Recovery without Hiring, United States International Trade Deficit and Fiscal Imbalance, Collapse of United States Dynamism of Income Growth and Employment Creation, International Financial Turbulence and the Global Recession Risk
Carlos M. Pelaez
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2010, 2011, 2012
Executive Summary
IA Recovery without Hiring
IA1 Hiring Collapse
IA2 Labor Underutilization
IA3 Ten Million Fewer Full-time Job
IA4 Youth and Middle-Aged Unemployment
IB Collapse of United States Dynamism of Income Growth and Employment Creation
II United States International Trade
IIA United States International Trade Deficit and Fiscal Imbalance
IIB Import Export Prices
III World Financial Turbulence
IIIA Financial Risks
IIIE Appendix Euro Zone Survival Risk
IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation
V World Economic Slowdown
VA United States
VB Japan
VC China
VD Euro Area
VE Germany
VF France
VG Italy
VH United Kingdom
VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets
VII Economic Indicators
VIII Interest Rates
IX Conclusion
References
Appendixes
Appendix I The Great Inflation
IIIB Appendix on Safe Haven Currencies
IIIC Appendix on Fiscal Compact
IIID Appendix on European Central Bank Large Scale Lender of Last Resort
IIIG Appendix on Deficit Financing of Growth and the Debt Crisis
IIIGA Monetary Policy with Deficit Financing of Economic Growth
IIIGB Adjustment during the Debt Crisis of the 1980s
Executive Summary
ESI Recovery without Hiring. Professor Edward P. Lazear (2012Jan19) at Stanford University finds that recovery of hiring in the US to peaks attained in 2007 requires an increase of hiring by 30 percent while hiring levels have increased by only 4 percent since Jan 2009. The high level of unemployment with low level of hiring reduces the statistical probability that the unemployed will find a job. According to Lazear (2012Jan19), the probability of finding a new job currently is about one third of the probability of finding a job in 2007. Improvements in labor markets have not increased the probability of finding a new job. Lazear (2012Jan19) quotes an essay coauthored with James R. Spletzer forthcoming in the American Economic Review on the concept of churn. A dynamic labor market occurs when a similar amount of workers is hired as those who are separated. This replacement of separated workers is called churn, which explains about two-thirds of total hiring. Typically, wage increases received in a new job are higher by 8 percent. Lazear (2012Jan19) argues that churn has declined 35 percent from the level before the recession in IVQ2007. Because of the collapse of churn there are no opportunities in escaping falling real wages by moving to another job. As this blog argues, there are meager chances of escaping unemployment because of the collapse of hiring and those employed cannot escape falling real wages by moving to another job (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/11/twenty-eight-million-unemployed-or.html). Lazear and Spletzer (2012Mar, 1) argue that reductions of churn reduce the operational effectiveness of labor markets. Churn is part of the allocation of resources or in this case labor to occupations of higher marginal returns. The decline in churn can harm static and dynamic economic efficiency. Losses from decline of churn during recessions can affect an economy over the long-term by preventing optimal growth trajectories because resources are not used in the occupations where they provide highest marginal returns. Lazear and Spletzer (2012Mar 7-8) conclude that: “under a number of assumptions, we estimate that the loss in output during the recession [of 2007 to 2009] and its aftermath resulting from reduced churn equaled $208 billion. On an annual basis, this amounts to about .4% of GDP for a period of 3½ years.”
There are two additional facts discussed below: (1) there are about ten million fewer full-time jobs currently than before the recession of 2008 and 2009; and (2) the extremely high and rigid rate of youth unemployment is denying an early start to young people ages 16 to 24 years while unemployment of ages 45 years or over has swelled.
An important characteristic of the current fractured labor market of the US is the closing of the avenue for exiting unemployment and underemployment normally available through dynamic hiring. Another avenue that is closed is the opportunity for advancement in moving to new jobs that pay better salaries and benefits again because of the collapse of hiring in the United States. Those who are unemployed or underemployed cannot find a new job even accepting lower wages and no benefits. The employed cannot escape declining inflation-adjusted earnings because there is no hiring. The objective of this section is to analyze hiring and labor underutilization in the United States.
An appropriate measure of job stress is considered by Blanchard and Katz (1997, 53):
“The right measure of the state of the labor market is the exit rate from unemployment, defined as the number of hires divided by the number unemployed, rather than the unemployment rate itself. What matters to the unemployed is not how many of them there are, but how many of them there are in relation to the number of hires by firms.”
The natural rate of unemployment and the similar NAIRU are quite difficult to estimate in practice (Ibid; see Ball and Mankiw 2002).
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) created the Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey (JOLTS) with the purpose that (http://www.bls.gov/jlt/jltover.htm#purpose):
“These data serve as demand-side indicators of labor shortages at the national level. Prior to JOLTS, there was no economic indicator of the unmet demand for labor with which to assess the presence or extent of labor shortages in the United States. The availability of unfilled jobs—the jobs opening rate—is an important measure of tightness of job markets, parallel to existing measures of unemployment.”
The BLS collects data from about 16,000 US business establishments in nonagricultural industries through the 50 states and DC. The data are released monthly and constitute an important complement to other data provided by the BLS (see also Lazear and Spletzer 2012Mar, 6-7).
Hiring in the nonfarm sector (HNF) has declined from 63.8 million in 2006 to 50.1 million in 2011 or by 13.7 million while hiring in the private sector (HP) has declined from 59.5 million in 2006 to 46.9 million in 2011 or by 12.6 million, as shown in Table ESI-1. The ratio of nonfarm hiring to employment (RNF) has fallen from 47.2 in 2005 to 38.1 in 2011 and in the private sector (RHP) from 52.1 in 2006 to 42.9 in 2011. The collapse of hiring in the US has not been followed by dynamic labor markets because of the low rate of economic growth of 2.2 percent in the first thirteen quarters of expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2012 compared with 6.2 percent in prior cyclical expansions (see table I-5 in http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/10/mediocre-and-decelerating-united-states.html).
Table ESI-1, US, Annual Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF) and Total Private Hiring (HP) in the US and Percentage of Total Employment
| HNF | Rate RNF | HP | Rate HP | |
| 2001 | 62,948 | 47.8 | 58,825 | 53.1 |
| 2002 | 58,583 | 44.9 | 54,759 | 50.3 |
| 2003 | 56,451 | 43.4 | 53,056 | 48.9 |
| 2004 | 60,367 | 45.9 | 56,617 | 51.6 |
| 2005 | 63,150 | 47.2 | 59,372 | 53.1 |
| 2006 | 63,773 | 46.9 | 59,494 | 52.1 |
| 2007 | 62,421 | 45.4 | 58,035 | 50.3 |
| 2008 | 55,166 | 40.3 | 51,606 | 45.2 |
| 2009 | 46,398 | 35.5 | 43,052 | 39.8 |
| 2010 | 48,647 | 37.5 | 44,826 | 41.7 |
| 2011 | 50,083 | 38.1 | 46,869 | 42.9 |
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Chart ESI-1 provides the yearly levels of total nonfarm hiring (NFH) in Table I-1. The fall of hiring during the contraction of 2007 to 2009 was much stronger than in the shallow recession of 2001 with GDP contraction of only 0.4 percent from Mar 2001 (IQ2001) to Dec 2001 (IVQ 2001) compared with 4.7 percent contraction in the much longer recession from Dec 2007 (IVQ2007) to Jun 2009 (IIQ2009) (http://www.nber.org/cycles/cyclesmain.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/10/mediocre-and-decelerating-united-states.html). Recovery is tepid.
Chart ESI-1, US, Level Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF), Annual, 2001-2011
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Chart ESI-2 shows the ratio or rate of nonfarm hiring to employment (RNF) that also fell much more in the recession of 2007 to 2009 than in the shallow recession of 2001. Recovery is weak.
Chart ESI-2, US, Rate Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF), Annual, 2001-2011
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Yearly percentage changes of total nonfarm hiring (HNF) are provided in Table ESI-2. There were much milder declines in 2002 of 6.9 percent and 3.6 percent in 2003 followed by strong rebounds of 6.9 percent in 2004 and 4.6 percent in 2005. In contrast, the contractions of nonfarm hiring in the recession after 2007 were much sharper in percentage points: 2.1 in 2007, 11.6 in 2008 and 15.9 percent in 2009. On a yearly basis, nonfarm hiring grew 4.8 percent in 2010 relative to 2009 and 3.0 percent in 2011.
Table ESI-2, US, Annual Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF), Annual Percentage Change, 2001-2011
| Year | Annual |
| 2002 | -6.9 |
| 2003 | -3.6 |
| 2004 | 6.9 |
| 2005 | 4.6 |
| 2006 | 1.0 |
| 2007 | -2.1 |
| 2008 | -11.6 |
| 2009 | -15.9 |
| 2010 | 4.8 |
| 2011 | 3.0 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Chart ESI-3 plots yearly percentage changes of nonfarm hiring. Percentage declines after 2007 were quite sharp.
Chart ESI-3, US, Annual Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF), Annual Percentage Change, 2001-2011
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Total private hiring (HP) yearly data are provided in Chart ESI-4. There has been sharp contraction of total private hiring in the US and only milder recovery in 2011 than in 2010.
Chart ESI-4, US, Total Private Hiring Level, Annual, 2001-2011
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Chart ESI-5 plots the rate of total private hiring relative to employment (RHP). The rate collapsed during the global recession after 2007 with insufficient recovery.
Chart ESI-5, US, Rate Total Private Hiring, Annual, 2001-2011
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Total nonfarm hiring (HNF), total private hiring (HP) and their respective rates are provided for the month of Sep in the years from 2001 to 2012 in Table ESI-3. Hiring numbers are in thousands. There is some recovery in HNF from 4093 thousand (or 4.7 million) in Sep 2009 to 4507 thousand in Sep 2011 and 4357 thousand in Sep 2012 for cumulative gain of 6.5 percent. HP rose from 3723 thousand in Sep 2009 to 4130 thousand in Sep 2011 and 3991 thousand in Sep 2012 for cumulative gain of 7.2 percent. HNF has fallen from 5674 in Sep 2006 to 4357 in Sep 2012 or by 23.2 percent. HP has fallen from 5215 in Sep 2005 to 3991 in Sep 2012 or by 23.5 percent. The labor market continues to be fractured, failing to provide an opportunity to exit from unemployment/underemployment or to find an opportunity for advancement away from declining inflation-adjusted earnings.
Table ESI-3, US, Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF) and Total Private Hiring (HP) in the US in Thousands and in Percentage of Total Employment Not Seasonally Adjusted
| HNF | Rate RNF | HP | Rate HP | |
| 2001 Sep | 5170 | 3.9 | 4716 | 4.3 |
| 2002 Sep | 5028 | 3.9 | 4622 | 4.2 |
| 2003 Sep | 4919 | 3.8 | 4548 | 4.2 |
| 2004 Sep | 5282 | 4.0 | 4776 | 4.3 |
| 2005 Sep | 5674 | 4.2 | 5215 | 4.6 |
| 2006 Sep | 5541 | 4.1 | 4934 | 4.3 |
| 2007 Sep | 5436 | 3.9 | 4880 | 4.2 |
| 2008 Sep | 4608 | 3.4 | 4200 | 3.7 |
| 2009 Sep | 4093 | 3.1 | 3723 | 3.5 |
| 2010 Sep | 4148 | 3.2 | 3811 | 3.5 |
| 2011 Sep | 4507 | 3.4 | 4130 | 3.8 |
| 2012 Sep | 4357 | 3.3 | 3991 | 3.6 |
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
ESII Ten Million Fewer Full-time Jobs. There is strong seasonality in US labor markets around the end of the year. The number employed part-time for economic reasons because they could not find full-time employment fell from 9.270 million in Sep 2011 to 8.031 million in Aug 2012, seasonally adjusted, or decline of 1.024 million in nine months, as shown in Table ESII-1, but then rebounded to 8.613 million in Sep 2012 for increase of 582,000 in one month from Aug to Sep 2012, declining to 8.344 in Oct 2012 or by 269,000 again in one month. There is an increase of 313,000 in part-time for economic reasons from Aug 2012 to Oct 2012. The number employed full-time increased from 112.841 million in Oct 2011 to 115.290 million in Mar 2012 or 2.449 million but then fell to 114.212 million in May 2012 or 1.078 million fewer full-time employed than in Mar 2012. The number employed full-time increased from 114,388 million in Aug 2012 to 115.459 million in Oct 2012 or increase of 1.071 million full-time jobs in two months. The number of employed part-time for economic reasons actually increased without seasonal adjustment from 8.271 million in Nov 2011 to 8.428 million in Dec 2011 or by 157,000 and then to 8.918 million in Jan 2012 or by an additional 490,000 for cumulative increase from Nov 2011 to Jan 2012 of 647,000. The level of employed part-time for economic reasons then fell from 8.918 million in Jan 2012 to 7.867 million in Mar 2012 or by 1.0151 million and to 7.694 million in Apr 2012 or 1.224 million fewer relative to Jan 2012. In Aug 2012, the number employed part-time for economic reasons reached 7.842 million NSA or 148,000 more than in Apr 2012. The number employed part-time for economic reasons increased from 7.842 million in Aug 2012 to 8.110 million in Sep 2012 or by 3.4 percent. The number part-time for economic reasons fell from 8.110 million in Sep 2012 to 7.870 million in Oct 2012 or by 240.000 in one month. The number employed full time without seasonal adjustment fell from 113.138 million in Nov 2011 to 113.050 million in Dec 2011 or by 88,000 and fell further to 111.879 in Jan 2012 for cumulative decrease of 1.259 million. The number employed full-time not seasonally adjusted fell from 113.138 million in Nov 2011 to 112.587 million in Feb 2012 or by 551.000 but increased to 116.214 million in Aug 2012 or 3.076 million more full-time jobs than in Nov 2011. The number employed full-time not seasonally adjusted decreased from 116.214 million in Aug 2012 to 115.678 million in Sep 2012 for loss of 536,000 full-time jobs and rose to 116.045 million in Oct 2012 or by 367,000 full-time jobs in one month relative to Sep 2012. Comparisons over long periods require use of NSA data. The number with full-time jobs fell from a high of 123.219 million in Jul 2007 to 108.777 million in Jan 2010 or by 14.442 million. The number with full-time jobs in Oct 2012 is 116.045 million, which is lower by 7.174 million relative to the peak of 123.219 million in Jul 2007. There appear to be around 10 million fewer full-time jobs in the US than before the global recession. Growth at 2.2 percent on average in the thirteen quarters of expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2012 compared with 6.2 percent on average in expansions from postwar cyclical contractions is the main culprit of the fractured US labor market (see table I-5 in http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/10/mediocre-and-decelerating-united-states.html).
Table ESII-1, US, Employed Part-time for Economic Reasons, Thousands, and Full-time, Millions
| Part-time Thousands | Full-time Millions | |
| Seasonally Adjusted | ||
| Oct 2012 | 8,344 | 115.459 |
| Sep 2012 | 8,613 | 115.226 |
| Aug 2012 | 8,031 | 114.388 |
| Jul 2012 | 8,246 | 114.345 |
| Jun 2012 | 8,210 | 114.573 |
| May 2012 | 8,098 | 114.212 |
| Apr 2012 | 7,853 | 114.478 |
| Mar 2012 | 7,672 | 115.290 |
| Feb 2012 | 8,119 | 114.408 |
| Jan 2012 | 8,230 | 113.845 |
| Dec 2011 | 8,098 | 113.765 |
| Nov 2011 | 8,469 | 113.212 |
| Oct 2011 | 8,790 | 112.841 |
| Sep 2011 | 9,270 | 112.479 |
| Aug 2011 | 8,787 | 112.406 |
| Jul 2011 | 8,437 | 112.006 |
| Not Seasonally Adjusted | ||
| Oct 2012 | 7,870 | 116.045 |
| Sep 2012 | 8,110 | 115.678 |
| Aug 2012 | 7,842 | 116.214 |
| Jul 2012 | 8,316 | 116.131 |
| Jun 2012 | 8,394 | 116.024 |
| May 2012 | 7,837 | 114.634 |
| Apr 2012 | 7,694 | 113.999 |
| Mar 2012 | 7,867 | 113.916 |
| Feb 2012 | 8,455 | 112.587 |
| Jan 2012 | 8,918 | 111.879 |
| Dec 2011 | 8,428 | 113.050 |
| Nov 2011 | 8,271 | 113.138 |
| Oct 2011 | 8,258 | 113.456 |
| Sep 2011 | 8,541 | 112.980 |
| Aug 2011 | 8,604 | 114.286 |
| Jul 2011 | 8,514 | 113.759 |
| Jun 2011 | 8,738 | 113.255 |
| May 2011 | 8,270 | 112.618 |
| Apr 2011 | 8,425 | 111.844 |
| Mar 2011 | 8,737 | 111.186 |
| Feb 2011 | 8,749 | 110.731 |
| Jan 2011 | 9,187 | 110.373 |
| Dec 2010 | 9,205 | 111.207 |
| Nov 2010 | 8,670 | 111.348 |
| Oct 2010 | 8,408 | 112.342 |
| Sep 2010 | 8,628 | 112.385 |
| Aug 2010 | 8,628 | 113.508 |
| Jul 2010 | 8,737 | 113.974 |
| Jun 2010 | 8,867 | 113.856 |
| May 2010 | 8,513 | 112.809 |
| Apr 2010 | 8,921 | 111.391 |
| Mar 2010 | 9,343 | 109.877 |
| Feb 2010 | 9,282 | 109.100 |
| Jan 2010 | 9,290 | 108.777 (low) |
| Dec 2009 | 9,354 (high) | 109.875 |
| Oct 2009 | 8,474 | 112.274 |
| Sep 2009 | 8,255 | 111.991 |
| Aug 2009 | 8,835 | 113.863 |
| Jul 2009 | 9,103 | 114.184 |
| Jun 2009 | 9,301 | 114.014 |
| May 2009 | 8,785 | 113.083 |
| Apr 2009 | 8,648 | 112.746 |
| Mar 2009 | 9,305 | 112.215 |
| Feb 2009 | 9,170 | 112.947 |
| Jan 2009 | 8,829 | 113.815 |
| Oct 2008 | 6,267 | 120.020 |
| Sep 2008 | 5,701 | 120.213 |
| Aug 2008 | 5,736 | 121.556 |
| Jul 2008 | 6,054 | 122.378 |
| Jun 2008 | 5,697 | 121.845 |
| May 2008 | 5,096 | 120.809 |
| Apr 2008 | 5,071 | 120.027 |
| Mar 2008 | 5,038 | 119.875 |
| Feb 2008 | 5,114 | 119.452 |
| Jan 2008 | 5,340 | 119.332 |
| Oct 2007 | 4,028 | 122.006 |
| Sep 2007 | 4,137 | 121.278 |
| Aug 2007 | 4,494 | 122.870 |
| Jul 2007 | 4,516 | 123.219 (high) |
| Jun 2007 | 4,469 | 122.150 |
| May 2007 | 4,315 | 120.846 |
| Apr 2007 | 4,205 | 119.609 |
| Mar 2007 | 4,384 | 119.640 |
| Feb 2007 | 4,417 | 119.041 |
| Jan 2007 | 4,726 | 119.094 |
| Oct 2006 | 4,010 | 121.199 |
| Sep 2006 | 3,735 (low) | 120.780 |
| Aug 2006 | 4,104 | 121.979 |
| Jul 2006 | 4,450 | 121.951 |
| Jun 2006 | 4,456 | 121.070 |
| May 2006 | 3,968 | 118.925 |
| Apr 2006 | 3,787 | 118.559 |
| Mar 2006 | 4,097 | 117.693 |
| Feb 2006 | 4,403 | 116.823 |
| Jan 2006 | 4,597 | 116.395 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
People lose their marketable job skills after prolonged unemployment and find increasing difficulty in finding another job. Chart ESII-1 shows the sharp rise in unemployed over 27 weeks and stabilization at an extremely high level.
Chart ESII-1, US, Number Unemployed for 27 Weeks or Over, Thousands SA Month 2001-2011
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/cps/data.htm
Another segment of U6 consists of people marginally attached to the labor force who continue to seek employment but less frequently on the frustration there may not be a job for them. Chart ESII-2 shows the sharp rise in people marginally attached to the labor force after 2007 and subsequent stabilization.
Chart ESII-2, US, Marginally Attached to the Labor Force, NSA Month 2001-2012
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/cps/data.htm
Chart ESII-3 reveals the fracture in the US labor market. The number of workers with full-time jobs not-seasonally-adjusted rose with fluctuations from 2002 to a peak in 2007, collapsing during the global recession. The terrible state of the job market is shown in the segment from 2009 to 2012 with fluctuations around the typical behavior of a stationary series: there is no improvement in the United States in creating full-time jobs.
Chart ESII-3, US, Full-time Employed, Thousands, NSA, 2001-2012
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/cps/data.htm
ESIII Youth and Middle Age Unemployment. The United States is experiencing high youth unemployment as in European economies. Table ESIII-1 provides the employment level for ages 16 to 24 years of age estimated by the Bureau of Labor Statistics. On an annual basis, youth employment fell from 20.041 million in 2006 to 17.362 million in 2011 or 2.679 million fewer youth jobs. During the seasonal peak months of youth employment in the summer from Jun to Aug, youth employment has fallen by more than two million jobs relative to 21.9 million in Jul 2006. There are two hardships behind these data. First, young people cannot find employment after finishing high-school and college, reducing prospects for achievement in older age. Second, students with more modest means cannot find employment to keep them in college.
Table ESIII-1, US, Employment Level 16-24 Years, Thousands, NSA
| Year | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Annual |
| 2001 | 21212 | 22042 | 20529 | 19706 | 19694 | 20088 |
| 2002 | 20828 | 21501 | 20653 | 19466 | 19542 | 19683 |
| 2003 | 20432 | 20950 | 20181 | 18909 | 19139 | 19351 |
| 2004 | 20587 | 21447 | 20660 | 19158 | 19609 | 19630 |
| 2005 | 20949 | 21749 | 20814 | 19503 | 19794 | 19770 |
| 2006 | 21268 | 21914 | 21167 | 19604 | 19853 | 20041 |
| 2007 | 21098 | 21717 | 20413 | 19498 | 19564 | 19875 |
| 2008 | 20466 | 21021 | 20096 | 18818 | 18757 | 19202 |
| 2009 | 18726 | 19304 | 18270 | 16972 | 16671 | 17601 |
| 2010 | 17920 | 18564 | 18061 | 16874 | 16867 | 17077 |
| 2011 | 18180 | 18632 | 18067 | 17238 | 17532 | 17362 |
| 2012 | 18907 | 19461 | 18171 | 17687 | 17842 |
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/cps/data.htm
Chart ESIII-1 provides US employment level ages 16 to 24 years from 2002 to 2012. Employment level is sharply lower in Jun 2012 relative to the peak in 2007.
Chart ESIII-1, US, Employment Level 16-24 Years, Thousands SA, 2001-2012
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Table ESIII-2 provides US unemployment level ages 16 to 24 years. The number unemployed ages 16 to 24 years increased from 2342 thousand in 2007 to 3634 thousand in 2011 or by 1.292 million. This situation may persist for many years.
Table ESIII-2, US, Unemployment Level 16-24 Years, Thousands NSA
| Year | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Annual |
| 2001 | 2775 | 2585 | 2461 | 2301 | 2424 | 2371 |
| 2002 | 3167 | 3034 | 2688 | 2506 | 2468 | 2683 |
| 2003 | 3542 | 3200 | 2724 | 2698 | 2522 | 2746 |
| 2004 | 3191 | 3018 | 2585 | 2493 | 2572 | 2638 |
| 2005 | 3010 | 2688 | 2519 | 2339 | 2285 | 2521 |
| 2006 | 2860 | 2750 | 2467 | 2297 | 2252 | 2353 |
| 2007 | 2883 | 2622 | 2388 | 2419 | 2258 | 2342 |
| 2008 | 3450 | 3408 | 2990 | 2904 | 2842 | 2830 |
| 2009 | 4653 | 4387 | 4004 | 3774 | 3789 | 3760 |
| 2010 | 4481 | 4374 | 3903 | 3604 | 3731 | 3857 |
| 2011 | 4248 | 4110 | 3820 | 3541 | 3386 | 3634 |
| 2012 | 4180 | 4011 | 3672 | 3174 | 3285 |
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart ESIII-2 provides the unemployment level ages 16 to 24 from 2002 to 2012. The level rose sharply from 2007 to 2010 with tepid improvement into 2012.
Chart ESIII-2, US, Unemployment Level 16-24 Years, Thousands SA, 2001-2012
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Table ESIII-3 provides the rate of unemployment of young peoples in ages 16 to 24 years. The annual rate jumped from 10.5 percent in 2007 to 18.4 percent in 2010 and 17.3 percent in 2011. During the seasonal peak in Jul 2011 the rate of youth unemployed was 18.1 percent and 17.1 percent in Jul 2012 compared with 10.8 percent in Jul 2007.
Table ESIII-3, US, Unemployment Rate 16-24 Years, Thousands, NSA
| Year | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Annual |
| 2001 | 10.0 | 11.6 | 10.5 | 10.7 | 10.5 | 11.0 | 11.2 | 10.6 |
| 2002 | 11.6 | 13.2 | 12.4 | 11.5 | 11.4 | 11.2 | 11.7 | 12.0 |
| 2003 | 13.0 | 14.8 | 13.3 | 11.9 | 12.5 | 11.6 | 11.6 | 12.4 |
| 2004 | 12.2 | 13.4 | 12.3 | 11.1 | 11.5 | 11.6 | 11.1 | 11.8 |
| 2005 | 11.9 | 12.6 | 11.0 | 10.8 | 10.7 | 10.3 | 10.7 | 11.3 |
| 2006 | 10.2 | 11.9 | 11.2 | 10.4 | 10.5 | 10.2 | 10.1 | 10.5 |
| 2007 | 10.2 | 12.0 | 10.8 | 10.5 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.3 | 10.5 |
| 2008 | 13.3 | 14.4 | 14.0 | 13.0 | 13.4 | 13.2 | 13.3 | 12.8 |
| 2009 | 18.0 | 19.9 | 18.5 | 18.0 | 18.2 | 18.5 | 18.1 | 17.6 |
| 2010 | 18.4 | 20.0 | 19.1 | 17.8 | 17.6 | 18.1 | 17.4 | 18.4 |
| 2011 | 17.5 | 18.9 | 18.1 | 17.5 | 17.0 | 16.2 | 15.9 | 17.3 |
| 2012 | 16.3 | 18.1 | 17.1 | 16.8 | 15.2 | 15.5 |
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart ESIII-3 provides the BLS estimate of the not-seasonally-adjusted rate of youth unemployment for ages 16 to 24 years from 2002 to 2012. The rate of youth unemployment increased sharply during the global recession of 2008 and 2009 but has failed to drop to earlier lower levels during the twelve consecutive quarters of expansion of the economy since IIIQ2009 because of much lower growth at 2.2 percent annual equivalent on average compared with 6.2 percent on average in cyclical expansions since World War II Table I -5 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/10/mediocre-and-decelerating-united-states.html).
Chart ESIII-3, US, Unemployment Rate 16-24 Years, Percent, NSA, 2001-2012
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart ESIII-4 provides longer perspective with the rate of youth unemployment in ages 16 to 24 years from 1948 to 2012. The rate of youth unemployment rose to 20 percent during the contractions of the early 1980s and also during the contraction of the global recession in 2008 and 2009. The data illustrate again the claim in this blog that the contractions of the early 1980s are the valid framework for comparison with the global recession of 2008 and 2009 instead of misleading comparisons with the 1930s. During the initial phase of recovery, the rate of youth unemployment 16 to 24 years NSA fell from 18.9 percent in Jun 1983 to 14.5 percent in Jun 1984 while the rate of youth unemployment 16 to 24 years was nearly the same during the expansion after IIIQ2009: 18.5 percent in Oct 2009, 18.1 percent in Oct 2010, 16.2 percent in Oct 2011 and 15.5 percent in Oct 2012. In Jul 2007, the rate of youth unemployment was 10.8 percent, increasing to 17.1 percent in Jul 2012. The difference originates in the vigorous seasonally-adjusted annual equivalent average rate of GDP growth of 5.7 percent during the recovery from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 compared with 2.2 percent on average during the first eleven quarters of expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2012 (see table I-5 in http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/10/mediocre-and-decelerating-united-states.html). The fractured US labor market denies an early start for young people.
Chart ESIII-4, US, Unemployment Rate 16-24 Years, Percent NSA, 1948-2012
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
It is more difficult to move to other jobs after a certain age because of fewer available opportunities for matured individuals than for new entrants into the labor force. Middle-aged unemployed are less likely to find another job. Table ESIII-4 provides the unemployment level ages 45 years and over. The number unemployed ages 45 years and over rose from 1.985 million in Jul 2006 to 4.821 million in July 2010 or by 142.9 percent. The number of unemployed ages 45 years and over declined to 4.405 million in Jul 2012 that is still higher by 121.9 percent than in Jul 2006. The number unemployed age 45 and over jumped from 1.607 million in Oct 2006 to 4.576 million in Oct 2010 or 184.8 percent and at 3.800 million in Oct 2012 is higher by 2.193 million or 136.5 percent higher than 1.607 million in Oct 2006.
Table ESIII-4, US, Unemployment Level 45 Years and Over, Thousands NSA
| Year | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Annual |
| 2001 | 1259 | 1371 | 1539 | 1640 | 1586 | 1722 | 1576 |
| 2002 | 1999 | 2190 | 2173 | 2114 | 1966 | 1945 | 2114 |
| 2003 | 2112 | 2212 | 2281 | 2301 | 2157 | 2032 | 2253 |
| 2004 | 2025 | 2182 | 2116 | 2082 | 1951 | 1931 | 2149 |
| 2005 | 1844 | 1868 | 2119 | 1895 | 1992 | 1875 | 2009 |
| 2006 | 1784 | 1813 | 1985 | 1869 | 1710 | 1607 | 1848 |
| 2007 | 1803 | 1805 | 2053 | 1956 | 1854 | 1885 | 1966 |
| 2008 | 2095 | 2211 | 2492 | 2695 | 2595 | 2728 | 2540 |
| 2009 | 4175 | 4505 | 4757 | 4683 | 4560 | 4492 | 4500 |
| 2010 | 4565 | 4564 | 4821 | 5128 | 4640 | 4576 | 4879 |
| 2011 | 4356 | 4559 | 4772 | 4592 | 4426 | 4375 | 4537 |
| 2012 | 4083 | 4084 | 4405 | 4179 | 3899 | 3800 |
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart ESIII-5 provides the level unemployed ages 45 years and over. There was sharp increase during the global recession and inadequate decline. There was an increase during the 2001 recession and then stability. The US is facing a major challenge of reemploying middle-aged workers.
Chart ESIII-5, US, Unemployment Level Ages 45 Years and Over, Thousands, NSA, 1976-2012
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
ESIV United States International Trade Deficit and Fiscal Imbalance. Chart ESIV-1 of the US Census Bureau provides the US trade account in goods and services SA from Jan 1992 to Sep 2012. There is a long-term trend of deterioration of the US trade deficit shown vividly by Chart ESIV-1. The trend of deterioration was reversed by the global recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. Deterioration resumed together with incomplete recovery and was influenced significantly by the carry trade from zero interest rates to commodity futures exposures (these arguments are elaborated in Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 157-66, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 217-27, International Financial Architecture (2005), 15-18, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 221-5, Globalization and the State Vol. II (2008b), 197-213, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 182-4 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/07/causes-of-2007-creditdollar-crisis.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/professor-mckinnons-bubble-economy.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/world-inflation-quantitative-easing.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/treasury-yields-valuation-of-risk.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/11/quantitative-easing-theory-evidence-and.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/12/is-fed-printing-money-what-are.html). Earlier research focused on the long-term external imbalance of the US in the form of trade and current account deficits (Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), Globalization and the State Vol. II (2008b) 183-94, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 167-71). US external imbalances have not been fully resolved and tend to widen together with improving world economic activity and commodity price shocks.
Chart ESIV-1. US, Balance of Trade SA, Monthly, Millions of Dollars, Jan 1992-Sep 2012
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
Chart ESIV-2 of the US Census Bureau provides US exports SA from Jan 1992 to Sep 2012. There was sharp acceleration from 2003 to 2007 during worldwide economic boom and increasing inflation. Exports fell sharply during the financial crisis and global recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. Growth picked up again together with world trade and inflation but stalled in the final segment.
Chart ESIV-2. US, Exports SA, Monthly, Millions of Dollars Jan 1992-Sep 2012
Source: US Census Bureau http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
Chart ESIV-3 of the US Census Bureau provides US imports SA from Jan 1992 to Sep 2012. Growth was stronger between 2003 and 2007 with worldwide economic boom and inflation. There was sharp drop during the financial crisis and global recession. There is stalling import levels in the final segment resulting from weaker world economic growth and diminishing inflation because of risk aversion.
Chart ESIV-3. US, Imports SA, Monthly, Millions of Dollars Jan 1992-Sep 2012
Source: US Census Bureau http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
The balance of international trade in goods of the US seasonally-adjusted is shown in Table ESIV-1. The US has a dynamic surplus in services that reduces the large deficit in goods for a still very sizeable deficit in international trade of goods and services. The balance in international trade of goods improved from $59.2 billion in Sep 2011 to $57.5 billion in Sep 2012. Improvement of the goods balance in Sep 2012 relative to Sep 2011 occurred mostly in the petroleum balance, exports less imports of goods other than petroleum, in the magnitude of reducing the deficit by $4.6 billion, while there was moderate deterioration in the nonpetroleum balance, exports less imports of petroleum goods, in the magnitude of increasing the deficit by $2.9 billion. US terms of trade, export prices relative to import prices, and the US trade account fluctuate in accordance with the carry trade from zero interest rates to commodity futures exposures, especially oil futures. Exports rose 3.8 percent with non-petroleum exports growing 3.3 percent. Total imports rose 1.5 percent with petroleum imports declining 9.3 percent and nonpetroleum imports increasing 4.5 percent.
