Geopolitics, Monetary Policy and Competitive Devaluations, Recovery without Hiring, Congressional Budget Office Budget Update, United States Services, United States Import and Export Prices, World Cyclical Slow Growth and Global Recession Risk
Carlos M. Pelaez
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014
I Recovery without Hiring
IA1 Hiring Collapse
IA2 Labor Underutilization
ICA3 Ten Million Fewer Full-time Jobs
IA4 Theory and Reality of Cyclical Slow Growth Not Secular Stagnation: Youth and
Middle-Age Unemployment
IIA The Congressional Budget Office Update of Budget Outlook and Long-term Budget Outlook
IIB United States Services
IIC United States Import and Export Prices
III World Financial Turbulence
IIIA Financial Risks
IIIE Appendix Euro Zone Survival Risk
IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation
IV Global Inflation
V World Economic Slowdown
VA United States
VB Japan
VC China
VD Euro Area
VE Germany
VF France
VG Italy
VH United Kingdom
VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets
VII Economic Indicators
VIII Interest Rates
IX Conclusion
References
Appendixes
Appendix I The Great Inflation
IIIB Appendix on Safe Haven Currencies
IIIC Appendix on Fiscal Compact
IIID Appendix on European Central Bank Large Scale Lender of Last Resort
IIIG Appendix on Deficit Financing of Growth and the Debt Crisis
IIIGA Monetary Policy with Deficit Financing of Economic Growth
IIIGB Adjustment during the Debt Crisis of the 1980s
I Recovery without Hiring. Professor Edward P. Lazear (2012Jan19) at Stanford University finds that recovery of hiring in the US to peaks attained in 2007 requires an increase of hiring by 30 percent while hiring levels increased by only 4 percent from Jan 2009 to Jan 2012. The high level of unemployment with low level of hiring reduces the statistical probability that the unemployed will find a job. According to Lazear (2012Jan19), the probability of finding a new job in early 2012 is about one third of the probability of finding a job in 2007. Improvements in labor markets have not increased the probability of finding a new job. Lazear (2012Jan19) quotes an essay coauthored with James R. Spletzer in the American Economic Review (Lazear and Spletzer 2012Mar, 2012May) on the concept of churn. A dynamic labor market occurs when a similar amount of workers is hired as those who are separated. This replacement of separated workers is called churn, which explains about two-thirds of total hiring. Typically, wage increases received in a new job are higher by 8 percent. Lazear (2012Jan19) argues that churn has declined 35 percent from the level before the recession in IVQ2007. Because of the collapse of churn, there are no opportunities in escaping falling real wages by moving to another job. As this blog argues, there are meager chances of escaping unemployment because of the collapse of hiring and those employed cannot escape falling real wages by moving to another job (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/weakening-world-economic-growth.html). Lazear and Spletzer (2012Mar, 1) argue that reductions of churn reduce the operational effectiveness of labor markets. Churn is part of the allocation of resources or in this case labor to occupations of higher marginal returns. The decline in churn can harm static and dynamic economic efficiency. Losses from decline of churn during recessions can affect an economy over the long-term by preventing optimal growth trajectories because resources are not used in the occupations where they provide highest marginal returns. Lazear and Spletzer (2012Mar 7-8) conclude that: “under a number of assumptions, we estimate that the loss in output during the recession [of 2007 to 2009] and its aftermath resulting from reduced churn equaled $208 billion. On an annual basis, this amounts to about .4% of GDP for a period of 3½ years.”
There are two additional facts discussed below: (1) there are about ten million fewer full-time jobs currently than before the recession of 2008 and 2009; and (2) the extremely high and rigid rate of youth unemployment is denying an early start to young people ages 16 to 24 years while unemployment of ages 45 years or over has swelled. There are four subsections. IA1 Hiring Collapse provides the data and analysis on the weakness of hiring in the United States economy. IA2 Labor Underutilization provides the measures of labor underutilization of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). Statistics on the decline of full-time employment are in IA3 Ten Million Fewer Full-time Jobs. IA4 Theory and Reality of Cyclical Slow Growth Not Secular Stagnation: Youth and Middle-Age Unemployment provides the data on high unemployment of ages 16 to 24 years and of ages 45 years or over.
IA1 Hiring Collapse. An important characteristic of the current fractured labor market of the US is the closing of the avenue for exiting unemployment and underemployment normally available through dynamic hiring. Another avenue that is closed is the opportunity for advancement in moving to new jobs that pay better salaries and benefits again because of the collapse of hiring in the United States. Those who are unemployed or underemployed cannot find a new job even accepting lower wages and no benefits. The employed cannot escape declining inflation-adjusted earnings because there is no hiring. The objective of this section is to analyze hiring and labor underutilization in the United States.
Blanchard and Katz (1997, 53 consider an appropriate measure of job stress:
“The right measure of the state of the labor market is the exit rate from unemployment, defined as the number of hires divided by the number unemployed, rather than the unemployment rate itself. What matters to the unemployed is not how many of them there are, but how many of them there are in relation to the number of hires by firms.”
The natural rate of unemployment and the similar NAIRU are quite difficult to estimate in practice (Ibid; see Ball and Mankiw 2002).
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) created the Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey (JOLTS) with the purpose that (http://www.bls.gov/jlt/jltover.htm#purpose):
“These data serve as demand-side indicators of labor shortages at the national level. Prior to JOLTS, there was no economic indicator of the unmet demand for labor with which to assess the presence or extent of labor shortages in the United States. The availability of unfilled jobs—the jobs opening rate—is an important measure of tightness of job markets, parallel to existing measures of unemployment.”
The BLS collects data from about 16,000 US business establishments in nonagricultural industries through the 50 states and DC. The data are released monthly and constitute an important complement to other data provided by the BLS (see also Lazear and Spletzer 2012Mar, 6-7).
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) revised on Mar 11, 2014 “job openings, hires and separations data to incorporate the annual update to the Current Employment Statistics employment estimates and the JOLTS seasonal adjustment factors. Unadjusted data and seasonally adjusted data from December 2000 forward are subject to revisions” (http://www.bls.gov/jlt/). Hiring in the nonfarm sector (HNF) has declined from 63.3 million in 2006 to 54.2 million in 2013 or by 9.1 million while hiring in the private sector (HP) has declined from 59.1 million in 2006 to 50.7 million in 2013 or by 8.4 million, as shown in Table I-1. The ratio of nonfarm hiring to employment (RNF) has fallen from 47.0 in 2005 to 39.7 in 2013 and in the private sector (RHP) from 52.7 in 2005 to 44.3 in 2013. Hiring has not recovered as in previous cyclical expansions because of the low rate of economic growth in the current cyclical expansion. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. US economic growth has been at only 2.2 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 20 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2014. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the second estimate of GDP for IIQ2014 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2014/pdf/gdp2q14_2nd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,745.9 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,355.6 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,745.9/$14,355.6 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/geopolitical-and-financial-risks.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/fluctuating-financial-valuations.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/geopolitical-and-financial-risks.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/fluctuating-financial-valuations.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIQ2014 would have accumulated to 22.1 percent. GDP in IIQ2014 would be $18,305.0 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2,310.7 billion than actual $15,994.3 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 26.9 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment of 16.4 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/competitive-monetary-policy-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/fluctuating-financial-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/financial-valuations-twenty-seven.html). US GDP in IIQ2014 is 12.6 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $15,994.3 billion in IIQ2014 or 6.7 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.0 percent. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. The long-term trend is growth at average 3.3 percent per year from Jan 1919 to Jul 2014. Growth at 3.3 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 99.2392 in Dec 2007 to 122.8881 in Jul 2014. The actual index NSA in Jul 2014 is 98.4978, which is 19.8 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.3 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2013, raising the index at trend to 115.2650 in Jul 2014. The output of manufacturing at 98.4978 in Jul 2014 is 14.5 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Table I-1, US, Annual Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF) and Total Private Hiring (HP) in the US in Thousands and Percentage of Total Employment
| HNF | Rate RNF | HP | Rate HP | |
| 2001 | 62,633 | 47.4 | 58,501 | 52.7 |
| 2002 | 58,479 | 44.8 | 54,665 | 50.1 |
| 2003 | 56,949 | 43.7 | 53,584 | 49.3 |
| 2004 | 60,263 | 45.7 | 56,573 | 51.4 |
| 2005 | 62,951 | 47.0 | 59,179 | 52.7 |
| 2006 | 63,327 | 46.4 | 59,128 | 51.7 |
| 2007 | 62,104 | 45.0 | 57,797 | 49.9 |
| 2008 | 54,745 | 39.9 | 51,316 | 44.8 |
| 2009 | 45,931 | 35.0 | 42,703 | 39.3 |
| 2010 | 48,743 | 37.4 | 44,914 | 41.7 |
| 2011 | 50,295 | 38.1 | 47,183 | 43.0 |
| 2012 | 52,360 | 39.0 | 48,915 | 43.6 |
| 2013 | 54,191 | 39.7 | 50,718 | 44.3 |
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-1 shows the annual level of total nonfarm hiring (HNF) that collapsed during the global recession after 2007 in contrast with milder decline in the shallow recession of 2001. Nonfarm hiring has not recovered, remaining at a depressed level.
Chart I-1, US, Level Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF), Annual, 2001-2013
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-2 shows the ratio or rate of nonfarm hiring to employment (RNF) that also fell much more in the recession of 2007 to 2009 than in the shallow recession of 2001. Recovery is weak in the current environment of cyclical slow growth.
Chart I-2, US, Rate Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF), Annual, 2001-2015
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Yearly percentage changes of total nonfarm hiring (HNF) are provided in Table I-2. There were much milder declines in 2002 of 6.6 percent and 2.6 percent in 2003 followed by strong rebounds of 5.8 percent in 2004 and 4.5 percent in 2005. In contrast, the contractions of nonfarm hiring in the recession after 2007 were much sharper in percentage points: 1.9 in 2007, 11.8 in 2008 and 16.1 percent in 2009. On a yearly basis, nonfarm hiring grew 6.1 percent in 2010 relative to 2009, 3.2 percent in 2011, 4.1 percent in 2012 and 3.5 percent in 2013. The relatively large length of 18 quarters of the current expansion reduces the likelihood of significant recovery of hiring levels in the United States because lower rates of growth and hiring in the final phase of expansions.
Table I-2, US, Annual Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF), Annual Percentage Change, 2002-2013
| Year | Annual ∆% |
| 2002 | -6.6 |
| 2003 | -2.6 |
| 2004 | 5.8 |
| 2005 | 4.5 |
| 2006 | 0.6 |
| 2007 | -1.9 |
| 2008 | -11.8 |
| 2009 | -16.1 |
| 2010 | 6.1 |
| 2011 | 3.2 |
| 2012 | 4.1 |
| 2013 | 3.5 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Total private hiring (HP) yearly data are provided in Chart I-4. There has been sharp contraction of total private hiring in the US and only milder recovery from 2010 to 2013.
Chart I-4, US, Total Nonfarm Hiring Level, Annual, ∆%, 2001-2013
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-5 plots the rate of total private hiring relative to employment (RHP). The rate collapsed during the global recession after 2007 with insufficient recovery.
Chart I-5, US, Total Private Hiring, Annual, 2001-2013
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-5A plots the rate of total private hiring relative to employment (RHP). The rate collapsed during the global recession after 2007 with insufficient recovery.
Chart I-5A, US, Rate Total Private Hiring Level, Annual, 2001-2013
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Total nonfarm hiring (HNF), total private hiring (HP) and their respective rates are provided for the month of Jul in the years from 2001 to 2014 in Table I-3. Hiring numbers are in thousands. There is moderate recovery in HNF from 4264 thousand (or 4.3 million) in Jul 2009 to 4566 thousand in Jul 2010, 4602 thousand in Jul 2011, 4689 thousand in Jul 2012, 4943 thousand in Jul 2013 and 5319 thousand in Jul 2014 for cumulative gain of 24.7 percent at average rate of 4.5 percent per year. HP rose from 3984 thousand in Jul 2009 to 4253 thousand in Jul 2010, 4326 thousand in Jul 2011, 4354 thousand in Jul 2012, 4632 thousand in Jul 2013 and 4982 thousand in Jul 2014 for cumulative gain of 25.1 percent at the average yearly rate of 4.6 percent. HNF has fallen from 5893 thousand in Jul 2006 to 5319 thousand in Jul 2014 or by 9.7 percent. HP has fallen from 5501 thousand in Jul 2006 to 4982 thousand in Jul 2014 or by 9.4 percent. The civilian noninstitutional population of the US, or individuals in condition to work, rose from 228.815 million in 2006 to 245.679 million in 2013 or by 16.864 million and the civilian labor force from 151.428 million in 2006 to 155.389 million in 2013 or by 3.961 million (http://www.bls.gov/data/). The number of nonfarm hires in the US fell from 63.327 million in 2006 to 54.191 million in 2013 or by 9.136 million and the number of private hires fell from 59.128 million in 2006 to 50.718 million in 2013 or by 8.410 million (http://www.bls.gov/jlt/). Private hiring of 59.128 million in 2006 was equivalent to 25.8 percent of the civilian noninstitutional population of 228.815, or those in condition of working, falling to 50.718 million in 2013 or 20.6 percent of the civilian noninstitutional population of 245.679 million in 2013. The percentage of hiring in civilian noninstitutional population of 25.8 percent in 2006 would correspond to 63.385 million of hiring in 2013, which would be 12.667 million higher than actual 50.718 million in 2013. Cyclical slow growth over the entire business cycle from IVQ2007 to the present in comparison with earlier cycles and long-term trend (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/geopolitical-and-financial-risks.html) explains the fact that there are many million fewer hires in the US than before the global recession. The labor market continues to be fractured, failing to provide an opportunity to exit from unemployment/underemployment or to find an opportunity for advancement away from declining inflation-adjusted earnings.
Table I-3, US, Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF) and Total Private Hiring (HP) in the US in
Thousands and in Percentage of Total Employment Not Seasonally Adjusted
| HNF | Rate RNF | HP | Rate HP | |
| 2001 Jul | 5732 | 4.3 | 5361 | 4.8 |
| 2002 Jul | 5554 | 4.3 | 5216 | 4.7 |
| 2003 Jul | 5222 | 4.0 | 4890 | 4.5 |
| 2004 Jul | 5361 | 4.1 | 5036 | 4.5 |
| 2005 Jul | 5828 | 4.4 | 5450 | 4.8 |
| 2006 Jul | 5893 | 4.3 | 5501 | 4.8 |
| 2007 Jul | 5644 | 4.1 | 5254 | 4.5 |
| 2008 Jul | 4949 | 3.6 | 4617 | 4.0 |
| 2009 Jul | 4264 | 3.3 | 3984 | 3.7 |
| 2010 Jul | 4566 | 3.5 | 4253 | 3.9 |
| 2011 Jul | 4602 | 3.5 | 4326 | 3.9 |
| 2012 Jul | 4689 | 3.5 | 4354 | 3.9 |
| 2013 Jul | 4943 | 3.6 | 4632 | 4.0 |
| 2014 Jul | 5319 | 3.8 | 4982 | 4.2 |
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-6 provides total nonfarm hiring on a monthly basis from 2001 to 2014. Nonfarm hiring rebounded in early 2010 but then fell and stabilized at a lower level than the early peak not-seasonally adjusted (NSA) of 4841 in May 2010 until it surpassed it with 4975 in Jun 2011 but declined to 3084 in Dec 2012. Nonfarm hiring fell to 3012 in Dec 2011 from 3810 in Nov and to revised 3614 in Feb 2012, increasing to 4220 in Mar 2012, 3084 in Dec 2012 and 4223 in Jan 2013 and declining to 3861 in Feb 2013. Nonfarm hires not seasonally adjusted increased to 4165 in Nov 2013 and 3271 in Dec 2013. Nonfarm hires reached 5319 in Jul 2014. Chart I-6 provides seasonally adjusted (SA) monthly data. The number of seasonally-adjusted hires in Oct 2011 was 4237 thousand, increasing to revised 4446 thousand in Feb 2012, or 4.9 percent, moving to 4343 in Dec 2012 for cumulative increase of 2.0 percent from 4256 in Dec 2011 and 4578 in Dec 2013 for increase of 5.4 percent relative to 4343 in Dec 2012. The number of hires not seasonally adjusted was 4975 in Jun 2011, falling to 3012 in Dec 2011 but increasing to 4112 in Jan 2012 and declining to 3084 in Dec 2012. The number of nonfarm hiring not seasonally adjusted fell by 39.5 percent from 4975 in Jun 2011 to 3012 in Dec 2011 and fell 38.7 percent from 5035 in Jun 2012 to 3084 in Dec 2012 in a yearly-repeated seasonal pattern. The number of nonfarm hires not seasonally adjusted fell from 5095 in Jun 2013 to 3271 in Dec 2013, or decline of 35.8 percent, showing strong seasonality.
Chart I-6, US, Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF), 2001-2014 Month SA
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Similar behavior occurs in the rate of nonfarm hiring in Chart I-7. Recovery in early 2010 was followed by decline and stabilization at a lower level but with stability in monthly SA estimates of 3.2 in Aug 2011 to 3.2 in Jan 2012, increasing to 3.3 in May 2012 and falling to 3.2 in Jun 2012. The rate stabilized at 3.2 in Jul 2012, increasing to 3.3 in Aug 2012 but falling to 3.2 in Dec 2012 and 3.3 in Dec 2013. The rate not seasonally adjusted fell from 3.7 in Jun 2011 to 2.3 in Dec 2011, climbing to 3.7 in Jun 2012 but falling to 2.3 in Dec 2012. The rate of nonfarm hires not seasonally adjusted fell from 3.7 in Jun 2013 to 2.4 in Dec 2013. Rates of nonfarm hiring NSA were in the range of 2.7 (Dec) to 4.4 (Jun) in 2006.
Chart I-7, US, Rate Total Nonfarm Hiring, Month SA 2001-2014
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
There is only milder improvement in total private hiring shown in Chart I-8. Hiring private (HP) rose in 2010 with stability and renewed increase in 2011 followed by almost stationary series in 2012. The number of private hiring seasonally adjusted fell from 4057 thousand in Sep 2011 to 3962 in Dec 2011 or by 2.3 percent, decreasing to 3998 in Jan 2012 or decline by 1.5 percent relative to the level in Sep 2011. Private hiring fell to 3959 in Sep 2012 or lower by 2.4 percent relative to Sep 2011, moving to 4061 in Dec 2012 for increase of 1.6 percent relative to 3998 in Jan 2012. The number of private hiring not seasonally adjusted fell from 4600 in Jun 2011 to 2833 in Dec 2011 or by 38.4 percent, reaching 3853 in Jan 2012 or decline of 16.2 percent relative to Jun 2011 and moving to 2911 in Dec 2012 or 37.1 percent lower relative to 4629 in Jun 2012. Hires fell from 4706 in Jun 2013 to 3098 in Dec 2013. Companies reduce hiring in the latter part of the year that explains the high seasonality in year-end employment data. For example, NSA private hiring fell from 5567 in Jun 2006 to 3568 in Dec 2006 or by 35.9 percent. Private hiring NSA data are useful in showing the huge declines from the period before the global recession. In Jul 2006, private hiring NSA was 5501, declining to 4326 in Jul 2011 or by 21.4 percent and to 4354 in Jul 2012 or lower by 20.9 percent relative to Jul 2006. Private hiring NSA fell from 5567 in Jun 2006 to 5164 in Jun 2014 or 7.2 percent. Private hiring fell from 5501 in Jul 2006 to 4632 in Jul 2013 or 15.8 percent. The conclusion is that private hiring in the US is around 20 percent below the hiring before the global recession while the noninstitutional population of the United States has grown from 228.815 million in 2006 to 245.679 million in 2013, by 16.864 million or 7.4 percent. The main problem in recovery of the US labor market has been the low rate of GDP growth. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent.
Chart I-8, US, Total Private Hiring Month SA 2001-2014
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-9 shows similar behavior in the rate of private hiring. The rate in 2011 in monthly SA data did not rise significantly above the peak in 2010. The rate seasonally adjusted fell from 3.7 in Sep 2011 to 3.6 in Dec 2011 and reached 3.6 in Dec 2012 and 3.7 in Dec 2013. The rate not seasonally adjusted (NSA) fell from 3.7 in Sep 2011 to 2.5 in Dec 2011, increasing to 3.8 in Oct 2012 but falling to 2.6 in Dec 2012 and 3.4 in Mar 2013. The NSA rate of private hiring fell from 4.8 in Jul 2006 to 3.4 in Aug 2009 but recovery was insufficient to only 3.9 in Aug 2012, 2.6 in Dec 2012 and 2.7 in Dec 2013. The NSA rate increased to 4.2 in Jul 2014.
Chart I-9, US, Rate Total Private Hiring Month SA 2001-2014
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
The JOLTS report of the Bureau of Labor Statistics also provides total nonfarm job openings (TNF JOB), TNF JOB rate and TNF LD (layoffs and discharges) shown in Table I-4 for the month of Jul from 2001 to 2014. The final column provides annual TNF LD for the years from 2001 to 2013. Nonfarm job openings (TNF JOB) increased from a peak of 4718 in Jul 2007 to 5016 in Jun 2014 or by 6.3 percent while the rate increased from 3.3 to 3.5. Nonfarm layoffs and discharges (TNF LD) rose from 1780 in Jul 2006 to 2286 in Jul 2009 or by 24.4 percent. The annual data show layoffs and discharges rising from 20.9 million in 2006 to 26.4 million in 2009 or by 26.3 percent. Business pruned payroll jobs to survive the global recession but there has not been hiring because of the low rate of GDP growth. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. US economic growth has been at only 2.2 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 20 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2014. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the second estimate of GDP for IIQ2014 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2014/pdf/gdp2q14_2nd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,745.9 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,355.6 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,745.9/$14,355.6 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/geopolitical-and-financial-risks.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/fluctuating-financial-valuations.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/geopolitical-and-financial-risks.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/fluctuating-financial-valuations.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIQ2014 would have accumulated to 22.1 percent. GDP in IIQ2014 would be $18,305.0 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2,310.7 billion than actual $15,994.3 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 26.9 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment of 16.4 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/competitive-monetary-policy-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/fluctuating-financial-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/financial-valuations-twenty-seven.html). US GDP in IIQ2014 is 12.6 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $15,994.3 billion in IIQ2014 or 6.7 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.0 percent. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. The long-term trend is growth at average 3.3 percent per year from Jan 1919 to Jul 2014. Growth at 3.3 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 99.2392 in Dec 2007 to 122.8881 in Jul 2014. The actual index NSA in Jul 2014 is 98.4978, which is 19.8 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.3 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2013, raising the index at trend to 115.2650 in Jul 2014. The output of manufacturing at 98.4978 in Jul 2014 is 14.5 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Table I-4, US, Total Nonfarm Job Openings and Total Nonfarm Layoffs and Discharges, Thousands NSA
| TNF JOB | TNF JOB | TNF LD | TNF LD | |
| Jul 2001 | 4760 | 3.5 | 1970 | 24138 |
| Jul 2002 | 3680 | 2.7 | 2021 | 22706 |
| Jul 2003 | 3510 | 2.6 | 2098 | 23490 |
| Jul 2004 | 4152 | 3.1 | 1821 | 22668 |
| Jul 2005 | 4474 | 3.2 | 1892 | 22243 |
| Jul 2006 | 4377 | 3.1 | 1780 | 20896 |
| Jul 2007 | 4718 | 3.3 | 1839 | 21958 |
| Jul 2008 | 4026 | 2.9 | 1934 | 24028 |
| Jul 2009 | 2328 | 1.8 | 2286 | 26444 |
| Jul 2010 | 3167 | 2.4 | 2072 | 21829 |
| Jul 2011 | 3661 | 2.7 | 1774 | 20805 |
| Jul 2012 | 3857 | 2.8 | 1611 | 20892 |
| Jul 2013 | 4098 | 2.9 | 1642 | 19964 |
| Jul 2014 | 5016 | 3.5 | 1632 |
Notes: TNF JOB: Total Nonfarm Job Openings; LD: Layoffs and Discharges
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-10 shows monthly job openings rising from the trough in 2009 to a high in the beginning of 2010. Job openings then stabilized into 2011 but have surpassed the peak of 3080 seasonally adjusted in Apr 2010 with 3646 seasonally adjusted in Dec 2012, which is higher by 18.4 percent relative to Apr 2010 but lower by 2.9 percent relative to 3755 in Nov 2012 and lower by 4.7 percent than 3827 in Mar 2012. Nonfarm job openings increased from 3646 in Dec 2012 to 3914 in Dec 2013 or by 7.4 percent. The high of job openings not seasonally adjusted was 3428 in Apr 2010 that was surpassed by 3661 in Jul 2011, increasing to 3939 in Oct 2012 but declining to 3152 in Dec 2012 and decreasing to 3387 in Dec 2013. The level of job openings not seasonally adjusted fell to 3152 in Dec 2012 or by 21.3 percent relative to 4005 in Apr 2012. There is here again the strong seasonality of year-end labor data. Job openings fell from 4209 in Apr 2013 to 3387 in Dec 2013, showing strong seasonal effects. The level of job openings of 5016 in Jul 2014 NSA is higher by 6.3 percent relative to 4718 in Jul 2007. The main problem in recovery of the US labor market has been the low rate of GDP growth. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent.
