Turbulence of Valuations of Financial Assets, Mediocre Cyclical United States Economic Growth with GDP Two Trillion Dollars below Trend, Stagnating Real Private Fixed Investment, United States House Prices and Rate of Homeownership, World Cyclical Slow Growth and Global Recession Risk
Carlos M. Pelaez
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015
I Mediocre Cyclical United States Economic Growth with GDP Two Trillion Dollars below Trend
IA Mediocre Cyclical United States Economic Growth
IA1 Stagnating Real Private Fixed Investment
II United States House Prices and Rate of Homeownership
III World Financial Turbulence
IIIA Financial Risks
IIIE Appendix Euro Zone Survival Risk
IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation
IV Global Inflation
V World Economic Slowdown
VA United States
VB Japan
VC China
VD Euro Area
VE Germany
VF France
VG Italy
VH United Kingdom
VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets
VII Economic Indicators
VIII Interest Rates
IX Conclusion
References
Appendixes
Appendix I The Great Inflation
IIIB Appendix on Safe Haven Currencies
IIIC Appendix on Fiscal Compact
IIID Appendix on European Central Bank Large Scale Lender of Last Resort
IIIG Appendix on Deficit Financing of Growth and the Debt Crisis
IIIGA Monetary Policy with Deficit Financing of Economic Growth
IIIGB Adjustment during the Debt Crisis of the 1980s
I Mediocre Cyclical United States Economic Growth with GDP Two Trillion Dollars below Trend. Section IA Mediocre Cyclical United States Economic Growth provides the analysis of long-term and cyclical growth of GDP in the US with GDP two trillion dollars or 12.4 percent below trend. Section IA1 Contracting Real Private Fixed Investment analyzes weakness in investment. There is socio-economic stress in the combination of adverse events and cyclical performance:
- Mediocre economic growth below potential and long-term trend, resulting in idle productive resources with GDP two trillion dollars below trend (Section I and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/international-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/dollar-revaluation-squeezing-corporate.html). US GDP grew at the average rate of 3.3 percent per year from 1929 to 2014 with similar performance in whole cycles of contractions and expansions but only at 1.1 percent per year on average from 2007 to 2014. GDP in IIQ2015 is 13.1 percent lower than what it would have been had it grown at trend of 3.0 percent
- Private fixed investment stagnating at increase of 4.7 percent in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIQ2015 Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/international-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/dollar-revaluation-squeezing-corporate.html)
- Twenty five million or 15.1 percent of the effective labor force unemployed or underemployed in involuntary part-time jobs with stagnating or declining real wages (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/turbulence-of-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html)
- Stagnating real disposable income per person or income per person after inflation and taxes (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/international-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/dollar-devaluation-and-carry-trade.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/volatility-of-valuations-of-financial.html)
- Depressed hiring that does not afford an opportunity for reducing unemployment/underemployment and moving to better-paid jobs (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/oscillating-valuations-of-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/volatility-of-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/volatility-of-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/fluctuating-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/dollar-revaluation-recovery-without.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/global-exchange-rate-struggle-recovery.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/02/g20-monetary-policy-recovery-without.html)
- Productivity growth fell from 2.2 percent per year on average from 1947 to 2014 and average 2.3 percent per year from 1947 to 2007 to 1.4 percent per year on average from 2007 to 2014, deteriorating future growth and prosperity (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/quite-high-equity-valuations-and.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/global-competitive-devaluation-rules.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/02/job-creation-and-monetary-policy-twenty.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/financial-risks-twenty-six-million.html)
- Output of manufacturing in Jun 2015 at 17.8 percent below long-term trend since 1919 and at 12.3 percent below trend since 1986 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/fluctuating-financial-asset-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/fluctuating-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/global-portfolio-reallocations-squeeze.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/impatience-with-monetary-policy-of.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/02/world-financial-turbulence-squeeze-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/01/exchange-rate-conflicts-squeeze-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/10/imf-view-squeeze-of-economic-activity.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html)
- Unsustainable government deficit/debt and balance of payments deficit (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/fluctuating-financial-asset-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/impatience-with-monetary-policy-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/irrational-exuberance-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/monetary-policy-world-inflation-waves.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/06/valuation-risks-world-inflation-waves.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/02/theory-and-reality-of-cyclical-slow.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/interest-rate-risks-world-inflation.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/tapering-quantitative-easing-mediocre.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/09/duration-dumping-and-peaking-valuations.html)
- Worldwide waves of inflation (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/fluctuating-financial-asset-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/interest-rate-policy-and-dollar.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/global-portfolio-reallocations-squeeze.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/dollar-revaluation-and-financial-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/irrational-exuberance-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/01/competitive-currency-conflicts-world.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/10/financial-oscillations-world-inflation.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/monetary-policy-world-inflation-waves.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/world-inflation-waves-united-states.html)
- Deteriorating terms of trade and net revenue margins of production across countries in squeeze of economic activity by carry trades induced by zero interest rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/fluctuating-financial-asset-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/global-portfolio-reallocations-squeeze.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/impatience-with-monetary-policy-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/02/world-financial-turbulence-squeeze-of.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/01/exchange-rate-conflicts-squeeze-of.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/patience-on-interest-rate-increases.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/squeeze-of-economic-activity-by-carry.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/10/imf-view-squeeze-of-economic-activity.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html)
- Financial repression of interest rates and credit affecting the most people without means and access to sophisticated financial investments with likely adverse effects on income distribution and wealth disparity (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/international-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/05/dollar-devaluation-and-carry-trade.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/04/volatility-of-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/global-competitive-devaluation-rules.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/02/job-creation-and-monetary-policy-twenty.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/11/growth-uncertainties-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/10/world-financial-turbulence-twenty-seven.html)
- 45 million in poverty and 41 million without health insurance with family income adjusted for inflation regressing to 1995 levels (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/financial-volatility-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/09/duration-dumping-and-peaking-valuations.html)
- Net worth of households and nonprofits organizations increasing by 13.2 percent after adjusting for inflation in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IQ2015 when it would have grown over 24.8 percent at trend of 3.1 percent per year in real terms from 1945 to 2014 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/fluctuating-financial-asset-valuations.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/03/dollar-revaluation-and-financial-risk.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/12/valuations-of-risk-financial-assets.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/09/financial-volatility-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/06/financial-indecision-mediocre-cyclical.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/03/global-financial-risks-recovery-without.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/12/collapse-of-united-states-dynamism-of.html). Financial assets increased $16.4 trillion while nonfinancial assets increased $1.5 trillion with likely concentration of wealth in those with access to sophisticated financial investments. Real estate assets adjusted for inflation fell 8.1 percent from 2007 to IQ2015
Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. US economic growth has been at only 2.1 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 24 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2015. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the first estimate of GDP for IIQ2015 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2015/pdf/gdp2q15_adv.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,745.9 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,355.6 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,745.9/$14,355.6 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/international-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/dollar-revaluation-squeezing-corporate.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1988 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/international-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/dollar-revaluation-squeezing-corporate.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIQ2015 would have accumulated to 24.8 percent. GDP in IIQ2015 would be $18,712.5 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2,442.1 billion than actual $16,270.4 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 25.0 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 15.1 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/turbulence-of-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html). US GDP in IIQ2015 is 13.1 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,270.4 billion in IIQ2015 or 8.5 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.1 percent. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth at average 3.3 percent per year from Jun 1919 to Jun 2015. Growth at 3.3 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 99.2392 in Dec 2007 to 126.6006 in Jun 2015. The actual index NSA in Jun 2015 is 104.0319, which is 17.8 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.4 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2014. Using trend growth of 2.4 percent per year, the index would increase to 118.5586 in Jun 2015. The output of manufacturing at 104.0319 in Jun 2015 is 12.3 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
The economy of the US can be summarized in growth of economic activity or GDP as fluctuating from mediocre growth of 2.5 percent on an annual basis in 2010 to 1.6 percent in 2011, 2.2 percent in 2012, 1.5 percent in 2013 and 2.4 percent in 2014. The following calculations show that actual growth is around 2.1 percent per year. The rate of growth of 1.0 percent in the entire cycle from 2007 to 2014 is well below 3 percent per year in trend from 1870 to 2010, which the economy of the US always attained for entire cycles in expansions after events such as wars and recessions (Lucas 2011May). Revisions and enhancements of United States GDP and personal income accounts by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) provide important information on long-term growth and cyclical behavior. Table Summary provides relevant data.
Table Summary, Long-term and Cyclical Growth of GDP, Real Disposable Income and Real Disposable Income per Capita
| GDP | ||
| Long-Term | ||
| 1929-2014 | 3.2 | |
| 1947-2014 | 3.2 | |
| Whole Cycles | ||
| 1980-1989 | 3.5 | |
| 2006-2014 | 1.2 | |
| 2007-2014 | 1.0 | |
| Cyclical Contractions ∆% | ||
| IQ1980 to IIIQ1980, IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 | -4.7 | |
| IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 | -4.2 | |
| Cyclical Expansions Average Annual Equivalent ∆% | ||
| IQ1983 to IVQ1985 IQ1983-IQ1986 IQ1983-IIIQ1986 IQ1983-IVQ1986 IQ1983-IQ1987 IQ1983-IIQ1987 IQ1983-IIIQ1987 IQ1983 to IVQ1987 IQ1983 to IQ1988 IQ1983 to IIQ1988 IQ1983 to IIIQ1988 | 5.9 5.7 5.4 5.2 5.0 5.0 4.9 5.0 4.9 4.9 4.8 | |
| First Four Quarters IQ1983 to IVQ1983 | 7.8 | |
| IIIQ2009 to IQ2015 | 2.2 | |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 | 2.7 | |
| Real Disposable Income | Real Disposable Income per Capita | |
| Long-Term | ||
| 1929-2014 | 3.2 | 2.0 |
| 1947-1999 | 3.7 | 2.3 |
| Whole Cycles | ||
| 1980-1989 | 3.5 | 2.6 |
| 2006-2014 | 1.5 | 0.7 |
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The revisions and enhancements of United States GDP and personal income accounts by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) also provide critical information in assessing the current rhythm of US economic growth. The economy appears to be moving at a pace around 2.1 percent per year. Table Summary GDP provides the data.
1. Average Annual Growth in the Past Twelve Quarters. GDP growth in the four quarters of 2012, the four quarters of 2013, the four quarters of 2014 and two quarters of Q2015 accumulated to 7.1 percent. This growth is equivalent to 2.0 percent per year, obtained by dividing GDP in IIQ2015 of $16,270.4 billion by GDP in IVQ2011 of $15,190.3 billion and compounding by 4/14: {[($16,270.4/$15,190.3)4/14 -1]100 = 2.0 percent.
2. Average Annual Growth in the Past Four Quarters. GDP growth in the four quarters of IIQ2014 to IIQ2015 accumulated to 2.3 percent that is equivalent to 2.3 percent in a year. This is obtained by dividing GDP in IIQ2015 of $16,270.4 billion by GDP in IIQ2014 of $15,901.5 billion and compounding by 4/4: {[($16,270.4/$15,901.5)4/4 -1]100 = 2.9 %}. The US economy grew 2.3 percent in IIQ2015 relative to the same quarter a year earlier in IIQ2014. Growth was at annual equivalent 4.6 percent in IIQ2014 and 4.3 percent IIIQ2014 and only at 2.1 percent in IVQ2014. GDP grew at annual equivalent 0.6 percent in IQ2015 and at 2.3 percent in IIQ2015. Another important revelation of the revisions and enhancements is that GDP was flat in IVQ2012, which is in the borderline of contraction, and negative in IQ2014. US GDP fell 0.2 percent in IQ2014. The rate of growth of GDP in the revision of IIIQ2013 is 3.0 percent in seasonally adjusted annual rate (SAAR).
Table Summary GDP, US, Real GDP and Percentage Change Relative to IVQ2007 and Prior Quarter, Billions Chained 2005 Dollars and ∆%
| Real GDP, Billions Chained 2009 Dollars | ∆% Relative to IVQ2007 | ∆% Relative to Prior Quarter | ∆% | |
| IVQ2007 | 14,991.8 | NA | 0.4 | 1.9 |
| IVQ2011 | 15,190.3 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 1.7 |
| IQ2012 | 15,291.0 | 2.0 | 0.7 | 2.8 |
| IIQ2012 | 15,362.4 | 2.5 | 0.5 | 2.5 |
| IIIQ2012 | 15,380.8 | 2.6 | 0.1 | 2.4 |
| IVQ2012 | 15,384.3 | 2.6 | 0.0 | 1.3 |
| IQ2013 | 15,457.2 | 3.1 | 0.5 | 1.1 |
| IIQ2013 | 15,500.2 | 3.4 | 0.3 | 0.9 |
| IIIQ2013 | 15,614.4 | 4.2 | 0.7 | 1.5 |
| IVQ2013 | 15,761.5 | 5.1 | 0.9 | 2.5 |
| IQ2014 | 15,724.9 | 4.9 | -0.2 | 1.7 |
| IIQ2014 | 15,901.5 | 6.1 | 1.1 | 2.6 |
| IIIQ2014 | 16,068.8 | 7.2 | 1.1 | 2.9 |
| IVQ2014 | 16,151.4 | 7.7 | 0.5 | 2.5 |
| IQ2015 | 16,177.3 | 7.9 | 0.2 | 2.9 |
| IIQ2015 | 16,270.4 | 8.5 | 0.6 | 2.3 |
| Cumulative ∆% IQ2012 to IQ2015 | 7.1 | 7.2 | ||
| Annual Equivalent ∆% | 2.0 | 2.0 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Historical parallels are instructive but have all the limitations of empirical research in economics. The more instructive comparisons are not with the Great Depression of the 1930s but rather with the recessions in the 1950s, 1970s and 1980s. The growth rates and job creation in the expansion of the economy away from recession are subpar in the current expansion compared to others in the past. Four recessions are initially considered, following the reference dates of the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER) (http://www.nber.org/cycles/cyclesmain.html ): IIQ1953-IIQ1954, IIIQ1957-IIQ1958, IIIQ1973-IQ1975 and IQ1980-IIIQ1980. The data for the earlier contractions illustrate that the growth rate and job creation in the current expansion are inferior. The sharp contractions of the 1950s and 1970s are considered in Table I-1, showing the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) quarter-to-quarter, seasonally adjusted (SA), yearly-equivalent growth rates of GDP. The recovery from the recession of 1953 consisted of four consecutive quarters of high percentage growth rates from IIIQ1954 to IIIQ1955: 4.6, 8.0, 11.9 and 6.7. The recession of 1957 was followed by four consecutive high percentage growth rates from IIIQ1958 to IIQ1959: 9.6, 9.7, 7.7 and 10.1. The recession of 1973-1975 was followed by high percentage growth rates from IIQ1975 to IQ1976: 3.1, 6.8, 5.5 and 9.3. The disaster of the Great Inflation and Unemployment of the 1970s, which made stagflation notorious, is even better in growth rates during the expansion phase in comparison with the current slow-growth recession.
Table I-1, US, Seasonally Adjusted Quarterly Percentage Growth Rates in Annual Equivalent of GDP in Cyclical Recessions and Following Four Quarter Expansions ∆%
| IQ | IIQ | IIIQ | IV | |
| R IIQ1953-IIQ1954 | ||||
| 1953 | -2.2 | -5.9 | ||
| 1954 | -1.8 | |||
| E IIIQ1954-IIQ1955 | ||||
| 1954 | 4.6 | 8.0 | ||
| 1955 | 11.9 | 6.7 | ||
| R IIIQ1957-IIQ1958 | ||||
| 1957 | -4.0 | |||
| 1958 | -10.0 | |||
| E IIIQ1958-IIQ1959 | ||||
| 1958 | 9.6 | 9.7 | ||
| 1959 | 7.7 | 10.1 | ||
| R IVQ1969-IV1970 | ||||
| 1969 | -1.7 | |||
| 1970 | -0.7 | |||
| E IIQ1970-IQ1971 | ||||
| 1970 | 0.7 | 3.6 | -4.0 | |
| 1971 | 11.1 | |||
| R IVQ1973-IQ1975 | ||||
| 1973 | 3.8 | |||
| 1974 | -3.3 | 1.1 | -3.8 | -1.6 |
| 1975 | -4.7 | |||
| E IIQ1975-IQ1976 | ||||
| 1975 | 3.1 | 6.8 | 5.5 | |
| 1976 | 9.3 | |||
| R IQ1980-IIIQ1980 | ||||
| 1980 | 1.3 | -7.9 | -0.6 | |
| R IQ1981-IVQ1982 | ||||
| 1981 | 8.5 | -2.9 | 4.7 | -4.6 |
| 1982 | -6.5 | 2.2 | -1.4 | 0.4 |
| E IQ1983-IVQ1983 | ||||
| 1983 | 5.3 | 9.4 | 8.1 | 8.5 |
| R IVQ2007-IIQ2009 | ||||
| 2008 | -2.7 | 2.0 | -1.9 | -8.2 |
| 2009 | -5.4 | -0.5 | ||
| E IIIQ2009-IIQ2010 | ||||
| 2009 | 1.3 | 3.9 | ||
| 2010 | 1.7 | 3.9 |
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The NBER dates another recession in 1980 that lasted about half a year. If the two recessions from IQ1980s to IIIQ1980 and IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 are combined, the impact of lost GDP of 4.7 percent is more comparable to the latest revised 4.2 percent drop of the recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. The recession in 1981-1982 is quite similar on its own to the 2007-2009 recession. In contrast, during the Great Depression in the four years of 1930 to 1933, GDP in constant dollars fell 26.4 percent cumulatively and fell 45.3 percent in current dollars (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 150-2, Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2009b), 205-7 and revisions in http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). Table I-2 provides the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) quarterly growth rates of GDP in SA yearly equivalents for the recessions of 1981 to 1982 and 2007 to 2009, using the latest major revision published on July 30, 2015 and the first estimate for IIQ2015 GDP (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2015/pdf/gdp2q15_adv.pdf), which are available in the dataset of the US Bureau of Economic Analysis (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). There were four quarters of contraction in 1981-1982 ranging in rate from -1.4 percent to -6.5 percent and five quarters of contraction in 2007-2009 ranging in rate from -0.5 percent to -8.2 percent. The striking difference is that in the first twenty-four quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1988, shown in Table I-2 in relief, GDP grew at the high quarterly percentage growth rates of 5.3, 9.4, 8.1, 8.5, 8.2, 7.2, 4.0, 3.2, 4.0, 3.7, 6.4, 3.0, 3.8, 1.9, 4.1, 2.1, 2.8, 4.6, 3.7, 6.8, 2.3, 5.4, 2.3 and 5.4. In contrast, the percentage growth rates in the first twenty-four quarters of expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2015 shown in relief in Table I-2 were mediocre: 1.3, 3.9, 1.7, 3.9, 2.7, 2.5, -1.5, 2.9, 0.8, 4.6, 2.7, 1.9, 0.5, 0.1, 1.9, 1.1, 3.0, 3.8, minus 0.9, 4.6, 4.3, 2.1, 0.6 and 2.3. Economic growth and employment creation continued at slow rhythm during 2012 and in 2013-2015 while much stronger growth would be required in movement to full employment. The cycle is now long by historical standards and growth rates are typically weaker in the final periods of cyclical expansions.
