Volatility of Valuations of Risk Financial Assets, Rules, Discretionary Authorities and Slow Productivity Growth, United States International Trade, World Cyclical Slow Growth and Global Recession Risk
Carlos M. Pelaez
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014
I Rules, Discretionary Authorities and Slow Productivity Growth
II United States International Trade
III World Financial Turbulence
IIIA Financial Risks
IIIE Appendix Euro Zone Survival Risk
IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation
IV Global Inflation
V World Economic Slowdown
VA United States
VB Japan
VC China
VD Euro Area
VE Germany
VF France
VG Italy
VH United Kingdom
VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets
VII Economic Indicators
VIII Interest Rates
IX Conclusion
References
Appendixes
Appendix I The Great Inflation
IIIB Appendix on Safe Haven Currencies
IIIC Appendix on Fiscal Compact
IIID Appendix on European Central Bank Large Scale Lender of Last Resort
IIIG Appendix on Deficit Financing of Growth and the Debt Crisis
IIIGA Monetary Policy with Deficit Financing of Economic Growth
IIIGB Adjustment during the Debt Crisis of the 1980s
I Rules, Discretionary Authorities and Slow Productivity Growth. The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) of the Department of Labor provides the quarterly report on productivity and costs. The operational definition of productivity used by the BLS is (http://www.bls.gov/news.release/pdf/prod2.pdf 1): “Labor productivity, or output per hour, is calculated by dividing an index of real output by an index of hours worked of all persons, including employees, proprietors, and unpaid family workers.” The BLS has revised the estimates for productivity and unit costs. Table II-1 provides the new estimate for IIQ2014 and revised data for nonfarm business sector productivity and unit labor costs for IQ2014 and IVQ2013 in seasonally adjusted annual equivalent (SAAE) rate and the percentage change from the same quarter a year earlier. Reflecting increases in output of 5.2 percent and increase of 2.7 percent in hours worked, nonfarm business sector labor productivity decreased at the SAAE rate of 2.5 percent in IIQ2014, as shown in column 2 “IIQ2014 SAEE.” The increase of labor productivity from IIQ2013 to IIQ2014 was 1.2 percent, reflecting increases in output of 3.2 percent and of hours worked of 2.0 percent, as shown in column 3 “IIQ2014 YoY.” Hours worked increased from 1.4 percent in IVQ2013 in SAAE to 2.1 percent in IQ2014 and increased to 2.7 percent in IIQ2014 while output growth decreased from 4.7 percent in IVQ2013 to minus 2.4 percent in IQ2014, increasing to 5.2 percent in IIQ2014. The BLS defines unit labor costs as (http://www.bls.gov/news.release/pdf/prod2.pdf 1): “BLS defines unit labor costs as the ratio of hourly compensation to labor productivity; increases in hourly compensation tend to increase unit labor costs and increases in output per hour tend to reduce them.” Unit labor costs increased at the SAAE rate of 0.6 percent in IIQ2014 and increased 1.9 percent in IIQ2014 relative to IIQ2013. Hourly compensation increased at the SAAE rate of 3.1 percent in IIQ2014, which deflating by the estimated consumer price increase SAAE rate in IIQ2014 results in increase of real hourly compensation at 0.1 percent. Real hourly compensation increased 1.0 percent in IIQ2014 relative to IIQ2013.
Table II-1, US, Nonfarm Business Sector Productivity and Costs %
| IIQ 2014 SSAE | IIQ 2014 YOY | IQ | IQ | IVQ 2013 SAAE | IVQ 2013 YoY | |
| Productivity | 2.5 | 1.2 | -4.5 | 0.7 | 3.3 | 2.0 |
| Output | 5.2 | 3.2 | -2.4 | 2.4 | 4.7 | 3.7 |
| Hours | 2.7 | 2.0 | 2.1 | 1.7 | 1.4 | 1.6 |
| Hourly | 3.1 | 3.1 | 6.8 | 3.3 | 1.9 | -0.1 |
| Real Hourly Comp. | 0.1 | 1.0 | 4.8 | 1.8 | 0.7 | -1.3 |
| Unit Labor Costs | 0.6 | 1.9 | 11.8 | 2.6 | -1.3 | -2.1 |
| Unit Nonlabor Payments | 3.5 | 0.9 | -12.0 | -0.1 | 5.0 | 6.2 |
| Implicit Price Deflator | 1.8 | 1.5 | 0.8 | 1.4 | 1.4 | 1.4 |
Notes: SAAE: seasonally adjusted annual equivalent; Comp.: compensation; YoY: Quarter on Same Quarter Year Earlier
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
The analysis by Kydland (http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/economic-sciences/laureates/2004/kydland-bio.html) and Prescott (http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/economic-sciences/laureates/2004/prescott-bio.html) (1977, 447-80, equation 5) uses the “expectation augmented” Phillips curve with the natural rate of unemployment of Friedman (1968) and Phelps (1968), which in the notation of Barro and Gordon (1983, 592, equation 1) is:
Ut = Unt – α(πt – πe) α > 0 (1)
Where Ut is the rate of unemployment at current time t, Unt is the natural rate of unemployment, πt is the current rate of inflation and πe is the expected rate of inflation by economic agents based on current information. Equation (1) expresses unemployment net of the natural rate of unemployment as a decreasing function of the gap between actual and expected rates of inflation. The system is completed by a social objective function, W, depending on inflation, π, and unemployment, U:
W = W(πt, Ut) (2)
The policymaker maximizes the preferences of the public, (2), subject to the constraint of the tradeoff of inflation and unemployment, (1). The total differential of W set equal to zero provides an indifference map in the Cartesian plane with ordered pairs (πt, Ut - Un) such that the consistent equilibrium is found at the tangency of an indifference curve and the Phillips curve in (1). The indifference curves are concave to the origin. The consistent policy is not optimal. Policymakers without discretionary powers following a rule of price stability would attain equilibrium with unemployment not higher than with the consistent policy. The optimal outcome is obtained by the rule of price stability, or zero inflation, and no more unemployment than under the consistent policy with nonzero inflation and the same unemployment. Taylor (1998LB) attributes the sustained boom of the US economy after the stagflation of the 1970s to following a monetary policy rule instead of discretion (see Taylor 1993, 1999). It is not uncommon for effects of regulation differing from those intended by policy. Professors Edward C. Prescott and Lee E. Ohanian (2014Feb), writing on “US productivity growth has taken a dive,” on Feb 3, 2014, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702303942404579362462611843696?KEYWORDS=Prescott), argue that impressive productivity growth over the long-term constructed US prosperity and wellbeing. Prescott and Ohanian (2014Feb) measure US productivity growth at 2.5 percent per year since 1948. Average US productivity growth has been only 1.1 percent on average since 2011. Prescott and Ohanian (2014Feb) argue that living standards in the US increased at 28 percent in a decade but with current slow growth of productivity will only increase 12 percent by 2024. There may be collateral effects on productivity growth from policy design similar to those in Kydland and Prescott (1977). The Bureau of Labor Statistics important report on productivity and costs released on Aug 8, 2014 (http://www.bls.gov/lpc/) supports the argument of decline of productivity growth in the US analyzed by Prescott and Ohanian (2014Feb). Table II-2 provides the annual percentage changes of productivity, real hourly compensation and unit labor costs for the entire economic cycle from 2007 to 2013. The data confirm the argument of Prescott and Ohanian (2014Feb): productivity increased cumulatively 2.5 percent from 2011 to 2013 at the average annual rate of 0.8 percent. The situation is direr by excluding growth of 1.5 percent in 2012, which leaves an average of 0.5 percent for 2011 and 2013. Average productivity growth for the entire economic cycle from 2007 to 2013 is only 1.6 percent. The argument by Prescott and Ohanian (2014Feb) is proper in choosing the tail of the business cycle because the increase in productivity in 2009 of 3.1 percent and 3.3 percent in 2013 consisted on reducing labor hours.
Table II-2, US, Revised Nonfarm Business Sector Productivity and Costs Annual Average, ∆% Annual Average
| 2013 ∆% | 2012 ∆% | 2011 ∆% | 2010 ∆% | 2009 ∆% | 2008 ∆% | 2007 ∆% | |
| Productivity | 0.9 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 3.3 | 3.2 | 0.8 | 1.6 |
| Real Hourly Compensation | -0.3 | 0.6 | -0.9 | 0.3 | 1.5 | -1.1 | 1.4 |
| Unit Labor Costs | 0.2 | 1.7 | 2.1 | -1.3 | -2.0 | 2.0 | 2.7 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics
Productivity jumped in the recovery after the recession from Mar IQ2001 to Nov IVQ2001 (http://www.nber.org/cycles.html). Table II-3 provides quarter on quarter and annual percentage changes in nonfarm business output per hour, or productivity, from 1999 to 2014. The annual average jumped from 2.7 percent in 2001 to 4.3 percent in 2002. Nonfarm business productivity increased at the SAAE rate of 9.4 percent in the first quarter after the recession in IQ2002. Productivity increases decline later in the expansion period. Productivity increases were mediocre during the recession from Dec IVQ2007 to Jun IIIQ2009 (http://www.nber.org/cycles.html) and increased during the first phase of expansion from IIQ2009 to IQ2010, trended lower and collapsed in 2011 and 2012 with sporadic jumps and declines. Productivity increased at 3.3 percent in IVQ2013 and contracted at 4.5 percent in IQ2014. Productivity increased at 2.5 percent in IIQ2014.
Table II-3, US, Nonfarm Business Output per Hour, Percent Change from Prior Quarter at Annual Rate, 1999-2014
| Year | Qtr1 | Qtr2 | Qtr3 | Qtr4 | Annual |
| 1999 | 3.8 | 0.7 | 3.5 | 6.8 | 3.3 |
| 2000 | -1.4 | 8.6 | 0.1 | 4.1 | 3.3 |
| 2001 | -1.2 | 6.8 | 2.2 | 5.0 | 2.7 |
| 2002 | 9.4 | 0.3 | 3.1 | -0.6 | 4.3 |
| 2003 | 4.0 | 5.6 | 9.0 | 3.9 | 3.7 |
| 2004 | -0.1 | 4.0 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 3.1 |
| 2005 | 4.4 | -0.4 | 3.0 | 0.2 | 2.1 |
| 2006 | 2.5 | -0.3 | -1.8 | 3.2 | 0.9 |
| 2007 | 0.4 | 2.6 | 4.6 | 1.8 | 1.6 |
| 2008 | -3.9 | 4.0 | 1.0 | -2.5 | 0.8 |
| 2009 | 3.2 | 7.9 | 6.0 | 4.8 | 3.2 |
| 2010 | 2.2 | 1.3 | 2.3 | 1.5 | 3.3 |
| 2011 | -3.2 | 1.3 | -0.9 | 3.1 | 0.1 |
| 2012 | 0.2 | 1.8 | 1.7 | -2.0 | 1.0 |
| 2013 | 0.8 | 0.5 | 3.6 | 3.3 | 0.9 |
| 2014 | -4.5 | 2.5 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/lpc/
Chart II-1 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) provides SAAE rates of nonfarm business productivity from 1999 to 2014. There is a clear pattern in both episodes of economic cycles in 2001 and 2007 of rapid expansion of productivity in the transition from contraction to expansion followed by more subdued productivity expansion. Part of the explanation is the reduction in labor utilization resulting from adjustment of business to the sudden shock of collapse of revenue. Productivity rose briefly in the expansion after 2009 but then collapsed and moved to negative change with some positive changes recently at lower rates. Contractions in the cycle from 2007 to 2014 have been more frequent and sharper.
Chart II-1, US, Nonfarm Business Output per Hour, Percent Change from Prior Quarter at Annual Rate, 1999-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/lpc/
Percentage changes from prior quarter at SAAE rates and annual average percentage changes of nonfarm business unit labor costs are provided in Table II-4. Unit labor costs fell during the contractions with continuing negative percentage changes in the early phases of the recovery. Weak labor markets partly explain the decline in unit labor costs. As the economy moves toward full employment, labor markets tighten with increase in unit labor costs. The expansion beginning in IIIQ2009 has been characterized by high unemployment and underemployment. Table II-4 shows continuing subdued increases in unit labor costs in 2011 but with increase at 11.4 percent in IQ2012 followed by decrease at 1.2 percent in IIQ2012, decline at 1.8 percent in IIIQ2012 and increase at 12.7 percent in IVQ2012. Unit labor costs decreased at 7.0 percent in IQ2013 and increased at 3.2 percent in IIQ2013. Unit labor costs decreased at 2.9 percent in IIIQ2013 and at 1.3 percent in IVQ2013. Unit labor costs increased at 11.8 percent in IQ2014 and at 0.6 percent in IIQ2014.
Table II-4, US, Nonfarm Business Unit Labor Costs, Percent Change from Prior Quarter at Annual Rate 1999-2014
| Year | Qtr1 | Qtr2 | Qtr3 | Qtr4 | Annual |
| 1999 | 2.8 | 0.2 | 0.0 | 1.7 | 0.9 |
| 2000 | 17.4 | -6.8 | 8.2 | -1.7 | 4.0 |
| 2001 | 11.4 | -5.4 | -1.7 | -1.4 | 1.6 |
| 2002 | -6.6 | 3.3 | -1.1 | 1.7 | -2.0 |
| 2003 | -1.5 | 1.6 | -2.6 | 1.5 | 0.1 |
| 2004 | -0.5 | 3.9 | 5.6 | 0.5 | 1.4 |
| 2005 | -1.3 | 2.6 | 1.9 | 2.3 | 1.6 |
| 2006 | 6.1 | 0.5 | 2.3 | 4.0 | 3.0 |
| 2007 | 9.8 | -2.7 | -3.2 | 2.6 | 2.7 |
| 2008 | 8.2 | -3.6 | 2.4 | 7.1 | 2.0 |
| 2009 | -12.3 | 2.1 | -3.0 | -2.3 | -2.0 |
| 2010 | -4.8 | 3.2 | -0.2 | 0.1 | -1.3 |
| 2011 | 11.0 | -3.5 | 3.3 | -7.7 | 2.1 |
| 2012 | 11.4 | -1.2 | -1.8 | 12.7 | 1.7 |
| 2013 | -7.0 | 3.2 | -2.9 | -1.3 | 0.2 |
| 2014 | 11.8 | 0.6 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/lpc/
Chart II-2 provides percentage change from prior quarter at annual rate of nonfarm business real hourly compensation from 1999 to 2014. There are significant fluctuations in quarterly percentage changes oscillating between positive and negative. There is no clear pattern in the two contractions in the 2000s.
