Contracting United States Industrial Production, World Inflation Waves, World Cyclical Slow Growth and Global Recession Risk
Carlos M. Pelaez
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016
I World Inflation Waves
IA Appendix: Transmission of Unconventional Monetary Policy
IB1 Theory
IB2 Policy
IB3 Evidence
IB4 Unwinding Strategy
IC United States Inflation
IC Long-term US Inflation
ID Current US Inflation
IE Theory and Reality of Economic History, Cyclical Slow Growth Not Secular Stagnation
II United States Industrial Production
III World Financial Turbulence
IIIA Financial Risks
IIIE Appendix Euro Zone Survival Risk
IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation
IV Global Inflation
V World Economic Slowdown
VA United States
VB Japan
VC China
VD Euro Area
VE Germany
VF France
VG Italy
VH United Kingdom
VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets
VII Economic Indicators
VIII Interest Rates
IX Conclusion
References
Appendixes
Appendix I The Great Inflation
IIIB Appendix on Safe Haven Currencies
IIIC Appendix on Fiscal Compact
IIID Appendix on European Central Bank Large Scale Lender of Last Resort
IIIG Appendix on Deficit Financing of Growth and the Debt Crisis
IIIGA Monetary Policy with Deficit Financing of Economic Growth
IIIGB Adjustment during the Debt Crisis of the 1980s
Appendix to Section VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets.
Preceding Table VI-6:
The Communiqué of Meeting of G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors in Moscow on February 16, 2013, available at the University of Toronto G20 Information Center (http://www.g8.utoronto.ca/g20/2013/2013-0216-finance.html), appears to rule out currency wars:
“Global Economy and G20 Framework for Strong, Sustainable and Balanced Growth
2. Thanks to the important policy actions in Europe, the US, Japan, and the resilience of the Chinese economy, tail risks to the global economy have receded and financial market conditions have improved. However, we recognize that important risks remain and global growth is still too weak, with unemployment remaining unacceptably high in many countries. We agree that the weak global performance derives from policy uncertainty, private deleveraging, fiscal drag, and impaired credit intermediation, as well as incomplete rebalancing of global demand. Under these circumstances, a sustained effort is required to continue building a stronger economic and monetary union in the euro area and to resolve uncertainties related to the fiscal situation in the United States and Japan, as well as to boost domestic sources of growth in surplus economies, taking into account special circumstances of large commodity producers.
3. To address the weakness of the global economy, ambitious reforms and coordinated policies are key to achieving strong, sustainable and balanced growth and restoring confidence. We will continue to implement our previous commitments, including on the financial reform agenda to build a more resilient financial system and on ambitious structural reforms to lift growth. We are committed to ensuring sustainable public finances. Advanced economies will develop credible medium-term fiscal strategies in line with the commitments made by our Leaders in Los Cabos by the St Petersburg Summit. Credible medium-term fiscal consolidation plans will be put in place, and implemented taking into account near-term economic conditions and fiscal space where available. We support action to improve the flow of credit to the economy, where necessary. Monetary policy should be directed toward domestic price stability and continuing to support economic recovery according to the respective mandates. We commit to monitor and minimize the negative spillovers on other countries of policies implemented for domestic purposes. We look forward to the results of the ongoing work on spillovers in the Framework Working Group.
4. We have adopted an assessment process on the implementation of our structural reform commitments, which will inform the direction of our future structural policies.
5. We reaffirm our commitment to cooperate for achieving a lasting reduction in global imbalances, and pursue structural reforms affecting domestic savings and improving productivity. We reiterate our commitments to move more rapidly toward more market-determined exchange rate systems and exchange rate flexibility to reflect underlying fundamentals, and avoid persistent exchange rate misalignments and in this regard, work more closely with one another so we can grow together. We reiterate that excess volatility of financial flows and disorderly movements in exchange rates have adverse implications for economic and financial stability. We will refrain from competitive devaluation. We will not target our exchange rates for competitive purposes, will resist all forms of protectionism and keep our markets open.”
The final phrases rule out “competitive devaluation” and the use of “exchange rates for competitive purposes.” What is seriously absent in this statement of intentions is monetary policy, which is precisely the mechanism by which competitive devaluations are currently implemented.
In the restatement of the liquidity trap and large-scale policies of monetary/fiscal stimulus, Krugman (1998, 162) finds:
“In the traditional open economy IS-LM model developed by Robert Mundell [1963] and Marcus Fleming [1962], and also in large-scale econometric models, monetary expansion unambiguously leads to currency depreciation. But there are two offsetting effects on the current account balance. On one side, the currency depreciation tends to increase net exports; on the other side, the expansion of the domestic economy tends to increase imports. For what it is worth, policy experiments on such models seem to suggest that these effects very nearly cancel each other out.
Krugman (1998) uses a different dynamic model with expectations that leads to similar conclusions.
The central bank could also be pursuing competitive devaluation of the national currency in the belief that it could increase inflation to a higher level and promote domestic growth and employment at the expense of growth and unemployment in the rest of the world. An essay by Chairman Bernanke in 1999 on Japanese monetary policy received attention in the press, stating that (Bernanke 2000, 165):
“Roosevelt’s specific policy actions were, I think, less important than his willingness to be aggressive and experiment—in short, to do whatever it took to get the country moving again. Many of his policies did not work as intended, but in the end FDR deserves great credit for having the courage to abandon failed paradigms and to do what needed to be done”
Quantitative easing has never been proposed by Chairman Bernanke or other economists as certain science without adverse effects. What has not been mentioned in the press is another suggestion to the Bank of Japan (BOJ) by Chairman Bernanke in the same essay that is very relevant to current events and the contentious issue of ongoing devaluation wars (Bernanke 2000, 161):
“The BOJ could probably undertake yen depreciation unilaterally; because the BOJ has a legal mandate to pursue price stability, it certainly could make a good argument that, with interest rates at zero, depreciation of the yen is the best available tool for achieving its mandated objective. Defenders of inaction on the yen claim that a large yen depreciation would therefore create serious international tensions. Whatever validity this political argument may have had at various times, it is of no relevance at the moment, for Japan has recently been urged by its most powerful allies and trading partners to weaken the yen—and refused! Moreover, the economic validity of the beggar-thy-neighbor thesis is doubtful, as depreciation creates trade—by raising home-country income—as well as diverting it. Perhaps not all those who cite the beggar-thy-neighbor thesis are aware that it had its origins in the Great Depression, when it was used as an argument against the very devaluations that ultimately proved crucial to world economic recovery. A yen trading at 100 to the dollar or less is in no one’s interest.”
Chairman Bernanke is referring to the argument by Joan Robinson based on the experience of the Great Depression that: “in times of general unemployment a game of beggar-my-neighbour is played between the nations, each one endeavouring to throw a larger share of the burden upon the others” (Robinson 1947, 156). Devaluation is one of the tools used in these policies (Robinson 1947, 157). Banking crises dominated the experience of the United States, but countries that recovered were those devaluing early such that competitive devaluations rescued many countries from a recession as strong as that in the US (see references to Ehsan Choudhri, Levis Kochin and Barry Eichengreen in Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 205-9; for the case of Brazil that devalued early in the Great Depression recovering with an increasing trade balance see Pelaez, 1968, 1968b, 1972; Brazil devalued and abandoned the gold standard during crises in the historical period as shown by Pelaez 1976, Pelaez and Suzigan 1981). Beggar-my-neighbor policies did work for individual countries but the criticism of Joan Robinson was that it was not optimal for the world as a whole.
Is depreciation of the dollar the best available tool currently for achieving the dual mandate of higher inflation and lower unemployment? Bernanke (2002) finds dollar devaluation against gold to have been important in preventing further deflation in the 1930s (http://www.federalreserve.gov/boarddocs/speeches/2002/20021121/default.htm):
“Although a policy of intervening to affect the exchange value of the dollar is nowhere on the horizon today, it's worth noting that there have been times when exchange rate policy has been an effective weapon against deflation. A striking example from U.S. history is Franklin Roosevelt's 40 percent devaluation of the dollar against gold in 1933-34, enforced by a program of gold purchases and domestic money creation. The devaluation and the rapid increase in money supply it permitted ended the U.S. deflation remarkably quickly. Indeed, consumer price inflation in the United States, year on year, went from -10.3 percent in 1932 to -5.1 percent in 1933 to 3.4 percent in 1934. The economy grew strongly, and by the way, 1934 was one of the best years of the century for the stock market. If nothing else, the episode illustrates that monetary actions can have powerful effects on the economy, even when the nominal interest rate is at or near zero, as was the case at the time of Roosevelt's devaluation.”
Should the US devalue following Roosevelt? Alternatively, has monetary policy intended devaluation? Fed policy is seeking, deliberately or as a side effect, what Irving Fisher proposed “that great depressions are curable and preventable through reflation and stabilization” (Fisher, 1933, 350). The Fed has created not only high volatility of assets but also what many countries are regarding as a competitive devaluation similar to those criticized by Nurkse (1944). Yellen (2011AS, 6) admits that Fed monetary policy results in dollar devaluation with the objective of increasing net exports, which was the policy that Joan Robinson (1947) labeled as “beggar-my-neighbor” remedies for unemployment. There is increasing unrest within the G20 and worldwide about the appreciation of exchange rates of most countries while the dollar devalues. Global coordination of policies with free riders in an institution of diverse interests such as the G20 is unlikely. Distortions of financial markets in the US and worldwide depend only on more sober evaluation of risks of unconventional policies at a body without free riders, such as the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC).
Chairman Bernanke (2013Mar 25) reinterprets devaluation and recovery from the Great Depression:
“The uncoordinated abandonment of the gold standard in the early 1930s gave rise to the idea of "beggar-thy-neighbor" policies. According to this analysis, as put forth by important contemporary economists like Joan Robinson, exchange rate depreciations helped the economy whose currency had weakened by making the country more competitive internationally. Indeed, the decline in the value of the pound after 1931 was associated with a relatively early recovery from the Depression by the United Kingdom, in part because of some rebound in exports. However, according to this view, the gains to the depreciating country were equaled or exceeded by the losses to its trading partners, which became less internationally competitive--hence, ‘beggar thy neighbor.’ Economists still agree that Smoot-Hawley and the ensuing tariff wars were highly counterproductive and contributed to the depth and length of the global Depression. However, modern research on the Depression, beginning with the seminal 1985 paper by Barry Eichengreen and Jeffrey Sachs, has changed our view of the effects of the abandonment of the gold standard. Although it is true that leaving the gold standard and the resulting currency depreciation conferred a temporary competitive advantage in some cases, modern research shows that the primary benefit of leaving gold was that it freed countries to use appropriately expansionary monetary policies. By 1935 or 1936, when essentially all major countries had left the gold standard and exchange rates were market-determined, the net trade effects of the changes in currency values were certainly small. Yet the global economy as a whole was much stronger than it had been in 1931. The reason was that, in shedding the strait jacket of the gold standard, each country became free to use monetary policy in a way that was more commensurate with achieving full employment at home.”
Nurkse (1944) raised concern on the contraction of trade by competitive devaluations during the 1930s. Haberler (1937) dwelled on the issue of flexible exchange rates. Bordo and James (2001) provide perceptive exegesis of the views of Haberler (1937) and Nurkse (1944) together with the evolution of thought by Haberler. Policy coordination among sovereigns may be quite difficult in practice even if there were sufficient knowledge and sound forecasts. Friedman (1953) provided strong case in favor of a system of flexible exchange rates.
Eichengreen and Sachs (1985) argue theoretically with measurements using a two-sector model that it is possible for series of devaluations to improve the welfare of all countries. There were adverse effects of depreciation on other countries but depreciation by many countries could be beneficial for all. The important counterfactual is if depreciations by many countries would have promoted faster recovery from the Great Depression. Depreciation in the model of Eichengreen and Sachs (1985) affected domestic and foreign economies through real wages, profitability, international competitiveness and world interest rates. Depreciation causes increase in the money supply that lowers world interest rates, promoting growth of world output. Lower world interest rates could compensate contraction of output from the shift of demand away from home goods originating in neighbor’s exchange depreciation. Eichengreen and Sachs (1985, 946) conclude:
“This much, however, is clear. We do not present a blanket endorsement of the competitive devaluations of the 1930s. Though it is indisputable that currency depreciation conferred macroeconomic benefits on the initiating country, because of accompanying policies the depreciations of the 1930s had beggar-thy-neighbor effects. Though it is likely that currency depreciation (had it been even more widely adopted) would have worked to the benefit of the world as a whole, the sporadic and uncoordinated approach taken to exchange-rate policy in the 1930s tended, other things being equal, to reduce the magnitude of the benefits.”
There could major difference in the current world economy. The initiating impulse for depreciation originates in zero interest rates on the fed funds rate. The dollar is the world’s reserve currency. Risk aversion intermittently channels capital flight to the safe haven of the dollar and US Treasury securities. In the absence of risk aversion, zero interest rates induce carry trades of short positions in dollars and US debt (borrowing) together with long leveraged exposures in risk financial assets such as stocks, emerging stocks, commodities and high-yield bonds. Without risk aversion, the dollar depreciates against every currency in the world. The dollar depreciated against the euro by 39.3 percent from USD 1.1423/EUR con Jun 26, 2003 to USD 1.5914/EUR on Jun 14, 2008 during unconventional monetary policy before the global recession (Table VI-1). Unconventional monetary policy causes devaluation of the dollar relative to other currencies, which can increases net exports of the US that increase aggregate economic activity (Yellen 2011AS). The country issuing the world’s reserve currency appropriates the advantage from initiating devaluation that in policy intends to generate net exports that increase domestic output.
Pelaez and Pelaez (Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 208-209) summarize the experience of Brazil as follows:
“During 1927–9, Brazil accumulated £30 million of foreign exchange of which £20 million were deposited at its stabilization fund (Pelaez 1968, 43–4). After the decline in coffee prices and the first impact of the Great Depression in Brazil, a hot money movement wiped out foreign exchange reserves. In addition, capital inflows stopped entirely. The deterioration of the terms of trade further complicated matters, as the value of exports in foreign currency declined abruptly. Because of this exchange crisis, the service of the foreign debt of Brazil became impossible. In August 1931, the federal government was forced to cancel the payment of principal on certain foreign loans. The balance of trade in 1931 was expected to yield £20 million whereas the service of the foreign debt alone amounted to £22.6 million. Part of the solution given to these problems was typical of the 1930s. In September 1931, the government of Brazil required that all foreign transactions were to be conducted through the Bank of Brazil. This monopoly of foreign exchange was exercised by the Bank of Brazil for the following three years. Export permits were granted only after the exchange derived from sales abroad was officially sold to the Bank, which in turn allocated it in accordance with the needs of the economy. An active black market in foreign exchange developed. Brazil was in the first group of countries that abandoned early the gold standard, in 1931, and suffered comparatively less from the Great Depression. The Brazilian federal government, advised by the BOE, increased taxes and reduced expenditures in 1931 to compensate a decline in custom receipts (Pelaez 1968, 40). Expenditures caused by a revolution in 1932 in the state of Sao Paulo and a drought in the northeast explain the deficit. During 1932–6, the federal government engaged in strong efforts to stabilize the budget. Apart from the deliberate efforts to balance the budget during the 1930s, the recovery in economic activity itself may have induced a large part of the reduction of the deficit (Ibid, 41). Brazil’s experience is similar to that of the United States in that fiscal policy did not promote recovery from the Great Depression.”
In remarkable anticipation in 2005, Professor Raghuram G. Rajan (2005) warned of low liquidity and high risks of central bank policy rates approaching the zero bound (Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 218-9). Professor Rajan excelled in a distinguished career as an academic economist in finance and was chief economist of the International Monetary Fund (IMF). Shefali Anand and Jon Hilsenrath, writing on Oct 13, 2013, on “India’s central banker lobbies Fed,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702304330904579133530766149484?KEYWORDS=Rajan), interviewed Raghuram G. Rajan, who is the current Governor of the Reserve Bank of India, which is India’s central bank (http://www.rbi.org.in/scripts/AboutusDisplay.aspx). In this interview, Rajan argues that central banks should avoid unintended consequences on emerging market economies of inflows and outflows of capital triggered by monetary policy. Portfolio reallocations induced by combination of zero interest rates and risk events stimulate carry trades that generate wide swings in world capital flows. Professor Raguram G Rajan, governor of the Reserve Bank of India, which is India’s central bank, warned about risks in high valuations of asset prices in an interview with Christopher Jeffery of Central Banking Journal on Aug 6, 2014 (http://www.centralbanking.com/central-banking-journal/interview/2358995/raghuram-rajan-on-the-dangers-of-asset-prices-policy-spillovers-and-finance-in-india). Professor Rajan demystifies in the interview “competitive easing” by major central banks as equivalent to competitive devaluation.
The Swiss National Bank (SNB) announced on Jan 15, 2015, the termination of its peg of the exchange rate of the Swiss franc to the euro (http://www.snb.ch/en/mmr/speeches/id/ref_20150115_tjn/source/ref_20150115_tjn.en.pdf):
“The Swiss National Bank (SNB) has decided to discontinue the minimum exchange rate of CHF 1.20 per euro with immediate effect and to cease foreign currency purchases associated with enforcing it.”
The SNB also lowered interest rates to nominal negative percentages (http://www.snb.ch/en/mmr/speeches/id/ref_20150115_tjn/source/ref_20150115_tjn.en.pdf):
“At the same time as discontinuing the minimum exchange rate, the SNB will be lowering the interest rate for balances held on sight deposit accounts to –0.75% from 22 January. The exemption thresholds remain unchanged. Further lowering the interest rate makes Swiss-franc investments considerably less attractive and will mitigate the effects of the decision to discontinue the minimum exchange rate. The target range for the three-month Libor is being lowered by 0.5 percentage points to between –1.25% and –0.25%.”
The Swiss franc rate relative to the euro (CHF/EUR) appreciated 18.7 percent on Jan 15, 2015. The Swiss franc rate relative to the dollar (CHF/USD) appreciated 17.7 percent. Central banks are taking measures in anticipation of the quantitative easing by the European Central Bank.
On Jan 22, 2015, the European Central Bank (ECB) decided to implement an “expanded asset purchase program” with combined asset purchases of €60 billion per month “until at least Sep 2016 (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pr/date/2015/html/pr150122_1.en.html). The objective of the program is that (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pr/date/2015/html/pr150122_1.en.html):
“Asset purchases provide monetary stimulus to the economy in a context where key ECB interest rates are at their lower bound. They further ease monetary and financial conditions, making access to finance cheaper for firms and households. This tends to support investment and consumption, and ultimately contributes to a return of inflation rates towards 2%.”
The President of the ECB, Mario Draghi, explains the coordination of asset purchases with NCBs (National Central Banks) of the euro area and risk sharing (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pressconf/2015/html/is150122.en.html):
“In March 2015 the Eurosystem will start to purchase euro-denominated investment-grade securities issued by euro area governments and agencies and European institutions in the secondary market. The purchases of securities issued by euro area governments and agencies will be based on the Eurosystem NCBs’ shares in the ECB’s capital key. Some additional eligibility criteria will be applied in the case of countries under an EU/IMF adjustment programme. As regards the additional asset purchases, the Governing Council retains control over all the design features of the programme and the ECB will coordinate the purchases, thereby safeguarding the singleness of the Eurosystem’s monetary policy. The Eurosystem will make use of decentralised implementation to mobilise its resources. With regard to the sharing of hypothetical losses, the Governing Council decided that purchases of securities of European institutions (which will be 12% of the additional asset purchases, and which will be purchased by NCBs) will be subject to loss sharing. The rest of the NCBs’ additional asset purchases will not be subject to loss sharing. The ECB will hold 8% of the additional asset purchases. This implies that 20% of the additional asset purchases will be subject to a regime of risk sharing.”
The President of the ECB, Mario Draghi, rejected the possibility of seigniorage in the new asset purchase program, or central bank financing of fiscal expansion (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pressconf/2015/html/is150122.en.html):
“As I just said, it would be a big mistake if countries were to consider that the presence of this programme might be an incentive to fiscal expansion. They would undermine the confidence, so it’s not directed to monetary financing at all. Actually, it’s been designed as to avoid any monetary financing.”
The President of the ECB, Mario Draghi, does not find effects of monetary policy in inflating asset prices (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pressconf/2015/html/is150122.en.html):
“On the first question, we monitor closely any potential instance of risk to financial stability. So we're very alert to that risk. So far we don't see bubbles. There may be some local episodes of certain specific markets where prices are going up fast. But to have a bubble, besides having that, one should also identify, detect an increase, dramatic increase in leverage or in bank credit, and we don't see that now. However, we, as I said, we are alert. If bubbles are of a local nature, they should be addressed by local instruments, namely macro-prudential instruments rather than by monetary policy.”
The DAX index of German equities increased 1.3 percent on Jan 22, 2015 and 2.1 percent on Jan 23, 2015. The euro depreciated from EUR 1.1611/USD (EUR 0.8613/USD) on Wed Jan 21, 2015, to EUR 1.1206/USD (EUR 0.8924/USD) on Fri Jan 23, 2015, or 3.6 percent. Yellen (2011AS, 6) admits that Fed monetary policy results in dollar devaluation with the objective of increasing net exports, which was the policy that Joan Robinson (1947) labeled as “beggar-my-neighbor” remedies for unemployment. Risk aversion erodes devaluation of the dollar.
Dan Strumpf and Pedro Nicolaci da Costa, writing on “Fed’s Yellen: Stock Valuations ‘Generally are Quite High,’” on May 6, 2015, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/feds-yellen-cites-progress-on-bank-regulation-1430918155?tesla=y ), quote Chair Yellen at open conversation with Christine Lagarde, Managing Director of the IMF, finding “equity-market valuations” as “quite high” with “potential dangers” in bond valuations. The DJIA fell 0.5 percent on May 6, 2015, after the comments and then increased 0.5 percent on May 7, 2015 and 1.5 percent on May 8, 2015.
| Fri May 1 | Mon 4 | Tue 5 | Wed 6 | Thu 7 | Fri 8 |
| DJIA 18024.06 -0.3% 1.0% | 18070.40 0.3% 0.3% | 17928.20 -0.5% -0.8% | 17841.98 -1.0% -0.5% | 17924.06 -0.6% 0.5% | 18191.11 0.9% 1.5% |
There are two approaches in theory considered by Bordo (2012Nov20) and Bordo and Lane (2013). The first approach is in the classical works of Milton Friedman and Anna Jacobson Schwartz (1963a, 1987) and Karl Brunner and Allan H. Meltzer (1973). There is a similar approach in Tobin (1969). Friedman and Schwartz (1963a, 66) trace the effects of expansionary monetary policy into increasing initially financial asset prices: “It seems plausible that both nonbank and bank holders of redundant balances will turn first to securities comparable to those they have sold, say, fixed-interest coupon, low-risk obligations. But as they seek to purchase these they will tend to bid up the prices of those issues. Hence they, and also other holders not involved in the initial central bank open-market transactions, will look farther afield: the banks, to their loans; the nonbank holders, to other categories of securities-higher risk fixed-coupon obligations, equities, real property, and so forth.”
The second approach is by the Austrian School arguing that increases in asset prices can become bubbles if monetary policy allows their financing with bank credit. Professor Michael D. Bordo provides clear thought and empirical evidence on the role of “expansionary monetary policy” in inflating asset prices (Bordo2012Nov20, Bordo and Lane 2013). Bordo and Lane (2013) provide revealing narrative of historical episodes of expansionary monetary policy. Bordo and Lane (2013) conclude that policies of depressing interest rates below the target rate or growth of money above the target influences higher asset prices, using a panel of 18 OECD countries from 1920 to 2011. Bordo (2012Nov20) concludes: “that expansionary money is a significant trigger” and “central banks should follow stable monetary policies…based on well understood and credible monetary rules.” Taylor (2007, 2009) explains the housing boom and financial crisis in terms of expansionary monetary policy. Professor Martin Feldstein (2016), at Harvard University, writing on “A Federal Reserve oblivious to its effects on financial markets,” on Jan 13, 2016, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/a-federal-reserve-oblivious-to-its-effect-on-financial-markets-1452729166), analyzes how unconventional monetary policy drove values of risk financial assets to high levels. Quantitative easing and zero interest rates distorted calculation of risks with resulting vulnerabilities in financial markets.