Chart I-10, US Job Openings, Thousands NSA, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The rate of job openings in Chart I-11 shows similar behavior. The rate seasonally adjusted increased from 2.2 in Jan 2011 to 2.6 in Dec 2011, 2.6 in Dec 2012 and 2.8 in Dec 2013. The rate seasonally adjusted stood at 3.3 in Jul 2014. The rate not seasonally adjusted rose from the high of 2.6 in Apr 2010 to 3.0 in Apr 2013 and 2.6 in Nov 2013. The rate of job openings NSA fell from 3.3 in Jul 2007 to 1.6 in Nov-Dec 2009, recovering insufficiently to 3.5 in Jul 2014.
Chart I-11, US, Rate of Job Openings, NSA, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Total separations are shown in Chart I-12. Separations are much lower in 2012-14 than before the global recession but hiring has not recovered.
Chart I-12, US, Total Nonfarm Separations, Month Thousands SA, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Annual total separations are shown in Chart I-13. Separations are much lower in 2011-2014 than before the global recession but without recovery in hiring.
Chart I-13, US, Total Separations, Annual, Thousands, 2001-2013
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Table I-5 provides total nonfarm total separations from 2001 to 2013. Separations fell from 61.1 million in 2006 to 47.8 million in 2010 or by 13.3 million and 48.2 million in 2011 or by 12.9 million. Total separations increased from 48.2 million in 2011 to 51.8 million in 2013 or by 3.6 million.
Table I-5, US, Total Nonfarm Total Separations, Thousands, 2001-2013
| Year | Annual |
| 2001 | 64472 |
| 2002 | 59003 |
| 2003 | 56970 |
| 2004 | 58238 |
| 2005 | 60494 |
| 2006 | 61117 |
| 2007 | 60838 |
| 2008 | 58227 |
| 2009 | 51127 |
| 2010 | 47750 |
| 2011 | 48220 |
| 2012 | 50070 |
| 2013 | 51837 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Monthly data of layoffs and discharges reach a peak in early 2009, as shown in Chart I-14. Layoffs and discharges dropped sharply with the recovery of the economy in 2010 and 2011 once employers reduced their job count to what was required for cost reductions and loss of business. Weak rates of growth of GDP (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/geopolitical-and-financial-risks.html) frustrated employment recovery. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent.
Chart I-14, US, Total Nonfarm Layoffs and Discharges, Monthly Thousands SA, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Layoffs and discharges in Chart I-15 rose sharply to a peak in 2009. There was pronounced drop into 2010 and 2011 with mild increase into 2012 and renewed decline into 2013.
Chart I-15, US, Total Nonfarm Layoffs and Discharges, Annual, 2001-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Table I-6 provides annual nonfarm layoffs and discharges from 2001 to 2013. Layoffs and discharges peaked at 26.4 million in 2009 and then fell to 20.8 million in 2011, by 5.6 million, or 21.2 percent. Total nonfarm layoffs and discharges increased mildly to 20.9 million in 2012, falling to 19.9 million in 2013.
Table I-6, US, Total Nonfarm Layoffs and Discharges, Thousands, 2001-2013
| Year | Annual |
| 2001 | 24138 |
| 2002 | 22706 |
| 2003 | 23490 |
| 2004 | 22668 |
| 2005 | 22243 |
| 2006 | 20896 |
| 2007 | 21958 |
| 2008 | 24028 |
| 2009 | 26444 |
| 2010 | 21829 |
| 2011 | 20805 |
| 2012 | 20892 |
| 2013 | 19964 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
IA2 Labor Underutilization. The Bureau of Labor Statistics also provides alternative measures of labor underutilization shown in Table I-7. The most comprehensive measure is U6 that consists of total unemployed plus total employed part time for economic reasons plus all marginally attached workers as percent of the labor force. U6 not seasonally adjusted has risen from 8.2 percent in 2006 to 12.0 percent in Aug 2014.
Table I-7, US, Alternative Measures of Labor Underutilization NSA %
| U1 | U2 | U3 | U4 | U5 | U6 | |
| 2014 | ||||||
| Aug | 2.8 | 3.0 | 6.3 | 6.7 | 7.5 | 12.0 |
| Jul | 2.8 | 3.1 | 6.5 | 7.0 | 7.8 | 12.6 |
| Jun | 2.8 | 3.0 | 6.3 | 6.7 | 7.5 | 12.4 |
| May | 3.1 | 3.0 | 6.1 | 6.5 | 7.3 | 11.7 |
| Apr | 3.3 | 3.2 | 5.9 | 6.3 | 7.2 | 11.8 |
| Mar | 3.7 | 3.7 | 6.8 | 7.2 | 8.1 | 12.8 |
| Feb | 3.6 | 3.9 | 7.0 | 7.5 | 8.4 | 13.1 |
| Jan | 3.5 | 4.0 | 7.0 | 7.5 | 8.6 | 13.5 |
| 2013 | ||||||
| Dec | 3.5 | 3.5 | 6.5 | 7.0 | 7.9 | 13.0 |
| Nov | 3.7 | 3.5 | 6.6 | 7.1 | 7.9 | 12.7 |
| Oct | 3.7 | 3.6 | 7.0 | 7.4 | 8.3 | 13.2 |
| Sep | 3.7 | 3.5 | 7.0 | 7.5 | 8.4 | 13.1 |
| Aug | 3.7 | 3.8 | 7.3 | 7.9 | 8.7 | 13.6 |
| Jul | 3.7 | 3.8 | 7.7 | 8.3 | 9.1 | 14.3 |
| Jun | 3.9 | 3.8 | 7.8 | 8.4 | 9.3 | 14.6 |
| May | 4.1 | 3.7 | 7.3 | 7.7 | 8.5 | 13.4 |
| Apr | 4.3 | 3.9 | 7.1 | 7.6 | 8.5 | 13.4 |
| Mar | 4.3 | 4.3 | 7.6 | 8.1 | 9.0 | 13.9 |
| Feb | 4.3 | 4.6 | 8.1 | 8.6 | 9.6 | 14.9 |
| Jan | 4.3 | 4.9 | 8.5 | 9.0 | 9.9 | 15.4 |
| 2012 | ||||||
| Dec | 4.2 | 4.3 | 7.6 | 8.3 | 9.2 | 14.4 |
| Nov | 4.2 | 3.9 | 7.4 | 7.9 | 8.8 | 13.9 |
| Oct | 4.3 | 3.9 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 9.0 | 13.9 |
| Sep | 4.2 | 4.0 | 7.6 | 8.0 | 9.0 | 14.2 |
| Aug | 4.3 | 4.4 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 9.7 | 14.6 |
| Jul | 4.3 | 4.6 | 8.6 | 9.1 | 10.0 | 15.2 |
| Jun | 4.5 | 4.4 | 8.4 | 8.9 | 9.9 | 15.1 |
| May | 4.7 | 4.3 | 7.9 | 8.4 | 9.3 | 14.3 |
| Apr | 4.8 | 4.3 | 7.7 | 8.3 | 9.1 | 14.1 |
| Mar | 4.9 | 4.8 | 8.4 | 8.9 | 9.7 | 14.8 |
| Feb | 4.9 | 5.1 | 8.7 | 9.3 | 10.2 | 15.6 |
| Jan | 4.9 | 5.4 | 8.8 | 9.4 | 10.5 | 16.2 |
| 2011 | ||||||
| Dec | 4.8 | 5.0 | 8.3 | 8.8 | 9.8 | 15.2 |
| Nov | 4.9 | 4.7 | 8.2 | 8.9 | 9.7 | 15.0 |
| Oct | 5.0 | 4.8 | 8.5 | 9.1 | 10.0 | 15.3 |
| Sep | 5.2 | 5.0 | 8.8 | 9.4 | 10.2 | 15.7 |
| Aug | 5.2 | 5.1 | 9.1 | 9.6 | 10.6 | 16.1 |
| Jul | 5.2 | 5.2 | 9.3 | 10.0 | 10.9 | 16.3 |
| Jun | 5.1 | 5.1 | 9.3 | 9.9 | 10.9 | 16.4 |
| May | 5.5 | 5.1 | 8.7 | 9.2 | 10.0 | 15.4 |
| Apr | 5.5 | 5.2 | 8.7 | 9.2 | 10.1 | 15.5 |
| Mar | 5.7 | 5.8 | 9.2 | 9.7 | 10.6 | 16.2 |
| Feb | 5.6 | 6.0 | 9.5 | 10.1 | 11.1 | 16.7 |
| Jan | 5.6 | 6.2 | 9.8 | 10.4 | 11.4 | 17.3 |
| Dec 2010 | 5.4 | 5.9 | 9.1 | 9.9 | 10.7 | 16.6 |
| Annual | ||||||
| 2013 | 3.9 | 3.9 | 7.4 | 7.9 | 8.8 | 13.8 |
| 2012 | 4.5 | 4.4 | 8.1 | 8.6 | 9.5 | 14.7 |
| 2011 | 5.3 | 5.3 | 8.9 | 9.5 | 10.4 | 15.9 |
| 2010 | 5.7 | 6.0 | 9.6 | 10.3 | 11.1 | 16.7 |
| 2009 | 4.7 | 5.9 | 9.3 | 9.7 | 10.5 | 16.2 |
| 2008 | 2.1 | 3.1 | 5.8 | 6.1 | 6.8 | 10.5 |
| 2007 | 1.5 | 2.3 | 4.6 | 4.9 | 5.5 | 8.3 |
| 2006 | 1.5 | 2.2 | 4.6 | 4.9 | 5.5 | 8.2 |
| 2005 | 1.8 | 2.5 | 5.1 | 5.4 | 6.1 | 8.9 |
| 2004 | 2.1 | 2.8 | 5.5 | 5.8 | 6.5 | 9.6 |
| 2003 | 2.3 | 3.3 | 6.0 | 6.3 | 7.0 | 10.1 |
| 2002 | 2.0 | 3.2 | 5.8 | 6.0 | 6.7 | 9.6 |
| 2001 | 1.2 | 2.4 | 4.7 | 4.9 | 5.6 | 8.1 |
| 2000 | 0.9 | 1.8 | 4.0 | 4.2 | 4.8 | 7.0 |
Note: LF: labor force; U1, persons unemployed 15 weeks % LF; U2, job losers and persons who completed temporary jobs %LF; U3, total unemployed % LF; U4, total unemployed plus discouraged workers, plus all other marginally attached workers; % LF plus discouraged workers; U5, total unemployed, plus discouraged workers, plus all other marginally attached workers % LF plus all marginally attached workers; U6, total unemployed, plus all marginally attached workers, plus total employed part time for economic reasons % LF plus all marginally attached workers
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Monthly seasonally adjusted measures of labor underutilization are provided in Table I-8. U6 climbed from 16.1 percent in Aug 2011 to 16.3 percent in Sep 2011 and then fell to 14.5 percent in Mar 2012, reaching 12.0 percent in Aug 2014. Unemployment is an incomplete measure of the stress in US job markets. A different calculation in this blog is provided by using the participation rate in the labor force before the global recession. This calculation shows 26.9 million in job stress of unemployment/underemployment in Jul 2013, not seasonally adjusted, corresponding to 16.4 percent of the labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/competitive-monetary-policy-and.html).
Table I-8, US, Alternative Measures of Labor Underutilization SA %
| U1 | U2 | U3 | U4 | U5 | U6 | |
| Aug 2014 | 2.9 | 3.1 | 6.1 | 6.6 | 7.4 | 12.0 |
| July | 2.9 | 3.1 | 6.2 | 6.6 | 7.5 | 12.2 |
| Jun | 2.9 | 3.1 | 6.1 | 6.5 | 7.3 | 12.1 |
| May | 3.1 | 3.2 | 6.3 | 6.7 | 7.6 | 12.2 |
| Apr | 3.2 | 3.4 | 6.3 | 6.7 | 7.6 | 12.3 |
| Mar | 3.5 | 3.5 | 6.7 | 7.1 | 8.0 | 12.7 |
| Feb | 3.5 | 3.5 | 6.7 | 7.2 | 8.1 | 12.6 |
| Jan | 3.4 | 3.5 | 6.6 | 7.1 | 8.1 | 12.7 |
| Dec 2013 | 3.6 | 3.5 | 6.7 | 7.2 | 8.1 | 13.1 |
| Nov | 3.7 | 3.7 | 7.0 | 7.4 | 8.2 | 13.1 |
| Oct | 3.8 | 4.0 | 7.2 | 7.7 | 8.6 | 13.7 |
| Sep | 3.8 | 3.7 | 7.2 | 7.7 | 8.6 | 13.6 |
| Aug | 3.8 | 3.8 | 7.2 | 7.8 | 8.6 | 13.6 |
| Jul | 3.9 | 3.8 | 7.3 | 7.9 | 8.7 | 13.9 |
| Jun | 4.0 | 3.9 | 7.5 | 8.1 | 9.0 | 14.2 |
| May | 4.0 | 3.9 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 8.8 | 13.8 |
| Apr | 4.1 | 4.1 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 8.9 | 13.9 |
| Mar | 4.1 | 4.1 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 8.9 | 13.8 |
| Feb | 4.2 | 4.2 | 7.7 | 8.3 | 9.3 | 14.3 |
| Jan | 4.2 | 4.3 | 7.9 | 8.4 | 9.3 | 14.4 |
| Dec 2012 | 4.3 | 4.2 | 7.9 | 8.5 | 9.4 | 14.4 |
| Nov | 4.2 | 4.1 | 7.8 | 8.3 | 9.2 | 14.4 |
| Oct | 4.4 | 4.2 | 7.8 | 8.3 | 9.2 | 14.4 |
| Sep | 4.3 | 4.2 | 7.8 | 8.3 | 9.3 | 14.7 |
| Aug | 4.4 | 4.5 | 8.1 | 8.6 | 9.6 | 14.7 |
| Jul | 4.5 | 4.6 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 9.7 | 14.9 |
| Jun | 4.6 | 4.6 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 9.6 | 14.8 |
| May | 4.6 | 4.5 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 9.6 | 14.8 |
| Apr | 4.6 | 4.4 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 9.5 | 14.6 |
| Mar | 4.7 | 4.6 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 9.6 | 14.5 |
| Feb | 4.8 | 4.6 | 8.3 | 8.9 | 9.8 | 15.0 |
| Jan | 4.8 | 4.7 | 8.2 | 8.8 | 9.8 | 15.1 |
| Dec 2011 | 4.9 | 4.9 | 8.5 | 9.1 | 10.0 | 15.2 |
| Nov | 5.0 | 5.0 | 8.6 | 9.3 | 10.2 | 15.6 |
| Oct | 5.1 | 5.1 | 8.8 | 9.4 | 10.3 | 15.9 |
| Sep | 5.4 | 5.2 | 9.0 | 9.6 | 10.5 | 16.3 |
| Aug | 5.3 | 5.2 | 9.0 | 9.6 | 10.5 | 16.1 |
| Jul | 5.3 | 5.3 | 9.0 | 9.7 | 10.6 | 16.0 |
| Jun | 5.3 | 5.3 | 9.1 | 9.7 | 10.7 | 16.1 |
| May | 5.3 | 5.4 | 9.0 | 9.5 | 10.3 | 15.8 |
| Apr | 5.2 | 5.4 | 9.1 | 9.7 | 10.5 | 16.1 |
| Mar | 5.3 | 5.4 | 9.0 | 9.5 | 10.4 | 15.9 |
| Feb | 5.4 | 5.5 | 9.0 | 9.6 | 10.6 | 16.0 |
| Jan | 5.5 | 5.5 | 9.1 | 9.7 | 10.7 | 16.1 |
Note: LF: labor force; U1, persons unemployed 15 weeks % LF; U2, job losers and persons who completed temporary jobs %LF; U3, total unemployed % LF; U4, total unemployed plus discouraged workers, plus all other marginally attached workers; % LF plus discouraged workers; U5, total unemployed, plus discouraged workers, plus all other marginally attached workers % LF plus all marginally attached workers; U6, total unemployed, plus all marginally attached workers, plus total employed part time for economic reasons % LF plus all marginally attached workers
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-16 provides U6 on a monthly basis from 2001 to 2014. There was a steep climb from 2007 into 2009 and then this measure of unemployment and underemployment stabilized at that high level but declined into 2012. The low of U6 SA was 8.0 percent in Mar 2007 and the peak was 17.1 percent in Apr 2010. The low NSA was 7.6 percent in Oct 2006 and the peak was 18.0 percent in Jan 2010.
Chart I-16, US, U6, total unemployed, plus all marginally attached workers, plus total employed Part-Time for Economic Reasons, Month, SA, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-17 provides the number employed part-time for economic reasons or who cannot find full-time employment. There are sharp declines at the end of 2009, 2010 and 2011 but an increase in 2012 followed by stability in 2013-2014.
Chart I-17, US, Working Part-time for Economic Reasons
Thousands, Month SA 2001-2014
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
ICA3 Ten Million Fewer Full-time Jobs. There is strong seasonality in US labor markets around the end of the year.
- Seasonally adjusted part-time for economic reasons. The number employed part-time for economic reasons because they could not find full-time employment fell from 9.068 million in Sep 2011 to 7.780 million in Mar 2012, seasonally adjusted, or decline of 1.288 million in six months, as shown in Table I-9. The number employed part-time for economic reasons rebounded to 8.572 million in Sep 2012 for increase of 527,000 in one month from Aug to Sep 2012. The number employed part-time for economic reasons declined to 8.231 million in Oct 2012 or by 341,000 again in one month, further declining to 8.164 million in Nov 2012 for another major one-month decline of 67,000 and 7.929 million in Dec 2012 or fewer 235,000 in just one month. The number employed part-time for economic reasons increased to 7.983 million in Jan 2013 or 54,000 more than in Dec 2012 and to 7,991 million in Feb 2013, declining to 7.917 million in May 2013 but increasing to 8.194 million in Jun 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 7.898 million in Aug 2013 for decline of 282,000 in one month from 8.180 million in Jul 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons increased 16,000 from 7.898 million in Aug 2013 to 7.914 million in Sep 2013. The number part-time for economic reasons rose to 8.016 million in Oct 2013, falling by 293,000 to 7.723 million in Nov 2013. The number part-time for economic reasons increased to 7.771 million in Dec 2013, decreasing to 7.257 million in Jan 2014. The number employed part-time for economic reasons fell from 7.257 million in Jan 2014 to 7.186 million in Feb 2014. The number employed part-time for economic reasons increased to 7.411 million in Mar 2014 and 7.465 million in Apr 2014. The number employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 7.269 million in May 2014, increasing to 7.544 million in Jun 2014. The level employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 7.511 million in Jul 2014 and 7.277 million in Aug 2014. There is an increase of 186,000 in part-time for economic reasons from Aug 2012 to Oct 2012 and of 119,000 from Aug 2012 to Nov 2012.
- Seasonally adjusted full-time. The number employed full-time increased from 112.906 million in Oct 2011 to 115.114 million in Mar 2012 or 2.208 million but then fell to 114.279 million in May 2012 or 0.835 million fewer full-time employed than in Mar 2012. The number employed full-time increased from 114.626 million in Aug 2012 to 115.531 million in Oct 2012 or increase of 0.905 million full-time jobs in two months and further to 115.821 million in Jan 2013 or increase of 1.195 million more full-time jobs in five months from Aug 2012 to Jan 2013. The number of full time jobs decreased slightly to 115.785 million in Feb 2013, increasing to 116.288 million in May 2013 and 116.087 million in Jun 2013. Then number of full-time jobs increased to 116.156 million in Jul 2013, 116.301 million in Aug 2013 and 116.883 million in Sep 2013. The number of full-time jobs fell to 116.306 million in Oct 2013 and increased to 116.951 in Nov 2013. The level of full-time jobs fell to 117.278 million in Dec 2013, increasing to 117.656 million in Jan 2014 and 117.819 million in Feb 2014. The level of employment full-time increased to 118.003 million in Mar 2014 and 118.415 million in Apr 2014. The level of full-time employment reached 118.727 million in May 2014, decreasing to 118.204 million in Jun 2014. The level of full-time jobs increased to 118.489 in Jul 2014 and 118.616 million in Aug 2014. Adjustments of benchmark and seasonality-factors at the turn of every year could affect comparability of labor market indicators (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/02/financial-instability-rules.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/02/thirty-one-million-unemployed-or.html).
