Recovery without Jobs, Stagnating Real Disposable per Capita Income and World Economy Growth Standstill with Global Recession Risk
Carlos M. Pelaez
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2010, 2011, 2012
Executive Summary
I Twenty Eight Million Unemployed and Underemployed and Stagnating Real Wages
IA Twenty Eight Million Unemployed or Underemployed
IA1 Summary of the Employment Situation
IA2 Number of People in Job Stress
IA3 Long-term and Cyclical Comparison of Employment
IA4 Job Creation
IB Stagnating Real Wages
II Stagnating Real Disposable Income and Consumption Expenditures and Financial Repression
IIA Stagnating Real Disposable Income and Consumption Expenditures
IIB Financial Repression
III World Financial Turbulence
IIIA Financial Risks
IIIB Appendix on Safe Haven Currencies
IIIC Appendix on Fiscal Compact
IIID Appendix on European Central Bank Large Scale Lender of Last Resort
IIIE Appendix Euro Zone Survival Risk
IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation
IIIG Appendix on Deficit Financing of Growth and the Debt Crisis
IIIGA Monetary Policy with Deficit Financing of Economic Growth
IIIGB Adjustment during the Debt Crisis of the 1980s
IV Global Inflation
V World Economic Slowdown
VA United States
VB Japan
VC China
VD Euro Area
VE Germany
VF France
VG Italy
VH United Kingdom
VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets
VII Economic Indicators
VIII Interest Rates
IX Conclusion
References
Appendix I The Great Inflation
VC China. China estimates an index of nonmanufacturing purchasing managers on the basis of a sample of 1200 nonmanufacturing enterprises across the country (http://www.stats.gov.cn/english/pressrelease/t20120704_402815668.htm). Table CIPMS provides this index and components from Jan to Jun 2012. The index fell from 57.3 in Mar to 55.2 in May but climbed to 56.7 in Jun, which is lower than 58.0 in Mar and 57.3 in Feb but higher than in any other of the months in 2012.
Table CIPMS, China, Nonmanufacturing Index of Purchasing Managers, %, Seasonally Adjusted
| Total Index | New Orders | Interm. | Subs Prices | Exp | |
| Jun | 56.7 | 53.7 | 52.1 | 48.6 | 65.5 |
| May | 55.2 | 52.5 | 53.6 | 48.5 | 65.4 |
| Apr | 56.1 | 52.7 | 57.9 | 50.3 | 66.1 |
| Mar | 58.0 | 53.5 | 60.2 | 52.0 | 66.6 |
| Feb | 57.3 | 52.7 | 59.0 | 51.2 | 63.8 |
| Jan | 55.7 | 52.2 | 58.2 | 51.1 | 65.3 |
Notes: Interm.: Intermediate; Subs: Subscription; Exp: Business Expectations
Source: National Bureau of Statistics of China
http://www.stats.gov.cn/english/pressrelease/t20120704_402815668.htm
Chart CIPMS provides China’s nonmanufacturing purchasing managers’ index from Jun 2011 to Jun 2012. There was slowing of the general index in Apr 2012 after the increase in Jan-Mar 2012 and further decline to 55.2 in May 2012 but increase to 56.7 in Jun 2012.
Chart CIPMS, China, Nonmanufacturing Index of Purchasing Managers, Seasonally Adjusted
Source: National Bureau of Statistics of China
http://www.stats.gov.cn/english/pressrelease/t20120704_402815668.htm
China estimates a manufacturing index of purchasing managers on the basis of a sample of 820 enterprises (http://www.stats.gov.cn/english/pressrelease/t20120703_402815318.htm). Chart CIPMM provides the index from Jun 2011 to Jun 2012. There is deceleration from 52.0 in May 2011 to marginal contraction at 49.0 in Nov 2011. Manufacturing activity recovered to 53.3 in Apr 2012 but then declined to 50.4 in May 2012 and 50.2 in Jun 2012, which is the lowest in a year with exception of contraction at 49.0 in Nov 2011.
Chart CIPMM, China, Manufacturing Index of Purchasing Managers, Seasonally Adjusted
Source: National Bureau of Statistics of China
http://www.stats.gov.cn/english/pressrelease/t20120703_402815318.htm
The HSBC China Services PMI™, compiled by Markit, moderating business activity in China with the HSBC Composite Output, combining manufacturing and services, decreasing from 51.9 in May to 50.6 in Jun, which is the lowest level in three months with contraction in manufacturing and slower activity in services (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9788). Hongbin Qu, Chief Economist, China and Co-Head of Asian Economic Research at HSBC, finds weak employment growth, suggesting that with lower inflation there is room for further stimulus (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9788).The HSBC Purchasing Managers’ Index™ (PMI™), compiled by Markit, fell slightly to 48.2 in Jun from 48.4 in May, for the lowest reading in IIQ2012 since IQ2009 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9721). Hongbin Qu, Chief Economist, China and Co-Head of Asian Economic Research at HSBC, finds continuing slowdown in China’s economy in IIQ2012, which requires further reduction of bank reserve requirements and the policy interest rate together with fiscal measures (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9721).
Wang Xiaotian, writing on China Daily, on “China cuts its reserve ratio again,” published by Xinhuanet on May 13, 2012 (http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/china/2012-05/13/c_131584252.htm), informs that the People’s Bank of China (PBC) (http://www.pbc.gov.cn/publish/english/963/index.html) reduced the reserve requirement imposed on Chinese lenders by 50 basis points with the objective of injecting liquidity to strengthen the economy. This is the second such reduction of reserve requirements in 2012. The reduction is estimated to release CNY 400 in China’s money market. The reserve requirement will be 20 percent for larger banks and 16.5 percent for smaller banks. The measures are intended to strengthen the economy. Xinhuanet, writing on “China announces surprise rate cuts amid economic downshift,” on Jun 5, 2012 (http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/china/2012-07/05/c_131697843.htm), informs that the central bank of China People’s Bank of China reduced the one year deposit rate by 25 basis points and the one year lending rate by 31 basis points effective Jun 6, 2012. The People’s Bank of China posts the new rates (http://www.pbc.gov.cn/publish/english/955/2012/20120608171005950734495/20120608171005950734495_.html). Table CNY provides the country data table for China.
Table CNY, China, Economic Indicators
| Price Indexes for Industry | May 12-month ∆%: minus 1.4 May month ∆%: minus 0.4 |
| Consumer Price Index | May month ∆%: -0.2 May 12 month ∆%: 3.0 |
| Value Added of Industry | May month ∆%: 0.89 Jan-May 2012/Jan-May 2011 ∆%: 10.7 |
| GDP Growth Rate | Year IQ2012 ∆%: 8.1 |
| Investment in Fixed Assets | Total Jan-May 2012 ∆%: 20.1 Real estate development: 18.5 |
| Retail Sales | May month ∆%: 0.84 Jan-May ∆%: 14.5 |
| Trade Balance | May balance $18.7 billion Cumulative May: $37.9 billion |
Links to blog comments in Table CNY:
6/17/12 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/05/world-financial-turbulence-global_27.html
4/15/12 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/04/fractured-labor-market-with-hiring_15.html
VD Euro Area. Table VD-EUR provides inflation, unemployment and real GDP growth in the euro area yearly from 1999 to 2011 together with growth forecasts of EUROSTAT for 2012 and 2013. Inflation in the euro zone remained subdued around 2 percent in the first five years of the euro zone from 1999 to 2004, as shown in Table VD-EUR. Inflation climbed above 2.0 percent after 2005, peaking at 3.3 percent in 2008 with the surge in commodity prices but falling to 0.3 percent in 2009 with the collapse of commodity prices. Inflation climbed back to 1.6 percent in 2010 and 2.7 percent in 2011. Under the regime of zero interest rates inflation returns worldwide during relaxation of risk aversion. The rate of unemployment increased in 2011 while the rate of GDP growth fell. EUROSTAT forecasts slightly negative growth of 0.3 percent in 2012 and growth of 1.0 percent in 2013.
Table VD-EUR, Euro Area, Yearly Percentage Change of Harmonized Index of Consumer Prices, Unemployment Rate and GDP, ∆%
| Year | HICP ∆% | Unemployment | GDP ∆% |
| 1999 | 1.2 | 9.6 | 2.9 |
| 2000 | 2.2 | 8.7 | 3.8 |
| 2001 | 2.4 | 8.1 | 2.0 |
| 2002 | 2.3 | 8.5 | 0.9 |
| 2003 | 2.1 | 9.0 | 0.7 |
| 2004 | 2.2 | 9.3 | 2.2 |
| 2005 | 2.2 | 9.2 | 1.7 |
| 2006 | 2.2 | 8.5 | 3.3 |
| 2007 | 2.1 | 7.6 | 3.0 |
| 2008 | 3.3 | 7.6 | 0.4 |
| 2009 | 0.3 | 9.6 | -4.4 |
| 2010 | 1.6 | 10.1 | 2.0 |
| 2011 | 2.7 | 10.2 | 1.5 |
| 2012* | -0.3 | ||
| 2013* | 1.0 |
*EUROSTAT forecast
http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/statistics/search_database
The Markit Eurozone PMI® Composite Output Index, combining services and manufacturing activity with close association with GDP, increased from 46.0 in May to 46.4 in Jun, which is still in sharp contraction (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9769) in the deepest contraction in three years. Chris Williamson, Chief Economist at Markit, finds that the data are consistent with decline of GDP at a quarterly rate of 0.6 percent IIQ2012, which could result in the third consecutive quarterly contraction of euro area GDP (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9769). The Markit Eurozone Manufacturing PMI® was unchanged at 45.1 in Jun, which indicates the sharpest deteriorating in activity in about three years (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9708). Chris Williamson, Chief Economist at Markit, finds that the index suggests manufacturing in the euro area declined at a quarterly rate of about 1 percent, exerting pressure on GDP in IIQ2012 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9708).
Table EUR provides the regional data table for the euro area.
Table EUR, Euro Area Economic Indicators
| GDP | IQ2012 ∆% 0.0; IQ2012/IQ2011 ∆% -0.1 Blog 6/10/12 |
| Unemployment | May 2012: 11.1% unemployment rate May 2012: 17.561 million unemployed Blog 7/8/12 |
| HICP | May month ∆%: -0.1 12 months May ∆%: 2.4 |
| Producer Prices | Euro Zone industrial producer prices May ∆%: -0.5 |
| Industrial Production | Apr month ∆%: -0.8; Apr 12 months ∆%: -2.3 |
| Retail Sales | May month ∆%: 0.6 |
| Confidence and Economic Sentiment Indicator | Sentiment 89.9 Jun 2012 Confidence minus 19.8 Jun 2012 Blog 7/2/12 |
| Trade | Jan-Apr 2012/Jan-Apr 2011 Exports ∆%: 7.9 Apr 2012 12-month Exports ∆% 6.1 Imports ∆% -0.9 |
Links to blog comments in Table EUR:
7/2/12 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/07/mediocre-economic-growth-united-states_03.html
6/17/12 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/05/world-financial-turbulence-global_27.html
6/10/12 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/rules-versus-discretionary-authorities_10.html
Eurostat estimates the rate of unemployment in the euro area as 11.1 percent in May 2012, as shown in Table VD-1. The number of unemployed in May 2012 was 17.561 million, which was 1.820 million higher than 15.741 million in May 2011. The rate of unemployment jumped from 10.0 percent in May 2011 to 11.1 percent in May 2012.
Table VD-1, Euro Area, Unemployment Rate and Number of Unemployed, % and Millions, SA
| Unemployment Rate % | Number Unemployed | |
| May 2012 | 11.1 | 17.561 |
| Apr | 11.0 | 17.473 |
| Mar | 11.0 | 17.357 |
| Feb | 10.8 | 17.174 |
| Jan | 10.8 | 17.022 |
| Dec 2011 | 10.7 | 16.862 |
| Nov | 10.6 | 16.773 |
| Oct | 10.5 | 16.537 |
| Sep | 10.3 | 16.342 |
| Aug | 10.2 | 16.099 |
| Jul | 10.1 | 15.994 |
| Jun | 10.0 | 15.821 |
| May | 10.0 | 15.741 |
| Apr | 9.9 | 15.602 |
| Mar | 9.9 | 15.600 |
| Feb | 9.9 | 15.604 |
| Jan | 10.0 | 15.660 |
| Dec 2010 | 10.0 | 15.764 |
Source: EUROSTAT
http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/statistics/search_database
Table VD-2 shows the disparity in rates of unemployment in the euro area with 11.1 percent for the region as a whole and 17.561 million unemployed but 5.6 percent in Germany and 2.341 million unemployed. At the other extreme is Spain with rate of unemployment of 24.6 percent and 5.701 million unemployed. The rate of unemployment of the European Union in May is 10.3 percent with 24.868 million unemployed.
Table VD-2, Unemployed and Unemployment Rate in Countries and Regions, Millions and %
| May 2012 | Unemployment Rate % | Unemployed Millions |
| Euro Zone | 11.1 | 17.561 |
| Germany | 5.6 | 2.341 |
| France | 10.1 | 2.942 |
| Netherlands | 5.1 | 0.455 |
| Finland | 7.6 | 0.204 |
| Portugal | 15.2 | 0.822 |
| Ireland | 14.6 | 0.307 |
| Italy | 10.1 | 2.584 |
| Greece | NA | NA |
| Spain | 24.6 | 5.701 |
| Belgium | 7.2 | 0.355 |
| European Union | 10.3 | 24.868 |
Source: EUROSTAT
http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/statistics/search_database
Chart VD-1 provides Eurosat estimates of unemployment rates in the European Union. There is significant diversity in the rates of unemployment in members of the euro zone and the European Union.
Chart VD-1, Unemployment Rate in Various Countries and Regions
Source: EUROSTAT
http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/statistics/search_database
Advanced economies are experiencing weak demand. Table VD-3 provides month and 12-month percentage changes of the volume of retail sales in the euro zone from Jan 2011 to May 2012. Retail sales increased 0.6 percent in May 2012 but fell 1.7 percent in 12 months. The 12-month rates of growth have become negative since Mar 2011 with exception of 1.0 percent in Apr 2011 and stability in Aug 2011 and Mar 2012. The lower part of Table VD-3 provides annual percentage changes of inflation-adjusted retail sales in the euro zone since 1990. Retail sales fell 2.4 percent in 2009 after falling 0.8 percent in 2008 and fell again by 0.6 percent in 2011. The average yearly rate of increase of retail sales from 1999 to 2007 was 2.0 percent but growth has not recovered. The average yearly rate of increase for the entire period 1999 to 2011 is lower at 1.1 percent.
Table VD-3, Euro Zone, Volume of Retail Sales, Deflated ∆%
| Month ∆% | 12-Month ∆% | |
| May 2012 | 0.6 | -1.7 |
| Apr | -1.4 | -3.4 |
| Mar | 0.4 | 0.0 |
| Feb | -0.2 | -2.0 |
| Jan | 1.2 | -1.1 |
| Dec 2011 | -1.3 | -1.7 |
| Nov | -0.3 | -1.4 |
| Oct | -0.2 | -0.7 |
| Sep | -0.6 | -1.1 |
| Aug | -0.1 | 0.0 |
| Jul | 0.5 | -0.4 |
| Jun | 0.8 | -0.8 |
| May | -1.6 | -1.8 |
| Apr | 1.1 | 1.0 |
| Mar | -1.2 | -1.4 |
| Feb | 0.3 | 1.1 |
| Jan | 0.3 | 0.9 |
| Annual ∆% | ||
| 2011 | -0.6 | |
| 2010 | 0.9 | |
| 2009 | -2.4 | |
| 2008 | -0.8 | |
| 2007 | 1.6 | |
| 2006 | 2.2 | |
| 2005 | 2.0 | |
| 2004 | 1.5 | |
| 2003 | 0.9 | |
| 2002 | 1.2 | |
| 2001 | 2.1 | |
| 2000 | 2.5 | |
| 1999 | 2.3 | |
| Average ∆% 1999-2007 | 2.0 | |
| Average ∆% 1999-2011 | 1.1 |
Source:
http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/statistics/search_database
Growth rates of retail sales of the euro zone by major segments are in Table VD-4. Total sales in increased 0.6 percent in May 2012 and declined 1.7 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2012. All 12-month percentage changes are negative with improvement in all monthly rates.
Table VD-4, Euro Zone, Volume of Retail Sales by Products, ∆%
| May 2012 | Month ∆% | 12-Month ∆% |
| Total | 0.6 | -1.7 |
| Food, Drinks, Tobacco | 0.2 | -1.1 |
| Nonfood Products ex Automotive Fuel | 1.0 | -1.5 |
Source:
http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/statistics/search_database
Month and 12-month percentage rates of change of retail sales by member countries of the euro zone are shown in Table VD-5 for May 2012. Retail sales are weak throughout the euro zone. The 12-month percentage changes are negative for all members in Table VD-5 with the exception of 2.3 percent for Germany, 0.6 percent for Finland and 1.7 percent for Ireland. The 12-month percentage change for the UK, which is not a member of the euro zone, was 3.7 percent. The European Union’s 12-month percentage change was also negative by 0.3 percent.
Table VD-5, Euro Zone, Volume of Retail Sales by Member Countries, ∆%
| May 2012 | Month ∆% | 12-Month ∆% |
| Euro Zone | 0.6 | -1.7 |
| Germany | -0.3 | 2.3 |
| France | 1.2 | -1.2 |
| Netherlands | NA | NA |
| Finland | 1.9 | 0.6 |
| Belgium | 0.2 | -2.2 |
| Portugal | 2.9 | -5.1 |
| Ireland | 1.7 | 1.7 |
| Italy | NA | NA |
| Greece | NA | NA |
| Spain | 1.2 | -4.8 |
| UK | 1.3 | 3.7 |
| European Union | 0.6 | -0.3 |
Source:
http://epp.eurostat.ec.europa.eu/portal/page/portal/statistics/search_database
VE Germany. Table VE-DE provides yearly growth rates of the German economy from 1992 to 2011, price adjusted chain-linked and price and calendar-adjusted chain-linked. Germany’s GDP fell 5.1 percent in 2009 after growing below trend at 1.1 percent in 2008. Recovery has been robust in contrast with other advanced economy. The German economy grew at 3.7 percent in 2010 and at 3.0 percent in 2011. Growth slowed in 2011 from 1.3 percent in IQ2011, 0.3 percent in IIQ2011 and 0.6 percent in IIIQ2011 to decline of 0.2 percent in IVQ2011 and growth of 0.5 percent in IQ2012. The Federal Statistical Agency of Germany analyzes the fall and recovery of the German economy (http://www.destatis.de/jetspeed/portal/cms/Sites/destatis/Internet/EN/Content/Statistics/VolkswirtschaftlicheGesamtrechnungen/Inlandsprodukt/Aktuell,templateId=renderPrint.psml):
“The German economy again grew strongly in 2011. The price-adjusted gross domestic product (GDP) increased by 3.0% compared with the previous year. Accordingly, the catching-up process of the German economy continued during the second year after the economic crisis. In the course of 2011, the price-adjusted GDP again exceeded its pre-crisis level. The economic recovery occurred mainly in the first half of 2011. In 2009, Germany experienced the most serious post-war recession, when GDP suffered a historic decline of 5.1%. The year 2010 was characterised by a rapid economic recovery (+3.7%).”
Table VE-DE, Germany, GDP Year ∆%
| Price Adjusted Chain-Linked | Price- and Calendar-Adjusted Chain Linked | |
| 2011 | 3.0 | 3.1 |
| 2010 | 3.7 | 3.6 |
| 2009 | -5.1 | -5.1 |
| 2008 | 1.1 | 0.8 |
| 2007 | 3.3 | 3.4 |
| 2006 | 3.7 | 3.9 |
| 2005 | 0.7 | 0.8 |
| 2004 | 1.2 | 0.7 |
| 2003 | -0.4 | -0.4 |
| 2002 | 0.0 | 0.0 |
| 2001 | 1.5 | 1.6 |
| 2000 | 3.1 | 3.3 |
| 1999 | 1.9 | 1.8 |
| 1998 | 1.9 | 1.7 |
| 1997 | 1.7 | 1.8 |
| 1996 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| 1995 | 1.7 | 1.8 |
| 1994 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| 1993 | -1.0 | -1.0 |
| 1992 | 1.9 | 1.5 |
Source: Statistiche Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/EN/PressServices/Press/pr/2012/05/PE12_178_811.html
The Markit Germany Composite Output Index of the Markit Germany Services PMI®, combining manufacturing and services with close association with Germany’s GDP, fell from 49.3 in May to 48.1 in Jun, indicating marginal deterioration in private sector output for the first time in six months and the deepest in three years (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9787). Tim Moore, Senior Economist at Markit and author of the report, finds that the index suggests flat GDP in Germany in IIQ2012 with possible deterioration in the future (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9787). The Markit/BME Germany Purchasing Managers’ Index® (PMI®), showing close association with Germany’s manufacturing output, fell from 45.2 in May to 45.0 in Jun, remaining below 50.0 during four consecutive months for the longest period since the global recession of 2008 and 2009 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9765). Tim Moore, Senior Economist at Markit and author of the report, finds that Germany’s manufacturing output is showing the sharpest drop in about three years with contracting orders from export markets (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9765).Table DE provides the country data table for Germany.
Table DE, Germany, Economic Indicators
| GDP | IQ2012 0.5 ∆%; I/Q2012/IQ2011 ∆% 1.7 2011/2010: 3.0% GDP ∆% 1992-2011 Blog 5/27/12 |
| Consumer Price Index | Jun month SA ∆%: -0.1 |
| Producer Price Index | May month ∆%: -0.3 |
| Industrial Production | Mfg May month SA ∆%: 1.9 |
| Machine Orders | May month ∆%: 0.6 |
| Retail Sales | Apr Month ∆% 0.6 12-Month ∆% minus 3.8 Blog 6/3/12 |
| Employment Report | Unemployment Rate May 5.5% |
| Trade Balance | Exports Apr 12-month NSA ∆%: 3.4 Blog 6/10/12 |
Links to blog comments in Table DE:
7/2/12 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/07/mediocre-economic-growth-united-states_03.html
6/24/12 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/recovery-without-hiring-continuance-of_24.html
6/10/12 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/rules-versus-discretionary-authorities_10.html
6/3/12 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/mediocre-recovery-without-jobs_04.html
5/27 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012_05_01_archive.html
The production industries index of Germany in Table VE-1 shows increase of 1.6 percent in May and decrease of 6.6 percent in the 12 months ending in May 2012. Germany’s production industries suffered decline of 7.3 percent in Dec 2008 relative to Dec 2007 and decline of 2.3 percent in 2009. Recovery was vigorous with 14.2 percent in the 12 months ending in Dec 2010. The first quarter of 2011 was quite strong when the German economy outperformed the other advanced economies. The performance of Germany’s production industries from 2003 to 2006 was vigorous with average rate of 4.4 percent. Data for the production industries index of Germany fluctuate sharply from month to month and also in 12-month rates.
Table VE-1, Germany, Production Industries, Month and 12-Month ∆%
| 12-Month ∆% NSA | Month ∆% Calendar SA | |
| May 2012 | -6.6 | 1.6 |
| Apr | -0.6 | -2.1 |
| Mar | -0.7 | 2.2 |
| Feb | 2.2 | -0.4 |
| Jan | 4.6 | 0.8 |
| Dec 2011 | 1.2 | -2.0 |
| Nov | 4.6 | 0.1 |
| Oct | 0.4 | 0.5 |
| Sep | 5.5 | -2.2 |
| Aug | 11.3 | -0.3 |
| Jul | 6.5 | 3.0 |
| Jun | 0.0 | -1.0 |
| May | 18.9 | 1.0 |
| Apr | 5.8 | -0.3 |
| Mar | 10.3 | 0.9 |
| Feb | 16.4 | 1.2 |
| Jan | 16.0 | 0.7 |
| Dec 2010 | 14.2 | |
| Dec 2009 | -2.3 | |
| Dec 2008 | -7.3 | |
| Dec 2007 | -0.1 | |
| Dec 2006 | 2.5 | |
| Dec 2005 | 4.9 | |
| Dec 2004 | 5.3 | |
| Dec 2003 | 5.1 | |
| Dec 2002 | 2.0 | |
| Average ∆% 2003-2006 | 4.4 |
Source: Statistiche Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
Table VE-2 provides monthly percentage changes of the German production industries index by components from Oct 2011 to May 2012. There were three sharp declines in the monthly production industries of 2.2 percent in Sep 2011, 2.0 percent in Dec and 2.1 percent in Apr 2012 with much milder recoveries in the other months. The declines of investment or capital goods were quite sharp with 4.0 percent in Sep 2011 and 3.7 percent in Apr 2012 with recovery by 1.7 percent in May 2012. Durable goods and nondurable goods fell in five of the nine months from Sep 2011 to May 2012.