Another hurdle of exit from zero interest rates is “competitive easing” that Professor Raghuram Rajan, governor of the Reserve Bank of India, characterizes as disguised “competitive devaluation” (http://www.centralbanking.com/central-banking-journal/interview/2358995/raghuram-rajan-on-the-dangers-of-asset-prices-policy-spillovers-and-finance-in-india). The fed has been considering increasing interest rates. The European Central Bank (ECB) announced, on Mar 5, 2015, the beginning on Mar 9, 2015 of its quantitative easing program denominated as Public Sector Purchase Program (PSPP), consisting of “combined monthly purchases of EUR 60 bn [billion] in public and private sector securities” (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/mopo/liq/html/pspp.en.html). Expectation of increasing interest rates in the US together with euro rates close to zero or negative cause revaluation of the dollar (or devaluation of the euro and of most currencies worldwide). US corporations suffer currency translation losses of their foreign transactions and investments (http://www.fasb.org/jsp/FASB/Pronouncement_C/SummaryPage&cid=900000010318) while the US becomes less competitive in world trade (Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. I (2008a), Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c)). The DJIA fell 1.5 percent on Mar 6, 2015 and the dollar revalued 2.2 percent from Mar 5 to Mar 6, 2015. The euro has devalued 40.9 percent relative to the dollar from the high on Jul 15, 2008 to Apr 15, 2016.
| Fri 27 Feb | Mon 3/2 | Tue 3/3 | Wed 3/4 | Thu 3/5 | Fri 3/6 |
| USD/ EUR 1.1197 1.6% 0.0% | 1.1185 0.1% 0.1% | 1.1176 0.2% 0.1% | 1.1081 1.0% 0.9% | 1.1030 1.5% 0.5% | 1.0843 3.2% 1.7% |
Chair Yellen explained the removal of the word “patience” from the advanced guidance at the press conference following the FOMC meeting on Mar 18, 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20150318.pdf):
“In other words, just because we removed the word “patient” from the statement doesn’t mean we are going to be impatient. Moreover, even after the initial increase in the target funds rate, our policy is likely to remain highly accommodative to support continued progress toward our objectives of maximum employment and 2 percent inflation.”
Exchange rate volatility is increasing in response of “impatience” in financial markets with monetary policy guidance and measures:
| Fri Mar 6 | Mon 9 | Tue 10 | Wed 11 | Thu 12 | Fri 13 |
| USD/ EUR 1.0843 3.2% 1.7% | 1.0853 -0.1% -0.1% | 1.0700 1.3% 1.4% | 1.0548 2.7% 1.4% | 1.0637 1.9% -0.8% | 1.0497 3.2% 1.3% |
| Fri Mar 13 | Mon 16 | Tue 17 | Wed 18 | Thu 19 | Fri 20 |
| USD/ EUR 1.0497 3.2% 1.3% | 1.0570 -0.7% -0.7% | 1.0598 -1.0% -0.3% | 1.0864 -3.5% -2.5% | 1.0661 -1.6% 1.9% | 1.0821 -3.1% -1.5% |
| Fri Apr 24 | Mon 27 | Tue 28 | Wed 29 | Thu 30 | May Fri 1 |
| USD/ EUR 1.0874 -0.6% -0.4% | 1.0891 -0.2% -0.2% | 1.0983 -1.0% -0.8% | 1.1130 -2.4% -1.3% | 1.1223 -3.2% -0.8% | 1.1199 -3.0% 0.2% |
In a speech at Brown University on May 22, 2015, Chair Yellen stated (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20150522a.htm):
“For this reason, if the economy continues to improve as I expect, I think it will be appropriate at some point this year to take the initial step to raise the federal funds rate target and begin the process of normalizing monetary policy. To support taking this step, however, I will need to see continued improvement in labor market conditions, and I will need to be reasonably confident that inflation will move back to 2 percent over the medium term. After we begin raising the federal funds rate, I anticipate that the pace of normalization is likely to be gradual. The various headwinds that are still restraining the economy, as I said, will likely take some time to fully abate, and the pace of that improvement is highly uncertain.”
The US dollar appreciated 3.8 percent relative to the euro in the week of May 22, 2015:
| Fri May 15 | Mon 18 | Tue 19 | Wed 20 | Thu 21 | Fri 22 |
| USD/ EUR 1.1449 -2.2% -0.3% | 1.1317 1.2% 1.2% | 1.1150 2.6% 1.5% | 1.1096 3.1% 0.5% | 1.1113 2.9% -0.2% | 1.1015 3.8% 0.9% |
The Managing Director of the International Monetary Fund (IMF), Christine Lagarde, warned on Jun 4, 2015, that: (http://blog-imfdirect.imf.org/2015/06/04/u-s-economy-returning-to-growth-but-pockets-of-vulnerability/):
“The Fed’s first rate increase in almost 9 years is being carefully prepared and telegraphed. Nevertheless, regardless of the timing, higher US policy rates could still result in significant market volatility with financial stability consequences that go well beyond US borders. I weighing these risks, we think there is a case for waiting to raise rates until there are more tangible signs of wage or price inflation than are currently evident. Even after the first rate increase, a gradual rise in the federal fund rates will likely be appropriate.”
The President of the European Central Bank (ECB), Mario Draghi, warned on Jun 3, 2015 that (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pressconf/2015/html/is150603.en.html):
“But certainly one lesson is that we should get used to periods of higher volatility. At very low levels of interest rates, asset prices tend to show higher volatility…the Governing Council was unanimous in its assessment that we should look through these developments and maintain a steady monetary policy stance.”
The Chair of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Janet L. Yellen, stated on Jul 10, 2015 that (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20150710a.htm):
“Based on my outlook, I expect that it will be appropriate at some point later this year to take the first step to raise the federal funds rate and thus begin normalizing monetary policy. But I want to emphasize that the course of the economy and inflation remains highly uncertain, and unanticipated developments could delay or accelerate this first step. I currently anticipate that the appropriate pace of normalization will be gradual, and that monetary policy will need to be highly supportive of economic activity for quite some time. The projections of most of my FOMC colleagues indicate that they have similar expectations for the likely path of the federal funds rate. But, again, both the course of the economy and inflation are uncertain. If progress toward our employment and inflation goals is more rapid than expected, it may be appropriate to remove monetary policy accommodation more quickly. However, if progress toward our goals is slower than anticipated, then the Committee may move more slowly in normalizing policy.”
There is essentially the same view in the Testimony of Chair Yellen in delivering the Semiannual Monetary Policy Report to the Congress on Jul 15, 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20150715a.htm).
At the press conference after the meeting of the FOMC on Sep 17, 2015, Chair Yellen states (http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20150917.pdf 4):
“The outlook abroad appears to have become more uncertain of late, and heightened concerns about growth in China and other emerging market economies have led to notable volatility in financial markets. Developments since our July meeting, including the drop in equity prices, the further appreciation of the dollar, and a widening in risk spreads, have tightened overall financial conditions to some extent. These developments may restrain U.S. economic activity somewhat and are likely to put further downward pressure on inflation in the near term. Given the significant economic and financial interconnections between the United States and the rest of the world, the situation abroad bears close watching.”
Some equity markets fell on Fri Sep 18, 2015:
| Fri Sep 11 | Mon 14 | Tue 15 | Wed 16 | Thu 17 | Fri 18 |
| DJIA 16433.09 2.1% 0.6% | 16370.96 -0.4% -0.4% | 16599.85 1.0% 1.4% | 16739.95 1.9% 0.8% | 16674.74 1.5% -0.4% | 16384.58 -0.3% -1.7% |
| Nikkei 225 18264.22 2.7% -0.2% | 17965.70 -1.6% -1.6% | 18026.48 -1.3% 0.3% | 18171.60 -0.5% 0.8% | 18432.27 0.9% 1.4% | 18070.21 -1.1% -2.0% |
| DAX 10123.56 0.9% -0.9% | 10131.74 0.1% 0.1% | 10188.13 0.6% 0.6% | 10227.21 1.0% 0.4% | 10229.58 1.0% 0.0% | 9916.16 -2.0% -3.1% |
Frank H. Knight (1963, 233), in Risk, uncertainty and profit, distinguishes between measurable risk and unmeasurable uncertainty. Chair Yellen, in a lecture on “Inflation dynamics and monetary policy,” on Sep 24, 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20150924a.htm), states that (emphasis added):
· “The economic outlook, of course, is highly uncertain”
· “Considerable uncertainties also surround the outlook for economic activity”
· “Given the highly uncertain nature of the outlook…”
Is there a “science” or even “art” of central banking under this extreme uncertainty in which policy does not generate higher volatility of money, income, prices and values of financial assets?
Lingling Wei, writing on Oct 23, 2015, on China’s central bank moves to spur economic growth,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/chinas-central-bank-cuts-rates-1445601495), analyzes the reduction by the People’s Bank of China (http://www.pbc.gov.cn/ http://www.pbc.gov.cn/english/130437/index.html) of borrowing and lending rates of banks by 50 basis points and reserve requirements of banks by 50 basis points. Paul Vigna, writing on Oct 23, 2015, on “Stocks rally out of correction territory on latest central bank boost,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://blogs.wsj.com/moneybeat/2015/10/23/stocks-rally-out-of-correction-territory-on-latest-central-bank-boost/), analyzes the rally in financial markets following the statement on Oct 22, 2015, by the President of the European Central Bank (ECB) Mario Draghi of consideration of new quantitative measures in Dec 2015 (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0814riKW25k&rel=0) and the reduction of bank lending/deposit rates and reserve requirements of banks by the People’s Bank of China on Oct 23, 2015. The dollar revalued 2.8 percent from Oct 21 to Oct 23, 2015, following the intended easing of the European Central Bank. The DJIA rose 2.8 percent from Oct 21 to Oct 23 and the DAX index of German equities rose 5.4 percent from Oct 21 to Oct 23, 2015.
| Fri Oct 16 | Mon 19 | Tue 20 | Wed 21 | Thu 22 | Fri 23 |
| USD/ EUR 1.1350 0.1% 0.3% | 1.1327 0.2% 0.2% | 1.1348 0.0% -0.2% | 1.1340 0.1% 0.1% | 1.1110 2.1% 2.0% | 1.1018 2.9% 0.8% |
| DJIA 17215.97 0.8% 0.4% | 17230.54 0.1% 0.1% | 17217.11 0.0% -0.1% | 17168.61 -0.3% -0.3% | 17489.16 1.6% 1.9% | 17646.70 2.5% 0.9% |
| Dow Global 2421.58 0.3% 0.6% | 2414.33 -0.3% -0.3% | 2411.03 -0.4% -0.1% | 2411.27 -0.4% 0.0% | 2434.79 0.5% 1.0% | 2458.13 1.5% 1.0% |
| DJ Asia Pacific 1402.31 1.1% 0.3% | 1398.80 -0.3% -0.3% | 1395.06 -0.5% -0.3% | 1402.68 0.0% 0.5% | 1396.03 -0.4% -0.5% | 1415.50 0.9% 1.4% |
| Nikkei 225 18291.80 -0.8% 1.1% | 18131.23 -0.9% -0.9% | 18207.15 -0.5% 0.4% | 18554.28 1.4% 1.9% | 18435.87 0.8% -0.6% | 18825.30 2.9% 2.1% |
| Shanghai 3391.35 6.5% 1.6% | 3386.70 -0.1% -0.1% | 3425.33 1.0% 1.1% | 3320.68 -2.1% -3.1% | 3368.74 -0.7% 1.4% | 3412.43 0.6% 1.3% |
| DAX 10104.43 0.1% 0.4% | 10164.31 0.6% 0.6% | 10147.68 0.4% -0.2% | 10238.10 1.3% 0.9% | 10491.97 3.8% 2.5% | 10794.54 6.8% 2.9% |
Ben Leubsdorf, writing on “Fed’s Yellen: December is “Live Possibility” for First Rate Increase,” on Nov 4, 2015, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/feds-yellen-december-is-live-possibility-for-first-rate-increase-1446654282) quotes Chair Yellen that a rate increase in “December would be a live possibility.” The remark of Chair Yellen was during a hearing on supervision and regulation before the Committee on Financial Services, US House of Representatives (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20151104a.htm) and a day before the release of the employment situation report for Oct 2015 (Section I). The dollar revalued 2.4 percent during the week. The euro has devalued 40.9 percent relative to the dollar from the high on Jul 15, 2008 to Apr 15, 2016.
| Fri Oct 30 | Mon 2 | Tue 3 | Wed 4 | Thu 5 | Fri 6 |
| USD/ EUR 1.1007 0.1% -0.3% | 1.1016 -0.1% -0.1% | 1.0965 0.4% 0.5% | 1.0867 1.3% 0.9% | 1.0884 1.1% -0.2% | 1.0742 2.4% 1.3% |
The release on Nov 18, 2015 of the minutes of the FOMC (Federal Open Market Committee) meeting held on Oct 28, 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/fomcminutes20151028.htm) states:
“Most participants anticipated that, based on their assessment of the current economic situation and their outlook for economic activity, the labor market, and inflation, these conditions [for interest rate increase] could well be met by the time of the next meeting. Nonetheless, they emphasized that the actual decision would depend on the implications for the medium-term economic outlook of the data received over the upcoming intermeeting period… It was noted that beginning the normalization process relatively soon would make it more likely that the policy trajectory after liftoff could be shallow.”
Markets could have interpreted a symbolic increase in the fed funds rate at the meeting of the FOMC on Dec 15-16, 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/fomccalendars.htm) followed by “shallow” increases, explaining the sharp increase in stock market values and appreciation of the dollar after the release of the minutes on Nov 18, 2015:
| Fri Nov 13 | Mon 16 | Tue 17 | Wed 18 | Thu 19 | Fri 20 |
| USD/ EUR 1.0774 -0.3% 0.4% | 1.0686 0.8% 0.8% | 1.0644 1.2% 0.4% | 1.0660 1.1% -0.2% | 1.0735 0.4% -0.7% | 1.0647 1.2% 0.8% |
| DJIA 17245.24 -3.7% -1.2% | 17483.01 1.4% 1.4% | 17489.50 1.4% 0.0% | 17737.16 2.9% 1.4% | 17732.75 2.8% 0.0% | 17823.81 3.4% 0.5% |
| DAX 10708.40 -2.5% -0.7% | 10713.23 0.0% 0.0% | 10971.04 2.5% 2.4% | 10959.95 2.3% -0.1% | 11085.44 3.5% 1.1% | 11119.83 3.8% 0.3% |
In testimony before The Joint Economic Committee of Congress on Dec 3, 2015 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20151203a.htm), Chair Yellen reiterated that the FOMC (Federal Open Market Committee) “anticipates that even after employment and inflation are near mandate-consistent levels, economic condition may, for some time, warrant keeping the target federal funds rate below the Committee views as normal in the longer run.” Todd Buell and Katy Burne, writing on “Draghi says ECB could step up stimulus efforts if necessary,” on Dec 4, 2015, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/draghi-says-ecb-could-step-up-stimulus-efforts-if-necessary-1449252934), analyze that the President of the European Central Bank (ECB), Mario Draghi, reassured financial markets that the ECB will increase stimulus if required to raise inflation the euro area to targets. The USD depreciated 3.1 percent on Thu Dec 3, 2015 after weaker than expected measures by the European Central Bank. DJIA fell 1.4 percent on Dec 3 and increased 2.1 percent on Dec 4. DAX fell 3.6 percent on Dec 3.
| Fri Nov 27 | Mon 30 | Tue 1 | Wed 2 | Thu 3 | Fri 4 |
| USD/ EUR 1.0594 0.5% 0.2% | 1.0565 0.3% 0.3% | 1.0634 -0.4% -0.7% | 1.0616 -0.2% 0.2% | 1.0941 -3.3% -3.1% | 1.0885 -2.7% 0.5% |
| DJIA 17798.49 -0.1% -0.1% | 17719.92 -0.4% -0.4% | 17888.35 0.5% 1.0% | 17729.68 -0.4% -0.9% | 17477.67 -1.8% -1.4% | 17847.63 0.3% 2.1% |
| DAX 11293.76 1.6% -0.2% | 11382.23 0.8% 0.8% | 11261.24 -0.3% -1.1% | 11190.02 -0.9% -0.6% | 10789.24 -4.5% -3.6% | 10752.10 -4.8% -0.3% |
At the press conference following the meeting of the FOMC on Dec 16, 2015, Chair Yellen states (http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20151216.pdf page 8):
“And we recognize that monetary policy operates with lags. We would like to be able to move in a prudent, and as we've emphasized, gradual manner. It's been a long time since the Federal Reserve has raised interest rates, and I think it's prudent to be able to watch what the impact is on financial conditions and spending in the economy and moving in a timely fashion enables us to do this.”
The implication of this statement is that the state of the art is not accurate in analyzing the effects of monetary policy on financial markets and economic activity. The US dollar appreciated and equities fluctuated:
| Fri Dec 11 | Mon 14 | Tue 15 | Wed 16 | Thu 17 | Fri 18 |
| USD/ EUR 1.0991 -1.0% -0.4% | 1.0993 0.0% 0.0% | 1.0932 0.5% 0.6% | 1.0913 0.7% 0.2% | 1.0827 1.5% 0.8% | 1.0868 1.1% -0.4% |
| DJIA 17265.21 -3.3% -1.8% | 17368.50 0.6% 0.6% | 17524.91 1.5% 0.9% | 17749.09 2.8% 1.3% | 17495.84 1.3% -1.4% | 17128.55 -0.8% -2.1% |
| DAX 10340.06 -3.8% -2.4% | 10139.34 -1.9% -1.9% | 10450.38 -1.1% 3.1% | 10469.26 1.2% 0.2% | 10738.12 3.8% 2.6% | 10608.19 2.6% -1.2% |
On January 29, 2016, the Policy Board of the Bank of Japan introduced a new policy to attain the “price stability target of 2 percent at the earliest possible time” (https://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2016/k160129a.pdf). The new framework consists of three dimensions: quantity, quality and interest rate. The interest rate dimension consists of rates paid to current accounts that financial institutions hold at the Bank of Japan of three tiers zero, positive and minus 0.1 percent. The quantitative dimension consists of increasing the monetary base at the annual rate of 80 trillion yen. The qualitative dimension consists of purchases by the Bank of Japan of Japanese government bonds (JGBs), exchange traded funds (ETFs) and Japan real estate investment trusts (J-REITS). The yen devalued sharply relative to the dollar and world equity markets soared after the new policy announced on Jan 29, 2016:
| Fri 22 | Mon 25 | Tue 26 | Wed 27 | Thu 28 | Fri 29 |
| JPY/ USD 118.77 -1.5% -0.9% | 118.30 0.4% 0.4% | 118.42 0.3% -0.1% | 118.68 0.1% -0.2% | 118.82 0.0% -0.1% | 121.13 -2.0% -1.9% |
| DJIA 16093.51 0.7% 1.3% | 15885.22 -1.3% -1.3% | 16167.23 0.5% 1.8% | 15944.46 -0.9% -1.4% | 16069.64 -0.1% 0.8% | 16466.30 2.3% 2.5% |
| Nikkei 16958.53 -1.1% 5.9% | 17110.91 0.9% 0.9% | 16708.90 -1.5% -2.3% | 17163.92 1.2% 2.7% | 17041.45 0.5% -0.7% | 17518.30 3.3% 2.8% |
| Shanghai 2916.56 0.5% 1.3 | 2938.51 0.8% 0.8% | 2749.79 -5.7% -6.4% | 2735.56 -6.2% -0.5% | 2655.66 -8.9% -2.9% | 2737.60 -6.1% 3.1% |
| DAX 9764.88 2.3% 2.0% | 9736.15 -0.3% -0.3% | 9822.75 0.6% 0.9% | 9880.82 1.2% 0.6% | 9639.59 -1.3% -2.4% | 9798.11 0.3% 1.6% |
In testimony on the Semiannual Monetary Policy Report to the Congress on Feb 10-11, 2016, Chair Yellen (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20160210a.htm) states: “U.S. real gross domestic product is estimated to have increased about 1-3/4 percent in 2015. Over the course of the year, subdued foreign growth and the appreciation of the dollar restrained net exports. In the fourth quarter of last year, growth in the gross domestic product is reported to have slowed more sharply, to an annual rate of just 3/4 percent; again, growth was held back by weak net exports as well as by a negative contribution from inventory investment.”
Jon Hilsenrath, writing on “Yellen Says Fed Should Be Prepared to Use Negative Rates if Needed,” on Feb 11, 2016, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://www.wsj.com/articles/yellen-reiterates-concerns-about-risks-to-economy-in-senate-testimony-1455203865), analyzes the statement of Chair Yellen in Congress that the FOMC (Federal Open Market Committee) is considering negative interest rates on bank reserves. The Wall Street Journal provides yields of two and ten-year sovereign bonds with negative interest rates on shorter maturities where central banks pay negative interest rates on excess bank reserves:
| Sovereign Yields 2/12/16 | Japan | Germany | USA |
| 2 Year | -0.168 | -0.498 | 0.694 |
| 10 Year | 0.076 | 0.262 | 1.744 |
On Mar 10, 2016, the European Central Bank (ECB) announced (1) reduction of the refinancing rate by 5 basis points to 0.00 percent; decrease the marginal lending rate to 0.25 percent; reduction of the deposit facility rate to 0,40 percent; increase of the monthly purchase of assets to €80 billion; include nonbank corporate bonds in assets eligible for purchases; and new long-term refinancing operations (https://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pr/date/2016/html/pr160310.en.html). The President of the ECB, Mario Draghi, stated in the press conference (https://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pressconf/2016/html/is160310.en.html): “How low can we go? Let me say that rates will stay low, very low, for a long period of time, and well past the horizon of our purchases…We don’t anticipate that it will be necessary to reduce rates further. Of course, new facts can change the situation and the outlook.”
The dollar devalued relative to the euro and open stock markets traded lower after the announcement on Mar 10, 2016, but stocks rebounded on Mar 11:
| Fri 4 | Mon 7 | Tue 8 | Wed 9 | Thu10 | Fri 11 |
| USD/ EUR 1.1006 -0.7% -0.4% | 1.1012 -0.1% -0.1% | 1.1013 -0.1% 0.0% | 1.0999 0.1% 0.1% | 1.1182 -1.6% -1.7% | 1.1151 -1.3% 0.3% |
| DJIA 17006.77 2.2% 0.4% | 17073.95 0.4% 0.4% | 16964.10 -0.3% -0.6% | 17000.36 0.0% 0.2% | 16995.13 -0.1% 0.0% | 17213.31 1.2% 1.3% |
| DAX 9824.17 3.3% 0.7% | 9778.93 -0.5% 0.5% | 9692.82 -1.3% -0.9% | 9723.09 -1.0% 0.3% | 9498.15 -3.3% -2.3% | 9831.13 0.1% 3.5% |
The Communiqué of the Istanbul meeting of G20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors on February 10, 2015, sanctions the need of unconventional monetary policy with warning on collateral effects (http://www.g20.utoronto.ca/2015/150210-finance.html):
“We agree that consistent with central banks' mandates, current economic conditions require accommodative monetary policies in some economies. In this regard, we welcome that central banks take appropriate monetary policy action. The recent policy decision by the ECB aims at fulfilling its price stability mandate, and will further support the recovery in the euro area. We also note that some advanced economies with stronger growth prospects are moving closer to conditions that would allow for policy normalization. In an environment of diverging monetary policy settings and rising financial market volatility, policy settings should be carefully calibrated and clearly communicated to minimize negative spillovers.”
Banking was important in facilitating economic growth in historical periods (Cameron 1961, 1967, 1972; Cameron et al. 1992). Banking is also important currently because small- and medium-size business may have no other form of financing than banks in contrast with many options for larger and more mature companies that have access to capital markets. Calomiris and Haber (2014) find that broad voting rights and institutions restricting coalitions of bankers and populists ensure stable banking systems and access to credit. Summerhill (2015) finds compelling evidence that sovereign credibility is insufficient to develop financial intermediation required for economic growth in the presence of inadequate political institutions.
Bernanke (2010WP) and Yellen (2011AS) reveal the emphasis of monetary policy on the impact of the rise of stock market valuations in stimulating consumption by wealth effects on household confidence. Table VI-5 shows a gain by Apr 29, 2011 in the DJIA of 14.3 percent and of the S&P 500 of 12.5 percent since Apr 26, 2010, around the time when sovereign risk issues in Europe began to be acknowledged in financial risk asset valuations. The last row of Table VI-5 for Apr 15, 2016, shows that the S&P 500 is now 71.7 percent above the Apr 26, 2010 level and the DJIA is 59.7 percent above the level on Apr 26, 2010. Multiple rounds of risk aversion eroded earlier gains, showing that risk aversion can destroy market value even with zero interest rates. Relaxed risk aversion has contributed to recovery of valuations. Much the same as zero interest rates and quantitative easing have not had any effects in recovering economic activity while distorting financial markets and resource allocation.