- Not seasonally adjusted part-time for economic reasons. The number of employed part-time for economic reasons actually increased without seasonal adjustment from 8.271 million in Nov 2011 to 8.428 million in Dec 2011 or by 157,000 and then to 8.918 million in Jan 2012 or by an additional 490,000 for cumulative increase from Nov 2011 to Jan 2012 of 647,000. The level of employed part-time for economic reasons then fell from 8.918 million in Jan 2012 to 7.867 million in Mar 2012 or by 1.051 million and to 7.694 million in Apr 2012 or 1.224 million fewer relative to Jan 2012. In Aug 2012, the number employed part-time for economic reasons reached 7.842 million NSA or 148,000 more than in Apr 2012. The number employed part-time for economic reasons increased from 7.842 million in Aug 2012 to 8.110 million in Sep 2012 or by 3.4 percent. The number part-time for economic reasons fell from 8.110 million in Sep 2012 to 7.870 million in Oct 2012 or by 240.000 in one month. The number employed part-time for economic reasons NSA increased to 8.628 million in Jan 2013 or 758,000 more than in Oct 2012. The number employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 8.298 million in Feb 2013, which is lower by 330,000 relative to 8.628 million in Jan 2013 but higher by 428,000 relative to 7.870 million in Oct 2012. The number employed part time for economic reasons fell to 7.734 million in Mar 2013 or 564,000 fewer than in Feb 2013 and fell to 7.709 million in Apr 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons reached 7.618 million in May 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons jumped from 7.618 million in May 2013 to 8.440 million in Jun 2013 or 822,000 in one month. The number employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 8.324 million in Jul 2013 and 7.690 million in Aug 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons NSA fell to 7.522 million in Sep 2013, increasing to 7.700 million in Oct 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 7.563 million in Nov 2013 and increased to 7.990 million in Dec 2013. The number employed part-time for economic reasons fell to 7.771 million in Jan 2014 and 7.397 million in Feb 2014. The level of part-time for economic reasons increased to 7.455 million in Mar 2014 and fell to 7.243 million in Apr 2014. The number of part-time for economic reasons fell to 6.960 million in May 2014, increasing to 7.805 million in Jun 2014. The level of part-time for economic reasons fell to 7.665 million in Jul 2014 and 7.083 million in Aug 2014.
- Not seasonally adjusted full-time. The number employed full time without seasonal adjustment fell from 113.138 million in Nov 2011 to 113.050 million in Dec 2011 or by 88,000 and fell further to 111.879 in Jan 2012 for cumulative decrease of 1.259 million. The number employed full-time not seasonally adjusted fell from 113.138 million in Nov 2011 to 112.587 million in Feb 2012 or by 551.000 but increased to 116.214 million in Aug 2012 or 3.076 million more full-time jobs than in Nov 2011. The number employed full-time not seasonally adjusted decreased from 116.214 million in Aug 2012 to 115.678 million in Sep 2012 for loss of 536,000 full-time jobs and rose to 116.045 million in Oct 2012 or by 367,000 full-time jobs in one month relative to Sep 2012. The number employed full-time NSA fell from 116.045 million in Oct 2012 to 115.515 million in Nov 2012 or decline of 530.000 in one month. The number employed full-time fell from 115.515 in Nov 2012 to 115.079 million in Dec 2012 or decline by 436,000 in one month. The number employed full time fell from 115.079 million in Dec 2012 to 113.868 million in Jan 2013 or decline of 1.211 million in one month. The number of full time jobs increased to 114.191 in Feb 2012 or by 323,000 in one month and increased to 114.796 million in Mar 2013 for cumulative increase from Jan by 928,000 full-time jobs but decrease of 283,000 from Dec 2012. The number employed full time reached 117.400 million in Jun 2013 and increased to 117.688 in Jul 2013 or by 288,000. The number employed full-time reached 117.868 million in Aug 2013 for increase of 180,000 in one month relative to Jul 2013. The number employed full-time fell to 117.308 million in Sep 2013 or by 560,000. The number employed full-time fell to 116.798 million in Oct 2013 or decline of 510.000 in one month. The number employed full-time rose to 116.875 million in Nov 2013, falling to 116.661 million in Dec 2013. The number employed full-time fell to 115.744 million in Jan 2014 but increased to 116.323 million in Feb 2014. The level of full-time jobs increased to 116.985 in Mar 2014 and 118.073 million in Apr 2014. The number of full-time jobs increased to 119.179 million in May 2014, increasing to 119.472 million in Jun 2014. The level of full-time jobs increased to 119.900 million in Jul 2014. Comparisons over long periods require use of NSA data. The number with full-time jobs fell from a high of 123.219 million in Jul 2007 to 108.777 million in Jan 2010 or by 14.442 million. The number with full-time jobs in Aug 2014 is 120.110 million, which is lower by 3.109 million relative to the peak of 123.219 million in Jul 2007.
- Loss of full-time jobs. The magnitude of the stress in US labor markets is magnified by the increase in the civilian noninstitutional population of the United States from 231.958 million in Jul 2007 to 248.229 million in Aug 2014 or by 16.271 million (http://www.bls.gov/data/) while in the same period the number of full-time jobs fell 3.109 million. The ratio of full-time jobs of 123.219 million Jul 2007 to civilian noninstitutional population of 231.958 million was 53.1 percent. If that ratio had remained the same, there would be 131.809 million full-time jobs with population of 248.229 million in Aug 2014 (0.531 x 248.229) or 11.699 million fewer full-time jobs relative to actual 120.110 million. There appear to be around 10 million fewer full-time jobs in the US than before the global recession while population increased around 15 million. Mediocre GDP growth is the main culprit of the fractured US labor market. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. US economic growth has been at only 2.2 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 20 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2014. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the second estimate of GDP for IIQ2014 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2014/pdf/gdp2q14_2nd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,745.9 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,355.6 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,745.9/$14,355.6 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/geopolitical-and-financial-risks.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/fluctuating-financial-valuations.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/geopolitical-and-financial-risks.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/fluctuating-financial-valuations.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIQ2014 would have accumulated to 22.1 percent. GDP in IIQ2014 would be $18,305.0 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2,310.7 billion than actual $15,994.3 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 26.9 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment of 16.4 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/competitive-monetary-policy-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/fluctuating-financial-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/financial-valuations-twenty-seven.html). US GDP in IIQ2014 is 12.6 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $15,994.3 billion in IIQ2014 or 6.7 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.0 percent. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. The long-term trend is growth at average 3.3 percent per year from Jan 1919 to Jul 2014. Growth at 3.3 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 99.2392 in Dec 2007 to 122.8881 in Jul 2014. The actual index NSA in Jul 2014 is 98.4978, which is 19.8 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.3 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2013, raising the index at trend to 115.2650 in Jul 2014. The output of manufacturing at 98.4978 in Jul 2014 is 14.5 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Table I-9, US, Employed Part-time for Economic Reasons, Thousands, and Full-time, Millions
| Part-time Thousands | Full-time Millions | |
| Seasonally Adjusted | ||
| Aug 2014 | 7,277 | 118.616 |
| Jul 2014 | 7,511 | 118.489 |
| Jun 2014 | 7,544 | 118.204 |
| May 2014 | 7,269 | 118.727 |
| Apr 2014 | 7,465 | 118.415 |
| Mar 2014 | 7,411 | 118.003 |
| Feb 2014 | 7,186 | 117.819 |
| Jan 2014 | 7,257 | 117.656 |
| Dec 2013 | 7,771 | 117.278 |
| Nov 2013 | 7,723 | 116.951 |
| Oct 2013 | 8,016 | 116.306 |
| Sep 2013 | 7,914 | 116.883 |
| Aug 2013 | 7,898 | 116.301 |
| Jul 2013 | 8,180 | 116.156 |
| Jun 2013 | 8,194 | 116.087 |
| May 2013 | 7,917 | 116.288 |
| Apr 2013 | 7,929 | 116.062 |
| Mar 2013 | 7,663 | 115.901 |
| Feb 2013 | 7,991 | 115.785 |
| Jan 2013 | 7,983 | 115.821 |
| Dec 2012 | 7,929 | 115.735 |
| Nov 2012 | 8,164 | 115.581 |
| Oct 2012 | 8,231 | 115.531 |
| Sep 2012 | 8,572 | 115.229 |
| Aug 2012 | 8,045 | 114.626 |
| Jul 2012 | 8,163 | 114.589 |
| Jun 2012 | 8,154 | 114.728 |
| May 2012 | 8,138 | 114.279 |
| Apr 2012 | 7,913 | 114.398 |
| Mar 2012 | 7,780 | 115.114 |
| Feb 2012 | 8,133 | 114.210 |
| Jan 2012 | 8,228 | 113.790 |
| Dec 2011 | 8,177 | 113.740 |
| Nov 2011 | 8,457 | 113.158 |
| Oct 2011 | 8,675 | 112.906 |
| Sep 2011 | 9,068 | 112.523 |
| Aug 2011 | 8,820 | 112.643 |
| Jul 2011 | 8,342 | 112.209 |
| Not Seasonally Adjusted | ||
| Aug 2014 | 7,083 | 120.110 |
| Jul 2014 | 7,665 | 119.900 |
| Jun 2014 | 7,805 | 119.472 |
| May 2014 | 6,960 | 119.179 |
| Apr 2014 | 7,243 | 118.073 |
| Mar 2014 | 7,455 | 116.985 |
| Feb 2014 | 7,397 | 116.323 |
| Jan 2014 | 7,771 | 115.744 |
| Dec 2013 | 7,990 | 116.661 |
| Nov 2013 | 7,563 | 116.875 |
| Oct 2013 | 7,700 | 116.798 |
| Sep 2013 | 7,522 | 117.308 |
| Aug 2013 | 7,690 | 117.868 |
| Jul 2013 | 8,324 | 117.688 |
| Jun 2013 | 8,440 | 117.400 |
| May 2013 | 7,618 | 116.643 |
| Apr 2013 | 7,709 | 115.674 |
| Mar 2013 | 7,734 | 114.796 |
| Feb 2013 | 8,298 | 114.191 |
| Jan 2013 | 8,628 | 113.868 |
| Dec 2012 | 8,166 | 115.079 |
| Nov 2012 | 7,994 | 115.515 |
| Oct 2012 | 7,870 | 116.045 |
| Sep 2012 | 8,110 | 115.678 |
| Aug 2012 | 7,842 | 116.214 |
| Jul 2012 | 8,316 | 116.131 |
| Jun 2012 | 8,394 | 116.024 |
| May 2012 | 7,837 | 114.634 |
| Apr 2012 | 7,694 | 113.999 |
| Mar 2012 | 7,867 | 113.916 |
| Feb 2012 | 8,455 | 112.587 |
| Jan 2012 | 8,918 | 111.879 |
| Dec 2011 | 8,428 | 113.050 |
| Nov 2011 | 8,271 | 113.138 |
| Oct 2011 | 8,258 | 113.456 |
| Sep 2011 | 8,541 | 112.980 |
| Aug 2011 | 8,604 | 114.286 |
| Jul 2011 | 8,514 | 113.759 |
| Jun 2011 | 8,738 | 113.255 |
| May 2011 | 8,270 | 112.618 |
| Apr 2011 | 8,425 | 111.844 |
| Mar 2011 | 8,737 | 111.186 |
| Feb 2011 | 8,749 | 110.731 |
| Jan 2011 | 9,187 | 110.373 |
| Dec 2010 | 9,205 | 111.207 |
| Nov 2010 | 8,670 | 111.348 |
| Oct 2010 | 8,408 | 112.342 |
| Sep 2010 | 8,628 | 112.385 |
| Aug 2010 | 8,628 | 113.508 |
| Jul 2010 | 8,737 | 113.974 |
| Jun 2010 | 8,867 | 113.856 |
| May 2010 | 8,513 | 112.809 |
| Apr 2010 | 8,921 | 111.391 |
| Mar 2010 | 9,343 | 109.877 |
| Feb 2010 | 9,282 | 109.100 |
| Jan 2010 | 9,290 | 108.777 (low) |
| Dec 2009 | 9,354 (high) | 109.875 |
| Nov 2009 | 8,894 | 111.274 |
| Oct 2009 | 8,474 | 111.599 |
| Sep 2009 | 8,255 | 111.991 |
| Aug 2009 | 8,835 | 113.863 |
| Jul 2009 | 9,103 | 114.184 |
| Jun 2009 | 9,301 | 114.014 |
| May 2009 | 8,785 | 113.083 |
| Apr 2009 | 8,648 | 112.746 |
| Mar 2009 | 9,305 | 112.215 |
| Feb 2009 | 9,170 | 112.947 |
| Jan 2009 | 8,829 | 113.815 |
| Dec 2008 | 8,250 | 116.422 |
| Nov 2008 | 7,135 | 118.432 |
| Oct 2008 | 6,267 | 120.020 |
| Sep 2008 | 5,701 | 120.213 |
| Aug 2008 | 5,736 | 121.556 |
| Jul 2008 | 6,054 | 122.378 |
| Jun 2008 | 5,697 | 121.845 |
| May 2008 | 5,096 | 120.809 |
| Apr 2008 | 5,071 | 120.027 |
| Mar 2008 | 5,038 | 119.875 |
| Feb 2008 | 5,114 | 119.452 |
| Jan 2008 | 5,340 | 119.332 |
| Dec 2007 | 4,750 | 121.042 |
| Nov 2007 | 4,374 | 121.846 |
| Oct 2007 | 4,028 | 122.006 |
| Sep 2007 | 4,137 | 121.728 |
| Aug 2007 | 4,494 | 122.870 |
| Jul 2007 | 4,516 | 123.219 (high) |
| Jun 2007 | 4,469 | 122.150 |
| May 2007 | 4,315 | 120.846 |
| Apr 2007 | 4,205 | 119.609 |
| Mar 2007 | 4,384 | 119.640 |
| Feb 2007 | 4,417 | 119.041 |
| Jan 2007 | 4,726 | 119.094 |
| Dec 2006 | 4,281 | 120.371 |
| Nov 2006 | 4,054 | 120.507 |
| Oct 2006 | 4,010 | 121.199 |
| Sep 2006 | 3,735 (low) | 120.780 |
| Aug 2006 | 4,104 | 121.979 |
| Jul 2006 | 4,450 | 121.951 |
| Jun 2006 | 4,456 | 121.070 |
| May 2006 | 3,968 | 118.925 |
| Apr 2006 | 3,787 | 118.559 |
| Mar 2006 | 4,097 | 117.693 |
| Feb 2006 | 4,403 | 116.823 |
| Jan 2006 | 4,597 | 116.395 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
People lose their marketable job skills after prolonged unemployment and face increasing difficulty in finding another job. Chart I-18 shows the sharp rise in unemployed over 27 weeks and stabilization at an extremely high level.
Chart I-18, US, Number Unemployed for 27 Weeks or Over, Thousands SA Month 2001-2014
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-19, US, Marginally Attached to the Labor Force, NSA Month, Thousands, 2001-2014
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The number with full-time jobs in Aug 2014 is 120.110 million, which is lower by 3.109 million relative to the peak of 123.219 million in Jul 2007. The magnitude of the stress in US labor markets is magnified by the increase in the civilian noninstitutional population of the United States from 231.958 million in Jul 2007 to 248.229 million in Aug 2014 or by 16.271 million (http://www.bls.gov/data/) while in the same period the number of full-time jobs fell 3.109 million. The ratio of full-time jobs of 123.219 million Jul 2007 to civilian noninstitutional population of 231.958 million was 53.1 percent. If that ratio had remained the same, there would be 131.809 million full-time jobs with population of 248.229 million in Aug 2014 (0.531 x 248.229) or 11.699 million fewer full-time jobs relative to actual 120.110 million. There appear to be around 10 million fewer full-time jobs in the US than before the global recession while population increased around 15 million. Mediocre GDP growth is the main culprit of the fractured US labor market.
Chart I-20 provides unadjusted full-time jobs in the US from 2001 to 2014 with sharp drop and incomplete recovery. There is current interest in past theories of “secular stagnation.” Alvin H. Hansen (1939, 4, 7; see Hansen 1938, 1941; for an early critique see Simons 1942) argues:
“Not until the problem of full employment of our productive resources from the long-run, secular standpoint was upon us, were we compelled to give serious consideration to those factors and forces in our economy which tend to make business recoveries weak and anaemic (sic) and which tend to prolong and deepen the course of depressions. This is the essence of secular stagnation-sick recoveries which die in their infancy and depressions which feed on them-selves and leave a hard and seemingly immovable core of unemployment. Now the rate of population growth must necessarily play an important role in determining the character of the output; in other words, the com-position of the flow of final goods. Thus a rapidly growing population will demand a much larger per capita volume of new residential building construction than will a stationary population. A stationary population with its larger proportion of old people may perhaps demand more personal services; and the composition of consumer demand will have an important influence on the quantity of capital required. The demand for housing calls for large capital outlays, while the demand for personal services can be met without making large investment expenditures. It is therefore not unlikely that a shift from a rapidly growing population to a stationary or declining one may so alter the composition of the final flow of consumption goods that the ratio of capital to output as a whole will tend to decline.”
The argument that anemic population growth causes “secular stagnation” in the US (Hansen 1938, 1939, 1941) is as misplaced currently as in the late 1930s (for early dissent see Simons 1942). This is merely another case of theory without reality with dubious policy proposals.
Inferior performance of the US economy and labor markets, during cyclical slow growth not secular stagnation, is the critical current issue of analysis and policy design.
Chart I-20, US, Full-time Employed, Thousands, NSA, 2001-2014
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-20A provides the noninstitutional civilian population of the United States from 2001 to 2014. There is clear trend of increase of the population while the number of full-time jobs collapsed after 2008 without sufficient recovery as shown in the preceding Chart I-20.
Chart I-20A, US, Noninstitutional Civilian Population, Thousands, 2001-2014
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-20B provides number of full-time jobs in the US from 1968 to 2014. There were multiple recessions followed by expansions without contraction of full-time jobs and without recovery as during the period after 2008. The problem is specific of the current cycle and not secular.
Chart I-20B, US, Full-time Employed, Thousands, NSA, 1968-2014
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-20C provides the noninstitutional civilian population of the United States from 1968 to 2013. Population expanded at a relatively constant rate of increase with the assurance of creation of full-time jobs that has been broken since 2008.
Chart I-20C, US, Noninstitutional Civilian Population, Thousands, 1968-2014
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
IA4 Theory and Reality of Secular Stagnation: Youth and Middle-Age Unemployment. Three tables support the argument that the proper comparison of the business cycle is between the recessions of the 1980s and the global recession after IVQ2007 and not as argued erroneously with the Great Depression of the 1930s.
Table I-5 provides percentage change of real GDP in the United States in the 1930s, 1980s and 2000s. The recession in 1981-1982 is quite similar on its own to the 2007-2009 recession. In contrast, during the Great Depression in the four years of 1930 to 1933, GDP in constant dollars fell 26.4 percent cumulatively and fell 45.3 percent in current dollars (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 150-2, Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2009b), 205-7 and revisions in http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). Data are available for the 1930s only on a yearly basis. US GDP fell 4.7 percent in the two recessions (1) from IQ1980 to IIIQ1980 and (2) from III1981 to IVQ1981 to IVQ1982 and 4.3 percent cumulatively in the recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. It is instructive to compare the first three years of the expansions in the 1980s and the current expansion. GDP grew at 4.6 percent in 1983, 7.3 percent in 1984, 4.2 percent in 1985, 3.5 percent in 1986 and 3.5 percent in 1987. In contrast, GDP grew 2.5 percent in 2010, 1.6 percent in 2011, 2.3 percent in 2012 and 2.2 percent in 2013. Actual annual equivalent GDP growth in the four quarters of 2012, and six quarters from IQ2013 to IIQ2014 is 2.1 percent and 2.5 percent in the four quarters ending in IIQ2014. GDP grew at 4.2 percent in 1985, 3.5 percent in 1986 and 3.5 percent in 1987 while the forecasts of the central tendency of participants of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) are in the range of 2.1 to 2.3 percent in 2014 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20140618.pdf) with less reliable forecast of 3.0 to 3.2 percent in 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20140618.pdf). Growth of GDP in the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2014 has been at average 2.2 percent in annual equivalent.
Table I-5, US, Percentage Change of GDP in the 1930s, 1980s and 2000s, ∆%
| Year | GDP ∆% | Year | GDP ∆% | Year | GDP ∆% |
| 1930 | -8.5 | 1980 | -0.2 | 2000 | 4.1 |
| 1931 | -6.4 | 1981 | 2.6 | 2001 | 1.0 |
| 1932 | -12.9 | 1982 | -1.9 | 2002 | 1.8 |
| 1933 | -1.3 | 1983 | 4.6 | 2003 | 2.8 |
| 1934 | 10.8 | 1984 | 7.3 | 2004 | 3.8 |
| 1935 | 8.9 | 1985 | 4.2 | 2005 | 3.3 |
| 1936 | 12.9 | 1986 | 3.5 | 2006 | 2.7 |
| 1937 | 5.1 | 1987 | 3.5 | 2007 | 1.8 |
| 1938 | -3.3 | 1988 | 4.2 | 2008 | -0.3 |
| 1930 | 8.0 | 1989 | 3.7 | 2009 | -2.8 |
| 1940 | 8.8 | 1990 | 1.9 | 2010 | 2.5 |
| 1941 | 17.7 | 1991 | -0.1 | 2011 | 1.6 |
| 1942 | 18.9 | 1992 | 3.6 | 2012 | 2.3 |
| 1943 | 17.0 | 1993 | 2.7 | 2013 | 2.2 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Characteristics of the four cyclical contractions are provided in Table I-6 with the first column showing the number of quarters of contraction; the second column the cumulative percentage contraction; and the final column the average quarterly rate of contraction. There were two contractions from IQ1980 to IIIQ1980 and from IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 separated by three quarters of expansion. The drop of output combining the declines in these two contractions is 4.7 percent, which is almost equal to the decline of 4.2 percent in the contraction from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. In contrast, during the Great Depression in the four years of 1930 to 1933, GDP in constant dollars fell 26.4 percent cumulatively and fell 45.3 percent in current dollars (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 150-2, Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2009b), 205-7 and revisions in http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). The comparison of the global recession after 2007 with the Great Depression is entirely misleading.
