9.7 | 10.2 | 11.9 | 11.2 | 10.4 | 10.5 | 10.2 | 10.1 | 9.1 | 10.5 |
| 2007 | 10.9 | 10.3 | 9.7 | 9.7 | 10.2 | 12.0 | 10.8 | 10.5 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.3 | 10.7 | 10.5 |
| 2008 | 12.3 | 11.8 | 11.1 | 10.3 | 13.3 | 14.4 | 14.0 | 13.0 | 13.4 | 13.2 | 13.3 | 13.7 | 12.8 |
| 2009 | 15.8 | 16.4 | 16.1 | 15.8 | 18.0 | 19.9 | 18.5 | 18.0 | 18.2 | 18.5 | 18.1 | 17.5 | 17.6 |
| 2010 | 19.8 | 19.2 | 18.4 | 18.5 | 18.4 | 20.0 | 19.1 | 17.8 | 17.6 | 18.1 | 17.4 | 16.7 | 18.4 |
| 2011 | 18.9 | 18.2 | 17.2 | 16.5 | 17.5 | 18.9 | 18.1 | 17.5 | 17.0 | 16.2 | 15.9 | 15.5 | 17.3 |
| 2012 | 16.8 | 17.0 | 16.0 | 15.4 | 16.3 | 18.1 | 17.1 | 16.8 | 15.2 | 15.5 | 14.8 | 15.2 | 16.2 |
| 2013 | 17.6 | 16.7 | 15.9 | 15.1 | 16.4 | 18.0 | 16.3 | 15.6 | 14.8 | 14.4 | 13.1 | 12.3 | 15.5 |
| 2014 | 14.9 | 14.9 | 14.3 | 11.9 | 13.4 | 15.0 | 14.3 | 13.0 | 13.6 | 12.2 | 11.7 | 11.2 | 13.4 |
| 2015 | 12.9 | 12.2 | 12.3 | 10.7 | 12.3 | 13.7 | 12.2 | 10.9 | 10.9 | 10.6 | 10.4 | 10.1 | 11.6 |
| 2016 | 10.8 | 10.8 | 10.4 | 9.9 | 10.6 | 12.3 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-23 provides the BLS estimate of the not-seasonally-adjusted rate of youth unemployment for ages 16 to 24 years from 2001 to 2016. The rate of youth unemployment increased sharply during the global recession of 2008 and 2009 but has failed to drop to earlier lower levels because of low growth of GDP. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E. Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent.
Chart I-23, US, Unemployment Rate 16-24 Years, Percent, NSA, 2001-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-24 provides longer perspective with the rate of youth unemployment in ages 16 to 24 years from 1948 to 2016. The rate of youth unemployment rose to 20 percent during the contractions of the early 1980s and also during the contraction of the global recession in 2008 and 2009. The data illustrate again the argument in this blog that the contractions of the early 1980s are the valid framework for comparison with the global recession of 2008 and 2009 instead of misleading comparisons with the 1930s. During the initial phase of recovery, the rate of youth unemployment 16 to 24 years NSA fell from 18.9 percent in Jun 1983 to 14.5 percent in Jun 1984. In contrast, the rate of youth unemployment 16 to 24 years was nearly the same during the expansion after IIIQ2009: 17.5 percent in Dec 2009, 16.7 percent in Dec 2010, 15.5 percent in Dec 2011, 15.2 percent in Dec 2012, 17.6 percent in Jan 2013, 16.7 percent in Feb 2013, 15.9 percent in Mar 2013, 15.1 percent in Apr 2013. The rate of youth unemployment was 16.4 percent in May 2013, 18.0 percent in Jun 2013, 16.3 percent in Jul 2013 and 15.6 percent in Aug 2013. In Sep 2006, the rate of youth unemployment was 10.5 percent, increasing to 14.8 percent in Sep 2013. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.3 in Oct 2007, increasing to 14.4 percent in Oct 2013. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.3 percent in Nov 2007, increasing to 13.1 percent in Nov 2013. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.7 percent in Dec 2013, increasing to 12.3 percent in Dec 2013. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.9 percent in Jan 2007, increasing to 14.9 percent in Jan 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.3 percent in Feb 2007, increasing to 14.9 percent in Feb 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 9.7 percent in Mar 2007, increasing to 14.3 percent in Mar 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 9.7 percent in Apr 2007, increasing to 11.9 percent in Apr 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.2 percent in May 2007, increasing to 13.4 percent in May 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 12.0 