Table I-2, US, Quarterly Growth Rates of GDP, % Annual Equivalent SA
| Q | 1981 | 1982 | 1983 | 1984 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 |
| I | 8.5 | -6.5 | 5.3 | 8.2 | -2.7 | -5.4 | 1.7 |
| II | -2.9 | 2.2 | 9.4 | 7.2 | 2.0 | -0.5 | 3.9 |
| III | 4.7 | -1.4 | 8.1 | 4.0 | -1.9 | 1.3 | 2.7 |
| IV | -4.6 | 0.4 | 8.5 | 3.2 | -8.2 | 3.9 | 2.5 |
| 1985 | 2011 | ||||||
| I | 4.0 | -1.5 | |||||
| II | 3.7 | 2.9 | |||||
| III | 6.4 | 0.8 | |||||
| IV | 3.0 | 4.6 | |||||
| 1986 | 2012 | ||||||
| I | 3.8 | 2.7 | |||||
| II | 1.9 | 1.9 | |||||
| III | 4.1 | 0.5 | |||||
| IV | 2.1 | 0.1 | |||||
| 1987 | 2013 | ||||||
| I | 2.8 | 1.9 | |||||
| II | 4.6 | 1.1 | |||||
| III | 3.7 | 3.0 | |||||
| IV | 6.8 | 3.8 | |||||
| 1988 | 2014 | ||||||
| I | 2.3 | -0.9 | |||||
| II | 5.4 | 4.6 | |||||
| III | 2.3 | 4.3 | |||||
| IV | 5.4 | 2.1 | |||||
| 2015 | |||||||
| I | 4.1 | 0.6 | |||||
| 3.2 | 2.3 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-1 of the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) provides strong growth of real GDP in the US between 1929 and 1999 at the yearly average rate of 3.5 percent. There is an evident acceleration of the rate of GDP growth in the 1990s as shown by a much sharper slope of the growth curve. Cobet and Wilson (2002) define labor productivity as the value of manufacturing output produced per unit of labor input used (see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 137-44). Between 1950 and 2000, labor productivity in the US grew less rapidly than in Germany and Japan. The major part of the increase in productivity in Germany and Japan occurred between 1950 and 1973 while the rate of productivity growth in the US was relatively subdued in several periods. While Germany and Japan reached their highest growth rates of productivity before 1973, the US accelerated its rate of productivity growth in the second half of the 1990s. Between 1950 and 2000, the rate of productivity growth in the US of 2.9 percent per year was much lower than 6.3 percent in Japan and 4.7 percent in Germany. Between 1995 and 2000, the rate of productivity growth of the US of 4.6 percent exceeded that of Japan of 3.9 percent and the rate of Germany of 2.6 percent.
Chart I-1, US, Real GDP 1929-1999
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-1A provides real GDP annually from 1929 to 2014. Growth after the global recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 has not been sufficiently high to compensate for the contraction as it had occurred in past economic cycles. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 25.0 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 15.1 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/turbulence-of-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html). US GDP in IIQ2015 is 13.1 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,270.4 billion in IIQ2015 or 8.5 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.1 percent. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth at average 3.3 percent per year from Jun 1919 to Jun 2015. Growth at 3.3 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 99.2392 in Dec 2007 to 126.6006 in Jun 2015. The actual index NSA in Jun 2015 is 104.0319, which is 17.8 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.4 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2014. Using trend growth of 2.4 percent per year, the index would increase to 118.5586 in Jun 2015. The output of manufacturing at 104.0319 in Jun 2015 is 12.3 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Chart I-1A, US, Real GDP 1929-2014
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-2 provides the growth of real quarterly GDP in the US between 1947 and 2014. The drop of output in the recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 has been followed by anemic recovery compared with return to trend at 3.0 percent from 1870 to 2010 after events such as wars and recessions (Lucas 2011May) and a standstill that can lead to growth recession, or low rates of economic growth. The expansion is relatively long compared to earlier expansion and there could be even another contraction or conventional recession in the future. The average rate of growth from 1947 to 2014 is 3.2 percent. The average growth rate from IV2007 to IIQ2015 is only 1.1 percent with 2.8 percent annual equivalent from the end of the recession in IVQ2001 to the end of the expansion in IVQ2007.
Chart I-2, US, Real GDP, Quarterly, 1947-2015
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-3 provides real GDP percentage change on the quarter a year earlier for 1983-1984. The objective is simply to compare expansion in two recoveries from sharp contractions as shown in Table I-5. Growth rates in the early phase of the recovery in 1983 and 1984 were very high, which is the opportunity to reduce unemployment that has characterized cyclical expansion in the postwar US economy.
Chart I-3, Real GDP Percentage Change on Quarter a Year Earlier 1983-1988
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
In contrast, growth rates in the comparable first twenty-three quarters of expansion from 2009 to 2015 in Chart I-4 have been mediocre. As a result, growth has not provided the exit from unemployment and underemployment as in other cyclical expansions in the postwar period. Growth rates did not rise in V shape as in earlier expansions and then declined close to the standstill of growth recessions.
Chart I-4, US, Real GDP Percentage Change on Quarter a Year Earlier 2009-2015
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table I-3 provides percentage change of real GDP in the United States in the 1930s, 1980s and 2000s. The recession in 1981-1982 is quite similar on its own to the 2007-2009 recession. In contrast, during the Great Depression in the four years of 1930 to 1933, GDP in constant dollars fell 26.4 percent cumulatively and fell 45.3 percent in current dollars (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 150-2, Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2009b), 205-7 and revisions in http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). Data are available for the 1930s only on a yearly basis. US GDP fell 4.7 percent in the two recessions (1) from IQ1980 to IIIQ1980 and (2) from III1981 to IVQ1981 to IVQ1982 and 4.2 percent cumulatively in the recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. It is instructive to compare the first years of the expansions in the 1980s and the current expansion. GDP grew at 4.6 percent in 1983, 7.3 percent in 1984, 4.2 percent in 1985, 3.5 percent in 1986, 3.5 percent in 1987 and 4.2 percent in 1988. In contrast, GDP grew 2.5 percent in 2010, 1.6 percent in 2011, 2.2 percent in 2012, 1.5 percent in 2013 and 2.4 percent in 2014. Actual annual equivalent GDP growth in the four quarters of 2012, and ten quarters from IQ2013 to IIQ2015 is 2.0 percent and 2.3 percent in the four quarters ending in IIQ2015. GDP grew at 4.2 percent in 1985, 3.5 percent in 1986, 3.5 percent in 1987 and 4.2 percent in 1988. The forecasts of the central tendency of participants of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) are in the range of 1.8 to 2.0 percent in 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20150617.pdf) with less reliable forecast of 2.4 to 2.7 percent in 2016 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcprojtabl20150617.pdf). Growth of GDP in the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2015 has been at average 2.1 percent in annual equivalent.
Table I-3, US, Percentage Change of GDP in the 1930s, 1980s and 2000s, ∆%
| Year | GDP ∆% | Year | GDP ∆% | Year | GDP ∆% |
| 1930 | -8.5 | 1980 | -0.2 | 2000 | 4.1 |
| 1931 | -6.4 | 1981 | 2.6 | 2001 | 1.0 |
| 1932 | -12.9 | 1982 | -1.9 | 2002 | 1.8 |
| 1933 | -1.3 | 1983 | 4.6 | 2003 | 2.8 |
| 1934 | 10.8 | 1984 | 7.3 | 2004 | 3.8 |
| 1935 | 8.9 | 1985 | 4.2 | 2005 | 3.3 |
| 1936 | 12.9 | 1986 | 3.5 | 2006 | 2.7 |
| 1937 | 5.1 | 1987 | 3.5 | 2007 | 1.8 |
| 1938 | -3.3 | 1988 | 4.2 | 2008 | -0.3 |
| 1930 | 8.0 | 1989 | 3.7 | 2009 | -2.8 |
| 1940 | 8.8 | 1990 | 1.9 | 2010 | 2.5 |
| 1941 | 17.7 | 1991 | -0.1 | 2011 | 1.6 |
| 1942 | 18.9 | 1992 | 3.6 | 2012 | 2.2 |
| 1943 | 17.0 | 1993 | 2.7 | 2013 | 1.5 |
| 1944 | 8.0 | 1994 | 4.0 | 2014 | 2.4 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-5 provides percentage change of GDP in the US during the 1930s. There is vast literature analyzing the Great Depression (Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009), 198-217). Cole and Ohanian (1999) find that US real per capita output was lower by 11 percent in 1939 than in 1929 while the typical expansion of real per capita output in the US during a decade is 31 percent. Private hours worked in the US were 25 percent lower in 1939 relative to 1929.
Chart I-5, US, Percentage Change of GDP in the 1930s
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
In contrast, Chart I-6 shows rapid recovery from the recessions in the 1980s. High growth rates in the initial quarters of expansion eliminated the unemployment and underemployment created during the contraction. The economy then returned to grow at the trend of expansion, interrupted by another contraction in 1991.
Chart I-6, US, Percentage Change of GDP in the 1980s
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis9
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-7 provides the rates of growth during the 2000s. Growth rates in the initial eighteen quarters of expansion have been relatively lower than during recessions after World War II. As a result, unemployment and underemployment continue at the rate of 15.1 percent of the effective US labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/turbulence-of-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html).
Chart I-7, US, Percentage Change of GDP in the 2000s
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Characteristics of the four cyclical contractions are provided in Table I-4 with the first column showing the number of quarters of contraction; the second column the cumulative percentage contraction; and the final column the average quarterly rate of contraction. There were two contractions from IQ1980 to IIIQ1980 and from IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 separated by three quarters of expansion. The drop of output combining the declines in these two contractions is 4.7 percent, which is almost equal to the decline of 4.2 percent in the contraction from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. In contrast, during the Great Depression in the four years of 1930 to 1933, GDP in constant dollars fell 26.4 percent cumulatively and fell 45.3 percent in current dollars (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 150-2, Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2009b), 205-7 and revisions in http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). The comparison of the global recession after 2007 with the Great Depression is entirely misleading.
Table I-4, US, Number of Quarters, GDP Cumulative Percentage Contraction and Average Percentage Annual Equivalent Rate in Cyclical Contractions
| Number of Quarters | Cumulative Percentage Contraction | Average Percentage Rate | |
| IIQ1953 to IIQ1954 | 3 | -2.4 | -0.8 |
| IIIQ1957 to IIQ1958 | 3 | -3.0 | -1.0 |
| IVQ1973 to IQ1975 | 5 | -3.1 | -0.6 |
| IQ1980 to IIIQ1980 | 2 | -2.2 | -1.1 |
| IIIQ1981 to IVQ1982 | 4 | -2.5 | -0.64 |
| IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 | 6 | -4.2 | -0.72 |
Sources: Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table I-5 shows the mediocre average annual equivalent growth rate of 2.1 percent of the US economy in the twenty-four quarters of the current cyclical expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2015. In sharp contrast, the average growth rate of GDP was:
- 5.7 percent in the first thirteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1986
- 5.4 percent in the first fifteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986
- 5.2 percent in the first sixteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1986
- 5.0 percent in the first seventeen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1987
- 5.0 percent in the first eighteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIQ1987
- 4.9 percent in the first nineteen quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987
- 5.0 percent in the first twenty quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1987
- 4.9 percent in the first twenty-first quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1988
- 4.9 percent in the first twenty-two quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIQ1988
- 4.8 percent in the first twenty-three quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988
- 4.8 percent in the first twenty-four quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1988
3. The line “average first four quarters in four expansions” provides the average growth rate of 7.7 percent with 7.8 percent from IIIQ1954 to IIQ1955, 9.2 percent from IIIQ1958 to IIQ1959, 6.1 percent from IIIQ1975 to IIQ1976 and 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983. The United States missed this opportunity of high growth in the initial phase of recovery. BEA data show the US economy in standstill with annual growth of 2.5 percent in 2010 decelerating to 1.6 percent annual growth in 2011, 2.2 percent in 2012, 1.5 percent in 2013 and 2.4 percent in 2014 (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) The expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1986 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.7 percent, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1988, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988. 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1988 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983. GDP grew 2.7 percent in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010. GDP growth in the four quarters of 2012, the four quarters of 2013, the four quarters of 2014 and two quarters of Q2015 accumulated to 7.1 percent. This growth is equivalent to 2.0 percent per year, obtained by dividing GDP in IIQ2015 of $16,270.4 billion by GDP in IVQ2011 of $15,190.3 billion and compounding by 4/14: {[($16,270.4/$15,190.3)4/14 -1]100 = 2.0 percent.
Table I-5, US, Number of Quarters, Cumulative Growth and Average Annual Equivalent Growth Rate in Cyclical Expansions
| Number | Cumulative Growth ∆% | Average Annual Equivalent Growth Rate | |
| IIIQ 1954 to IQ1957 | 11 | 12.8 | 4.5 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ1954 to IIQ1955 | 4 | 7.8 | |
| IIQ1958 to IIQ1959 | 5 | 10.0 | 7.9 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ1958 to IIQ1959 | 4 | 9.2 | |
| IIQ1975 to IVQ1976 | 8 | 8.3 | 4.1 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ1975 to IIQ1976 | 4 | 6.1 | |
| IQ1983-IQ1986 IQ1983-IIIQ1986 IQ1983-IVQ1986 IQ1983-IQ1987 IQ1983-IIQ1987 IQ1983 to IIIQ1987 IQ1983 to IVQ1987 IQ1983 to IQ1988 IQ1983 to IIQ1988 IQ1983 to IIIQ1988 IQ1983 to IVQ1988 | 13 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 | 19.9 21.6 22.3 23.1 24.5 25.6 27.7 28.4 30.1 30.9 32.6 | 5.7 5.4 5.2 5.0 5.0 4.9 5.0 4.9 4.9 4.8 4.8 |
| First Four Quarters IQ1983 to IVQ1983 | 4 | 7.8 | |
| Average First Four Quarters in Four Expansions* | 7.7 | ||
| IIIQ2009 to IIQ2015 | 24 | 13.3 | 2.1 |
| First Four Quarters IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 | 2.7 |
*First Four Quarters: 7.8% IIIQ1954-IIQ1955; 9.2% IIIQ1958-IIQ1959; 6.1% IIIQ1975-IQ1976; 7.8% IQ1983-IVQ1983
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-8 shows US real quarterly GDP growth from 1980 to 1989. The economy contracted during the recession and then expanded vigorously throughout the 1980s, rapidly eliminating the unemployment caused by the contraction.
Chart I-8, US, Real GDP, 1980-1989
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-9 shows the entirely different situation of real quarterly GDP in the US between 2007 and 2015. The economy has underperformed during the first twenty-four quarters of expansion for the first time in the comparable contractions since the 1950s. The US economy is now in a perilous standstill.
Chart I-9, US, Real GDP, 2007-2015
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
As shown in Tables I-4 and I-5 above the loss of real GDP in the US during the contraction was 4.2 percent but the gain in the cyclical expansion has been only 13.3 percent (first to the last row in Table I-5), using all latest revisions. As a result, the level of real GDP in IIQ2015 with the first estimate and revisions is higher by only 8.5 percent than the level of real GDP in IVQ2007. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIQ2015 would have accumulated to 24.8 percent. GDP in IIQ2015 would be $18,712.5 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2,442.1 billion than actual $16,270.4 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 25.0 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 15.1 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/turbulence-of-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html). US GDP in IIQ2015 is 13.1 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,270.4 billion in IIQ2015 or 8.5 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.1 percent. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth at average 3.3 percent per year from Jun 1919 to Jun 2015. Growth at 3.3 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 99.2392 in Dec 2007 to 126.6006 in Jun 2015. The actual index NSA in Jun 2015 is 104.0319, which is 17.8 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.4 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2014. Using trend growth of 2.4 percent per year, the index would increase to 118.5586 in Jun 2015. The output of manufacturing at 104.0319 in Jun 2015 is 12.3 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Table I-6 shows that the contraction actually concentrated in two quarters: decline of 2.1 percent in IVQ2008 relative to the prior quarter and decline of 1.4 percent in IQ2009 relative to IVQ2008. The combined fall of GDP in IVQ2008 and IQ2009 was 3.5 percent {[(1-0.021) x (1-0.014) -1]100 = -3.5%}, or {[(IQ2009 $14,375.0)/(IIIQ2008 $14,891.6) – 1]100 = -3.5%} except for rounding. Those two quarters coincided with the worst effects of the financial crisis (Cochrane and Zingales 2009). GDP fell 0.1 percent in IIQ2009 but grew 0.3 percent in IIIQ2009, which is the beginning of recovery in the cyclical dates of the NBER. Most of the recovery occurred in five successive quarters from IVQ2009 to IVQ2010 of growth of 1.0 percent in IVQ2009, 0.4 percent in IQ2010, 1.0 percent in IIQ2010 and nearly equal growth at 0.7 percent in IIIQ2010 and 0.6 percent in IVQ2010 for cumulative growth in those five quarters of 3.8 percent, obtained by accumulating the quarterly rates {[(1.01 x 1.004 x 1.01 x 1.007 x 1.006) – 1]100 = 3.8%} or {[(IVQ2010 $14,939.0)/(IIIQ2009 $14,402.5) – 1]100 = 3.7%} with minor rounding difference. The economy then stalled during the first half of 2011 with decline of 0.4 percent in IQ2011 and growth of 0.7 percent in IIQ2011 for combined annual equivalent rate of 0.6 percent {(0.996 x 1.007)2}. The economy grew 0.2 percent in IIIQ2011 for annual equivalent growth of 0.7 percent in the first three quarters {[(0.996 x 1.007 x 1.002)4/3 -1]100 = 0.7%}. Growth picked up in IVQ2011 with 1.1 percent relative to IIIQ2011. Growth in a quarter relative to a year earlier in Table I-6 slows from over 2.7 percent during three consecutive quarters from IIQ2010 to IVQ2010 to 1.9 percent in IQ2011, 1.7 percent in IIQ2011, 1.2 percent in IIIQ2011 and 1.7 percent in IVQ2011. As shown below, growth of 1.1 percent in IVQ2011 was partly driven by inventory accumulation. In IQ2012, GDP grew 0.7 percent relative to IVQ2011 and 2.8 percent relative to IQ2011, decelerating to 0.5 percent in IIQ2012 and 2.5 percent relative to IIQ2011 and 0.1 percent in IIIQ2012 and 2.4 percent relative to IIIQ2011. Growth was 0.0 percent in IVQ2012 with 1.3 percent relative to a year earlier but mostly because of deduction of 1.54 percentage points of inventory divestment and 0.42 percentage points of reduction of one-time national defense expenditures. Growth was 0.5 percent in IQ2013 and 1.1 percent relative to IQ2012 in large part because of burning savings to consume caused by financial repression of zero interest rates. There is similar growth of 0.3 percent in IIQ2013 and 0.9 percent relative to a year earlier. In IIIQ2013, GDP grew 0.7 percent relative to the prior quarter and 1.5 percent relative to the same quarter a year earlier with inventory accumulation contributing 1.48 percentage points to growth at 3.0 percent SAAR in IIIQ2013. GDP increased 0.9 percent in IVQ2013 and 2.5 percent relative to a year earlier. GDP fell 0.2 percent in IQ2014 and grew 1.7 percent relative to a year earlier. Inventory divestment deducted 1.29 percentage points from GDP growth in IQ2014. GDP grew 1.1 percent in IIQ2014, 2.6 percent relative to a year earlier and at 4.3 SAAR with inventory change contributing 1.12 percentage points. GDP grew 1.1 percent in IIIQ2014 and 2.9 percent relative to a year earlier. GDP grew 0.5 percent in IVQ2014 and 2.5 percent relative to a year earlier. GDP increased 0.2 percent in IQ2015 and increased 2.9 percent relative to a year earlier partly because of low level during contraction of 0.2 percent in IQ2014. GDP grew 0.6 percent in IIQ2015 and 2.3 percent relative to a year earlier. Rates of a quarter relative to the prior quarter capture better deceleration of the economy than rates on a quarter relative to the same quarter a year earlier. The critical question for which there is not yet definitive solution is whether what lies ahead is continuing growth recession with the economy crawling and unemployment/underemployment at extremely high levels or another contraction or conventional recession. Forecasts of various sources continued to maintain high growth in 2011 without taking into consideration the continuous slowing of the economy in late 2010 and the first half of 2011. The sovereign debt crisis in the euro area and growth in China are common sources of doubts on the rate and direction of economic growth in the US. There is weak internal demand in the US with almost no investment and spikes of consumption driven by burning saving because of financial repression forever in the form of zero interest rates.