Table I-6, US, Number of Quarters, GDP Cumulative Percentage Contraction and Average Percentage Annual Equivalent Rate in Cyclical Contractions
| Number of Quarters | Cumulative Percentage Contraction | Average Percentage Rate | |
| IIQ1953 to IIQ1954 | 3 | -2.4 | -0.8 |
| IIIQ1957 to IIQ1958 | 3 | -3.0 | -1.0 |
| IVQ1973 to IQ1975 | 5 | -3.1 | -0.6 |
| IQ1980 to IIIQ1980 | 2 | -2.2 | -1.1 |
| IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 | 4 | -2.5 | -0.64 |
| IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 | 6 | -4.2 | -0.72 |
Sources: Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table I-7 shows the mediocre average annual equivalent growth rate of 2.2 percent of the US economy in the twenty quarters of the current cyclical expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2014. In sharp contrast, the average growth rate of GDP was:
- 5.7 percent in the first thirteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1986
- 5.4 percent in the first fifteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986
- 5.2 percent in the first sixteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1986
- 5.0 percent in the first seventeen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1987
- 5.0 percent in the first eighteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIQ1987
- 4.9 percent in the first nineteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987
- 5.0 percent in the first twenty quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1987
The line “average first four quarters in four expansions” provides the average growth rate of 7.7 percent with 7.8 percent from IIIQ1954 to IIQ1955, 9.2 percent from IIIQ1958 to IIQ1959, 6.1 percent from IIIQ1975 to IIQ1976 and 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983. The United States missed this opportunity of high growth in the initial phase of recovery. BEA data show the US economy in standstill with annual growth of 2.5 percent in 2010 decelerating to 1.6 percent annual growth in 2011, 2.3 percent in 2012 and 2.2 percent in 2013 (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) The expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1986 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.7 percent, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983. GDP growth in the four quarters of 2012, the four quarters of 2013 and the first two quarters of 2014 accumulated to 5.3 percent. This growth is equivalent to 2.1 percent per year, obtained by dividing GDP in IIQ2014 of $15,994.3 billion by GDP in IVQ2011 of $15,190.3 billion and compounding by 4/10: {[($15,994.3/$15,190.3)4/10 -1]100 = 2.1 percent. The rate of growth of GDP in the revision of the third estimate of IIIQ2013 is 4.5 percent in seasonally adjusted annual rate (SAAR). Inventory accumulation contributed 1.49 percentage points to this rate of growth. The actual rate without this impulse of unsold inventories would have been 3.0 percent, or 0.74 percent in IIIQ2013, such that annual equivalent growth in 2013 is closer to 2.8 percent {[(1.007)(1.004)(1.0074)(1.009)4/4-1]100 = 2.8%}, compounding the quarterly rates and converting into annual equivalent. Inventory divestment deducted 1.16 percentage points from GDP growth in IQ2014. Without this deduction of inventory divestment, GDP growth would have been minus 0.9 percent in IQ2014, such that the actual growth rates in the four quarters ending in IQ2014 is closer to 2.2 percent {[(1.004)(1.011)(1.009)(0.9977)]4/4 -1]100 = 2.2%}.
Table I-7, US, Number of Quarters, Cumulative Growth and Average Annual Equivalent Growth Rate in Cyclical Expansions
| Number | Cumulative Growth ∆% | Average Annual Equivalent Growth Rate | |
| IIIQ 1954 to IQ1957 | 11 | 12.8 | 4.5 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ1954 to IIQ1955 | 4 | 7.8 | |
| IIQ1958 to IIQ1959 | 5 | 10.0 | 7.9 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ1958 to IIQ1959 | 4 | 9.2 | |
| IIQ1975 to IVQ1976 | 8 | 8.3 | 4.1 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ1975 to IIQ1976 | 4 | 6.1 | |
| IQ1983-IQ1986 IQ1983-IIIQ1986 IQ1983-IVQ1986 IQ1983-IQ1987 IQ1983-IIQ1987 IQ1983 to IIIQ1987 IQ1983 to IVQ1987 | 13 15 16 17 18 19 20 | 19.9 21.6 22.3 23.1 24.5 25.6 27.7 | 5.7 5.4 5.2 5.0 5.0 4.9 5.0 |
| First Four Quarters IQ1983 to IVQ1983 | 4 | 7.8 | |
| Average First Four Quarters in Four Expansions* | 7.7 | ||
| IIIQ2009 to IIQ2014 | 20 | 11.4 | 2.2 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 | 2.7 |
*First Four Quarters: 7.8% IIIQ1954-IIQ1955; 9.2% IIIQ1958-IIQ1959; 6.1% IIIQ1975-IQ1976; 7.8% IQ1983-IVQ1983
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table EMP provides the comparison between the labor market in the current whole cycle from 2007 to 2013 and the whole cycle from 1979 to 1986. In the entire cycle from 2007 to 2013, the number employed fell 2.118 million, full-time employed fell 4.777 million, part-time for economic reasons increased 3.534 and population increased 13.812 million. The number employed fell 1.5 percent, full-time employed fell 3.9 percent, part-time for economic reasons increased 80.3 percent and population increased 6.0 percent. There is sharp contrast with the contractions of the 1980s and with most economic history of the United States. In the whole cycle from 1979 to 1986, the number employed increased 10.773 million, full-time employed increased 7.875 million, part-time for economic reasons 2.011 million and population 15.724 million. In the entire cycle from 1979 to 1986, the number employed increased 10.9 percent, full-time employed 9.5 percent, part-time for economic reasons 56.2 percent and population 9.5 million. The difference between the 1980s and the current cycle after 2007 is in the high rate of growth after the contraction that maintained trend growth around 3.0 percent for the entire cycle and per capital growth at 2.0 percent. The evident fact is that current weakness in labor markets originates in cyclical slow growth and not in imaginary secular stagnation.
Table EMP, US, Annual Level of Employed, Full-Time Employed, Employed Part-Time for Economic Reasons and Noninstitutional Civilian Population, Millions
| Employed | Full-Time Employed | Part Time Economic Reasons | Noninstitutional Civilian Population | |
| 2000s | ||||
| 2000 | 136.891 | 113.846 | 3.227 | 212.577 |
| 2001 | 136.933 | 113.573 | 3.715 | 215.092 |
| 2002 | 136.485 | 112.700 | 4.213 | 217.570 |
| 2003 | 137.736 | 113.324 | 4.701 | 221.168 |
| 2004 | 139.252 | 114.518 | 4.567 | 223.357 |
| 2005 | 141.730 | 117.016 | 4.350 | 226.082 |
| 2006 | 144.427 | 119.688 | 4.162 | 228.815 |
| 2007 | 146.047 | 121.091 | 4.401 | 231.867 |
| 2008 | 145.362 | 120.030 | 5.875 | 233.788 |
| 2009 | 139.877 | 112.634 | 8.913 | 235.801 |
| 2010 | 139.064 | 111.714 | 8.874 | 237.830 |
| 2011 | 139.869 | 112.556 | 8.560 | 239.618 |
| 2012 | 142.469 | 114.809 | 8.122 | 243.284 |
| 2013 | 143.929 | 116.314 | 7.935 | 245.679 |
| ∆2007-2013 | -2.118 | -4.777 | 3.534 | 13.812 |
| ∆% 2007-2013 | -1.5 | -3.9 | 80.3 | 6.0 |
| 1980s | ||||
| 1979 | 98.824 | 82.654 | 3.577 | 164.863 |
| 1980 | 99.303 | 82.562 | 4.321 | 167.745 |
| 1981 | 100.397 | 83.243 | 4.768 | 170.130 |
| 1982 | 99.526 | 81.421 | 6.170 | 172.271 |
| 1983 | 100.834 | 82.322 | 6.266 | 174.215 |
| 1984 | 105.005 | 86.544 | 5.744 | 176.383 |
| 1985 | 107.150 | 88.534 | 5.590 | 178.206 |
| 1986 | 109.597 | 90.529 | 5.588 | 180.587 |
| 1987 | 112.440 | 92.957 | 5.401 | 182.753 |
| 1988 | 114.968 | 95.214 | 5.206 | 184.613 |
| 1989 | 117.342 | 97.369 | 4.894 | 186.393 |
| ∆1979-1986 | 10.773 | 7.875 | 2.011 | 15.724 |
| ∆% 1979-86 | 10.9 | 9.5 | 56.2 | 9.5 |
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
There is current interest in past theories of “secular stagnation.” Alvin H. Hansen (1939, 4, 7; see Hansen 1938, 1941; for an early critique see Simons 1942) argues:
“Not until the problem of full employment of our productive resources from the long-run, secular standpoint was upon us, were we compelled to give serious consideration to those factors and forces in our economy which tend to make business recoveries weak and anaemic (sic) and which tend to prolong and deepen the course of depressions. This is the essence of secular stagnation-sick recoveries which die in their infancy and depressions which feed on them-selves and leave a hard and seemingly immovable core of unemployment. Now the rate of population growth must necessarily play an important role in determining the character of the output; in other words, the com-position of the flow of final goods. Thus a rapidly growing population will demand a much larger per capita volume of new residential building construction than will a stationary population. A stationary population with its larger proportion of old people may perhaps demand more personal services; and the composition of consumer demand will have an important influence on the quantity of capital required. The demand for housing calls for large capital outlays, while the demand for personal services can be met without making large investment expenditures. It is therefore not unlikely that a shift from a rapidly growing population to a stationary or declining one may so alter the composition of the final flow of consumption goods that the ratio of capital to output as a whole will tend to decline.”
The argument that anemic population growth causes “secular stagnation” in the US (Hansen 1938, 1939, 1941) is as misplaced currently as in the late 1930s (for early dissent see Simons 1942). Youth workers would obtain employment at a premium in an economy with declining population. In fact, there is currently population growth in the ages of 16 to 24 years but not enough job creation and discouragement of job searches for all ages. This is merely another case of theory without reality with dubious policy proposals. Inferior performance of the US economy and labor markets is the critical current issue of analysis and policy design.
In revealing research, Edward P. Lazear and James R. Spletzer (2012JHJul22) use the wealth of data in the valuable database and resources of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (http://www.bls.gov/data/) in providing clear thought on the nature of the current labor market of the United States. The critical issue of analysis and policy currently is whether unemployment is structural or cyclical. Structural unemployment could occur because of (1) industrial and demographic shifts and (2) mismatches of skills and job vacancies in industries and locations. Consider the aggregate unemployment rate, Y, expressed in terms of share si of a demographic group in an industry i and unemployment rate yi of that demographic group (Lazear and Spletzer 2012JHJul22, 5-6):
Y = ∑isiyi (1)
This equation can be decomposed for analysis as (Lazear and Spletzer 2012JHJul22, 6):
∆Y = ∑i∆siy*i + ∑i∆yis*i (2)
The first term in (2) captures changes in the demographic and industrial composition of the economy ∆si multiplied by the average rate of unemployment y*i , or structural factors. The second term in (2) captures changes in the unemployment rate specific to a group, or ∆yi, multiplied by the average share of the group s*i, or cyclical factors. There are also mismatches in skills and locations relative to available job vacancies. A simple observation by Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22) casts intuitive doubt on structural factors: the rate of unemployment jumped from 4.4 percent in the spring of 2007 to 10 percent in October 2009. By nature, structural factors should be permanent or occur over relative long periods. The revealing result of the exhaustive research of Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22) is:
“The analysis in this paper and in others that we review do not provide any compelling evidence that there have been changes in the structure of the labor market that are capable of explaining the pattern of persistently high unemployment rates. The evidence points to primarily cyclic factors.”
The theory of secular stagnation cannot explain sudden collapse of the US economy and labor markets. There are accentuated cyclic factors for both the entire population and the young population of ages 16 to 24 years. Table Summary provides the total noninstitutional population (ICP) of the US, full-time employment level (FTE), employment level (EMP), civilian labor force (CLF), civilian labor force participation rate (CLFP), employment/population ratio (EPOP) and unemployment level (UNE). Secular stagnation would spread over long periods instead of immediately. All indicators of the labor market weakened sharply during the contraction and did not recover. Population continued to grow but all other variables collapsed and did not recover. The theory of secular stagnation departs from an aggregate production function in which output grows with the use of labor, capital and technology (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. I (2008a), 11-6). Hansen (1938, 1939) finds secular stagnation in lower growth of an aging population. In the current US economy, Table Summary shows that population is dynamic while the labor market is fractured. There is key explanation in the behavior of the civilian labor force participation rate (CLFP) and the employment population ratio (EPOP) that collapsed during the global recession with inadequate recovery. Abandoning job searches are difficult to capture in labor statistics but likely explain the decline in the participation of the population in the labor force. Allowing for abandoning job searches, the total number of people unemployed or underemployed is 26.9 million or 16.4 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/competitive-monetary-policy-and.html).
Table Summary Total, US, Total Noninstitutional Civilian Population, Full-time Employment, Employment, Civilian Labor Force, Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate, Employment Population Ratio, Unemployment, NSA, Millions and Percent
| ICP | FTE | EMP | CLF | CLFP | EPOP | UNE | |
| 2006 | 228.8 | 119.7 | 144.4 | 151.4 | 66.2 | 63.1 | 7.0 |
| 2009 | 235.8 | 112.6 | 139.9 | 154.1 | 65.4 | 59.3 | 14.3 |
| 2012 | 243.3 | 114.8 | 142.5 | 155.0 | 63.7 | 58.6 | 12.5 |
| 2013 | 245.7 | 116.3 | 143.9 | 155.4 | 63.2 | 58.6 | 11.5 |
| 12/07 | 233.2 | 121.0 | 146.3 | 153.7 | 65.9 | 62.8 | 7.4 |
| 9/09 | 236.3 | 112.0 | 139.1 | 153.6 | 65.0 | 58.9 | 14.5 |
| 8/14 | 248.2 | 120.0 | 146.6 | 156.4 | 63.0 | 59.1 | 9.8 |
ICP: Total Noninstitutional Civilian Population; FT: Full-time Employment Level, EMP: Total Employment Level; CLF: Civilian Labor Force; CLFP: Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate; EPOP: Employment Population Ratio; UNE: Unemployment
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
The same situation is present in the labor market for young people in ages 16 to 24 years with data in Table Summary Youth. The youth noninstitutional civilian population (ICP) continued to increase during and after the global recession. There is the same disastrous labor market with decline for young people in employment (EMP), civilian labor force (CLF), civilian labor force participation rate (CLFP) and employment population ratio (EPOP). There are only increases for unemployment of young people (UNE) and youth unemployment rate (UNER). If aging were a factor of secular stagnation, growth of population of young people would attract a premium in remuneration in labor markets. The sad fact is that young people are also facing tough labor markets. The application of the theory of secular stagnation to the US economy and labor markets is void of reality in the form of key facts, which are best explained by accentuated cyclic factors analyzed by Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22).
Table Summary Youth, US, Youth, Ages 16 to 24 Years, Noninstitutional Civilian Population, Full-time Employment, Employment, Civilian Labor Force, Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate, Employment Population Ratio, Unemployment, NSA, Millions and Percent
| ICP | EMP | CLF | CLFP | EPOP | UNE | UNER | |
| 2006 | 36.9 | 20.0 | 22.4 | 60.6 | 54.2 | 2.4 | 10.5 |
| 2009 | 37.6 | 17.6 | 21.4 | 56.9 | 46.9 | 3.8 | 17.6 |
| 2012 | 38.7 | 17.8 | 21.3 | 54.9 | 46.0 | 3.5 | 16.2 |
| 2013 | 38.8 | 18.1 | 21.4 | 55.0 | 46.5 | 3.3 | 15.5 |
| 12/07 | 37.5 | 19.4 | 21.7 | 57.8 | 51.6 | 2.3 | 10.7 |
| 9/09 | 37.6 | 17.0 | 20.7 | 55.2 | 45.1 | 3.8 | 18.2 |
| 8/14 | 38.7 | 19.0 | 21.8 | 56.4 | 49.0 | 2.8 | 13.0 |
ICP: Youth Noninstitutional Civilian Population; EMP: Youth Employment Level; CLF: Youth Civilian Labor Force; CLFP: Youth Civilian Labor Force Participation Rate; EPOP: Youth Employment Population Ratio; UNE: Unemployment; UNER: Youth Unemployment Rate
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
The United States is experiencing high youth unemployment as in European economies. Table I-10 provides the employment level for ages 16 to 24 years of age estimated by the Bureau of Labor Statistics. On an annual basis, youth employment fell from 20.041 million in 2006 to 17.362 million in 2011 or 2.679 million fewer youth jobs and to 17.834 million in 2012 or 2.207 million fewer jobs. Youth employment fell from 20.041 million in 2006 to 18.057 million in 2013 or 1.984 million fewer jobs. During the seasonal peak months of youth employment in the summer from Jun to Aug, youth employment has fallen by more than two million jobs relative to 21.167 million in Aug 2006 to 18.972 million in Aug 2014 for 2.195 million fewer jobs. Youth employment fell from 21.914 million in Jul 2006 to 20.085 million in Jul 2014 for 1.829 million fewer youth jobs. The number of youth jobs fell from 21.268 million in Jun 2006 million to 19.421 million in Jun 2014 or 1.847 million fewer youth jobs. The number of jobs ages 16 to 24 years fell from 21.167 million in Aug 2006 to 18.636 million in Aug 2013 or by 2.531 million. The number of youth jobs fell from 19.604 million in Sep 2006 to 18.043 million in Sep 2013 or 1.561 million fewer youth jobs. The number of youth jobs fell from 20.129 million in Dec 2006 to 18.106 million in Dec 2013 or 2.023 million fewer jobs. The civilian noninstitutional population ages 16 to 24 years increased from 37.443 million in Jul 2007 to 38.861 million in Jul 2013 or by 1.418 million while the number of jobs for ages 16 to 24 years fell by 2.230 million from 21.914 million in Jul 2006 to 19.684 million in Jul 2013. The civilian noninstitutional population for ages 16 to 24 years increased from 37.455 million in Aug 2007 to 38.841 million in Aug 2013 or by 1.386 million while the number of youth jobs fell by 1.777 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.467 million in Sep 2007 to 38.822 million in Sep 2013 or by 1.355 million while the number of youth jobs fell by 1.455 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.480 million in Oct 2007 to 38.804 million in Oct 2013 or by 1.324 million while the number of youth jobs decreased 1.877 million from Oct 2006 to Oct 2013. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.798 million in Nov 2013 or by 1.722 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.799 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.518 million in Dec 2007 to 38.790 million in Dec 2013 or by 1.272 million while the number of youth jobs fell 2.023 million from Dec 2006 to Dec 2013. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.488 million from 37.282 million in in Jan 2007 to 38.770 million in Jan 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 2.035 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.464 million from 37.302 in Feb 2007 to 38.766 million in Feb 2014 while the number of youth jobs decreased 2.058 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.437 million from 37.324 million in Mar 2007 to 38.761 million in Mar 2014 while jobs for ages 16 to 24 years decreased 1.599 million from 19.538 million in Mar 2007 to 17.939 million in Mar 2014. The civilian noninstitutional population ages 16 to 24 years increased 1.410 million from 37.349 million in Apr 2007 to 38.759 million in Apr 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.347 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.370 million from 37.379 million in May 2007 to 38.749 million in May 2014 while the number of youth jobs decreased 1.128 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.330 million from 37.410 million in Jun 2007 to 38.740 million in Jun 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.847 million from 21.268 million in Jun 2006 to 19.421 million in Jun 2014. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased by 1.292 million from 37.443 million in Jul 2007 to 38.735 million in Jul 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.632 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.445 million in Aug 2007 to 38.706 million in Aug 2014 or 1.251 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.441 million. The hardship does not originate in low growth of population but in underperformance of the economy in the expansion from the business cycle. There are two hardships behind these data. First, young people cannot find employment after finishing high school and college, reducing prospects for achievement in older age. Second, students with more modest means cannot find employment to keep them in college.
Table I-10, US, Employment Level 16-24 Years, Thousands, NSA
| Year | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug |
| 2001 | 19678 | 19745 | 19800 | 19778 | 19648 | 21212 | 22042 | 20529 |
| 2002 | 18653 | 19074 | 19091 | 19108 | 19484 | 20828 | 21501 | 20653 |
| 2003 | 18811 | 18880 | 18709 | 18873 | 19032 | 20432 | 20950 | 20181 |
| 2004 | 18852 | 18841 | 18752 | 19184 | 19237 | 20587 | 21447 | 20660 |
| 2005 | 18858 | 18670 | 18989 | 19071 | 19356 | 20949 | 21749 | 20814 |
| 2006 | 19003 | 19182 | 19291 | 19406 | 19769 | 21268 | 21914 | 21167 |
| 2007 | 19407 | 19415 | 19538 | 19368 | 19457 | 21098 | 21717 | 20413 |
| 2008 | 18724 | 18546 | 18745 | 19161 | 19254 | 20466 | 21021 | 20096 |
| 2009 | 17467 | 17606 | 17564 | 17739 | 17588 | 18726 | 19304 | 18270 |
| 2010 | 16166 | 16412 | 16587 | 16764 | 17039 | 17920 | 18564 | 18061 |
| 2011 | 16512 | 16638 | 16898 | 16970 | 17045 | 18180 | 18632 | 18067 |
| 2012 | 16944 | 17150 | 17301 | 17387 | 17681 | 18907 | 19461 | 18171 |
| 2013 | 17183 | 17257 | 17271 | 17593 | 17704 | 19125 | 19684 | 18636 |
| 2014 | 17372 | 17357 | 17939 | 18021 | 18329 | 19421 | 20085 | 18972 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-21 provides US employment level ages 16 to 24 years from 2002 to 2014. Employment level is sharply lower in Jun 2014 relative to the peak in 2007. The following Chart I-21A relates youth employment and youth civilian noninstitutional population.
Chart I-21, US, Employment Level 16-24 Years, Thousands SA, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-21A provides the US civilian noninstitutional population ages 16 to 24 years not seasonally adjusted from 2001 to 2014. The civilian noninstitutional population ages 16 to 24 years increased from 37.443 million in Jul 2007 to 38.861 million in Jul 2013 or by 1.418 million while the number of jobs for ages 16 to 24 years fell by 2.230 million from 21.914 million in Jul 2006 to 19.684 million in Jul 2013. The civilian noninstitutional population for ages 16 to 24 years increased from 37.455 million in Aug 2007 to 38.841 million in Aug 2013 or by 1.386 million while the number of youth jobs fell by 1.777 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.467 million in Sep 2007 to 38.822 million in Sep 2013 or by 1.355 million while the number of youth jobs fell by 1.455 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.480 million in Oct 2007 to 38.804 million in Oct 2013 or by 1.324 million while the number of youth jobs decreased 1.877 million from Oct 2006 to Oct 2013. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.798 million in Nov 2013 or by 1.722 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.799 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.518 million in Dec 2007 to 38.790 million in Dec 2013 or by 1.272 million while the number of youth jobs fell 2.023 million from Dec 2006 to Dec 2013. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.488 million from 37.282 million in in Jan 2007 to 38.770 million in Jan 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 2.035 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.464 million from 37.302 in Feb 2007 to 38.766 million in Feb 2014 while the number of youth jobs decreased 2.058 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.437 million from 37.324 million in Mar 2007 to 38.761 million in Mar 2014 while jobs for ages 16 to 24 years decreased 1.599 million from 19.538 million in Mar 2007 to 17.939 million in Mar 2014. The civilian noninstitutional population ages 16 to 24 years increased 1.410 million from 37.349 million in Apr 2007 to 38.759 million in Apr 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.347 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.370 million from 37.379 million in May 2007 to 38.749 million in May 2014 while the number of youth jobs decreased 1.128 million. The civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.330 million from 37.410 million in Jun 2007 to 38.740 million in Jun 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.847 million from 21.268 million in Jun 2006 to 19.421 million in Jun 2014. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased by 1.292 million from 37.443 million in Jul 2007 to 38.735 million in Jul 2014 while the number of youth jobs fell 1.632 million. The youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.445 million in Aug 2007 to 38.706 million in Aug 2014 or 1.251 million while the number of youth jobs fell 1.441 million. The hardship does not originate in low growth of population but in underperformance of the economy in the expansion from the business cycle. There are two hardships behind these data. First, young people cannot find employment after finishing high school and college, reducing prospects for achievement in older age. Second, students with more modest means cannot find employment to keep them in college.
