IMF View of World Economy and Finance, Global Financial and Economic Risk and World Economic Slowdown
Carlos M. Pelaez
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2010, 2011, 2012
Executive Summary
I IMF View of World Economy and Finance
IA IMF Diagnosis and Policy
IA1 World Economy
IA2 Global Finance
IA3 Fiscal Imbalances
IA4 IMF Firewall
IB IMF Projections
II Global Financial and Economic Risk
III World Financial Turbulence
IIIA Financial Risks
IIIB Appendix on Safe Haven Currencies
IIIC Appendix on Fiscal Compact
IIID Appendix on European Central Bank Large Scale Lender of Last Resort
IIIE Appendix Euro Zone Survival Risk
IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation
II Global Financial and Economic Risk
IV Global Inflation
V World Economic Slowdown
VA United States
VB Japan
VC China
VD Euro Area
VE Germany
VF France
VG Italy
VH United Kingdom
VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets
VII Economic Indicators
VIII Interest Rates
IX Conclusion
References
Appendix I The Great Inflation
Executive Summary
ESI IMF Role. The International Financial Institutions (IFI) consist of the International Monetary Fund, World Bank Group, Bank for International Settlements (BIS) and the multilateral development banks, which are the European Investment Bank, Inter-American Development Bank and the Asian Development Bank (Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), The Global Recession Risk (2007), 8-19, 218-29, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008b), 114-48, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 145-54). There are four types of contributions of the IFIs:
1. Safety Net. The IFIs contribute to crisis prevention and crisis resolution.
i. Crisis Prevention. An important form of contributing to crisis prevention is by surveillance of the world economy and finance by regions and individual countries. The IMF and World Bank conduct periodic regional and country evaluations and recommendations in consultations with member countries and also jointly with other international organizations. The IMF and the World Bank have been providing the Financial Sector Assessment Program (FSAP) by monitoring financial risks in member countries that can serve to mitigate them before they can become financial crises.
ii. Crisis Resolution. The IMF jointly with other IFIs provides assistance to countries in resolution of those crises that do occur. Currently, the IMF is cooperating with the government of Greece, European Union and European Central Bank in resolving the debt difficulties of Greece as it has done in the past in numerous other circumstances. Programs with other countries involved in the European debt crisis may also be developed.
2. Surveillance. The IMF conducts surveillance of the world economy, finance and public finance with continuous research and analysis. Important documents of this effort are the World Economic Outlook of which the current one is IMF (2012WEOApr), Global Financial Stability Report of which the current one is IMF (2012 GFSRApr) and Fiscal Monitor of which the current one is IMF (2012FMApr).
3. Infrastructure and Development. The IFIs also engage in infrastructure and development, in particular the World Bank Group and the multilateral development banks.
4. Soft Law. Significant activity by IFIs has consisted of developing standards and codes under multiple forums. It is easier and faster to negotiate international agreements under soft law that are not binding but can be very effective (on soft law see Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008c), 114-25). These norms and standards can solidify world economic and financial arrangements.
ESII IMF Firewall. A critical development in the resolution of the European debt crisis is the increase in available resources of the IMF announced in a joint statement of the IMFC and the Group of 20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors (IMFC 2012Apr20):
“There are firm commitments to increase resources made available to the IMF by over $430 billion in addition to the quota increase under the 2010 reform. These resources will be available for the whole membership of the IMF, and not earmarked for any particular region.”
Resources are not earmarked for the European debt crisis but it is the most threatening current vulnerability in the world economy.
ESIII IMF World Economy. Blanchard (2012WEOApr) finds that interest rates close to zero in advanced economies have not induced higher economic growth because of two main factors—fiscal consolidation and deleveraging—that restrict economic growth in the short-term. First, Blanchard (2012WEOApr, XIII) finds that assuming a multiplier of unity of the fiscal deficit on GDP, decrease of the cyclically-adjusted deficit of advanced economies by 1 percent would reduce economic growth by one percentage point. Second, deleveraging by banks, occurring mainly in Europe, tightens credit supply with similar reduction of euro area economic growth by one percentage point in 2012. The baseline of the World Economic Outlook (WEO) of the IMF (2012WEOApr) for Apr 2012 incorporates both effects, which results in weak economic growth, in particular in Europe, and prolonged unemployment. An important analysis by Blanchard (2012WEOApr, XIII) is that “financial uncertainty, together with sharp shifts in risk appetite, has led to volatile capital flows.” Blanchard (2012WEOApr) still finds that the greatest vulnerability is another profound crisis in Europe (ECB). Crisis prevention should buttress the resilience of affected countries during those shifts in risk appetite. The role of the enhanced firewall of the IMF, European Union (EU) and European Central Bank is gaining time during which countries could engage in fiscal consolidation and structural reforms that would diminish the shifts in risk appetite, preventing devastating effects of financial crises. Volatility in capital flows is equivalent to volatility of valuations of risk financial assets. The challenge to the policy mix consists in balancing the adverse short-term effects of fiscal consolidation and deleveraging with the beneficial long-term effects of eliminating the vulnerability to shocks of risk aversion. Blanchard (2012WEOApr) finds that policy should seek short-term credibility while implementing measures that restrict the path of expenditures together with simultaneous development of institutions and rules that constrain deficits and spending in the future. There is similar policy challenge in deleveraging banks, which is required for sound lending institutions, but without causing an adverse credit crunch. Advanced economies face a tough policy challenge of increasing demand and potential growth. Although the forecasts of the WEO (IMF 2012WEOApr) reduce growth of emerging economies relative to the forecasts of Sep 2012, the projections still show emerging economies enjoying sustained economic growth.
ESMIV IMF Global Finance. The Global Financial Stability Report (GFSR) of the IMF (2012GFSRApr, 31) finds three drivers of balance sheets of European banks. (1) There are still loans in bank balance sheets that have not been adequately resolved; banks receiving government support must increase their competitiveness, requiring changing in volume and structure of assets; and there are requirements to dispose of some business lines. (2) Increasing capital buffers requires reduction of assets. (3) Reduction of reliance on less reliable wholesale funding prompts changes in volume and structure of bank assets. The policy challenge consists in improving the soundness of the financial system without creating a credit crunch with damaging effects on growth and employment. The IMF (2012GFSRApr, 33) estimates that after using retained earnings and new capital provided in stress tests of the European Banking Authority (EBA), banks would still have to reduce assets by $2.6 trillion, or about €2.0 trillion, which is equivalent to reducing the size of the total balance sheet by 7 percent. The estimate of the Global Financial Stability Report (GFSR) is that one quarter of the reduction of the balance sheets of banks would be obtained by reducing loans with the remainder in the form of selling subsidiaries, noncore assets and securities (IMF 2012GFSRApr, 33). Banks in the sample used by the IMF reduced their assets by $580 billion in IVQ2011.
Spain continues to drive euro area credit risk with hurdles in adjusting its high fiscal deficit, domestic economic recession, high unemployment and unresolved bank balance sheets. The Bank of Spain released on Apr 18 new worrisome data on delinquent credit in Spain’s credit institutions (http://www.bde.es/webbde/es/secciones/prensa/Agenda/Datos_de_credit_c62379ebaa85631.html). The aggregate balance sheet of institutions supervised by the Bank of Spain registered total credit of €1,508,626 million in 2006 with delinquent credit of €10,859 million or 0.7 percent. The latest available data for Feb 2012 registers total credit of €1,763,312 million with delinquent credit of €143,815 million or 8.2 percent. Total credit has contracted from a peak of €1,869,882 million in 2008 to €1,763,313 on Feb 2012 or by 5.7 percent. Delinquent credit has risen from €10,859 million in 2006 to €143,815 million in Feb 2012 or by 1224 percent. The credit standing of Spain may be further imperiled if the country is forced into bank nationalizations or absorptions of bad loans by the government. There is troubled history of government ownership and control of banks (Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance: Theory and Policy after the Credit Crisis (2009b), 227-9; Pelaez 1975, Pelaez and Suzigan 1981, following Cameron 1961, 1967, 1972).
ESV IMF Projections. Table ESV-1 is constructed with the database of the IMF (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/index.aspx) to show GDP in dollars in 2010 and the growth rate of real GDP of the world and selected regional countries from 2011 to 2014. The data illustrate the concept often repeated of “two-speed recovery” of the world economy from the recession of 2007 to 2009. The IMF has lowered its forecast of the world economy to 3.5 percent in 2012 but accelerating to 4.1 percent in 2013, 4.4 percent in 2014 and 4.5 percent in 2015. Slow-speed recovery occurs in the “major advanced economies” of the G7 that account for $33,670 billion of world output of $69,660 billion, or 48.3 percent, but are projected to grow at much lower rates than world output, 2.1 percent on average from 2012 to 2015 in contrast with 4.1 percent for the world as a whole. While the world would grow 17.6 percent in the four years from 2012 to 2015, the G7 as a whole would grow 8.5 percent. The difference in dollars of 2011 is rather high: growing by 17.6 percent would add $12.3 trillion of output to the world economy, or roughly two times the output of the economy of Japan of $5,869 but growing by 8.5 percent would add $5.9 trillion of output to the world, or about the output of Japan in 2011. The “two speed” concept is in reference to the growth of the 150 countries labeled as emerging and developing economies (EMDE) with joint output in 2011 of $25,237 billion, or 36.2 percent of world output. The EMDEs would grow cumulatively 26.5 percent or at the average yearly rate of 6.1 percent, contributing $6.7 trillion from 2012 to 2015 or the equivalent of somewhat less than the GDP of $7,298 billion of China in 2011. The final four countries in Table ESV-1 often referred as BRIC (Brazil, Russia, India, China), are large, rapidly growing emerging economies. Their combined output adds to $13,317 billion, or 19.1 percent of world output, which is equivalent to 39.6 percent of the combined output of the major advanced economies of the G7.
Table ESV-1, IMF World Economic Outlook Database Projections of Real GDP Growth
| GDP USD 2011 | Real GDP ∆% | Real GDP ∆% | Real GDP ∆% | Real GDP ∆% | |
| World | 69,660 | 3.5 | 4.1 | 4.4 | 4.5 |
| G7 | 33,670 | 1.5 | 1.9 | 2.3 | 2.5 |
| Canada | 1,737 | 2.1 | 2.2 | 2.4 | 2.4 |
| France | 2,776 | 0.5 | 1.1 | 1.9 | 1.9 |
| DE | 3,577 | 0.6 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.3 |
| Italy | 2,199 | -1.9 | -0.3 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
| Japan | 5,869 | 2.0 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 1.3 |
| UK | 2,418 | 0.8 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 2.6 |
| US | 15,094 | 2.1 | 2.4 | 2.9 | 3.3 |
| Euro Area | 13,115 | -0.3 | 0.9 | 1.4 | 1.6 |
| DE | 3,577 | 0.6 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.3 |
| France | 2,776 | 0.5 | 1.1 | 1.9 | 1.9 |
| Italy | 2,199 | -1.9 | -0.3 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
| POT | 239 | -3.3 | 0.3 | 2.1 | 1.9 |
| Ireland | 218 | 0.5 | 2.1 | 2.5 | 2.8 |
| Greece | 303 | -4.7 | 0.0 | 2.5 | 3.1 |
| Spain | 1,494 | -1.8 | 0.1 | 1.6 | 1.6 |
| EMDE | 25,237 | 5.7 | 6.0 | 6.2 | 6.3 |
| Brazil | 2,493 | 3.0 | 4.2 | 4.0 | 4.1 |
| Russia | 1,850 | 4.0 | 3.9 | 3.9 | 3.9 |
| India | 1,676 | 6.9 | 7.3 | 7.5 | 7.7 |
| China | 7,298 | 8.2 | 8.8 | 8.7 | 8.7 |
Notes; DE: Germany; EMDE: Emerging and Developing Economies (150 countries); POT: Portugal
Source: IMF World Economic Outlook databank
http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/index.aspx
Continuing high rates of unemployment in advanced economies constitute another characteristic of the database of the WEO (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/index.aspx). Table ESV-2 is constructed with the WEO database to provide rates of unemployment from 2011 to 2015 for major countries and regions. In fact, unemployment rates for 2011 in Table ESV-2 are high for all countries: unusually high for countries with high rates most of the time and unusually high for countries with low rates most of the time. The rates of unemployment are particularly high for the countries with sovereign debt difficulties in Europe: 12.7 percent for Portugal (POT), 14.4 percent for Ireland, 17.3 percent for Greece, 21.6 percent for Spain and 8.4 percent for Italy, which is lower but still high. The G7 rate of unemployment is 7.7 percent. Unemployment rates are not likely to decrease substantially if slow growth persists in advanced economies.
Table ESV-2, IMF World Economic Outlook Database Projections of Unemployment Rate as Percent of Labor Force
| % Labor Force 2011 | % Labor Force 2012 | % Labor Force 2013 | % Labor Force 2014 | % Labor Force 2015 | |
| World | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| G7 | 7.7 | 7.4 | 7.3 | 7.0 | 6.7 |
| Canada | 7.5 | 7.4 | 7.3 | 7.1 | 6.9 |
| France | 9.7 | 9.9 | 10.1 | 9.8 | 9.4 |
| DE | 6.0 | 5.6 | 5.5 | 5.3 | 5.3 |
| Italy | 8.4 | 9.5 | 9.7 | 9.8 | 9.5 |
| Japan | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.4 | 4.3 | 4.2 |
| UK | 8.0 | 8.3 | 8.2 | 7.8 | 7.4 |
| US | 8.9 | 8.2 | 7.9 | 7.5 | 6.9 |
| Euro Area | 10.1 | 10.9 | 10.8 | 10.5 | 10.1 |
| DE | 6.0 | 5.6 | 5.5 | 5.3 | 5.3 |
| France | 9.7 | 9.9 | 10.1 | 9.8 | 9.4 |
| Italy | 8.4 | 9.5 | 9.7 | 9.8 | 9.5 |
| POT | 12.7 | 14.3 | 13.9 | 13.2 | 12.4 |
| Ireland | 14.4 | 14.5 | 13.8 | 12.9 | 12.0 |
| Greece | 17.3 | 19.4 | 19.4 | 18.2 | 16.8 |
| Spain | 21.6 | 24.2 | 23.9 | 22.8 | 21.9 |
| EMDE | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Brazil | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.5 | 7.0 | 7.0 |
| Russia | 7.5 | 6.5 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 |
| India | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| China | 4.1 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 |
Notes; DE: Germany; EMDE: Emerging and Developing Economies (150 countries)
Source: IMF World Economic Outlook databank http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/weoselgr.aspx
ESVI Euro Area Survival. Brazil faced in the debt crisis of 1982 a more complex policy mix. Between 1977 and 1983, Brazil’s terms of trade, export prices relative to import prices, deteriorated 47 percent and 36 percent excluding oil (Pelaez 1987, 176-79; Pelaez 1986, 37-66; see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 178-87). Brazil had accumulated unsustainable foreign debt by borrowing to finance balance of payments deficits during the 1970s. Foreign lending virtually stopped. The German mark devalued strongly relative to the dollar such that Brazil’s products lost competitiveness in Germany and in multiple markets in competition with Germany. The resolution of the crisis was devaluation of the Brazilian currency by 30 percent relative to the dollar and subsequent maintenance of parity by monthly devaluation equal to inflation and indexing that resulted in financial stability by parity in external and internal interest rates avoiding capital flight. With a combination of declining imports, domestic import substitution and export growth, Brazil followed rapid growth in the US and grew out of the crisis with surprising GDP growth of 4.5 percent in 1984.
The euro zone faces a critical survival risk because several of its members may default on their sovereign obligations if not bailed out by the other members. The valuation equation of bonds is essential to understanding the stability of the euro area. An explanation is provided in this paragraph and readers interested in technical details are referred Subsection IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation. Contrary to the Wriston doctrine, investing in sovereign obligations is a credit decision. The value of a bond today is equal to the discounted value of future obligations of interest and principal until maturity. On Dec 30 the yield of the 2-year bond of the government of Greece was quoted around 100 percent. In contrast, the 2-year US Treasury note traded at 0.239 percent and the 10-year at 2.871 percent while the comparable 2-year government bond of Germany traded at 0.14 percent and the 10-year government bond of Germany traded at 1.83 percent. There is no need for sovereign ratings: the perceptions of investors are of relatively higher probability of default by Greece, defying Wriston (1982), and nil probability of default of the US Treasury and the German government. The essence of the sovereign credit decision is whether the sovereign will be able to finance new debt and refinance existing debt without interrupting service of interest and principal. Prices of sovereign bonds incorporate multiple anticipations such as inflation and liquidity premiums of long-term relative to short-term debt but also risk premiums on whether the sovereign’s debt can be managed as it increases without bound. The austerity measures of Italy are designed to increase the primary surplus, or government revenues less expenditures excluding interest, to ensure investors that Italy will have the fiscal strength to manage its debt of 120 percent of GDP, which is the third largest in the world after the US and Japan. Appendix IIIE links the expectations on the primary surplus to the real current value of government monetary and fiscal obligations. As Blanchard (2011SepWEO) analyzes, fiscal consolidation to increase the primary surplus is facilitated by growth of the economy. Italy and the other indebted sovereigns in Europe face the dual challenge of increasing primary surpluses while maintaining growth of the economy (for the experience of Brazil in the debt crisis of 1982 see Pelaez 1986, 1987).
Much of the analysis and concern over the euro zone centers on the lack of credibility of the debt of a few countries while there is credibility of the debt of the euro zone as a whole. In practice, there is convergence in valuations and concerns toward the fact that there may not be credibility of the euro zone as a whole. The fluctuations of financial risk assets of members of the euro zone move together with risk aversion toward the countries with lack of debt credibility. This movement raises the need to consider analytically sovereign debt valuation of the euro zone as a whole in the essential analysis of whether the single-currency will survive without major changes.
Welfare economics considers the desirability of alternative states, which in this case would be evaluating the “value” of Germany (1) within and (2) outside the euro zone. Is the sum of the wealth of euro zone countries outside of the euro zone higher than the wealth of these countries maintaining the euro zone? On the choice of indicator of welfare, Hicks (1975, 324) argues:
“Partly as a result of the Keynesian revolution, but more (perhaps) because of statistical labours that were initially quite independent of it, the Social Product has now come right back into its old place. Modern economics—especially modern applied economics—is centered upon the Social Product, the Wealth of Nations, as it was in the days of Smith and Ricardo, but as it was not in the time that came between. So if modern theory is to be effective, if it is to deal with the questions which we in our time want to have answered, the size and growth of the Social Product are among the chief things with which it must concern itself. It is of course the objective Social Product on which attention must be fixed. We have indexes of production; we do not have—it is clear we cannot have—an Index of Welfare.”
If the burden of the debt of the euro zone falls on Germany and France or only on Germany, is the wealth of Germany and France or only Germany higher after breakup of the euro zone or if maintaining the euro zone? In practice, political realities will determine the decision through elections.
The prospects of survival of the euro zone are dire. Table ESVI-1 is constructed with IMF World Economic Outlook database (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/index.aspx) for GDP in USD billions, primary net lending/borrowing as percent of GDP and general government debt as percent of GDP for selected regions and countries in 2010.
Table ESVI-1, World and Selected Regional and Country GDP and Fiscal Situation
| GDP 2012 | Primary Net Lending Borrowing | General Government Net Debt | |
| World | 69,660 | ||
| Euro Zone | 12,586 | -0.5 | 70.3 |
| Portugal | 221 | 0.1 | 110.9 |
| Ireland | 210 | -4.4 | 102.9 |
| Greece | 271 | -1.0 | 153.2 |
| Spain | 1,398 | -3.6 | 67.0 |
| Major Advanced Economies G7 | 34,106 | -4.8 | 88.3 |
| United States | 15,610 | -6.1 | 83.7 |
| UK | 2,453 | -5.3 | 84.2 |
| Germany | 3,479 | 1.0 | 54.1 |
| France | 2,712.0 | -2.2 | 83.2 |
| Japan | 5,981 | -8.9 | 135.2 |
| Canada | 1,805 | -3.1 | 35.4 |
| Italy | 2,067 | 2.9 | 102.3 |
| China | 7992 | -1.3* | 22.0** |
*Net Lending/borrowing**Gross Debt
Source: http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/weoselgr.aspx
The data in Table ESVI-1 are used for some very simple calculations in Table ESVI-2. The column “Net Debt USD Billions” in Table ESVI-1 is generated by applying the percentage in Table ESVI-2 column “General Government Net Debt % GDP 2010” to the column “GDP USD Billions.” The total debt of France and Germany in 2012 is $4138.5 billion, as shown in row “B+C” in column “Net Debt USD Billions” The sum of the debt of Italy, Spain, Portugal, Greece and Ireland is $3927.8 billion, adding rows D+E+F+G+H in column “Net Debt USD billions.” There is some simple “unpleasant bond arithmetic” in the two final columns of Table ESVI-2. Suppose the entire debt burdens of the five countries with probability of default were to be guaranteed by France and Germany, which de facto would be required by continuing the euro zone. The sum of the total debt of these five countries and the debt of France and Germany is shown in column “Debt as % of Germany plus France GDP” to reach $8066.3 billion, which would be equivalent to 130.3 percent of their combined GDP in 2012. Under this arrangement the entire debt of the euro zone including debt of France and Germany would not have nil probability of default. The final column provides “Debt as % of Germany GDP” that would exceed 231.9 percent if including debt of France and 167.0 percent of German GDP if excluding French debt. The unpleasant bond arithmetic illustrates that there is a limit as to how far Germany and France can go in bailing out the countries with unsustainable sovereign debt without incurring severe pains of their own such as downgrades of their sovereign credit ratings. A central bank is not typically engaged in direct credit because of remembrance of inflation and abuse in the past. There is also a limit to operations of the European Central Bank in doubtful credit obligations. Wriston (1982) would prove to be wrong again that countries do not bankrupt but would have a consolation prize that similar to LBOs the sum of the individual values of euro zone members outside the current agreement exceeds the value of the whole euro zone. Internal rescues of French and German banks may be less costly than bailing out other euro zone countries so that they do not default on French and German banks.
Table ESVI-2, Guarantees of Debt of Sovereigns in Euro Area as Percent of GDP of Germany and France, USD Billions and %
| Net Debt USD Billions | Debt as % of Germany Plus France GDP | Debt as % of Germany GDP | |
| A Euro Area | 8,847.9 | ||
| B Germany | 1,882.1 | $8066.3 as % of $3479 =231.9% $5809.9 as % of $3479 =167.0% | |
| C France | 2,256.4 | ||
| B+C | 4,138.5 | GDP $6,191.0 Total Debt $8066.3 Debt/GDP: 130.3% | |
| D Italy | 2,114.5 | ||
| E Spain | 936.7 | ||
| F Portugal | 245.3 | ||
| G Greece | 415.2 | ||
| H Ireland | 216.1 | ||
| Subtotal D+E+F+G+H | 3,927.8 |
Source: calculation with IMF data http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/index.aspx
ESVII Global Imbalances. The database of the World Economic Outlook (WEO) of the IMF (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/index.aspx) is used to contract Table ESVII-1 with fiscal and current account imbalances projected for 2011 and 2015. The WEO finds the need to rebalance external and domestic demand (IMF 2011WEOSep xvii):
“Progress on this front has become even more important to sustain global growth. Some emerging market economies are contributing more domestic demand than is desirable (for example, several economies in Latin America); others are not contributing enough (for example, key economies in emerging Asia). The first set needs to restrain strong domestic demand by considerably reducing structural fiscal deficits and, in some cases, by further removing monetary accommodation. The second set of economies needs significant currency appreciation alongside structural reforms to reduce high surpluses of savings over investment. Such policies would help improve their resilience to shocks originating in the advanced economies as well as their medium-term growth potential.”
The IMF (2012WEOApr, XVII) explains decreasing importance of the issue of global imbalances as follows:
“The latest developments suggest that global current account imbalances are no longer expected to widen again, following their sharp reduction during the Great Recession. This is largely because the excessive consumption growth that characterized economies that ran large external deficits prior to the crisis has been wrung out and has not been offset by stronger consumption in surplus economies. Accordingly, the global economy has experienced a loss of demand and growth in all regions relative to the boom years just before the crisis. Rebalancing activity in key surplus economies toward higher consumption, supported by more market-determined exchange rates, would help strengthen their prospects as well as those of the rest of the world.”
Table ESVII-1, Fiscal Deficit, Current Account Deficit and Government Debt as % of GDP and 2011 Dollar GDP
| GDP 2011 | FD | CAD | Debt | FD%GDP | CAD%GDP | Debt | |
| US | 15094 | -7.3 | -3.1 | 80.3 | -2.3 | -3.2 | 88.3 |
| Japan | 5869 | -9.1 | 2.0 | 126.6 | -5.8 | 2.4 | 155.0 |
| UK | 2418 | -5.8 | -1.9 | 78.3 | -0.8 | -0.4 | 88.1 |
| Euro | 13115 | -1.6 | 0.3 | 68.4 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 71.3 |
| Ger | 3577 | 0.7 | 5.7 | 56.1 | 1.4 | 4.3 | 52.4 |
| France | 2776 | -2.9 | -2.2 | 80.4 | 0.3 | -0.8 | 83.8 |
| Italy | 2199 | 0.8 | -3.2 | 99.6 | 4.4 | -1.6 | 101.5 |
| Can | 1737 | -4.1 | -2.8 | 33.3 | -1.1 | -2.5 | 37.4 |
| China | 7298 | -1.2 | 2.7 | 25.8 | -0.1 | 3.4 | 14.8 |
| Brazil | 2493 | 3.1 | -2.1 | 36.4 | 3.1 | -3.4 | 31.9 |
Note: GER = Germany; Can = Canada; FD = fiscal deficit; CAD = current account deficit
FD is primary except total for China; Debt is net except gross for China
Source: http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/weoselgr.aspx
ESVIII Global Financial and Economic Risk. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) provides an international safety net for prevention and resolution of international financial crises. The IMF’s Financial Sector Assessment Program (FSAP) provides analysis of the economic and financial sectors of countries (see Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), 101-62, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008), 114-23). Relating economic and financial sectors is a challenging task both for theory and measurement. The IMF provides surveillance of the world economy with its Global Economic Outlook (WEO) (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/update/01/index.htm), of the world financial system with its Global Financial Stability Report (GFSR) (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fmu/eng/2012/01/index.htm) and of fiscal affairs with the Fiscal Monitor (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fm/2012/update/01/fmindex.htm). There appears to be a moment of transition in global economic and financial variables that may prove of difficult analysis and measurement. It is useful to consider a summary of global economic and financial risks, which are analyzed in detail in the comments of this blog in Section VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets, Table VI-4.
Economic risks include the following:
1. China’s Economic Growth. China is lowering its growth target to 7.5 percent per year. The growth rate of GDP of China in the first quarter of 2012 of 1.8 percent is equivalent to 7.4 percent per year
2. United States Economic Growth, Labor Markets and Budget/Debt Quagmire. The US is growing slowly with 30.5 million in job stress, fewer 10 million full-time jobs, high youth unemployment, historically-low hiring and declining real wages.
3. Economic Growth and Labor Markets in Advanced Economies. Advanced economies are growing slowly. There is still high unemployment in advanced economies.
4. World Inflation Waves. Inflation continues in repetitive waves globally (see Section I Inflation Waves at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/03/global-financial-and-economic-risk.html).
A list of financial uncertainties includes:
1. Euro Area Survival Risk. The resilience of the euro to fiscal and financial doubts on larger member countries is still an unknown risk.
2. Foreign Exchange Wars. Exchange rate struggles continue as zero interest rates in advanced economies induce devaluation of their currencies.
3. Valuation of Risk Financial Assets. Valuations of risk financial assets have reached extremely high levels in markets with lower volumes.
4. Duration Trap of the Zero Bound. The yield of the US 10-year Treasury rose from 2.031 percent on Mar 9, 2012, to 2.294 percent on Mar 16, 2012. Considering a 10-year Treasury with coupon of 2.625 percent and maturity in exactly 10 years, the price would fall from 105.3512 corresponding to yield of 2.031 percent to 102.9428 corresponding to yield of 2.294 percent, for loss in a week of 2.3 percent but far more in a position with leverage of 10:1. Min Zeng, writing on “Treasurys fall, ending brutal quarter,” published on Mar 30, 2012, in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052702303816504577313400029412564.html?mod=WSJ_hps_sections_markets), informs that Treasury bonds maturing in more than 20 years lost 5.52 percent in the first quarter of 2012.
5. Credibility and Commitment of Central Bank Policy. There is a credibility issue of the commitment of monetary policy (Sargent and Silber 2012Mar20).