Table ESIV-1, US, International Trade in Goods Balance, Exports and Imports $ Millions and ∆% SA
| Sep 2012 | Sep 2011 | ∆% | |
| Total Balance | -57,454 | -59,522 | |
| Petroleum | -21,670 | -26,255 | |
| Non Petroleum | -35,169 | -32,281 | |
| Total Exports | 134,016 | 129,053 | 3.8 |
| Petroleum | 11,179 | 9,974 | 12.1 |
| Non Petroleum | 121,438 | 117,532 | 3.3 |
| Total Imports | 191,470 | 188,575 | 1.5 |
| Petroleum | 32,849 | 36,229 | -9.3 |
| Non Petroleum | 156,607 | 149,813 | 4.5 |
Details may not add because of rounding and seasonal adjustment
Source: US Census Bureau http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
US exports and imports of goods not seasonally adjusted in Jan-Sep 2012 and Jan-Sep 2011 are shown in Table ESIV-2. The rate of growth of exports was 5.1 percent and 3.9 percent for imports. The US has partial hedge of commodity price increases in exports of agricultural commodities that fell 0.6 percent and of mineral fuels that increased 7.3 percent both because of higher prices of raw materials and commodities increase and fall recurrently because of shocks of risk aversion. The US exports an insignificant amount of crude oil. US exports and imports consist mostly of manufactured products, with less rapidly increasing prices. US manufactured exports rose 6.1 percent while imports rose 7.3 percent. Significant part of the US trade imbalance originates in imports of mineral fuels decreasing 4.9 percent and crude oil decreasing 3.6 percent with wide oscillations in oil prices. The limited hedge in exports of agricultural commodities and mineral fuels compared with substantial imports of mineral fuels and crude oil results in waves of deterioration of the terms of trade of the US, or export prices relative to import prices, originating in commodity price increases caused by carry trades from zero interest rates. These waves are similar to those in worldwide inflation (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/10/world-inflation-waves-stagnating-united.html).
Table ESIV-2, US, Exports and Imports of Goods, Not Seasonally Adjusted Millions of Dollars and %
| Jan-Sep 2012 $ Millions | Jan-Sep 2011 $ Millions | ∆% | |
| Exports | 1,152,293 | 1,096,638 | 5.1 |
| Manufactured | 765,714 | 721,399 | 6.1 |
| Agricultural | 99,348 | 99,942 | -0.6 |
| Mineral Fuels | 100,196 | 93,401 | 7.3 |
| Crude Oil | 1,380 | 984 | 40.2 |
| Imports | 1,705,322 | 1,641,307 | 3.9 |
| Manufactured | 1,268,104 | 1,191,614 | 6.4 |
| Agricultural | 78,128 | 73,551 | 6.2 |
| Mineral Fuels | 327,034 | 344,110 | -4.9 |
| Crude Oil | 244,513 | 253,609 | -3.6 |
Source: US Census Bureau http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
In their classic work on “unpleasant monetarist arithmetic,” Sargent and Wallace (1981, 2) consider a regime of domination of monetary policy by fiscal policy (emphasis added):
“Imagine that fiscal policy dominates monetary policy. The fiscal authority independently sets its budgets, announcing all current and future deficits and surpluses and thus determining the amount of revenue that must be raised through bond sales and seignorage. Under this second coordination scheme, the monetary authority faces the constraints imposed by the demand for government bonds, for it must try to finance with seignorage any discrepancy between the revenue demanded by the fiscal authority and the amount of bonds that can be sold to the public. Suppose that the demand for government bonds implies an interest rate on bonds greater than the economy’s rate of growth. Then if the fiscal authority runs deficits, the monetary authority is unable to control either the growth rate of the monetary base or inflation forever. If the principal and interest due on these additional bonds are raised by selling still more bonds, so as to continue to hold down the growth of base money, then, because the interest rate on bonds is greater than the economy’s growth rate, the real stock of bonds will growth faster than the size of the economy. This cannot go on forever, since the demand for bonds places an upper limit on the stock of bonds relative to the size of the economy. Once that limit is reached, the principal and interest due on the bonds already sold to fight inflation must be financed, at least in part, by seigniorage, requiring the creation of additional base money.”
The current real value of government debt plus monetary liabilities depends on the expected discounted values of future primary surpluses or difference between tax revenue and government expenditure excluding interest payments (Cochrane 2011Jan, 27, equation (16)). There is a point when adverse expectations about the capacity of the government to generate primary surpluses to honor its obligations can result in increases in interest rates on government debt.
This analysis suggests that there may be a point of saturation of demand for United States financial liabilities without an increase in interest rates on Treasury securities. A risk premium may develop on US debt. Such premium is not apparent currently because of distressed conditions in the world economy and international financial system. Risk premiums are observed in the spread of bonds of highly indebted countries in Europe relative to bonds of the government of Germany.
The issue of global imbalances centered on the possibility of a disorderly correction (Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), Globalization and the State Vol. II (2008b) 183-94, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 167-71). Such a correction has not occurred historically but there is no argument proving that it could not occur. The need for a correction would originate in unsustainable large and growing United States current account deficits (CAD) and net international investment position (NIIP) or excess of financial liabilities of the US held by foreigners net of financial liabilities of foreigners held by US residents. The IMF estimated that the US could maintain a CAD of two to three percent of GDP without major problems (Rajan 2004). The threat of disorderly correction is summarized by Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 15):
“It is possible that foreigners may be unwilling to increase their positions in US financial assets at prevailing interest rates. An exit out of the dollar could cause major devaluation of the dollar. The depreciation of the dollar would cause inflation in the US, leading to increases in American interest rates. There would be an increase in mortgage rates followed by deterioration of real estate values. The IMF has simulated that such an adjustment would cause a decline in the rate of growth of US GDP to 0.5 percent over several years. The decline of demand in the US by four percentage points over several years would result in a world recession because the weakness in Europe and Japan could not compensate for the collapse of American demand. The probability of occurrence of an abrupt adjustment is unknown. However, the adverse effects are quite high, at least hypothetically, to warrant concern.”
The United States could be moving toward a situation typical of heavily indebted countries, requiring fiscal adjustment and increases in productivity to become more competitive internationally. The CAD and NIIP of the United States are not observed in full deterioration because the economy is well below potential. There are two complications in the current environment relative to the concern with disorderly correction in the first half of the past decade. Table ESIV-3 provides data on the US fiscal and balance of payments imbalances. In 2007, the federal deficit of the US was $161 billion corresponding to 1.2 percent of GDP while the Congressional Budget Office (CBO 2011AugBEO, 2) estimates the federal deficit in 2012 at $1128 billion or 7.3 percent of GDP (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/08/expanding-bank-cash-and-deposits-with.html). The combined record federal deficits of the US from 2009 to 2012 are $5135 billion or 33 percent of the estimate of GDP of $15,538 billion for fiscal year 2012 by the CBO (http://www.cbo.gov/publication/43542 2012AugBEO). The deficits from 2009 to 2012 exceed one trillion dollars per year, adding to $5.096 trillion in four years, using the fiscal year deficit of $1089.4 billion for fiscal year 2012 (http://www.fms.treas.gov/mts/mts0912.txt), which is the worst fiscal performance since World War II. Federal debt in 2007 was $5035 billion, less than the combined deficits from 2009 to 2012 of $5135 billion using the CBO forecast or $5096 billion using the fiscal year 2012 value of $1089 billion (http://www.fms.treas.gov/mts/mts0912.txt), and corresponded to 36.3 percent of GDP. Federal debt in 2011 was 67.7 percent of GDP and is estimated to reach 72.8 percent of GDP in 2012 (CBO2012AugBEO). This situation may worsen in the future (CBO 2012LTBO):
“The budget outlook is much bleaker under the extended alternative fiscal scenario, which maintains what some analysts might consider “current policies,” as opposed to current laws. Federal debt would grow rapidly from its already high level, exceeding 90 percent of GDP in 2022. After that, the growing imbalance between revenues and spending, combined with spiraling interest payments, would swiftly push debt to higher and higher levels. Debt as a share of GDP would exceed its historical peak of 109 percent by 2026, and it would approach 200 percent in 2037.
The changes under this scenario would result in much lower revenues than would occur under the extended baseline scenario because almost all expiring tax provisions are assumed to be extended through 2022 (with the exception of the current reduction in the payroll tax rate for Social Security). After 2022, revenues under this scenario are assumed to remain at their 2022 level of 18.5 percent of GDP, just above the average of the past 40 years.
Outlays would be much higher than under the other scenario. This scenario incorporates assumptions that through 2022, lawmakers will act to prevent Medicare’s payment rates for physicians from declining; that after 2022, lawmakers will not allow various restraints on the growth of Medicare costs and health insurance subsidies to exert their full effect; and that the automatic reductions in spending required by the Budget Control Act of 2011 will not occur (although the original caps on discretionary appropriations in that law are assumed to remain in place). Finally, under this scenario, federal spending as a percentage of GDP for activities other than Social Security, the major health care programs, and interest payments is assumed to return to its average level during the past two decades, rather than fall significantly below that level, as it does under the extended baseline scenario.”
Table ESIV-3, US, Current Account, NIIP, Fiscal Balance, Nominal GDP, Federal Debt and Direct Investment, Dollar Billions and %
| 2000 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | |
| Goods & | -377 | -697 | -698 | -379 | -495 | -559 |
| Income | 19 | 101 | 147 | 119 | 184 | 227 |
| UT | -58 | -115 | -126 | -122 | -131 | -133 |
| Current Account | -416 | -710 | -677 | -382 | -442 | -466 |
| NGDP | 9951 | 14028 | 14291 | 13974 | 14499 | 15076 |
| Current Account % GDP | -3.8 | -5.1 | -4.7 | -2.7 | -3.1 | -3.1 |
| NIIP | -1337 | -1796 | -3260 | -2321 | -2474 | -4030 |
| US Owned Assets Abroad | 6239 | 18399 | 19464 | 18512 | 20298 | 21132 |
| Foreign Owned Assets in US | 7576 | 20195 | 22724 | 20833 | 22772 | 25162 |
| NIIP % GDP | -13.4 | -12.8 | -22.8 | -16.6 | -17.1 | 26.7 |
| Exports | 1425 | 2488 | 2657 | 2181 | 2519 | 2848 |
| NIIP % | -94 | -72 | -123 | -106 | -98 | -142 |
| DIA MV | 2694 | 5274 | 3102 | 4287 | 4767 | 4450 |
| DIUS MV | 2783 | 3551 | 2486 | 2995 | 3397 | 3509 |
| Fiscal Balance | +236 | -161 | -459 | -1413 | -1294 | -1300 |
| Fiscal Balance % GDP | +2.4 | -1.2 | -3.2 | -10.1 | -9.0 | -8.7 |
| Federal Debt | 3410 | 5035 | 5803 | 7545 | 9019 | 10128 |
| Federal Debt % GDP | 34.7 | 36.3 | 40.5 | 54.1 | 62.8 | 67.7 |
| Federal Outlays | 1789 | 2729 | 2983 | 3518 | 3456 | 3603 |
| ∆% | 5.1 | 2.8 | 9.3 | 17.9 | -1.8 | 4.3 |
| % GDP | 18.2 | 19.7 | 20.8 | 25.2 | 24.1 | 24.1 |
| Federal Revenue | 2052 | 2568 | 2524 | 2105 | 2162 | 2303 |
| ∆% | 10.8 | 6.7 | -1.7 | -16.6 | 2.7 | 6.5 |
| % GDP | 20.6 | 18.5 | 17.6 | 15.1 | 15.1 | 15.4 |
Sources:
Notes: UT: unilateral transfers; NGDP: nominal GDP or in current dollars; NIIP: Net International Investment Position; DIA MV: US Direct Investment Abroad at Market Value; DIUS MV: Direct Investment in the US at Market Value. There are minor discrepancies in the decimal point of percentages of GDP between the balance of payments data and federal debt, outlays, revenue and deficits in which the original number of the CBO source is maintained. These discrepancies do not alter conclusions.
Sources: Balance of Payments and NIIP, Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) http://www.bea.gov/international/index.htm#bop
Gross Domestic Product, Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) http://www.bea.gov/national/index.htm#gdp
ESV Global Financial and Economic Risk. The International Monetary Fund (IMF) provides an international safety net for prevention and resolution of international financial crises. The IMF’s Financial Sector Assessment Program (FSAP) provides analysis of the economic and financial sectors of countries (see Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), 101-62, Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008), 114-23). Relating economic and financial sectors is a challenging task both for theory and measurement. The IMF provides surveillance of the world economy with its Global Economic Outlook (WEO) (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/weo/2012/02/pdf/text.pdf), of the world financial system with its Global Financial Stability Report (GFSR) (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/gfsr/2012/02/index.htm) and of fiscal affairs with the Fiscal Monitor (http://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fm/2012/02/pdf/fm1202.pdf). There appears to be a moment of transition in global economic and financial variables that may prove of difficult analysis and measurement. It is useful to consider a summary of global economic and financial risks, which are analyzed in detail in the comments of this blog in Section VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets, Table VI-4.
Economic risks include the following:
1. China’s Economic Growth. China is lowering its growth target to 7.5 percent per year. The growth rate of GDP of China in the third quarter of 2012 of 2.2 percent is equivalent to 9.1 percent per year and GDP increased 7.4 percent relative to the third quarter of 2011.
2. United States Economic Growth, Labor Markets and Budget/Debt Quagmire. The US is growing slowly with 28.7 million in job stress, fewer 10 million full-time jobs, high youth unemployment, historically-low hiring and declining real wages.
3. Economic Growth and Labor Markets in Advanced Economies. Advanced economies are growing slowly. There is still high unemployment in advanced economies.
4. World Inflation Waves. Inflation continues in repetitive waves globally (see Section I).
A list of financial uncertainties includes:
1. Euro Area Survival Risk. The resilience of the euro to fiscal and financial doubts on larger member countries is still an unknown risk.
2. Foreign Exchange Wars. Exchange rate struggles continue as zero interest rates in advanced economies induce devaluation of their currencies.
3. Valuation of Risk Financial Assets. Valuations of risk financial assets have reached extremely high levels in markets with lower volumes.
4. Duration Trap of the Zero Bound. The yield of the US 10-year Treasury rose from 2.031 percent on Mar 9, 2012, to 2.294 percent on Mar 16, 2012. Considering a 10-year Treasury with coupon of 2.625 percent and maturity in exactly 10 years, the price would fall from 105.3512 corresponding to yield of 2.031 percent to 102.9428 corresponding to yield of 2.294 percent, for loss in a week of 2.3 percent but far more in a position with leverage of 10:1. Min Zeng, writing on “Treasurys fall, ending brutal quarter,” published on Mar 30, 2012, in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424052702303816504577313400029412564.html?mod=WSJ_hps_sections_markets), informs that Treasury bonds maturing in more than 20 years lost 5.52 percent in the first quarter of 2012.
5. Credibility and Commitment of Central Bank Policy. There is a credibility issue of the commitment of monetary policy (Sargent and Silber 2012Mar20).
6. Carry Trades. Commodity prices driven by zero interest rates have resumed their increasing path with fluctuations caused by intermittent risk aversion.
It is in this context of economic and financial uncertainties that decisions on portfolio choices of risk financial assets must be made. There is a new carry trade that learned from the losses after the crisis of 2007 or learned from the crisis how to avoid losses. The sharp rise in valuations of risk financial assets shown in Table VI-1 in the text after the first policy round of near zero fed funds and quantitative easing by the equivalent of withdrawing supply with the suspension of the 30-year Treasury auction was on a smooth trend with relatively subdued fluctuations. The credit crisis and global recession have been followed by significant fluctuations originating in sovereign risk issues in Europe, doubts of continuing high growth and accelerating inflation in China now complicated by political developments, events such as in the Middle East and Japan and legislative restructuring, regulation, insufficient growth, falling real wages, depressed hiring and high job stress of unemployment and underemployment in the US now with realization of growth standstill. The “trend is your friend” motto of traders has been replaced with a “hit and realize profit” approach of managing positions to realize profits without sitting on positions. There is a trend of valuation of risk financial assets driven by the carry trade from zero interest rates with fluctuations provoked by events of risk aversion or the “sharp shifts in risk appetite” of Blanchard (2012WEOApr, XIII). Table ESV-1, which is updated for every comment of this blog, shows the deep contraction of valuations of risk financial assets after the Apr 2010 sovereign risk issues in the fourth column “∆% to Trough.” There was sharp recovery after around Jul 2010 in the last column “∆% Trough to 11/9/12,” which has been recently stalling or reversing amidst bouts of risk aversion.
Continuing risk aversion originates in the week of Nov 9 from the unresolved European debt crisis, world economic slowdown and low growth with fiscal challenges in the United States. The highest valuations in column “∆% Trough to 11/9/12” are by US equities indexes: DJIA 32.3 percent and S&P 500 34.9 percent, driven by stronger earnings and economy in the US than in other advanced economies but with doubts on the relation of business revenue to the weakening economy and fractured job market. The DJIA reached 13,703.53 on Oct 5, 2012, which is the highest level in 52 weeks (http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_PRO_hps_marketdata). The carry trade from zero interest rates to leveraged positions in risk financial assets had proved strongest for commodity exposures but US equities have regained leadership. Before the current round of risk aversion, almost all assets in the column “∆% Trough to 11/9/12” had double digit gains relative to the trough around Jul 2, 2010 but now some valuations of equity indexes show varying behavior: China’s Shanghai Composite is 13.2 percent below the trough; Japan’s Nikkei Average is 0.8 percent below the trough; DJ Asia Pacific TSM is 8.1 percent above the trough; Dow Global is 10.5 percent above the trough; STOXX 50 of 50 blue-chip European equities (http://www.stoxx.com/indices/index_information.html?symbol=sx5E) is 9.8 percent above the trough; and NYSE Financial is 11.6 percent above the trough. DJ UBS Commodities is 13.6 percent above the trough. DAX index of German equities (http://www.bloomberg.com/quote/DAX:IND) is 26.3 percent above the trough. Japan’s Nikkei Average is 0.8 percent below the trough on Aug 31, 2010 and 23.1 percent below the peak on Apr 5, 2010. The Nikkei Average closed at 8757.60 on Fri Nov 9, 2012 (http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_PRO_hps_marketdata), which is 14.6 percent lower than 10,254.43 on Mar 11, 2011, on the date of the Tōhoku or Great East Japan Earthquake/tsunami. Global risk aversion erased the earlier gains of the Nikkei. The dollar depreciated by 6.6 percent relative to the euro and even higher before the new bout of sovereign risk issues in Europe. The column “∆% week to 11/9/12” in Table ESV-1 shows that there were decreases of valuations of risk financial assets in the week of Nov 9, 2012 such as 2.6 percent for Dow Global, 2.8 percent for NYSE Financial, 1.6 percent for STOXX 50, 2.7 percent for DAX and 1.0 percent for DJ Asia Pacific TSM. Nikkei Average decreased 3.2 percent in the week. DJ UBS Commodities increased 0.3 percent. China’s Shanghai Composite decreased 2.3 percent in the week of Nov 9, 2012. The DJIA decreased 2.1 percent and S&P 500 decreased 2.4 percent. The USD appreciated 1.0 percent. There are still high uncertainties on European sovereign risks and banking soundness, US and world growth slowdown and China’s growth tradeoffs. Sovereign problems in the “periphery” of Europe and fears of slower growth in Asia and the US cause risk aversion with trading caution instead of more aggressive risk exposures. There is a fundamental change in Table ESV-1 from the relatively upward trend with oscillations since the sovereign risk event of Apr-Jul 2010. Performance is best assessed in the column “∆% Peak to 11/9/12” that provides the percentage change from the peak in Apr 2010 before the sovereign risk event to Nov 9, 2012. Most risk financial assets had gained not only relative to the trough as shown in column “∆% Trough to 11/9/12” but also relative to the peak in column “∆% Peak to 11/9/12.” There are now only three equity indexes above the peak in Table ESV-1: DJIA 14.4 percent, S&P 500 13.4 percent and DAX 13.1 percent. There are several indexes below the peak: NYSE Financial Index (http://www.nyse.com/about/listed/nykid.shtml) by 11.1 percent, Nikkei Average by 23.1 percent, Shanghai Composite by 34.6 percent, DJ Asia Pacific by 5.4 percent, STOXX 50 by 7.0 percent and Dow Global by 9.9 percent. DJ UBS Commodities Index is now 2.9 percent below the peak. The US dollar strengthened 16.0 percent relative to the peak. The factors of risk aversion have adversely affected the performance of risk financial assets. The performance relative to the peak in Apr 2010 is more important than the performance relative to the trough around early Jul 2010 because improvement could signal that conditions have returned to normal levels before European sovereign doubts in Apr 2010. Kate Linebaugh, writing on “Falling revenue dings stocks,” on Oct 20, 2012, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10000872396390444592704578066933466076070.html?mod=WSJPRO_hpp_LEFTTopStories), identifies a key financial vulnerability: falling revenues across markets for United States reporting companies. Global economic slowdown is reducing corporate sales and squeezing corporate strategies. Linebaugh quotes data from Thomson Reuters that 100 companies of the S&P 500 index have reported declining revenue only 1 percent higher in Jun-Sep 2012 relative to Jun-Sep 2011 but about 60 percent of the companies are reporting lower sales than expected by analysts with expectation that revenue for the S&P 500 will be lower in Jun-Sep 2012 for the entities represented in the index. Results of US companies are likely repeated worldwide. It may be quite painful to exit QE∞ or use of the balance sheet of the central together with zero interest rates forever. The basic valuation equation that is also used in capital budgeting postulates that the value of stocks or of an investment project is given by:
Where Rτ is expected revenue in the time horizon from τ =1 to T; Cτ denotes costs; and ρ is an appropriate rate of discount. In words, the value today of a stock or investment project is the net revenue, or revenue less costs, in the investment period from τ =1 to T discounted to the present by an appropriate rate of discount. In the current weak economy, revenues have been increasing more slowly than anticipated in investment plans. An increase in interest rates would affect discount rates used in calculations of present value, resulting in frustration of investment decisions. If V represents value of the stock or investment project, as ρ → ∞, meaning that interest rates increase without bound, then V → 0, or
declines. Equally, decline in expected revenue from the stock or project, Rτ, causes decline in valuation. An intriguing issue is the difference in performance of valuations of risk financial assets and economic growth and employment. Paul A. Samuelson (http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/economics/laureates/1970/samuelson-bio.html) popularized the view of the elusive relation between stock markets and economic activity in an often-quoted phrase “the stock market has predicted nine of the last five recessions.” In the presence of zero interest rates forever, valuations of risk financial assets are likely to differ from the performance of the overall economy. The interrelations of financial and economic variables prove difficult to analyze and measure.
Table ESV-1, Stock Indexes, Commodities, Dollar and 10-Year Treasury
| Peak | Trough | ∆% to Trough | ∆% Peak to 11/9/ /12 | ∆% Week 11/9/12 | ∆% Trough to 11/9/ 12 | |
| DJIA | 4/26/ | 7/2/10 | -13.6 | 14.4 | -2.1 | 32.3 |
| S&P 500 | 4/23/ | 7/20/ | -16.0 | 13.4 | -2.4 | 34.9 |
| NYSE Finance | 4/15/ | 7/2/10 | -20.3 | -11.1 | -2.8 | 11.6 |
| Dow Global | 4/15/ | 7/2/10 | -18.4 | -9.9 | -2.6 | 10.5 |
| Asia Pacific | 4/15/ | 7/2/10 | -12.5 | -5.4 | -1.0 | 8.1 |
| Japan Nikkei Aver. | 4/05/ | 8/31/ | -22.5 | -23.1 | -3.2 | -0.8 |
| China Shang. | 4/15/ | 7/02 | -24.7 | -34.6 | -2.3 | -13.2 |
| STOXX 50 | 4/15/10 | 7/2/10 | -15.3 | -7.0 | -1.6 | 9.8 |
| DAX | 4/26/ | 5/25/ | -10.5 | 13.1 | -2.7 | 26.3 |
| Dollar | 11/25 2009 | 6/7 | 21.2 | 16.0 | 1.0 | -6.6 |
| DJ UBS Comm. | 1/6/ | 7/2/10 | -14.5 | -2.9 | 0.3 | 13.6 |
| 10-Year T Note | 4/5/ | 4/6/10 | 3.986 | 1.614 |
T: trough; Dollar: positive sign appreciation relative to euro (less dollars paid per euro), negative sign depreciation relative to euro (more dollars paid per euro)
Source: http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_hps_marketdata
IA Recovery without Hiring. Professor Edward P. Lazear (2012Jan19) at Stanford University finds that recovery of hiring in the US to peaks attained in 2007 requires an increase of hiring by 30 percent while hiring levels have increased by only 4 percent since Jan 2009. The high level of unemployment with low level of hiring reduces the statistical probability that the unemployed will find a job. According to Lazear (2012Jan19), the probability of finding a new job currently is about one third of the probability of finding a job in 2007. Improvements in labor markets have not increased the probability of finding a new job. Lazear (2012Jan19) quotes an essay coauthored with James R. Spletzer forthcoming in the American Economic Review on the concept of churn. A dynamic labor market occurs when a similar amount of workers is hired as those who are separated. This replacement of separated workers is called churn, which explains about two-thirds of total hiring. Typically, wage increases received in a new job are higher by 8 percent. Lazear (2012Jan19) argues that churn has declined 35 percent from the level before the recession in IVQ2007. Because of the collapse of churn there are no opportunities in escaping falling real wages by moving to another job. As this blog argues, there are meager chances of escaping unemployment because of the collapse of hiring and those employed cannot escape falling real wages by moving to another job (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/11/twenty-eight-million-unemployed-or.html). Lazear and Spletzer (2012Mar, 1) argue that reductions of churn reduce the operational effectiveness of labor markets. Churn is part of the allocation of resources or in this case labor to occupations of higher marginal returns. The decline in churn can harm static and dynamic economic efficiency. Losses from decline of churn during recessions can affect an economy over the long-term by preventing optimal growth trajectories because resources are not used in the occupations where they provide highest marginal returns. Lazear and Spletzer (2012Mar 7-8) conclude that: “under a number of assumptions, we estimate that the loss in output during the recession [of 2007 to 2009] and its aftermath resulting from reduced churn equaled $208 billion. On an annual basis, this amounts to about .4% of GDP for a period of 3½ years.”
There are two additional facts discussed below: (1) there are about ten million fewer full-time jobs currently than before the recession of 2008 and 2009; and (2) the extremely high and rigid rate of youth unemployment is denying an early start to young people ages 16 to 24 years while unemployment of ages 45 years or over has swelled. There are four subsections. IA1 Hiring Collapse provides the data and analysis on the weakness of hiring in the United States economy. IA2 Labor Underutilization provides the measures of labor underutilization of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). Statistics on the decline of full-time employment are in IA3 Ten Million Fewer Full-time Jobs. IA4 Youth and Middle-Age Unemployment provides the data on high unemployment of ages 16 to 24 years and of ages 45 years or over.
IA1 Hiring Collapse. An important characteristic of the current fractured labor market of the US is the closing of the avenue for exiting unemployment and underemployment normally available through dynamic hiring. Another avenue that is closed is the opportunity for advancement in moving to new jobs that pay better salaries and benefits again because of the collapse of hiring in the United States. Those who are unemployed or underemployed cannot find a new job even accepting lower wages and no benefits. The employed cannot escape declining inflation-adjusted earnings because there is no hiring. The objective of this section is to analyze hiring and labor underutilization in the United States.
An appropriate measure of job stress is considered by Blanchard and Katz (1997, 53):
“The right measure of the state of the labor market is the exit rate from unemployment, defined as the number of hires divided by the number unemployed, rather than the unemployment rate itself. What matters to the unemployed is not how many of them there are, but how many of them there are in relation to the number of hires by firms.”
The natural rate of unemployment and the similar NAIRU are quite difficult to estimate in practice (Ibid; see Ball and Mankiw 2002).
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) created the Job Openings and Labor Turnover Survey (JOLTS) with the purpose that (http://www.bls.gov/jlt/jltover.htm#purpose):
“These data serve as demand-side indicators of labor shortages at the national level. Prior to JOLTS, there was no economic indicator of the unmet demand for labor with which to assess the presence or extent of labor shortages in the United States. The availability of unfilled jobs—the jobs opening rate—is an important measure of tightness of job markets, parallel to existing measures of unemployment.”
The BLS collects data from about 16,000 US business establishments in nonagricultural industries through the 50 states and DC. The data are released monthly and constitute an important complement to other data provided by the BLS (see also Lazear and Spletzer 2012Mar, 6-7).
Hiring in the nonfarm sector (HNF) has declined from 63.8 million in 2006 to 50.1 million in 2011 or by 13.7 million while hiring in the private sector (HP) has declined from 59.5 million in 2006 to 46.9 million in 2011 or by 12.6 million, as shown in Table I-1. The ratio of nonfarm hiring to employment (RNF) has fallen from 47.2 in 2005 to 38.1 in 2011 and in the private sector (RHP) from 52.1 in 2006 to 42.9 in 2011. The collapse of hiring in the US has not been followed by dynamic labor markets because of the low rate of economic growth of 2.2 percent in the first thirteen quarters of expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2012 compared with 6.2 percent in prior cyclical expansions (see table I-5 in http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/10/mediocre-and-decelerating-united-states.html).
Table I-1, US, Annual Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF) and Total Private Hiring (HP) in the US and Percentage of Total Employment
| HNF | Rate RNF | HP | Rate HP | |
| 2001 | 62,948 | 47.8 | 58,825 | 53.1 |
| 2002 | 58,583 | 44.9 | 54,759 | 50.3 |
| 2003 | 56,451 | 43.4 | 53,056 | 48.9 |
| 2004 | 60,367 | 45.9 | 56,617 | 51.6 |
| 2005 | 63,150 | 47.2 | 59,372 | 53.1 |
| 2006 | 63,773 | 46.9 | 59,494 | 52.1 |
| 2007 | 62,421 | 45.4 | 58,035 | 50.3 |
| 2008 | 55,166 | 40.3 | 51,606 | 45.2 |
| 2009 | 46,398 | 35.5 | 43,052 | 39.8 |
| 2010 | 48,647 | 37.5 | 44,826 | 41.7 |
| 2011 | 50,083 | 38.1 | 46,869 | 42.9 |
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Chart I-1 provides the yearly levels of total nonfarm hiring (NFH) in Table I-1. The fall of hiring during the contraction of 2007 to 2009 was much stronger than in the shallow recession of 2001 with GDP contraction of only 0.4 percent from Mar 2001 (IQ2001) to Dec 2001 (IVQ 2001) compared with 4.7 percent contraction in the much longer recession from Dec 2007 (IVQ2007) to Jun 2009 (IIQ2009) (http://www.nber.org/cycles/cyclesmain.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/10/mediocre-and-decelerating-united-states.html). Recovery is tepid.
Chart I-1, US, Level Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF), Annual, 2001-2011
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Chart I-2 shows the ratio or rate of nonfarm hiring to employment (RNF) that also fell much more in the recession of 2007 to 2009 than in the shallow recession of 2001. Recovery is weak.
Chart I-2, US, Rate Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF), Annual, 2001-2011
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Yearly percentage changes of total nonfarm hiring (HNF) are provided in Table I-2. There were much milder declines in 2002 of 6.9 percent and 3.6 percent in 2003 followed by strong rebounds of 6.9 percent in 2004 and 4.6 percent in 2005. In contrast, the contractions of nonfarm hiring in the recession after 2007 were much sharper in percentage points: 2.1 in 2007, 11.6 in 2008 and 15.9 percent in 2009. On a yearly basis, nonfarm hiring grew 4.8 percent in 2010 relative to 2009 and 3.0 percent in 2011.
Table I-2, US, Annual Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF), Annual Percentage Change, 2001-2011
| Year | Annual |
| 2002 | -6.9 |
| 2003 | -3.6 |
| 2004 | 6.9 |
| 2005 | 4.6 |
| 2006 | 1.0 |
| 2007 | -2.1 |
| 2008 | -11.6 |
| 2009 | -15.9 |
| 2010 | 4.8 |
| 2011 | 3.0 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Chart I-3 plots yearly percentage changes of nonfarm hiring. Percentage declines after 2007 were quite sharp.
Chart I-3, US, Annual Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF), Annual Percentage Change, 2001-2011
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Total private hiring (HP) yearly data are provided in Chart I-4. There has been sharp contraction of total private hiring in the US and only milder recovery in 2011 than in 2010.
Chart I-4, US, Total Private Hiring Level, Annual, 2001-2011
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Chart I-5 plots the rate of total private hiring relative to employment (RHP). The rate collapsed during the global recession after 2007 with insufficient recovery.
Chart I-5, US, Rate Total Private Hiring, Annual, 2001-2011
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Total nonfarm hiring (HNF), total private hiring (HP) and their respective rates are provided for the month of Sep in the years from 2001 to 2012 in Table I-3. Hiring numbers are in thousands. There is some recovery in HNF from 4093 thousand (or 4.7 million) in Sep 2009 to 4507 thousand in Sep 2011 and 4357 thousand in Sep 2012 for cumulative gain of 6.5 percent. HP rose from 3723 thousand in Sep 2009 to 4130 thousand in Sep 2011 and 3991 thousand in Sep 2012 for cumulative gain of 7.2 percent. HNF has fallen from 5674 in Sep 2006 to 4357 in Sep 2012 or by 23.2 percent. HP has fallen from 5215 in Sep 2005 to 3991 in Sep 2012 or by 23.5 percent. The labor market continues to be fractured, failing to provide an opportunity to exit from unemployment/underemployment or to find an opportunity for advancement away from declining inflation-adjusted earnings.