Chart I-21A, US, Civilian Noninstitutional Population Ages 16 to 24 Years, Thousands NSA, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-21B provides the civilian labor force of the US ages 16 to 24 years NSA from 2001 to 2014. The US civilian labor force ages 16 to 24 years fell from 24.339 million in Jul 2007 to 23.506 million in Jul 2013, by 0.833 million or decline of 3.4 percent, while the civilian noninstitutional population NSA increased from 37.443 million in Jul 2007 to 38.861 million in Jul 2013, by 1.418 million or 3.8 percent. The US civilian labor force ages 16 to 24 fell from 22.801 million in Aug 2007 to 22.089 million in Aug 2013, by 0.712 million or 3.1 percent, while the noninstitutional population for ages 16 to 24 years increased from 37.455 million in Aug 2007 to 38.841 million in Aug 2013, by 1.386 million or 3.7 percent. The US civilian labor force ages 16 to 24 years fell from 21.917 million in Sep 2007 to 21.183 million in Sep 2013, by 0.734 million or 3.3 percent while the civilian noninstitutional youth population increased from 37.467 million in Sep 2007 to 38.822 million in Sep 2013 by 1.355 million or 3.6 percent. The US civilian labor force fell from 21.821 million in Oct 2007 to 21.003 million in Oct 2013, by 0.818 million or 3.7 percent while the noninstitutional youth population increased from 37.480 million in Oct 2007 to 38.804 million in Oct 2013, by 1.324 million or 3.5 percent. The US youth civilian labor force fell from 21.909 million in Nov 2007 to 20.825 million in Nov 2013, by 1.084 million or 4.9 percent while the civilian noninstitutional youth population increased from 37.076 million in Nov 2006 to 38.798 million in Nov 2013 or by 1.722 million. The US youth civilian labor force fell from 21.684 million in Dec 2007 to 20.642 million in Dec 2013, by 1.042 million or 4.8 percent, while the civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.518 million in Dec 2007 to 38.790 million in Dec 2013, by 1.272 million or 3.4 percent. The youth civilian labor force of the US fell from 21.770 million in Jan 2007 to 20.423 million in Jan 2014, by 1.347 million or 6.2 percent while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 37.282 million in Jan 2007 to 38.770 million in Jan 2014, by 1.488 million or 4.0 percent. The youth civilian labor force of the US fell 1.255 million from 21.645 million in Feb 2007 to 20.390 million in Feb 2014 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.464 million from 37.302 million in Feb 2007 to 38.766 million in Feb 2014. The youth civilian labor force of the US fell 0.693 million from 21.634 million in Mar 2007 to 20.941 million in Mar 2014 or 3.2 person while the youth noninstitutional civilian population 1.437 million from 37.324 million in Mar 2007 to 38.761 million in Mar 2014 or 3.9 percent. The US youth civilian labor force fell 981 thousand from 21.442 million in Apr 2007 to 20.461 million in Apr 2014 while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.349 million in Apr 2007 to 38.759 million in Apr 2014 by 1.410 thousand or 3.8 percent. The youth civilian labor force decreased from 21.659 million in May 2007 to 21.160 million in May 2014 by 499 thousand or 2.3 percent while the youth civilian noninstitutional population increased 1.370 million from 37.739 million in May 2007 to 38.749 million in May 2007 or by 2.7 percent. The youth civilian labor force decreased from 24.128 million in Jun 2006 to 22.851 million in Jun 2014 by 1.277 million or 5.3 percent while the civilian noninstitutional population increased from 36.943 million in Jun 2006 to 38.740 million in Jun 2014 by 1.797 million or 4.9 percent. The youth civilian labor force fell from 24.664 million in Jul 2006 to 23.437 million in Jul 2014 while the civilian noninstitutional population increased from 36.989 million in Jul 2006 to 38.735 million in Jul 2014. The youth civilian labor force fell 1.818 million from 23.634 million in Aug 2006 to 21.816 million in Aug 2014 while the civilian noninstitutional population increased from 37.008 million in Aug 2006 to 38.706 million in Aug 2914 or 1.698 million. Youth in the US abandoned their participation in the labor force because of the frustration that there are no jobs available for them.
Chart I-21B, US, Civilian Labor Force Ages 16 to 24 Years, Thousands NSA, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-21C provides the ratio of labor force to noninstitutional population or labor force participation of ages 16 to 24 years not seasonally adjusted. The US labor force participation rates for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 66.7 in Jul 2006 to 60.5 in Jul 2013 because of the frustration of young people who believe there may not be jobs available for them. The US labor force participation rate of young people fell from 63.9 in Aug 2006 to 56.9 in Aug 2013. The US labor force participation rate of young people fell from 59.1 percent in Sep 2006 to 54.6 percent in Sep 2013. The US labor force participation rate of young people fell from 59.7 percent in Oct 2006 to 54.1 in Oct 2013. The US labor force participation rate of young people fell from 59.7 percent in Nov 2006 to 53.7 percent in Nov 2013. The US labor force participation rate fell from 57.8 in Dec 2007 to 53.2 in Dec 2013. The youth labor force participation rate fell from 58.4 in Jan 2007 to 52.7 in Jan 2014. The US youth labor force participation rate fell from 58.0 percent in Feb 2007 to 52.6 percent in Feb 2013. The labor force participation rate of ages 16 to 24 years fell from 58.0 in Mar 2007 to 54.0 in Mar 2014. The labor force participation rate of ages 16 to 24 years fell from 57.4 in Apr 2007 to 52.8 in Apr 2014. The labor force participation rate of ages 16 to 24 years fell from 57.9 in May 2007 to 54.6 in May 2014. The labor force participation rate of ages 16 to 24 years fell from 65.3 in Jun 2006 to 59.0 in Jun 2014. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 years fell from 66.7 in Jul 2006 to 60.5 in Jul 2014. The labor force participation rate ages 16 to 24 years fell from 63.9 in Aug 2006 to 56.4 in Aug 2014. Many young people abandoned searches for employment, dropping from the labor force.
Chart I-21C, US, Labor Force Participation Rate Ages 16 to 24 Years, NSA, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
An important measure of the job market is the number of people with jobs relative to population available for work (civilian noninstitutional population) or employment/population ratio. Chart I-21D provides the employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years. The US employment/population ratio NSA for ages 16 to 24 years collapsed from 59.2 in Jul 2006 to 50.7 in Jul 2013. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years dropped from 57.2 in Aug 2006 to 48.0 in Aug 2013. The employment population ratio for ages to 16 to 24 years declined from 52.9 in Sep 2006 to 46.5 in Sep 2013. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 53.6 in Oct 2006 to 46.3 in Oct 2013. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 53.7 in Nov 2007 to 46.7 in Nov 2013. The US employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 51.6 in Dec 2007 to 46.7 in Dec 2013. The US employment population ratio fell from 52.1 in Jan 2007 to 44.8 in Jan 2014. The US employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 fell from 52.0 in Feb 2007 to 44.8 in Feb 2014. The US employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 52.3 in Mar 2007 to 46.3 in Mar 2014. The US employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 51.9 in Apr 2007 to 46.5 in Apr 2014. The US employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 52.1 in May 2007 to 47.3 in May 2014. The US employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 57.6 in Jun 2006 to 50.1 in Jun 2014. The US employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 59.2 in Jul 2006 to 50.1 in Jul 2014. The employment population ratio for ages 16 to 24 years fell from 57.2 in Aug 2006 to 49.0 in Aug 2014. Chart I-21D shows vertical drop during the global recession without recovery.
Chart I-21D, US, Employment Population Ratio Ages 16 to 24 Years, Thousands NSA, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Table I-11 provides US unemployment level ages 16 to 24 years. The number unemployed ages 16 to 24 years increased from 2342 thousand in 2007 to 3634 thousand in 2011 or by 1.292 million and 3451 thousand in 2012 or by 1.109 million. The unemployment level ages 16 to 23 years increased from 2342 in 2007 to 3324 thousand in 2013 or by 0.982 million. The unemployment level ages 16 to 24 years rose from 2.388 million in Aug 2007 to 2.844 million in Aug 2014 or by 0.456 million. This situation may persist for many years.
Table I-11, US, Unemployment Level 16-24 Years, NSA, Thousands
| Year | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Annual |
| 2001 | 2258 | 2253 | 2095 | 2171 | 2775 | 2585 | 2461 | 2371 |
| 2002 | 2731 | 2822 | 2515 | 2568 | 3167 | 3034 | 2688 | 2683 |
| 2003 | 2740 | 2601 | 2572 | 2838 | 3542 | 3200 | 2724 | 2746 |
| 2004 | 2631 | 2588 | 2387 | 2684 | 3191 | 3018 | 2585 | 2638 |
| 2005 | 2787 | 2520 | 2398 | 2619 | 3010 | 2688 | 2519 | 2521 |
| 2006 | 2433 | 2216 | 2092 | 2254 | 2860 | 2750 | 2467 | 2353 |
| 2007 | 2230 | 2096 | 2074 | 2203 | 2883 | 2622 | 2388 | 2342 |
| 2008 | 2480 | 2347 | 2196 | 2952 | 3450 | 3408 | 2990 | 2830 |
| 2009 | 3457 | 3371 | 3321 | 3851 | 4653 | 4387 | 4004 | 3760 |
| 2010 | 3888 | 3748 | 3803 | 3854 | 4481 | 4374 | 3903 | 3857 |
| 2011 | 3696 | 3520 | 3365 | 3628 | 4248 | 4110 | 3820 | 3634 |
| 2012 | 3507 | 3294 | 3175 | 3438 | 4180 | 4011 | 3672 | 3451 |
| 2013 | 3449 | 3261 | 3129 | 3478 | 4198 | 3821 | 3453 | 3324 |
| 2014 | 3033 | 3002 | 2440 | 2831 | 3429 | 3353 | 2844 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-22 provides the unemployment level for ages 16 to 24 from 2001 to 2014. The level rose sharply from 2007 to 2010 with tepid improvement into 2012 and deterioration into 2013-2014 with recent marginal improvement alternating with deterioration.
Chart I-22, US, Unemployment Level 16-24 Years, Thousands SA, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Table I-12 provides the rate of unemployment of young peoples in ages 16 to 24 years. The annual rate jumped from 10.5 percent in 2007 to 18.4 percent in 2010, 17.3 percent in 2011 and 16.2 percent in 2012. The rate of youth unemployment fell marginally to 15.5 percent in 2013. During the seasonal peak in Jul, the rate of youth unemployed was 18.1 percent in Jul 2011, 17.1 percent in Jul 2012 and 16.3 percent in Jul 2013 compared with 10.8 percent in Jul 2007. The rate of youth unemployment rose from 11.2 percent in Jul 2006 to 16.3 percent in Jul 2013 and likely higher if adding those who ceased searching for a job in frustration none may be available. The rate of youth unemployment rose from 10.8 in Jul 2007 to 14.3 in Jul 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 9.1 percent in Dec 2006 to 12.3 percent in Dec 2013. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.9 percent in Jan 2007 to 14.9 percent in Jan and Feb 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 9.7 percent in Mar 2007 to 14.3 percent in Mar 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 9.7 percent in Apr 2007 to 11.9 percent in Apr 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.2 percent in May 2007 to 13.4 percent in May 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 12.0 percent in Jun 2007 to 15.0 percent in Jun 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.8 in Jul 2007 to 14.3 in Jul 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased from 10.5 in Aug 2007 to 13.0 in Aug 2014. The actual rate is higher because of the difficulty in counting those dropping from the labor force because they believe there are no jobs available for them.
Table I-12, US, Unemployment Rate 16-24 Years, Thousands, NSA
| Year | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Dec | Annual |
| 2001 | 10.3 | 10.3 | 10.2 | 9.6 | 10.0 | 11.6 | 10.5 | 10.7 | 11.0 | 10.6 |
| 2002 | 12.9 | 12.5 | 12.9 | 11.6 | 11.6 | 13.2 | 12.4 | 11.5 | 10.9 | 12.0 |
| 2003 | 12.7 | 12.7 | 12.2 | 12.0 | 13.0 | 14.8 | 13.3 | 11.9 | 10.5 | 12.4 |
| 2004 | 12.8 | 12.3 | 12.1 | 11.1 | 12.2 | 13.4 | 12.3 | 11.1 | 10.5 | 11.8 |
| 2005 | 12.4 | 13.0 | 11.7 | 11.2 | 11.9 | 12.6 | 11.0 | 10.8 | 9.4 | 11.3 |
| 2006 | 11.1 | 11.3 | 10.3 | 9.7 | 10.2 | 11.9 | 11.2 | 10.4 | 9.1 | 10.5 |
| 2007 | 10.9 | 10.3 | 9.7 | 9.7 | 10.2 | 12.0 | 10.8 | 10.5 | 10.7 | 10.5 |
| 2008 | 12.3 | 11.8 | 11.1 | 10.3 | 13.3 | 14.4 | 14.0 | 13.0 | 13.7 | 12.8 |
| 2009 | 15.8 | 16.4 | 16.1 | 15.8 | 18.0 | 19.9 | 18.5 | 18.0 | 17.5 | 17.6 |
| 2010 | 19.8 | 19.2 | 18.4 | 18.5 | 18.4 | 20.0 | 19.1 | 17.8 | 16.7 | 18.4 |
| 2011 | 18.9 | 18.2 | 17.2 | 16.5 | 17.5 | 18.9 | 18.1 | 17.5 | 15.5 | 17.3 |
| 2012 | 16.8 | 17.0 | 16.0 | 15.4 | 16.3 | 18.1 | 17.1 | 16.8 | 15.2 | 16.2 |
| 2013 | 17.6 | 16.7 | 15.9 | 15.1 | 16.4 | 18.0 | 16.3 | 15.6 | 12.3 | 15.5 |
| 2014 | 14.9 | 14.9 | 14.3 | 11.9 | 13.4 | 15.0 | 14.3 | 13.0 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-23 provides the BLS estimate of the not-seasonally-adjusted rate of youth unemployment for ages 16 to 24 years from 2001 to 2014. The rate of youth unemployment increased sharply during the global recession of 2008 and 2009 but has failed to drop to earlier lower levels because of low growth of GDP. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E. Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent.
Chart I-23, US, Unemployment Rate 16-24 Years, Percent, NSA, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-24 provides longer perspective with the rate of youth unemployment in ages 16 to 24 years from 1948 to 2014. The rate of youth unemployment rose to 20 percent during the contractions of the early 1980s and also during the contraction of the global recession in 2008 and 2009. The data illustrate again the argument in this blog that the contractions of the early 1980s are the valid framework for comparison with the global recession of 2008 and 2009 instead of misleading comparisons with the 1930s. During the initial phase of recovery, the rate of youth unemployment 16 to 24 years NSA fell from 18.9 percent in Jun 1983 to 14.5 percent in Jun 1984. In contrast, the rate of youth unemployment 16 to 24 years was nearly the same during the expansion after IIIQ2009: 17.5 percent in Dec 2009, 16.7 percent in Dec 2010, 15.5 percent in Dec 2011, 15.2 percent in Dec 2012, 17.6 percent in Jan 2013, 16.7 percent in Feb 2013, 15.9 percent in Mar 2013, 15.1 percent in Apr 2013. The rate of youth unemployment was 16.4 percent in May 2013, 18.0 percent in Jun 2013, 16.3 percent in Jul 2013 and 15.6 percent in Aug 2013. In Sep 2006, the rate of youth unemployment was 10.5 percent, increasing to 14.8 percent in Sep 2013. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.3 in Oct 2007, increasing to 14.4 percent in Oct 2013. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.3 percent in Nov 2007, increasing to 13.1 percent in Nov 2013. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.7 percent in Dec 2013, increasing to 12.3 percent in Dec 2013. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.9 percent in Jan 2007, increasing to 14.9 percent in Jan 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.3 percent in Feb 2007, increasing to 14.9 percent in Feb 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 9.7 percent in Mar 2007, increasing to 14.3 percent in Mar 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 9.7 percent in Apr 2007, increasing to 11.9 percent in Apr 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.2 percent in May 2007, increasing to 13.4 percent in May 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 12.0 percent in Jun 2007, increasing to 15.0 percent in Jun 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.8 percent in Jul 2007, increasing to 14.3 percent in Jul 2014. The rate of youth unemployment was 10.5 in Aug 2007, increasing to 13.0 percent in Aug 2014. The difference originates in the vigorous seasonally-adjusted annual equivalent average rate of GDP growth of 5.9 percent during the recovery from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 and 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987 compared with 2.2 percent on average during the first 20 quarters of expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2014 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/geopolitical-and-financial-risks.html). US economic growth has been at only 2.2 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 20 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2014. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the second estimate of GDP for IIQ2014 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2014/pdf/gdp2q14_2nd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,745.9 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,355.6 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,745.9/$14,355.6 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/geopolitical-and-financial-risks.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/fluctuating-financial-valuations.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/geopolitical-and-financial-risks.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/fluctuating-financial-valuations.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIQ2014 would have accumulated to 22.1 percent. GDP in IIQ2014 would be $18,305.0 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2,310.7 billion than actual $15,994.3 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 26.9 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment of 16.4 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/competitive-monetary-policy-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/fluctuating-financial-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/financial-valuations-twenty-seven.html). US GDP in IIQ2014 is 12.6 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $15,994.3 billion in IIQ2014 or 6.7 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.0 percent. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. The long-term trend is growth at average 3.3 percent per year from Jan 1919 to Jul 2014. Growth at 3.3 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 99.2392 in Dec 2007 to 122.8881 in Jul 2014. The actual index NSA in Jul 2014 is 98.4978, which is 19.8 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.3 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2013, raising the index at trend to 115.2650 in Jul 2014. The output of manufacturing at 98.4978 in Jul 2014 is 14.5 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Chart I-24, US, Unemployment Rate 16-24 Years, Percent NSA, 1948-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
It is more difficult to move to other jobs after a certain age because of fewer available opportunities for mature individuals than for new entrants into the labor force. Middle-aged unemployed are less likely to find another job. Table I-13 provides the unemployment level ages 45 years and over. The number unemployed ages 45 years and over rose from 1.607 million in Oct 2006 to 4.576 million in Oct 2010 or by 184.8 percent. The number of unemployed ages 45 years and over declined to 3.800 million in Oct 2012 that is still higher by 136.5 percent than in Oct 2006. The number unemployed age 45 and over increased from 1.704 million in Nov 2006 to 3.861 million in Nov 2012, or 126.6 percent. The number unemployed age 45 and over is still higher by 98.5 percent at 3.383 million in Nov 2013 than 1.704 million in Nov 2006. The number unemployed age 45 and over jumped from 1.794 million in Dec 2006 to 4.762 million in Dec 2010 or 165.4 percent. At 3.927 million in Dec 2012, mature unemployment is higher by 2.133 million or 118.9 percent higher than 1.794 million in Dec 2006. The level of unemployment of those aged 45 year or more of 3.632 million in Oct 2013 is higher by 2.025 million than 1.607 million in Oct 2006 or higher by 126.0 percent. The number of unemployed 45 years and over increased from 1.794 million in Dec 2006 to 3.378 million in Nov 2013 or 88.3 percent. The annual number of unemployed 45 years and over increased from 1.848 million in 2006 to 3.719 million in 2013 or 101.2 percent. The number of unemployed 45 years and over increased from 2.126 million in Jan 2006 to 4.394 million in Jan 2013, by 2.618 million or 106.7 percent. The number of unemployed 45 years and over rose from 2.126 million in Jan 2006 to 3.508 million in Jan 2014, by 1.382 million or 65.0 percent. The level of unemployed 45 years or older increased 2.051 million or 99.8 percent from 2.056 million in Feb 2006 to 4.107 million in Feb 2013 and at 3.490 million in Feb 2014 is higher by 69.7 percent than in Feb 2006. The number of unemployed 45 years and over increased 2.048 million or 108.9 percent from 1.881 million in Mar 2006 to 3.929 million in Mar 2013 and at 3.394 million in Mar 2014 is higher by 80.4 percent than in Mar 2006. The number of unemployed 45 years and over increased 1.846 million or 100.2 percent from 1.843 million in Apr 2006 to 3.689 million in Apr 2013 and at 3.006 million in Apr 2014 is higher by 1.163 million or 63.1 percent. The number of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 102.1 percent from 1.784 million in May 2006 to 3.605 million in May 2014 and at 2.913 million in May 2014 is higher by 63.3 percent than in May 2007.
The number of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 102.1 percent from 1.805 million in Jun 2007 to 3.648 million in Jun 2013 and at 2.832 million in Jun 2014 is higher by 56.9 percent than in Jun 2007. The number of unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 81.5 percent from 2.053 million in Jul 2007 to 3.727 million in Jul 2013 and at 3.083 million in Jul 2014 is higher by 50.2 percent than in Jul 2007. The level unemployed ages 45 years and over increased 84.4 percent from 1.956 million in Aug 2007 to 3.607 million in Aug 2013 and at 3.037 million in Aug 2014 is 55.2 percent higher than in Aug 2007. The actual number unemployed is likely much higher because many are not accounted who abandoned job searches in frustration there may not be a job for them. Recent improvements may be illusory.
Table I-13, US, Unemployment Level 45 Years and Over, Thousands NSA
| Year | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Annual |
| 2000 | 1392 | 1291 | 1062 | 1074 | 1163 | 1253 | 1339 | 1249 |
| 2001 | 1587 | 1533 | 1421 | 1259 | 1371 | 1539 | 1640 | 1576 |
| 2002 | 2280 | 2138 | 2101 | 1999 | 2190 | 2173 | 2114 | 2114 |
| 2003 | 2415 | 2485 | 2287 | 2112 | 2212 | 2281 | 2301 | 2253 |
| 2004 | 2397 | 2354 | 2160 | 2025 | 2182 | 2116 | 2082 | 2149 |
| 2005 | 2286 | 2126 | 1939 | 1844 | 1868 | 2119 | 1895 | 2009 |
| 2006 | 2056 | 1881 | 1843 | 1784 | 1813 | 1985 | 1869 | 1848 |
| 2007 | 2138 | 2031 | 1871 | 1803 | 1805 | 2053 | 1956 | 1966 |
| 2008 | 2336 | 2326 | 2104 | 2095 | 2211 | 2492 | 2695 | 2540 |
| 2009 | 4380 | 4518 | 4172 | 4175 | 4505 | 4757 | 4683 | 4500 |
| 2010 | 5307 | 5194 | 4770 | 4565 | 4564 | 4821 | 5128 | 4879 |
| 2011 | 4837 | 4748 | 4373 | 4356 | 4559 | 4772 | 4592 | 4537 |
| 2012 | 4472 | 4390 | 4037 | 4083 | 4084 | 4405 | 4179 | 4133 |
| 2013 | 4107 | 3929 | 3689 | 3605 | 3648 | 3727 | 3607 | 3719 |
| 2014 | 3490 | 3394 | 3006 | 2913 | 2832 | 3083 | 3037 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-25 provides the level unemployed ages 45 years and over. There was an increase in the recessions of the 1980s, 1991 and 2001 followed by declines to earlier levels. The current expansion of the economy after IIIQ2009 has not been sufficiently vigorous to reduce significantly middle-age unemployment. Recent improvements could be illusory because many abandoned job searches in frustration that there may not be jobs for them and are not counted as unemployed.