6. Carry Trades. Commodity prices driven by zero interest rates have resumed their increasing path.
It is in this context of economic and financial uncertainties that decisions on portfolio choices of risk financial assets must be made. There is a new carry trade that learned from the losses after the crisis of 2007 or learned from the crisis how to avoid losses. The sharp rise in valuations of risk financial assets shown in Table VI-1 after the first policy round of near zero fed funds and quantitative easing by the equivalent of withdrawing supply with the suspension of the 30-year Treasury auction was on a smooth trend with relatively subdued fluctuations. The credit crisis and global recession have been followed by significant fluctuations originating in sovereign risk issues in Europe, doubts of continuing high growth and accelerating inflation in China now complicated by political developments, events such as in the Middle East and Japan and legislative restructuring, regulation, insufficient growth, falling real wages, depressed hiring and high job stress of unemployment and underemployment in the US now with realization of growth standstill. The “trend is your friend” motto of traders has been replaced with a “hit and realize profit” approach of managing positions to realize profits without sitting on positions. There is a trend of valuation of risk financial assets driven by the carry trade from zero interest rates with fluctuations provoked by events of risk aversion or the “sharp shifts in risk appetite” of Blanchard (2012WEOApr, XIII). Table ESVIII-1, which is updated for every comment of this blog, shows the deep contraction of valuations of risk financial assets after the Apr 2010 sovereign risk issues in the fourth column “∆% to Trough.” There was sharp recovery after around Jul 2010 in the last column “∆% Trough to 4/20/12,” which has been recently stalling or reversing amidst profound risk aversion. “Let’s twist again” monetary policy during the week of Sep 23 caused deep worldwide risk aversion and selloff of risk financial assets (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/09/imf-view-of-world-economy-and-finance.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/09/collapse-of-household-income-and-wealth.html). Monetary policy was designed to increase risk appetite but instead suffocated risk exposures. There has been rollercoaster fluctuation in risk aversion and financial risk asset valuations: surge in the week of Dec 2, mixed performance of markets in the week of Dec 9, renewed risk aversion in the week of Dec 16, end-of-the-year relaxed risk aversion in thin markets in the weeks of Dec 23 and Dec 30, mixed sentiment in the weeks of Jan 6 and Jan 13 2012 and strength in the weeks of Jan 20, Jan 27 and Feb 3 followed by weakness in the week of Feb 10 but strength in the weeks of Feb 17 and 24 followed by uncertainty on financial counterparty risk in the weeks of Mar 2 and Mar 9. All financial values have fluctuated with events such as the surge in the week of Mar 16 on favorable news of Greece’s bailout even with new risk issues arising in the week of Mar 23 but renewed risk appetite in the week of Mar 30 because of the end of the quarter and the increase in the firewall of support of sovereign debts in the euro area. New risks developed in the week of Apr 6 with increase of yields of sovereign bonds of Spain and Italy, doubts on Fed policy and weak employment report. Asia and financial entities are experiencing their own risk environments. Financial markets were under stress in the week of Apr 13 because of the large exposure of Spanish banks to lending by the European Central Bank and the annual equivalent growth rate of China’s GDP of 7.4 percent in IQ2012. There was strength again in the week of Apr 20 because of the enhanced IMF firewall and Spain placement of debt. The highest valuations in column “∆% Trough to 4/20/12” are by US equities indexes: DJIA 34.5 percent and S&P 500 34.8 percent, driven by stronger earnings and economy in the US than in other advanced economies. The DJIA reached in intraday trading 13,331.77 on Mar 16, which is the highest level in 52 weeks (http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_PRO_hps_marketdata). The carry trade from zero interest rates to leveraged positions in risk financial assets had proved strongest for commodity exposures but US equities have regained leadership. Before the current round of risk aversion, all assets in the column “∆% Trough to 4/20/12” had double digit gains relative to the trough around Jul 2, 2010 but now only three valuation show increase of less than 10 percent: China’s Shanghai Composite is 1.0 percent above the trough; STOXX 50 of Europe is 5.6 percent above the trough; and Japan’s Nikkei Average is 8.4 percent above the trough. DJ UBS Commodities is 11.5 percent above the trough; Dow Global is 13.2 percent above the trough; and DAX is 19.0 percent above the trough. Japan’s Nikkei Average is 8.4 percent above the trough on Aug 31, 2010 and 16.1 percent below the peak on Apr 5, 2010. The Nikkei Average closed at 9561.36 on Fri Apr 20, 2012 (http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_PRO_hps_marketdata), which is 6.8 percent lower than 10,254.43 on Mar 11, 2011, on the date of the Great East Japan Earthquake/tsunami. Global risk aversion erased the earlier gains of the Nikkei. The dollar depreciated by 10.9 percent relative to the euro and even higher before the new bout of sovereign risk issues in Europe. The column “∆% week to 4/20/12” in Table ESVIII-1 shows increases of most valuations of risk financial assets in the week of Apr 20, 2012, with exception of decline of 0.8 percent by Japan’s Nikkei Average and decline of 0.6 percent for DJ Asia Pacific. There are still high uncertainties on European sovereign risks, US and world growth slowdown and China’s growth tradeoffs. Sovereign problems in the “periphery” of Europe and fears of slower growth in Asia and the US cause risk aversion with trading caution instead of more aggressive risk exposures. There is a fundamental change in Table ESVIII-1 from the relatively upward trend with oscillations since the sovereign risk event of Apr-Jul 2010. Performance is best assessed in the column “∆% Peak to 4/20/12” that provides the percentage change from the peak in Apr 2010 before the sovereign risk event to Apr 6, 2012. Most risk financial assets had gained not only relative to the trough as shown in column “∆% Trough to 4/20/12” but also relative to the peak in column “∆% Peak to 4/20/12.” There are now only three equity indexes above the peak in Table ESVIII-1: DJIA 16.3 percent, S&P 500 13.2 percent and Dax 6.6 percent. There are several indexes below the peak: NYSE Financial Index (http://www.nyse.com/about/listed/nykid.shtml) by 13.1 percent, Nikkei Average by 16.1 percent, Shanghai Composite by 23.9 percent, STOXX 50 by 10.6 percent and Dow Global by 7.7 percent. DJ UBS Commodities Index is now 4.7 percent below the peak. The factors of risk aversion have adversely affected the performance of risk financial assets. The performance relative to the peak in Apr 2010 is more important than the performance relative to the trough around early Jul because improvement could signal that conditions have returned to normal levels before European sovereign doubts in Apr 2010. An intriguing issue is the difference in performance of valuations of risk financial assets and economic growth and employment. Paul A. Samuelson (http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/economics/laureates/1970/samuelson-bio.html) popularized the view of the troubled relation between stock markets and economic activity in an often-quoted phrase “the stock market has forecast nine of the last five recessions.” In the presence of zero interest rates forever, valuations of risk financial assets are likely to differ from the performance of the overall economy.
Table ESVIII-1, Stock Indexes, Commodities, Dollar and 10-Year Treasury
| Peak | Trough | ∆% to Trough | ∆% Peak to 4/20 /12 | ∆% Week 4/20/ 12 | ∆% Trough to 4/20 12 | |
| DJIA | 4/26/ | 7/2/10 | -13.6 | 16.3 | 1.4 | 34.5 |
| S&P 500 | 4/23/ | 7/20/ | -16.0 | 13.2 | 0.6 | 34.8 |
| NYSE Finance | 4/15/ | 7/2/10 | -20.3 | -13.1 | 1.0 | 9.0 |
| Dow Global | 4/15/ | 7/2/10 | -18.4 | -7.7 | 0.9 | 13.2 |
| Asia Pacific | 4/15/ | 7/2/10 | -12.5 | -2.9 | -0.6 | 10.9 |
| Japan Nikkei Aver. | 4/05/ | 8/31/ | -22.5 | -16.1 | -0.8 | 8.4 |
| China Shang. | 4/15/ | 7/02 | -24.7 | -23.9 | 2.0 | 1.0 |
| STOXX 50 | 4/15/10 | 7/2/10 | -15.3 | -10.6 | 2.4 | 5.6 |
| DAX | 4/26/ | 5/25/ | -10.5 | 6.6 | 2.5 | 19.0 |
| Dollar | 11/25 2009 | 6/7 | 21.2 | 12.6 | -1.1 | -10.9 |
| DJ UBS Comm. | 1/6/ | 7/2/10 | -14.5 | -4.7 | -0.9 | 11.5 |
| 10-Year T Note | 4/5/ | 4/6/10 | 3.986 | 1.959 |
T: trough; Dollar: positive sign appreciation relative to euro (less dollars paid per euro), negative sign depreciation relative to euro (more dollars paid per euro)
Source: http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_hps_marketdata
I IMF View of World Economy and Finance. The International Financial Institutions (IFI) consist of the International Monetary Fund, World Bank Group, Bank for International Settlements (BIS) and the multilateral development banks, which are the European Investment Bank, Inter-American Development Bank and the Asian Development Bank (Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), The Global Recession Risk (2007), 8-19, 218-29, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008b), 114-48, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 145-54). There are four types of contributions of the IFIs:
1. Safety Net. The IFIs contribute to crisis prevention and crisis resolution.
i. Crisis Prevention. An important form of contributing to crisis prevention is by surveillance of the world economy and finance by regions and individual countries. The IMF and World Bank conduct periodic regional and country evaluations and recommendations in consultations with member countries and also jointly with other international organizations. The IMF and the World Bank have been providing the Financial Sector Assessment Program (FSAP) by monitoring financial risks in member countries that can serve to mitigate them before they can become financial crises.
ii. Crisis Resolution. The IMF jointly with other IFIs provides assistance to countries in resolution of those crises that do occur. Currently, the IMF is cooperating with the government of Greece, European Union and European Central Bank in resolving the debt difficulties of Greece as it has done in the past in numerous other circumstances. Programs with other countries involved in the European debt crisis may also be developed.
2. Surveillance. The IMF conducts surveillance of the world economy, finance and public finance with continuous research and analysis. Important documents of this effort are the World Economic Outlook of which the current one is IMF (2012WEOApr), Global Financial Stability Report of which the current one is IMF (2012 GFSRApr) and Fiscal Monitor of which the current one is IMF (2012FMApr).
3. Infrastructure and Development. The IFIs also engage in infrastructure and development, in particular the World Bank Group and the multilateral development banks.
4. Soft Law. Significant activity by IFIs has consisted of developing standards and codes under multiple forums. It is easier and faster to negotiate international agreements under soft law that are not binding but can be very effective (on soft law see Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008c), 114-25). These norms and standards can solidify world economic and financial arrangements.
The objective of this section is to analyze the current view of the IMF on selected critical issues of the world economy (IMF 2012WEOApr), international finance (IMF2012GFSRApr) and global fiscal affairs (IMF2012FMApr). Subsection IA IMF Diagnosis and Policy reviews the mains elements of analysis and policy proposals in the IMF view. Subsection IB IMF Projections provides searches of the IMF database for the most important indicators.
IA IMF Diagnosis and Policy. There are four subsections: IB1 World Economy; IB2 Global Finance; IB3 Fiscal Imbalances; and IB4 IMF Firewall.
IA1 World Economy. Blanchard (2012WEOApr) finds that interest rates close to zero in advanced economies have not induced higher economic growth because of two main factors—fiscal consolidation and deleveraging—that restrict economic growth in the short-term. First, Blanchard (2012WEOApr, XIII) finds that assuming a multiplier of unity of the fiscal deficit on GDP, decrease of the cyclically-adjusted deficit of advanced economies by 1 percent would reduce economic growth by one percentage point. Second, deleveraging by banks, occurring mainly in Europe, tightens credit supply with similar reduction of euro area economic growth by one percentage point in 2012. The baseline of the World Economic Outlook (WEO) of the IMF (2012WEOApr) for Apr 2012 incorporates both effects, which results in weak economic growth, in particular in Europe, and prolonged unemployment. An important analysis by Blanchard (2012WEOApr, XIII) is that “financial uncertainty, together with sharp shifts in risk appetite, has led to volatile capital flows.” Blanchard (2012WEOApr) still finds that the greatest vulnerability is another profound crisis in Europe (ECB). Crisis prevention should buttress the resilience of affected countries during those shifts in risk appetite. The role of the enhanced firewall of the IMF, European Union (EU) and European Central Bank is gaining time during which countries could engage in fiscal consolidation and structural reforms that would diminish the shifts in risk appetite, preventing devastating effects of financial crises. Volatility in capital flows is equivalent to volatility of valuations of risk financial assets. The challenge to the policy mix consists in balancing the adverse short-term effects of fiscal consolidation and deleveraging with the beneficial long-term effects of eliminating the vulnerability to shocks of risk aversion. Blanchard (2012WEOApr) finds that policy should seek short-term credibility while implementing measures that restrict the path of expenditures together with simultaneous development of institutions and rules that constrain deficits and spending in the future. There is similar policy challenge in deleveraging banks, which is required for sound lending institutions, but without causing an adverse credit crunch. Advanced economies face a tough policy challenge of increasing demand and potential growth. Although the forecasts of the WEO (IMF 2012WEOApr) reduce growth of emerging economies relative to the forecasts of Sep 2012, the projections still show emerging economies enjoying sustained economic growth.
IA2 Global Finance. The Global Financial Stability Report (GFSR) of the IMF (2012GFSRApr, 31) finds three drivers of balance sheets of European banks. (1) There are still loans in bank balance sheets that have not been adequately resolved; banks receiving government support must increase their competitiveness, requiring changing in volume and structure of assets; and there are requirements to dispose of some business lines. (2) Increasing capital buffers requires reduction of assets. (3) Reduction of reliance on less reliable wholesale funding prompts changes in volume and structure of bank assets. The policy challenge consists in improving the soundness of the financial system without creating a credit crunch with damaging effects on growth and employment. The IMF (2012GFSRApr, 33) estimates that after using retained earnings and new capital provided in stress tests of the European Banking Authority (EBA), banks would still have to reduce assets by $2.6 trillion, or about €2.0 trillion, which is equivalent to reducing the size of the total balance sheet by 7 percent. The estimate of the Global Financial Stability Report (GFSR) is that one quarter of the reduction of the balance sheets of banks would be obtained by reducing loans with the remainder in the form of selling subsidiaries, noncore assets and securities (IMF 2012GFSRApr, 33). Banks in the sample used by the IMF reduced their assets by $580 billion in IVQ2011.
IA3 Fiscal Imbalances. The Fiscal Monitor (FM) for Apr 2012 of the IMF (2012FMApr) finds tough choices for fiscal management in advanced economies. Choices are constrained by the type of fiscal imbalances in individual countries. There are two broad categories of fiscal situations. First, countries with “fiscal space” may be more careful in maintaining growth and employment in the short term while at the same implementing credible measures and reforms during the medium term. Policies could consist of permitting the deficit to increase by use of automatic stabilizers to avoid excessive fiscal contraction that could reduce growth and employment. The FM finds that the fiscal space lost between 2008 and 2009 should be entirely rebuilt. Second, countries without fiscal space may be more constrained in designing and implementing credible policies. The IMF (2012FM, IX) finds need of analyzing the rise of seigniorage (see http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/05/global-inflation-seigniorage-monetary.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/05/global-inflation-seigniorage-financial.html) and accumulation of government paper in monetary authorities:
“Since 2008 the rise in general government gross debt ratios may have overstated short-term pressures on the public finances in some countries, primarily because of the surge in seigniorage and the accumulation of assets by central banks (including government paper). This comes to light when looking at consolidated net balance sheets of governments and central banks. However, large central bank holdings of government debt and other assets will need to be liquidated or rolled over to the private sector as the demand for base money returns to more normal levels, meaning that gross general government debt, alongside net debt, remains a key indicator of public indebtedness over the longer term. The process of reducing central bank balance sheets will be difficult to manage without previous or parallel medium-term fiscal consolidation.”
The International Monetary and Financial Committee (IFMC 2012Apr21) formulated a policy of caution with respect to fiscal consolidation in the midst of fragile world economic recovery and unemployment:
“In advanced economies, further actions are needed in many countries to achieve credible fiscal consolidation and government debt reduction, while avoiding excessively contractionary fiscal policies. Where conditions permit, automatic fiscal stabilizers should be allowed to operate. In all countries, viable medium-term consolidation strategies should be in place. Monetary policy will need to remain accommodative as long as inflation prospects remain anchored and weak growth persists. The potential impact and cross-border spillovers of such a policy should be closely monitored. Structural reforms to boost potential output and employment are critical, and need further momentum. In the euro area, continued progress on ensuring debt sustainability, securing financial stability, and undertaking bold structural reforms will be crucial to boosting confidence and productivity, facilitating rebalancing within the monetary union, and promoting strong and balanced growth.”
IA4. IMF Firewall. A critical development in the resolution of the European debt crisis is the increase in available resources of the IMF announced in a joint statement of the IMFC and the Group of 20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors (IMFC 2012Apr20):
“There are firm commitments to increase resources made available to the IMF by over $430 billion in addition to the quota increase under the 2010 reform. These resources will be available for the whole membership of the IMF, and not earmarked for any particular region.”
Resources are not earmarked for the European debt crisis but it is the most threatening current vulnerability in the world economy.
IB IMF Projections. Table I-1 is constructed with the database of the IMF (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/index.aspx) to show GDP in dollars in 2010 and the growth rate of real GDP of the world and selected regional countries from 2011 to 2014. The data illustrate the concept often repeated of “two-speed recovery” of the world economy from the recession of 2007 to 2009. The IMF has lowered its forecast of the world economy to 3.5 percent in 2012 but accelerating to 4.1 percent in 2013, 4.4 percent in 2014 and 4.5 percent in 2015. Slow-speed recovery occurs in the “major advanced economies” of the G7 that account for $33,670 billion of world output of $69,660 billion, or 48.3 percent, but are projected to grow at much lower rates than world output, 2.1 percent on average from 2012 to 2015 in contrast with 4.1 percent for the world as a whole. While the world would grow 17.6 percent in the four years from 2012 to 2015, the G7 as a whole would grow 8.5 percent. The difference in dollars of 2011 is rather high: growing by 17.6 percent would add $12.3 trillion of output to the world economy, or roughly two times the output of the economy of Japan of $5,869 but growing by 8.5 percent would add $5.9 trillion of output to the world, or about the output of Japan in 2011. The “two speed” concept is in reference to the growth of the 150 countries labeled as emerging and developing economies (EMDE) with joint output in 2011 of $25,237 billion, or 36.2 percent of world output. The EMDEs would grow cumulatively 26.5 percent or at the average yearly rate of 6.1 percent, contributing $6.7 trillion from 2012 to 2015 or the equivalent of somewhat less than the GDP of $7,298 billion of China in 2011. The final four countries in Table 1 often referred as BRIC (Brazil, Russia, India, China), are large, rapidly growing emerging economies. Their combined output adds to $13,317 billion, or 19.1 percent of world output, which is equivalent to 39.6 percent of the combined output of the major advanced economies of the G7.
Table I-1, IMF World Economic Outlook Database Projections of Real GDP Growth
| GDP USD 2011 | Real GDP ∆% | Real GDP ∆% | Real GDP ∆% | Real GDP ∆% | |
| World | 69,660 | 3.5 | 4.1 | 4.4 | 4.5 |
| G7 | 33,670 | 1.5 | 1.9 | 2.3 | 2.5 |
| Canada | 1,737 | 2.1 | 2.2 | 2.4 | 2.4 |
| France | 2,776 | 0.5 | 1.1 | 1.9 | 1.9 |
| DE | 3,577 | 0.6 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.3 |
| Italy | 2,199 | -1.9 | -0.3 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
| Japan | 5,869 | 2.0 | 1.7 | 1.5 | 1.3 |
| UK | 2,418 | 0.8 | 2.0 | 2.5 | 2.6 |
| US | 15,094 | 2.1 | 2.4 | 2.9 | 3.3 |
| Euro Area | 13,115 | -0.3 | 0.9 | 1.4 | 1.6 |
| DE | 3,577 | 0.6 | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.3 |
| France | 2,776 | 0.5 | 1.1 | 1.9 | 1.9 |
| Italy | 2,199 | -1.9 | -0.3 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
| POT | 239 | -3.3 | 0.3 | 2.1 | 1.9 |
| Ireland | 218 | 0.5 | 2.1 | 2.5 | 2.8 |
| Greece | 303 | -4.7 | 0.0 | 2.5 | 3.1 |
| Spain | 1,494 | -1.8 | 0.1 | 1.6 | 1.6 |
| EMDE | 25,237 | 5.7 | 6.0 | 6.2 | 6.3 |
| Brazil | 2,493 | 3.0 | 4.2 | 4.0 | 4.1 |
| Russia | 1,850 | 4.0 | 3.9 | 3.9 | 3.9 |
| India | 1,676 | 6.9 | 7.3 | 7.5 | 7.7 |
| China | 7,298 | 8.2 | 8.8 | 8.7 | 8.7 |
Notes; DE: Germany; EMDE: Emerging and Developing Economies (150 countries); POT: Portugal
Source: IMF World Economic Outlook databank
http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/index.aspx
Continuing high rates of unemployment in advanced economies constitute another characteristic of the database of the WEO (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/index.aspx). Table I-2 is constructed with the WEO database to provide rates of unemployment from 2011 to 2015 for major countries and regions. In fact, unemployment rates for 2011 in Table I-2 are high for all countries: unusually high for countries with high rates most of the time and unusually high for countries with low rates most of the time. The rates of unemployment are particularly high for the countries with sovereign debt difficulties in Europe: 12.7 percent for Portugal (POT), 14.4 percent for Ireland, 17.3 percent for Greece, 21.6 percent for Spain and 8.4 percent for Italy, which is lower but still high. The G7 rate of unemployment is 7.7 percent. Unemployment rates are not likely to decrease substantially if slow growth persists in advanced economies.
Table I-2, IMF World Economic Outlook Database Projections of Unemployment Rate as Percent of Labor Force
| % Labor Force 2011 | % Labor Force 2012 | % Labor Force 2013 | % Labor Force 2014 | % Labor Force 2015 | |
| World | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| G7 | 7.7 | 7.4 | 7.3 | 7.0 | 6.7 |
| Canada | 7.5 | 7.4 | 7.3 | 7.1 | 6.9 |
| France | 9.7 | 9.9 | 10.1 | 9.8 | 9.4 |
| DE | 6.0 | 5.6 | 5.5 | 5.3 | 5.3 |
| Italy | 8.4 | 9.5 | 9.7 | 9.8 | 9.5 |
| Japan | 4.5 | 4.5 | 4.4 | 4.3 | 4.2 |
| UK | 8.0 | 8.3 | 8.2 | 7.8 | 7.4 |
| US | 8.9 | 8.2 | 7.9 | 7.5 | 6.9 |
| Euro Area | 10.1 | 10.9 | 10.8 | 10.5 | 10.1 |
| DE | 6.0 | 5.6 | 5.5 | 5.3 | 5.3 |
| France | 9.7 | 9.9 | 10.1 | 9.8 | 9.4 |
| Italy | 8.4 | 9.5 | 9.7 | 9.8 | 9.5 |
| POT | 12.7 | 14.3 | 13.9 | 13.2 | 12.4 |
| Ireland | 14.4 | 14.5 | 13.8 | 12.9 | 12.0 |
| Greece | 17.3 | 19.4 | 19.4 | 18.2 | 16.8 |
| Spain | 21.6 | 24.2 | 23.9 | 22.8 | 21.9 |
| EMDE | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Brazil | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.5 | 7.0 | 7.0 |
| Russia | 7.5 | 6.5 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.0 |
| India | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| China | 4.1 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 | 4.0 |
Notes; DE: Germany; EMDE: Emerging and Developing Economies (150 countries)
Source: IMF World Economic Outlook databank http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/weoselgr.aspx
The database of the WEO (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/index.aspx) is used to construct the debt/GDP ratios of regions and countries in Table I-3. The concept used is general government debt, which consists of central government debt, such as Treasury debt in the US, and all state and municipal debt. Net debt is provided for all countries except for gross debt for China, Russia and India. The net debt/GDP ratio of the G7 jumps from 84.5 in 2011 to 93.7 in 2015. G7 debt is pulled by the high debt of Japan that grows from 126.6 percent of GDP in 2011 to 154.9 percent of GDP in 2015. US general government debt grows from 80.3 percent of GDP in 2011 to 88.3 percent of GDP in 2015. Debt/GDP ratios of countries with sovereign debt difficulties in Europe are particularly worrisome. General government net debts of Italy, Ireland, Greece and Portugal exceed 100 percent of GDP or are expected to exceed 100 percent of GDP by 2015. The only country with relatively low debt/GDP ratio is Spain with 56.9 in 2010 but growing to 76.9 in 2014. Fiscal adjustment, voluntary or forced by defaults, may squeeze further economic growth and employment in many countries as analyzed by Blanchard (2012WEOApr). Defaults could feed through exposures of banks and investors to financial institutions and economies in countries with sounder fiscal affairs.
Table I-3, IMF World Economic Outlook Database Projections, General Government Net Debt as Percent of GDP
| % Debt/ | % Debt/ | % Debt/ | % Debt/ | % Debt/ | |
| World | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| G7 | 84.5 | 88.3 | 91.2 | 92.8 | 93.7 |
| Canada | 33.3 | 35.4 | 36.9 | 37.5 | 37.4 |
| France | 80.4 | 83.2 | 84.9 | 84.8 | 83.8 |
| DE | 56.1 | 54.1 | 53.4 | 54.4 | 52.4 |
| Italy | 99.6 | 102.3 | 102.6 | 102.5 | 101.5 |
| Japan | 126.6 | 135.2 | 142.7 | 149.1 | 154.9 |
| UK | 78.3 | 84.2 | 87.2 | 88.6 | 88.1 |
| US | 80.3 | 83.7 | 86.7 | 88.0 | 88.3 |
| Euro Area | 68.4 | 70.3 | 71.5 | 71.6 | 71.3 |
| DE | 56.1 | 54.1 | 53.4 | 54.4 | 52.4 |
| France | 80.4 | 83.2 | 84.9 | 84.8 | 83.8 |
| Italy | 99.6 | 102.3 | 102.6 | 102.5 | 101.5 |
| POT | 100.4 | 110.9 | 113.9 | 112.9 | 111.4 |
| Ireland | 95.9 | 102.9 | 106.9 | 107.5 | 105.8 |
| Greece | 160.8 | 153.2 | 160.9 | 158.1 | 150.9 |
| Spain | 56.9 | 67.0 | 71.8 | 75.1 | 76.9 |
| EMDE | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Brazil | 36.4 | 36.0 | 34.5 | 33.2 | 31.9 |
| Russia* | 9.6 | 8.4 | 7.9 | 9.0 | 9.7 |
| India* | 68.1 | 67.6 | 66.8 | 66.2 | 65.8 |
| China* | 25.8 | 22.0 | 19.4 | 17.1 | 14.8 |
Notes; DE: Germany; EMDE: Emerging and Developing Economies (150 countries)
Source: IMF World Economic Outlook databank http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2011/02/weodata/index.aspx
The primary balance consists of revenues less expenditures but excluding interest revenues and interest payments. It measures the capacity of a country to generate sufficient current revenue to meet current expenditures. Brazil is the only country in Table I-4 with sizeable surplus of primary net lending/borrowing of 3.1 percent in 2011 followed by 1.9 percent for Russia and smaller ones of 0.8 percent for Italy and 0.7 percent for Germany. Most countries in Table I-4 face significant fiscal adjustment in the future without “fiscal space.” Investors in government securities may require higher yields when the share of individual government debts hit saturation shares in portfolios. The tool of analysis of Cochrane (2011Jan, 27, equation (16)) is the government debt valuation equation:
(Mt + Bt)/Pt = Et∫(1/Rt, t+τ)st+τdτ (1)
Equation (1) expresses the monetary, Mt, and debt, Bt, liabilities of the government, divided by the price level, Pt, in terms of the expected value discounted by the ex-post rate on government debt, Rt, t+τ, of the future primary surpluses st+τ, which are equal to Tt+τ – Gt+τ or difference between taxes, T, and government expenditures, G. Cochrane (2010A) provides the link to a web appendix demonstrating that it is possible to discount by the ex post Rt, t+τ. Expectations by investors of future primary balances of indebted governments may be less optimistic than those in Table I-4 because of government revenues constrained by low growth and government expenditures rigid because of entitlements. Political realities may also jeopardize structural reforms and fiscal austerity.
Table I-4, IMF World Economic Outlook Database Projections of Primary General Government Net Lending/Borrowing as Percent of GDP
| % GDP 2011 | % GDP 2012 | % GDP 2013 | % GDP 2014 | % GDP 2015 | |
| World | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| G7 | -5.6 | -4.8 | -3.5 | -2.3 | -1.7 |
| Canada | -4.1 | -3.1 | -2.5 | -1.8 | -1.1 |
| France | -2.9 | -2.2 | -1.5 | -0.6 | 0.3 |
| DE | 0.7 | 1.0 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.4 |
| Italy | 0.8 | 2.9 | 4.0 | 4.1 | 4.4 |
| Japan | -9.1 | -8.9 | -7.5 | -6.4 | -5.8 |
| UK | -5.8 | -5.3 | -4.0 | -2.3 | -0.8 |
| US | -7.3 | -6.1 | -4.4 | -2.8 | -2.2 |
| Euro Area | -1.6 | -0.5 | 0.1 | 0.7 | 1.1 |
| DE | 0.7 | 1.0 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.4 |
| France | -2.9 | -2.2 | -1.5 | -0.6 | 0.3 |
| Italy | 0.8 | 2.9 | 4.0 | 4.1 | 4.4 |
| POT | -0.2 | 0.1 | 1.5 | 2.4 | 2.7 |
| Ireland | -6.7 | -4.4 | -1.8 | 0.9 | 2.8 |
| Greece | -2.3 | -1.0 | 1.8 | 4.4 | 4.4 |
| Spain | -6.6 | -3.6 | -3.0 | -2.2 | -1.4 |
| EMDE* | -1.1 | -1.0 | -1.1 | -1.2 | -1.2 |
| Brazil | 3.1 | 3.1 | 3.1 | 3.1 | 3.1 |
| Russia | 1.9 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 0.1 | -0.9 |
| India | -4.4 | -3.9 | -3.6 | -3.6 | -3.5 |
| China* | -1.2 | -1.3 | -1.0 | -0.6 | -0.1 |
*General Government Net Lending/Borrowing
Notes; DE: Germany; EMDE: Emerging and Developing Economies (150 countries)
Source: IMF World Economic Outlook databank http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/weoselgr.aspx
The database of the World Economic Outlook of the IMF (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/index.aspx) is used to obtain government net lending/borrowing as percent of GDP in Table I-5. Interest on government debt is added to the primary balance to obtain overall government fiscal balance in Table I-5. For highly indebted countries there is an even tougher challenge of fiscal consolidation. Adverse expectations on the success of fiscal consolidation may drive up yields on government securities that could create hurdles to adjustment, growth and employment.