Table VI-5, Percentage Changes of DJIA and S&P 500 in Selected Dates
| ∆% DJIA from prior date | ∆% DJIA from | ∆% S&P 500 from prior date | ∆% S&P 500 from | |
| Apr 26, 2010 | ||||
| May 6/10 | -6.1 | -6.1 | -6.9 | -6.9 |
| May 26/10 | -5.2 | -10.9 | -5.4 | -11.9 |
| Jun 8/10 | -1.2 | -11.3 | 2.1 | -12.4 |
| Jul 2/10 | -2.6 | -13.6 | -3.8 | -15.7 |
| Aug 9/10 | 10.5 | -4.3 | 10.3 | -7.0 |
| Aug 31/10 | -6.4 | -10.6 | -6.9 | -13.4 |
| Nov 5/10 | 14.2 | 2.1 | 16.8 | 1.0 |
| Nov 30/10 | -3.8 | -3.8 | -3.7 | -2.6 |
| Dec 17/10 | 4.4 | 2.5 | 5.3 | 2.6 |
| Dec 23/10 | 0.7 | 3.3 | 1.0 | 3.7 |
| Dec 31/10 | 0.03 | 3.3 | 0.07 | 3.8 |
| Jan 7 2011 | 0.8 | 4.2 | 1.1 | 4.9 |
| Jan 14/11 | 0.9 | 5.2 | 1.7 | 6.7 |
| Jan 21/11 | 0.7 | 5.9 | -0.8 | 5.9 |
| Jan 28/11 | -0.4 | 5.5 | -0.5 | 5.3 |
| Feb 4/11 | 2.3 | 7.9 | 2.7 | 8.1 |
| Feb 11/11 | 1.5 | 9.5 | 1.4 | 9.7 |
| Feb 18/11 | 0.9 | 10.6 | 1.0 | 10.8 |
| Feb 25/11 | -2.1 | 8.3 | -1.7 | 8.9 |
| Mar 4/11 | 0.3 | 8.6 | 0.1 | 9.0 |
| Mar 11/11 | -1.0 | 7.5 | -1.3 | 7.6 |
| Mar 18/11 | -1.5 | 5.8 | -1.9 | 5.5 |
| Mar 25/11 | 3.1 | 9.1 | 2.7 | 8.4 |
| Apr 1/11 | 1.3 | 10.5 | 1.4 | 9.9 |
| Apr 8/11 | 0.03 | 10.5 | -0.3 | 9.6 |
| Apr 15/11 | -0.3 | 10.1 | -0.6 | 8.9 |
| Apr 22/11 | 1.3 | 11.6 | 1.3 | 10.3 |
| Apr 29/11 | 2.4 | 14.3 | 1.9 | 12.5 |
| May 6/11 | -1.3 | 12.8 | -1.7 | 10.6 |
| May 13/11 | -0.3 | 12.4 | -0.2 | 10.4 |
| May 20/11 | -0.7 | 11.7 | -0.3 | 10.0 |
| May 27/11 | -0.6 | 11.0 | -0.2 | 9.8 |
| Jun 3/11 | -2.3 | 8.4 | -2.3 | 7.3 |
| Jun 10/11 | -1.6 | 6.7 | -2.2 | 4.9 |
| Jun 17/11 | 0.4 | 7.1 | 0.04 | 4.9 |
| Jun 24/11 | -0.6 | 6.5 | -0.2 | 4.6 |
| Jul 1/11 | 5.4 | 12.3 | 5.6 | 10.5 |
| Jul 8/11 | 0.6 | 12.9 | 0.3 | 10.9 |
| Jul 15/11 | -1.4 | 11.4 | -2.1 | 8.6 |
| Jul 22/11 | 1.6 | 13.2 | 2.2 | 10.9 |
| Jul 29/11 | -4.2 | 8.4 | -3.9 | 6.6 |
| Aug 05/11 | -5.8 | 2.1 | -7.2 | -1.0 |
| Aug 12/11 | -1.5 | 0.6 | -1.7 | -2.7 |
| Aug 19/11 | -4.0 | -3.5 | -4.7 | -7.3 |
| Aug 26/11 | 4.3 | 0.7 | 4.7 | -2.9 |
| Sep 02 | -0.4 | 0.3 | -0.2 | -3.1 |
| Sep 09/11 | -2.2 | -1.9 | -1.7 | -4.8 |
| Sep 16/11 | 4.7 | 2.7 | 5.4 | 0.3 |
| Sep 23/11 | -6.4 | -3.9 | -6.5 | -6.2 |
| Sep 30/11 | 1.3 | -2.6 | -0.4 | -6.7 |
| Oct 7/11 | 1.7 | -0.9 | 2.1 | -4.7 |
| Oct 14/11 | 4.9 | 3.9 | 5.9 | 1.0 |
| Oct 21/11 | 1.4 | 5.4 | 1.1 | 2.2 |
| Oct 28/11 | 3.6 | 9.2 | 3.8 | 6.0 |
| Nov 04/11 | -2.0 | 6.9 | -2.5 | 3.4 |
| Nov 11/11 | 1.4 | 8.5 | 0.8 | 4.3 |
| Nov 18/11 | -2.9 | 5.3 | -3.8 | 0.3 |
| Nov 25/11 | -4.8 | 0.2 | -4.7 | -4.4 |
| Dec 02/11 | 7.0 | 7.3 | 7.4 | 2.7 |
| Dec 09/11 | 1.4 | 8.7 | 0.9 | 3.6 |
| Dec 16/11 | -2.6 | 5.9 | -2.8 | 0.6 |
| Dec 23/11 | 3.6 | 9.7 | 3.7 | 4.4 |
| Dec 30/11 | -0.6 | 9.0 | -0.6 | 3.8 |
| Jan 6 2012 | 1.2 | 10.3 | 1.6 | 5.4 |
| Jan 13/12 | 0.5 | 10.9 | 0.9 | 6.4 |
| Jan 20/12 | 2.4 | 13.5 | 2.0 | 8.5 |
| Jan 27/12 | -0.5 | 13.0 | 0.1 | 8.6 |
| Feb 3/12 | 1.6 | 14.8 | 2.2 | 11.0 |
| Feb 10/12 | -0.5 | 14.2 | -0.2 | 10.8 |
| Feb 17/12 | 1.2 | 15.6 | 1.4 | 12.3 |
| Feb 24/12 | 0.3 | 15.9 | 0.3 | 12.7 |
| Mar 2/12 | 0.0 | 15.8 | 0.3 | 13.0 |
| Mar 9/12 | -0.4 | 15.3 | 0.1 | 13.1 |
| Mar 16/12 | 2.4 | 18.1 | 2.4 | 15.9 |
| Mar 23/12 | -1.1 | 16.7 | -0.5 | 15.3 |
| Mar 30/12 | 1.0 | 17.9 | 0.8 | 16.2 |
| Apr 6/12 | -1.1 | 16.6 | -0.7 | 15.3 |
| Apr 13/12 | -1.6 | 14.7 | -2.0 | 13.1 |
| Apr 20/12 | 1.4 | 16.3 | 0.6 | 13.7 |
| Apr 27/12 | 1.5 | 18.1 | 1.8 | 15.8 |
| May 4/12 | -1.4 | 16.4 | -2.3 | 12.9 |
| May 11/12 | -1.7 | 14.4 | -1.1 | 11.7 |
| May 18/12 | -3.5 | 10.4 | -4.3 | 6.4 |
| May 25/12 | 0.7 | 11.2 | 1.7 | 8.7 |
| Jun 1/12 | -2.7 | 8.2 | -3.0 | 5.4 |
| Jun 8/12 | 3.6 | 12.0 | 3.7 | 9.4 |
| Jun 15/12 | 1.7 | 13.9 | 1.3 | 10.8 |
| Jun 22/12 | -1.0 | 12.8 | -0.6 | 10.1 |
| Jun 29/12 | 1.9 | 14.9 | 2.0 | 12.4 |
| Jul 6/12 | -0.8 | 14.0 | -0.5 | 11.8 |
| Jul 13/12 | 0.0 | 14.0 | 0.2 | 11.9 |
| Jul 20/12 | 0.4 | 14.4 | 0.4 | 12.4 |
| Jul 27/12 | 2.0 | 16.7 | 1.7 | 14.3 |
| Aug 3/12 | 0.2 | 16.9 | 0.4 | 14.8 |
| Aug 10/12 | 0.9 | 17.9 | 1.1 | 16.0 |
| Aug 17/12 | 0.5 | 18.5 | 0.9 | 17.0 |
| Aug 24/12 | -0.9 | 17.4 | -0.5 | 16.4 |
| Aug 31/12 | -0.5 | 16.8 | -0.3 | 16.0 |
| Sep 7/12 | 1.6 | 18.8 | 2.2 | 18.6 |
| Sep 14/12 | 2.2 | 21.3 | 1.90 | 20.9 |
| Sep 21/12 | -0.1 | 21.2 | -0.4 | 20.5 |
| Sep 28/12 | -1.0 | 19.9 | -1.3 | 18.9 |
| Oct 5/12 | 1.3 | 21.5 | 1.4 | 20.5 |
| Oct 12/12 | -2.1 | 18.9 | -2.2 | 17.9 |
| Oct 19/12 | 0.1 | 19.1 | 0.3 | 18.3 |
| Oct 26/12 | -1.8 | 17.0 | -1.5 | 16.5 |
| Nov 2/12 | -0.1 | 16.9 | 0.2 | 16.7 |
| Nov 9/12 | -2.1 | 14.4 | -2.4 | 13.8 |
| Nov 16/12 | -1.8 | 12.3 | -1.4 | 12.2 |
| Nov 23/12 | 3.3 | 16.1 | 3.6 | 16.3 |
| Nov 30/12 | 0.1 | 16.2 | 0.5 | 16.8 |
| Dec 7/12 | 1.0 | 17.4 | 0.1 | 17.0 |
| Dec 14/12 | -0.2 | 17.2 | -0.3 | 16.6 |
| Dec 21/12 | 0.4 | 17.7 | 1.2 | 18.0 |
| Dec 28/12 | -1.9 | 15.5 | -1.9 | 15.7 |
| Jan 4 2013 | 3.8 | 19.9 | 4.6 | 21.0 |
| Jan 11/13 | 0.4 | 20.4 | 0.4 | 21.5 |
| Jan 18/13 | 1.2 | 21.8 | 0.9 | 22.6 |
| Jan 25/13 | 1.8 | 24.0 | 1.1 | 24.0 |
| Feb 1/13 | 0.8 | 25.0 | 0.7 | 24.8 |
| Feb 8/13 | -0.1 | 24.9 | 0.3 | 25.2 |
| Feb 15/13 | -0.1 | 24.8 | 0.1 | 25.4 |
| Feb 22/13 | 0.1 | 24.9 | -0.3 | 25.0 |
| Mar 1/13 | 0.6 | 25.7 | 0.2 | 25.3 |
| Mar 8/13 | 2.2 | 28.5 | 2.2 | 28.0 |
| Mar 15/13 | 0.8 | 29.5 | 0.6 | 28.8 |
| Mar 22/13 | 0.0 | 29.5 | -0.2 | 28.5 |
| Mar 29/13 | 0.5 | 30.1 | 0.8 | 29.5 |
| Apr 5/13 | -0.1 | 30.0 | -1.0 | 28.2 |
| Apr 12/13 | 2.1 | 32.7 | 2.3 | 31.1 |
| Apr 19/13 | -2.1 | 29.8 | -2.1 | 28.3 |
| Aug 26/13 | 1.1 | 31.3 | 1.7 | 30.5 |
| May 3/13 | 1.8 | 33.6 | 2.0 | 33.2 |
| May 10/13 | 1.0 | 34.9 | 1.2 | 34.8 |
| May 17/13 | 1.6 | 37.0 | 2.1 | 37.6 |
| May 24/13 | -0.3 | 36.6 | -1.1 | 36.1 |
| May 31/13 | -1.2 | 34.9 | -1.1 | 34.5 |
| Jun 7/13 | 0.9 | 36.1 | 0.8 | 35.6 |
| Jun 14/13 | -1.2 | 34.5 | -0.9 | 34.4 |
| Jun 21/13 | -1.8 | 32.1 | -2.2 | 31.4 |
| Jun 28/13 | 0.7 | 33.1 | 0.9 | 32.5 |
| Jul 5/13 | 1.5 | 35.1 | 1.6 | 34.6 |
| Jul 12/13 | 2.2 | 38.0 | 3.0 | 38.6 |
| Jul 19/13 | 0.5 | 38.7 | 0.7 | 39.6 |
| Jul 26/13 | 0.1 | 38.9 | 0.0 | 39.6 |
| Aug 2/13 | 0.6 | 39.7 | 1.1 | 41.1 |
| Aug 9/13 | -1.5 | 37.7 | -1.1 | 39.6 |
| Aug 16/13 | -2.2 | 34.6 | -2.1 | 36.6 |
| Aug 23/13 | -0.5 | 34.0 | 0.5 | 37.2 |
| Aug 30/13 | -1.3 | 32.2 | -1.8 | 34.7 |
| Sep 6/13 | 0.8 | 33.2 | 1.4 | 36.6 |
| Sep 13/13 | 3.0 | 37.2 | 2.0 | 39.3 |
| Sep 20/13 | 0.5 | 37.9 | 1.3 | 41.1 |
| Sep 27/13 | -1.2 | 36.2 | -1.1 | 39.6 |
| Oct 4/13 | -1.2 | 34.5 | -0.1 | 39.5 |
| Oct 11/13 | 1.1 | 36.0 | 0.8 | 40.5 |
| Oct 18/13 | 1.1 | 37.4 | 2.4 | 43.9 |
| Oct 25/13 | 1.1 | 39.0 | 0.9 | 45.2 |
| Nov 1/13 | 0.3 | 39.4 | 0.1 | 45.3 |
| Nov 8/13 | 0.9 | 40.7 | 0.5 | 46.1 |
| Nov 15/13 | 1.3 | 42.5 | 1.6 | 48.4 |
| Nov 22/13 | 0.6 | 43.4 | 0.4 | 48.9 |
| Nov 29/13 | 0.1 | 43.6 | 0.1 | 49.0 |
| Dec 6/13 | -0.4 | 43.0 | 0.0 | 48.9 |
| Dec 13/13 | -1.7 | 40.6 | -1.6 | 46.5 |
| Dec 20/13 | 3.0 | 44.8 | 2.4 | 50.0 |
| Dec 27/13 | 1.6 | 47.1 | 1.3 | 51.9 |
| Jan 3, 2014 | -0.1 | 47.0 | -0.5 | 79.1 |
| Jan 10/14 | -0.2 | 46.7 | 0.6 | 52.0 |
| Jan 17/14 | 0.1 | 46.9 | -0.2 | 51.7 |
| Jan 24/14 | -3.5 | 41.7 | -2.6 | 47.7 |
| Jan 31/14 | -1.1 | 40.1 | -0.4 | 47.1 |
| Feb 7/14 | 0.6 | 41.0 | 0.8 | 48.3 |
| Feb 14/14 | 2.3 | 44.2 | 2.3 | 51.7 |
| Feb 21/14 | -0.3 | 43.7 | -0.1 | 51.5 |
| Feb 28/14 | 1.4 | 45.7 | 1.3 | 53.4 |
| Mar 7/14 | 0.8 | 46.8 | 1.0 | 54.9 |
| Mar 14/14 | -2.4 | 43.4 | -2.0 | 51.9 |
| Mar 21/14 | 1.5 | 45.5 | 1.4 | 54.0 |
| Mar 28/14 | 0.1 | 45.7 | -0.5 | 53.3 |
| Apr 4/14 | 0.5 | 46.5 | 0.4 | 53.9 |
| Apr 11/14 | -2.4 | 43.0 | -2.6 | 49.8 |
| Apr 17/14 | 2.4 | 46.4 | 2.7 | 53.9 |
| Apr 25/14 | -0.3 | 46.0 | -0.1 | 53.7 |
| May 2/14 | 0.9 | 47.4 | 1.0 | 55.2 |
| May 9/14 | 0.4 | 48.0 | -0.1 | 55.0 |
| May 16, 14 | -0.6 | 47.2 | 0.0 | 54.9 |
| May 23, 14 | 0.7 | 48.2 | 1.2 | 56.8 |
| May 30, 14 | 0.7 | 49.2 | 1.2 | 58.7 |
| Jun 6, 14 | 1.2 | 51.0 | 1.3 | 60.8 |
| Jun 13, 14 | -0.9 | 49.7 | -0.7 | 59.7 |
| Jun 20, 14 | 1.0 | 51.2 | 1.4 | 61.9 |
| Jun 27, 14 | -0.6 | 50.4 | -0.1 | 61.8 |
| Jul 4, 14 | 1.3 | 52.3 | 1.2 | 63.8 |
| Jul 11, 14 | -0.7 | 51.2 | -0.9 | 62.3 |
| Jul 18, 14 | 0.9 | 52.6 | 0.5 | 63.2 |
| Jul 25, 14 | -0.8 | 51.4 | 0.0 | 63.2 |
| Aug 1, 14 | -2.8 | 47.2 | -2.7 | 58.8 |
| Aug 8, 14 | 0.4 | 47.7 | 0.3 | 59.4 |
| Aug 15, 14 | 0.7 | 48.7 | 1.2 | 61.3 |
| Aug 22, 14 | 2.0 | 51.7 | 1.7 | 64.1 |
| Aug 29, 14 | 0.6 | 52.6 | 0.8 | 65.3 |
| Sep 5, 14 | 0.2 | 52.9 | 0.2 | 65.6 |
| Sep 12, 14 | -0.9 | 51.6 | -1.1 | 63.8 |
| Sep 19, 14 | 1.7 | 54.2 | 1.3 | 65.9 |
| Sep 26,14 | -1.0 | 52.7 | -1.4 | 63.6 |
| Oct 3, 14 | -0.6 | 51.8 | -0.8 | 62.4 |
| Oct 10, 14 | -2.7 | 47.6 | -3.1 | 57.3 |
| Oct 17, 14 | -1.0 | 46.2 | -1.0 | 55.7 |
| Oct 24, 14 | 2.6 | 50.0 | 4.1 | 62.1 |
| Oct 31, 14 | 3.5 | 55.2 | 2.7 | 66.5 |
| Nov 7, 14 | 1.1 | 56.8 | 0.7 | 67.6 |
| Nov 14, 14 | 0.3 | 57.4 | 0.4 | 68.3 |
| Nov 21,14 | 1.0 | 58.9 | 1.2 | 70.2 |
| Nov 28, 14 | 0.1 | 59.1 | 0.2 | 70.6 |
| Dec 5, 14 | 0.7 | 60.3 | 0.4 | 71.2 |
| Dec 12, 14 | -3.8 | 54.2 | -3.5 | 65.2 |
| Dec 19, 14 | 3.0 | 58.9 | 3.4 | 70.8 |
| Dec 26, 2014 | 1.4 | 61.1 | 0.9 | 72.3 |
| Jan 2, 2015 | -1.2 | 59.2 | -1.5 | 69.8 |
| Jan 9, 15 | -0.5 | 58.3 | -0.7 | 68.7 |
| Jan 16, 15 | -1.3 | 56.3 | -1.2 | 66.6 |
| Jan 23, 15 | 0.9 | 57.7 | 1.6 | 69.3 |
| Jan 30, 15 | -2.9 | 53.2 | -2.8 | 64.6 |
| Feb 6, 15 | 3.8 | 59.1 | 3.0 | 69.6 |
| Feb 13, 15 | 1.1 | 60.8 | 2.0 | 73.0 |
| Feb 20, 15 | 0.7 | 61.9 | 0.6 | 74.1 |
| Feb 27, 15 | 0.0 | 61.8 | -0.3 | 73.6 |
| Feb 6, 2015 | -1.5 | 59.4 | -1.6 | 70.9 |
| Feb 13, 2015 | -0.6 | 58.4 | -0.9 | 69.4 |
| Feb 20, 2015 | 2.1 | 61.8 | 2.7 | 73.9 |
| Feb 27, 2015 | -2.3 | 58.1 | -2.2 | 70.0 |
| Apr 03,2015 | 0.3 | 58.5 | 0.3 | 70.5 |
| Apr 10,2015 | 1.7 | 61.2 | 1.7 | 73.4 |
| Apr 17, 2015 | -1.3 | 59.1 | -1.0 | 71.7 |
| Apr 24, 2015 | 1.4 | 61.4 | 1.8 | 74.7 |
| May 1, 2015 | -0.3 | 60.9 | -0.4 | 73.9 |
| May 8, 2015 | 0.9 | 62.3 | 0.4 | 74.6 |
| May 15, 2015 | 0.4 | 63.1 | 0.3 | 75.1 |
| May 22, 2015 | -0.2 | 62.7 | 0.2 | 75.4 |
| May 29, 2015 | -1.2 | 60.7 | -0.9 | 73.9 |
| Jun 5, 2015 | -0.9 | 59.3 | -0.7 | 72.7 |
| Jun 12, 2015 | 0.3 | 59.7 | 0.1 | 72.8 |
| Jun 19, 2015 | 0.7 | 60.8 | 0.8 | 74.1 |
| Jun 26, 2015 | -0.4 | 60.2 | -0.4 | 73.4 |
| Jul 3, 2015 | -1.2 | 58.2 | -1.2 | 71.3 |
| Jul 10, 2015 | 0.2 | 58.5 | 0.0 | 71.3 |
| Jul 17, 2015 | 1.8 | 61.4 | 2.4 | 75.5 |
| Jul 24, 2015 | -2.9 | 56.8 | -2.2 | 71.6 |
| Jul 31, 2015 | 0.7 | 57.9 | 1.2 | 73.6 |
| Aug 7, 2015 | -1.8 | 55.0 | -1.2 | 71.4 |
| Aug 14, 2015 | 0.6 | 56.0 | 0.7 | 72.6 |
| Aug 21, 2015 | -5.8 | 46.9 | -5.8 | 62.6 |
| Aug 28, 2015 | 1.1 | 48.5 | 0.9 | 64.1 |
| Sep 4, 2015 | -3.2 | 43.7 | -3.4 | 58.5 |
| Sep 11, 2015 | 2.1 | 46.7 | 2.1 | 61.8 |
| Sep 18, 2015 | -0.3 | 46.2 | -0.2 | 61.5 |
| Sep 25, 2015 | -0.4 | 45.6 | -1.4 | 59.3 |
| Oct 2, 2015 | 1.0 | 47.0 | 1.0 | 70.1 |
| Oct 9, 2015 | 3.7 | 52.5 | 3.3 | 66.2 |
| Oct 16, 2015 | 0.8 | 53.6 | 0.9 | 67.7 |
| Oct 23, 2015 | 2.5 | 57.5 | 2.1 | 71.2 |
| Oct 30, 2015 | 0.1 | 57.6 | 0.2 | 71.6 |
| Nov 6, 2015 | 0.4 | 59.8 | 1.0 | 73.2 |
| Nov 13, 2015 | -3.7 | 53.9 | -3.6 | 66.9 |
| Nov 20, 2015 | 3.4 | 59.1 | 3.3 | 72.4 |
| Nov 27, 2015 | -0.1 | 58.8 | 0.0 | 72.4 |
| Dec 4, 2015 | 0.3 | 59.3 | 0.1 | 72.6 |
| Dec 11, 2015 | -3.3 | 54.1 | -3.8 | 66.0 |
| Dec 18, 2015 | -0.8 | 52.9 | -0.3 | 65.5 |
| Dec 23, 2015 | 2.5 | 56.6 | 2.8 | 70.0 |
| Dec 31, 2015 | -0.7 | 55.5 | -0.8 | 68.6 |
| Jan 08, 2016 | -6.2 | 45.9 | -6.0 | 58.6 |
| Jan 15, 2016 | -2.2 | 42.7 | -2.2 | 55.1 |
| Jan 22, 2016 | 0.7 | 43.6 | 1.4 | 57.3 |
| Jan 29, 2016 | 2.3 | 47.0 | 1.7 | 60.1 |
| Feb 05, 2016 | -1.6 | 44.6 | -3.1 | 55.1 |
| Feb 12, 2016 | -1.4 | 42.6 | -0.8 | 53.9 |
| Feb 19, 2016 | 2.6 | 46.3 | 2.8 | 58.2 |
| Feb 26, 2016 | 1.5 | 48.5 | 1.6 | 60.7 |
| Mar 04, 2016 | 2.2 | 51.8 | 2.7 | 65.0 |
| Mar 11, 2016 | 1.2 | 53.6 | 1.1 | 66.8 |
| Mar 18, 2016 | 2.3 | 57.1 | 1.4 | 69.1 |
| Mar 25, 2016 | -0.5 | 56.3 | -0.7 | 68.0 |
| Apr 01, 2016 | 1.6 | 58.8 | 1.8 | 71.0 |
| Apr 08, 2016 | -1.2 | 56.9 | -1.2 | 68.9 |
| Apr 15, 2016 | 1.8 | 59.7 | 1.6 | 71.7 |
Source:
http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/mdc_us_stocks.html?mod=mdc_topnav_2_3014
IX Conclusion. The departing theoretical framework of Bordo and Haubrich (2012DR) is the plucking model of Friedman (1964, 1988). Friedman (1988, 1) recalls, “I was led to the model in the course of investigating the direction of influence between money and income. Did the common cyclical fluctuation in money and income reflect primarily the influence of money on income or of income on money?” Friedman (1964, 1988) finds useful for this purpose to analyze the relation between expansions and contractions. Analyzing the business cycle in the United States between 1870 and 1961, Friedman (1964, 15) found that “a large contraction in output tends to be followed on the average by a large business expansion; a mild contraction, by a mild expansion.” The depth of the contraction opens up more room in the movement toward full employment (Friedman 1964, 17):
“Output is viewed as bumping along the ceiling of maximum feasible output except that every now and then it is plucked down by a cyclical contraction. Given institutional rigidities and prices, the contraction takes in considerable measure the form of a decline in output. Since there is no physical limit to the decline short of zero output, the size of the decline in output can vary widely. When subsequent recovery sets in, it tends to return output to the ceiling; it cannot go beyond, so there is an upper limit to output and the amplitude of the expansion tends to be correlated with the amplitude of the contraction.”