percent in Jun 2007, increasing to 15.0 percent in Jun 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.8 percent in Jul 2007, increasing to 14.3 percent in Jul 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.5 percent in Aug 2007, increasing to 13.0 percent in Aug 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 11.0 percent in Sep 2007, increasing to 13.6 percent in Sep 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.3 in Oct 2007 to 12.2 in Oct 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.3 percent in Nov 2007 to 11.7 percent in Nov 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.7 in Dec 2007 to 11.2 in Dec 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 9.7 in Mar 2007 to 12.3 in Mar 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 9.7 in Apr 2007 to 10.7 in Apr 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.2 in May 2007 to 12.3 in May 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 12.0 in Jun 2007 to 13.7 in Jun 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.8 in Jul 2007 to 12.2 in Jul 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.5 in Aug 2007 to 10.9 in Aug 2015. The rate of youth unemployment decreased from 11.0 in Sep 2007 to 10.9 in Sep 2015. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.3 in Oct 2007 to 10.6 in Oct 2015, decreasing to 10.4 in Nov 2015. The rate of youth unemployment decreased to 10.1 in Dec 2015. The rate of youth unemployment stood at 10.8 in Jan 2016, 10.8 in Feb 2016, 10.4 in Mar 2016 and 9.9 in Apr 2016. The rate of youth unemployment increased to 10.6 in May 2016 and 12.3 in Jun 2016. The actual rate is higher because of the difficulty in counting those dropping from the labor force because they believe there are no jobs available for them. The difference originates in the vigorous seasonally adjusted annual equivalent average rate of GDP growth of 5.9 percent during the recovery from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 and 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1989 compared with 2.1 percent on average during the first 26 quarters of expansion from IIIQ2009 to IVQ2015. US economic growth has been at only 2.1 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 27 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IQ2016. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the third estimate of GDP for IQ2016 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2016/pdf/gdp1q16_3rd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,745.9 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,355.6 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,745.9/$14,355.6 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/financial-asset-values-rebound-from.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/appropriate-for-fed-to-increase.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1989 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/financial-asset-values-rebound-from.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/appropriate-for-fed-to-increase.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IQ2016 would have accumulated to 27.6 percent. GDP in IQ2016 would be $19,129.5 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2614.9 billion than actual $16,514.6 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 23.7 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 14.1 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/fluctuating-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/financial-turbulence-twenty-four.html). US GDP in IQ2016 is 13.7 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,514.6 billion in IQ2016 or 10.2 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.2 percent. Professor John H. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. Cochrane (2016May02) measures GDP growth in the US at average 3.5 percent per year from 1950 to 2000 and only at 1.76 percent per year from 2000 to 2015 with only at 2.0 percent annual equivalent in the current expansion. Cochrane (2016May02) proposes drastic changes in regulation and legal obstacles to private economic activity. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth of manufacturing at average 3.2 percent per year from May 1919 to May 2016. Growth at 3.2 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 108.2316 in Dec 2007 to 141.0886 in May 2016. The actual index NSA in May 2016 is 103.0898, which is 26.9 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.1 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2015. Using trend growth of 2.1 percent per year, the index would increase to 128.9038 in May 2016. The output of manufacturing at 103.0898 in May 2016 is 20.0 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Chart I-24, US, Unemployment Rate 16-24 Years, Percent NSA, 1948-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
It is more difficult to move to other jobs after a certain age because of fewer available opportunities for mature individuals than for new entrants into the labor force. Middle-aged unemployed are less likely to find another job. Table I-13 provides the unemployment level ages 45 years and over. The number unemployed ages 45 years and over rose from 1.607 million in Oct 2006 to 4.576 million in Oct 2010 or by 184.8 percent. The number of unemployed ages 45 years and over declined to 3.800 million in Oct 2012 that is still higher by 136.5 percent than in Oct 2006. The number unemployed age 45 and over increased from 1.704 million in Nov 2006 to 3.861 million in Nov 2012, or 126.6 percent. The number unemployed age 45 and over is still higher by 98.5 percent at 3.383 million in Nov 2013 than 1.704 million in Nov 2006. The number unemployed age 45 and over jumped from 1.794 million in Dec 2006 to 4.762 million in Dec 2010 or 165.4 percent. At 3.927 million in Dec 2012, mature unemployment is higher by 2.133 million or 118.9 percent higher than 1.794 million in Dec 2006. The level of unemployment of those aged 45 year or more of 3.632 million in Oct 2013 is higher by 2.025 million than 1.607 million in Oct 2006 or higher by 126.0 percent. The number of unemployed 45 years and over increased from 1.794 million in Dec 2006 to 3.378 million in Nov 2013 or 88.3 percent. The annual number of unemployed 45 years and over increased from 1.848 million in 2006 to 3.719 million in 2013 or 101.2 percent. The number of unemployed 45 years and over increased from 2.126 million in Jan 2006 to 4.394 million in Jan 2013, by 2.618 million or 106.7 percent. The number of unemployed 45 years and over rose from 2.126 million in Jan 2006 to 3.508 million in Jan 2014, by 1.382 million or 65.0 percent. The level of unemployed 45 years or older increased 2.051 million or 99.8 percent from 2.056 million in Feb 2006 to 4.107 million in Feb 2013 and at 3.490 million in Feb 2014 is higher by 69.7 percent than in Feb 2006. The number of unemployed 45 years and over increased 2.048 million or 108.9 percent from 1.881 million in Mar 2006 to 3.929 million in Mar 2013 and at 3.394 million in Mar 2014 is higher by 80.4 percent than in Mar 2006. The number of unemployed 45 years and over increased 1.846 million or 100.2 percent from 1.843 million in Apr 2006 to 3.689 million in Apr 2013 and at 3.006 million in Apr 2014 is higher by 1.163 million or 63.1 percent. The number of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 102.1 percent from 1.784 million in May 2006 to 3.605 million in May 2014 and at 2.913 million in May 2014 is higher by 63.3 percent than in May 2007.