Table I-5, IMF World Economic Outlook Database Projections of General Government Net Lending/Borrowing as Percent of GDP
| % GDP 2011 | % GDP 2012 | % GDP 2013 | % GDP 2014 | % GDP 2015 | |
| World | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| G7 | -7.7 | -6.8 | -5.5 | -4.5 | -4.0 |
| Canada | -4.5 | -3.7 | -2.9 | -2.1 | -1.5 |
| France | -5.3 | -4.6 | -3.9 | -3.1 | -2.2 |
| DE | -1.0 | -0.8 | -0.6 | -0.3 | -0.2 |
| Italy | -3.9 | -2.4 | -1.5 | -1.6 | -1.5 |
| Japan | -10.1 | -10.0 | -8.7 | -7.9 | -7.6 |
| UK | -8.7 | -7.9 | -6.6 | -5.0 | -3.6 |
| US | -9.6 | -8.1 | -6.3 | -4.9 | -4.4 |
| Euro Area | -4.1 | -3.2 | -2.7 | -2.3 | -1.8 |
| DE | -1.0 | -0.8 | -0.6 | -0.3 | -0.2 |
| France | -5.3 | -4.6 | -3.9 | -3.1 | -2.2 |
| Italy | -3.9 | -2.4 | -1.5 | -1.6 | -1.5 |
| POT | -0.2 | 0.1 | 1.5 | 2.4 | 2.7 |
| Ireland | -9.8 | -8.5 | -7.4 | -4.9 | -2.9 |
| Greece | -9.2 | -7.2 | -4.6 | -2.1 | -1.6 |
| Spain | -8.5 | -6.0 | -5.7 | -5.2 | -4.8 |
| EMDE | -1.2 | -1.0 | -1.1 | -1.2 | -1.2 |
| Brazil | -2.6 | -2.4 | -2.4 | -2.3 | -2.3 |
| Russia | 1.6 | 0.6 | -0.3 | -0.5 | -1.6 |
| India | -8.7 | -8.3 | -8.2 | -8.1 | -7.9 |
| China | -1.2 | -1.3 | -1.0 | -0.6 | -0.1 |
Notes; DE: Germany; EMDE: Emerging and Developing Economies (150 countries)
Source: IMF World Economic Outlook databank http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/weoselgr.aspx
There were some hopes that the sharp contraction of output during the global recession would eliminate current account imbalances. Table I-6 constructed with the database of the WEO (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/index.aspx) shows that external imbalances have been maintained in the form of current account deficits and surpluses. China’s current account surplus is 2.8 percent of GDP for 2011 and is projected to climb to 3.4 percent of GDP in 2015. At the same time the current account deficit of the US is 3.1 percent of GDP and is projected to remain almost unchanged at 3.2 percent of GDP in 2015. The current account surplus of Germany is 5.7 percent for 2011 and remains at a high 4.3 percent of GDP in 2015. Japan’s current account surplus is 2.0 percent of GDP in 2011 and increases slightly to 2.4 percent of GDP in 2015.
Table I-6, IMF World Economic Outlook Databank Projections, Current Account of Balance of Payments as Percent of GDP
| % CA/ | % CA/ | % CA/ | % CA/ | % CA/ | |
| World | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| G7 | -1.1 | -1.1 | -0.9 | -0.9 | -1.0 |
| Canada | -2.8 | -2.7 | -2.7 | -2.7 | -2.5 |
| France | -2.2 | -1.9 | -1.5 | -1.0 | -0.8 |
| DE | 5.7 | 5.1 | 4.9 | 4.6 | 4.3 |
| Italy | -3.2 | -2.2 | -1.6 | -1.5 | -1.6 |
| Japan | 2.0 | 2.2 | 2.7 | 2.6 | 2.4 |
| UK | -1.9 | -1.7 | -1.1 | -0.8 | -0.4 |
| US | -3.1 | -3.3 | -3.1 | -3.0 | -3.2 |
| Euro Area | 0.3 | 0.7 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 1.2 |
| DE | 5.7 | 5.1 | 4.9 | 4.6 | 4.3 |
| France | -2.2 | -1.9 | -1.5 | -1.0 | -0.8 |
| Italy | -3.2 | -2.2 | -1.6 | -1.5 | -1.6 |
| POT | -6.4 | -4.2 | -3.5 | -3.1 | -3.0 |
| Ireland | 0.1 | 0.9 | 1.7 | 3.0 | 3.8 |
| Greece | -9.7 | -7.4 | -6.3 | -5.4 | -3.3 |
| Spain | -3.7 | -2.1 | -1.7 | -1.3 | -0.8 |
| EMDE | 1.9 | 1.7 | 1.3 | 0.9 | 0.8 |
| Brazil | -2.1 | -3.2 | -3.2 | -3.3 | -3.4 |
| Russia | 5.5 | 4.8 | 1.9 | 0.4 | -0.7 |
| India | -2.8 | -3.2 | -2.9 | -2.8 | -2.7 |
| China | 2.8 | 2.3 | 2.6 | 3.0 | 3.4 |
Notes; DE: Germany; EMDE: Emerging and Developing Economies (150 countries)
Source: IMF World Economic Outlook databank http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/weoselgr.aspx
The G7 meeting in Washington on Apr 21 2006 of finance ministers and heads of central bank governors of the G7 established the “doctrine of shared responsibility” (G7 2006Apr):
“We, Ministers and Governors, reviewed a strategy for addressing global imbalances. We recognized that global imbalances are the product of a wide array of macroeconomic and microeconomic forces throughout the world economy that affect public and private sector saving and investment decisions. We reaffirmed our view that the adjustment of global imbalances:
- Is shared responsibility and requires participation by all regions in this global process;
- Will importantly entail the medium-term evolution of private saving and investment across countries as well as counterpart shifts in global capital flows; and
- Is best accomplished in a way that maximizes sustained growth, which requires strengthening policies and removing distortions to the adjustment process.
In this light, we reaffirmed our commitment to take vigorous action to address imbalances. We agreed that progress has been, and is being, made. The policies listed below not only would be helpful in addressing imbalances, but are more generally important to foster economic growth.
- In the United States, further action is needed to boost national saving by continuing fiscal consolidation, addressing entitlement spending, and raising private saving.
- In Europe, further action is needed to implement structural reforms for labor market, product, and services market flexibility, and to encourage domestic demand led growth.
- In Japan, further action is needed to ensure the recovery with fiscal soundness and long-term growth through structural reforms.
Others will play a critical role as part of the multilateral adjustment process.
- In emerging Asia, particularly China, greater flexibility in exchange rates is critical to allow necessary appreciations, as is strengthening domestic demand, lessening reliance on export-led growth strategies, and actions to strengthen financial sectors.
- In oil-producing countries, accelerated investment in capacity, increased economic diversification, enhanced exchange rate flexibility in some cases.
- Other current account surplus countries should encourage domestic consumption and investment, increase micro-economic flexibility and improve investment climates.
We recognized the important contribution that the IMF can make to multilateral surveillance.”
The concern at that time was that fiscal and current account global imbalances could result in disorderly correction with sharp devaluation of the dollar after an increase in premiums on yields of US Treasury debt (see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007)). The IMF was entrusted with monitoring and coordinating action to resolve global imbalances. The G7 was eventually broadened to the formal G20 in the effort to coordinate policies of countries with external surpluses and deficits.
The database of the WEO (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/index.aspx) is used to contract Table I-7 with fiscal and current account imbalances projected for 2011 and 2015. The WEO finds the need to rebalance external and domestic demand (IMF 2011WEOSep xvii):
“Progress on this front has become even more important to sustain global growth. Some emerging market economies are contributing more domestic demand than is desirable (for example, several economies in Latin America); others are not contributing enough (for example, key economies in emerging Asia). The first set needs to restrain strong domestic demand by considerably reducing structural fiscal deficits and, in some cases, by further removing monetary accommodation. The second set of economies needs significant currency appreciation alongside structural reforms to reduce high surpluses of savings over investment. Such policies would help improve their resilience to shocks originating in the advanced economies as well as their medium-term growth potential.”
The IMF (2012WEOApr, XVII) explains decreasing importance of the issue of global imbalances as follows:
“The latest developments suggest that global current account imbalances are no longer expected to widen again, following their sharp reduction during the Great Recession. This is largely because the excessive consumption growth that characterized economies that ran large external deficits prior to the crisis has been wrung out and has not been offset by stronger consumption in surplus economies. Accordingly, the global economy has experienced a loss of demand and growth in all regions relative to the boom years just before the crisis. Rebalancing activity in key surplus economies toward higher consumption, supported by more market-determined exchange rates, would help strengthen their prospects as well as those of the rest of the world.”
Table I-7, Fiscal Deficit, Current Account Deficit and Government Debt as % of GDP and 2011 Dollar GDP
| GDP 2011 | FD | CAD | Debt | FD%GDP | CAD%GDP | Debt | |
| US | 15094 | -7.3 | -3.1 | 80.3 | -2.3 | -3.2 | 88.3 |
| Japan | 5869 | -9.1 | 2.0 | 126.6 | -5.8 | 2.4 | 155.0 |
| UK | 2418 | -5.8 | -1.9 | 78.3 | -0.8 | -0.4 | 88.1 |
| Euro | 13115 | -1.6 | 0.3 | 68.4 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 71.3 |
| Ger | 3577 | 0.7 | 5.7 | 56.1 | 1.4 | 4.3 | 52.4 |
| France | 2776 | -2.9 | -2.2 | 80.4 | 0.3 | -0.8 | 83.8 |
| Italy | 2199 | 0.8 | -3.2 | 99.6 | 4.4 | -1.6 | 101.5 |
| Can | 1737 | -4.1 | -2.8 | 33.3 | -1.1 | -2.5 | 37.4 |
| China | 7298 | -1.2 | 2.7 | 25.8 | -0.1 | 3.4 | 14.8 |
| Brazil | 2493 | 3.1 | -2.1 | 36.4 | 3.1 | -3.4 | 31.9 |
Note: GER = Germany; Can = Canada; FD = fiscal deficit; CAD = current account deficit
FD is primary except total for China; Debt is net except gross for China
Source: http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/weoselgr.aspx
Brazil faced in the debt crisis of 1982 a more complex policy mix. Between 1977 and 1983, Brazil’s terms of trade, export prices relative to import prices, deteriorated 47 percent and 36 percent excluding oil (Pelaez 1987, 176-79; Pelaez 1986, 37-66; see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 178-87). Brazil had accumulated unsustainable foreign debt by borrowing to finance balance of payments deficits during the 1970s. Foreign lending virtually stopped. The German mark devalued strongly relative to the dollar such that Brazil’s products lost competitiveness in Germany and in multiple markets in competition with Germany. The resolution of the crisis was devaluation of the Brazilian currency by 30 percent relative to the dollar and subsequent maintenance of parity by monthly devaluation equal to inflation and indexing that resulted in financial stability by parity in external and internal interest rates avoiding capital flight. With a combination of declining imports, domestic import substitution and export growth, Brazil followed rapid growth in the US and grew out of the crisis with surprising GDP growth of 4.5 percent in 1984.
The euro zone faces a critical survival risk because several of its members may default on their sovereign obligations if not bailed out by the other members. The valuation equation of bonds is essential to understanding the stability of the euro area. An explanation is provided in this paragraph and readers interested in technical details are referred to the Subsection IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation. Contrary to the Wriston doctrine, investing in sovereign obligations is a credit decision. The value of a bond today is equal to the discounted value of future obligations of interest and principal until maturity. On Dec 30 the yield of the 2-year bond of the government of Greece was quoted around 100 percent. In contrast, the 2-year US Treasury note traded at 0.239 percent and the 10-year at 2.871 percent while the comparable 2-year government bond of Germany traded at 0.14 percent and the 10-year government bond of Germany traded at 1.83 percent. There is no need for sovereign ratings: the perceptions of investors are of relatively higher probability of default by Greece, defying Wriston (1982), and nil probability of default of the US Treasury and the German government. The essence of the sovereign credit decision is whether the sovereign will be able to finance new debt and refinance existing debt without interrupting service of interest and principal. Prices of sovereign bonds incorporate multiple anticipations such as inflation and liquidity premiums of long-term relative to short-term debt but also risk premiums on whether the sovereign’s debt can be managed as it increases without bound. The austerity measures of Italy are designed to increase the primary surplus, or government revenues less expenditures excluding interest, to ensure investors that Italy will have the fiscal strength to manage its debt of 120 percent of GDP, which is the third largest in the world after the US and Japan. Appendix IIIE links the expectations on the primary surplus to the real current value of government monetary and fiscal obligations. As Blanchard (2011SepWEO) analyzes, fiscal consolidation to increase the primary surplus is facilitated by growth of the economy. Italy and the other indebted sovereigns in Europe face the dual challenge of increasing primary surpluses while maintaining growth of the economy (for the experience of Brazil in the debt crisis of 1982 see Pelaez 1986, 1987).
Much of the analysis and concern over the euro zone centers on the lack of credibility of the debt of a few countries while there is credibility of the debt of the euro zone as a whole. In practice, there is convergence in valuations and concerns toward the fact that there may not be credibility of the euro zone as a whole. The fluctuations of financial risk assets of members of the euro zone move together with risk aversion toward the countries with lack of debt credibility. This movement raises the need to consider analytically sovereign debt valuation of the euro zone as a whole in the essential analysis of whether the single-currency will survive without major changes.
Welfare economics considers the desirability of alternative states, which in this case would be evaluating the “value” of Germany (1) within and (2) outside the euro zone. Is the sum of the wealth of euro zone countries outside of the euro zone higher than the wealth of these countries maintaining the euro zone? On the choice of indicator of welfare, Hicks (1975, 324) argues:
“Partly as a result of the Keynesian revolution, but more (perhaps) because of statistical labours that were initially quite independent of it, the Social Product has now come right back into its old place. Modern economics—especially modern applied economics—is centered upon the Social Product, the Wealth of Nations, as it was in the days of Smith and Ricardo, but as it was not in the time that came between. So if modern theory is to be effective, if it is to deal with the questions which we in our time want to have answered, the size and growth of the Social Product are among the chief things with which it must concern itself. It is of course the objective Social Product on which attention must be fixed. We have indexes of production; we do not have—it is clear we cannot have—an Index of Welfare.”
If the burden of the debt of the euro zone falls on Germany and France or only on Germany, is the wealth of Germany and France or only Germany higher after breakup of the euro zone or if maintaining the euro zone? In practice, political realities will determine the decision through elections.
The prospects of survival of the euro zone are dire. Table I-8 is constructed with IMF World Economic Outlook database (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/index.aspx) for GDP in USD billions, primary net lending/borrowing as percent of GDP and general government debt as percent of GDP for selected regions and countries in 2010.
Table I-8, World and Selected Regional and Country GDP and Fiscal Situation
| GDP 2012 | Primary Net Lending Borrowing | General Government Net Debt | |
| World | 69,660 | ||
| Euro Zone | 12,586 | -0.5 | 70.3 |
| Portugal | 221 | 0.1 | 110.9 |
| Ireland | 210 | -4.4 | 102.9 |
| Greece | 271 | -1.0 | 153.2 |
| Spain | 1,398 | -3.6 | 67.0 |
| Major Advanced Economies G7 | 34,106 | -4.8 | 88.3 |
| United States | 15,610 | -6.1 | 83.7 |
| UK | 2,453 | -5.3 | 84.2 |
| Germany | 3,479 | 1.0 | 54.1 |
| France | 2,712.0 | -2.2 | 83.2 |
| Japan | 5,981 | -8.9 | 135.2 |
| Canada | 1,805 | -3.1 | 35.4 |
| Italy | 2,067 | 2.9 | 102.3 |
| China | 7992 | -1.3* | 22.0** |
*Net Lending/borrowing**Gross Debt
Source: http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/weoselgr.aspx
The data in Table I-8 are used for some very simple calculations in Table I-9. The column “Net Debt USD Billions” in Table I-9 is generated by applying the percentage in Table I-8 column “General Government Net Debt % GDP 2010” to the column “GDP USD Billions.” The total debt of France and Germany in 2012 is $4138.5 billion, as shown in row “B+C” in column “Net Debt USD Billions” The sum of the debt of Italy, Spain, Portugal, Greece and Ireland is $3927.8 billion, adding rows D+E+F+G+H in column “Net Debt USD billions.” There is some simple “unpleasant bond arithmetic” in the two final columns of Table I-9. Suppose the entire debt burdens of the five countries with probability of default were to be guaranteed by France and Germany, which de facto would be required by continuing the euro zone. The sum of the total debt of these five countries and the debt of France and Germany is shown in column “Debt as % of Germany plus France GDP” to reach $8066.3 billion, which would be equivalent to 130.3 percent of their combined GDP in 2012. Under this arrangement the entire debt of the euro zone including debt of France and Germany would not have nil probability of default. The final column provides “Debt as % of Germany GDP” that would exceed 231.9 percent if including debt of France and 167.0 percent of German GDP if excluding French debt. The unpleasant bond arithmetic illustrates that there is a limit as to how far Germany and France can go in bailing out the countries with unsustainable sovereign debt without incurring severe pains of their own such as downgrades of their sovereign credit ratings. A central bank is not typically engaged in direct credit because of remembrance of inflation and abuse in the past. There is also a limit to operations of the European Central Bank in doubtful credit obligations. Wriston (1982) would prove to be wrong again that countries do not bankrupt but would have a consolation prize that similar to LBOs the sum of the individual values of euro zone members outside the current agreement exceeds the value of the whole euro zone. Internal rescues of French and German banks may be less costly than bailing out other euro zone countries so that they do not default on French and German banks.
Table I-9, Guarantees of Debt of Sovereigns in Euro Area as Percent of GDP of Germany and France, USD Billions and %
| Net Debt USD Billions | Debt as % of Germany Plus France GDP | Debt as % of Germany GDP | |
| A Euro Area | 8,847.9 | ||
| B Germany | 1,882.1 | $8066.3 as % of $3479 =231.9% $5809.9 as % of $3479 =167.0% | |
| C France | 2,256.4 | ||
| B+C | 4,138.5 | GDP $6,191.0 Total Debt $8066.3 Debt/GDP: 130.3% | |
| D Italy | 2,114.5 | ||
| E Spain | 936.7 | ||
| F Portugal | 245.3 | ||
| G Greece | 415.2 | ||
| H Ireland | 216.1 | ||
| Subtotal D+E+F+G+H | 3,927.8 |
Source: calculation with IMF data http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/index.aspx
II Global Financial and Economic Risk. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) provides an international safety net for prevention and resolution of international financial crises. The IMF’s Financial Sector Assessment Program (FSAP) provides analysis of the economic and financial sectors of countries (see Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), 101-62, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008), 114-23). Relating economic and financial sectors is a challenging task both for theory and measurement. The IMF (2012WEOApr) provides surveillance of the world economy with its Global Economic Outlook (WEO) (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/pdf/text.pdf), of the world financial system with its Global Financial Stability Report (GFSR) (IMF 2012GFSRApr) (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/gfsr/2012/01/pdf/text.pdf) and of fiscal affairs with the Fiscal Monitor (IMF 2012FMApr) (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fm/2012/01/pdf/fm1201.pdf). There appears to be a moment of transition in global economic and financial variables that may prove of difficult analysis and measurement. It is useful to consider global economic and financial risks, which are analyzed in the comments of this blog.
Economic risks include the following:
1. China’s Economic Growth. China is lowering its growth target to 7.5 percent per year. Lu Hui, writing on “China lowers GDP target to achieve quality economic growth, on Mar 12, 2012, published in Beijing by Xinhuanet (http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/china/2012-03/12/c_131461668.htm), informs that Premier Jiabao wrote in a government work report that the GDP growth target will be lowered to 7.5 percent to enhance the quality and level of development of China over the long term. The quarterly growth rate of GDP in IQ2012 of 1.8 percent is equivalent to 7.4 percent per year (see subsection VC at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/04/fractured-labor-market-with-hiring_15.html). There is also ongoing political development in China during a decennial political reorganization
2. United States Economic Growth, Labor Markets and Budget/Debt Quagmire. (i) The US economy grew at 1.6 percent in 2011 (Section I in http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/04/mediocre-economic-growth-falling-real.html). (ii) The labor market continues fractured with 29.4 million unemployed or underemployed (see Section I http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/04/thirty-million-unemployed-or.html). There are over 10 million fewer full-time jobs and hiring has collapsed (see Section II at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/04/fractured-labor-market-with-hiring.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/03/global-financial-and-economic-risk.html). (iii) There is a difficult climb from the record deficit of 9.9 percent in 2009 and cumulative deficit of $5,082 in four consecutive years of deficits exceeding one trillion dollars from 2009 to 2012 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/02/thirty-one-million-unemployed-or.html). There is no subsequent jump of debt in US peacetime history as the one from 40.5 percent of GDP in 2008 to 62.8 percent of GDP in 2011 and projected by the Congressional Budget Office (CBO 2012JanBEO) at 67.7 percent in 2012. The CBO (2012JanBEO) must use current law without any changes in the baseline scenario but also calculates another alternative scenario with different assumptions. In the alternative scenario, the debt/GDP ratio rises to 94.2 percent by 2022. The US is facing an unsustainable debt/GDP path. Feldstein (2012Mar19) finds that the most troubling uncertainty in the US is the programmed tax increases projected by the CBO (2012JanBEO) under current law with federal government revenue increasing from $2.4 trillion in fiscal year 2012 to $2.9 trillion in fiscal year 2013. The increase of $512 billion of federal revenue would be about 2.9 percent of GDP, raising the share of federal revenue in GDP from 15.8 percent in fiscal year 2012 to 18.7 percent of GDP in fiscal year 2013. In the analysis of Feldstein (2012Mar19), increasing revenue would originate in higher personal tax rates, payroll tax contributions and taxes on dividends, capital gains and corporate income tax. The share of federal revenue in GDP would increase to 19.8 percent in 2014, remaining above 20 percent during the rest of the decade. Feldstein (2012Mar19) finds that such a shock of sustained tax increases would risk another recession in 2013, requiring preventive legislation to smooth tax increases
3. Economic Growth and Labor Markets in Advanced Economies. Advanced economies are growing slowly. Japan’s GDP fell 0.6 percent in IVQ2011 relative to a year earlier. The euro zone’s GDP fell 0.3 percent in IVQ2011; Germany’s GDP fell 0.2 percent in IVQ2011; and the UK’s GDP fell 0.3 percent in IVQ2011. There is still high unemployment in advanced economies
4. World Inflation Waves. Inflation continues in repetitive waves globally (see Section I Inflation Waves at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/04/fractured-labor-market-with-hiring.html and earlier at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/03/global-financial-and-economic-risk.html)
A list of financial uncertainties includes:
1. Euro Area Survival Risk. The resilience of the euro to fiscal and financial doubts on larger member countries is still an unknown risk. Adjustment programs consist of immediate adoption of economic reforms that would increase future growth permitting fiscal consolidation, which would reduce risk spreads on sovereign debt. Fiscal consolidation is challenging in an environment of weak economic growth as analyzed by Blanchard (2011WEOSep) and consolidation can restrict growth as analyzed by Blanchard (2012WEOApr). Adjustment of countries such as Italy requires depreciation of the currency to parity, as proposed by Caballero and Giavazzi (2012Jan15), but it is not workable within the common currency and zero interest rates in the US. Bailouts of euro area member countries with temporary liquidity challenges cannot be permanently provided by stronger members at the risk of impairing their own sovereign debt credibility
2. Foreign Exchange Wars. Exchange rate struggles continue as zero interest rates in advanced economies induce devaluation. After deep global recession, regulation, trade and devaluation wars were to be expected (Pelaez and Pelaez, Government Intervention in Globalization: Regulation, Trade and Devaluation Wars (2008c), 181): “There are significant grounds for concern on the basis of this experience. International economic cooperation and the international financial framework can collapse during extreme events. It is unlikely that there will be a repetition of the disaster of the Great Depression. However, a milder contraction can trigger regulatory, trade and exchange wars”
3. Valuation of Risk Financial Assets. Valuations of risk financial assets have reached extremely high levels in markets with lower volumes. For example, the DJIA has increased 34.5 percent since the trough of the sovereign debt crisis in Europe on Jul 2, 2010, and the S&P 500 has gained 34.8 percent. It is challenging in theory and practice to assess when variables have peaked but sustained valuations to very high levels could be followed by contractions of valuations. Jonathan Cheng, writing on “Stocks add 66 points, post first-quarter record,” published on Mar 30, 2012, in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052702303816504577313123753822852.html?mod=WSJ_Markets_LEFTTopStories&mg=reno64-sec-wsj), finds that the DJIA rose 8.1 percent in IQ2012, which is the highest since 1998, while the S&P 500 gained 12 percent
4. Duration Trap of the Zero Bound. The yield of the US 10-year Treasury rose from 2.031 percent on Mar 9, 2012, to 2.294 percent on Mar 16, 2012. Considering a 10-year Treasury with coupon of 2.625 percent and maturity in exactly 10 years, the price would fall from 105.3512 corresponding to yield of 2.031 percent to 102.9428 corresponding to yield of 2.294 percent, for loss in a week of 2.3 percent but far more in a position with leverage of 10:1. Min Zeng, writing on “Treasurys fall, ending brutal quarter,” published on Mar 30, 2012, in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052702303816504577313400029412564.html?mod=WSJ_hps_sections_markets), informs that Treasury bonds maturing in more than 20 years lost 5.52 percent in the first quarter of 2012
5. Credibility and Commitment of Central Bank Policy. There is a credibility issue of the commitment of monetary policy. The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) advised on its Mar 13, 2012 statement that: “To support a stronger economic recovery and to help ensure that inflation, over time, is at the rate most consistent with its dual mandate, the Committee expects to maintain a highly accommodative stance for monetary policy. In particular, the Committee decided today to keep the target range for the federal funds rate at 0 to ¼ percent and currently anticipates that economic conditions—including low rates of resource utilization and a subdued outlook for inflation over the medium run—are likely to warrant exceptionally low levels of the federal funds rate at least through late 2014” (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20120313a.htm). At its meeting on Jan 25, the FOMC began to provide to the public the specific forecasts of interest rates and other economic variables by FOMC members (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20120125.pdf). These forecasts are analyzed in Section IV Global Inflation. Thomas J. Sargent and William L. Silber, writing on “The challenges of the Fed’s bid for transparency,” on Mar 20, published in the Financial Times (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20120125.pdf
), analyze the costs and benefits of transparency by the Fed. In the analysis of Sargent and Silber (2012Mar20), benefits of transparency by the Fed will exceed costs if the Fed is successful in conveying to the public what policies would be implemented and how forcibly in the presence of unforeseen economic events. History has been unkind to policy commitments. The risk in this case is if the Fed would postpone adjustment because of political pressures as has occurred in the past or because of errors of evaluation and forecasting of economic and financial conditions. Both political pressures and errors abounded in the unhappy stagflation of the 1970s also known as the US Great Inflation (see http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/05/slowing-growth-global-inflation-great.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/04/new-economics-of-rose-garden-turned.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/03/is-there-second-act-of-us-great.html and Appendix I The Great Inflation; see Taylor 1993, 1997, 1998LB, 1999, 2012FP, 2012Mar27, 2012Mar28, 2012JMCB). The challenge of the Fed, in the view of Sargent and Silber 2012Mar20), is to convey to the public the need to deviate from the commitment to interest rates of zero to ¼ percent because conditions have changed instead of unwarranted inaction or policy changes. Errors have abounded such as a critical cause of the global recession pointed by Sargent and Silber (2012Mar20): “While no president is known to have explicitly pressurized Mr. Bernanke’s predecessor, Alan Greenspan, he found it easy to maintain low interest rates for too long, fuelling the credit boom and housing bubble that led to the financial crisis in 2008.” Sargent and Silber (2012Mar20) also find need of commitment of fiscal authorities to consolidation needed to attain sustainable path of debt.
The analysis by Kydland and Prescott (1977, 447-80, equation 5) uses the “expectation augmented” Phillips curve with the natural rate of unemployment of Friedman (1968) and Phelps (1968), which in the notation of Barro and Gordon (1983, 592, equation 1) is:
Ut = Unt – α(πt – πe) α > 0 (1)
Where Ut is the rate of unemployment at current time t, Unt is the natural rate of unemployment, πt is the current rate of inflation and πe is the expected rate of inflation by economic agents based on current information. Equation (1) expresses unemployment net of the natural rate of unemployment as a decreasing function of the gap between actual and expected rates of inflation. The system is completed by a social objective function, W, depending on inflation, π, and unemployment, U:
W = W(πt, Ut) (2)
The policymaker maximizes the preferences of the public, (2), subject to the constraint of the tradeoff of inflation and unemployment, (1). The total differential of W set equal to zero provides an indifference map in the Cartesian plane with ordered pairs (πt, Ut - Un) such that the consistent equilibrium is found at the tangency of an indifference curve and the Phillips curve in (1). The indifference curves are concave to the origin. The consistent policy is not optimal. Policymakers without discretionary powers following a rule of price stability would attain equilibrium with unemployment not higher than with the consistent policy. The optimal outcome is obtained by the rule of price stability, or zero inflation, and no more unemployment than under the consistent policy with nonzero inflation and the same unemployment. Taylor (1998LB) attributes the sustained boom of the US economy after the stagflation of the 1970s to following a monetary policy rule instead of discretion (see Taylor 1993, 1999).
6. Carry Trades. Commodity prices driven by zero interest rates have resumed their increasing path. Some analytical aspects of the carry trade are instructive (Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. I (2008a), 101-5, Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008b), 202-4), Government Intervention in Globalization: Regulation, Trade and Devaluation Wars (2008c), 70-4). Consider the following symbols: Rt is the exchange rate of a country receiving carry trade denoted in units of domestic currency per dollars at time t of initiation of the carry trade; Rt+τ is the exchange of the country receiving carry trade denoted in units of domestic currency per dollars at time t+τ when the carry trade is unwound; if is the domestic interest rate of the high-yielding country where investment will be made; iusd is the interest rate on short-term dollar debt assumed to be 0.5 percent per year; if >iusd, which expresses the fact that the interest rate on the foreign country is much higher than that in short-term USD (US dollars); St is the dollar value of the investment principal; and π is the dollar profit from the carry trade. The investment of the principal St in the local currency debt of the foreign country provides a profit of:
π = (1 + if)(RtSt)(1/Rt+τ) – (1 + iusd)St (3)
The profit from the carry trade, π, is nonnegative when:
(1 + if)/ (1 + iusd) ≥ Rt+τ/Rt (4)
In words, the difference in interest rate differentials, left-hand side of inequality (4), must exceed the percentage devaluation of the currency of the host country of the carry trade, right hand side of inequality (4). The carry trade must earn enough in the host-country interest rate to compensate for depreciation of the host-country at the time of return to USD. A simple example explains the vulnerability of the carry trade in fixed-income. Let if be 0.10 (10 percent), iusd 0.005 (0.5 percent), St USD100 and Rt CUR 1.00/USD. Adopt the fixed-income rule of months of 30 days and years of 360 days. Consider a strategy of investing USD 100 at 10 percent for 30 days with borrowing of USD 100 at 0.5 percent for 30 days. At time t, the USD 100 are converted into CUR 100 and invested at [(30/360)10] equal to 0.833 percent for thirty days. At the end of the 30 days, assume that the rate Rt+30 is still CUR 1/USD such that the return amount from the carry trade is USD 0.833. There is still a loan to be paid [(0.005)(30/360)USD100] equal to USD 0.042. The investor receives the net amount of USD 0.833 minus USD 0.042 or US 0.791. The rate of return on the investment of the USD 100 is 0.791 percent, which is equivalent to the annual rate of return of 9.49 percent {(0.791)(360/30)}. This is incomparably better than earning 0.5 percent. There are alternatives of hedging by buying forward the exchange for conversion back into USD.