Chart I-25, US, Unemployment Level Ages 45 Years and Over, Thousands, NSA, 1976-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
IIA The Congressional Budget Office Update of Budget Outlook and Long-term Budget Outlook. Table IIA1-1 of the CBO (2012NovMBR, 2013BEOFeb5, 2013HBDFFeb5, 2013MEFFeb5, 2013Aug12, CBO, Feb 2014, CBO, Apr 2014) shows the significant worsening of United States fiscal affairs from 2007-2008 to 2009-2012 with marginal improvement in 2013 but with much higher debt relative to GDP. The deficit of $1.1 trillion in fiscal year 2012 was the fourth consecutive federal deficit exceeding one trillion dollars. All four deficits are the highest in share of GDP since 1946 (CBO 2012MBR, 2013HBDFeb5, 2013Aug12, 2013AugHBD).
Table IAI-1, US, Budget Fiscal Year Totals, Billions of Dollars and % GDP
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | |
| Receipts | 2568 | 2524 | 2105 | 2163 | 2304 | 2450 | 2775 |
| Outlays | 2729 | 2983 | 3518 | 3457 | 3603 | 3537 | 3455 |
| Deficit | -161 | -459 | 1413 | 1294 | 1300 | 1087 | 680 |
| % GDP | -1.1 | -3.1 | -9.8 | -8.8 | -8.4 | -6.8 | -4.1 |
Source: CBO (2012NovMBR), CBO (2013BEOFeb5), CBO (2013HBDFeb5), CBO (2013Aug12). CBO, Historical Budget Data—February 2014, Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb. CBO, Historical Budget Data—April 2014, Washington DC, Congressional Budget Office, Apr 14.
Table VA-6 provides additional information required for understanding the deficit/debt situation of the United States. The table is divided into four parts: Treasury budget in the 2014 fiscal year beginning on Oct 1, 2013 and ending on Sep 30, 2014; federal fiscal data for the years from 2009 to 2013; federal fiscal data for the years from 2005 to 2008; and Treasury debt held by the public from 2005 to 2013. Receipts increased 7.7 percent in the cumulative fiscal year 2014 ending in Aug 2014 relative to the cumulative in fiscal year 2013. Individual income taxes increased 4.9 percent relative to the same fiscal period a year earlier. Outlays increased 0.8 percent relative to a year earlier. There are also receipts, outlays, deficit and debt for fiscal year 2013. Total revenues of the US from 2009 to 2012 accumulate to $9021 billion, or $9.0 trillion, while expenditures or outlays accumulate to $14,109 billion, or $14.1 trillion, with the deficit accumulating to $5090 billion, or $5.1 trillion. Revenues decreased 6.5 percent from $9653 billion in the four years from 2005 to 2008 to $9021 billion in the years from 2009 to 2012. Decreasing revenues were caused by the global recession from IVQ2007 (Dec) to IIQ2009 (Jun) and also by growth of only 2.2 percent on average in the cyclical expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2014. In contrast, the expansion from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987 was at the average annual growth rate of 4.9 percent and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/geopolitical-and-financial-risks.html). Because of mediocre GDP growth, there are 26.9 million unemployed or underemployed in the United States for an effective unemployment rate of 16.4 percent (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/competitive-monetary-policy-and.html). Weakness of growth and employment creation is analyzed in II Collapse of United States Dynamism of Income Growth and Employment Creation (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/monetary-policy-world-inflation-waves.html). In contrast with the decline of revenue, outlays or expenditures increased 30.2 percent from $10,839 billion, or $10.8 trillion, in the four years from 2005 to 2008, to $14,109 billion, or $14.1 trillion, in the four years from 2009 to 2012. Increase in expenditures by 30.2 percent while revenue declined by 6.5 percent caused the increase in the federal deficit from $1186 billion in 2005-2008 to $5090 billion in 2009-2012. Federal revenue was 14.9 percent of GDP on average in the years from 2009 to 2012, which is well below 17.4 percent of GDP on average from 1973 to 2012. Federal outlays were 23.3 percent of GDP on average from 2009 to 2012, which is well above 20.4 percent of GDP on average from 1973 to 2012. The lower part of Table VA-6 shows that debt held by the public swelled from $5803 billion in 2008 to $11,982 billion in 2013, by $5478 billion or 106.5 percent. Debt held by the public as percent of GDP or economic activity jumped from 39.3 percent in 2008 to 72.1 percent in 2013, which is well above the average of 38.0 percent from 1973 to 2012. The United States faces tough adjustment because growth is unlikely to recover, creating limits on what can be obtained by increasing revenues, while continuing stress of social programs restricts what can be obtained by reducing expenditures.
Table VA-6, US, Treasury Budget in Fiscal Year to Date Million Dollars
| Aug 2014 | Fiscal Year 2014 | Fiscal Year 2013 | ∆% |
| Receipts | 2,663,426 | 2,472,542 | 7.7 |
| Outlays | 3,252,611 | 3,227,877 | 0.8 |
| Deficit | -589,185 | -755,334 | |
| Individual Income Tax | 1,233,274 | 1,175,536 | 4.9 |
| Corporation Income Tax | 247,200 | 216,360 | 14.3 |
| Social Insurance | 674,338 | 614,010 | 9.8 |
| Receipts | Outlays | Deficit (-), Surplus (+) | |
| $ Billions | |||
| Fiscal Year 2013 | 2,775 | 3,455 | -680 |
| % GDP | 16.7 | 20.8 | -4.1 |
| Fiscal Year 2012 | 2,450 | 3,537 | -1,087 |
| % GDP | 15.2 | 22.0 | -6.8 |
| Fiscal Year 2011 | 2,304 | 3,603 | -1,300 |
| % GDP | 15.0 | 23.4 | -8.4 |
| Fiscal Year 2010 | 2,163 | 3,457 | -1,294 |
| % GDP | 14.6 | 23.4 | -8.8 |
| Fiscal Year 2009 | 2,105 | 3,518 | -1,413 |
| % GDP | 14.6 | 24.4 | -9.8 |
| Total 2009-2012 | 9,021 | 14,109 | -5,090 |
| Average % GDP 2009-2012 | 14.9 | 23.3 | -8.4 |
| Fiscal Year 2008 | 2,524 | 2,983 | -459 |
| % GDP | 17.1 | 20.2 | -3.1 |
| Fiscal Year 2007 | 2,568 | 2,729 | -161 |
| % GDP | 17.9 | 19.0 | -1.1 |
| Fiscal Year 2006 | 2,407 | 2,655 | -248 |
| % GDP | 17.6 | 19.4 | -1.8 |
| Fiscal Year 2005 | 2,154 | 2,472 | -318 |
| % GDP | 16.7 | 19.2 | -2.5 |
| Total 2005-2008 | 9,653 | 10,839 | -1,186 |
| Average % GDP 2005-2008 | 17.3 | 19.5 | -2.1 |
| Debt Held by the Public | Billions of Dollars | Percent of GDP | |
| 2005 | 4,592 | 35.6 | |
| 2006 | 4,829 | 35.3 | |
| 2007 | 5,035 | 35.1 | |
| 2008 | 5,803 | 39.3 | |
| 2009 | 7,545 | 52.3 | |
| 2010 | 9,019 | 61.0 | |
| 2011 | 10,128 | 65.8 | |
| 2012 | 11,281 | 70.1 | |
| 2013 | 11,982 | 72.0 |
Source: http://www.fms.treas.gov/mts/index.html CBO (2012NovMBR). CBO (2011AugBEO); Office of Management and Budget 2011. Historical Tables. Budget of the US Government Fiscal Year 2011. Washington, DC: OMB; CBO. 2011JanBEO. Budget and Economic Outlook. Washington, DC, Jan. CBO. 2012AugBEO. Budget and Economic Outlook. Washington, DC, Aug 22. CBO. 2012Jan31. Historical budget data. Washington, DC, Jan 31. CBO. 2012NovCDR. Choices for deficit reduction. Washington, DC. Nov. CBO. 2013HBDFeb5. Historical budget data—February 2013 baseline projections. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb 5. CBO. 2013HBDFeb5. Historical budget data—February 2013 baseline projections. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb 5. CBO (2013Aug12). 2013AugHBD. Historical budget data—August 2013. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Aug. CBO, Historical Budget Data—February 2014, Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb. CBO, Historical budget data—April 2014 release. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Apr. Congressional Budget Office, August 2014 baseline: an update to the budget and economic outlook: 2014 to 2024. Washington, DC, CBO, Aug 27, 2014.
Table IIAI-3 provides total United States federal receipts from 2010 to 2013. Individual income taxes of $1132 billion, or $1.1 trillion, increased 25.9 percent from 2010 to 2012 and account for 46.2 percent of US total receipts in 2012. Individual income taxes increased 16.3 percent from $1132 billion in 2012 to $1316 billion in 2013, contributing 47.4 percent of total receipts. Total receipts stood at 15.2 percent of GDP in 2012, which is lower than 17.4 percent in the past 40 years (CBO 2013Aug12Av). Total receipts increased to 16.7 percent of GDP in 2013.
Table IIA1-3, United States, Total Receipts, Billions of Dollars and ∆%
| Major Source | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | ∆% 2012-2013 |
| Individual Income Taxes | 899 | 1092 | 1132 | 1316 | 16.3 |
| Corporate Income Taxes | 191 | 181 | 242 | 274 | 13.2 |
| Social Insurance | 865 | 819 | 845 | 948 | 12.2 |
| Other | 208 | 212 | 231 | 236 | 10.0 |
| Total | 2163 | 2304 | 2450 | 2775 | 13.3 |
| % of GDP | 14.6 | 15.0 | 15.2 | 16.7 | NA |
Source: CBO (2012NovMBR), CBO (2013BEOFeb5), CBO 2013HBDFeb5), CBO (2013Aug12). CBO, Historical Budget Data—February 2014, Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb. CBO, Historical budget data—April 2014 release. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Apr.
Total outlays of the federal government of the United States have grown to extremely high levels. Table IIA1-4 of the CBO (2014Feb, Apr 2014) provides total outlays in 2006 and 2013. Total outlays of $3454.6 billion in 2013, or $3.5 trillion, are higher by $799.5 billion, or $0.8 trillion, relative to $2655.1 billion in 2006, or $2.7 trillion. Outlays have grown from 19.4 percent of GDP in 2007 to 20.8 percent of GDP in 2013. Outlays as percent of GDP were on average 20.4 percent from 1973 to 2012 and receipts as percent of GDP were on average 17.4 percent of GDP. It has proved extremely difficult to increase receipts above 19 percent of GDP. Mandatory outlays increased from $1411.8 billion in 2006 to $2031.8 billion in 2013, by $620 billion. The first to the final row shows that the total of social security, Medicare, Medicaid, Income Security, net interest and defense absorbs 82.3 percent of US total outlays, which is equal to 17.1 percent of GDP. There has been no meaningful constraint of spending, which is quite difficult because of the rigid structure of social programs.
Table IIA1-4, US, Central Government Total Revenue and Outlays, Billions of Dollars and Percent
| 2006 | % Total | 2013 | % Total | |
| I TOTAL REVENUE $B | 2406.9 | 100.0 | 2775 | 100.0 |
| % GDP | 17.6 | 16.7 | ||
| Individual Income Taxes $B | 1043.9 | 1316.4 | ||
| % GDP | 7.6 | 7.9 | ||
| Corporate Income Taxes $B | 353.9 | 273.5 | ||
| % GDP | 2.6 | 5.7 | ||
| Social Insurance Taxes | 837.8 | 947.8 | ||
| % GDP | 6.1 | 1.6 | ||
| II TOTAL OUTLAYS | 2655.1 | 3454.6 | ||
| % GDP | 19.4 | 20.8 | ||
| Discretionary | 1016.6 | 1202.2 | ||
| % GDP | 7.4 | 7.2 | ||
| Defense | 520.0 | 625.8 | ||
| % GDP | 3.8 | 3.8 | ||
| Nondefense | 496.7 | 576.4 | ||
| % GDP | 3.6 | 3.5 | ||
| Mandatory | 1411.8 | 2031.8 | ||
| % GDP | 10.3 | 12.2 | ||
| Social Security | 543.9 | 807.8 | ||
| % GDP | 4.0 | 4.9 | ||
| Medicare | 376.8 | 585.2 | ||
| % GDP | 2.8 | 3.5 | ||
| Medicaid | 180.6 | 265.4 | ||
| % GDP | 1.3 | 1.6 | ||
| Income Security | 200.0 | 339.5 | ||
| % GDP | 1.5 | 2.0 | ||
| Offsetting Receipts | -144.3 | -304.8 | ||
| % GDP | -1.1 | -1.8 | ||
| Net Interest | 226.6 | 220.9 | ||
| % GDP | 1.7 | 1.3 | ||
| Defense +Medicare | 2047.9 | 77.1* | 2844.6 | 82.3* |
| % GDP | 15.1 | 17.1 |
*Percent of Total Outlays
Source: CBO (2013Aug12). 2013AugHBD. Historical budget data—August 2013. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Aug. CBO, Historical Budget Data—February 2014, Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb. CBO, Historical budget data—April 2014 release. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Apr.
The US is facing a major fiscal challenge. Table IIA1-5 provides federal revenues, expenditures, deficit and debt as percent of GDP and the yearly change in GDP in the more than eight decades from 1930 to 2013. The most recent period of debt exceeding 90 percent of GDP based on yearly observations in Table IIA1-5 is between 1944 and 1948. The data in Table IIA-15 use the earlier GDP estimates of the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) until 1972 for the ratios to GDP of revenue, expenditures, deficit and debt and the revised CBO (2013Aug12) after 1973 that incorporate the new BEA GDP estimates (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). The percentage change of GDP is based on the new BEA estimates for all years. The debt/GDP ratio actually rose to 106.2 percent of GDP in 1945 and to 108.7 percent of GDP in 1946. GDP fell revised 11.6 percent in 1946, which is only matched in Table I-5 by the decline of revised 12.9 percent in 1932. Part of the decline is explained by the bloated US economy during World War II, growing at revised 17.7 percent in 1941, 18.9 percent in 1942 and 17.0 percent in 1943. Expenditures as a share of GDP rose to their highest in the series: 43.6 percent in 1943, 43.6 percent in 1944 and 41.9 percent in 1945. The repetition of 43.6 percent in 1943 and 1944 is in the original source of Table IIA1-5. During the Truman administration from Apr 1945 to Jan 1953, the federal debt held by the public fell systematically from the peak of 108.7 percent of GDP in 1946 to 61.6 percent of GDP in 1952. During the Eisenhower administration from Jan 1953 to Jan 1961, the federal debt held by the public fell from 58.6 percent of GDP in 1953 to 45.6 percent of GDP in 1960. The Truman and Eisenhower debt reductions were facilitated by diverse factors such as low interest rates, lower expenditure/GDP ratios that could be attained again after lowering war outlays and less rigid structure of mandatory expenditures than currently. There is no subsequent jump of debt as the one from revised 39.3 percent of GDP in 2008 to 65.8 percent of GDP in 2011, 70.1 percent in 2012 and 72.0 percent in 2013.
Table IIA1-5, United States Central Government Revenue, Expenditure, Deficit, Debt and GDP Growth 1930-2011
| Rev | Exp | Deficit | Debt | GDP | |
| 1930 | 4.2 | 3.4 | 0.8 | -8.5 | |
| 1931 | 3.7 | 4.3 | -0.6 | -6.4 | |
| 1932 | 2.8 | 6.9 | -4.0 | -12.9 | |
| 1933 | 3.5 | 8.0 | -4.5 | -1.3 | |
| 1934 | 4.8 | 10.7 | -5.9 | 10.8 | |
| 1935 | 5.2 | 9.2 | -4.0 | 8.9 | |
| 1936 | 5.0 | 10.5 | -5.5 | 12.9 | |
| 1937 | 6.1 | 8.6 | -2.5 | 5.1 | |
| 1938 | 7.6 | 7.7 | -0.1 | -3.3 | |
| 1939 | 7.1 | 10.3 | -3.2 | 8.0 | |
| 1940s | |||||
| 1940 | 6.8 | 9.8 | -3.0 | 44.2 | 8.8 |
| 1941 | 7.6 | 12.0 | -4.3 | 42.3 | 17.7 |
| 1942 | 10.1 | 24.3 | -14.2 | 47.0 | 18.9 |
| 1943 | 13.3 | 43.6 | -30.3 | 70.9 | 17.0 |
| 1944 | 20.9 | 43.6 | -22.7 | 88.3 | 8.0 |
| 1945 | 20.4 | 41.9 | -21.5 | 106.2 | -1.0 |
| 1946 | 17.7 | 24.8 | -7.2 | 108.7 | -11.6 |
| 1947 | 16.5 | 14.8 | 1.7 | 96.2 | -1.1 |
| 1948 | 16.2 | 11.6 | 4.6 | 84.3 | 4.1 |
| 1949 | 14.5 | 14.3 | 0.2 | 79.0 | -0.5 |
| 1950s | |||||
| 1950 | 14.4 | 15.6 | -1.1 | 80.2 | 8.7 |
| 1951 | 16.1 | 14.2 | 1.9 | 66.9 | 8.1 |
| 1952 | 19.0 | 19.4 | -0.4 | 61.6 | 4.1 |
| 1953 | 18.7 | 20.4 | -1.7 | 58.6 | 4.7 |
| 1954 | 18.5 | 18.8 | -0.3 | 59.5 | -0.6 |
| 1955 | 16.5 | 17.3 | -0.8 | 57.2 | 7.1 |
| 1956 | 17.5 | 16.5 | 0.9 | 52.0 | 2.1 |
| 1957 | 17.7 | 17.0 | 0.8 | 48.6 | 2.1 |
| 1958 | 17.3 | 17.9 | -0.6 | 49.2 | -0.7 |
| 1959 | 16.2 | 18.8 | -2.6 | 47.9 | 6.9 |
| 1960s | |||||
| 1960 | 17.8 | 17.8 | 0.1 | 45.6 | 2.6 |
| 1961 | 17.8 | 18.4 | -0.6 | 45.0 | 2.6 |
| 1962 | 17.6 | 18.8 | -1.3 | 43.7 | 6.1 |
| 1963 | 17.8 | 18.6 | -0.8 | 42.4 | 4.4 |
| 1964 | 17.6 | 18.5 | -0.9 | 40.0 | 5.8 |
| 1965 | 17.0 | 17.2 | -0.2 | 37.9 | 6.5 |
| 1966 | 17.3 | 17.8 | -0.5 | 34.9 | 6.6 |
| 1967 | 18.4 | 19.4 | -1.1 | 32.9 | 2.7 |
| 1968 | 17.6 | 20.5 | -2.9 | 33.9 | 4.9 |
| 1969 | 19.7 | 19.4 | 0.3 | 29.3 | 3.1 |
| 1970s | |||||
| 1970 | 19.0 | 19.3 | -0.3 | 28.0 | 0.2 |
| 1971 | 17.3 | 19.5 | -2.1 | 28.1 | 3.3 |
| 1972 | 17.6 | 19.6 | -2.0 | 27.4 | 5.2 |
| 1973 | 17.0 | 18.1 | -1.1 | 25.1 | 5.6 |
| 1974 | 17.7 | 18.1 | -0.4 | 23.1 | -0.5 |
| 1975 | 17.3 | 20.6 | -3.3 | 24.5 | -0.2 |
| 1976 | 16.6 | 20.8 | -4.1 | 26.7 | 5.4 |
| 1977 | 17.5 | 20.2 | -2.6 | 27.1 | 4.6 |
| 1978 | 17.5 | 20.1 | -2.6 | 26.6 | 5.6 |
| 1979 | 18.0 | 19.6 | -1.6 | 24.9 | 3.2 |
| 1980s | |||||
| 1980 | 18.5 | 21.1 | -2.6 | 25.5 | -0.2 |
| 1981 | 19.1 | 21.6 | -2.5 | 25.2 | 2.6 |
| 1982 | 18.6 | 22.5 | -3.9 | 27.9 | -1.9 |
| 1983 | 17.0 | 22.8 | -5.9 | 32.1 | 4.6 |
| 1984 | 16.9 | 21.5 | -4.7 | 33.1 | 7.3 |
| 1985 | 17.2 | 22.2 | -5.0 | 35.3 | 4.2 |
| 1986 | 17.0 | 21.8 | -4.9 | 38.4 | 3.5 |
| 1987 | 17.9 | 21.0 | -3.1 | 39.5 | 3.5 |
| 1988 | 17.6 | 20.6 | -3.0 | 39.8 | 4.2 |
| 1989 | 17.8 | 20.5 | -2.7 | 39.3 | 3.7 |
| 1990s | |||||
| 1990 | 17.4 | 21.2 | -3.7 | 40.8 | 1.9 |
| 1991 | 17.3 | 21.7 | -4.4 | 44.0 | -0.1 |
| 1992 | 17.0 | 21.5 | -4.5 | 46.6 | 3.6 |
| 1993 | 17.0 | 20.7 | -3.8 | 47.8 | 2.7 |
| 1994 | 17.5 | 20.3 | -2.8 | 47.7 | 4.0 |
| 1995 | 17.8 | 20.0 | -2.2 | 47.5 | 2.7 |
| 1996 | 18.2 | 19.6 | -1.3 | 46.8 | 3.8 |
| 1997 | 18.6 | 18.9 | -0.3 | 44.5 | 4.5 |
| 1998 | 19.2 | 18.5 | 0.8 | 41.6 | 4.4 |
| 1999 | 19.2 | 17.9 | 1.3 | 38.2 | 4.8 |
| 2000s | |||||
| 2000 | 19.9 | 17.6 | 2.3 | 33.6 | 4.1 |
| 2001 | 18.8 | 17.6 | 1.2 | 31.4 | 1.0 |
| 2002 | 17.0 | 18.5 | -1.5 | 32.5 | 1.8 |
| 2003 | 15.7 | 19.1 | -3.3 | 34.5 | 2.8 |
| 2004 | 15.6 | 19.0 | -3.4 | 35.5 | 3.8 |
| 2005 | 16.7 | 19.2 | -2.5 | 35.6 | 3.4 |
| 2006 | 17.6 | 19.4 | -1.8 | 35.3 | 2.7 |
| 2007 | 17.9 | 19.0 | -1.1 | 35.1 | 1.8 |
| 2008 | 17.1 | 20.2 | -3.1 | 39.3 | -0.3 |
| 2009 | 14.6 | 24.4 | -9.8 | 52.3 | -2.8 |
| 2010s | |||||
| 2010 | 14.6 | 23.4 | -8.8 | 61.0 | 2.5 |
| 2011 | 15.0 | 23.4 | -8.4 | 65.8 | 1.8 |
| 2012 | 15.2 | 22.0 | -6.8 | 70.1 | 2.8 |
| 2013 | 16.7 | 20.8 | -4.1 | 72.0 | 1.9 |
Sources:
Office of Management and Budget. 2011. Historical Tables. Budget of the US Government Fiscal Year 2011. Washington, DC: OMB. CBO (2012JanBEO). CBO (2012Jan31). CBO (2012AugBEO). CBO (2013BEOFeb5). CBO2013HBDFeb5), CBO (2013Aug12). CBO, Historical Budget Data—February 2014, Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb. CBO, Historical budget data—April 2014 release. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Apr 14, 2014. Congressional Budget Office, August 2014 baseline: an update to the budget and economic outlook: 2014 to 2024. Washington, DC, CBO, Aug 27, 2014.