Kim and Nelson (1999) test the asymmetric plucking model of Friedman (1964, 1988) relative to a symmetric model using reference cycles of the NBER and find evidence supporting the Friedman model. Bordo and Haubrich (2012DR) analyze 27 cycles beginning in 1872, using various measures of financial crises while considering different regulatory and monetary regimes. The revealing conclusion of Bordo and Haubrich (2012DR, 2) is that:
“Our analysis of the data shows that steep expansions tend to follow deep contractions, though this depends heavily on when the recovery is measured. In contrast to much conventional wisdom, the stylized fact that deep contractions breed strong recoveries is particularly true when there is a financial crisis. In fact, on average, it is cycles without a financial crisis that show the weakest relation between contraction depth and recovery strength. For many configurations, the evidence for a robust bounce-back is stronger for cycles with financial crises than those without.”
The average rate of growth of real GDP in expansions after recessions with financial crises was 8 percent but only 6.9 percent on average for recessions without financial crises (Bordo 2012Sep27). Real GDP declined 12 percent in the Panic of 1907 and increased 13 percent in the recovery, consistent with the plucking model of Friedman (Bordo 2012Sep27). Bordo (2012Sep27) finds two probable explanations for the weak recovery during the current economic cycle: (1) collapse of United States housing; and (2) uncertainty originating in fiscal policy, regulation and structural changes. There are serious doubts if monetary policy is adequate to recover the economy under these conditions.
Lucas (2011May) estimates US economic growth in the long-term at 3 percent per year and about 2 percent per year in per capita terms. There are displacements from this trend caused by events such as wars and recessions but the economy grows much faster during the expansion, compensating for the contraction and maintaining trend growth over the entire cycle. Historical US GDP data exhibit remarkable growth: Lucas (2011May) estimates an increase of US real income per person by a factor of 12 in the period from 1870 to 2010. The explanation by Lucas (2011May) of this remarkable growth experience is that government provided stability and education while elements of “free-market capitalism” were an important driver of long-term growth and prosperity. Lucas sharpens this analysis by comparison with the long-term growth experience of G7 countries (US, UK, France, Germany, Canada, Italy and Japan) and Spain from 1870 to 2010. Countries benefitted from “common civilization” and “technology” to “catch up” with the early growth leaders of the US and UK, eventually growing at a faster rate. Significant part of this catch up occurred after World War II. Lucas (2011May) finds that the catch up stalled in the 1970s. The analysis of Lucas (2011May) is that the 20-40 percent gap that developed originated in differences in relative taxation and regulation that discouraged savings and work incentives in comparison with the US. A larger welfare and regulatory state, according to Lucas (2011May), could be the cause of the 20-40 percent gap. Cobet and Wilson (2002) provide estimates of output per hour and unit labor costs in national currency and US dollars for the US, Japan and Germany from 1950 to 2000 (see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 137-44). The average yearly rate of productivity change from 1950 to 2000 was 2.9 percent in the US, 6.3 percent for Japan and 4.7 percent for Germany while unit labor costs in USD increased at 2.6 percent in the US, 4.7 percent in Japan and 4.3 percent in Germany. From 1995 to 2000, output per hour increased at the average yearly rate of 4.6 percent in the US, 3.9 percent in Japan and 2.6 percent in Germany while unit labor costs in USD fell at minus 0.7 percent in the US, 4.3 percent in Japan and 7.5 percent in Germany. There was increase in productivity growth in Japan and France within the G7 in the second half of the 1990s but significantly lower than the acceleration of 1.3 percentage points per year in the US. The key indicator of growth of real income per capita, which is what a person earns after inflation, measures long-term economic growth and prosperity. A refined concept would include real disposable income per capita, which is what a person earns after inflation and taxes.
Table IB-1 provides the data required for broader comparison of long-term and cyclical performance of the United States economy. Revisions and enhancements of United States GDP and personal income accounts by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) provide important information on long-term growth and cyclical behavior. First, Long-term performance. Using annual data, US GDP grew at the average rate of 3.2 percent per year from 1929 to 2015 and at 3.2 percent per year from 1947 to 2015. Real disposable income grew at the average yearly rate of 3.2 percent from 1929 to 2015 and at 3.7 percent from 1947 to 1999. Real disposable income per capita grew at the average yearly rate of 2.0 percent from 1929 to 2015 and at 2.3 percent from 1947 to 1999. US economic growth was much faster during expansions, compensating contractions in maintaining trend growth for whole cycles. Using annual data, US real disposable income grew at the average yearly rate of 3.5 percent from 1980 to 1989 and real disposable income per capita at 2.6 percent. The US economy has lost its dynamism in the current cycle: real disposable income grew at the yearly average rate of 1.6 percent from 2006 to 2015 and real disposable income per capita at 0.8 percent. Real disposable income grew at the average rate of 1.6 percent from 2007 to 2015 and real disposable income per capita at 0.7 percent. Table IB-1 illustrates the contradiction of long-term growth with the proposition of secular stagnation (Hansen 1938, 1938, 1941 with early critique by Simons (1942). Secular stagnation would occur over long periods. Table IB-1 also provides the corresponding rates of population growth that is only marginally lower at 0.8 to 0.9 percent recently from 1.1 percent over the long-term. GDP growth fell abruptly from 2.6 percent on average from 2000 to 2006 to 1.3 percent from 2006 to 2015 and 1.2 percent from 2007 to 2015 and real disposable income growth fell from 2.9 percent on average from 2000 to 2006 to 1.6 percent from 2006 to 2015. The decline of growth of real per capita disposable income is even sharper from average 2.0 percent from 2000 to 2006 to 0.8 percent from 2006 to 2015 and 0.7 percent from 2007 to 2015 while population growth was 0.8 percent on average. Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul122) provide theory and measurements showing that cyclic factors explain currently depressed labor markets. This is also the case of the overall economy. Second, first four quarters of expansion. Growth in the first four quarters of expansion is critical in recovering loss of output and employment occurring during the contraction. In the first four quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1983: GDP increased 7.8 percent, real disposable personal income 5.3 percent and real disposable income per capita 4.4 percent. In the first four quarters of expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010: GDP increased 2.7 percent, real disposable personal income 0.2 percent and real disposable income per capita decreased 0.7 percent. Third, first 26 quarters of expansion. In the expansion from IQ1983 to IIQ1989: GDP grew 35.0 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 4.7 percent; real disposable income grew 28.7 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 4.0 percent; and real disposable income per capita grew 21.5 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 3.0 percent. In the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IVQ2015: GDP grew 14.6 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 2.1 percent; real disposable income grew 12.1 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 1.8 percent; and real disposable personal income per capita grew 6.6 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 1.0 percent. Fourth, entire quarterly cycle. In the entire cycle combining contraction and expansion from IQ1980 to IIQ1989: GDP grew 34.8 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 3.1 percent; real disposable personal income grew 36.2 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 3.2 percent; and real disposable personal income per capita 24.7 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 2.3 percent. In the entire cycle combining contraction and expansion from IVQ2007 to IVQ2015: GDP grew 9.8 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 1.2 percent; real disposable personal income increased 14.0 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 1.7 percent; and real disposable personal income per capita grew 7.0 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 0.8 percent. The United States grew during its history at high rates of per capita income that made its economy the largest in the world. That dynamism is disappearing. Bordo (2012 Sep27) and Bordo and Haubrich (2012DR) provide strong evidence that recoveries have been faster after deeper recessions and recessions with financial crises, casting serious doubts on the conventional explanation of weak growth during the current expansion allegedly because of the depth of the contraction of 4.2 percent from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 and the financial crisis. The proposition of secular stagnation should explain a long-term process of decay and not the actual abrupt collapse of the economy and labor markets currently.
Table IB-1, US, GDP, Real Disposable Personal Income, Real Disposable Income per Capita and Population Long-term and in 1983-88 and 2007-2014, %
| Long-term Average ∆% per Year | GDP | Population | |
| 1929-2015 | 3.2 | 1.1 | |
| 1947-2015 | 3.2 | 1.2 | |
| 1947-1999 | 3.6 | 1.3 | |
| 1980-1989 | 3.5 | 0.9 | |
| 2000-2015 | 1.8 | 0.9 | |
| 2000-2006 | 2.6 | 0.9 | |
| 2006-2015 | 1.3 | 0.8 | |
| 2007-2015 | 1.2 | 0.8 | |
| Long-term Average ∆% per Year | Real Disposable Income | Real Disposable Income per Capita | Population |
| 1929-2015 | 3.2 | 2.0 | 1.1 |
| 1947-1999 | 3.7 | 2.3 | 1.3 |
| 2000-2015 | 2.2 | 1.3 | 0.9 |
| 2000-2006 | 2.9 | 2.0 | 0.9 |
| 2006-2015 | 1.6 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| 2007-2015 | 1.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 |
| Whole Cycles Average ∆% per Year | |||
| 1980-1989 | 3.5 | 2.6 | 0.9 |
| 2006-2015 | 1.6 | 0.8 | 0.8 |
| 2007-2015 | 1.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 |
| Comparison of Cycles | # Quarters | ∆% | ∆% Annual Equivalent |
| GDP | |||
| I83 to IV83 I83 to IQ87 I83 to II87 I83 to III87 I83 to IV87 I83 to I88 I83 to II88 I83 to III88 I83 to IV88 I83 to I89 I83 to II89 | 4 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | 7.8 23.1 24.5 25.6 27.7 28.4 30.1 30.9 32.6 34.0 35.0 | 7.8 5.0 5.0 4.9 5.0 4.9 4.9 4.8 4.8 4.8 4.7 |
| RDPI | |||
| I83 to IV83 I83 to I87 I83 to III87 I83 to IV87 I83 to I88 I83 to II88 I83 to III88 I83 to IV88 I83 to I89 IQ83 to II89 | 4 17 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | 5.3 19.5 20.5 22.1 23.8 25.1 26.3 27.5 29.1 28.7 | 5.3 4.3 4.0 4.1 4.2 4.2 4.1 4.1 4.2 4.0 |
| RDPI Per Capita | |||
| I83 to IV83 I83 to I87 I83 to III87 I83 to IV87 I83 to I88 I83 to II88 I83 to III88 I83 to IV88 I83 to I89 I83 to II89 | 4 17 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 | 4.4 15.1 15.5 16.7 18.2 19.2 20.0 20.9 22.1 21.5 | 4.4 3.4 3.1 3.1 3.2 3.2 3.2 3.2 3.2 3.0 |
| Whole Cycle IQ1980 to IIQ1989 | |||
| GDP | 39 | 34.8 | 3.1 |
| RDPI | 39 | 36.2 | 3.2 |
| RDPI per Capita | 39 | 24.7 | 2.3 |
| Population | 39 | 9.2 | 0.9 |
| GDP | |||
| III09 to II10 III09 to IV15 | 4 26 | 2.7 14.6 | 2.7 2.1 |
| RDPI | |||
| III09 to II10 III09 to IV15 | 4 26 | 0.2 12.1 | 0.2 1.8 |
| RDPI per Capita | |||
| III09 to II10 III09 to IV15 | 4 26 | -0.7 6.6 | -0.7 1.0 |
| Population | |||
| III09 to II10 III09 to IV15 | 4 26 | 0.8 5.2 | 0.8 0.8 |
| IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 | 32 | ||
| GDP | 32 | 9.8 | 1.2 |
| RDPI | 32 | 14.0 | 1.7 |
| RDPI per Capita | 32 | 7.0 | 0.8 |
| Population | 32 | 6.6 | 0.8 |
RDPI: Real Disposable Personal Income
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
There are seven basic facts illustrating the current economic disaster of the United States:
- GDP maintained trend growth in the entire business cycle from IQ1980 to IIQI989, including contractions and expansions. GDP is well below trend in the entire business cycle from IVQ2007 to IVQ2015, including contractions and expansions
- Per capita real disposable income exceeded trend growth in the 1980s but is substantially below trend in IVQ2015
- Level of employed persons increased in the 1980s but declined/stagnated into IVQ2015
- Level of full-time employed persons increased in the 1980s but declined/stagnated into IVQ2015
- Level unemployed, unemployment rate and employed part-time for economic reasons fell in the recovery from the recessions in the 1980s but not substantially in the recovery since IVQ2009
- Wealth of households and nonprofit organizations soared in the 1980s but stagnated in real terms into IVQ2015
- Gross private domestic investment increased sharply from IQ1980 to IIQ1989 but gross private domestic investment stagnated and private fixed investment stagnated from IVQ2007 into IVQ2015
There is a critical issue of the United States economy will be able in the future to attain again the level of activity and prosperity of projected trend growth. Growth at trend during the entire business cycles built the largest economy in the world but there may be an adverse, permanent weakness in United States economic performance and prosperity. Table IB-2 provides data for analysis of these seven basic facts. The seven blocks of Table IB-2 are separated initially after individual discussion of each one followed by the full Table IB-2.
1. Trend Growth.
i. As shown in Table IB-2, actual GDP grew cumulatively 34.3 percent from IQ1980 to IIQ1989, which is relatively close to what trend growth would have been at 33.4 percent. Real GDP grew 34.8 percent from IVQ1979 to IIQ1989. Rapid growth at the average annual rate of 4.8 percent per quarter during the expansion from IQ1983 to IIQ1989 erased the loss of GDP of 4.7 percent during the contractions and maintained trend growth at 3.1 percent for GDP and 3.2 percent for real disposable personal income over the entire cycle.
ii. In contrast, cumulative growth from IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 was 9.8 percent while trend growth would have been 26.7 percent. GDP in IVQ2015 would be $18,994.6 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2539.5 billion than actual $16,455.1 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 25.1 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 15.0 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets-in.html). US GDP in IVQ2015 is 13.4 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,445.1 billion in IVQ2015 or 9.8 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.2 percent. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth of manufacturing at average 3.2 percent per year from Jan 1919 to Jan 2016. Growth at 3.2 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 107.6075 in Dec 2007 to 138.8098 in Jan 2016. The actual index NSA in Jan 2016 is 103.8436, which is 25.2 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.2 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2015. Using trend growth of 2.2 percent per year, the index would increase to 128.3031 in Jan 2016. The output of manufacturing at 103.8436 in Jan 2016 is 19.1 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
The civilian labor force consists of people who are available and willing to work and who have searched for employment recently. The labor force of the US grew 9.4 percent from 142.828 million in Jan 2001 to 156.255 million in Jul 2009. The civilian labor force is 1.3 percent higher at 158.279 million in Feb 2016 than in Jul 2009, all numbers not seasonally adjusted. Chart I-3 shows the flattening of the curve of expansion of the labor force and its decline in 2010 and 2011. The ratio of the labor force of 154.871 million in Jul 2007 to the noninstitutional population of 231.958 million in Jul 2007 was 66.8 percent while the ratio of the labor force of 158.279 million in Feb 2016 to the noninstitutional population of 252.577 million in Feb 2016 was 62.7 percent. The labor force of the US in Feb 2016 corresponding to 66.8 percent of participation in the population would be 168.721 million (0.668 x 252.577). The difference between the measured labor force in Feb 2016 of 158.279 million and the labor force in Feb 2016 with participation rate of 66.8 percent (as in Jul 2007) of 168.721 million is 10.442 million. The level of the labor force in the US has stagnated and is 10.442 million lower than what it would have been had the same participation rate been maintained. Millions of people have abandoned their search for employment because they believe there are no jobs available for them. The key issue is whether the decline in participation of the population in the labor force is the result of people giving up on finding another job.
| Period IQ1980 to IIQ1989 | |
| GDP SAAR USD Billions | |
| IQ1980 | 6,524.9 |
| IIQ1989 | 8,766.1 |
| ∆% IQ1980 to IIQ1989 (34.8 percent from IVQ1979 $6503.9 billion) | 34.3 |
| ∆% Trend Growth IQ1980 to IIQ1989 | 33.4 |
| Period IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 | |
| GDP SAAR USD Billions | |
| IVQ2007 | 14,991.8 |
| IVQ2015 | 16,455,1 |
| ∆% IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 | 9.8 |
| ∆% IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 Trend Growth | 26.7 |
2. Real Disposable Income
i. In the entire business cycle from IQ1980 to IIQ1989, as shown in Table IB-2, per capita real disposable income, or what is left per person after inflation and taxes, grew cumulatively 24.6 percent, which is close to what would have been trend growth of 21.3 percent.
ii. In contrast, in the entire business cycle from IVQ2007 to IVQ2015, per capita real disposable income increased 7.3 percent while trend growth would have been 17.2 percent. Income available after inflation and taxes is about the same as before the contraction after 26 consecutive quarters of GDP growth at mediocre rates relative to those prevailing during historical cyclical expansions. Growth of personal income during the expansion has been tepid even with the new revisions. In IVQ2012, nominal disposable personal income grew at the SAAR of 13.3 percent and real disposable personal income at 10.9 percent (Table 2.1 http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm). The BEA explains as follows: “Personal income in November and December was boosted by accelerated and special dividend payments to persons and by accelerated bonus payments and other irregular pay in private wages and salaries in anticipation of changes in individual income tax rates. Personal income in December was also boosted by lump-sum social security benefit payments” (page 2 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi1212.pdf pages 1-2 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi0113.pdf). The Bureau of Economic Analysis explains as (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi0213.pdf 2-3): “The January estimate of employee contributions for government social insurance reflected the expiration of the “payroll tax holiday,” that increased the social security contribution rate for employees and self-employed workers by 2.0 percentage points, or $114.1 billion at an annual rate. For additional information, see FAQ on “How did the expiration of the payroll tax holiday affect personal income for January 2013?” at www.bea.gov. The January estimate of employee contributions for government social insurance also reflected an increase in the monthly premiums paid by participants in the supplementary medical insurance program, in the hospital insurance provisions of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, and in the social security taxable wage base.”
The increase was provided in the “fiscal cliff” law H.R. 8 American Taxpayer Relief Act of 2012 (http://www.gpo.gov/fdsys/pkg/BILLS-112hr8eas/pdf/BILLS-112hr8eas.pdf).
In IQ2013, personal income fell at the SAAR of minus 11.4 percent; real personal income excluding current transfer receipts at minus 11.9 percent; and real disposable personal income at minus 15.9 percent (Table 14 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2015/pdf/pi0615.pdf).The BEA explains as follows (page 3 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2013/pdf/pi0313.pdf):
“The February and January changes in disposable personal income (DPI) mainly reflected the effect of special factors in January, such as the expiration of the “payroll tax holiday” and the acceleration of bonuses and personal dividends to November and to December in anticipation of changes in individual tax rates.”
In IIIQ2014, personal income grew at 4.5 percent, real personal income excluding current transfers at 2.8 percent, nominal disposable income at 3.9 percent and real disposable personal income at 2.7 percent (Table 6 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2016/pdf/pi0116.pdf). In IVQ2014, personal income grew at 5.0 percent in nominal terms and at 6.0 percent in real terms excluding current transfers while nominal disposable income grew at 4.2 percent in nominal terms and at 4.7 percent in real terms (Table 6 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2016/pdf/pi0116.pdf). In IQ2015, nominal personal income grew at 3.4 percent and at 4.3 percent in real terms excluding current transfer receipts while nominal disposable income grew at 1.9 percent and at 3.9 percent in real terms (Table 6 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2016/pdf/pi0116.pdf). In IIQ2015, nominal personal income grew at 5.3 percent and at 3.3 percent in real terms excluding current transfer receipts while nominal disposable income grew at 4.9 percent and real disposable income grew at 2.6 percent (Table 6 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2016/pdf/pi0116.pdf). In IIIQ2015, nominal personal income grew at 4.4 percent and 3.3 percent excluding transfer receipts while nominal disposable income grew at 4.5 percent and real disposable income grew at 3.2 percent (Table 6 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2016/pdf/pi0116.pdf). In IVQ2015, nominal personal income grew at 3.2 percent and 2.8 percent excluding transfer receipts while nominal disposable income grew at 2.9 percent and real disposable income at 2.5 percent (Table 6 at http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/pi/2016/pdf/pi0116.pdf).
| Period IQ1980 to IIQ1989 | |
| Real Disposable Personal Income per Capita IQ1980 Chained 2009 USD | 20,241 |
| Real Disposable Personal Income per Capita IIQ1989 Chained 2009 USD | 25,222 |
| ∆% IQ1980 to IIQ1989 (25.3 percent from IVQ1979 $20,230 billion) | 24.6 |
| ∆% Trend Growth | 21.3 |
| Period IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 | |
| Real Disposable Personal Income per Capita IVQ2007 Chained 2009 USD | 35,819 |
| Real Disposable Personal Income per Capita IVQ2015 Chained 2009 USD | 38,320 |
| ∆% IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 | 7.0 |
| ∆% Trend Growth | 17.2 |
3. Number of Employed Persons
i. As shown in Table IB-2, the number of employed persons increased over the entire business cycle from 98.527 million not seasonally adjusted (NSA) in IQ1980 to 118.719 million NSA in IIQ1989 or by 120.5 percent.
ii. In contrast, during the entire business cycle the number employed stagnated from 146.334 million in IVQ2007 to 149.703 million in IVQ2015 or by 2.3 percent higher. There are 25.1 million persons unemployed or underemployed, which is 15.0 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets-in.html).The number employed in Feb 2016 was 150.060 million (NSA) or 2.745 million more people with jobs relative to the peak of 147.315 million in Jul 2007 while the civilian noninstitutional population of ages 16 years and over increased from 231.958 million in Jul 2007 to 252.577 million in Feb 2016 or by 20.619 million. The number employed increased 1.9 percent from Jul 2007 to Feb 2016 while the noninstitutional civilian population of ages of 16 years and over, or those available for work, increased 8.9 percent. The ratio of employment to population in Jul 2007 was 63.5 percent (147.315 million employment as percent of population of 231.958 million). The same ratio in Feb 2016 would result in 160.386 million jobs (0.635 multiplied by noninstitutional civilian population of 252.577 million). There are effectively 10.326 million fewer jobs in Feb 2016 than in Jul 2007, or 160.386 million minus 150.060 million. There is actually not sufficient job creation in merely absorbing new entrants in the labor force because of those dropping from job searches, worsening the stock of unemployed or underemployed in involuntary part-time jobs.
| Period IQ1980 to IIQ1989 | |
| Employed Millions IQ1980 NSA End of Quarter | 98.527 |
| Employed Millions IIQ1989 NSA End of Quarter | 118.719 |
| ∆% Employed IIQ1980 to IIQ1989 | 20.5 |
| Period IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 | |
| Employed Millions IVQ2007 NSA End of Quarter | 146.334 |
| Employed Millions IVQ2015 NSA End of Quarter | 149.703 |
| ∆% Employed IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 | 2.3 |
4. Number of Full-Time Employed Persons
i. As shown in Table IB-2, during the entire business cycle in the 1980s, including contractions and expansion, the number of employed full-time rose from 81.280 million NSA in IQ1980 to 99.539 million NSA in IIQ1989 or 22.5 percent.
ii. In contrast, during the entire current business cycle, including contraction and expansion, the number of persons employed full-time increased from 121.042 million in IVQ2007 to 122.013 million in IVQ2015 or 0.8 percent. The number with full-time jobs fell from a high of 123.219 million in Jul 2007 to 108.777 million in Jan 2010 or by 14.442 million. The number with full-time jobs in Jan 2016 is 121.411 million, which is lower by 1.808 million relative to the peak of 123.219 million in Jul 2007.