Table I-3, US, Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF) and Total Private Hiring (HP) in the US in Thousands and in Percentage of Total Employment Not Seasonally Adjusted
| HNF | Rate RNF | HP | Rate HP | |
| 2001 Sep | 5170 | 3.9 | 4716 | 4.3 |
| 2002 Sep | 5028 | 3.9 | 4622 | 4.2 |
| 2003 Sep | 4919 | 3.8 | 4548 | 4.2 |
| 2004 Sep | 5282 | 4.0 | 4776 | 4.3 |
| 2005 Sep | 5674 | 4.2 | 5215 | 4.6 |
| 2006 Sep | 5541 | 4.1 | 4934 | 4.3 |
| 2007 Sep | 5436 | 3.9 | 4880 | 4.2 |
| 2008 Sep | 4608 | 3.4 | 4200 | 3.7 |
| 2009 Sep | 4093 | 3.1 | 3723 | 3.5 |
| 2010 Sep | 4148 | 3.2 | 3811 | 3.5 |
| 2011 Sep | 4507 | 3.4 | 4130 | 3.8 |
| 2012 Sep | 4357 | 3.3 | 3991 | 3.6 |
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Chart I-6 provides total nonfarm hiring on a monthly basis from 2001 to 2012. Nonfarm hiring rebounded in early 2010 but then fell and stabilized at a lower level than the early peak not-seasonally adjusted (NSA) of 4786 in May 2010 until it surpassed it in with 4869 in Jun 2011 but declined to 4357 in Sep 2012. Nonfarm hiring fell again in Dec 2011 to 3038 from 3844 in Nov and to revised 3633 in Feb 2012, increasing to 4127 in Mar 2012, 4490 in Apr 2012, 4926 in May 2012, 4988 in Jun 2012, 4732 in Jul 2012, 4962 in Aug 2012 and 4357 in Sep 2012. Chart I-6 provides seasonally-adjusted (SA) monthly data. The number of seasonally-adjusted hires in Aug 2011 was 4221 thousand, increasing to revised 4444 thousand in Feb 2012, or 5.3 percent, but falling to revised 4335 thousand in Mar 2012 and 4213 in Apr 2012, or cumulative decline of 0.2 percent relative to Aug 2011, moving to 4185 in Sep 2012 for cumulative decrease of 2.1 percent from 4276 in Sep 2011. The number of hires not seasonally adjusted was 4655 in Aug 2011, falling to 3038 in Dec but increasing to 4072 in Jan 2012 and 4357 in Sep 2012. The number of nonfarm hiring not seasonally adjusted fell by 34.7 percent from 4655 in Aug 2011 to 3038 in Dec 2011 in a yearly-repeated seasonal pattern.
Chart I-6, US, Total Nonfarm Hiring (HNF), 2001-2012 Month SA
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Similar behavior occurs in the rate of nonfarm hiring plot in Chart I-7. Recovery in early 2010 was followed by decline and stabilization at a lower level but with stability in monthly SA estimates of 3.2 in Sep 2011 to 3.2 in Jan 2012, increasing to 3.4 in May 2012 and falling to 3.2 in both Jun and Jul 2012, increasing to 3.3 in Aug 2012 but falling to 3.1 in Sep 2012. The rate not seasonally adjusted fell from 3.7 in Jun 2011 to 2.3 in Dec, climbing to 3.1 in Jan 2012, 3.7 in both May and Jun 2012 and falling to 36 in both Jul, increasing to 3.7 in Aug and falling to 3.3 in Sep 2012. Rates of nonfarm hiring NSA were in the range of 2.8 (Dec) to 4.5 (Jun) in 2006.
Chart I-7, US, Rate Total Nonfarm Hiring, Month SA 2001-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
There is only milder improvement in total private hiring shown in Chart I-8. Hiring private (HP) rose in 2010 followed by stability and renewed increase in 2011 followed by stationary series in 2012. The number of private hiring seasonally adjusted fell from 4002 thousand in Sep 2011 to 3889 in Dec 2011 or by 2.8 percent, increasing to 3945 in Jan 2012 or decline by 1.4 relative to the level in Sep 2011 but decreasing to 3908 in Sep 2012 or lower by 2.3 percent relative to Sep 2011. The number of private hiring not seasonally adjusted fell from 4130 in Sep 2011 to 2856 in Dec or by 30.8 percent, reaching 3782 in Jan 2012 or decline of 8.4 percent relative to Sep 2011 and decreasing to 3991 in Sep 2012 or 3.4 percent lower relative to Sep 2011. Companies do not hire in the latter part of the year that explains the high seasonality in year-end employment data. For example, NSA private hiring fell from 4934 in Sep 2006 to 3635 in Dec 2006 or by 26.3 percent. Private hiring NSA data are useful in showing the huge declines from the period before the global recession. In Jul 2006 private hiring NSA was 5555, declining to 4293 in Jul 2011 or by 22.7 percent and to 4403 in Jul 2012 or lower by 20.7 percent relative to Jul 2006. Private hiring NSA fell from 5215in Sep 2005 to 3991 in Sep 2012 or 23.5 percent. The conclusion is that private hiring in the US is around 20 percent below the hiring before the global recession. The main problem in recovery of the US labor market has been the low rate of growth of 2.2 percent in the twelve quarters of expansion of the economy from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2012 compared with average 6.2 percent in prior expansions from contractions (see table I-5 in http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/10/mediocre-and-decelerating-united-states.html). The US missed the opportunity to recover employment as in past cyclical expansions from contractions.
Chart I-8, US, Total Private Hiring Month SA 2011-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Chart I-9 shows similar behavior in the rate of private hiring. The rate in 2011 in monthly SA data did not rise significantly above the peak in 2010. The rate seasonally adjusted fell from 3.6 in Sep 2011 to 3.5 in Dec 2011 and 3.5 in Sep 2012. The rate not seasonally adjusted (NSA) fell from 3.8 in Sep 2011 to 2.6 in Dec 2011, increasing to 3.6 in Sep 2012. The NSA rate of private hiring fell from 4.8 in Jul 2006 to 3.4 in Jul 2009 but recovery was insufficient to only 3.6 in Sep 2012.
Chart I-9, US, Rate Total Private Hiring Month SA 2011-2011
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
The JOLTS report of the Bureau of Labor Statistics also provides total nonfarm job openings (TNF JOB), TNF JOB rate and TNF LD (layoffs and discharges) shown in Table I-4 for the month of Sep from 2001 to 2012. The final column provides annual TNF LD for the years from 2001 to 2011. Nonfarm job openings fell from a peak of 4542 in Sep 2006 to 3602 in Sep 2012 or by 20.7 percent while the rate dropped from 3.2 to 2.6. Nonfarm layoffs and discharges (TNF LD) rose from 1840 in Sep 2006 to 2235 in Sep 2009 or by 21.5 percent. The annual data show layoffs and discharges rising from 21.2 million in 2006 to 26.8 million in 2009 or by 26.4 percent.
Table I-4, US, Job Openings and Total Separations, Thousands NSA
| TNF JOB | TNF JOB | TNF LD | TNF LD | |
| Sep 2001 | 3880 | 2.9 | 2178 | 24499 |
| Sep 2002 | 3207 | 2.4 | 2017 | 22922 |
| Sep 2003 | 2990 | 2.2 | 1929 | 23294 |
| Sep 2004 | 3708 | 2.7 | 2065 | 22802 |
| Sep 2005 | 4219 | 3.0 | 2050 | 22185 |
| Sep 2006 | 4542 | 3.2 | 1840 | 21157 |
| Sep 2007 | 4531 | 3.2 | 2173 | 22142 |
| Sep 2008 | 3232 | 2.3 | 2054 | 24166 |
| Sep 2009 | 2498 | 1.9 | 2235 | 26783 |
| Sep 2010 | 2798 | 2.1 | 1788 | 21784 |
| Sep 2011 | 3546 | 2.6 | 1886 | 20718 |
| Sep 2012 | 3602 | 2.6 | 1789 |
Notes: TNF JOB: Total Nonfarm Job Openings; LD: Layoffs and Discharges
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Chart I-10 shows monthly job openings rising from the trough in 2009 to a high in the beginning of 2010. Job openings then stabilized into 2011 but have surpassed the peak of 3057 seasonally adjusted in Nov 2010 with 3561 seasonally adjusted in Sep 2012, which is higher by 16.5 percent than 3501 in Sep 2011 and lower than 3741 in Mar 2012 by 4.8 percent. The high of job openings not seasonally adjusted in 2010 was 3221 in Oct 2010 that was surpassed by 3659 in Oct 2011, decreasing to 3602 in Sep 2012. The level of job openings not seasonally adjusted fell to 2912 in Nov 2011 or by 17.9 percent relative to 3546 in Sep 2011. There is here again the strong seasonality of year-end labor data. Job openings NSA fell from 4678 in Oct 2006 to 2547 in Oct 2009 or by 45.6 percent, recovering to 3221 in Oct 2010 or by 26.5 percent, which is still 21.8 percent lower at 3659 in Oct 2011 relative to Oct 2006. The level of job openings of 3602 in Sep 2012 NSA is lower by 20.5 percent relative to 4531 in Sep 2007. Again, the main problem in recovery of the US labor market has been the low rate of growth of 2.2 percent in the thirteen quarters of expansion of the economy since IIIQ2009 compared with average 6.2 percent in prior expansions from contractions (see table I-5 in http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/10/mediocre-and-decelerating-united-states.html). The US missed the opportunity to recover employment as in past cyclical expansions from contractions.
Chart I-10, US Job Openings, Thousands NSA, 2001-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
The rate of job openings in Chart I-11 shows similar behavior. The rate seasonally adjusted rose from 2.1 percent in Jan 2011 to 2.6 percent in Dec 2011 and 2.6 in Sep 2012. The rate not seasonally adjusted rose from the high of 2.6 in Apr 2010 to 2.7 in Jul 2011 and 2.7 in all months from Jan to Jun 2012 with exception of 2.5 in Feb 2012 and then to 2.9 in Jul 2012 but back to 2.7 in Aug 2012 and 2.6 in Sep 2012. The rate of job openings NSA fell from 3.0 in Sep 2005 to 1.9 in Sep 2009, recovering insufficiently to 2.6 in Sep 2012.
Chart I-11, US, Rate of Job Openings, NSA, 2001-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Total separations are shown in Chart I-12. Separations are much lower in 2012 than before the global recession.
Chart I-12, US, Total Nonfarm Separations, Month SA, 2001-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Annual total separations are shown in Chart I-13. Separations are much lower in 2011 than before the global recession.
Chart I-13, US, Total Separations, Annual, 2001-2011
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Table I-5 provides total nonfarm total separations from 2001 to 2011. Separations fell from 61.6 million in 2006 to 47.6 million in 2010 or by 14.0 million and 48.2 million in 2011 or by 13.4 million.
Table I-5, US, Total Nonfarm Total Separations, Thousands, 2001-201
| Year | Annual |
| 2001 | 64765 |
| 2002 | 59190 |
| 2003 | 56487 |
| 2004 | 58340 |
| 2005 | 60733 |
| 2006 | 61565 |
| 2007 | 61162 |
| 2008 | 58601 |
| 2009 | 51527 |
| 2010 | 47641 |
| 2011 | 48242 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Monthly data of layoffs and discharges reach a peak in early 2009, as shown in Chart I-14. Layoffs and discharges dropped sharply with the recovery of the economy in 2010 and 2011 once employers reduced their job count to what was required for cost reductions and loss of business.
Chart I-14, US, Total Nonfarm Layoffs and Discharges, Monthly SA, 2011-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Layoffs and discharges in Chart I-15 rose sharply to a peak in 2009. There was pronounced drop into 2010 and 2011.
Chart I-15, US, Total Nonfarm Layoffs and Discharges, Annual, 2001-2011
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
Table I-6 provides annual nonfarm layoffs and discharges from 2001 to 2011. Layoffs and discharges peaked at 26.8 million in 2009 and then fell to 20.7 million in 2011, by 6.1 million, or 22.8 percent.
Table I-6, US, Total Nonfarm Layoffs and Discharges, 2001-2011
| Year | Annual |
| 2001 | 24499 |
| 2002 | 22922 |
| 2003 | 23294 |
| 2004 | 22802 |
| 2005 | 22185 |
| 2006 | 21157 |
| 2007 | 22142 |
| 2008 | 24166 |
| 2009 | 26783 |
| 2010 | 21784 |
| 2011 | 20718 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/jlt/data.htm
IA2 Labor Underutilization. The Bureau of Labor Statistics also provides alternative measures of labor underutilization shown in Table I-7. The most comprehensive measure is U6 that consists of total unemployed plus total employed part time for economic reasons plus all marginally attached workers as percent of the labor force. U6 not seasonally annualized has risen from 8.2 percent in 2006 to 13.9 percent in Oct 2012.
Table I-7, US, Alternative Measures of Labor Underutilization NSA %
| U1 | U2 | U3 | U4 | U5 | U6 | |
| 2012 | ||||||
| Oct | 4.3 | 3.9 | 7.5 | 8.0 | 9.0 | 13.9 |
| Sep | 4.2 | 4.0 | 7.6 | 8.0 | 9.0 | 14.2 |
| Aug | 4.3 | 4.4 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 9.7 | 14.6 |
| Jul | 4.3 | 4.6 | 8.6 | 9.1 | 10.0 | 15.2 |
| Jun | 4.5 | 4.4 | 8.4 | 8.9 | 9.9 | 15.1 |
| May | 4.7 | 4.3 | 7.9 | 8.4 | 9.3 | 14.3 |
| Apr | 4.8 | 4.3 | 7.7 | 8.3 | 9.1 | 14.1 |
| Mar | 4.9 | 4.8 | 8.4 | 8.9 | 9.7 | 14.8 |
| Feb | 4.9 | 5.1 | 8.7 | 9.3 | 10.2 | 15.6 |
| Jan | 4.9 | 5.4 | 8.8 | 9.4 | 10.5 | 16.2 |
| 2011 | ||||||
| Dec | 4.8 | 5.0 | 8.3 | 8.8 | 9.8 | 15.2 |
| Nov | 4.9 | 4.7 | 8.2 | 8.9 | 9.7 | 15.0 |
| Oct | 5.0 | 4.8 | 8.5 | 9.1 | 10.0 | 15.3 |
| Sep | 5.2 | 5.0 | 8.8 | 9.4 | 10.2 | 15.7 |
| Aug | 5.2 | 5.1 | 9.1 | 9.6 | 10.6 | 16.1 |
| Jul | 5.2 | 5.2 | 9.3 | 10.0 | 10.9 | 16.3 |
| Jun | 5.1 | 5.1 | 9.3 | 9.9 | 10.9 | 16.4 |
| May | 5.5 | 5.1 | 8.7 | 9.2 | 10.0 | 15.4 |
| Apr | 5.5 | 5.2 | 8.7 | 9.2 | 10.1 | 15.5 |
| Mar | 5.7 | 5.8 | 9.2 | 9.7 | 10.6 | 16.2 |
| Feb | 5.6 | 6.0 | 9.5 | 10.1 | 11.1 | 16.7 |
| Jan | 5.6 | 6.2 | 9.8 | 10.4 | 11.4 | 17.3 |
| Dec 2010 | 5.4 | 5.9 | 9.1 | 9.9 | 10.7 | 16.6 |
| Annual | ||||||
| 2011 | 5.3 | 5.3 | 8.9 | 9.5 | 10.4 | 15.9 |
| 2010 | 5.7 | 6.0 | 9.6 | 10.3 | 11.1 | 16.7 |
| 2009 | 4.7 | 5.9 | 9.3 | 9.7 | 10.5 | 16.2 |
| 2008 | 2.1 | 3.1 | 5.8 | 6.1 | 6.8 | 10.5 |
| 2007 | 1.5 | 2.3 | 4.6 | 4.9 | 5.5 | 8.3 |
| 2006 | 1.5 | 2.2 | 4.6 | 4.9 | 5.5 | 8.2 |
| 2005 | 1.8 | 2.5 | 5.1 | 5.4 | 6.1 | 8.9 |
| 2004 | 2.1 | 2.8 | 5.5 | 5.8 | 6.5 | 9.6 |
| 2003 | 2.3 | 3.3 | 6.0 | 6.3 | 7.0 | 10.1 |
| 2002 | 2.0 | 3.2 | 5.8 | 6.0 | 6.7 | 9.6 |
| 2001 | 1.2 | 2.4 | 4.7 | 4.9 | 5.6 | 8.1 |
| 2000 | 0.9 | 1.8 | 4.0 | 4.2 | 4.8 | 7.0 |
Note: LF: labor force; U1, persons unemployed 15 weeks % LF; U2, job losers and persons who completed temporary jobs %LF; U3, total unemployed % LF; U4, total unemployed plus discouraged workers, plus all other marginally attached workers; % LF plus discouraged workers; U5, total unemployed, plus discouraged workers, plus all other marginally attached workers % LF plus all marginally attached workers; U6, total unemployed, plus all marginally attached workers, plus total employed part time for economic reasons % LF plus all marginally attached workers
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Monthly seasonally adjusted measures of labor underutilization are provided in Table I-8. U6 climbed from 16.2 percent in Aug 2011 to 16.4 percent in Sep 2011 and then fell to 14.5 percent in Apr 2012, increasing to 15.0 percent in Jul 2012, 14.7 percent in both Aug and Sep 2012 and 14.6 percent in Oct 2012. Unemployment is an incomplete measure of the stress in US job markets. A different calculation in this blog is provided by using the participation rate in the labor force before the global recession. This calculation shows 28.1 million in job stress of unemployment/underemployment in Oct 2012, not seasonally adjusted, corresponding to 17.4 percent of the labor force (Table I-4 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/11/twenty-eight-million-unemployed-or.html).
Table I-8, US, Alternative Measures of Labor Underutilization SA %
| U1 | U2 | U3 | U4 | U5 | U6 | |
| Oct 2012 | 4.4 | 4.2 | 7.9 | 8.4 | 9.3 | 14.6 |
| Sep | 4.3 | 4.2 | 7.8 | 8.3 | 9.3 | 14.7 |
| Aug | 4.4 | 4.5 | 8.1 | 8.6 | 9.6 | 14.7 |
| Jul | 4.5 | 4.6 | 8.3 | 8.8 | 9.7 | 15.0 |
| Jun | 4.6 | 4.6 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 9.7 | 14.9 |
| May | 4.6 | 4.5 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 9.6 | 14.8 |
| Apr | 4.5 | 4.4 | 8.1 | 8.7 | 9.5 | 14.5 |
| Mar | 4.6 | 4.5 | 8.2 | 8.7 | 9.6 | 14.5 |
| Feb | 4.8 | 4.7 | 8.3 | 8.9 | 9.8 | 14.9 |
| Jan | 4.9 | 4.7 | 8.3 | 8.9 | 9.9 | 15.1 |
| Dec 2011 | 5.0 | 4.9 | 8.5 | 9.1 | 10.0 | 15.2 |
| Nov | 5.0 | 4.9 | 8.7 | 9.3 | 10.2 | 15.6 |
| Oct | 5.1 | 5.1 | 8.9 | 9.5 | 10.4 | 16.0 |
| Sep | 5.3 | 5.2 | 9.0 | 9.6 | 10.5 | 16.4 |
| Aug | 5.3 | 5.3 | 9.1 | 9.6 | 10.6 | 16.2 |
| Jul | 5.3 | 5.3 | 9.1 | 9.7 | 10.7 | 16.1 |
| Jun | 5.3 | 5.4 | 9.1 | 9.7 | 10.7 | 16.2 |
| May | 5.3 | 5.4 | 9.0 | 9.5 | 10.3 | 15.8 |
| Apr | 5.2 | 5.3 | 9.0 | 9.6 | 10.4 | 15.9 |
| Mar | 5.3 | 5.4 | 8.9 | 9.4 | 10.3 | 15.7 |
| Feb | 5.4 | 5.4 | 9.0 | 9.6 | 10.6 | 15.9 |
| Jan | 5.5 | 5.5 | 9.1 | 9.7 | 10.7 | 16.1 |
Note: LF: labor force; U1, persons unemployed 15 weeks % LF; U2, job losers and persons who completed temporary jobs %LF; U3, total unemployed % LF; U4, total unemployed plus discouraged workers, plus all other marginally attached workers; % LF plus discouraged workers; U5, total unemployed, plus discouraged workers, plus all other marginally attached workers % LF plus all marginally attached workers; U6, total unemployed, plus all marginally attached workers, plus total employed part time for economic reasons % LF plus all marginally attached workers
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
Chart I-16 provides U6 on a monthly basis from 2001 to 2012. There was a steep climb from 2007 into 2009 and then this measure of unemployment and underemployment stabilized at that high level but declined into 2012. The low of U16 SA was 7.9 percent in Dec 2006 and the peak was 17.2 percent in Oct 2009. The low NSA was 7.6 percent in Oct 2006 and the peak was 18.0 percent in Jan 2010.
Chart I-16, US, U6, total unemployed, plus all marginally attached workers, plus total employed part Month, SA, 2001-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/cps/data.htm
Chart I-17 provides the number employed part-time for economic reasons or who cannot find full-time employment. There are sharp declines at the end of 2009, 2010 and 2011 but an increase in 2012.
Chart I-17, US, Working Part-time for Economic Reasons
Thousands, Month SA 2001-2012
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/cps/data.htm
There is strong seasonality in US labor markets around the end of the year. The number employed part-time for economic reasons because they could not find full-time employment fell from 9.270 million in Sep 2011 to 8.031 million in Aug 2012, seasonally adjusted, or decline of 1.024 million in nine months, as shown in Table I-9, but then rebounded to 8.613 million in Sep 2012 for increase of 582,000 in one month from Aug to Sep 2012, declining to 8.344 in Oct 2012 or by 269,000 again in one month. There is an increase of 313,000 in part-time for economic reasons from Aug 2012 to Oct 2012. The number employed full-time increased from 112.841 million in Oct 2011 to 115.290 million in Mar 2012 or 2.449 million but then fell to 114.212 million in May 2012 or 1.078 million fewer full-time employed than in Mar 2012. The number employed full-time increased from 114,388 million in Aug 2012 to 115.459 million in Oct 2012 or increase of 1.071 million full-time jobs in two months. The number of employed part-time for economic reasons actually increased without seasonal adjustment from 8.271 million in Nov 2011 to 8.428 million in Dec 2011 or by 157,000 and then to 8.918 million in Jan 2012 or by an additional 490,000 for cumulative increase from Nov 2011 to Jan 2012 of 647,000. The level of employed part-time for economic reasons then fell from 8.918 million in Jan 2012 to 7.867 million in Mar 2012 or by 1.0151 million and to 7.694 million in Apr 2012 or 1.224 million fewer relative to Jan 2012. In Aug 2012, the number employed part-time for economic reasons reached 7.842 million NSA or 148,000 more than in Apr 2012. The number employed part-time for economic reasons increased from 7.842 million in Aug 2012 to 8.110 million in Sep 2012 or by 3.4 percent. The number part-time for economic reasons fell from 8.110 million in Sep 2012 to 7.870 million in Oct 2012 or by 240.000 in one month. The number employed full time without seasonal adjustment fell from 113.138 million in Nov 2011 to 113.050 million in Dec 2011 or by 88,000 and fell further to 111.879 in Jan 2012 for cumulative decrease of 1.259 million. The number employed full-time not seasonally adjusted fell from 113.138 million in Nov 2011 to 112.587 million in Feb 2012 or by 551.000 but increased to 116.214 million in Aug 2012 or 3.076 million more full-time jobs than in Nov 2011. The number employed full-time not seasonally adjusted decreased from 116.214 million in Aug 2012 to 115.678 million in Sep 2012 for loss of 536,000 full-time jobs and rose to 116.045 million in Oct 2012 or by 367,000 full-time jobs in one month relative to Sep 2012. Comparisons over long periods require use of NSA data. The number with full-time jobs fell from a high of 123.219 million in Jul 2007 to 108.777 million in Jan 2010 or by 14.442 million. The number with full-time jobs in Oct 2012 is 116.045 million, which is lower by 7.174 million relative to the peak of 123.219 million in Jul 2007. There appear to be around 10 million fewer full-time jobs in the US than before the global recession. Growth at 2.2 percent on average in the thirteen quarters of expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2012 compared with 6.2 percent on average in expansions from postwar cyclical contractions is the main culprit of the fractured US labor market (see table I-5 in http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/10/mediocre-and-decelerating-united-states.html).
Table I-9, US, Employed Part-time for Economic Reasons, Thousands, and Full-time, Millions
| Part-time Thousands | Full-time Millions | |
| Seasonally Adjusted | ||
| Oct 2012 | 8,344 | 115.459 |
| Sep 2012 | 8,613 | 115.226 |
| Aug 2012 | 8,031 | 114.388 |
| Jul 2012 | 8,246 | 114.345 |
| Jun 2012 | 8,210 | 114.573 |
| May 2012 | 8,098 | 114.212 |
| Apr 2012 | 7,853 | 114.478 |
| Mar 2012 | 7,672 | 115.290 |
| Feb 2012 | 8,119 | 114.408 |
| Jan 2012 | 8,230 | 113.845 |
| Dec 2011 | 8,098 | 113.765 |
| Nov 2011 | 8,469 | 113.212 |
| Oct 2011 | 8,790 | 112.841 |
| Sep 2011 | 9,270 | 112.479 |
| Aug 2011 | 8,787 | 112.406 |
| Jul 2011 | 8,437 | 112.006 |
| Not Seasonally Adjusted | ||
| Oct 2012 | 7,870 | 116.045 |
| Sep 2012 | 8,110 | 115.678 |
| Aug 2012 | 7,842 | 116.214 |
| Jul 2012 | 8,316 | 116.131 |
| Jun 2012 | 8,394 | 116.024 |
| May 2012 | 7,837 | 114.634 |
| Apr 2012 | 7,694 | 113.999 |
| Mar 2012 | 7,867 | 113.916 |
| Feb 2012 | 8,455 | 112.587 |
| Jan 2012 | 8,918 | 111.879 |
| Dec 2011 | 8,428 | 113.050 |
| Nov 2011 | 8,271 | 113.138 |
| Oct 2011 | 8,258 | 113.456 |
| Sep 2011 | 8,541 | 112.980 |
| Aug 2011 | 8,604 | 114.286 |
| Jul 2011 | 8,514 | 113.759 |
| Jun 2011 | 8,738 | 113.255 |
| May 2011 | 8,270 | 112.618 |
| Apr 2011 | 8,425 | 111.844 |
| Mar 2011 | 8,737 | 111.186 |
| Feb 2011 | 8,749 | 110.731 |
| Jan 2011 | 9,187 | 110.373 |
| Dec 2010 | 9,205 | 111.207 |
| Nov 2010 | 8,670 | 111.348 |
| Oct 2010 | 8,408 | 112.342 |
| Sep 2010 | 8,628 | 112.385 |
| Aug 2010 | 8,628 | 113.508 |
| Jul 2010 | 8,737 | 113.974 |
| Jun 2010 | 8,867 | 113.856 |
| May 2010 | 8,513 | 112.809 |
| Apr 2010 | 8,921 | 111.391 |
| Mar 2010 | 9,343 | 109.877 |
| Feb 2010 | 9,282 | 109.100 |
| Jan 2010 | 9,290 | 108.777 (low) |
| Dec 2009 | 9,354 (high) | 109.875 |
| Oct 2009 | 8,474 | 112.274 |
| Sep 2009 | 8,255 | 111.991 |
| Aug 2009 | 8,835 | 113.863 |
| Jul 2009 | 9,103 | 114.184 |
| Jun 2009 | 9,301 | 114.014 |
| May 2009 | 8,785 | 113.083 |
| Apr 2009 | 8,648 | 112.746 |
| Mar 2009 | 9,305 | 112.215 |
| Feb 2009 | 9,170 | 112.947 |
| Jan 2009 | 8,829 | 113.815 |
| Oct 2008 | 6,267 | 120.020 |
| Sep 2008 | 5,701 | 120.213 |
| Aug 2008 | 5,736 | 121.556 |
| Jul 2008 | 6,054 | 122.378 |
| Jun 2008 | 5,697 | 121.845 |
| May 2008 | 5,096 | 120.809 |
| Apr 2008 | 5,071 | 120.027 |
| Mar 2008 | 5,038 | 119.875 |
| Feb 2008 | 5,114 | 119.452 |
| Jan 2008 | 5,340 | 119.332 |
| Oct 2007 | 4,028 | 122.006 |
| Sep 2007 | 4,137 | 121.278 |
| Aug 2007 | 4,494 | 122.870 |
| Jul 2007 | 4,516 | 123.219 (high) |
| Jun 2007 | 4,469 | 122.150 |
| May 2007 | 4,315 | 120.846 |
| Apr 2007 | 4,205 | 119.609 |
| Mar 2007 | 4,384 | 119.640 |
| Feb 2007 | 4,417 | 119.041 |
| Jan 2007 | 4,726 | 119.094 |
| Oct 2006 | 4,010 | 121.199 |
| Sep 2006 | 3,735 (low) | 120.780 |
| Aug 2006 | 4,104 | 121.979 |
| Jul 2006 | 4,450 | 121.951 |
| Jun 2006 | 4,456 | 121.070 |
| May 2006 | 3,968 | 118.925 |
| Apr 2006 | 3,787 | 118.559 |
| Mar 2006 | 4,097 | 117.693 |
| Feb 2006 | 4,403 | 116.823 |
| Jan 2006 | 4,597 | 116.395 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/
People lose their marketable job skills after prolonged unemployment and find increasing difficulty in finding another job. Chart I-18 shows the sharp rise in unemployed over 27 weeks and stabilization at an extremely high level.
Chart I-18, US, Number Unemployed for 27 Weeks or Over, Thousands SA Month 2001-2011
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/cps/data.htm
Another segment of U6 consists of people marginally attached to the labor force who continue to seek employment but less frequently on the frustration there may not be a job for them. Chart I-19 shows the sharp rise in people marginally attached to the labor force after 2007 and subsequent stabilization.
Chart I-19, US, Marginally Attached to the Labor Force, NSA Month 2001-2012
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/cps/data.htm
IA3 Ten Million Fewer Full-time Jobs. Chart I-20 reveals the fracture in the US labor market. The number of workers with full-time jobs not-seasonally-adjusted rose with fluctuations from 2002 to a peak in 2007, collapsing during the global recession. The terrible state of the job market is shown in the segment from 2009 to 2012 with fluctuations around the typical behavior of a stationary series: there is no improvement in the United States in creating full-time jobs.
Chart I-20, US, Full-time Employed, Thousands, NSA, 2001-2012
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/cps/data.htm
IA4 Youth Unemployment and Middle-Aged Unemployment. The United States is experiencing high youth unemployment as in European economies. Table I-10 provides the employment level for ages 16 to 24 years of age estimated by the Bureau of Labor Statistics. On an annual basis, youth employment fell from 20.041 million in 2006 to 17.362 million in 2011 or 2.679 million fewer youth jobs. During the seasonal peak months of youth employment in the summer from Jun to Aug, youth employment has fallen by more than two million jobs relative to 21.9 million in Jul 2006. There are two hardships behind these data. First, young people cannot find employment after finishing high-school and college, reducing prospects for achievement in older age. Second, students with more modest means cannot find employment to keep them in college.
Table I-10, US, Employment Level 16-24 Years, Thousands, NSA
| Year | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Annual |
| 2001 | 21212 | 22042 | 20529 | 19706 | 19694 | 20088 |
| 2002 | 20828 | 21501 | 20653 | 19466 | 19542 | 19683 |
| 2003 | 20432 | 20950 | 20181 | 18909 | 19139 | 19351 |
| 2004 | 20587 | 21447 | 20660 | 19158 | 19609 | 19630 |
| 2005 | 20949 | 21749 | 20814 | 19503 | 19794 | 19770 |
| 2006 | 21268 | 21914 | 21167 | 19604 | 19853 | 20041 |
| 2007 | 21098 | 21717 | 20413 | 19498 | 19564 | 19875 |
| 2008 | 20466 | 21021 | 20096 | 18818 | 18757 | 19202 |
| 2009 | 18726 | 19304 | 18270 | 16972 | 16671 | 17601 |
| 2010 | 17920 | 18564 | 18061 | 16874 | 16867 | 17077 |
| 2011 | 18180 | 18632 | 18067 | 17238 | 17532 | 17362 |
| 2012 | 18907 | 19461 | 18171 | 17687 | 17842 |
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/cps/data.htm
I-21 provides US employment level ages 16 to 24 years from 2002 to 2012. Employment level is sharply lower in Jun 2012 relative to the peak in 2007.
Chart I-21, US, Employment Level 16-24 Years, Thousands SA, 2001-2012
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Table I-11 provides US unemployment level ages 16 to 24 years. The number unemployed ages 16 to 24 years increased from 2342 thousand in 2007 to 3634 thousand in 2011 or by 1.292 million. This situation may persist for many years.
Table I-11, US, Unemployment Level 16-24 Years, Thousands NSA
| Year | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Annual |
| 2001 | 2775 | 2585 | 2461 | 2301 | 2424 | 2371 |
| 2002 | 3167 | 3034 | 2688 | 2506 | 2468 | 2683 |
| 2003 | 3542 | 3200 | 2724 | 2698 | 2522 | 2746 |
| 2004 | 3191 | 3018 | 2585 | 2493 | 2572 | 2638 |
| 2005 | 3010 | 2688 | 2519 | 2339 | 2285 | 2521 |
| 2006 | 2860 | 2750 | 2467 | 2297 | 2252 | 2353 |
| 2007 | 2883 | 2622 | 2388 | 2419 | 2258 | 2342 |
| 2008 | 3450 | 3408 | 2990 | 2904 | 2842 | 2830 |
| 2009 | 4653 | 4387 | 4004 | 3774 | 3789 | 3760 |
| 2010 | 4481 | 4374 | 3903 | 3604 | 3731 | 3857 |
| 2011 | 4248 | 4110 | 3820 | 3541 | 3386 | 3634 |
| 2012 | 4180 | 4011 | 3672 | 3174 | 3285 |
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-22 provides the unemployment level ages 16 to 24 from 2002 to 2012. The level rose sharply from 2007 to 2010 with tepid improvement into 2012.
Chart I-22, US, Unemployment Level 16-24 Years, Thousands SA, 2001-2012
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Table I-12 provides the rate of unemployment of young peoples in ages 16 to 24 years. The annual rate jumped from 10.5 percent in 2007 to 18.4 percent in 2010 and 17.3 percent in 2011. During the seasonal peak in Jul 2011 the rate of youth unemployed was 18.1 percent and 17.1 percent in Jul 2012 compared with 10.8 percent in Jul 2007.