Chart II-2, US, Nonfarm Business Unit Labor Costs, Percent Change from Prior Quarter at Annual Rate 1999-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/lpc/
Table II-5 provides percentage change from prior quarter at annual rates for nonfarm business real hourly worker compensation. The expansion after the contraction of 2001 was followed by strong recovery of real hourly compensation. Real hourly compensation increased at the rate of 3.1 percent in IQ2011 but fell at annual rates of 6.9 percent in IIQ2011 and 6.2 percent in IVQ2011. Real hourly compensation increased at 9.3 percent in IQ2012, decreasing at 0.7 percent in IIQ2012, declining at 1.8 percent in IIIQ2012 and increasing at 7.8 percent in IVQ2012. Real hourly compensation fell at 0.9 percent in 2011 and increased at 0.6 percent in 2012. Real hourly compensation fell at 7.4 percent in IQ2013 and increased at 3.2 percent in IIQ2013, falling at 1.4 percent in IIIQ2013. Real hourly compensation increased at 0.7 percent in IVQ2013 and at 4.8 percent in IQ2014. Real hourly compensation increased at 0.1 percent in IIQ2014. The annual rate of increase of real hourly compensation for 2013 is minus 0.3 percent.
Table II-5, Nonfarm Business Real Hourly Compensation, Percent Change from Prior Quarter at Annual Rate 1999-2014
| Year | Qtr1 | Qtr2 | Qtr3 | Qtr4 | Annual |
| 1999 | 5.0 | -2.0 | 0.3 | 5.5 | 2.0 |
| 2000 | 11.5 | -1.8 | 4.4 | -0.5 | 3.9 |
| 2001 | 6.0 | -1.8 | -0.7 | 4.0 | 1.5 |
| 2002 | 0.7 | 0.4 | -0.2 | -1.4 | 0.7 |
| 2003 | -1.5 | 8.0 | 2.9 | 3.9 | 1.5 |
| 2004 | -3.9 | 4.8 | 4.2 | -2.5 | 1.8 |
| 2005 | 1.2 | -0.6 | -1.1 | -1.2 | 0.3 |
| 2006 | 6.4 | -3.3 | -3.4 | 9.2 | 0.6 |
| 2007 | 6.0 | -4.5 | -1.2 | -0.5 | 1.4 |
| 2008 | -0.5 | -4.7 | -2.7 | 14.6 | -1.1 |
| 2009 | -7.1 | 7.9 | -0.6 | -0.8 | 1.5 |
| 2010 | -3.1 | 4.5 | 0.8 | -1.4 | 0.3 |
| 2011 | 3.1 | -6.9 | -0.3 | -6.2 | -0.9 |
| 2012 | 9.3 | -0.7 | -1.8 | 7.8 | 0.6 |
| 2013 | -7.4 | 3.2 | -1.4 | 0.7 | -0.3 |
| 2014 | 4.8 | 0.1 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/lpc/
Chart II-3 provides percentage change from prior quarter at annual rate of nonfarm business real hourly compensation. There have been multiple negative percentage quarterly changes in the current cycle since IVQ2007.
Chart II-3, US, Nonfarm Business Real Hourly Compensation, Percent Change from Prior Quarter at Annual Rate 1999-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/lpc/
Chart II-4 provides percentage change of nonfarm business output per hour in a quarter relative to the same quarter a year earlier. As in most series of real output, productivity increased sharply in 2010 but the momentum was lost after 2011 as with the rest of the real economy.
Chart II-4, US, Nonfarm Business Output per Hour, Percent Change from Same Quarter a Year Earlier 1999-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/lpc/
Chart II-5 provides percentage changes of nonfarm business unit labor costs relative to the same quarter a year earlier. Softening of labor markets caused relatively high yearly percentage changes in the recession of 2001 repeated in the recession in 2009. Recovery was strong in 2010 but then weakened.
Chart II-5, US, Nonfarm Business Unit Labor Costs, Percent Change from Same Quarter a Year Earlier 1999-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/lpc/
Chart II-6 provides percentage changes in a quarter relative to the same quarter a year earlier for nonfarm business real hourly compensation. Labor compensation eroded sharply during the recession with brief recovery in 2010 and another fall until recently.
Chart II-6, US, Nonfarm Business Real Hourly Compensation, Percent Change from Same Quarter a Year Earlier 1999-2014
Source: US Bureau of Labor S In the analysis of Hansen (1939, 3) of secular stagnation, economic progress consists of growth of real income per person driven by growth of productivity. The “constituent elements” of economic progress are “(a) inventions, (b) the discovery and development of new territory and new resources, and (c) the growth of population” (Hansen 1939, 3). Secular stagnation originates in decline of population growth and discouragement of inventions. According to Hansen (1939, 2), US population grew by 16 million in the 1920s but grew by one half or about 8 million in the 1930s with forecasts at the time of Hansen’s writing in 1938 of growth of around 5.3 million in the 1940s. Hansen (1939, 2) characterized demography in the US as “a drastic decline in the rate of population growth.” Hansen’s plea was to adapt economic policy to stagnation of population in ensuring full employment. In the analysis of Hansen (1939, 8), population caused half of the growth of US GDP per year. Growth of output per person in the US and Europe was caused by “changes in techniques and to the exploitation of new natural resources.” In this analysis, population caused 60 percent of the growth of capital formation in the US. Declining population growth would reduce growth of capital formation. Residential construction provided an important share of growth of capital formation. Hansen (1939, 12) argues that market power of imperfect competition discourages innovation with prolonged use of obsolete capital equipment. Trade unions would oppose labor-savings innovations. The combination of stagnating and aging population with reduced innovation caused secular stagnation. Hansen (1939, 12) concludes that there is role for public investments to compensate for lack of dynamism of private investment but with tough tax/debt issues.
The current application of Hansen’s (1938, 1939, 1941) proposition argues that secular stagnation occurs because full employment equilibrium can be attained only with negative real interest rates between minus 2 and minus 3 percent. Professor Lawrence H. Summers (2013Nov8) finds that “a set of older ideas that went under the phrase secular stagnation are not profoundly important in understanding Japan’s experience in the 1990s and may not be without relevance to America’s experience today” (emphasis added). Summers (2013Nov8) argues there could be an explanation in “that the short-term real interest rate that was consistent with full employment had fallen to -2% or -3% sometime in the middle of the last decade. Then, even with artificial stimulus to demand coming from all this financial imprudence, you wouldn’t see any excess demand. And even with a relative resumption of normal credit conditions, you’d have a lot of difficulty getting back to full employment.” The US economy could be in a situation where negative real rates of interest with fed funds rates close to zero as determined by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) do not move the economy to full employment or full utilization of productive resources. Summers (2013Oct8) finds need of new thinking on “how we manage an economy in which the zero nominal interest rates is a chronic and systemic inhibitor of economy activity holding our economies back to their potential.”
Former US Treasury Secretary Robert Rubin (2014Jan8) finds three major risks in prolonged unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates and quantitative easing: (1) incentive of delaying action by political leaders; (2) “financial moral hazard” in inducing excessive exposures pursuing higher yields of risker credit classes; and (3) major risks in exiting unconventional policy. Rubin (2014Jan8) proposes reduction of deficits by structural reforms that could promote recovery by improving confidence of business attained with sound fiscal discipline.
Professor John B. Taylor (2014Jan01, 2014Jan3) provides clear thought on the lack of relevance of Hansen’s contention of secular stagnation to current economic conditions. The application of secular stagnation argues that the economy of the US has attained full-employment equilibrium since around 2000 only with negative real rates of interest of minus 2 to minus 3 percent. At low levels of inflation, the so-called full-employment equilibrium of negative interest rates of minus 2 to minus 3 percent cannot be attained and the economy stagnates. Taylor (2014Jan01) analyzes multiple contradictions with current reality in this application of the theory of secular stagnation:
- Secular stagnation would predict idle capacity, in particular in residential investment when fed fund rates were fixed at 1 percent from Jun 2003 to Jun 2004. Taylor (2014Jan01) finds unemployment at 4.4 percent with house prices jumping 7 percent from 2002 to 2003 and 14 percent from 2004 to 2005 before dropping from 2006 to 2007. GDP prices doubled from 1.7 percent to 3.4 percent when interest rates were low from 2003 to 2005.
- Taylor (2014Jan01, 2014Jan3) finds another contradiction in the application of secular stagnation based on low interest rates because of savings glut and lack of investment opportunities. Taylor (2009) shows that there was no savings glut. The savings rate of the US in the past decade is significantly lower than in the 1980s.
- Taylor (2014Jan01, 2014Jan3) finds another contradiction in the low ratio of investment to GDP currently and reduced investment and hiring by US business firms.
- Taylor (2014Jan01, 2014Jan3) argues that the financial crisis and global recession were caused by weak implementation of existing regulation and departure from rules-based policies.
- Taylor (2014Jan01, 2014Jan3) argues that the recovery from the global recession was constrained by a change in the regime of regulation and fiscal/monetary policies.
The analysis by Kydland (http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/economic-sciences/laureates/2004/kydland-bio.html) and Prescott (http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/economic-sciences/laureates/2004/prescott-bio.html) (1977, 447-80, equation 5) uses the “expectation augmented” Phillips curve with the natural rate of unemployment of Friedman (1968) and Phelps (1968), which in the notation of Barro and Gordon (1983, 592, equation 1) is:
Ut = Unt – α(πt – πe) α > 0 (1)
Where Ut is the rate of unemployment at current time t, Unt is the natural rate of unemployment, πt is the current rate of inflation and πe is the expected rate of inflation by economic agents based on current information. Equation (1) expresses unemployment net of the natural rate of unemployment as a decreasing function of the gap between actual and expected rates of inflation. The system is completed by a social objective function, W, depending on inflation, π, and unemployment, U:
W = W(πt, Ut) (2)
The policymaker maximizes the preferences of the public, (2), subject to the constraint of the tradeoff of inflation and unemployment, (1). The total differential of W set equal to zero provides an indifference map in the Cartesian plane with ordered pairs (πt, Ut - Un) such that the consistent equilibrium is found at the tangency of an indifference curve and the Phillips curve in (1). The indifference curves are concave to the origin. The consistent policy is not optimal. Policymakers without discretionary powers following a rule of price stability would attain equilibrium with unemployment not higher than with the consistent policy. The optimal outcome is obtained by the rule of price stability, or zero inflation, and no more unemployment than under the consistent policy with nonzero inflation and the same unemployment. Taylor (1998LB) attributes the sustained boom of the US economy after the stagflation of the 1970s to following a monetary policy rule instead of discretion (see Taylor 1993, 1999). It is not uncommon for effects of regulation differing from those intended by policy. Professors Edward C. Prescott and Lee E. Ohanian (2014Feb), writing on “US productivity growth has taken a dive,” on Feb 3, 2014, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702303942404579362462611843696?KEYWORDS=Prescott), argue that impressive productivity growth over the long-term constructed US prosperity and wellbeing. Prescott and Ohanian (2014Feb) measure US productivity growth at 2.5 percent per year since 1948. Average US productivity growth has been only 1.1 since 2011. Prescott and Ohanian (2014Feb) argue that living standards in the US increased at 28 percent in a decade but with current slow growth of productivity will only increase 12 percent by 2024. There may be collateral effects on productivity growth from policy design similar to those in Kydland and Prescott (1977). The Bureau of Labor Statistics important report on productivity and costs released on Mar 6, 2014 (http://www.bls.gov/lpc/) supports the argument of decline of productivity in the US analyzed by Prescott and Ohanian (2014Feb). Table II-2 provides the annual percentage changes of productivity, real hourly compensation and unit labor costs for the entire economic cycle from 2007 to 2013. The data confirm the argument of Prescott and Ohanian (2014Feb): productivity increased cumulatively 2.5 percent from 2011 to 2013 at the average annual rate of 0.8 percent. The situation is direr by excluding growth of 1.5 percent in 2013, which leaves an average of 0.5 percent for 2011 and 2013. Average productivity growth for the entire economic cycle from 2007 to 2013 is only 1.6 percent. The argument by Prescott and Ohanian (2014Feb) is proper in choosing the tail of the business cycle because the increase in productivity in 2009 of 3.1 percent and 3.3 percent in 2013 consisted on reducing labor hours.
In revealing research, Edward P. Lazear and James R. Spletzer (2012JHJul22) use the wealth of data in the valuable database and resources of the Bureau of Labor Statistics (http://www.bls.gov/data/) in providing clear thought on the nature of the current labor market of the United States. The critical issue of analysis and policy currently is whether unemployment is structural or cyclical. Structural unemployment could occur because of (1) industrial and demographic shifts and (2) mismatches of skills and job vacancies in industries and locations. Consider the aggregate unemployment rate, Y, expressed in terms of share si of a demographic group in an industry i and unemployment rate yi of that demographic group (Lazear and Spletzer 2012JHJul22, 5-6):
Y = ∑isiyi (1)
This equation can be decomposed for analysis as (Lazear and Spletzer 2012JHJul22, 6):
∆Y = ∑i∆siy*i + ∑i∆yis*i (2)
The first term in (2) captures changes in the demographic and industrial composition of the economy ∆si multiplied by the average rate of unemployment y*i , or structural factors. The second term in (2) captures changes in the unemployment rate specific to a group, or ∆yi, multiplied by the average share of the group s*i, or cyclical factors. There are also mismatches in skills and locations relative to available job vacancies. A simple observation by Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22) casts intuitive doubt on structural factors: the rate of unemployment jumped from 4.4 percent in the spring of 2007 to 10 percent in October 2009. By nature, structural factors should be permanent or occur over relative long periods. The revealing result of the exhaustive research of Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22) is:
“The analysis in this paper and in others that we review do not provide any compelling evidence that there have been changes in the structure of the labor market that are capable of explaining the pattern of persistently high unemployment rates. The evidence points to primarily cyclic factors.”