Research by the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis finds that the dollar declined on average by 6.56 percent in the events of quantitative easing, ranging from depreciation of 10.8 percent relative to the Japanese yen to 3.6 percent relative to the pound sterling (http://research.stlouisfed.org/wp/2010/2010-018.pdf). A critical assumption of Rudiger Dornbusch (1976) in his celebrated analysis of overshooting (Rogoff 2002MF http://www.imf.org/external/np/speeches/2001/kr/112901.pdf) is “that exchange rates and asset markets adjust fast relative to goods markets” (Rudiger Dornbusch 1976, 1162). The market response of a monetary expansion is “to induce an immediate depreciation in the exchange rate and accounts therefore for fluctuations in the exchange rate and the terms of trade. During the adjustment process, rising prices may be accompanied by an appreciating exchange rate so that the trend behavior of exchange rates stands potentially in strong contrast with the cyclical behavior of exchange rates and prices” (Dornbusch 1976, 1162). The volatility of the exchange rate “is needed to temporarily equilibrate the system in response to monetary shocks, because underlying national prices adjust so slowly” (Rogoff 2002MF http://www.imf.org/external/np/speeches/2001/kr/112901.pdf 3). The exchange rate “is identified as a critical channel for the transmission of monetary policy to aggregate demand for domestic output” (Dornbusch 1976, 1162).
In a world of exchange wars, depreciation of the host-country currency can move even faster such that the profits from the carry trade may become major losses. Depreciation is the percentage change in instants against which the interest rate of a day is in the example [(10)(1/360)] or 0.03 percent. Exchange rates move much faster in the real world as in the overshooting model of Dornbusch (1976). Profits in carry trades have greater risks but equally greater returns when the short position in zero interest rates, or borrowing, and on the dollar, are matched with truly agile financial risk assets such as commodities and equities. A simplified analysis could consider the portfolio balance equations Aij = f(r, x) where Aij is the demand for i = 1,2,∙∙∙n assets from j = 1,2, ∙∙∙m sectors, r the 1xn vector of rates of return, ri, of n assets and x a vector of other relevant variables. Tobin (1969) and Brunner and Meltzer (1973) assume imperfect substitution among capital assets such that the own first derivatives of Aij are positive, demand for an asset increases if its rate of return (interest plus capital gains) is higher, and cross first derivatives are negative, demand for an asset decreases if the rate of return of alternative assets increases. Theoretical purity would require the estimation of the complete model with all rates of return. In practice, it may be impossible to observe all rates of return such as in the critique of Roll (1976). Policy proposals and measures by the Fed have been focused on the likely impact of withdrawals of stocks of securities in specific segments, that is, of effects of one or several specific rates of return among the n possible rates. In fact, the central bank cannot influence investors and arbitrageurs to allocate funds to assets of desired categories such as asset-backed securities that would lower the costs of borrowing for mortgages and consumer loans. Floods of cheap money may simply induce carry trades in arbitrage of opportunities in fast moving assets such as currencies, commodities and equities instead of much lower returns in fixed income securities (see http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/07/causes-of-2007-creditdollar-crisis.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/07/causes-of-2007-creditdollar-crisis.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/professor-mckinnons-bubble-economy.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/world-inflation-quantitative-easing.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/treasury-yields-valuation-of-risk.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/11/quantitative-easing-theory-evidence-and.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/12/is-fed-printing-money-what-are.html).
It is in this context of economic and financial uncertainties that decisions on portfolio choices of risk financial assets must be made. There is a new carry trade that learned from the losses after the crisis of 2007 or learned from the crisis how to avoid losses. The sharp rise in valuations of risk financial assets shown in Table VI-1 after the first policy round of near zero fed funds and quantitative easing by the equivalent of withdrawing supply with the suspension of the 30-year Treasury auction was on a smooth trend with relatively subdued fluctuations. The credit crisis and global recession have been followed by significant fluctuations originating in sovereign risk issues in Europe, doubts of continuing high growth and accelerating inflation in China now complicated by political developments, events such as in the Middle East and Japan and legislative restructuring, regulation, insufficient growth, falling real wages, depressed hiring and high job stress of unemployment and underemployment in the US now with realization of growth standstill. The “trend is your friend” motto of traders has been replaced with a “hit and realize profit” approach of managing positions to realize profits without sitting on positions. There is a trend of valuation of risk financial assets driven by the carry trade from zero interest rates with fluctuations provoked by events of risk aversion or the “sharp shifts in risk appetite” of Blanchard (2012WEOApr, XIII). Table II-1, which is updated for every comment of this blog, shows the deep contraction of valuations of risk financial assets after the Apr 2010 sovereign risk issues in the fourth column “∆% to Trough.” There was sharp recovery after around Jul 2010 in the last column “∆% Trough to 4/20/12,” which has been recently stalling or reversing amidst profound risk aversion. “Let’s twist again” monetary policy during the week of Sep 23 caused deep worldwide risk aversion and selloff of risk financial assets (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/09/imf-view-of-world-economy-and-finance.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/09/collapse-of-household-income-and-wealth.html). Monetary policy was designed to increase risk appetite but instead suffocated risk exposures. There has been rollercoaster fluctuation in risk aversion and financial risk asset valuations: surge in the week of Dec 2, mixed performance of markets in the week of Dec 9, renewed risk aversion in the week of Dec 16, end-of-the-year relaxed risk aversion in thin markets in the weeks of Dec 23 and Dec 30, mixed sentiment in the weeks of Jan 6 and Jan 13 2012 and strength in the weeks of Jan 20, Jan 27 and Feb 3 followed by weakness in the week of Feb 10 but strength in the weeks of Feb 17 and 24 followed by uncertainty on financial counterparty risk in the weeks of Mar 2 and Mar 9. All financial values have fluctuated with events such as the surge in the week of Mar 16 on favorable news of Greece’s bailout even with new risk issues arising in the week of Mar 23 but renewed risk appetite in the week of Mar 30 because of the end of the quarter and the increase in the firewall of support of sovereign debts in the euro area. New risks developed in the week of Apr 6 with increase of yields of sovereign bonds of Spain and Italy, doubts on Fed policy and weak employment report. Asia and financial entities are experiencing their own risk environments. Financial markets were under stress in the week of Apr 13 because of the large exposure of Spanish banks to lending by the European Central Bank and the annual equivalent growth rate of China’s GDP of 7.4 percent in IQ2012. There was strength again in the week of Apr 20 because of the enhanced IMF firewall and Spain placement of debt. The highest valuations in column “∆% Trough to 4/20/12” are by US equities indexes: DJIA 34.5 percent and S&P 500 34.8 percent, driven by stronger earnings and economy in the US than in other advanced economies. The DJIA reached in intraday trading 13,331.77 on Mar 16, which is the highest level in 52 weeks (http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_PRO_hps_marketdata). The carry trade from zero interest rates to leveraged positions in risk financial assets had proved strongest for commodity exposures but US equities have regained leadership. Before the current round of risk aversion, all assets in the column “∆% Trough to 4/20/12” had double digit gains relative to the trough around Jul 2, 2010 but now only three valuation show increase of less than 10 percent: China’s Shanghai Composite is 1.0 percent above the trough; STOXX 50 of Europe is 5.6 percent above the trough; and Japan’s Nikkei Average is 8.4 percent above the trough. DJ UBS Commodities is 11.5 percent above the trough; Dow Global is 13.2 percent above the trough; and DAX is 19.0 percent above the trough. Japan’s Nikkei Average is 8.4 percent above the trough on Aug 31, 2010 and 16.1 percent below the peak on Apr 5, 2010. The Nikkei Average closed at 9561.36 on Fri Apr 20, 2012 (http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_PRO_hps_marketdata), which is 6.8 percent lower than 10,254.43 on Mar 11, 2011, on the date of the Great East Japan Earthquake/tsunami. Global risk aversion erased the earlier gains of the Nikkei. The dollar depreciated by 10.9 percent relative to the euro and even higher before the new bout of sovereign risk issues in Europe. The column “∆% week to 4/20/12” in Table II-1 shows increases of most valuations of risk financial assets in the week of Apr 20, 2012, with exception of decline of 0.8 percent by Japan’s Nikkei Average and decline of 0.6 percent for DJ Asia Pacific. There are still high uncertainties on European sovereign risks, US and world growth slowdown and China’s growth tradeoffs. Sovereign problems in the “periphery” of Europe and fears of slower growth in Asia and the US cause risk aversion with trading caution instead of more aggressive risk exposures. There is a fundamental change in Table II-1 from the relatively upward trend with oscillations since the sovereign risk event of Apr-Jul 2010. Performance is best assessed in the column “∆% Peak to 4/20/12” that provides the percentage change from the peak in Apr 2010 before the sovereign risk event to Apr 6, 2012. Most risk financial assets had gained not only relative to the trough as shown in column “∆% Trough to 4/20/12” but also relative to the peak in column “∆% Peak to 4/20/12.” There are now only three equity indexes above the peak in Table II-1: DJIA 16.3 percent, S&P 500 13.2 percent and Dax 6.6 percent. There are several indexes below the peak: NYSE Financial Index (http://www.nyse.com/about/listed/nykid.shtml) by 13.1 percent, Nikkei Average by 16.1 percent, Shanghai Composite by 23.9 percent, STOXX 50 by 10.6 percent and Dow Global by 7.7 percent. DJ UBS Commodities Index is now 4.7 percent below the peak. The factors of risk aversion have adversely affected the performance of risk financial assets. The performance relative to the peak in Apr 2010 is more important than the performance relative to the trough around early Jul because improvement could signal that conditions have returned to normal levels before European sovereign doubts in Apr 2010. An intriguing issue is the difference in performance of valuations of risk financial assets and economic growth and employment. Paul A. Samuelson (http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/economics/laureates/1970/samuelson-bio.html) popularized the view of the troubled relation between stock markets and economic activity in an often-quoted phrase “the stock market has forecast nine of the last five recessions.” In the presence of zero interest rates forever, valuations of risk financial assets are likely to differ from the performance of the overall economy.
Tabl II-1, Stock Indexes, Commodities, Dollar and 10-Year Treasury
| Peak | Trough | ∆% to Trough | ∆% Peak to 4/20 /12 | ∆% Week 4/20/ 12 | ∆% Trough to 4/20 12 | |
| DJIA | 4/26/ | 7/2/10 | -13.6 | 16.3 | 1.4 | 34.5 |
| S&P 500 | 4/23/ | 7/20/ | -16.0 | 13.2 | 0.6 | 34.8 |
| NYSE Finance | 4/15/ | 7/2/10 | -20.3 | -13.1 | 1.0 | 9.0 |
| Dow Global | 4/15/ | 7/2/10 | -18.4 | -7.7 | 0.9 | 13.2 |
| Asia Pacific | 4/15/ | 7/2/10 | -12.5 | -2.9 | -0.6 | 10.9 |
| Japan Nikkei Aver. | 4/05/ | 8/31/ | -22.5 | -16.1 | -0.8 | 8.4 |
| China Shang. | 4/15/ | 7/02 | -24.7 | -23.9 | 2.0 | 1.0 |
| STOXX 50 | 4/15/10 | 7/2/10 | -15.3 | -10.6 | 2.4 | 5.6 |
| DAX | 4/26/ | 5/25/ | -10.5 | 6.6 | 2.5 | 19.0 |
| Dollar | 11/25 2009 | 6/7 | 21.2 | 12.6 | -1.1 | -10.9 |
| DJ UBS Comm. | 1/6/ | 7/2/10 | -14.5 | -4.7 | -0.9 | 11.5 |
| 10-Year T Note | 4/5/ | 4/6/10 | 3.986 | 1.959 |
T: trough; Dollar: positive sign appreciation relative to euro (less dollars paid per euro), negative sign depreciation relative to euro (more dollars paid per euro)
Source: http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_hps_marketdata
III World Financial Turbulence. Financial markets are being shocked by multiple factors including (1) world economic slowdown; (2) growth in China with political development, Japan and world trade; (3) slow growth propelled by savings reduction in the US with high unemployment/underemployment, falling wages and hiring collapse; and (3) the outcome of the sovereign debt crisis in Europe. This section provides current data and analysis. Subsection IIIA Financial Risks provides analysis of the evolution of valuations of risk assets during the week. There are various appendixes at the end of this section for convenience of reference of material related to the euro area debt crisis. Some of this material is updated in Subsection IIIA when new data are available and then maintained in the appendixes for future reference until updated again in Subsection IIIA. Subsection IIIB Appendix on Safe Haven Currencies discusses arguments and measures of currency intervention. Subsection IIIC Appendix on Fiscal Compact provides analysis of the restructuring of the fiscal affairs of the European Union in the agreement of European leaders reached on Dec 9, 2011. Subsection IIID Appendix on European Central Bank Large Scale Lender of Last Resort considers the policies of the European Central Bank. Appendix IIIE Euro Zone Survival Risk analyzes the threats to survival of the European Monetary Union. Subsection IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation provides more technical analysis.
IIIA Financial Risks. The past half year has been characterized by financial turbulence, attaining unusual magnitude in recent months. Table III-1, updated with every comment in this blog, provides beginning values on Fr Apr 13 and daily values throughout the week ending on Fri Apr 20 of various financial assets. Section VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets provides a set of more complete values. All data are for New York time at 5 PM. The first column provides the value on Fri Apr 13 and the percentage change in that prior week below the label of the financial risk asset. For example, the US dollar (USD) appreciated 0.1 percent to USD 1.3078/EUR in the week ending on Apr 13. The first five asset rows provide five key exchange rates versus the dollar and the percentage cumulative appreciation (positive change or no sign) or depreciation (negative change or negative sign). Positive changes constitute appreciation of the relevant exchange rate and negative changes depreciation. Financial turbulence has been dominated by reactions to the new program for Greece (see section IB in http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/07/debt-and-financial-risk-aversion-and.html), modifications and new approach adopted in the Euro Summit of Oct 26 (European Commission 2011Oct26SS, 2011Oct26MRES), doubts on the larger countries in the euro zone with sovereign risks such as Spain and Italy but expanding into possibly France and Germany, the growth standstill recession and long-term unsustainable government debt in the US, worldwide deceleration of economic growth and continuing waves of inflation. The most important current shock is that resulting from the agreement by European leaders at their meeting on Dec 9 (European Council 2911Dec9), which is analyzed in IIIC Appendix on Fiscal Compact. European leaders reached a new agreement on Jan 30 (http://www.consilium.europa.eu/uedocs/cms_data/docs/pressdata/en/ec/127631.pdf).
The dollar/euro rate is quoted as number of US dollars USD per one euro EUR, USD 1.3078/EUR in the first row, first column in the block for currencies in Table III-1 for Fri Apr 13, depreciating to USD 1.3143/EUR on Mon Apr 16, or by 0.5 percent. The dollar depreciated because more dollars, $1.3143, were required on Mon Apr 16 to buy one euro than $1.3078 on Apr 13. Table III-1 defines a country’s exchange rate as number of units of domestic currency per unit of foreign currency. USD/EUR would be the definition of the exchange rate of the US and the inverse [1/(USD/EUR)] is the definition in this convention of the rate of exchange of the euro zone, EUR/USD. A convention used throughout this blog is required to maintain consistency in characterizing movements of the exchange rate in Table III-1 as appreciation and depreciation. The first row for each of the currencies shows the exchange rate at 5 PM New York time, such as USD 1.3143/EUR on Apr 16; the second row provides the cumulative percentage appreciation or depreciation of the exchange rate from the rate on the last business day of the prior week, in this case Fri Apr 13, to the last business day of the current week, in this case Fri Apr 20, such as depreciation by 1.1 percent to USD 1.3220/EUR by Apr 120; and the third row provides the percentage change from the prior business day to the current business day. For example, the USD depreciated (denoted by positive sign) by 1.1 percent from the rate of USD 1.3078/EUR on Fri Apr 13 to the rate of USD 1.3220/EUR on Fri Apr 20 {[(1.3220/1.3078) – 1]100 = 1.1%} and depreciated (denoted by negative sign) by 0.6 percent from the rate of USD 1.3139 on Thu Apr 19 to USD 1.3220/EUR on Fri Apr 20 {[(1.3220/1.3139) -1]100 = 0.6%}. Other factors constant, appreciation of the dollar relative to the euro is caused by increasing risk aversion, with rising uncertainty on European sovereign risks increasing dollar-denominated assets with sales of risk financial investments. Funds move away from higher yielding risk financial assets to the safety of dollar investments. When risk aversion declines, funds have been moving away from safe assets in dollars to risk financial assets, depreciating the dollar.
Table III-I, Weekly Financial Risk Assets Apr 16 to Apr 20, 2012
| Fri Apr 13, 2012 | M 16 | Tue 17 | W 18 | Thu 19 | Fr 20 |
| USD/EUR 1.3078 0.1% | 1.3143 -0.5% -0.55 | 1.3127 -0.4% 0.1% | 1.3122 -0.3% 0.0% | 1.3139 -0.5% -0.1% | 1.3220 -1.1% -0.6% |
| JPY/ USD 80.92 0.9% | 80.39 0.7% 0.7% | 80.91 0.0% -0.6% | 81.25 -0.4% -0.4% | 81.62 -0.9% -0.5% | 81.51 -0.7% 0.1% |
| CHF/ USD 0.9195 -0.3% | 0.9145 0.5% 0.5% | 0.9153 0.5% -0.1% | 0.9161 0.4% -0.1% | 0.9151 0.5% 0.1% | 0.9088 1.2% 0.7% |
| CHF/ EUR 1.2024 -0.1% | 1.2020 0.0% 0.0% | 1.2014 0.1% 0.0% | 1.2020 0.0% 0.0% | 1.2022 0.0% 0.0% | 1.2014 0.1% 0.1% |
| USD/ AUD 1.0372 0.9641 0.6% | 1.0357 0.9655 -0.1% -0.1% | 1.0395 0.9620 0.2% 0.4% | 1.0355 0.9657 -0.2% -0.4% | 1.0335 0.9676 -0.4% -0.2% | 1.0378 0.9636 0.1% 0.4% |
| 10 Year T Note 1.987 | 1.98 | 1.99 | 1.98 | 1.97 | 1.959 |
| 2 Year T Note 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.27 | 0.268 |
| German Bond 2Y 0.13 10Y 1.74 | 2Y 0.14 10Y 1.72 | 2Y 0.15 10Y 1.75 | 2Y 0.14 10Y 1.72 | 2Y 0.13 10Y 1.69 | 2Y 0.14 10Y 1.71 |
| DJIA 12849.59 -1.6% | 12921.41 0.6% 0.6% | 13115.54 2.1% 1.5% | 13032.75 1.4% -0.6% | 12964.10 0.9% -0.5% | 13029.26 1.4% 0.5% |
| DJ Global 1909.67 -2.1% | 1905.90 -0.2% -0.2% | 1935.58 1.4% 1.6% | 1929.18 1.0% -0.3% | 1921.34 0.6% -0.4% | 1926.87 0.9% 0.3% |
| DJ Asia Pacific 1278.01 0.2% | 1270.00 -0.6% -0.6% | 1265.29 -1.0% -0.4% | 1277.96 0.0% 1.0% | 1274.56 -0.3% -0.3% | 1270.07 -0.6% -0.4% |
| Nikkei 9637.99 -0.5% | 9470.64 -1.7% -1.7% | 9464.71 -1.8% -0.1% | 9667.26 0.3% 2.1% | 9588.38 -0.5% -0.8% | 9561.36 -0.8% -0.3% |
| Shanghai 2359.16 2.3% | 2357.03 -0.1% -0.1% | 2334.98 -1.0% -0.9% | 2380.85 0.9% 2.0% | 2378.63 0.8% -0.1% | 2406.86 2.0% 1.2% |
| DAX 6583.90 -2.8% | 6625.19 0.6% 0.6% | 6801.00 3.3% 2.7% | 6732.03 2.2% -1.0% | 6671.22 1.3% -0.9% | 6750.12 2.5% 1.2% |
| DJ UBS Comm. 139.46 -1.6% | 138.24 -0.9% -0.9% | 138.46 -0.7% 0.2% | 137.17 -1.6% -0.9% | 137.52 -1.4% 0.3% | 138.20 -0.9% 0.5% |
| WTI $ B 102.83 -0.5% | 103.62 0.8% 0.8% | 104.22 1.4% 0.6% | 102.72 -0.1% -1.4% | 102.59 -0.2% -0.1% | 104.03 1.2% 1.4% |
| Brent $/B 121.22 -1.8% | 118.92 -1.9% -1.9% | 118.65 -2.1% -0.2% | 118.09 -2.6% -0.5% | 118.03 -2.6% -0.1% | 118.85 -1.9% 0.7% |
| Gold $/OZ 1658.2 1.7% | 1653.6 -0.3% -0.3% | 1651.3 -0.4% -0.1% | 1641.6 -1.0% -0.6% | 1643.1 -0.9% 0.1% | 1643.0 -0.9% 0.0% |
Note: USD: US dollar; JPY: Japanese Yen; CHF: Swiss
Franc; AUD: Australian dollar; Comm.: commodities; OZ: ounce
Sources: http://www.bloomberg.com/markets/
http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_hps_marketdata
Spain continues to drive euro area credit risk with hurdles in adjusting its high fiscal deficit, domestic economic recession, high unemployment and unresolved bank balance sheets. The Bank of Spain released on Apr 18 new worrisome data on delinquent credit in Spain’s credit institutions (http://www.bde.es/webbde/es/secciones/prensa/Agenda/Datos_de_credit_c62379ebaa85631.html). The aggregate balance sheet of institutions supervised by the Bank of Spain registered total credit of €1,508,626 million in 2006 with delinquent credit of €10,859 million or 0.7 percent. The latest available data for Feb 2012 registers total credit of €1,763,312 million with delinquent credit of €143,815 million or 8.2 percent. Total credit has contracted from a peak of €1,869,882 million in 2008 to €1,763,313 on Feb 2012 or by 5.7 percent. Delinquent credit has risen from €10,859 million in 2006 to €143,815 million in Feb 2012 or by 1224 percent. The credit standing of Spain may be further imperiled if the country is forced into bank nationalizations or absorptions of bad loans by the government. There is troubled history of government ownership and control of banks (Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance: Theory and Policy after the Credit Crisis (2009b), 227-9; Pelaez 1975, Pelaez and Suzigan 1981, following Cameron 1961, 1967, 1972). Christopher Bjork and Jonathan House, writing on “Spanish banks’ ECB borrowing hits high,” on Apr 13, published by the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052702304356604577341133498311916.html?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection), analyze the impact on valuations of risk financial assets from new data on Spanish bank borrowing. The Bank of Spain, as quoted by Bjork and House, provided information on average Spanish bank borrowing from the European Central Bank increasing from €169.85 billion in Feb to €316.3 billion in Mar, or USD 417.10 billion, which are substantially higher than €106.3 billion before long-term refinancing operations (LTRO). Spain borrowed 28 percent of lending of €1.1 trillion by the ECB to banks in the euro zone. A crucial fact provided by Bjork and House is that Spanish banks devoted €40.6 billion of their assigned LTROs to buying Spanish government debt, which is equivalent to one half of the needs of Spain in 2012. LTROs are effectively a bailout of Spain in which the European Central Bank (ECB) is taking credit risks in contrast with mostly rate risks in quantitative easing by the Fed.
A critical development in the resolution of the European debt crisis is the increase in available resources of the IMF announced in a joint statement of the IMFC and the Group of 20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors (IMFC 2012Apr20):
“There are firm commitments to increase resources made available to the IMF by over $430 billion in addition to the quota increase under the 2010 reform. These resources will be available for the whole membership of the IMF, and not earmarked for any particular region.”
Resources are not earmarked for the European debt crisis but it is the most threatening current vulnerability in the world economy.
The JPY reversed recent appreciation, depreciating 0.7 percent during the week of Apr 20. Japan’s has not been very successful in the past in foreign exchange interventions (Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 107-9). Japan is currently combining unconventional monetary policy and exchange intervention. The Policy Board of the Bank of Japan decided at its meeting on April 10, 2010 to continue “powerful easing” (http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2012/k120410a.pdf 2):
“The Bank recognizes that Japan's economy faces the critical challenge of overcoming deflation and returning to a sustainable growth path with price stability. The goal of overcoming deflation will be achieved both through efforts to strengthen the economy's growth potential and support from the financial side. With this in mind, the Bank will pursue powerful monetary easing, and will support private financial institutions in their efforts to strengthen the foundations for Japan's economic growth via the fund-provisioning measure to support strengthening the foundations for economic growth. At today's meeting, as shown in the Attachment, the Bank established detailed rules for a new U.S. dollar lending arrangement equivalent to 1 trillion yen, of which a preliminary outline was released at the previous meeting in March.”
The Policy Board of the Bank of Japan decided three important measures of enhancing monetary easing at the meeting held on Feb 14, 2012 (Bank of Japan 2012EME, 2012PSG and 2012APP). First, the Bank of Japan (2012Feb14EME, 2012Feb14PSG) adopted a “price stability goal” for the “medium term” of 2 percent of the “year-on-year rate of change of the CPI” with the immediate goal of inflation of 1 percent. Japan’s CPI inflation in the 12 months ending in Dec was minus 0.2 percent. Second, the Bank of Japan (2012Feb14EME, 1-2) will conduct “virtually zero interest rate policy” by maintaining “the uncollateralized overnight call rate at around 0 to 0.1 percent.” Third, the Bank of Japan (20012Feb13EME, 2014Feb14APP) is increasing the size of its quantitative easing:
“The Bank increases the total size of the Asset Purchase Program by about 10 trillion yen, from about 55 trillion yen to about 65 trillion yen. The increase in the Program is earmarked for the purchase of Japanese government bonds. By fully implementing the Program including the additional expansion decided today, by the end of 2012, the amount outstanding of the Program will be increased by about 22 trillion yen from the current level of around 43 trillion yen.”
IIIB Appendix on Safe Haven Currencies analyzes the burden on the Japanese economy of yen appreciation. Policy rates close to zero by major central banks in the world together with quantitative easing tend to depreciate currencies. Monetary policy is an indirect form of currency intervention.
The Swiss franc appreciated 1.2 percent in the week of Apr 20 to CHF 0.9088/USD relative to the dollar and appreciated 0.1 percent relative to the euro to CHF 1.2014, as shown in Table III-1. The important event in the prior weeks was appreciation of 0.3 percent by Apr 6 relative to the euro to the very bottom of the exchange rate floor at CHF 1.2009/EUR. William L. Watts, writing on “Euro weakness triggers Swissie showdown,” on Apr 5, published by MarketWatch (http://www.marketwatch.com/story/euro-weakness-triggers-swissie-showdown-2012-04-05), quotes exchange strategists claiming that at point on Apr 5 the Swiss franc traded at CHF 1.1990/EUR. Some participants believe that there was intervention by the Swiss National Bank to defend the floor of CHF `1.2000/EUR. The Australian dollar appreciated 0.1 percent to USD 1.0378/AUD by Apr 20 because of unfavorable environment for carry trades. The AUD is considered a carry trade commodity currency.
Risk aversion is captured by flight of investors from risk financial assets to the government securities of the US and Germany. Increasing aversion is captured by decrease of the yield of the ten-year Treasury. As shown in past updates of Table III-1, the ten-year Treasury yield fell from 2.234 percent on Mar 23 to 2.214 percent on Mar 30, collapsing to 2.058 percent on Apr 6 after the employment report and declining further to 1.987 on Apr 13 and 1.959 on Apr 20 because of increasing risk aversion. The ten-year Treasury yield is still at a level well below consumer price inflation of 2.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Mar (see subsection IB United States Inflation at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/04/fractured-labor-market-with-hiring.html). Treasury securities continue to be safe haven for investors fearing risk but with concentration in shorter maturities such as the two-year Treasury. As shown in past updates of Table III-1, the two-year Treasury yield fell marginally from 0.35 percent on Mar 23 to 0.335 percent on Mar 30 and then to 0.31 percent on Apr 6 and 0.27 percent on Apr 13, remaining almost unchanged at 0.268 percent on Apr 20. Investors are willing to sacrifice yield relative to inflation in defensive actions to avoid turbulence in valuations of risk financial assets but may be managing duration more carefully. During the financial panic of Sep 2008, funds moved away from risk exposures to government securities. The latest statement of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) on March 13, 2012 does not have sufficient changes suggesting that it contributed to the rise in Treasury yields. The statement continues to consider inflation low, unemployment high and growth at a moderate pace. Because of the “slack” in the economy, the FOMC maintained the zero interest rate policy until 2014 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20120313a.htm):
“In particular, the Committee decided today to keep the target range for the federal funds rate at 0 to 1/4 percent and currently anticipates that economic conditions--including low rates of resource utilization and a subdued outlook for inflation over the medium run--are likely to warrant exceptionally low levels for the federal funds rate at least through late 2014.”
A similar risk aversion phenomenon occurred in Germany. Eurostat confirmed euro zone CPI inflation is at 2.7 percent for the 12 months ending in Mar 2012 but jumping 1.3 percent in the month of Mar (http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/cache/ITY_PUBLIC/2-17042012-AP/EN/2-17042012-AP-EN.PDF) but the yield of the two-year German government bond fell from 0.23 percent on Mar 23 to 0.21 percent on Mar 30, 0.14 percent on Apr 6 and 0.13 percent on Apr 13 with 0.14 percent on Apr 20 while the yield of the ten-year German government bond fell from 1.87 on Mar 23 to 1.79 percent on Mar 30 and then to 1.74 on Apr 6 and also on Apr 13 with 1.71 percent on Apr 20, as shown in Table III-1 and past updates. Safety overrides inflation-adjusted yield but there could be duration aversion. Turbulence has also affected the market for German sovereign bonds.
Equity indexes in Table III-1 were mostly strong during the week of Apr 20 because of hope of resolution with the enhanced firewall of the IMF. Germany’s Dax jumped 2.5 percent while DJIA gained 1.4 percent in the week of Apr 20 and Dow Global increased 0.9 percent. Japan’s Nikkei Average interrupted recent increases with decline of 3.9 percent in the week of Apr 6, decline of 0.5 percent in the week of Apr 13 and another decline of 08 percent in the week of Apr 20. Dow Asia Pacific dropped 0.6 percent in the week of Apr 20 while Shanghai’s composite increased 2.0 percent.