The number of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 102.1 percent from 1.805 million in Jun 2007 to 3.648 million in Jun 2013 and at 2.832 million in Jun 2014 is higher by 56.9 percent than in Jun 2007. The number of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 81.5 percent from 2.053 million in Jul 2007 to 3.727 million in Jul 2013 and at 3.083 million in Jul 2014 is higher by 50.2 percent than in Jul 2007. The level unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 84.4 percent from 1.956 million in Aug 2007 to 3.607 million in Aug 2013 and at 3.037 million in Aug 2014 is 55.2 percent higher than in Aug 2007. The level unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 90.7 percent from 1.854 million in Sep 2007 to 3.535 million in Sep 2013 and at 2.640 million in Sep 2014 is 42.4 percent higher than in Sep 2007. The level unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 1.747 million from 1.885 million in Oct 2007 to 3.632 million in Oct 2013 and at 2.606 million in Oct 2014 is 38.2 percent higher than in Oct 2007. The level unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 1.458 million from 1.925 million in Nov 2007 to 3.383 million in Nov 2013 and at 2.829 million in Nov 2014 is 47.0 percent higher than in Nov 2007. The level of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 1.258 million from Dec 2007 to Dec 2013 and at 2.667 million in Dec 2014 is 25.8 higher than in Dec 2007. The level unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 1.353 million from Jan 2007 to Jan 2015 and at 3.077 million in Jan 2015 is 42.8 percent higher than in Jan 2007. The level unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 1.352 million from 2.138 million in Feb 2007 to 3.490 million in Feb 2014 and at 2.991 million in Feb 2015 is 39.9 percent higher than in Feb 2007. The level of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 1.363 million from 2.031 million in Mar 2007 to 3.394 million in Mar 2014 and at 2.724 million in Mar 2015 is 34.1 percent higher than in Mar 2007. The level of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased from 1.871 million in Apr 2007 to 3.006 million in Apr 2014 and at 2.579 million in Apr 2015 is 37.8 higher than in Apr 2007. The level of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased from 1.803 million in May 2007 to 2.913 million in Jun 2014 and at 2.457 million in May 2015 is 36.3 percent higher than in May 2007. The level of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased from 1.805 million in Jun 2007 to 2.832 million in Jun 2014 and at 2.359 million in Jun 2015 is 30.7 percent higher than in Jun 2007. The level of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased from 2.053 million in Jul 2007 to 3.083 million in Jul 2014 and at 2.666 million in Jul 2015 is 30.0 percent higher than in Jul 2007. The level of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased from 1.956 million in Aug 2007 to 3.037 million in Aug 2014 and at 2.693 million in Aug 2015 is 37.7 higher than in Aug 2007. The level of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased from 1.854 million in Sep 2007 to 2.640 million in Sep 2015 and at 2.388 million in Sep 2015 is 28.8 percent higher than in Sep 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 years and over increased from 1.885 million in Oct 2007 to 2.606 million in Oct 2014 and at 2.290 million in Oct 2015 is 21.5 percent higher than in Oct 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 years and over increased from 1.925 million in Nov 2007 to 2.829 million in Nov 2014 and at 2.349 million in Nov 2015 is 22.0 percent higher than in Nov 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 years and over increased from 2.120 million in Dec 2007 to 2.667 million in Dec 2014 and at 2.317 million in Dec 