The theory of secular stagnation cannot explain sudden collapse of the US economy and labor markets. The theory of secular stagnation departs from an aggregate production function in which output grows with the use of labor, capital and technology (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Globalization and the State, Vol. I (2008a), 11-6). Simon Kuznets (1971) analyzes modern economic growth in his Lecture in Memory of Alfred Nobel:
“The major breakthroughs in the advance of human knowledge, those that constituted dominant sources of sustained growth over long periods and spread to a substantial part of the world, may be termed epochal innovations. And the changing course of economic history can perhaps be subdivided into economic epochs, each identified by the epochal innovation with the distinctive characteristics of growth that it generated. Without considering the feasibility of identifying and dating such economic epochs, we may proceed on the working assumption that modern economic growth represents such a distinct epoch - growth dating back to the late eighteenth century and limited (except in significant partial effects) to economically developed countries. These countries, so classified because they have managed to take adequate advantage of the potential of modern technology, include most of Europe, the overseas offshoots of Western Europe, and Japan—barely one quarter of world population.”
Chart II-7 provides nonfarm-business labor productivity, measured by output per hour, from 1947 to 2014. The rate of productivity increase continued in the early part of the 2000s but then softened and fell during the global recession. The interruption of productivity increases occurred exclusively in the current business cycle. Lazear and Spletzer (2012JHJul22) find “primarily cyclic” factors in explaining the frustration of currently depressed labor markets in the United States. Stagnation of productivity is another cyclic event and not secular trend. The theory and application of secular stagnation to current US economic conditions is void of reality.
Chart II-7, US, Nonfarm Business Labor Productivity, Output per Hour, 1947-2014, Index 2005=100
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/lpc/
Table II-6 expands Table II-2 providing more complete measurements of the Productivity and Cost research of the Bureau of Labor Statistics. The proper emphasis of Prescott and Ohanian (2014Feb) is on the low productivity increases from 2011 to 2013. Labor productivity increased 3.3 percent in 2010 and 3.2 percent in 2009. There is much stronger yet not sustained performance in 2010 with productivity growing 3.3 percent because of growth of output of 3.2 percent with decline of hours worked of 0.1 percent. Productivity growth of 3.2 percent in 2009 consists of decline of output by 4.3 percent while hours worked collapsed 7.2 percent, which is not a desirable route to progress. The expansion phase of the economic cycle concentrated in one year, 2010, with underperformance in the remainder of the expansion from 2011 to 2013 of productivity growth at average 0.7 percent per year.
Table II-6, US, Productivity and Costs, Annual Percentage Changes 2007-2013
| 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | |
| Productivity | 0.9 | 1.0 | 0.1 | 3.3 | 3.2 | 0.8 | 1.6 |
| Output | 2.6 | 3.2 | 2.2 | 3.2 | -4.3 | -1.3 | 2.3 |
| Hours Worked | 1.7 | 2.2 | 2.1 | -0.1 | -7.2 | -2.0 | 0.7 |
| Employment | 1.8 | 2.0 | 1.6 | -1.2 | -5.7 | -1.5 | 0.9 |
| Average Weekly Hours Worked | -0.2 | 0.2 | 0.5 | 1.1 | -1.6 | -0.6 | -0.2 |
| Unit Labor Costs | 0.2 | 1.7 | 2.1 | -1.3 | -2.0 | 2.0 | 2.7 |
| Hourly Compensation | 1.1 | 2.7 | 2.2 | 2.0 | 1.1 | 2.7 | 4.3 |
| Consumer Price Inflation | 1.5 | 2.1 | 3.2 | 1.6 | -0.4 | 3.8 | 2.8 |
| Real Hourly Compensation | -0.3 | 0.6 | -0.9 | 0.3 | 1.5 | -1.1 | 1.4 |
| Non-labor Payments | 5.5 | 5.3 | 3.7 | 7.5 | 0.0 | -0.4 | 3.4 |
| Output per Job | 0.7 | 1.2 | 0.6 | 4.5 | 1.5 | 0.2 | 1.4 |
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/lpc/
Productivity growth can bring about prosperity while productivity regression can jeopardize progress. Cobet and Wilson (2002) provide estimates of output per hour and unit labor costs in national currency and US dollars for the US, Japan and Germany from 1950 to 2000 (see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 137-44). The average yearly rate of productivity change from 1950 to 2000 was 2.9 percent in the US, 6.3 percent for Japan and 4.7 percent for Germany while unit labor costs in USD increased at 2.6 percent in the US, 4.7 percent in Japan and 4.3 percent in Germany. From 1995 to 2000, output per hour increased at the average yearly rate of 4.6 percent in the US, 3.9 percent in Japan and 2.6 percent in Germany while unit labor costs in USD fell at minus 0.7 percent in the US, 4.3 percent in Japan and 7.5 percent in Germany. There was increase in productivity growth in Japan and France within the G7 in the second half of the 1990s but significantly lower than the acceleration of 1.3 percentage points per year in the US. Table II-7 provides average growth rates of indicators in the research of productivity and growth of the US Bureau of Labor Statistics. There is dramatic decline of productivity growth from 2.2 percent per year on average from 1947 to 2013 to 1.5 percent per year on average in the whole cycle from 2007 to 2013. Productivity increased at the average rate of 2.3 percent from 1947 to 2007. There is profound drop in the average rate of output growth from 3.4 percent on average from 1947 to 2013 to 0.9 percent from 2007 to 2013. Output grew at 3.7 percent per year on average from 1947 to 2007. The US maintained growth at 3.0 percent on average over entire cycles with expansions at higher rates compensating for contractions. Growth at trend in the entire cycle from IVQ2007 to IIQ2014 would have accumulated to 22.1 percent. GDP in IIQ2014 would be $18,305.0 billion (in constant dollars of 2009) if the US had grown at trend, which is higher by $2,319.3 billion than actual $15,985.7 billion. There are about two trillion dollars of GDP less than at trend, explaining the 26.8 million unemployed or underemployed equivalent to actual unemployment of 16.3 percent of the effective labor force (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/fluctuating-financial-valuations.html
and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/financial-valuations-twenty-seven.html). US GDP in IIQ2014 is 12.7 percent lower than at trend. US GDP grew from $14,991.8 billion in IVQ2007 in constant dollars to $15,985.7 billion in IIQ2014 or 6.6 percent at the average annual equivalent rate of 1.0 percent. Cochrane (2014Jul2) estimates US GDP at more than 10 percent below trend. The US missed the opportunity to grow at higher rates during the expansion and it is difficult to catch up because growth rates in the final periods of expansions tend to decline. The US missed the opportunity for recovery of output and employment always afforded in the first four quarters of expansion from recessions. Zero interest rates and quantitative easing were not required or present in successful cyclical expansions and in secular economic growth at 3.0 percent per year and 2.0 percent per capita as measured by Lucas (2011May). There is cyclical uncommonly slow growth in the US instead of allegations of secular stagnation. There is similar behavior in manufacturing. The long-term trend is growth at average 3.3 percent per year from Jan 1919 to Jun 2014. Growth at 3.3 percent per year would raise the NSA index of manufacturing output from 111.7242 in Dec 2007 to 120.3775 in Jun 2014. The actual index NSA in Jun 2014 is 101.9337, which is 15.3 percent below trend. Manufacturing output grew at average 2.3 percent between Dec 1986 and Dec 2013, raising the index at trend to 113.0017 in Jun 2014. The output of manufacturing at 101.9337 in Jun 2014 is 9.8 percent below trend under this alternative calculation. United States policy design deserves consideration of Kydland and Prescott (1977) and Prescott and Ohanian (2014Feb, 2014Jun) to induce productivity growth for future progress. Hourly compensation increased at the average yearly rate of 5.1 percent from 1947 to 2013 and consumer price inflation at 3.6 percent with real hourly compensation increasing at the average yearly rate of 1.6 percent. Hourly compensation increased at the average yearly rate of 2.0 percent from 2007 to 2013 while consumer price inflation increased at 2.0 percent with real hourly compensation changing at the average yearly rate of 0.0 percent. Hourly compensation increased at the average rate of 5.4 percent from 1947 to 2007 and the consumer price index at 3.8 percent for real hourly compensation of 1.7 percent per year. While hours worked increased at the average yearly rate of 1.2 percent from 1947 to 2013, hours worked fell 3.7 percent from 2007 to 2013. Hours worked increased at the average rate of 1.4 percent from 1947 to 2007. While employment increased at the average yearly rate of 1.6 percent from 1947 to 2013, employment fell 3.3 percent from 2007 to 2013. Employment increased at the average rate of 1.6 percent from 1947 to 2007.
Table II-7, US, Productivity and Costs, Average Annual Percentage Changes 2007-2013 and 1947-2013
| Average Annual Percentage Rate 2007-2013 | Average Annual Percentage Rate 1947-2007 | Average Annual Percentage Rate 1947-2013 | |
| Productivity | 1.5 | 2.3 | 2.2 |
| Output | 0.9 | 3.7 | 3.4 |
| Hours | -3.7* | 1.4 | 1.2 |
| Employment | -3.3* | 1.6 | 1.4 |
| Average Weekly Hours | -0.5* | -14.6* | -15.0* |
| Hourly Compensation | 2.0 | 5.4 | 5.1 |
| Consumer Price Inflation | 2.0 | 3.8 | 3.6 |
| Real Hourly Compensation | 0.0 | 1.7 | 1.6 |
| Unit Labor Costs | 0.4 | 3.0 | 2.8 |
| Unit Non-labor Payments | 2.6 | 3.5 | 3.4 |
| Output per Job | 1.5 | 2.0 | 2.0 |
* Percentage Change
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/lpc/
Unit labor costs increased sharply during the Great Inflation from the late 1960s to 1981 as shown by sharper slope in Chart II-8. Unit labor costs continued to increase but at a lower rate because of cyclic factors and not because of imaginary secular stagnation.
Chart II-8, US, Nonfarm Business, Unit Labor Costs, 1947-2014, Index 2009=100
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/lpc/
Real hourly compensation increased at relatively high rates after 1947 to the early 1970s but reached a plateau that lasted until the early 1990s, as shown in Chart II-9. There were rapid increases until the global recession. Cyclic factors and not alleged secular stagnation explain the interruption of increases in real hourly compensation.
Chart II-9, US, Nonfarm Business, Real Hourly Compensation, 1947-2014, Index 2009=100
Source: US Bureau of Labor Statistics http://www.bls.gov/lpc/
IIA United States International Trade. Table IIA-1 provides the trade balance of the US and monthly growth of exports and imports seasonally adjusted with the latest release and revisions (http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/). Because of heavy dependence on imported oil, fluctuations in the US trade account originate largely in fluctuations of commodity futures prices caused by carry trades from zero interest rates into commodity futures exposures in a process similar to world inflation waves (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/world-inflation-waves-united-states.html). The Census Bureau revised data for 2013 and 2012. The US trade balance improved from deficits of $39,083 million in Oct 2013 and $42,263 million in Sep 2013 to deficit of $35,972 million in Nov 2013 but higher deficit of $37,393 million in Dec 2013. The trade deficit increased to $40,052 million in Jan 2014 and deficit of $42,586 million in Feb 2014. The trade deficit increased to $44,176 million in Mar 2014 and $47,037 million in Apr 2014. The deficit improved to $44,663 million in May 2014 and $41,538 million in Jun 2014. Exports increased 0.5 percent in Nov 2013 while imports fell 0.9 percent. Exports fell 1.1 percent in Dec 2013 while imports decreased 0.3 percent. Exports decreased 0.3 percent in Jan 2014 and imports increased 0.9 percent. In Feb 2014, exports fell 2.1 percent while imports decreased 0.6 percent. Exports increased 2.9 percent in Mar 2013 while imports increased 3.1 percent. In Apr 2014, exports fell 0.1 percent while imports increased 1.1 percent. Exports increased 1.1 percent in May 2014 while imports fell 0.1 percent. Imports increased 0.1 percent in Jun 2014 while imports fell 1.2 percent. The trade balance deteriorated from cumulative deficit of $494,658 million in Jan-Dec 2010 to deficit of $548,625 million in Jan-Dec 2011 and improved to marginally lower deficit of $537,605 million in Jan-Dec 2012. The trade deficit improved to $476,392 million in Jan-Dec 2013.
Table IIA-1, US, Trade Balance of Goods and Services Seasonally Adjusted Millions of Dollars and ∆%
| Trade Balance | Exports | Month ∆% | Imports | Month ∆% | |
| Jun 2014 | -41,538 | 195,863 | 0.1 | 237,401 | -1.2 |
| May | -44,663 | 195,598 | 1.1 | 240,261 | -0.1 |
| Apr | -47,037 | 193,505 | -0.1 | 240,541 | 1.1 |
| Mar | -44,176 | 193,657 | 2.9 | 237,833 | 3.1 |
| Feb | -42,586 | 188,149 | -2.1 | 230,735 | -0.6 |
| Jan | -40,052 | 192,184 | -0.3 | 232,236 | 0.9 |
| Dec 2013 | -37,393 | 192,799 | -1.1 | 230,193 | -0.3 |
| Nov | -35,972 | 194,922 | 0.5 | 230,894 | -0.9 |
| Oct | -39,083 | 193,971 | 2.0 | 233,053 | 0.2 |
| Sep | -42,263 | 190,249 | -0.2 | 232,512 | 1.0 |
| Aug | -39,515 | 190,606 | 0.4 | 230,121 | 0.3 |
| Jul | -39,419 | 189,902 | -0.2 | 229,321 | 1.1 |
| Jun | -36,552 | 190,366 | 1.7 | 226,918 | -2.2 |
| May | -44,831 | 187,206 | -0.3 | 232,037 | 1.7 |
| Apr | -40,417 | 187,763 | 0.5 | 228,180 | 1.9 |
| Mar | -36,973 | 186,903 | -0.6 | 223,876 | -2.6 |
| Feb | -41,770 | 188,030 | 0.3 | 229,800 | 0.1 |
| Jan | -42,205 | 187,478 | -1.2 | 229,683 | 1.0 |
| Jan-Dec 2013 | -476,392 | 2,280,194 | 2,756,586 | ||
| Dec 2012 | -37,634 | 189,765 | 1.9 | 227,399 | -2.4 |
| Nov | -46,604 | 186,286 | 1.5 | 232,891 | 3.1 |
| Oct | -42,358 | 183,512 | -2.7 | 225,870 | -1.3 |
| Sep | -40,150 | 188,696 | 3.2 | 228,846 | 0.6 |
| Aug | -44,536 | 182,845 | -0.5 | 227,380 | -0.1 |
| Jul | -43,834 | 183,673 | -0.9 | 227,507 | -0.4 |
| Jun | -43,078 | 185,330 | 0.6 | 228,408 | -1.3 |
| May | -47,184 | 184,306 | -0.1 | 231,490 | -0.4 |
| Apr | -47,773 | 184,543 | -0.9 | 232,317 | -1.6 |
| Mar | -49,850 | 186,257 | 2.5 | 236,107 | 4.9 |
| Feb | -43,338 | 181,720 | 1.8 | 225,058 | -2.5 |
| Jan | -51,266 | 179,606 | 0.2 | 230,873 | 0.2 |
| Jan-Dec 2012 | -537,605 | 2,216,540 | 2,754,145 | ||
| Jan-Dec | -548,625 | 2,127,021 | 2,675,646 | ||
| Jan-Dec | -494,658 | 1,853,606 | 2,348,263 |
Note: Trade Balance of Goods = Exports of Goods less Imports of Goods. Trade balance may not add exactly because of errors of rounding and seasonality. Source: US Census Bureau, Foreign Trade Division
http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
Table IIA-1B provides US exports, imports and the trade balance of goods. The US has not shown a trade surplus in trade of goods since 1976. The deficit of trade in goods deteriorated sharply during the boom years from 2000 to 2007. The deficit improved during the contraction in 2009 but deteriorated in the expansion after 2009. The deficit could deteriorate sharply with growth at full employment.