Commodities were mostly weak during the week of Apr 20. The DJ UBS Commodities Index dropped 0.9 percent. WTI gained 1.2 percent and Brent decreased 1.9 percent. Gold fell 0.9 percent.
Risk aversion during the week of Mar 2, 2012, was dominated by the long-term refinancing operations (LTRO) of the European Central Bank. LTROs and related principles are analyzed in subsection IIID Appendix on European Central Bank Large Scale Lender of Last Resort. First, as analyzed by David Enrich, writing on “ECB allots €529.5 billion in long-term refinancing operations,” published on Feb 29, 2012 by the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052970203986604577252803223310964.html?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection), the ECB provided a second round of three-year loans at 1.0 percent to about 800 banks. The earlier round provided €489 billion to more than 500 banks. Second, the ECB sets the fixed-rate for main refinancing operations at 1.00 percent and the overnight deposit facility at 0.25 percent (http://www.ecb.int/home/html/index.en.html) for negative spread of 75 basis points. That is, if a bank borrows at 1.0 percent for three years through the LTRO and deposits overnight at the ECB, it incurs negative spread of 75 basis points. An alternative allocation could be to lend for a positive spread to other banks. Richard Milne, writing on “Banks deposit record cash with ECB,” on Mar 2, 2012, published in the Financial Times (http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/9798fd36-644a-11e1-b30e-00144feabdc0.html#axzz1nxeicB6H), provides important information and analysis that banks deposited a record €776.9 billion at the ECB on Fri Mar 2 at interest receipt of 0.25 percent, just two days after receiving €529.5 billion of LTRO loans at interest cost of 1.0 percent. The main issue here is whether there is ongoing perceptions of high risks in counterparties in financial transactions that froze credit markets in 2008 (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009a), 57-60, 217-27, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009b), 155-67). Richard Milne and Mary Watkins, writing on “European finance: the leaning tower of perils,” on Mar 27, 2012, published in the Financial Times (http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/82205f6e-7735-11e1-baf3-00144feab49a.html#axzz1qOqWaqF2), raise concerns that the large volume of LTROs can create future problems for banks and the euro area. An important issue is if the cheap loans at 1 percent for three-year terms finance the carry trade into securities of the governments of banks. Balance sheets of banks may be stressed during future sovereign-credit events. Sam Jones, writing on “ECB liquidity fuels high stakes hedging,” on Apr 4, 2012, published in the Financial Times (http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/cb74d63a-7e75-11e1-b009-00144feab49a.html#axzz1qyDYxLjS), analyzes unusually high spreads in government bond markets in Europe that could have been caused by LTROs. There has been active relative value arbitrage of these spreads similar to the strategies of Long-Term Capital Management (LTCM) of capturing high spreads in mortgage-backed securities jointly with hedges in Treasury securities (on LTCM see Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), 108-12, 87-9, The Global Recession Risk (2007) 12-3, 102, 176, Globalization and the State, Vol. I (2008a), 59-64).
Table III-1A provides an update of the consolidated financial statement of the Eurosystem. The balance sheet has swollen with the LTROs. Line 5 “Lending to Euro Area Credit Institutions Related to Monetary Policy” increasing from €546,747 million on Dec 31, 2010, to €870,130 million on Dec 28, 2011 and €1,147,981 million on Apr 13, 2012. The sum of line 5 and line 7 (“Securities of Euro Area Residents Denominated in Euro”) has increased to €1,775,693 million in the statement of Apr 13.
Table III-1A, Consolidated Financial Statement of the Eurosystem, Million EUR
| Dec 31, 2010 | Dec 28, 2011 | Apr 13, 2012 | |
| 1 Gold and other Receivables | 367,402 | 419,822 | 423,706 |
| 2 Claims on Non Euro Area Residents Denominated in Foreign Currency | 223,995 | 236,826 | 239,669 |
| 3 Claims on Euro Area Residents Denominated in Foreign Currency | 26,941 | 95,355 | 55,513 |
| 4 Claims on Non-Euro Area Residents Denominated in Euro | 22,592 | 25,982 | 20,106 |
| 5 Lending to Euro Area Credit Institutions Related to Monetary Policy Operations Denominated in Euro | 546,747 | 879,130 | 1,147,981 |
| 6 Other Claims on Euro Area Credit Institutions Denominated in Euro | 45,654 | 94,989 | 62,548 |
| 7 Securities of Euro Area Residents Denominated in Euro | 457,427 | 610,629 | 627,712 |
| 8 General Government Debt Denominated in Euro | 34,954 | 33,928 | 31,131 |
| 9 Other Assets | 278,719 | 336,574 | 358,493 |
| TOTAL ASSETS | 2,004, 432 | 2,733,235 | 2,974,859 |
| Memo Items | |||
| Sum of 5 and 7 | 1,004,174 | 1,489,759 | 1,775,693 |
| Capital and Reserves | 78,143 | 81,481 | 85,819 |
Source: European Central Bank
http://www.ecb.int/press/pr/wfs/2011/html/fs110105.en.html
http://www.ecb.int/press/pr/wfs/2011/html/fs111228.en.html
http://www.ecb.int/press/pr/wfs/2012/html/fs120417.en.html
Brazil faced in the debt crisis of 1982 a more complex policy mix. Between 1977 and 1983, Brazil’s terms of trade, export prices relative to import prices, deteriorated 47 percent and 36 percent excluding oil (Pelaez 1987, 176-79; Pelaez 1986, 37-66; see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 178-87). Brazil had accumulated unsustainable foreign debt by borrowing to finance balance of payments deficits during the 1970s. Foreign lending virtually stopped. The German mark devalued strongly relative to the dollar such that Brazil’s products lost competitiveness in Germany and in multiple markets in competition with Germany. The resolution of the crisis was devaluation of the Brazilian currency by 30 percent relative to the dollar and subsequent maintenance of parity by monthly devaluation equal to inflation and indexing that resulted in financial stability by parity in external and internal interest rates avoiding capital flight. With a combination of declining imports, domestic import substitution and export growth, Brazil followed rapid growth in the US and grew out of the crisis with surprising GDP growth of 4.5 percent in 1984.
The euro zone faces a critical survival risk because several of its members may default on their sovereign obligations if not bailed out by the other members. The valuation equation of bonds is essential to understanding the stability of the euro area. An explanation is provided in this paragraph and readers interested in technical details are referred to the following Subsection IIID Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation. Contrary to the Wriston doctrine, investing in sovereign obligations is a credit decision. The value of a bond today is equal to the discounted value of future obligations of interest and principal until maturity. On Dec 30 the yield of the 2-year bond of the government of Greece was quoted around 100 percent. In contrast, the 2-year US Treasury note traded at 0.239 percent and the 10-year at 2.871 percent while the comparable 2-year government bond of Germany traded at 0.14 percent and the 10-year government bond of Germany traded at 1.83 percent. There is no need for sovereign ratings: the perceptions of investors are of relatively higher probability of default by Greece, defying Wriston (1982), and nil probability of default of the US Treasury and the German government. The essence of the sovereign credit decision is whether the sovereign will be able to finance new debt and refinance existing debt without interrupting service of interest and principal. Prices of sovereign bonds incorporate multiple anticipations such as inflation and liquidity premiums of long-term relative to short-term debt but also risk premiums on whether the sovereign’s debt can be managed as it increases without bound. The austerity measures of Italy are designed to increase the primary surplus, or government revenues less expenditures excluding interest, to ensure investors that Italy will have the fiscal strength to manage its debt of 120 percent of GDP, which is the third largest in the world after the US and Japan. Appendix IIIE links the expectations on the primary surplus to the real current value of government monetary and fiscal obligations. As Blanchard (2011SepWEO) analyzes, fiscal consolidation to increase the primary surplus is facilitated by growth of the economy. Italy and the other indebted sovereigns in Europe face the dual challenge of increasing primary surpluses while maintaining growth of the economy (for the experience of Brazil in the debt crisis of 1982 see Pelaez 1986, 1987).
Much of the analysis and concern over the euro zone centers on the lack of credibility of the debt of a few countries while there is credibility of the debt of the euro zone as a whole. In practice, there is convergence in valuations and concerns toward the fact that there may not be credibility of the euro zone as a whole. The fluctuations of financial risk assets of members of the euro zone move together with risk aversion toward the countries with lack of debt credibility. This movement raises the need to consider analytically sovereign debt valuation of the euro zone as a whole in the essential analysis of whether the single-currency will survive without major changes.
Welfare economics considers the desirability of alternative states, which in this case would be evaluating the “value” of Germany (1) within and (2) outside the euro zone. Is the sum of the wealth of euro zone countries outside of the euro zone higher than the wealth of these countries maintaining the euro zone? On the choice of indicator of welfare, Hicks (1975, 324) argues:
“Partly as a result of the Keynesian revolution, but more (perhaps) because of statistical labours that were initially quite independent of it, the Social Product has now come right back into its old place. Modern economics—especially modern applied economics—is centered upon the Social Product, the Wealth of Nations, as it was in the days of Smith and Ricardo, but as it was not in the time that came between. So if modern theory is to be effective, if it is to deal with the questions which we in our time want to have answered, the size and growth of the Social Product are among the chief things with which it must concern itself. It is of course the objective Social Product on which attention must be fixed. We have indexes of production; we do not have—it is clear we cannot have—an Index of Welfare.”
If the burden of the debt of the euro zone falls on Germany and France or only on Germany, is the wealth of Germany and France or only Germany higher after breakup of the euro zone or if maintaining the euro zone? In practice, political realities will determine the decision through elections.
The prospects of survival of the euro zone are dire. Table III-B is constructed with IMF World Economic Outlook database (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/index.aspx) for GDP in USD billions, primary net lending/borrowing as percent of GDP and general government debt as percent of GDP for selected regions and countries in 2010.
Table III-1B, World and Selected Regional and Country GDP and Fiscal Situation
| GDP 2012 | Primary Net Lending Borrowing | General Government Net Debt | |
| World | 69,660 | ||
| Euro Zone | 12,586 | -0.5 | 70.3 |
| Portugal | 221 | 0.1 | 110.9 |
| Ireland | 210 | -4.4 | 102.9 |
| Greece | 271 | -1.0 | 153.2 |
| Spain | 1,398 | -3.6 | 67.0 |
| Major Advanced Economies G7 | 34,106 | -4.8 | 88.3 |
| United States | 15,610 | -6.1 | 83.7 |
| UK | 2,453 | -5.3 | 84.2 |
| Germany | 3,479 | 1.0 | 54.1 |
| France | 2,712.0 | -2.2 | 83.2 |
| Japan | 5,981 | -8.9 | 135.2 |
| Canada | 1,805 | -3.1 | 35.4 |
| Italy | 2,067 | 2.9 | 102.3 |
| China | 7992 | -1.3* | 22.0** |
*Net Lending/borrowing**Gross Debt
Source: http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/weoselgr.aspx
The data in Table III-1B are used for some very simple calculations in Table I-9. The column “Net Debt USD Billions” in Table III-1C is generated by applying the percentage in Table III-1B column “General Government Net Debt % GDP 2010” to the column “GDP USD Billions.” The total debt of France and Germany in 2012 is $4138.5 billion, as shown in row “B+C” in column “Net Debt USD Billions” The sum of the debt of Italy, Spain, Portugal, Greece and Ireland is $3927.8 billion, adding rows D+E+F+G+H in column “Net Debt USD billions.” There is some simple “unpleasant bond arithmetic” in the two final columns of Table III-B. Suppose the entire debt burdens of the five countries with probability of default were to be guaranteed by France and Germany, which de facto would be required by continuing the euro zone. The sum of the total debt of these five countries and the debt of France and Germany is shown in column “Debt as % of Germany plus France GDP” to reach $8066.3 billion, which would be equivalent to 130.3 percent of their combined GDP in 2012. Under this arrangement the entire debt of the euro zone including debt of France and Germany would not have nil probability of default. The final column provides “Debt as % of Germany GDP” that would exceed 231.9 percent if including debt of France and 167.0 percent of German GDP if excluding French debt. The unpleasant bond arithmetic illustrates that there is a limit as to how far Germany and France can go in bailing out the countries with unsustainable sovereign debt without incurring severe pains of their own such as downgrades of their sovereign credit ratings. A central bank is not typically engaged in direct credit because of remembrance of inflation and abuse in the past. There is also a limit to operations of the European Central Bank in doubtful credit obligations. Wriston (1982) would prove to be wrong again that countries do not bankrupt but would have a consolation prize that similar to LBOs the sum of the individual values of euro zone members outside the current agreement exceeds the value of the whole euro zone. Internal rescues of French and German banks may be less costly than bailing out other euro zone countries so that they do not default on French and German banks.
Table III-1C, Guarantees of Debt of Sovereigns in Euro Area as Percent of GDP of Germany and France, USD Billions and %
| Net Debt USD Billions | Debt as % of Germany Plus France GDP | Debt as % of Germany GDP | |
| A Euro Area | 8,847.9 | ||
| B Germany | 1,882.1 | $8066.3 as % of $3479 =231.9% $5809.9 as % of $3479 =167.0% | |
| C France | 2,256.4 | ||
| B+C | 4,138.5 | GDP $6,191.0 Total Debt $8066.3 Debt/GDP: 130.3% | |
| D Italy | 2,114.5 | ||
| E Spain | 936.7 | ||
| F Portugal | 245.3 | ||
| G Greece | 415.2 | ||
| H Ireland | 216.1 | ||
| Subtotal D+E+F+G+H | 3,927.8 |
Source: calculation with IMF data http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/index.aspx
IIIB Appendix on Safe Haven Currencies. Safe-haven currencies, such as the Swiss franc (CHF) and the Japanese yen (JPY) have been under threat of appreciation but also remained relatively unchanged. A characteristic of the global recession would be struggle for maintaining competitiveness by policies of regulation, trade and devaluation (Pelaez and Pelaez, Government Intervention in Globalization: Regulation, Trade and Devaluation War (2008c)). Appreciation of the exchange rate causes two major effects on Japan.
1. Trade. Consider an example with actual data (Pelaez and Pelaez, Government Intervention in Globalization: Regulation, Trade and Devaluation Wars (2008c), 70-72). The yen traded at JPY 117.69/USD on Apr 2, 2007 and at JPY 102.77/USD on Apr 2, 2008, or appreciation of 12.7 percent. This meant that an export of JPY 10,000 to the US sold at USD 84.97 on Apr 2, 2007 [(JPY 10,000)/(USD 117.69/USD)], rising to USD 97.30 on Apr 2, 2008 [(JPY 10,000)/(JPY 102.77)]. If the goods sold by Japan were invoiced worldwide in dollars, Japanese’s companies would suffer a reduction in profit margins of 12.7 percent required to maintain the same dollar price. An export at cost of JPY 10,000 would only bring JPY 8,732 when converted at JPY 102.77 to maintain the price of USD 84.97 (USD 84.97 x JPY 102.77/USD). If profit margins were already tight, Japan would be uncompetitive and lose revenue and market share. The pain of Japan from dollar devaluation is illustrated by Table 58 in the Nov 6 comment of this blog (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/10/slow-growth-driven-by-reducing-savings.html): The yen traded at JPY 110.19/USD on Aug 18, 2008 and at JPY 75.812/USD on Oct 28, 2011, for cumulative appreciation of 31.2 percent. Cumulative appreciation from Sep 15, 2010 (JPY 83.07/USD) to Oct 28, 2011 (JPY 75.812) was 8.7 percent. The pain of Japan from dollar devaluation continues as illustrated by Table VI-6 in Section VII Valuation of Risk Financial Assets: The yen traded at JPY 110.19/USD on Aug 18, 2008 and at JPY 78.08/USD on Dec 23, 2011, for cumulative appreciation of 29.1 percent. Cumulative appreciation from Sep 15, 2010 (JPY 83.07/USD) to Dec 23, 2011 (JPY 78.08) was 6.0 percent.
2. Foreign Earnings and Investment. Consider the case of a Japanese company receiving earnings from investment overseas. Accounting the earnings and investment in the books in Japan would also result in a loss of 12.7 percent. Accounting would show fewer yen for investment and earnings overseas.
There is a point of explosion of patience with dollar devaluation and domestic currency appreciation. Andrew Monahan, writing on “Japan intervenes on yen to cap sharp rise,” on Oct 31, 2011, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052970204528204577009152325076454.html?mod=WSJPRO_hpp_MIDDLETopStories), analyzes the intervention of the Bank of Japan, at request of the Ministry of Finance, on Oct 31, 2011. Traders consulted by Monahan estimate that the Bank of Japan sold JPY 7 trillion, about $92.31 billion, against the dollar, exceeding the JPY 4.5 trillion on Aug 4, 2011. The intervention caused an increase of the yen rate to JPY 79.55/USD relative to earlier trading at a low of JPY 75.31/USD. The JPY appreciated to JPY76.88/USD by Fri Nov 18 for cumulative appreciation of 3.4 percent from JPY 79.55 just after the intervention. The JPY appreciated another 0.3 percent in the week of Nov 18 but depreciated 1.1 percent in the week of Nov 25. There was mild depreciation of 0.3 percent in the week of Dec 2 that was followed by appreciation of 0.4 percent in the week of Dec 9. The JPY was virtually unchanged in the week of Dec 16 with depreciation of 0.1 percent but depreciated by 0.5 percent in the week of Dec 23, appreciating by 1.5 percent in the week of Dec 30. Historically, interventions in yen currency markets have been unsuccessful (Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 107-109). Interventions are even more difficult currently with daily trading of some $4 trillion in world currency markets. Risk aversion with zero interest rates in the US diverts hot capital movements toward safe-haven currencies such as Japan, causing appreciation of the yen. Mitsuru Obe, writing on Nov 25, on “Japanese government bonds tumble,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052970204452104577060231493070676.html?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection), analyzes the increase in yields of the Japanese government bond with 10 year maturity to a high for one month of 1.025 percent at the close of market on Nov 25. Thin markets in after-hours trading may have played an important role in this increase in yield but there may have been an effect of a dreaded reduction in positions of bonds by banks under pressure of reducing assets. The report on Japan sustainability by the IMF (2011JSRNov23, 2), analyzes how rising yields could threaten Japan:
· “As evident from recent developments, market sentiment toward sovereigns with unsustainably large fiscal imbalances can shift abruptly, with adverse effects on debt dynamics. Should JGB yields increase, they could initiate an adverse feedback loop from rising yields to deteriorating confidence, diminishing policy space, and a contracting real economy.
· Higher yields could result in a withdrawal of liquidity from global capital markets, disrupt external positions and, through contagion, put upward pressure on sovereign bond yields elsewhere.”
Exchange rate controls by the Swiss National Bank (SNB) fixing the rate at a minimum of CHF 1.20/EUR (http://www.snb.ch/en/mmr/reference/pre_20110906/source/pre_20110906.en.pdf) has prevented flight of capital into the Swiss franc. The Swiss franc remained unchanged relative to the USD in the week of Dec 23 and appreciated 0.2 percent in the week of Dec 30 relative to the USD and 0.5 percent relative to the euro, as shown in Table II-1. Risk aversion is evident in the depreciation of the Australian dollar by cumulative 2.5 percent in the week of Fr Dec 16 after no change in the week of Dec 9. In the week of Dec 23, the Australian dollar appreciated 1.9 percent, appreciating another 0.5 percent in the week of Dec 30 as shown in Table II-1. Risk appetite would be revealed by carry trades from zero interest rates in the US and Japan into high yielding currencies such as in Australia with appreciation of the Australian dollar (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008b), 202-4, Pelaez and Pelaez, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 70-4).
IIIC Appendix on Fiscal Compact. There are three types of actions in Europe to steer the euro zone away from the threats of fiscal and banking crises: (1) fiscal compact; (2) enhancement of stabilization tools and resources; and (3) bank capital requirements. The first two consist of agreements by the Euro Area Heads of State and government while the third one consists of measurements and recommendations by the European Banking Authority.
1. Fiscal Compact. The “fiscal compact” consists of (1) conciliation of fiscal policies and budgets within a “fiscal rule”; and (2) establishment of mechanisms of governance, monitoring and enforcement of the fiscal rule.
i. Fiscal Rule. The essence of the fiscal rule is that “general government budgets shall be balanced or in surplus” by compliance of members countries that “the annual structural deficit does not exceed 0.5% of nominal GDP” (European Council 2011Dec9, 3). Individual member states will create “an automatic correction mechanism that shall be triggered in the event of deviation” (European Council 2011Dec9, 3). Member states will define their automatic correction mechanisms following principles proposed by the European Commission. Those member states falling into an “excessive deficit procedure” will provide a detailed plan of structural reforms to correct excessive deficits. The European Council and European Commission will monitor yearly budget plans for consistency with adjustment of excessive deficits. Member states will report in anticipation their debt issuance plans. Deficits in excess of 3 percent of GDP and/or debt in excess of 60 percent of GDP will trigger automatic consequences.
ii. Policy Coordination and Governance. The euro area is committed to following common economic policy. In accordance, “a procedure will be established to ensure that all major economic policy reforms planned by euro area member states will be discussed and coordinated at the level of the euro area, with a view to benchmarking best practices” (European Council 2011Dec9, 5). Governance of the euro area will be strengthened with regular euro summits at least twice yearly.
2. Stabilization Tools and Resources. There are several enhancements to the bailouts of member states.
i. Facilities. The European Financial Stability Facility (EFSF) will use leverage and the European Central Bank as agent of its market operations. The European Stability Mechanism (ESM) or permanent bailout facility will be operational as soon as 90 percent of the capital commitments are ratified by member states. The ESM is planned to begin in Jul 2012.
ii. Financial Resources. The overall ceiling of the EFSF/ESM of €500 billion (USD 670 billion) will be reassessed in Mar 2012. Measures will be taken to maintain “the combined effective lending capacity of EUR 500 billion” (European Council 2011Dec9, 6). Member states will “consider, and confirm within 10 days, the provision of additional resources for the IMF of up to EUR 200 billion (USD 270 billion), in the form of bilateral loans, to ensure that the IMF has adequate resources to deal with the crisis. We are looking forward to parallel contributions from the international community” (European Council 2011Dec9, 6). Matthew Dalton and Matina Stevis, writing on Dec 20, 2011, on “Euro Zone Agrees to New IMF Loans,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052970204791104577107974167166272.html?mod=WSJPRO_hps_MIDDLESecondNews), inform that at a meeting on Dec 20, finance ministers of the euro-zone developed plans to contribute €150 billion in bilateral loans to the IMF as provided in the agreement of Dec 9. Bailouts “will strictly adhere to the well established IMF principles and practices.” There is a specific statement on private sector involvement and its relation to recent experience: “We clearly reaffirm that the decisions taken on 21 July and 26/27 October concerning Greek debt are unique and exceptional; standardized and identical Collective Action clauses will be included, in such a way as to preserve market liquidity, in the terms and conditions of all new euro government bonds” (European Council 2011Dec9, 6). Will there be again “unique and exceptional” conditions? The ESM is authorized to take emergency decisions with “a qualified majority of 85% in case the Commission and the ECB conclude that an urgent decision related to financial assistance is needed when the financial and economic sustainability of the euro area is threatened” (European Council 2011Dec9, 6).
3. Bank Capital. The European Banking Authority (EBA) finds that European banks have a capital shortfall of €114.7 billion (http://stress-test.eba.europa.eu/capitalexercise/Press%20release%20FINAL.pdf). To avoid credit difficulties, the EBA recommends “that the credit institutions build a temporary capital buffer to reach a 9% Core Tier 1 ratio by 30 June 2012” (http://stress-test.eba.europa.eu/capitalexercise/EBA%20BS%202011%20173%20Recommendation%20FINAL.pdf 6). Patrick Jenkins, Martin Stabe and Stanley Pignal, writing on Dec 9, 2011, on “EU banks slash sovereign holdings,” published in the Financial Times (http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/a6d2fd4e-228f-11e1-acdc-00144feabdc0.html#axzz1gAlaswcW), analyze the balance sheets of European banks released by the European Banking Authority. They conclude that European banks have reduced their holdings of riskier sovereign debt of countries in Europe by €65 billion from the end of 2010 to Sep 2011. Bankers informed that the European Central Bank and hedge funds acquired those exposures that represent 13 percent of their holdings of debt to Greece, Ireland, Italy, Portugal and Spain, which are down to €513 billion by the end of IIIQ2011.
The members of the European Monetary Union (EMU), or euro area, established the European Financial Stability Facility (EFSF), on May 9, 2010, to (http://www.efsf.europa.eu/about/index.htm):
- “Provide loans to countries in financial difficulties
- Intervene in the debt primary and secondary markets. Intervention in the secondary market will be only on the basis of an ECB analysis recognising the existence of exceptional financial market circumstances and risks to financial stability
- Act on the basis of a precautionary programme
- Finance recapitalisations of financial institutions through loans to governments”
The EFSF will be replaced by the permanent European Stability Mechanism (ESM) in 2013. On Mar 30, 2012, members of the euro area reached an agreement providing for sufficient funding required in rescue programs of members countries facing funding and fiscal difficulties and the transition from the EFSF to the ESM. The agreement of Mar 30, 2012 of the euro area members provides for the following (http://www.consilium.europa.eu/media/1513204/eurogroup_statement_30_march_12.pdf):
· Acceleration of ESM paid-in capital. The acceleration of paid-in capital for the ESM provides for two tranches paid in 2012, in July and Oct; another two tranches in 2013; and a final tranche in the first half of 2014. There could be acceleration of paid-in capital is required to maintain a 15 percent relation of paid-in capital and the outstanding issue of the ESM
· ESM Operation and EFSF transition. ESM will assume all new rescue programs beginning in Jul 2012. EFSF will administer programs begun before initiation of ESM activities. There will be a transition period for the EFSF until mid 2013 in which it can engage in new programs if required to maintain the full lending limit of €500 billion.
· Increase of ESM/EFSF lending limit. The combined ceiling of the ESM and EFSF will be increased to €700 billion to facilitate operation of the transition of the EFSF to the ESM. The ESM lending ceiling will be €500 billion by mid 2013. The combined lending ceiling of the ESM and EFSF will continue to €700 billion
· Prior lending. The bilateral Greek loan facility of €53 billion and €49 billion of the EFSF have been paid-out in supporting programs of countries: “all together the euro area is mobilizing an overall firewall of approximately EUR 800 billion, more than USD 1 trillion” (http://www.consilium.europa.eu/media/1513204/eurogroup_statement_30_march_12.pdf)
· Bilateral IMF contributions. Members of the euro area have made commitments of bilateral contributions to the IMF of €150 billion
A key development in the bailout of Greece is the approval by the Executive Board of the International Monetary Fund (IMF) on Mar 15, 2012, of a new four-year financing in the value of €28 billion to be disbursed in equal quarterly disbursements (http://www.imf.org/external/np/tr/2012/tr031512.htm). The sovereign debt crisis of Europe has moderated significantly with the elimination of immediate default of Greece. New economic and financial risk factors have developed, which are covered in VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets and V World Economic Slowdown.
IIID Appendix on European Central Bank Large Scale Lender of Last Resort. European Central Bank. The European Central Bank (ECB) has been pressured to assist in the bailouts by acquiring sovereign debts. The ECB has been providing liquidity lines to banks under pressure and has acquired sovereign debts but not in the scale desired by authorities. In an important statement to the European Parliament, the President of the ECB Mario Draghi (2011Dec1) opened the possibility of further ECB actions but after a decisive “fiscal compact:”
“What I believe our economic and monetary union needs is a new fiscal compact – a fundamental restatement of the fiscal rules together with the mutual fiscal commitments that euro area governments have made.
Just as we effectively have a compact that describes the essence of monetary policy – an independent central bank with a single objective of maintaining price stability – so a fiscal compact would enshrine the essence of fiscal rules and the government commitments taken so far, and ensure that the latter become fully credible, individually and collectively.
We might be asked whether a new fiscal compact would be enough to stabilise markets and how a credible longer-term vision can be helpful in the short term. Our answer is that it is definitely the most important element to start restoring credibility.
Other elements might follow, but the sequencing matters. And it is first and foremost important to get a commonly shared fiscal compact right. Confidence works backwards: if there is an anchor in the long term, it is easier to maintain trust in the short term. After all, investors are themselves often taking decisions with a long time horizon, especially with regard to government bonds.
A new fiscal compact would be the most important signal from euro area governments for embarking on a path of comprehensive deepening of economic integration. It would also present a clear trajectory for the future evolution of the euro area, thus framing expectations.”
An important statement of Draghi (2011Dec15) focuses on the role of central banking: “You all know that the statutes of the ECB inherited this important principle and that central bank independence and the credible pursuit of price stability go hand in hand.”
Draghi (2011Dec19) explains measures to ensure “access to funding markets” by euro zone banks:
§ “We have decided on three-year refinancing operations to support the supply of credit to the euro area economy. These measures address the risk that persistent financial markets tensions could affect the capacity of euro area banks to obtain refinancing over longer horizons.
§ Earlier, in October, the Governing Council had already decided to have two more refinancing operations with a maturity of around one year.
§ Also, it was announced then that in all refinancing operations until at least the first half of 2012 all liquidity demand by banks would be fully allotted at fixed rate.
§ Funding via the covered bonds market was also facilitated by the ECB deciding in October to introduce a new Covered Bond Purchase Programme of €40 billion.
§ Funding in US dollar is facilitated by lowering the pricing on the temporary US dollar liquidity swap arrangements.”
Lionel Barber and Ralph Atkins interviewed Mario Draghi on Dec 14 with the transcript published in the Financial Times on Dec 18 (http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/25d553ec-2972-11e1-a066-00144feabdc0.html#axzz1gzoHXOj6) as “FT interview transcript: Mario Draghi.” A critical question in the interview is if the new measures are a European version of quantitative easing. Draghi analyzes the difference between the measures of the European Central Bank (ECB) and quantitative easing such as in Japan, US and UK:
1. The measures are termed “non-standard” instead of “unconventional.” While quantitative easing attempts to lower the yield of targeted maturities, the three-year facility operates through the “bank channel.” Quantitative easing would not be feasible because the ECB is statutorily prohibited of funding central governments. The ECB would comply with its mandate of medium-term price stability.
2. There is a critical difference in the two programs. Quantitative easing has been used as a form of financial repression known as “directed lending.” For example, the purchase of mortgage-backed securities more recently or the suspension of the auctions of 30-year bonds in response to the contraction early in the 2000s has the clear objective of directing spending to housing. The ECB gives the banks entire discretion on how to use the funding within their risk/return decisions, which could include purchase of government bonds.