Table IIA1-6 provides 40-year average ratios of fiscal variables to GDP before and after the revision by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) in Aug 2013 (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). The ratios are equal or slightly higher because of the addition of intellectual property to GDP estimates. There are no major changes.
Table IIA1-6, US, Congressional Budget Office, 40-Year Averages of Revenues and Outlays Before and After Update of the US National Income Accounts by the Bureau of Economic Analysis, % of GDP
| Before Update | After Update | |
| Revenues | ||
| Individual Income Taxes | 8.2 | 7.9 |
| Social Insurance Taxes | 6.2 | 6.0 |
| Corporate Income Taxes | 1.9 | 1.9 |
| Other | 1.6 | 1.6 |
| Total Revenues | 17.9 | 17.4 |
| Outlays | ||
| Mandatory | 10.2 | 9.9 |
| Discretionary | 8.6 | 8.4 |
| Net Interest | 2.2 | 2.2 |
| Total Outlays | 21.0 | 20.4 |
| Deficit | -3.1 | -3.0 |
| Debt Held by the Public | 39.2 | 38.0 |
Source: CBO (2013Aug12Av). Kim Kowaleski and Amber Marcellino.
Table IIA1-7 provides the latest exercise by the CBO (2013BEOFeb5, 2012AugBEO, CBO2012NovCDR, 2013Sep11, CBO Feb2014, CBO Apr2014, CBOAug2014) of projecting the fiscal accounts of the US. Table IIA1-7 extends data back to 1995 with the projections of the CBO from 2014 to 2024, using the new estimates of the Bureau of Economic Analysis of US GDP (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). Budget analysis in the US uses a ten-year horizon. The significant event in the data before 2011 is the budget surpluses from 1998 to 2001, from 0.8 percent of GDP in 1998 to 2.3 percent of GDP in 2000 and 1.2 percent of GDP in 2001. Debt held by the public fell from 47.5 percent of GDP in 1995 to 31.4 percent of GDP in 2001.
Table IIA1-7, US, CBO Baseline Budget Outlook 2014-2024
| Out | Out | Deficit | Deficit | Debt | Debt | |
| 1995 | 1,516 | 20.0 | -164 | -2.2 | 3,604 | 47.5 |
| 1996 | 1,560 | 19.6 | -107 | -1.3 | 3,734 | 46.8 |
| 1997 | 1,601 | 18.9 | -22 | -0.3 | 3,772 | 44.5 |
| 1998 | 1,652 | 18.5 | +69 | +0.8 | 3,721 | 41.6 |
| 1999 | 1,702 | 17.9 | +126 | +1.3 | 3,632 | 38.2 |
| 2000 | 1,789 | 17.6 | +236 | +2.3 | 3,410 | 33.6 |
| 2001 | 1,863 | 17.6 | +128 | +1.2 | 3,320 | 31.4 |
| 2002 | 2,011 | 18.5 | -158 | -1.5 | 3,540 | 32.5 |
| 2003 | 2,159 | 19.1 | -378 | -3.3 | 3,913 | 34.5 |
| 2004 | 2,293 | 19.0 | -413 | -3.4 | 4,295 | 35.5 |
| 2005 | 2,472 | 19.2 | -318 | -2.5 | 4,592 | 35.6 |
| 2006 | 2,655 | 19.4 | -248 | -1.8 | 4,829 | 35.3 |
| 2007 | 2,729 | 19.0 | -161 | -1.1 | 5,035 | 35.1 |
| 2008 | 2,983 | 20.2 | -459 | -3.1 | 5,803 | 39.3 |
| 2009 | 3,518 | 24.4 | -1,413 | -9.8 | 7,545 | 52.3 |
| 2010 | 3,457 | 23.4 | -1,294 | -8.7 | 9,019 | 61.0 |
| 2011 | 3,603 | 23.4 | -1,300 | -8.4 | 10,128 | 65.8 |
| 2012 | 3,537 | 22.0 | -1,087 | -6.8 | 11,281 | 70.1 |
| 2013 | 3,455 | 20.8 | -680 | -4.1 | 11,983 | 72.0 |
| 2014 | 3,512 | 20.4 | -506 | -2.9 | 12,797 | 74.4 |
| 2015 | 3,750 | 20.9 | -469 | -2.6 | 13,305 | 74.0 |
| 2016 | 3,979 | 21.0 | -556 | -2.9 | 13,927 | 73.6 |
| 2017 | 4,135 | 20.8 | -530 | -2.7 | 14,521 | 73.0 |
| 2018 | 4,308 | 20.7 | -560 | -2.7 | 15,135 | 72.8 |
| 2019 | 4,569 | 21.1 | -661 | -3.0 | 15,850 | 73.1 |
| 2020 | 4,820 | 21.3 | -737 | -3.3 | 16,642 | 73.6 |
| 2021 | 5,076 | 21.5 | -820 | -3.5 | 17,518 | 74.3 |
| 2022 | 5,391 | 21.9 | -946 | -3.8 | 18,520 | 75.4 |
| 2023 | 5,601 | 21.9 | -957 | -3.7 | 19,534 | 76.4 |
| 2024 | 5,810 | 21.8 | -960 | -3.6 | 20,554 | 77.2 |
| 2015 to 2019 | 20,741 | 20.9 | -2,777 | -2.8 | NA | NA |
| 2015 | 47,439 | 21.3 | -7,196 | -3.2 | NA | NA |
Note: Out = outlays
Sources: CBO (2011AugBEO); Office of Management and Budget. 2011. Historical Tables. Budget of the US Government Fiscal Year 2011. Washington, DC: OMB; CBO. 2011JanBEO. Budget and Economic Outlook. Washington, DC, Jan. CBO. 2012AugBEO. Budget and Economic Outlook. Washington, DC, Aug 22. CBO. 2012Jan31. Historical budget data. Washington, DC, Jan 31. CBO. 2012NovCDR. Choices for deficit reduction. Washington, DC. Nov. CBO. 2013HBDFeb5. Historical budget data—February 2013 baseline projections. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb 5. CBO. 2013HBDFeb5. Historical budget data—February 2013 baseline projections. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb 5. CBO (2013Sep11). CBO, Historical Budget Data—February 2014, Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb. CBO, The Budget and Economic Outlook 2014 to 2024. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb 2014. CBO, Historical budget data—April 2014 release. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Apr 14, 2014. CBO, Updated Budget Projections: 2014 to 2024. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Apr 14, 2014.
Congressional Budget Office, August 2014 baseline: an update to the budget and economic outlook: 2014 to 2024. Washington, DC, CBO, Aug 27, 2014.
Chart IIA1-1 of the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) provides the deficits of the US as percent of GDP from 1974 to 2013 followed on the right with the projections of the CBO in Feb 2014. Large deficits from 2009 to 2013, all above the average from 1974 to 2013, doubled the debt held by the public. Fiscal adjustment is now more challenging with rigidities in revenues and expenditures. The projections of the CBO in Apr 2014 for the years from 2014 to 2024 show lower deficits in proportion of GDP in the initial years that eventually become larger than the average in the second half of the ten-year window.
Chart IIA1-1, US, Total Federal Deficits and Surpluses
Source: Congressional Budget Office
CBO, Updated Budget Projections: 2014 to 2024. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Apr 14, 2014. http://www.cbo.gov/publication/45229
The Budget and Economic Outlook 2014 to 2024. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb 2014.
http://www.cbo.gov/publication/45073
Table IIA1-8 provides baseline CBO projections of federal revenues, outlays, deficit and debt as percent of GDP. The adjustment depends on increasing revenues from 15.0 percent of GDP in 2011 and 16.7 percent in 2013 to 18.2 percent of GDP in 2024, which is above the 40-year average of 17.4 percent of GDP. Outlays fall from 23.4 percent of GDP in 2011 and 20.8 percent of GDP in 2013 to 21.8 percent of GDP in 2024. The last row of Table IIA1-8 provides the CBO estimates of averages for 1973 to 2012 of 17.4 percent for revenues/GDP, 20.4 percent for outlays/GDP and 38.0 percent for debt/GDP. The debt/GDP ratio increases to 77.2 percent of GDP in 2014. The United States faces tough adjustment of its fiscal accounts. There is an additional source of pressure on financing the current account deficit of the balance of payments.
Table IIA1-8, US, Baseline CBO Projections of Federal Government Revenues, Outlays, Deficit and Debt as Percent of GDP
| Revenues | Outlays | Deficit | Debt | |
| 2011 | 15.0 | 23.4 | -8.4 | 65.8 |
| 2012 | 15.2 | 22.0 | -6.8 | 70.1 |
| 2013 | 16.7 | 20.8 | -4.1 | 72.0 |
| 2014 | 17.5 | 20.4 | -2.9 | 74.4 |
| 2015 | 18.3 | 20.9 | -2.6 | 74.0 |
| 2016 | 18.1 | 21.0 | -2.9 | 73.6 |
| 2017 | 18.1 | 20.8 | -2.7 | 73.0 |
| 2018 | 18.0 | 20.7 | -2.7 | 72.8 |
| 2019 | 18.0 | 21.1 | -3.0 | 73.1 |
| 2020 | 18.1 | 21.3 | -3.3 | 73.6 |
| 2021 | 18.1 | 21.5 | -3.5 | 74.3 |
| 2022 | 18.1 | 21.9 | -3.8 | 75.4 |
| 2023 | 18.2 | 21.9 | -3.7 | 76.4 |
| 2024 | 18.2 | 21.8 | -3.6 | 77.2 |
| Total 2015-2019 | 18.1 | 20.9 | -2.8 | NA |
| Total 2015-2024 | 18.1 | 21.3 | -3.2 | NA |
| Average | 17.4 | 20.4 | -3.0 | 38.0 |
Source: CBO (2012AugBEO). CBO (2012NovCDR). CBO (2013BEOFeb5). CBO 2013HBDFeb5), CBO (2013Sep11), CBO (2013Aug12Av). Kim Kowaleski and Amber Marcellino. CBO, Historical Budget Data—February 2014, Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb. CBO, The Budget and Economic Outlook 2014 to 2024. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb 2014. CBO, Historical budget data—April 2014 release. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Apr 14, 2014. CBO, Updated Budget Projections: 2014 to 2024. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Apr 14, 2014.
Chart IIA1-2 of the Congressional Budget Office (CBO) provides the actual federal debt as percent of GDP from 1940 to 2013 and the projected path by the CBO from 2014 to 2024. The federal debt exceeded 100 percent of GDP because of the war effort during World War II. Adjustment was swift and continuous during rapid economic growth in large part because of less rigid structures of expenditures and revenues. The jump of the federal debt from 35.1 percent of GDP in 2007 to 72.0 percent of GDP in 2013 with CBO projection of 77.2 percent of GDP in 2024 poses a major challenge of fiscal adjustment.
Chart IIA1-2, US, Federal Debt Held by the Public
Source: Congressional Budget Office
Congressional Budget Office, August 2014 baseline: an update to the budget and economic outlook: 2014 to 2024. Washington, DC, CBO, Aug 27, 2014.
http://www.cbo.gov/publication/45653
Table IIA1-9 provides the long-term budget outlook of the CBO for 2014, 2024 and 2039. Revenues increase from 17.6 percent of GDP in 2014 to 19.4 percent in 2038. The growing stock of debt raises net interest spending from 1.3 percent of GDP in 2014 to 3.3 percent in 2024 and 4.7 percent 2039. Total spending increases from 20.4 percent of GDP in 2014 to 25.9 percent in 2039. Federal debt held by the public rises to 106.0 percent of GDP in 2039. US fiscal affairs are in an unsustainable path with tough rigidities in spending and revenues.
Table IIA1-9, Congressional Budget Office, Long-term Budget Outlook, % of GDP
| 2014 | 2024 | 2039 | |
| Revenues | 17.6 | 18.3 | 19.4 |
| Total Noninterest Spending | 19.1 | 18.8 | 21.2 |
| Social Security | 4.9 | 5.6 | 6.3 |
| Medicare | 3.0 | 3.2 | 4.6 |
| Medicaid, CHIP and Exchange Subsidies | 1.9 | 2.7 | 3.4 |
| Other | 9.3 | 7.3 | 6.8 |
| Net Interest | 1.3 | 3.3 | 4.7 |
| Total Spending | 20.4 | 22.1 | 25.9 |
| Revenues Minus Total Noninterest Spending | -1.5 | -0.5 | -1.7 |
| Revenues Minus Total Spending | -2.8 | -3.7 | -6.4 |
| Federal Debt Held by the Public | 74.0 | 78.0 | 106.0 |
Source: CBO (2014Jul25). The 2014 long-term budget outlook. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Jul 25.
Chart IIA1-3 provides actual federal debt held by the public as percent of GDP from 1790 to 2012 and projected by the CBO (2013Sep17) from 2013 to 2038. The ratio of debt to GDP climbed from 42.3 percent in 1941 to a peak of 108.7 percent in 1946 because of the Second World War. The ratio of debt to GDP declined to 80.2 percent in 1950 and 66.9 percent in 1951 because of unwinding war effort, economy growing to capacity and less rigid mandatory expenditures. The ratio of debt to GDP of 70.1 percent in 2012 is the highest in the United States since 1950. The CBO (2013BEOJul25) projects the ratio of debt of GDP of the United States to reach 106.0 percent in 2039, which will be more than double the average ratio of 38.0 percent in 1973-2012. The misleading debate on the so-called “fiscal cliff” has disguised the unsustainable path of United States fiscal affairs.
Chart IIA1-3, Congressional Budget Office, Federal Debt Held by the Public, Extended Baseline Projection, % of GDP
Source: CBO. 2013Sep17. The 2013 long-term budget outlook. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Sep 17.
Chart IIIA1-4 of the Congressional Budget Office provides actual and extended baseline projections of federal debt held by the public, spending and revenues. The excess of spending over revenues increases from 2.8 percent in 2014 to 3.7 percent in 2024 and 6.4 percent in 2039. Federal debt held by the public rises from 74.0 percent of GDP in 2014 to 78.0 percent of GDP in 2024 and 106 percent of GDP in 2039.
Chart IIA1-4, Congressional Budget Office, Federal Debt Held by the Public, % of GDP
Source: CBO (2014Jul25). The 2014 long-term budget outlook. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Jul 25.
Chart IIA1-5 of the Congressional Budget Office provides actual and baseline projections of components of federal spending, illustrating the rigidity of US federal government spending. The combined spending in social security, Medicare and Medicaid increases from 9.8 percent of GDP in 2014 to 14.3 percent of GDP in 2039. Interest spending on a rising federal debt increases from 1.3 percent of GDP in 2014 to 4.7 percent of GDP in 2039.
Chart IIA1-5, Congressional Budget Office, Actual and Extended Baseline Projections of Components of Total Spending, % of GDP
Source: CBO (2014Jul25). The 2014 long-term budget outlook. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Jul 25.
Chart IIA1-6 of the Congressional Budget Office provides similar rigidity in the components of federal revenues. Individual income taxes increase from 8.0 percent of GDP in 2014 to 10.5 percent of GDP in 2039. Corporate income taxes decrease from 2.0 percent of GDP in 2014 to 1.8 percent of GDP in 2039. Payroll (social insurance) taxes decrease from 6.0 percent of GDP in 2014 to 5.7 percent of GDP in 2039. Other revenue sources decrease from 1.5 percent of GDP in 2014 to 1.4 percent of GDP in 2039. There is limited space for reduction of expenditures and increases of revenue.
Chart IIA1-6, Congressional Budget Office, Actual and Extended Baseline Projections of Components of Total Revenue, % of GDP
Source: CBO (2014Jul25). The 2014 long-term budget outlook. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Jul 25.
IIB United States Services. Chart II-1 of the US Census Bureau of the Department of Commerce provides the quarterly service report SA from IIIQ2003 to IIQ2014. Services revenue contracted during the recession from IVQ2007 (December) to IIQ2009 (June) (http://wwwdev.nber.org/cycles/cyclesmain.html) but there appears to be continuing growth especially for professional, scientific and technical services with steeper slope from IVQ2010 through IIQ2014.
Chart II-1, US, Quarterly Revenue for Selected Services, SA $ Billions
Note: _____ Information Seasonally Adjusted (SA)
_____ Professional, Scientific and Technical Services (SA)
_____ Administrative and Support and Waste Management (SA)
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www2.census.gov/services/qss/qss.gif
Total revenues of information services not seasonally adjusted in millions of current dollars are shown in Table II-1 from IVQ2003, when they become available, to IIQ2014. The row below current values provides percentage change in the quarter from the quarter a year earlier. Growth rates were robust before the global recession in the range from 3.7 percent in IVQ2004 to 5.5 percent in IQ2005. Percentage changes were negative in all quarters in 2009 with the deepest declines in the first three quarters. Growth was milder in the expansion phase than before the global recession. As with most indicators of the US, growth was robust in the final three quarters of 2010 and initial quarters of 2011. Growth rates recovered to 5.6 percent in IVQ2012, 4.8 percent in IQ2013 and 4.4 percent in IIQ2013. Growth continued with 5.3 percent in IIIQ2013 relative to a year earlier and 5.5 percent in IVQ2013. Growth strengthened with 6.0 percent in IQ2014 relative to a year earlier and 5.6 percent in IIQ2014 relative to a year earlier.
Table II-1, US, Information Services Revenue Not Seasonally Adjusted, Millions of Dollars, 2003-2014
| Year | 1st Quarter | 2nd Quarter | 3rd Quarter | 4th Quarter |
| 2003 | NA | NA | NA | 237,399 |
| 2004 | 223,675 | 233,241 | 232,983 | 246,201 |
| ∆% | NA | NA | NA | 3.7 |
| 2005 | 236,033 | 244,136 | 244,711 | 255,856 |
| ∆% | 5.5 | 4.7 | 5.0 | 3.9 |
| 2006 | 245,182 | 254,735 | 255,745 | 271,401 |
| ∆% | 3.9 | 4.3 | 4.5 | 6.1 |
| 2007 | 257,973 | 265,739 | 267,325 | 281,304 |
| ∆% | 5.2 | 4.3 | 4.5 | 3.6 |
| 2008 | 270,223 | 277,650 | 277,603 | 282,873 |
| ∆% | 4.7 | 4.5 | 3.8 | 0.6 |
| 2009 | 261,921 | 266,862 | 265,511 | 280,665 |
| ∆% | -3.1 | -3.9 | -4.4 | -0.8 |
| 2010 | 267,597 | 274,785 | 276,049 | 291,794 |
| ∆% | 2.2 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 |
| 2011 | 277,416 | 289,110 | 288,779 | 305,253 |
| ∆% | 3.7 | 5.2 | 4.6 | 4.6 |
| 2012 | 291,952 | 300,081 | 298,950 | 322,308 |
| ∆% | 5.2 | 3.8 | 3.5 | 5.6 |
| 2013 | 306,040 | 313,234 | 314,646 | 340,055 |
| ∆% | 4.8 | 4.4 | 5.3 | 5.5 |
| 2014 | 324,502 | 330,908 | NA | NA |
| ∆% | 6.0 | 5.6 |
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/services/index.html
Chart II-2 provides total revenue of information services not seasonally adjusted from IVQ2013 to IIQ2014 in current millions of dollars not seasonally adjusted. Oscillating growth was strong before the drop of the global recession. Growth recovered in recent quarters relative to the same quarter a year earlier with strong increase in IVQ2012 followed by increases in all quarters in 2013. Growth continued in IQ2014 and IIQ2014.
Chart II-2, Quarterly Revenue for Information Services Not Seasonally Adjusted, Millions of Dollars 2003-2014
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/services/index.html
There is similar pattern in Chart II-3 with quarterly total revenue of information services in current millions of dollars adjusted for seasonality. There is the same hump of the global recession followed by resumption of growth.
Chart II-3, Quarterly Revenue for Information Services Seasonally Adjusted, Millions of Dollars 2003-2014
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/services/index.html
Table II-2 provides total revenue of financial services and insurance in current million dollars not seasonally adjusted from IIIQ2009, when data first become available, to IIQ2014. The row below values provides percentage changes in a quarter relative to the same quarter a year earlier. Percentage changes were negative until 2012 with 3.0 percent in IQ2012, 1.3 percent in IIQ2012, 5.4 percent in IIIQ2012 and 3.8 percent in IVQ2012. Revenue increased 1.1 percent in IQ2013 relative to a year earlier and increased 3.9 percent in IIQ2013. Revenue growth moderated to 0.4 percent in IIIQ2013 and recovered to 5.6 percent in IVQ2013. Growth strengthened with 5.0 percent in IQ2014 relative to a year earlier and 4.8 percent in IIQ2014 relative to a year earlier.
Table II-2, US, Financial Services and Insurance Total Revenue Not Seasonally Adjusted, Millions of Dollars, 2003-2013
| 2009 | NA | NA | 844,210 | 842,875 |
| 2010 | 831,167 | 831,769 | 831,075 | 832,059 |
| ∆% | NA | NA | -1.6 | -1.3 |
| 2011 | 830,076 | 828,539 | 814,472 | 820,554 |
| ∆% | -0.1 | -0.4 | -2.0 | -1.4 |
| 2012 | 854,954 | 839,140 | 858,619 | 851,997 |
| ∆% | 3.0 | 1.3 | 5.4 | 3.8 |
| 2013 | 864,479 | 871,496 | 862,024 | 894,022 |
| ∆% | 1.1 | 3.9 | 0.4 | 4.9 |
| 2014 | 907,418 | 912,985 | NA | NA |
| ∆% | 5.0 | 4.8 | NA | NA |
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/services/index.html
Chart II-4 provides total quarterly revenue of financial services and insurance from IIIQ2009, when data first become available, to IIQ2014. Total revenue of financial services and insurance contracted 1.3 percent between IVQ2009 and IVQ2011 and grew 3.8 percent between IVQ2011 and IVQ2012. Revenue increased 1.1 percent in IQ2013 relative to a year earlier and 3.9 percent in IIQ2013. Revenue growth slowed to 0.4 percent in IIIQ2013 and jumped to 4.9 percent in IVQ2013. Growth continued with 5.0 percent in IQ2014 relative to a year earlier and 4.8 percent in IIQ2014 relative to a year earlier.