Table IIA-1B, US, International Trade Balance of Goods, Exports and Imports of Goods, Millions of Dollars, Census Basis
| Balance | ∆% | Exports | ∆% | Imports | ∆% | |
| 1960 | 4,608 | (X) | 19,626 | (X) | 15,018 | (X) |
| 1961 | 5,476 | 18.8 | 20,190 | 2.9 | 14,714 | -2.0 |
| 1962 | 4,583 | -16.3 | 20,973 | 3.9 | 16,390 | 11.4 |
| 1963 | 5,289 | 15.4 | 22,427 | 6.9 | 17,138 | 4.6 |
| 1964 | 7,006 | 32.5 | 25,690 | 14.5 | 18,684 | 9.0 |
| 1965 | 5,333 | -23.9 | 26,699 | 3.9 | 21,366 | 14.4 |
| 1966 | 3,837 | -28.1 | 29,379 | 10.0 | 25,542 | 19.5 |
| 1967 | 4,122 | 7.4 | 30,934 | 5.3 | 26,812 | 5.0 |
| 1968 | 837 | -79.7 | 34,063 | 10.1 | 33,226 | 23.9 |
| 1969 | 1,289 | 54.0 | 37,332 | 9.6 | 36,043 | 8.5 |
| 1970 | 3,224 | 150.1 | 43,176 | 15.7 | 39,952 | 10.8 |
| 1971 | -1,476 | -145.8 | 44,087 | 2.1 | 45,563 | 14.0 |
| 1972 | -5,729 | 288.1 | 49,854 | 13.1 | 55,583 | 22.0 |
| 1973 | 2,389 | -141.7 | 71,865 | 44.2 | 69,476 | 25.0 |
| 1974 | -3,884 | -262.6 | 99,437 | 38.4 | 103,321 | 48.7 |
| 1975 | 9,551 | -345.9 | 108,856 | 9.5 | 99,305 | -3.9 |
| 1976 | -7,820 | -181.9 | 116,794 | 7.3 | 124,614 | 25.5 |
| 1977 | -28,352 | 262.6 | 123,182 | 5.5 | 151,534 | 21.6 |
| 1978 | -30,205 | 6.5 | 145,847 | 18.4 | 176,052 | 16.2 |
| 1979 | -23,922 | -20.8 | 186,363 | 27.8 | 210,285 | 19.4 |
| 1980 | -19,696 | -17.7 | 225,566 | 21.0 | 245,262 | 16.6 |
| 1981 | -22,267 | 13.1 | 238,715 | 5.8 | 260,982 | 6.4 |
| 1982 | -27,510 | 23.5 | 216,442 | -9.3 | 243,952 | -6.5 |
| 1983 | -52,409 | 90.5 | 205,639 | -5.0 | 258,048 | 5.8 |
| 1984 | -106,702 | 103.6 | 223,976 | 8.9 | 330,678 | 28.1 |
| 1985 | -117,711 | 10.3 | 218,815 | -2.3 | 336,526 | 1.8 |
| 1986 | -138,279 | 17.5 | 227,159 | 3.8 | 365,438 | 8.6 |
| 1987 | -152,119 | 10.0 | 254,122 | 11.9 | 406,241 | 11.2 |
| 1988 | -118,526 | -22.1 | 322,426 | 26.9 | 440,952 | 8.5 |
| 1989 | -109,399 | -7.7 | 363,812 | 12.8 | 473,211 | 7.3 |
| 1990 | -101,719 | -7.0 | 393,592 | 8.2 | 495,311 | 4.7 |
| 1991 | -66,723 | -34.4 | 421,730 | 7.1 | 488,453 | -1.4 |
| 1992 | -84,501 | 26.6 | 448,164 | 6.3 | 532,665 | 9.1 |
| 1993 | -115,568 | 36.8 | 465,091 | 3.8 | 580,659 | 9.0 |
| 1994 | -150,630 | 30.3 | 512,626 | 10.2 | 663,256 | 14.2 |
| 1995 | -158,801 | 5.4 | 584,742 | 14.1 | 743,543 | 12.1 |
| 1996 | -170,214 | 7.2 | 625,075 | 6.9 | 795,289 | 7.0 |
| 1997 | -180,522 | 6.1 | 689,182 | 10.3 | 869,704 | 9.4 |
| 1998 | -229,758 | 27.3 | 682,138 | -1.0 | 911,896 | 4.9 |
| 1999 | -328,821 | 43.1 | 695,797 | 2.0 | 1,024,618 | 12.4 |
| 2000 | -436,104 | 32.6 | 781,918 | 12.4 | 1,218,022 | 18.9 |
| 2001 | -411,899 | -5.6 | 729,100 | -6.8 | 1,140,999 | -6.3 |
| 2002 | -468,263 | 13.7 | 693,103 | -4.9 | 1,161,366 | 1.8 |
| 2003 | -532,350 | 13.7 | 724,771 | 4.6 | 1,257,121 | 8.2 |
| 2004 | -654,830 | 23.0 | 814,875 | 12.4 | 1,469,704 | 16.9 |
| 2005 | -772,373 | 18.0 | 901,082 | 10.6 | 1,673,455 | 13.9 |
| 2006 | -827,971 | 7.2 | 1,025,967 | 13.9 | 1,853,938 | 10.8 |
| 2007 | -808,763 | -2.3 | 1,148,199 | 11.9 | 1,956,962 | 5.6 |
| 2008 | -816,199 | 0.9 | 1,287,442 | 12.1 | 2,103,641 | 7.5 |
| 2009 | -503,582 | -38.3 | 1,056,043 | -18.0 | 1,559,625 | -25.9 |
| 2010 | -635,362 | 26.2 | 1,278,495 | 21.1 | 1,913,857 | 22.7 |
| 2011 | -725,447 | 14.2 | 1,482,508 | 16.0 | 2,207,954 | 15.4 |
| 2012 | -730,599 | 0.7 | 1,545,703 | 4.3 | 2,276,302 | 3.1 |
| 2013 | -688,728 | -5.7 | 1,579,593 | 2.2 | 2,268,321 | -0.4 |
Source: US Census Bureau, Foreign Trade Division
http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
Chart IIA-1 of the US Census Bureau of the Department of Commerce shows that the trade deficit (gap between exports and imports) fell during the economic contraction after 2007 but has grown again during the expansion. The low average rate of growth of GDP of 2.1 percent during the expansion beginning since IIIQ2009 does not deteriorate further the trade balance. Higher rates of growth may cause sharper deterioration.
Chart IIA-1, US, International Trade Balance, Exports and Imports of Goods and Services USD Billions
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/briefrm/esbr/www/esbr042.html
Table IIA-2B provides the US international trade balance, exports and imports of goods and services on an annual basis from 1992 to 2013. The trade balance deteriorated sharply over the long term. The US has a large deficit in goods or exports less imports of goods but it has a surplus in services that helps to reduce the trade account deficit or exports less imports of goods and services. The current account deficit of the US not seasonally adjusted increased from $81.0 billion in IQ2013 to $86.1 billion in IQ2014. The current account deficit seasonally adjusted at annual rate fell from 2.6 percent of GDP in IQ2013 to 2.0 percent of GDP in IVQ2013, increasing to 2.6 percent of GDP in IQ2014 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/06/valuation-risks-world-inflation-waves.html). The ratio of the current account deficit to GDP has stabilized around 3 percent of GDP compared with much higher percentages before the recession (see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008b), 183-94, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 167-71). The last row of Table IIA-2B shows marginal improvement of the trade deficit from $548,625 million in 2011 to lower $537,605 million in 2012 with exports growing 4.2 percent and imports 2.9 percent. The trade balance improved further to deficit of $476,392 million in 2013 with growth of exports of 2.9 percent while imports stagnated. Growth and commodity shocks under alternating inflation waves (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/world-inflation-waves-united-states.html) have deteriorated the trade deficit from the low of $383,774 million in 2009.
Table IIA-2B, US, International Trade Balance of Goods and Services, Exports and Imports of Goods and Services, SA, Millions of Dollars, Balance of Payments Basis
| Balance | Exports | ∆% | Imports | ∆% | |
| 1960 | 3,508 | 25,940 | NA | 22,432 | NA |
| 1961 | 4,195 | 26,403 | 1.8 | 22,208 | -1.0 |
| 1962 | 3,370 | 27,722 | 5.0 | 24,352 | 9.7 |
| 1963 | 4,210 | 29,620 | 6.8 | 25,410 | 4.3 |
| 1964 | 6,022 | 33,341 | 12.6 | 27,319 | 7.5 |
| 1965 | 4,664 | 35,285 | 5.8 | 30,621 | 12.1 |
| 1966 | 2,939 | 38,926 | 10.3 | 35,987 | 17.5 |
| 1967 | 2,604 | 41,333 | 6.2 | 38,729 | 7.6 |
| 1968 | 250 | 45,543 | 10.2 | 45,293 | 16.9 |
| 1969 | 91 | 49,220 | 8.1 | 49,129 | 8.5 |
| 1970 | 2,254 | 56,640 | 15.1 | 54,386 | 10.7 |
| 1971 | -1,302 | 59,677 | 5.4 | 60,979 | 12.1 |
| 1972 | -5,443 | 67,222 | 12.6 | 72,665 | 19.2 |
| 1973 | 1,900 | 91,242 | 35.7 | 89,342 | 23.0 |
| 1974 | -4,293 | 120,897 | 32.5 | 125,190 | 40.1 |
| 1975 | 12,404 | 132,585 | 9.7 | 120,181 | -4.0 |
| 1976 | -6,082 | 142,716 | 7.6 | 148,798 | 23.8 |
| 1977 | -27,246 | 152,301 | 6.7 | 179,547 | 20.7 |
| 1978 | -29,763 | 178,428 | 17.2 | 208,191 | 16.0 |
| 1979 | -24,565 | 224,131 | 25.6 | 248,696 | 19.5 |
| 1980 | -19,407 | 271,834 | 21.3 | 291,241 | 17.1 |
| 1981 | -16,172 | 294,398 | 8.3 | 310,570 | 6.6 |
| 1982 | -24,156 | 275,236 | -6.5 | 299,391 | -3.6 |
| 1983 | -57,767 | 266,106 | -3.3 | 323,874 | 8.2 |
| 1984 | -109,072 | 291,094 | 9.4 | 400,166 | 23.6 |
| 1985 | -121,880 | 289,070 | -0.7 | 410,950 | 2.7 |
| 1986 | -138,538 | 310,033 | 7.3 | 448,572 | 9.2 |
| 1987 | -151,684 | 348,869 | 12.5 | 500,552 | 11.6 |
| 1988 | -114,566 | 431,149 | 23.6 | 545,715 | 9.0 |
| 1989 | -93,141 | 487,003 | 13.0 | 580,144 | 6.3 |
| 1990 | -80,864 | 535,233 | 9.9 | 616,097 | 6.2 |
| 1991 | -31,135 | 578,344 | 8.1 | 609,479 | -1.1 |
| 1992 | -39,212 | 616,882 | 6.7 | 656,094 | 7.6 |
| 1993 | -70,311 | 642,863 | 4.2 | 713,174 | 8.7 |
| 1994 | -98,493 | 703,254 | 9.4 | 801,747 | 12.4 |
| 1995 | -96,384 | 794,387 | 13.0 | 890,771 | 11.1 |
| 1996 | -104,065 | 851,602 | 7.2 | 955,667 | 7.3 |
| 1997 | -108,273 | 934,453 | 9.7 | 1,042,726 | 9.1 |
| 1998 | -166,140 | 933,174 | -0.1 | 1,099,314 | 5.4 |
| 1999 | -258,617 | 969,867 | 3.9 | 1,228,485 | 11.8 |
| 2000 | -372,517 | 1,075,321 | 10.9 | 1,447,837 | 17.9 |
| 2001 | -361,511 | 1,005,654 | -6.5 | 1,367,165 | -5.6 |
| 2002 | -418,955 | 978,706 | -2.7 | 1,397,660 | 2.2 |
| 2003 | -493,890 | 1,020,418 | 4.3 | 1,514,308 | 8.3 |
| 2004 | -609,883 | 1,161,549 | 13.8 | 1,771,433 | 17.0 |
| 2005 | -714,245 | 1,286,022 | 10.7 | 2,000,267 | 12.9 |
| 2006 | -761,716 | 1,457,642 | 13.3 | 2,219,358 | 11.0 |
| 2007 | -705,375 | 1,653,548 | 13.4 | 2,358,922 | 6.3 |
| 2008 | -708,726 | 1,841,612 | 11.4 | 2,550,339 | 8.1 |
| 2009 | -383,774 | 1,583,053 | -14.0 | 1,966,827 | -22.9 |
| 2010 | -494,658 | 1,853,606 | 17.1 | 2,348,263 | 19.4 |
| 2011 | -548,625 | 2,127,021 | 14.8 | 2,675,646 | 13.9 |
| 2012 | -537,605 | 2,216,540 | 4.2 | 2,754,145 | 2.9 |
| 2013 | -476,392 | 2,280,194 | 2.9 | 2,756,586 | 0.1 |
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/briefrm/esbr/www/esbr042.html
Chart IIA-2 of the US Census Bureau provides the US trade account in goods and services SA from Jan 1992 to Jun 2014. There is long-term trend of deterioration of the US trade deficit shown vividly by Chart IIA-2. The global recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 reversed the trend of deterioration. Deterioration resumed together with incomplete recovery and was influenced significantly by the carry trade from zero interest rates to commodity futures exposures (these arguments are elaborated in Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession (2009a), 157-66, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 217-27, International Financial Architecture (2005), 15-18, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 221-5, Globalization and the State Vol. II (2008b), 197-213, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 182-4 http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/07/causes-of-2007-creditdollar-crisis.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/professor-mckinnons-bubble-economy.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/world-inflation-quantitative-easing.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/01/treasury-yields-valuation-of-risk.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/11/quantitative-easing-theory-evidence-and.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2010/12/is-fed-printing-money-what-are.html). Earlier research focused on the long-term external imbalance of the US in the form of trade and current account deficits (Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), Globalization and the State Vol. II (2008b) 183-94, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 167-71). US external imbalances have not been fully resolved and tend to widen together with improving world economic activity and commodity price shocks.