The question on the similarity of the ECB three-year lending facility and quantitative easing is quite valid. Tracy Alloway, writing on Oct 10, 2011, on “Investors worry over cheap ECB money side effects,” published in the Financial Times (http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/d2f87d16-f339-11e0-8383-00144feab49a.html#axzz1hAqMH1vn), analyzes the use of earlier long-term refinancing operations (LTRO) of the ECB. LTROs by the ECB in Jun, Sep and Dec 2009 lent €614 billion at 1 percent. Alloway quotes estimates of Deutsche Bank that banks used €442billion to acquire assets with higher yields. Carry trades developed from LTRO funds at 1 percent into liquid investments at a higher yield to earn highly profitable spreads. Alloway quotes estimates of Morgan Stanley that European debt of GIIPS (Greece, Ireland, Italy, Portugal and Spain) in European bank balance sheets is €700 billion. Tracy Alloway, writing on Dec 21, 2011, on “Demand for ECB loans rises to €489bn,” published in the Financial Times (http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/d6ddd0ae-2bbd-11e1-98bc-00144feabdc0.html#axzz1hAqMH1vn), informs that European banks borrowed the largest value of €489 billion in all LTROs of the ECB. Tom Fairless and David Cottle, writing on Dec 21, 2011, on “ECB sees record refinancing demand,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052970204464404577111983838592746.html?mod=WSJPRO_hpp_LEFTTopStories), inform that the first of three operations of the ECB lent €489.19 billion, or $639.96 billion, to 523 banks. Three such LTROs could add to $1.9 trillion, which is not far from the value of quantitative easing in the US of $2.5 trillion. Fairless and Cottle find that there could be renewed hopes that banks could use the LTROs to support euro zone bond markets. It is possible that there could be official moral suasion by governments on banks to increase their holdings of government bonds or at least not to sell existing holdings. Banks are not free to choose assets in evaluation of risk and returns. Floods of cheap money at 1 percent per year induce carry trades to high-risk assets and not necessarily financing of growth with borrowing and lending decisions constrained by shocks of confidence.
The LTROs of the ECB are not very different from the liquidity facilities of the Fed during the financial crisis. Kohn (2009Sep10) finds that the trillions of dollars in facilities provided by the Fed (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 157-64, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 224-7) could fall under normal principles of “lender of last resort” of central banks:
“The liquidity measures we took during the financial crisis, although unprecedented in their details, were generally consistent with Bagehot's principles and aimed at short-circuiting these feedback loops. The Federal Reserve lends only against collateral that meets specific quality requirements, and it applies haircuts where appropriate. Beyond the collateral, in many cases we also have recourse to the borrowing institution for repayment. In the case of the TALF, we are backstopped by the Treasury. In addition, the terms and conditions of most of our facilities are designed to be unattractive under normal market conditions, thus preserving borrowers' incentives to obtain funds in the market when markets are operating normally. Apart from a very small number of exceptions involving systemically important institutions, such features have limited the extent to which the Federal Reserve has taken on credit risk, and the overall credit risk involved in our lending during the crisis has been small.
In Ricardo's view, if the collateral had really been good, private institutions would have lent against it. However, as has been recognized since Bagehot, private lenders, acting to protect themselves, typically severely curtail lending during a financial crisis, irrespective of the quality of the available collateral. The central bank--because it is not liquidity constrained and has the infrastructure in place to make loans against a variety of collateral--is well positioned to make those loans in the interest of financial stability, and can make them without taking on significant credit risk, as long as its lending is secured by sound collateral. A key function of the central bank is to lend in such circumstances to contain the crisis and mitigate its effects on the economy.”
The Bagehot (1873) principle is that central banks should provide a safety net, lending to temporarily illiquid but solvent banks and not to insolvent banks (see Cline 2001, 2002; Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), 175-8). Kohn (2009Apr18) characterizes “quantitative easing” as “large scale purchases of assets:”
“Another aspect of our efforts to affect financial conditions has been the extension of our open market operations to large-scale purchases of agency mortgage-backed securities (MBS), agency debt, and longer-term Treasury debt. We initially announced our intention to undertake large-scale asset purchases last November, when the federal funds rate began to approach its zero lower bound and we needed to begin applying stimulus through other channels as the economic contraction deepened. These purchases are intended to reduce intermediate- and longer-term interest rates on mortgages and other credit to households and businesses; those rates influence decisions about investments in long-lived assets like houses, consumer durable goods, and business capital. In ordinary circumstances, the typically quite modest volume of central bank purchases and sales of such assets has only small and temporary effects on their yields. However, the extremely large volume of purchases now underway does appear to have substantially lowered yields. The decline in yields reflects "preferred habitat" behavior, meaning that there is not perfect arbitrage between the yields on longer-term assets and current and expected short-term interest rates. These preferences are likely to be especially strong in current circumstances, so that long-term asset prices rise and yields fall as the Federal Reserve acquires a significant portion of the outstanding stock of securities held by the public.”
Non-standard ECB policy and unconventional Fed policy have a common link in the scale of implementation or policy doses. Direct lending by the central bank to banks is the function “large scale lender of last resort.” If there is moral suasion by governments to coerce banks into increasing their holdings of government bonds, the correct term would be financial repression.
An important additional measure discussed by Draghi (2011Nov19) is relaxation on the collateral pledged by banks in LTROs:
“Some banks’ access to refinancing operations may be restricted by lack of eligible collateral. To overcome this, a temporary expansion of the list of collateral has been decided. Furthermore, the ECB intends to enhance the use of bank loans as collateral in Eurosystem operations. These measures should support bank lending, by increasing the amount of assets on euro area banks’ balance sheets that can be used to obtain central bank refinancing.”
There are collateral concerns about European banks. David Enrich and Sara Schaefer Muñoz, writing on Dec 28, on “European bank worry: collateral,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052970203899504577126430202451796.html?mod=WSJPRO_hpp_LEFTTopStories), analyze the strain on bank funding from a squeeze in the availability of high-quality collateral as guarantee in funding. High-quality collateral includes government bonds and investment-grade non-government debt. There could be difficulties in funding for a bank without sufficient available high-quality collateral to offer in guarantee of loans. It is difficult to assess from bank balance sheets the availability of sufficient collateral to support bank funding requirements. There has been erosion in the quality of collateral as a result of the debt crisis and further erosion could occur. Perceptions of counterparty risk among financial institutions worsened the credit/dollar crisis of 2007 to 2009. The banking theory of Diamond and Rajan (2000, 2001a, 2001b) and the model of Diamond Dybvig (1983, 1986) provide the analysis of bank functions that explains the credit crisis of 2007 to 2008 (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 155-7, 48-52, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 52-66, 217-24). In fact, Rajan (2005, 339-41) anticipated the role of low interest rates in causing a hunt for yields in multiple financial markets from hedge funds to emerging markets and that low interest rates foster illiquidity. Rajan (2005, 341) argued:
“The point, therefore, is that common factors such as low interest rates—potentially caused by accommodative monetary policy—can engender excessive tolerance for risk on both sides of financial transactions.”
A critical function of banks consists of providing transformation services that convert illiquid risky loans and investment that the bank monitors into immediate liquidity such as unmonitored demand deposits. Credit in financial markets consists of the transformation of asset-backed securities (SRP) constructed with monitoring by financial institutions into unmonitored immediate liquidity by sale and repurchase agreements (SRP). In the financial crisis financial institutions distrusted the quality of their own balance sheets and those of their counterparties in SRPs. The financing counterparty distrusted that the financed counterparty would not repurchase the assets pledged in the SRP that could collapse in value below the financing provided. A critical problem was the unwillingness of banks to lend to each other in unsecured short-term loans. Emse Bartha, writing on Dec 28, on “Deposits at ECB hit high,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052970204720204577125913779446088.html?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection), informs that banks deposited €453.034 billion, or $589.72 billion, at the ECB on Dec 28, which is a record high in two consecutive days. The deposit facility is typically used by banks when they do prefer not to extend unsecured loans to other banks. In addition, banks borrowed €6.225 billion from the overnight facility on Dec 28, when in normal times only a few hundred million euro are borrowed. The collateral issues and the possible increase in counterparty risk occurred a week after large-scale lender of last resort by the ECB in the value of €489 billion in the prior week. The ECB may need to extend its lender of last resort operations.
The financial reform of the United States around the proposal of a national bank by Alexander Hamilton (1780) to develop the money economy with specialization away from the barter economy is credited with creating the financial system that brought prosperity over a long period (see Pelaez 2008). Continuing growth and prosperity together with sound financial management earned the US dollar the role as reserve currency and the AAA rating of its Treasury securities. McKinnon (2011Dec18) analyzes the resolution of the European debt crisis by comparison with the reform of Alexander Hamilton. Northern states of the US had financed the revolutionary war with the issue of paper notes that were at risk of default by 1890. Alexander Hamilton proposed the purchase of the states’ paper notes by the Federal government without haircuts. McKinnon (2011Dec18) describes the conflicts before passing the assumption bill in 1790 for federal absorption of the debts of states. Other elements in the Hamilton reform consisted of creation of a market for US Treasury bonds by their use as paid-in capital in the First Bank of the United States. McKinnon (2011Dec18) finds growth of intermediation in the US by the branching of the First Bank of the United States throughout several states, accepting deposits to provide commercial short-term credit. The reform consolidated the union of states, fiscal credibility for the union and financial intermediation required for growth. The reform also introduced low tariffs and an excise tax on whisky to service the interest on the federal debt. Trade relations among members of the euro zone are highly important to economic activity. There are two lessons drawn by McKinnon (2011Dec18) from the experience of Hamilton for the euro zone currently. (1) The reform of Hamilton included new taxes for the assumption of debts of states with concrete provisions for their credibility. (2) Commercial lending was consolidated with a trusted bank both for accepting private deposits and for commercial lending, creating the structure of financial intermediation required for growth.
IIIE Appendix Euro Zone Survival Risk. Markets have been dominated by rating actions of Standard & Poor’s Ratings Services (S&PRS) (2012Jan13) on 16 members of the European Monetary Union (EMU) or eurozone. The actions by S&PRS (2012Jan13) are of several types:
1. Downgrades by two notches of long-term credit ratings of Cyprus (from BBB/Watch/NegA-3+ to BB+/Neg/B), Italy (from A/Watch Neg/A-1 to BBB+/Neg/A-2), Portugal (from BBB-/Watch Neg/A-3 to BB/Neg/B) and Spain (from AA-/Watch Neg/A-1+ to A/Neg/A-1).
2. Downgrades by one notch of long-term credit ratings of Austria (from AAA/Watch Neg/A-1+ to AA+/Neg/A-1+), France (from AAA/Watch Neg/A-1+ to AA+/Neg A-1+), Malta (from A/Watch, Neg/A-1 to A-/Neg/A-2), Slovakia (from A+/Watch Neg/A-1 to A/Stable/A-1) and Slovenia (AA-/Watch Neg/A-1+ to A+/Neg/A-1).
3. Affirmation of long-term ratings of Belgium (AA/Neg/A-1+), Estonia (AA-/Neg/A-1+), Finland (AAA/Neg/A-1+), Germany (AAA/Stable/A-1+), Ireland (BBB+/Neg/A-2), Luxembourg (AAA/Neg/A-1+) and the Netherlands (AAA/Neg/A-1+) with removal from CreditWatch.
4. Negative outlook on the long-term credit ratings of Austria, Belgium, Cyprus, Estonia, Finland, France, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, Malta, the Netherlands, Portugal, Slovenia and Spain, meaning that S&PRS (2012Jan13) finds that the ratings of these sovereigns have a chance of at least 1-to-3 of downgrades in 2012 or 2013.
S&PRS (2012Jan13) finds that measures by European policymakers may not be sufficient to contain sovereign risks in the eurozone. The sources of stress according to S&PRS (2012Jan13) are:
1. Worsening credit environment
2. Increases in risk premiums for many eurozone borrowers
3. Simultaneous attempts at reducing debts by both eurozone governments and households
4. More limited perspectives of economic growth
5. Deepening and protracted division among Europe’s policymakers in agreeing to approaches to resolve the European debt crisis
There is now only one major country in the eurozone with AAA rating of its long-term debt by S&PRS (2012Jan13): Germany. IIIE Appendix Euro Zone Survival Risk analyzes the hurdle of financial bailouts of euro area members by the strength of the credit of Germany alone. The sum of the debt of Italy, Spain, Portugal, Greece and Ireland is abouy $3531.6 billion. There is some simple “unpleasant bond arithmetic.” Suppose the entire debt burdens of the five countries with probability of default were to be guaranteed by France and Germany, which de facto would be required by continuing the euro zone. The sum of the total debt of these five countries and the debt of France and Germany is about $7385.1 billion, which would be equivalent to 126.3 percent of their combined GDP in 2010. Under this arrangement the entire debt of the euro zone including debt of France and Germany would not have nil probability of default. Debt as percent of Germany’s GDP would exceed 224 percent if including debt of France and 165 percent of German GDP if excluding French debt. The unpleasant bond arithmetic illustrates that there is a limit as to how far Germany and France can go in bailing out the countries with unsustainable sovereign debt without incurring severe pains of their own such as downgrades of their sovereign credit ratings. A central bank is not typically engaged in direct credit because of remembrance of inflation and abuse in the past. There is also a limit to operations of the European Central Bank in doubtful credit obligations. Charles Forelle, writing on Jan 14, 2012, on “Downgrade hurts euro rescue fund,” published by the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052970204409004577159210191567778.html), analyzes the impact of the downgrades on the European Financial Stability Facility (EFSF). The EFSF is a special purpose vehicle that has not capital but can raise funds to be used in bailouts by issuing AAA-rated debt. S&P may cut the rating of the EFSF to the new lowest rating of the six countries with AAA rating, which are now down to four with the downgrades of France and Austria. The other rating agencies Moody’s and Fitch have not taken similar action. On Jan, S&PRS (2012Jan16) did cut the long-term credit rating of the EFSF to AA+ and affirmed the short-term credit rating at A-+. The decision is derived from the reduction in credit rating of the countries guaranteeing the EFSF. In the view of S&PRS (2012Jan16), there are not sufficient credit enhancements after the reduction in the creditworthiness of the countries guaranteeing the EFSF. The decision could be reversed if credit enhancements were provided.
The flow of cash from safe havens to risk financial assets is processed by carry trades from zero interest rates that are frustrated by episodes of risk aversion or encouraged with return of risk appetite. European sovereign risk crises are closely linked to the exposures of regional banks to government debt. An important form of financial repression consists of changing the proportions of debt held by financial institutions toward higher shares in government debt. The financial history of Latin America, for example, is rich in such policies. Bailouts in the euro zone have sanctioned “bailing in” the private sector, which means that creditors such as banks will participate by “voluntary” reduction of the principal in government debt (see Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), 163-202). David Enrich, Sara Schaeffer Muñoz and Patricia Knowsmann, writing on “European nations pressure own banks for loans,” on Nov 29, 2011, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052970204753404577066431341281676.html?mod=WSJPRO_hpp_MIDDLETopStories), provide important data and analysis on the role of banks in the European sovereign risk crisis. They assemble data from various sources showing that domestic banks hold 16.2 percent of Italy’s total government securities outstanding of €1,617.4 billion, 22.9 percent of Portugal’s total government securities of €103.9 billion and 12.3 percent of Spain’s total government securities of €535.3 billion. Capital requirements force banks to hold government securities to reduce overall risk exposure in balance sheets. Enrich, Schaeffer Muñoz and Knowsmann find information that governments are setting pressures on banks to acquire more government debt or at least to stop selling their holdings of government debt.
Bond auctions are also critical in episodes of risk aversion. David Oakley, writing on Jan 3, 2012, on “Sovereign issues draw euro to crunch point,” published by the Financial Times (http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/63b9d7ca-2bfa-11e1-98bc-00144feabdc0.html#axzz1iLNRyEbs), estimates total euro area sovereign issues in 2012 at €794 billion, much higher than the long-term average of €670 billion. Oakley finds that the sovereign issues are: Italy €220 billion, France €197 billion, Germany €178 billion and Spain €81 billion. Bond auctions will test the resilience of the euro. Victor Mallet and Robin Wigglesworth, writing on Jan 12, 2012, on “Spain and Italy raise €22bn in debt sales,” published in the Financial Times (http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/e22c4e28-3d05-11e1-ae07-00144feabdc0.html#axzz1j4euflAi), analyze debt auctions during the week. Spain placed €10 billion of new bonds with maturities in 2015 and 2016, which was twice the maximum planned for the auction. Italy placed €8.5 billion of one-year bills at average yield of 2.735 percent, which was less than one-half of the yield of 5.95 percent a month before. Italy also placed €3.5 billion of 136-day bills at 1.64 percent. There may be some hope in the sovereign debt market. The yield of Italy’s 10-year bond dropped from around 7.20 percent on Jan 9 to about 6.70 percent on Jan 13 and then to around 6.30 percent on Jan 20. The yield of Spain’s 10-year bond fell from about 6.60 percent on Jan 9 to around 5.20 percent on Jan 13 and then to 5.50 percent on Jan 20.
A combination of strong economic data in China analyzed in subsection VC and the realization of the widely expected downgrade could explain the strength of the European sovereign debt market. Emese Bartha, Art Patnaude and Nick Cawley, writing on January 17, 2012, on “European T-bills see solid demand,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052970204555904577166363369792848.html?mod=WSJPRO_hpp_LEFTTopStories), analyze successful auctions treasury bills by Spain and Greece. A day after the downgrade, the EFSF found strong demand on Jan 17 for its six-month debt auction at the yield of 0.2664 percent, which is about the same as sovereign bills of France with the same maturity.
There may be some hope in the sovereign debt market. The yield of Italy’s 10-year bond dropped from around 7.20 percent on Jan 9 to about 6.70 percent on Jan 13 and then to around 6.30 percent on Jan 20. The yield of Spain’s 10-year bond fell from about 6.60 percent on Jan 9 to around 5.20 percent on Jan 13 and then to 5.50 percent on Jan 20. Paul Dobson, Emma Charlton and Lucy Meakin, writing on Jan 20, 2012, on “Bonds show return of crisis once ECB loans expire,” published in Bloomberg (http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2012-01-20/bonds-show-return-of-crisis-once-ecb-loans-expire-euro-credit.html), analyze sovereign debt and analysis of market participants. Large-scale lending of last resort by the European Central Bank, considered in VD Appendix on European Central Bank Large Scale Lender of Last Resort, provided ample liquidity in the euro zone for banks to borrow at 1 percent and lend at higher rates, including to government. Dobson, Charlton and Meakin trace the faster decline of yields of short-term sovereign debt relative to decline of yields of long-term sovereign debt. The significant fall of the spread of short relative to long yields could signal concern about the resolution of the sovereign debt while expanding lender of last resort operations have moderated relative short-term sovereign yields. Normal conditions would be attained if there is definitive resolution of long-term sovereign debt that would require fiscal consolidation in an environment of economic growth.
Charles Forelle and Stephen Fidler, writing on Dec 10, 2011, on “Questions place EU pact,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052970203413304577087562993283958.html?mod=WSJPRO_hpp_LEFTTopStories#project%3DEUSUMMIT121011%26articleTabs%3Darticle), provide data, information and analysis of the agreement of Dec 9. There are multiple issues centering on whether investors will be reassured that the measures have reduced the risks of European sovereign obligations. While the European Central Bank has welcomed the measures, it is not yet clear of its future role in preventing erosion of sovereign debt values.
Another complicating factor is whether there will be further actions on sovereign debt ratings. On Dec 5, 2011, four days before the conclusion of the meeting of European leaders, Standard & Poor’s (2011Dec5) placed the sovereign ratings of 15 members of the euro zone on “CreditWatch with negative implications.” S&P finds five conditions that trigger the action: (1) worsening credit conditions in the euro area; (2) differences among member states on how to manage the debt crisis in the short run and on measures to move toward enhanced fiscal convergence; (3) household and government debt at high levels throughout large parts of the euro area; (4) increasing risk spreads on euro area sovereigns, including those with AAA ratings; and (5) increasing risks of recession in the euro zone. S&P also placed the European Financial Stability Facility (EFSF) in CreditWatch with negative implications (http://www.standardandpoors.com/ratings/articles/en/us/?articleType=HTML&assetID=1245325307963). On Dec 9, 2011, Moody’s Investors Service downgraded the ratings of the three largest French banks (http://www.moodys.com/research/Moodys-downgrades-BNP-Paribass-long-term-ratings-to-Aa3-concluding--PR_232989 http://www.moodys.com/research/Moodys-downgrades-Credit-Agricole-SAs-long-term-ratings-to-Aa3--PR_233004 http://www.moodys.com/research/Moodys-downgrades-Socit-Gnrales-long-term-ratings-to-A1--PR_232986 ).
Improving equity markets and strength of the euro appear related to developments in sovereign debt negotiations and markets. Alkman Granitsas and Costas Paris, writing on Jan 29, 2012, on “Greek debt deal, new loan agreement to finish next week,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052970204573704577189021923288392.html?mod=WSJPRO_hpp_LEFTTopStories), inform that Greece and its private creditors were near finishing a deal of writing off €100 billion, about $132 billion, of Greece’s debt depending on the conversations between Greece, the euro area and the IMF on the new bailout. An agreement had been reached in Oct 2011 for a new package of fresh money in the amount of €130 billion to fill needs through 2015 but was contingent on haircuts reducing Greece’s debt from 160 percent of GDP to 120 percent of GDP. The new bailout would be required to prevent default by Greece of €14.4 billion maturing on Mar 20, 2012. There has been increasing improvement of sovereign bond yields. Italy’s ten-year bond yield fell from over 6.30 percent on Jan 20, 2012 to slightly above 5.90 percent on Jan 27. Spain’s ten-year bond yield fell from slightly above 5.50 percent on Jan 20 to just below 5 percent on Jan 27.
An important difference, according to Beim (2011Oct9), between large-scale buying of bonds by the central bank between the Federal Reserve of the US and the European Central Bank (ECB) is that the Fed and most banks do not buy local and state government obligations with lower creditworthiness. The European Monetary Union (EMU) that created the euro and the ECB did not include common fiscal policy and affairs. Thus, EMU cannot issue its own treasury obligations. The line “Reserve bank credit” in the Fed balance sheet for Jan 25, 2012, is $2902 billion of which $2570 billion consisting of $1565 billion US Treasury notes and bonds, $68 billion inflation-indexed bonds and notes, $101 billion Federal agency debt securities and $836 billion mortgage-backed securities (http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h41/current/h41.htm#h41tab1). The Fed has been careful in avoiding credit risk in its portfolio of securities. The 11 exceptional liquidity facilities of several trillion dollars created during the financial crisis (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 157-62) have not resulted in any losses. The Fed has used unconventional monetary policy without credit risk as in classical central banking.
Beim (2011Oct9, 6) argues:
“In short, the ECB system holds more than €1 trillion of debt of the banks and governments of the 17 member states. The state-by-state composition of this debt is not disclosed, but the events of the past year suggest that a disproportionate fraction of these assets are likely obligations of stressed countries. If a significant fraction of the €1 trillion were to be restructured at 40-60% discounts, the ECB would have a massive problem: who would bail out the ECB?
This is surely why the ECB has been so shrill in its antagonism to the slightest mention of default and restructuring. They need to maintain the illusion of risk-free sovereign debt because confidence in the euro itself is built upon it.”
Table III-2 provides an update of the consolidated financial statement of the Eurosystem. The balance sheet has swollen with the LTROs. Line 5 “Lending to Euro Area Credit Institutions Related to Monetary Policy” increasing from €546,747 million on Dec 31, 2010, to €870,130 million on Dec 28, 2011 and €1,147,981 million on Apr 13, 2012. The sum of line 5 and line 7 (“Securities of Euro Area Residents Denominated in Euro”) has increased to €1,775,693 million in the statement of Apr 13.
This sum is roughly what concerns Beim (2012Oct9) because of the probable exposure relative to capital to institutions and sovereigns with higher default risk. To be sure, there is no precise knowledge of the composition of the ECB portfolio of loans and securities with weights and analysis of the risks of components. Javier E. David, writing on Jan 16, 2012, on “The risks in ECB’s crisis moves,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052970204542404577158753459542024.html?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection), informs that the estimated debt of weakest euro zone sovereigns held by the ECB is €211 billion, with Greek debt in highest immediate default risk being only 17 percent of the total. Another unknown is whether there is high risk collateral in the €489 billion three-year loans to credit institutions at 1 percent interest rates. The potential risk is the need for recapitalization of the ECB that could find similar political hurdles as the bailout fund EFSF. There is a recurring issue of whether the ECB should accept a haircut on its portfolio of Greek bonds of €40 billion acquired at discounts from face value. An article on “Haircut for the ECB? Not so fast,” published by the Wall Street Journal on Jan 28, 2012 (http://blogs.wsj.com/davos/2012/01/28/haircut-for-the-ecb-not-so-fast/), informs of the remarks by Mark Carney, Governor of the Bank of Canada and President of the Financial Stability Board (FSB) (http://www.financialstabilityboard.org/about/overview.htm), expressing what appears to be correct doctrine that there could conceivably be haircuts for official debt but that such a decision should be taken by governments and not by central banks.
Table III-2, Consolidated Financial Statement of the Eurosystem, Million EUR
| Dec 31, 2010 | Dec 28, 2011 | Apr 6, 2012 | |
| 1 Gold and other Receivables | 367,402 | 419,822 | 423,706 |
| 2 Claims on Non Euro Area Residents Denominated in Foreign Currency | 223,995 | 236,826 | 239,669 |
| 3 Claims on Euro Area Residents Denominated in Foreign Currency | 26,941 | 95,355 | 55,513 |
| 4 Claims on Non-Euro Area Residents Denominated in Euro | 22,592 | 25,982 | 20,106 |
| 5 Lending to Euro Area Credit Institutions Related to Monetary Policy Operations Denominated in Euro | 546,747 | 879,130 | 1,147,981 |
| 6 Other Claims on Euro Area Credit Institutions Denominated in Euro | 45,654 | 94,989 | 62,548 |
| 7 Securities of Euro Area Residents Denominated in Euro | 457,427 | 610,629 | 627,712 |
| 8 General Government Debt Denominated in Euro | 34,954 | 33,928 | 31,131 |
| 9 Other Assets | 278,719 | 336,574 | 358,493 |
| TOTAL ASSETS | 2,004, 432 | 2,733,235 | 2,974,859 |
| Memo Items | |||
| Sum of 5 and 7 | 1,004,174 | 1,489,759 | 1,775,693 |
| Capital and Reserves | 78,143 | 81,481 | 85,819 |
Source: European Central Bank
http://www.ecb.int/press/pr/wfs/2011/html/fs110105.en.html
http://www.ecb.int/press/pr/wfs/2011/html/fs111228.en.html
http://www.ecb.int/press/pr/wfs/2012/html/fs120417.en.html
Professors Ricardo Caballero and Francesco Giavazzi (2012Jan15) find that the resolution of the European sovereign crisis with survival of the euro area would require success in the restructuring of Italy. That success would be assured with growth of the Italian economy. A critical problem is that the common euro currency prevents Italy from devaluing the exchange rate to parity or the exchange rate that would permit export growth to promote internal economic activity, which could generate fiscal revenues for primary fiscal surplus that ensure creditworthiness. Fiscal consolidation and restructuring are important but of long-term gestation. Immediate growth of the Italian economy would consolidate the resolution of the sovereign debt crisis. Caballero and Giavazzi (2012Jan15) argue that 55 percent of the exports of Italy are to countries outside the euro area such that devaluation of 15 percent would be effective in increasing export revenue. Newly available data in Table III-3 providing Italy’s trade with regions and countries supports the argument of Caballero and Giavazzi (2012Jan15). Italy’s exports to the European Monetary Union (EMU) are only 42.7 percent of the total. Exports to the non-European Union area are growing at 11.8 percent in Feb 2012 relative to Feb 2011 while those to EMU are growing at 3.5 percent.
Table III-3, Italy, Exports and Imports by Regions and Countries, % Share and 12-Month ∆%
| Feb 2012 | Exports | ∆% Feb 2012/ Feb 2011 | Imports | Imports |
| EU | 56.0 | 4.1 | 53.3 | -2.4 |
| EMU 17 | 42.7 | 3.5 | 43.2 | -1.5 |
| France | 11.6 | 5.4 | 8.3 | -1.5 |
| Germany | 13.1 | 7.4 | 15.6 | -4.4 |
| Spain | 5.3 | -7.4 | 4.5 | -6.0 |
| UK | 4.7 | 9.5 | 2.7 | -9.1 |
| Non EU | 44.0 | 11.8 | 46.7 | 4.6 |
| Europe non EU | 13.3 | 16.7 | 11.1 | 8.6 |
| USA | 6.1 | 21.5 | 3.3 | 7.2 |
| China | 2.7 | -4.8 | 7.3 | -11.5 |
| OPEC | 4.7 | 2.9 | 8.6 | 15.9 |
| Total | 100.0 | 7.3 | 100.0 | 0.8 |
Notes: EU: European Union; EMU: European Monetary Union (euro zone)
Source: http://www.istat.it/it/archivio/59291
Table III-4 provides Italy’s trade balance by regions and countries. Italy had trade deficit of €493 million with the 17 countries of the euro zone (EMU 17) in Feb and €535 million in Jan-Feb. Depreciation to parity could permit greater competitiveness in improving the trade surpluses of €699 million in Jan-Feb with Europe non European Union and of €1093 million with the US. There is significant rigidity in the trade deficits in Jan-Feb of €3209 million with China and €4472 million with members of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC).
Table III-4, Italy, Trade Balance by Regions and Countries, Millions of Euro
| Regions and Countries | Trade Balance Feb 2012 Millions of Euro | Trade Balance Cumulative Jan-Feb 2012 Millions of Euro |
| EU | 439 | 1,199 |
| EMU 17 | -493 | -535 |
| France | 964 | 1,796 |
| Germany | -470 | -870 |
| Spain | 158 | 484 |
| UK | 664 | 1,301 |
| Non EU | -1,552 | -6,658 |
| Europe non EU | 601 | 699 |
| USA | 837 | 1,093 |
| China | -1,477 | -3,209 |
| OPEC | -1,892 | -4,472 |
| Total | -1,113 | -5,549 |
Notes: EU: European Union; EMU: European Monetary Union (euro zone)
Source: http://www.istat.it/it/archivio/59291
Growth rates of Italy’s trade and major products are provided in Table III-5 for the period Feb 2012 relative to Feb 2011. Growth rates are high for the total and all segments of exports. Imports of nondurable goods increased 3.8 percent and imports of energy increased 29.7 percent driven by carry trades into commodities futures. The higher rate of growth of exports of 7.3 percent relative to imports of 0.8 percent may reflect weak demand in Italy.