Table I-6, US, Real GDP and Percentage Change Relative to IVQ2007 and Prior Quarter, Billions Chained 2009 Dollars and ∆%
| Real GDP, Billions Chained 2009 Dollars | ∆% Relative to IVQ2007 | ∆% Relative to Prior Quarter | ∆% | |
| IVQ2007 | 14,991.8 | NA | 0.4 | 1.9 |
| IQ2008 | 14,889.5 | -0.7 | -0.7 | 1.1 |
| IIQ2008 | 14,963.4 | -0.2 | 0.5 | 0.8 |
| IIIQ2008 | 14,891.6 | -0.7 | -0.5 | -0.3 |
| IVQ2008 | 14,577.0 | -2.8 | -2.1 | -2.8 |
| IQ2009 | 14,375.0 | -4.1 | -1.4 | -3.5 |
| IIQ2009 | 14,355.6 | -4.2 | -0.1 | -4.1 |
| IIIQ2009 | 14,402.5 | -3.9 | 0.3 | -3.3 |
| IV2009 | 14,541.9 | -3.0 | 1.0 | -0.2 |
| IQ2010 | 14,604.8 | -2.6 | 0.4 | 1.6 |
| IIQ2010 | 14,745.9 | -1.6 | 1.0 | 2.7 |
| IIIQ2010 | 14,845.5 | -1.0 | 0.7 | 3.1 |
| IVQ2010 | 14,939.0 | -0.4 | 0.6 | 2.7 |
| IQ2011 | 14,881.3 | -0.7 | -0.4 | 1.9 |
| IIQ2011 | 14,989.6 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 1.7 |
| IIIQ2011 | 15,021.1 | 0.2 | 0.2 | 1.2 |
| IVQ2011 | 15,190.3 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 1.7 |
| IQ2012 | 15,291.0 | 2.0 | 0.7 | 2.8 |
| IIQ2012 | 15,362.4 | 2.5 | 0.5 | 2.5 |
| IIIQ2012 | 15,380.8 | 2.6 | 0.1 | 2.4 |
| IVQ2012 | 15,384.3 | 2.6 | 0.0 | 1.3 |
| IQ2013 | 15,457.2 | 3.1 | 0.5 | 1.1 |
| IIQ2013 | 15,500.2 | 3.4 | 0.3 | 0.9 |
| IIIQ2013 | 15,614.4 | 4.2 | 0.7 | 1.5 |
| IVQ2013 | 15,761.5 | 5.1 | 0.9 | 2.5 |
| IQ2014 | 15,724.9 | 4.9 | -0.2 | 1.7 |
| IIQ2014 | 15,901.5 | 6.1 | 1.1 | 2.6 |
| IIIQ2014 | 16,068.8 | 7.2 | 1.1 | 2.9 |
| IVQ2014 | 16,151.4 | 7.7 | 0.5 | 2.5 |
| IQ2015 | 16,177.3 | 7.9 | 0.2 | 2.9 |
| IIQ2015 | 16,270.4 | 8.5 | 0.6 | 2.3 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-10 provides the percentage change of real GDP from the same quarter a year earlier from 1980 to 1989. There were two contractions almost in succession in 1980 and from 1981 to 1983. The expansion was marked by initial high rates of growth as in other recession in the postwar US period during which employment lost in the contraction was recovered. Growth rates continued to be high after the initial phase of expansion.
Chart I-10, Percentage Change of Real Gross Domestic Product from Quarter a Year Earlier 1980-1989
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The experience of recovery after 2009 is not as complete as during the 1980s. Chart I-11 shows the much lower rates of growth in the early phase of the current expansion and sharp decline from an early peak. The US missed the initial high growth rates in cyclical expansions that eliminate unemployment and underemployment.
Chart I-11, Percentage Change of Real Gross Domestic Product from Quarter a Year Earlier 2007-2015
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-12 provides growth rates from a quarter relative to the prior quarter during the 1980s. There is the same strong initial growth followed by a long period of sustained growth.
Chart I-12, Percentage Change of Real Gross Domestic Product from Prior Quarter 1980-1989
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart I-13 provides growth rates in a quarter relative to the prior quarter from 2007 to 2015. Growth in the current expansion after IIIQ2009 has not been as strong as in other postwar cyclical expansions.
Chart I-13, Percentage Change of Real Gross Domestic Product from Prior Quarter 2007-2015
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The revised estimates and earlier estimates from IQ2008 to IQ2014 in seasonally adjusted annual equivalent rates are shown in Table I-7. The strongest revision is for IVQ2008 for which the contraction of GDP is revised from minus 6.8 percent to minus 8.9 percent and minus 8.2 percent. IQ2009 is also revised from contraction of minus 4.9 percent to minus 6.7 percent but then lowered to contraction of 5.3 percent and 5.4 percent. There is only minor revision in IIIQ2008 of the contraction of minus 4.0 percent to minus 3.7 percent and much lower to minus 1.9 percent. Growth of 5.0 percent in IV2009 is revised to 3.8 percent and then increased to 4.0 percent but lowered to 3.9 percent. Growth in IQ2010 is lowered from 3.9 percent to 2.3 percent and 1.7 percent. Growth in IIQ2010 is upwardly revised to 3.8 percent but then lowered to 2.2 percent. The final revision increased growth in IIQ2010 to 3.9 percent. Revisions lowered growth of 1.9 percent in IQ2011 to minus 1.5 percent. The revisions increased growth of 1.8 percent in IQ2013 to 2.7 percent and increased growth of 2.0 percent in IQ2012 to 2.3 percent. The revision reduced the decline of GDP from 2.9 percent in IQ2014 to 2.1 percent. The latest revision reduced significantly the rate of growth in 2013. The revisions do not alter the conclusion that the current expansion is much weaker than historical sharp contractions since the 1950s and is now changing into slow growth recession with higher risks of contraction and continuing underperformance.
Table I-7, US, Quarterly Growth Rates of GDP, % Annual Equivalent SA, Revised and Earlier Estimates
| Quarters | Rev Jul 30, 2015 | Rev Jul 30, 2014 | Rev Jul 31, 2013 | Rev Jul 27, 2012 | Rev Jul 29, 2011 | Earlier Estimate |
| 2008 | ||||||
| I | -2.7 | -2.7 | -1.8 | -0.7 | ||
| II | 2.0 | 2.0 | 1.3 | 0.6 | ||
| III | -1.9 | -2.0 | -3.7 | -4.0 | ||
| IV | -8.2 | -8.3 | -8.9 | -6.8 | ||
| 2009 | ||||||
| I | -5.4 | -5.4 | -5.3 | -6.7 | -4.9 | |
| II | -0.5 | -0.4 | -0.3 | -0.7 | -0.7 | |
| III | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.4 | 1.7 | 1.6 | |
| IV | 3.9 | 3.9 | 4.0 | 3.8 | 5.0 | |
| 2010 | ||||||
| I | 1.7 | 1.6 | 2.3 | 3.9 | 3.7 | |
| II | 3.9 | 3.9 | 2.2 | 3.8 | 1.7 | |
| III | 2.7 | 2.8 | 2.6 | 2.5 | 2.6 | |
| IV | 2.5 | 2.8 | 2.4 | 2.3 | 3.1 | |
| 2011 | ||||||
| I | -1.5 | -1.3 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 1.9 | |
| II | 2.9 | 3.2 | 2.5 | |||
| III | 0.8 | 1.4 | 1.3 | |||
| IV | 4.6 | 4.9 | 4.1 | |||
| 2012 | ||||||
| I | 2.7 | 2.3 | 3.7 | 2.0 | ||
| II | 1.9 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 1.3 | ||
| III | 0.5 | 2.5 | 2.8 | 3.1 | ||
| IV | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 0.4 | ||
| 2013 | ||||||
| I | 1.9 | 2.7 | 1.1 | 1.8 | ||
| II | 1.1 | 1.8 | 2.5 | |||
| III | 3.0 | 4.5 | 4.1 | |||
| IV | 3.8 | 3.5 | 2.6 | |||
| 2014 | ||||||
| I | -0.9 | -2.1 | -2.9 | |||
| II | 4.6 | |||||
| III | 4.3 | |||||
| IV | 2.1 | |||||
| 2015 | ||||||
| I | 0.6 |
Note: Rev: Revision
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Aggregate demand, personal consumption expenditures (PCE) and gross private domestic investment (GDI) were much stronger during the expansion phase from IQ1983 to IIQ1988 than from IIIQ2009 to IQ2015, as shown in Table I-8. GDI provided the impulse of growth in 1983 and 1984, which has not been the case from 2009 to 2015. The investment decision in the US economy has been frustrated in the current cyclical expansion. Growth of GDP in IIIQ2013 at seasonally adjusted annual rate of 3.0 percent consisted of positive contribution of 1.17 percentage points of personal consumption expenditures (PCE) plus positive contribution of 2.07 percentage points of gross private domestic investment (GDI) of which 1.48 percentage points of inventory investment (∆PI), contribution of net exports (trade or exports less imports) of 0.16 percentage points and deduction of 0.36 percentage points of government consumption expenditures and gross investment (GOV) partly because of one-time contribution of national defense expenditures of 0.03 percentage points. Growth at 3.8 percent in IVQ2013 had strongest contributions of 2.36 percentage points of PCE and 1.26 percentage points of trade. Growth of GDP at minus 0.9 percent in IQ2014 is mostly contribution of 0.85 percentage points by PCE with deduction of 0.38 percentage points by GDI, inventory divestment of 1.29 percentage points and trade deducting 1.39 percentage points. Growth at 4.6 percent in IIQ2014 consists of contributions of 2.60 percentage points by PCE and 1.99 percentage points by GDI with 1.12 percentage points by inventory change. Trade deducted 0.24 percentage points and government added 0.21 percentage points mostly because of contribution of 0.29 percentage points of expenditures by state and local government. Growth at 4.3 percent in IIIQ2014 consists of contribution of 2.34 percentage points by PCE, 1.22 percentage points by GDI, 0.39 percentage points by trade and 0.33 percentage points by government of which 0.19 percentage points by national defense expenditures growing at 4.5 percent in annual equivalent. Growth at 2.1 percent in IVQ2014 consists of contribution of 2.86 percentage points by PCE, 0.36 percentage points by GDI with deduction of 0.03 percentage points by inventory investment. Net trade deducted 0.89 percentage points while government deducted 0.26 percentage mostly because of deduction of 0.47 percentage points by national defense expenditure declining at 10.3 percent in IVQ2014. Growth of GDP at 0.6 percent in IQ2015 consisted mostly of contributions of 1.19 percentage points by personal consumption expenditures and 0.87 percentage points by inventory accumulation while trade deducted 1.92 percentage points and government deducted 0.01 percentage points. Growth at 2.3 percentage points in IIQ2015 consisted mostly of contributions of 1.99 percentage points by personal consumption expenditures, 0.13 percentage points by net trade and 0.14 percent by government consumption and expenditures. The economy of the United States has lost the dynamic growth impulse of earlier cyclical expansions with mediocre growth resulting from consumption forced by one-time effects of financial repression, national defense expenditures and inventory accumulation.
Table I-8, US, Contributions to the Rate of Growth of GDP in Percentage Points
| GDP | PCE | GDI | ∆ PI | Trade | GOV | |
| 2015 | ||||||
| I | 0.6 | 1.19 | 1.39 | 0.87 | -1.92 | -0.01 |
| II | 2.3 | 1.99 | 0.06 | -0.08 | 0.13 | 0.14 |
| 2014 | ||||||
| I | -0.9 | 0.85 | -0.38 | -1.29 | -1.39 | 0.00 |
| II | 4.6 | 2.60 | 1.99 | 1.12 | -0.24 | 0.21 |
| III | 4.3 | 2.34 | 1.22 | -0.01 | 0.39 | 0.33 |
| IV | 2.1 | 2.86 | 0.36 | -0.03 | -0.89 | -0.26 |
| 2013 | ||||||
| I | 1.9 | 1.74 | 1.05 | 0.28 | -0.01 | -0.88 |
| II | 1.1 | 0.96 | 0.78 | 0.38 | -0.24 | -0.38 |
| III | 3.0 | 1.17 | 2.07 | 1.48 | 0.16 | -0.42 |
| IV | 3.8 | 2.36 | 0.71 | -0.08 | 1.26 | -0.51 |
| 2012 | ||||||
| I | 2.7 | 1.63 | 1.47 | -0.53 | -0.02 | -0.40 |
| II | 1.9 | 0.45 | 1.53 | 0.56 | 0.28 | -0.39 |
| III | 0.5 | 0.72 | -0.18 | -0.18 | 0.16 | -0.22 |
| IV | 0.1 | 0.78 | -0.51 | -1.54 | 0.58 | -0.75 |
| 2011 | ||||||
| I | -1.5 | 1.38 | -1.07 | -0.96 | -0.24 | -1.60 |
| II | 2.9 | 0.57 | 2.14 | 1.04 | 0.31 | -0.08 |
| III | 0.8 | 1.20 | 0.15 | -2.10 | 0.01 | -0.52 |
| IV | 4.6 | 0.94 | 4.16 | 2.80 | -0.21 | -0.31 |
| 2010 | ||||||
| I | 1.7 | 1.46 | 1.77 | 1.66 | -0.85 | -0.63 |
| II | 3.9 | 2.23 | 2.86 | 1.09 | -1.77 | 0.61 |
| III | 2.7 | 1.77 | 1.86 | 1.90 | -0.83 | -0.07 |
| IV | 2.5 | 2.79 | -0.51 | -1.63 | 1.12 | -0.87 |
| 2009 | ||||||
| I | -5.4 | -0.86 | -7.02 | -2.26 | 2.30 | 0.15 |
| II | -0.5 | -1.19 | -3.25 | -1.12 | 2.34 | 1.56 |
| III | 1.3 | 1.68 | -0.40 | -0.38 | -0.45 | 0.48 |
| IV | 3.9 | -0.01 | 4.05 | 4.40 | 0.06 | -0.17 |
| 1982 | ||||||
| I | -6.5 | 1.61 | -7.59 | -5.33 | -0.49 | -0.05 |
| II | 2.2 | 0.89 | -0.06 | 2.26 | 0.81 | 0.56 |
| III | -1.4 | 1.88 | -0.62 | 1.11 | -3.22 | 0.53 |
| IV | 0.4 | 4.51 | -5.37 | -5.33 | -0.10 | 1.35 |
| 1983 | ||||||
| I | 5.3 | 2.45 | 2.36 | 0.92 | -0.29 | 0.82 |
| II | 9.4 | 5.06 | 5.96 | 3.43 | -2.46 | 0.89 |
| III | 8.1 | 4.50 | 4.40 | 0.57 | -2.25 | 1.42 |
| IV | 8.5 | 4.06 | 6.94 | 3.01 | -1.14 | -1.36 |
| 1984 | ||||||
| I | 8.2 | 2.26 | 7.23 | 4.94 | -2.31 | 1.01 |
| II | 7.2 | 3.64 | 2.57 | -0.29 | -0.87 | 1.87 |
| III | 4.0 | 1.95 | 1.69 | 0.21 | -0.36 | 0.70 |
| IV | 3.2 | 3.29 | -1.08 | -2.44 | -0.56 | 1.58 |
| 1985 | ||||||
| I | 4.0 | 4.23 | -2.14 | -2.86 | 0.94 | 1.01 |
| II | 3.7 | 2.35 | 1.34 | 0.35 | -1.90 | 1.93 |
| III | 6.4 | 4.82 | -0.43 | -0.15 | -0.01 | 1.98 |
| IV | 3.0 | 0.62 | 2.80 | 1.40 | -0.66 | 0.27 |
| 1986 | ||||||
| I | 3.8 | 2.10 | 0.04 | -0.17 | 0.92 | 0.70 |
| II | 1.9 | 2.77 | -1.30 | -1.30 | -1.33 | 1.70 |
| III | 4.1 | 4.55 | -1.97 | -1.62 | -0.45 | 1.95 |
| IV | 2.1 | 1.62 | 0.24 | -0.29 | 0.71 | -0.48 |
| 1987 | ||||||
| I | 2.8 | 0.05 | 1.98 | 3.28 | 0.23 | 0.57 |
| II | 4.6 | 3.54 | 0.08 | -0.99 | 0.14 | 0.81 |
| III | 3.7 | 2.97 | 0.03 | -1.19 | 0.45 | 0.23 |
| IV | 6.8 | 0.57 | 4.94 | 4.95 | 0.18 | 1.08 |
| 1988 | ||||||
| I | 2.3 | 4.49 | -3.62 | -3.68 | 1.94 | -0.54 |
| II | 5.4 | 1.89 | 1.72 | 0.33 | 1.44 | 0.34 |
| III | 2.3 | 2.17 | 0.38 | 0.05 | -0.31 | 0.08 |
| IV | 5.4 | 2.93 | 1.11 | 0.27 | -0.21 | 1.56 |
Note: PCE: personal consumption expenditures; GDI: gross private domestic investment; ∆ PI: change in private inventories; Trade: net exports of goods and services; GOV: government consumption expenditures and gross investment; – is negative and no sign positive
GDP: percent change at annual rate; percentage points at annual rates
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (pages 1) conducted the annual revision of GDP (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2015/pdf/gdp2q15_adv.pdf):
“The estimates released today reflect the results of the annual revision of the national income and
product accounts (NIPAs) in conjunction with the "advance" estimate of GDP for the second quarter of 2015. In addition to the regular revision of the estimates for the most recent 3 years and for the first quarter of 2015, some series are revised back further (see the Technical Note). More information is available in "Preview of the 2015 Annual Revision of the NIPAs" in the June Survey of Current Business and on BEA's Web site. The August Survey will contain an article that describes the results.“
The Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (pages 1-2 http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2015/pdf/gdp2q15_adv.pdf) explains growth of GDP in IQ2015 as follows:
“Real gross domestic product -- the value of the production of goods and services in the United
States, adjusted for price changes -- increased at an annual rate of 2.3 percent in the second quarter of 2015, according to the "advance" estimate released by the Bureau of Economic Analysis. In the first quarter, real GDP increased 0.6 percent (revised).
The Bureau emphasized that the second-quarter advance estimate released today is based on source data that are incomplete or subject to further revision by the source agency (see the box on page 3 and "Comparisons of Revisions to GDP" on page 10). The "second" estimate for the second quarter, based on more complete data, will be released on August 27, 2015.