Table I-12, US, Unemployment Rate 16-24 Years, Thousands, NSA
| Year | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Annual |
| 2001 | 10.0 | 11.6 | 10.5 | 10.7 | 10.5 | 11.0 | 11.2 | 10.6 |
| 2002 | 11.6 | 13.2 | 12.4 | 11.5 | 11.4 | 11.2 | 11.7 | 12.0 |
| 2003 | 13.0 | 14.8 | 13.3 | 11.9 | 12.5 | 11.6 | 11.6 | 12.4 |
| 2004 | 12.2 | 13.4 | 12.3 | 11.1 | 11.5 | 11.6 | 11.1 | 11.8 |
| 2005 | 11.9 | 12.6 | 11.0 | 10.8 | 10.7 | 10.3 | 10.7 | 11.3 |
| 2006 | 10.2 | 11.9 | 11.2 | 10.4 | 10.5 | 10.2 | 10.1 | 10.5 |
| 2007 | 10.2 | 12.0 | 10.8 | 10.5 | 11.0 | 10.3 | 10.3 | 10.5 |
| 2008 | 13.3 | 14.4 | 14.0 | 13.0 | 13.4 | 13.2 | 13.3 | 12.8 |
| 2009 | 18.0 | 19.9 | 18.5 | 18.0 | 18.2 | 18.5 | 18.1 | 17.6 |
| 2010 | 18.4 | 20.0 | 19.1 | 17.8 | 17.6 | 18.1 | 17.4 | 18.4 |
| 2011 | 17.5 | 18.9 | 18.1 | 17.5 | 17.0 | 16.2 | 15.9 | 17.3 |
| 2012 | 16.3 | 18.1 | 17.1 | 16.8 | 15.2 | 15.5 |
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-23 provides the BLS estimate of the not-seasonally-adjusted rate of youth unemployment for ages 16 to 24 years from 2002 to 2012. The rate of youth unemployment increased sharply during the global recession of 2008 and 2009 but has failed to drop to earlier lower levels during the twelve consecutive quarters of expansion of the economy since IIIQ2009 because of much lower growth at 2.2 percent annual equivalent on average compared with 6.2 percent on average in cyclical expansions since World War II Table I -5 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/10/mediocre-and-decelerating-united-states.html).
Chart I-23, US, Unemployment Rate 16-24 Years, Percent, NSA, 2001-2012
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-24 provides longer perspective with the rate of youth unemployment in ages 16 to 24 years from 1948 to 2012. The rate of youth unemployment rose to 20 percent during the contractions of the early 1980s and also during the contraction of the global recession in 2008 and 2009. The data illustrate again the claim in this blog that the contractions of the early 1980s are the valid framework for comparison with the global recession of 2008 and 2009 instead of misleading comparisons with the 1930s. During the initial phase of recovery, the rate of youth unemployment 16 to 24 years NSA fell from 18.9 percent in Jun 1983 to 14.5 percent in Jun 1984 while the rate of youth unemployment 16 to 24 years was nearly the same during the expansion after IIIQ2009: 18.5 percent in Oct 2009, 18.1 percent in Oct 2010, 16.2 percent in Oct 2011 and 15.5 percent in Oct 2012. In Jul 2007, the rate of youth unemployment was 10.8 percent, increasing to 17.1 percent in Jul 2012. The difference originates in the vigorous seasonally-adjusted annual equivalent average rate of GDP growth of 5.7 percent during the recovery from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 compared with 2.2 percent on average during the first eleven quarters of expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2012 (see table I-5 in http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/10/mediocre-and-decelerating-united-states.html). The fractured US labor market denies an early start for young people.
Chart I-24, US, Unemployment Rate 16-24 Years, Percent NSA, 1948-2012
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
It is more difficult to move to other jobs after a certain age because of fewer available opportunities for matured individuals than for new entrants into the labor force. Middle-aged unemployed are less likely to find another job. Table I-13 provides the unemployment level ages 45 years and over. The number unemployed ages 45 years and over rose from 1.985 million in Jul 2006 to 4.821 million in July 2010 or by 142.9 percent. The number of unemployed ages 45 years and over declined to 4.405 million in Jul 2012 that is still higher by 121.9 percent than in Jul 2006. The number unemployed age 45 and over jumped from 1.607 million in Oct 2006 to 4.576 million in Oct 2010 or 184.8 percent and at 3.800 million in Oct 2012 is higher by 2.193 million or 136.5 percent higher than 1.607 million in Oct 2006.
Table I-13, US, Unemployment Level 45 Years and Over, Thousands NSA
| Year | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Annual |
| 2001 | 1259 | 1371 | 1539 | 1640 | 1586 | 1722 | 1576 |
| 2002 | 1999 | 2190 | 2173 | 2114 | 1966 | 1945 | 2114 |
| 2003 | 2112 | 2212 | 2281 | 2301 | 2157 | 2032 | 2253 |
| 2004 | 2025 | 2182 | 2116 | 2082 | 1951 | 1931 | 2149 |
| 2005 | 1844 | 1868 | 2119 | 1895 | 1992 | 1875 | 2009 |
| 2006 | 1784 | 1813 | 1985 | 1869 | 1710 | 1607 | 1848 |
| 2007 | 1803 | 1805 | 2053 | 1956 | 1854 | 1885 | 1966 |
| 2008 | 2095 | 2211 | 2492 | 2695 | 2595 | 2728 | 2540 |
| 2009 | 4175 | 4505 | 4757 | 4683 | 4560 | 4492 | 4500 |
| 2010 | 4565 | 4564 | 4821 | 5128 | 4640 | 4576 | 4879 |
| 2011 | 4356 | 4559 | 4772 | 4592 | 4426 | 4375 | 4537 |
| 2012 | 4083 | 4084 | 4405 | 4179 | 3899 | 3800 |
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Chart I-25 provides the level unemployed ages 45 years and over. There was sharp increase during the global recession and inadequate decline. There was an increase during the 2001 recession and then stability. The US is facing a major challenge of reemploying middle-aged workers.
Chart I-25, US, Unemployment Level Ages 45 Years and Over, Thousands, NSA, 1976-2012
Sources: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
IB Collapse of United States Dynamism of Income Growth and Employment Creation. There are four major approaches to the analysis of the depth of the financial crisis and global recession from IVQ2007 (Dec) to IIQ2009 (Jun) and the subpar recovery from IIIQ2009 (Jul) to the present IIIQ2012: (1) deeper contraction and slower recovery in recessions with financial crises; (2) counterfactual of avoiding deeper contraction by fiscal and monetary policies; (3) counterfactual that the financial crises and global recession would have been avoided had economic policies been different; and (4) evidence that growth rates are higher after deeper recessions with financial crises. A counterfactual consists of theory and measurements of what would have occurred otherwise if economic policies or institutional arrangements had been different. This task is quite difficult because economic data are observed with all effects as they actually occurred while the counterfactual attempts to evaluate how data would differ had policies and institutional arrangements been different (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. I (2008b), 125, 136). Counterfactual data are unobserved and must be calculated using theory and measurement methods. The measurement of costs and benefits of projects or applied welfare economics (Harberger 1971, 1997) specifies and attempts to measure projects such as what would be economic welfare with or without a bridge or whether markets would be more or less competitive in the absence of antitrust and regulation laws (Winston 2006). Counterfactuals were used in the “new economic history” of the United States to measure the economy with or without railroads (Fishlow 1965, Fogel 1964) and also in analyzing slavery (Fogel and Engerman 1974). A critical counterfactual in economic history is how Britain surged ahead of France (North and Weingast 1989). These four approaches are discussed below in turn followed with comparison of the two recessions of the 1980s from IQ1980 (Jan) to IIIQ1980 (Jul) and from IIIQ1981 (Jul) to IVQ1982 (Nov) as dated by the National Bureau of Economic Research (NBER http://www.nber.org/cycles.html). These comparisons are not idle exercises, defining the interpretation of history and even possibly critical policies and institutional arrangements. There is active debate on these issues (Bordo 2012Oct 21 http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2012-10-21/why-this-u-s-recovery-is-weaker.html Reinhart and Rogoff, 2012Oct14 http://www.economics.harvard.edu/faculty/rogoff/files/Is_US_Different_RR_3.pdf Taylor 2012Oct 25 http://www.johnbtaylorsblog.blogspot.co.uk/2012/10/an-unusually-weak-recovery-as-usually.html, Wolf 2012Oct23 http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/791fc13a-1c57-11e2-a63b-00144feabdc0.html#axzz2AotsUk1q).
(1) Lower Growth Rates in Recessions with Financial Crises. A monumental effort of data gathering, calculation and analysis by Professors Carmen M. Reinhart and Kenneth Rogoff at Harvard University is highly relevant to banking crises, financial crash, debt crises and economic growth (Reinhart 2010CB; Reinhart and Rogoff 2011AF, 2011Jul14, 2011EJ, 2011CEPR, 2010FCDC, 2010GTD, 2009TD, 2009AFC, 2008TDPV; see also Reinhart and Reinhart 2011Feb, 2010AF and Reinhart and Sbrancia 2011). See http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/07/debt-and-financial-risk-aversion-and.html. The dataset of Reinhart and Rogoff (2010GTD, 1) is quite unique in breadth of countries and over time periods:
“Our results incorporate data on 44 countries spanning about 200 years. Taken together, the data incorporate over 3,700 annual observations covering a wide range of political systems, institutions, exchange rate and monetary arrangements and historic circumstances. We also employ more recent data on external debt, including debt owed by government and by private entities.”
Reinhart and Rogoff (2010GTD, 2011CEPR) classify the dataset of 2317 observations into 20 advanced economies and 24 emerging market economies. In each of the advanced and emerging categories, the data for countries is divided into buckets according to the ratio of gross central government debt to GDP: below 30, 30 to 60, 60 to 90 and higher than 90 (Reinhart and Rogoff 2010GTD, Table 1, 4). Median and average yearly percentage growth rates of GDP are calculated for each of the buckets for advanced economies. There does not appear to be any relation for debt/GDP ratios below 90. The highest growth rates are for debt/GDP ratios below 30: 3.7 percent for the average and 3.9 for the median. Growth is significantly lower for debt/GDP ratios above 90: 1.7 for the average and 1.9 percent for the median. GDP growth rates for the intermediate buckets are in a range around 3 percent: the highest 3.4 percent average is for the bucket 60 to 90 and 3.1 percent median for 30 to 60. There is even sharper contrast for the United States: 4.0 percent growth for debt/GDP ratio below 30; 3.4 percent growth for debt/GDP ratio of 30 to 60; 3.3 percent growth for debt/GDP ratio of 60 to 90; and minus 1.8 percent, contraction, of GDP for debt/GDP ratio above 90.
For the five countries with systemic financial crises—Iceland, Ireland, UK, Spain and the US—real average debt levels have increased by 75 percent between 2007 and 2009 (Reinhart and Rogoff 2010GTD, Figure 1). The cumulative increase in public debt in the three years after systemic banking crisis in a group of episodes after World War II is 86 percent (Reinhart and Rogoff 2011CEPR, Figure 2, 10).
An important concept is “this time is different syndrome,” which “is rooted in the firmly-held belief that financial crises are something that happens to other people in other countries at other times; crises do not happen here and now to us” (Reinhart and Rogoff 2010FCDC, 9). There is both an arrogance and ignorance in “this time is different” syndrome, as explained by Reinhart and Rogoff (2010FCDC, 34):
“The ignorance, of course, stems from the belief that financial crises happen to other people at other time in other places. Outside a small number of experts, few people fully appreciate the universality of financial crises. The arrogance is of those who believe they have figured out how to do things better and smarter so that the boom can long continue without a crisis.”
There is sober warning by Reinhart and Rogoff (2011CEPR, 42) on the basis of the momentous effort of their scholarly data gathering, calculation and analysis:
“Despite considerable deleveraging by the private financial sector, total debt remains near its historic high in 2008. Total public sector debt during the first quarter of 2010 is 117 percent of GDP. It has only been higher during a one-year sting at 119 percent in 1945. Perhaps soaring US debt levels will not prove to be a drag on growth in the decades to come. However, if history is any guide, that is a risky proposition and over-reliance on US exceptionalism may only be one more example of the “This Time is Different” syndrome.”
As both sides of the Atlantic economy maneuver around defaults the experience on debt and growth deserves significant emphasis in research and policy. The world economy is slowing with high levels of unemployment in advanced economies. Countries do not grow themselves out of unsustainable debts but rather through de facto defaults by means of financial repression and in some cases through inflation. The conclusion is that this time is not different.
Professor Alan M. Taylor (2012) at the University of Virginia analyzes own and collaborative research on 140 years of history with data from 14 advanced economies in the effort to elucidate experience anticipating, during and after financial crises. The conclusion is (Allan M. Taylor 2012, 8):
“Recessions might be painful, but they tend to be even more painful when combined with financial crises or (worse) global crises, and we already know that post-2008 experience will not overturn this conclusion. The impact on credit is also very strong: financial crises lead to strong setbacks in the rate of growth of loans as compared to what happens in normal recessions, and this effect is strong for global crises. Finally, inflation generally falls in recessions, but the downdraft is stronger in financial crisis times.”
Alan M. Taylor (2012) also finds that advanced economies entered the global recession with the largest financial sector in history. There was doubling after 1980 of the ratio of loans to GDP and tripling of the size of bank balance sheets. In contrast, in the period from 1950 to 1970 there was high investment, savings and growth in advanced economies with firm regulation of finance and controls of foreign capital flows.
(2) Counterfactual of the Global Recession. There is a difficult decision on when to withdraw the fiscal stimulus that could have adverse consequences on current growth and employment analyzed by Krugman (2011Jun18). CBO (2011JunLTBO, Chapter 2) considers the timing of withdrawal as well as the equally tough problems that result from not taking prompt action to prevent a possible debt crisis in the future. Krugman (2011Jun18) refers to Eggertsson and Krugman (2010) on the possible contractive effects of debt. The world does not become poorer as a result of debt because an individual’s asset is another’s liability. Past levels of credit may become unacceptable by credit tightening, such as during a financial crisis. Debtors are forced into deleveraging, which results in expenditure reduction, but there may not be compensatory effects by creditors who may not be in need of increasing expenditures. The economy could be pushed toward the lower bound of zero interest rates, or liquidity trap, remaining in that threshold of deflation and high unemployment.
Analysis of debt can lead to the solution of the timing of when to cease stimulus by fiscal spending (Krugman 2011Jun18). Excessive debt caused the financial crisis and global recession and it is difficult to understand how more debt can recover the economy. Krugman (2011Jun18) argues that the level of debt is not important because one individual’s asset is another individual’s liability. The distribution of debt is important when economic agents with high debt levels are encountering different constraints than economic agents with low debt levels. The opportunity for recovery may exist in borrowing by some agents that can adjust the adverse effects of past excessive borrowing by other agents. As Krugman (2011Jun18, 20) states:
“Suppose, in particular, that the government can borrow for a while, using the borrowed money to buy useful things like infrastructure. The true social cost of these things will be very low, because the spending will be putting resources that would otherwise be unemployed to work. And government spending will also make it easier for highly indebted players to pay down their debt; if the spending is sufficiently sustained, it can bring the debtors to the point where they’re no longer so severely balance-sheet constrained, and further deficit spending is no longer required to achieve full employment. Yes, private debt will in part have been replaced by public debt – but the point is that debt will have been shifted away from severely balance-sheet-constrained players, so that the economy’s problems will have been reduced even if the overall level of debt hasn’t fallen. The bottom line, then, is that the plausible-sounding argument that debt can’t cure debt is just wrong. On the contrary, it can – and the alternative is a prolonged period of economic weakness that actually makes the debt problem harder to resolve.”
Besides operational issues, the consideration of this argument would require specifying and measuring two types of gains and losses from this policy: (1) the benefits in terms of growth and employment currently; and (2) the costs of postponing the adjustment such as in the exercise by CBO (2011JunLTO, 28-31) in Table 11. It may be easier to analyze the costs and benefits than actual measurement.
An analytical and empirical approach is followed by Blinder and Zandi (2010), using the Moody’s Analytics model of the US economy with four different scenarios: (1) baseline with all policies used; (2) counterfactual including all fiscal stimulus policies but excluding financial stimulus policies; (3) counterfactual including all financial stimulus policies but excluding fiscal stimulus; and (4) a scenario excluding all policies. The scenario excluding all policies is an important reference or the counterfactual of what would have happened if the government had been entirely inactive. A salient feature of the work by Blinder and Zandi (2010) is the consideration of both fiscal and financial policies. There was probably more activity with financial policies than with fiscal policies. Financial policies included the Fed balance sheet, 11 facilities of direct credit to illiquid segments of financial markets, interest rate policy, the Financial Stability Plan including stress tests of banks, the Troubled Asset Relief Program (TARP) and others (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009b), 157-67; Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009a), 224-7).
Blinder and Zandi (2010, 4) find that:
“In the scenario that excludes all the extraordinary policies, the downturn continues into 2011. Real GDP falls a stunning 7.4% in 2009 and another 3.7% in 2010 (see Table 3). The peak-to-trough decline in GDP is therefore close to 12%, compared to an actual decline of about 4%. By the time employment hits bottom, some 16.6 million jobs are lost in this scenario—about twice as many as actually were lost. The unemployment rate peaks at 16.5%, and although not determined in this analysis, it would not be surprising if the underemployment rate approached one-fourth of the labor force. The federal budget deficit surges to over $2 trillion in fiscal year 2010, $2.6 trillion in fiscal year 2011, and $2.25 trillion in FY 2012. Remember, this is with no policy response. With outright deflation in prices and wages in 2009-2011, this dark scenario constitutes a 1930s-like depression.”
The conclusion by Blinder and Zandi (2010) is that if the US had not taken massive fiscal and financial measures the economy could have suffered far more during a prolonged period. There are still a multitude of questions that cloud understanding of the impact of the recession and what would have happened without massive policy impulses. Some effects are quite difficult to measure. An important argument by Blinder and Zandi (2010) is that this evaluation of counterfactuals is relevant to the need of stimulus if economic conditions worsened again.
(3) Counterfactual of Policies Causing the Financial Crisis and Global Recession. The counterfactual of avoidance of deeper and more prolonged contraction by fiscal and monetary policies is not the critical issue. As Professor John B. Taylor (2012Oct25) argues the critically important counterfactual is that the financial crisis and global recessions would have not occurred in the first place if different economic policies had been followed. The counterfactual intends to verify that a combination of housing policies and discretionary monetary policies instead of rules (Taylor 1993) caused, deepened and prolonged the financial crisis (Taylor 2007, 2008Nov, 2009, 2012FP, 2012Mar27, 2012Mar28, 2012JMCB; see http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/rules-versus-discretionary-authorities.html) and that the experience resembles that of the Great Inflation of the 1960s and 1970s with stop-and-go growth/inflation that coined the term stagflation (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/rules-versus-discretionary-authorities.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/05/slowing-growth-global-inflation-great.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/04/new-economics-of-rose-garden-turned.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/03/is-there-second-act-of-us-great.html and Appendix I).
The explanation of the sharp contraction of United States housing can probably be found in the origins of the financial crisis and global recession. Let V(T) represent the value of the firm’s equity at time T and B stand for the promised debt of the firm to bondholders and assume that corporate management, elected by equity owners, is acting on the interests of equity owners. Robert C. Merton (1974, 453) states:
“On the maturity date T, the firm must either pay the promised payment of B to the debtholders or else the current equity will be valueless. Clearly, if at time T, V(T) > B, the firm should pay the bondholders because the value of equity will be V(T) – B > 0 whereas if they do not, the value of equity would be zero. If V(T) ≤ B, then the firm will not make the payment and default the firm to the bondholders because otherwise the equity holders would have to pay in additional money and the (formal) value of equity prior to such payments would be (V(T)- B) < 0.”
Pelaez and Pelaez (The Global Recession Risk (2007), 208-9) apply this analysis to the US housing market in 2005-2006 concluding:
“The house market [in 2006] is probably operating with low historical levels of individual equity. There is an application of structural models [Duffie and Singleton 2003] to the individual decisions on whether or not to continue paying a mortgage. The costs of sale would include realtor and legal fees. There could be a point where the expected net sale value of the real estate may be just lower than the value of the mortgage. At that point, there would be an incentive to default. The default vulnerability of securitization is unknown.”
There are multiple important determinants of the interest rate: “aggregate wealth, the distribution of wealth among investors, expected rate of return on physical investment, taxes, government policy and inflation” (Ingersoll 1987, 405). Aggregate wealth is a major driver of interest rates (Ibid, 406). Unconventional monetary policy, with zero fed funds rates and flattening of long-term yields by quantitative easing, causes uncontrollable effects on risk taking that can have profound undesirable effects on financial stability. Excessively aggressive and exotic monetary policy is the main culprit and not the inadequacy of financial management and risk controls.
The net worth of the economy depends on interest rates. In theory, “income is generally defined as the amount a consumer unit could consume (or believe that it could) while maintaining its wealth intact” (Friedman 1957, 10). Income, Y, is a flow that is obtained by applying a rate of return, r, to a stock of wealth, W, or Y = rW (Ibid). According to a subsequent restatement: “The basic idea is simply that individuals live for many years and that therefore the appropriate constraint for consumption decisions is the long-run expected yield from wealth r*W. This yield was named permanent income: Y* = r*W” (Darby 1974, 229), where * denotes permanent. The simplified relation of income and wealth can be restated as:
W = Y/r (1)
Equation (1) shows that as r goes to zero, r →0, W grows without bound, W→∞.
Lowering the interest rate near the zero bound in 2003-2004 caused the illusion of permanent increases in wealth or net worth in the balance sheets of borrowers and also of lending institutions, securitized banking and every financial institution and investor in the world. The discipline of calculating risks and returns was seriously impaired. The objective of monetary policy was to encourage borrowing, consumption and investment but the exaggerated stimulus resulted in a financial crisis of major proportions as the securitization that had worked for a long period was shocked with policy-induced excessive risk, imprudent credit, high leverage and low liquidity by the incentive to finance everything overnight at close to zero interest rates, from adjustable rate mortgages (ARMS) to asset-backed commercial paper of structured investment vehicles (SIV).
The consequences of inflating liquidity and net worth of borrowers were a global hunt for yields to protect own investments and money under management from the zero interest rates and unattractive long-term yields of Treasuries and other securities. Monetary policy distorted the calculations of risks and returns by households, business and government by providing central bank cheap money. Short-term zero interest rates encourage financing of everything with short-dated funds, explaining the SIVs created off-balance sheet to issue short-term commercial paper to purchase default-prone mortgages that were financed in overnight or short-dated sale and repurchase agreements (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession, 50-1, Regulation of Banks and Finance, 59-60, Globalization and the State Vol. I, 89-92, Globalization and the State Vol. II, 198-9, Government Intervention in Globalization, 62-3, International Financial Architecture, 144-9). ARMS were created to lower monthly mortgage payments by benefitting from lower short-dated reference rates. Financial institutions economized in liquidity that was penalized with near zero interest rates. There was no perception of risk because the monetary authority guaranteed a minimum or floor price of all assets by maintaining low interest rates forever or equivalent to writing an illusory put option on wealth. Subprime mortgages were part of the put on wealth by an illusory put on house prices. The housing subsidy of $221 billion per year created the impression of ever increasing house prices. The suspension of auctions of 30-year Treasuries was designed to increase demand for mortgage-backed securities, lowering their yield, which was equivalent to lowering the costs of housing finance and refinancing. Fannie and Freddie purchased or guaranteed $1.6 trillion of nonprime mortgages and worked with leverage of 75:1 under Congress-provided charters and lax oversight. The combination of these policies resulted in high risks because of the put option on wealth by near zero interest rates, excessive leverage because of cheap rates, low liquidity because of the penalty in the form of low interest rates and unsound credit decisions because the put option on wealth by monetary policy created the illusion that nothing could ever go wrong, causing the credit/dollar crisis and global recession (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession, 157-66, Regulation of Banks, and Finance, 217-27, International Financial Architecture, 15-18, The Global Recession Risk, 221-5, Globalization and the State Vol. II, 197-213, Government Intervention in Globalization, 182-4).
There are significant elements of the theory of bank financial fragility of Diamond and Dybvig (1983) and Diamond and Rajan (2000, 2001a, 2001b) that help to explain the financial fragility of banks during the credit/dollar crisis (see also Diamond 2007). The theory of Diamond and Dybvig (1983) as exposed by Diamond (2007) is that banks funding with demand deposits have a mismatch of liquidity (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 58-66). A run occurs when too many depositors attempt to withdraw cash at the same time. All that is needed is an expectation of failure of the bank. Three important functions of banks are providing evaluation, monitoring and liquidity transformation. Banks invest in human capital to evaluate projects of borrowers in deciding if they merit credit. The evaluation function reduces adverse selection or financing projects with low present value. Banks also provide important monitoring services of following the implementation of projects, avoiding moral hazard that funds be used for, say, real estate speculation instead of the original project of factory construction. The transformation function of banks involves both assets and liabilities of bank balance sheets. Banks convert an illiquid asset or loan for a project with cash flows in the distant future into a liquid liability in the form of demand deposits that can be withdrawn immediately.
In the theory of banking of Diamond and Rajan (2000, 2001a, 2001b), the bank creates liquidity by tying human assets to capital. The collection skills of the relationship banker convert an illiquid project of an entrepreneur into liquid demand deposits that are immediately available for withdrawal. The deposit/capital structure is fragile because of the threat of bank runs. In these days of online banking, the run on Washington Mutual was through withdrawals online. A bank run can be triggered by the decline of the value of bank assets below the value of demand deposits.
Pelaez and Pelaez (Regulation of Banks and Finance 2009b, 60, 64-5) find immediate application of the theories of banking of Diamond, Dybvig and Rajan to the credit/dollar crisis after 2007. It is a credit crisis because the main issue was the deterioration of the credit portfolios of securitized banks as a result of default of subprime mortgages. It is a dollar crisis because of the weakening dollar resulting from relatively low interest rate policies of the US. It caused systemic effects that converted into a global recession not only because of the huge weight of the US economy in the world economy but also because the credit crisis transferred to the UK and Europe. Management skills or human capital of banks are illustrated by the financial engineering of complex products. The increasing importance of human relative to inanimate capital (Rajan and Zingales 2000) is revolutionizing the theory of the firm (Zingales 2000) and corporate governance (Rajan and Zingales 2001). Finance is one of the most important examples of this transformation. Profits were derived from the charter in the original banking institution. Pricing and structuring financial instruments was revolutionized with option pricing formulas developed by Black and Scholes (1973) and Merton (1973, 1974, 1998) that permitted the development of complex products with fair pricing. The successful financial company must attract and retain finance professionals who have invested in human capital, which is a sunk cost to them and not of the institution where they work.
The complex financial products created for securitized banking with high investments in human capital are based on houses, which are as illiquid as the projects of entrepreneurs in the theory of banking. The liquidity fragility of the securitized bank is equivalent to that of the commercial bank in the theory of banking (Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 65). Banks created off-balance sheet structured investment vehicles (SIV) that issued commercial paper receiving AAA rating because of letters of liquidity guarantee by the banks. The commercial paper was converted into liquidity by its use as collateral in SRPs at the lowest rates and minimal haircuts because of the AAA rating of the guarantor bank. In the theory of banking, default can be triggered when the value of assets is perceived as lower than the value of the deposits. Commercial paper issued by SIVs, securitized mortgages and derivatives all obtained SRP liquidity on the basis of illiquid home mortgage loans at the bottom of the pyramid. The run on the securitized bank had a clear origin (Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 65):
“The increasing default of mortgages resulted in an increase in counterparty risk. Banks were hit by the liquidity demands of their counterparties. The liquidity shock extended to many segments of the financial markets—interbank loans, asset-backed commercial paper (ABCP), high-yield bonds and many others—when counterparties preferred lower returns of highly liquid safe havens, such as Treasury securities, than the risk of having to sell the collateral in SRPs at deep discounts or holding an illiquid asset. The price of an illiquid asset is near zero.”
Gorton and Metrick (2010H, 507) provide a revealing quote to the work in 1908 of Edwin R. A. Seligman, professor of political economy at Columbia University, founding member of the American Economic Association and one of its presidents and successful advocate of progressive income taxation. The intention of the quote is to bring forth the important argument that financial crises are explained in terms of “confidence” but as Professor Seligman states in reference to historical banking crises in the US the important task is to explain what caused the lack of confidence. It is instructive to repeat the more extended quote of Seligman (1908, xi) on the explanations of banking crises:
“The current explanations may be divided into two categories. Of these the first includes what might be termed the superficial theories. Thus it is commonly stated that the outbreak of a crisis is due to lack of confidence,--as if the lack of confidence was not in itself the very thing which needs to be explained. Of still slighter value is the attempt to associate a crisis with some particular governmental policy, or with some action of a country’s executive. Such puerile interpretations have commonly been confined to countries like the United States, where the political passions of democracy have had the fullest way. Thus the crisis of 1893 was ascribed by the Republicans to the impending Democratic tariff of 1894; and the crisis of 1907 has by some been termed the ‘[Theodore] Roosevelt panic,” utterly oblivious of the fact that from the time of President Jackson, who was held responsible for the troubles of 1837, every successive crisis had had its presidential scapegoat, and has been followed by a political revulsion. Opposed to these popular, but wholly unfounded interpretations, is the second class of explanations, which seek to burrow beneath the surface and to discover the more occult and fundamental causes of the periodicity of crises.”
Scholars ignore superficial explanations in the effort to seek good and truth. The problem of economic analysis of the credit/dollar crisis is the lack of a structural model with which to attempt empirical determination of causes (Gorton and Metrick 2010SB). There would still be doubts even with a well-specified structural model because samples of economic events do not typically permit separating causes and effects. There is also confusion is separating the why of the crisis and how it started and propagated, all of which are extremely important.
In true heritage of the principles of Seligman (1908), Gorton (2009EFM) discovers a prime causal driver of the credit/dollar crisis. The objective of subprime and Alt-A mortgages was to facilitate loans to populations with modest means so that they could acquire a home. These borrowers would not receive credit because of (1) lack of funds for down payments; (2) low credit rating and information; (3) lack of information on income; and (4) errors or lack of other information. Subprime mortgage “engineering” was based on the belief that both lender and borrower could benefit from increases in house prices over the short run. The initial mortgage would be refinanced in two or three years depending on the increase of the price of the house. According to Gorton (2009EFM, 13, 16):
“The outstanding amounts of Subprime and Alt-A [mortgages] combined amounted to about one quarter of the $6 trillion mortgage market in 2004-2007Q1. Over the period 2000-2007, the outstanding amount of agency mortgages doubled, but subprime grew 800%! Issuance in 2005 and 2006 of Subprime and Alt-A mortgages was almost 30% of the mortgage market. Since 2000 the Subprime and Alt-A segments of the market grew at the expense of the Agency (i.e., the government sponsored entities of Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac) share, which fell from almost 80% (by outstanding or issuance) to about half by issuance and 67% by outstanding amount. The lender’s option to rollover the mortgage after an initial period is implicit in the subprime mortgage. The key design features of a subprime mortgage are: (1) it is short term, making refinancing important; (2) there is a step-up mortgage rate that applies at the end of the first period, creating a strong incentive to refinance; and (3) there is a prepayment penalty, creating an incentive not to refinance early.”
The prime objective of successive administrations in the US during the past 20 years and actually since the times of Roosevelt in the 1930s has been to provide “affordable” financing for the “American dream” of home ownership. The US housing finance system is mixed with public, public/private and purely private entities. The Federal Home Loan Bank (FHLB) system was established by Congress in 1932 that also created the Federal Housing Administration in 1934 with the objective of insuring homes against default. In 1938, the government created the Federal National Mortgage Association, or Fannie Mae, to foster a market for FHA-insured mortgages. Government-insured mortgages were transferred from Fannie Mae to the Government National Mortgage Association, or Ginnie Mae, to permit Fannie Mae to become a publicly-owned company. Securitization of mortgages began in 1970 with the government charter to the Federal Home Loan Mortgage Corporation, or Freddie Mac, with the objective of bundling mortgages created by thrift institutions that would be marketed as bonds with guarantees by Freddie Mac (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 42-8). In the third quarter of 2008, total mortgages in the US were $12,057 billion of which 43.5 percent, or $5423 billion, were retained or guaranteed by Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 45). In 1990, Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac had a share of only 25.4 percent of total mortgages in the US. Mortgages in the US increased from $6922 billion in 2002 to $12,088 billion in 2007, or by 74.6 percent, while the retained or guaranteed portfolio of Fannie and Freddie rose from $3180 billion in 2002 to $4934 billion in 2007, or by 55.2 percent.
According to Pinto (2008) in testimony to Congress:
“There are approximately 25 million subprime and Alt-A loans outstanding, with an unpaid principal amount of over $4.5 trillion, about half of them held or guaranteed by Fannie and Freddie. Their high risk activities were allowed to operate at 75:1 leverage ratio. While they may deny it, there can be no doubt that Fannie and Freddie now own or guarantee $1.6 trillion in subprime, Alt-A and other default prone loans and securities. This comprises over 1/3 of their risk portfolios and amounts to 34% of all the subprime loans and 60% of all Alt-A loans outstanding. These 10.5 million unsustainable, nonprime loans are experiencing a default rate 8 times the level of the GSEs’ 20 million traditional quality loans. The GSEs will be responsible for a large percentage of an estimated 8.8 million foreclosures expected over the next 4 years, accounting for the failure of about 1 in 6 home mortgages. Fannie and Freddie have subprimed America.”
In perceptive analysis of growth and macroeconomics in the past six decades, Rajan (2012FA) argues that “the West can’t borrow and spend its way to recovery.” The Keynesian paradigm is not applicable in current conditions. Advanced economies in the West could be divided into those that reformed regulatory structures to encourage productivity and others that retained older structures. In the period from 1950 to 2000, Cobet and Wilson (2002) find that US productivity, measured as output/hour, grew at the average yearly rate of 2.9 percent while Japan grew at 6.3 percent and Germany at 4.7 percent (see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 135-44). In the period from 1995 to 2000, output/hour grew at the average yearly rate of 4.6 percent in the US but at lower rates of 3.9 percent in Japan and 2.6 percent in the US. Rajan (2012FA) argues that the differential in productivity growth was accomplished by deregulation in the US at the end of the 1970s and during the 1980s. In contrast, Europe did not engage in reform with the exception of Germany in the early 2000s that empowered the German economy with significant productivity advantage. At the same time, technology and globalization increased relative remunerations in highly-skilled, educated workers relative to those without skills for the new economy. It was then politically appealing to improve the fortunes of those left behind by the technological revolution by means of increasing cheap credit. As Rajan (2012FA) argues:
“In 1992, Congress passed the Federal Housing Enterprises Financial Safety and Soundness Act, partly to gain more control over Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, the giant private mortgage agencies, and partly to promote affordable homeownership for low-income groups. Such policies helped money flow to lower-middle-class households and raised their spending—so much so that consumption inequality rose much less than income inequality in the years before the crisis. These policies were also politically popular. Unlike when it came to an expansion in government welfare transfers, few groups opposed expanding credit to the lower-middle class—not the politicians who wanted more growth and happy constituents, not the bankers and brokers who profited from the mortgage fees, not the borrowers who could now buy their dream houses with virtually no money down, and not the laissez-faire bank regulators who thought they could pick up the pieces if the housing market collapsed. The Federal Reserve abetted these shortsighted policies. In 2001, in response to the dot-com bust, the Fed cut short-term interest rates to the bone. Even though the overstretched corporations that were meant to be stimulated were not interested in investing, artificially low interest rates acted as a tremendous subsidy to the parts of the economy that relied on debt, such as housing and finance. This led to an expansion in housing construction (and related services, such as real estate brokerage and mortgage lending), which created jobs, especially for the unskilled. Progressive economists applauded this process, arguing that the housing boom would lift the economy out of the doldrums. But the Fed-supported bubble proved unsustainable. Many construction workers have lost their jobs and are now in deeper trouble than before, having also borrowed to buy unaffordable houses. Bankers obviously deserve a large share of the blame for the crisis. Some of the financial sector’s activities were clearly predatory, if not outright criminal. But the role that the politically induced expansion of credit played cannot be ignored; it is the main reason the usual checks and balances on financial risk taking broke down.”