The magnitude of the stress in US labor markets is magnified by the increase in the civilian noninstitutional population of the United States from 231.958 million in Jul 2007 to 252.397 million in Jan 2016 or by 20.439 million (http://www.bls.gov/data/) while in the same period the number of full-time jobs decreased 1.808 million. The ratio of full-time jobs of 123.219 million in Jul 2007 to civilian noninstitutional population of 231.958 million was 53.1 percent. If that ratio had remained the same, there would be 134,023 million full-time jobs with population of 252.397 million in Jan 2016 (0.531 x 252.397) or 12.612 million fewer full-time jobs relative to actual 121.411 million. There appear to be around 10 million fewer full-time jobs in the US than before the global recession while population increased around 20 million. Mediocre GDP growth is the main culprit of the fractured US labor market.
| Period IQ1980 to IIQ1989 | |
| Employed Full-time Millions IQ1980 NSA End of Quarter | 81.280 |
| Employed Full-time Millions IIQ1989 NSA End of Quarter | 99.539 |
| ∆% Full-time Employed IQ1980 to IIQ1989 | 22.5 |
| Period IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 | |
| Employed Full-time Millions IVQ2007 NSA End of Quarter | 121.042 |
| Employed Full-time Millions IVQ2015 NSA End of Quarter | 122.013 |
| ∆% Full-time Employed IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 | 0.8 |
5. Unemployed, Unemployment Rate and Employed Part-time for Economic Reasons.
i. As shown in Table IB-2 and in the following block, in the cycle from IQ1980 to IIQ1989: (a) The rate of unemployment was lower at 5.5 percent in IIQ1989 relative to 6.6 percent in IQ1980. (b) The number unemployed decreased from 6.983 million in IQ1980 to 6.850 million in IIQ1989 or 1.9 percent. (c) The number employed part-time for economic reasons increased 49.4 percent from 3.624 million in IQ1980 to 5.413 million in IIQ1989.
ii. In contrast, in the economic cycle from IVQ2007 to IVQ2015: (a) The rate of unemployment did not change from 4.8 percent in IVQ2007 to 4.8 percent in IVQ2015. (b) The number unemployed increased 2.3 percent from 7.371 million in IVQ2007 to 7.542 million in IVQ2015. (c) The number employed part-time for economic reasons because they could not find any other job increased 30.1 percent from 4.750 million in IVQ2007 to 6.179 million in IVQ2015. (d) U6 Total Unemployed plus all marginally attached workers plus total employed part time for economic reasons as percent of all civilian labor force plus all marginally attached workers NSA increased from 8.7 percent in IVQ2007 to 9.8 percent in IVQ2015.
| Period IQ1980 to IIQ1989 | |
| Unemployment Rate IQ1980 NSA End of Quarter | 6.6 |
| Unemployment Rate IIQ1989 NSA End of Quarter | 5.5 |
| Unemployed IQ1980 Millions NSA End of Quarter | 6.983 |
| Unemployed IIQ1989 Millions NSA End of Quarter | 6.850 |
| ∆% | -1.9 |
| Employed Part-time Economic Reasons IQ1980 Millions NSA End of Quarter | 3.624 |
| Employed Part-time Economic Reasons Millions IIQ1989 NSA End of Quarter | 5.413 |
| ∆% | 49.4 |
| Period IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 | |
| Unemployment Rate IVQ2007 NSA End of Quarter | 4.8 |
| Unemployment Rate IVQ2015 NSA End of Quarter | 4.8 |
| Unemployed IVQ2007 Millions NSA End of Quarter | 7.371 |
| Unemployed IVQ2015 Millions NSA End of Quarter | 7.542 |
| ∆% | 2.3 |
| Employed Part-time Economic Reasons IVQ2007 Millions NSA End of Quarter | 4.750 |
| Employed Part-time Economic Reasons Millions IVQ2015 NSA End of Quarter | 6,179 |
| ∆% | 30.1 |
| U6 Total Unemployed plus all marginally attached workers plus total employed part time for economic reasons as percent of all civilian labor force plus all marginally attached workers NSA | |
| IVQ2007 | 8.7 |
| IVQ2015 | 9.8 |
6. Wealth of Households and Nonprofit Organizations.
The comparison of net worth of households and nonprofit organizations in the entire economic cycle from IQ1980 (and from IVQ1979) to IIQ1989 and from IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 is in Table IIA-5. The data reveal the following facts for the cycles in the 1980s:
- IVQ1979 to IIQ1989. Net worth increased 126.9 percent from IVQ1979 to IIQ1989, the all items CPI index increased 61.8 percent from 76.7 in Dec 1979 to 124.1 in Jun 1989 and real net worth increased 40.2 percent.
- IQ1980 to IVQ1985. Net worth increased 65.4 percent, the all items CPI index increased 36.5 percent from 80.1 in Mar 1980 to 109.3 in Dec 1985 and real net worth increased 21.2 percent.
- IVQ1979 to IVQ1985. Net worth increased 68.9 percent, the all items CPI index increased 42.5 percent from 76.7 in Dec 1979 to 109.3 in Dec 1985 and real net worth increased 18.5 percent.
- IQ1980 to IQ1989. Net worth increased 118.0 percent, the all items CPI index increased 52.7 percent from 80.1 in Mar 1980 to 122.3 in Mar 1989 and real net worth increased 42.8 percent.
- IQ1980 to IIQ1989. Net worth increased 122.2 percent, the all items CPI index increased 54.9 percent from 80.1 in Mar 1980 to 124.1 in Jun 1989 and real net worth increased 43.4 percent.
There is disastrous performance in the current economic cycle:
- IVQ2007 to IVQ2015. Net worth increased 30.4 percent, the all items CPI increased 12.6 percent from 210.036 in Dec 2007 to 236.525 in Dec 2015 and real or inflation adjusted net worth increased 15.8 percent. Real estate assets adjusted for inflation fell 4.0 percent.
The explanation is partly in the sharp decline of wealth of households and nonprofit organizations and partly in the mediocre growth rates of the cyclical expansion beginning in IIIQ2009. Long-term economic performance in the United States consisted of trend growth of GDP at 3 percent per year and of per capita GDP at 2 percent per year as measured for 1870 to 2010 by Robert E Lucas (2011May). The economy returned to trend growth after adverse events such as wars and recessions. The key characteristic of adversities such as recessions was much higher rates of growth in expansion periods that permitted the economy to recover output, income and employment losses that occurred during the contractions. Over the business cycle, the economy compensated the losses of contractions with higher growth in expansions to maintain trend growth of GDP of 3 percent and of GDP per capita of 2 percent. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. US economic growth has been at only 2.1 percent on average in the cyclical expansion in the 26 quarters from IIIQ2009 to IVQ2015. Boskin (2010Sep) measures that the US economy grew at 6.2 percent in the first four quarters and 4.5 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the second quarter of 1975; and at 7.7 percent in the first four quarters and 5.8 percent in the first 12 quarters after the trough in the first quarter of 1983 (Professor Michael J. Boskin, Summer of Discontent, Wall Street Journal, Sep 2, 2010 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html). There are new calculations using the revision of US GDP and personal income data since 1929 by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and the second estimate of GDP for IVQ2015 (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2016/pdf/gdp4q15_2nd.pdf). The average of 7.7 percent in the first four quarters of major cyclical expansions is in contrast with the rate of growth in the first four quarters of the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2010 of only 2.7 percent obtained by diving GDP of $14,745.9 billion in IIQ2010 by GDP of $14,355.6 billion in IIQ2009 {[$14,745.9/$14,355.6 -1]100 = 2.7%], or accumulating the quarter on quarter growth rates (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/closely-monitoring-global-economic-and.html). The expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 was at the average annual growth rate of 5.9 percent, 5.4 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1986, 5.2 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1986, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1987, 5.0 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1987, 4.9 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IIIQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1988, 4.8 percent from IQ1983 to IQ1989 4.7 percent from IQ1983 to IIQ1989 and at 7.8 percent from IQ1983 to IVQ1983 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/closely-monitoring-global-economic-and.html). The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 would have accumulated to 26.7 percent. GDP in IVQ2015 would be $18,994.6 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2539.5 billion than actual $16,455.1 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 25.1 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment/underemployment of 15.0 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets-in.html). US GDP in IVQ2015 is 13.4 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $16,445.1 billion in IVQ2015 or 9.8 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.2 percent. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. There is classic research on analyzing deviations of output from trend (see for example Schumpeter 1939, Hicks 1950, Lucas 1975, Sargent and Sims 1977). The long-term trend is growth of manufacturing at average 3.2 percent per year from Jan 1919 to Jan 2016. Growth at 3.2 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 107.6075 in Dec 2007 to 138.8098 in Jan 2016. The actual index NSA in Jan 2016 is 103.8436, which is 25.2 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.2 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2015. Using trend growth of 2.2 percent per year, the index would increase to 128.3031 in Jan 2016. The output of manufacturing at 103.8436 in Jan 2016 is 19.1 percent below trend under this alternative calculation.
| Period IQ1980 to IIQ1988 | |
| Net Worth of Households and Nonprofit Organizations USD Millions | |
| IVQ1979 IQ1980 | 9,047.8 9,238.6 |
| IVQ1985 IIIQ1986 IVQ1986 IQ1987 IIQ1987 IIIQ1987 IVQ1987 IQ1988 IIQ1988 IIIQ1988 IVQ1988 IQ1989 IIQ1989 | 15,277.3 16,290.8 16,840.3 17,494.7 17,784.1 18,195.3 18,022.0 18,495.3 18,900.3 19,209.4 19,691.2 20,138.2 20,530.4 |
| ∆ USD Billions IVQ1985 IVQ1979 to IIQ1989 IQ1980-IVQ1985 IQ1980-IIIQ1986 IQ1980-IVQ1986 IQ1980-IQ1987 IQ1980-IIQ1987 IQ1980-IIIQ1987 IQ1980-IVQ1987 IQ1980-IQ1988 IQ1980-IIQ1988 IQ1980-IIIQ1988 IQ1980-IVQ1988 IQ1980-IQ1989 IQ1980-IIQ1989 | +6,229.5 ∆%68.9 R∆%18.5 +11482.6 ∆%126.9 R∆%40.2 +6,038.7 ∆%65.4 R∆%21.2 +7,052.2 ∆%76.3 R∆%28.2 +7,601.8 ∆%82.3 R∆%32.1 +8,256.1 ∆%89.4 R∆%35.3 +8,545.5 ∆%92.5 R∆%35.9 +8,956.8 ∆%96.9 R∆%37.2 +8783.4 ∆%95.1 R∆%35.4 +9256.7 ∆%100.2 R∆%37.6 +9661.7 ∆%104.6 R∆%38.9 +9970.7 ∆%107.9 R∆%39.0 +10452.6 ∆%113.1 R∆%41.7 +10899.6 ∆%118.0 R∆%42.8 +11,291.8 ∆%122.2 R∆% 43.4 |
| Period IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 | |
| Net Worth of Households and Nonprofit Organizations USD Millions | |
| IVQ2007 | 66,536.0 |
| IVQ2015 | 86,796.0 |
| ∆ USD Billions | +20,260 ∆%30.4 R∆%15.8 |
Net Worth = Assets – Liabilities. R∆% real percentage change or adjusted for CPI percentage change.
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. 2016. Flow of funds, balance sheets and integrated macroeconomic accounts: fourth quarter 2015. Washington, DC, Federal Reserve System, Mar 10. http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/z1/.
7. Gross Private Domestic Investment.
i. The comparison of gross private domestic investment in the entire economic cycles from IQ1980 to IIQ1989 and from IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 is in the following block and in Table IB-2. Gross private domestic investment increased from $951.6 billion in IQ1980 to $1,278.3 billion in IIQ1989 or by 34.3 percent.
ii In the current cycle, gross private domestic investment increased from $2,605.2 billion in IVQ2007 to $2,854.7 billion in IVQ2015, or 9.6 percent. Private fixed investment edged from $2,586.3 billion in IVQ2007 to $2,761.5 billion in IVQ2015, or increase by 6.8 percent.
| Period IQ1980-IQ1989 | |
| Gross Private Domestic Investment USD 2009 Billions | |
| IQ1980 | 951.6 |
| IIQ1989 | 1278.3 |
| ∆% | 34.3 |
| Period IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 | |
| Gross Private Domestic Investment USD Billions | |
| IVQ2007 | 2,605.2 |
| IVQ2015 | 2,854.7 |
| ∆% | 9.6 |
| Private Fixed Investment USD 2009 Billions | |
| IVQ2007 | 2,586.3 |
| IVQ2015 | 2,761.5 |
| ∆% | 6.8 |
Table IB-2, US, GDP and Real Disposable Personal Income per Capita Actual and Trend Growth and Employment, 1980-1989 and 2007-2015, SAAR USD Billions, Millions of Persons and ∆%
| Period IQ1980 to IIQ1989 | |
| GDP SAAR USD Billions | |
| IQ1980 | 6,524.9 |
| IIQ1989 | 8,766.1 |
| ∆% IQ1980 to IIQ1989 (34.8 percent from IVQ1979 $6503.9 billion) | 34.3 |
| ∆% Trend Growth IQ1980 to IIQ1989 | 33.4 |
| Real Disposable Personal Income per Capita IQ1980 Chained 2009 USD | 20,241 |
| Real Disposable Personal Income per Capita IIQ1989 Chained 2009 USD | 25,222 |
| ∆% IQ1980 to IIQ1989 (25.3 percent from IVQ1979 $20,230 billion) | 24.6 |
| ∆% Trend Growth | 21.3 |
| Employed Millions IQ1980 NSA End of Quarter | 98.527 |
| Employed Millions IIQ1989 NSA End of Quarter | 118.719 |
| ∆% Employed IQ1980 to IIQ1989 | 20.5 |
| Employed Full-time Millions IQ1980 NSA End of Quarter | 81.280 |
| Employed Full-time Millions IIQ1989 NSA End of Quarter | 99.539 |
| ∆% Full-time Employed IIQ1980 to IIQ1989 | 22.5 |
| Unemployment Rate IQ1980 NSA End of Quarter | 6.6 |
| Unemployment Rate IIQ1989 NSA End of Quarter | 5.5 |
| Unemployed IQ1980 Millions NSA End of Quarter | 6.983 |
| Unemployed IIQ1989 Millions NSA End of Quarter | 6.850 |
| ∆% | -1.9 |
| Employed Part-time Economic Reasons IQ1980 Millions NSA End of Quarter | 3.624 |
| Employed Part-time Economic Reasons Millions IIQ1989 NSA End of Quarter | 5.413 |
| ∆% | 49.4 |
| Net Worth of Households and Nonprofit Organizations USD Billions | |
| IVQ1979 | 9,047.8 |
| IIQ1989 | 20,530.4 |
| ∆ USD Billions | +11,482.6 |
| ∆% CPI Adjusted | 40.2 |
| Gross Private Domestic Investment USD 2009 Billions | |
| IQ1980 | 951.6 |
| IIQ1989 | 1278.3 |
| ∆% | 34.3 |
| Period IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 | |
| GDP SAAR USD Billions | |
| IVQ2007 | 14,991.8 |
| IVQ2015 | 16,455.1 |
| ∆% IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 | 9.8 |
| ∆% IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 Trend Growth | 26.7 |
| Real Disposable Personal Income per Capita IVQ2007 Chained 2009 USD | 35,819 |
| Real Disposable Personal Income per Capita IVQ2015 Chained 2009 USD | 38,320 |
| ∆% IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 | 7.0 |
| ∆% Trend Growth | 17.2 |
| Employed Millions IVQ2007 NSA End of Quarter | 146.334 |
| Employed Millions IVQ2015 NSA End of Quarter | 149.703 |
| ∆% Employed IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 | 2.3 |
| Employed Full-time Millions IVQ2007 NSA End of Quarter | 121.042 |
| Employed Full-time Millions IVQ2015 NSA End of Quarter | 122.013 |
| ∆% Full-time Employed IVQ2007 to IVQ2015 | 0.8 |
| Unemployment Rate IVQ2007 NSA End of Quarter | 4.8 |
| Unemployment Rate IVQ2015 NSA End of Quarter | 4.8 |
| Unemployed IVQ2007 Millions NSA End of Quarter | 7.371 |
| Unemployed IVQ2015 Millions NSA End of Quarter | 7.542 |
| ∆% | 2.3 |
| Employed Part-time Economic Reasons IVQ2007 Millions NSA End of Quarter | 4.750 |
| Employed Part-time Economic Reasons Millions IVQ2015 NSA End of Quarter | 6.179 |
| ∆% | 30.1 |
| U6 Total Unemployed plus all marginally attached workers plus total employed part time for economic reasons as percent of all civilian labor force plus all marginally attached workers NSA | |
| IVQ2007 | 8.7 |
| IVQ2015 | 9.8 |
| Net Worth of Households and Nonprofit Organizations USD Billions | |
| IVQ2007 | 66,536.0 |
| IVQ2015 | 86,796.0 |
| ∆ USD Billions | +20,260 ∆%30.4 R∆%15.8 |
| Gross Private Domestic Investment USD Billions | |
| IVQ2007 | 2,605.2 |
| IVQ2015 | 2,854.7 |
| ∆% | 9.6 |
| Private Fixed Investment USD 2009 Billions | |
| IVQ2007 | 2,586.3 |
| IVQ2015 | 2,761.5 |
| ∆% | 6.8 |
Note: GDP trend growth used is 3.0 percent per year and GDP per capita is 2.0 percent per year as estimated by Lucas (2011May) on data from 1870 to 2010.
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/. Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. 2015. Flow of funds, balance sheets and integrated macroeconomic accounts: third quarter 2015. Washington, DC, Federal Reserve System, Dec 10. http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/z1/.
The Congressional Budget Office (CBO 2014BEOFeb4) estimates potential GDP, potential labor force and potential labor productivity provided in Table IB-3. The CBO estimates average rate of growth of potential GDP from 1950 to 2014 at 3.3 percent per year. The projected path is significantly lower at 2.1 percent per year from 2015 to 2025. The legacy of the economic cycle expansion from IIIQ2009 to IVQ2015 at 2.1 percent on average is in contrast with 4.7 percent on average in the expansion from IQ1983 to IIQ1989 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/closely-monitoring-global-economic-and.html). Subpar economic growth may perpetuate unemployment and underemployment estimated at 25.1 million or 15.0 percent of the effective labor force in Feb 2016 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets-in.html). There is much lower hiring than in the period before the current cycle (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/subdued-foreign-growth-and-dollar.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/unconventional-monetary-policy-and.html).
Table IB-3, US, Congressional Budget Office History and Projections of Potential GDP of US Overall Economy, ∆%
| Potential GDP | Potential Labor Force | Potential Labor Productivity* | |
| Average Annual ∆% | |||
| 1950-1973 | 4.0 | 1.6 | 2.4 |
| 1974-1981 | 3.3 | 2.5 | 0.8 |
| 1982-1990 | 3.2 | 1.6 | 1.6 |
| 1991-2001 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 1.9 |
| 2002-2007 | 2.8 | 0.9 | 1.9 |
| 2008-2014 | 1.4 | 0.5 | 0.9 |
| Total 1950-2014 | 3.3 | 1.5 | 1.8 |
| Projected Average Annual ∆% | |||
| 2015-2019 | 2.1 | 0.5 | 1.6 |
| 2019-2025 | 2.2 | 0.6 | 1.6 |
| 2015-2025 | 2.1 | 0.5 | 1.6 |
*Ratio of potential GDP to potential labor force
Source: CBO (2014BEOFeb4), CBO, Key assumptions in projecting potential GDP—February 2014 baseline. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb 4, 2014. CBO, The budget and economic outlook: 2015 to 2025. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Jan 26, 2015.
Chart IB-1A of the Congressional Budget Office provides historical and projected potential and actual US GDP. The gap between actual and potential output closes by 2017. Potential output expands at a lower rate than historically. Growth is even weaker relative to trend.
Chart IB-1A, Congressional Budget Office, Estimate of Potential GDP and Gap
Source: Congressional Budget Office
https://www.cbo.gov/publication/49890
Chart IB-1 of the Congressional Budget Office (CBO 2013BEOFeb5) provides actual and potential GDP of the United States from 2000 to 2011 and projected to 2024. Lucas (2011May) estimates trend of United States real GDP of 3.0 percent from 1870 to 2010 and 2.2 percent for per capita GDP. The United States successfully returned to trend growth of GDP by higher rates of growth during cyclical expansion as analyzed by Bordo (2012Sep27, 2012Oct21) and Bordo and Haubrich (2012DR). Growth in expansions following deeper contractions and financial crises was much higher in agreement with the plucking model of Friedman (1964, 1988). The unusual weakness of growth at 2.1 percent on average from IIIQ2009 to IVQ2015 during the current economic expansion in contrast with 4.7 percent on average in the cyclical expansion from IQ1983 to IIQ1989 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/mediocre-cyclical-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/closely-monitoring-global-economic-and.html) cannot be explained by the contraction of 4.2 percent of GDP from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 and the financial crisis. Weakness of growth in the expansion is perpetuating unemployment and underemployment of 25.1 million or 15.0 percent of the labor force as estimated for Feb 2016 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/03/twenty-five-million-unemployed-or.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/fluctuating-risk-financial-assets-in.html). There is no exit from unemployment/underemployment and stagnating real wages because of the collapse of hiring (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/02/subdued-foreign-growth-and-dollar.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2016/01/unconventional-monetary-policy-and.html). The US economy and labor markets collapsed without recovery. Abrupt collapse of economic conditions can be explained only with cyclic factors (Lazear and Spletzer 2012Jul22) and not by secular stagnation (Hansen 1938, 1939, 1941 with early dissent by Simons 1942).
Chart IB-1, US, Congressional Budget Office, Actual and Projections of Potential GDP, 2000-2024, Trillions of Dollars
Source: Congressional Budget Office, CBO (2013BEOFeb5). The last year in common in both projections is 2017. The revision lowers potential output in 2017 by 7.3 percent relative to the projection in 2007.
Chart IB-2 provides differences in the projections of potential output by the CBO in 2007 and more recently on Feb 4, 2014, which the CBO explains in CBO (2014Feb28).
Chart IB-2, Congressional Budget Office, Revisions of Potential GDP
Source: Congressional Budget Office, 2014Feb 28. Revisions to CBO’s Projection of Potential Output since 2007. Washington, DC, CBO, Feb 28, 2014.
Chart IB-3 provides actual and projected potential GDP from 2000 to 2024. The gap between actual and potential GDP disappears at the end of 2017 (CBO2014Feb4). GDP increases in the projection at 2.5 percent per year.
Chart IB-3, Congressional Budget Office, GDP and Potential GDP
Source: CBO (2013BEOFeb5), CBO, Key assumptions in projecting potential GDP—February 2014 baseline. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb 4, 2014.
References
Abraham, Katharine G., John C. Haltiwanger, Kristin Sandusky and James Spletzer. 2009. Exploring differences in employment between household and establishment data. Cambridge, MA, National Bureau of Economic Research, Mar 2009.
Allen, William R. 1993. Irving Fisher and the 100 percent reserve proposal. Journal of Law and Economics 36 (2, Oct): 703-17.
Andrés, Javier, J. David López-Salido and Edward Nelson. 2004. Tobin’s imperfect asset substitution in optimizing equilibrium. Journal of Money, Credit and Banking 36 (4, Aug): 665-90.
Asso, Pier Francesco, George A. Kahn and Robert Leeson. 2007. The Taylor Rule and the transformation of monetary policy. Kansas City: Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City RWP 07-II, Dec.
Asso, Pier Francesco, George A. Kahn and Robert Leeson. 2010. The Taylor Rule and the practice of central banking. Kansas City: Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City, RWP 10-05, Feb.
Atkeson, Andrew and Patrick J. Kehoe. 1998. Paths of development for early- and late-bloomers in a dynamic Heckscher-Ohlin world. Minneapolis, Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis, Staff Report No. 256, Oct.
Atkeson, Andrew and Patrick J. Kehoe. 2004. Deflation and depression: is there an empirical link. American Economic Review 94 (2, May): 99-103.
Bagehot, Walter. 1873. Lombard Street, 14th edn. London: Kegan, Paul & Co, 1917.
Ball, Laurence and N. Gregory Mankiw. 2002. The NAIRU in theory and practice. Journal of Economic Perspectives 16 (4, Autumn): 115-36.