The increase in real GDP in the second quarter reflected positive contributions from personal consumption expenditures (PCE), exports, state and local government spending, and residential fixed investment that were partly offset by negative contributions from federal government spending, private inventory investment, and nonresidential fixed investment. Imports, which are a subtraction in the calculation of GDP, increased. “
There are positive contributions to growth in IIQ2015 shown in Table I-9:
- Personal consumption expenditures (PCE) growing at 2.9 percent
- Consumption of durable goods growing at 7.3 percent
- Residential fixed investment growing at 6.6 percent
- Exports growing at 5.3 percent
- Government expenditures growing at 0.8 percent
There were negative contributions in IIQ2015:
- Imports, which are a deduction from growth, growing at 3.5 percent
- Nonresidential investment falling at 0.6 percent
- Inventory accumulation deducting 0.08 percentage points
The BEA explains acceleration in real GDP growth in IIQ2015 by:
- Growth of consumption of durable goods at 7.3 percent in IIQ2015 compared with 2.0 percent in IIQ2015
- Growth of personal consumption expenditures at 2.9 percent in IIQ2015 compared with 1.8 percent in IQ2015
- Growth of exports at 5.3 percent compared with contraction at 6.0 percent in IQ2015
The BEA finds offsetting accelerating factors:
· Growth of imports at 3.5 percent in IIQ2015 compared with 7.1 percent in the prior quarter
· Contraction of government expenditures at 0.8 percent in IIQ2015 compared with contraction at 0.1 percent in the prior quarter
An important aspect of growth in the US is the decline in growth of real disposable personal income, or what is left after taxes and inflation, which decreased at the rate of 0.5 percent in IIIQ2013 compared with a year earlier. Contraction of real disposable income of 2.9 percent in IVQ2013 relative to a year earlier is largely due to comparison with an artificially higher level in anticipations of income in Nov and Dec 2012 to avoid increases in taxes in 2013, an episode known as “fiscal cliff.” Real disposable personal income increased 2.3 percent in IQ2014 relative to a year earlier and 2.4 percent in IIQ2014 relative to a year earlier. Real disposable personal income increased 2.5 percent in IIIQ2014 relative to a year earlier and 3.6 percent in IVQ2014 compared with a year earlier. Real disposable personal income grew 3.5 percent in IQ2015 relative to a year earlier partly because of contraction of energy prices and increased 3.1 percent in IIQ2015. The effects of financial repression, or zero interest, are vividly shown in the decline of the savings rate, or personal saving as percent of disposable income from 9.2 percent in IVQ2012 to 5.1 percent in IIIQ2013 and 4.4 percent in IVQ2013. The savings rate eased to 5.0 percent in IQ2014, decreasing to 4.8 percent in IIQ2014 and moving to 4.7 percent in IIIQ2014. The savings rate fell to 4.7 percent in IVQ2014, increasing to 5.2 percent in IQ2015. The savings rate fell to 4.8 percent in IIQ2015. Anticipation of income in IVQ2012 to avoid higher taxes in 2013 caused increases in income and savings while higher payroll taxes in 2013 restricted income growth and savings in IQ2013. Zero interest rates induce risky investments with high leverage and can contract balance sheets of families, business and financial institutions when interest rates inevitably increase in the future. There is a tradeoff of weaker economy in the future when interest rates increase by meager growth in the present with forced consumption by zero interest rates. Microeconomics consists of the analysis of allocation of scarce resources to alternative and competing ends. Zero interest rates cloud he calculus of risk and returns in consumption and investment, disrupting decisions that maintain the economy in its long-term growth path.
Table I-9, US, Percentage Seasonally Adjusted Annual Equivalent Quarterly Rates of Increase, %
| IIQ 2014 | IIIQ 2014 | IVQ 2014 | IQ 2015 | IIQ 2015 | |
| GDP | 4.6 | 4.3 | 2.1 | 0.6 | 2.3 |
| PCE | 3.8 | 3.5 | 4.3 | 1.8 | 2.9 |
| Durable Goods | 13.9 | 7.5 | 6.1 | 2.0 | 7.3 |
| NRFI | 4.4 | 9.0 | 0.7 | 1.6 | -0.6 |
| RFI | 10.4 | 3.4 | 10.0 | 10.1 | 6.6 |
| Exports | 9.8 | 1.8 | 5.4 | -6.0 | 5.3 |
| Imports | 9.6 | -0.8 | 10.3 | 7.1 | 3.5 |
| GOV | 1.2 | 1.8 | -1.4 | -0.1 | 0.8 |
| Federal GOV | -1.2 | 3.7 | -5.7 | 1.1 | -1.1 |
| National Defense | -0.5 | 4.5 | -10.3 | 1.0 | -1.5 |
| Cont to GDP Growth % Points | -0.02 | 0.19 | -0.47 | 0.04 | -0.06 |
| State/Local GOV | 2.6 | 0.6 | 1.3 | -0.8 | 2.0 |
| ∆ PI (PP) | 1.12 | -0.01 | -0.03 | 0.87 | -0.08 |
| Final Sales of Domestic Product | 3.5 | 4.3 | 2.1 | -0.2 | 2.4 |
| Gross Domestic Purchases | 4.7 | 3.8 | 2.9 | 2.5 | 2.1 |
| Prices Gross | 2.0 | 1.4 | -0.1 | -1.6 | 1.4 |
| Prices of GDP | 2.2 | 1.6 | 0.1 | 0.1 | 2.0 |
| Prices of GDP Excluding Food and Energy | 1.9 | 1.8 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 1.4 |
| Prices of PCE | 2.1 | 1.2 | -0.4 | -1.9 | 2.2 |
| Prices of PCE Excluding Food and Energy | 2.0 | 1.4 | 1.0 | 1.0 | 1.8 |
| Prices of Market Based PCE | 1.9 | 1.1 | -0.9 | -2.5 | 2.1 |
| Prices of Market Based PCE Excluding Food and Energy | 1.7 | 1.3 | 0.7 | 0.7 | 1.7 |
| Real Disposable Personal Income* | 2.4 | 2.5 | 3.6 | 3.5 | 3.1 |
| Personal Saving As % Disposable Income | 4.8 | 4.7 | 4.7 | 5.2 | 4.8 |
Note: PCE: personal consumption expenditures; NRFI: nonresidential fixed investment; RFI: residential fixed investment; GOV: government consumption expenditures and gross investment; ∆ PI: change in
private inventories; GDP - ∆ PI: final sales of domestic product; PP: percentage points; Personal savings rate: savings as percent of disposable income
*Percent change from quarter one year ago
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Percentage shares of GDP are shown in Table I-10. PCE (personal consumption expenditures) is equivalent to 68.4 percent of GDP and is under pressure with stagnant real disposable income per person, high levels of unemployment and underemployment and higher savings rates than before the global recession, temporarily interrupted by financial repression in the form of zero interest rates. Gross private domestic investment is also growing slowly even with about two trillion dollars in cash holdings by companies. In a slowing world economy, it may prove more difficult to grow exports faster than imports to generate higher growth. Bouts of risk aversion revalue the dollar relative to most currencies in the world as investors increase their holdings of dollar-denominated assets.
Table I-10, US, Percentage Shares of GDP, %
| IIQ2015 | |
| GDP | 100.0 |
| PCE | 68.4 |
| Goods | 22.3 |
| Durable | 7.4 |
| Nondurable | 14.8 |
| Services | 46.2 |
| Gross Private Domestic Investment | 16.8 |
| Fixed Investment | 16.1 |
| NRFI | 12.7 |
| Structures | 2.8 |
| Equipment & Software | 5.9 |
| Intellectual Property | 4.1 |
| RFI | 3.3 |
| Change in Private | 0.7 |
| Net Exports of Goods and Services | -2.9 |
| Exports | 12.8 |
| Goods | 8.6 |
| Services | 4.2 |
| Imports | 15.7 |
| Goods | 12.9 |
| Services | 2.8 |
| Government | 17.7 |
| Federal | 6.8 |
| National Defense | 4.1 |
| Nondefense | 2.7 |
| State and Local | 10.9 |
PCE: personal consumption expenditures; NRFI: nonresidential fixed investment; RFI: residential fixed investment
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table I-11 shows percentage point (PP) contributions to the annual levels of GDP growth in the earlier recessions 1958-1959, 1975-1976, 1982-1983 and 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013 and 2014. The data incorporate the new revisions released by the BEA. The most striking contrast is in the rates of growth of annual GDP in the expansion phases of 6.9 percent in 1959, 5.4 percent in 1976, and 4.6 percent in 1983 followed by 7.3 percent in 1984 and 4.2 percent in 1985. In contrast, GDP grew 2.5 percent in 2010 after six consecutive quarters of growth, 1.6 percent in 2011 after ten consecutive quarters of expansion, 2.2 percent in 2012 after 14 quarters of expansion, 1.5 percent in 2013 after 18 consecutive quarters of expansion and 2.4 percent in 2014 after 22 consecutive quarters of expansion. Annual levels also show much stronger growth of PCEs in the expansions after the earlier contractions than in the expansion after the global recession of 2007. Gross domestic investment was much stronger in the earlier expansions than in 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013 and 2014.
Table I-11, US, Percentage Point Contributions to the Annual Growth Rate of GDP
| GDP | PCE | GDI | ∆ PI | Trade | GOV | |
| 1958 | -0.7 | 0.52 | -1.16 | -0.17 | -0.87 | 0.77 |
| 1959 | 6.9 | 3.49 | 2.82 | 0.83 | 0.00 | 0.59 |
| 1975 | -0.2 | 1.36 | -2.90 | -1.23 | 0.86 | 0.49 |
| 1976 | 5.4 | 3.41 | 2.91 | 1.37 | -1.05 | 0.12 |
| 1982 | -1.9 | 0.86 | -2.55 | -1.30 | -0.59 | 0.38 |
| 1983 | 4.6 | 3.54 | 1.60 | 0.28 | -1.32 | 0.81 |
| 1984 | 7.3 | 3.32 | 4.73 | 1.90 | -1.54 | 0.76 |
| 1985 | 4.2 | 3.25 | -0.01 | -1.03 | -0.39 | 1.38 |
| 1986 | 3.5 | 2.63 | 0.03 | -0.31 | -0.29 | 1.14 |
| 1987 | 3.5 | 2.14 | 0.53 | 0.41 | 0.17 | 0.63 |
| 2009 | -2.8 | -1.08 | -3.52 | -0.76 | 1.19 | 0.64 |
| 2010 | 2.5 | 1.32 | 1.66 | 1.45 | -0.46 | 0.02 |
| 2011 | 1.6 | 1.55 | 0.73 | -0.14 | -0.02 | -0.65 |
| 2012 | 2.2 | 1.01 | 1.52 | 0.14 | 0.08 | -0.38 |
| 2013 | 1.5 | 1.16 | 0.70 | 0.06 | 0.20 | -0.58 |
| 2014 | 2.4 | 1.84 | 0.87 | 0.05 | -0.18 | -0.11 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table I-12 provides more detail of the contributions to growth of GDP from 2009 to 2014 using annual-level data. PCEs contributed 1.32 PPs to GDP growth in 2010 of which 0.77 percentage points (PP) in goods and 0.55 PP in services. Gross private domestic investment (GPDI) deducted 3.52 PPs of GDP growth in 2009 of which -2.77 PPs by fixed investment and -0.76 PPs of inventory change (∆PI) and added 1.66 PPs of GPDI in 2010 of which 0.21 PPs of fixed investment and 1.45 PPs of inventory accumulation (∆PI). Trade, or exports of goods and services net of imports, contributed 1.19 PPs in 2009 of which exports deducted 1.07 PPs and imports added 2.26 PPs. In 2010, trade deducted 0.46 PPs with exports contributing 1.33 PPs and imports deducting 1.79 PPs likely benefitting from dollar revaluation. In 2009, government added 0.64 PP of which 0.44 PPs by the federal government and 0.20 PPs by state and local government; in 2010, government added 0.02 PPs of which 0.37 PPs by the federal government with state and local government deducting 0.35 PPs. Table I-12 provides the estimates for 2011, 2012, 2013 and 2014. PCE contributed 1.55 PPs in 2011 after 1.32 PPs in 2010. The contribution of PCE fell to 1.01 points in 2012 and increased to 1.16 PPs in 2013 and 1.84 PPs in 2014. The breakdown into goods and services is similar but with contributions in 2012 of 0.63 PPs of goods and 0.38 PPs of services. In 2013, goods contributed 0.71 PPs and services 0.45 PPs. Goods contributed 0.75 PPs in 2014 and services contributed 1.09 PPS. Gross private domestic investment contributed 1.66 PPs in 2010 with 1.45 PPs of change of private inventories but the contribution of gross private domestic investment was only 0.73 PPs in 2011. The contribution of GDI in 2012 increased to 1.52 PPs with fixed investment increasing its contribution to 1.38 PPs and residential investment contributing 0.33 PPs for the first time since 2009. GDI contributed 1.52 PPs in 2012 with 1.05 PPs from fixed investment and 0.33 PPs from inventory change. GDI contribute 0.70 PPs in 2013 and 0.87 PPs in 2014. Net exports of goods and services deducted marginally in 2011 with 0.02 PPs and added 0.08 PPs in 2012. Net trade contributed 0.20 PPs in 2013 and deducted 0.18 PPs in 2014. The contribution of exports fell from 1.33 PPs in 2010 and 0.87 PPs in 2011 to only 0.46 PPs in 2012, 0.38 PPs in 2013 and 0.46 PPs in 2014. Government deducted 0.65 PPs in 2011, 0.38 PPs in 2012 and 0.58 PPs in 2013. Government deducted 0.11 PPs in 2014. Demand weakened in 2013 with higher contribution of personal consumption expenditures of 1.16 PPs and of gross domestic investment of 0.70 PPs. PCE contributed 1.84 PPs in 2014 and GDI 0.87 PPs. Net trade contributed only 0.20 PPs in 2013 and deducted 0.18 PPs in 2014. The expansion since IIIQ2009 has been characterized by weak contributions of aggregate demand, which is the sum of personal consumption expenditures plus gross private domestic investment. The US did not recover strongly from the global recessions as typical in past cyclical expansions. Recoveries tend to be more sluggish as expansions mature. At the margin in IVQ2011, the acceleration of expansion was driven by inventory accumulation instead of aggregate demand of consumption and investment. Growth of PCE was partly the result of burning savings because of financial repression, which may not be sustainable in the future while creating multiple distortions of resource allocation and growth restraint.
Table I-12, US, Contributions to Growth of Gross Domestic Product in Percentage Points
| 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | |
| GDP Growth ∆% | -2.8 | 2.5 | 1.6 | 2.2 | 1.5 | 2.4 |
| Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) | -1.08 | 1.32 | 1.55 | 1.01 | 1.16 | 1.84 |
| Goods | -0.68 | 0.77 | 0.71 | 0.63 | 0.71 | 0.75 |
| Durable | -0.41 | 0.43 | 0.43 | 0.53 | 0.42 | 0.43 |
| Nondurable | -0.27 | 0.34 | 0.28 | 0.10 | 0.29 | 0.32 |
| Services | -0.40 | 0.55 | 0.84 | 0.38 | 0.45 | 1.09 |
| Gross Private Domestic Investment (GPDI) | -3.52 | 1.66 | 0.73 | 1.52 | 0.70 | 0.87 |
| Fixed Investment | -2.77 | 0.21 | 0.86 | 1.38 | 0.64 | 0.82 |
| Nonresidential | -2.04 | 0.28 | 0.85 | 1.05 | 0.38 | 0.77 |
| Structures | -0.70 | -0.49 | 0.06 | 0.32 | 0.04 | 0.23 |
| Equipment, software | -1.29 | 0.70 | 0.66 | 0.58 | 0.19 | 0.34 |
| Intellectual Property | -0.05 | 0.07 | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.20 |
| Residential | -0.73 | -0.07 | 0.01 | 0.33 | 0.27 | 0.05 |
| Change Private Inventories | -0.76 | 1.45 | -0.14 | 0.14 | 0.06 | 0.05 |
| Net Exports of Goods and Services | 1.19 | -0.46 | -0.02 | 0.08 | 0.20 | -0.18 |
| Exports | -1.07 | 1.33 | 0.87 | 0.46 | 0.38 | 0.46 |
| Goods | -1.03 | 1.08 | 0.57 | 0.34 | 0.26 | 0.41 |
| Services | -0.04 | 0.25 | 0.29 | 0.12 | 0.11 | 0.05 |
| Imports | 2.26 | -1.79 | -0.89 | -0.38 | -0.18 | -0.63 |
| Goods | 2.15 | -1.69 | -0.78 | -0.30 | -0.14 | -0.59 |
| Services | 0.10 | -0.10 | -0.11 | -0.09 | -0.04 | -0.05 |
| Government Consumption Expenditures and Gross Investment | 0.64 | 0.02 | -0.65 | -0.38 | -0.58 | -0.11 |
| Federal | 0.44 | 0.37 | -0.24 | -0.15 | -0.46 | -0.18 |
| National Defense | 0.27 | 0.18 | -0.13 | -0.18 | -0.34 | -0.18 |
| Nondefense | 0.17 | 0.19 | -0.11 | 0.03 | -0.12 | 0.00 |
| State and Local | 0.20 | -0.35 | -0.41 | -0.22 | -0.12 | 0.07 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Manufacturing jobs not seasonally adjusted increased 160,000 from Jun 2014 to
Jun 2015 or at the average monthly rate of 13,333. There are effects of the weaker economy and international trade together with the yearly adjustment of labor statistics. The report of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System states (http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/g17/Current/default.htm):
“Industrial production increased 0.3 percent in June but fell at an annual rate of 1.4 percent for the second quarter of 2015. In June, manufacturing output was unchanged: The output of motor vehicles and parts fell 3.7 percent, but production elsewhere in manufacturing rose 0.3 percent. The indexes for mining and utilities advanced 1.0 percent and 1.5 percent, respectively. At 105.7 percent of its 2007 average, total industrial production in June was 1.5 percent above its year-earlier level. Capacity utilization for the industrial sector increased 0.2 percentage point in June to 78.4 percent, a rate that is 1.7 percentage points below its long-run (1972–2014) average.” In the six months ending in Jun 2015, United States national industrial production accumulated change of minus 0.6 percent at the annual equivalent rate of minus 1.2 percent, which is lower than growth of 1.5 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2015. Excluding growth of 0.3 percent in Dec 2014, growth in the remaining five months from Jan 2014 to Jun 2015 accumulated to minus 0.9 percent or minus 2.1 percent annual equivalent. Industrial production declined in three of the past six months and changed 0.0 percent in one months. Industrial production contracted at annual equivalent 1.6 percent in the most recent quarter from Apr 2015 to Jun 2015 and contracted at 0.8 percent in the prior quarter Jan 2015 to Mar 2015. Business equipment accumulated increase of 0.9 percent in the six months from Jan 2015 to Jun 2015 at the annual equivalent rate of 1.8 percent, which is higher than growth of 3.0 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2015. The Fed analyzes capacity utilization of total industry in its report (http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/g17/Current/default.htm): “Capacity utilization for the industrial sector increased 0.2 percentage point in June to 78.4 percent, a rate that is 1.7 percentage points below its long-run (1972–2014) average.” United States industry apparently decelerated to a lower growth rate followed by possible acceleration and weakening growth in past months.
Manufacturing fell 21.9 from the peak in Jun 2007 to the trough in Apr 2009 and increased by 25.1 percent from the trough in Apr 2009 to Dec 2014. Manufacturing grew 29.3 percent from the trough in Apr 2009 to Jun 2015. Manufacturing output in Jun 2015 is 1.0 percent above the peak in Jun 2007. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IQ2015 would have accumulated to 23.9 percent. GDP in IQ2015 would be $18,574.8 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2,287.1 billion than actual $16,287.7 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 25.0 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 15.1 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/turbulence-of-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html). US GDP in IQ2015 is 12.3 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,287.7 billion in IQ2015 or 8.6 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.2 percent. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth at average 3.3 percent per year from Jun 1919 to Jun 2015. Growth at 3.3 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 99.2392 in Dec 2007 to 126.6006 in Jun 2015. The actual index NSA in Jun 2015 is 104.0319, which is 17.8 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.4 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2014. Using trend growth of 2.4 percent per year, the index would increase to 118.5586 in Jun 2015. The output of manufacturing at 104.0319 in Jun 2015 is 12.3 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
Table I-13 provides national income by industry without capital consumption adjustment (WCCA). “Private industries” or economic activities have share of 87.1 percent in IQ2015. Most of US national income is in the form of services. In Jun 2015, there were 142.817 million nonfarm jobs NSA in the US, according to estimates of the establishment survey of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) (http://www.bls.gov/news.release/empsit.nr0.htm Table B-1). Total private jobs of 120.959 million NSA in Jun 2015 accounted for 84.7 percent of total nonfarm jobs of 142.817 million, of which 12.415 million, or 10.3 percent of total private jobs and 8.7 percent of total nonfarm jobs, were in manufacturing. Private service-providing jobs were 101.128 million NSA in Jun 2015, or 70.8 percent of total nonfarm jobs and 83.6 percent of total private-sector jobs. Manufacturing has share of 11.3 percent in US national income in IQ2015 and durable goods 6.5 percent, as shown in Table I-13. Most income in the US originates in services. Subsidies and similar measures designed to increase manufacturing jobs will not increase economic growth and employment and may actually reduce growth by diverting resources away from currently employment-creating activities because of the drain of taxation.