Chart II-4, Total Quarterly Revenue for Financial Services and Insurance Not Seasonally Adjusted, Millions of Dollars 2003-2014
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/services/index.html
IIC United States Import and Export Prices. Chart IIA2-1 provides prices of total US imports 2001-2014. Prices fell during the contraction of 2001. Import price inflation accelerated after unconventional monetary policy of near zero interest rates in 2003-2004 and quantitative easing by withdrawing supply with the suspension of 30-year Treasury bond auctions. Slow pace of adjusting fed funds rates from 1 percent by increments of 25 basis points in 17 consecutive meetings of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) between Jun 2004 and Jun 2006 continued to give impetus to carry trades. The reduction of fed funds rates toward zero in 2008 fueled a spectacular global hunt for yields that caused commodity price inflation in the middle of a global recession. After risk aversion in 2009 because of the announcement of TARP (Troubled Asset Relief Program) creating anxiety on “toxic assets” in bank balance sheets (see Cochrane and Zingales 2009), prices collapsed because of unwinding carry trades. Renewed price increases returned with zero interest rates and quantitative easing. Monetary policy impulses in massive doses have driven inflation and valuation of risk financial assets in wide fluctuations over a decade.
Chart IIA2-1, US, Prices of Total US Imports 2001=100, 2001-2014
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIA2-2 provides 12-month percentage changes of prices of total US imports from 2001 to 2014. The only plausible explanation for the wide oscillations is by the carry trade originating in unconventional monetary policy. Import prices jumped in 2008 during deep and protracted global recession driven by carry trades from zero interest rates to long, leveraged positions in commodity futures. Carry trades were unwound during the financial panic in the final quarter of 2008 that resulted in flight to government obligations. Import prices jumped again in 2009 with subdued risk aversion because US banks did not have unsustainable toxic assets. Import prices then fluctuated as carry trades were resumed during periods of risk appetite and unwound during risk aversion resulting from the European debt crisis.
Chart IIA2-2, US, Prices of Total US Imports, 12-Month Percentage Changes, 2001-2014
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIA2-3 provides prices of US imports from 1982 to 2014. There is no similar episode to that of the increase of commodity prices in 2008 during a protracted and deep global recession with subsequent collapse during a flight into government obligations. Trade prices have been driven by carry trades created by unconventional monetary policy in the past decade.
Chart IIA2-3, US, Prices of Total US Imports, 2001=100, 1982-2014
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIA2-4 provides 12-month percentage changes of US total imports from 1982 to 2014. There have not been wide consecutive oscillations as the ones during the global recession of IVQ2007 to IIQ2009.
Chart IIA2-4, US, Prices of Total US Imports, 12-Month Percentage Changes, 1982-2014
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIA2-5 provides the index of US export prices from 2001 to 2014. Import and export prices have been driven by impulses of unconventional monetary policy in massive doses. The most recent segment in Chart IIA2-5 shows declining trend resulting from a combination of the world economic slowdown and the decline of commodity prices as carry trade exposures are unwound because of risk aversion to the sovereign debt crisis in Europe and slowdown in the world economy.
Chart IIA2-5, US, Prices of Total US Exports, 2001=100, 2001-2014
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIA2-6 provides prices of US total exports from 1982 to 2014. The rise before the global recession from 2003 to 2008, driven by carry trades, is also unique in the series and is followed by another steep increase after risk aversion moderated in IQ2009.
Chart IIA2-6, US, Prices of Total US Exports, 2001=100, 1982-2014
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIA2-7 provides 12-month percentage changes of total US exports from 1982 to 2014. The uniqueness of the oscillations around the global recession of IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 is clearly revealed.
Chart IIA2-7, US, Prices of Total US Exports, 12-Month Percentage Changes, 1982-2014
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Twelve-month percentage changes of US prices of exports and imports are provided in Table IIA2-1. Import prices have been driven since 2003 by unconventional monetary policy of near zero interest rates influencing commodity prices according to moods of risk aversion and portfolio reallocations. In a global recession without risk aversion until the panic of Sep 2008 with flight to government obligations, import prices increased 21.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Jul 2008, 18.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2008, 13.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep 2008, 4.9 percent in the twelve months ending in Oct 2008. Import prices fell 10.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2008 when risk aversion developed in 2008 until mid 2009 (http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm). Import prices rose again sharply in Dec 2009 by 8.6 percent and in Dec 2010 by 5.3 percent in the presence of zero interest rates with relaxed mood of risk aversion. Carry trades were unwound in May 2011 and following months as shown by decrease of import prices by 2.0 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2012 and 1.1 percent in Dec 2013. Import prices increased 16.9 percent in the 12 months ending in Apr 2008, fell 16.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Apr 2009 and increased 11.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Apr 2010. Fluctuations are much sharper in imports because of the high content of oil that as all commodities futures contracts increases sharply with zero interest rates and risk appetite, contracting under risk aversion. There is similar behavior of prices of imports ex fuels, exports and exports ex agricultural goods but less pronounced than for commodity-rich prices dominated by carry trades from zero interest rates. A critical event resulting from unconventional monetary policy driving higher commodity prices by carry trades is the deterioration of the terms of trade, or export prices relative to import prices, that has adversely affected US real income growth relative to what it would have been in the absence of unconventional monetary policy. Europe, Japan and other advanced economies have experienced similar deterioration of their terms of trade. Because of unwinding carry trades of commodity futures resulting from risk aversion and portfolio reallocations, import prices decreased 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2014, export prices increased 0.4 percent and prices of nonagricultural exports increased 0.5 percent. Imports excluding fuel increased 0.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Aug 2014. At the margin, price changes over the year in world exports and imports are decreasing or increasing moderately because of unwinding carry trades in a temporary mood of risk aversion and relative allocation of asset classes toward equities that reverses exposures in commodity futures.
Table IIA2-1, US, Twelve-Month Percentage Rates of Change of Prices of Exports and Imports
| Imports | Imports Ex Fuels | Exports | Exports Non-Ag | |
| Aug 2014 | -0.4 | 0.7 | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| Aug 2013 | 0.0 | -1.0 | -1.1 | -0.6 |
| Aug 2012 | -1.8 | -0.4 | -0.9 | -1.9 |
| Aug 2011 | 12.9 | 5.4 | 9.4 | 8.0 |
| Aug 2010 | 3.8 | 2.7 | 4.1 | 3.9 |
| Aug 2009 | -15.3 | -5.1 | -6.2 | -5.3 |
| Aug 2008 | 18.1 | 6.6 | 8.3 | 6.8 |
| Aug 2007 | 1.9 | 2.4 | 3.7 | 2.5 |
| Aug 2006 | 6.0 | 2.9 | 5.2 | 5.3 |
| Aug 2005 | 8.2 | 1.3 | 3.1 | 2.8 |
| Aug 2004 | 7.1 | 2.8 | 4.0 | 3.9 |
| Aug 2003 | 2.0 | 0.3 | 0.9 | 0.8 |
| Aug 2002 | -1.3 | NA | -0.3 | -0.6 |
| Aug 2001 | -4.4 | NA | -1.0 | -1.6 |
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Table IIA2-2 provides 12-month percentage changes of the import price index all commodities from 2001 to 2014. Interest rates moving toward zero during unconventional monetary policy in 2008 induced carry trades into highly leveraged commodity derivatives positions that caused increases in 12-month percentage changes of import prices of around 20 percent. The flight into dollars and Treasury securities by fears of toxic assets in banks in the proposal of TARP (Cochrane and Zingales 2009) caused reversion of carry trades and collapse of commodity futures explaining sharp declines in trade prices in 2009. Twelve-month percentage changes of import prices at the end of 2012 and into 2013 occurred during another bout of risk aversion and portfolio reallocation. There is a new shock of risk aversion in late 2013 with marginally increasing exposures in commodities followed by reversals of exposures into 2014.
Table IIA2-2, US, Twelve-Month Percentage Changes of Import Price Index All Commodities, 2001-2014
| Year | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Dec |
| 2001 | 2.8 | 0.2 | -1.6 | -0.7 | -0.8 | -2.6 | -4.1 | -4.4 | -9.1 |
| 2002 | -8.9 | -8.3 | -5.6 | -3.6 | -3.7 | -3.6 | -1.7 | -1.3 | 4.2 |
| 2003 | 5.8 | 7.5 | 6.8 | 1.8 | 1.0 | 2.2 | 2.3 | 2.0 | 2.4 |
| 2004 | 2.2 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 4.6 | 6.9 | 5.7 | 5.6 | 7.1 | 6.7 |
| 2005 | 5.7 | 6.1 | 7.6 | 8.4 | 5.9 | 7.4 | 8.2 | 8.2 | 8.0 |
| 2006 | 8.7 | 6.9 | 4.5 | 5.8 | 8.6 | 7.4 | 7.0 | 6.0 | 2.5 |
| 2007 | 0.0 | 1.2 | 2.8 | 2.1 | 1.2 | 2.3 | 2.8 | 1.9 | 10.6 |
| 2008 | 13.6 | 13.5 | 15.2 | 16.9 | 19.1 | 21.3 | 21.4 | 18.1 | -10.1 |
| 2009 | -12.5 | -12.7 | -14.9 | -16.4 | -17.3 | -17.5 | -19.1 | -15.3 | 8.6 |
| 2010 | 11.4 | 11.3 | 11.2 | 11.2 | 8.5 | 4.3 | 4.9 | 3.8 | 5.3 |
| 2011 | 5.6 | 7.6 | 10.3 | 11.9 | 12.9 | 13.6 | 13.7 | 12.9 | 8.5 |
| 2012 | 6.9 | 5.1 | 3.5 | 0.8 | -0.8 | -2.5 | -3.3 | -1.8 | -2.0 |
| 2013 | -1.5 | -0.6 | -2.1 | -2.7 | -1.8 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 0.0 | -1.1 |
| 2014 | -1.3 | -1.1 | -0.5 | -0.4 | 0.5 | 1.2(R) | 0.8 | -0.4 |
R: Revised
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
There is finer detail in one-month percentage changes of imports of the US in Table IIA2-3. Carry trades into commodity futures induced by interest rates moving to zero in unconventional monetary policy caused sharp monthly increases in import prices for cumulative increase of 13.8 percent from Mar to Jul 2008 at average rate of 2.6 percent per month or annual equivalent in five months of 36.4 percent (3.1 percent in Mar 2008, 2.8 percent in Apr 2008, 2.8 percent in May 2008, 3.0 percent in Jun 2008 and 1.4 percent in Jul 2008, data from http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm). There is no other explanation for increases in import prices during sharp global recession and contracting world trade. Import prices then fell 23.4 percent from Aug 2008 to Jan 2009 or at the annual equivalent rate of minus 41.4 percent in the flight to US government securities in fear of the need to buy toxic assets from banks in the TARP program (Cochrane and Zingales 2009). Risk aversion during the first sovereign debt crisis of the euro area in May-Jun 2010 caused decline of US import prices at the annual equivalent rate of 11.4 percent. US import prices have been driven by combinations of carry trades induced by unconventional monetary policy and bouts of risk aversion and portfolio reallocation (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/monetary-policy-world-inflation-waves.html). US import prices increased 0.5 percent in Jan 2013 and 0.9 percent in Feb 2013 for annual equivalent rate of 8.7 percent, similar to those in national price indexes worldwide, originating in carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures. Import prices fell 0.1 percent in Mar 2013, 0.7 percent in Apr 2013, 0.6 percent in May 2013 and 0.4 percent in Jun 2013. Import prices changed 0.1 percent in Jul 2013, increased 0.4 percent in Aug 2013 and increased 0.3 percent in Sep 2013. Portfolio reallocations into asset classes other than commodities explains declines of import prices by 0.6 percent in Oct 2013 and 0.9 percent in Nov 2013. Import prices increased 0.1 percent in Dec 2013, 0.4 percent in Jan 2014, 1.1 percent in Feb 2014 and 0.5 percent in Mar 2014. Import prices fell 0.6 percent in Apr 2014 and increased 0.3 percent in May 2014. Import prices increased 0.2 percent in Jun 2014 and contracted 0.3 percent in Jul 2014. Import prices fell 0.9 percent in Aug 2014.
Table IIA2-3, US, One-Month Percentage Changes of Import Price Index All Commodities, 2001-2014
| Year | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Dec |
| 2001 | 0.0 | -0.6 | -1.6 | -0.5 | 0.2 | -0.4 | -1.5 | -0.1 | -1.0 |
| 2002 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 0.1 | -0.3 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.6 |
| 2003 | 1.8 | 1.7 | 0.6 | -3.1 | -0.7 | 0.9 | 0.5 | 0.0 | 0.7 |
| 2004 | 1.5 | 0.4 | 0.8 | 0.2 | 1.5 | -0.2 | 0.4 | 1.5 | -1.4 |
| 2005 | 0.6 | 0.9 | 2.2 | 0.9 | -0.8 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 1.4 | 0.0 |
| 2006 | 1.2 | -0.8 | -0.1 | 2.1 | 1.8 | 0.1 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 1.1 |
| 2007 | -1.2 | 0.4 | 1.6 | 1.4 | 0.9 | 1.2 | 1.3 | -0.3 | -0.2 |
| 2008 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 3.1 | 2.8 | 2.8 | 3.0 | 1.4 | -3.1 | -4.6 |
| 2009 | -1.3 | 0.0 | 0.5 | 1.1 | 1.7 | 2.7 | -0.6 | 1.5 | 0.2 |
| 2010 | 1.2 | -0.1 | 0.4 | 1.1 | -0.8 | -1.2 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 1.4 |
| 2011 | 1.5 | 1.7 | 3.0 | 2.6 | 0.1 | -0.6 | 0.1 | -0.4 | 0.0 |
| 2012 | 0.0 | 0.0 | 1.4 | -0.1 | -1.5 | -2.3 | -0.7 | 1.2 | -0.6 |
| 2013 | 0.5 | 0.9 | -0.1 | -0.7 | -0.6 | -0.4 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 0.1 |
| 2014 | 0.4 | 1.1 | 0.5 | -0.6 | 0.3 | 0.2(R) | -0.3(R) | -0.9 |
R: Revised
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIA2-8 shows the US monthly import price index of all commodities excluding fuels from 2001 to 2014. All curves of nominal values follow the same behavior under the influence of unconventional monetary policy. Zero interest rates without risk aversion result in jumps of nominal values while under strong risk aversion even with zero interest rates there are declines of nominal values.
Chart IIA2-8, US, Import Price Index All Commodities Excluding Fuels, 2001=100, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIA2-9 provides 12-month percentage changes of the US import price index excluding fuels between 2001 and 2014. There is the same behavior of carry trades driving up without risk aversion and down with risk aversion prices of raw materials, commodities and food in international trade during the global recession of IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 and in previous and subsequent periods.
Chart IIA2-9, US, Import Price Index All Commodities Excluding Fuels, 12-Month Percentage Changes, 2002-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIA2-10 provides the monthly US import price index ex petroleum from 2001 to 2014. Prices including or excluding commodities follow the same fluctuations and trends originating in impulses of unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates.
Chart IIA2-10, US, Import Price Index ex Petroleum, 2001=100, 2000-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIA2-11 provides the US import price index ex petroleum from 1985 to 2014. There is the same unique hump in 2008 caused by carry trades from zero interest rates to prices of commodities and raw materials.
Chart IIA2-11, US, Import Price Index ex Petroleum, 2001=100, 1985-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIA2-12 provides 12-month percentage changes of the import price index ex petroleum from 1986 to 2014. The oscillations caused by the carry trade in increasing prices of commodities and raw materials without risk aversion and subsequently decreasing them during risk aversion are unique.
Chart IIA2-12, US, Import Price Index ex Petroleum, 12-Month Percentage Changes, 1986-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIA2-13 of the US Energy Information Administration shows the price of WTI crude oil since the 1980s. Chart IA2-13 captures commodity price shocks during the past decade. The costly mirage of deflation was caused by the decline in oil prices during the recession of 2001. The upward trend after 2003 was promoted by the carry trade from near zero interest rates. The jump above $140/barrel during the global recession in 2008 at $145.29/barrel on Jul 3, 2008, can only be explained by the carry trade promoted by monetary policy of zero fed funds rate. After moderation of risk aversion, the carry trade returned with resulting sharp upward trend of crude prices. Risk aversion resulted in another drop in recent weeks followed by some recovery and renewed deterioration/increase.
Chart IIA2-13, US, Crude Oil Futures Contract
Source: US Energy Information Administration
http://www.eia.gov/dnav/pet/hist/LeafHandler.ashx?n=PET&s=RCLC1&f=D
The price index of US imports of petroleum and petroleum products in shown in Chart IIA2-14. There is similar behavior of the curves all driven by the same impulses of monetary policy.
Chart IIA2-14, US, Import Price Index of Petroleum and Petroleum Products, 2001=100, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIA2-15 provides the price index of petroleum and petroleum products from 1982 to 2014. The rise in prices during the global recession in 2008 and the decline after the flight to government obligations is unique in the history of the series. Increases in prices of trade in petroleum and petroleum products were induced by carry trades and declines by unwinding carry trades in flight to government obligations.
Chart IIA2-15, US, Import Price Index of Petroleum and Petroleum Products, 2001=100, 1982-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIA2-16 provides 12-month percentage changes of the price index of US imports of petroleum and petroleum products from 1982 to 2014. There were wider oscillations in this index from 1999 to 2001 (see Barsky and Killian 2004 for an explanation).
Chart IIA2-16, US, Import Price Index of Petroleum and Petroleum Products, 12-Month Percentage Changes, 1982-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
The price index of US exports of agricultural commodities is in Chart IIA2-17 from 2001 to 2014. There are similar fluctuations and trends as in all other price index originating in unconventional monetary policy repeated over a decade. The most recent segment in 2011 has declining trend in a new flight from risk resulting from the sovereign debt crisis in Europe followed by declines in Jun 2012 and Nov 2012 with stability/decline in Dec 2012 into 2013. Prices rebounded into 2014.
Chart IIA2-17, US, Exports Price Index of Agricultural Commodities, 2001=100, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIA2-18 provides the price index of US exports of agricultural commodities from 1982 to 2014. The increase in 2008 in the middle of deep, protracted contraction was induced by unconventional monetary policy. The decline from 2008 into 2009 was caused by unwinding carry trades in a flight to government obligations. The increase into 2011 and current pause with marginal rebound were also induced by unconventional monetary policy in waves of increases during relaxed risk aversion and declines during unwinding of positions because of aversion to financial risk.
Chart IIA2-18, US, Exports Price Index of Agricultural Commodities, 2001=100, 1982-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIA2-19 provides 12-month percentage changes of the index of US exports of agricultural commodities from 1986 to 2014. The wide swings in 2008, 2009 and 2011 are only explained by unconventional monetary policy inducing carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures and reversals during risk aversion.
Chart IIA2-19, US, Exports Price Index of Agricultural Commodities, 12-Month Percentage Changes, 1986-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIA2-20 shows the export price index of nonagricultural commodities from 2001 to 2014. Unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates drove price behavior during the past decade. Policy has been based on the myth of stimulating the economy by climbing the negative slope of an imaginary short-term Phillips curve.
Chart IIA2-20, US, Exports Price Index of Nonagricultural Commodities, 2001=100, 2001-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIA2-21 provides a longer perspective of the price index of US nonagricultural commodities from 1982 to 2014. Increases and decreases around the global contraction after 2007 were caused by carry trade induced by unconventional monetary policy.
Chart IIA2-21, US, Exports Price Index of Nonagricultural Commodities, 2001=100, 1982-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Finally, Chart IIA2-22 provides 12-month percentage changes of the price index of US exports of nonagricultural commodities from 1986 to 2014. The wide swings before, during and after the global recession beginning in 2007 were caused by carry trades induced by unconventional monetary policy.
Chart IIA2-22, US, Exports Price Index of Nonagricultural Commodities, 12-Month Percentage Changes, 1986-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014.




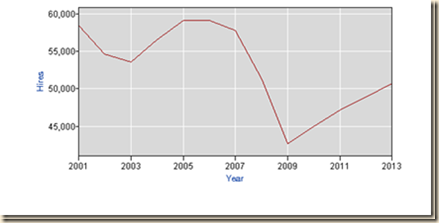






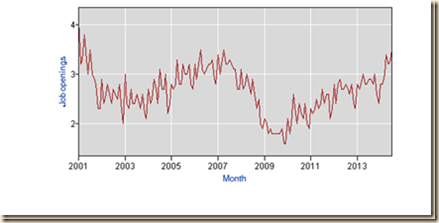




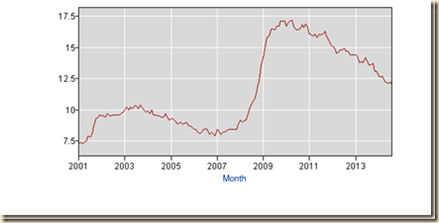
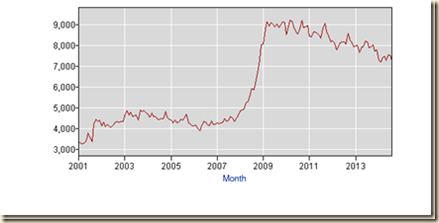


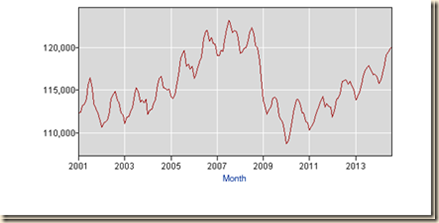


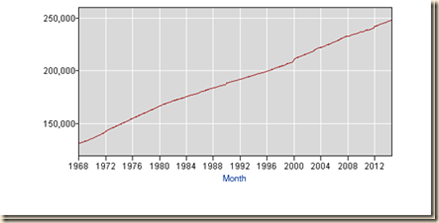

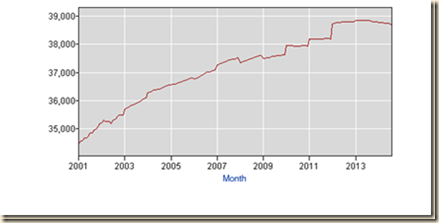
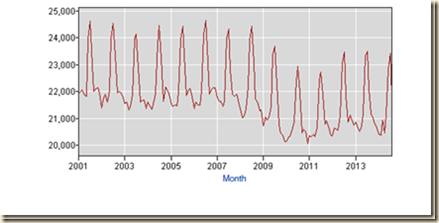





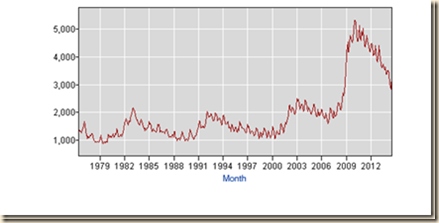













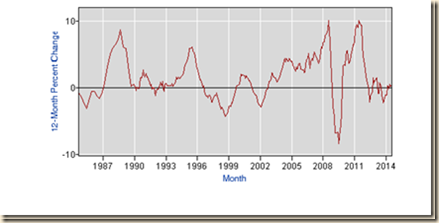



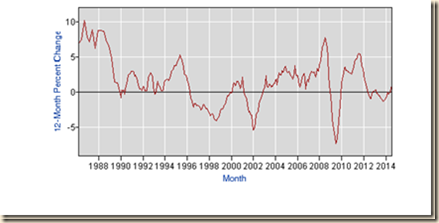









No comments:
Post a Comment