Bank of Japan. 2012Feb14APP. Amendment to “Principal Terms and Conditions for the Asset Purchase Program.” Tokyo, Bank of Japan, Feb 14 http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2012/rel120214a.pdf
Bank of Japan. 2012Feb14PSG. The price stability goal in the medium to long term. Tokyo, Bank of Japan, Feb 14 http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2012/k120214b.pdf
Bank of Japan. 2012Feb14EME. Enhancement of monetary easing. Tokyo, Bank of Japan, Feb 14 http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2012/k120214a.pdf
Barbosa, Fernando de Holanda. 1987. Domestic and international sources of Brazilian inflation: 1947-80. In Luigi L. Pasinetti and P.J. Lloyd, eds. Structural change, economic interdependence and world development. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.
Barro, Robert J. and David B. Gordon. 1983a. Rules, discretion and reputation in a model of monetary policy. Journal of Monetary Economics 12 (1): 101-121.
Barro, Robert J. and David B. Gordon. 1983b. A positive theory of monetary policy in a natural rate model. Journal of Political Economy 91 (4, Aug): 589-610.
Barsky, Robert B. and Lutz Kilian. 2004. Oil and the macroeconomy since the 1970s. Journal of Economic Perspectives 18 (4, Autumn): 115-34.
Barth, James R., Gerard Caprio, Jr. and Ross Levine. 2006. Rethinking bank regulation. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
Basel Committee on Banking Supervision. 2011Jun. Basel II: a global regulatory framework for more resilient banks and banking systems. Basel, Switzerland: BIS, Jun 2011 http://www.bis.org/publ/bcbs189.pdf
Batini, Nicoletta and Edward Nelson. 2002. The lag from monetary policy actions to inflation: Friedman revisited. London, Bank of England, External MPC Unit Discussion Paper No. 6, Jan.
Beim, David O. 2011Oct9. Can the euro be saved? New York City, Columbia University, Oct 9 http://www1.gsb.columbia.edu/mygsb/faculty/research/pubfiles/5573/Can%20the%20Euro%20be%20Saved.pdf
Benhabib, Jess and Mark M. Spiegel. 2009. Moderate inflation and the deflation-depression link. 2009. Journal of Money, Credit and Banking 41 (4, Jun): 787-798.
Benston, George J. and George G. Kaufman. 1997. The FDICA after five years. Journal of Economic Perspectives 11 (3, Summer, 1997): 139-58.
Bernanke, Ben S. 2002. Deflation: making sure “it” doesn’t happen here. Washington, DC, National Economists Club, Nov 21 http://www.federalreserve.gov/boarddocs/speeches/2002/20021121/default.htm
Bernanke, Ben S. 2000. Japanese monetary policy: a case of self-induced paralysis? In Ryoichi Mikitani and Adam S. Posen, Japan’s financial crisis and its parallels to US experience. Washington, DC, Institute for International Economics, Special Report 13, Sep 2000.
Bernanke, Ben S. 2002. Deflation: making sure “it” doesn’t happen here. Washington, DC, Before the National Economists Club, Nov 21 http://www.federalreserve.gov/boarddocs/speeches/2002/20021121/default.htm
Bernanke, Ben S. 2003. A perspective on inflation targeting. Business Economics 38 (3, Jul): 7–15.
Bernanke, Ben S. 2003JPY. Some thoughts on monetary policy in Japan. Tokyo, Before the Japan Society of Monetary Economics, May 31 http://www.federalreserve.gov/boarddocs/speeches/2003/20030531/default.htm
Bernanke, Ben S. 2009SL. The crisis and the policy response. London, London School of Economics, Stamp Lecture, Jan 13 http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/bernanke20090113a.htm
Bernanke, Ben S. 2010WP. What the Fed did and why: supporting the recovery and sustaining price stability. Washington Post, Nov 4. http://www.washingtonpost.com/wp-dyn/content/article/2010/11/03/AR2010110307372_pf.html
Bernanke, Ben S. 2011Oct4JEC. Statement. Washington, DC, Joint Economic Committee, US Congress, Oct 4 http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/bernanke20111004a.pdf
Bernanke, Ben S. 2012Apr25. Transcript of Chairman Bernanke’s press conference April 25, 2012. Washington, DC, Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Apr 25 http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20120425.pdf
Bernanke, Ben S. 2012Aug22. Letter to The Honorable Darrell E. Issa. Washington, DC, Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Aug 22 http://online.wsj.com/public/resources/documents/Bernankeletter0812.pdf
Bernanke, Ben S. 2012Oct14IMF. US monetary policy and international implications. Tokyo, Japan, Challenges of the Global Financial System: Risks and Governance under Evolving Globalization, High-level Seminar sponsored by Bank of Japan-International Monetary Fund, Oct 14 http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/bernanke20121014a.htm
Bernanke, Ben S. 2012JHAug31. Monetary policy since the onset of the crisis. Jackson Hole, WY, Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City Economic Symposium, Aug 31 http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/bernanke20120831a.htm
Bernanke, Ben S. 2012Nov20. The economic recovery and economic policy. New York City, NY, Economic Club, Nov 20 http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/bernanke20121120a.htm
Bernanke, Ben S. 2013Mar25. Monetary policy and the global economy. London, Bank of England and London School of Economics, Mar 25 http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/bernanke20130325a.htm
Bernanke, Ben S. 2013Jul17. Statement on semiannual monetary policy report to the Congress. Washington, DC, Jul 17, US House of Representatives, Jul 18, US Senate http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/bernanke20130717a.htm
Bernanke, Ben S. and Frederic S. Mishkin. 1997. Inflation targeting: a new framework for monetary policy? Journal of Economic Perspectives 11 (2, Spring): 97–116.
Bernanke, Ben S. and Vincent R. Reinhart. 2004. Conducting monetary policy at very low short-term interest rates. American Economic Review 94 (2): 85-90.
Black, Fischer and Myron Scholes. 1973. The pricing of options and corporate liabilities. Journal of Political Economy 81 (May/June): 637-54.
Blanchard, Olivier. 2011WEOSep. Foreword to IMF 2011WEOSep: XIII-XIV.
Blanchard, Olivier. 2012WEOApr. Foreword to IMF 2012WEOApr: XIII-XIV
Blanchard, Olivier and Lawrence F. Katz. 1997. What we know and do not know about the natural rate of unemployment. Journal of Economic Perspectives 11 (1, Winter): 51-72.
Blinder, Alan S. 2000. Monetary policy at the zero lower bound: balancing the risks. Journal of Money, Credit and Banking 32 (4, Nov): 1093-1099.
Blinder, Alan S. and Mark Zandi. 2010Jul27. How the Great Recession was brought to an end. Princeton, NJ, http://www.princeton.edu/~blinder/End-of-Great-Recession.pdf
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. 2012Dec6. Flow of funds accounts of the United States. Washington, DC, Federal Reserve System, Dec 6 http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/z1/default.htm
Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. 2017Jul17. Monetary policy report. Washington, DC, Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve, Jul 17 http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/mpr_default.htm
Bordo, Michael D. 2012Sep27. Financial recessions don’t lead to weak recoveries. Wall Street Journal, Sep 27 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10000872396390444506004577613122591922992.html
Bordo, Michael D. 2012Oct21. Why this US recovery is weaker. Bloomberg View, Oct 21 http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2012-10-21/why-this-u-s-recovery-is-weaker.html
Bordo, Michael D. 2012Nov20. Expansionary monetary policy can create asset price booms. Washington, DC, Shadow Open Market Committee, Nov 20 http://shadowfed.org/wp-content/uploads/2012/11/Bordo-SOMC-Nov2012.pdf
Bordo, Michael D. and Hugh Rockoff. 2011. The influence of Irving Fisher on Milton Friedman’s monetary economics. Denver, CO, AEA Session on Irving Fisher and Modern Economics: 100 years after the Purchasing Power of Money, Jan 8 www.aeaweb.org/aea/2011conference/program/retrieve.php?pdfid
Bordo, Michael D, Ehsan Choudhri and Anna J. Schwartz. 1995. Could stable money have averted the Great Contraction. Economic Inquiry 33 (3, Jul): 484-505.
Bordo, Michael D. and Harold James. 2001. The Adam Klug Memorial Lecture: Haberler versus Nurkse: the case for floating exchange rates as an alternative to Bretton Woods? Cambridge, MA: NBER, WP 8545, Oct.
Bordo, Michael D. and Jopseh G. Haubrich. 2012DR. Deep recessions, fast recoveries, and financial crises: evidence from the American record. Cleveland, OH, Federal Reserve Bank of Cleveland, WP 12/14 http://www.clevelandfed.org/research/workpaper/2012/wp1214.pdf
Bordo, Michael D. and John Landon-Lane. 2013. Does expansionary monetary policy cause asset price booms; some historical and empirical evidence. Cambridge, MA, National Bureau of Economic Research, Working Paper 19585, Oct 2013 http://www.nber.org/papers/w19585
Bordo, Michael D. and Peter Rousseau. 2006. Legal political factors and the historical evolution of the finance-growth link. NBER Working Paper No. 12035. Cambridge, MA, National Bureau of Economic Research, Feb. Earlier presented at CPRN/ONB Workshop on International Financial Integration: The Role of Intermediaries, Vienna, 30 Sep-1Oct 2005.
Boskin, Michael J. 2010Sep. Summer of economic discontent. Wall Street Journal, Sep 2 http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052748703882304575465462926649950.html?KEYWORDS=michael+boskin
Bricker, Jesse, Arthur B. Kennickell, Kevin B. Moore and John Sabelhaus. 2012. Changes in US family finances from 2007 to 2010: evidence from the Survey of Consumer Finances. Federal Reserve Bulletin 98 (2, Jun): 2-80 http://www.federalreserve.gov/pubs/bulletin/2012/PDF/scf12.pdf
Brunner, Karl and Allan H. Meltzer. 1973. Mr. Hicks and the “monetarists.” Economica NS 40 (157, Feb): 44-59.
Brunnermeier, Markus K. and Lasse Hege Pedersen. 2009. Market liquidity and funding liquidity. Review of Financial Studies 22 (6): 2201-38.
Buiter, Willem. 2011Oct31. EFSF needs bigger bazooka to maximize its firepower. Financial Times, Oct 31 http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/c4886f7a-03d3-11e1-bbc5-00144feabdc0.html#axzz1cMoq63R5
Buiter, Willem. 2012Oct15. Only big debt restructuring can save euro. Financial Times, Oct 15 http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/edd92eee-12de-11e2-aa9c-00144feabdc0.html#axzz29OP0k8cX
Buiter, Willem. 2014Feb4. The Fed’s bad manners risk offending foreigners. Financial Times, Feb 4 http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/fbb09572-8d8d-11e3-9dbb-00144feab7de.html#axzz2suwrwkFs
Brunner, Karl and Allan H. Meltzer. 1973. Mr. Hicks and the “monetarists.” Economica NS 40 (157, Feb): 44-59.
Burdekin, Richard C. 2005. US pressure on China’s currency: Milton Friedman and the silver episode revisited. Claremont McKenna College, Nov 2005 http://www.claremontmckenna.edu/rdschool/papers/2005-07.pdf
Bureau of Labor Statistics. 2011Feb11. Overview of seasonal adjustment of the current employment statistics program. Washington, Feb 11, 2011 http://www.bls.gov/ces/cessa_oview.pdf
Bureau of Labor Statistics. 2012Feb3. Seasonal adjustment files and documentation. Washington, BLD, Feb 3 http://www.bls.gov/web/empsit/cesseasadj.htm
Caballero, Ricardo and Francsco Giavazzi. 2012Jan15. Parity may be euro’s last chance. Bloomberg, Jan 15 http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2012-01-16/dollar-parity-may-be-euro-salvation-commentary-by-caballero-and-giavazzi.html
Cagan, Phillip. 1965. Determinants and effects of changes in the stock of money, 1875-1960. New York: Columbia University Press.
Calomiris, Charles C. and Gary B. Gorton. 1991. The origins of banking panics: models, facts and bank regulation. In R. Glenn Hubbard, ed. Financial markets and financial crises. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Calomiris, Charles W. and Stephen H. Haber. 2014. Fragile by design: the political origins of banking crises and scarce credit. Princeton: Princeton University Press http://press.princeton.edu/titles/10177.html
Cameron, Rondo E. 1961. France and the economic development of Europe 1800-1914: conquests of peace and seeds of war. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Cameron, Rondo E. 1967. Banking in the early stages of industrialization. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Cameron, Rondo E. 1972. Banking and economic development. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Cameron, Rondo E. 1989. A concise economic history of the world: from Paleolithic times to the present. New York and Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Cameron, Rondo E., V.I. Bovkyn, Richard Sylla, Mira Wilkins, Boris Anan’ich, and A. A. Fursenko, eds. 1992. International Banking 1870-1914. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
CBO. 2011JunLTBO. CBO’s long-term budget outlook. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Jun http://www.cbo.gov/ftpdocs/122xx/doc12212/06-21-Long-Term_Budget_Outlook.pdf
CBO. 2012JanBEO. The budget and economic outlook: fiscal years 2012 to 2022. Washington, DC: Congressional Budget Office, Jan http://www.cbo.gov/ftpdocs/126xx/doc12699/01-31-2012_Outlook.pdf
CBO. 2012Jan31. Historical budget data. Washington, DC, Jan 31.
CBO. 2012MarBEO. Updated budget projections: fiscal years 2012 to 2022. Washington, DC: Congressional Budget Office, Mar http://www.cbo.gov/sites/default/files/cbofiles/attachments/March2012Baseline.pdf
CBO. 2012LTBO. The 2012 long-term budget outlook. Washington, DC: Congressional Budget Office, Jun http://www.cbo.gov/sites/default/files/cbofiles/attachments/06-05-Long-Term_Budget_Outlook.pdf
CBO. 2012AugBEO. An update to the budget and economic outlook: fiscal years 2012 to 2022. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Aug http://www.cbo.gov/publication/43539
CBO. 2012NovMBR. Monthly budget review fiscal year 2012. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Nov 7 http://www.cbo.gov/publication/43698
CBO. 2012NovCDR. Choices for deficit reduction. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office http://www.cbo.gov/publication/43692
CBO. 2012NovEEP. Economic effects of policies contributing to fiscal tightening in 2013. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Nov http://www.cbo.gov/publication/43694
CBO. 2013BEOFeb5. The budget and economic outlook: fiscal years 2013 to 2023. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office http://www.cbo.gov/publication/43907
CBO. 2013HBDFeb5. Historical budget data—February 2013 baseline projections. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office http://www.cbo.gov/publication/43904
CBO. 2013MEFeb5. Macroeconomic effects of alternative budget paths. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb 5 http://www.cbo.gov/publication/43769
CBO (2013Aug12). 2013AugHBD. Historical budget data—August 2013. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Aug 12 http://www.cbo.gov/publication/44507
CBO (2013Aug12Av). Kim Kowaleski and Amber Marcellino. Updated historical budget data. CBO, Aug 12 http://www.cbo.gov/publication/44508
CBO (2013Sep11). 2013Sep11. CBO’s baseline budget projections updated. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Sep 11 http://www.cbo.gov/publication/44574
CBO (2013Sep17). The 2013 long-term budget outlook. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Sep 17 http://www.cbo.gov/publication/44521
Chung, Hess, Jean-Philippe Laforte, David Reifschneider and John C. Williams. 2011. Have we underestimated the likelihood and severity of zero lower bound events? San Francisco, FRBSF, WP 2011-01 http://www.frbsf.org/publications/economics/papers/2011/wp11-01bk.pdf
Cline, William. 2001. The role of the private sector in resolving financial crises in emerging markets. Cambridge, MA, NBER, Jun.
Cline, William. 2002. Private sector involvement: definition, measurement and implementation. London, Bank of England Conference, Jul-23-4.
Cobet, Aaron E. and Gregory A. Wilson. 2002. Comparing 50 years of labor productivity in US and foreign manufacturing. Monthly Labor Review (Jun): 51-65.
Cochrane, John A. 2010A. The government debt valuation equation. An appendix to “Understanding policy.” http://faculty.chicagobooth.edu/john.cochrane/research/Papers/
Cochrane, John H. 2011Jan. Understanding policy in the great recession: some unpleasant fiscal arithmetic. European Economic Review 55 (1, Jan): 2-30.
Cochrane, John H. 2012Aug31. The Federal Reserve: from central bank to central planner. Wall Street Journal, Aug 31 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10000872396390444812704577609384030304936.html?mod=WSJ_hps_sections_opinion
Cochrane, John H. 2014Jul2. The failure of macroeconomics. Wall Street Journal, Jul 2. http://online.wsj.com/articles/john-cochrane-new-keynesian-macroeconomic-models-dont-support-more-stimulus-spending-1404342631?KEYWORDS=john+h+cochrane
Cochrane, John H. and Luigi Zingales. 2009. Lehman and the financial crisis. Wall Street Journal, Sep 15.
Cohen, Morris Raphael and Ernest Nagel. 1934. An introduction to logic and scientific method. New York: Harcourt, Brace and Company.
Cole, Harold L. and Lee E. Ohanian. 1999. The Great Depression in the United States from a neoclassical perspective. Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis Quarterly Review 23 (1, Winter): 2-24.
Cole, Harold L. and Narayana Kocherlakota. 1998. Zero nominal interest rates: why they are good and how to get them. Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis Quarterly Review 22 (2, Spring): 2-10.
Cooley, Thomas F. and Lee E. Ohanian. 2010. FDR and the lessons of the Depression. Wall Street Journal, Aug 27 http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052748703461504575443402028756986?KEYWORDS=Thomas+Cooley
Contador, Cláudio R. and Haddad, Cláudio L. 1975. Produto real, moeda e preços. Revista Brasileira de Estatística 36(143, jul/set): 407-40.
Cox, John C., Jonathan E. Ingersoll, Jr. and Stephen A. Ross. 1981. A re-examination of traditional hypotheses about the term structure of interest rates. Journal of Finance 36 (4, Sep): 769-99.
Cox, John C., Jonathan E. Ingersoll, Jr. and Stephen A. Ross. 1985. A theory of the term structure of interest rates. Econometrica 53 (2, Mar): 385-407.
Culbertson, John M. 1957. The term structure of interest rates. Quarterly Journal of Economics 71 (4, Nov): 485-517.
Culbertson, J. M. 1960. Friedman on the lag in effect of monetary policy. Journal of Political Economy 68 (6, Dec): 617-21.
Culbertson, J. M. 1961. The lag in effect of monetary policy: reply. Journal of Political Economy 69 (5, Oct): 467-77.
Culbertson, John M. 1963. The term structure of interest rates: reply. Quarterly Journal of Economics 77 (4, Nov): 691-6.
D’Amico Stefania and Thomas B. King. 2010. Flow and stock effects of large-sale Treasury purchases. Washington, DC, Federal Reserve board, Sep.
Darby, Michael R. Darby. 1974. The permanent income theory of consumption—a restatement. Quarterly Journal of Economics (88, 2): 228-50.
Deane, Phyllis. 1968. New estimates of gross national product for the United Kingdom 1830-1914. Review of Income and Wealth 14 (2, Jun): 95-112.
Delfim Netto, Antonio. 1959. O problema do café no Brasil. São Paulo: Faculdade de Economia e Administração da Universidade de São Paulo. Partly reprinted in Pelaez (1973).
De Long, J. Bradford. 1997. America’s peacetime inflation: the 1970s. In Christina D. Romer and David H. Romer, eds. Reducing inflation: motivation and strategy. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 1997.
DeLong, J. Bradford and Barry Eichengreen. 2001Jul. Between meltdown and moral hazard: the international monetary and financial policies of the Clinton Administration. Cambridge, MA, Conference on the Economic Policies of the Clinton Administration, Kennedy School of Government, Jun 26-29 http://eml.berkeley.edu/~eichengr/research/clintonfinancialpolicies9.pdf
DeNavas-Walt, Carmen, Bernadette D. Proctor and Jessica C. Smith. 2012Sep. Income, poverty and health insurance coverage in the United States: 2011. Washington, DC, US Census Bureau http://www.census.gov/prod/2012pubs/p60-243.pdf
DeNavas-Walt, Carmen, Bernadette D. Proctor and Jessica C. Smith. 2013. Income, poverty, and health insurance coverage in the United States: 2012. Washington, DC: US Census Bureau, Current Population Reports, P60-245, US Government Printing Office http://www.census.gov/prod/2013pubs/p60-245.pdf
DeNavas-Walt, Carmen and Bernadette D. Proctor. 2014. Income and poverty in the United States: 2013. Washington, DC: US Census Bureau, Current Population Reports P60-249, US Government Printing Office, Sep 18.
DeNavas-Walt, Carmen and Bernadette D. Proctor. 2015. Income and poverty in the United States: 2014. Washington, DC: US Census Bureau, Current Population Reports P60-252, US Government Printing Office, Sep.
Doh, Taeyoung. 2010. The efficacy of large-scale asset purchases at the zero lower bound. Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City Economic Review Second Quarter 2010: 5-34 http://www.kansascityfed.org/Publicat/EconRev/PDF/10q2Doh.pdf
Dorrance, G. S. 1948. The income terms of trade. Review of Economic Studies 16 (1, 1948-1949): 50-6.
Draghi, Mario. 2011Dec1. Introductory statement by Mario Draghi, President of the ECB. Brussels, Hearing before the Plenary of the European Parliament, Dec 1 http://www.ecb.int/press/key/date/2011/html/sp111201.en.html
Draghi, Mario. 2011Dec8. Introductory statement to the press conference. Frankfurt am Main, ECB, Dec 8 http://www.ecb.int/press/pressconf/2011/html/is111208.en.html
Draghi, Mario. 2012May26. Speech by Mario Draghi, President of the European Central Bank. London, Global Investment Conference, Jul 26 http://www.ecb.int/press/key/date/2012/html/sp120726.en.html
Draghi, Mario. 2012Aug29. The future of the euro: stability through change. Frankfurt am Main, ECB, published in Die Zeit, 29 Aug 2012 http://www.ecb.int/press/key/date/2012/html/sp120829.en.html
Duffie, Darell and Kenneth J. Singleton. 2003. Credit risk: pricing, measurement and management. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Eggertsson, Gauti B. and Paul Krugman. 2010. Debt, deleveraging and the liquidity trap: A Fisher-Minsky-Koo approach. Princeton, Princeton University, Nov 16 http://www.princeton.edu/~pkrugman/debt_deleveraging_ge_pk.pdf
European Council. 2011Dec9. Statements by the euro area heads of state or government. Brussels, European Union, Dec 9 http://www.consilium.europa.eu/uedocs/cms_Data/docs/pressdata/en/ec/126658.pdf
European Council. 2012Oct19. Conclusions. Brussels, European Union, Oct 19 http://www.consilium.europa.eu/uedocs/cms_data/docs/pressdata/en/ec/133004.pdf
DeNavas-Walt, Carmen, Bernadette D. Proctor and Jessica C. Smith. 2012Sep. Income, poverty and health insurance coverage in the United States: 2011. Washington, DC, US Census Bureau, US Government Printing Office, Sep http://www.census.gov/prod/2012pubs/p60-243.pdf
Diamond, DouglasW. 1984. Financial intermediation and delegated monitoring. Review of Economic Studies 51: 393-414.
Diamond, Douglas W. 1996. Financial intermediation as delegated monitoring: a simple example. Economic Quarterly Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond 82 (3): 51-66.
Diamond, Douglas W. and Philip H. Dybvig. 1983. Bank runs, deposit insurance and liquidity. Journal of Political Economy 91 (3, Jun): 401-49.
Diamond, Douglas W. and Philip H. Dybvig. 1986. Banking theory, deposit insurance and bank regulation. Journal of Business 59 (1, Jan): 55-68.
Diamond, Douglas W. and Raghuram G. Rajan. 2000. A theory of bank capital. Journal of Finance 55 (6, Dec): 2431-65.
Diamond, Douglas W. and Raghuram G. Rajan. 2001a. Banks and liquidity. American Economic Review 91 (2, May): 422-5.
Diamond, Douglas W. and Raghuram G. Rajan. 2001b. Liquidity Risk, liquidity creation and financial fragility: a theory of banking. Journal of Political Economy 109 (2, Apr): 287-327.
Dornbusch, Rudiger. 1976. Expectations and exchange rate dynamics. Journal of Political Economy 84 (6, Dec): 1161-76.