Chart IIA-2, US, Balance of Trade SA, Monthly, Millions of Dollars, Jan 1992-Jun 2014
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
Chart IIA-3 of the US Census Bureau provides US exports SA from Jan 1992 to Jun 2014. There was sharp acceleration from 2003 to 2007 during worldwide economic boom and increasing inflation. Exports fell sharply during the financial crisis and global recession from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009. Growth picked up again together with world trade and inflation but stalled in the final segment with less rapid global growth and inflation.
Chart IIA-3, US, Exports SA, Monthly, Millions of Dollars Jan 1992-Jun 2014
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
Chart IIA-4 of the US Census Bureau provides US imports SA from Jan 1992 to Jun 2014. Growth was stronger between 2003 and 2007 with worldwide economic boom and inflation. There was sharp drop during the financial crisis and global recession. There is stalling import levels in the final segment resulting from weaker world economic growth and diminishing inflation because of risk aversion and portfolio reallocations from commodity exposures to equities.
Chart IIA-4, US, Imports SA, Monthly, Millions of Dollars Jan 1992-Jun 2014
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
There is deterioration of the US trade balance in goods from deficit of $54,973 million in Jun 2013 to deficit of $60,285 million in Jun 2014. The nonpetroleum deficit increased by $9,179 million while the petroleum deficit shrank by $3,275 million. Total exports of goods increased 2.6 percent in Jun 2014 relative to a year earlier while total imports increased 4.7 percent. Nonpetroleum exports increased 1.3 percent from Jun 2013 to Jun 2014 while nonpetroleum imports increased 6.9 percent. Petroleum imports fell 6.9 percent.
Table IIA-3, US, International Trade in Goods Balance, Exports and Imports $ Millions and ∆% SA
| Jun 2014 | Jun 2013 | ∆% | |
| Total Balance | -60,285 | -54,973 | |
| Petroleum | -14,656 | -17,931 | |
| Non Petroleum | -44,816 | -35,637 | |
| Total Exports | 136,870 | 133,343 | 2.6 |
| Petroleum | 12,728 | 11,476 | 10.9 |
| Non Petroleum | 122,815 | 121,236 | 1.3 |
| Total Imports | 197,155 | 188,316 | 4.7 |
| Petroleum | 27,385 | 29,407 | -6.9 |
| Non Petroleum | 167,631 | 156,873 | 6.9 |
Details may not add because of rounding and seasonal adjustment
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
US exports and imports of goods not seasonally adjusted in Jan-Jun 2014 and Jan-Jun 2013 are in Table IIA-4. The rate of growth of exports was 2.9 percent and 3.2 percent for imports. The US has partial hedge of commodity price increases in exports of agricultural commodities that increased 11.6 percent and of mineral fuels that increased 17.5 percent both because prices of raw materials and commodities increase and fall recurrently as a result of shocks of risk aversion and portfolio reallocations. The US exports an insignificant amount of crude oil. US exports and imports consist mostly of manufactured products, with less rapidly increasing prices. US manufactured exports increased 0.4 percent while manufactured imports rose 4.3 percent. Significant part of the US trade imbalance originates in imports of mineral fuels decreasing 4.2 percent and petroleum decreasing 5.8 percent with wide oscillations in oil prices. The limited hedge in exports of agricultural commodities and mineral fuels compared with substantial imports of mineral fuels and crude oil results in waves of deterioration of the terms of trade of the US, or export prices relative to import prices, originating in commodity price increases caused by carry trades from zero interest rates. These waves are similar to those in worldwide inflation (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/world-inflation-waves-united-states.html).
Table IIA-4, US, Exports and Imports of Goods, Not Seasonally Adjusted Millions of Dollars and %, Census Basis
| Jan-Jun 2014 $ Millions | Jan-Jun 2014 $ Millions | ∆% | |
| Exports | 803,597 | 780,729 | 2.9 |
| Manufactured | 591,166 | 588,579 | 0.4 |
| Agricultural | 75,855 | 67,987 | 11.6 |
| Mineral Fuels | 78,587 | 66,895 | 17.5 |
| Petroleum | 63,800 | 54,844 | 16.3 |
| Imports | 1,145,596 | 1,109,615 | 3.2 |
| Manufactured | 929,980 | 891,641 | 4.3 |
| Agricultural | 56,835 | 54,200 | 4.9 |
| Mineral Fuels | 182,483 | 190,477 | -4.2 |
| Petroleum | 171,510 | 182,013 | -5.8 |
Source: US Census Bureau
http://www.census.gov/foreign-trade/
The current account of the US balance of payments is provided in Table IIA-5 for IQ2013 and IQ2014. The US has a large deficit in goods or exports less imports of goods but it has a surplus in services that helps to reduce the trade account deficit or exports less imports of goods and services. The current account deficit of the US not seasonally adjusted increased from $81.0 billion in IQ2013 to $86.1 billion in IQ2014. The current account deficit seasonally adjusted at annual rate fell from 2.6 percent of GDP in IQ2013 to 2.0 percent of GDP in IVQ2013, increasing to 2.6 percent of GDP in IQ2014. The ratio of the current account deficit to GDP has stabilized below 3 percent of GDP compared with much higher percentages before the recession but is combined now with much higher imbalance in the Treasury budget (see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), Globalization and the State, Vol. II (2008b), 183-94, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 167-71).
Table IIA-5, US, Balance of Payments, Millions of Dollars NSA
| IQ2013 | IQ2014 | Difference | |
| Goods Balance | -156,922 | -158,746 | -1,824 |
| X Goods | 386,924 | 396,135 | 2.4 ∆% |
| M Goods | -543,846 | -554,881 | 2.0 ∆% |
| Services Balance | 58,560 | 57,565 | -995 |
| X Services | 166,192 | 170,588 | 2.6 ∆% |
| M Services | -107,632 | -113,023 | 5.0 ∆% |
| Balance Goods and Services | -98,362 | -101,181 | -2,819 |
| Exports of Goods and Services and Income Receipts | 772,204 | 794,134 | |
| Imports of Goods and Services and Income Payments | -853,226 | -880,265 | |
| Current Account Balance | -81,022 | -86,131 | -5,109 |
| % GDP | IQ2013 | IQ2014 | IVQ2013 |
| 2.6 | 2.6 | 2.0 |
X: exports; M: imports
Balance on Current Account = Exports of Goods and Services – Imports of Goods and Services and Income Payments
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/international/index.htm#bop
In their classic work on “unpleasant monetarist arithmetic,” Sargent and Wallace (1981, 2) consider a regime of domination of monetary policy by fiscal policy (emphasis added):
“Imagine that fiscal policy dominates monetary policy. The fiscal authority independently sets its budgets, announcing all current and future deficits and surpluses and thus determining the amount of revenue that must be raised through bond sales and seignorage. Under this second coordination scheme, the monetary authority faces the constraints imposed by the demand for government bonds, for it must try to finance with seignorage any discrepancy between the revenue demanded by the fiscal authority and the amount of bonds that can be sold to the public. Suppose that the demand for government bonds implies an interest rate on bonds greater than the economy’s rate of growth. Then if the fiscal authority runs deficits, the monetary authority is unable to control either the growth rate of the monetary base or inflation forever. If the principal and interest due on these additional bonds are raised by selling still more bonds, so as to continue to hold down the growth of base money, then, because the interest rate on bonds is greater than the economy’s growth rate, the real stock of bonds will growth faster than the size of the economy. This cannot go on forever, since the demand for bonds places an upper limit on the stock of bonds relative to the size of the economy. Once that limit is reached, the principal and interest due on the bonds already sold to fight inflation must be financed, at least in part, by seignorage, requiring the creation of additional base money.”
The alternative fiscal scenario of the CBO (2012NovCDR, 2013Sep17) resembles an economic world in which eventually the placement of debt reaches a limit of what is proportionately desired of US debt in investment portfolios. This unpleasant environment is occurring in various European countries.
The current real value of government debt plus monetary liabilities depends on the expected discounted values of future primary surpluses or difference between tax revenue and government expenditure excluding interest payments (Cochrane 2011Jan, 27, equation (16)). There is a point when adverse expectations about the capacity of the government to generate primary surpluses to honor its obligations can result in increases in interest rates on government debt.
Fiscal policy is described by Sargent and Wallace (1981, 3, equation 1) as a time sequence of D(t), t = 1, 2,…t, …, where D is real government expenditures, excluding interest on government debt, less real tax receipts. D(t) is the real deficit excluding real interest payments measured in real time t goods. Monetary policy is described by a time sequence of H(t), t=1,2,…t, …, with H(t) being the stock of base money at time t. In order to simplify analysis, all government debt is considered as being only for one time period, in the form of a one-period bond B(t), issued at time t-1 and maturing at time t. Denote by R(t-1) the real rate of interest on the one-period bond B(t) between t-1 and t. The measurement of B(t-1) is in terms of t-1 goods and [1+R(t-1)] “is measured in time t goods per unit of time t-1 goods” (Sargent and Wallace 1981, 3). Thus, B(t-1)[1+R(t-1)] brings B(t-1) to maturing time t. B(t) represents borrowing by the government from the private sector from t to t+1 in terms of time t goods. The price level at t is denoted by p(t). The budget constraint of Sargent and Wallace (1981, 3, equation 1) is:
D(t) = {[H(t) – H(t-1)]/p(t)} + {B(t) – B(t-1)[1 + R(t-1)]} (1)
Equation (1) states that the government finances its real deficits into two portions. The first portion, {[H(t) – H(t-1)]/p(t)}, is seigniorage, or “printing money.” The second part,
{B(t) – B(t-1)[1 + R(t-1)]}, is borrowing from the public by issue of interest-bearing securities. Denote population at time t by N(t) and growing by assumption at the constant rate of n, such that:
N(t+1) = (1+n)N(t), n>-1 (2)
The per capita form of the budget constraint is obtained by dividing (1) by N(t) and rearranging:
B(t)/N(t) = {[1+R(t-1)]/(1+n)}x[B(t-1)/N(t-1)]+[D(t)/N(t)] – {[H(t)-H(t-1)]/[N(t)p(t)]} (3)
On the basis of the assumptions of equal constant rate of growth of population and real income, n, constant real rate of return on government securities exceeding growth of economic activity and quantity theory equation of demand for base money, Sargent and Wallace (1981) find that “tighter current monetary policy implies higher future inflation” under fiscal policy dominance of monetary policy. That is, the monetary authority does not permanently influence inflation, lowering inflation now with tighter policy but experiencing higher inflation in the future.
Second, Unpleasant Fiscal Arithmetic. The tool of analysis of Cochrane (2011Jan, 27, equation (16)) is the government debt valuation equation:
(Mt + Bt)/Pt = Et∫(1/Rt, t+τ)st+τdτ (4)
Equation (4) expresses the monetary, Mt, and debt, Bt, liabilities of the government, divided by the price level, Pt, in terms of the expected value discounted by the ex-post rate on government debt, Rt, t+τ, of the future primary surpluses st+τ, which are equal to Tt+τ – Gt+τ or difference between taxes, T, and government expenditures, G. Cochrane (2010A) provides the link to a web appendix demonstrating that it is possible to discount by the ex post Rt, t+τ. The second equation of Cochrane (2011Jan, 5) is:
MtV(it, ·) = PtYt (5)
Conventional analysis of monetary policy contends that fiscal authorities simply adjust primary surpluses, s, to sanction the price level determined by the monetary authority through equation (5), which deprives the debt valuation equation (4) of any role in price level determination. The simple explanation is (Cochrane 2011Jan, 5):
“We are here to think about what happens when [4] exerts more force on the price level. This change may happen by force, when debt, deficits and distorting taxes become large so the Treasury is unable or refuses to follow. Then [4] determines the price level; monetary policy must follow the fiscal lead and ‘passively’ adjust M to satisfy [5]. This change may also happen by choice; monetary policies may be deliberately passive, in which case there is nothing for the Treasury to follow and [4] determines the price level.”
An intuitive interpretation by Cochrane (2011Jan 4) is that when the current real value of government debt exceeds expected future surpluses, economic agents unload government debt to purchase private assets and goods, resulting in inflation. If the risk premium on government debt declines, government debt becomes more valuable, causing a deflationary effect. If the risk premium on government debt increases, government debt becomes less valuable, causing an inflationary effect.
There are multiple conclusions by Cochrane (2011Jan) on the debt/dollar crisis and Global recession, among which the following three:
(1) The flight to quality that magnified the recession was not from goods into money but from private-sector securities into government debt because of the risk premium on private-sector securities; monetary policy consisted of providing liquidity in private-sector markets suffering stress
(2) Increases in liquidity by open-market operations with short-term securities have no impact; quantitative easing can affect the timing but not the rate of inflation; and purchase of private debt can reverse part of the flight to quality
(3) The debt valuation equation has a similar role as the expectation shifting the Phillips curve such that a fiscal inflation can generate stagflation effects similar to those occurring from a loss of anchoring expectations.