Table I-13, US, National Income without Capital Consumption Adjustment by Industry, Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rates, Billions of Dollars, % of Total
| SAAR | % Total | SAAR IQ2015 | % Total | |
| National Income WCCA | 15,314.2 | 100.0 | 15,577.7 | 100.0 |
| Domestic Industries | 15,049.5 | 98.3 | 15,350.2 | 98.5 |
| Private Industries | 13,277.9 | 86.7 | 13,566.0 | 87.1 |
| Agriculture | 173.5 | 1.1 | 161.7 | 1.0 |
| Mining | 264.7 | 1.7 | 255.7 | 1.6 |
| Utilities | 169.6 | 1.1 | 190.8 | 1.2 |
| Construction | 690.1 | 4.5 | 696.9 | 4.5 |
| Manufacturing | 1678.3 | 11.0 | 1759.2 | 11.3 |
| Durable Goods | 966.1 | 6.3 | 1005.7 | 6.5 |
| Nondurable Goods | 712.2 | 4.7 | 753.4 | 4.8 |
| Wholesale Trade | 932.9 | 6.1 | 947.3 | 6.1 |
| Retail Trade | 1065.0 | 7.0 | 1074.0 | 6.9 |
| Transportation & WH | 453.5 | 3.0 | 492.0 | 3.2 |
| Information | 542.0 | 3.5 | 577.3 | 3.7 |
| Finance, Insurance, RE | 2659.4 | 17.4 | 2723.1 | 17.5 |
| Professional & Business Services | 2067.9 | 13.5 | 2083.8 | 13.4 |
| Education, Health Care | 1515.2 | 9.9 | 1521.6 | 9.8 |
| Arts, Entertainment | 623.6 | 4.1 | 641.3 | 4.1 |
| Other Services | 442.4 | 2.9 | 441.3 | 2.8 |
| Government | 1771.6 | 11.6 | 1784.2 | 11.5 |
| Rest of the World | 264.7 | 1.7 | 227.5 | 1.5 |
Notes: SSAR: Seasonally-Adjusted Annual Rate; WCCA: Without Capital Consumption Adjustment by Industry; WH: Warehousing; RE, includes rental and leasing: Real Estate; Art, Entertainment includes recreation, accommodation and food services; BS: business services
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
IA1. Contracting Real Private Fixed Investment. The United States economy has grown at the average yearly rate of 3 percent per year and 2 percent per year in per capita terms from 1870 to 2010, as measured by Lucas (2011May). An important characteristic of the economic cycle in the US has been rapid growth in the initial phase of expansion after recessions. US economic growth has been at only 2.1 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 24 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2015. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the first estimate of GDP for IIQ2015 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2015/pdf/gdp2q15_adv.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,745.9 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,355.6 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,745.9/$14,355.6 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/international-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/dollar-revaluation-squeezing-corporate.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1988 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/international-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/dollar-revaluation-squeezing-corporate.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIQ2015 would have accumulated to 24.8 percent. GDP in IIQ2015 would be $18,712.5 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2,442.1 billion than actual $16,270.4 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 25.0 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 15.1 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/07/turbulence-of-financial-asset.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/higher-volatility-of-asset-prices-at.html). US GDP in IIQ2015 is 13.1 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,270.4 billion in IIQ2015 or 8.5 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.1 percent. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth at average 3.3 percent per year from Jun 1919 to Jun 2015. Growth at 3.3 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 99.2392 in Dec 2007 to 126.6006 in Jun 2015. The actual index NSA in Jun 2015 is 104.0319, which is 17.8 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.4 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2014. Using trend growth of 2.4 percent per year, the index would increase to 118.5586 in Jun 2015. The output of manufacturing at 104.0319 in Jun 2015 is 12.3 percent below trend under this alternative calculation. Inferior performance of the US economy and labor markets is the critical current issue of analysis and policy design. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. Table IA1-1 provides quarterly seasonally adjusted annual rates (SAAR) of growth of private fixed investment for the recessions of the 1980s and the current economic cycle. In the cyclical expansion beginning in IQ1983 (http://www.nber.org/cycles.html), real private fixed investment in the United States grew at the average annual rate of 14.7 percent in the first eight quarters from IQ1983 to IVQ1984. Growth rates fell to an average of 2.2 percent in the following eight quarters from IQ1985 to IVQ1986 and to an average of 1.9 percent in the 12 quarters of 1985, 1986 and 1987. The average rate of growth in the four quarters of 1988 was 3.7 percent. There were only four quarters of contraction of private fixed investment from IQ1983 to IVQ1987. There is quite different behavior of private fixed investment in the twenty-four quarters of cyclical expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2015. The average annual growth rate in the first eight quarters of expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2011 was 3.2 percent, which is significantly lower than 14.7 percent in the first eight quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1984. There is only strong growth of private fixed investment in the four quarters of expansion from IIQ2011 to IQ2012 at the average annual rate of 12.5 percent. Growth has fallen from the SAAR of 17.3 percent in IIIQ2011 to 0.1 percent in IIIQ2012, recovering to 6.9 percent in IVQ2012 and falling to 4.9 percent in IQ2013. The SAAR of fixed investment rose to 3.8 percent in IIIQ2013 and to 5.1 percent in IVQ2013. The SAAR of fixed investment increased to 6.0 percent in IQ2014. Fixed investment grew at the SAAR of 5.6 percent in IIQ2014 and at 7.9 percent in IIIQ2014. Fixed investment grew at 2.5 percent in IVQ2014, 3.3 percent in IQ2015 and 0.8 percent in IIQ2015. Sudeep Reddy and Scott Thurm, writing on “Investment falls off a cliff,” on Nov 18, 2012, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887324595904578123593211825394.html?mod=WSJPRO_hpp_LEFTTopStories) analyze the decline of private investment in the US and inform that a review by the Wall Street Journal of filing and conference calls finds that 40 of the largest publicly traded corporations in the US have announced intentions to reduce capital expenditures in 2012.
Table IA1-1, US, Quarterly Growth Rates of Real Private Fixed Investment, % Annual Equivalent SA
| Q | 1981 | 1982 | 1983 | 1984 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 |
| I | 3.8 | -12.2 | 9.4 | 13.1 | -7.1 | -27.4 | 0.8 |
| II | 3.2 | -12.1 | 16.0 | 16.6 | -5.5 | -14.2 | 13.6 |
| III | 0.1 | -9.3 | 24.4 | 8.2 | -12.1 | -0.5 | -0.4 |
| IV | -1.5 | 0.2 | 24.3 | 7.3 | -23.9 | -2.8 | 8.5 |
| 1985 | 2011 | ||||||
| I | 3.7 | -0.9 | |||||
| II | 5.2 | 8.2 | |||||
| III | -1.6 | 17.3 | |||||
| IV | 7.8 | 9.9 | |||||
| 1986 | 2012 | ||||||
| I | 1.1 | 14.7 | |||||
| II | 0.1 | 6.9 | |||||
| III | -1.8 | 0.1 | |||||
| IV | 3.1 | 6.9 | |||||
| 1987 | 2013 | ||||||
| I | -6.7 | 4.9 | |||||
| II | 6.3 | 2.6 | |||||
| III | 7.1 | 3.8 | |||||
| IV | -0.2 | 5.1 | |||||
| 1988 | 2014 | ||||||
| I | 0.2 | 6.0 | |||||
| II | 8.1 | 5.6 | |||||
| III | 1.9 | 7.9 | |||||
| IV | 4.8 | 2.5 | |||||
| 1989 | 2015 | ||||||
| IQ | 3.6 | 3.3 | |||||
| IIQ | 0.5 | 0.8 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-1 of the US Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) provides seasonally adjusted annual rates of growth of real private fixed investment from 1981 to 1988. Growth rates recovered sharply during the first eight quarters, which was essential in returning the economy to trend growth and eliminating unemployment and most underemployment accumulated during the contractions.
Chart IA1-1, US, Real Private Fixed Investment, Seasonally-Adjusted Annual Rates Percent Change from Prior Quarter, 1981-1988
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-2, US, Real Private Fixed Investment, Seasonally-Adjusted Annual Rates Percent Change from Prior Quarter, 2007-2015
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table IA1-2 provides real private fixed investment at seasonally adjusted annual rates from IVQ2007 to IVQ2014 or for the complete economic cycle. The first column provides the quarter, the second column percentage change relative to IVQ2007, the third column the quarter percentage change in the quarter relative to the prior quarter and the final column percentage change in a quarter relative to the same quarter a year earlier. In IQ1980, real gross private domestic investment in the US was $951.6 billion of chained 2009 dollars, growing to $1,248.4 billion in IVQ1988 or 31.2 percent. Real gross private domestic investment in the US increased 8.7 percent from $2605.2 billion in IVQ2007 to $2,832.5 billion in IIQ2015. As shown in Table IAI-2, real private fixed investment increased 4.7 percent from $2,586.3 billion of chained 2009 dollars in IVQ2007 to $2,707.1 billion in IIQ2015. Private fixed investment fell relative to IVQ2007 in all quarters preceding IIQ2014. Growth of real private investment in Table IA1-2 is mediocre for all but four quarters from IIQ2011 to IQ2012. The investment decision of United States corporations has been fractured in the current economic cycle in preference of cash.
Table IA1-2, US, Real Private Fixed Investment and Percentage Change Relative to IVQ2007 and Prior Quarter, Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars and ∆%
| Real PFI, Billions Chained 2009 Dollars | ∆% Relative to IVQ2007 | ∆% Relative to Prior Quarter | ∆% | |
| IVQ2007 | 2586.3 | NA | -0.9 | -1.4 |
| IQ2008 | 2539.1 | -1.8 | -1.8 | -3.0 |
| IIQ2008 | 2503.4 | -3.2 | -1.4 | -4.6 |
| IIIQ2008 | 2424.1 | -6.3 | -3.2 | -7.1 |
| IV2008 | 2263.8 | -12.5 | -6.6 | -12.5 |
| IQ2009 | 2089.3 | -19.2 | -7.7 | -17.7 |
| IIQ2009 | 2011.0 | -22.2 | -3.7 | -19.7 |
| IIIQ2009 | 2008.4 | -22.3 | -0.1 | -17.1 |
| IVQ2009 | 1994.1 | -22.9 | -0.7 | -11.9 |
| IQ2010 | 1997.9 | -22.8 | 0.2 | -4.4 |
| IIQ2010 | 2062.8 | -20.2 | 3.2 | 2.6 |
| IIIQ2010 | 2060.8 | -20.3 | -0.1 | 2.6 |
| IVQ2010 | 2103.1 | -18.7 | 2.1 | 5.5 |
| IQ2011 | 2098.4 | -18.9 | -0.2 | 5.0 |
| IIQ2011 | 2140.2 | -17.2 | 2.0 | 3.8 |
| IIIQ2011 | 2227.5 | -13.9 | 4.1 | 8.1 |
| IVQ2011 | 2280.6 | -11.8 | 2.4 | 8.4 |
| IQ2012 | 2360.4 | -8.7 | 3.5 | 12.5 |
| IIQ2012 | 2399.8 | -7.2 | 1.7 | 12.1 |
| IIIQ2012 | 2400.4 | -7.2 | 0.0 | 7.8 |
| IVQ2012 | 2441.0 | -5.6 | 1.7 | 7.0 |
| IQ2013 | 2470.6 | -4.5 | 1.2 | 4.7 |
| IIQ2013 | 2486.3 | -3.9 | 0.6 | 3.6 |
| IIIQ2013 | 2509.5 | -3.0 | 0.9 | 4.5 |
| IVQ2013 | 2541.0 | -1.8 | 1.3 | 4.1 |
| IQ2014 | 2578.3 | -0.3 | 1.5 | 4.4 |
| IIQ2014 | 2613.4 | 1.0 | 1.4 | 5.1 |
| IIIQ2014 | 2663.5 | 3.0 | 1.9 | 6.1 |
| IVQ2014 | 2679.7 | 3.6 | 0.6 | 5.5 |
| IQ2015 | 2701.4 | 4.5 | 0.8 | 4.8 |
| IIQ2015 | 2707.1 | 4.7 | 0.2 | 3.6 |
PFI: Private Fixed Investment
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-3 provides real private fixed investment in billions of chained 2009 dollars from IQ2007 to IQ2015. Real private fixed investment has not recovered, stabilizing at a level in IQ2015 that is barely higher relative to that in IVQ2007.
Chart IA1-3, US, Real Private Fixed Investment, Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars, IQ2007 to IQ2015
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-4 provides real gross private domestic investment in chained dollars of 2009 from 1980 to 1988. Real gross private domestic investment climbed 31.2 percent to $1,248.4 billion of 2009 dollars in IVQ1988 above the level of $951.6 billion in IQ1980.
Chart IA1-4, US, Real Gross Private Domestic Investment, Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars at Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rate, 1980-1988
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-5 provides real gross private domestic investment in the United States in billions of chained dollars of 2009 from 2006 to 2014. Real gross private domestic investment reached a level of $2,832.5 billion in IIQ2015, which was only 8.7 percent higher than the level of $2605.2 billion in IVQ2007 (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm).
Chart IA1-5, US, Real Gross Private Domestic Investment, Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars at Seasonally Adjusted Annual Rate, 2007-2015
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
The share of gross private domestic investment in GDP has fallen from 20.2 percent in IIQ2000 and 19.5 percent in IIQ2006 to 16.8 percent in IIQ2015. There are declines in percentage shares in GDP of all components with sharp reduction of residential investment from 4.7 percent in IIQ2000 and 6.2 percent in IIQ2006 to 3.3 percent in IIQ2015. The share of fixed investment in GDP fell from 19.3 percent in IIQ2000 and 19.0 percent in IIQ2006 to 16.1 percent in IIQ2015.
Table IA1-3, Percentage Shares of Gross Private Domestic Investment and Components in Gross Domestic Product, % of GDP, IQ2013
| IIQ2015 | IIQ2006 | IIQ2000 | |
| Gross Private Domestic Investment | 16.8 | 19.5 | 20.2 |
| Fixed Investment | 16.1 | 19.0 | 19.3 |
| Nonresidential | 12.7 | 12.8 | 14.5 |
| Structures | 2.8 | 3.0 | 3.0 |
| Equipment and Software | 5.9 | 6.2 | 7.5 |
| Intellectual | 4.1 | 3.6 | 4.0 |
| Residential | 3.3 | 6.2 | 4.7 |
| Change in Private Inventories | 0.7 | 0.6 | 0.9 |
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Broader perspective is provided in Chart IA1-6 with the percentage share of gross private domestic investment in GDP in annual data from 1929 to 2014. There was sharp drop during the current economic cycle with almost no recovery in contrast with sharp recovery after the recessions of the 1980s.
Chart IA1-6, US, Percentage Share of Gross Private Domestic Investment in Gross Domestic Product, Annual, 1929-2014
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-7 provides percentage shares of private fixed investment in GDP with annual data from 1929 to 2014. The sharp contraction after the recessions of the 1980s was followed by sustained recovery while the sharp drop in the current economic cycle has not been recovered.
Chart IA1-7, US, Percentage Share of Private Fixed Investment in Gross Domestic Product, Annual, 1929-2014
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-8 provides percentage shares in GDP of nonresidential investment from 1929 to 2014. There is again recovery from sharp contraction in the 1980s but inadequate recovery in the current economic cycle.
Chart IA1-8, US, Percentage Share of Nonresidential Investment in Gross Domestic Product, Annual, 1929-2014
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-9 provides percentage shares of business equipment and software in GDP with annual data from 1929 to 2014. There is again inadequate recovery in the current economic cycle.
Chart IA1-9, US, Percentage Share of Business Equipment and Software in Gross Domestic Product, Annual, 1929-2014
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-10 provides percentage shares of residential investment in GDP with annual data from 1929 to 2014. The salient characteristic of Chart IA1-10 is the vertical increase of the share of residential investment in GDP up to 2006 and subsequent collapse.
Chart IA1-10, US, Percentage Share of Residential Investment in Gross Domestic Product, Annual, 1929-2014
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Finer detail is provided by the quarterly share of residential investment in GDP from 1979 to 2015 in Chart IA1-11. There was protracted growth of that share, accelerating sharply into 2006 followed with nearly vertical drop. The explanation of the sharp contraction of United States housing can probably be found in the origins of the financial crisis and global recession. Let V(T) represent the value of the firm’s equity at time T and B stand for the promised debt of the firm to bondholders and assume that corporate management, elected by equity owners, is acting on the interests of equity owners. Robert C. Merton (1974, 453) states:
“On the maturity date T, the firm must either pay the promised payment of B to the debtholders or else the current equity will be valueless. Clearly, if at time T, V(T) > B, the firm should pay the bondholders because the value of equity will be V(T) – B > 0 whereas if they do not, the value of equity would be zero. If V(T) ≤ B, then the firm will not make the payment and default the firm to the bondholders because otherwise the equity holders would have to pay in additional money and the (formal) value of equity prior to such payments would be (V(T)- B) < 0.”
Pelaez and Pelaez (The Global Recession Risk (2007), 208-9) apply this analysis to the US housing market in 2005-2006 concluding:
“The house market [in 2006] is probably operating with low historical levels of individual equity. There is an application of structural models [Duffie and Singleton 2003] to the individual decisions on whether or not to continue paying a mortgage. The costs of sale would include realtor and legal fees. There could be a point where the expected net sale value of the real estate may be just lower than the value of the mortgage. At that point, there would be an incentive to default. The default vulnerability of securitization is unknown.”
There are multiple important determinants of the interest rate: “aggregate wealth, the distribution of wealth among investors, expected rate of return on physical investment, taxes, government policy and inflation” (Ingersoll 1987, 405). Aggregate wealth is a major driver of interest rates (Ingersoll 1987, 406). Unconventional monetary policy, with zero fed funds rates and flattening of long-term yields by quantitative easing, causes uncontrollable effects on risk taking that can have profound undesirable effects on financial stability. Excessively aggressive and exotic monetary policy is the main culprit and not the inadequacy of financial management and risk controls.
The net worth of the economy depends on interest rates. In theory, “income is generally defined as the amount a consumer unit could consume (or believe that it could) while maintaining its wealth intact” (Friedman 1957, 10). Income, Y, is a flow that is obtained by applying a rate of return, r, to a stock of wealth, W, or Y = rW (Ibid). According to a subsequent restatement: “The basic idea is simply that individuals live for many years and that therefore the appropriate constraint for consumption decisions is the long-run expected yield from wealth r*W. This yield was named permanent income: Y* = r*W” (Darby 1974, 229), where * denotes permanent. The simplified relation of income and wealth can be restated as:
W = Y/r (1)
Equation (1) shows that as r goes to zero, r →0, W grows without bound, W→∞.
Lowering the interest rate near the zero bound in 2003-2004 caused the illusion of permanent increases in wealth or net worth in the balance sheets of borrowers and also of lending institutions, securitized banking and every financial institution and investor in the world. The discipline of calculating risks and returns was seriously impaired. The objective of monetary policy was to encourage borrowing, consumption and investment but the exaggerated stimulus resulted in a financial crisis of major proportions as the securitization that had worked for a long period was shocked with policy-induced excessive risk, imprudent credit, high leverage and low liquidity by the incentive to finance everything overnight at close to zero interest rates, from adjustable rate mortgages (ARMS) to asset-backed commercial paper of structured investment vehicles (SIV).