In fact, Raghuram G. Rajan (2005) anticipated low liquidity in financial markets resulting from low interest rates before the financial crisis that caused distortions of risk/return decisions provoking the credit/dollar crisis and global recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. Near zero interest rates of unconventional monetary policy induced excessive risks and low liquidity in financial decisions that were critical as a cause of the credit/dollar crisis after 2007. Rajan (2012FA) argues that it is not feasible to return to the employment and income levels before the credit/dollar crisis because of the bloated construction sector, financial system and government budgets.
(4) Historically Sharper Recoveries from Deeper Contractions and Financial Crises. Professor Michael D. Bordo (2012Sep27), at Rutgers University, is providing clear thought on the correct comparison of the current business cycles in the United States with those in United States history. There are two issues raised by Professor Bordo: (1) lumping together countries with different institutions, economic policies and financial systems; and (2) the conclusion that growth is mediocre after financial crises and deep recessions, which is repeated daily in the media, but that Bordo and Haubrich (2012DR) persuasively demonstrate to be inconsistent with United States experience.
Depriving economic history of institutions is perilous as is illustrated by the economic history of Brazil. Douglass C. North (1994) emphasized the key role of institutions in explaining economic history. Rondo E. Cameron (1961, 1967, 1972) applied institutional analysis to banking history. Friedman and Schwartz (1963) analyzed the relation of money, income and prices in the business cycle and related the monetary policy of an important institution, the Federal Reserve System, to the Great Depression. Bordo, Choudhri and Schwartz (1995) analyze the counterfactual of what would have been economic performance if the Fed had used during the Great Depression the Friedman (1960) monetary policy rule of constant growth of money(for analysis of the Great Depression see Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 198-217). Alan Meltzer (2004, 2010a,b) analyzed the Federal Reserve System over its history. The reader would be intrigued by Figure 5 in Reinhart and Rogoff (2010FCDC, 15) in which Brazil is classified in external default for seven years between 1828 and 1834 but not again until 64 years later in 1989, above the 50 years of incidence for “serial default”. This void has been filled in scholarly research on nineteenth-century Brazil by William R. Summerhill, Jr. (2007SC, 2007IR). There are important conclusions by Summerhill on the exceptional sample of institutional change or actually lack of change, public finance and financial repression in Brazil between 1822 an 1899, combining tools of economics, political science and history. During seven continuous decades, Brazil did not miss a single interest payment with government borrowing without repudiation of debt or default. What is really surprising is that Brazil borrowed by means of long-term bonds and even more surprising interest rates fell over time. The external debt of Brazil in 1870 was ₤41,275,961 and the domestic debt in the internal market was ₤25,708,711, or 62.3 percent of the total (Summerhill 2007IR, 73).
The experience of Brazil differed from that of Latin America (Summerhill 2007IR). During the six decades when Brazil borrowed without difficulty, Latin American countries becoming independent after 1820 engaged in total defaults, suffering hardship in borrowing abroad. The countries that borrowed again fell again in default during the nineteenth century. Venezuela defaulted in four occasions. Mexico defaulted in 1827, rescheduling its debt eight different times and servicing the debt sporadically. About 44 percent of Latin America’s sovereign debt was in default in 1855 and approximately 86 percent of total government loans defaulted in London originated in Spanish American borrowing countries.
External economies of commitment to secure private rights in sovereign credit would encourage development of private financial institutions, as postulated in classic work by North and Weingast (1989), Summerhill 2007IR, 22). This is how banking institutions critical to the Industrial Revolution were developed in England (Cameron 1967). The obstacle in Brazil found by Summerhill (2007IR) is that sovereign debt credibility was combined with financial repression. There was a break in Brazil of the chain of effects from protecting public borrowing, as in North and Weingast (1989), to development of private financial institutions. According to Pelaez 1976, 283) following Cameron:
“The banking law of 1860 placed severe restrictions on two basic modern economic institutions—the corporation and the commercial bank. The growth of the volume of bank credit was one of the most significant factors of financial intermediation and economic growth in the major trading countries of the gold standard group. But Brazil placed strong restrictions on the development of banking and intermediation functions, preventing the channeling of coffee savings into domestic industry at an earlier date.”
Brazil actually abandoned the gold standard during multiple financial crises in the nineteenth century, as it should have to protect domestic economic activity. Pelaez (1975, 447) finds similar experience in the first half of nineteenth-century Brazil:
“Brazil’s experience is particularly interesting in that in the period 1808-1851 there were three types of monetary systems. Between 1808 and 1829, there was only one government-related Bank of Brazil, enjoying a perfect monopoly of banking services. No new banks were established in the 1830s after the liquidation of the Bank of Brazil in 1829. During the coffee boom in the late 1830s and 1840s, a system of banks of issue, patterned after similar institutions in the industrial countries, supplied the financial services required in the first stage of modernization of the export economy.”
Financial crises in the advanced economies were transmitted to nineteenth-century Brazil by the arrival of a ship (Pelaez and Suzigan 1981). The explanation of those crises and the economy of Brazil requires knowledge and roles of institutions, economic policies and the financial system chosen by Brazil, in agreement with Bordo (2012Sep27).
The departing theoretical framework of Bordo and Haubrich (2012DR) is the plucking model of Friedman (1964, 1988). Friedman (1988, 1) recalls “I was led to the model in the course of investigating the direction of influence between money and income. Did the common cyclical fluctuation in money and income reflect primarily the influence of money on income or of income on money?” Friedman (1964, 1988) finds useful for this purpose to analyze the relation between expansions and contractions. Analyzing the business cycle in the United States between 1870 and 1961, Friedman (1964, 15) found that “a large contraction in output tends to be followed on the average by a large business expansion; a mild contraction, by a mild expansion.” The depth of the contraction opens up more room in the movement toward full employment (Friedman 1964, 17):
“Output is viewed as bumping along the ceiling of maximum feasible output except that every now and then it is plucked down by a cyclical contraction. Given institutional rigidities and prices, the contraction takes in considerable measure the form of a decline in output. Since there is no physical limit to the decline short of zero output, the size of the decline in output can vary widely. When subsequent recovery sets in, it tends to return output to the ceiling; it cannot go beyond, so there is an upper limit to output and the amplitude of the expansion tends to be correlated with the amplitude of the contraction.”
Kim and Nelson (1999) test the asymmetric plucking model of Friedman (1964, 1988) relative to a symmetric model using reference cycles of the NBER and find evidence supporting the Friedman model. Bordo and Haubrich (2012DR) analyze 27 cycles beginning in 1872, using various measures of financial crises while considering different regulatory and monetary regimes. The revealing conclusion of Bordo and Haubrich (2012DR, 2) is that:
“Our analysis of the data shows that steep expansions tend to follow deep contractions, though this depends heavily on when the recovery is measured. In contrast to much conventional wisdom, the stylized fact that deep contractions breed strong recoveries is particularly true when there is a financial crisis. In fact, on average, it is cycles without a financial crisis that show the weakest relation between contraction depth and recovery strength. For many configurations, the evidence for a robust bounce-back is stronger for cycles with financial crises than those without.”
The average rate of growth of real GDP in expansions after recessions with financial crises was 8 percent but only 6.9 percent on average for recessions without financial crises (Bordo 2012Sep27). Real GDP declined 12 percent in the Panic of 1907 and increased 13 percent in the recovery, consistent with the plucking model of Friedman (Bordo 2012Sep27). Bordo (2012Sep27) finds two probable explanations for the weak recovery during the current economic cycles: (1) collapse of United States housing; and (2) uncertainty originating in fiscal policy, regulation and structural changes. There are serious doubts if monetary policy is adequate to recover the economy under these conditions.
Lucas (2011May) estimates US economic growth in the long-term at 3 percent per year and about 2 percent per year in per capita terms. There are displacements from this trend caused by events such as wars and recessions but the economy then returns to trend. Historical US GDP data exhibit remarkable growth: Lucas (2011May) estimates an increase of US real income per person by a factor of 12 in the period from 1870 to 2010. The explanation by Lucas (2011May) of this remarkable growth experience is that government provided stability and education while elements of “free-market capitalism” were an important driver of long-term growth and prosperity. The analysis is sharpened by comparison with the long-term growth experience of G7 countries (US, UK, France, Germany, Canada, Italy and Japan) and Spain from 1870 to 2010. Countries benefitted from “common civilization” and “technology” to “catch up” with the early growth leaders of the US and UK, eventually growing at a faster rate. Significant part of this catch up occurred after World War II. Lucas (2011May) finds that the catch up stalled in the 1970s. The analysis of Lucas (2011May) is that the 20-40 percent gap that developed originated in differences in relative taxation and regulation that discouraged savings and work incentives in comparison with the US. A larger welfare and regulatory state, according to Lucas (2011May), could be the cause of the 20-40 percent gap. Cobet and Wilson (2002) provide estimates of output per hour and unit labor costs in national currency and US dollars for the US, Japan and Germany from 1950 to 2000 (see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 137-44). The average yearly rate of productivity change from 1950 to 2000 was 2.9 percent in the US, 6.3 percent for Japan and 4.7 percent for Germany while unit labor costs in USD increased at 2.6 percent in the US, 4.7 percent in Japan and 4.3 percent in Germany. From 1995 to 2000, output per hour increased at the average yearly rate of 4.6 percent in the US, 3.9 percent in Japan and 2.6 percent in Germany while unit labor costs in USD fell at minus 0.7 percent in the US, 4.3 percent in Japan and 7.5 percent in Germany. There was increase in productivity growth in Japan and France within the G7 in the second half of the 1990s but significantly lower than the acceleration of 1.3 percentage points per year in the US. Long-term economic growth and prosperity are measured by the key indicators of growth of real income per capita, or what is earned per person after inflation. A refined concept would include real disposable income per capita, or what is earned per person after inflation and taxes.
Table IB-1 provides the data required for broader comparison of the cyclical expansions of IQ1983 to IVQ1985 and the current one from 2009 to 2012. First, in the 13 quarters from IQ1983 to IVQ1985, GDP increased 19.6 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 5.7 percent; real disposable personal income (RDPI) increased 14.5 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 4.3 percent; RDPI per capita increased 11.5 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 3.4 percent; and population increased 2.7 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 0.8 percent. Second, in the 13 quarters of the current cyclical expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2012, GDP increased 7.2 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 2.2 percent. In the 12 quarters of cyclical expansion real disposable personal income (RDPI) increased 5.7 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 1.7 percent; RDPI per capita increased 3.3 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 1.0 percent; and population increased 2.3 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 0.7 percent. Third, since the beginning of the recession in IVQ2007 to IIIQ2012, GDP increased 2.2 percent, or barely above the level before the recession. Since the beginning of the recession in IVQ2007 to IIIQ2012, real disposable personal income increased 3.7 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 0.7 percent; population increased 3.9 percent at the annual equivalent rate of 0.8 percent; and real disposable personal income per capita is 0.2 percent lower than the level before the recession. Real disposable personal income is the actual take home pay after inflation and taxes and real disposable income per capita is what is left per inhabitant. The current cyclical expansion is the worst in the period after World War II in terms of growth of economic activity and income. The United States grew during its history at high rates of per capita income that made its economy the largest in the world. That dynamism is disappearing. Bordo (2012 Sep27) and Bordo and Haubrich (2012DR) provide strong evidence that recoveries have been faster after deeper recessions and recessions with financial crises, casting serious doubts on the conventional explanation of weak growth during the current expansion allegedly because of the depth of the contraction from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 of 4.7 percent and the financial crisis.
Table IB-1, US, GDP, Real Disposable Personal Income, Real Disposable Income per Capita and Population in 1983-85 and 2007-2011, %
| # Quarters | ∆% | ∆% Annual Equivalent | |
| IQ1983 to IVQ1985 | 13 | ||
| GDP | 19.6 | 5.7 | |
| RDPI | 14.5 | 4.3 | |
| RDPI Per Capita | 11.5 | 3.4 | |
| Population | 2.7 | 0.8 | |
| IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2012 | 13 | ||
| GDP | 7.2 | 2.2 | |
| RDPI | 5.7 | 1.7 | |
| RDPI per Capita | 3.3 | 1.0 | |
| Population | 2.3 | 0.7 | |
| IVQ2007 to IIIQ2012 | 20 | ||
| GDP | 2.2 | 0.4 | |
| RDPI | 3.7 | 0.7 | |
| RDPI per Capita | -0.2 | ||
| Population | 3.9 | 0.8 |
RDPI: Real Disposable Personal Income
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
There are six basic facts illustrating the current economic disaster of the United States: (1) GDP maintained trend growth in the entire business cycle from IQ1980 to IV1985, including contractions and expansions, but is well below trend in the entire business cycle from IVQ2007 to IIQ2012, including contractions and expansions; (2) per capita real disposable income exceeded trend growth in the 1980s but is substantially below trend in IIQ2012; (3) the number of employed persons increased in the 1980s but declined into IIQ2012; (4) the number of full-time employed persons increased in the 1980s but declined into IIQ2012; (5) the number unemployed, unemployment rate and number employed part-time for economic reasons fell in the recovery from the recessions of the 1980s but not substantially in the recovery after IIQ2009; and (6) wealth of households and nonprofit organizations soared in the 1980s but declined into IIQ2012. There is a critical issue of whether the United States economy will be able in the future to attain again the level of activity and prosperity of projected trend growth. Growth at trend during the entire business cycles built the largest economy in the world but there may be an adverse, permanent weakness in United States economic performance and prosperity. Table IB-2 provides data for analysis of these five basic facts. The six blocks of Table IB-2 are separated initially after individual discussion of each one followed by the full Table IB-2.
1. Trend Growth.
i. As shown in Table IB-2, actual GDP grew cumulatively 17.7 percent from IQ1980 to IVQ1985, which is relatively close to what trend growth would have been at 18.5 percent. Rapid growth at 5.7 percent annual rate on average per quarter during the expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 erased the loss of GDP of 4.8 percent during the contraction and maintained trend growth at 3 percent over the entire cycle.
ii. In contrast, cumulative growth from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2012 was 2.2 percent while trend growth would have been 15.1 percent. GDP in IIIQ2012 at seasonally adjusted annual rate is estimated at $13,616.2 percent by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) (http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm) and would have been $15,338.2 billion, or $1,722 billion higher, had the economy grown at trend over the entire business cycle as it happened during the 1980s and throughout most of US history. There is $1.7 trillion of foregone GDP that would have been created as it occurred during past cyclical expansions, which explains why employment has not rebounded to even higher than before. There would not be recovery of full employment even with growth of 3 percent per year beginning immediately because the opportunity was lost to grow faster during the expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIIQ2012 after the recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. The United States has acquired a heavy social burden of unemployment and underemployment of 28.1 million people or 17.4 percent of the effective labor force (Section I, Table I-4 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/11/twenty-eight-million-unemployed-or.html) that will not be significantly diminished even with return to growth of GDP of 3 percent per year because of growth of the labor force by new entrants. The US labor force grew from 142.583 million in 2000 to 153.124 million in 2007 or by 7.4 percent at the average yearly rate of 1.0 percent per year. The civilian noninstitutional population increased from 212.577 million in 2000 to 231.867 million in 2007 or 9.1 percent at the average yearly rate of 1.3 percent per year (data from http://www.bls.gov/data/). Data for the past five years cloud accuracy because of the number of people discouraged from seeking employment. The noninstitutional population of the United States increased from 231.867 million in 2007 to 239.618 million in 2011 or by 3.3 percent while the labor force increased from 153.124 million in 2007 to 153.617 million in 2011 or by 0.3 percent (data from http://www.bls.gov/data/). People ceased to seek jobs because they do not believe that there is a job available for them (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/11/twenty-eight-million-unemployed-or.html ).
| Period IQ1980 to IVQ1985 | |
| GDP SAAR USD Billions | |
| IQ1980 | 5,903.4 |
| IVQ1985 | 6,950.0 |
| ∆% IQ1980 to IVQ1985 | 17.7 |
| ∆% Trend Growth IQ1980 to IVQ1985 | 18.5 |
| Period IVQ2007 to IIIQ2012 | |
| GDP SAAR USD Billions | |
| IVQ2007 | 13,326.0 |
| IIIQ2012 | 13,616.2 |
| ∆% IVQ2007 to IIIQ2012 Actual | 2.2 |
| ∆% IVQ2007 to IIIQ2012 Trend | 15.1 |
2. Decline of Per Capita Real Disposable Income
i. In the entire business cycle from IQ1980 to IVQ1985, as shown in Table IB-2 trend growth of per capita real disposable income, or what is left per person after inflation and taxes, grew cumulatively 14.5 percent, which is close to what would have been trend growth of 12.1 percent.
ii. In contrast, in the entire business cycle from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2012, per capita real disposable income fell 0.2 percent while trend growth would have been 10.4 percent. Income available after inflation and taxes is lower than before the contraction after 13 consecutive quarters of GDP growth at mediocre rates relative to those prevailing during historical cyclical expansions.
| Period IQ1980 to IVQ1985 |
| Real Disposable Personal Income per Capita IQ1980 Chained 2005 USD | 18,938 |
| Real Disposable Personal Income per Capita IVQ1985 Chained 2005 USD | 21,687 |
| ∆% IQ1980 to IVQ1985 | 14.5 |
| ∆% Trend Growth | 12.1 |
| Period IVQ2007 to IIIQ2012 |
| Real Disposable Personal Income per Capita IVQ2007 Chained 2005USD | 32,837 |
| Real Disposable Personal Income per Capita IIIQ2012 Chained 2005 USD | 32,778 |
| ∆% IVQ2007 to IIIQ2012 | -0.2 |
| ∆% Trend Growth | 10.4 |
3. Number of Employed Persons
i. As shown in Table IB-2, the number of employed persons increased over the entire business cycle from 98.527 million not seasonally adjusted (NSA) in IQ1980 to 107.819 million NSA in IVQ1985 or by 9.4 percent.
ii. In contrast, during the entire business cycle the number employed fell from 146.334 million in IVQ2007 to 143.202 million in IIIQ2012 or by 2.1 percent. There are 28.1 million persons unemployed or underemployed, which is 17.4 percent of the effective labor force (Section I, Table I-4 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/11/twenty-eight-million-unemployed-or.html).
| Period IQ1980 to IVQ1985 |
| Employed Millions IQ1980 NSA End of Quarter | 98.527 |
| Employed Millions IV1985 NSA End of Quarter | 107.819 |
| ∆% Employed IQ1980 to IV1985 | 9.4 |
| Period IVQ2007 to IIIQ2012 |
| Employed Millions IVQ2007 NSA End of Quarter | 146.334 |
| Employed Millions IIIQ2012 NSA End of Quarter | 143.333 |
| ∆% Employed IVQ2007 to IIIQ2012 | -2.1 |
4. Number of Full-Time Employed Persons
i. As shown in Table IB-2, during the entire business cycle in the 1980s, including contractions and expansion, the number of employed full-time rose from 81.280 million NSA in IQ1980 to 88.757 million NSA in IVQ1985 or 9.2 percent.
ii. In contrast, during the entire current business cycle, including contraction and expansion, the number of persons employed full-time fell from 121.042 million in IVQ2007 to 115.678 million in IIIQ2012 or by minus 4.4 percent.
| Period IQ1980 to IVQ1985 |
| Employed Full-time Millions IQ1980 NSA End of Quarter | 81.280 |
| Employed Full-time Millions IV1985 NSA End of Quarter | 88.757 |
| ∆% Full-time Employed IQ1980 to IV1985 | 9.2 |
| Period IVQ2007 to IIIQ2012 |
| Employed Full-time Millions IVQ2007 NSA End of Quarter | 121.042 |
| Employed Full-time Millions IIIQ2012 NSA End of Quarter | 115.678 |
| ∆% Full-time Employed IVQ2007 to IIIQ2012 | -4.4 |
5. Unemployed, Unemployment Rate and Employed Part-time for Economic Reasons.
i. As shown in Table IB-2 and in the following block, in the cycle from IQ1980 to IVQ1985: (a) the rate of unemployment was virtually the same at 6.7 percent in IQ1985 relative to 6.6 percent in IQ1980; (b) the number unemployed increased from 6.983 million in IQ1980 to 7.717 million in IVQ1985 or 10.5 percent; and (c) the number employed part-time for economic reasons increased 49.1 percent from 3.624 million in IQ1980 to 5.402 million in IVQ1985.
ii. In contrast, in the economic cycle from IVQ2007 to IIIQ2012: (a) the rate of unemployment increased from 4.8 percent in IVQ2007 to 7.6 percent in IIIQ2012; (b) the number unemployed increased 59.3 percent from 7.371 million in IVQ2007 to 11.742 million in IIIQ2012; (c) the number employed part-time for economic reasons increased 70.7 percent from 4.750 million in IVQ2007 to 8.110 million in IIIQ2012; and (d) U6 Total Unemployed plus all marginally attached workers plus total employed part time for economic reasons as percent of all civilian labor force plus all marginally attached workers NSA increased from 8.7 percent in IVQ2007 to 14.2 percent in IIIQ2012.
| Period IQ1980 to IVQ1985 |
| Unemployment Rate IQ1980 NSA End of Quarter | 6.6 |
| Unemployment Rate IV1985 NSA End of Quarter | 6.7 |
| Unemployed IQ1980 Millions End of Quarter | 6.983 |
| Unemployed IV 1985 Millions End of Quarter | 7.717 |
| Employed Part-time Economic Reasons Millions IQ1980 End of Quarter | 3.624 |
| Employed Part-time Economic Reasons Millions IVQ1985 End of Quarter | 5.402 |
| ∆% | 49.1 |
| Period IVQ2007 to IIIQ2012 |
| Unemployment Rate IVQ2007 NSA End of Quarter | 4.8 |
| Unemployment Rate IIIQ2012 NSA End of Quarter | 7.6 |
| Unemployed IVQ2007 Millions End of Quarter | 7.371 |
| Unemployed IIIQ2009 Millions End of Quarter | 11.742 |
| ∆% | 59.3 |
| Employed Part-time Economic Reasons IVQ2007 Millions End of Quarter | 4.750 |
| Employed Part-time Economic Reasons Millions IIIQ2009 End of Quarter | 8.110 |
| ∆% | 70.7 |
| U6 Total Unemployed plus all marginally attached workers plus total employed part time for economic reasons as percent of all civilian labor force plus all marginally attached workers NSA | |
| IVQ2007 | 8.7 |
| IIIQ2012 | 14.2 |
6. Wealth of Households and Nonprofit Organizations.
i. The comparison of net worth of households and nonprofit organizations in the entire economic cycle from IQ1980 (and also from IVQ1979) to IVQ1985 and from IVQ2007 to IIQ2012 is provided in the following block and in Table IB-2. Net worth of households and nonprofit organizations increased from $8,326.4 billion in IVQ1979 to $14,395.2 billion in IVQ1985 or 72.9 percent or 69.3 percent from $8,502.9 billion in IQ1980. The starting quarter does not bias the results. The US consumer price index not seasonally adjusted increased from 76.7 in Dec 1979 to 109.3 in Dec 1985 or 42.5 percent or 36.5 percent from 80.1 in Mar 1980 (using consumer price index data from the US Bureau of Labor Statistics at http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm). In terms of purchasing power measured by the consumer price index, real wealth of households and nonprofit organizations increased 21.3 percent in constant purchasing power from IVQ1979 to IVQ1985 or 24.0 percent from IQ1980.
ii. In contrast, as shown in the following block and in Table IB-2, net worth of households and nonprofit organizations fell from $66,057.1 billion in IVQ2007 to $62,668.4 billion in IIQ2012 by $3,388.7 billion or 5.1 percent. The US consumer price index was 210.036 in Dec 2007 and 229.478 in Jun 2012 for increase of 9.3 percent. In purchasing power of Dec 2007, wealth of households and nonprofit organizations is lower by 13.2 percent in Jun 2012 after 12 consecutive quarters of expansion from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2012 relative to IVQ2012 when the recession began. The explanation is partly in the sharp decline of wealth of households and nonprofit organizations and partly in the mediocre growth rates of the cyclical expansion beginning in IIIQ2009. The average growth rate from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2012 has been 2.2 percent, which is substantially lower than the average of 6.2 percent in cyclical expansions after World War II and 5.7 percent in the expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1985 (see Table I-5 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/10/mediocre-and-decelerating-united-states.html). The US missed the opportunity of high growth rates that has been available in past cyclical expansions.
| Period IQ1980 to IVQ1985 | |
| Net Worth of Households and Nonprofit Organizations USD Billions | |
| IVQ1979 | 8,326.4 |
| IVQ1985 | 14,395.2 |
| ∆ USD Billions | +6,068.8 |
| Period IVQ2007 to IIQ2012 | |
| Net Worth of Households and Nonprofit Organizations USD Billions | |
| IVQ2007 | 66,057.1 |
| IIQ2012 | 62,668.4 |
| ∆ USD Billions | -3,388.7 |
Table IB-2, US, GDP and Real Disposable Personal Income per Capita Actual and Trend Growth and Employment, 1980-1985 and 2007-2012, SAAR USD Billions, Millions of Persons and ∆%
| Period IQ1980 to IVQ1985 | |
| GDP SAAR USD Billions | |
| IQ1980 | 5,903.4 |
| IVQ1985 | 6,950.0 |
| ∆% IQ1980 to IVQ1985 | 17.7 |
| ∆% Trend Growth IQ1980 to IVQ1985 | 18.5 |
| Real Disposable Personal Income per Capita IQ1980 Chained 2005 USD | 18,938 |
| Real Disposable Personal Income per Capita IVQ1985 Chained 2005 USD | 21,687 |
| ∆% IQ1980 to IVQ1985 | 14.5 |
| ∆% Trend Growth | 12.1 |
| Employed Millions IQ1980 NSA End of Quarter | 98.527 |
| Employed Millions IV1985 NSA End of Quarter | 107.819 |
| ∆% Employed IQ1980 to IV1985 | 9.4 |
| Employed Full-time Millions IQ1980 NSA End of Quarter | 81.280 |
| Employed Full-time Millions IV1985 NSA End of Quarter | 88.757 |
| ∆% Full-time Employed IQ1980 to IV1985 | 9.2 |
| Unemployment Rate IQ1980 NSA End of Quarter | 6.6 |
| Unemployment Rate IV1985 NSA End of Quarter | 6.7 |
| Unemployed IQ1980 Millions NSA End of Quarter | 6.983 |
| Unemployed IV 1985 Millions NSA End of Quarter | 7.717 |
| ∆% | 11.9 |
| Employed Part-time Economic Reasons IVQ2007 Millions NSA End of Quarter | 4.750 |
| Employed Part-time Economic Reasons Millions IIQ2009 NSA End of Quarter | 8.394 |
| ∆% | 76.7 |
| Net Worth of Households and Nonprofit Organizations USD Billions | |
| IVQ1979 | 8,326.4 |
| IVQ1985 | 14,395.2 |
| ∆ USD Billions | +6,068.8 |
| Period IVQ2007 to IIIQ2012 | |
| GDP SAAR USD Billions | |
| IVQ2007 | 13,326.0 |
| IIIQ2012 | 13,616.2 |
| ∆% IVQ2007 to IIIQ2012 | 2.2 |
| ∆% IVQ2007 to IIIQ2012 Trend Growth | 15.1 |
| Real Disposable Personal Income per Capita IVQ2007 Chained 2005USD | 32,837 |
| Real Disposable Personal Income per Capita IIIQ2012 Chained 2005 USD | 32,778 |
| ∆% IVQ2007 to IIIQ2012 | -0.2 |
| ∆% Trend Growth | 10.4 |
| Employed Millions IVQ2007 NSA End of Quarter | 146.334 |
| Employed Millions IIIQ2012 NSA End of Quarter | 143.333 |
| ∆% Employed IVQ2007 to IIIQ2012 | -2.1 |
| Employed Full-time Millions IVQ2007 NSA End of Quarter | 121.042 |
| Employed Full-time Millions IIIQ2012 NSA End of Quarter | 115.678 |
| ∆% Full-time Employed IVQ2007 to IIIQ2012 | -4.4 |
| Unemployment Rate IVQ2007 NSA End of Quarter | 4.8 |
| Unemployment Rate IIIQ2012 NSA End of Quarter | 7.6 |
| Unemployed IVQ2007 Millions NSA End of Quarter | 7.371 |
| Unemployed IIIQ2009 Millions NSA End of Quarter | 11.742 |
| ∆% | 59.3 |
| Employed Part-time Economic Reasons IVQ2007 Millions NSA End of Quarter | 4.750 |
| Employed Part-time Economic Reasons Millions IIIQ2009 NSA End of Quarter | 8.110 |
| ∆% | 70.7 |
| U6 Total Unemployed plus all marginally attached workers plus total employed part time for economic reasons as percent of all civilian labor force plus all marginally attached workers NSA | |
| IVQ2007 | 8.7 |
| IIIQ2012 | 14.2 |
| Net Worth of Households and Nonprofit Organizations USD Billions | |
| IVQ2007 | 66,057.1 |
| IIQ2012 | 62,668.4 |
| ∆ USD Billions | -3,388.7 |
Note: GDP trend growth used is 3.0 percent per year and GDP per capita is 2.0 percent per year as estimated by Lucas (2011May) on data from 1870 to 2010.
Source: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/data/. Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System. 2012Sep20. Flow of funds accounts of the United States. Washington, DC, Federal Reserve System.
II United States International Trade. Subsection IIA United States International Trade provides data and analysis of US foreign trade. Subsection IIB Import Export Prices provides analysis of prices in US foreign trade.
IIA United States International Trade Deficit and Fiscal Imbalance. The United States Census Bureau has released revisions of trade statistics from Jan 2009 to Mar 2012 (http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/Press-Release/2011pr/final_revisions/). Table IIA-1 provides the trade balance of the US and monthly growth of exports and imports seasonally adjusted with the latest release and revisions (http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/). Because of heavy dependence on imported oil, fluctuations in the US trade account originate largely in fluctuations of commodity futures prices caused by carry trades from zero interest rates into commodity futures exposures in a process similar to world inflation waves (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/10/world-inflation-waves-stagnating-united.html). The US trade balance improved from deficit of $51,647 million in Mar 2012 to deficit of $49,826 million in Apr 2012 and lower deficits of $47,596 million in May, $41,899 million in Jun and $42,466 million in Jul 2012 but with increase to 43,790 million in Aug 2012. The increase of exports in Sep of 3.1 percent was higher than increase of imports of 1.5 percent, resulting in decrease of the trade deficit in Sep to $41,545 million. The deterioration of the trade deficit from $44,507 million in Feb 2012 to $51,647 million in Mar 2012 resulted from growth of exports of 2.5 percent while imports jumped 5.2 percent. The US trade balance had improved from deficit of $52,209 million in Jan 2012 to lower deficit of $44,507 million in Feb 2012 mostly because of decline of imports by 2.7 percent while exports increased 0.9 percent. The US trade balance deteriorated sharply from Nov 2011 to Jan 2012 with growth of imports by cumulative 3.0 percent and cumulative increase of exports of 0.1 percent, resulting in deficits of $48,835 million in Nov, $51,748 million in Dec and $52,209 million in Jan, which are the highest since $50,234 million in Jun 2011. In the months of Jun to Oct 2011, exports increased 1.8 percent while imports increased 0.5 percent, resulting in improvement of the trade deficit from $50,234 million in Jun to $45,703 million in Oct. The trade balance deteriorated from cumulative deficit of $494,737 million in Jan-Dec 2010 to deficit of $559,880 million in Jan-Dec 2011.
Table IIA-1, US, Trade Balance of Goods and Services Seasonally Adjusted Millions of Dollars and ∆%
| Trade Balance | Exports | Month ∆% | Imports | Month ∆% | |
| Sep 2012 | -41,545 | 186,996 | 3.1 | 228,541 | 1.5 |
| Aug | -43,790 | 181,375 | -1.0 | 225,165 | -0.2 |
| Jul | -42,466 | 183,188 | -1.1 | 225,654 | -0.6 |
| Jun | -41,899 | 185,182 | 1.2 | 227,081 | -1.5 |
| May | -47,596 | 183,058 | 0.1 | 230,654 | -0.9 |
| Apr | -49,826 | 182,825 | -1.1 | 232,651 | -1.6 |
| Mar | -51,647 | 184,867 | 2.5 | 236,514 | 5.2 |
| Feb | -44,507 | 180,348 | 0.9 | 224,855 | -2.7 |
| Jan | -52,209 | 178,802 | 0.6 | 231,011 | 0.7 |
| Dec 2011 | -51,748 | 177,751 | 0.6 | 229,499 | 1.8 |
| Nov | -48,835 | 176,710 | -1.1 | 225,545 | 0.5 |
| Oct | -45,703 | 178,742 | -1.0 | 224,445 | -0.3 |
| Sep | -44,467 | 180,629 | 1.3 | 225,096 | 0.9 |
| Aug | -44,775 | 178,382 | 0.0 | 223,157 | -0.3 |
| Jul | -45,580 | 178,339 | 3.3 | 223,919 | 0.4 |
| Jun | -50,234 | 172,664 | -1.7 | 222,988 | -0.2 |
| May | -47,669 | 175,673 | 0.0 | 223,343 | 1.9 |
| Apr | -43,556 | 175,662 | 0.9 | 219,218 | 0.1 |
| Mar | -44,902 | 174,169 | 4.6 | 219,071 | 3.7 |
| Feb | -44,801 | 166,545 | -0.9 | 211,346 | -2.0 |
| Jan | -47,523 | 168,098 | 1.6 | 215,621 | 4.6 |
| Dec 2010 | -40,677 | 165,499 | 1.7 | 206,176 | 2.2 |
| Jan-Dec | -559,880 | 2,103,367 | 2,663,247 | ||
| Jan-Dec | -494,737 | 1,842,485 | 2,337,222 |
Note: Trade Balance of Goods and Services = Exports of Goods and Services less Imports of Goods and Services. Trade balance may not add exactly because of errors of rounding and seasonality. Source: US Census Bureau http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
Table IIA-2 provides the US international trade balance, exports and imports on an annual basis from 1992 to 2011. The trade balance deteriorated sharply over the long term. The US has a large deficit in goods or exports less imports of goods but it has a surplus in services that helps to reduce the trade account deficit or exports less imports of goods and services. The current account deficit of the US decreased from $124.5 billion in IIQ2011, or 3.2 percent of GDP to $123.2 billion in IIQ2012, or 3.1 percent of GDP (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/09/collapse-of-united-states-creation-of.html). The ratio of the current account deficit to GDP has stabilized around 3 percent of GDP compared with much higher percentages before the recession (see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008b), 183-94, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 167-71).