This analysis suggests that there may be a point of saturation of demand for United States financial liabilities without an increase in interest rates on Treasury securities. A risk premium may develop on US debt. Such premium is not apparent currently because of distressed conditions in the world economy and international financial system. Risk premiums are observed in the spread of bonds of highly indebted countries in Europe relative to bonds of the government of Germany.
The issue of global imbalances centered on the possibility of a disorderly correction (Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), Globalization and the State Vol. II (2008b) 183-94, Government Intervention in Globalization (2008c), 167-71). Such a correction has not occurred historically but there is no argument proving that it could not occur. The need for a correction would originate in unsustainable large and growing United States current account deficits (CAD) and net international investment position (NIIP) or excess of financial liabilities of the US held by foreigners net relative to financial liabilities of foreigners held by US residents. The IMF estimated that the US could maintain a CAD of two to three percent of GDP without major problems (Rajan 2004). The threat of disorderly correction is summarized by Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 15):
“It is possible that foreigners may be unwilling to increase their positions in US financial assets at prevailing interest rates. An exit out of the dollar could cause major devaluation of the dollar. The depreciation of the dollar would cause inflation in the US, leading to increases in American interest rates. There would be an increase in mortgage rates followed by deterioration of real estate values. The IMF has simulated that such an adjustment would cause a decline in the rate of growth of US GDP to 0.5 percent over several years. The decline of demand in the US by four percentage points over several years would result in a world recession because the weakness in Europe and Japan could not compensate for the collapse of American demand. The probability of occurrence of an abrupt adjustment is unknown. However, the adverse effects are quite high, at least hypothetically, to warrant concern.”
The United States could be moving toward a situation typical of heavily indebted countries, requiring fiscal adjustment and increases in productivity to become more competitive internationally. The CAD and NIIP of the United States are not observed in full deterioration because the economy is well below trend. There are two complications in the current environment relative to the concern with disorderly correction in the first half of the past decade. In the release of Jun 14, 2013, the Bureau of Economic Analysis (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/international/transactions/2013/pdf/trans113.pdf) informs of revisions of US data on US international transactions since 1999:
“The statistics of the U.S. international transactions accounts released today have been revised for the first quarter of 1999 to the fourth quarter of 2012 to incorporate newly available and revised source data, updated seasonal adjustments, changes in definitions and classifications, and improved estimating methodologies.”
The BEA introduced new concepts and methods (http://www.bea.gov/international/concepts_methods.htm) in comprehensive restructuring on Jun 18, 2014 (http://www.bea.gov/international/modern.htm):
“BEA introduced a new presentation of the International Transactions Accounts on June 18, 2014 and will introduce a new presentation of the International Investment Position on June 30, 2014. These new presentations reflect a comprehensive restructuring of the international accounts that enhances the quality and usefulness of the accounts for customers and bring the accounts into closer alignment with international guidelines.”
Table IIA-6 provides data on the US fiscal and balance of payments imbalances incorporating all revisions and methods. In 2007, the federal deficit of the US was $161 billion corresponding to 1.1 percent of GDP while the Congressional Budget Office estimates the federal deficit in 2012 at $1087 billion or 6.8 percent of GDP. The estimate of the deficit for 2013 is $680 billion or 4.1 percent of GDP. The combined record federal deficits of the US from 2009 to 2012 are $5090 billion or 31.6 percent of the estimate of GDP for fiscal year 2012 implicit in the CBO (CBO 2013Sep11) estimate of debt/GDP. The deficits from 2009 to 2012 exceed one trillion dollars per year, adding to $5.090 trillion in four years, using the fiscal year deficit of $1087 billion for fiscal year 2012, which is the worst fiscal performance since World War II. Federal debt in 2007 was $5035 billion, less than the combined deficits from 2009 to 2012 of $5090 billion. Federal debt in 2012 was 70.1 percent of GDP (CBO 2013Sep11) and 72.1 percent of GDP in 2013 (http://www.cbo.gov/). This situation may worsen in the future (CBO 2013Sep17):
“Between 2009 and 2012, the federal government recorded the largest budget deficits relative to the size of the economy since 1946, causing federal debt to soar. Federal debt held by the public is now about 73 percent of the economy’s annual output, or gross domestic product (GDP). That percentage is higher than at any point in U.S. history except a brief period around World War II, and it is twice the percentage at the end of 2007. If current laws generally remained in place, federal debt held by the public would decline slightly relative to GDP over the next several years, CBO projects. After that, however, growing deficits would ultimately push debt back above its current high level. CBO projects that federal debt held by the public would reach 100 percent of GDP in 2038, 25 years from now, even without accounting for the harmful effects that growing debt would have on the economy. Moreover, debt would be on an upward path relative to the size of the economy, a trend that could not be sustained indefinitely.
The gap between federal spending and revenues would widen steadily after 2015 under the assumptions of the extended baseline, CBO projects. By 2038, the deficit would be 6½ percent of GDP, larger than in any year between 1947 and 2008, and federal debt held by the public would reach 100 percent of GDP, more than in any year except 1945 and 1946. With such large deficits, federal debt would be growing faster than GDP, a path that would ultimately be unsustainable.
Incorporating the economic effects of the federal policies that underlie the extended baseline worsens the long-term budget outlook. The increase in debt relative to the size of the economy, combined with an increase in marginal tax rates (the rates that would apply to an additional dollar of income), would reduce output and raise interest rates relative to the benchmark economic projections that CBO used in producing the extended baseline. Those economic differences would lead to lower federal revenues and higher interest payments. With those effects included, debt under the extended baseline would rise to 108 percent of GDP in 2038.”
Table IIA-6, US, Current Account, NIIP, Fiscal Balance, Nominal GDP, Federal Debt and Direct Investment, Dollar Billions and %
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | |
| Goods & | -705 | -709 | -384 | -495 | -549 | -538 | -476 |
| Primary Income | 101 | 146 | 124 | 178 | 221 | 203 | 200 |
| Second-ary Income | -114 | -124 | -121 | -127 | -132 | -126 | -124 |
| Current Account | -719 | -687 | -381 | -444 | -459 | -461 | -400 |
| NGDP | 14480 | 14720 | 14418 | 14958 | 15534 | 16245 | 16799 |
| Current Account % GDP | -4.9 | -4.7 | -2.6 | -3.0 | -2.9 | -2.8 | -2.4 |
| NIIP | -1279 | -3995 | -2628 | -2512 | -4455 | -4578 | -5383 |
| US Owned Assets Abroad | 20705 | 19423 | 19426 | 21768 | 22209 | 22520 | 23710 |
| Foreign Owned Assets in US | 21984 | 23418 | 22054 | 24280 | 26664 | 27098 | 29093 |
| NIIP % GDP | -8.8 | -27.1 | -18.2 | -16.8 | -28.7 | -28.2 | -32.0 |
| Exports | 2569 | 2751 | 2286 | 2631 | 2988 | 3085 | 3179 |
| NIIP % | -50 | -145 | -115 | -95 | -149 | -148 | -169 |
| DIA MV | 5858 | 3707 | 4945 | 5486 | 5215 | 5938 | 7080 |
| DIUS MV | 4134 | 3091 | 3619 | 4099 | 4199 | 4671 | 5791 |
| Fiscal Balance | -161 | -459 | -1413 | -1294 | -1300 | -1087 | -680 |
| Fiscal Balance % GDP | -1.1 | -3.1 | -9.8 | -8.8 | -8.4 | -6.8 | -4.1 |
| Federal Debt | 5035 | 5803 | 7545 | 9019 | 10128 | 11281 | 11982 |
| Federal Debt % GDP | 35.1 | 39.3 | 52.3 | 61.0 | 65.8 | 70.1 | 72.1 |
| Federal Outlays | 2729 | 2983 | 3518 | 3457 | 3603 | 3537 | 3455 |
| ∆% | 2.8 | 9.3 | 17.9 | -1.7 | 4.2 | -1.8 | -2.3 |
| % GDP | 19.0 | 20.2 | 24.4 | 23.4 | 23.4 | 22.0 | 20.8 |
| Federal Revenue | 2568 | 2524 | 2105 | 2163 | 2304 | 2450 | 2775 |
| ∆% | 6.7 | -1.7 | -16.6 | 2.7 | 6.5 | 6.3 | 13.3 |
| % GDP | 17.9 | 17.1 | 14.6 | 14.6 | 15.0 | 15.2 | 16.7 |
Sources:
Notes: NGDP: nominal GDP or in current dollars; NIIP: Net International Investment Position; DIA MV: US Direct Investment Abroad at Market Value; DIUS MV: Direct Investment in the US at Market Value. There are minor discrepancies in the decimal point of percentages of GDP between the balance of payments data and federal debt, outlays, revenue and deficits in which the original number of the CBO source is maintained. See Bureau of Economic Analysis, US International Economic Accounts: Concepts and Methods. 2014. Washington, DC: BEA, Department of Commerce, Jun 2014 http://www.bea.gov/international/concepts_methods.htm These discrepancies do not alter conclusions. Budget http://www.cbo.gov/ Balance of Payments and NIIP http://www.bea.gov/international/index.htm#bop Gross Domestic Product, Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Table IIA-7 provides quarterly estimates NSA of the external imbalance of the United States. The current account deficit seasonally adjusted falls from 2.6 percent of GDP in IVQ2012 to 2.6 percent in IQ2013, 2.5 percent in IIQ2013, 2.4 percent of GDP in IIIQ2013 and 2.0 percent of GDP in IVQ2013. The deficit increases to 2.6 percent of GDP in IQ2014. The net international investment position increases from $4.6 trillion in IVQ2012 to $5.1 trillion in IQ2013 and $5.5 trillion in IIQ2013, decreasing to $5.0 trillion in IIIQ2013 but increasing to $5.4 trillion in IVQ2013 and $5.5 trillion in IQ2014.
Table IIA-7, US, Current Account, NIIP, Fiscal Balance, Nominal GDP, Federal Debt and Direct Investment, Dollar Billions and % NSA
| IQ2013 | IIQ2013 | IIIQ2013 | IVQ2013 | IQ2014 | |
| Goods & | -98 | -130 | -137 | -111 | -101 |
| Primary Income | 48 | 47 | 51 | 53 | 47 |
| Secondary Income | -31 | -30 | -33 | -29 | -32 |
| Current Account | -81 | -113 | -119 | -87 | -86 |
| Current Account % GDP | -2.6 | -2.5 | -2.4 | -2.0 | -2.6 |
| NIIP | -5111 | -5524 | -4995 | -5383 | -5539 |
| US Owned Assets Abroad | 22650 | 21904 | 22954 | 23710 | 23601 |
| Foreign Owned Assets in US | -27761 | -27428 | -27949 | -29093 | -29141 |
| DIA MV | 6185 | 6147 | 6690 | 7080 | 7143 |
| DIA MV Equity | 5237 | 5162 | 5699 | 6070 | 6135 |
| DIUS MV | 5019 | 5132 | 5342 | 5791 | 5698 |
| DIUS MV Equity | 3753 | 3845 | 4041 | 4462 | 4393 |
Notes: NIIP: Net International Investment Position; DIA MV: US Direct Investment Abroad at Market Value; DIUS MV: Direct Investment in the US at Market Value. See Bureau of Economic Analysis, US International Economic Accounts: Concepts and Methods. 2014. Washington, DC: BEA, Department of Commerce, Jun 2014 http://www.bea.gov/international/concepts_methods.htm
Sources: US Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/international/index.htm#bop
Chart VI-10 of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System provides the overnight Fed funds rate on business days from Jul 1, 1954 at 1.13 percent through Jan 10, 1979, at 9.91 percent per year, to Aug 7, 2014, at 0.09 percent per year. US recessions are in shaded areas according to the reference dates of the NBER (http://www.nber.org/cycles.html). In the Fed effort to control the “Great Inflation” of the 1930s (see http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/05/slowing-growth-global-inflation-great.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/04/new-economics-of-rose-garden-turned.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/03/is-there-second-act-of-us-great.html and Appendix I The Great Inflation; see Taylor 1993, 1997, 1998LB, 1999, 2012FP, 2012Mar27, 2012Mar28, 2012JMCB and http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2012/06/rules-versus-discretionary-authorities.html), the fed funds rate increased from 8.34 percent on Jan 3, 1979 to a high in Chart VI-10 of 22.36 percent per year on Jul 22, 1981 with collateral adverse effects in the form of impaired savings and loans associations in the United States, emerging market debt and money-center banks (see Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 72-7; Pelaez 1986, 1987). Another episode in Chart VI-10 is the increase in the fed funds rate from 3.15 percent on Jan 3, 1994, to 6.56 percent on Dec 21, 1994, which also had collateral effects in impairing emerging market debt in Mexico and Argentina and bank balance sheets in a world bust of fixed income markets during pursuit by central banks of non-existing inflation (Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), 113-5). Another interesting policy impulse is the reduction of the fed funds rate from 7.03 percent on Jul 3, 2000, to 1.00 percent on Jun 22, 2004, in pursuit of equally non-existing deflation (Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture (2005), 18-28, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 83-85), followed by increments of 25 basis points from Jun 2004 to Jun 2006, raising the fed funds rate to 5.25 percent on Jul 3, 2006 in Chart VI-10. Central bank commitment to maintain the fed funds rate at 1.00 percent induced adjustable-rate mortgages (ARMS) linked to the fed funds rate. Lowering the interest rate near the zero bound in 2003-2004 caused the illusion of permanent increases in wealth or net worth in the balance sheets of borrowers and also of lending institutions, securitized banking and every financial institution and investor in the world. The discipline of calculating risks and returns was seriously impaired. The objective of monetary policy was to encourage borrowing, consumption and investment but the exaggerated stimulus resulted in a financial crisis of major proportions as the securitization that had worked for a long period was shocked with policy-induced excessive risk, imprudent credit, high leverage and low liquidity by the incentive to finance everything overnight at interest rates close to zero, from adjustable rate mortgages (ARMS) to asset-backed commercial paper of structured investment vehicles (SIV).