Table VE-2, Germany, Production Industries, Industry and Components, Month ∆%
| May | Apr | Mar | Feb | Jan | Dec | Nov | Oct | |
| Production | 1.6 | -2.1 | 2.2 | -0.4 | 0.8 | -2.0 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| Industry | 1.8 | -2.3 | 1.1 | 0.2 | 0.6 | -1.5 | -0.3 | 0.5 |
| Mfg | 1.9 | -2.3 | 1.1 | 0.3 | 0.6 | -1.4 | -0.3 | 0.5 |
| Intermediate Goods | 1.0 | -0.3 | 0.2 | -0.1 | 0.9 | -1.8 | -0.3 | -0.2 |
| Investment | 1.7 | -3.7 | 1.6 | 1.0 | 0.7 | -1.4 | -0.2 | 1.4 |
| Durable Goods | 2.7 | -1.6 | 0.5 | -1.5 | 1.2 | -1.6 | -2.0 | 1.4 |
| Nondurable Goods | 4.0 | -3.8 | 2.6 | -1.2 | -0.6 | -0.7 | 0.0 | -0.2 |
| Energy | -1.6 | 2.4 | -2.0 | 6.7 | 1.1 | -6.8 | 1.6 | 1.5 |
Seasonally Calendar Adjusted
Source: Statistiche Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
Table VE-3 provides 12-month unadjusted percentage changes of industry and components in Germany. Although there are sharp fluctuations in the data there is suggestion of deceleration that would be expected from much higher earlier rates. The deceleration is quite evident in single-digit percentage changes from Sep 2011 to May 2012 relative to high double-digit percentage changes in Jan-Mar 2011. There are multiple negative 12-month percentage changes across many segments. Growth rates in the recovery from the global recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 were initially very vigorous in comparison with the growth rates before the contraction that are shown in the bottom part of Table VE-3.
Table VE-3, Germany, Industry and Components, 12-Month ∆% Unadjusted
| IND | MFG | INTG | INVG | DG | NDG | EN | |
| 2012 | |||||||
| May | -7.2 | -7.0 | 6.8 | -7.3 | -11.7 | -7.7 | 3.5 |
| Apr | -1.0 | -0.8 | -1.2 | 1.2 | -6.5 | -5.7 | 3.4 |
| Mar | -0.2 | -0.2 | -2.0 | 2.9 | -6.5 | -3.2 | -6.3 |
| Feb | 3.5 | 3.6 | 1.8 | 7.4 | -0.7 | -2.0 | 0.0 |
| Jan | 6.2 | 6.1 | 4.6 | 9.7 | 4.3 | 1.4 | -12.0 |
| 2011 | |||||||
| Dec | 1.4 | 1.4 | 2.5 | 1.0 | -0.4 | 0.2 | -16.4 |
| Nov | 4.9 | 5.1 | 3.9 | 7.9 | 1.9 | 0.0 | -4.0 |
| Oct | 1.1 | 1.2 | 0.4 | 3.6 | -2.7 | -2.8 | -7.2 |
| Sep | 6.4 | 6.5 | 6.4 | 8.9 | 3.6 | 0.2 | -6.3 |
| Aug | 12.8 | 12.6 | 10.8 | 20.2 | 4.5 | 1.2 | -3.5 |
| Jul | 8.0 | 8.1 | 6.5 | 13.1 | 7.7 | -0.5 | -8.1 |
| Jun | 0.9 | 0.9 | 1.6 | 2.0 | -10.5 | -2.0 | -7.4 |
| May | 21.4 | 21.4 | 17.7 | 28.3 | 21.7 | 13.4 | -12.0 |
| Apr | 7.4 | 7.5 | 5.9 | 11.1 | 4.9 | 2.2 | -8.2 |
| Mar | 10.7 | 10.9 | 10.0 | 14.9 | 8.5 | 2.1 | 1.2 |
| Feb | 16.8 | 17.0 | 16.1 | 22.4 | 11.0 | 6.1 | -2.2 |
| Jan | 16.8 | 17.1 | 16.7 | 23.2 | 11.2 | 4.2 | -1.8 |
| 2010 | |||||||
| Dec | 17.5 | 17.6 | 14.5 | 26.3 | 9.1 | 2.9 | 4.8 |
| Nov | 13.8 | 13.8 | 13.1 | 19.0 | 7.9 | 3.6 | 2.9 |
| Oct | 9.9 | 10.1 | 10.1 | 13.9 | 6.5 | 0.9 | 0.2 |
| Sep | 9.5 | 9.3 | 12.1 | 10.0 | 7.9 | 1.7 | -2.4 |
| Aug | 17.2 | 17.2 | 19.0 | 20.3 | 19.5 | 6.9 | -2.1 |
| Jul | 9.1 | 8.8 | 12.7 | 8.7 | 7.2 | 0.9 | -0.2 |
| Jun | 16.2 | 16.1 | 20.5 | 16.0 | 20.5 | 5.3 | -2.5 |
| May | 13.3 | 13.3 | 20.2 | 11.6 | 10.7 | 1.7 | 12.8 |
| Apr | 14.9 | 14.8 | 21.8 | 15.3 | 8.5 | 0.0 | 9.9 |
| Mar | 14.2 | 14.5 | 20.4 | 11.7 | 11.8 | 6.4 | 7.2 |
| Feb | 7.1 | 7.5 | 10.8 | 7.0 | 7.4 | -1.2 | 5.4 |
| Jan | 0.6 | 0.9 | 6.7 | -3.4 | -0.4 | -3.9 | 3.3 |
| Dec 2010 | 17.5 | 17.6 | 14.5 | 26.3 | 9.1 | 2.9 | 4.8 |
| Dec 2009 | -3.3 | -3.2 | 3.3 | -9.9 | -0.1 | 1.1 | 3.8 |
| Dec 2008 | -7.6 | -7.4 | -14.4 | -5.5 | -11.2 | 3.7 | -9.0 |
| Dec 2007 | 0.1 | -0.3 | -0.6 | 2.5 | -10.0 | -2.6 | 1.7 |
| Dec 2006 | 3.1 | 3.1 | 5.2 | 2.3 | 8.7 | -1.0 | -5.4 |
| Dec 2005 | 5.8 | 5.8 | 3.5 | 8.9 | 3.2 | 2.2 | 0.6 |
| Dec 2004 | 5.2 | 5.6 | 7.6 | 3.4 | 0.9 | 5.7 | 9.6 |
| Dec 2003 | 5.5 | 5.3 | 5.6 | 6.3 | 1.6 | 4.6 | 0.3 |
| Dec 2002 | 3.7 | 3.4 | 5.3 | 3.4 | -5.9 | 2.2 | -2.6 |
Note: IND: Industry; MFG: Manufacturing; INTG: Intermediate Goods; INVG: Investment Goods; DG: Durable Goods; NDG: Nondurable Goods; EN: Energy
Source: Statistiche Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
Broader perspective since 2002 is provided by Chart VE-1 of the Statistiche Bundesamt Deutschland, Federal Statistical Agency of Germany. The index rises by more than one third between 2003 and 2008 with sharp fluctuations and then collapses during the global recession in 2008. Recovery has been in a steep upward trajectory that has recovered at the more recent peaks the losses during the contraction. Recovery was reversed by the drop in Dec with strong rebound into 2012 and another sharp drop in Apr 2012 with recovery in May 2012.
Chart VE-1, Germany, Production Industries, Not Adjusted, 2005=100
Source: Statistiche Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
More detail is provided by Chart VE-2 of the Statistiche Bundesamt Deutschland, or Federal Statistical Agency of Germany, with the unadjusted production industries index and trend from 2007 to 2012. There could be some flattening in recent months as depicted by trend.
Chart VE-2, Germany, Production Index, Production Industries, Not Adjusted Index and Trend, 2005=100
Source: Statistiche Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
Table VE-4 provides month and 12-month rates of growth of manufacturing in Germany in 2011 from Jan 2011 to May 2012. There are fluctuations in both monthly rates and in the past 12 months. Recovery is strong in Jan-Mar 2012 with cumulative growth of 2.1 percent at the high annual equivalent rate of 8.7 percent but the drop in Apr 2012 of 2.3 percent results in decline of 0.2 percent in the first four months of 2012 that pulls down the 12-month rate of Apr 2012 to minus 0.8 percent. Growth of 1.9 percent in May 2012 is insufficient to prevent decline of 7.0 percent in 12 months because production was quite strong in the first part of 2011.
Table VE-4, Germany, Manufacturing Month and 12-Month ∆%
| 12-Month ∆% NSA | Month ∆% SA and Calendar Adjusted | |
| May 2012 | -7.0 | 1.9 |
| Apr | -0.8 | -2.3 |
| Mar | -0.2 | 1.1 |
| Feb | 3.6 | 0.3 |
| Jan | 6.1 | 0.7 |
| Dec 2011 | 1.4 | -1.4 |
| Nov | 5.1 | -0.3 |
| Oct | 1.2 | 0.5 |
| Sep | 6.5 | -2.3 |
| Aug | 12.6 | -0.3 |
| Jul | 8.1 | 3.2 |
| Jun | 0.9 | -1.1 |
| May | 21.4 | 1.4 |
| Apr | 7.5 | 0.4 |
| Mar | 10.9 | 0.7 |
| Feb | 17.0 | 1.4 |
| Jan | 17.1 | -0.6 |
| Dec | 17.6 | 1.9 |
Source: Statistiche Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
Chart VE-3 of the Statistiche Bundesamt Deutschland, or Federal Statistical Office of Germany, provides the manufacturing index of Germany from 2007 to 2012. Manufacturing was already flattening in 2007 and fell sharply in 2008 to the beginning of 2010. Manufacturing grew sharply in the initial phase of recovery but has flattened in recent months as revealed by the trend.
Chart VE-3, Germany, Manufacturing Index, Not Adjusted Index and Trend, 2005=100
Source: Statistiche Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
Several tables and charts facilitate analysis of machinery orders in Germany. Table VE-5 reveals strong fluctuations in an evident deceleration of total orders for industry of Germany. The same behavior is observed for total, foreign and domestic orders with decline in 12-month rates from two-digit levels to single digits and some negative changes. An important aspect of Germany is that the bulk of orders is domestic or from other European countries while foreign orders have been growing rapidly. Total orders increased 0.6 percent in May 2012 with decrease of 1.3 percent in domestic orders and sharp compensatory increase of 2.3 percent of foreign orders. In contrast, there was weakness in Apr 2012 with decreases of total orders by 1.4 percent and foreign orders by 3.1 percent while domestic orders increased 1.3 percent. As in other countries, data on orders for manufacturing are highly volatile. All 12-month percentage changes from Jan 2012 to May 2012 in Table VE-5 are negative largely because of the unusual strength of the Germany economy in the beginning of 2011.
Table VE-5, Germany, Volume of Orders Received in Manufacturing, Total, Domestic and Foreign, ∆%
| Total | Total | Foreign 12 M | Foreign M | Home | Home | |
| 2012 | ||||||
| May | -10.6 | 0.6 | -3.3 | 2.3 | -18.3 | -1.3 |
| Apr | -3.4 | -1.4 | -4.0 | -3.1 | -2.5 | 0.6 |
| Mar | -2.0 | 3.0 | -0.9 | 4.4 | -3.3 | 1.3 |
| Feb | -4.5 | 0.6 | -4.9 | 1.7 | -3.9 | -0.8 |
| Jan | -3.1 | -1.4 | -5.7 | -3.8 | 0.1 | 1.7 |
| 2011 | ||||||
| Dec | -0.2 | 0.7 | -0.8 | 3.7 | 0.6 | -2.8 |
| Nov | -4.2 | -2.8 | -7.6 | -4.4 | 0.0 | -0.7 |
| Oct | 0.6 | 2.7 | 2.2 | 4.7 | -1.3 | 0.5 |
| Sep | 2.4 | -4.6 | 1.2 | -6.2 | 3.8 | -2.7 |
| Aug | 6.8 | -0.4 | 4.3 | 0.3 | 10.1 | -1.3 |
| Jul | 5.6 | -3.2 | 5.7 | -7.5 | 5.6 | 2.6 |
| Jun | 3.8 | 0.8 | 8.0 | 10.8 | -1.6 | -10.0 |
| May | 22.7 | 2.8 | 16.2 | -3.3 | 30.2 | 10.2 |
| Apr | 6.9 | 1.8 | 9.9 | 1.7 | 3.4 | 1.8 |
| Mar | 9.1 | -2.8 | 11.9 | -2.3 | 5.8 | -3.2 |
| Feb | 21.5 | 0.7 | 24.8 | -0.3 | 17.8 | 1.9 |
| Jan | 22.4 | 4.2 | 26.5 | 3.4 | 17.6 | 5.5 |
| 2010 | ||||||
| Dec | 22.2 | -3.3 | 27.3 | -3.5 | 15.8 | -3.2 |
| Nov | 21.5 | 5.6 | 26.8 | 8.8 | 15.6 | 1.8 |
| Oct | 14.1 | 1.3 | 17.7 | 0.9 | 10.4 | 1.8 |
| Sep | 13.9 | -2.8 | 16.0 | -5.3 | 11.6 | 0.4 |
| Aug | 23.5 | 3.5 | 31.9 | 6.1 | 14.4 | 0.3 |
| Jul | 14.2 | -2.2 | 21.7 | -3.2 | 6.3 | -1.2 |
| Jun | 28.5 | 3.9 | 32.0 | 6.3 | 24.3 | 1.2 |
| May | 24.4 | 0.1 | 28.9 | 0.3 | 19.9 | -0.1 |
| Apr | 29.3 | 2.2 | 33.0 | 2.1 | 25.2 | 2.2 |
| Mar | 29.4 | 6.0 | 32.3 | 6.9 | 26.4 | 5.0 |
| Feb | 23.4 | -0.3 | 27.6 | -0.2 | 18.6 | -0.4 |
| Jan | 16.7 | 4.5 | 23.6 | 4.2 | 9.7 | 4.8 |
| Dec 2009 | 9.2 | -2.4 | 10.6 | -2.7 | 7.4 | -1.9 |
| Dec 2008 | -28.2 | -7.1 | -31.5 | -9.7 | -23.7 | -4.1 |
| Dec 2007 | 7.1 | -1.8 | 9.1 | -2.9 | 4.5 | -0.6 |
| Dec 2006 | 2.9 | 0.4 | 3.4 | 0.3 | 2.2 | 0.5 |
| Dec 2005 | 4.9 | -0.5 | 10.5 | -0.8 | -1.5 | 0.1 |
| Dec 2004 | 12.7 | 6.6 | 12.9 | 8.4 | 12.7 | 4.9 |
| Dec 2003 | 10.7 | 2.4 | 16.4 | 5.4 | 5.1 | -0.8 |
| Dec 2002 | -0.2 | -3.4 | -0.8 | -6.6 | 0.2 | -0.3 |
| Average ∆% 2003-2007 | 7.6 | 10.4 | 4.5 | |||
| Average ∆% 2003-2011 | 3.6 | 5.1 | 1.9 |
Notes: AE: Annual Equivalent; M: Month; M: Calendar and seasonally-adjusted; 12 M: Non-adjusted
Source: Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
Orders for investment goods of Germany are shown in Table VE-6. Total investment goods orders increased 0.2 percent in May 2012 with foreign orders increasing 1.6 percent and domestic orders decreasing 2.0 percent. There has been evident deceleration from 2010 and early 2011 with growth rates falling from two digit levels to single digits and multiple negative changes. An important aspect of Germany’s economy shown in Tables VE-5 and VE-6 is the success in increasing the competitiveness of its economic activities as shown by rapid growth of orders for industry after the recession of 2001 in the period before the global recession beginning in late 2007. Germany adopted fiscal and labor market reforms to increase productivity.
Table VE-6, Germany, Volume of Orders Received of Capital Goods Industries, Total, Foreign and Domestic, ∆%
| Total 12 M | Total M | Foreign 12 M | Foreign M | Domestic 12 M | Domestic M | |
| 2012 | ||||||
| May | -11.0 | 0.2 | -1.9 | 1.6 | -22.9 | -2.0 |
| Apr | -2.3 | -2.9 | -3.7 | -5.2 | 0.0 | 1.1 |
| Mar | 1.9 | 5.8 | 3.8 | 9.8 | -1.1 | -0.2 |
| Feb | -5.9 | 1.3 | -7.4 | 1.0 | -3.6 | 1.8 |
| Jan | -3.6 | -4.4 | -6.0 | -5.2 | 0.6 | -3.2 |
| 2011 | ||||||
| Dec | 1.6 | 2.8 | 0.5 | 4.0 | 3.5 | 1.0 |
| Nov | -5.9 | -3.6 | -9.4 | -6.2 | -0.1 | 0.6 |
| Oct | 3.6 | 5.0 | 7.5 | 7.9 | -2.3 | 0.6 |
| Sep | 2.9 | -5.5 | 1.8 | -6.9 | 4.9 | -3.3 |
| Aug | 6.3 | 0.6 | 3.5 | 1.8 | 11.1 | -1.2 |
| Jul | 7.7 | -8.1 | 6.9 | -13.7 | 8.9 | 2.0 |
| Jun | 8.9 | 3.4 | 13.6 | 17.5 | 1.0 | -15.1 |
| May | 26.8 | 4.4 | 18.0 | -4.6 | 40.3 | 19.1 |
| Apr | 11.3 | 3.1 | 14.7 | 3.8 | 6.2 | 1.8 |
| Mar | 11.0 | -5.0 | 13.7 | -4.1 | 7.0 | -6.4 |
| Feb | 29.4 | 2.5 | 33.1 | 1.2 | 23.9 | 4.8 |
| Jan | 26.4 | 3.2 | 32.4 | 3.2 | 17.5 | 2.9 |
| 2010 | ||||||
| Dec | 27.3 | -4.9 | 31.0 | -6.2 | 21.3 | -2.7 |
| Nov | 30.1 | 9.4 | 35.9 | 14.3 | 21.5 | 2.2 |
| Oct | 20.6 | 1.2 | 23.9 | -0.6 | 16.0 | 4.1 |
| Sep | 18.1 | -4.6 | 20.4 | -7.2 | 14.6 | -0.1 |
| Aug | 29.3 | 6.8 | 42.8 | 9.7 | 12.0 | 2.3 |
| Jul | 14.1 | -4.7 | 28.4 | -6.3 | -2.3 | -2.1 |
| Jun | 33.5 | 6.4 | 41.3 | 10.3 | 22.2 | 0.4 |
| May | 25.9 | 1.3 | 35.6 | 0.6 | 13.6 | 2.6 |
| Apr | 30.1 | 1.3 | 40.1 | 1.7 | 17.4 | 0.6 |
| Mar | 26.2 | 8.4 | 33.8 | 10.2 | 16.1 | 5.6 |
| Feb | 20.3 | -1.3 | 30.3 | -0.3 | 8.1 | -2.5 |
| Jan | 16.9 | 4.3 | 29.5 | 2.2 | 2.5 | 7.2 |
| Dec 2009 | 8.1 | -1.4 | 13.6 | -1.6 | 0.5 | -1.2 |
| Dec 2008 | -32.2 | -7.2 | -36.7 | -9.9 | -24.4 | -3.5 |
| Dec 2007 | 9.6 | -1.2 | 11.6 | -3.3 | 6.3 | 2.2 |
| Dec 2006 | 3.6 | 2.2 | 3.8 | 2.7 | 3.1 | 1.4 |
| Dec 2005 | 1.9 | -1.9 | 9.8 | -2.1 | -8.5 | -1.6 |
| Dec 2004 | 19.4 | 11.2 | 18.6 | 12.2 | 20.5 | 9.8 |
| Dec 2003 | 11.7 | 2.1 | 17.2 | 5.0 | 5.4 | -1.6 |
| Dec 2002 | -2.8 | -4.3 | -3.7 | -8.1 | -1.8 | 0.2 |
| Average ∆% 2003-2007 | 9.1 | 12.1 | 4.9 | |||
| Average ∆% 2003-2011 | 3.4 | 4.4 | 2.1 |
Notes: AE: Annual Equivalent; M: Month; M: Calendar and seasonally-adjusted; 12 M: Non-adjusted
Source: Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
Chart VE-4 of the German Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland shows the sharp upward trend of total orders in manufacturing before the global recession. There is also an obvious upward trend in the recovery from the recession with Germany’s economy being among the most dynamic in the advanced economies until the slowdown beginning in the final months of 2011 and what could be stationary series from late 2011 into 2012.
Chart VE-4, Germany, Volume of Total Orders in Manufacturing, Non-Adjusted, 2005=100
Source: Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
Chart VE-5 of the German Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland provides unadjusted volume of total orders in manufacturing and a trend curve. The final segment on the right could be the beginning of flattening or even decline of the trend curve but it is early to reach conclusions.
Chart VE-5, Germany, Volume of Total Orders in Manufacturing and Trend, Non-Adjusted, 2005=100
Source: Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
VF France. The Markit France Composite Output Index, combining services and manufacturing with close association with French GDP, increased from 44.6 in May to 47.3 in Jun, indicating contraction of private sector activity at a more moderate rate (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9783). Jack Kennedy, Senior Economist at Markit and author of the France Services PMI®, finds that weak services and manufacturing survey data suggest contraction of GDP in IIQ2012 after no growth in IQ2012 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9783).The Markit France Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index® increased to 45.2 in Jun from 44.7 in May, which was the sharpest decline of the manufacturing economy in three years (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9727). Jack Kennedy, Senior Economist at Markit and author of the France Manufacturing PMI®, finds continuing deterioration in manufacturing with IIQ2012 being the weakest quarter for French manufacturing in three years (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9727). Table FR provides the country data table for France.
Table FR, France, Economic Indicators
| CPI | May month ∆% -0.1 |
| PPI | May month ∆%: -1.1 Blog 7/2/12 |
| GDP Growth | IQ2012/IVQ2011 ∆%: 0.0 |
| Industrial Production | Apr SA ∆%: |
| Consumer Spending | May Manufactured Goods |
| Employment | IQ2012 Unemployed 2.746 million |
| Trade Balance | May Exports ∆%: month 1.3, 12 months 7.8 Apr Imports ∆%: month 0.1, 12 months 3.2 Blog 7/8/12 |
| Confidence Indicators | Historical averages 100 Jun Mfg Business Climate 92 Blog 6/24/12 |
Links to blog comments in Table FR:
7/2/12 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/07/mediocre-economic-growth-united-states_03.html
6/24/12 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/recovery-without-hiring-continuance-of_24.html
6/17/12 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/05/world-financial-turbulence-global_27.html
6/10/12 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/rules versus-discretionary-authorities_10.html
France has been running a trade deficit fluctuating around €6,000 million, as shown in Table VF-1. Exports increased 1.3 percent in Apr while imports increased 0.1 percent, resulting in decrease of the trade deficit from revised €5768 million in Apr to €5325 million in May.
Table VF-1, France, Exports, Imports and Trade Balance, € Millions
| Exports | Imports | Trade Balance | |
| May 2012 | 37,440 | 42,765 | -5,325 |
| Apr | 36,969 | 42,737 | -5,768 |
| Mar | 36,316 | 41,876 | -5,560 |
| Feb | 36,945 | 43,355 | -6,410 |
| Jan | 36,728 | 43,127 | -5,399 |
| Dec 2011 | 36,143 | 41,428 | -5,285 |
| Nov | 37,122 | 41,504 | -4,382 |
| Oct | 35,813 | 41,711 | -5,898 |
| Sep | 35,677 | 42,091 | -6,414 |
| Aug | 37,576 | 42,158 | -4,582 |
| Jul | 34,938 | 41,436 | -6,498 |
| Jun | 34,746 | 40,065 | -5,319 |
| May | 34,732 | 41,458 | -6,726 |
| Apr | 34,558 | 41,445 | -6,887 |
| Mar | 35,233 | 41,394 | -6,161 |
| Feb | 34,716 | 41,086 | -6,370 |
| Jan | 34,320 | 40,879 | -6,559 |
| Dec 2010 | 33,975 | 39,496 | -5,521 |
Source: http://lekiosque.finances.gouv.fr/AppChiffre/Portail_default.asp
Monthly and 12-month rates of growth of exports and imports of France are provided in Table VF-2. Exports increased 1.3 percent in Apr and 7.8 percent in the 12 months ending in May. Imports increased 0.1 percent in May and 3.2 percent in12 months. Growth of exports and imports has fluctuated in 2011 as a result of price surges of commodities and raw materials.