Table IIA-2, US, International Trade Balance, Exports and Imports SA, Millions of Dollars
| Period | Balance | Exports | Imports |
| Total | |||
| Annual | |||
| 1992 | -39,212 | 616,882 | 656,094 |
| 1993 | -70,311 | 642,863 | 713,174 |
| 1994 | -98,493 | 703,254 | 801,747 |
| 1995 | -96,384 | 794,387 | 890,771 |
| 1996 | -104,065 | 851,602 | 955,667 |
| 1997 | -108,273 | 934,453 | 1,042,726 |
| 1998 | -166,140 | 933,174 | 1,099,314 |
| 1999 | -263,160 | 967,008 | 1,230,168 |
| 2000 | -376,749 | 1,072,783 | 1,449,532 |
| 2001 | -361,771 | 1,007,726 | 1,369,496 |
| 2002 | -417,432 | 980,879 | 1,398,311 |
| 2003 | -490,984 | 1,023,519 | 1,514,503 |
| 2004 | -605,357 | 1,163,146 | 1,768,502 |
| 2005 | -708,624 | 1,287,441 | 1,996,065 |
| 2006 | -753,288 | 1,459,823 | 2,213,111 |
| 2007 | -696,728 | 1,654,561 | 2,351,289 |
| 2008 | -698,338 | 1,842,682 | 2,541,020 |
| 2009 | -379,154 | 1,578,945 | 1,958,099 |
| 2010 | -494,737 | 1,842,485 | 2,337,222 |
| 2011 | -559,880 | 2,103,367 | 2,663,247 |
Source: US Census Bureau http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
Chart IIA-1 of the US Census Bureau of the Department of Commerce shows that the trade deficit (gap between exports and imports) fell during the economic contraction after 2007 but has grown again during the expansion. There was slight improvement at the margin from Jul to Oct 2011 but new increase in the gap from Nov 2011 to Jan 2012 and again in Mar as exports grow less rapidly than imports. There is improvement in Apr 2012 with imports declining at a faster rate of 1.6 percent than decline of exports by 1.1 percent and growth of exports of 0.1 percent in May 2012 with imports declining 0.9 percent. Further improvement occurred in Jun with imports increasing 1.2 percent and exports declining 1.5 percent. There was deterioration in Jul with exports declining 1.1 percent and imports only 0.6 percent but deterioration in Aug with exports decreasing 1.0 percent while imports declined only 0.2 percent. In Sep 2012, exports increased 3.1 percent while imports increased only 1.5 percent. Weaker world and internal demand and fluctuating commodity price increases explain the declining or less dynamic changes in exports and imports in Chart IIA-1.
Chart IIA-1, US Balance, Exports and Imports of Goods and Services $ Billions
Source: US Census Bureau http://www.census.gov/briefrm/esbr/www/esbr042.html
Chart IIA-2 of the US Census Bureau provides the US trade account in goods and services SA from Jan 1992 to Sep 2012. There is a long-term trend of deterioration of the US trade deficit shown vividly by Chart IIA-2. The trend of deterioration was reversed by the global recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. Deterioration resumed together with incomplete recovery and was influenced significantly by the carry trade from zero interest rates to commodity futures exposures (these arguments are elaborated in Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 157-66, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 217-27, International Financial Architecture (2005), 15-18, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 221-5, Globalization and the State Vol. II (2008b), 197-213, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 182-4 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/07/causes-of-2007-creditdollar-crisis.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/professor-mckinnons-bubble-economy.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/world-inflation-quantitative-easing.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/treasury-yields-valuation-of-risk.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/11/quantitative-easing-theory-evidence-and.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/12/is-fed-printing-money-what-are.html). Earlier research focused on the long-term external imbalance of the US in the form of trade and current account deficits (Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), Globalization and the State Vol. II (2008b) 183-94, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 167-71). US external imbalances have not been fully resolved and tend to widen together with improving world economic activity and commodity price shocks.
Chart IIA-2. US, Balance of Trade SA, Monthly, Millions of Dollars, Jan 1992-Sep 2012
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
Chart IIA-3 of the US Census Bureau provides US exports SA from Jan 1992 to Sep 2012. There was sharp acceleration from 2003 to 2007 during worldwide economic boom and increasing inflation. Exports fell sharply during the financial crisis and global recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. Growth picked up again together with world trade and inflation but stalled in the final segment.
Chart IIA-3. US, Exports SA, Monthly, Millions of Dollars Jan 1992-Sep 2012
Source: US Census Bureau http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
Chart IIA-4 of the US Census Bureau provides US imports SA from Jan 1992 to Sep 2012. Growth was stronger between 2003 and 2007 with worldwide economic boom and inflation. There was sharp drop during the financial crisis and global recession. There is stalling import levels in the final segment resulting from weaker world economic growth and diminishing inflation because of risk aversion.
Chart IIA-4. US, Imports SA, Monthly, Millions of Dollars Jan 1992-Sep 2012
Source: US Census Bureau http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
The balance of international trade in goods of the US seasonally-adjusted is shown in Table IIA-3. The US has a dynamic surplus in services that reduces the large deficit in goods for a still very sizeable deficit in international trade of goods and services. The balance in international trade of goods improved from $59.2 billion in Sep 2011 to $57.5 billion in Sep 2012. Improvement of the goods balance in Sep 2012 relative to Sep 2011 occurred mostly in the petroleum balance, exports less imports of goods other than petroleum, in the magnitude of reducing the deficit by $4.6 billion, while there was moderate deterioration in the nonpetroleum balance, exports less imports of petroleum goods, in the magnitude of increasing the deficit by $2.9 billion. US terms of trade, export prices relative to import prices, and the US trade account fluctuate in accordance with the carry trade from zero interest rates to commodity futures exposures, especially oil futures. Exports rose 3.8 percent with non-petroleum exports growing 3.3 percent. Total imports rose 1.5 percent with petroleum imports declining 9.3 percent and nonpetroleum imports increasing 4.5 percent.
Table IIA-3, US, International Trade in Goods Balance, Exports and Imports $ Millions and ∆% SA
| Sep 2012 | Sep 2011 | ∆% | |
| Total Balance | -57,454 | -59,522 | |
| Petroleum | -21,670 | -26,255 | |
| Non Petroleum | -35,169 | -32,281 | |
| Total Exports | 134,016 | 129,053 | 3.8 |
| Petroleum | 11,179 | 9,974 | 12.1 |
| Non Petroleum | 121,438 | 117,532 | 3.3 |
| Total Imports | 191,470 | 188,575 | 1.5 |
| Petroleum | 32,849 | 36,229 | -9.3 |
| Non Petroleum | 156,607 | 149,813 | 4.5 |
Details may not add because of rounding and seasonal adjustment
Source: US Census Bureau http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
US exports and imports of goods not seasonally adjusted in Jan-Sep 2012 and Jan-Sep 2011 are shown in Table IIA-4. The rate of growth of exports was 5.1 percent and 3.9 percent for imports. The US has partial hedge of commodity price increases in exports of agricultural commodities that fell 0.6 percent and of mineral fuels that increased 7.3 percent both because of higher prices of raw materials and commodities increase and fall recurrently because of shocks of risk aversion. The US exports an insignificant amount of crude oil. US exports and imports consist mostly of manufactured products, with less rapidly increasing prices. US manufactured exports rose 6.1 percent while imports rose 7.3 percent. Significant part of the US trade imbalance originates in imports of mineral fuels decreasing 4.9 percent and crude oil decreasing 3.6 percent with wide oscillations in oil prices. The limited hedge in exports of agricultural commodities and mineral fuels compared with substantial imports of mineral fuels and crude oil results in waves of deterioration of the terms of trade of the US, or export prices relative to import prices, originating in commodity price increases caused by carry trades from zero interest rates. These waves are similar to those in worldwide inflation (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/10/world-inflation-waves-stagnating-united.html).
Table IIA-4, US, Exports and Imports of Goods, Not Seasonally Adjusted Millions of Dollars and %
| Jan-Sep 2012 $ Millions | Jan-Sep 2011 $ Millions | ∆% | |
| Exports | 1,152,293 | 1,096,638 | 5.1 |
| Manufactured | 765,714 | 721,399 | 6.1 |
| Agricultural | 99,348 | 99,942 | -0.6 |
| Mineral Fuels | 100,196 | 93,401 | 7.3 |
| Crude Oil | 1,380 | 984 | 40.2 |
| Imports | 1,705,322 | 1,641,307 | 3.9 |
| Manufactured | 1,268,104 | 1,191,614 | 6.4 |
| Agricultural | 78,128 | 73,551 | 6.2 |
| Mineral Fuels | 327,034 | 344,110 | -4.9 |
| Crude Oil | 244,513 | 253,609 | -3.6 |
Source: US Census Bureau http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
In their classic work on “unpleasant monetarist arithmetic,” Sargent and Wallace (1981, 2) consider a regime of domination of monetary policy by fiscal policy (emphasis added):
“Imagine that fiscal policy dominates monetary policy. The fiscal authority independently sets its budgets, announcing all current and future deficits and surpluses and thus determining the amount of revenue that must be raised through bond sales and seignorage. Under this second coordination scheme, the monetary authority faces the constraints imposed by the demand for government bonds, for it must try to finance with seignorage any discrepancy between the revenue demanded by the fiscal authority and the amount of bonds that can be sold to the public. Suppose that the demand for government bonds implies an interest rate on bonds greater than the economy’s rate of growth. Then if the fiscal authority runs deficits, the monetary authority is unable to control either the growth rate of the monetary base or inflation forever. If the principal and interest due on these additional bonds are raised by selling still more bonds, so as to continue to hold down the growth of base money, then, because the interest rate on bonds is greater than the economy’s growth rate, the real stock of bonds will growth faster than the size of the economy. This cannot go on forever, since the demand for bonds places an upper limit on the stock of bonds relative to the size of the economy. Once that limit is reached, the principal and interest due on the bonds already sold to fight inflation must be financed, at least in part, by seigniorage, requiring the creation of additional base money.”
The current real value of government debt plus monetary liabilities depends on the expected discounted values of future primary surpluses or difference between tax revenue and government expenditure excluding interest payments (Cochrane 2011Jan, 27, equation (16)). There is a point when adverse expectations about the capacity of the government to generate primary surpluses to honor its obligations can result in increases in interest rates on government debt.
This analysis suggests that there may be a point of saturation of demand for United States financial liabilities without an increase in interest rates on Treasury securities. A risk premium may develop on US debt. Such premium is not apparent currently because of distressed conditions in the world economy and international financial system. Risk premiums are observed in the spread of bonds of highly indebted countries in Europe relative to bonds of the government of Germany.
The issue of global imbalances centered on the possibility of a disorderly correction (Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), Globalization and the State Vol. II (2008b) 183-94, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 167-71). Such a correction has not occurred historically but there is no argument proving that it could not occur. The need for a correction would originate in unsustainable large and growing United States current account deficits (CAD) and net international investment position (NIIP) or excess of financial liabilities of the US held by foreigners net of financial liabilities of foreigners held by US residents. The IMF estimated that the US could maintain a CAD of two to three percent of GDP without major problems (Rajan 2004). The threat of disorderly correction is summarized by Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 15):
“It is possible that foreigners may be unwilling to increase their positions in US financial assets at prevailing interest rates. An exit out of the dollar could cause major devaluation of the dollar. The depreciation of the dollar would cause inflation in the US, leading to increases in American interest rates. There would be an increase in mortgage rates followed by deterioration of real estate values. The IMF has simulated that such an adjustment would cause a decline in the rate of growth of US GDP to 0.5 percent over several years. The decline of demand in the US by four percentage points over several years would result in a world recession because the weakness in Europe and Japan could not compensate for the collapse of American demand. The probability of occurrence of an abrupt adjustment is unknown. However, the adverse effects are quite high, at least hypothetically, to warrant concern.”
The United States could be moving toward a situation typical of heavily indebted countries, requiring fiscal adjustment and increases in productivity to become more competitive internationally. The CAD and NIIP of the United States are not observed in full deterioration because the economy is well below potential. There are two complications in the current environment relative to the concern with disorderly correction in the first half of the past decade. Table VI-3B provides data on the US fiscal and balance of payments imbalances. In 2007, the federal deficit of the US was $161 billion corresponding to 1.2 percent of GDP while the Congressional Budget Office (CBO 2011AugBEO, 2) estimates the federal deficit in 2012 at $1128 billion or 7.3 percent of GDP (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/08/expanding-bank-cash-and-deposits-with.html). The combined record federal deficits of the US from 2009 to 2012 are $5135 billion or 33 percent of the estimate of GDP of $15,538 billion for fiscal year 2012 by the CBO (http://www.cbo.gov/publication/43542 2012AugBEO). The deficits from 2009 to 2012 exceed one trillion dollars per year, adding to $5.096 trillion in four years, using the fiscal year deficit of $1089.4 billion for fiscal year 2012 (http://www.fms.treas.gov/mts/mts0912.txt), which is the worst fiscal performance since World War II. Federal debt in 2007 was $5035 billion, less than the combined deficits from 2009 to 2012 of $5135 billion using the CBO forecast or $5096 billion using the fiscal year 2012 value of $1089 billion (http://www.fms.treas.gov/mts/mts0912.txt), and corresponded to 36.3 percent of GDP. Federal debt in 2011 was 67.7 percent of GDP and is estimated to reach 72.8 percent of GDP in 2012 (CBO2012AugBEO). This situation may worsen in the future (CBO 2012LTBO):
“The budget outlook is much bleaker under the extended alternative fiscal scenario, which maintains what some analysts might consider “current policies,” as opposed to current laws. Federal debt would grow rapidly from its already high level, exceeding 90 percent of GDP in 2022. After that, the growing imbalance between revenues and spending, combined with spiraling interest payments, would swiftly push debt to higher and higher levels. Debt as a share of GDP would exceed its historical peak of 109 percent by 2026, and it would approach 200 percent in 2037.
The changes under this scenario would result in much lower revenues than would occur under the extended baseline scenario because almost all expiring tax provisions are assumed to be extended through 2022 (with the exception of the current reduction in the payroll tax rate for Social Security). After 2022, revenues under this scenario are assumed to remain at their 2022 level of 18.5 percent of GDP, just above the average of the past 40 years.
Outlays would be much higher than under the other scenario. This scenario incorporates assumptions that through 2022, lawmakers will act to prevent Medicare’s payment rates for physicians from declining; that after 2022, lawmakers will not allow various restraints on the growth of Medicare costs and health insurance subsidies to exert their full effect; and that the automatic reductions in spending required by the Budget Control Act of 2011 will not occur (although the original caps on discretionary appropriations in that law are assumed to remain in place). Finally, under this scenario, federal spending as a percentage of GDP for activities other than Social Security, the major health care programs, and interest payments is assumed to return to its average level during the past two decades, rather than fall significantly below that level, as it does under the extended baseline scenario.”
Table IIA-5, US, Current Account, NIIP, Fiscal Balance, Nominal GDP, Federal Debt and Direct Investment, Dollar Billions and %
| 2000 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | |
| Goods & | -377 | -697 | -698 | -379 | -495 | -559 |
| Income | 19 | 101 | 147 | 119 | 184 | 227 |
| UT | -58 | -115 | -126 | -122 | -131 | -133 |
| Current Account | -416 | -710 | -677 | -382 | -442 | -466 |
| NGDP | 9951 | 14028 | 14291 | 13974 | 14499 | 15076 |
| Current Account % GDP | -3.8 | -5.1 | -4.7 | -2.7 | -3.1 | -3.1 |
| NIIP | -1337 | -1796 | -3260 | -2321 | -2474 | -4030 |
| US Owned Assets Abroad | 6239 | 18399 | 19464 | 18512 | 20298 | 21132 |
| Foreign Owned Assets in US | 7576 | 20195 | 22724 | 20833 | 22772 | 25162 |
| NIIP % GDP | -13.4 | -12.8 | -22.8 | -16.6 | -17.1 | 26.7 |
| Exports | 1425 | 2488 | 2657 | 2181 | 2519 | 2848 |
| NIIP % | -94 | -72 | -123 | -106 | -98 | -142 |
| DIA MV | 2694 | 5274 | 3102 | 4287 | 4767 | 4450 |
| DIUS MV | 2783 | 3551 | 2486 | 2995 | 3397 | 3509 |
| Fiscal Balance | +236 | -161 | -459 | -1413 | -1294 | -1300 |
| Fiscal Balance % GDP | +2.4 | -1.2 | -3.2 | -10.1 | -9.0 | -8.7 |
| Federal Debt | 3410 | 5035 | 5803 | 7545 | 9019 | 10128 |
| Federal Debt % GDP | 34.7 | 36.3 | 40.5 | 54.1 | 62.8 | 67.7 |
| Federal Outlays | 1789 | 2729 | 2983 | 3518 | 3456 | 3603 |
| ∆% | 5.1 | 2.8 | 9.3 | 17.9 | -1.8 | 4.3 |
| % GDP | 18.2 | 19.7 | 20.8 | 25.2 | 24.1 | 24.1 |
| Federal Revenue | 2052 | 2568 | 2524 | 2105 | 2162 | 2303 |
| ∆% | 10.8 | 6.7 | -1.7 | -16.6 | 2.7 | 6.5 |
| % GDP | 20.6 | 18.5 | 17.6 | 15.1 | 15.1 | 15.4 |
Sources:
Notes: UT: unilateral transfers; NGDP: nominal GDP or in current dollars; NIIP: Net International Investment Position; DIA MV: US Direct Investment Abroad at Market Value; DIUS MV: Direct Investment in the US at Market Value. There are minor discrepancies in the decimal point of percentages of GDP between the balance of payments data and federal debt, outlays, revenue and deficits in which the original number of the CBO source is maintained. These discrepancies do not alter conclusions.
Sources: Balance of Payments and NIIP, Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) http://www.bea.gov/international/index.htm#bop
Gross Domestic Product, Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) http://www.bea.gov/national/index.htm#gdp
IIB Import Export Prices. Chart IIB-1 provides prices of total US imports 2001-2012. Prices fell during the contraction of 2001. Import price inflation accelerated after unconventional monetary policy of near zero interest rates in 2003-2004 and quantitative easing by withdrawing supply with the suspension of 30-year Treasury bond auctions. Slow pace of adjusting fed funds rates from 1 percent by increments of 25 basis points in 17 consecutive meetings of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) between Jun 2004 and Jun 2006 continued to give impetus to carry trades. The reduction of fed funds rates toward zero in 2008 fueled a spectacular global hunt for yields that caused commodity price inflation in the middle of a global recession. After risk aversion in 2009 because of the announcement of TARP (Troubled Asset Relief Program) creating anxiety on “toxic assets” in bank balance sheets (see Cochrane and Zingales 2009), prices collapsed because of unwinding carry trades. Renewed price increases returned with zero interest rates and quantitative easing. Monetary policy impulses in massive doses have driven inflation and valuation of risk financial assets in wide fluctuations over a decade.
Chart IIB-1, US, Prices of Total US Imports 2001=100, 2001-2012
Source: http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIB-2 provides 12-month percentage changes of prices of total US imports from 2001 to 2012. The only plausible explanation for the wide oscillations is by the carry trade originating in unconventional monetary policy. Import prices jumped in 2008 during deep and protracted global recession driven by carry trades from zero interest rates to long, leveraged positions in commodity futures. Carry trades were unwound during the financial panic in the final quarter of 2008 that resulted in flight to government obligations. Import prices jumped again in 2009 with subdued risk aversion because US banks did not have unsustainable toxic assets. Import prices then fluctuated as carry trades were resumed during periods of risk appetite and unwound during risk aversion resulting from the European debt crisis.
Chart IIB-2, US, Prices of Total US Imports, 12-Month Percentage Changes, 2001-2012
Source: http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIB-3 provides prices of US imports from 1982 to 2012. There is no similar episode to that of the increase of commodity prices in 2008 during a protracted and deep global recession with subsequent collapse during a flight into government obligations. Trade prices have been driven by carry trades created by unconventional monetary policy in the past decade.
Chart IIB-3, US, Prices of Total US Imports, 2001=100, 1982-2012
Source: http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIB-4 provides 12-month percentage changes of US total imports from 1982 to 2012. There have not been wide consecutive oscillations as the ones during the global recession of IVQ2007 to IIQ2009.
Chart IIB-4, US, Prices of Total US Imports, 12-Month Percentage Changes, 1982-2012
Source: http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIB-5 provides the index of US export prices from 2001 to 2012. Import and export prices have been driven by impulses of unconventional monetary policy in massive doses. The most recent segment in Chart IIB2-5 shows declining trend resulting from a combination of the world economic slowdown and the decline of commodity prices as carry trade exposures are unwound because of risk aversion to the sovereign debt crisis in Europe.
Chart IIB-5, US, Prices of Total US Exports, 2001=100, 2001-2012
Source: http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIB-6 provides prices of US total exports from 1982 to 2012. The rise before the global recession from 2003 to 2008, driven by carry trades, is also unique in the series and is followed by another steep increase after risk aversion moderated in IQ2009.
Chart IIB-6, US, Prices of Total US Exports, 2001=100, 1982-2012
Source: http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIB-7 provides 12-month percentage changes of total US exports from 1982 to 2012. The uniqueness of the oscillations around the global recession of IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 is clearly revealed.
Chart IIB-7, US, Prices of Total US Exports, 12-Month Percentage Changes, 1982-2012
Source: http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Twelve-month percentage changes of US prices of exports and imports are provided in Table IIB-1. Import prices have been driven since 2003 by unconventional monetary policy of near zero interest rates influencing commodity prices according to moods of risk aversion. In a global recession without risk aversion until the panic of Sep 2008 with flight to government obligations, import prices rose 4.9 percent in the twelve months ending in Oct 2008 and fell 5.6 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2009 when risk aversion developed in 2008 until mid 2009. Import prices rose again sharply in Oct 2010 by 3.9 percent and in Oct 2011 by 11.1 percent in the presence of zero interest rates with relaxed mood of risk aversion until carry trades were unwound in May 2011 and following months as shown by increase of import prices by 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2012 and of 1.4 percent in exports. Fluctuations are much sharper in imports because of the high content of oil that as all commodities futures contracts increases sharply with zero interest rates and risk appetite, contracting under risk aversion. There is similar behavior of prices of imports ex fuels, exports and exports ex agricultural goods but less pronounced than for commodity-rich prices dominated by carry trades from zero interest rates. A critical event resulting from unconventional monetary policy driving higher commodity prices by carry trades is the deterioration of the terms of trade, or export prices relative to import prices, that has adversely affected US real income growth relative to what it would have been in the absence of unconventional monetary policy. Europe, Japan and other advanced economies have experienced similar deterioration of their terms of trade. Because of unwinding carry trades of commodity futures as a result of risk aversion, import prices increased only 0.4 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2012, export prices increased 1.4 percent and prices of nonagricultural exports increased only 0.2 percent. Imports excluding fuel increased only 0.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Oct 2012. At the margin, prices in world exports and imports are increasing again because of carry trades in a temporary mood of risk appetite.
Table IIB-1, US, Twelve-Month Percentage Rates of Change of Prices of Exports and Imports
| Imports | Imports Ex Fuels | Exports | Exports Non-Ag | |
| Oct 2012 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 1.4 | 0.2 |
| Oct 2011 | 11.1 | 4.8 | 6.3 | 5.8 |
| Oct 2010 | 3.9 | 2.5 | 5.8 | 4.8 |
| Oct 2009 | -5.6 | -3.1 | -3.6 | -2.9 |
| Oct 2008 | 4.9 | 4.8 | 4.0 | 3.8 |
| Oct 2007 | 9.1 | 2.7 | 5.6 | 3.9 |
| Oct 2006 | -1.0 | 2.6 | 2.9 | 2.6 |
| Oct 2005 | 8.2 | 1.6 | 3.7 | 3.6 |
| Oct 2004 | 9.9 | 2.7 | 4.4 | 5.0 |
| Oct 2003 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 1.3 | 0.6 |
| Oct 2002 | 1.9 | NA | 0.4 | 0.0 |
| Oct 2001 | -7.4 | NA | -2.0 | -2.2 |
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIB-8 shows the US monthly import price index of all commodities excluding fuels from 2001 to 2012. All curves of nominal values follow the same behavior under the influence of unconventional monetary policy. Zero interest rates without risk aversion result in jumps of nominal values while under strong risk aversion even with zero interest rates there are declines of nominal values.
Chart IIB-8, US, Import Price Index All Commodities Excluding Fuels, 2001=100, 2001-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIB-9 provides 12-month percentage changes of the US import price index excluding fuels between 2001 and 2012. There is the same behavior of carry trades driving up without risk aversion and down with risk aversion prices of raw materials, commodities and food in international trade during the global recession of IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 and in previous and subsequent periods.
Chart IIB-9, US, Import Price Index All Commodities Excluding Fuels, 12-Month Percentage Changes, 2002-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIB-10 provides the monthly US import price index ex petroleum from 2001 to 2012. Prices including or excluding commodities follow the same fluctuations and trends originating in impulses of unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates.
Chart IIB-10, US, Import Price Index ex Petroleum, 2001=100, 2001-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIB-11 provides the US import price index ex petroleum from 1982 to 2012. There is the same unique hump in 2008 caused by carry trades from zero interest rates to prices of commodities and raw materials.
Chart IIB-11, US, Import Price Index ex Petroleum, 2001=100, 1982-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIB-12 provides 12-month percentage changes of the import price index ex petroleum from 1986 to 2012. The oscillations caused by the carry trade in increasing prices of commodities and raw materials without risk aversion and subsequently decreasing them during risk aversion are quite unique.
Chart IIB-12, US, Import Price Index ex Petroleum, 12-Month Percentage Changes, 1986-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIB-13 of the US Energy Information Administration provides the price of the crude oil futures contract from 1985 to 2012. There is the same hump in 2008 as in all charts caused by the common factor of carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures positions with risk appetite and subsequent decline when carry trades were unwound during shocks of risk aversion.
Chart IIB-13, US, Crude Oil Futures Contract
Source: US Energy Information Administration
http://www.eia.gov/dnav/pet/hist/LeafHandler.ashx?n=PET&s=RCLC1&f=D
The price index of US imports of petroleum and petroleum products in shown in Chart IIB-14. There is similar behavior of the curves all driven by the same impulses of monetary policy.
Chart IIB-14, US, Import Price Index of Petroleum and Petroleum Products, 2001=100, 2001-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIB-15 provides the price index of petroleum and petroleum products from 1982 to 2012. The rise in prices during the global recession in 2008 and the decline after the flight to government obligations is unique in the history of the series. Increases in prices of trade in petroleum and petroleum products were induced by carry trades and declines by unwinding carry trades in flight to government obligations.
Chart IIB-15, US, Import Price Index of Petroleum and Petroleum Products, 2001=100, 1982-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIB-16 provides 12-month percentage changes of the price index of US imports of petroleum and petroleum products from 1982 to 2012. There were wider oscillations in this index from 1999 to 2001 (see Barsky and Killian 2004 for an explanation).
Chart IIB-16, US, Import Price Index of Petroleum and Petroleum Products, 12-Month Percentage Changes, 1982-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
The price index of US exports of agricultural commodities is in Chart IIB-17 from 2001 to 2012. There are similar fluctuations and trends as in all other price index originating in unconventional monetary policy repeated over a decade. The most recent segment in 2011 has declining trend in a new flight from risk resulting from the sovereign debt crisis in Europe followed by another decline in Jun 2012.
Chart IIB-17, US, Exports Price Index of Agricultural Commodities, 2001=100, 2001-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIB-18 provides the price index of US exports of agricultural commodities from 1982 to 2012. The increase in 2008 in the middle of deep, protracted contraction was induced by unconventional monetary policy. The decline from 2008 into 2009 was caused by unwinding carry trades in a flight to government obligations. The increase into 2011 and current pause were also induced by unconventional monetary policy in waves of increases during relaxed risk aversion and declines during unwinding of positions because of aversion to financial risk.
Chart IIB-18, US, Exports Price Index of Agricultural Commodities, 2001=100, 1982-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIB-19 provides 12-month percentage changes of the index of US exports of agricultural commodities from 1986 to 2012. The wide swings in 2008, 2009 and 2011 are only explained by unconventional monetary policy inducing carry trades from zero interest rates to commodity futures and reversals during risk aversion.
Chart IIB-19, US, Exports Price Index of Agricultural Commodities, 12-Month Percentage Changes, 1986-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIB-20 shows the export price index of nonagricultural commodities from 2001 to 2012. Unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates drove price behavior during the past decade. Policy has been based on the myth of stimulating the economy by climbing the negative slope of an imaginary short-term Phillips curve.
Chart IIB-20, US, Exports Price Index of Nonagricultural Commodities, 2001=100, 2001-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Chart IIB-21 provides a longer perspective of the price index of US nonagricultural commodities from 1982 to 2012. Increases and decreases around the global contraction after 2007 were caused by carry trade induced by unconventional monetary policy.
Chart IIB-21, US, Exports Price Index of Nonagricultural Commodities, 2001=100, 1982-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
Finally, Chart IIB-22 provides 12-month percentage changes of the price index of US exports of nonagricultural commodities from 1986 to 2012. The wide swings before, during and after the global recession beginning in 2007 were caused by carry trades induced by unconventional monetary policy.
Chart IIB-22, US, Exports Price Index of Nonagricultural Commodities, 12-Month Percentage Changes, 1986-2012
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/mxp/data.htm
III World Financial Turbulence. Financial markets are being shocked by multiple factors including (1) world economic slowdown; (2) slowing growth in China with political development and slowing growth in Japan and world trade; (3) slow growth propelled by savings reduction in the US with high unemployment/underemployment, falling wages and hiring collapse; and (3) the outcome of the sovereign debt crisis in Europe. This section provides current data and analysis. Subsection IIIA Financial Risks provides analysis of the evolution of valuations of risk financial assets during the week. There are various appendixes for convenience of reference of material related to the euro area debt crisis. Some of this material is updated in Subsection IIIA when new data are available and then maintained in the appendixes for future reference until updated again in Subsection IIIA. Subsection IIIB Appendix on Safe Haven Currencies discusses arguments and measures of currency intervention and is available in the Appendixes section at the end of the blog comment. Subsection IIIC Appendix on Fiscal Compact provides analysis of the restructuring of the fiscal affairs of the European Union in the agreement of European leaders reached on Dec 9, 2011 and is available in the Appendixes section at the end of the blog comment. Subsection IIID Appendix on European Central Bank Large Scale Lender of Last Resort considers the policies of the European Central Bank and is available in the Appendixes section at the end of the blog comment. Appendix IIIE Euro Zone Survival Risk analyzes the threats to survival of the European Monetary Union and is available following Subsection IIIA. Subsection IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation provides more technical analysis and is available following Subsection IIIA. Subsection IIIG Appendix on Deficit Financing of Growth and the Debt Crisis provides analysis of proposals to finance growth with budget deficits together with experience of the economic history of Brazil and is available in the Appendixes section at the end of the blog comment.
IIIA Financial Risks. The past half year has been characterized by financial turbulence, attaining unusual magnitude in recent months. Table III-1, updated with every comment in this blog, provides beginning values on Fr Nov 2 and daily values throughout the week ending on Nov 9 of various financial assets. Section VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets provides a set of more complete values. All data are for New York time at 5 PM. The first column provides the value on Fri Nov 2 and the percentage change in that prior week below the label of the financial risk asset. For example, the first column “Fri Nov 2, 2012”, first row “USD/EUR 1.2838 0.8 %,” provides the information that the US dollar (USD) appreciated 0.8 percent to USD 1.2838/EUR in the week ending on Fri Nov 2 relative to the exchange rate on Fri Oct 26. The first five asset rows provide five key exchange rates versus the dollar and the percentage cumulative appreciation (positive change or no sign) or depreciation (negative change or negative sign). Positive changes constitute appreciation of the relevant exchange rate and negative changes depreciation. Financial turbulence has been dominated by reactions to the new program for Greece (see section IB in http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/07/debt-and-financial-risk-aversion-and.html), modifications and new approach adopted in the Euro Summit of Oct 26 (European Commission 2011Oct26SS, 2011Oct26MRES), doubts on the larger countries in the euro zone with sovereign risks such as Spain and Italy but expanding into possibly France and Germany, the growth standstill recession and long-term unsustainable government debt in the US, worldwide deceleration of economic growth and continuing waves of inflation. The most important current shock is that resulting from the agreement by European leaders at their meeting on Dec 9 (European Council 2911Dec9), which is analyzed in IIIC Appendix on Fiscal Compact. European leaders reached a new agreement on Jan 30 (http://www.consilium.europa.eu/uedocs/cms_data/docs/pressdata/en/ec/127631.pdf) and another agreement on Jun 29, 2012 (http://www.consilium.europa.eu/uedocs/cms_data/docs/pressdata/en/ec/131388.pdf).