2015 is 9.3 percent higher than in Dec 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 and over increased from 2.155 million in Jan 2007 to 3.077 million in Jan 2015 and at 2.736 million in Jan 2016 is 27.0 percent higher than in Jan 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 and over increased from 2.138 million in Feb 2007 to 2.991 million in Feb 2015 and at 2.744 million in Feb 2016 is 28.3 percent higher than in Feb 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 and over increased from 2.031 million in Mar 2007 to 2.724 million in Mar 2015 and at 2.747 million in Mar 2016 is 35.3 percent higher than in Mar 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 and over increased from 1.871 million in Apr 2007 to 2.579 million in Apr 2015 and at 2.410 million in Apr 2016 is 28.8 percent higher than in Apr 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 and over increased from 1.803 million in May 2007 to 2.457 million in May 2015 and at 2.190 million in May 2016 is 21.5 percent higher than in May 2007. The level of unemployment ages 45 and over increased from 1.805 million in Jun 2007 to 2.359 million in Jun 2015 and at 2.345 million in Jun 2016 is 29.9 percent higher than in Jun 2007. The actual number unemployed is likely much higher because many are not accounted who abandoned job searches in frustration there may not be a job for them. Recent improvements may be illusory. US economic growth has been at only 2.1 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 27 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IQ2016. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the third estimate of GDP for IQ2016 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2016/pdf/gdp1q16_3rd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,745.9 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,355.6 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,745.9/$14,355.6 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/financial-asset-values-rebound-from.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/appropriate-for-fed-to-increase.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1989, 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1989 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/financial-asset-values-rebound-from.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/05/appropriate-for-fed-to-increase.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IQ2016 would have accumulated to 27.6 percent. GDP in IQ2016 would be $19,129.5 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2614.9 billion than actual $16,514.6 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 23.7 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 14.1 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/07/fluctuating-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/06/financial-turbulence-twenty-four.html). US GDP in IQ2016 is 13.7 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,514.6 billion in IQ2016 or 10.2 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.2 percent. Professor John H. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. Cochrane (2016May02) measures GDP growth in the US at average 3.5 percent per year from 1950 to 2000 and only at 1.76 percent per year from 2000 to 2015 with only at 2.0 percent annual equivalent in the current expansion. Cochrane (2016May02) proposes drastic changes in regulation and legal obstacles to private economic activity. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth of manufacturing at average 3.2 percent per year from May 1919 to May 2016. Growth at 3.2 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 108.2316 in Dec 2007 to 141.0886 in May 2016. The actual index NSA in May 2016 is 103.0898, which is 26.9 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.1 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2015. Using trend growth of 2.1 percent per year, the index would increase to 128.9038 in May 2016. The output of manufacturing at 103.0898 in May 2016 is 20.0 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Table I-13, US, Unemployment Level 45 Years and Over, Thousands NSA