Draghi, Mario. 2011Dec15. The euro, monetary stability and the design of a fiscal compact. Berlin, Dec 15 http://www.ecb.int/press/key/date/2011/html/sp111215.en.html
Draghi, Mario. 2012May3. Introductory statement to the press conference. Barcelona, May 3 http://www.ecb.int/press/pressconf/2012/html/is120503.en.html
Draghi, Mario. 2012Jun15. President’s address at the 14th ECB and its Watchers Conference. Frankfurt am Main, European Central Bank, Jun 15 http://www.ecb.int/press/key/date/2012/html/sp120615.en.html
Economides, Nicholas, Yannis Ioannides, Emmanuel Petrakis, Christopher Pissarides and Thanasis Stengos. 2012. What’s at stake in the Greek vote. Wall Street Journal, Jun 14 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052702303822204577466541312448940.html?mod=WSJ_hps_sections_opinion
Eichengreen, Barry and Jeffrey Sachs. 1985. Exchange rates and economic recovery in the 1930s. Journal of Economic History 45 (4, Dec): 925-46.
Eggertson, Gauti B. and Michael Woodford. 2003. The zero bound on interest rates and optimal monetary policy. Brookings Papers on Economic Activity I (2003): 139-211.
European Central Bank. 2011MBDec. Editorial. Monthly Bulletin December 2011, 5-9 http://www.ecb.int/pub/pdf/mobu/mb201112en.pdf
European Commission. 2011Oct26SS. Euro summit statement. Brussels, European Commission, Oct 26 http://ec.europa.eu/news/economy/111027_en.htm
European Commission. 2011Oct26MRES. Main results of Euro Summit. Brussels, European Commission, Oct 26 http://www.consilium.europa.eu/uedocs/cms_Data/docs/pressdata/en/ec/125645.pdf
European Council. 2011Dec9. Statements by the euro area heads of state or government. Brussels, European Union, Dec 9 http://www.consilium.europa.eu/uedocs/cms_Data/docs/pressdata/en/ec/126658.pdf
Evans, Charles. 2010. Monetary policy in a low-inflation environment: developing a state-contingent price-level target. Boston, Federal Reserve Bank of Boston’s 55th Economic Conference, Oct 16 http://chicagofed.org/webpages/publications/speeches/2010/10_16_boston_speech.cfm#_ftn1
Evans, Charles. 2012Aug27. Some thoughts on global risks and monetary policy. Hong Kong, China, Market News International Seminar, Aug 27 http://www.chicagofed.org/webpages/publications/speeches/2012/08_27_12_hongkong.cfm
Evans, Charles. 2012Nov27. Monetary policy in challenging times. Toronto, Canada, Howe Institute, Nov 27
http://www.chicagofed.org/webpages/publications/speeches/2012/11_27_12_cdhowe.cfm
Fabozi, Frank J., Gerald W. Buestow, Jr., and Robert R. Johnson. Measuring interest rate risk. In Frank J. Fabozzi, ed. The handbook of fixed income securities, 7th Edition. New York, McGraw, 2006.
Fama, Eugene F. 1970. Efficient capital markets: a review of theory and empirical work. Journal of Finance 25 (2): 383-417.
Fama, Eugene F. and Robert R. Bliss. 1987. The information in long-maturity forward rates. American Economic Review 77 (4, Sep): 680-92.
Feldstein, Martin. 2016. A Federal Reserve oblivious to its effect on financial markets. Wall Street Journal, Jan 13 http://www.wsj.com/articles/a-federal-reserve-oblivious-to-its-effect-on-financial-markets-1452729166
Fisher, Irving. 1930. The theory of interest. New York: The Macmillan Company http://www.econlib.org/library/YPDBooks/Fisher/fshToI19.html
Fisher, Irving. 1933. The debt-deflation theory of great depressions. Econometrica 1(4): 337-57.
Fisher, Irving. 100% Money. 1936. New York: Adelphi Company.
Fishlow, Albert. 1965. American railroads and the transformation of the ante-bellum economy. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Feldstein, Martin. 2012Mar19. Obama’s tax hikes threaten a new US recession. Financial Times, Mar 19 http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/0d0e7acc-6f7d-11e1-9c57-00144feab49a.html#axzz1pexRlsiQ
Fleming, J. Marcus. 1962. Domestic financial policies under fixed and under floating exchange rates. IMF Staff Papers 9: 369-79.
Fogel, Robert W. 1964. Railroads and American economic growth: essays in econometric history. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Fogel, Robert W. and Stanley Engerman. 1974. Time on the cross. Boston: Little Brown.
Forbes, Kristin J. 2012JHAug9. The big “C”: identifying and mitigating contagion. Jackson Hole, WY, Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City Symposium, Aug 31 http://www.kansascityfed.org/publicat/sympos/2012/kf.pdf
Friedman, Milton. 1953. The effects of a full-employment policy on economic stability: a formal analysis. In Milton Friedman, Essays on positive economics. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Friedman, Milton. 1953b. The case for flexible exchange rates. In Milton Friedman, Essays on positive economics. Chicago: University of Chicago Press: 157-203.
Friedman, Milton. 1957. A Theory of the Consumption Function. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Friedman, Milton. 1961. The lag in effect of monetary policy. Journal of Political Economy 69 (5, Oct): 447-66.
Friedman, Milton. 1964. The monetary studies of the National Bureau. In The National Bureau enters its forty-fifth year. New York, NY: National Bureau of Economic Research, Inc., Forty-Fourth Annual Report: 7-25 http://www.nber.org/chapters/c4453.pdf
Friedman, Milton. 1968. The role of monetary policy. American Economic Review 58 (1, Mar): 1-17.
Friedman, Milton. 1969. The optimum quantity of money. In Milton Friedman, The optimum quantity of money and other essays. Chicago: Aldine, 1969.
Friedman, Milton. 1970. Controls on interest rates paid by banks. Journal of Money, Credit and Banking 2 (1, Feb): 15-32.
Friedman, Milton. 1982. Monetary policy: theory and practice. Journal of Money, Credit and Banking 14 (1, Feb): 98-118.
Friedman, Milton. 1988. The “plucking model” of business fluctuations revisited. Palo Alto, CA, The Hoover Institution, Stanford University, Working Papers in Economics E-88-48, Dec 1988.
Friedman, Milton. 1989. Bimetalism revisited. Palo Alto, CA, The Hoover Institution, Stanford University, Working Papers in Economics E-89-24. Aug 1989.
Friedman, Milton. Franklin D. Roosevelt, Silver and China. Journal of Political Economy 100 (1, Feb): 62-83.
Friedman, Milton and Anna Jacobson Schwartz. 1963. A monetary history of the United States, 1867-1960. Princeton: Princeton University Press.
Friedman, Milton and Anna Jacobson Schwartz. 1963a. Money and business cycles. Review of Economics and Statistics 45, Supplement (Feb): 32-64.
Friedman, Milton and Anna Jacobson Schwartz. 1970. Monetary statistics of the United States: estimates, sources, and methods. New York: Columbia University Press.
Friedman, Milton and Anna Jacobson Schwartz. 1987. Money and business cycles. In Anna Jacobson Schwartz, ed. Money in historical perspective. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
FOMC. 2006Dec12. Meeting of the Federal Open Market Committee December 12, 2006. Washington, DC, Federal Reserve, Dec 12 http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/FOMC20061212meeting.pdf
Gagnon, Joseph, Matthew Raskin, Julie Remache and Brian Sack. 2010. Large-scale asset purchases by the Federal Reserve: did they work. New York, FRBNY Staff Report no. 441, Mar http://data.newyorkfed.org/research/staff_reports/sr441.pdf
Georgescu-Rogen, Nicholas. 1960. Economic theory and agrarian economics. Oxford Economic Papers New Series 12 (1, Feb): 1-40.
Gorton, Gary. 2009EFM. The subprime panic. European Financial Management 15 (1): 10-46.
Graham, Frank D. 1936. Partial reserve money and the 100 per cent proposal. American Economic Review (26, 3): 428-40.
Gorton, Gary and Andrew Metrick. 2010H. Haircuts. Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis Review 92 (6, Nov/Dec): 507-19 http://research.stlouisfed.org/publications/review/10/11/Gorton.pdf
Gorton, Gary and Andrew Metrick. 2010SB. Securitized banking and the run on repo. New Haven, Yale University, 2010, Nov.
Greenspan, Alan. 1996. The challenge of central banking in a democratic society. Washingotn, DC, American Enterprise Institute, Dec 5 http://www.federalreserve.gov/boarddocs/speeches/1996/19961205.htm
Greenspan, Alan. 2004. Risk and uncertainty in monetary policy. American Economic Review 94 (2, May): 33-40. Also available at http://www.federalreserve.gov/boarddocs/speeches/2004/20040103/default.htm
Gürkaynak, Refet S., Brian Sack and Eric T. Swanson. 2005. Do actions speak louder than words? The response of asset prices to monetary policy actions and statements. International Journal of Central Banking 1 (May): 55-93.
Haber, Stephen. 2011. Differential paths of financial development: evidence from new world economies. In Dora L. Costa and Naomi R. Lamoreaux, eds. Understanding long-run economic growth: geography, institutions and the knowledge economy. Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2011, 89-120.
Haberler, Gottfried. 1937. Prosperity and depression. Lake Success, New York: United Nations. http://mises.org/document/4617/
Haddad, Cláudio L. 1974. Growth of Brazilian real output. Chicago, Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Chicago, Jun.
Hamilton, Alexander. 1780. The national Bank. In Henry Cabot Lodge, ed. The works of Alexander Hamilton. New York and London: G. P. Putnam & Sons, 1904: 319-45. http://oll.libertyfund.org/?option=com_staticxt&staticfile=show.php%3Ftitle=1380&chapter=64319&layout=html#a_1594266
Hamilton, James D. and Jing Wu. 2010. The effectiveness of alternative monetary policy tools in a zero lower bound environment. San Diego, University of California San Diego, Nov 3 http://dss.ucsd.edu/~jhamilto/zlb.pdf
Hansen, Alvin H. 1938. Full recovery of stagnation? New York: W. W. Norton & Co., 1938.
Hansen, Alvin H. 1939. Economic progress and declining population growth. American Economic Review 29, 1 (Mar, 1939): 1-15.
Hansen, Alvin H. 1941. Fiscal policy and business cycles. New York: W. W. Norton & Co., 1941.
Harberger, Arnold C. 1971. Three basic postulates for applied welfare economics: an interpretive essay. Journal of Economic Literature 9 (3): 785-97.
Harberger, Arnold C. 1997. New frontiers in project evaluation? World Bank Research Observer 12 (1): 73-9.
Harris, Jennifer M. 2011BA. Benchmark article. Washington, DC, Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/ces/cesbmart.pdf
Hetzel, Robert L. and Ralph F. Leach. 2001. The Treasury-Fed accord: a new narrative account. Federal Reserve Bank of Richmond Economic Quarterly 87 (1, Winter): 33-55.
Hicks, John R. 1935. A suggestion for simplifying the theory of money. Economica NS 2 (5, Feb): 1-19.
Hicks, John R. 1937. Mr. Keynes and the “classics”: a suggested interpretation. Econometrica 5 (2, Apr): 147-59.
Hicks, John R. 1950. A contribution to the theory of the trade cycle. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1950.
Hicks, John R. 1962. Liquidity. Economic Journal 72 (288, Dec): 787-802.
Hicks, John R. 1975. The scope and status of welfare economics. Oxford Economic Papers 27 (3): 307-26.
Imlah, Albert H. 1958. Economic elements in the Pax Britannica. Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1958.
Hallerbach, Winfried G. 2001. Duration and Dimension. Tinbergen Institute Working Paper No. TI 99-047/2, Erasmus University, Amsterdam, the Netherlands http://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/cf_dev/AbsByAuth.cfm?per_id=89567
Ho, Tai-kuang and Cheng-chung Lai. 2012. Silver fetters? The rise and fall of Chinese price level under fluctuating world silver price, 1928-34. Hsinchu, Taiwan, National Tsiang Hua University, Nov http://apebh2013.files.wordpress.com/2013/02/ho-lai-textrv.pdf
Hobbs, Frank and Nicole Stoops. 2002. Demographic trends in the 20th century. Washington, DC, US Government Printing Office http://www.census.gov/prod/2002pubs/censr-4.pdf
Hoover, Ethel D. 1958. Wholesale and retail prices in the nineteenth century. Journal of Economic History 18 (3, Sep): 298-316.
Hoover, Ethel D. 1960. Retail prices after 1850. In Trends in the American economy in the nineteenth century. New York: National Bureau of Economic Research, 1960.
IMF. 2011WEOSep. World economic outlook Sep 11: slowing growth, rising risks. Washington, DC, IMF Sep http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2011/02/pdf/text.pdf
IMF. 2011JSRNov23. Japan sustainability report. Washington, DC, IMF, Nov 23 http://www.imf.org/external/np/country/2011/mapjapanpdf.pdf
IMF. 2012GFSRJan24. Global Financial Stability Report: market update. Washington, DC, IMF, Jan 24 http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fmu/eng/2012/01/index.htm
IMF. 2012FMJan24. Fiscal Monitor Update. Washington, DC, IMF, Jan 24 http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fm/2012/update/01/fmindex.htm
IMF. 2012WEOJan24. World Economic Outlook Update: an update of the key WEO projections. Washington, DC, IMF, Jan 24 http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/update/01/index.htm
IMF. 2012WEOApr. World Economic Outlook April 2012: growth resuming, dangers remains. Washington, DC, IMF, 2012, Apr http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/01/pdf/text.pdf
IMF. 2012GFSRApr. Global financial stability report: the quest for lasting stability. Washington, DC, IMF 2012, Apr http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/gfsr/2012/01/pdf/text.pdf
IMF. 2012FMApr. Fiscal monitor: balancing fiscal policy risks. Washington, DC, IMF, Apr
http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fm/2012/01/pdf/fm1201.pdf
IMFC. 2012Apr20. Joint Statement of the International Monetary and Financial Committee and the Group of 20 Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors on IMF Resources. Washington, DC, IMF, Apr 20 http://www.imf.org/external/np/sec/pr/2012/pr12144.htm
IMFC. 2012Apr21. Communiqué of the Twenty-Fifth Meeting of the IMFC. Washington, DC, IMF, Apr 21 http://www.imf.org/external/np/sec/pr/2012/pr12145.htm
IMF. 2012FSAPJun8. Spain: Financial Stability Assessment. Washington, DC, International Monetary Fund, Jun http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/scr/2012/cr12137.pdf
IMF. 2012FMOct. Fiscal Monitor: taking stock a progress report on fiscal adjustment. Washington, DC, International Monetary Fund, Oct http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fm/2012/02/pdf/fm1202.pdf
IMF. 2012GFSROct. Global Financial and Stability Report: restoring confidence and progressing on reforms. Washington, DC, International Monetary Fund, Oct http://www.imf.org/External/Pubs/FT/GFSR/2012/02/pdf/text.pdf
IMF. 2012WEOOct. World Economic Outlook October 2012: coping with high debt and sluggish growth. Washington, DC, International Monetary Fund, Oct http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/02/pdf/text.pdf
Ingersoll, Jonathan. 1987. Theory of Financial Decision Making. New Jersey: Rowman.
Ireland, Peter N. 1999. Does the time-consistency problem explain the behavior of inflation in the United States. Journal of Monetary Economics 44 (2): 279-91.
Ireland, Peter N. 2003. Implementing the Friedman rule. Review of Economic Dynamics 6(2003): 120-134.
Issa, Darrell E. 2012Aug1. Letter to the Honorable Ben Bernanke. Washington DC, Committee on Oversight and Government Reform, Congress of the United States, House of Representatives, Aug 1 http://online.wsj.com/public/resources/documents/Bernankeletter0812.pdf
Ito, Takatoshi. Interventions and Japanese economic recovery. YenMacro, Michigan 2004 1 http://www.fordschool.umich.edu/rsie/Conferences/CGP/Oct2004Papers/Ito.pdf
Jensen, Michael C. 1993. The modern industrial revolution, exit and the failure of internal control systems. Journal of Finance 48 (3, Jul): 831-80.
Joint Forum of the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision, International Organization of Securities Commissions and the International Association of Supervisors. 2004. Credit risk transfer. BCBS, BIS, Oct. http://www.bis.org/publ/joint10.pdf
Kahil, Raouf. 1973. Inflation and economic development in Brazil. Oxford: Clarendon Press.
Kendall, Maurice G. and Alan Stuart. 1968. The advanced theory of statistics, III. New York: Hafner, 1968.
Kim, Chang-Jin and Charles R. Nelson. 1999. Friedman’s plucking model of business fluctuations: tests and estimates of permanent and transitory components. Journal of Money, Credit and Banking 31 (3, Part 1, Aug): 317-334.
Kohn, Donald L. 2009Apr18. Monetary policy in the financial crisis. Nashville, TN, Conference in Honor of Dewey Daane, Apr 18 http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/kohn20090418a.htm
Kohn, Donald L. 2009Sep10. Comments on “Interpreting the Unconventional US Monetary policy of 2007-2009.” Washington, Brookings Institution, Sep 10 http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/kohn20090910a.htm
Knight, Frank H. 1964. Risk, uncertainty and profit. New York: Reprints of Economic Classics, August M. Kelley, New York.
Krugman, Paul. 1998. It’s baaack: Japan’s slump and the return of the liquidity trap. Brookings Papers on Economic Activity 2 (1998): 137-205.
Krugman, Paul. 2011Jun 18. Mr. Keynes and the moderns. Princeton, Princeton University Jun 18. Prepared for Conference on 75th Anniversary of Keynes’ General Theory, Cambridge, Cambridge University, Jun 19-21 http://www.princeton.edu/~pkrugman/keynes_and_the_moderns.pdf
Krugman, Paul. 2012Apr24. Earth to Ben Bernanke: chairman Bernanke should listen to Professor Bernanke. New York Times Magazine, Apr 24 http://www.nytimes.com/2012/04/29/magazine/chairman-bernanke-should-listen-to-professor-bernanke.html?pagewanted=all
Kuznets, Simon. 1971. Modern economic growth: findings and reflections. Lecture to the memory of Alfred Nobel, Dec 11, 1971 http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/economics/laureates/1971/kuznets-lecture.html
Kydland, Finn E. and Edward C. Prescott. 1977. Rules rather than discretion: the inconsistency of optimal plans. Journal of Political Economy 85 (3, Jun): 473-92.
Lazear, Edward P. 2012Jan19. The jobs picture is still far from rosy. Wall Street Journal, Jan 19 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052970204468004577165292033648810.html
Lazear, Edward P. 2013Jan7. Chinese “currency manipulation” is not the problem. Wall Street Journal, Jan 7 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887323320404578213203581231448.html
Lazear, Edward P. and Spletzer, James R. 2012JHJul22. The United States labor market: status quo or a new normal? Jackson, Hole, WY, Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City Symposium, Sep 1 http://www.kansascityfed.org/publicat/sympos/2012/el-js.pdf
Lazear, Edward P. and James R. Spletzer. 2012Mar. Hiring, churn and the business cycle. Cambridge, MA, NBER, Mar http://www.nber.org/papers/w17910
Lazear, Edward P. and James R. Spletzer. 2012May. Hiring, churn and the business cycle. American Economic Review Papers and Proceedings 102 (May, No. 3): 575-579.
Leff, Nathaniel H. 1975. Review of Inflation and Economic Development in Brazil, 1946-1963 by Raouf Kahil. Journal of Economic Literature 12 (2, Jun): 510-11.
Levin, Andrew and John B. Taylor. 2009. Falling behind the curve: a positive analysis of stop-start monetary policies and the Great Inflation. Cambridge, MA, NBER, Dec.
Lintner, John. 1965. The valuation of risk assets and the selection of risky investments in stock portfolios and capital budgets. Review of Economics and Statistics 47 (1, Feb): 12-37.
Lucas, Robert E. 1975. An equilibrium model of the business cycle. Journal of Political Economy (83, 6): 1113-1144.
Lucas, Robert E. 1976. Econometric policy evaluation: a critique. Carnegie Rochester Conference Series on Public Policy I (1976): 16-46.
Lucas, Robert E. 2004. The industrial revolution: past and future. In Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis 2003Annual Report, May 1, 2004 http://www.minneapolisfed.org/publications_papers/pub_display.cfm?id=3333
Lucas, Robert E. 2011May. The US recession of 2007-201? Washington, University of Washington, Milliman Lecture, May 19 http://www.econ.washington.edu/news/millimansl.pdf
Macaulay, Frederick R. 1938. Some theoretical problems suggested by the movement of interest rates, bond yields and stock prices in the United States since 1856. New York, National Bureau of Economic Research http://papers.nber.org/books/maca38-1
MacFarlane, Helen and Paul Mortimer-Lee. 1994. Inflation over 300 years. Bank of England Quarterly Bulletin, May 1994, 156-162.
McGrattan, Ellen R. 2010. Capital taxation during the US Great Depression. Minneapolis, MN, Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis, Working Paper 670, Oct 2010 http://www.minneapolisfed.org/research/wp/wp670.pdf
Mann, Henry B. 1945. Nonparametric tests against trend. Econometrica 13 (3, Jul): 245-259.
Markowitz, Harry. 1952. Portfolio selection. Journal of Finance 7 (1, Mar): 77-91.
McCallum, Bennett. 1999. Issues in the design of monetary policy rules. In John B. Taylor and Michael Woodford, eds. Handbook of Macroeconomics Volume 1A. Amsterdam: Elsevier North Holland.
McKinnon, Ronald I. 1973. Money and Capital in Economic Development. Washington, DC: Brookings Institution.
McKinnon, Ronald I. 2011Dec18. Oh, for Alexander Hamilton to save Europe! Financial Times, Dec 18 http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/811611d6-273a-11e1-b7ec-00144feabdc0.html#axzz1gzoHXOj6
McKinnon, Ronald I. 2013Oct27. Tapering without tears—how to end QE3. Wall Street Journal, Oct 27.
McKinsey & Co. 2007. Sustaining New York and the US’ global financial services leadership. New York: McKinsey & Co.
Meltzer, Allan H. 2005. Origins of the Great Inflation. Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis Review 87 (2, Part 2, Mar/Apr): 145-72.
Meltzer, Allan H. 2004. A history of the federal reserve, Volume 1: 1913-1951. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Meltzer, Allan H. 2010a. A history of the Federal Reserve, Volume 2, Book 1, 1951-1969. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Meltzer, Allan H. 2010b. A history of the Federal Reserve, Volume 2, Book 2, 1970-1986. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Metzler, Lloyd A. The nature and stability of inventory cycles. 1941. Review of Economics and Statistics 23 (3, Aug): 113-29.
Merton, Robert C. 1973. Theory of rational option pricing. Bell Journal of Economics and Management Science 4 (1, Spring): 141-83.
Merton, Robert C. 1974. On the pricing of corporate debt: the risk structure of interest rates. Journal of Finance 29 (2, May): 449-70.
Merton, Robert C. 1998. Applications of option-pricing theory: twenty-five years later. American Economic Review 88 (3): 323-49.
Meulendyke, Ann-Marie. 1998. U.S. monetary policy and financial markets. New York: Federal Reserve Bank of New York http://www.newyorkfed.org/education/addpub/monpol/
Modigliani, Franco and Richard Sutch. 1966. Innovations in interest rate policy. American Economic Review 56 (1/2, Mar): 178-97.
Modigliani, Franco and Richard Sutch. 1967. Debt management and the term structure of interest rates: an empirical analysis of recent experience. Journal of Political Economy 75 (4, Aug): 569-89.
Mossin, Jan. 1966. 1966. Equilibrium in a capital asset market. Econometrica 34 (4, Oct): 768-83.
Mundell, Robert A. 1963. Capital mobility and stabilization policy under fixed and flexible exchange rates. Canadian Journal of Economics and Political Science 29 (4): 475-85.
North, Douglass C. 1994. Economic performance through time. American Economic Review 84 (3): 359-68.
North, Douglass C. and Barry R. Weingast. 1989. Constitutions and commitments: the evolution of institutional governing public choice in seventeenth-century England. Journal of Economic History 49 (4): 803-32.
Nurkse, Ragnar. 1944. International currency experience: lessons of the interwar experience. Geneva, League of Nations.
Nurkse, Ragnar. 1959. Patterns of trade and development. Stockholm: Almquist & Wicksell.
O’Donoghue, Jim and Louise Goulding, 2004. Consumer Price Inflation since 1750. UK Office for National Statistics Economic Trends 604, Mar 2004, 38-46.
Pelaez, Carlos A. 2008. The reform of Alexander Hamilton. Philadelphia, University of Pennsylvania Law School, Unpublished manuscript.