Table III-5, Italy, Exports and Imports % Share of Products in Total and ∆%
| Exports | Exports | Imports | Imports | |
| Consumer | 28.9 | 8.0 | 25.0 | 2.5 |
| Durable | 5.9 | 2.8 | 3.0 | -6.6 |
| Non | 23.0 | 9.4 | 22.0 | 3.8 |
| Capital Goods | 32.2 | 5.8 | 20.8 | -5.2 |
| Inter- | 34.3 | 6.3 | 34.5 | -10.8 |
| Energy | 4.7 | 20.7 | 19.7 | 29.7 |
| Total ex Energy | 95.3 | 6.7 | 80.3 | -5.4 |
| Total | 100.0 | 7.3 | 100.0 | 0.8 |
Source: http://www.istat.it/it/archivio/59291
Table III-6 provides Italy’s trade balance by product categories in Feb 2012 and cumulative Jan-Feb 2012. Italy’s trade balance excluding energy generated surplus of €6475 million in Feb 2012 but the energy trade balance created deficit of €11,934 million. The overall deficit was €5459 million. Italy has significant competitiveness in various economic activities in contrast with some other countries with debt difficulties.
Table III-6, Italy, Trade Balance by Product Categories, € Millions
| Feb 2012 | Cumulative Jan-Feb 2012 | |
| Consumer Goods | 1,264 | 1,425 |
| Durable | 953 | 1,428 |
| Nondurable | 311 | -3 |
| Capital Goods | 3,161 | 5,160 |
| Intermediate Goods | 264 | -111 |
| Energy | -5,802 | -11,934 |
| Total ex Energy | 4,689 | 6,475 |
| Total | -1,113 | -5,459 |
Source: http://www.istat.it/it/archivio/59291
Brazil faced in the debt crisis of 1982 a more complex policy mix. Between 1977 and 1983, Brazil’s terms of trade, export prices relative to import prices, deteriorated 47 percent and 36 percent excluding oil (Pelaez 1987, 176-79; Pelaez 1986, 37-66; see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 178-87). Brazil had accumulated unsustainable foreign debt by borrowing to finance balance of payments deficits during the 1970s. Foreign lending virtually stopped. The German mark devalued strongly relative to the dollar such that Brazil’s products lost competitiveness in Germany and in multiple markets in competition with Germany. The resolution of the crisis was devaluation of the Brazilian currency by 30 percent relative to the dollar and subsequent maintenance of parity by monthly devaluation equal to inflation and indexing that resulted in financial stability by parity in external and internal interest rates avoiding capital flight. With a combination of declining imports, domestic import substitution and export growth, Brazil followed rapid growth in the US and grew out of the crisis with surprising GDP growth of 4.5 percent in 1984.
The euro zone faces a critical survival risk because several of its members may default on their sovereign obligations if not bailed out by the other members. The valuation equation of bonds is essential to understanding the stability of the euro area. An explanation is provided in this paragraph and readers interested in technical details are referred to the following Subsection IIID Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation. Contrary to the Wriston doctrine, investing in sovereign obligations is a credit decision. The value of a bond today is equal to the discounted value of future obligations of interest and principal until maturity. On Dec 30 the yield of the 2-year bond of the government of Greece was quoted around 100 percent. In contrast, the 2-year US Treasury note traded at 0.239 percent and the 10-year at 2.871 percent while the comparable 2-year government bond of Germany traded at 0.14 percent and the 10-year government bond of Germany traded at 1.83 percent. There is no need for sovereign ratings: the perceptions of investors are of relatively higher probability of default by Greece, defying Wriston (1982), and nil probability of default of the US Treasury and the German government. The essence of the sovereign credit decision is whether the sovereign will be able to finance new debt and refinance existing debt without interrupting service of interest and principal. Prices of sovereign bonds incorporate multiple anticipations such as inflation and liquidity premiums of long-term relative to short-term debt but also risk premiums on whether the sovereign’s debt can be managed as it increases without bound. The austerity measures of Italy are designed to increase the primary surplus, or government revenues less expenditures excluding interest, to ensure investors that Italy will have the fiscal strength to manage its debt of 120 percent of GDP, which is the third largest in the world after the US and Japan. Appendix IIIE links the expectations on the primary surplus to the real current value of government monetary and fiscal obligations. As Blanchard (2011SepWEO) analyzes, fiscal consolidation to increase the primary surplus is facilitated by growth of the economy. Italy and the other indebted sovereigns in Europe face the dual challenge of increasing primary surpluses while maintaining growth of the economy (for the experience of Brazil in the debt crisis of 1982 see Pelaez 1986, 1987).
Much of the analysis and concern over the euro zone centers on the lack of credibility of the debt of a few countries while there is credibility of the debt of the euro zone as a whole. In practice, there is convergence in valuations and concerns toward the fact that there may not be credibility of the euro zone as a whole. The fluctuations of financial risk assets of members of the euro zone move together with risk aversion toward the countries with lack of debt credibility. This movement raises the need to consider analytically sovereign debt valuation of the euro zone as a whole in the essential analysis of whether the single-currency will survive without major changes.
Welfare economics considers the desirability of alternative states, which in this case would be evaluating the “value” of Germany (1) within and (2) outside the euro zone. Is the sum of the wealth of euro zone countries outside of the euro zone higher than the wealth of these countries maintaining the euro zone? On the choice of indicator of welfare, Hicks (1975, 324) argues:
“Partly as a result of the Keynesian revolution, but more (perhaps) because of statistical labours that were initially quite independent of it, the Social Product has now come right back into its old place. Modern economics—especially modern applied economics—is centered upon the Social Product, the Wealth of Nations, as it was in the days of Smith and Ricardo, but as it was not in the time that came between. So if modern theory is to be effective, if it is to deal with the questions which we in our time want to have answered, the size and growth of the Social Product are among the chief things with which it must concern itself. It is of course the objective Social Product on which attention must be fixed. We have indexes of production; we do not have—it is clear we cannot have—an Index of Welfare.”
If the burden of the debt of the euro zone falls on Germany and France or only on Germany, is the wealth of Germany and France or only Germany higher after breakup of the euro zone or if maintaining the euro zone? In practice, political realities will determine the decision through elections.
The prospects of survival of the euro zone are dire. Table III-7 is constructed with IMF World Economic Outlook database (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/index.aspx) for GDP in USD billions, primary net lending/borrowing as percent of GDP and general government debt as percent of GDP for selected regions and countries in 2010.
Table III-7, World and Selected Regional and Country GDP and Fiscal Situation
| GDP 2012 | Primary Net Lending Borrowing | General Government Net Debt | |
| World | 69,660 | ||
| Euro Zone | 12,586 | -0.5 | 70.3 |
| Portugal | 221 | 0.1 | 110.9 |
| Ireland | 210 | -4.4 | 102.9 |
| Greece | 271 | -1.0 | 153.2 |
| Spain | 1,398 | -3.6 | 67.0 |
| Major Advanced Economies G7 | 34,106 | -4.8 | 88.3 |
| United States | 15,610 | -6.1 | 83.7 |
| UK | 2,453 | -5.3 | 84.2 |
| Germany | 3,479 | 1.0 | 54.1 |
| France | 2,712.0 | -2.2 | 83.2 |
| Japan | 5,981 | -8.9 | 135.2 |
| Canada | 1,805 | -3.1 | 35.4 |
| Italy | 2,067 | 2.9 | 102.3 |
| China | 7992 | -1.3* | 22.0** |
*Net Lending/borrowing**Gross Debt
Source: http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/weoselgr.aspx
The data in Table III-7 are used for some very simple calculations in Table III-8. The column “Net Debt USD Billions” in Table III-8 is generated by applying the percentage in Table III-7 column “General Government Net Debt % GDP 2010” to the column “GDP USD Billions.” The total debt of France and Germany in 2012 is $4138.5 billion, as shown in row “B+C” in column “Net Debt USD Billions” The sum of the debt of Italy, Spain, Portugal, Greece and Ireland is $3927.8 billion, adding rows D+E+F+G+H in column “Net Debt USD billions.” There is some simple “unpleasant bond arithmetic” in the two final columns of Table III-8. Suppose the entire debt burdens of the five countries with probability of default were to be guaranteed by France and Germany, which de facto would be required by continuing the euro zone. The sum of the total debt of these five countries and the debt of France and Germany is shown in column “Debt as % of Germany plus France GDP” to reach $8066.3 billion, which would be equivalent to 130.3 percent of their combined GDP in 2012. Under this arrangement the entire debt of the euro zone including debt of France and Germany would not have nil probability of default. The final column provides “Debt as % of Germany GDP” that would exceed 231.9 percent if including debt of France and 167.0 percent of German GDP if excluding French debt. The unpleasant bond arithmetic illustrates that there is a limit as to how far Germany and France can go in bailing out the countries with unsustainable sovereign debt without incurring severe pains of their own such as downgrades of their sovereign credit ratings. A central bank is not typically engaged in direct credit because of remembrance of inflation and abuse in the past. There is also a limit to operations of the European Central Bank in doubtful credit obligations. Wriston (1982) would prove to be wrong again that countries do not bankrupt but would have a consolation prize that similar to LBOs the sum of the individual values of euro zone members outside the current agreement exceeds the value of the whole euro zone. Internal rescues of French and German banks may be less costly than bailing out other euro zone countries so that they do not default on French and German banks.
Table III-8, Guarantees of Debt of Sovereigns in Euro Area as Percent of GDP of Germany and France, USD Billions and %
| Net Debt USD Billions | Debt as % of Germany Plus France GDP | Debt as % of Germany GDP | |
| A Euro Area | 8,847.9 | ||
| B Germany | 1,882.1 | $8066.3 as % of $3479 =231.9% $5809.9 as % of $3479 =167.0% | |
| C France | 2,256.4 | ||
| B+C | 4,138.5 | GDP $6,191.0 Total Debt $8066.3 Debt/GDP: 130.3% | |
| D Italy | 2,114.5 | ||
| E Spain | 936.7 | ||
| F Portugal | 245.3 | ||
| G Greece | 415.2 | ||
| H Ireland | 216.1 | ||
| Subtotal D+E+F+G+H | 3,927.8 |
Source: calculation with IMF data http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/index.aspx
There is extremely important information in Table III-9 for the current sovereign risk crisis in the euro zone. Table III-9 provides the structure of regional and country relations of Germany’s exports and imports with newly available data for Feb. German exports to other European Union (EU) members are 58.5 percent of total exports in Feb 2012 and 58.9 percent in Jan-Feb 2012. Exports to the euro area are 38.8 percent in Feb and 39.3 percent in Jan-Feb. Exports to third countries are 37.9 percent of the total in Feb and 41.1 percent in Jan-Feb. There is similar distribution for imports. Economic performance in Germany is closely related to its high competitiveness in world markets. Weakness in the euro zone and the European Union in general could affect the German economy. This may be the major reason for choosing the “fiscal abuse” of the European Central Bank considered by Buiter (2011Oct31) over the breakdown of the euro zone. There is a tough analytical, empirical and forecasting doubt of growth and trade in the euro zone and the world with or without maintenance of the European Monetary Union (EMU) or euro zone. Germany could benefit from depreciation of the euro because of its high share in exports to countries not in the euro zone but breakdown of the euro zone raises doubts on the region’s economic growth that could affect German exports to other member states.
Table III-9, Germany, Structure of Exports and Imports by Region, € Billions and ∆%
| Feb 2012 | Feb 12-Month | Jan–Feb 2012 € Billions | Jan-Feb 2012/ | |
| Total | 91.3 | 8.6 | 177.3 | 8.9 |
| A. EU | 53.4 % 58.5 | 5.4 | 104.4 % 58.9 | 5.4 |
| Euro Area | 35.4 % 38.8 | 3.3 | 69.7 % 39.3 | 4.0 |
| Non-euro Area | 18.0 % 19.7 | 9.7 | 34.7 % 19.6 | 8.5 |
| B. Third Countries | 37.9 % 41.5 | 13.4 | 72.9 % 41.1 | 14.4 |
| Total Imports | 76.5 | 6.1 | 149.3 | 6.2 |
| C. EU Members | 48.7 % 63.7 | 6.6 | 93.6 % 62.7 | 6.9 |
| Euro Area | 34.1 % 44.6 | 5.5 | 65.5 % 43.9 | 6.3 |
| Non-euro Area | 14.6 % 19.1 | 9.3 | 28.1 % 18.8 | 8.6 |
| D. Third Countries | 27.8 % 36.3 | 5.2 | 55.8 % 37.4 | 4.9 |
Notes: Total Exports = A+B; Total Imports = C+D
Source:
Statistiche Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/EN/PressServices/Press/pr/2012/04/PE12_129_51.html
IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation. There are two approaches to government finance and their implications: (1) simple unpleasant monetarist arithmetic; and (2) simple unpleasant fiscal arithmetic. Both approaches illustrate how sovereign debt can be perceived riskier under profligacy.
First, Unpleasant Monetarist Arithmetic. Fiscal policy is described by Sargent and Wallace (1981, 3, equation 1) as a time sequence of D(t), t = 1, 2,…t, …, where D is real government expenditures, excluding interest on government debt, less real tax receipts. D(t) is the real deficit excluding real interest payments measured in real time t goods. Monetary policy is described by a time sequence of H(t), t=1,2,…t, …, with H(t) being the stock of base money at time t. In order to simplify analysis, all government debt is considered as being only for one time period, in the form of a one-period bond B(t), issued at time t-1 and maturing at time t. Denote by R(t-1) the real rate of interest on the one-period bond B(t) between t-1 and t. The measurement of B(t-1) is in terms of t-1 goods and [1+R(t-1)] “is measured in time t goods per unit of time t-1 goods” (Sargent and Wallace 1981, 3). Thus, B(t-1)[1+R(t-1)] brings B(t-1) to maturing time t. B(t) represents borrowing by the government from the private sector from t to t+1 in terms of time t goods. The price level at t is denoted by p(t). The budget constraint of Sargent and Wallace (1981, 3, equation 1) is:
D(t) = {[H(t) – H(t-1)]/p(t)} + {B(t) – B(t-1)[1 + R(t-1)]} (1)
Equation (1) states that the government finances its real deficits into two portions. The first portion, {[H(t) – H(t-1)]/p(t)}, is seigniorage, or “printing money.” The second part,
{B(t) – B(t-1)[1 + R(t-1)]}, is borrowing from the public by issue of interest-bearing securities. Denote population at time t by N(t) and growing by assumption at the constant rate of n, such that:
N(t+1) = (1+n)N(t), n>-1 (2)
The per capita form of the budget constraint is obtained by dividing (1) by N(t) and rearranging:
B(t)/N(t) = {[1+R(t-1)]/(1+n)}x[B(t-1)/N(t-1)]+[D(t)/N(t)] – {[H(t)-H(t-1)]/[N(t)p(t)]} (3)
On the basis of the assumptions of equal constant rate of growth of population and real income, n, constant real rate of return on government securities exceeding growth of economic activity and quantity theory equation of demand for base money, Sargent and Wallace (1981) find that “tighter current monetary policy implies higher future inflation” under fiscal policy dominance of monetary policy. That is, the monetary authority does not permanently influence inflation, lowering inflation now with tighter policy but experiencing higher inflation in the future.
Second, Unpleasant Fiscal Arithmetic. The tool of analysis of Cochrane (2011Jan, 27, equation (16)) is the government debt valuation equation:
(Mt + Bt)/Pt = Et∫(1/Rt, t+τ)st+τdτ (4)
Equation (4) expresses the monetary, Mt, and debt, Bt, liabilities of the government, divided by the price level, Pt, in terms of the expected value discounted by the ex-post rate on government debt, Rt, t+τ, of the future primary surpluses st+τ, which are equal to Tt+τ – Gt+τ or difference between taxes, T, and government expenditures, G. Cochrane (2010A) provides the link to a web appendix demonstrating that it is possible to discount by the ex post Rt, t+τ. The second equation of Cochrane (2011Jan, 5) is:
MtV(it, ·) = PtYt (5)
Conventional analysis of monetary policy contends that fiscal authorities simply adjust primary surpluses, s, to sanction the price level determined by the monetary authority through equation (5), which deprives the debt valuation equation (4) of any role in price level determination. The simple explanation is (Cochrane 2011Jan, 5):
“We are here to think about what happens when [4] exerts more force on the price level. This change may happen by force, when debt, deficits and distorting taxes become large so the Treasury is unable or refuses to follow. Then [4] determines the price level; monetary policy must follow the fiscal lead and ‘passively’ adjust M to satisfy [5]. This change may also happen by choice; monetary policies may be deliberately passive, in which case there is nothing for the Treasury to follow and [4] determines the price level.”
An intuitive interpretation by Cochrane (2011Jan 4) is that when the current real value of government debt exceeds expected future surpluses, economic agents unload government debt to purchase private assets and goods, resulting in inflation. If the risk premium on government debt declines, government debt becomes more valuable, causing a deflationary effect. If the risk premium on government debt increases, government debt becomes less valuable, causing an inflationary effect.
There are multiple conclusions by Cochrane (2011Jan) on the debt/dollar crisis and Global recession, among which the following three:
(1) The flight to quality that magnified the recession was not from goods into money but from private-sector securities into government debt because of the risk premium on private-sector securities; monetary policy consisted of providing liquidity in private-sector markets suffering stress
(2) Increases in liquidity by open-market operations with short-term securities have no impact; quantitative easing can affect the timing but not the rate of inflation; and purchase of private debt can reverse part of the flight to quality
(3) The debt valuation equation has a similar role as the expectation shifting the Phillips curve such that a fiscal inflation can generate stagflation effects similar to those occurring from a loss of anchoring expectations.
IV Global Inflation. There is inflation everywhere in the world economy, with slow growth and persistently high unemployment in advanced economies. Table IV-1, updated with every blog comment, provides the latest annual data for GDP, consumer price index (CPI) inflation, producer price index (PPI) inflation and unemployment (UNE) for the advanced economies, China and the highly-indebted European countries with sovereign risk issues. The table now includes the Netherlands and Finland that with Germany make up the set of northern countries in the euro zone that hold key votes in the enhancement of the mechanism for solution of sovereign risk issues (Peter Spiegel and Quentin Peel, “Europe: Northern Exposures,” Financial Times, Mar 9, 2011 http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/55eaf350-4a8b-11e0-82ab-00144feab49a.html#axzz1gAlaswcW). Newly available data on inflation is considered below in this section. Data in Table IV-1 for the euro zone and its members are updated from information provided by Eurostat but individual country information is provided in this section as soon as available, following Table IV-1. Data for other countries in Table IV-1 are also updated with reports from their statistical agencies. Economic data for major regions and countries is considered in Section V World Economic Slowdown following with individual country and regional data tables.
Table IV-1, GDP Growth, Inflation and Unemployment in Selected Countries, Percentage Annual Rates
| GDP | CPI | PPI | UNE | |
| US | 1.6 | 2.7 | 2.8 | 8.2 |
| Japan | -0.6 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 4.5 |
| China | 8.9 | 3.6 | -0.3 | |
| UK | 0.5 | 3.5* | 3.6* output | 8.3 |
| Euro Zone | 0.7 | 2.7 | 3.6 | 10.8 |
| Germany | 2.0 | 2.3 | 3.2 | 5.7 |
| France | 0.2 | 2.6 | 4.3 | 10.0 |
| Nether-lands | -0.7 | 2.9 | 4.2 | 4.9 |
| Finland | 1.2 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 7.4 |
| Belgium | 0.9 | 3.1 | 3.6 | 7.2 |
| Portugal | -2.7 | 3.1 | 4.2 | 15.0 |
| Ireland | NA | 2.2 | 3.8 | 14.7 |
| Italy | -0.5 | 3.8 | 3.2 | 9.3 |
| Greece | -7.0 | 1.4 | 6.9 | NA |
| Spain | 0.3 | 1.8 | 3.4 | 23.6 |
Notes: GDP: rate of growth of GDP; CPI: change in consumer price inflation; PPI: producer price inflation; UNE: rate of unemployment; all rates relative to year earlier
*Office for National Statistics http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/cpi/consumer-price-indices/march-2012/index.html **Core
PPI http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/ppi2/producer-price-index/march-2012/index.html
Source: EUROSTAT; country statistical sources http://www.census.gov/aboutus/stat_int.html
Table IV-1 shows the simultaneous occurrence of low growth, inflation and unemployment in advanced economies. The US grew at 1.6 percent in IVQ2011 relative to IVQ2010 (Table 8, p 11 in http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2012/pdf/gdp4q11_3rd.pdf). Japan’s GDP fell 0.6 percent in IVQ2011 relative to IVQ2010 and contracted 1.7 percent in IIQ2011 relative to IIQ2010 because of the Tōhoku or Great East Earthquake and Tsunami of Mar 11, 2011 but grew at the seasonally-adjusted annual rate (SAAR) of 7.1 percent in IIIQ2011 to decline at the SAAR of 0.7 percent in IVQ 2011 (see Section VB at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/03/thirty-million-unemployed-or_11.html); the UK grew at 0.5 percent in IVQ2011 relative to IVQ2010 and GDP fell 0.3 percent in IVQ2011 relative to IIIQ2011 (http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/naa2/quarterly-national-accounts/q4-2011/index.html); and the Euro Zone grew at 0.7 percent in IVQ2011 relative to IVQ2010 but declined 0.3 percent in IVQ2011 relative to IIIQ2011 (see Section VD at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/03/thirty-million-unemployed-or_11.html and http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/cache/ITY_PUBLIC/2-06032012-AP/EN/2-06032012-AP-EN.PDF). These are stagnating or “growth recession” rates, which are positive growth rates instead of contractions but insufficient to recover employment. The rates of unemployment are quite high: 8.2 percent in the US but 18.3 percent for unemployment/underemployment (see Table I-4 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/04/thirty-million-unemployed-or.html), 4.5 percent for Japan, 8.3 percent for the UK with high rates of unemployment for young people (see the labor statistics of the UK in Subsection VH in this comment and earlier at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/03/global-financial-and-economic-risk_18.html) and 10.8 percent in the Euro Zone (section VD in http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/04/thirty-million-unemployed-or_08.html). Twelve-month rates of inflation have been quite high, even when some are moderating at the margin: 2.7 percent in the US, 0.3 percent for Japan, 3.6 percent for China, 2.7 percent for the Euro Zone and 3.5 percent for the UK (http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/cpi/consumer-price-indices/march-2012/index.html). Stagflation is still an unknown event but the risk is sufficiently high to be worthy of consideration (see http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/06/risk-aversion-and-stagflation.html). The analysis of stagflation also permits the identification of important policy issues in solving vulnerabilities that have high impact on global financial risks. There are six key interrelated vulnerabilities in the world economy that have been causing global financial turbulence: (1) sovereign risk issues in Europe resulting from countries in need of fiscal consolidation and enhancement of their sovereign risk ratings (see Section III in this post and the earlier post http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/04/fractured-labor-market-with-hiring.html); (2) the tradeoff of growth and inflation in China now with change in growth strategy to domestic consumption instead of investment and political developments in a decennial transition; (3) slow growth by repression of savings with de facto interest rate controls (see section II http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/04/mediocre-economic-growth-falling-real.html), weak hiring with the loss of 10 million full-time jobs (see section II in http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/04/fractured-labor-market-with-hiring.html and earlier at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/03/global-financial-and-economic-risk.html and http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/02/hiring-collapse-ten-million-fewer-full.html) and continuing job stress of 24 to 30 million people in the US and stagnant wages in a fractured job market (see Section I Thirty Million Unemployed or Underemployed in http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/04/thirty-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/03/thirty-million-unemployed-or.html); (4) the timing, dose, impact and instruments of normalizing monetary and fiscal policies (see IV Budget/Debt Quagmire in http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/02/thirty-one-million-unemployed-or.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/08/united-states-gdp-growth-standstill.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/03/is-there-second-act-of-us-great.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/03/global-financial-risks-and-fed.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/02/policy-inflation-growth-unemployment.html) in advanced and emerging economies; (5) the Tōhoku or Great East Earthquake and Tsunami of Mar 11, 2011 that had repercussions throughout the world economy because of Japan’s share of about 9 percent in world output, role as entry point for business in Asia, key supplier of advanced components and other inputs as well as major role in finance and multiple economic activities (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748704461304576216950927404360.html?mod=WSJ_business_AsiaNewsBucket&mg=reno-wsj); and (6) geopolitical events in the Middle East.
In the effort to increase transparency, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) provides both economic projections of its participants and views on future paths of the policy rate that in the US is the federal funds rate or interest on interbank lending of reserves deposited at Federal Reserve Banks. These projections and views are discussed initially followed with appropriate analysis.
The statement of the FOMC at the conclusion of its meeting on Jan 25, 2012, revealed the following policy intentions (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20120125a.htm):
“Information received since the Federal Open Market Committee met in December suggests that the economy has been expanding moderately, notwithstanding some slowing in global growth. While indicators point to some further improvement in overall labor market conditions, the unemployment rate remains elevated. Household spending has continued to advance, but growth in business fixed investment has slowed, and the housing sector remains depressed. Inflation has been subdued in recent months, and longer-term inflation expectations have remained stable.
Consistent with its statutory mandate, the Committee seeks to foster maximum employment and price stability. The Committee expects economic growth over coming quarters to be modest and consequently anticipates that the unemployment rate will decline only gradually toward levels that the Committee judges to be consistent with its dual mandate. Strains in global financial markets continue to pose significant downside risks to the economic outlook. The Committee also anticipates that over coming quarters, inflation will run at levels at or below those consistent with the Committee's dual mandate.
To support a stronger economic recovery and to help ensure that inflation, over time, is at levels consistent with the dual mandate, the Committee expects to maintain a highly accommodative stance for monetary policy. In particular, the Committee decided today to keep the target range for the federal funds rate at 0 to 1/4 percent and currently anticipates that economic conditions--including low rates of resource utilization and a subdued outlook for inflation over the medium run--are likely to warrant exceptionally low levels for the federal funds rate at least through late 2014.
The Committee also decided to continue its program to extend the average maturity of its holdings of securities as announced in September. The Committee is maintaining its existing policies of reinvesting principal payments from its holdings of agency debt and agency mortgage-backed securities in agency mortgage-backed securities and of rolling over maturing Treasury securities at auction. The Committee will regularly review the size and composition of its securities holdings and is prepared to adjust those holdings as appropriate to promote a stronger economic recovery in a context of price stability. ”
There are several important issues in this statement.
1. Mandate. The FOMC pursues a policy of attaining its “dual mandate” of (http://www.federalreserve.gov/aboutthefed/mission.htm):
“Conducting the nation's monetary policy by influencing the monetary and credit conditions in the economy in pursuit of maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates”
2. Extending Average Maturity of Holdings of Securities. The statement of Jan 25, 2012, invokes the mandate that inflation is subdued but employment below maximum such that further accommodation is required. Accommodation consists of low interest rates. The new “Operation Twist” (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011_09_01_archive.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/09/collapse-of-household-income-and-wealth.html) or restructuring the portfolio of securities of the Fed by selling short-dated securities and buying long-term securities has the objective of reducing long-term interest rates. Lower interest rates would stimulate consumption and investment, or aggregate demand, increasing the rate of economic growth and thus reducing stress in job markets.
3. Target of Fed Funds Rate. The FOMC continues to maintain the target of fed funds rate at 0 to ¼ percent.
4. Advance Guidance. The FOMC increases transparency by advising on the expectation of the future path of fed funds rate. This guidance is the view that conditions such as “low rates of resource utilization and a subdued outlook for inflation over the medium run are likely to warrant exceptionally low levels for the federal funds rate at least through late 2014.”
5. Monitoring and Policy Focus. The FOMC reconsiders its policy continuously in accordance with available information: “The Committee will regularly review the size and composition of its securities holdings and is prepared to adjust those holdings as appropriate to promote a stronger economic recovery in a context of price stability.”
These policy statements are carefully crafted to express the intentions of the FOMC. The main objective of the statements is to communicate as clearly and firmly as possible the intentions of the FOMC to fulfill its dual mandate. During periods of low inflation and high unemployment and underemployment such as currently the FOMC may be more biased toward measures that stimulate the economy to reduce underutilization of workers and other productive resources. The FOMC also is vigilant about inflation and ready to change policy in the effort to attain its dual mandate.
The FOMC also released the economic projections of governors of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve and Federal Reserve Banks presidents shown in Table IV-2. The Fed releases the data with careful explanations (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20120125.pdf). Columns “∆% GDP,” “∆% PCE Inflation” and “∆% Core PCE Inflation” are changes “from the fourth quarter of the previous year to the fourth quarter of the year indicated.” The GDP report for IVQ2011 is analyzed in the current post of this blog in section I. The Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) provides the GDP report with the second estimate for IVQ2011 to be released on Feb 29 and the third estimate on Mar 29 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/gdpnewsrelease.htm). PCE inflation is the index of personal consumption expenditures (PCE) of the report of the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) on “Personal Income and Outlays” (http://www.bea.gov/national/index.htm#personal), which is analyzed in this blog as soon as available. The next report will be released at 8:30 AM on Jan 30, 2012. PCE core inflation consists of PCE inflation excluding food and energy. Column “UNEMP %” is the rate of unemployment measured as the average civilian unemployment rate in the fourth quarter of the year. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) provides the Employment Situation Report with the civilian unemployment rate in the first Friday of every month, which is analyzed in this blog. The report for February will be released on Feb 3, 2012 (http://www.bls.gov/cps/). “Longer term projections represent each participant’s assessment of the rate to which each variable would be expected to converge under appropriate monetary policy and in the absence of further shocks to the economy” (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20120125.pdf).
It is instructive to focus on 2012, as 2013, 2014 and longer term are too far away, and there is not much information on what will happen in 2013 and beyond. The central tendency should provide reasonable approximation of the view of the majority of members of the FOMC but the second block of numbers provides the range of projections by FOMC participants. The first row for each year shows the projection introduced after the meeting of Jan 25 and the second row “Nov PR” the projection of the Nov meeting. There are three major changes in the view.