| Year | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Dec | Annual |
| 2000 | 1498 | 1392 | 1291 | 1062 | 1074 | 1163 | 1217 | 1249 |
| 2001 | 1572 | 1587 | 1533 | 1421 | 1259 | 1371 | 1901 | 1576 |
| 2002 | 2235 | 2280 | 2138 | 2101 | 1999 | 2190 | 2210 | 2114 |
| 2003 | 2495 | 2415 | 2485 | 2287 | 2112 | 2212 | 2130 | 2253 |
| 2004 | 2453 | 2397 | 2354 | 2160 | 2025 | 2182 | 2086 | 2149 |
| 2005 | 2286 | 2286 | 2126 | 1939 | 1844 | 1868 | 1963 | 2009 |
| 2006 | 2126 | 2056 | 1881 | 1843 | 1784 | 1813 | 1794 | 1848 |
| 2007 | 2155 | 2138 | 2031 | 1871 | 1803 | 1805 | 2120 | 1966 |
| 2008 | 2336 | 2336 | 2326 | 2104 | 2095 | 2211 | 3485 | 2540 |
| 2009 | 4138 | 4380 | 4518 | 4172 | 4175 | 4505 | 4960 | 4500 |
| 2010 | 5314 | 5307 | 5194 | 4770 | 4565 | 4564 | 4762 | 4879 |
| 2011 | 5027 | 4837 | 4748 | 4373 | 4356 | 4559 | 4182 | 4537 |
| 2012 | 4458 | 4472 | 4390 | 4037 | 4083 | 4084 | 3927 | 4133 |
| 2013 | 4394 | 4107 | 3929 | 3689 | 3605 | 3648 | 3378 | 3719 |
| 2014 | 3508 | 3490 | 3394 | 3006 | 2913 | 2832 | 2667 | 3000 |
| 2015 | 3077 | 2991 | 2724 | 2579 | 2457 | 2359 | 2317 | 2574 |
| 2016 | 2736 | 2744 | 2747 | 2410 | 2190 | 2345 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-25 provides the level unemployed ages 45 years and over. There was an increase in the recessions of the 1980s, 1991 and 2001 followed by declines to earlier levels. The current expansion of the economy after IIIQ2009 has not been sufficiently vigorous to reduce significantly middle-age unemployment. Recent improvements could be illusory because many abandoned job searches in frustration that there may not be jobs for them and are not counted as unemployed.
Chart I-25, US, Unemployment Level Ages 45 Years and Over, Thousands, NSA, 1976-2016
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016.






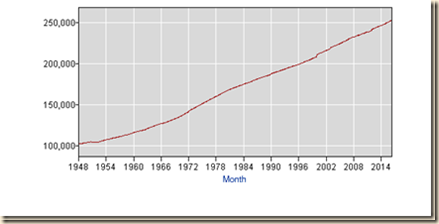

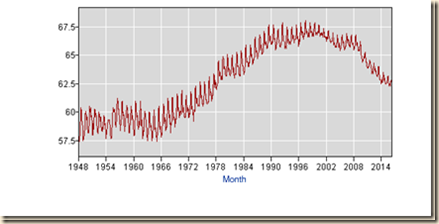







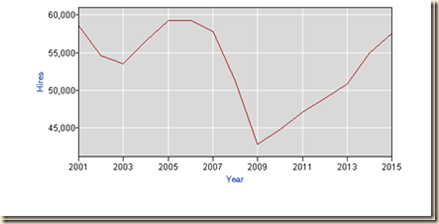

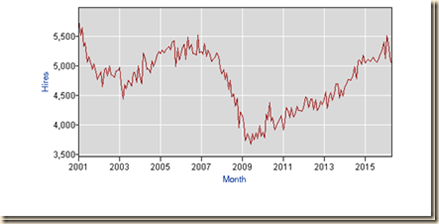





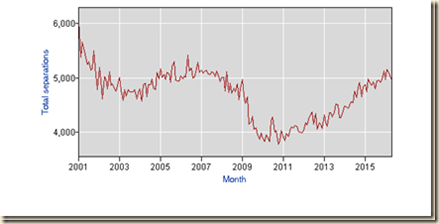




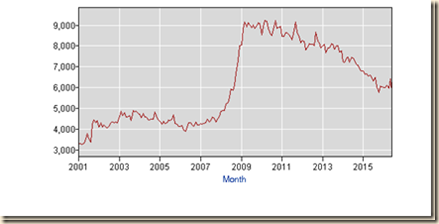


![clip_image009[1] clip_image009[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiMA4z5ktiNh7_dygcHYLecRvsCVZC7MavSFntqEE6qN8b-tS8vBKs9_kAqD8qQRqnxBiiiObN3P0aejcWeZJdwd_sKKJOBW1GUEnZJ2MANgbbLPKZgf1MnaFoKLNDe0-8UeLXzB3CBgPE/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image010[1] clip_image010[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgu11XEcqmDsd0yy-sww0cIY438jyKWYDqUiY6we_hTwau2S4-tJbUmrfxYi4OypsVT9a1KhP_uafdNVogov2app6lKR31LHi9YMgHJgHk9pGQ-I2y1NeXK7wbr3S-gRdBLg9261HL-2AE/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image011[1] clip_image011[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhaI7tccJb-nZaGieUa3vY0pgpRcXweT-CzZSyM8vq3OSBnQRyAyiJfzD7xNvNx35v80lMFXCIhO02ZAnWixRLDdzHJFaSvYyqgZ6GfV8KbXA6DIVrFbIHkidjmuRnqPh2N2E3lonUAO38/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image012[1] clip_image012[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgI23RwHQsA9pBvBynYaZEegBPF9dSsyzDXU9qWzrAAAQQZgrZ0BAhyk4ZctVVwAThNv3bLYGnceiadrRJLw96OUQY9AErAYZbkG3ChEPTP6kqrRxssbfrhfNKWZo0_I7py5GEvAizQHSAl/?imgmax=800)
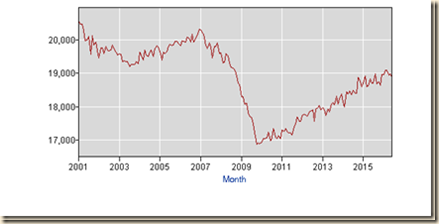
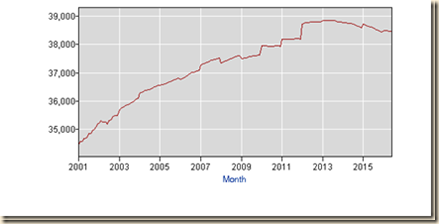
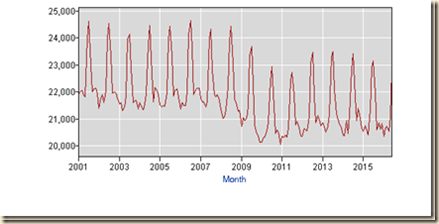
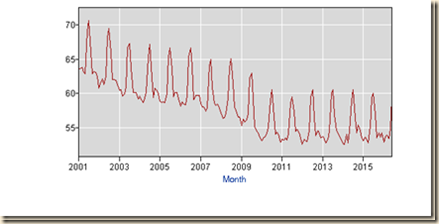
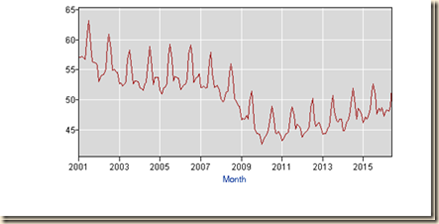



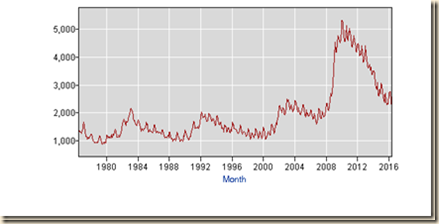
No comments:
Post a Comment