Table VF-2, France, Exports and Imports, Month and 12-Month ∆%
| Exports | Exports | Imports | Imports 12-Month ∆% | |
| May 2012 | 1.3 | 7.8 | 0.1 | 3.2 |
| Apr | 1.8 | 7.0 | 2.1 | 3.1 |
| Mar | -1.7 | 3.1 | -3.4 | 1.2 |
| Feb | 0.6 | 6.4 | 2.9 | 5.5 |
| Jan | 1.6 | 7.0 | 1.7 | 3.1 |
| Dec 2011 | -2.6 | 6.4 | -0.2 | 4.9 |
| Nov | 3.7 | 7.4 | -0.5 | 4.6 |
| Oct | 0.4 | 8.6 | -0.9 | 14.3 |
| Sep | -5.1 | 7.6 | -0.2 | 10.8 |
| Aug | 7.6 | 10.8 | 1.7 | 8.6 |
| Jul | 0.6 | 1.7 | 3.4 | 8.8 |
| Jun | 0.0 | 3.5 | -3.4 | 8.2 |
| May | 0.5 | 15.5 | 0.0 | 16.4 |
| Apr | -1.9 | 7.7 | 0.1 | 14.4 |
| Mar | 1.5 | 11.6 | 0.7 | 15.0 |
| Feb | 1.2 | 13.9 | 0.5 | 21.8 |
| Jan | 1.0 | 13.8 | 3.5 | 20.4 |
| Dec 2011 | 6.4 | 4.9 | ||
| Dec 2010 | 14.4 | 15.0 | ||
| Dec 2009 | -9.8 | -1.8 | ||
| Dec 2008 | -7.3 | -11.3 | ||
| Dec 2007 | 6.1 | 8.3 | ||
| Dec 2006 | 7.2 | 6.8 | ||
| Dec 2005 | 11.3 | 15.1 | ||
| Dec 2004 | -3.5 | 6.0 | ||
| Dec 2003 | 7.1 | 1.6 |
Source: http://lekiosque.finances.gouv.fr/AppChiffre/Portail_default.asp
Annual data for France’s exports, imports and trade balance are provided in Table VF-3. France’s trade balance deteriorated sharply from 2007 to 2011 with the deficit increasing from €42,494 million in 2007 to €70,799 million in 2011. Annual growth rates of exports have not been sufficiently high to compensate for growth of imports driven in part by commodity price increases.
Table VF-3, France, Exports, Imports and Balance Year € Millions and ∆%
| Exports € Millions | ∆% | Imports € Millions | ∆% | Balance € Millions | |
| May 2012 12 Months | 432,118 | 499,677 | -67,559 | ||
| Year | |||||
| 2011 | 427,061 | 8.3 | 497,860 | 11.5 | -70,799 |
| 2010 | 394,269 | 13.8 | 446,536 | 14.0 | -52,267 |
| 2009 | 346,340 | -17.1 | 391,667 | -17.3 | -45,327 |
| 2008 | 417,634 | 2.7 | 473,853 | 5.5 | -56,219 |
| 2007 | 406,487 | 3.0 | 448,981 | 5.8 | -42,494 |
| 2006 | 394,621 | 9.5 | 424,549 | 10.4 | -29,928 |
| 2005 | 360,376 | 4.4 | 384,588 | 9.6 | -24,212 |
| 2004 | 345,256 | 5.4 | 350,996 | 7.0 | -5,740 |
| 2003 | 327,653 | 327,884 | -231 |
Source: http://lekiosque.finances.gouv.fr/AppChiffre/Portail_default.asp
VG Italy. The Markit/ADACI Business Activity Index increased from 42.8 in May to 43.1 in Jun, indicating sharp contraction of output of Italy’s services sector in 13 consecutive months of contraction (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9785). Phil Smith, economist at Markit and author of the Italy Services PMI®, finds that the combined manufacturing and services indexes suggest continuing recession in IIQ2012 at the sharpest rate since IIQ2009 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9785). The Markit/ADACI Purchasing Managers’ Index® (PMI®), fell slightly from 44.8 in May to 44.6 in Jun for nine consecutive months of contraction of Italy’s manufacturing quite sharp relative to the history of the index (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9744). Phil Smith, economist at Markit and author of the Italian Manufacturing PMI®, finds continuing sharp contraction of new orders of manufacturing in Italy and manufacturing output lower than in the first quarter when it fell at a quarterly rate of 2 percent (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9744). Table IT provides the country data table for Italy.
Table IT, Italy, Economic Indicators
| Consumer Price Index | Jun month ∆%: 0.3 |
| Producer Price Index | May month ∆%: -0.3 Blog 7/2/12 |
| GDP Growth | IQ2012/IVQ2011 SA ∆%: minus 0.8 |
| Labor Report | Apr 2012 Participation rate 63.4% Employment ratio 57.0% Unemployment rate 10.2% Blog 6/3/12 |
| Industrial Production | Apr month ∆%: -1.9 |
| Retail Sales | Apr month ∆%: -1.6 Apr 12-month ∆%: -6.9 Blog 7/2/12 |
| Business Confidence | Mfg Jun 88.9, Feb 90.9 Construction Jun 85.6, Feb 84.6 Blog 7/2/12 |
| Consumer Confidence | Consumer Confidence May 86.5, Apr 88.8 Economy May 64.4, Apr 71.6 Blog 5/27/12 |
| Trade Balance | Balance Apr SA -€36 million versus Mar +€714 |
Links to blog comments in Table IT:
7/2/12 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/07/mediocre-economic-growth-united-states_03.html
6/17/12 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/05/world-financial-turbulence-global_27.html
6/10/12 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/rules-versus-discretionary-authorities_10.html
6/3/12 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/mediocre-recovery-without-jobs_04.html
5/27/12 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/05/world-financial-turbulence-global_27.html
VH United Kingdom. Revised annual data in Table VH-UK show the strong impact of the global recession in the UK with decline of GDP of revised 4.0 percent in 2009 after dropping revised 1.0 percent in 2008. Recovery of 1.8 percent in 2010 is relatively low compared to annual growth rates in 2007 and earlier years. Growth was only 0.8 percent in 2011. The bottom part of Table VH-UK provides average growth rates of UK GDP since 1948. The UK economy grew at 2.7 percent on average between 1948 and 2011, which is relatively high for an advanced economy. The growth rate of GDP between 2000 and 2007 is higher at 3.0 percent. Growth in the current cyclical expansion has been only at 1.3 percent as advanced economies struggle with weak internal demand and world trade.
Table VH-UK, UK, Gross Domestic Product, ∆%
| ∆% on Prior Year | |
| 1998 | 3.5 |
| 1999 | 3.2 |
| 2000 | 4.2 |
| 2001 | 2.9 |
| 2002 | 2.4 |
| 2003 | 3.8 |
| 2004 | 2.9 |
| 2005 | 2.8 |
| 2006 | 2.6 |
| 2007 | 3.6 |
| 2008 | -1.0 |
| 2009 | -4.0 |
| 2010 | 1.8 |
| 2011 | 0.8 |
| Average ∆% per Year | |
| 1948-2011 | 2.7 |
| 1948-1959 | 2.9 |
| 1960-1969 | 3.3 |
| 1970-1979 | 2.5 |
| 1980-1989 | 3.2 |
| 1990-1999 | 2.6 |
| 2000-2011 | 1.7 |
| 2000-2007 | 3.0 |
| 2009-2011 | 1.3 |
Source: UK Office for National Statistics
http://www.ons.gov.uk/ons/rel/naa2/quarterly-national-accounts/q1-2012/index.html
http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/recovery-without-hiring-continuance-of_24.html
The Business Activity Index of the Markit/CIPS UK Services PMI® fell from 53.3 in May to 51.3 in Jun with growth during 18 months but at the weakest level since Oct 2011 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9784). Chris Williamson, Chief Economist at Markit, finds that services grew only around 0.2 percent in IIQ2012, stagnating at the margin in Jun (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9784). The Markit/CIPS UK Manufacturing Purchasing Managers’ Index® (PMI®) increased from the three-year low of 45.9 in May to 48.6 in Jun with the average quarterly reading of 48.2 being the lowest since IIQ2009 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9748). The decline of 4.3 points in May is the second sharpest decline in the history of 20 years of the index. Rob Dobson, Senior Economist at Markit and author of the Markit/CIPS Manufacturing PMI®, finds significant volatility from factors such as the jubilee holidays with production increase in Jun raising more favorable views but manufacturing output probably falling by around 0.5 percent in IIQ2012 (http://www.markiteconomics.com/MarkitFiles/Pages/ViewPressRelease.aspx?ID=9748).
Table UK, UK Economic Indicators
| CPI | May month ∆%: -0.1 |
| Output/Input Prices | Output Prices: |
| GDP Growth | IQ2012 prior quarter ∆% minus 0.3; year earlier same quarter ∆%: minus 0.2 |
| Industrial Production | Apr 2012/Apr 2011 NSA ∆%: Production Industries minus 1.0; Manufacturing minus 0.3 |
| Retail Sales | May month SA ∆%: +1.4 |
| Labor Market | Feb-Apr Unemployment Rate: 8.2%; Claimant Count 4.9%; Earnings Growth 1.4% |
| Trade Balance | Balance Apr minus ₤4421 million |
Links to blog comments in Table UK:
7/2/12 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/07/mediocre-economic-growth-united-states_03.html
6/24/12 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/recovery-without-hiring-continuance-of_24.html
6/17/12 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/05/world-financial-turbulence-global_27.html
VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets. The financial crisis and global recession were caused by interest rate and housing subsidies and affordability policies that encouraged high leverage and risks, low liquidity and unsound credit (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 157-66, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 217-27, International Financial Architecture (2005), 15-18, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 221-5, Globalization and the State Vol. II (2008b), 197-213, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 182-4). Several past comments of this blog elaborate on these arguments, among which: http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/07/causes-of-2007-creditdollar-crisis.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/professor-mckinnons-bubble-economy.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/world-inflation-quantitative-easing.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/treasury-yields-valuation-of-risk.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/11/quantitative-easing-theory-evidence-and.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/12/is-fed-printing-money-what-are.html
Table VI-1 shows the phenomenal impulse to valuations of risk financial assets originating in the initial shock of near zero interest rates in 2003-2004 with the fed funds rate at 1 percent, in fear of deflation that never materialized, and quantitative easing in the form of suspension of the auction of 30-year Treasury bonds to lower mortgage rates. World financial markets were dominated by monetary and housing policies in the US. Between 2002 and 2008, the DJ UBS Commodity Index rose 165.5 percent largely because of unconventional monetary policy encouraging carry trades from low US interest rates to long leveraged positions in commodities, exchange rates and other risk financial assets. The charts of risk financial assets show sharp increase in valuations leading to the financial crisis and then profound drops that are captured in Table VI-1 by percentage changes of peaks and troughs. The first round of quantitative easing and near zero interest rates depreciated the dollar relative to the euro by 39.3 percent between 2003 and 2008, with revaluation of the dollar by 25.1 percent from 2008 to 2010 in the flight to dollar-denominated assets in fear of world financial risks and then devaluation of the dollar of 3.1 percent by Fri Jul 6, 2012. Dollar devaluation is a major vehicle of monetary policy in reducing the output gap that is implemented in the probably erroneous belief that devaluation will not accelerate inflation, misallocating resources toward less productive economic activities and disrupting financial markets. The last row of Table VI-1 shows CPI inflation in the US rising from 1.9 percent in 2003 to 4.1 percent in 2007 even as monetary policy increased the fed funds rate from 1 percent in Jun 2004 to 5.25 percent in Jun 2006.
Table VI-1, Volatility of Assets
| DJIA | 10/08/02-10/01/07 | 10/01/07-3/4/09 | 3/4/09- 4/6/10 | |
| ∆% | 87.8 | -51.2 | 60.3 | |
| NYSE Financial | 1/15/04- 6/13/07 | 6/13/07- 3/4/09 | 3/4/09- 4/16/07 | |
| ∆% | 42.3 | -75.9 | 121.1 | |
| Shanghai Composite | 6/10/05- 10/15/07 | 10/15/07- 10/30/08 | 10/30/08- 7/30/09 | |
| ∆% | 444.2 | -70.8 | 85.3 | |
| STOXX EUROPE 50 | 3/10/03- 7/25/07 | 7/25/07- 3/9/09 | 3/9/09- 4/21/10 | |
| ∆% | 93.5 | -57.9 | 64.3 | |
| UBS Com. | 1/23/02- 7/1/08 | 7/1/08- 2/23/09 | 2/23/09- 1/6/10 | |
| ∆% | 165.5 | -56.4 | 41.4 | |
| 10-Year Treasury | 6/10/03 | 6/12/07 | 12/31/08 | 4/5/10 |
| % | 3.112 | 5.297 | 2.247 | 3.986 |
| USD/EUR | 6/26/03 | 7/14/08 | 6/07/10 | 7/6/2012 |
| Rate | 1.1423 | 1.5914 | 1.192 | 1.2288 |
| CNY/USD | 01/03 | 07/21 | 7/15 | 7/6/ 2012 |
| Rate | 8.2798 | 8.2765 | 6.8211 | 6.3658 |
| New House | 1963 | 1977 | 2005 | 2009 |
| Sales 1000s | 560 | 819 | 1283 | 375 |
| New House | 2000 | 2007 | 2009 | 2010 |
| Median Price $1000 | 169 | 247 | 217 | 203 |
| 2003 | 2005 | 2007 | 2010 | |
| CPI | 1.9 | 3.4 | 4.1 | 1.5 |
Sources: http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_hps_marketdata
http://www.census.gov/const/www/newressalesindex_excel.html
http://federalreserve.gov/releases/h10/Hist/dat00_eu.htm
ftp://ftp.bls.gov/pub/special.requests/cpi/cpiai.txt
Table VI-2 extracts four rows of Table VI-I with the Dollar/Euro (USD/EUR) exchange rate and Chinese Yuan/Dollar (CNY/USD) exchange rate that reveal pursuit of exchange rate policies resulting from monetary policy in the US and capital control/exchange rate policy in China. The ultimate intentions are the same: promoting internal economic activity at the expense of the rest of the world. The easy money policy of the US was deliberately or not but effectively to devalue the dollar from USD 1.1423/EUR on Jun 26, 2003 to USD 1.5914/EUR on Jul 14, 2008, or by 39.3 percent. The flight into dollar assets after the global recession caused revaluation to USD 1.192/EUR on Jun 7, 2010, or by 25.1 percent. After the temporary interruption of the sovereign risk issues in Europe from Apr to Jul, 2010, shown in Table VI-4 below, the dollar has devalued again to USD 1.2288/EUR on Jul 6, 2012 or by 3.1 percent {[(1.2288/1.192)-1]100 = 3.1%}. Yellen (2011AS, 6) admits that Fed monetary policy results in dollar devaluation with the objective of increasing net exports, which was the policy that Joan Robinson (1947) labeled as “beggar-my-neighbor” remedies for unemployment. Risk aversion erodes devaluation of the dollar. China fixed the CNY to the dollar for a long period at a highly undervalued level of around CNY 8.2765/USD subsequently revaluing to CNY 6.8211/USD until Jun 7, 2010, or by 17.6 percent and after fixing it again to the dollar, revalued to CNY 6.3658/USD on Fri Jul 6, 2012, or by an additional 6.7 percent, for cumulative revaluation of 23.1 percent.
Table VI-2, Dollar/Euro (USD/EUR) Exchange Rate and Chinese Yuan/Dollar (CNY/USD) Exchange Rate
| USD/EUR | 12/26/03 | 7/14/08 | 6/07/10 | 7/6/ |
| Rate | 1.1423 | 1.5914 | 1.192 | 1.2288 |
| CNY/USD | 01/03 | 07/21 | 7/15 | 7/6/ 2012 |
| Rate | 8.2798 | 8.2765 | 6.8211 | 6.3658 |
| Weekly Rates | 6/15/2012 | 6/22/2012 | 6/29/2012 | 7/6/ 2012 |
| CNY/USD | 6.3678 | 6.3650 | 6.3552 | 6.3658 |
| ∆% from Earlier Week* | 0.1 | 0.0 | 0.2 | -0.2 |
*Negative sign is depreciation, positive sign is appreciation
Source:
http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/mdc_currencies.html?mod=mdc_topnav_2_3000
http://federalreserve.gov/releases/h10/Hist/dat00_ch.htm
The Dow Jones Newswires informs on Oct 15 that the premier of China Wen Jiabao announced that the Chinese yuan will not be further appreciated to prevent adverse effects on exports (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052970203914304576632790881396896.html?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection). Table VI-2A provides the CNY/USD rate from Oct 28, 2011 to Jun 29, 2012 in selected intervals. The CNY/USD revalued by 0.9 percent from Oct 28, 2012 to Apr 27, 2012. After depreciation of 0.5 percent in the week of Jun 5 and 0.1 percent in the week of Jun 8 but appreciation of 0.1 percent in the week of Jun 15 and no change in the week of Jun 22 but revaluation of 0.2 percent in the week of Jun 29 (see Table VI-2), the CNY has appreciated 0.1 percent relative to Oct 28, 2011, as shown in Table VI-2A. The CNY devalued by 0.2 percent relative to the USD in the week of Jul 6, 2012 such that, as shown in Table VI-2A, there is marginal devaluation of 0.1 percent on Jul 6, 2012 relative to Oct 28, 2011. Meanwhile, the Senate of the US is proceeding with a bill on China’s trade that could create a confrontation but may not be approved by the entire Congress. An important statement by the People’s Bank of China (PBC), China’s central bank, on Apr 14, 2012, announced the widening of the daily maximum band of fluctuation of the renminbi (RMB) yuan (http://www.pbc.gov.cn/publish/english/955/2012/20120414090756030448561/20120414090756030448561_.html):
“Along with the development of China’s foreign exchange market, the pricing and risk management capabilities of market participants are gradually strengthening. In order to meet market demands, promote price discovery, enhance the flexibility of RMB exchange rate in both directions, further improve the managed floating RMB exchange rate regime based on market supply and demand with reference to a basket of currencies, the People’s Bank of China has decided to enlarge the floating band of RMB’s trading prices against the US dollar and is hereby making a public announcement as follows:
Effective from April 16, 2012 onwards, the floating band of RMB’s trading prices against the US dollar in the inter-bank spot foreign exchange market is enlarged from 0.5 percent to 1 percent, i.e., on each business day, the trading prices of the RMB against the US dollar in the inter-bank spot foreign exchange market will fluctuate within a band of ±1 percent around the central parity released on the same day by the China Foreign Exchange Trade System. The spread between the RMB/USD selling and buying prices offered by the foreign exchange-designated banks to their customers shall not exceed 2 percent of the central parity, instead of 1 percent, while other provisions in the Circular of the PBC on Relevant Issues Managing the Trading Prices in the Inter-bank Foreign Exchange Market and Quoted Exchange Rates of Exchange-Designated Banks(PBC Document No.[2010]325) remain valid.
In view of the domestic and international economic and financial conditions, the People’s Bank of China will continue to fulfill its mandates in relation to the RMB exchange rate, keeping RMB exchange rate basically stable at an adaptive and equilibrium level based on market supply and demand with reference to a basket of currencies to preserve stability of the Chinese economy and financial markets.”
Table VI-2A, Renminbi Yuan US Dollar Rate
| CNY/USD | ∆% from 10/28/2011 | |
| 7/6/12 | 6.3658 | -0.1% |
| 6/29/12 | 6.3552 | 0.1 |
| 6/22/12 | 6.3650 | -0.1 |
| 6/15/12 | 6.3678 | -0.1 |
| 6/8/2012 | 6.3752 | -0.3 |
| 6/1/2012 | 6.3708 | -0.2 |
| 4/27/2012 | 6.3016 | 0.9 |
| 3/23/2012 | 6.3008 | 0.9 |
| 2/3/2012 | 6.3030 | 0.9 |
| 12/30/2011 | 6.2940 | 1.0 |
| 11/25/2011 | 6.3816 | -0.4 |
| 10/28/2011 | 6.3588 | - |
Source:
http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/mdc_currencies.html?mod=mdc_topnav_2_3000
http://federalreserve.gov/releases/h10/Hist/dat00_ch.htm
The database of the World Economic Outlook (WEO) of the IMF (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/index.aspx) is used to contract Table VI-3 with fiscal and current account imbalances projected for 2011 and 2015. The WEO finds the need to rebalance external and domestic demand (IMF 2011WEOSep xvii):
“Progress on this front has become even more important to sustain global growth. Some emerging market economies are contributing more domestic demand than is desirable (for example, several economies in Latin America); others are not contributing enough (for example, key economies in emerging Asia). The first set needs to restrain strong domestic demand by considerably reducing structural fiscal deficits and, in some cases, by further removing monetary accommodation. The second set of economies needs significant currency appreciation alongside structural reforms to reduce high surpluses of savings over investment. Such policies would help improve their resilience to shocks originating in the advanced economies as well as their medium-term growth potential.”
The IMF (2012WEOApr, XVII) explains decreasing importance of the issue of global imbalances as follows:
“The latest developments suggest that global current account imbalances are no longer expected to widen again, following their sharp reduction during the Great Recession. This is largely because the excessive consumption growth that characterized economies that ran large external deficits prior to the crisis has been wrung out and has not been offset by stronger consumption in surplus economies. Accordingly, the global economy has experienced a loss of demand and growth in all regions relative to the boom years just before the crisis. Rebalancing activity in key surplus economies toward higher consumption, supported by more market-determined exchange rates, would help strengthen their prospects as well as those of the rest of the world.”
Table VI-3, Fiscal Deficit, Current Account Deficit and Government Debt as % of GDP and 2011 Dollar GDP
| GDP 2011 | FD | CAD | Debt | FD%GDP | CAD%GDP | Debt | |
| US | 15094 | -7.3 | -3.1 | 80.3 | -2.3 | -3.2 | 88.3 |
| Japan | 5869 | -9.1 | 2.0 | 126.6 | -5.8 | 2.4 | 155.0 |
| UK | 2418 | -5.8 | -1.9 | 78.3 | -0.8 | -0.4 | 88.1 |
| Euro | 13115 | -1.6 | 0.3 | 68.4 | 1.1 | 1.2 | 71.3 |
| Ger | 3577 | 0.7 | 5.7 | 56.1 | 1.4 | 4.3 | 52.4 |
| France | 2776 | -2.9 | -2.2 | 80.4 | 0.3 | -0.8 | 83.8 |
| Italy | 2199 | 0.8 | -3.2 | 99.6 | 4.4 | -1.6 | 101.5 |
| Can | 1737 | -4.1 | -2.8 | 33.3 | -1.1 | -2.5 | 37.4 |
| China | 7298 | -1.2 | 2.7 | 25.8 | -0.1 | 3.4 | 14.8 |
| Brazil | 2493 | 3.1 | -2.1 | 36.4 | 3.1 | -3.4 | 31.9 |
Note: GER = Germany; Can = Canada; FD = fiscal deficit; CAD = current account deficit
FD is primary except total for China; Debt is net except gross for China
Source: http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/weodata/weoselgr.aspx
The current account of the US balance of payments is provided in Table VI-A for IQ2011 and IQ2012. The US has a large deficit in goods or exports less imports of goods but it has a surplus in services that helps to reduce the trade account deficit or exports less imports of goods and services. The current account deficit of the US increased from $119.9 billion in IQ2011, or 3.2 percent of GDP to $137.3 billion in IQ2012, or 3.6 percent of GDP. The ratio of the current account deficit to GDP has stabilized around 3 percent of GDP compared with much higher percentages before the recession (see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008b), 183-94, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 167-71).
Table VI-3A, US Balance of Payments, Millions of Dollars NSA
| IQ2011 | IQ2012 | Difference | |
| Goods Balance | -181,358 | -194,462 | -13,104 |
| X Goods | 360,917 | 388,501 | 11.0 ∆% |
| M Goods | -542,276 | -582.963 | 12.9 ∆% |
| Services Balance | 44,133 | 43,465 | -668 |
| X Services | 147,894 | 154,420 | 9.1 ∆% |
| M Services | -103,761 | -110,955 | 8.0 ∆% |
| Balance Goods and Services | -137,225 | -150,997 | -13,772 |
| Balance Income | 52,451 | 47,571 | -4,880 |
| Unilateral Transfers | -35,223 | -33,887 | 1,336 |
| Current Account Balance | -119,997 | -137,313 | -17,316 |
| % GDP | IQ2011 | IVQ2011 | IQ2012 |
| 3.2 | 3.1 | 3.6 |
X: exports; M: imports
Balance on Current Account = Balance on Goods and Services + Balance on Income + Unilateral Transfers
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/international/index.htm#bop
In their classic work on “unpleasant monetarist arithmetic,” Sargent and Wallace (1981, 2) consider a regime of domination of monetary policy by fiscal policy (emphasis added):
“Imagine that fiscal policy dominates monetary policy. The fiscal authority independently sets its budgets, announcing all current and future deficits and surpluses and thus determining the amount of revenue that must be raised through bond sales and seignorage. Under this second coordination scheme, the monetary authority faces the constraints imposed by the demand for government bonds, for it must try to finance with seignorage any discrepancy between the revenue demanded by the fiscal authority and the amount of bonds that can be sold to the public. Suppose that the demand for government bonds implies an interest rate on bonds greater than the economy’s rate of growth. Then if the fiscal authority runs deficits, the monetary authority is unable to control either the growth rate of the monetary base or inflation forever. If the principal and interest due on these additional bonds are raised by selling still more bonds, so as to continue to hold down the growth of base money, then, because the interest rate on bonds is greater than the economy’s growth rate, the real stock of bonds will growth faster than the size of the economy. This cannot go on forever, since the demand for bonds places an upper limit on the stock of bonds relative to the size of the economy. Once that limit is reached, the principal and interest due on the bonds already sold to fight inflation must be financed, at least in part, by seignorage, requiring the creation of additional base money.”