The consequences of inflating liquidity and net worth of borrowers were a global hunt for yields to protect own investments and money under management from the zero interest rates and unattractive long-term yields of Treasuries and other securities. Monetary policy distorted the calculations of risks and returns by households, business and government by providing central bank cheap money. Short-term zero interest rates encourage financing of everything with short-dated funds, explaining the SIVs created off-balance sheet to issue short-term commercial paper to purchase default-prone mortgages that were financed in overnight or short-dated sale and repurchase agreements (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession, 50-1, Regulation of Banks and Finance, 59-60, Globalization and the State Vol. I, 89-92, Globalization and the State Vol. II, 198-9, Government Intervention in Globalization, 62-3, International Financial Architecture, 144-9). ARMS were created to lower monthly mortgage payments by benefitting from lower short-dated reference rates. Financial institutions economized in liquidity that was penalized with near zero interest rates. There was no perception of risk because the monetary authority guaranteed a minimum or floor price of all assets by maintaining low interest rates forever or equivalent to writing an illusory put option on wealth. Subprime mortgages were part of the put on wealth by an illusory put on house prices. The housing subsidy of $221 billion per year created the impression of ever increasing house prices. The suspension of auctions of 30-year Treasuries was designed to increase demand for mortgage-backed securities, lowering their yield, which was equivalent to lowering the costs of housing finance and refinancing. Fannie and Freddie purchased or guaranteed $1.6 trillion of nonprime mortgages and worked with leverage of 75:1 under Congress-provided charters and lax oversight. The combination of these policies resulted in high risks because of the put option on wealth by near zero interest rates, excessive leverage because of cheap rates, low liquidity because of the penalty in the form of low interest rates and unsound credit decisions because the put option on wealth by monetary policy created the illusion that nothing could ever go wrong, causing the credit/dollar crisis and global recession (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession, 157-66, Regulation of Banks, and Finance, 217-27, International Financial Architecture, 15-18, The Global Recession Risk, 221-5, Globalization and the State Vol. II, 197-213, Government Intervention in Globalization, 182-4).
Chart IA1-11, US, Percentage Share of Residential Investment in Gross Domestic Product, Quarterly, 1979-2015
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-12 provides the share of intellectual property products investment in GDP with annual data from 1929 to 2014. This is an important addition in the revision and enhancement of GDP provided by the Bureau of Economic Analysis. The share rose sharply over time but stabilized at a lower level in the past decade.
Chart IA1-12, US, Percentage Share of Intellectual Property Products Investment in Gross Domestic Product, Annual, 1929-2014
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IA1-13 provides the percentage share of intellectual property investment in GDP on a quarterly basis from 1979 to 2015. The share stabilized in the 2000s.
Chart IA1-13, US, Percentage Share of Intellectual Property Investment in Gross Domestic Product, Quarterly, 1979-2015
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table IA1-4 provides the seasonally adjusted annual rate of real GDP percentage change and contributions in percentage points in annual equivalent rate of gross domestic investment (GDI), real private fixed investment (PFI), nonresidential investment (NRES), business equipment and software (BES), residential investment (RES), intellectual property products (IPP) and change in inventories (∆INV) for the cyclical expansions from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 and from IIIQ2009 to IQ2015. GDI contributed 0.52 percentage points to GDP in IQ2015 with 0.87 percentage points by inventory accumulation and 0.29 percentage points by intellectual property products. GDI contributed 0.06 percentage points to GDP growth in IIQ2015: 0.14 percentage points in PFI, minus 0.07 percentage points in NRES and 0.21 percentage points in RES. Inventory investment deducted 0.08 percentage points and IPP added 0.22 percentage points.
Table IA1-4, US, Contributions to the Rate of Growth of Real GDP in Percentage Points
| GDP | GDI | PFI | NRES | BES | IPP | RES | ∆INV | |
| 2015 | ||||||||
| I | 0.6 | 1.39 | 0.52 | 0.20 | -0.22 | 0.29 | 0.32 | 0.87 |
| II | 2.3 | 0.06 | 0.14 | -0.07 | -0.04 | 0.22 | 0.21 | -0.08 |
| 2014 | ||||||||
| I | -0.9 | -0.38 | 0.91 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 0.30 | -0.09 | -1.29 |
| II | 4.6 | 1.99 | 0.87 | 0.56 | 0.00 | 0.19 | 0.31 | 1.12 |
| III | 4.3 | 1.22 | 1.23 | 1.12 | -0.05 | 0.25 | 0.11 | -0.01 |
| IV | 2.1 | 0.36 | 0.39 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.27 | 0.31 | -0.03 |
| 2013 | ||||||||
| I | 1.9 | 1.05 | 0.77 | 0.51 | -0.16 | 0.30 | 0.26 | 0.28 |
| II | 1.1 | 0.78 | 0.40 | 0.14 | 0.30 | -0.13 | 0.27 | 0.38 |
| III | 3.0 | 2.07 | 0.59 | 0.44 | 0.46 | 0.20 | 0.15 | 1.48 |
| IV | 3.8 | 0.71 | 0.79 | 1.05 | 0.11 | 0.13 | -0.26 | -0.08 |
| 2012 | ||||||||
| I | 2.7 | 1.47 | 2.00 | 1.37 | 0.48 | 0.07 | 0.63 | -0.53 |
| II | 1.9 | 1.53 | 0.98 | 0.88 | 0.27 | 0.14 | 0.10 | 0.56 |
| III | 0.5 | -0.18 | 0.00 | -0.27 | -0.12 | 0.05 | 0.27 | -0.18 |
| IV | 0.1 | -0.51 | 1.03 | 0.46 | -0.21 | 0.26 | 0.57 | -1.54 |
| 2011 | ||||||||
| I | -1.5 | -1.07 | -0.11 | -0.09 | -0.73 | 0.05 | -0.02 | -0.96 |
| II | 2.9 | 2.14 | 1.10 | 0.97 | 0.63 | 0.12 | 0.13 | 1.04 |
| III | 0.8 | 0.15 | 2.25 | 2.06 | 0.56 | 0.19 | 0.19 | -2.10 |
| IV | 4.6 | 4.16 | 1.36 | 1.08 | 0.34 | 0.26 | 0.28 | 2.80 |
| 2010 | ||||||||
| I | 1.7 | 1.77 | 0.11 | 0.46 | 1.25 | -0.07 | -0.35 | 1.66 |
| II | 3.9 | 2.86 | 1.76 | 1.21 | 1.02 | -0.08 | 0.56 | 1.09 |
| III | 2.7 | 1.86 | -0.04 | 0.90 | 0.83 | 0.22 | -0.94 | 1.90 |
| IV | 2.5 | -0.51 | 1.13 | 0.94 | 0.57 | 0.19 | 0.19 | -1.63 |
| 2009 | ||||||||
| I | -5.4 | -7.02 | -4.75 | -3.58 | -2.25 | -0.23 | -1.17 | -2.26 |
| II | -0.5 | -3.25 | -2.13 | -1.46 | -0.60 | 0.16 | -0.66 | -1.12 |
| III | 1.3 | -0.40 | -0.02 | -0.54 | 0.25 | 0.04 | 0.52 | -0.38 |
| IV | 3.9 | 4.05 | -0.36 | -0.37 | 0.36 | 0.25 | 0.01 | 4.40 |
| 1982 | ||||||||
| I | -6.5 | -7.59 | -2.26 | -1.45 | -0.83 | 0.14 | -0.81 | -5.33 |
| II | 2.2 | -0.06 | -2.32 | -1.89 | -1.20 | 0.08 | -0.44 | 2.26 |
| III | -1.4 | -0.62 | -1.73 | -1.72 | -0.55 | 0.06 | -0.02 | 1.11 |
| IV | 0.4 | -5.37 | -0.03 | -1.05 | -0.57 | 0.00 | 1.01 | -5.33 |
| 1983 | ||||||||
| I | 5.3 | 2.36 | 1.44 | -0.92 | -0.27 | 0.16 | 2.36 | 0.92 |
| II | 9.4 | 5.96 | 2.53 | 0.67 | 1.24 | 0.29 | 1.86 | 3.43 |
| III | 8.1 | 4.40 | 3.82 | 2.13 | 1.43 | 0.31 | 1.70 | 0.57 |
| IV | 8.5 | 6.94 | 3.93 | 3.14 | 2.32 | 0.35 | 0.79 | 3.01 |
| 1984 | ||||||||
| I | 8.2 | 7.23 | 2.29 | 1.71 | 0.46 | 0.30 | 0.58 | 4.94 |
| II | 7.2 | 2.57 | 2.86 | 2.52 | 1.36 | 0.29 | 0.34 | -0.29 |
| III | 4.0 | 1.69 | 1.48 | 1.70 | 0.88 | 0.25 | -0.22 | 0.21 |
| IV | 3.2 | -1.08 | 1.36 | 1.34 | 0.86 | 0.29 | 0.02 | -2.44 |
| 1985 | ||||||||
| I | 4.0 | -2.14 | 0.72 | 0.67 | -0.23 | 0.14 | 0.05 | -2.86 |
| II | 3.7 | 1.34 | 0.99 | 0.83 | 0.64 | 0.20 | 0.16 | 0.35 |
| III | 6.4 | -0.43 | -0.28 | -0.62 | -0.38 | 0.13 | 0.34 | -0.15 |
| IV | 3.0 | 2.80 | 1.40 | 1.00 | 0.53 | 0.26 | 0.40 | 1.40 |
| 1986 | ||||||||
| I | 3.8 | 0.04 | 0.21 | -0.55 | -0.28 | 0.17 | 0.76 | -0.17 |
| II | 1.9 | -1.30 | 0.00 | -1.12 | 0.34 | 0.15 | 1.12 | -1.30 |
| III | 4.1 | -1.97 | -0.34 | -0.63 | -0.17 | 0.10 | 0.28 | -1.62 |
| IV | 2.1 | 0.24 | 0.53 | 0.48 | 0.30 | 0.10 | 0.05 | -0.29 |
| 1987 | ||||||||
| I | 2.8 | 1.98 | -1.30 | -1.26 | -0.97 | 0.07 | -0.04 | 3.28 |
| II | 4.6 | 0.08 | 1.07 | 1.00 | 0.76 | 0.08 | 0.07 | -0.99 |
| III | 3.7 | 0.03 | 1.22 | 1.39 | 0.70 | 0.11 | -0.17 | -1.19 |
| IV | 6.8 | 4.94 | -0.01 | -0.05 | -0.48 | 0.16 | 0.04 | 4.95 |
| 1988 | ||||||||
| I | 2.3 | -3.62 | 0.06 | 0.41 | 0.82 | 0.15 | -0.36 | -3.68 |
| II | 5.4 | 1.72 | 1.39 | 1.14 | 0.67 | 0.18 | 0.25 | 0.33 |
| III | 2.3 | 0.38 | 0.33 | 0.32 | 0.29 | 0.22 | 0.01 | 0.05 |
| IV | 5.4 | 1.11 | 0.84 | 0.71 | 0.34 | 0.40 | 0.13 | 0.27 |
GDP: Gross Domestic Product; GDI: Gross Domestic Investment; PFI: Private Fixed Investment; NRES: Nonresidential; BES: Business Equipment and Software; IPP: Intellectual Property Products; RES: Residential; ∆INV: Change in Private Inventories.
GDI = PFI + ∆INV, may not add exactly because of errors of rounding.
GDP: Seasonally adjusted annual equivalent rate of growth in a quarter; components: percentage points at annual rate.
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
II United States House Prices and Homeownership Rate. The valuable report on Financial Accounts of the United States formerly Flow of Funds Accounts of the United States provided by the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/z1/Current/ http://www.federalreserve.gov/apps/fof/) is rich in important information and analysis. Table IIA-1, updated in this blog for every new quarterly release, shows the balance sheet of US households combined with nonprofit organizations in 2007, 2011, 2014 and IQ2015. The data show the strong shock to US wealth during the contraction. Assets fell from $81.1 trillion in 2007 to $77.4 trillion in 2011 even after nine consecutive quarters of growth beginning in IIIQ2009 (Section I and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/international-valuations-of-financial.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2015/06/dollar-revaluation-squeezing-corporate.html), for decline of $3.7 trillion or 4.5 percent. Assets stood at $97.5 trillion in 2014 for gain of $16.4 trillion relative to $81.1 trillion in 2007 or increase by 20.2 percent. Assets increased to $99.1 trillion in IQ2015 by $18.0 trillion relative to 2007 or 22.1 percent. Liabilities declined from $14.4 trillion in 2007 to $13.6 trillion in 2011 or by $824.4 billion equivalent to decline by 5.7 percent. Liabilities declined $226.4 billion or 1.6 percent from 2007 to 2014. Liabilities fell from $14.4 trillion in 2007 to $14.1 trillion in IQ2015, by $243.7 billion or decline of 1.7 percent. Net worth shrank from $66.7 trillion in 2007 to $63.9 trillion in 2011, that is, $2.8 trillion equivalent to decline of 4.3 percent. Net worth increased from $66,721.8 billion in 2007 to $84,924.6 billion in IQ2015 by $18,202.8 billion or 27.3 percent. The US consumer price index for all items increased from 210.036 in Dec 2007 to 236.119 in Mar 2015 (http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm) or 12.4 percent. Net worth adjusted by CPI inflation increased 13.2 percent from 2007 to IQ2015. Nonfinancial assets increased $898.5 billion from $28,149.7 billion in 2007 to $29,693.7 billion in IQ2015 or 5.5 percent. There was increase from 2007 to IQ2015 of $778.5 billion in real estate assets or by 3.3 percent. Real estate assets adjusted for CPI inflation fell 8.1 percent between 2007 and IQ2015. The National Association of Realtors estimated that the gains in net worth in homes by Americans were about $4 trillion between 2000 and 2005 (quoted in Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 224-5).
Table IIA-1, US, Balance Sheet of Households and Nonprofit Organizations, Billions of Dollars Outstanding End of Period, NSA
| 2007 | 2011 | 2014 | IQ2015 | |
| Assets | 81,117.1 | 77,449.5 | 97,464.9 | 99,076.3 |
| Nonfinancial | 28,149.7 | 23,378.2 | 29,150.2 | 29,693.7 |
| Real Estate | 23,340.2 | 18,252.6 | 23,615.4 | 24,118.7 |
| Durable Goods | 4,476.0 | 4,723.3 | 5,085.5 | 5,121.1 |
| Financial | 52,967.4 | 54,071.3 | 68,314.7 | 69,382.6 |
| Deposits | 7,560.4 | 8,716.1 | 10,144.1 | 10,287.2 |
| Credit Market | 3,997.0 | 4,395.5 | 3,314.5 | 3,271.4 |
| Mutual Fund Shares | 4,591.5 | 4,622.5 | 7,695.3 | 7,918.8 |
| Equities Corporate | 9,912.5 | 8,498.4 | 13,360.7 | 13,640.8 |
| Equity Noncorporate | 8,933.1 | 7,587.0 | 9,924.7 | 10,156.2 |
| Pension | 15,267.2 | 17,447.7 | 20,783.7 | 20,991.9 |
| Liabilities | 14,395.3 | 13,570.9 | 14,168.9 | 14,151.6 |
| Home Mortgages | 10,613.3 | 9,695.9 | 9,403.1 | 9,370.5 |
| Consumer Credit | 2,615.1 | 2,755.4 | 3,317.2 | 3,321.6 |
| Net Worth | 66,721.8 | 63,878.6 | 83,296.0 | 84,924.6 |
Net Worth = Assets – Liabilities
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. 2015. Flow of funds, balance sheets and integrated macroeconomic accounts: first quarter 2015. Washington, DC, Federal Reserve System, Jun 11. http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/z1/.
The explanation of the sharp contraction of household wealth can probably be found in the origins of the financial crisis and global recession. Let V(T) represent the value of the firm’s equity at time T and B stand for the promised debt of the firm to bondholders and assume that corporate management, elected by equity owners, is acting on the interests of equity owners. Robert C. Merton (1974, 453) states:
“On the maturity date T, the firm must either pay the promised payment of B to the debtholders or else the current equity will be valueless. Clearly, if at time T, V(T) > B, the firm should pay the bondholders because the value of equity will be V(T) – B > 0 whereas if they do not, the value of equity would be zero. If V(T) ≤ B, then the firm will not make the payment and default the firm to the bondholders because otherwise the equity holders would have to pay in additional money and the (formal) value of equity prior to such payments would be (V(T)- B) < 0.”
Pelaez and Pelaez (The Global Recession Risk (2007), 208-9) apply this analysis to the US housing market in 2005-2006 concluding:
“The house market [in 2006] is probably operating with low historical levels of individual equity. There is an application of structural models [Duffie and Singleton 2003] to the individual decisions on whether or not to continue paying a mortgage. The costs of sale would include realtor and legal fees. There could be a point where the expected net sale value of the real estate may be just lower than the value of the mortgage. At that point, there would be an incentive to default. The default vulnerability of securitization is unknown.”
There are multiple important determinants of the interest rate: “aggregate wealth, the distribution of wealth among investors, expected rate of return on physical investment, taxes, government policy and inflation” (Ingersoll 1987, 405). Aggregate wealth is a major driver of interest rates (Ibid, 406). Unconventional monetary policy, with zero fed funds rates and flattening of long-term yields by quantitative easing, causes uncontrollable effects on risk taking that can have profound undesirable effects on financial stability. Excessively aggressive and exotic monetary policy is the main culprit and not the inadequacy of financial management and risk controls.
The net worth of the economy depends on interest rates. In theory, “income is generally defined as the amount a consumer unit could consume (or believe that it could) while maintaining its wealth intact” (Friedman 1957, 10). Income, Y, is a flow that is obtained by applying a rate of return, r, to a stock of wealth, W, or Y = rW (Ibid). According to a subsequent restatement: “The basic idea is simply that individuals live for many years and that therefore the appropriate constraint for consumption decisions is the long-run expected yield from wealth r*W. This yield was named permanent income: Y* = r*W” (Darby 1974, 229), where * denotes permanent. The simplified relation of income and wealth can be restated as:
W = Y/r (1)
Equation (1) shows that as r goes to zero, r →0, W grows without bound, W→∞.
Lowering the interest rate near the zero bound in 2003-2004 caused the illusion of permanent increases in wealth or net worth in the balance sheets of borrowers and also of lending institutions, securitized banking and every financial institution and investor in the world. The discipline of calculating risks and returns was seriously impaired. The objective of monetary policy was to encourage borrowing, consumption and investment but the exaggerated stimulus resulted in a financial crisis of major proportions as the securitization that had worked for a long period was shocked with policy-induced excessive risk, imprudent credit, high leverage and low liquidity by the incentive to finance everything overnight at close to zero interest rates, from adjustable rate mortgages (ARMS) to asset-backed commercial paper of structured investment vehicles (SIV).
The consequences of inflating liquidity and net worth of borrowers were a global hunt for yields to protect own investments and money under management from the zero interest rates and unattractive long-term yields of Treasuries and other securities. Monetary policy distorted the calculations of risks and returns by households, business and government by providing central bank cheap money. Short-term zero interest rates encourage financing of everything with short-dated funds, explaining the SIVs created off-balance sheet to issue short-term commercial paper to purchase default-prone mortgages that were financed in overnight or short-dated sale and repurchase agreements (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession, 50-1, Regulation of Banks and Finance, 59-60, Globalization and the State Vol. I, 89-92, Globalization and the State Vol. II, 198-9, Government Intervention in Globalization, 62-3, International Financial Architecture, 144-9). ARMS were created to lower monthly mortgage payments by benefitting from lower short-dated reference rates. Financial institutions economized in liquidity that was penalized with near zero interest rates. There was no perception of risk because the monetary authority guaranteed a minimum or floor price of all assets by maintaining low interest rates forever or equivalent to writing an illusory put option on wealth. Subprime mortgages were part of the put on wealth by an illusory put on house prices. The housing subsidy of $221 billion per year created the impression of ever increasing house prices. The suspension of auctions of 30-year Treasuries was designed to increase demand for mortgage-backed securities, lowering their yield, which was equivalent to lowering the costs of housing finance and refinancing. Fannie and Freddie purchased or guaranteed $1.6 trillion of nonprime mortgages and worked with leverage of 75:1 under Congress-provided charters and lax oversight. The combination of these policies resulted in high risks because of the put option on wealth by near zero interest rates, excessive leverage because of cheap rates, low liquidity because of the penalty in the form of low interest rates and unsound credit decisions because the put option on wealth by monetary policy created the illusion that nothing could ever go wrong, causing the credit/dollar crisis and global recession (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession, 157-66, Regulation of Banks, and Finance, 217-27, International Financial Architecture, 15-18, The Global Recession Risk, 221-5, Globalization and the State Vol. II, 197-213, Government Intervention in Globalization, 182-4).