The dollar/euro rate is quoted as number of US dollars USD per one euro EUR, USD 1.2838/EUR in the first row, first column in the block for currencies in Table III-1 for Fri Nov 2, appreciating to USD 1.2796/EUR on Mon Nov 5, or by 0.3 percent. The dollar appreciated because fewer dollars, $1.2796, were required on Mon Nov 5 to buy one euro than $1.2838 on Nov 2. Table III-1 defines a country’s exchange rate as number of units of domestic currency per unit of foreign currency. USD/EUR would be the definition of the exchange rate of the US and the inverse [1/(USD/EUR)] is the definition in this convention of the rate of exchange of the euro zone, EUR/USD. A convention used throughout this blog is required to maintain consistency in characterizing movements of the exchange rate such as in Table III-1 as appreciation and depreciation. The first row for each of the currencies shows the exchange rate at 5 PM New York time, such as USD 1.2838/EUR on Nov 2; the second row provides the cumulative percentage appreciation or depreciation of the exchange rate from the rate on the last business day of the prior week, in this case Fri Nov 2, to the last business day of the current week, in this case Fri Nov 9, such as appreciation by 1.0 percent to USD 1.2711/EUR by Nov 9; and the third row provides the percentage change from the prior business day to the current business day. For example, the USD appreciated (denoted by positive sign) by 1.0 percent from the rate of USD 1.2838/EUR on Fri Nov 2 to the rate of USD 1.2711/EUR on Fri Nov 9 {[(1.2711/1.2838) – 1]100 = -1.0%} and appreciated (denoted by positive sign) by 0.3 percent from the rate of USD 1.2747 on Thu Nov 8 to USD 1.2711/EUR on Fri Nov 9 {[(1.2711/1.2747) -1]100 = -0.3%}. Other factors constant, appreciation of the dollar relative to the euro is caused by increasing risk aversion, with rising uncertainty on European sovereign risks increasing dollar-denominated assets with sales of risk financial investments. Funds move away from higher yielding risk financial assets to the safety of dollar investments. When risk aversion declines, funds have been moving away from safe assets in dollars to risk financial assets, depreciating the dollar.
Table III-I, Weekly Financial Risk Assets Nov 5 to Nov 9, 2012
| Fri Nov 2, 2012 | M 5 | Tue 6 | W 7 | Thu 8 | Fr 9 |
| USD/EUR 1.2838 0.8% | 1.2796 0.3% 0.3% | 1.2813 0.2% -0.1% | 1.2774 0.5% 0.3% | 1.2747 0.7% 0.2% | 1.2711 1.0% 0.3% |
| JPY/ USD 80.43 -1.0% | 80.29 0.2% 0.2% | 80.34 0.1% -0.1% | 79.93 0.6% 0.5% | 79.48 1.2% 0.6% | 79.49 1.2% 0.0% |
| CHF/ USD 0.9405 -0.6 | 0.9435 -0.3% -0.3% | 0.9429 -0.3% 0.1% | 0.9450 -0.5% -0.2% | 0.9459 -0.6% -0.1% | 0.9488 -0.9% -0.3% |
| CHF/ EUR 1.2071 0.2% | 1.2073 0.0% 0.0% | 1.2082 -0.1% -0.1% | 1.2070 0.0% 0.1% | 1.2058 0.1% 0.1% | 1.2059 0.1% 0.0% |
| USD/ AUD 1.0337 0.9674 -0.4% | 1.0366 0.9647 0.3% 0.3% | 1.0435 0.9583 0.9% 0.7% | 1.0405 0.9611 0.7% -0.3% | 1.0407 0.9609 0.7% 0.0% | 1.0385 0.9629 0.5% -0.2% |
| 10 Year T Note 1.715 | 1.68 | 1.75 | 1.65 | 1.61 | 1.614 |
| 2 Year T Note 0.274 | 0.27 | 0.30 | 0.27 | 0.26 | 0.256 |
| German Bond 2Y 0.01 10Y 1.45 | 2Y -0.01 10Y 1.43 | 2Y -0.01 10Y 1.44 | 2Y -0.04 10Y 1.38 | 2Y -0.03 10Y 1.36 | 2Y -0.03 10Y 1.35 |
| DJIA 13093.16 -0.1% | 13112.44 0.1% 0.1% | 13245.68 1.2% 1.0% | 12932.73 -1.2% -2.4% | 12811.32 -2.2% -0.9% | 12815.39 -2.1% 0.0% |
| DJ Global 1932.44 0.9% | 1922.98 -0.5% -0.5% | 1933.23 0.0% 0.5% | 1905.80 -1.4% -1.4% | 1886.64 -2.4% -1.0% | 1881.43 -2.6% -0.3% |
| DJ Asia Pacific 1249.69 0.8% | 1246.92 -0.2% -0.2% | 1248.03 -0.1% 0.1% | 1256.58 0.6% 0.7% | 1241.24 -0.7% -1.2% | 1237.15 -1.0% -0.3% |
| Nikkei 9051.22 0.6% | 9007.44 -0.5% -0.5% | 8975.15 -0.8% -0.4% | 8972.89 -0.9% 0.0% | 8837.15 -2.4% -1.5% | 8757.60 -3.2% -0.9% |
| Shanghai 2117.05 2.5% | 2114.03 -0.1% -0.1% | 2106.00 -0.5% -0.4% | 2105.73 -0.5% 0.0% | 2071.51 -2.2% -1.6% | 2069.07 -2.3% -0.1% |
| DAX 7363.85 1.8% | 7326.47 -0.5% -0.5% | 7377.76 0.2% 0.7% | 7232.83 -1.8% -2.0% | 7204.96 -2.2% -0.4% | 7163.50 -2.7% -0.6% |
| DJ UBS Comm. 140.37 -1.8% | 140.23 -0.1% -0.1% | 142.47 1.5% 1.6% | 140.99 0.4% -1.0% | 141.55 0.8% 0.4% | 140.79 0.3% -0.5% |
| WTI $ B 84.86 -1.6% | 85.78 1.1% 1.1% | 88.45 4.2% 3.1% | 84.44 -0.5% -4.5% | 85.01 0.2% 0.7% | 86.12 1.5% 1.3% |
| Brent $/B 105.68 -3.5% | 108.09 2.3% 2.3% | 111.03 5.1% 2.7% | 106.70 1.0% -3.9% | 107.03 1.3% 0.3% | 109.44 3.6% 2.3% |
| Gold $/OZ 1675.20 -2.1% | 1684.90 0.6% 0.6% | 1716.0 2.4% 1.8% | 1714.0 2.3% -0.1% | 1731.1 3.3% 1.0% | 1731.0 3.3% 0.0% |
Note: USD: US dollar; JPY: Japanese Yen; CHF: Swiss
Franc; AUD: Australian dollar; Comm.: commodities; OZ: ounce
Sources: http://www.bloomberg.com/markets/
http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_hps_marketdata
Discussion of current and recent risk-determining events is followed below by analysis of risk-measuring yields of the US and Germany and the USD/EUR rate.
First, Risk-Determining Events. The European Council (2012Oct19 http://www.consilium.europa.eu/uedocs/cms_data/docs/pressdata/en/ec/133004.pdf ) reached conclusions on strengthening the euro area and providing unified financial supervision:
“The European Council called for work to proceed on the proposals on the Single Supervisory Mechanism as a matter of priority with the objective of agreeing on the legislative framework by 1st January 2013 and agreed on a number of orientations to that end. It also took note of issues relating to the integrated budgetary and economic policy frameworks and democratic legitimacy and accountability which should be further explored. It agreed that the process towards deeper economic and monetary union should build on the EU's institutional and legal framework and be characterised by openness and transparency towards non-euro area Member States and respect for the integrity of the Single Market. It looked forward to a specific and time-bound roadmap to be presented at its December 2012 meeting, so that it can move ahead on all essential building blocks on which a genuine EMU should be based.”
Buiter (2012Oct15) finds that resolution of the euro crisis requires full banking union together with restructuring the sovereign debt of at least four and possibly total seven European countries. The Bank of Spain released new data on doubtful debtors in Spain’s credit institutions (http://www.bde.es/bde/en/secciones/prensa/Agenda/Datos_de_credit_a6cd708c59cf931.html). In 2006, the value of doubtful credits reached €10,859 million or 0.7 percent of total credit of €1,508,626 million. In Aug 2012, doubtful credit reached €178,579 million or 10.5 percent of total credit of €1,698,714 million.
There are three critical factors influencing world financial markets. (1) Spain could request formal bailout from the European Stability Mechanism (ESM) that may also affect Italy’s international borrowing. David Roman and Jonathan House, writing on “Spain risks backlash with budget plan,” on Sep 27, 2012, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10000872396390443916104578021692765950384.html?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection) analyze Spain’s proposal of reducing government expenditures by €13 billion, or around $16.7 billion, increasing taxes in 2013, establishing limits on early retirement and cutting the deficit by €65 billion through 2014. Banco de España, Bank of Spain, contracted consulting company Oliver Wyman to conduct rigorous stress tests of the resilience of its banking system. (Stress tests and their use are analyzed by Pelaez and Pelaez Globalization and the State Vol. I (2008b), 95-100, International Financial Architecture (2005) 112-6, 123-4, 130-3).) The results are available from Banco de España (http://www.bde.es/bde/en/secciones/prensa/infointeres/reestructuracion/ http://www.bde.es/f/webbde/SSICOM/20120928/informe_ow280912e.pdf). The assumptions of the adverse scenario used by Oliver Wyman are quite tough for the three-year period from 2012 to 2014: “6.5 percent cumulative decline of GDP, unemployment rising to 27.2 percent and further declines of 25 percent of house prices and 60 percent of land prices (http://www.bde.es/f/webbde/SSICOM/20120928/informe_ow280912e.pdf). Fourteen banks were stress tested with capital needs estimates of seven banks totaling €59.3 billion. The three largest banks of Spain, Banco Santander (http://www.santander.com/csgs/Satellite/CFWCSancomQP01/es_ES/Corporativo.html), BBVA (http://www.bbva.com/TLBB/tlbb/jsp/ing/home/index.jsp) and Caixabank (http://www.caixabank.com/index_en.html), with 43 percent of exposure under analysis, have excess capital of €37 billion in the adverse scenario in contradiction with theories that large, international banks are necessarily riskier. Jonathan House, writing on “Spain expects wider deficit on bank aid,” on Sep 30, 2012, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10000872396390444138104578028484168511130.html?mod=WSJPRO_hpp_LEFTTopStories), analyzes the 2013 budget plan of Spain that will increase the deficit of 7.4 percent of GDP in 2012, which is above the target of 6.3 percent under commitment with the European Union. The ratio of debt to GDP will increase to 85.3 percent in 2012 and 90.5 percent in 2013 while the 27 members of the European Union have an average debt/GDP ratio of 83 percent at the end of IIQ2012. (2) Symmetric inflation targets appear to have been abandoned in favor of a self-imposed single jobs mandate of easing monetary policy even after the economy grows again at or close to potential output. Monetary easing by unconventional measures is now apparently open ended in perpetuity as provided in the statement of the meeting of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) on Sep 13, 2012 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20120913a.htm):
“To support a stronger economic recovery and to help ensure that inflation, over time, is at the rate most consistent with its dual mandate, the Committee agreed today to increase policy accommodation by purchasing additional agency mortgage-backed securities at a pace of $40 billion per month. The Committee also will continue through the end of the year its program to extend the average maturity of its holdings of securities as announced in June, and it is maintaining its existing policy of reinvesting principal payments from its holdings of agency debt and agency mortgage-backed securities in agency mortgage-backed securities. These actions, which together will increase the Committee’s holdings of longer-term securities by about $85 billion each month through the end of the year, should put downward pressure on longer-term interest rates, support mortgage markets, and help to make broader financial conditions more accommodative.
To support continued progress toward maximum employment and price stability, the Committee expects that a highly accommodative stance of monetary policy will remain appropriate for a considerable time after the economic recovery strengthens.”
In fact, it is evident to the public that this policy will be abandoned if inflation costs rise. There is the concern of the production and employment costs of controlling future inflation.
(2) The European Central Bank (ECB) approved a new program of bond purchases under the name “Outright Monetary Transactions” (OMT). The ECB will purchase sovereign bonds of euro zone member countries that have a program of conditionality under the European Financial Stability Facility (EFSF) that is converting into the European Stability Mechanism (ESM). These programs provide enhancing the solvency of member countries in a transition period of structural reforms and fiscal adjustment. The purchase of bonds by the ECB would maintain debt costs of sovereigns at sufficiently low levels to permit adjustment under the EFSF/ESM programs. Purchases of bonds are not limited quantitatively with discretion by the ECB as to how much is necessary to support countries with adjustment programs. Another feature of the OMT of the ECB is sterilization of bond purchases: funds injected to pay for the bonds would be withdrawn or sterilized by ECB transactions. The statement by the European Central Bank on the program of OTM is as follows (http://www.ecb.int/press/pr/date/2012/html/pr120906_1.en.html):
“6 September 2012 - Technical features of Outright Monetary Transactions
As announced on 2 August 2012, the Governing Council of the European Central Bank (ECB) has today taken decisions on a number of technical features regarding the Eurosystem’s outright transactions in secondary sovereign bond markets that aim at safeguarding an appropriate monetary policy transmission and the singleness of the monetary policy. These will be known as Outright Monetary Transactions (OMTs) and will be conducted within the following framework:
Conditionality
A necessary condition for Outright Monetary Transactions is strict and effective conditionality attached to an appropriate European Financial Stability Facility/European Stability Mechanism (EFSF/ESM) programme. Such programmes can take the form of a full EFSF/ESM macroeconomic adjustment programme or a precautionary programme (Enhanced Conditions Credit Line), provided that they include the possibility of EFSF/ESM primary market purchases. The involvement of the IMF shall also be sought for the design of the country-specific conditionality and the monitoring of such a programme.
The Governing Council will consider Outright Monetary Transactions to the extent that they are warranted from a monetary policy perspective as long as programme conditionality is fully respected, and terminate them once their objectives are achieved or when there is non-compliance with the macroeconomic adjustment or precautionary programme.
Following a thorough assessment, the Governing Council will decide on the start, continuation and suspension of Outright Monetary Transactions in full discretion and acting in accordance with its monetary policy mandate.
Coverage
Outright Monetary Transactions will be considered for future cases of EFSF/ESM macroeconomic adjustment programmes or precautionary programmes as specified above. They may also be considered for Member States currently under a macroeconomic adjustment programme when they will be regaining bond market access.
Transactions will be focused on the shorter part of the yield curve, and in particular on sovereign bonds with a maturity of between one and three years.
No ex ante quantitative limits are set on the size of Outright Monetary Transactions.
Creditor treatment
The Eurosystem intends to clarify in the legal act concerning Outright Monetary Transactions that it accepts the same (pari passu) treatment as private or other creditors with respect to bonds issued by euro area countries and purchased by the Eurosystem through Outright Monetary Transactions, in accordance with the terms of such bonds.
Sterilisation
The liquidity created through Outright Monetary Transactions will be fully sterilised.
Transparency
Aggregate Outright Monetary Transaction holdings and their market values will be published on a weekly basis. Publication of the average duration of Outright Monetary Transaction holdings and the breakdown by country will take place on a monthly basis.
Securities Markets Programme
Following today’s decision on Outright Monetary Transactions, the Securities Markets Programme (SMP) is herewith terminated. The liquidity injected through the SMP will continue to be absorbed as in the past, and the existing securities in the SMP portfolio will be held to maturity.”
Jon Hilsenrath, writing on “Fed sets stage for stimulus,” on Aug 31, 2012, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10000872396390443864204577623220212805132.html?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection), analyzes the essay presented by Chairman Bernanke at the Jackson Hole meeting of central bankers, as defending past stimulus with unconventional measures of monetary policy that could be used to reduce extremely high unemployment. Chairman Bernanke (2012JHAug31, 18-9) does support further unconventional monetary policy impulses if required by economic conditions (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/bernanke20120831a.htm):
“Over the past five years, the Federal Reserve has acted to support economic growth and foster job creation, and it is important to achieve further progress, particularly in the labor market. Taking due account of the uncertainties and limits of its policy tools, the Federal Reserve will provide additional policy accommodation as needed to promote a stronger economic recovery and sustained improvement in labor market conditions in a context of price stability.”
Professor John H Cochrane (2012Aug31), at the University of Chicago Booth School of Business, writing on “The Federal Reserve: from central bank to central planner,” on Aug 31, 2012, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10000872396390444812704577609384030304936.html?mod=WSJ_hps_sections_opinion), analyzes that the departure of central banks from open market operations into purchase of assets with risks to taxpayers and direct allocation of credit subject to political influence has caused them to abandon their political independence and accountability. Cochrane (2012Aug31) finds a return to the proposition of Milton Friedman in the 1960s that central banks can cause inflation and macroeconomic instability.
Mario Draghi (2012Aug29), President of the European Central Bank, also reiterated the need of exceptional and unconventional central bank policies (http://www.ecb.int/press/key/date/2012/html/sp120829.en.html):
“Yet it should be understood that fulfilling our mandate sometimes requires us to go beyond standard monetary policy tools. When markets are fragmented or influenced by irrational fears, our monetary policy signals do not reach citizens evenly across the euro area. We have to fix such blockages to ensure a single monetary policy and therefore price stability for all euro area citizens. This may at times require exceptional measures. But this is our responsibility as the central bank of the euro area as a whole.
The ECB is not a political institution. But it is committed to its responsibilities as an institution of the European Union. As such, we never lose sight of our mission to guarantee a strong and stable currency. The banknotes that we issue bear the European flag and are a powerful symbol of European identity.”
Buiter (2011Oct31) analyzes that the European Financial Stability Fund (EFSF) would need a “bigger bazooka” to bail out euro members in difficulties that could possibly be provided by the ECB. Buiter (2012Oct15) finds that resolution of the euro crisis requires full banking union together with restructuring the sovereign debt of at least four and possibly total seven European countries. Table III-7 in IIIE Appendix Euro Zone Survival Risk below provides the combined GDP in 2012 of the highly indebted euro zone members estimated in the latest World Economic Outlook of the IMF at $4167 billion or 33.1 percent of total euro zone GDP of $12,586 billion. Using the WEO of the IMF, Table III-8 in IIIE Appendix Euro Zone Survival Risk below provides debt of the highly indebted euro zone members at $3927.8 billion in 2012 that increases to $5809.9 billion when adding Germany’s debt, corresponding to 167.0 percent of Germany’s GDP. There are additional sources of debt in bailing out banks. The dimensions of the problem may require more firepower than a bazooka perhaps that of the largest conventional bomb of all times of 44,000 pounds experimentally detonated only once by the US in 1948 (http://www.airpower.au.af.mil/airchronicles/aureview/1967/mar-apr/coker.html).
Second, Risk-Measuring Yields and Exchange Rate. The ten-year government bond of Spain was quoted at 6.868 percent on Aug 10, declining to 6.447 percent on Aug 17 and 6.403 percent on Aug 24, and the ten-year government bond of Italy fell from 5.894 percent on Aug 10 to 5.709 percent on Aug 17 and 5.618 percent on Aug 24. On Aug 31, the yield of the 10-year sovereign bond of Italy rose to 5.787 percent and that of Spain to 6.832 percent. The announcement of the OMT of bond-buying by the ECB together with weak employment creation in the US created risk appetite with the yield of the ten-year government bond of Spain collapsing to 5.708 percent on Sep 7 and the yield of the ten-year government bond of Italy to 5.008 percent (http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_PRO_hps_marketdata). The yield of the ten-year government bond of Spain traded at 5.770 percent on Sep 14 and at 5.739 percent on Sep 21 and ten-year government of Italy traded at 4.953 percent on Sep 14 and 4.982 on Sep 21. The imminence of a bailout of Spain drove the yield of the ten-year sovereign bond of Spain to 5.979 percent on Fri Sep 28 and that of Italy to 5.031 percent but both traded higher during the day. Sovereign yields continued to decline by Oct 5 with the yield of the ten-year sovereign bond of Spain trading at 5.663 percent and that of Italy at 4.922 percent. On Oct 12, 2012, the yield of the ten-year sovereign bond of Spain traded at 5.612 percent and that of Italy at 4.856 percent. Sovereign bonds continued to decline in the week of Oct 19 with the ten-year government bond Spain trading at 5.289 percent and that of Italy at 4.655 percent. On Oct 26, the yield of the ten-year government bond of Spain traded at 5.574 percent and that of Italy at 4.838 percent. On Nov 2, the ten-year government bond of Spain traded at 5.649 percent, increasing to 5.820 percent on Nov 9 while the ten-year bond of Italy traded at 4.879 percent on Nov 2, increasing o 4.898 percent on Nov 9 under renewed concerns about Greece. Risk aversion is captured by flight of investors from risk financial assets to the government securities of the US and Germany. Diminishing aversion is captured by increase of the yield of the two- and ten-year Treasury notes and the two- and ten-year government bonds of Germany. Table III-1A provides yields of US and German governments bonds and the rate of USD/EUR. Yields of US and German government bonds decline during shocks of risk aversion and the dollar strengthens in the form of fewer dollars required to buy one euro. The yield of the US ten-year Treasury note fell from 2.202 percent on Aug 26, 2011 to 1.459 percent on Jul 20, 2012, reminiscent of experience during the Treasury-Fed accord of the 1940s that placed a ceiling on long-term Treasury debt (Hetzel and Leach 2001), while the yield of the ten-year government bond of Germany fell from 2.16 percent to 1.17 percent. Under increasing risk appetite, the yield of the ten-year Treasury rose to 1.544 on Jul 27, 2012 and 1.569 percent on Aug 3, 2012, while the yield of the ten-year Government bond of Germany rose to 1.40 percent on Jul 27 and 1.42 percent on Aug 3. Yields moved on an increasing trend with the US ten-year note at 1.814 percent on Aug 17 and the German ten-year bond at 1.50 percent with sharp decline on Aug 24 to 1.684 percent for the yield of the US ten-year note and 1.35 for the yield of the German ten-year bond. The trend was interrupted with decline of the yield of the ten-year Treasury note to 1.543 percent on Aug 31, 2012, and of the ten-year German bond to 1.33 percent. The US dollar strengthened significantly from USD 1.450/EUR on Aug 26, 2011, to USD 1.2158 on Jul 20, 2012, or by 16.2 percent, but depreciated to USD 1.2320/EUR on Jul 27, 2012 and 1.2387 on Aug 3, 2012 in expectation of massive support of highly indebted euro zone members. Doubts returned at the end of the week of Aug 10, 2012 with appreciation to USD 1.2290/EUR and decline of the yields of the two-year government bond of Germany to -0.07 percent and of the ten-year to 1.38 percent. On Aug 17, the US dollar depreciated by 0.4 percent to USD 1.2335/EUR and the ten-year bond of Germany yielded -0.04 percent. Risk appetite returned in the week of Aug 24 with depreciation by 1.4 percent to USD 1.2512/EUR and lower yield of the German two-year bond to -0.01 percent and of the US two-year note to 0.266 percent. Further risk aversion is captured by decline of yield of the two-year Treasury note to 0.225 percent on Aug 31, 2012, and to -0.03 percent for the two-year sovereign bond of Germany while the USD moved in opposite direction, depreciating to USD 1.2575/EUR. The almost simultaneous announcement of the bond-buying OMT of the ECB on Sep 6 and the weak employment report on Sep 7 suggesting further easing by the FOMC caused risk appetite shown by the increase in yields of government bonds of the US on Sep 7 to 1.668 percent for the ten-year note and 0.252 percent for the two-year while the two-year yield of Germany rose from -0.03 percent to 0.03 percent and the ten-year yield from 1.33 percent to 1.52 percent. Risk aversion retreated again on Sep 14, 2012 because of the open-ended monetary policy of the FOMC with the dollar devaluing to USD 1.3130 and the ten-year yield of the US Treasury note increasing to 1.863 percent (also in part because of bond buying by the Fed at shorter maturities) and the yield of the ten-year German bond increasing to 1.71 percent. Risk aversions returned because of weak flash purchasing managers indices with appreciation to USD1.2981 in the week of Sep 21 and declines of the yield of the ten-year Treasury note to 1.753 percent and of the yield of the ten-year government bond to 1.60 percent. Risk aversion because of the potential bailout of Spain drove down the US ten-year yield to 1.631 and the ten-year yield of Germany to 1.44 percent while the dollar appreciated to USD 1.2859/EUR. Increasing risk appetite drove the yield of the ten-year Treasury to 1.737 percent on Oct 5, 2012 and depreciated the dollar to USD 1.3036 with more muted response in the yield of the ten-year bond of Germany rising to 1.52 percent and the two-year yield to 0.06 percent. There is indication of some risk aversion in the week of Oct 12, 2012, with decline of the yield of the ten-year Treasury to 1.663 percent and that of Germany to 1.45 percent, stability of the two-year Treasury yield at 0.264 percent and marginal decline of the yield of the two-year German bond to 0.04 percent while the dollar appreciated to USD 1.2953/EUR. Risk aversion fluctuated in the week of Oct 19 but the week ended with the increase of the yield of the two-year note of the US to 0.296 percent and of the ten-year note to 1.766 percent; there was similar increase of the yield of the two-year government bond of Germany to 0.11 percent and of the ten-year yield to 1.59 percent; and the dollar depreciated 0.5 percent to USD 1.3023 percent. Mild risk aversion returned in the week of Oct 26, with the 10-year Treasury yield declining marginally to 1.748 percent and that of Germany to 1.54 percent while the dollar appreciated to USD 1.2942/EUR. Mild risk aversion continued in the week of Nov 2 with declines in the yield of the ten-year Treasury note to 1.715 percent and of the ten-year government bond of Germany to 1.45 percent while the dollar appreciated to USD 1.2838/EUR. Risk aversion deepened in the week of Nov 9 with the two-year Treasury trading at 0.256 percent and the ten-year at 1.614 percent while the two-year government bond of Germany traded at minus 0.03 percent and the ten-year at 1.35 percent while the dollar strengthened to USD 1.2711/EUR. Under zero interest rates for the monetary policy rate of the US, or fed funds rate, carry trades ensure devaluation of the dollar if there is no risk aversion but the dollar appreciates in flight to safe haven during episodes of risk aversion. Unconventional monetary policy induces significant global financial instability, excessive risks and low liquidity. The ten-year Treasury yield is below consumer price inflation of 2.0 percent in the 12 months ending in Sep (see http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/10/world-inflation-waves-stagnating-united_21.html) and the expectation of higher inflation if risk aversion diminishes. Treasury securities continue to be safe haven for investors fearing risk but with concentration in shorter maturities such as the two-year Treasury. The lower part of Table III-1A provides the same flight to government securities of the US and Germany and the USD during the financial crisis and global recession and the beginning of the European debt crisis in the spring of 2010 with the USD trading at USD 1.192/EUR on Jun 7, 2010.
Table III-1A, Two- and Ten-Year Yields of Government Bonds of the US and Germany and US Dollar/EUR Exchange rate
| US 2Y | US 10Y | DE 2Y | DE 10Y | USD/ EUR | |
| 11/9/12 | 0.256 | 1.614 | -0.03 | 1.35 | 1.2711 |
| 11/2/12 | 0.274 | 1.715 | 0.01 | 1.45 | 1.2838 |
| 10/26/12 | 0.299 | 1.748 | 0.05 | 1.54 | 1.2942 |
| 10/19/12 | 0.296 | 1.766 | 0.11 | 1.59 | 1.3023 |
| 10/12/12 | 0.264 | 1.663 | 0.04 | 1.45 | 1.2953 |
| 10/5/12 | 0.26 | 1.737 | 0.06 | 1.52 | 1.3036 |
| 9/28/12 | 0.236 | 1.631 | 0.02 | 1.44 | 1.2859 |
| 9/21/12 | 0.26 | 1.753 | 0.04 | 1.60 | 1.2981 |
| 9/14/12 | 0.252 | 1.863 | 0.10 | 1.71 | 1.3130 |
| 9/7/12 | 0.252 | 1.668 | 0.03 | 1.52 | 1.2816 |
| 8/31/12 | 0.225 | 1.543 | -0.03 | 1.33 | 1.2575 |
| 8/24/12 | 0.266 | 1.684 | -0.01 | 1.35 | 1.2512 |
| 8/17/12 | 0.288 | 1.814 | -0.04 | 1.50 | 1.2335 |
| 8/10/12 | 0.267 | 1.658 | -0.07 | 1.38 | 1.2290 |
| 8/3/12 | 0.242 | 1.569 | -0.02 | 1.42 | 1.2387 |
| 7/27/12 | 0.244 | 1.544 | -0.03 | 1.40 | 1.2320 |
| 7/20/12 | 0.207 | 1.459 | -0.07 | 1.17 | 1.2158 |
| 7/13/12 | 0.24 | 1.49 | -0.04 | 1.26 | 1.2248 |
| 7/6/12 | 0.272 | 1.548 | -0.01 | 1.33 | 1.2288 |
| 6/29/12 | 0.305 | 1.648 | 0.12 | 1.58 | 1.2661 |
| 6/22/12 | 0.309 | 1.676 | 0.14 | 1.58 | 1.2570 |
| 6/15/12 | 0.272 | 1.584 | 0.07 | 1.44 | 1.2640 |
| 6/8/12 | 0.268 | 1.635 | 0.04 | 1.33 | 1.2517 |
| 6/1/12 | 0.248 | 1.454 | 0.01 | 1.17 | 1.2435 |
| 5/25/12 | 0.291 | 1.738 | 0.05 | 1.37 | 1.2518 |
| 5/18/12 | 0.292 | 1.714 | 0.05 | 1.43 | 1.2780 |
| 5/11/12 | 0.248 | 1.845 | 0.09 | 1.52 | 1.2917 |
| 5/4/12 | 0.256 | 1.876 | 0.08 | 1.58 | 1.3084 |
| 4/6/12 | 0.31 | 2.058 | 0.14 | 1.74 | 1.3096 |
| 3/30/12 | 0.335 | 2.214 | 0.21 | 1.79 | 1.3340 |
| 3/2/12 | 0.29 | 1.977 | 0.16 | 1.80 | 1.3190 |
| 2/24/12 | 0.307 | 1.977 | 0.24 | 1.88 | 1.3449 |
| 1/6/12 | 0.256 | 1.957 | 0.17 | 1.85 | 1.2720 |
| 12/30/11 | 0.239 | 1.871 | 0.14 | 1.83 | 1.2944 |
| 8/26/11 | 0.20 | 2.202 | 0.65 | 2.16 | 1.450 |
| 8/19/11 | 0.192 | 2.066 | 0.65 | 2.11 | 1.4390 |
| 6/7/10 | 0.74 | 3.17 | 0.49 | 2.56 | 1.192 |
| 3/5/09 | 0.89 | 2.83 | 1.19 | 3.01 | 1.254 |
| 12/17/08 | 0.73 | 2.20 | 1.94 | 3.00 | 1.442 |
| 10/27/08 | 1.57 | 3.79 | 2.61 | 3.76 | 1.246 |
| 7/14/08 | 2.47 | 3.88 | 4.38 | 4.40 | 1.5914 |
| 6/26/03 | 1.41 | 3.55 | NA | 3.62 | 1.1423 |
Note: DE: Germany
Source:
http://www.bloomberg.com/markets/
http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_hps_marketdata
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/data.htm
http://www.ecb.int/stats/money/long/html/index.en.html
Chart III-1A of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System provides the ten-year and two-year Treasury constant maturity yields. The combination of zero fed funds rate and quantitative easing caused sharp decline of the yields from 2008 and 2009. Yield declines have also occurred during periods of financial risk aversion, including the current one of stress of financial markets in Europe.
Chart III-1A, US, Ten-Year and Two-Year Treasury Constant Maturity Yields Jul 31, 2001-Nov 8, 2012
Note: US Recessions in shaded areas
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/update/
Kate Linebaugh, writing on “Falling revenue dings stocks,” on Oct 20, 2012, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10000872396390444592704578066933466076070.html?mod=WSJPRO_hpp_LEFTTopStories), identifies a key financial vulnerability: falling revenues across markets for United States reporting companies. Global economic slowdown is reducing corporate sales and squeezing corporate strategies. Linebaugh quotes data from Thomson Reuters that 100 companies of the S&P 500 index have reported declining revenue only 1 percent higher in Jun-Sep 2012 relative to Jun-Sep 2011 but about 60 percent of the companies are reporting lower sales than expected by analysts with expectation that revenue for the S&P 500 will be lower in Jun-Sep 2012 for the entities represented in the index. Results of US companies are likely repeated worldwide. The basic valuation equation that is also used in capital budgeting postulates that the value of stocks or of an investment project is given by:
Where Rτ is expected revenue in the time horizon from τ =1 to T; Cτ denotes costs; and ρ is an appropriate rate of discount. In words, the value today of a stock or investment project is the net revenue, or revenue less costs, in the investment period from τ =1 to T discounted to the present by an appropriate rate of discount. In the current weak economy, revenues have been increasing more slowly than anticipated in investment plans. An increase in interest rates would affect discount rates used in calculations of present value, resulting in frustration of investment decisions. If V represents value of the stock or investment project, as ρ → ∞, meaning that interest rates increase without bound, then V → 0, or
declines.
Equity indexes in Table III-1 weakened the week ending on Nov 9, 2012. Stagnating revenues are causing reevaluation of discounted net earnings with deteriorating views on the world economy. DJIA dropped 2.4 percent on Nov 7, declining 2.1 percent in the week. Germany’s Dax increased 0.6 percent on Fri Nov 9 and decreased 2.7 percent in the week. Dow Global decreased 0.3 percent on Nov 9 and lost 2.6 percent in the week. Japan’s Nikkei Average decreased 0.9 percent on Fri Nov 9 and decreased 3.2 percent in the week. Dow Asia Pacific TSM decreased 0.3 percent on Nov 9 and decreased 1.0 percent in the week while Shanghai Composite decreased 0.1 percent on Nov 9 and increased 2.3 percent in the week. There is evident trend of deceleration of the world economy that could affect corporate revenue and equity valuations.
Commodities were mostly higher in the week of Nov 9, 2012. The DJ UBS Commodities Index decreased 0.5 percent on Fri Nov 9 and increased 0.3 percent in the week, as shown in Table III-1. WTI increased 1.5 percent in the week of Nov 9 while Brent increased 3.6 percent in the week. Gold increased 0.0 percent on Fri Nov 9 and increased 3.3 percent in the week.
Table III-2 provides an update of the consolidated financial statement of the Eurosystem. The balance sheet has swollen with the long-term refinancing operations (LTROs). Line 5 “Lending to Euro Area Credit Institutions Related to Monetary Policy” increased from €546,747 million on Dec 31, 2010, to €879,130 million on Dec 28, 2011 and €1,131,744 million on Nov 2, 2012. The sum of line 5 and line 7 (“Securities of Euro Area Residents Denominated in Euro”) has increased to €1,721,948 million in the statement of Nov 2. There is high credit risk in these transactions with capital of only €85,551 million as analyzed by Cochrane (2012Aug31).