The current real value of government debt plus monetary liabilities depends on the expected discounted values of future primary surpluses or difference between tax revenue and government expenditure excluding interest payments (Cochrane 2011Jan, 27, equation (16)). There is a point when adverse expectations about the capacity of the government to generate primary surpluses to honor its obligations can result in increases in interest rates on government debt.
This analysis suggests that there may be a point of saturation of demand for United States financial liabilities without an increase in interest rates on Treasury securities. A risk premium may develop on US debt. Such premium is not apparent currently because of distressed conditions in the world economy and international financial system. Risk premiums are observed in the spread of bonds of highly indebted countries in Europe relative to bonds of the government of Germany.
The issue of global imbalances centered on the possibility of a disorderly correction (Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), Globalization and the State Vol. II (2008b) 183-94, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 167-71). Such a correction has not occurred historically but there is no argument proving that it could not occur. The need for a correction would originate in unsustainable large and growing United States current account deficits (CAD) and net international investment position (NIIP) or excess of financial liabilities of the US held by foreigners net of financial liabilities of foreigners held by US residents. The IMF estimated that the US could maintain a CAD of two to three percent of GDP without major problems (Rajan 2004). The threat of disorderly correction is summarized by Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 15):
“It is possible that foreigners may be unwilling to increase their positions in US financial assets at prevailing interest rates. An exit out of the dollar could cause major devaluation of the dollar. The depreciation of the dollar would cause inflation in the US, leading to increases in American interest rates. There would be an increase in mortgage rates followed by deterioration of real estate values. The IMF has simulated that such an adjustment would cause a decline in the rate of growth of US GDP to 0.5 percent over several years. The decline of demand in the US by four percentage points over several years would result in a world recession because the weakness in Europe and Japan could not compensate for the collapse of American demand. The probability of occurrence of an abrupt adjustment is unknown. However, the adverse effects are quite high, at least hypothetically, to warrant concern.”
The United States could be moving toward a situation typical of heavily indebted countries, requiring fiscal adjustment and increases in productivity to become more competitive internationally. The CAD and NIIP of the United States are not observed in full deterioration because the economy is well below potential. There are two complications in the current environment relative to the concern with disorderly correction in the first half of the past decade. Table VI-3B provides data on US fiscal and balance of payments imbalances. In 2007, the federal deficit of the US was $161 billion corresponding to 1.2 percent of GDP while the Congressional Budget Office (CBO 2012MarBEO, 2) estimates the federal deficit in 2012 at $1171 billion or 7.6 percent of GDP. The combined record federal deficits of the US from 2009 to 2012 are $5178 billion or 33 percent of the estimate of GDP of $15,508 billion for 2012 by the CBO (2012MarBEO, 2). Federal debt in 2007 was $5035 billion, less than the combined deficits from 2009 to 2012 of $5178 billion, and corresponded to 36.3 percent of GDP. Federal debt in 2011 was 67.7 percent of GDP and is estimated to reach 73.2 percent of GDP in 2012 (CBO2012MarBEO, 2). This situation may worsen in the future (CBO 2012LTBO):
“The budget outlook is much bleaker under the extended alternative fiscal scenario, which maintains what some analysts might consider “current policies,” as opposed to current laws. Federal debt would grow rapidly from its already high level, exceeding 90 percent of GDP in 2022. After that, the growing imbalance between revenues and spending, combined with spiraling interest payments, would swiftly push debt to higher and higher levels. Debt as a share of GDP would exceed its historical peak of 109 percent by 2026, and it would approach 200 percent in 2037.
The changes under this scenario would result in much lower revenues than would occur under the extended baseline scenario because almost all expiring tax provisions are assumed to be extended through 2022 (with the exception of the current reduction in the payroll tax rate for Social Security). After 2022, revenues under this scenario are assumed to remain at their 2022 level of 18.5 percent of GDP, just above the average of the past 40 years.
Outlays would be much higher than under the other scenario. This scenario incorporates assumptions that through 2022, lawmakers will act to prevent Medicare’s payment rates for physicians from declining; that after 2022, lawmakers will not allow various restraints on the growth of Medicare costs and health insurance subsidies to exert their full effect; and that the automatic reductions in spending required by the Budget Control Act of 2011 will not occur (although the original caps on discretionary appropriations in that law are assumed to remain in place). Finally, under this scenario, federal spending as a percentage of GDP for activities other than Social Security, the major health care programs, and interest payments is assumed to return to its average level during the past two decades, rather than fall significantly below that level, as it does under the extended baseline scenario.”
Table VI-3B, US, Current Account, NIIP, Fiscal Balance, Nominal GDP, Federal Debt and Direct Investment, Dollar Billions and %
| 2000 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | |
| Goods & | -377 | -697 | -698 | -379 | -495 | -559 |
| Income | 19 | 101 | 147 | 119 | 184 | 227 |
| UT | -58 | -115 | -126 | -122 | -131 | -133 |
| Current Account | -416 | -710 | -677 | -382 | -442 | -466 |
| NGDP | 9951 | 14028 | 14291 | 13939 | 14526 | 15094 |
| Current Account % GDP | -3.8 | -5.0 | -4.9 | -2.7 | -3.4 | -3.7 |
| NIIP | -1337 | -1796 | -3260 | -2396 | -2471 | NA |
| NIIP % GDP | -13.4 | -12.8 | -22.8 | -17.2 | -17.0 | NA |
| Exports | 1425 | 2488 | 2657 | 2181 | 2519 | 2848 |
| NIIP % | -94 | -72 | -123 | -110 | -98 | NA |
| DIA MV | 2694 | 5274 | 3102 | 4331 | 4843 | NA |
| DIUS MV | 2783 | 3551 | 2486 | 3027 | 3451 | NA |
| Fiscal Balance | +236 | -161 | -459 | -1413 | -1294 | -1300 |
| Fiscal Balance % GDP | +2.4 | -1.2 | -3.2 | -9.9 | -8.9 | -8.7 |
| Federal Debt | 3410 | 5035 | 5803 | 7545 | 9019 | 10128 |
| Federal Debt % GDP | 34.7 | 36.3 | 40.5 | 54.1 | 62.8 | 67.7 |
| Federal Outlays | 1789 | 2729 | 2983 | 3518 | 3456 | 3598 |
| ∆% | 5.1 | 2.8 | 9.3 | 17.9 | -1.8 | 4.1 |
| % GDP | 18.2 | 19.7 | 20.8 | 25.2 | 24.1 | 24.1 |
| Federal Revenue | 2052 | 2568 | 2524 | 2105 | 2162 | 2303 |
| ∆% | 10.8 | 6.7 | -1.7 | -16.6 | 2.7 | 6.5 |
| % GDP | 20.6 | 18.5 | 17.6 | 15.1 | 15.1 | 15.4 |
Sources:
Notes: UT: unilateral transfers; NGDP: nominal GDP or in current dollars; NIIP: Net International Investment Position; DIA MV: US Direct Investment Abroad at Market Value; DIUS MV: Direct Investment in the US at Market Value. There are minor discrepancies in the decimal point of percentages of GDP between the balance of payments data and federal debt, outlays, revenue and deficits in which they original number of the CBO source is maintained. These discrepancies do not alter conclusions.
Sources: Balance of Payments and NIIP, Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) http://www.bea.gov/international/index.htm#bop
Gross Domestic Product, Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) http://www.bea.gov/national/index.htm#gdp
Federal Outlays, Revenues and Debt, Congressional Budget Office (CBO) http://www.cbo.gov/publication/42911
The International Monetary Fund (IMF) provides an international safety net for prevention and resolution of international financial crises. The IMF’s Financial Sector Assessment Program (FSAP) provides analysis of the economic and financial sectors of countries (see Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), 101-62, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008), 114-23). Relating economic and financial sectors is a challenging task both for theory and measurement. The IMF (2012WEOApr) provides surveillance of the world economy with its Global Economic Outlook (WEO) (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/pdf/text.pdf), of the world financial system with its Global Financial Stability Report (GFSR) (IMF 2012GFSRApr) (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/gfsr/2012/01/pdf/text.pdf) and of fiscal affairs with the Fiscal Monitor (IMF 2012FMApr) (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fm/2012/01/pdf/fm1201.pdf). There appears to be a moment of transition in global economic and financial variables that may prove of difficult analysis and measurement. It is useful to consider global economic and financial risks, which are analyzed in the comments of this blog.
Economic risks include the following:
1. China’s Economic Growth. China is lowering its growth target to 7.5 percent per year. Lu Hui, writing on “China lowers GDP target to achieve quality economic growth, on Mar 12, 2012, published in Beijing by Xinhuanet (http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/china/2012-03/12/c_131461668.htm), informs that Premier Jiabao wrote in a government work report that the GDP growth target will be lowered to 7.5 percent to enhance the quality and level of development of China over the long term. The quarterly growth rate of GDP in IQ2012 of 1.8 percent is equivalent to 7.4 percent per year (see subsection VC at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/04/fractured-labor-market-with-hiring_15.html). There is also ongoing political development in China during a decennial political reorganization. Xinhuanet informs that Premier Wen Jiabao considers the need for macroeconomic stimulus, arguing that “we should continue to implement proactive fiscal policy and a prudent monetary policy, while giving more priority to maintaining growth” (http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/china/2012-05/20/c_131599662.htm). Premier Wen elaborates that “the country should properly handle the relationship between maintaining growth, adjusting economic structures and managing inflationary expectations” (http://news.xinhuanet.com/english/china/2012-05/20/c_131599662.htm).
2. United States Economic Growth, Labor Markets and Budget/Debt Quagmire. (i) The US economy grew at 1.7 percent in 2011 (Section I), 1.7 percent in annual equivalent in the five quarters from IQ2011 to IQ2012 and 2.0 percent in IQ2012 relative to IQ2011 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/07/mediocre-economic-growth-united-states.html). (ii) The labor market continues fractured with 28.4 million unemployed or underemployed (see Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/mediocre-recovery-without-jobs.html). There are over 10 million fewer full-time jobs and hiring has collapsed (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/recovery-without-hiring-continuance-of.html). (iii) There is a difficult climb from the record federal deficit of 9.9 percent of GDP in 2009 and cumulative deficit of $5178 in four consecutive years of deficits exceeding one trillion dollars from 2009 to 2012 (see Section VA http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/destruction-of-three-trillion-dollars_17.html). There is no subsequent jump of debt in US peacetime history as the one from 40.5 percent of GDP in 2008 to 67.7 percent of GDP in 2011 and projected by the Congressional Budget Office (CBO 2012MarBEO, 2) at 73.2 percent in 2012. The CBO (2012MarBEO) must use current law without any changes in the baseline scenario but also calculates another alternative scenario with different assumptions. In the alternative scenario, the debt/GDP ratio rises to 94.2 percent by 2022. The US is facing an unsustainable debt/GDP path. Feldstein (2012Mar19) finds that the most troubling uncertainty in the US is the programmed tax increases projected by the CBO (2012JanBEO) under current law with federal government revenue increasing from $2.4 trillion in fiscal year 2012 to $2.9 trillion in fiscal year 2013. The increase of $512 billion of federal revenue would be about 2.9 percent of GDP, raising the share of federal revenue in GDP from 15.8 percent in fiscal year 2012 to 18.7 percent of GDP in fiscal year 2013. In the analysis of Feldstein (2012Mar19), increasing revenue would originate in higher personal tax rates, payroll tax contributions and taxes on dividends, capital gains and corporate income tax. The share of federal revenue in GDP would increase to 19.8 percent in 2014, remaining above 20 percent during the rest of the decade. Feldstein (2012Mar19) finds that such a shock of sustained tax increases would risk another recession in 2013, requiring preventive legislation to smooth tax increases
3. Economic Growth and Labor Markets in Advanced Economies. Advanced economies are growing slowly. Japan’s GDP fell 0.6 percent in IVQ2011 relative to a year earlier but grew 2.8 percent in IQ2012 relative to a year earlier and 1.2 percent in IQ2012 relative to IVQ2011. The euro zone’s GDP fell 0.3 percent in IVQ2011 and was flat in IQ2012, falling 0.1 percent relative to a year earlier in IQ2011; Germany’s GDP fell 0.2 percent in IVQ2011 but grew 0.5 percent in IQ2012; and the UK’s GDP fell 0.3 percent in IVQ2011 and 0.3 percent in IQ2012. There is still high unemployment in advanced economies
4. World Inflation Waves. Inflation continues in repetitive waves globally (see Section I Inflation Waves http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/destruction-of-three-trillion-dollars.html and earlier at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/05/world-inflation-waves-monetary-policy.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/04/fractured-labor-market-with-hiring.html and http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/03/global-financial-and-economic-risk.html)
A list of financial uncertainties includes:
1. Euro Area Survival Risk. The resilience of the euro to fiscal and financial doubts on larger member countries is still an unknown risk. Adjustment programs consist of immediate adoption of economic reforms that would increase future growth permitting fiscal consolidation, which would reduce risk spreads on sovereign debt. Fiscal consolidation is challenging in an environment of weak economic growth as analyzed by Blanchard (2011WEOSep) and consolidation can restrict growth as analyzed by Blanchard (2012WEOApr). Adjustment of countries such as Italy requires depreciation of the currency to parity, as proposed by Caballero and Giavazzi (2012Jan15), but it is not workable within the common currency and zero interest rates in the US. Bailouts of euro area member countries with temporary liquidity challenges cannot be permanently provided by stronger members at the risk of impairing their own sovereign debt credibility
2. Foreign Exchange Wars. Exchange rate struggles continue as zero interest rates in advanced economies induce devaluation. After deep global recession, regulation, trade and devaluation wars were to be expected (Pelaez and Pelaez, Government Intervention in Globalization: Regulation, Trade and Devaluation Wars (2008c), 181): “There are significant grounds for concern on the basis of this experience. International economic cooperation and the international financial framework can collapse during extreme events. It is unlikely that there will be a repetition of the disaster of the Great Depression. However, a milder contraction can trigger regulatory, trade and exchange wars”
3. Valuation of Risk Financial Assets. Valuations of risk financial assets have reached extremely high levels in markets with lower volumes. For example, the DJIA has increased 31.9 percent since the trough of the sovereign debt crisis in Europe on Jul 2, 2010, and the S&P 500 has gained 32.5 percent. It is challenging in theory and practice to assess when variables have peaked but sustained valuations to very high levels could be followed by contractions of valuations. Jonathan Cheng, writing on “Stocks add 66 points, post first-quarter record,” published on Mar 30, 2012, in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052702303816504577313123753822852.html?mod=WSJ_Markets_LEFTTopStories&mg=reno64-sec-wsj), finds that the DJIA rose 8.1 percent in IQ2012, which is the highest since 1998, while the S&P 500 gained 12 percent. Paul A. Samuelson remarked that “the stock market has predicted nine of the last five recessions.” Another version of this phrase would be that “the stock market has predicted nine of the last five economic booms.” The tool of analysis of Cochrane (2011Jan, 27, equation (16)) is the government debt valuation equation:
(Mt + Bt)/Pt = Et∫(1/Rt, t+τ)st+τdτ (1)
Equation (1) expresses the monetary, Mt, and debt, Bt, liabilities of the government, divided by the price level, Pt, in terms of the expected value discounted by the ex-post rate on government debt, Rt, t+τ, of the future primary surpluses st+τ, which are equal to Tt+τ – Gt+τ or difference between taxes, T, and government expenditures, G. Cochrane (2010A) provides the link to a web appendix demonstrating that it is possible to discount by the ex post Rt, t+τ. The present value of the firm can also be expressed as the discounted future value of net cash flows. Equities can inflate beyond sound values if cash flows that depend on economic activity prove to be illusory in continuing mediocre growth
4. Duration Trap of the Zero Bound. The yield of the US 10-year Treasury rose from 2.031 percent on Mar 9, 2012, to 2.294 percent on Mar 16, 2012. Considering a 10-year Treasury with coupon of 2.625 percent and maturity in exactly 10 years, the price would fall from 105.3512 corresponding to yield of 2.031 percent to 102.9428 corresponding to yield of 2.294 percent, for loss in a week of 2.3 percent but far more in a position with leverage of 10:1. Min Zeng, writing on “Treasurys fall, ending brutal quarter,” published on Mar 30, 2012, in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052702303816504577313400029412564.html?mod=WSJ_hps_sections_markets), informs that Treasury bonds maturing in more than 20 years lost 5.52 percent in the first quarter of 2012
5. Credibility and Commitment of Central Bank Policy. There is a credibility issue of the commitment of monetary policy. The Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) advised on its Jun 20, 2012 statement that: “To support a stronger economic recovery and to help ensure that inflation, over time, is at the rate most consistent with its dual mandate, the Committee expects to maintain a highly accommodative stance for monetary policy. In particular, the Committee decided today to keep the target range for the federal funds rate at 0 to 1/4 percent and currently anticipates that economic conditions--including low rates of resource utilization and a subdued outlook for inflation over the medium run--are likely to warrant exceptionally low levels for the federal funds rate at least through late 2014.” (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20120620a.htm). At its meeting on Jan 25, the FOMC began to provide to the public the specific forecasts of interest rates and other economic variables by FOMC members. These forecasts are analyzed in Section IV Global Inflation. Thomas J. Sargent and William L. Silber, writing on “The challenges of the Fed’s bid for transparency,” on Mar 20, published in the Financial Times (http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/778eb1ce-7288-11e1-9c23-00144feab49a.html#axzz1pexRlsiQ), analyze the costs and benefits of transparency by the Fed. In the analysis of Sargent and Silber (2012Mar20), benefits of transparency by the Fed will exceed costs if the Fed is successful in conveying to the public what policies would be implemented and how forcibly in the presence of unforeseen economic events. History has been unkind to policy commitments. The risk in this case is if the Fed would postpone adjustment because of political pressures as has occurred in the past or because of errors of evaluation and forecasting of economic and financial conditions. Both political pressures and errors abounded in the unhappy stagflation of the 1970s also known as the US Great Inflation (see http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/05/slowing-growth-global-inflation-great.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/04/new-economics-of-rose-garden-turned.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/03/is-there-second-act-of-us-great.html and Appendix I The Great Inflation; see Taylor 1993, 1997, 1998LB, 1999, 2012FP, 2012Mar27, 2012Mar28, 2012JMCB and http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/rules-versus-discretionary-authorities.html). The challenge of the Fed, in the view of Sargent and Silber 2012Mar20), is to convey to the public the need to deviate from the commitment to interest rates of zero to ¼ percent because conditions have changed instead of unwarranted inaction or policy changes. Errors have abounded such as a critical cause of the global recession pointed by Sargent and Silber (2012Mar20): “While no president is known to have explicitly pressurized Mr. Bernanke’s predecessor, Alan Greenspan, he found it easy to maintain low interest rates for too long, fuelling the credit boom and housing bubble that led to the financial crisis in 2008.” Sargent and Silber (2012Mar20) also find need of commitment of fiscal authorities to consolidation needed to attain sustainable path of debt.
The analysis by Kydland and Prescott (1977, 447-80, equation 5) uses the “expectation augmented” Phillips curve with the natural rate of unemployment of Friedman (1968) and Phelps (1968), which in the notation of Barro and Gordon (1983, 592, equation 1) is:
Ut = Unt – α(πt – πe) α > 0 (1)
Where Ut is the rate of unemployment at current time t, Unt is the natural rate of unemployment, πt is the current rate of inflation and πe is the expected rate of inflation by economic agents based on current information. Equation (1) expresses unemployment net of the natural rate of unemployment as a decreasing function of the gap between actual and expected rates of inflation. The system is completed by a social objective function, W, depending on inflation, π, and unemployment, U:
W = W(πt, Ut) (2)
The policymaker maximizes the preferences of the public, (2), subject to the constraint of the tradeoff of inflation and unemployment, (1). The total differential of W set equal to zero provides an indifference map in the Cartesian plane with ordered pairs (πt, Ut - Un) such that the consistent equilibrium is found at the tangency of an indifference curve and the Phillips curve in (1). The indifference curves are concave to the origin. The consistent policy is not optimal. Policymakers without discretionary powers following a rule of price stability would attain equilibrium with unemployment not higher than with the consistent policy. The optimal outcome is obtained by the rule of price stability, or zero inflation, and no more unemployment than under the consistent policy with nonzero inflation and the same unemployment. Taylor (1998LB) attributes the sustained boom of the US economy after the stagflation of the 1970s to following a monetary policy rule instead of discretion (see Taylor 1993, 1999).
6. Carry Trades. Commodity prices driven by zero interest rates have resumed their increasing path. Some analytical aspects of the carry trade are instructive (Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. I (2008a), 101-5, Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008b), 202-4), Government Intervention in Globalization: Regulation, Trade and Devaluation Wars (2008c), 70-4). Consider the following symbols: Rt is the exchange rate of a country receiving carry trade denoted in units of domestic currency per dollars at time t of initiation of the carry trade; Rt+τ is the exchange of the country receiving carry trade denoted in units of domestic currency per dollars at time t+τ when the carry trade is unwound; if is the domestic interest rate of the high-yielding country where investment will be made; iusd is the interest rate on short-term dollar debt assumed to be 0.5 percent per year; if >iusd, which expresses the fact that the interest rate on the foreign country is much higher than that in short-term USD (US dollars); St is the dollar value of the investment principal; and π is the dollar profit from the carry trade. The investment of the principal St in the local currency debt of the foreign country provides a profit of:
π = (1 + if)(RtSt)(1/Rt+τ) – (1 + iusd)St (3)
The profit from the carry trade, π, is nonnegative when:
(1 + if)/ (1 + iusd) ≥ Rt+τ/Rt (4)
In words, the difference in interest rate differentials, left-hand side of inequality (4), must exceed the percentage devaluation of the currency of the host country of the carry trade, right hand side of inequality (4). The carry trade must earn enough in the host-country interest rate to compensate for depreciation of the host-country at the time of return to USD. A simple example explains the vulnerability of the carry trade in fixed-income. Let if be 0.10 (10 percent), iusd 0.005 (0.5 percent), St USD100 and Rt CUR 1.00/USD. Adopt the fixed-income rule of months of 30 days and years of 360 days. Consider a strategy of investing USD 100 at 10 percent for 30 days with borrowing of USD 100 at 0.5 percent for 30 days. At time t, the USD 100 are converted into CUR 100 and invested at [(30/360)10] equal to 0.833 percent for thirty days. At the end of the 30 days, assume that the rate Rt+30 is still CUR 1/USD such that the return amount from the carry trade is USD 0.833. There is still a loan to be paid [(0.005)(30/360)USD100] equal to USD 0.042. The investor receives the net amount of USD 0.833 minus USD 0.042 or US 0.791. The rate of return on the investment of the USD 100 is 0.791 percent, which is equivalent to the annual rate of return of 9.49 percent {(0.791)(360/30)}. This is incomparably better than earning 0.5 percent. There are alternatives of hedging by buying forward the exchange for conversion back into USD.
Research by the Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis finds that the dollar declined on average by 6.56 percent in the events of quantitative easing, ranging from depreciation of 10.8 percent relative to the Japanese yen to 3.6 percent relative to the pound sterling (http://research.stlouisfed.org/wp/2010/2010-018.pdf). A critical assumption of Rudiger Dornbusch (1976) in his celebrated analysis of overshooting (Rogoff 2002MF http://www.imf.org/external/np/speeches/2001/kr/112901.pdf) is “that exchange rates and asset markets adjust fast relative to goods markets” (Rudiger Dornbusch 1976, 1162). The market response of a monetary expansion is “to induce an immediate depreciation in the exchange rate and accounts therefore for fluctuations in the exchange rate and the terms of trade. During the adjustment process, rising prices may be accompanied by an appreciating exchange rate so that the trend behavior of exchange rates stands potentially in strong contrast with the cyclical behavior of exchange rates and prices” (Dornbusch 1976, 1162). The volatility of the exchange rate “is needed to temporarily equilibrate the system in response to monetary shocks, because underlying national prices adjust so slowly” (Rogoff 2002MF http://www.imf.org/external/np/speeches/2001/kr/112901.pdf 3). The exchange rate “is identified as a critical channel for the transmission of monetary policy to aggregate demand for domestic output” (Dornbusch 1976, 1162).