Pelaez, Carlos M. and Carlos A. Pelaez. 2005. International Financial Architecture. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. http://us.macmillan.com/QuickSearchResults.aspx?search=pelaez%2C+carlos&ctl00%24ctl00%24cphContent%24ucAdvSearch%24imgGo.x=26&ctl00%24ctl00%24cphContent%24ucAdvSearch%24imgGo.y=14 http://www.amazon.com/Carlos-Manuel-Pel%C3%A1ez/e/B001HCUT10
Pelaez, Carlos M. and Carlos A. Pelaez. 2007. The Global Recession Risk. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. http://www.amazon.com/Carlos-Manuel-Pel%C3%A1ez/e/B001HCUT10
Pelaez, Carlos M. and Carlos A. Pelaez. 2008a. Globalization and the State: Vol. I. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. http://www.amazon.com/Carlos-Manuel-Pel%C3%A1ez/e/B001HCUT10
Pelaez, Carlos M. and Carlos A. Pelaez. 2008b. Globalization and the State: Vol. II. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.
Pelaez, Carlos M. and Carlos A. Pelaez. 2008c. Government Intervention in Globalization. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. http://www.amazon.com/Carlos-Manuel-Pel%C3%A1ez/e/B001HCUT10
Pelaez, Carlos M. and Carlos A. Pelaez. 2009a. Financial Regulation after the Global Recession. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan. http://www.amazon.com/Carlos-Manuel-Pel%C3%A1ez/e/B001HCUT10
Pelaez, Carlos M. and Carlos A. Pelaez. 2009b. Regulation of Banks and Finance. Basingstoke: Palgrave Macmillan.http://www.amazon.com/Carlos-Manuel-Pel%C3%A1ez/e/B001HCUT10
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel. 1968. The State, the Great Depression and the Industrialization of Brazi. New York, PhD Dissertation, Columbia University in the City of New York, Jun.
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel. 1968b. A Balança Comercial, a Grande Depressão e a Industrialização Brasileira. Revista Brasileira de Economia 22 (1, Jan/Mar): 15-47.
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel 1971. Análise econômica do programa brasileiro de sustentação do café—1906-1945. Revista Brasileira de Economia 25 (4, Out/Dez): 5-211.
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel. 1972. História da Industrialização Brasileira. Rio de Janeiro: APEC.
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel, ed. 1973. Essays on Coffee and Economic Development. Rio de Janeiro, IBC, 1973. Portuguese edition: Ensaios sobre Café e Desenvolvimento Econômico. Rio de Janeiro: Instituto Brasileiro do Café, 1973.
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel. 1974. Long-run Monetary Behavior and Institutions in an Underdeveloped Economy, 1800-1971. Copenhaguen, Paper Presented at the VI International Congress on Economic History, Session on Monetary Inflation in Historical Perspective, International Economic History Association, Aug 22.
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel. 1975. The Establishment of Banking Institutions in a Backward Economy: Brazil, 1800-1851. Business History Review 49 (4, Winter): 446-472.
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel. 1976a. The Theory and Reality of Imperialism in the Coffee Economy of Nineteenth-Century Brazil. Economic History Review 29, Second Series (May): 276-294.
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel. 1976b. A Comparison of Long-term Monetary Behavior and Institutions in Brazil, Europe and the United States. Journal of European Economic History 5 (2, Fall): 439-450.
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel. 1977. World War I and the Economy of Brazil: Some Evidence from Monetary Statistics. Journal of Interdisciplinary History (7, Apr): 683-680.
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel. 1979. História Econômica do Brasil: Um Elo entre a Teoria e a Realidade Econômica. São Paulo: Editora Atlas.
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel. 1986. O Cruzado e o Austral: Análise das Reformas Monetárias do Brasil e da Argentina. São Paulo: Editora Atlas.
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel. 1987. Economia Brasileira Contemporânea: Origens e Conjuntura Atual. São Paulo: Editora Atlas.
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel and Wilson Suzigan. 1978. Economia Monetária: Teoria, Política e Evidência Empírica. São Paulo, Atlas.
Pelaez, Carlos Manuel and Wilson Suzigan. 1981. História Monetária do Brasil Segunda Edição. Coleção Temas Brasileiros. Brasília: Universidade de Brasília.
Phelps, Edmund S. 1968. Money-wage dynamics and labor market equilibrium. Journal of Political Economy 76 (4, 2, Jul-Aug): 678-711.
Pinto, Edward J. 2008. Statement. Washington, DC, US House of Representatives, Committee on Oversight and Government Reform, Dec 9.
Pozsar, Zoltan, Adrian Tobias, Adam Ashcraft and Hayley Boesky. 2012RFeb. Shadow banking. New York: Federal Reserve Bank of New York, Staff Report No. 458, Revised Feb 2012 http://www.newyorkfed.org/research/staff_reports/sr458.pdf
Prescott, Edward C. and Lee E. Ohanian. 2014Feb. US productivity growth has taken a dive. Wall Street Journal, Feb 4 http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702303942404579362462611843696?KEYWORDS=Prescott
Prescott, Edward C. and Lee E. Ohanian. 2014Jun. Behind the productivity plunge: fewer startups. Wall Street Journal, Jun 25 http://online.wsj.com/articles/behind-the-productivity-plunge-fewer-startups-1403737197?KEYWORDS=Prescott
Reinhart, Carmen M. and Kenneth Rogoff. 2010GTD. Growth in a time of debt. American Economic Review 100 (2): 1-9.
Rajan, Raghuram G. 2004. Remarks. Sydney, Australia, Australasian Finance and Banking Conference, Dec 15.
Rajan, Raghuram G. 2005. Has financial development made the world riskier? Jackson Hole, WY, Symposium sponsored by the Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City. http://www.kc.frb.org/publicat/sympos/2005/PDF/Rajan2005.pdf
Rajan, Raghuram G. 2012May8. Stop beating up on Ben Bernanke. Financial Times, May 8 http://blogs.ft.com/the-a-list/2012/05/08/stop-beating-up-on-ben-bernanke/
Rajan, Raghuram G. 2012FA. The true lessons of the recession: the West can’t borrow and spend its way to recovery. Foreign Affairs 91 (May/June, 3): 69-79.
Rajan, Raghuram G. 2014Apr10. Competitive monetary easing: is it yesterday once more? Washington DC, Brookings Institution, Apr 10 http://www.brookings.edu/~/media/events/2014/04/10%20global%20monetary%20policy%20hutchins/rajan_remarks_at_brookings.pdf
Rajan, Raghuram G. and Luigi Zingales. 2001. The influence of the financial revolution on the nature of the firm. American Economic Review 91 (2): 206-11.
Robinson, Joan. 1947. Beggar-my-neighbour remedies for unemployment. In Joan Robinson, Essays in the Theory of Employment, Oxford, Basil Blackwell, 1947.
Reinhart, Carmen M. 2010CB. This time is different chartbook: country histories on debt, default and financial crises. Cambridge, MA, NBER WP 15815, Mar http://www.nber.org/papers/w15815
Reinhart, Carmen M. and Vincent R. Reinhart. 2011Feb. Pride goes before a fall: Federal Reserve policy and asset markets. Cambridge, MA, NBER WP 16815, Feb http://www.nber.org/papers/w16815
Reinhart, Carmen M. and Vincent R. Reinhart. 2010AF. After the fall. Cambridge, MA, NBER WP 16634, Sep http://www.nber.org/papers/w16334
Reinhart Carmen M., Kenneth S. Rogoff and Miguel A. Savastano. 2003. Debt intolerance. Brookings Papers on Economic Activity 1 (2003): 1-74.
Reinhart, Carmen M. and Kenneth S. Rogoff. 2008TDPV. This time is different: a panoramic view of eight centuries of financial crises. Cambridge, MA, WP 13882, Mar http://www.nber.org/papers/w13882
Reinhart, Carmen M. and Kenneth S. Rogoff. 2009AFC. The aftermath of financial crises. Cambridge, MA, WP 14656, Jan http://www.nber.org/papers/w14656
Reinhart, Carmen M. and Kenneth Rogoff. 2009TD. This time is different: eight centuries of financial folly. Princeton: Princeton University Press http://www.amazon.com/This-Time-Different-Centuries-Financial/dp/0691142165/ref=pd_sim_b_6
Reinhart, Carmen M. and Kenneth Rogoff. 2010GTD. Growth in a time of debt. American Economic Review 100 (2): 1-9.
Reinhart, Carmen M. and Kenneth S. Rogoff. 2010FCDC. From financial crash to debt crisis. Cambridge, MA, NBER WP 15795, Mar http://www.nber.org/papers/w15795 forthcoming in American Economic Review http://www.aeaweb.org/forthcoming/output/acceptedAER.php
Reinhart, Carmen M. and Kenneth S. Rogoff. 2011CEPR. A decade of debt. Washington, DC, Center for Economic and Policy Research, Discussion Paper No. 8310, Apr. Cambridge, MA, NBER WP 16827, Feb http://www.nber.org/papers/w16827
Reinhart, Carmen M. and Kenneth S. Rogoff. 2011EJ. The forgotten history of domestic debt. Economic Journal 121 (May): 319-350.
Reinhart, Carmen M. and Kenneth S. Rogoff. 2011Jul14. Debt endangers growth. Bloomberg, Jul14 http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2011-07-14/too-much-debt-means-economy-can-t-grow-commentary-by-reinhart-and-rogoff.html
Reinhart, Carmen M. and M. Belen Sbrancia. 2011LD. The liquidation of government debt. Cambridge, MA, NBER WP 16893, Mar http://www.nber.org/papers/w16893
Reinhart, Carmen M. and Kenneth S. Rogoff. 2012Oct14. This time is different, again? The United States five years after the onset of subprime. Cambridge, MA, Harvard University, Oct 14 http://www.economics.harvard.edu/faculty/rogoff/files/Is_US_Different_RR_3.pdf
Rogoff, Kenneth. 2002MF. Dornbusch’s overshooting model after twenty-five years. Washington, DC, IMF, Mundell-Fleming Lecture http://www.imf.org/external/np/speeches/2001/kr/112901.pdf
Roll, Richard. 1977. A critique of the asset pricing theory’s tests. Part I: on past and potential testability of the theory. Journal of Financial Economics 4 (2, Mar): 129-76.
Romer, Christina D. 1992. What ended the Great Depression? Journal of Economic History 52 (4, Dec): 757-84.
Romer, Christina D. 2009. Lessons from the New Deal. Washington DC, Testimony of Christina D. Romer, Chair, President’s Council of Economic Advisers, Before the Economic Policy Subcommittee, Senate Committee on Banking, Housing and Urban Affairs, Mar 31 http://www.whitehouse.gov/assets/documents/Testimony_of_Christina_D.pdf
Romer, Christina D. and David H. Romer. 2004. A new measure of monetary shocks: derivation and implications. American Economic Review 94 (4, Sep): 1055-84.
Rubin, Robert. 2014Jan8. Sound government finances will promote recovery. Financial Times, Jan 8.
Samuelson, Paul A. 1965. Proof that properly anticipated stock prices fluctuate randomly. Industrial Management Review 6 (2): 41-9.
Samuelson, Paul A. 1974. Lessons from the current economic expansion. American Economic Review 64 (2, May): 75-7.
Sargent, Thomas J. 1983. The end of four big inflations. In Robert E. Hall, ed. Inflation: causes and effects. Chicago: Chicago University Press.
Sargent, Thomas J. and Christopher A. Sims. 1977. Business cycle modelling without pretending to have too much a priori economic theory. In Christopher A. Sims, ed. New methods in business cycle research. Minneapolis: Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis.
Sargent, Thomas J. and Neil Wallace. 1973. The stability of models of money and growth with perfect foresight. Econometrica 41 (6, Nov): 1043-8.
Sargent, Thomas J. and Neil Wallace. 1981. Some unpleasant monetarist arithmetic. Federal Reserve Bank of Minneapolis Quarterly Review 5 (3, Fall): 1-17.
Sargent, Thomas J. and William L. Silber. 2012Mar20. The challenges of the Fed’s bid for transparency. Financial Times, Mar 20 http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/778eb1ce-7288-11e1-9c23-00144feab49a.html#axzz1pexRlsiQ
Schumpeter, Joseph A. 1939. Business cycles: a theoretical, historical and statistical analysis of the capitalist process. New York and London: McCraw Hill Book Company.
Seers, Dudley. 1962. A theory of inflation and growth in under-developed economies based on the experience of Latin America. Oxford Economic Papers New Series 14 (Jun, 2): 173-95.
Seligman, Edwin R. A. 1908. The crisis of 1907 in the light of history. Introduction to The currency problem and the present financial situation. New York: Columbia University Press http://fraser.stlouisfed.org/docs/publications/books/currencyprob/1908currencyproblem_introduction.pdf
Sharpe, William F. 1964. Capital asset prices: a theory of market equilibrium under conditions of risk. Journal of Finance 19 (3, Sep): 425-42.
Shaw, Edward S. 1973. Financial Deepening in Economic Development. New York: Oxford University Press.
Shultz, George P., Michael J. Boskin, John F. Cogan, Allan H. Meltzer and John B. Taylor. 2012. The magnitude of the mess we’re in. Wall Street Journal, Sep 16, 2012 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052702303561504577497442109193610.html?mod=WSJ_hps_sections_opinion
Simons, Henry C. 1936. Rules versus authorities in monetary policy. Journal of Political Economy 44 (1, Feb): 1-30.
Simons, Henry C. 1942. Hansen on fiscal policy. Journal of Political Economy 50 (2, Apr): 161-96.
Simons, Henry C. 1948. Economic Policy for a free society. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Sims, Christopher A. 1972. Money, income and causality. American Economic Review 62 (4, Sep): 540-52.
Singer, Hans W. 1950. The distribution of gains between investing and borrowing countries. American Economic Review 40 (2, May): 473-485.
Smith, Jessica C. and Carla Medalia. 2014. Health insurance coverage in the United States: 2013. US Current Population Reports, P60-250, US Census Bureau. Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office, Sep 18.
Smith, Jessica C. and Carla Medalia. 2015. Health insurance coverage in the United States: 2014. US Current Population Reports, P60-253, US Census Bureau. Washington, DC: US Government Printing Office, Sep.
Standard & Poor’s Rating Services (S&PRS). 2012Jan13. Standard & Poor’s takes various rating actions on 16 eurozone sovereign governments. Frankfurt, S&P Rating Services, Jan 13 http://www.standardandpoors.com/ratings/articles/en/us/?articleType=HTML&assetID=1245327294763
Standard & Poor’s Rating Services (S&PRS). 2012Jan16. European Financial Stability Facility long-term Ratings Cut to ‘AA+’; short-term ratings affirmed; outlook developing. Frankfurt, S&P Rating Services, Jan 16 http://www.standardandpoors.com/ratings/articles/en/us/?articleType=HTML&assetID=1245327337060
Stein, Stanley J. and Barbara H. Stein. 1970. The colonial heritage of Latin America. New York and London: Oxford University Press.
Summerhill, Jr., William R. 2007SC. Sovereign credibility with financial underdevelopment. Palo Alto, CA, Hoover Seminar on Collective Choice, Mar 6.
Summerhill, Jr., William R. 2007IR. Inglorious revolution: political institutions, sovereign debt and financial underdevelopment in Imperial Brazil. Los Angeles, CA, UCLA, Book Manuscript.
Summerhill, William R. 2015. Inglorious revolution: political institutions, sovereign debt, and financial underdevelopment in Brazil. New Haven, CT, Yale University Press https://yalepress.yale.edu/yupbooks/book.asp?isbn=9780300139273
Summers, Lawrence H. 2013Nov8. Presentation. Washington, DC, IMF Fourteenth Annual Research Conference in Honor of Stanley Fischer, IMF, Nov 8 http://larrysummers.com/imf-fourteenth-annual-research-conference-in-honor-of-stanley-fischer/
Svensson, Lars E. 2003. What is wrong with Taylor rules? Using judgment in monetary policy through targeting rules. Journal of Economic Literature 41 (2 Jun): 426–77.
Svensson, Lars E. 2003LT. Escaping from a liquidity trap and deflation: the foolproof way and others. Journal of Economic Perspectives 17 (4, Autumn): 145-66.
Swanson, Eric T. 2011Mar. Let’s twist again: a high-frequency event-study analysis of operation twist and its implication for QE2. Forthcoming in Brookings Papers on Economic Activity http://www.brookings.edu/~/media/Files/Programs/ES/BPEA/2011_spring_bpea_papers/2011_spring_bpea_conference_swanson.pdf
Taylor, Alan M. 2012. The great leveraging. Basel, Switzerland, Bank for International Settlements, Jul http://www.bis.org/events/conf120621/taylor.pdf
Taylor, John B. 1993. Discretion versus policy rules in practice. Carnegie-Rochester Conference Series on Public Policy 39 (1993): 195-214.
Taylor, John B. 1997. Comment. In Christina Romer and David Romer, eds. Reducing inflation: motivation and strategy. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Taylor, John B. 1998LB. Monetary policy and the long boom. Federal Reserve Bank of St. Louis Review (Nov-Dec): 3-11.
Taylor, John B. 1999. An historical analysis of monetary policy rules. In John B. Taylor, ed. Monetary policy rules. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Taylor, John B. 2007JH. Housing and monetary policy. Jackson Hole, WY, Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City Symposium http://www.kansascityfed.org/PUBLICAT/SYMPOS/2007/PDF/Taylor_0415.pdf
Taylor, John B. 2008Nov. The financial crisis and the policy responses: an empirical analysis of what went wrong. Bank of Canada, Nov 2008 http://www.stanford.edu/~johntayl/Onlinepaperscombinedbyyear/2008/The_Financial_Crisis_and_the_Policy_Responses_An_Empirical_Analysis_of_What_Went_Wrong.pdf
Taylor, John B. 2009. Getting off track: how government actions and interventions caused, prolonged, and worsened the financial crisis. Stanford, CA, Hoover Institution Press.
Taylor, John B. 2012FP. First principles: five keys to restoring America’s prosperity. New York: W. W. Norton.
Taylor, John B. 2012Mar27. Testimony before the Joint Economic Committee at the Hearing on “Monetary Policy Going Forward: Why a Sound Dollar Boosts Growth and Employment.” Washington, DC, JEC, Mar 27 http://jec.senate.gov/republicans/public/?a=Files.Serve&File_id=f002b5f0-9fc0-45f9-9d53-e563137c040e
Taylor, John B. 2012Mar28. The dangers of an interventionist Fed. Wall Street Journal, Mar 28 http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052702303816504577307403971824094.html?mod=WSJ_hps_sections_opinion
Taylor, John B. 2012JMCB. Monetary policy rules work and discretion doesn’t: a tale of two eras. Palo Alto, CA, Stanford University, Mar 2012, forthcoming in the Journal of Money, Credit and Banking, 2012 http://www.stanford.edu/~johntayl/JMCB%20lecture.pdf
Taylor, John B. 2012Oct25. An unusually weak recovery as usually defined. Economics One, A Blog by John B. Taylor, Oct 25 http://www.johnbtaylorsblog.blogspot.co.uk/2012/10/an-unusually-weak-recovery-as-usually.html
Taylor, John B. 2013Oct28. Economic failure causes political polarization. Wall Street Journal, Oct 28.
Taylor, John B. 2014Jan01. The economic Hokum of “Secular Stagnation.” Wall Street Journal, Jan 1 http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702304858104579263953449606842?KEYWORDS=john+b+taylor
Taylor, John B. 2014Jan3. The role of policy in the Great Recession and the weak recovery. Palo Alto, Stanford University, prepared for Allied Social Science Associations, Recessions and Recoveries, American Economic Association, Philadelphia, Jan 3 http://www.aeaweb.org/aea/2014conference/program/preliminary.php?search_string=taylor&search_type=last_name&association=&jel_class=&search=Search#search_box
Taylor, Jonn B. 2014Jun26. The Fed needs to return to monetary rules, Wall Street Journal, Jun 26 http://online.wsj.com/articles/john-taylor-the-fed-needs-to-return-to-monetary-rules-1403823464?KEYWORDS=john+b+taylor
Taylor, John B. 2014Jul15. How to spark another ‘Great Moderation,” Wall Street Journal, Jul 15 http://online.wsj.com/articles/john-taylor-how-to-spark-another-great-moderation-1405469227?KEYWORDS=john+b+taylor
Taylor, John B. and John C. Williams. 2010. Simple and robust rules for monetary policy. In Benjamin Friedman and Michael Woodford, eds. Handbook of monetary economics Volume 3B. Amsterdam: Elsevier North Holland.
Temin, Peter. 1997. Two views of the British industrial revolution. Journal of Economic History 57 (1, Mar): 63-82.
Tobias, Adrian and Adam B. Aschraft. 2012Apr. Shawdow banking regulation. New York, Federal Reserve Bank of New York, Staff Report No. 559, Apr http://www.newyorkfed.org/research/staff_reports/sr559.pdf
Tobin, James. 1958. Liquidity preference as behavior toward risk. Review of Economic Studies 26 (Feb): 65-86.
Tobin, James. 1961. Money, capital, and other stores of value. American Economic Review 51 (2, May): 26-37.
Tobin, James. 1969. A general equilibrium approach to monetary theory. Journal of Money, Credit and Banking 1 (1, Feb): 15-29.
Tobin, James. 1974. Monetary policy in 1974 and beyond. Brookings Papers on Economic Activity 1 (1974): 219-32.
Treynor, Jack L. 1962. Toward a theory of market value of risky assets, unpublished manuscript, 1962, provided by Craig W. French, http://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=628187
Vayanos, Dimitri and Jean-Luc Vila. 2009. A preferred-habitat model of the term structure of interest rates. New Orleans, AFA Meetings Paper, Nov 1. http://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=971439
Vilela Luz, Nícia. 1961. A luta pela industrialização do Brasil (1808 a 1930). São Paulo: Difusão Europeia do Livro.
Vilela Luz, Nicia and Carlos Manuel Peláez. 1972. Economia e história: o encontro dos dois campos de conhecimento. Revista Brasileira de Economia 26 (3, Jul/Sep): 273-301.
Villela, Annibal V. and Wilson Suzigan. 1973. Política do governo e crescimento da economia brasileira. Rio de Janeiro: IPEA/INPES.
Viner, Jacob. 1937. Studies in the theory of international trade. New York: Harper and Brothers, 1965. Available at http://oll.libertyfund.org/?option=com_staticxt&staticfile=show.php%3Ftitle=1414
Wallis, W. Allen and Geoffrey H. Moore. 1941. A significance test for time series and other ordered observations. New York: National Bureau of Economic Research, 1941.
Williams, David, C.A. E. Goodhart and D. H. Gowland. 1976. Money, income and causality: the UK experience. American Economic Review 66 (3, Jun): 417-23.
Winston, Clifford. 2006. Government failure versus market failure. Washington, DC: American Enterprise Institute/Brookings Joint Center for Regulatory Studies, Brookings Institution Press.
Wolf, Martin. 2012Oct23. A slow convalescence under Obama. Financial Times, Oct 23, 2012 http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/791fc13a-1c57-11e2-a63b-00144feabdc0.html#axzz2AotsUk1q
Wriston, Walter B. 1982. Banking against disaster. New York Times, Sep 14.
Yellen, Janet L. 2011AS. The Federal’s Reserve’s asset purchase program. Denver, Colorado, Allied Social Science Association Annual Meeting, Jan 8 http://federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20110108a.pdf
Yellen, Janet L. 2013Nov14. Testimony. Washington, DC. Committee on Banking, Housing and Urban Affairs, US Senate, Nov 14 http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20131114a.htm
Yellen, Janet L. 2014Jul15. Semiannual Monetary Policy Report to Congress. Washington DC, US Senate, Committee on Banking, Housing and Urban Affairs, Jul 15 2014 http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20140715a.htm
Yellen, Janet L. 20014Aug22. Labor market dynamics and monetary policy. Jackson Hole, WY, Federal Reserve Bank of Kansas City Economic Symposium, Aug 22 http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20140822a.htm
Zingales, Luigi. 2000. In search of new foundations. Journal of Finance 55 (4, Aug): 1623-54.
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014, 2015, 2016.

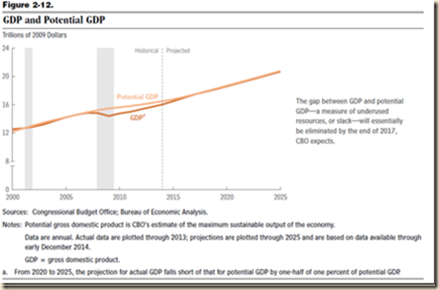

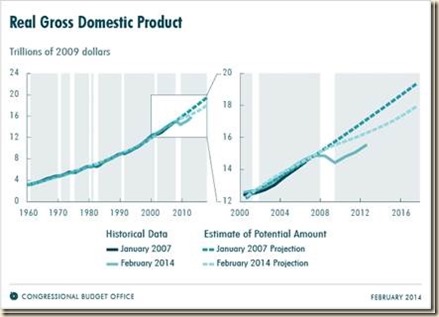

No comments:
Post a Comment