The consequences of inflating liquidity and net worth of borrowers were a global hunt for yields to protect own investments and money under management from the zero interest rates and unattractive long-term yields of Treasuries and other securities. Monetary policy distorted the calculations of risks and returns by households, business and government by providing central bank cheap money. Short-term zero interest rates encourage financing of everything with short-dated funds, explaining the SIVs created off-balance sheet to issue short-term commercial paper with the objective of purchasing default-prone mortgages that were financed in overnight or short-dated sale and repurchase agreements (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession, 50-1, Regulation of Banks and Finance, 59-60, Globalization and the State Vol. I, 89-92, Globalization and the State Vol. II, 198-9, Government Intervention in Globalization, 62-3, International Financial Architecture, 144-9). ARMS were created to lower monthly mortgage payments by benefitting from lower short-dated reference rates. Financial institutions economized in liquidity that was penalized with near zero interest rates. There was no perception of risk because the monetary authority guaranteed a minimum or floor price of all assets by maintaining low interest rates forever or equivalent to writing an illusory put option on wealth. Subprime mortgages were part of the put on wealth by an illusory put on house prices. The housing subsidy of $221 billion per year created the impression of ever-increasing house prices. The suspension of auctions of 30-year Treasuries was designed to increase demand for mortgage-backed securities, lowering their yield, which was equivalent to lowering the costs of housing finance and refinancing. Fannie and Freddie purchased or guaranteed $1.6 trillion of nonprime mortgages and worked with leverage of 75:1 under Congress-provided charters and lax oversight. The combination of these policies resulted in high risks because of the put option on wealth by near zero interest rates, excessive leverage because of cheap rates, low liquidity because of the penalty in the form of low interest rates and unsound credit decisions because the put option on wealth by monetary policy created the illusion that nothing could ever go wrong, causing the credit/dollar crisis and global recession (Pelaez and Pelaez, Financial Regulation after the Global Recession, 157-66, Regulation of Banks, and Finance, 217-27, International Financial Architecture, 15-18, The Global Recession Risk, 221-5, Globalization and the State Vol. II, 197-213, Government Intervention in Globalization, 182-4). A final episode in Chart VI-10 is the reduction of the fed funds rate from 5.41 percent on Aug 9, 2007, to 2.97 percent on October 7, 2008, to 0.12 percent on Dec 5, 2008 and close to zero throughout a long period with the final point at 0.09 percent on Aug 7, 2014. Evidently, this behavior of policy would not have occurred had there been theory, measurements and forecasts to avoid these violent oscillations that are clearly detrimental to economic growth and prosperity without inflation. Current policy consists of forecast mandate of maintaining policy accommodation until the forecast of the rate of unemployment reaches 6.5 percent and the rate of personal consumption expenditures excluding food and energy reaches 2.5 percent (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20121212a.htm). The FOMC dropped the numbers but affirmed guidance (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20140319a.htm): “With the unemployment rate nearing 6-1/2 percent, the Committee has updated its forward guidance. The change in the Committee's guidance does not indicate any change in the Committee's policy intentions as set forth in its recent statements.” It is a forecast mandate because of the lags in effect of monetary policy impulses on income and prices (Romer and Romer 2004). The intention is to reduce unemployment close to the “natural rate” (Friedman 1968, Phelps 1968) of around 5 percent and inflation at or below 2.0 percent. If forecasts were reasonably accurate, there would not be policy errors. A commonly analyzed risk of zero interest rates is the occurrence of unintended inflation that could precipitate an increase in interest rates similar to the Himalayan rise of the fed funds rate from 9.91 percent on Jan 10, 1979, at the beginning in Chart VI-10, to 22.36 percent on Jul 22, 1981. There is a less commonly analyzed risk of the development of a risk premium on Treasury securities because of the unsustainable Treasury deficit/debt of the United States (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/02/theory-and-reality-of-cyclical-slow.html and earlier (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/02/united-states-unsustainable-fiscal.html) together with unresolved external imbalances (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/06/valuation-risks-world-inflation-waves.html). There is not a fiscal cliff or debt limit issue ahead but rather free fall into a fiscal abyss. The combination of the fiscal abyss with zero interest rates could trigger the risk premium on Treasury debt or Himalayan hike in interest rates.
Chart VI-10, US, Fed Funds Rate, Business Days, Jul 1, 1954 to Aug 7, 2014, Percent per Year
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/update/
Chart VI-14 provides the overnight fed funds rate, the yield of the 10-year Treasury constant maturity bond, the yield of the 30-year constant maturity bond and the conventional mortgage rate from Jan 1991 to Dec 1996. In Jan 1991, the fed funds rate was 6.91 percent, the 10-year Treasury yield 8.09 percent, the 30-year Treasury yield 8.27 percent and the conventional mortgage rate 9.64 percent. Before monetary policy tightening in Oct 1993, the rates and yields were 2.99 percent for the fed funds, 5.33 percent for the 10-year Treasury, 5.94 for the 30-year Treasury and 6.83 percent for the conventional mortgage rate. After tightening in Nov 1994, the rates and yields were 5.29 percent for the fed funds rate, 7.96 percent for the 10-year Treasury, 8.08 percent for the 30-year Treasury and 9.17 percent for the conventional mortgage rate.
Chart VI-14, US, Overnight Fed Funds Rate, 10-Year Treasury Constant Maturity, 30-Year Treasury Constant Maturity and Conventional Mortgage Rate, Monthly, Jan 1991 to Dec 1996
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/update/
Chart VI-15 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides the all items consumer price index from Jan 1991 to Dec 1996. There does not appear acceleration of consumer prices requiring aggressive tightening.
Chart VI-15, US, Consumer Price Index All Items, Jan 1991 to Dec 1996
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm
Chart IV-16 of the Bureau of Labor Statistics provides 12-month percentage changes of the all items consumer price index from Jan 1991 to Dec 1996. Inflation collapsed during the recession from Jul 1990 (III) and Mar 1991 (I) and the end of the Kuwait War on Feb 25, 1991 that stabilized world oil markets. CPI inflation remained almost the same and there is no valid counterfactual that inflation would have been higher without monetary policy tightening because of the long lag in effect of monetary policy on inflation (see Culbertson 1960, 1961, Friedman 1961, Batini and Nelson 2002, Romer and Romer 2004). Policy tightening had adverse collateral effects in the form of emerging market crises in Mexico and Argentina and fixed income markets worldwide.
Chart VI-16, US, Consumer Price Index All Items, Twelve-Month Percentage Change, Jan 1991 to Dec 1996
Source: Bureau of Labor Statistics
http://www.bls.gov/cpi/data.htm
The Congressional Budget Office (CBO 2014BEOFeb4) estimates potential GDP, potential labor force and potential labor productivity provided in Table IB-3. The CBO estimates average rate of growth of potential GDP from 1950 to 2012 at 3.3 percent per year. The projected path is significantly lower at 2.1 percent per year from 2013 to 2024. The legacy of the economic cycle expansion from IIIQ2009 to IVQ2013 at 2.1 percent on average is in contrast with 5.0 percent on average in the expansion from IQ1983 to IIQ1987 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/06/financial-indecision-mediocre-cyclical.html). Subpar economic growth may perpetuate unemployment and underemployment estimated at 26.8 million or 16.2 percent of the effective labor force in Jun 2014 (Section I and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/06/financial-risks-rules-discretionary.html) with much lower hiring than in the period before the current cycle (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/06/financialgeopolitical-risks-recovery.html).
Table IB-3, US, Congressional Budget Office History and Projections of Potential GDP of US Overall Economy, ∆%
| Potential GDP | Potential Labor Force | Potential Labor Productivity* | |
| Average Annual ∆% | |||
| 1950-1973 | 3.9 | 1.6 | 2.3 |
| 1974-1981 | 3.2 | 2.5 | 0.8 |
| 1982-1990 | 3.2 | 1.6 | 1.6 |
| 1991-2001 | 3.2 | 1.3 | 1.9 |
| 2002-2012 | 2.2 | 0.8 | 1.4 |
| 2007-2012 | 1.7 | 0.6 | 1.1 |
| Total 1950-2012 | 3.3 | 1.5 | 1.8 |
| Projected Average Annual ∆% | |||
| 2013-2018 | 2.1 | 0.6 | 1.5 |
| 2019-2024 | 2.1 | 0.5 | 1.6 |
| 2013-2024 | 2.1 | 0.5 | 1.6 |
*Ratio of potential GDP to potential labor force
Source: CBO (2014BEOFeb4), CBO, Key assumptions in projecting potential GDP—February 2014 baseline. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb 4, 2014.
Chart IB-1 of the Congressional Budget Office (CBO 2013BEOFeb5) provides actual and potential GDP of the United States from 2000 to 2011 and projected to 2024. Lucas (2011May) estimates trend of United States real GDP of 3.0 percent from 1870 to 2010 and 2.2 percent for per capita GDP. The United States successfully returned to trend growth of GDP by higher rates of growth during cyclical expansion as analyzed by Bordo (2012Sep27, 2012Oct21) and Bordo and Haubrich (2012DR). Growth in expansions following deeper contractions and financial crises was much higher in agreement with the plucking model of Friedman (1964, 1988). The unusual weakness of growth at 2.2 percent on average from IIIQ2009 to IIQ2014 during the current economic expansion in contrast with 5.0 percent on average in the cyclical expansion from IQ1983 to IQ1987 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/fluctuating-financial-valuations.html) cannot be explained by the contraction of 4.3 percent of GDP from IVQ2007 to IIQ2009 and the financial crisis. Weakness of growth in the expansion is perpetuating unemployment and underemployment of 26.8 million or 16.3 percent of the labor force as estimated for Jul 2014 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/08/fluctuating-financial-valuations.html). There is no exit from unemployment/underemployment and stagnating real wages because of the collapse of hiring (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/financial-risk-recovery-without-hiring.html). The US economy and labor markets collapsed without recovery. Abrupt collapse of economic conditions can be explained only with cyclic factors (Lazear and Spletzer 2012Jul22) and not by secular stagnation (Hansen 1938, 1939, 1941 with early dissent by Simons 1942).
Chart IB-1, US, Congressional Budget Office, Actual and Projections of Potential GDP, 2000-2024, Trillions of Dollars
Source: Congressional Budget Office, CBO (2013BEOFeb5). The last year in common in both projections is 2017. The revision lowers potential output in 2017 by 7.3 percent relative to the projection in 2007.
Chart IB-2 provides differences in the projections of potential output by the CBO in 2007 and more recently on Feb 4, 2014, which the CBO explains in CBO (2014Feb28).
Chart IB-2, Congressional Budget Office, Revisions of Potential GDP
Source: Congressional Budget Office, 2014Feb 28. Revisions to CBO’s Projection of Potential Output since 2007. Washington, DC, CBO, Feb 28, 2014.
Chart IB-3 provides actual and projected potential GDP from 2000 to 2024. The gap between actual and potential GDP disappears at the end of 2017 (CBO2014Feb4). GDP increases in the projection at 2.5 percent per year.
Chart IB-3, Congressional Budget Office, GDP and Potential GDP
Source: CBO (2013BEOFeb5), CBO, Key assumptions in projecting potential GDP—February 2014 baseline. Washington, DC, Congressional Budget Office, Feb 4, 2014.
Chart IIA2-3 of the Bureau of Economic Analysis of the Department of Commerce shows on the lower negative panel the sharp increase in the deficit in goods and the deficits in goods and services from 1960 to 2012. The upper panel shows the increase in the surplus in services that was insufficient to contain the increase of the deficit in goods and services. The adjustment during the global recession has been in the form of contraction of economic activity that reduced demand for goods.
Chart IIA2-3, US, Balance of Goods, Balance on Services and Balance on Goods and Services, 1960-2013, Millions of Dollars
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_ita.cfm
Chart IIA2-4 of the Bureau of Economic Analysis shows exports and imports of goods and services from 1960 to 2012. Exports of goods and services in the upper positive panel have been quite dynamic but have not compensated for the sharp increase in imports of goods. The US economy apparently has become less competitive in goods than in services.
Chart IIA2-4, US, Exports and Imports of Goods and Services, 1960-2013, Millions of Dollars
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_ita.cfm
Chart IIA2-5 of the Bureau of Economic Analysis shows the US balance on current account from 1960 to 2012. The sharp devaluation of the dollar resulting from unconventional monetary policy of zero interest rates and elimination of auctions of 30-year Treasury bonds did not adjust the US balance of payments. Adjustment only occurred after the contraction of economic activity during the global recession.
Chart IIA2-5, US, Balance on Current Account, 1960-2013, Millions of Dollars
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_ita.cfm
Chart IIA2-6 of the Bureau of Economic Analysis provides real GDP in the US from 1960 to 2013. The contraction of economic activity during the global recession was a major factor in the reduction of the current account deficit as percent of GDP.
Chart IIA2-6, US, Real GDP, 1960-2013, Billions of Chained 2009 Dollars
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Chart IIA-7 provides the US current account deficit on a quarterly basis from 1980 to IQ2013. The deficit is at a lower level because of growth below potential not only in the US but worldwide. The combination of high government debt and deficit with external imbalance restricts potential prosperity in the US.
Chart IIA-7, US, Balance on Current Account, Quarterly, 1980-2013
Source: Bureau of Economic Analysis
http://www.bea.gov/iTable/index_nipa.cfm
Risk aversion channels funds toward US long-term and short-term securities that finance the US balance of payments and fiscal deficits benefitting from risk flight to US dollar denominated assets. There are now temporary interruptions because of fear of rising interest rates that erode prices of US government securities because of mixed signals on monetary policy and exit from the Fed balance sheet of four trillion dollars of securities held outright. Net foreign purchases of US long-term securities (row C in Table VA-8) increased from minus $41.2 billion in Apr 2014 to $19.4 billion in May 2014. Foreign (residents) purchases minus sales of US long-term securities (row A in Table VA-8) in Apr 2014 of minus $14.0 billion increased to $34.6 billion in May 2014. Net US (residents) purchases of long-term foreign securities (row B in Table VA-8) improved from minus $27.2 billion in Apr 2014 to minus $15.2 billion in May 2014. In May 2014,
C = A + B = $34.6 billion - $15.2 billion = $19.4 billion
There are minor rounding errors. There is strengthening demand in Table VA-8 in May in A1 private purchases by residents overseas of US long-term securities of $10.2 billion of which improvement in A11 Treasury securities of $5.3 billion, improvement in A12 of $0.4 billion in agency securities, improvement of minus $6.6 billion of corporate bonds and stability of $11.0 billion in equities, coincidentally equal to $11.0 billion in Apr. Worldwide risk aversion causes flight into US Treasury obligations with significant oscillations. Official purchases of securities in row A2 increased $24.4 billion with increase of Treasury securities of $19.7 billion in May 2014. Official purchases of agency securities increased $3.7 billion in May. Row D shows increase in May 2014 of $0.5 billion in purchases of short-term dollar denominated obligations. Foreign private holdings of US Treasury bills decreased $1.7 billion (row D11) with foreign official holdings decreasing $3.2 billion while the category “other” increased $5.4 billion. Foreign private holdings of US Treasury bills decreased $1.7 billion in what could be arbitrage of duration exposures. Risk aversion of default losses in foreign securities dominates decisions to accept zero interest rates in Treasury securities with no perception of principal losses. In the case of long-term securities, investors prefer to sacrifice inflation and possible duration risk to avoid principal losses with significant oscillations in risk perceptions.