In a world of exchange wars, depreciation of the host-country currency can move even faster such that the profits from the carry trade may become major losses. Depreciation is the percentage change in instants against which the interest rate of a day is in the example [(10)(1/360)] or 0.03 percent. Exchange rates move much faster in the real world as in the overshooting model of Dornbusch (1976). Profits in carry trades have greater risks but equally greater returns when the short position in zero interest rates, or borrowing, and on the dollar, are matched with truly agile financial risk assets such as commodities and equities. A simplified analysis could consider the portfolio balance equations Aij = f(r, x) where Aij is the demand for i = 1,2,∙∙∙n assets from j = 1,2, ∙∙∙m sectors, r the 1xn vector of rates of return, ri, of n assets and x a vector of other relevant variables. Tobin (1969) and Brunner and Meltzer (1973) assume imperfect substitution among capital assets such that the own first derivatives of Aij are positive, demand for an asset increases if its rate of return (interest plus capital gains) is higher, and cross first derivatives are negative, demand for an asset decreases if the rate of return of alternative assets increases. Theoretical purity would require the estimation of the complete model with all rates of return. In practice, it may be impossible to observe all rates of return such as in the critique of Roll (1976). Policy proposals and measures by the Fed have been focused on the likely impact of withdrawals of stocks of securities in specific segments, that is, of effects of one or several specific rates of return among the n possible rates. In fact, the central bank cannot influence investors and arbitrageurs to allocate funds to assets of desired categories such as asset-backed securities that would lower the costs of borrowing for mortgages and consumer loans. Floods of cheap money may simply induce carry trades in arbitrage of opportunities in fast moving assets such as currencies, commodities and equities instead of much lower returns in fixed income securities (see http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/07/causes-of-2007-creditdollar-crisis.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/professor-mckinnons-bubble-economy.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/world-inflation-quantitative-easing.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/treasury-yields-valuation-of-risk.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/11/quantitative-easing-theory-evidence-and.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/12/is-fed-printing-money-what-are.html).
It is in this context of economic and financial uncertainties that decisions on portfolio choices of risk financial assets must be made. There is a new carry trade that learned from the losses after the crisis of 2007 or learned from the crisis how to avoid losses. The sharp rise in valuations of risk financial assets shown in Table VI-1 after the first policy round of near zero fed funds and quantitative easing by the equivalent of withdrawing supply with the suspension of the 30-year Treasury auction was on a smooth trend with relatively subdued fluctuations. The credit crisis and global recession have been followed by significant fluctuations originating in sovereign risk issues in Europe, doubts of continuing high growth and accelerating inflation in China now complicated by political developments, events such as in the Middle East and Japan and legislative restructuring, regulation, insufficient growth, falling real wages, depressed hiring and high job stress of unemployment and underemployment in the US now with realization of growth standstill. The “trend is your friend” motto of traders has been replaced with a “hit and realize profit” approach of managing positions to realize profits without sitting on positions. There is a trend of valuation of risk financial assets driven by the carry trade from zero interest rates with fluctuations provoked by events of risk aversion or the “sharp shifts in risk appetite” of Blanchard (2012WEOApr, XIII). Table VI-4, which is updated for every comment of this blog, shows the deep contraction of valuations of risk financial assets after the Apr 2010 sovereign risk issues in the fourth column “∆% to Trough.” There was sharp recovery after around Jul 2010 in the last column “∆% Trough to 7/6/12,” which has been recently stalling or reversing amidst profound risk aversion. “Let’s twist again” monetary policy during the week of Sep 23 caused deep worldwide risk aversion and selloff of risk financial assets (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/09/imf-view-of-world-economy-and-finance.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/09/collapse-of-household-income-and-wealth.html). Monetary policy was designed to increase risk appetite but instead suffocated risk exposures. There has been rollercoaster fluctuation in risk aversion and financial risk asset valuations: surge in the week of Dec 2, mixed performance of markets in the week of Dec 9, renewed risk aversion in the week of Dec 16, end-of-the-year relaxed risk aversion in thin markets in the weeks of Dec 23 and Dec 30, mixed sentiment in the weeks of Jan 6 and Jan 13 2012 and strength in the weeks of Jan 20, Jan 27 and Feb 3 followed by weakness in the week of Feb 10 but strength in the weeks of Feb 17 and 24 followed by uncertainty on financial counterparty risk in the weeks of Mar 2 and Mar 9. All financial values have fluctuated with events such as the surge in the week of Mar 16 on favorable news of Greece’s bailout even with new risk issues arising in the week of Mar 23 but renewed risk appetite in the week of Mar 30 because of the end of the quarter and the increase in the firewall of support of sovereign debts in the euro area. New risks developed in the week of Apr 6 with increase of yields of sovereign bonds of Spain and Italy, doubts on Fed policy and weak employment report. Asia and financial entities are experiencing their own risk environments. Financial markets were under stress in the week of Apr 13 because of the large exposure of Spanish banks to lending by the European Central Bank and the annual equivalent growth rate of China’s GDP of 7.4 percent in IQ2012 [(1.018)4]. There was strength again in the week of Apr 20 because of the enhanced IMF firewall and Spain placement of debt, continuing into the week of Apr 27. Risk aversion returned in the week of May 4 because of the expectation of elections in Europe and the new trend of deterioration of job creation in the US. Europe’s sovereign debt crisis and the fractured US job market continued to influence risk aversion in the week of May 11. Politics in Greece and banking issues in Spain were important factors of sharper risk aversion in the week of May 18. Risk aversion continued during the week of May 25 and exploded in the week of Jun 1. Expectations of stimulus by central banks caused valuation of risk financial assets in the week of Jun 8 and in the week of Jun 15. Expectations of major stimulus were frustrated by minor continuance of maturity extension policy in the week of Jun 22 together with doubts on the silent bank run in highly indebted euro area member countries. There was a major rally of valuations of risk financial assets in the week of Jun 29 with the announcement of new measures by the European Council on bank resolutions. New doubts surfaced in the week of Jul 6, 2012 on the implementation of the bank resolution mechanism and on the outlook for the world economy because of interest rate reductions by the European Central, Bank of England and People’s Bank of China. The highest valuations in column “∆% Trough to 7/6/12” are by US equities indexes: DJIA 31.9 percent and S&P 500 32.5 percent, driven by stronger earnings and economy in the US than in other advanced economies but with doubts on the relation of business revenue to the weakening economy and fractured job market. The DJIA reached 13,331.77 in intraday trading on Mar 16, which is the highest level in 52 weeks (http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_PRO_hps_marketdata). The carry trade from zero interest rates to leveraged positions in risk financial assets had proved strongest for commodity exposures but US equities have regained leadership. Before the current round of risk aversion, almost all assets in the column “∆% Trough to 7/6/12” had double digit gains relative to the trough around Jul 2, 2010 but now most valuations of equity indexes show increase of less than 10 percent: China’s Shanghai Composite is 6.7 percent below the trough; STOXX 50 of Europe is 5.5 percent above the trough; Japan’s Nikkei Average is 2.2 percent above the trough; DJ Asia Pacific TSM is 5.8 percent above the trough; Dow Global is 6.5 percent above the trough; and NYSE Financial is 4.0 percent above the trough. DJ UBS Commodities is 10.4 percent above the trough. DAX is 13.0 percent above the trough. Japan’s Nikkei Average is 2.2 percent above the trough on Aug 31, 2010 and 20.8 percent below the peak on Apr 5, 2010. The Nikkei Average closed at 9020.75 on Fri Jul 6, 2012 (http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_PRO_hps_marketdata), which is 12.0 percent lower than 10,254.43 on Mar 11, 2011, on the date of the Tōhoku or Great East Japan Earthquake/tsunami. Global risk aversion erased the earlier gains of the Nikkei. The dollar depreciated by 3.1 percent relative to the euro and even higher before the new bout of sovereign risk issues in Europe. The column “∆% week to 7/6/12” in Table VI-4 shows that there were increases of valuations of risk financial assets in the week of Jul 7, 2012 such as 1.2 percent for DJ Asia Pacific, 0.2 percent for Nikkei Average and 1.8 percent for STOXX 50. DJ UBS Commodities increased 1.1 percent. Other valuations decreased such as 0.8 percent for NYSE Financial, 0.9 percent for Dow Global and 0.1 percent for DAX. The DJIA fell 0.8 percent and S&P 500 decreased 0.5 percent. There are still high uncertainties on European sovereign risks and banking soundness, US and world growth slowdown and China’s growth tradeoffs. Sovereign problems in the “periphery” of Europe and fears of slower growth in Asia and the US cause risk aversion with trading caution instead of more aggressive risk exposures. There is a fundamental change in Table VI-4 from the relatively upward trend with oscillations since the sovereign risk event of Apr-Jul 2010. Performance is best assessed in the column “∆% Peak to 7/6/12” that provides the percentage change from the peak in Apr 2010 before the sovereign risk event to Jul 6, 2012. Most risk financial assets had gained not only relative to the trough as shown in column “∆% Trough to 7/6/12” but also relative to the peak in column “∆% Peak to 7/6/12.” There are now only three equity indexes above the peak in Table VI-4: DJIA 14.0 percent, S&P 500 11.3 percent and DAX 1.2 percent. There are several indexes below the peak: NYSE Financial Index (http://www.nyse.com/about/listed/nykid.shtml) by 17.2 percent, Nikkei Average by 20.8 percent, Shanghai Composite by 29.7 percent, DJ Asia Pacific by 7.3 percent, STOXX 50 by 10.6 percent and Dow Global by 13.1 percent. DJ UBS Commodities Index is now 5.6 percent below the peak. The factors of risk aversion have adversely affected the performance of risk financial assets. The performance relative to the peak in Apr 2010 is more important than the performance relative to the trough around early Jul 2010 because improvement could signal that conditions have returned to normal levels before European sovereign doubts in Apr 2010. An intriguing issue is the difference in performance of valuations of risk financial assets and economic growth and employment. Paul A. Samuelson (http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/economics/laureates/1970/samuelson-bio.html) popularized the view of the elusive relation between stock markets and economic activity in an often-quoted phrase “the stock market has predicted nine of the last five recessions.” In the presence of zero interest rates forever, valuations of risk financial assets are likely to differ from the performance of the overall economy. The interrelations of financial and economic variables prove difficult to analyze and measure.
Table VI-4, Stock Indexes, Commodities, Dollar and 10-Year Treasury
| Peak | Trough | ∆% to Trough | ∆% Peak to 7/6 /12 | ∆% Week 7/6/12 | ∆% Trough to 7/6 12 | |
| DJIA | 4/26/ | 7/2/10 | -13.6 | 14.0 | -0.8 | 31.9 |
| S&P 500 | 4/23/ | 7/20/ | -16.0 | 11.3 | -0.5 | 32.5 |
| NYSE Finance | 4/15/ | 7/2/10 | -20.3 | -17.2 | -0.8 | 4.0 |
| Dow Global | 4/15/ | 7/2/10 | -18.4 | -13.1 | -0.9 | 6.5 |
| Asia Pacific | 4/15/ | 7/2/10 | -12.5 | -7.3 | 1.2 | 5.8 |
| Japan Nikkei Aver. | 4/05/ | 8/31/ | -22.5 | -20.8 | 0.2 | 2.2 |
| China Shang. | 4/15/ | 7/02 | -24.7 | -29.7 | -0.1 | -6.7 |
| STOXX 50 | 4/15/10 | 7/2/10 | -15.3 | -10.6 | 1.8 | 5.5 |
| DAX | 4/26/ | 5/25/ | -10.5 | 1.2 | -0.1 | 13.0 |
| Dollar | 11/25 2009 | 6/7 | 21.2 | 18.8 | 2.9 | -3.1 |
| DJ UBS Comm. | 1/6/ | 7/2/10 | -14.5 | -5.6 | 1.1 | 10.4 |
| 10-Year T Note | 4/5/ | 4/6/10 | 3.986 | 1.548 |
T: trough; Dollar: positive sign appreciation relative to euro (less dollars paid per euro), negative sign depreciation relative to euro (more dollars paid per euro)
Source: http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_hps_marketdata
Bernanke (2010WP) and Yellen (2011AS) reveal the emphasis of monetary policy on the impact of the rise of stock market valuations in stimulating consumption by wealth effects on household confidence. Table VI-5 shows a gain by Apr 29, 2011 in the DJIA of 14.3 percent and of the S&P 500 of 12.5 percent since Apr 26, 2010, around the time when sovereign risk issues in Europe began to be acknowledged in financial risk asset valuations. The last row of Table VI-5 for Jul 6, 2012, shows that the S&P 500 is now 11.8 percent above the Apr 26, 2010 level and the DJIA is 14.0 percent above the level on Apr 26, 2010. Multiple rounds of risk aversion eroded earlier gains, showing that risk aversion can destroy market value even with zero interest rates. Relaxed risk aversion has contributed to recovery of valuations. Much the same as zero interest rates and quantitative easing have not had any effects in recovering economic activity while distorting financial markets and resource allocation.
Table VI-5, Percentage Changes of DJIA and S&P 500 in Selected Dates
| 2010 | ∆% DJIA from prior date | ∆% DJIA from | ∆% S&P 500 from prior date | ∆% S&P 500 from |
| Apr 26 | ||||
| May 6 | -6.1 | -6.1 | -6.9 | -6.9 |
| May 26 | -5.2 | -10.9 | -5.4 | -11.9 |
| Jun 8 | -1.2 | -11.3 | 2.1 | -12.4 |
| Jul 2 | -2.6 | -13.6 | -3.8 | -15.7 |
| Aug 9 | 10.5 | -4.3 | 10.3 | -7.0 |
| Aug 31 | -6.4 | -10.6 | -6.9 | -13.4 |
| Nov 5 | 14.2 | 2.1 | 16.8 | 1.0 |
| Nov 30 | -3.8 | -3.8 | -3.7 | -2.6 |
| Dec 17 | 4.4 | 2.5 | 5.3 | 2.6 |
| Dec 23 | 0.7 | 3.3 | 1.0 | 3.7 |
| Dec 31 | 0.03 | 3.3 | 0.07 | 3.8 |
| Jan 7 | 0.8 | 4.2 | 1.1 | 4.9 |
| Jan 14 | 0.9 | 5.2 | 1.7 | 6.7 |
| Jan 21 | 0.7 | 5.9 | -0.8 | 5.9 |
| Jan 28 | -0.4 | 5.5 | -0.5 | 5.3 |
| Feb 4 | 2.3 | 7.9 | 2.7 | 8.1 |
| Feb 11 | 1.5 | 9.5 | 1.4 | 9.7 |
| Feb 18 | 0.9 | 10.6 | 1.0 | 10.8 |
| Feb 25 | -2.1 | 8.3 | -1.7 | 8.9 |
| Mar 4 | 0.3 | 8.6 | 0.1 | 9.0 |
| Mar 11 | -1.0 | 7.5 | -1.3 | 7.6 |
| Mar 18 | -1.5 | 5.8 | -1.9 | 5.5 |
| Mar 25 | 3.1 | 9.1 | 2.7 | 8.4 |
| Apr 1 | 1.3 | 10.5 | 1.4 | 9.9 |
| Apr 8 | 0.03 | 10.5 | -0.3 | 9.6 |
| Apr 15 | -0.3 | 10.1 | -0.6 | 8.9 |
| Apr 22 | 1.3 | 11.6 | 1.3 | 10.3 |
| Apr 29 | 2.4 | 14.3 | 1.9 | 12.5 |
| May 6 | -1.3 | 12.8 | -1.7 | 10.6 |
| May 13 | -0.3 | 12.4 | -0.2 | 10.4 |
| May 20 | -0.7 | 11.7 | -0.3 | 10.0 |
| May 27 | -0.6 | 11.0 | -0.2 | 9.8 |
| Jun 3 | -2.3 | 8.4 | -2.3 | 7.3 |
| Jun 10 | -1.6 | 6.7 | -2.2 | 4.9 |
| Jun 17 | 0.4 | 7.1 | 0.04 | 4.9 |
| Jun 24 | -0.6 | 6.5 | -0.2 | 4.6 |
| Jul 1 | 5.4 | 12.3 | 5.6 | 10.5 |
| Jul 8 | 0.6 | 12.9 | 0.3 | 10.9 |
| Jul 15 | -1.4 | 11.4 | -2.1 | 8.6 |
| Jul 22 | 1.6 | 13.2 | 2.2 | 10.9 |
| Jul 29 | -4.2 | 8.4 | -3.9 | 6.6 |
| Aug 05 | -5.8 | 2.1 | -7.2 | -1.0 |
| Aug 12 | -1.5 | 0.6 | -1.7 | -2.7 |
| Aug 19 | -4.0 | -3.5 | -4.7 | -7.3 |
| Aug 26 | 4.3 | 0.7 | 4.7 | -2.9 |
| Sep 02 | -0.4 | 0.3 | -0.2 | -3.1 |
| Sep 09 | -2.2 | -1.9 | -1.7 | -4.8 |
| Sep 16 | 4.7 | 2.7 | 5.4 | 0.3 |
| Sep 23 | -6.4 | -3.9 | -6.5 | -6.2 |
| Sep 30 | 1.3 | -2.6 | -0.4 | -6.7 |
| Oct 7 | 1.7 | -0.9 | 2.1 | -4.7 |
| Oct 14 | 4.9 | 3.9 | 5.9 | 1.0 |
| Oct 21 | 1.4 | 5.4 | 1.1 | 2.2 |
| Oct 28 | 3.6 | 9.2 | 3.8 | 6.0 |
| Nov 04 | -2.0 | 6.9 | -2.5 | 3.4 |
| Nov 11 | 1.4 | 8.5 | 0.8 | 4.3 |
| Nov 18 | -2.9 | 5.3 | -3.8 | 0.3 |
| Nov 25 | -4.8 | 0.2 | -4.7 | -4.4 |
| Dec 02 | 7.0 | 7.3 | 7.4 | 2.7 |
| Dec 09 | 1.4 | 8.7 | 0.9 | 3.6 |
| Dec 16 | -2.6 | 5.9 | -2.8 | 0.6 |
| Dec 23 | 3.6 | 9.7 | 3.7 | 4.4 |
| Dec 30 | -0.6 | 9.0 | -0.6 | 3.8 |
| Jan 6 2012 | 1.2 | 10.3 | 1.6 | 5.4 |
| Jan 13 | 0.5 | 10.9 | 0.9 | 6.4 |
| Jan 20 | 2.4 | 13.5 | 2.0 | 8.5 |
| Jan 27 | -0.5 | 13.0 | 0.1 | 8.6 |
| Feb 3 | 1.6 | 14.8 | 2.2 | 11.0 |
| Feb 10 | -0.5 | 14.2 | -0.2 | 10.8 |
| Feb 17 | 1.2 | 15.6 | 1.4 | 12.3 |
| Feb 24 | 0.3 | 15.9 | 0.3 | 12.7 |
| Mar 2 | 0.0 | 15.8 | 0.3 | 13.0 |
| Mar 9 | -0.4 | 15.3 | 0.1 | 13.1 |
| Mar 16 | 2.4 | 18.1 | 2.4 | 15.9 |
| Mar 23 | -1.1 | 16.7 | -0.5 | 15.3 |
| Mar 30 | 1.0 | 17.9 | 0.8 | 16.2 |
| Apr 6 | -1.1 | 16.6 | -0.7 | 15.3 |
| Apr 13 | -1.6 | 14.7 | -2.0 | 13.1 |
| Apr 20 | 1.4 | 16.3 | 0.6 | 13.7 |
| Apr 27 | 1.5 | 18.1 | 1.8 | 15.8 |
| May 4 | -1.4 | 16.4 | -2.3 | 12.9 |
| May 11 | -1.7 | 14.4 | -1.1 | 11.7 |
| May 18 | -3.5 | 10.4 | -4.3 | 6.4 |
| May 25 | 0.7 | 11.2 | 1.7 | 8.7 |
| Jun 1 | -2.7 | 8.2 | -3.0 | 5.4 |
| Jun 8 | 3.6 | 12.0 | 3.7 | 9.4 |
| Jun 15 | 1.7 | 13.9 | 1.3 | 10.8 |
| Jun 22 | -1.0 | 12.8 | -0.6 | 10.1 |
| Jun 29 | 1.9 | 14.9 | 2.0 | 12.4 |
| Jul 6 | -0.8 | 14.0 | -0.5 | 11.8 |
Source: http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/mdc_us_stocks.html?mod=mdc_topnav_2_3014
Table VI-6, updated with every blog comment, shows that exchange rate valuations affect a large variety of countries, in fact, almost the entire world, in magnitudes that cause major problems for domestic monetary policy and trade flows. Dollar devaluation is expected to continue because of zero fed funds rate, expectations of rising inflation, large budget deficit of the federal government (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703907004576279321350926848.html?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection) and now zero interest rates indefinitely but with interruptions caused by risk aversion events. Such an event actually occurred in the week of Sep 23 reversing the devaluation of the dollar in the form of sharp appreciation of the dollar relative to other currencies from all over the world including the offshore Chinese yuan market. Column “Peak” in Table VI-6 shows exchange rates during the crisis year of 2008. There was a flight to safety in dollar-denominated government assets as a result of the arguments in favor of TARP (Cochrane and Zingales 2009). This is evident in various exchange rates that depreciated sharply against the dollar such as the South African rand (ZAR) at the peak of depreciation of ZAR 11.578/USD on Oct 22, 2008, subsequently appreciating to the trough of ZAR 7.238/USD by Aug 15, 2010 but now depreciating by 13.9 percent to ZAR 8.2483/USD on Jul 6, 2012, which is still 28.8 percent stronger than on Oct 22, 2008. An example from Asia is the Singapore Dollar (SGD) highly depreciated at the peak of SGD 1.553/USD on Mar 3, 2009 but subsequently appreciating by 13.2 percent to the trough of SGD 1.348/USD on Aug 9, 2010 but is now only 5.6 percent stronger at SGD 1.2719/USD on Jul 6, 2012 relative to the trough of depreciation but still stronger by 18.1 percent relative to the peak of depreciation on Mar 3, 2009. Another example is the Brazilian real (BRL) that depreciated at the peak to BRL 2.43/USD on Dec 5, 2008 but appreciated 28.5 percent to the trough at BRL 1.737/USD on Apr 30, 2010, showing depreciation of 16.8 percent relative to the trough to BRL 2.0281/USD on Jul 6, 2012 but still stronger by 16.5 percent relative to the peak on Dec 5, 2008. At one point in 2011 the Brazilian real traded at BRL 1.55/USD and in the week of Sep 23 surpassed BRL 1.90/USD in intraday trading for depreciation of more than 20 percent. The Banco Central do Brasil, Brazil’s central bank, lowered its policy rate SELIC by 50 basis points for the sixth consecutive meeting of its monetary policy committee, COPOM (http://www.bcb.gov.br/textonoticia.asp?codigo=3554&IDPAI=NEWS):
“Copom reduces the Selic rate to 8.5 percent
30/05/2012 8:04:00 PM
Brasília - Continuing the adjustment process of monetary conditions, the Copom unanimously decided to reduce the Selic rate to 8.50 percent.”
Jeffrey T. Lewis, writing on “Brazil steps up battle to curb real’s rise,” on Mar 1, 2012, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052970203986604577255793224099580.html?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection), analyzes new measures by Brazil to prevent further appreciation of its currency, including the extension of the tax on foreign capital for three years terms, subsequently broadened to five years, and intervention in the foreign exchange market by the central bank. Unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates and quantitative easing creates trends such as the depreciation of the dollar followed by Table VI-6 but with abrupt reversals during risk aversion. The main effects of unconventional monetary policy are on valuations of risk financial assets and not necessarily on consumption and investment or aggregate demand.
Table VI-6, Exchange Rates
| Peak | Trough | ∆% P/T | Jul 6, 2012 | ∆% T Jul 6, 2012 | ∆% P Jul 6, 2012 | |
| EUR USD | 7/15 | 6/7 2010 | 7/6 2012 | |||
| Rate | 1.59 | 1.192 | 1.2288 | |||
| ∆% | -33.4 | 3.0 | -29.4 | |||
| JPY USD | 8/18 | 9/15 | 7/6 2012 | |||
| Rate | 110.19 | 83.07 | 79.66 | |||
| ∆% | 24.6 | 4.1 | 27.7 | |||
| CHF USD | 11/21 2008 | 12/8 2009 | 7/6 2012 | |||
| Rate | 1.225 | 1.025 | 0.9774 | |||
| ∆% | 16.3 | 4.6 | 20.2 | |||
| USD GBP | 7/15 | 1/2/ 2009 | 7/6 2012 | |||
| Rate | 2.006 | 1.388 | 1.5489 | |||
| ∆% | -44.5 | 10.4 | -29.5 | |||
| USD AUD | 7/15 2008 | 10/27 2008 | 7/6 | |||
| Rate | 1.0215 | 1.6639 | 1.0211 | |||
| ∆% | -62.9 | 41.1 | 4.1 | |||
| ZAR USD | 10/22 2008 | 8/15 | 6/29 2012 | |||
| Rate | 11.578 | 7.238 | 8.2483 | |||
| ∆% | 37.5 | -13.9 | 28.8 | |||
| SGD USD | 3/3 | 8/9 | 7/6 | |||
| Rate | 1.553 | 1.348 | 1.2719 | |||
| ∆% | 13.2 | 5.6 | 18.1 | |||
| HKD USD | 8/15 2008 | 12/14 2009 | 7/6 | |||
| Rate | 7.813 | 7.752 | 7.7542 | |||
| ∆% | 0.8 | 0.0 | 0.8 | |||
| BRL USD | 12/5 2008 | 4/30 2010 | 7/6 2012 | |||
| Rate | 2.43 | 1.737 | 2.0281 | |||
| ∆% | 28.5 | -16.8 | 16.5 | |||
| CZK USD | 2/13 2009 | 8/6 2010 | 7/6 | |||
| Rate | 22.19 | 18.693 | 20.92 | |||
| ∆% | 15.7 | -11.9 | 5.7 | |||
| SEK USD | 3/4 2009 | 8/9 2010 | 7/6 2012 | |||
| Rate | 9.313 | 7.108 | 7.0204 | |||
| ∆% | 23.7 | 1.2 | 24.6 | |||
| CNY USD | 7/20 2005 | 7/15 | 7/6 | |||
| Rate | 8.2765 | 6.8211 | 6.3658 | |||
| ∆% | 17.6 | 6.7 | 23.1 |
Symbols: USD: US dollar; EUR: euro; JPY: Japanese yen; CHF: Swiss franc; GBP: UK pound; AUD: Australian dollar; ZAR: South African rand; SGD: Singapore dollar; HKD: Hong Kong dollar; BRL: Brazil real; CZK: Czech koruna; SEK: Swedish krona; CNY: Chinese yuan; P: peak; T: trough
Note: percentages calculated with currencies expressed in units of domestic currency per dollar; negative sign means devaluation and no sign appreciation
Source:
http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/mdc_currencies.html?mod=mdc_topnav_2_3000
http://federalreserve.gov/releases/h10/Hist/dat00_ch.htm
Chart VI-1 of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System provides indexes of the dollar from 2010 to 2012. The dollar depreciates during episodes of risk appetite but appreciate during risk aversion as funds seek dollar-denominated assets in avoiding financial risk.