There are significant elements of the theory of bank financial fragility of Diamond and Dybvig (1983) and Diamond and Rajan (2000, 2001a, 2001b) that help to explain the financial fragility of banks during the credit/dollar crisis (see also Diamond 2007). The theory of Diamond and Dybvig (1983) as exposed by Diamond (2007) is that banks funding with demand deposits have a mismatch of liquidity (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 58-66). A run occurs when too many depositors attempt to withdraw cash at the same time. All that is needed is an expectation of failure of the bank. Three important functions of banks are providing evaluation, monitoring and liquidity transformation. Banks invest in human capital to evaluate projects of borrowers in deciding if they merit credit. The evaluation function reduces adverse selection or financing projects with low present value. Banks also provide important monitoring services of following the implementation of projects, avoiding moral hazard that funds be used for, say, real estate speculation instead of the original project of factory construction. The transformation function of banks involves both assets and liabilities of bank balance sheets. Banks convert an illiquid asset or loan for a project with cash flows in the distant future into a liquid liability in the form of demand deposits that can be withdrawn immediately.
In the theory of banking of Diamond and Rajan (2000, 2001a, 2001b), the bank creates liquidity by tying human assets to capital. The collection skills of the relationship banker convert an illiquid project of an entrepreneur into liquid demand deposits that are immediately available for withdrawal. The deposit/capital structure is fragile because of the threat of bank runs. In these days of online banking, the run on Washington Mutual was through withdrawals online. A bank run can be triggered by the decline of the value of bank assets below the value of demand deposits.
Pelaez and Pelaez (Regulation of Banks and Finance 2009b, 60, 64-5) find immediate application of the theories of banking of Diamond, Dybvig and Rajan to the credit/dollar crisis after 2007. It is a credit crisis because the main issue was the deterioration of the credit portfolios of securitized banks as a result of default of subprime mortgages. It is a dollar crisis because of the weakening dollar resulting from relatively low interest rate policies of the US. It caused systemic effects that converted into a global recession not only because of the huge weight of the US economy in the world economy but also because the credit crisis transferred to the UK and Europe. Management skills or human capital of banks are illustrated by the financial engineering of complex products. The increasing importance of human relative to inanimate capital (Rajan and Zingales 2000) is revolutionizing the theory of the firm (Zingales 2000) and corporate governance (Rajan and Zingales 2001). Finance is one of the most important examples of this transformation. Profits were derived from the charter in the original banking institution. Pricing and structuring financial instruments was revolutionized with option pricing formulas developed by Black and Scholes (1973) and Merton (1973, 1974, 1998) that permitted the development of complex products with fair pricing. The successful financial company must attract and retain finance professionals who have invested in human capital, which is a sunk cost to them and not of the institution where they work.
The complex financial products created for securitized banking with high investments in human capital are based on houses, which are as illiquid as the projects of entrepreneurs in the theory of banking. The liquidity fragility of the securitized bank is equivalent to that of the commercial bank in the theory of banking (Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 65). Banks created off-balance sheet structured investment vehicles (SIV) that issued commercial paper receiving AAA rating because of letters of liquidity guarantee by the banks. The commercial paper was converted into liquidity by its use as collateral in SRPs at the lowest rates and minimal haircuts because of the AAA rating of the guarantor bank. In the theory of banking, default can be triggered when the value of assets is perceived as lower than the value of the deposits. Commercial paper issued by SIVs, securitized mortgages and derivatives all obtained SRP liquidity on the basis of illiquid home mortgage loans at the bottom of the pyramid. The run on the securitized bank had a clear origin (Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 65):
“The increasing default of mortgages resulted in an increase in counterparty risk. Banks were hit by the liquidity demands of their counterparties. The liquidity shock extended to many segments of the financial markets—interbank loans, asset-backed commercial paper (ABCP), high-yield bonds and many others—when counterparties preferred lower returns of highly liquid safe havens, such as Treasury securities, than the risk of having to sell the collateral in SRPs at deep discounts or holding an illiquid asset. The price of an illiquid asset is near zero.”
Gorton and Metrick (2010H, 507) provide a revealing quote to the work in 1908 of Edwin R. A. Seligman, professor of political economy at Columbia University, founding member of the American Economic Association and one of its presidents and successful advocate of progressive income taxation. The intention of the quote is to bring forth the important argument that financial crises are explained in terms of “confidence” but as Professor Seligman states in reference to historical banking crises in the US the important task is to explain what caused the lack of confidence. It is instructive to repeat the more extended quote of Seligman (1908, xi) on the explanations of banking crises:
“The current explanations may be divided into two categories. Of these the first includes what might be termed the superficial theories. Thus it is commonly stated that the outbreak of a crisis is due to lack of confidence,--as if the lack of confidence was not in itself the very thing which needs to be explained. Of still slighter value is the attempt to associate a crisis with some particular governmental policy, or with some action of a country’s executive. Such puerile interpretations have commonly been confined to countries like the United States, where the political passions of democracy have had the fullest way. Thus the crisis of 1893 was ascribed by the Republicans to the impending Democratic tariff of 1894; and the crisis of 1907 has by some been termed the ‘[Theodore] Roosevelt panic,” utterly oblivious of the fact that from the time of President Jackson, who was held responsible for the troubles of 1837, every successive crisis had had its presidential scapegoat, and has been followed by a political revulsion. Opposed to these popular, but wholly unfounded interpretations, is the second class of explanations, which seek to burrow beneath the surface and to discover the more occult and fundamental causes of the periodicity of crises.”
Scholars ignore superficial explanations in the effort to seek good and truth. The problem of economic analysis of the credit/dollar crisis is the lack of a structural model with which to attempt empirical determination of causes (Gorton and Metrick 2010SB). There would still be doubts even with a well-specified structural model because samples of economic events do not typically permit separating causes and effects. There is also confusion is separating the why of the crisis and how it started and propagated, all of which are extremely important.
In true heritage of the principles of Seligman (1908), Gorton (2009EFM) discovers a prime causal driver of the credit/dollar crisis. The objective of subprime and Alt-A mortgages was to facilitate loans to populations with modest means so that they could acquire a home. These borrowers would not receive credit because of (1) lack of funds for down payments; (2) low credit rating and information; (3) lack of information on income; and (4) errors or lack of other information. Subprime mortgage “engineering” was based on the belief that both lender and borrower could benefit from increases in house prices over the short run. The initial mortgage would be refinanced in two or three years depending on the increase of the price of the house. According to Gorton (2009EFM, 13, 16):
“The outstanding amounts of Subprime and Alt-A [mortgages] combined amounted to about one quarter of the $6 trillion mortgage market in 2004-2007Q1. Over the period 2000-2007, the outstanding amount of agency mortgages doubled, but subprime grew 800%! Issuance in 2005 and 2006 of Subprime and Alt-A mortgages was almost 30% of the mortgage market. Since 2000 the Subprime and Alt-A segments of the market grew at the expense of the Agency (i.e., the government sponsored entities of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac) share, which fell from almost 80% (by outstanding or issuance) to about half by issuance and 67% by outstanding amount. The lender’s option to rollover the mortgage after an initial period is implicit in the subprime mortgage. The key design features of a subprime mortgage are: (1) it is short term, making refinancing important; (2) there is a step-up mortgage rate that applies at the end of the first period, creating a strong incentive to refinance; and (3) there is a prepayment penalty, creating an incentive not to refinance early.”
The prime objective of successive administrations in the US during the past 20 years and actually since the times of Roosevelt in the 1930s has been to provide “affordable” financing for the “American dream” of home ownership. The US housing finance system is mixed with public, public/private and purely private entities. The Federal Home Loan Bank (FHLB) system was established by Congress in 1932 that also created the Federal Housing Administration in 1934 with the objective of insuring homes against default. In 1938, the government created the Federal National Mortgage Association, or Fannie Mae, to foster a market for FHA-insured mortgages. Government-insured mortgages were transferred from Fannie Mae to the Government National Mortgage Association, or Ginnie Mae, to permit Fannie Mae to become a publicly-owned company. Securitization of mortgages began in 1970 with the government charter to the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation, or Freddie Mac, with the objective of bundling mortgages created by thrift institutions that would be marketed as bonds with guarantees by Freddie Mac (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 42-8). In the third quarter of 2008, total mortgages in the US were $12,057 billion of which 43.5 percent, or $5423 billion, were retained or guaranteed by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 45). In 1990, Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac had a share of only 25.4 percent of total mortgages in the US. Mortgages in the US increased from $6922 billion in 2002 to $12,088 billion in 2007, or by 74.6 percent, while the retained or guaranteed portfolio of Fannie and Freddie rose from $3180 billion in 2002 to $4934 billion in 2007, or by 55.2 percent.
According to Pinto (2008) in testimony to Congress:
“There are approximately 25 million subprime and Alt-A loans outstanding, with an unpaid principal amount of over $4.5 trillion, about half of them held or guaranteed by Fannie and Freddie. Their high risk activities were allowed to operate at 75:1 leverage ratio. While they may deny it, there can be no doubt that Fannie and Freddie now own or guarantee $1.6 trillion in subprime, Alt-A and other default prone loans and securities. This comprises over 1/3 of their risk portfolios and amounts to 34% of all the subprime loans and 60% of all Alt-A loans outstanding. These 10.5 million unsustainable, nonprime loans are experiencing a default rate 8 times the level of the GSEs’ 20 million traditional quality loans. The GSEs will be responsible for a large percentage of an estimated 8.8 million foreclosures expected over the next 4 years, accounting for the failure of about 1 in 6 home mortgages. Fannie and Freddie have subprimed America.”
In perceptive analysis of growth and macroeconomics in the past six decades, Rajan (2012FA) argues that “the West can’t borrow and spend its way to recovery.” The Keynesian paradigm is not applicable in current conditions. Advanced economies in the West could be divided into those that reformed regulatory structures to encourage productivity and others that retained older structures. In the period from 1950 to 2000, Cobet and Wilson (2002) find that US productivity, measured as output/hour, grew at the average yearly rate of 2.9 percent while Japan grew at 6.3 percent and Germany at 4.7 percent (see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 135-44). In the period from 1995 to 2000, output/hour grew at the average yearly rate of 4.6 percent in the US but at lower rates of 3.9 percent in Japan and 2.6 percent in the US. Rajan (2012FA) argues that the differential in productivity growth was accomplished by deregulation in the US at the end of the 1970s and during the 1980s. In contrast, Europe did not engage in reform with the exception of Germany in the early 2000s that empowered the German economy with significant productivity advantage. At the same time, technology and globalization increased relative remunerations in highly-skilled, educated workers relative to those without skills for the new economy. It was then politically appealing to improve the fortunes of those left behind by the technological revolution by means of increasing cheap credit. As Rajan (2012FA) argues:
“In 1992, Congress passed the Federal Housing Enterprises Financial Safety and Soundness Act, partly to gain more control over Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, the giant private mortgage agencies, and partly to promote affordable homeownership for low-income groups. Such policies helped money flow to lower-middle-class households and raised their spending—so much so that consumption inequality rose much less than income inequality in the years before the crisis. These policies were also politically popular. Unlike when it came to an expansion in government welfare transfers, few groups opposed expanding credit to the lower-middle class—not the politicians who wanted more growth and happy constituents, not the bankers and brokers who profited from the mortgage fees, not the borrowers who could now buy their dream houses with virtually no money down, and not the laissez-faire bank regulators who thought they could pick up the pieces if the housing market collapsed. The Federal Reserve abetted these shortsighted policies. In 2001, in response to the dot-com bust, the Fed cut short-term interest rates to the bone. Even though the overstretched corporations that were meant to be stimulated were not interested in investing, artificially low interest rates acted as a tremendous subsidy to the parts of the economy that relied on debt, such as housing and finance. This led to an expansion in housing construction (and related services, such as real estate brokerage and mortgage lending), which created jobs, especially for the unskilled. Progressive economists applauded this process, arguing that the housing boom would lift the economy out of the doldrums. But the Fed-supported bubble proved unsustainable. Many construction workers have lost their jobs and are now in deeper trouble than before, having also borrowed to buy unaffordable houses. Bankers obviously deserve a large share of the blame for the crisis. Some of the financial sector’s activities were clearly predatory, if not outright criminal. But the role that the politically induced expansion of credit played cannot be ignored; it is the main reason the usual checks and balances on financial risk taking broke down.”
In fact, Raghuram G. Rajan (2005) anticipated low liquidity in financial markets resulting from low interest rates before the financial crisis that caused distortions of risk/return decisions provoking the credit/dollar crisis and global recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. Near zero interest rates of unconventional monetary policy induced excessive risks and low liquidity in financial decisions that were critical as a cause of the credit/dollar crisis after 2007. Rajan (2012FA) argues that it is not feasible to return to the employment and income levels before the credit/dollar crisis because of the bloated construction sector, financial system and government budgets.
Table IIA-1 shows the euphoria of prices during the housing boom and the subsequent decline. House prices rose 94.1 percent in the 10-city composite of the Case-Shiller home price index, 78.0 percent in the 20-city composite and 63.5 percent in the US national home price index between May 2000 and May 2005. Prices rose around 100 percent from May 2000 to May 2006, increasing 113.2 percent for the 10-city composite, 95.7 percent for the 20-city composite and 77.8 percent in the US national index. House prices rose 38.9 percent between May 2003 and May 2005 for the 10-city composite, 33.7 percent for the 20-city composite and 28.6 percent for the US national propelled by low fed funds rates of 1.0 percent between Jun 2003 and Jun 2004. Fed funds rates increased by 0.25 basis points at every meeting of the Federal Open Aprket Committee (FOMC) from Jun 2004 until Jun 2006, reaching 5.25 percent. Simultaneously, the suspension of auctions of the 30-year Treasury bond caused decline of yields of mortgage-backed securities with intended decrease in mortgage rates. Similarly, between May 2003 and May 2006, the 10-city index gained 52.5 percent, the 20-city index increased 47.0 percent and the US national 40.0 percent. House prices have fallen from May 2006 to May 2015 by 14.2 percent for the 10-city composite, 13.0 percent for the 20-city composite and 6.7 percent for the US national. Measuring house prices is quite difficult because of the lack of homogeneity that is typical of standardized commodities. In the 12 months ending in May 2015, house prices increased 4.7 percent in the 10-city composite, increased 4.9 percent in the 20-city composite and 4.4 percent in the US national. Table IIA-6 also shows that house prices increased 83.1 percent between May 2000 and May 2015 for the 10-city composite, increased 70.2 percent for the 20-city composite and 65.9 percent for the US national. House prices are close to the lowest level since peaks during the boom before the financial crisis and global recession. The 10-city composite fell 14.3 percent from the peak in Jun 2006 to May 2015 and the 20-city composite fell 13.3 percent from the peak in Jul 2006 to May 2015. The US national fell 6.8 percent from the peak of the 10-city composite to May 2015 and 6.8 percent from the peak of the 20-city composite to May 2015. The final part of Table II-2 provides average annual percentage rates of growth of the house price indexes of Standard & Poor’s Case-Shiller. The average annual growth rate between Dec 1987 and Dec 2014 for the 10-city composite was 3.7 percent and 3.4 percent for the US national. Data for the 20-city composite are available only beginning in Jan 2000. House prices accelerated in the 1990s with the average rate of the 10-city composite of 5.0 percent between Dec 1992 and Dec 2000 while the average rate for the period Dec 1987 to Dec 2000 was 3.8 percent. The average rate for the US national was 3.4 percent from Dec 1987 to Dec 2014 and 3.6 percent from Dec 1987 to Dec 2000. Although the global recession affecting the US between IVQ2007 (Dec) and IIQ2009 (Jun) caused decline of house prices of slightly above 30 percent, the average annual growth rate of the 10-city composite between Dec 2000 and Dec 2014 was 3.7 percent while the rate of the 20-city composite was 3.2 percent and 3.1 percent for the US national.
Table IIA-1, US, Percentage Changes of Standard & Poor’s Case-Shiller Home Price Indices, Not Seasonally Adjusted, ∆%
| 10-City Composite | 20-City Composite | US National | |
| ∆% May 2000 to May 2003 | 39.8 | 33.1 | 27.1 |
| ∆% May 2000 to May 2005 | 94.1 | 78.0 | 63.5 |
| ∆% May 2003 to May 2005 | 38.9 | 33.7 | 28.6 |
| ∆% May 2000 to May 2006 | 113.2 | 95.7 | 77.8 |
| ∆% May 2003 to May 2006 | 52.5 | 47.0 | 40.0 |
| ∆% May 2005 to May 2015 | -5.7 | -4.4 | 1.5 |
| ∆% May 2006 to May 2015 | -14.2 | -13.0 | -6.7 |
| ∆% May 2009 to May 2015 | 28.3 | 27.9 | 16.1 |
| ∆% May 2010 to May 2015 | 21.7 | 22.2 | 17.0 |
| ∆% May 2011 to May 2015 | 26.5 | 28.0 | 22.3 |
| ∆% May 2012 to May 2015 | 27.8 | 28.6 | 21.9 |
| ∆% May 2013 to May 2015 | 14.5 | 14.7 | 11.8 |
| ∆% May 2014 to May 2015 | 4.7 | 4.9 | 4.4 |
| ∆% May 2000 to May 2015 | 83.1 | 70.2 | 65.9 |
| ∆% Peak Jun 2006 May 2015 | -14.3 | -6.8 | |
| ∆% Peak Jul 2006 May 2015 | -13.3 | -6.8 | |
| Average ∆% Dec 1987-Dec 2014 | 3.7 | NA | 3.4 |
| Average ∆% Dec 1987-Dec 2000 | 3.8 | NA | 3.6 |
| Average ∆% Dec 1992-Dec 2000 | 5.0 | NA | 4.5 |
| Average ∆% Dec 2000-Dec 2014 | 3.7 | 3.2 | 3.1 |
Source: http://us.spindices.com/index-family/real-estate/sp-case-shiller
Price increases measured by the Case-Shiller house price indices show that “home prices continued their rise across the country over the last 12 months” (https://www.spice-indices.com/idpfiles/spice-assets/resources/public/documents/212743_cshomeprice-release-0728.pdf?force_download=true). Monthly house prices increased sharply from Feb 2013 to Jan 2014 for both the 10- and 20-city composites, as shown in Table IIA-2. In Jan 2013, the seasonally adjusted 10-city composite increased 0.9 percent and the 20-city increased 1.0 percent while the 10-city not seasonally adjusted changed 0.0 percent and the 20-city changed 0.0 percent. House prices increased at high monthly percentage rates from Feb to Nov 2013. With the exception of Mar through Apr 2012, house prices seasonally adjusted declined in most month for both the 10-city and 20-city Case-Shiller composites from Dec 2010 to Jan 2012, as shown in Table IIA-2. The most important seasonal factor in house prices is school changes for wealthier homeowners with more expensive houses. Without seasonal adjustment, house prices fell from Dec 2010 throughout Mar 2011 and then increased in every month from Apr to Aug 2011 but fell in every month from Sep 2011 to Feb 2012. The not seasonally adjusted index registers decline in Mar 2012 of 0.1 percent for the 10-city composite and is flat for the 20-city composite. Not seasonally adjusted house prices increased 1.4 percent in Apr 2012 and at high monthly percentage rates until Sep 2012. House prices not seasonally adjusted stalled from Oct 2012 to Jan 2013 and surged from Feb to Sep 2013, decelerating in Oct 2013-Feb 2014. House prices grew at fast rates in Mar 2014. The 10-city NSA index increased 1.1 percent in May 2015 and the 20-city increased 1.1 percent. The 10-city SA decreased 0.2 percent in May 2015 and the 20-city composite SA decreased 0.2 percent. Declining house prices cause multiple adverse effects of which two are quite evident. (1) There is a disincentive to buy houses in continuing price declines. (2) More mortgages could be losing fair market value relative to mortgage debt. Another possibility is a wealth effect that consumers restrain purchases because of the decline of their net worth in houses.