Table III-2, Consolidated Financial Statement of the Eurosystem, Million EUR
| Dec 31, 2010 | Dec 28, 2011 | Nov 2, 2012 | |
| 1 Gold and other Receivables | 367,402 | 419,822 | 479,108 |
| 2 Claims on Non Euro Area Residents Denominated in Foreign Currency | 223,995 | 236,826 | 258,358 |
| 3 Claims on Euro Area Residents Denominated in Foreign Currency | 26,941 | 95,355 | 37,275 |
| 4 Claims on Non-Euro Area Residents Denominated in Euro | 22,592 | 25,982 | 16,560 |
| 5 Lending to Euro Area Credit Institutions Related to Monetary Policy Operations Denominated in Euro | 546,747 | 879,130 | 1,131,744 |
| 6 Other Claims on Euro Area Credit Institutions Denominated in Euro | 45,654 | 94,989 | 232,223 |
| 7 Securities of Euro Area Residents Denominated in Euro | 457,427 | 610,629 | 590,204 |
| 8 General Government Debt Denominated in Euro | 34,954 | 33,928 | 30,010 |
| 9 Other Assets | 278,719 | 336,574 | 265,211 |
| TOTAL ASSETS | 2,004, 432 | 2,733,235 | 3,046,693 |
| Memo Items | |||
| Sum of 5 and 7 | 1,004,174 | 1,489,759 | 1,721,948 |
| Capital and Reserves | 78,143 | 85,748 | 85,551 |
Source: European Central Bank
http://www.ecb.int/press/pr/wfs/2011/html/fs110105.en.html
http://www.ecb.int/press/pr/wfs/2011/html/fs111228.en.html
http://www.ecb.int/press/pr/wfs/2012/html/fs121106.en.html
IIIE Appendix Euro Zone survival risk. European sovereign crisis with survival of the euro area would require success in the restructuring of Italy. That success would be assured with growth of the Italian economy. A critical problem is that the common euro currency prevents Italy from devaluing the exchange rate to parity or the exchange rate that would permit export growth to promote internal economic activity, which could generate fiscal revenues for primary fiscal surplus that ensure creditworthiness. Fiscal consolidation and restructuring are important but of long-term gestation. Immediate growth of the Italian economy would consolidate the resolution of the sovereign debt crisis. Professors Ricardo Caballero and Francesco Giavazzi (2012Jan15) find that the resolution of the European sovereign crisis with survival of the euro area would require success in the restructuring of Italy. That success would be assured with growth of the Italian economy. A critical problem is that the common euro currency prevents Italy from devaluing the exchange rate to parity or the exchange rate that would permit export growth to promote internal economic activity, which could generate fiscal revenues for primary fiscal surplus that ensure creditworthiness. Fiscal consolidation and restructuring are important but of long-term gestation. Immediate growth of the Italian economy would consolidate the resolution of the sovereign debt crisis. Caballero and Giavazzi (2012Jan15) argue that 55 percent of the exports of Italy are to countries outside the euro area such that devaluation of 15 percent would be effective in increasing export revenue. Newly available data in Table III-3 providing Italy’s trade with regions and countries supports the argument of Caballero and Giavazzi (2012Jan15). Italy’s exports to the European Monetary Union (EMU), or euro area, are only 42.7 percent of the total. Exports to the non-European Union area with share of 44.0 percent in Italy’s total exports are growing at 10.3 percent in Jan-Aug 2012 relative to Jan-Aug 2011 while those to EMU are falling at 1.0 percent.
Table III-3, Italy, Exports and Imports by Regions and Countries, % Share and 12-Month ∆%
| Jul 2012 | Exports | ∆% Jan-Aug 2012/ Jan-Aug 2011 | Imports | Imports |
| EU | 56.0 | 0.3 | 53.3 | -6.6 |
| EMU 17 | 42.7 | -1.0 | 43.2 | -6.3 |
| France | 11.6 | 0.4 | 8.3 | -4.5 |
| Germany | 13.1 | 0.5 | 15.6 | -10.7 |
| Spain | 5.3 | -8.0 | 4.5 | -5.7 |
| UK | 4.7 | 10.5 | 2.7 | -12.8 |
| Non EU | 44.0 | 10.3 | 46.7 | -3.4 |
| Europe non EU | 13.3 | 11.5 | 11.1 | -4.6 |
| USA | 6.1 | 18.7 | 3.3 | 3.7 |
| China | 2.7 | -11.4 | 7.3 | -16.2 |
| OPEC | 4.7 | 24.2 | 8.6 | 23.6 |
| Total | 100.0 | 8.4 | 100.0 | -5.1 |
Notes: EU: European Union; EMU: European Monetary Union (euro zone)
Source: Istituto Nazionale di Statistica http://www.istat.it/it/archivio/72548
Table III-4 provides Italy’s trade balance by regions and countries. Italy had trade deficit of €674 million with the 17 countries of the euro zone (EMU 17) in Aug 2012 and deficit of €1375 million in Jan-Aug 2012. Depreciation to parity could permit greater competitiveness in improving the trade surpluses of €7128 million in Jan-Aug with Europe non European Union and of €8973 million with the US. There is significant rigidity in the trade deficits in Jan-Aug of €11,378 million with China and €14,150 million with members of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC). Higher exports could drive economic growth in the economy of Italy that would permit less onerous adjustment of the country’s fiscal imbalances, raising the country’s credit rating.
Table III-4, Italy, Trade Balance by Regions and Countries, Millions of Euro
| Regions and Countries | Trade Balance Aug 2012 Millions of Euro | Trade Balance Cumulative Jan-Aug 2012 Millions of Euro |
| EU | 374 | 8,176 |
| EMU 17 | -674 | -1,375 |
| France | 637 | 7,926 |
| Germany | -449 | -3,600 |
| Spain | -26 | 1,136 |
| UK | 683 | 6,300 |
| Non EU | -972 | -4,351 |
| Europe non EU | 534 | 7,128 |
| USA | 902 | 8,973 |
| China | -1,345 | -11,378 |
| OPEC | -1,478 | -14,150 |
| Total | -598 | 3,825 |
Notes: EU: European Union; EMU: European Monetary Union (euro zone)
Source: Istituto Nazionale di Statistica http://www.istat.it/it/archivio/72548
Growth rates of Italy’s trade and major products are provided in Table III-5 for the period Jan-Aug 2012 relative to Jan-Aug 2011. Growth rates in 12 months of imports are negative with the exception of 9.7 percent for energy. The higher rate of growth of exports of 5.9 percent in Jan-Aug 2012/Jan-Jul 2011 relative to imports of minus 2.6 percent may reflect weak demand in Italy with GDP declining during four consecutive quarters from IIIQ2011 through IIQ2012.
Table III-5, Italy, Exports and Imports % Share of Products in Total and ∆%
| Exports | Exports | Imports | Imports | |
| Consumer | 28.9 | 5.9 | 25.0 | -2.6 |
| Durable | 5.9 | 2.5 | 3.0 | -6.2 |
| Non | 23.0 | 6.8 | 22.0 | -2.1 |
| Capital Goods | 32.2 | 3.1 | 20.8 | -11.5 |
| Inter- | 34.3 | 3.3 | 34.5 | -11.3 |
| Energy | 4.7 | 17.0 | 19.7 | 9.7 |
| Total ex Energy | 95.3 | 4.0 | 80.3 | -8.7 |
| Total | 100.0 | 4.6 | 100.0 | -5.1 |
Source: Istituto Nazionale di Statistica http://www.istat.it/it/archivio/72548
Table III-6 provides Italy’s trade balance by product categories in Aug 2012 and cumulative Jan-Aug 2012. Italy’s trade balance excluding energy generated surplus of €5163 million in Aug 2012 and €47,109 million in Jan-Aug 2012 but the energy trade balance created deficit of €5761 million in Aug 2012 and €43,284 million in Jan-Aug 2012. The overall deficit in Aug 2012 was €598 million with surplus of €3825 million in Jan-Aug 2012. Italy has significant competitiveness in various economic activities in contrast with some other countries with debt difficulties.
Table III-6, Italy, Trade Balance by Product Categories, € Millions
| Aug 2012 | Cumulative Jan-Aug 2012 | |
| Consumer Goods | 745 | 10,426 |
| Durable | 589 | 7,432 |
| Nondurable | 156 | 2,994 |
| Capital Goods | 3,808 | 32,763 |
| Intermediate Goods | 610 | 3,920 |
| Energy | -5,761 | -43,284 |
| Total ex Energy | 5,163 | 47,109 |
| Total | -598 | 3,825 |
Source: Istituto Nazionale di Statistica http://www.istat.it/it/archivio/72548
Brazil faced in the debt crisis of 1982 a more complex policy mix. Between 1977 and 1983, Brazil’s terms of trade, export prices relative to import prices, deteriorated 47 percent and 36 percent excluding oil (Pelaez 1987, 176-79; Pelaez 1986, 37-66; see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 178-87). Brazil had accumulated unsustainable foreign debt by borrowing to finance balance of payments deficits during the 1970s. Foreign lending virtually stopped. The German mark devalued strongly relative to the dollar such that Brazil’s products lost competitiveness in Germany and in multiple markets in competition with Germany. The resolution of the crisis was devaluation of the Brazilian currency by 30 percent relative to the dollar and subsequent maintenance of parity by monthly devaluation equal to inflation and indexing that resulted in financial stability by parity in external and internal interest rates avoiding capital flight. With a combination of declining imports, domestic import substitution and export growth, Brazil followed rapid growth in the US and grew out of the crisis with surprising GDP growth of 4.5 percent in 1984.
The euro zone faces a critical survival risk because several of its members may default on their sovereign obligations if not bailed out by the other members. The valuation equation of bonds is essential to understanding the stability of the euro area. An explanation is provided in this paragraph and readers interested in technical details are referred to the Subsection IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation. Contrary to the Wriston doctrine, investing in sovereign obligations is a credit decision. The value of a bond today is equal to the discounted value of future obligations of interest and principal until maturity. On Dec 30 the yield of the 2-year bond of the government of Greece was quoted around 100 percent. In contrast, the 2-year US Treasury note traded at 0.239 percent and the 10-year at 2.871 percent while the comparable 2-year government bond of Germany traded at 0.14 percent and the 10-year government bond of Germany traded at 1.83 percent. There is no need for sovereign ratings: the perceptions of investors are of relatively higher probability of default by Greece, defying Wriston (1982), and nil probability of default of the US Treasury and the German government. The essence of the sovereign credit decision is whether the sovereign will be able to finance new debt and refinance existing debt without interrupting service of interest and principal. Prices of sovereign bonds incorporate multiple anticipations such as inflation and liquidity premiums of long-term relative to short-term debt but also risk premiums on whether the sovereign’s debt can be managed as it increases without bound. The austerity measures of Italy are designed to increase the primary surplus, or government revenues less expenditures excluding interest, to ensure investors that Italy will have the fiscal strength to manage its debt of 120 percent of GDP, which is the third largest in the world after the US and Japan. Appendix IIIE links the expectations on the primary surplus to the real current value of government monetary and fiscal obligations. As Blanchard (2011SepWEO) analyzes, fiscal consolidation to increase the primary surplus is facilitated by growth of the economy. Italy and the other indebted sovereigns in Europe face the dual challenge of increasing primary surpluses while maintaining growth of the economy (for the experience of Brazil in the debt crisis of 1982 see Pelaez 1986, 1987).
Much of the analysis and concern over the euro zone centers on the lack of credibility of the debt of a few countries while there is credibility of the debt of the euro zone as a whole. In practice, there is convergence in valuations and concerns toward the fact that there may not be credibility of the euro zone as a whole. The fluctuations of financial risk assets of members of the euro zone move together with risk aversion toward the countries with lack of debt credibility. This movement raises the need to consider analytically sovereign debt valuation of the euro zone as a whole in the essential analysis of whether the single-currency will survive without major changes.
Welfare economics considers the desirability of alternative states, which in this case would be evaluating the “value” of Germany (1) within and (2) outside the euro zone. Is the sum of the wealth of euro zone countries outside of the euro zone higher than the wealth of these countries maintaining the euro zone? On the choice of indicator of welfare, Hicks (1975, 324) argues:
“Partly as a result of the Keynesian revolution, but more (perhaps) because of statistical labours that were initially quite independent of it, the Social Product has now come right back into its old place. Modern economics—especially modern applied economics—is centered upon the Social Product, the Wealth of Nations, as it was in the days of Smith and Ricardo, but as it was not in the time that came between. So if modern theory is to be effective, if it is to deal with the questions which we in our time want to have answered, the size and growth of the Social Product are among the chief things with which it must concern itself. It is of course the objective Social Product on which attention must be fixed. We have indexes of production; we do not have—it is clear we cannot have—an Index of Welfare.”
If the burden of the debt of the euro zone falls on Germany and France or only on Germany, is the wealth of Germany and France or only Germany higher after breakup of the euro zone or if maintaining the euro zone? In practice, political realities will determine the decision through elections.
The prospects of survival of the euro zone are dire. Table III-7 is constructed with IMF World Economic Outlook database (http://www.imf.org/external/datamapper/index.php?db=WEO) for GDP in USD billions, primary net lending/borrowing as percent of GDP and general government debt as percent of GDP for selected regions and countries in 2010.
Table III-7, World and Selected Regional and Country GDP and Fiscal Situation
| GDP 2012 | Primary Net Lending Borrowing | General Government Net Debt | |
| World | 71,277 | ||
| Euro Zone | 12,065 | -0.5 | 73.4 |
| Portugal | 211 | -0.7 | 110.9 |
| Ireland | 205 | -4.4 | 103.0 |
| Greece | 255 | -1.7 | 170.7 |
| Spain | 1,340 | -4.5 | 78.6 |
| Major Advanced Economies G7 | 33,769 | -5.1 | 89.0 |
| United States | 15,653 | -6.5 | 83.8 |
| UK | 2,434 | -5.6 | 83.7 |
| Germany | 3,367 | 1.4 | 58.4 |
| France | 2,580 | -2.2 | 83.7 |
| Japan | 5,984 | -9.1 | 135.4 |
| Canada | 1,770 | -3.2 | 35.8 |
| Italy | 1,980 | 2.6 | 103.1 |
| China | 8,250 | -1.3* | 22.2** |
*Net Lending/borrowing**Gross Debt
Source: IMF World Economic Outlook databank http://www.imf.org/external/datamapper/index.php?db=WEO
The data in Table III-7 are used for some very simple calculations in Table III-8. The column “Net Debt USD Billions” in Table III-8 is generated by applying the percentage in Table III-7 column “General Government Net Debt % GDP 2010” to the column “GDP USD Billions.” The total debt of France and Germany in 2012 is $4155.8 billion, as shown in row “B+C” in column “Net Debt USD Billions” The sum of the debt of Italy, Spain, Portugal, Greece and Ireland is $3975.1 billion, adding rows D+E+F+G+H in column “Net Debt USD billions.” There is some simple “unpleasant bond arithmetic” in the two final columns of Table III-8. Suppose the entire debt burdens of the five countries with probability of default were to be guaranteed by France and Germany, which de facto would be required by continuing the euro zone. The sum of the total debt of these five countries and the debt of France and Germany is shown in column “Debt as % of Germany plus France GDP” to reach $8130.8 billion, which would be equivalent to 136.7 percent of their combined GDP in 2012. Under this arrangement the entire debt of the euro zone including debt of France and Germany would not have nil probability of default. The final column provides “Debt as % of Germany GDP” that would exceed 241.5 percent if including debt of France and 177.4 percent of German GDP if excluding French debt. The unpleasant bond arithmetic illustrates that there is a limit as to how far Germany and France can go in bailing out the countries with unsustainable sovereign debt without incurring severe pains of their own such as downgrades of their sovereign credit ratings. A central bank is not typically engaged in direct credit because of remembrance of inflation and abuse in the past. There is also a limit to operations of the European Central Bank in doubtful credit obligations. Wriston (1982) would prove to be wrong again that countries do not bankrupt but would have a consolation prize that similar to LBOs the sum of the individual values of euro zone members outside the current agreement exceeds the value of the whole euro zone. Internal rescues of French and German banks may be less costly than bailing out other euro zone countries so that they do not default on French and German banks.
Table III-8, Guarantees of Debt of Sovereigns in Euro Area as Percent of GDP of Germany and France, USD Billions and %
| Net Debt USD Billions | Debt as % of Germany Plus France GDP | Debt as % of Germany GDP | |
| A Euro Area | 8,855.7 | ||
| B Germany | 1,996.3 | $8130.9 as % of $3367 =241.5% $5971.4 as % of $3367 =177.4% | |
| C France | 2,159.5 | ||
| B+C | 4,155.8 | GDP $5,947.0 Total Debt $8130.9 Debt/GDP: 136.7% | |
| D Italy | 2,041.4 | ||
| E Spain | 1,053.2 | ||
| F Portugal | 234.0 | ||
| G Greece | 435.3 | ||
| H Ireland | 211.2 | ||
| Subtotal D+E+F+G+H | 3,975.1 |
Source: calculation with IMF data http://www.imf.org/external/datamapper/index.php?db=WEO
There is extremely important information in Table III-9 for the current sovereign risk crisis in the euro zone. Table III-9 provides the structure of regional and country relations of Germany’s exports and imports with newly available data for Sep 2012. German exports to other European Union (EU) members are 57.4 percent of total exports in Sep 2012 and 57.2 percent in Jan-Sep 2012. Exports to the euro area are 37.6 percent in Sep and 37.6 percent in Jan-Sep. Exports to third countries are 42.8 percent of the total in Sep and 42.8 percent in Jan-Sep. There is similar distribution for imports. Exports to non-euro countries are decreasing at 2.7 percent in Sep 2012 and increasing 3.8 percent in Jan-Sep 2012 while exports to the euro area are decreasing 9.1 percent in Sep and decreasing 2.1 percent in Jan-Sep 2012. Exports to third countries, accounting for 42.8 percent of the total in Sep 2012, are increasing at 1.8 percent, and 10.4 percent in Jan-Sep, accounting for 42.8 percent of the cumulative total in Jan-Sep 2012. Price competitiveness through devaluation could improve export performance and growth. Economic performance in Germany is closely related to its high competitiveness in world markets. Weakness in the euro zone and the European Union in general could affect the German economy. This may be the major reason for choosing the “fiscal abuse” of the European Central Bank considered by Buiter (2011Oct31) over the breakdown of the euro zone. There is a tough analytical, empirical and forecasting doubt of growth and trade in the euro zone and the world with or without maintenance of the European Monetary Union (EMU) or euro zone. Germany could benefit from depreciation of the euro because of high share in its exports to countries not in the euro zone but breakdown of the euro zone raises doubts on the region’s economic growth that could affect German exports to other member states.
Table III-9, Germany, Structure of Exports and Imports by Region, € Billions and ∆%
| Sep 2012 | Sep 12-Month | Jan–Sep 2012 € Billions | Jan-Sep 2012/ | |
| Total | 91.7 | -3.4 | 825.9 | 4.1 |
| A. EU | 52.6 % 57.4 | -7.0 | 472.2 % 57.2 | -0.2 |
| Euro Area | 34.5 % 37.6 | -9.1 | 310.7 % 37.6 | -2.1 |
| Non-euro Area | 18.1 % 19.7 | -2.7 | 161.4 % 19.5 | 3.8 |
| B. Third Countries | 39.2 % 42.8 | 1.8 | 353.7 % 42.8 | 10.4 |
| Total Imports | 74.9 | -3.6 | 682.4 | 1.2 |
| C. EU Members | 47.5 % 63.4 | -4.8 | 432.5 % 63.3 | 1.3 |
| Euro Area | 32.7 % 43.7 | -5.7 | 303.7 % 44.5 | 0.9 |
| Non-euro Area | 14.8 % 19.8 | -2.8 | 128.8 % 18.9 | 2.1 |
| D. Third Countries | 27.4 % 36.6 | -1.4 | 249.9 % 36.6 | 1.1 |
Notes: Total Exports = A+B; Total Imports = C+D
Source:
Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland https://www.destatis.de/EN/PressServices/Press/pr/2012/11/PE12_385_51.html;jsessionid=61633506F891355DDF446AAB5332A764.cae4 https://www.destatis.de/EN/FactsFigures/Indicators/ShortTermIndicators/ShortTermIndicators.html
IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation. There are two approaches to government finance and their implications: (1) simple unpleasant monetarist arithmetic; and (2) simple unpleasant fiscal arithmetic. Both approaches illustrate how sovereign debt can be perceived riskier under profligacy.
First, Unpleasant Monetarist Arithmetic. Fiscal policy is described by Sargent and Wallace (1981, 3, equation 1) as a time sequence of D(t), t = 1, 2,…t, …, where D is real government expenditures, excluding interest on government debt, less real tax receipts. D(t) is the real deficit excluding real interest payments measured in real time t goods. Monetary policy is described by a time sequence of H(t), t=1,2,…t, …, with H(t) being the stock of base money at time t. In order to simplify analysis, all government debt is considered as being only for one time period, in the form of a one-period bond B(t), issued at time t-1 and maturing at time t. Denote by R(t-1) the real rate of interest on the one-period bond B(t) between t-1 and t. The measurement of B(t-1) is in terms of t-1 goods and [1+R(t-1)] “is measured in time t goods per unit of time t-1 goods” (Sargent and Wallace 1981, 3). Thus, B(t-1)[1+R(t-1)] brings B(t-1) to maturing time t. B(t) represents borrowing by the government from the private sector from t to t+1 in terms of time t goods. The price level at t is denoted by p(t). The budget constraint of Sargent and Wallace (1981, 3, equation 1) is:
D(t) = {[H(t) – H(t-1)]/p(t)} + {B(t) – B(t-1)[1 + R(t-1)]} (1)
Equation (1) states that the government finances its real deficits into two portions. The first portion, {[H(t) – H(t-1)]/p(t)}, is seigniorage, or “printing money.” The second part,
{B(t) – B(t-1)[1 + R(t-1)]}, is borrowing from the public by issue of interest-bearing securities. Denote population at time t by N(t) and growing by assumption at the constant rate of n, such that:
N(t+1) = (1+n)N(t), n>-1 (2)
The per capita form of the budget constraint is obtained by dividing (1) by N(t) and rearranging:
B(t)/N(t) = {[1+R(t-1)]/(1+n)}x[B(t-1)/N(t-1)]+[D(t)/N(t)] – {[H(t)-H(t-1)]/[N(t)p(t)]} (3)
On the basis of the assumptions of equal constant rate of growth of population and real income, n, constant real rate of return on government securities exceeding growth of economic activity and quantity theory equation of demand for base money, Sargent and Wallace (1981) find that “tighter current monetary policy implies higher future inflation” under fiscal policy dominance of monetary policy. That is, the monetary authority does not permanently influence inflation, lowering inflation now with tighter policy but experiencing higher inflation in the future.
Second, Unpleasant Fiscal Arithmetic. The tool of analysis of Cochrane (2011Jan, 27, equation (16)) is the government debt valuation equation:
(Mt + Bt)/Pt = Et∫(1/Rt, t+τ)st+τdτ (4)
Equation (4) expresses the monetary, Mt, and debt, Bt, liabilities of the government, divided by the price level, Pt, in terms of the expected value discounted by the ex-post rate on government debt, Rt, t+τ, of the future primary surpluses st+τ, which are equal to Tt+τ – Gt+τ or difference between taxes, T, and government expenditures, G. Cochrane (2010A) provides the link to a web appendix demonstrating that it is possible to discount by the ex post Rt, t+τ. The second equation of Cochrane (2011Jan, 5) is:
MtV(it, ·) = PtYt (5)
Conventional analysis of monetary policy contends that fiscal authorities simply adjust primary surpluses, s, to sanction the price level determined by the monetary authority through equation (5), which deprives the debt valuation equation (4) of any role in price level determination. The simple explanation is (Cochrane 2011Jan, 5):
“We are here to think about what happens when [4] exerts more force on the price level. This change may happen by force, when debt, deficits and distorting taxes become large so the Treasury is unable or refuses to follow. Then [4] determines the price level; monetary policy must follow the fiscal lead and ‘passively’ adjust M to satisfy [5]. This change may also happen by choice; monetary policies may be deliberately passive, in which case there is nothing for the Treasury to follow and [4] determines the price level.”
An intuitive interpretation by Cochrane (2011Jan 4) is that when the current real value of government debt exceeds expected future surpluses, economic agents unload government debt to purchase private assets and goods, resulting in inflation. If the risk premium on government debt declines, government debt becomes more valuable, causing a deflationary effect. If the risk premium on government debt increases, government debt becomes less valuable, causing an inflationary effect.
There are multiple conclusions by Cochrane (2011Jan) on the debt/dollar crisis and Global recession, among which the following three:
(1) The flight to quality that magnified the recession was not from goods into money but from private-sector securities into government debt because of the risk premium on private-sector securities; monetary policy consisted of providing liquidity in private-sector markets suffering stress
(2) Increases in liquidity by open-market operations with short-term securities have no impact; quantitative easing can affect the timing but not the rate of inflation; and purchase of private debt can reverse part of the flight to quality
(3) The debt valuation equation has a similar role as the expectation shifting the Phillips curve such that a fiscal inflation can generate stagflation effects similar to those occurring from a loss of anchoring expectations.
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2010, 2011, 2012

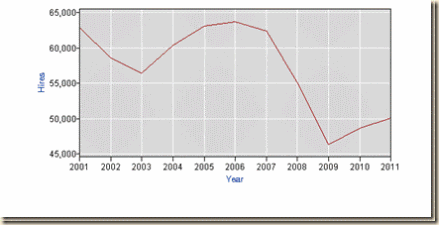

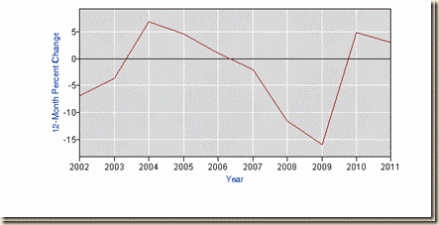




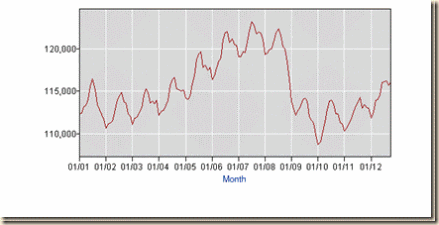



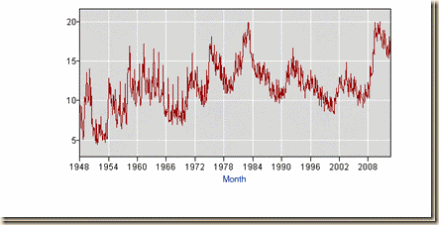




![clip_image002[1] clip_image002[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEi4FIGPlGug11gfuvdZfNiqcDfOVsTNfzgSDY2c2ooF867D71SiBxkmgGe7CR2qlQ3se_nfZLlGlO0Yk-mQhWl4Z1XbkjcDAdVacwJxAGUE6uMxCyod-VBShBWsG2wfDjDBPXCrALXhkAk/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image004[1] clip_image004[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEh9-o7Ll25eonHbveETuGSlzS7qhB0zaPkHMCZy5ZKFvvNG0NATvR0BmWgTuObVJd1tYIHDIf7ML7AxB8UsOlfOytMPHbjYJEcGEw_KbkvGyTNZLrkoQoxO26ue9MQLT5EEriDdkZHSRUg/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image006[1] clip_image006[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiIi_Jn1JqAU5vC6R3OK5ZmztJbAbCU_gQlPVEBbacI8UxZhTtUEtmcBehBACcqLEDJ-X4PZUlhCxAx-sfKq0VNX3nIpEOzXdh_FxbTf2ERagRdCx51NFJt2m_HxFcbCwd-v-NWO8TXveXM/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image008[1] clip_image008[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhWe3xJj7w_psmjvwvaKsMyjp5C0n9jV7c3P48V9Yb5F2oGgGt5ZB9xMy-1ZSEQ1AKSxO7aQ0HUkQXqUCLbHpto04_oOY8FmYrYYkFYmvEm0ogtUHbZtI7Achg_IzW3hp8tFXjCXmOGg9EH/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image010[1] clip_image010[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhGsqzZduY9ccoSk15m_owjYvglHS3JXz3V5ZbBEqFLXwlGZK6ICHv_huAZnOm0359jNYls52AAJykebigDth198L6wmyTC9JlCbxudC481EbTqWqhZBYRVrWRaX-DMznfIm1M-sw12ZKw/?imgmax=800)



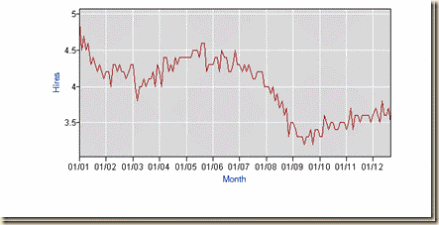




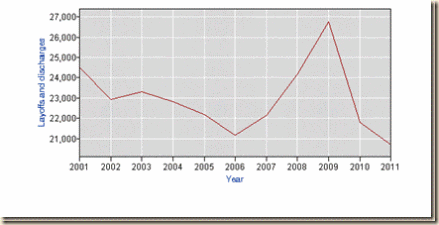


![clip_image012[1] clip_image012[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiSk0__Splqum-WtkxJhGAtpEWUeTfJGmEf0NKBNZ6lY-YOXzjbeljDLYbIJjOrnkrVOrr4lW8mnPqlvKBwovcaBP6B4sQEV6V1lEyhMtvm9TBKj6NH2jcVQosB-EIf1u-MjU_tPL3DLj8/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image014[1] clip_image014[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEif03gtrTHr2j-s6G7iUJz1GKMEMLxF-Y3Bu71biWyLRk2wBuELavmpTM4nBSYkNMF0nhy6zfOdQzhidZy56SO8X8cp-P9QGJiaxgVAM8leFPQYLPEKh7tEVyhukW0VZuicuGfkzd6GTwY/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image016[1] clip_image016[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhhBMyxCtGBG4NuHsVlan7T-bip68lEJK3KwTOdumJTmQo63JLhHtKQ_RNWapXnZ7-o7VJos2b11ictKpw34Ls6HVqeH6j6UttRRq5_j7pyWou3X8W_8pNvNko3RRSNEbKb2ArlUmRvVTo5/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image018[1] clip_image018[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgZP7Gwo9AN7dpyqQNUHNm8N-Il4pfur41mnvM2ldnZm77ODFxqMR7HaGmQqdz6SZ7_oCISp_tWgrS-Pt6zxIzXP9A8LcVNXNhdVKD7ldDMkXyA1uNeCn8ju2YCeKk03_MVEiltKna3rcA/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image020[1] clip_image020[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEg087MxO2fbOPFcT0Fr4WgxP5h5NQ0_ZuMolVSlZpbz24BtNij1AOGEI_8bo30mnE8tiPu4eOnL57FgDHgVeTvVCIf5Yy-0h8xkg-YG80b_6rQetCN9U_EhP6cWhEWyB6BZiny7dipqmqQ/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image022[1] clip_image022[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEghdF29ZwbMK-Fl_YM8lLilXsYFjxYFLdB4FRdvo-EGoVghw1ot9FCecCn1BgCCxSmmTVQPSYDIQVS6qGg2odGi5nteQqB9b5KDGNHw2fKtiKzyezj9T9qlKEo1H90ge72EQSdND39JdsI/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image024[1] clip_image024[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhFxuqVriUixQmn2dS4sVqx5pnXOOKQPfWziDQ6XynhgeyO1E_VHX-BhIJDNms6qivbihvw8sU14gD-Fsp7ngk_ksIi2MAthnyNsLDdw2Hf-zQ7y9LbGSNUjBzpi6aPJY8I9DS12mfYwlk/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image026[1] clip_image026[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgSQl6tgL4ffgVBXCQLpYS-gktYWNlvOGwQXR-4NDTd-8ksuLjnE8Jvaj-rP5VzLcinls3T55v9GDn_EHIcl4X8FyT7VRTXqvPHBdYSgWnJFUz6ssuTS4yfxG4X7FohhVGqd3OMChT6eQk/?imgmax=800)

![clip_image027[1] clip_image027[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEicqgdtVwxdnCXkNZVRwRVKqHie-odBhMqoLTO0V7yH5kPOGoJSPU5nNneUs5d9JrKGJBowf4krIM-100XH1k4VT_WAXOLKL6c4ETSBPPMKB7BsHmaTygPuHHE-2u2b_yYsID6A-R_lIUw/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image028[1] clip_image028[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj8fHg5R6mIv8-YSF_SkojeWUzsJeJBryGFOWr140xmYZ6dQcvNnDoNXgLS6WK4G43MFl_9dMNctOF8GKVCkOLabsh8TaVgjL3JyO3Bz7hYGkc3wO5Z6nXGypLGoVk_ukGrX_mLzKbIYdw/?imgmax=800)
![clip_image029[1] clip_image029[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgV2gOmF7VjWL_wMYzJ6GrDZpi4JwdZ3M2aMXhEbzuGzn6TfVBOl_i1hGdb19Lz0SaRN3g1YpU9jGROUhc9ecpTyuSZp21XjT4CDj1zFN98Hj2O7-NeKyFi3zHwr0lpmL8pD8bKMuKqCKQ/?imgmax=800)

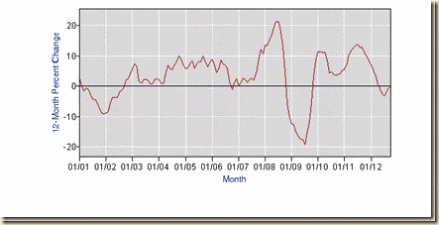




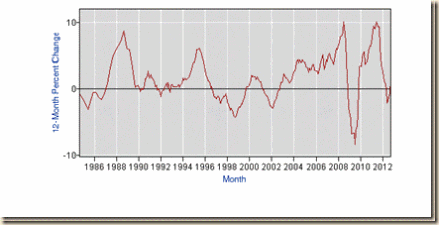










![clip_image095[1] clip_image095[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEj5v9Zj5BsiZN8xo0hiVzs-3oKA9ZHB_3sqtUrLQjgHo67Hk8CN7x0wcYwQzf3sa1ZNcKZAiy1kwsDLIwXDKhz99U5g_oYrP2FlcqkBkzXsGS1PP4RJUYVFuYBk1SR0XV-7eHQZVExDQRU/?imgmax=800)



No comments:
Post a Comment