Chart VI-1, US Dollar Currency Indexes
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
Chart VI-2 of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System provides the exchange rate of the US relative to the euro, or USD/EUR. During maintenance of the policy of zero fed funds rates the dollar appreciates during periods of significant risk aversion such as the flight into US government obligations in late 2008 and early 2009 and during the various fears generated by the European sovereign debt crisis.
Chart VI-2, US Dollars per Euro, 2009-2012
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
Table VI-7, updated with every blog comment, provides in the second column the yield at the close of market of the 10-year Treasury note on the date in the first column. The price in the third column is calculated with the coupon of 2.625 percent of the 10-year note current at the time of the second round of quantitative easing after Nov 3, 2010 and the final column “∆% 11/04/10” calculates the percentage change of the price on the date relative to that of 101.2573 at the close of market on Nov 4, 2010, one day after the decision on quantitative easing by the Fed on Nov 3, 2010. Prices with new coupons such as 2.0 percent in recent auctions (http://www.treasurydirect.gov/RI/OFAuctions?form=extended&cusip=912828RR3) are not comparable to prices in Table VI-7. The highest yield in the decade was 5.510 percent on May 1, 2001 that would result in a loss of principal of 22.9 percent relative to the price on Nov 4. Monetary policy has created a “duration trap” of bond prices. Duration is the percentage change in bond price resulting from a percentage change in yield or what economists call the yield elasticity of bond price. Duration is higher the lower the bond coupon and yield, all other things constant. This means that the price loss in a yield rise from low coupons and yields is much higher than with high coupons and yields. Intuitively, the higher coupon payments offset part of the price loss. Prices/yields of Treasury securities were affected by the combination of Fed purchases for its program of quantitative easing and also by the flight to dollar-denominated assets because of geopolitical risks in the Middle East, subsequently by the tragic Great East Japan Earthquake and Tsunami and now again by the sovereign risk doubts in Europe and the growth recession in the US and the world. The yield of 1.548 percent at the close of market on Fri Jul 6, 2012 would be equivalent to price of 109.9423 in a hypothetical bond maturing in 10 years with coupon of 2.625 percent for price gain of 8.6 percent relative to the price on Nov 4, 2010, one day after the decision on the second program of quantitative easing, as shown in the first to the last row of Table VI-7. The price loss between Jun 1, 2012 and Jun 8, 2012 would have been 1.6 percent, in just a week, and much higher with leverage of 10:1 as typical in Treasury positions. The price loss between Mar 9, 2012 and Mar 16, 2012 is 2.3 percent but much higher when using common leverage of 10:1. These losses defy annualizing. If inflation accelerates, yields of Treasury securities may rise sharply. Yields are not observed without special yield-lowering effects such as the flight into dollars caused by the events in the Middle East, continuing purchases of Treasury securities by the Fed, the tragic Tōhoku or Great East Earthquake and Tsunami of Mar 11, 2011 affecting Japan, recurring fears on European sovereign credit issues and worldwide risk aversion in the week of Sep 30 caused by “let’s twist again” monetary policy. The realization of a growth standstill recession is also influencing yields. Important causes of the earlier rise in yields shown in Table VI-7 are expectations of rising inflation and US government debt estimated to be around 70 percent of GDP in 2012 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/02/thirty-one-million-unemployed-or.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/08/united-states-gdp-growth-standstill.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/02/policy-inflation-growth-unemployment.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/04/budget-quagmire-fed-commodities_10.html), rising from 40.5 percent of GDP in 2008, 54.1 percent in 2009 (Table IV-1 at http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/02/thirty-one-million-unemployed-or.html and Table 2 in http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/04/budget-quagmire-fed-commodities_10.html) and 67.7 percent in 2011. On Jul 4, 2012, the line “Reserve Bank credit” in the Fed balance sheet stood at $2848 billion, or $2.8 trillion, with portfolio of long-term securities of $2584 billion, or $2.6 trillion, consisting of $1570 billion Treasury nominal notes and bonds, $68 billion of notes and bonds inflation-indexed, $91 billion Federal agency debt securities and $855 billion mortgage-backed securities; reserve balances deposited with Federal Reserve Banks reached $1506 billion or $1.5 trillion (http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h41/current/h41.htm#h41tab1). There is no simple exit of this trap created by the highest monetary policy accommodation in US history together with the highest deficits and debt in percent of GDP since World War II. Risk aversion from various sources, discussed in section III World Financial Turbulence, has been affecting financial markets for several months. The risk is that in a reversal of risk aversion that has been typical in this cyclical expansion of the economy yields of Treasury securities may back up sharply.
Table VI-7, Yield, Price and Percentage Change to November 4, 2010 of Ten-Year Treasury Note
| Date | Yield | Price | ∆% 11/04/10 |
| 05/01/01 | 5.510 | 78.0582 | -22.9 |
| 06/10/03 | 3.112 | 95.8452 | -5.3 |
| 06/12/07 | 5.297 | 79.4747 | -21.5 |
| 12/19/08 | 2.213 | 104.4981 | 3.2 |
| 12/31/08 | 2.240 | 103.4295 | 2.1 |
| 03/19/09 | 2.605 | 100.1748 | -1.1 |
| 06/09/09 | 3.862 | 89.8257 | -11.3 |
| 10/07/09 | 3.182 | 95.2643 | -5.9 |
| 11/27/09 | 3.197 | 95.1403 | -6.0 |
| 12/31/09 | 3.835 | 90.0347 | -11.1 |
| 02/09/10 | 3.646 | 91.5239 | -9.6 |
| 03/04/10 | 3.605 | 91.8384 | -9.3 |
| 04/05/10 | 3.986 | 88.8726 | -12.2 |
| 08/31/10 | 2.473 | 101.3338 | 0.08 |
| 10/07/10 | 2.385 | 102.1224 | 0.8 |
| 10/28/10 | 2.658 | 99.7119 | -1.5 |
| 11/04/10 | 2.481 | 101.2573 | - |
| 11/15/10 | 2.964 | 97.0867 | -4.1 |
| 11/26/10 | 2.869 | 97.8932 | -3.3 |
| 12/03/10 | 3.007 | 96.7241 | -4.5 |
| 12/10/10 | 3.324 | 94.0982 | -7.1 |
| 12/15/10 | 3.517 | 92.5427 | -8.6 |
| 12/17/10 | 3.338 | 93.9842 | -7.2 |
| 12/23/10 | 3.397 | 93.5051 | -7.7 |
| 12/31/10 | 3.228 | 94.3923 | -6.7 |
| 01/07/11 | 3.322 | 94.1146 | -7.1 |
| 01/14/11 | 3.323 | 94.1064 | -7.1 |
| 01/21/11 | 3.414 | 93.4687 | -7.7 |
| 01/28/11 | 3.323 | 94.1064 | -7.1 |
| 02/04/11 | 3.640 | 91.750 | -9.4 |
| 02/11/11 | 3.643 | 91.5319 | -9.6 |
| 02/18/11 | 3.582 | 92.0157 | -9.1 |
| 02/25/11 | 3.414 | 93.3676 | -7.8 |
| 03/04/11 | 3.494 | 92.7235 | -8.4 |
| 03/11/11 | 3.401 | 93.4727 | -7.7 |
| 03/18/11 | 3.273 | 94.5115 | -6.7 |
| 03/25/11 | 3.435 | 93.1935 | -7.9 |
| 04/01/11 | 3.445 | 93.1129 | -8.0 |
| 04/08/11 | 3.576 | 92.0635 | -9.1 |
| 04/15/11 | 3.411 | 93.3874 | -7.8 |
| 04/22/11 | 3.402 | 93.4646 | -7.7 |
| 04/29/11 | 3.290 | 94.3759 | -6.8 |
| 05/06/11 | 3.147 | 95.5542 | -5.6 |
| 05/13/11 | 3.173 | 95.3387 | -5.8 |
| 05/20/11 | 3.146 | 95.5625 | -5.6 |
| 05/27/11 | 3.068 | 96.2089 | -4.9 |
| 06/03/11 | 2.990 | 96.8672 | -4.3 |
| 06/10/11 | 2.973 | 97.0106 | -4.2 |
| 06/17/11 | 2.937 | 97.3134 | -3.9 |
| 06/24/11 | 2.872 | 97.8662 | -3.3 |
| 07/01/11 | 3.186 | 95.2281 | -5.9 |
| 07/08/11 | 3.022 | 96.5957 | -4.6 |
| 07/15/11 | 2.905 | 97.5851 | -3.6 |
| 07/22/11 | 2.964 | 97.0847 | -4.1 |
| 07/29/11 | 2.795 | 98.5258 | -2.7 |
| 08/05/11 | 2.566 | 100.5175 | -0.7 |
| 08/12/11 | 2.249 | 103.3504 | 2.1 |
| 08/19/11 | 2.066 | 105.270 | 3.7 |
| 08/26/11 | 2.202 | 103.7781 | 2.5 |
| 09/02/11 | 1.992 | 105.7137 | 4.4 |
| 09/09/11 | 1.918 | 106.4055 | 5.1 |
| 09/16/11 | 2.053 | 101.5434 | 0.3 |
| 09/23/11 | 1.826 | 107.2727 | 5.9 |
| 09/30/11 | 1.912 | 106.4602 | 5.1 |
| 10/07/11 | 2.078 | 104.9161 | 3.6 |
| 10/14/11 | 2.251 | 103.3323 | 2.0 |
| 10/21/11 | 2.220 | 103.6141 | 2.3 |
| 10/28/11 | 2.326 | 102.6540 | 1.4 |
| 11/04/11 | 2.066 | 105.0270 | 3.7 |
| 11/11/11 | 2.057 | 105.1103 | 3.8 |
| 11/18/11 | 2.003 | 105.6113 | 4.3 |
| 11/25/11 | 1.964 | 105.9749 | 4.7 |
| 12/02/11 | 2.042 | 105.2492 | 3.9 |
| 12/09/11 | 2.065 | 105.0363 | 3.7 |
| 12/16/11 | 1.847 | 107.0741 | 5.7 |
| 12/23/11 | 2.027 | 105.3883 | 4.1 |
| 12/30/11 | 1.871 | 106.8476 | 5.5 |
| 01/06/12 | 1.957 | 106.0403 | 4.7 |
| 01/13/12 | 1.869 | 106.8664 | 5.5 |
| 01/20/12 | 2.026 | 105.3976 | 4.1 |
| 01/27/12 | 1.893 | 106.6404 | 5.3 |
| 02/03/12 | 1.923 | 106.3586 | 5.0 |
| 02/10/12 | 1.974 | 105.8815 | 4.6 |
| 02/17/12 | 2.000 | 105.6392 | 4.3 |
| 02/24/12 | 1.977 | 105.8535 | 4.5 |
| 03/02/12 | 1.977 | 105.8535 | 4.5 |
| 03/09/12 | 2.031 | 105.3512 | 4.0 |
| 03/16/12 | 2.294 | 102.9428 | 1.7 |
| 03/23/12 | 2.234 | 103.4867 | 2.2 |
| 03/30/12 | 2.214 | 103.6687 | 2.4 |
| 04/06/12 | 2.058 | 105.1010 | 3.8 |
| 04/13/12 | 1.987 | 105.7603 | 4.4 |
| 04/20/12 | 1.959 | 106.0216 | 4.7 |
| 04/27/12 | 1.931 | 106.2836 | 5.0 |
| 05/04/12 | 1.876 | 106.8004 | 5.5 |
| 05/11/12 | 1.845 | 107.0930 | 5.8 |
| 05/18/12 | 1.714 | 108.3393 | 7.0 |
| 05/25/12 | 1.738 | 108.1098 | 6.8 |
| 06/01/12 | 1.454 | 110.8618 | 9.5 |
| 06/08/12 | 1.635 | 109.0989 | 7.7 |
| 06/15/12 | 1.584 | 109.5924 | 8.2 |
| 06/22/12 | 1.676 | 108.7039 | 7.4 |
| 06/29/12 | 1.648 | 108.9734 | 7.6 |
| 07/06/12 | 1.548 | 109.9423 | 8.6 |
Note: price is calculated for an artificial 10-year note paying semi-annual coupon and maturing in ten years using the actual yields traded on the dates and the coupon of 2.625% on 11/04/10
Source:
http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/mdc_bonds.html?mod=mdc_topnav_2_3000
VII Economic Indicators. Crude oil input in refineries increased 0.3 percent to 15,626 thousand barrels per day on average in the four weeks ending on Jun 29, 2012 from 15,585 thousand barrels per day in the four weeks ending on Jun 22, 2012, as shown in Table VII-1. The rate of capacity utilization in refineries continues at a relatively high level of 92.1 percent on Jun 29, 2012, which is higher than 88.0 percent on Jul 1, 2011 and higher than 91.9 percent on Jun 22, 2012. Imports of crude oil decreased 0.5 percent from 9,120 thousand barrels per day on average in the four weeks ending on Jun 22 to 9,075 thousand barrels per day in the week of Jun 29. The Energy Information Administration (EIA) informs that “US crude oil imports averaged 8.8 million barrels per day last week, down by 344 thousand barrels per day from the previous week [Jun 22]” (http://www.eia.gov/pub/oil_gas/petroleum/data_publications/weekly_petroleum_status_report/current/pdf/highlights.pdf). Increasing utilization in refineries with decreasing imports at the margin in the prior week resulted in decrease of commercial crude oil stocks by 4.3 million barrels from 387.2 million barrels on Jun 22 to 382.9 million barrels on Jun 29. Motor gasoline production increased 0.9 percent to 9,310 thousand barrels per day in the week of Jun 29 from 9,227 thousand barrels per day on average in the week of Jun 22. Gasoline stocks increased 0.2 million barrels and stocks of fuel oil decreased 1.1 million barrels. Supply of gasoline decreased from 9,315 thousand barrels per day on Jul 1, 2011, to 8,918 thousand barrels per day on Jun 29, 2012, or by 4.3 percent, while fuel oil supply increased 3.8 percent. Part of the fall in consumption of gasoline is due to high prices and part to the growth recession. WTI crude oil price traded at $85.04/barrel on Jun 29, 2012, decreasing 10.3 percent relative to $94.81/barrel on Jul 1, 2011. Gasoline prices fell 6.2 percent from Jul 4, 2011 to Jul 2, 2012. Increases in prices of crude oil and gasoline relative to a year earlier are moderating because year earlier prices are already reflecting the commodity price surge and commodity prices have been declining recently during worldwide risk aversion. Gasoline prices had been increasing to the highest levels at this time of the year.
Table VII-1, US, Energy Information Administration Weekly Petroleum Status Report
| Four Weeks Ending Thousand Barrels/Day | 6/29/12 | 6/22/12 | 7/1/11 |
| Crude Oil Refineries Input | 15,626 Week ∆%: 0.3 | 15,585 | 15,177 |
| Refinery Capacity Utilization % | 92.1 | 91.9 | 88.0 |
| Motor Gasoline Production | 9,310 Week ∆%: 0.9 | 9,227 | 9,409 |
| Distillate Fuel Oil Production | 4,668 Week ∆%: 0.3 | 4,654 | 4,362 |
| Crude Oil Imports | 9,075 Week ∆%: -0.5 | 9,120 | 9,095 |
| Motor Gasoline Supplied | 8,918 ∆% 2012/2011= -4.3% | 8,829 | 9,315 |
| Distillate Fuel Oil Supplied | 3,717 ∆% 2012/2011 = 3.8% | 3,599 | 3,580 |
| 6/29/12 | 6/22/12 | 7/1/11 | |
| Crude Oil Stocks | 382.9 ∆= -4.3 MB | 387.2 | 358.6 |
| Motor Gasoline Million B | 205.0 ∆= +0.2 MB | 204.8 | 212.5 |
| Distillate Fuel Oil Million B | 117.8 | 118.9 | 142.1 |
| WTI Crude Oil Price $/B | 85.04 ∆% 2012/2011 -10.3 | 79.33 | 94.81 |
| 7/2/12 | 6/25/12 | 7/4/11 | |
| Regular Motor Gasoline $/G | 3.356 ∆% 2012/2011 | 3.437 | 3.579 |
B: barrels; G: gallon
Source: US Energy Information Administration
Chart VII-1 of the US Energy Information Administration shows commercial stocks of crude oil of the US. There have been fluctuations around an upward trend since 2005. Crude oil stocks trended downwardly during a few weeks but with fluctuations followed by several sharp weekly increases.
Chart VII-1, US, Weekly Crude Oil Ending Stocks
Source: US Energy Information Administration
http://www.eia.gov/dnav/pet/hist/LeafHandler.ashx?n=PET&s=WCESTUS1&f=W
Chart VII-2 provides the evolution of distillate fuel oil stocks in the US since 2007. There have been oscillations around a downward trend.
Chart VII-2, US, Total Distillate Fuel Oil Stocks
Source: US Energy Information Administration
Chart VII-3 of the US Energy Information Administration shows the price of WTI crude oil since the 1980s. Chart VII-3 captures commodity price shocks during the past decade. The costly mirage of deflation was caused by the decline in oil prices during the recession of 2001. The upward trend after 2003 was promoted by the carry trade from near zero interest rates. The jump above $140/barrel during the global recession in 2008 can only be explained by the carry trade promoted by monetary policy of zero fed funds rate. After moderation of risk aversion, the carry trade returned with resulting sharp upward trend of crude prices. Risk aversion resulted in another drop in recent weeks.
Chart VII-3, US, Crude Oil Futures Contract
Source: US Energy Information Administration
http://www.eia.gov/dnav/pet/hist/LeafHandler.ashx?n=PET&s=RCLC1&f=D
There is typically significant difference between initial claims for unemployment insurance adjusted and not adjusted for seasonality provided in Table VII-2. Seasonally adjusted claims decreased 14,000 from 388,000 on Jun 23, 2012, to 374,000 on Jun 30. Claims not adjusted for seasonality decreased 3,129 from 370,460 on Jun 23, 2012 to 367,331 on Jun 30. Strong seasonality is preventing clear analysis of labor markets.
Table VII-2, US, Initial Claims for Unemployment Insurance
| SA | NSA | 4-week MA SA | |
| June 30, 12 | 374,000 | 367,331 | 385,750 |
| June 23, 12 | 388,000 | 370,460 | 387,250 |
| Change | -14,000 | -3,129 | -1,500 |
| Jun 16, 12 | 392,000 | 364,548 | 387,500 |
| Prior Year | 422,000 | 425,640 | 422,250 |
Note: SA: seasonally adjusted; NSA: not seasonally adjusted; MA: moving average
Source: http://www.dol.gov/opa/media/press/eta/ui/current.htm
Table VII-3 provides seasonally and not seasonally adjusted claims in the comparable week for the years from 2001 to 2012. Seasonally adjusted claims typically are lower than claims not adjusted for seasonality. Claims not seasonally adjusted have declined from 563,387 on Jun 27, 2009 to 406,633 on Jun 25, 2011, and 367,331 on Jun 30, 2012. There is strong indication of significant decline in the level of layoffs in the US but some doubts at the margin after the high increase in unadjusted claims in the week of Jun 9, 2012. Hiring has not recovered (see http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/recovery-without-hiring-continuance-of.html).
Table VII-3, US, Unemployment Insurance Weekly Claims
| Not Seasonally Adjusted Claims | Seasonally Adjusted Claims | |
| Jun 30, 2001 | 375,885 | 394,000 |
| Jun 29, 2002 | 358,658 | 386,00 |
| Jun 28, 2003 | 394,214 | 429,000 |
| Jun 26, 2004 | 318,746 | 348,000 |
| Jun 25, 2005 | 286,681 | 311,000 |
| Jun 24, 2006 | 287,503 | 309,000 |
| Jun 30, 2007 | 300,348 | 317,000 |
| Jun 28, 2008 | 368,544 | 392,000 |
| Jun 27, 2009 | 563,387 | 595,000 |
| Jun 26, 2010 | 444,712 | 466,000 |
| Jun 25, 2011 | 406,633 | 425,000 |
| Jun 30, 2012 | 367,331 | 374,000 |
Source: http://workforcesecurity.doleta.gov/unemploy/claims.asp
VIII Interest Rates. It is quite difficult to measure inflationary expectations because they tend to break abruptly from past inflation. There could still be an influence of past and current inflation in the calculation of future inflation by economic agents. Table VIII-1 provides inflation of the CPI. In the four months Jan to May 2012, CPI inflation for all items seasonally adjusted was 1.4 percent in annual equivalent, that is, compounding inflation in Jan-May 2012 and assuming it would be repeated for a full year. In the 12 months ending in May, CPI inflation of all items not seasonally adjusted was 1.7 percent. Inflation in May 2012 not seasonally adjusted was minus 0.1 percent relative to Apr 2012 and minus 0.3 percent seasonally adjusted (http://www.bls.gov/cpi/). The second row provides the same measurements for the CPI of all items excluding food and energy: 2.3 percent in 12 months and 2.2 percent in annual equivalent Jan-May 2012. Bloomberg provides the yield curve of US Treasury securities (http://www.bloomberg.com/markets/rates-bonds/government-bonds/us/). The lowest yield is 0.07 percent for three months, 0.14 percent for six months, 0.18 percent for 12 months, 0.27 percent for two years, 0.36 percent for three years, 0.64 percent for five years, 1.01 percent for seven years, 1.55 percent for ten years and 2.66 percent for 30 years. The Irving Fisher definition of real interest rates is approximately the difference between nominal interest rates, which are those estimated by Bloomberg, and the rate of inflation expected in the term of the security, which could behave as in Table VIII-1. May inflation is low because of the unwinding of carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures prices but could ignite again with subdued risk aversion. Real interest rates in the US have been negative during substantial periods in the past decade while monetary policy pursues a policy of attaining its “dual mandate” of (http://www.federalreserve.gov/aboutthefed/mission.htm):
“Conducting the nation's monetary policy by influencing the monetary and credit conditions in the economy in pursuit of maximum employment, stable prices, and moderate long-term interest rates”
Negative real rates of interest distort calculations of risk and returns from capital budgeting by firms, through lending by financial intermediaries to decisions on savings, housing and purchases of households. Inflation on near zero interest rates misallocates resources away from their most productive uses and creates uncertainty of the future path of adjustment to higher interest rates that inhibit sound decisions.
Table VIII-1, US, Consumer Price Index Percentage Changes 12 months NSA and Annual Equivalent ∆%
| ∆% 12 Months May 2012/May | ∆% Annual Equivalent Jan-May 2012 SA | |
| CPI All Items | 1.7 | 1.4 |
| CPI ex Food and Energy | 2.3 | 2.2 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/cpi/
IX Conclusion. Table IX-1 provides the data required for broader comparison of the cyclical expansions of IQ1983 to IVQ1985 and the current one from 2009 to 2012. First, in the 13 quarters from IQ1983 to IVQ1985, GDP increased 19.6 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 5.7 percent; real disposable personal income (RDPI) increased 14.5 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 4.3 percent; RDPI per capita increased 11.5 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 3.4 percent; and population increased 2.7 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 0.8 percent. Second, in the 11 quarters of the current cyclical expansion from IIIQ2009 to IQ2012, GDP increased 6.7 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 2.4 percent; real disposable personal income (RDPI) increased 2.5 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 0.9 percent; RDPI per capita increased 0.4 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 0.1 percent; and population increased 2.1 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 0.8 percent. Third, since the beginning of the recession in IVQ2007 to IQ2012, GDP increased 1.2 percent, or barely above the level before the recession; real disposable personal income increased 2.7 percent; population increased 3.5 percent; and real disposable personal income per capita is 0.8 percent lower than the level before the recession. Real disposable personal income is the actual take home pay after inflation and taxes and real disposable income per capita is what is left per inhabitant. The current cyclical expansion is the worst in the period after World War II in terms of growth of economic activity and income. The United States grew during its history at high rates of per capita income that made its economy the largest in the world. That dynamism is disappearing.