Table IIA-2, US, Monthly Percentage Change of S&P Case-Shiller Home Price Indices, Seasonally Adjusted and Not Seasonally Adjusted, ∆%
| 10-City Composite SA | 10-City Composite NSA | 20-City Composite SA | 20-City Composite NSA | |
| May 2015 | -0.2 | 1.1 | -0.2 | 1.1 |
| Apr | 0.0 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 1.1 |
| Mar | 0.9 | 0.7 | 1.0 | 0.9 |
| Feb | 1.1 | 0.5 | 1.2 | 0.5 |
| Jan | 0.8 | -0.1 | 0.8 | -0.1 |
| Dec 2014 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 0.0 |
| Nov | 0.7 | -0.3 | 0.7 | -0.2 |
| Oct | 0.7 | -0.1 | 0.7 | -0.1 |
| Sep | 0.2 | -0.1 | 0.3 | -0.1 |
| Aug | -0.1 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 0.2 |
| Jul | -0.3 | 0.6 | -0.3 | 0.6 |
| Jun | -0.1 | 1.0 | -0.2 | 1.0 |
| May | -0.2 | 1.1 | -0.2 | 1.1 |
| Apr | 0.0 | 1.1 | 0.0 | 1.2 |
| Mar | 1.0 | 0.8 | 1.0 | 0.9 |
| Feb | 0.7 | 0.0 | 0.7 | 0.0 |
| Jan | 0.8 | -0.1 | 0.8 | -0.1 |
| Dec 2013 | 0.7 | -0.1 | 0.7 | -0.1 |
| Nov | 0.9 | 0.0 | 0.9 | -0.1 |
| Oct | 1.0 | 0.2 | 1.0 | 0.2 |
| Sep | 1.0 | 0.7 | 1.1 | 0.7 |
| Aug | 1.1 | 1.3 | 1.1 | 1.3 |
| Jul | 0.9 | 1.9 | 0.9 | 1.8 |
| Jun | 1.0 | 2.2 | 1.0 | 2.2 |
| May | 1.2 | 2.5 | 1.1 | 2.5 |
| Apr | 1.6 | 2.6 | 1.5 | 2.6 |
| Mar | 1.5 | 1.3 | 1.5 | 1.3 |
| Feb | 1.1 | 0.3 | 1.1 | 0.2 |
| Jan | 0.9 | 0.0 | 1.0 | 0.0 |
| Dec 2012 | 1.0 | 0.2 | 1.0 | 0.2 |
| Nov | 0.7 | -0.3 | 0.8 | -0.2 |
| Oct | 0.6 | -0.2 | 0.7 | -0.1 |
| Sep | 0.5 | 0.3 | 0.6 | 0.3 |
| Aug | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.9 |
| Jul | 0.4 | 1.5 | 0.5 | 1.6 |
| Jun | 0.9 | 2.1 | 1.0 | 2.3 |
| May | 0.9 | 2.2 | 1.0 | 2.4 |
| Apr | 0.4 | 1.4 | 0.4 | 1.4 |
| Mar | 0.2 | -0.1 | 0.3 | 0.0 |
| Feb | -0.1 | -0.9 | 0.0 | -0.8 |
| Jan | -0.2 | -1.1 | -0.1 | -1.0 |
| Dec 2011 | -0.5 | -1.2 | -0.4 | -1.1 |
| Nov | -0.5 | -1.4 | -0.5 | -1.3 |
| Oct | -0.6 | -1.3 | -0.6 | -1.4 |
| Sep | -0.4 | -0.6 | -0.4 | -0.7 |
| Aug | -0.2 | 0.1 | -0.2 | 0.1 |
| Jul | -0.1 | 0.9 | -0.1 | 1.0 |
| Jun | -0.1 | 1.0 | 0.0 | 1.2 |
| May | -0.3 | 1.0 | -0.3 | 1.0 |
| Apr | -0.2 | 0.6 | -0.3 | 0.6 |
| Mar | -0.5 | -1.0 | -0.6 | -1.0 |
| Feb | -0.4 | -1.3 | -0.3 | -1.2 |
| Jan | -0.2 | -1.1 | -0.2 | -1.1 |
| Dec 2010 | -0.2 | -0.9 | -0.2 | -1.0 |
Source: http://us.spindices.com/index-family/real-estate/sp-case-shiller
The US Census Bureau measures the homeownership rate by “dividing the number of owner-occupied housing units by the number of occupied housing units or households” (http://quickfacts.census.gov/qfd/meta/long_HSG445213.htm). The rate of homeownership of the US quarterly from 1965 to 2015 is in Table IIA-3. The rate of homeownership increased from 62.9 in IQ1966 to 64.4 in IVQ1969. The rate of homeownership rose from 64.0 in IVQ21970 to 65.5 in IVQ1980, declining to 63.8 in IVQ1989. The rate of homeownership increased to 66.9 in IVQ1999, reaching 69.0 in IVQ2005. The rate of homeownership fell to 63.4 in IIQ2015.
Table IIA-3, US, Home Ownership Rate, NSA, %
| Year | 1st Quarter | 2nd Quarter | 3rd Quarter | 4th Quarter |
| 1965 | 62.9 | 62.9 | 62.9 | 63.4 |
| 1966 | 63.5 | 63.2 | 63.3 | 63.8 |
| 1967 | 63.3 | 63.9 | 63.8 | 63.5 |
| 1968 | 63.6 | 64.1 | 64.1 | 63.6 |
| 1969 | 64.1 | 64.4 | 64.4 | 64.4 |
| 1970 | 64.3 | 64.0 | 64.4 | 64.0 |
| 1971 | 64.0 | 64.1 | 64.4 | 64.5 |
| 1972 | 64.3 | 64.5 | 64.3 | 64.4 |
| 1973 | 64.9 | 64.4 | 64.4 | 64.4 |
| 1974 | 64.8 | 64.8 | 64.6 | 64.4 |
| 1975 | 64.4 | 64.9 | 64.6 | 64.5 |
| 1976 | 64.6 | 64.6 | 64.9 | 64.8 |
| 1977 | 64.8 | 64.5 | 65.0 | 64.9 |
| 1978 | 64.8 | 64.4 | 65.2 | 65.4 |
| 1979 | 64.8 | 64.9 | 65.8 | 65.4 |
| 1980 | 65.5 | 65.5 | 65.8 | 65.5 |
| 1981 | 65.6 | 65.3 | 65.6 | 65.2 |
| 1982 | 64.8 | 64.9 | 64.9 | 64.5 |
| 1983 | 64.7 | 64.7 | 64.8 | 64.4 |
| 1984 | 64.6 | 64.6 | 64.6 | 64.1 |
| 1985 | 64.1 | 64.1 | 63.9 | 63.5 |
| 1986 | 63.6 | 63.8 | 63.8 | 63.9 |
| 1987 | 63.8 | 63.8 | 64.2 | 64.1 |
| 1988 | 63.7 | 63.7 | 64.0 | 63.8 |
| 1989 | 63.9 | 63.8 | 64.1 | 63.8 |
| 1990 | 64.0 | 63.7 | 64.0 | 64.1 |
| 1991 | 63.9 | 63.9 | 64.2 | 64.2 |
| 1992 | 64.0 | 63.9 | 64.3 | 64.4 |
| 1993 | 64.2 | 64.4 | 64.7 | 64.6 |
| 1994 | 63.8 | 63.8 | 64.1 | 64.2 |
| 1995 | 64.2 | 64.7 | 65.0 | 65.1 |
| 1996 | 65.1 | 65.4 | 65.6 | 65.4 |
| 1997 | 65.4 | 65.7 | 66.0 | 65.7 |
| 1998 | 65.9 | 66.0 | 66.8 | 66.4 |
| 1999 | 66.7 | 66.6 | 67.0 | 66.9 |
| 2000 | 67.1 | 67.2 | 67.7 | 67.5 |
| 2001 | 67.5 | 67.7 | 68.1 | 68.0 |
| 2002 | 67.8 | 67.6 | 68.0 | 68.3 |
| 2003 | 68.0 | 68.0 | 68.4 | 68.6 |
| 2004 | 68.6 | 69.2 | 69.0 | 69.2 |
| 2005 | 69.1 | 68.6 | 68.8 | 69.0 |
| 2006 | 68.5 | 68.7 | 69.0 | 68.9 |
| 2007 | 68.4 | 68.2 | 68.2 | 67.8 |
| 2008 | 67.8 | 68.1 | 67.9 | 67.5 |
| 2009 | 67.3 | 67.4 | 67.6 | 67.2 |
| 2010 | 67.1 | 66.9 | 66.9 | 66.5 |
| 2011 | 66.4 | 65.9 | 66.3 | 66.0 |
| 2012 | 65.4 | 65.5 | 65.5 | 65.4 |
| 2013 | 65.0 | 65.0 | 65.3 | 65.2 |
| 2014 | 64.8 | 64.7 | 64.4 | 64.0 |
| 2015 | 63.7 | 63.4 | NA | NA |
Source: US Bureau of the Census
http://www.census.gov/housing/hvs/index.html
Chart IIA-1 of the US Census Bureau provides the rate of homeownership of the US from 1965 to 2015. There are four periods in US homeownership. The rate of homeownership increased in an upward trend from 1965 to 1980. The rate fell in the 1980s and stabilized until 1995. The rate then increased sharply from 1996 to 2005. In the current period, the rate of homeownership shows the sharpest downward trend in available data from 2005 to 2015.
Chart IIA-1, US Home Ownership Rate, Quarterly, 1965-2015, %
Source: US Bureau of the Census
http://www.census.gov/housing/hvs/index.html
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015.

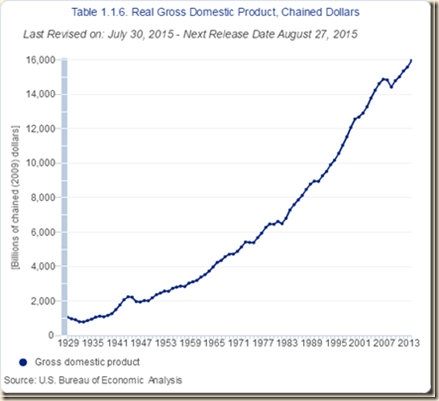
![clip_image001[1] clip_image001[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjGiaG_W3UKMxnayWWMQOJfxv64bR3nTfjW9lfcsRg9z_0PK9Ht7RE8ENwHfyAOzn7lC9d0Ip_AVvgp4RimkMeQ4KU76FzS2UZSO6ojbdnfchLxzUQZTJ7Nq4dwY3aUtiU-uILqwjSNNiE/?imgmax=800)

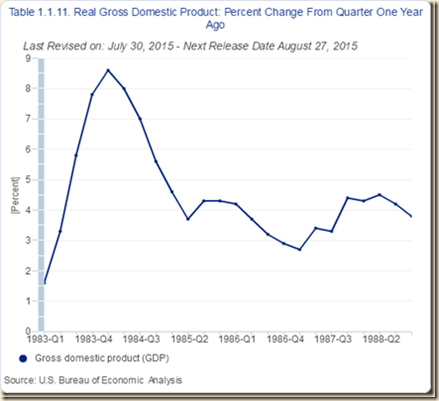
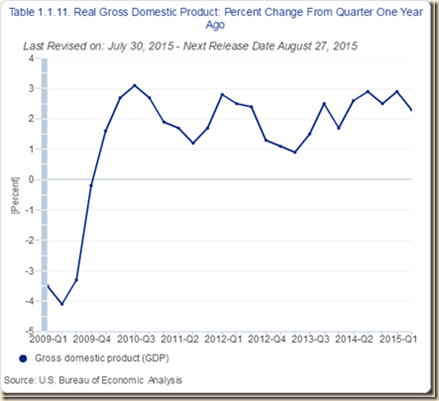
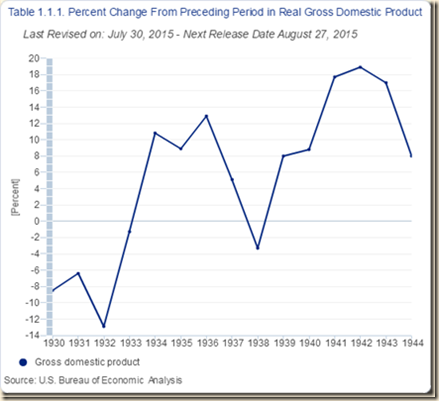
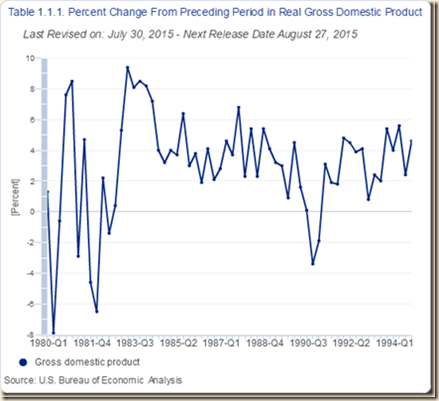

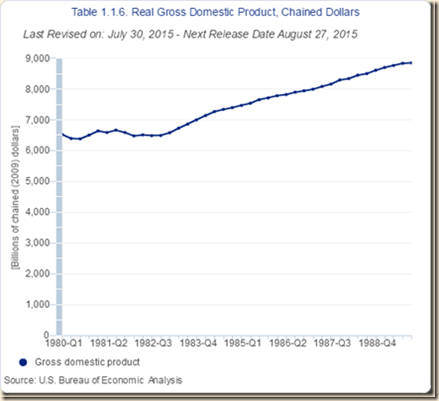



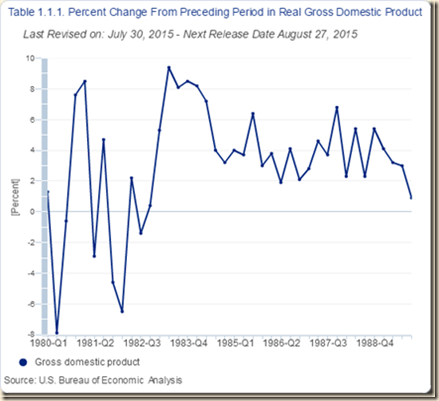




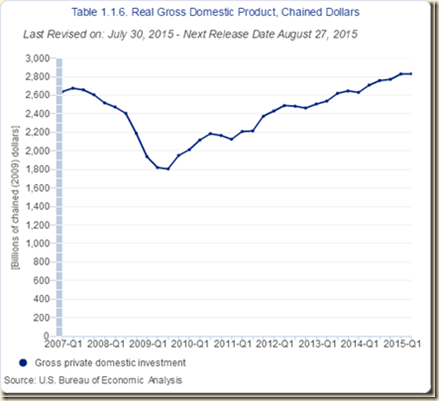
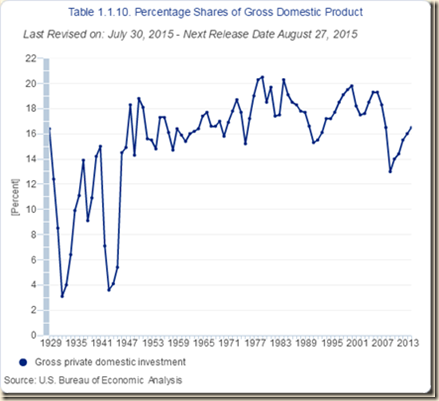
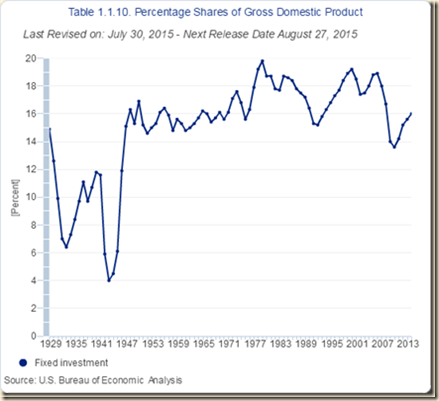
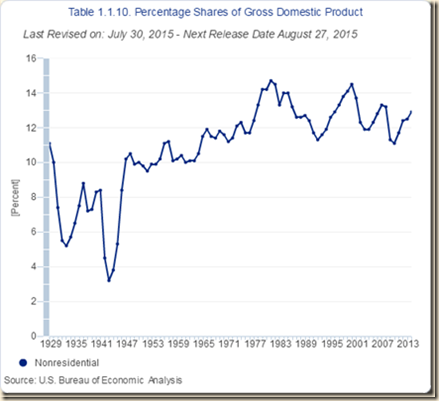
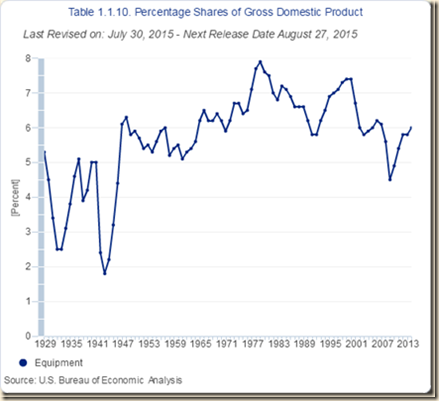
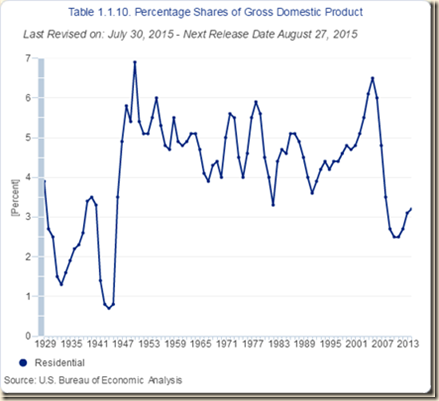
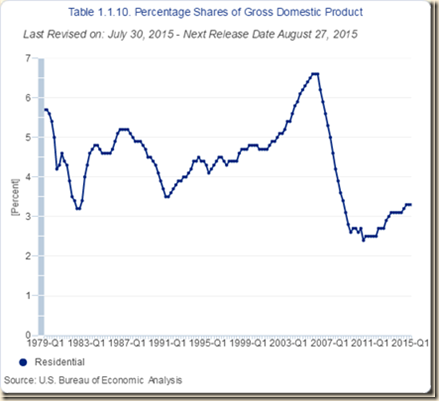

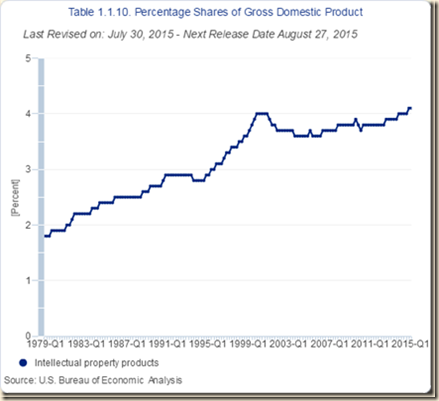
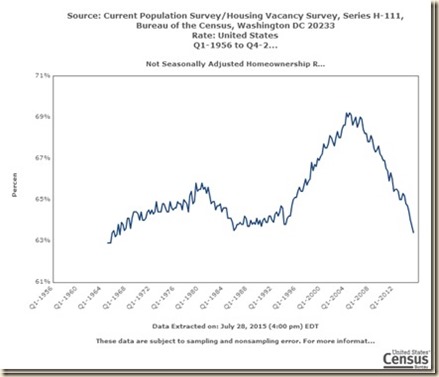
No comments:
Post a Comment