1. Growth “GDP ∆.” The FOMC has reduced the forecast of GDP growth in 2012 from 3.3 to 3.7 percent in Jun to 2.5 to 2.9 percent in Nov and now to 2.2 to 2.7 percent at the Jan 25 meeting.
2. Rate of Unemployment “UNEM%.” The FOMC increased the rate of unemployment from 7.8 to 8.2 percent in Jun to 8.5 to 8.7 percent in Nov but has reduced it to 8.2 to 8.5 percent at the Jan 25 meeting.
3. Inflation “∆% PCE Inflation.” The FOMC changed the forecast of personal consumption expenditures (PCE) inflation from 1.5 to 2.0 percent in Jun to virtually the same of 1.4 to 2.0 percent in Nov but has reduced it to 1.4 to 1.8 percent at the Jan 25 meeting.
4. Core Inflation “∆% Core PCE Inflation.” Core inflation is PCE inflation excluding food and energy. There is again not much of a difference of the projection for 2012 in Jun of 1.4 to 2.0 percent and the Nov projection of 1.5 to 2.0 percent, which has been reduced slightly to 1.5 to 1.8 percent at the Jan 25 meeting.
Table IV-2, US, Economic Projections of Federal Reserve Board Members and Federal Reserve Bank Presidents in FOMC, January 2012 and November 2011
| ∆% GDP | UNEM % | ∆% PCE Inflation | ∆% Core PCE Inflation | |
| Central | ||||
| 2012 | 2.2 to 2.7 | 8.2 to 8.5 | 1.4 to 1.8 | 1.5 to 1.8 |
| 2013 | 2.8 to 3.2 | 7.4 to 8.1 | 1.4 to 2.0 | 1.5 to 2.0 |
| 2014 | 3.3 to 4.0 | 6.7 to 7.6 | 1.6 to 2.0 | 1.6 to 2.0 |
| Longer Run | 2.3 to 2.6 | 5.2 to 6.0 | 2.0 | |
| Range | ||||
| 2012 | 2.1 to 3.0 | 7.8 to 8.6 | 1.3 to 2.5 | 1.3 to 2.0 |
| 2013 | 2.4 to 3.8 | 7.0 to 8.2 | 1.4 to 2.3 | 1.4 to 2.0 |
| 2014 | 2.8 to 4.3 | 6.3 to 7.7 | 1.5 to 2.1 | 1.4 to 2.0 |
| Longer Run | 2.2 to 3.0 | 5.0 to 6.0 | 2.0 |
Notes: UEM: unemployment; PR: Projection
Source: http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20120125.pdf
Another important decision at the FOMC meeting on Jan 25, 2012, is formal specification of the goal of inflation of 2 percent per year but without specific goal for unemployment (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20120125c.htm):
“Following careful deliberations at its recent meetings, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) has reached broad agreement on the following principles regarding its longer-run goals and monetary policy strategy. The Committee intends to reaffirm these principles and to make adjustments as appropriate at its annual organizational meeting each January.
The FOMC is firmly committed to fulfilling its statutory mandate from the Congress of promoting maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates. The Committee seeks to explain its monetary policy decisions to the public as clearly as possible. Such clarity facilitates well-informed decisionmaking by households and businesses, reduces economic and financial uncertainty, increases the effectiveness of monetary policy, and enhances transparency and accountability, which are essential in a democratic society.
Inflation, employment, and long-term interest rates fluctuate over time in response to economic and financial disturbances. Moreover, monetary policy actions tend to influence economic activity and prices with a lag. Therefore, the Committee's policy decisions reflect its longer-run goals, its medium-term outlook, and its assessments of the balance of risks, including risks to the financial system that could impede the attainment of the Committee's goals.
The inflation rate over the longer run is primarily determined by monetary policy, and hence the Committee has the ability to specify a longer-run goal for inflation. The Committee judges that inflation at the rate of 2 percent, as measured by the annual change in the price index for personal consumption expenditures, is most consistent over the longer run with the Federal Reserve's statutory mandate. Communicating this inflation goal clearly to the public helps keep longer-term inflation expectations firmly anchored, thereby fostering price stability and moderate long-term interest rates and enhancing the Committee's ability to promote maximum employment in the face of significant economic disturbances.
The maximum level of employment is largely determined by nonmonetary factors that affect the structure and dynamics of the labor market. These factors may change over time and may not be directly measurable. Consequently, it would not be appropriate to specify a fixed goal for employment; rather, the Committee's policy decisions must be informed by assessments of the maximum level of employment, recognizing that such assessments are necessarily uncertain and subject to revision. The Committee considers a wide range of indicators in making these assessments. Information about Committee participants' estimates of the longer-run normal rates of output growth and unemployment is published four times per year in the FOMC's Summary of Economic Projections. For example, in the most recent projections, FOMC participants' estimates of the longer-run normal rate of unemployment had a central tendency of 5.2 percent to 6.0 percent, roughly unchanged from last January but substantially higher than the corresponding interval several years earlier.
In setting monetary policy, the Committee seeks to mitigate deviations of inflation from its longer-run goal and deviations of employment from the Committee's assessments of its maximum level. These objectives are generally complementary. However, under circumstances in which the Committee judges that the objectives are not complementary, it follows a balanced approach in promoting them, taking into account the magnitude of the deviations and the potentially different time horizons over which employment and inflation are projected to return to levels judged consistent with its mandate. ”
The probable intention of this specific inflation goal is to “anchor” inflationary expectations. Massive doses of monetary policy of promoting growth to reduce unemployment could conflict with inflation control. Economic agents could incorporate inflationary expectations in their decisions. As a result, the rate of unemployment could remain the same but with much higher rate of inflation (see Kydland and Prescott 1977 and Barro and Gordon 1983; http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/05/slowing-growth-global-inflation-great.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/04/new-economics-of-rose-garden-turned.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/03/is-there-second-act-of-us-great.html). Strong commitment to maintaining inflation at 2 percent could control expectations of inflation.
The FOMC continues its efforts of increasing transparency that can improve the credibility of its firmness in implementing its dual mandate. Table IV-3 provides the views by participants of the FOMC of the levels at which they expect the fed funds rate in 2012, 2013, 2014 and the in the longer term. The table is inferred from a chart provided by the FOMC with the number of participants expecting the target of fed funds rate (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20120125.pdf). There are 14 participants expecting the rate to remain at 0 to ¼ percent in 2012 and only three to be higher. Not much change is expected in 2013 either with 11 participants anticipating the rate at the current target of 0 to ¼ percent and only six expecting higher rates. The rate would still remain at 0 to ¼ percent in 2014 for six participants with five expecting the rate to be in the range of 0.5 to 1 percent and two participants expecting rates from 1 to 1.5 percent but only 4 with rates exceeding 2.5 percent. This table is consistent with the guidance statement of the FOMC that rates will remain at low levels until late in 2014.
Table IV-3, US, Views of Target Federal Funds Rate at Year-End of Federal Reserve Board Members and Federal Reserve Bank Presidents Participating in FOMC, January 25, 2012
| 0 to 0.25 | 0.5 to 1.0 | 1.0 to 1.5 | 1.75 to 2.0 | 2.5 to 2.75 | 3.75 to 4.5 | |
| 2012 | 14 | 1 | 2 | |||
| 2013 | 11 | 4 | 2 | |||
| 2014 | 6 | 5 | 2 | 4 | ||
| Longer Run | 17 |
Source: http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20120125.pdf
Additional information is provided in Table IV-4 with the number of participants expecting increasing interest rates in the years from 2012 to 2016. It is evident from Table IV-4 that the prevailing view in the FOMC is for interest rates to continue at low levels in future years. This view is consistent with the economic projections of low economic growth, relatively high unemployment and subdued inflation provided in Table IV-2.
Table IV-4, US, Views of Appropriate Year of Increasing Target Federal Funds Rate of Federal Reserve Board Members and Federal Reserve Bank Presidents Participating in FOMC, January 25, 2012
| Appropriate Year of Increasing Target Fed Funds Rate | Number of Participants |
| 2012 | 3 |
| 2013 | 3 |
| 2014 | 5 |
| 2015 | 4 |
| 2016 | 2 |
Source: http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20120125.pdf
There are two categories of responses in the Empire State Manufacturing Survey of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York (http://www.newyorkfed.org/survey/empire/empiresurvey_overview.html): current conditions and expectations for the next six months. There are responses in the survey for two types of prices: prices received or inputs of production and prices paid or sales prices of products. Table IV-2 provides the responses and indexes for the two categories and within them for the two types of prices from Jan 2011 to Apr 2012. Current prices paid were rising at an accelerating rate from 35.79 in Jan to 69.89 in May but the rate of increase dropped significantly to 25.88 in Feb 2012, increasing sharply to 50.62 in Mar in the current commodity price shock but falling to 45.78 in Apr. The index of current prices received also fell sharply from 27.96 in May to 4.49 in Oct, meaning that prices were increasing at a very low rate and then rose to 13.58 in Mar 2012, increasing to 18.28 in Apr, which is also relatively low. In the expectations for the next six months, the index of prices paid also declined from 68.82 in May to 56.98 in Dec, rising to 66.67 in Mar but declining to 50.60 in Apr 2012. Expected prices received also rose in the first five months of 2011, declining from 35.48 in May to 15.22 in Aug but then rising to 32.10 in Mar and declining to 22.89 in Apr 2012.
Table IV-2, US, FRBNY Empire State Manufacturing Survey, Diffusion Indexes, Prices Paid and Prices Received, SA
| Current Prices Paid | Current Prices Received | Six Months Prices Paid | Six Months Prices Received | |
| Apr 2012 | 45.78 | 19.28 | 50.60 | 22.89 |
| Mar 2012 | 50.62 | 13.58 | 66.67 | 32.10 |
| Feb | 25.88 | 15.29 | 62.35 | 34.12 |
| Jan | 26.37 | 23.08 | 53.85 | 30.77 |
| Dec 20111 | 24.42 | 3.49 | 56.98 | 36.05 |
| Nov | 18.29 | 6.10 | 36.59 | 25.61 |
| Oct | 24.47 | 4.49 | 40.45 | 17.98 |
| Sep | 32.61 | 8.70 | 53.26 | 22.83 |
| Aug | 28.26 | 2.17 | 42.39 | 15.22 |
| Jul | 43.33 | 5.56 | 51.11 | 30.0 |
| Jun | 56.12 | 11.22 | 55.10 | 19.39 |
| May | 69.89 | 27.96 | 68.82 | 35.48 |
| Apr | 57.69 | 26.92 | 56.41 | 38.46 |
| Mar | 53.25 | 20.78 | 71.43 | 36.36 |
| Feb | 45.78 | 16.87 | 55.42 | 27.71 |
| Jan | 35.79 | 15.79 | 60.00 | 42.11 |
Source: http://www.newyorkfed.org/survey/empire/empiresurvey_overview.html
Price indexes of the Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia Outlook Survey are provided in Table IV-3. As inflation waves throughout the world (analyzed in section I World Inflation Waves http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/04/fractured-labor-market-with-hiring.html), indexes of both current and expectations of future prices paid and received were quite high until May. Prices paid, or inputs, were more dynamic, reflecting carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures. All indexes softened after May with even decline of prices received in Aug during the first round of risk aversion. Current and future price indexes have increased again but not back to the levels in the beginning of 2011 because of risk aversion frustrating carry trades even under zero interest rates.
Table IV-3, US, Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia Business Outlook Survey, Current and Future Prices Paid and Prices Received, SA
| Current Prices Paid | Current Prices Received | Future Prices Paid | Future Prices Received | |
| Apr 2012 | 22.5 | 9.4 | 35.2 | 20.4 |
| Mar | 18.7 | 8.4 | 39.4 | 25.6 |
| Feb | 38.7 | 15.0 | 50.4 | 32.0 |
| Jan | 31.8 | 11.2 | 52.7 | 23.8 |
| Dec 2011 | 30.4 | 10.3 | 49.4 | 26.4 |
| Nov | 25.9 | 6.2 | 41.0 | 28.1 |
| Oct | 23.5 | 1.6 | 44.8 | 27.2 |
| Sep | 25.0 | 3.9 | 37.8 | 22.0 |
| Aug | 20.1 | -6.0 | 40.2 | 20.1 |
| Jul | 30.2 | 3.9 | 44.2 | 12.7 |
| Jun | 32.8 | 5.2 | 30.5 | 4.1 |
| May | 46.4 | 16.3 | 53.4 | 27.0 |
| Apr | 54.4 | 23.0 | 55.4 | 33.5 |
| Mar | 59.8 | 19.3 | 63.6 | 34.8 |
| Feb | 63.2 | 17.5 | 67.8 | 35.9 |
| Jan | 51.9 | 14.5 | 62.8 | 36.0 |
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia
http://www.phil.frb.org/index.cfm
Inflation waves in the diffusion index of the Philadelphia Fed are quite clear in Chart IV-1 of the Business Outlook Survey of the Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia. The index collapsed from the highs of the year that were driven by carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures and increased slightly again but under check by risk aversion from the European debt crisis. The decline into Mar is different than the increase into Mar in the index of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York.
Chart IV-1, Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia Business Outlook Survey Current Prices Paid Diffusion Index SA
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia
http://www.phil.frb.org/index.cfm
Chart IV-2 of the Business Outlook Survey of the Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia provides the current diffusion index of prices received, which are prices of sales of products by companies. There is much less dynamism than in prices paid because commodity-rich inputs are only part of total costs. The high levels early in 2011 have not been realized again under the pressure on carry trades of risk financial assets from the European debt crisis.
Chart IV-2, Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia Business Outlook Survey Current Prices Received Diffusion Index SA
Source: Federal Reserve Bank of Philadelphia
http://www.phil.frb.org/index.cfm
Table IV-4, Euro Area Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices Month and 12 Months ∆%
| Month ∆% | 12 Months ∆% | |
| Mar 2012 | 1.3 | 2.7 |
| Feb | 0.5 | 2.7 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Mar | 11.3 | |
| Jan | -0.8 | 2.7 |
| Dec 2011 | 0.3 | 2.7 |
| AE ∆% Dec-Jan | -3.0 | |
| Nov | 0.1 | 3.0 |
| Oct | 0.3 | 3.0 |
| Sep | 0.7 | 3.0 |
| Aug | 0.2 | 2.6 |
| AE ∆% Aug-Dec | 4.0 | |
| Jul | -0.6 | 2.6 |
| Jun | 0.0 | 2.7 |
| May | 0.0 | 2.7 |
| AE ∆% May-Jul | -2.4 | |
| Apr | 0.6 | 2.8 |
| Mar | 1.4 | 2.7 |
| Feb | 0.4 | 2.4 |
| Jan | -0.7 | 2.3 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr | 5.2 | |
| Dec 2010 | 0.6 | 2.2 |
AE: annual equivalent
Source: EUROSTAT
http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/cache/ITY_PUBLIC/2-17042012-AP/EN/2-17042012-AP-EN.PDF
Table IV-5 provides inflation, unemployment and real GDP growth in the euro area yearly from 1999 to 2011 together with growth forecasts of EUROSTAT for 2012 and 2013. Inflation in the euro zone remained subdued around 2 percent in the first five years of the euro zone from 1999 to 2004, as shown in Table IV-5. Inflation climbed above 2.0 percent after 2005, peaking at 3.3 percent in 2008 with the surge in commodity prices but falling to 0.3 percent in 2009 with the collapse of commodity prices. Inflation climbed back to 1.6 percent in 2010 and 2.7 percent in 2011.
Table IV-5, Euro Area, Yearly Percentage Change of Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices, ∆%
| Year | HICP ∆% | Unemployment | GDP ∆% |
| 1999 | 1.2 | 9.6 | 2.9 |
| 2000 | 2.2 | 8.7 | 3.8 |
| 2001 | 2.4 | 8.1 | 2.0 |
| 2002 | 2.3 | 8.5 | 0.9 |
| 2003 | 2.1 | 9.0 | 0.7 |
| 2004 | 2.2 | 9.3 | 2.2 |
| 2005 | 2.2 | 9.2 | 1.7 |
| 2006 | 2.2 | 8.5 | 3.3 |
| 2007 | 2.1 | 7.6 | 3.0 |
| 2008 | 3.3 | 7.6 | 0.4 |
| 2009 | 0.3 | 9.6 | -4.3 |
| 2010 | 1.6 | 10.1 | 1.9 |
| 2011 | 2.7 | 10.2 | 1.5 |
| 2012* | -0.3 | ||
| 2013* | 1.3 |
*EUROSTAT forecast
Source: http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/statistics/search_database
EUROSTAT provides the decomposition in percentage point contributions of the rate of inflation of 2.7 percent in the 12 months ending in Mar 2012 relative to Mar 2011 shown in Table IV-6. Energy-rich components dominate the 12-month rate of inflation with percentage point contributions: 0.36 by fuel for transport, 0.14 by bas and 0.08 by heating oil. Table IV-14 only lists highest magnitudes of positive and negative contributions.
Table IV-6, Euro Area, Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices Sub-Indices with Most Important Impact %
| Mar 2012/ | Weight 2012 % | Rate ∆% | Impact |
| Positive Contribution | |||
| Fuel for Transport | 48.5 | 9.6 | 0.36 |
| Gas | 18.3 | 10.6 | 0.14 |
| Heating Oil | 8.9 | 11.1 | 0.08 |
| Tobacco | 23.4 | 5.4 | 0.07 |
| Jewelry and Watches | 5.9 | 11.3 | 0.05 |
| District Heating | 6.8 | 11.0 | 0.05 |
| Negative Contribution | |||
| Accommodation Services | 16.5 | -0.6 | -0.06 |
| Fruit | 11.8 | -1.9 | -0.06 |
| Audio-visual Equipment | 5.0 | -9.4 | -0.06 |
| Cars | 36.2 | 0.9 | -0.07 |
| Rents | 60.5 | 1.4 | -0.08 |
| Telecom | 29.8 | -3.1 | -0.18 |
PP: percentage points
Source: EUROSTAT http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/cache/ITY_PUBLIC/2-17042012-AP/EN/2-17042012-AP-EN.PDF
EUROSTAT provides the decomposition in percentage point contributions of the rate of inflation of 1.3 percent in Mar 2012 relative to Feb 2012 shown in Table IV-7. The largest positive contributions originated in 0.74 by package garments, 0.15 percentage points from footwear and 0.10 percentage points for fuel for transport. The largest contributions to decline were 0.03 percentage points for bread and cereals and various individual contributions.
Table IV-7, Euro Area, Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices Sub-Indices with Most Important Impact %
| Mar 2012/ | Weight 2012 % | Rate ∆% | Impact Percentage Points |
| Garments | 50.7 | 17.6 | 0.74 |
| Footwear | 13.6 | 13.5 | 0.15 |
| Fuel for Transport | 48.5 | 3.1 | 0.10 |
| Air Transport | 6.3 | 6.4 | 0.03 |
| Clothing Accessories | 2.0 | 10.5 | 0.02 |
| Other Personal Effects | 4.3 | 4.5 | 0.01 |
| Negative Contribution | |||
| Bread and Cereals | 25.6 | 0.0 | -0.03 |
| Telecom | 29.8 | 0.0 | -0.04 |
| Cars | 36.2 | 0.1 | -0.04 |
| Meat | 35.8 | 0.1 | -0.05 |
| Rents | 60.5 | 0.1 | -0.08 |
| Restaurants and Cafes | 68.8 | 0.2 | -0.09 |
Source: EUROSTAT http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/cache/ITY_PUBLIC/2-17042012-AP/EN/2-17042012-AP-EN.PDF
The producer price index of Germany increased 0.6 percent in Mar relative to Feb and increased 3.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Feb, as shown in Table IV-8. The producer price index of Germany has similar waves of inflation as in many other countries (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/04/fractured-labor-market-with-hiring.html). In the first wave from Jan to Apr, the annual equivalent rate of producer price inflation was 10.3 percent, propelled by carry trades from zero interest rates to exposures in commodity futures in a mood of risk appetite. In the second wave in May and Jun, the annual equivalent rate of producer price inflation was only 0.6 percent because of the collapse of the carry trade in fear of risks of European sovereign debt. In the third wave from Jul to Sep, annual-equivalent producer price inflation in Germany 2.8 percent with fluctuations in commodity prices resulting from perceptions of the sovereign risk crisis in Europe. In the fourth wave from Oct to Nov, annual equivalent inflation was minus 1.8 percent as financial markets were shocked with strong risk aversion. In the fifth wave from Dec to Jan, annual equivalent inflation was at 1.2 percent. In the sixth wave, annual equivalent inflation increased to 6.2 percent in Feb-Mar. Annual data in the bottom of Table IV-8 show that the producer price index fell 5.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2009 as a result of the fall of commodity prices originating in risk aversion after the panic of 2008.
Table IV-8, Germany, Producer Price Index ∆%
| 12 Months ∆% NSA | Month ∆% Calendar and SA | |
| Mar 2012 | 3.3 | 0.6 |
| Feb | 3.2 | 0.4 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Mar | 6.2 | |
| Jan | 3.4 | 0.6 |
| Dec 2011 | 4.0 | -0.4 |
| AE ∆% Dec-Jan | 1.2 | |
| Nov | 5.2 | 0.1 |
| Oct | 5.3 | 0.2 |
| AE ∆% Oct-Nov | 1.8 | |
| Sep | 5.5 | 0.3 |
| Aug | 5.5 | -0.3 |
| Jul | 5.8 | 0.7 |
| AE ∆% Jul-Sep | 2.8 | |
| Jun | 5.6 | 0.1 |
| May | 6.1 | 0.0 |
| AE ∆% May-Jun | 0.6 | |
| Apr | 6.4 | 1.0 |
| Mar | 6.2 | 0.4 |
| Feb | 6.4 | 0.7 |
| Jan | 5.7 | 1.2 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr | 10.4 | |
| Dec 2010 | 5.3 | 0.7 |
| Nov | 4.4 | 0.2 |
| Oct | 4.3 | 0.4 |
| Sep | 3.9 | 0.3 |
| Aug | 3.2 | 0.0 |
| Jul | 3.7 | 0.5 |
| Jun | 1.7 | 0.6 |
| May | 0.9 | 0.3 |
| Apr | 0.6 | 0.8 |
| Mar | -1.5 | 0.7 |
| Feb | -2.9 | 0.0 |
| Jan | -3.4 | 0.8 |
| Dec 2009 | -5.2 | -0.1 |
| Dec 2008 | 4.0 | -0.8 |
| Dec 2007 | 1.9 | -0.1 |
| Dec 2006 | 4.2 | 0.1 |
| Dec 2005 | 4.8 | 0.3 |
| Dec 2004 | 2.9 | 0.1 |
| Dec 2003 | 1.8 | 0.0 |
| Dec 2002 | 0.5 | 0.1 |
| Dec 2001 | 0.1 | -0.2 |
Source: https://www.destatis.de/DE/ZahlenFakten/Indikatoren/Konjunkturindikatoren/Konjunkturindikatoren.html
Chart IV-3 of the Federal Statistical Agency of Germany Statistiche Bundesamt Deutschland provides the producer price index of Germany from 2003 to 2012. Producer price inflation peaked in 2008 with the rise of commodity prices induced by the carry trade from zero interest rates to commodity futures. Prices then declined with the flight away from risk financial assets to government obligations after the financial panic in Sep 2008. With zero interest rates and no risk aversion, the carry trade pushed commodity future prices upwardly resulting in new rising trend of the producer price index. The right-hand side of the chart shows moderation and even decline in prices because of severe risk aversion frustrating carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures but then return of risk appetite with another surge of the index in annual equivalent rate at 6.2 percent in Feb-Mar 2012.
Chart IV-3, Germany, Index of Producer Prices for Industrial Products, 2005=100
Source: Statistiche Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/DE/ZahlenFakten/Indikatoren/Konjunkturindikatoren/Konjunkturindikatoren.html
Chart IV-4 of the Federal Statistical Agency of Germany Statistiche Bundesamt Deutschland provides the unadjusted producer price index and trend. There is a clear upward trend of prices after the end of risk aversion with zero interest rates in 2009. The actual curve fell below trend in the current episode of severe risk aversion but rose again in Feb-Mar.
Chart IV-4, Germany, Producer Price Index, Non-adjusted Value and Trend, 2005=100
Source: Statistiche Bundesamt Deutschland
Consumer price inflation in the UK is shown in Table IV-9. The CPI index increased 0.3 percent in Mar after 0.6 percent in Feb. The same inflation waves are present in UK CPI inflation (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/04/fractured-labor-market-with-hiring.html). In the first wave in Jan-Apr, annual equivalent inflation was at a high 6.5 percent. In the second wave in May-Jul, annual equivalent inflation fell to only 0.4 percent. In the third wave in Aug-Dec, annual equivalent inflation returned at 4.6 percent. In the fourth wave in Dec to Jan, annual equivalent inflation was minus 0.6 percent because of decline of 0.5 percent in Jan. In the fifth wave, annual equivalent inflation increased to 5.5 percent in Feb-Mar.
Table IV-9, UK, Consumer Price Index All Items, Month and 12 Months ∆%
| Month ∆% | 12 Months ∆% | |
| Mar 2012 | 0.3 | 3.5 |
| Feb | 0.6 | 3.4 |
| AE ∆% Feb-Mar | 5.5 | |
| Jan | -0.5 | 3.6 |
| Dec 2011 | 0.4 | 4.2 |
| AE ∆% Dec-Jan | -0.6 | |
| Nov | 0.2 | 4.8 |
| Oct | 0.1 | 5.0 |
| Sep | 0.6 | 5.2 |
| Aug | 0.6 | 4.5 |
| AE ∆% Aug-Dec | 4.6 | |
| Jul | 0.0 | 4.4 |
| Jun | -0.1 | 4.2 |
| May | 0.2 | 4.5 |
| May-Jul | 0.4 | |
| Apr | 1.0 | 4.5 |
| Mar | 0.3 | 4.0 |
| Feb | 0.7 | 4.4 |
| Jan | 0.1 | 4.0 |
| AE ∆% Jan-Apr | 6.5 | |
| Dec 2010 | 1.0 | 3.7 |
| Nov | 0.4 | 3.3 |
| Oct | 0.3 | 3.2 |
| Sep | 0.0 | 3.1 |
| Aug | 0.5 | 3.1 |
| Jul | -0.2 | 3.1 |
| Jun | 0.1 | 3.2 |
| May | 0.2 | 3.4 |
| Apr | 0.6 | 3.7 |
| Mar | 0.6 | 3.4 |
| Feb | 0.4 | 3.0 |
| Jan | -0.2 | 3.5 |
Source: http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/cpi/consumer-price-indices/march-2012/index.html
Inflation has been unusually high in the UK since 2006, as shown in Table IV-10. There were no rates of inflation close to 2.0 percent in the period from 1997 to 2004. Inflation has exceeded 2 percent since 2005, reaching 3.6 percent in 2008, 3.3 percent in 2010 and 4.5 percent in 2011.
Table IV-10, UK, Consumer Price Index, Annual ∆%
| 1997 | 1.8 |
| 1998 | 1.6 |
| 1999 | 1.3 |
| 2000 | 0.8 |
| 2001 | 1.2 |
| 2002 | 1.3 |
| 2003 | 1.4 |
| 2004 | 1.3 |
| 2005 | 2.1 |
| 2006 | 2.3 |
| 2007 | 2.3 |
| 2008 | 3.6 |
| 2009 | 2.2 |
| 2010 | 3.3 |
| 2011 | 4.5 |
Source: http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/cpi/consumer-price-indices/march-2012/index.html
Table IV-11 provides the analysis of inflation in Mar by the UK Office for National Statistics. The drivers of monthly inflation of 0.3 percent were 0.14 percentage points of clothing and footwear, 0.12 percentage points of transportation and 0.08 percentage points of furniture and household goods. Contributions of percentage points to the 12-month rate of consumer price inflation of 3.5 percent are provided by the final two columns in Table IV-11. Housing and household services rose 6.2 percent in 12 months, contributing 0.79 percentage points. Transport rose 3.3 percent in 12 months, contributing 0.53 percentage points. Food & nonalcoholic beverages rose 4.6 percent in 12 months, contributing 0.53 percentage points. There is only negative change of 0.6 percent in recreation and culture but with negligible impact on the index of 0.09 percentage points.
Table IV-11, UK, Consumer Price Index Month ∆% and Percentage Point Contribution by Components
| Mar 2012 | Month ∆% | Percentage Point Contribution | 12 Months ∆% | Percentage Point Contribution |
| CPI All Items | 0.3 | 3.5 | ||
| Food & Non-Alcoholic Beverages | -0.5 | -0.06 | 4.6 | 0.53 |
| Alcohol & Tobacco | 0.2 | 0.01 | 8.0 | 0.33 |
| Clothing & Footwear | 2.2 | 0.14 | 3.2 | 0.22 |
| Housing & Household Services | -0.2 | -0.02 | 6.2 | 0.79 |
| Furniture & Household Goods | 1.3 | 0.08 | 4.1 | 0.26 |
| Health | 0.0 | 0.0 | 2.8 | 0.07 |
| Transport | 0.8 | 0.12 | 3.3 | 0.53 |
| Communication | 0.6 | 0.02 | 4.8 | 0.13 |
| Recreation & Culture | -0.1 | -0.01 | -0.6 | -0.09 |
| Education | 0.0 | 0.00 | 5.1 | 0.09 |
| Restaurants & Hotels | 0.2 | 0.03 | 2.9 | 0.35 |
| Miscellaneous Goods & Services | 0.0 | 0.03 | 2.7 | 0.26 |
Source: http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/cpi/consumer-price-indices/march-2012/index.html
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2010, 2011, 2012


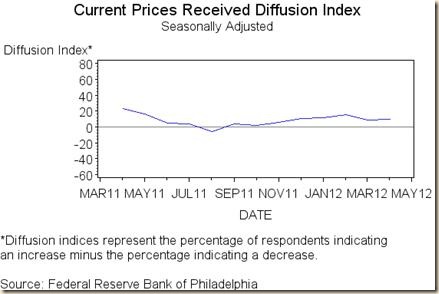
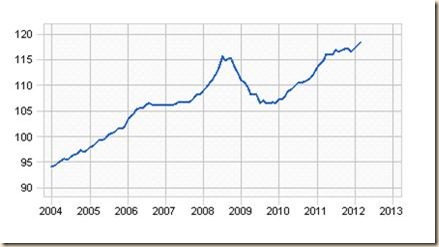

No comments:
Post a Comment