Table IX-1, US, GDP, Real Disposable Personal Income, Real Disposable Income per Capita and Population in 1983-85 and 2007-2011, %
| # Quarters | ∆% | ∆% Annual Equivalent | |
| IQ1983 to IVQ1985 | 13 | ||
| GDP | 19.6 | 5.7 | |
| RDPI | 14.5 | 4.3 | |
| RDPI Per Capita | 11.5 | 3.4 | |
| Population | 2.7 | 0.8 | |
| IIIQ2009 to IQ2012 | 11 | ||
| GDP | 6.7 | 2.4 | |
| RDPI | 2.5 | 0.9 | |
| RDPI per Capita | 0.4 | 0.1 | |
| Population | 2.1 | 0.8 | |
| IVQ2007 to IQ2012 | 18 | ||
| GDP | 1.2 | ||
| RDPI | 2.7 | ||
| RDPI per Capita | -0.8 | ||
| Population | 3.5 |
RDPI: Real Disposable Personal Income
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
References
Abraham, Katharine G., John C. Haltiwanger, Kristin Sandusky and James Spletzer. 2009. Exploring differences in employment between household and establishment data. Cambridge, MA, National Bureau of Economic Research, Mar 2009.
Allen, William R. 1993. Irving Fisher and the 100 percent reserve proposal. Journal of Law and Economics 36 (2, Oct): 703-17.
Andrés, Javier, J. David López-Salido and Edward Nelson. 2004. Tobin’s imperfect asset substitution in optimizing equilibrium. Journal of Money, Credit and Banking 36 (4, Aug): 665-90.
Asso, Pier Francesco, George A. Kahn and Robert Leeson. 2007. The Taylor Rule and the transformation of monetary policy. Kansas City: Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City RWP 07-II, Dec.
Asso, Pier Francesco, George A. Kahn and Robert Leeson. 2010. The Taylor Rule and the practice of central banking. Kansas City: Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City, RWP 10-05, Feb.
Bagehot, Walter. 1873. Lombard Street, 14th edn. London: Kegan, Paul & Co, 1917.
Ball, Laurence and N. Gregory Mankiw. 2002. The NAIRU in theory and practice. Journal of Economic Perspectives 16 (4, Autumn): 115-36.
Bank of Japan. 2012Feb14APP. Amendment to “Principal Terms and Conditions for the Asset Purchase Program.” Tokyo, Bank of Japan, Feb 14 http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2012/rel120214a.pdf
Bank of Japan. 2012Feb14PSG. The price stability goal in the medium to long term. Tokyo, Bank of Japan, Feb 14 http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2012/k120214b.pdf
Bank of Japan. 2012Feb14EME. Enhancement of monetary easing. Tokyo, Bank of Japan, Feb 14 http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2012/k120214a.pdf
Barbosa, Fernando de Holanda. 1987. Domestic and international sources of Brazilian inflation: 1947-80. In Luigi L. Pasinetti and P.J. Lloyd, eds. Structural change, economic interdependence and world development. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.
Barro, Robert J. and David B. Gordon. 1983a. Rules, discretion and reputation in a model of monetary policy. Journal of Monetary Economics 12 (1): 101-121.
Barro, Robert J. and David B. Gordon. 1983b. A positive theory of monetary policy in a natural rate model. Journal of Political Economy 91 (4, Aug): 589-610.
Barsky, Robert B. and Lutz Kilian. 2004. Oil and the macroeconomy since the 1970s. Journal of Economic Perspectives 18 (4, Autumn): 115-34.
Basel Committee on Banking Supervision. 2011Jun. Basel II: a global regulatory framework for more resilient banks and banking systems. Basel, Switzerland: BIS, Jun 2011 http://www.bis.org/publ/bcbs189.pdf
Batini, Nicoletta and Edward Nelson. 2002. The lag from monetary policy actions to inflation: Friedman revisited. London, Bank of England, External MPC Unit Discussion Paper No. 6, Jan.
Beim, David O. 2011Oct9. Can the euro be saved? New York City, Columbia University, Oct 9 http://www1.gsb.columbia.edu/mygsb/faculty/research/pubfiles/5573/Can%20the%20Euro%20be%20Saved.pdf
Bernanke, Ben S. 2002. Deflation: making sure “it” doesn’t happen here. Washington, DC, National Economists Club, Nov 21 http://www.federalreserve.gov/boarddocs/speeches/2002/20021121/default.htm
Bernanke, Ben S. 2000. Japanese monetary policy: a case of self-induced paralysis? In Ryoichi Mikitani and Adam S. Posen, Japan’s financial crisis and its parallels to US experience. Washington, DC, Institute for International Economics, Special Report 13, Sep 2000.
Bernanke, Ben S. 2003. A perspective on inflation targeting. Business Economics 38 (3, Jul): 7–15.
Bernanke, Ben S. 2009SL. The crisis and the policy response. London, London School of Economics, Stamp Lecture, Jan 13 http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/bernanke20090113a.htm
Bernanke, Ben S. 2010WP. What the Fed did and why: supporting the recovery and sustaining price stability. Washington Post, Nov 4. http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2010/11/03/AR2010110307372_pf.html
Bernanke, Ben S. 2011Oct4JEC. Statement. Washington, DC, Joint Economic Committee, US Congress, Oct 4 http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/bernanke20111004a.pdf
Bernanke, Ben S. 2012Apr25. Transcript of Chairman Bernanke’s press conference April 25, 2012. Washington, DC, Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Apr 25 http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20120425.pdf
Bernanke, Ben S. and Frederic S. Mishkin. 1997. Inflation targeting: a new framework for monetary policy? Journal of Economic Perspectives 11 (2, Spring): 97–116.
Bernanke, Ben S. and Vincent R. Reinhart. 2004. Conducting monetary policy at very low short-term interest rates. American Economic Review 94 (2): 85-90.
Black, Fischer and Myron Scholes. 1973. The pricing of options and corporate liabilities. Journal of Political Economy 81 (May/June): 637-54.
Blanchard, Olivier. 2011WEOSep. Foreword to IMF 2011WEOSep: XIII-XIV.
Blanchard, Olivier. 2012WEOApr. Foreword to IMF 2012WEOApr: XIII-XIV
Blanchard, Olivier and Lawrence F. Katz. 1997. What we know and do not know about the natural rate of unemployment. Journal of Economic Perspectives 11 (1, Winter): 51-72.
Blinder, Alan S. 2000. Monetary policy at the zero lower bound: balancing the risks. Journal of Money, Credit and Banking 32 (4, Nov): 1093-1099.
Bordo, Michael D. and Hugh Rockoff. 2011. The influence of Irving Fisher on Milton Friedman’s monetary economics. Denver, CO, AEA Session on Irving Fisher and Modern Economics: 100 years after the Purchasing Power of Money, Jan 8 www.aeaweb.org/aea/2011conference/program/retrieve.php?pdfid
Bricker, Jesse, Arthur B. Kennickell, Kevin B. Moore and John Sabelhaus. 2012. Changes in US family finances from 2007 to 2010: evidence from the Survey of Consumer Finances. Federal Reserve Bulletin 98 (2, Jun): 2-80 http://www.federalreserve.gov/pubs/bulletin/2012/PDF/scf12.pdf
Brunner, Karl and Allan H. Meltzer. 1973. Mr. Hicks and the “monetarists.” Economica NS 40 (157, Feb): 44-59.
Buiter, Willem. 2011Oct31. EFSF needs bigger bazooka to maximize its firepower. Financial Times, Oct 31 http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/c4886f7a-03d3-11e1-bbc5-00144feabdc0.html#axzz1cMoq63R5
Brunner, Karl and Allan H. Meltzer. 1973. Mr. Hicks and the “monetarists.” Economica NS 40 (157, Feb): 44-59.
Bureau of Labor Statistics. 2011Feb11. Overview of seasonal adjustment of the current employment statistics program. Washington, Feb 11, 2011 http://www.bls.gov/ces/cessa_oview.pdf
Bureau of Labor Statistics. 2012Feb3. Seasonal adjustment files and documentation. Washington, BLD, Feb 3 http://www.bls.gov/web/empsit/cesseasadj.htm
Caballero, Ricardo and Francsco Giavazzi. 2012Jan15. Parity may be euro’s last chance. Bloomberg, Jan 15 http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2012-01-16/dollar-parity-may-be-euro-salvation-commentary-by-caballero-and-giavazzi.html
Cagan, Phillip. 1965. Determinants and effects of changes in the stock of money, 1875-1960. New York: Columbia University Press.
Calomiris, Charles C. and Gary B. Gorton. 1991. The origins of banking panics: models, facts and bank regulation. In R. Glenn Hubbard, ed. Financial markets and financial crises. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Cameron, Rondo E. 1961. France and the economic development of Europe 1800-1914: conquests of peace and seeds of war. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Cameron, Rondo E. 1967. Banking in the early stages of industrialization. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Cameron, Rondo E. 1972. Banking and economic development. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Cameron, Rondo E., V.I. Bovkyn, Richard Sylla, Mira Wilkins, Boris Anan’ich, and A. A. Fursenko, eds. 1992. International Banking 1870-1914. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
CBO. 2012JanBEO. The budget and economic outlook: fiscal years 2012 to 2022. Washington, DC: Congressional Budget Office, Jan http://www.cbo.gov/ftpdocs/126xx/doc12699/01-31-2012_Outlook.pdf
CBO. 2012MarBEO. Updated budget projections: fiscal years 2012 to 2022. Washington, DC: Congressional Budget Office, Mar http://www.cbo.gov/sites/default/files/cbofiles/attachments/March2012Baseline.pdf
CBO. 2012LTBO. The 2012 long-term budget outlook. Washington, DC: Congressional Budget Office, Jun http://www.cbo.gov/sites/default/files/cbofiles/attachments/06-05-Long-Term_Budget_Outlook.pdf
Chung, Hess, Jean-Philippe Laforte, David Reifschneider and John C. Williams. 2011. Have we underestimated the likelihood and severity of zero lower bound events? San Francisco, FRBSF, WP 2011-01 http://www.frbsf.org/publications/economics/papers/2011/wp11-01bk.pdf
Cline, William. 2001. The role of the private sector in resolving financial crises in emerging markets. Cambridge, MA, NBER, Jun.
Cline, William. 2002. Private sector involvement: definition, measurement and implementation. London, Bank of England Conference, Jul-23-4.
Cobet, Aaron E. and Gregory A. Wilson. 2002. Comparing 50 years of labor productivity in US and foreign manufacturing. Monthly Labor Review (Jun): 51-65.
Cochrane, John A. 2010A. The government debt valuation equation. An appendix to “Understanding policy.” http://faculty.chicagobooth.edu/john.cochrane/research/Papers/
Cochrane, John H. 2011Jan. Understanding policy in the great recession: some unpleasant fiscal arithmetic. European Economic Review 55 (1, Jan): 2-30.
Cochrane, John H. and Luigi Zingales. 2009. Lehman and the financial crisis. Wall Street Journal, Sep 15.
Cole, Harold L. and Lee E. Ohanian. 1999. The Great Depression in the United States from a neoclassical perspective. Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis Quarterly Review 23 (1, Winter): 2-24.
Contador, Cláudio R. and Haddad, Cláudio L. 1975. Produto real, moeda e preços. Revista Brasileira de Estatística 36(143, jul/set): 407-40.
Cox, John C., Jonathan E. Ingersoll, Jr. and Stephen A. Ross. 1981. A re-examination of traditional hypotheses about the term structure of interest rates. Journal of Finance 36 (4, Sep): 769-99.
Cox, John C., Jonathan E. Ingersoll, Jr. and Stephen A. Ross. 1985. A theory of the term structure of interest rates. Econometrica 53 (2, Mar): 385-407.
Culbertson, John M. 1957. The term structure of interest rates. Quarterly Journal of Economics 71 (4, Nov): 485-517.
Culbertson, J. M. 1960. Friedman on the lag in effect of monetary policy. Journal of Political Economy 68 (6, Dec): 617-21.
Culbertson, J. M. 1961. The lag in effect of monetary policy: reply. Journal of Political Economy 69 (5, Oct): 467-77.
Culbertson, John M. 1963. The term structure of interest rates: reply. Quarterly Journal of Economics 77 (4, Nov): 691-6.
D’Amico Stefania and Thomas B. King. 2010. Flow and stock effects of large-sale Treasury purchases. Washington, DC, Federal Reserve board, Sep.
Darby, Michael R. Darby. 1974. The permanent income theory of consumption—a restatement. Quarterly Journal of Economics (88, 2): 228-50.
De Long, J. Bradford. 1997. America’s peacetime inflation: the 1970s. In Christina D. Romer and David H. Romer, eds. Reducing inflation: motivation and strategy. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1997.
Doh, Taeyoung. 2010. The efficacy of large-scale asset purchases at the zero lower bound. Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City Economic Review Second Quarter 2010: 5-34 http://www.kansascityfed.org/Publicat/EconRev/PDF/10q2Doh.pdf
Draghi, Mario. 2011Dec1. Introductory statement by Mario Draghi, President of the ECB. Brussels, Hearing before the Plenary of the European Parliament, Dec 1 http://www.ecb.int/press/key/date/2011/html/sp111201.en.html
Draghi, Mario. 2011Dec8. Introductory statement to the press conference. Frankfurt am Main, ECB, Dec 8 http://www.ecb.int/press/pressconf/2011/html/is111208.en.html
Duffie, Darell and Kenneth J. Singleton. 2003. Credit risk: pricing, measurement and management. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
European Council. 2011Dec9. Statements by the euro area heads of state or government. Brussels, European Union, Dec 9 http://www.consilium.europa.eu/uedocs/cms_Data/docs/pressdata/en/ec/126658.pdf
De Long, J. Bradford. 1997. America’s peacetime inflation: the 1970s. In Christina D. Romer and David H. Romer, eds. Reducing inflation: motivation and strategy. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1997.
Diamond, Douglas W. and Philip H. Dybvig. 1983. Bank runs, deposit insurance and liquidity. Journal of Political Economy 91 (3, Jun): 401-49.
Diamond, Douglas W. and Philip H. Dybvig. 1986. Banking theory, deposit insurance and bank regulation. Journal of Business 59 (1, Jan): 55-68.
Diamond, Douglas W. and Raghuram G. Rajan. 2000. A theory of bank capital. Journal of Finance 55 (6, Dec): 2431-65.
Diamond, Douglas W. and Raghuram G. Rajan. 2001a. Banks and liquidity. American Economic Review 91 (2, May): 422-5.
Diamond, Douglas W. and Raghuram G. Rajan. 2001b. Banks and liquidity. American Economic Review 91 (2, May): 422-5.
Dornbusch, Rudiger. 1976. Expectations and exchange rate dynamics. Journal of Political Economy 84 (6, Dec): 1161-76.
Draghi, Mario. 2011Dec15. The euro, monetary stability and the design of a fiscal compact. Berlin, Dec 15 http://www.ecb.int/press/key/date/2011/html/sp111215.en.html
Draghi, Mario. 2012May3. Introductory statement to the press conference. Barcelona, May 3 http://www.ecb.int/press/pressconf/2012/html/is120503.en.html
Draghi, Mario. 2012Jun15. President’s address at the 14th ECB and its Watchers Conference. Frankfurt am Main, European Central Bank, Jun 15 http://www.ecb.int/press/key/date/2012/html/sp120615.en.html
Economides, Nicholas, Yannis Ioannides, Emmanuel Petrakis, Christopher Pissarides and Thanasis Stengos. 2012. What’s at stake in the Greek vote. Wall Street Journal, Jun 14 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052702303822204577466541312448940.html?mod=WSJ_hps_sections_opinion
European Central Bank. 2011MBDec. Editorial. Monthly Bulletin December 2011, 5-9 http://www.ecb.int/pub/pdf/mobu/mb201112en.pdf
European Commission. 2011Oct26SS. Euro summit statement. Brussels, European Commission, Oct 26 http://ec.europa.eu/news/economy/111027_en.htm
European Commission. 2011Oct26MRES. Main results of Euro Summit. Brussels, European Commission, Oct 26 http://www.consilium.europa.eu/uedocs/cms_Data/docs/pressdata/en/ec/125645.pdf
European Council. 2011Dec9. Statements by the euro area heads of state or government. Brussels, European Union, Dec 9 http://www.consilium.europa.eu/uedocs/cms_Data/docs/pressdata/en/ec/126658.pdf
Fama, Eugene F. 1970. Efficient capital markets: a review of theory and empirical work. Journal of Finance 25 (2): 383-417.
Fisher, Irving. 100% Money. 1936. New York: Adelphi Company
Feldstein, Martin. 2012Mar19. Obama’s tax hikes threaten a new US recession. Financial Times, Mar 19 http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/0d0e7acc-6f7d-11e1-9c57-00144feab49a.html#axzz1pexRlsiQ
Friedman, Milton. 1953. The effects of a full-employment policy on economic stability: a formal analysis. In Milton Friedman, Essays on positive economics. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Friedman, Milton. 1957. A Theory of the Consumption Function. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Friedman, Milton. 1961. The lag in effect of monetary policy. Journal of Political Economy 69 (5, Oct): 447-66.
Friedman, Milton. 1968. The role of monetary policy. American Economic Review 58 (1, Mar): 1-17.
Friedman, Milton. 1970. Controls on interest rates paid by banks. Journal of Money, Credit and Banking 2 (1, Feb): 15-32.
Friedman, Milton. 1982. Monetary policy: theory and practice. Journal of Money, Credit and Banking 14 (1, Feb): 98-118.
Friedman, Milton and Anna Jacobson Schwartz. 1963. A monetary history of the United States, 1867-1960. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Friedman, Milton and Anna Jacobson Schwartz. 1970. Monetary statistics of the United States: estimates, sources, and methods. New York: Columbia University Press.
FOMC. 2006Dec12. Meeting of the Federal Open Market Committee December 12, 2006. Washington, DC, Federal Reserve, Dec 12 http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/FOMC20061212meeting.pdf
Gagnon, Joseph, Matthew Raskin, Julie Remache and Brian Sack. 2010. Large-scale asset purchases by the Federal Reserve: did they work. New York, FRBNY Staff Report no. 441, Mar http://data.newyorkfed.org/research/staff_reports/sr441.pdf
Gorton, Gary. 2009EFM. The subprime panic. European Financial Management 15 (1): 10-46.
Graham, Frank D. 1936. Partial reserve money and the 100 per cent proposal. American Economic Review (26, 3): 428-40.
Gorton, Gary and Andrew Metrick. 2010H. Haircuts. Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis Review 92 (6, Nov/Dec): 507-19 http://research.stlouisfed.org/publications/review/10/11/Gorton.pdf
Gorton, Gary and Andrew Metrick. 2010SB. Securitized banking and the run on repo. New Haven, Yale University, 2010, Nov.
Greenspan, Alan. 2004. Risk and uncertainty in monetary policy. American Economic Review 94 (2, May): 33-40. Also available at http://www.federalreserve.gov/boarddocs/speeches/2004/20040103/default.htm
Gürkaynak, Refet S., Brian Sack and Eric T. Swanson. 2005. Do actions speak louder than words? The response of asset prices to monetary policy actions and statements. International Journal of Central Banking 1 (May): 55-93.
Haddad, Cláudio L. 1974. Growth of Brazilian real output. Chicago, Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Chicago, Jun.
Hamilton, Alexander. 1780. The national Bank. In Henry Cabot Lodge, ed. The works of Alexander Hamilton. New York and London: G. P. Putnam & Sons, 1904: 319-45. http://oll.libertyfund.org/?option=com_staticxt&staticfile=show.php%3Ftitle=1380&chapter=64319&layout=html#a_1594266
Hamilton, James D. and Jing Wu. 2010. The effectiveness of alternative monetary policy tools in a zero lower bound environment. San Diego, University of California San Diego, Nov 3 http://dss.ucsd.edu/~jhamilto/zlb.pdf
Harris, Jennifer M. 2011BA. Benchmark article. Washington, DC, Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/ces/cesbmart.pdf
Hetzel, Robert L. and Ralph F. Leach. 2001. The Treasury-Fed accord: a new narrative account. Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond Economic Quarterly 87 (1, Winter): 33-55.
Hicks, John R. 1935. A suggestion for simplifying the theory of money. Economica NS 2 (5, Feb): 1-19.
Hicks, John R. 1962. Liquidity. Economic Journal 72 (288, Dec): 787-802.
Hicks, John R. 1975. The scope and status of welfare economics. Oxford Economic Papers 27 (3): 307-26.
Hobbs, Frank and Nicole Stoops. 2002. Demographic trends in the 20th century. Washington, DC, US Government Printing Office http://www.census.gov/prod/2002pubs/censr-4.pdf
IMF. 2011WEOSep. World economic outlook Sep 11: slowing growth, rising risks. Washington, DC, IMF Sep http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2011/02/pdf/text.pdf
IMF. 2011JSRNov23. Japan sustainability report. Washington, DC, IMF, Nov 23 http://www.imf.org/external/np/country/2011/mapjapanpdf.pdf
IMF. 2012GFSRJan24. Global Financial Stability Report: market update. Washington, DC, IMF, Jan 24 http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fmu/eng/2012/01/index.htm
IMF. 2012FMJan24. Fiscal Monitor Update. Washington, DC, IMF, Jan 24 http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fm/2012/update/01/fmindex.htm
IMF. 2012WEOJan24. World Economic Outlook Update: an update of the key WEO projections. Washington, DC, IMF, Jan 24 http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/update/01/index.htm
IMF. 2012WEOApr. World Economic Outlook April 2012: growth resuming, dangers remains. Washington, DC, IMF, 2012, Apr http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/pdf/text.pdf
IMF. 2012GFSRApr. Global financial stability report: the quest for lasting stability. Washington, DC, IMF 2012, Apr http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/gfsr/2012/01/pdf/text.pdf
IMF. 2012FMApr. Fiscal monitor: balancing fiscal policy risks. Washington, DC, IMF, Apr
http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fm/2012/01/pdf/fm1201.pdf
IMFC. 2012Apr20. Joint Statement of the International Monetary and Financial Committee and the Group of 20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors on IMF Resources. Washington, DC, IMF, Apr 20 http://www.imf.org/external/np/sec/pr/2012/pr12144.htm
IMFC. 2012Apr21. Communiqué of the Twenty-Fifth Meeting of the IMFC. Washington, DC, IMF, Apr 21 http://www.imf.org/external/np/sec/pr/2012/pr12145.htm
IMF. 2012FSAPJun8. Spain: Financial Stability Assessment. Washington, DC, International Monetary Fund, Jun http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/scr/2012/cr12137.pdf
Ingersoll, Jonathan. 1987. Theory of Financial Decision Making. New Jersey: Rowman.
Ireland, Peter N. 1999. Does the time-consistency problem explain the behavior of inflation in the United States. Journal of Monetary Economics 44 (2): 279-91.
Ito, Takatoshi. Interventions and Japanese economic recovery. YenMacro, Michigan 2004 1 http://www.fordschool.umich.edu/rsie/Conferences/CGP/Oct2004Papers/Ito.pdf
Jensen, Michael C. 1993. The modern industrial revolution, exit and the failure of internal control systems. Journal of Finance 48 (3, Jul): 831-80.
Joint Forum of the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision, International Organization of Securities Commissions and the International Association of Supervisors. 2004. Credit risk transfer. BCBS, BIS, Oct. http://www.bis.org/publ/joint10.pdf
Kahil, Raouf. 1973. Inflation and economic development in Brazil. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
Kohn, Donald L. 2009Apr18. Monetary policy in the financial crisis. Nashville, TN, Conference in Honor of Dewey Daane, Apr 18 http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/kohn20090418a.htm
Kohn, Donald L. 2009Sep10. Comments on “Interpreting the Unconventional US Monetary policy of 2007-2009.” Washington, Brookings Institution, Sep 10 http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/kohn20090910a.htm
Krugman, Paul. 1998. It’s baaack: Japan’s slump and the return of the liquidity trap. Brookings Papers on Economic Activity 2 (1998): 137-205.
Krugman, Paul. 2012Apr24. Earth to Ben Bernanke: chairman Bernanke should listen to Professor Bernanke. New York Times Magazine, Apr 24 http://www.nytimes.com/2012/04/29/magazine/chairman-bernanke-should-listen-to-professor-bernanke.html?pagewanted=all
Kydland, Finn E. and Edward C. Prescott. 1977. Rules rather than discretion: the inconsistency of optimal plans. Journal of Political Economy 85 (3, Jun): 473-92.
Lazear, Edward P. 2012Jan19. The jobs picture is still far from rosy. Wall Street Journal, Jan 19 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052970204468004577165292033648810.html
Lazear, Edward P. and James R. Spletzer. 2012Mar. Hiring, churn and the business cycle. Cambridge, MA, NBER, Mar http://www.nber.org/papers/w17910
Leff, Nathaniel H. 1975. Review of Inflation and Economic Development in Brazil, 1946-1963 by Raouf Kahil. Journal of Economic Literature 12 (2, Jun): 510-11.
Levin, Andrew and John B. Taylor. 2009. Falling behind the curve: a positive analysis of stop-start monetary policies and the Great Inflation. Cambridge, MA, NBER, Dec.
Lintner, John. 1965. The valuation of risk assets and the selection of risky investments in stock portfolios and capital budgets. Review of Economics and Statistics 47 (1, Feb): 12-37.
Markowitz, Harry. 1952. Portfolio selection. Journal of Finance 7 (1, Mar): 77-91.
McCallum, Bennett. 1999. Issues in the design of monetary policy rules. In John B. Taylor and Michael Woodford, eds. Handbook of Macroeconomics Volume 1A. Amsterdam: Elsevier North Holland.
McKinnon, Ronald I. 1973. Money and Capital in Economic Development. Washington, DC: Brookings Institution.
McKinnon, Ronald I. 2011Dec18. Oh, for Alexander Hamilton to save Europe! Financial Times, Dec 18 http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/811611d6-273a-11e1-b7ec-00144feabdc0.html#axzz1gzoHXOj6
McKinsey & Co. 2007. Sustaining New York and the US’ global financial services leadership. New York: McKinsey & Co.
Meltzer, Allan H. 2005. Origins of the Great Inflation. Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis Review 87 (2, Part 2, Mar/Apr): 145-72.
Meltzer, Allan H. 2010a. A history of the Federal Reserve, Volume 2, Book 1, 1951-1969. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Meltzer, Allan H. 2010b. A history of the Federal Reserve, Volume 2, Book 2, 1970-1986. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Metzler, Lloyd A. The nature and stability of inventory cycles. 1941. Review of Economics and Statistics 23 (3, Aug): 113-29.
Merton, Robert C. 1973. Theory of rational option pricing. Bell Journal of Economics and Management Science 4 (1, Spring): 141-83.
Merton, Robert C. 1974. On the pricing of corporate debt: the risk structure of interest rates. Journal of Finance 29 (2, May): 449-70.
Merton, Robert C. 1998. Applications of option-pricing theory: twenty-five years later. American Economic Review 88 (3): 323-49.
Meulendyke, Ann-Marie. 1998. U.S. monetary policy and financial markets. New York: Federal Reserve Bank of New York http://www.newyorkfed.org/education/addpub/monpol/
Modigliani, Franco and Richard Sutch. 1966. Innovations in interest rate policy. American Economic Review 56 (1/2, Mar): 178-97.
Modigliani, Franco and Richard Sutch. 1967. Debt management and the term structure of interest rates: an empirical analysis of recent experience. Journal of Political Economy 75 (4, Aug): 569-89.
Mossin, Jan. 1966. 1966. Equilibrium in a capital asset market. Econometrica 34 (4, Oct): 768-83.
Pelaez, Carlos A. 2008. The reform of Alexander Hamilton. Philadelphia, University of Pennsylvania Law School, Unpublished manuscript.
Pelaez, Carlos M. and Carlos A. Pelaez. 2005. International Financial Architecture. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. http://us.macmillan.com/QuickSearchResults.aspx?search=pelaez%2C+carlos&ctl00%24ctl00%24cphContent%24ucAdvSearch%24imgGo.x=26&ctl00%24ctl00%24cphContent%24ucAdvSearch%24imgGo.y=14 http://www.amazon.com/Carlos-Manuel-Pel%C3%A1ez/e/B001HCUT10
Pelaez, Carlos M. and Carlos A. Pelaez. 2007. The Global Recession Risk. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. http://www.amazon.com/Carlos-Manuel-Pel%C3%A1ez/e/B001HCUT10
Pelaez, Carlos M. and Carlos A. Pelaez. 2008a. Globalization and the State: Vol. I. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. http://www.amazon.com/Carlos-Manuel-Pel%C3%A1ez/e/B001HCUT10
Pelaez, Carlos M. and Carlos A. Pelaez. 2008b. Globalization and the State: Vol. II. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.
Pelaez, Carlos M. and Carlos A. Pelaez. 2008c. Government Intervention in Globalization. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. http://www.amazon.com/Carlos-Manuel-Pel%C3%A1ez/e/B001HCUT10
Pelaez, Carlos M. and Carlos A. Pelaez. 2009a. Financial Regulation after the Global Recession. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. http://www.amazon.com/Carlos-Manuel-Pel%C3%A1ez/e/B001HCUT10
Pelaez, Carlos M. and Carlos A. Pelaez. 2009b. Regulation of Banks and Finance. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.http://www.amazon.com/Carlos-Manuel-Pel%C3%A1ez/e/B001HCUT10
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel. 1974. Long-run Monetary Behavior and Institutions in an Underdeveloped Economy, 1800-1971. Copenhaguen, Paper Presented at the VI International Congress on Economic History, Session on Monetary Inflation in Historical Perspective, International Economic History Association, Aug 22.
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel. 1975. The Establishment of Banking Institutions in a Backward Economy: Brazil, 1800-1851. Business History Review 49 (4, Winter): 446-472.
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel. 1976a. The Theory and Reality of Imperialism in the Coffee Economy of Nineteenth-Century Brazil. Economic History Review 29, Second Series (May): 276-294.
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel. 1976b. A Comparison of Long-term Monetary Behavior and Institutions in Brazil, Europe and the United States. Journal of European Economic History 5 (2, Fall): 439-450.
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel. 1977. World War I and the Economy of Brazil: Some Evidence from Monetary Statistics. Journal of Interdisciplinary History (7, Apr): 683-680.
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel. 1979. História Econômica do Brasil. São Paulo: Editora Atlas.
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel and Wilson Suzigan. 1978. Economia Monetária. São Paulo, Atlas.
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel and Wilson Suzigan. 1981. História Monetária do Brasil Segunda Edição. Coleção Temas Brasileiros. Brasília: Universidade de Brasília.
Phelps, Edmund S. 1968. Money-wage dynamics and labor market equilibrium. Journal of Political Economy 76 (4, 2, Jul-Aug): 678-711.
Pozsar, Zoltan, Adrian Tobias, Adam Ashcraft and Hayley Boesky. 2012RFeb. Shadow banking. New York: Federal Reserve Bank of New York, Staff Report No. 458, Revised Feb 2012 http://www.newyorkfed.org/research/staff_reports/sr458.pdf
Reinhart, Carmen M. and Kenneth Rogoff. 2010GTD. Growth in a time of debt. American Economic Review 100 (2): 1-9.
Rajan, Raghuram G. 2004. Remarks. Sydney, Australia, Australasian Finance and Banking Conference, Dec 15.
Rajan, Raghuram G. 2005. Has financial development made the world riskier? Jackson Hole, WY, Symposium sponsored by the Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City. http://www.kc.frb.org/publicat/sympos/2005/PDF/Rajan2005.pdf
Rajan, Raghuram G. 2012May8. Stop beating up on Ben Bernanke. Financial Times, May 8 http://blogs.ft.com/the-a-list/2012/05/08/stop-beating-up-on-ben-bernanke/
Rajan, Raghuram G. 2012FA. The true lessons of the recession: the West can’t borrow and spend its way to recovery. Foreign Affairs 91 (May/June, 3): 69-79.
Rajan, Raghuram G. and Luigi Zingales. 2001. The influence of the financial revolution on the nature of the firm. American Economic Review 91 (2): 206-11.
Robinson, Joan. 1947. Beggar-my-neighbour remedies for unemployment. In Joan Robinson, Essays in the Theory of Employment, Oxford, Basil Blackwell, 1947.
Rogoff, Kenneth. 2002MF. Dornbusch’s overshooting model after twenty-five years. Washington, DC, IMF, Mundell-Fleming Lecture http://www.imf.org/external/np/speeches/2001/kr/112901.pdf
Roll, Richard. 1977. A critique of the asset pricing theory’s tests. Part I: on past and potential testability of the theory. Journal of Financial Economics 4 (2, Mar): 129-76.
Romer, Christina D. and David H. Romer. 2004. A new measure of monetary shocks: derivation and implications. American Economic Review 94 (4, Sep): 1055-84.
Samuelson, Paul A. 1965. Proof that properly anticipated stock prices fluctuate randomly. Industrial Management Review 6 (2): 41-9.
Samuelson, Paul A. 1974. Lessons from the current economic expansion. American Economic Review 64 (2, May): 75-7.
Sargent, Thomas J. 1983. The end of four big inflations. In Robert E. Hall, ed. Inflation: causes and effects. Chicago: Chicago University Press.
Sargent, Thomas J. and Neil Wallace. 1973. The stability of models of money and growth with perfect foresight. Econometrica 41 (6, Nov): 1043-8.
Sargent, Thomas J. and Neil Wallace. 1981. Some unpleasant monetarist arithmetic. Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis Quarterly Review 5 (3, Fall): 1-17.
Sargent, Thomas J. and William L. Silber. 2012Mar20. The challenges of the Fed’s bid for transparency. Financial Times, Mar 20 http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/778eb1ce-7288-11e1-9c23-00144feab49a.html#axzz1pexRlsiQ
Seers, Dudley. 1962. A theory of inflation and growth in under-developed economies based on the experience of Latin America. Oxford Economic Papers New Series 14 (Jun, 2): 173-95.
Sharpe, William F. 1964. Capital asset prices: a theory of market equilibrium under conditions of risk. Journal of Finance 19 (3, Sep): 425-42.
Shaw, Edward S. 1973. Financial Deepening in Economic Development. New York: Oxford University Press.
Simons, Henry C. 1936. Rules versus authorities in monetary policy. Journal of Political Economy 44 (1, Feb): 1-30.
Simons, Henry C. 1948. Economic Policy for a free society. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Sims, Christopher A. 1972. Money, income and causality. American Economic Review 62 (4, Sep): 540-52.
Standard & Poor’s Rating Services (S&PRS). 2012Jan13. Standard & Poor’s takes various rating actions on 16 eurozone sovereign governments. Frankfurt, S&P Rating Services, Jan 13 http://www.standardandpoors.com/ratings/articles/en/us/?articleType=HTML&assetID=1245327294763
Standard & Poor’s Rating Services (S&PRS). 2012Jan16. European Financial Stability Facility long-term Ratings Cut to ‘AA+’; short-term ratings affirmed; outlook developing. Frankfurt, S&P Rating Services, Jan 16 http://www.standardandpoors.com/ratings/articles/en/us/?articleType=HTML&assetID=1245327337060
Svensson, Lars E. 2003. What is wrong with Taylor rules? Using judgment in monetary policy through targeting rules. Journal of Economic Literature 41 (2 Jun): 426–77.
Swanson, Eric T. 2011Mar. Let’s twist again: a high-frequency event-study analysis of operation twist and its implication for QE2. Forthcoming in Brookings Papers on Economic Activity http://www.brookings.edu/~/media/Files/Programs/ES/BPEA/2011_spring_bpea_papers/2011_spring_bpea_conference_swanson.pdf
Taylor, John B. 1993. Discretion versus policy rules in practice. Carnegie-Rochester Conference Series on Public Policy 39 (1993): 195-214.
Taylor, John B. 1997. Comment. In Christina Romer and David Romer, eds. Reducing inflation: motivation and strategy. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Taylor, John B. 1998LB. Monetary policy and the long boom. Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis Review (Nov-Dec): 3-11.
Taylor, John B. 1999. An historical analysis of monetary policy rules. In John B. Taylor, ed. Monetary policy rules. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Taylor, John B. 2012FP. First principles: five keys to restoring America’s prosperity. New York: W. W. Norton.
Taylor, John B. 2012Mar27. Testimony before the Joint Economic Committee at the Hearing on “Monetary Policy Going Forward: Why a Sound Dollar Boosts Growth and Employment.” Washington, DC, JEC, Mar 27 http://jec.senate.gov/republicans/public/?a=Files.Serve&File_id=f002b5f0-9fc0-45f9-9d53-e563137c040e
Taylor, John B. 2012Mar28. The dangers of an interventionist Fed. Wall Street Journal, Mar 28 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052702303816504577307403971824094.html?mod=WSJ_hps_sections_opinion
Taylor, John B. 2012JMCB. Monetary policy rules work and discretion doesn’t: a tale of two eras. Palo Alto, CA, Stanford University, Mar 2012, forthcoming in the Journal of Money, Credit and Banking, 2012 http://www.stanford.edu/~johntayl/JMCB%20lecture.pdf
Taylor, John B. and John C. Williams. 2010. Simple and robust rules for monetary policy. In Benjamin Friedman and Michael Woodford, eds. Handbook of monetary economics Volume 3B. Amsterdam: Elsevier North Holland.
Tobias, Adrian and Adam B. Aschraft. 2012Apr. Shawdow banking regulation. New York, Federal Reserve Bank of New York, Staff Report No. 559, Apr http://www.newyorkfed.org/research/staff_reports/sr559.pdf
Tobin, James. 1958. Liquidity preference as behavior toward risk. Review of Economic Studies 26 (Feb): 65-86.
Tobin, James. 1969. A general equilibrium approach to monetary theory. Journal of Money, Credit and Banking 1 (1, Feb): 15-29.
Tobin, James. 1974. Monetary policy in 1974 and beyond. Brookings Papers on Economic Activity 1 (1974): 219-32.
Treynor, Jack L. 1962. Toward a theory of market value of risky assets, unpublished manuscript, 1962, provided by Craig W. French, http://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=628187
Vayanos, Dimitri and Jean-Luc Vila. 2009. A preferred-habitat model of the term structure of interest rates. New Orleans, AFA Meetings Paper, Nov 1. http://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=971439
Villela, Annibal V. and Wilson Suzigan. 1973. Política do governo e crescimento da economia brasileira. Rio de Janeiro: IPEA/INPES.
Williams, David, C.A. E. Goodhart and D. H. Gowland. 1976. Money, income and causality: the UK experience. American Economic Review 66 (3, Jun): 417-23.
Wriston, Walter B. 1982. Banking against disaster. New York Times, Sep 14.
Yellen, Janet L. 2011AS. The Federal’s Reserve’s asset purchase program. Denver, Colorado, Allied Social Science Association Annual Meeting, Jan 8 http://federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20110108a.pdf
Zingales, Luigi. 2000. In search of new foundations. Journal of Finance 55 (4, Aug): 1623-54.
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2010, 2011, 2012
Appendix I. The Great Inflation
Inflation and unemployment in the period 1966 to 1985 is analyzed by Cochrane (2011Jan, 23) by means of a Phillips circuit joining points of inflation and unemployment. Chart I1 for Brazil in Pelaez (1986, 94-5) was reprinted in The Economist in the issue of Jan 17-23, 1987 as updated by the author. Cochrane (2011Jan, 23) argues that the Phillips circuit shows the weakness in Phillips curve correlation. The explanation is by a shift in aggregate supply, rise in inflation expectations or loss of anchoring. The case of Brazil in Chart I1 cannot be explained without taking into account the increase in the fed funds rate that reached 22.36 percent on Jul 22, 1981 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/data.htm) in the Volcker Fed that precipitated the stress on a foreign debt bloated by financing balance of payments deficits with bank loans in the 1970s; the loans were used in projects, many of state-owned enterprises with low present value in long gestation. The combination of the insolvency of the country because of debt higher than its ability of repayment and the huge government deficit with declining revenue as the economy contracted caused adverse expectations on inflation and the economy. This interpretation is consistent with the case of the 24 emerging market economies analyzed by Reinhart and Rogoff (2010GTD, 4), concluding that “higher debt levels are associated with significantly higher levels of inflation in emerging markets. Median inflation more than doubles (from less than seven percent to 16 percent) as debt rises from the low (0 to 30 percent) range to above 90 percent. Fiscal dominance is a plausible interpretation of this pattern.”
The reading of the Phillips circuits of the 1970s by Cochrane (2011Jan, 25) is doubtful about the output gap and inflation expectations:
“So, inflation is caused by ‘tightness’ and deflation by ‘slack’ in the economy. This is not just a cause and forecasting variable, it is the cause, because given ‘slack’ we apparently do not have to worry about inflation from other sources, notwithstanding the weak correlation of [Phillips circuits]. These statements [by the Fed] do mention ‘stable inflation expectations. How does the Fed know expectations are ‘stable’ and would not come unglued once people look at deficit numbers? As I read Fed statements, almost all confidence in ‘stable’ or ‘anchored’ expectations comes from the fact that we have experienced a long period of low inflation (adaptive expectations). All these analyses ignore the stagflation experience in the 1970s, in which inflation was high even with ‘slack’ markets and little ‘demand, and ‘expectations’ moved quickly. They ignore the experience of hyperinflations and currency collapses, which happen in economies well below potential.”
Chart I1, Brazil, Phillips Circuit 1963-1987
©Carlos Manuel Pelaez, O cruzado e o austral. São Paulo: Editora Atlas, 1986, pages 94-5. Reprinted in: Brazil. Tomorrow’s Italy, The Economist, 17-23 January 1987, page 25.
DeLong (1997, 247-8) shows that the 1970s were the only peacetime period of inflation in the US without parallel in the prior century. The price level in the US drifted upward since 1896 with jumps resulting from the two world wars: “on this scale, the inflation of the 1970s was as large an increase in the price level relative to drift as either of this century’s major wars” (DeLong, 1997, 248). Monetary policy focused on accommodating higher inflation, with emphasis solely on the mandate of promoting employment, has been blamed as deliberate or because of model error or imperfect measurement for creating the Great Inflation (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/05/slowing-growth-global-inflation-great.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/04/new-economics-of-rose-garden-turned.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/03/is-there-second-act-of-us-great.html). As DeLong (1997) shows, the Great Inflation began in the mid 1960s, well before the oil shocks of the 1970s (see also the comment to DeLong 1997 by Taylor 1997, 276-7). TableI1 provides the change in GDP, CPI and the rate of unemployment from 1960 to 1990. There are three waves of inflation (1) in the second half of the 1960s; (2) from 1973 to 1975; and (3) from 1978 to 1981. In one of his multiple important contributions to understanding the Great Inflation, Meltzer (2005) distinguishes between one-time price jumps, such as by oil shocks, and a “maintained” inflation rate. Meltzer (2005) uses a dummy variable to extract the one-time oil price changes, resulting in a maintained inflation rate that was never higher than 8 to 10 percent in the 1970s. There is revealing analysis of the Great Inflation and its reversal by Meltzer (2005, 2010a, 2010b).
Table I1, US Annual Rate of Growth of GDP and CPI and Unemployment Rate 1960-1982
| ∆% GDP | ∆% CPI | UNE | |
| 1960 | 2.5 | 1.4 | 6.6 |
| 1961 | 2.3 | 0.7 | 6.0 |
| 1962 | 6.1 | 1.3 | 5.5 |
| 1963 | 4.4 | 1.6 | 5.5 |
| 1964 | 5.8 | 1.0 | 5.0 |
| 1965 | 6.4 | 1.9 | 4.0 |
| 1966 | 6.5 | 3.5 | 3.8 |
| 1967 | 2.5 | 3.0 | 3.8 |
| 1968 | 4.8 | 4.7 | 3.4 |
| 1969 | 3.1 | 6.2 | 3.5 |
| 1970 | 0.2 | 5.6 | 6.1 |
| 1971 | 3.4 | 3.3 | 6.0 |
| 1972 | 5.3 | 3.4 | 5.2 |
| 1973 | 5.8 | 8.7 | 4.9 |
| 1974 | -0.6 | 12.3 | 7.2 |
| 1975 | -0.2 | 6.9 | 8.2 |
| 1976 | 5.4 | 4.9 | 7.8 |
| 1977 | 4.6 | 6.7 | 6.4 |
| 1978 | 5.6 | 9.0 | 6.0 |
| 1979 | 3.1 | 13.3 | 6.0 |
| 1980 | -0.3 | 12.5 | 7.2 |
| 1981 | 2.5 | 8.9 | 8.5 |
| 1982 | -1.9 | 3.8 | 10.8 |
| 1983 | 4.5 | 3.8 | 8.3 |
| 1984 | 7.2 | 3.9 | 7.3 |
| 1985 | 4.1 | 3.8 | 7.0 |
| 1986 | 3.5 | 1.1 | 6.6 |
| 1987 | 3.2 | 4.4 | 5.7 |
| 1988 | 4.1 | 4.4 | 5,3 |
| 1989 | 3.6 | 4.6 | 5.4 |
| 1990 | 1.9 | 6.1 | 6.3 |
Note: GDP: Gross Domestic Product; CPI: consumer price index; UNE: rate of unemployment; CPI and UNE are at year end instead of average to obtain a complete series
Source: ftp://ftp.bls.gov/pub/special.requests/cpi/cpiai.txt
http://www.bls.gov/web/empsit/cpseea01.htm
http://data.bls.gov/pdq/SurveyOutputServlet
There is a false impression of the existence of a monetary policy “science,” measurements and forecasting with which to steer the economy into “prosperity without inflation.” Market participants are remembering the Great Bond Crash of 1994 shown in Table I2 when monetary policy pursued nonexistent inflation, causing trillions of dollars of losses in fixed income worldwide while increasing the fed funds rate from 3 percent in Jan 1994 to 6 percent in Dec. The exercise in Table I2 shows a drop of the price of the 30-year bond by 18.1 percent and of the 10-year bond by 14.1 percent. CPI inflation remained almost the same and there is no valid counterfactual that inflation would have been higher without monetary policy tightening because of the long lag in effect of monetary policy on inflation (see Culbertson 1960, 1961, Friedman 1961, Batini and Nelson 2002, Romer and Romer 2004). The pursuit of nonexistent deflation during the past ten years has resulted in the largest monetary policy accommodation in history that created the 2007 financial market crash and global recession and is currently preventing smoother recovery while creating another financial crash in the future. The issue is not whether there should be a central bank and monetary policy but rather whether policy accommodation in doses from zero interest rates to trillions of dollars in the fed balance sheet endangers economic stability.
Table I2, Fed Funds Rates, Thirty and Ten Year Treasury Yields and Prices, 30-Year Mortgage Rates and 12-month CPI Inflation 1994
| 1994 | FF | 30Y | 30P | 10Y | 10P | MOR | CPI |
| Jan | 3.00 | 6.29 | 100 | 5.75 | 100 | 7.06 | 2.52 |
| Feb | 3.25 | 6.49 | 97.37 | 5.97 | 98.36 | 7.15 | 2.51 |
| Mar | 3.50 | 6.91 | 92.19 | 6.48 | 94.69 | 7.68 | 2.51 |
| Apr | 3.75 | 7.27 | 88.10 | 6.97 | 91.32 | 8.32 | 2.36 |
| May | 4.25 | 7.41 | 86.59 | 7.18 | 88.93 | 8.60 | 2.29 |
| Jun | 4.25 | 7.40 | 86.69 | 7.10 | 90.45 | 8.40 | 2.49 |
| Jul | 4.25 | 7.58 | 84.81 | 7.30 | 89.14 | 8.61 | 2.77 |
| Aug | 4.75 | 7.49 | 85.74 | 7.24 | 89.53 | 8.51 | 2.69 |
| Sep | 4.75 | 7.71 | 83.49 | 7.46 | 88.10 | 8.64 | 2.96 |
| Oct | 4.75 | 7.94 | 81.23 | 7.74 | 86.33 | 8.93 | 2.61 |
| Nov | 5.50 | 8.08 | 79.90 | 7.96 | 84.96 | 9.17 | 2.67 |
| Dec | 6.00 | 7.87 | 81.91 | 7.81 | 85.89 | 9.20 | 2.67 |
Notes: FF: fed funds rate; 30Y: yield of 30-year Treasury; 30P: price of 30-year Treasury assuming coupon equal to 6.29 percent and maturity in exactly 30 years; 10Y: yield of 10-year Treasury; 10P: price of 10-year Treasury assuming coupon equal to 5.75 percent and maturity in exactly 10 years; MOR: 30-year mortgage; CPI: percent change of CPI in 12 months
Sources: yields and mortgage rates http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/data.htm CPI ftp://ftp.bls.gov/pub/special.requests/cpi/cpiai.t
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2010, 2011, 2012





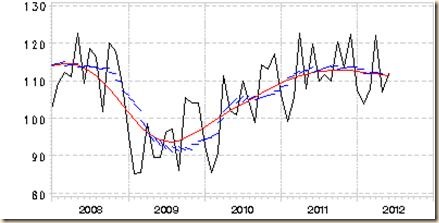








No comments:
Post a Comment