Table VA-8, Net Cross-Borders Flows of US Long-Term Securities, Billion Dollars, NSA
| May 2013 12 Months | May 2014 12 Months | Apr 2014 | May 2014 | |
| A Foreign Purchases less Sales of | 411.9 | 139.5 | -14.0 | 34.6 |
| A1 Private | 215.1 | 111.6 | -31.9 | 10.2 |
| A11 Treasury | 38.0 | 180.6 | -32.4 | 5.3 |
| A12 Agency | 91.9 | -16.2 | -2.4 | 0.4 |
| A13 Corporate Bonds | -2.3 | -16.4 | -8.2 | -6.6 |
| A14 Equities | 87.5 | -36.4 | 11.0 | 11.0 |
| A2 Official | 196.8 | 27.9 | 18.0 | 24.4 |
| A21 Treasury | 133.6 | -3.6 | 18.8 | 19.7 |
| A22 Agency | 35.3 | 40.0 | 0.3 | 3.7 |
| A23 Corporate Bonds | 14.8 | 8.9 | -0.3 | 1.2 |
| A24 Equities | 13.0 | -17.4 | -0.9 | -0.2 |
| B Net US Purchases of LT Foreign Securities | -151.4 | -182.3 | -27.2 | -15.2 |
| B1 Foreign Bonds | -38.4 | 6.5 | 0.8 | 0.2 |
| B2 Foreign Equities | -113.0 | -188.8 | -28.0 | -15.3 |
| C Net Foreign Purchases of US LT Securities | 260.4 | -42.8 | -41.2 | 19.4 |
| D Increase in Foreign Holdings of Dollar Denominated Short-term | 43.5 | -42.4 | -17.1 | 0.5 |
| D1 US Treasury Bills | 37.8 | -25.2 | -41.6 | -4.9 |
| D11 Private | 20.1 | -6.5 | -22.2 | -1.7 |
| D12 Official | 17.8 | -18.6 | -19.4 | -3.2 |
| D2 Other | 5.7 | -17.3 | 24.5 | 5.4 |
C = A + B;
A = A1 + A2
A1 = A11 + A12 + A13 + A14
A2 = A21 + A22 + A23 + A24
B = B1 + B2
D = D1 + D2
Sources: United States Treasury
http://www.treasury.gov/resource-center/data-chart-center/tic/Pages/ticpress.aspx
Table VA-5 provides major foreign holders of US Treasury securities. China is the largest holder with $1270.9 billion in May 2014, decreasing 2.0 percent from $1297.3 billion in May 2013 while increasing $7.7 billion from Apr 2014 or 0.6 percent. The United States Treasury estimates US government debt held by private investors at $9800 billion in Mar 2014. China’s holding of US Treasury securities represent 13.0 percent of US government marketable interest-bearing debt held by private investors (http://www.fms.treas.gov/bulletin/index.html). Min Zeng, writing on “China plays a big role as US Treasury yields fall,” on Jul 16, 2004, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/articles/china-plays-a-big-role-as-u-s-treasury-yields-fall-1405545034?tesla=y&mg=reno64-wsj), finds that acceleration in purchases of US Treasury securities by China has been an important factor in the decline of Treasury yields in 2014. Japan increased its holdings from $1103.7 billion in May 2013 to $1220.1 billion in May 2014 or 10.5 percent. The combined holdings of China and Japan in May 2014 add to $2491 billion, which is equivalent to 25 .4 percent of US government marketable interest-bearing securities held by investors of $9800 billion in Mar 2014 (http://www.fms.treas.gov/bulletin/index.html). Total foreign holdings of Treasury securities rose from $5658.1 billion in May 2013 to $5976.0 billion in May 2014, or 5.6 percent. The US continues to finance its fiscal and balance of payments deficits with foreign savings (see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007)). A point of saturation of holdings of US Treasury debt may be reached as foreign holders evaluate the threat of reduction of principal by dollar devaluation and reduction of prices by increases in yield, including possibly risk premium. Shultz et al (2012) find that the Fed financed three-quarters of the US deficit in fiscal year 2011, with foreign governments financing significant part of the remainder of the US deficit while the Fed owns one in six dollars of US national debt. Concentrations of debt in few holders are perilous because of sudden exodus in fear of devaluation and yield increases and the limit of refinancing old debt and placing new debt. In their classic work on “unpleasant monetarist arithmetic,” Sargent and Wallace (1981, 2) consider a regime of domination of monetary policy by fiscal policy (emphasis added):
“Imagine that fiscal policy dominates monetary policy. The fiscal authority independently sets its budgets, announcing all current and future deficits and surpluses and thus determining the amount of revenue that must be raised through bond sales and seignorage. Under this second coordination scheme, the monetary authority faces the constraints imposed by the demand for government bonds, for it must try to finance with seignorage any discrepancy between the revenue demanded by the fiscal authority and the amount of bonds that can be sold to the public. Suppose that the demand for government bonds implies an interest rate on bonds greater than the economy’s rate of growth. Then if the fiscal authority runs deficits, the monetary authority is unable to control either the growth rate of the monetary base or inflation forever. If the principal and interest due on these additional bonds are raised by selling still more bonds, so as to continue to hold down the growth of base money, then, because the interest rate on bonds is greater than the economy’s growth rate, the real stock of bonds will growth faster than the size of the economy. This cannot go on forever, since the demand for bonds places an upper limit on the stock of bonds relative to the size of the economy. Once that limit is reached, the principal and interest due on the bonds already sold to fight inflation must be financed, at least in part, by seignorage, requiring the creation of additional base money.”
Table VA-9, US, Major Foreign Holders of Treasury Securities $ Billions at End of Period
| May 2014 | Apr 2014 | May 2013 | |
| Total | 5976.0 | 5960.9 | 5658.1 |
| China | 1270.9 | 1263.2 | 1297.3 |
| Japan | 1220.1 | 1209.7 | 1103.7 |
| Belgium | 362.4 | 366.4 | 175.2 |
| Caribbean Banking Centers | 310.8 | 308.4 | 281.3 |
| Oil Exporters | 257.9 | 255.5 | 264.5 |
| Brazil | 250.1 | 245.8 | 255.2 |
| United Kingdom | 179.8 | 185.5 | 155.8 |
| Taiwan | 174.4 | 175.7 | 188.8 |
| Switzerland | 174.0 | 177.6 | 182.6 |
| Hong Kong | 155.8 | 155.1 | 136.4 |
| Luxembourg | 141.9 | 141.3 | 143.2 |
| Russia | 111.4 | 116.4 | 143.4 |
| Ireland | 107.9 | 112.1 | 120.5 |
| Foreign Official Holdings | 4092.2 | 4067.5 | 4075.9 |
| A. Treasury Bills | 361.2 | 364.4 | 379.8 |
| B. Treasury Bonds and Notes | 3731.0 | 3703.1 | 3696.1 |
Source: United States Treasury
http://www.treasury.gov/resource-center/data-chart-center/tic/Pages/ticpress.aspx
III World Financial Turbulence. Financial markets are being shocked by multiple factors including:
(1) World economic slowdown
(2) Slowing growth in China with political development and slowing growth in Japan and world trade
(3) Slow growth propelled by savings/investment reduction in the US with high unemployment/underemployment, falling wages, hiring collapse, contraction of real private fixed investment, increase of wealth of households over the business cycle by total 7.3 percent adjusted for inflation from IVQ2007 to IVQ2013 while growing at 3.1 percent per year adjusted for inflation from IVQ1945 to IVQ2013 and unsustainable fiscal deficit/debt threatening prosperity that can cause risk premium on Treasury debt with Himalayan interest rate hikes
(4) Outcome of the sovereign debt crisis in Europe.
This section provides current data and analysis. Subsection IIIA Financial Risks provides analysis of the evolution of valuations of risk financial assets during the week. There are various appendixes for convenience of reference of material related to the debt crisis of the euro area. Some of this material is updated in Subsection IIIA when new data are available and then maintained in the appendixes for future reference until updated again in Subsection IIIA. Subsection IIIB Appendix on Safe Haven Currencies discusses arguments and measures of currency intervention and is available in the Appendixes section at the end of the blog comment. Subsection IIIC Appendix on Fiscal Compact provides analysis of the restructuring of the fiscal affairs of the European Union in the agreement of European leaders reached on Dec 9, 2011 and is available in the Appendixes section at the end of the blog comment. Subsection IIID Appendix on European Central Bank Large Scale Lender of Last Resort considers the policies of the European Central Bank and is available in the Appendixes section at the end of the blog comment. Appendix IIIE Euro Zone Survival Risk analyzes the threats to survival of the European Monetary Union and is available following Subsection IIIA. Subsection IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation provides more technical analysis and is available following Subsection IIIA. Subsection IIIG Appendix on Deficit Financing of Growth and the Debt Crisis provides analysis of proposals to finance growth with budget deficits together with experience of the economic history of Brazil and is available in the Appendixes section at the end of the blog comment.
IIIA Financial Risks. Financial turbulence, attaining unusual magnitude in recent months, characterized the expansion from the global recession since IIIQ2009. Table III-1, updated with every comment in this blog, provides beginning values on Aug 1 and daily values throughout the week ending on Aug 8, 2014 of various financial assets. Section VI Valuation of Risk Financial Assets provides a set of more complete values. All data are for New York time at 5 PM. The first column provides the value on Fri Aug 1 and the percentage change in that prior week below the label of the financial risk asset. For example, the first column “Fri Aug 1, 2014”, first row “USD/EUR 1.3430 0.0% -0.3%,” provides the information that the US dollar (USD) changed 0.0 percent to USD 1.3430/EUR in the week ending on Fri Aug 1 relative to the exchange rate on Fri Jul 25 and depreciated 0.3 percent relative to Thu Jul 31. The first five asset rows provide five key exchange rates versus the dollar and the percentage cumulative appreciation (positive change or no sign) or depreciation (negative change or negative sign). Positive changes constitute appreciation of the relevant exchange rate and negative changes depreciation. Financial turbulence has been dominated by reactions to the new program for Greece (see section IB in http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2011/07/debt-and-financial-risk-aversion-and.html), modifications and new approach adopted in the Euro Summit of Oct 26 (European Commission 2011Oct26SS, 2011Oct26MRES), doubts on the larger countries in the euro zone with sovereign risks such as Spain and Italy but expanding into possibly France and Germany, the growth standstill recession and long-term unsustainable government debt in the US, worldwide deceleration of economic growth and continuing waves of inflation. An important current shock is that resulting from the agreement by European leaders at their meeting on Dec 9 (European Council 2911Dec9), which is analyzed in IIIC Appendix on Fiscal Compact. European leaders reached a new agreement on Jan 30 (http://www.consilium.europa.eu/uedocs/cms_data/docs/pressdata/en/ec/127631.pdf) and another agreement on Jun 29, 2012 (http://www.consilium.europa.eu/uedocs/cms_data/docs/pressdata/en/ec/131388.pdf). The most important source of financial turbulence is shifting toward fluctuating interest rates. The dollar/euro rate is quoted as number of US dollars USD per one euro EUR, USD 1.3430/EUR in the first row, first column in the block for currencies in Table III-1 for Fri Aug 1, appreciating to USD 1.3422/EUR on Mon Aug 4, 2014, or by 0.1 percent. The dollar appreciated because fewer dollars, 1.3422, were required on Mon Aug 4 to buy one euro than $1.3430 on Fri Aug 1. Table III-1 defines a country’s exchange rate as number of units of domestic currency per unit of foreign currency. USD/EUR would be the definition of the exchange rate of the US and the inverse [1/(USD/EUR)] is the definition in this convention of the rate of exchange of the euro zone, EUR/USD. A convention used throughout this blog is required to maintain consistency in characterizing movements of the exchange rate such as in Table III-1 as appreciation and depreciation. The first row for each of the currencies shows the exchange rate at 5 PM New York time, such as USD 1.3430/EUR on Aug 1. The second row provides the cumulative percentage appreciation or depreciation of the exchange rate from the rate on the last business day of the prior week, in this case Fri Aug 1, to the last business day of the current week, in this case Fri Aug 8, such as appreciation of 0.1 percent to USD 1.3411/EUR by Aug 8. The third row provides the percentage change from the prior business day to the current business day. For example, the USD appreciated (denoted by positive sign) by 0.1 percent from the rate of USD 1.3430/EUR on Fri Aug 1 to the rate of USD 1.3411/EUR on Fri Aug 8 {[(1.3411/1.3430) – 1]100 = -0.1%}. The dollar depreciated (denoted by negative sign) by 0.4 percent from the rate of USD 1.3364 on Thu Aug 7 to USD 1.3411/EUR on Fri Aug 8 {[(1.3411/1.3360) -1]100 = 0.4%}. Other factors constant, appreciation of the dollar relative to the euro is caused by increasing risk aversion, with rising uncertainty on European and global sovereign risks increasing dollar-denominated assets with sales of risk financial investments. Funds move away from higher yielding risk assets to the safety of dollar-denominated assets during risk aversion and return to higher yielding risk assets during risk appetite.
Table III-I, Weekly Financial Risk Assets Aug 4 to Aug 8, 2014
| Fri Aug 1 2014 | Mon 4 | Tue 5 | Wed 6 | Thu 7 | Fri 8 |
| USD/ EUR 1.3430 0.0% -0.3% | 1.3422 0.1% 0.1% | 1.3376 0.4% 0.3% | 1.3383 -0.3% 0.1% | 1.3364 0.5% 0.1% | 1.3411 0.1% -0.4% |
| JPY/ USD 102.60 -0.7% 0.2% | 102.58 0.0% 0.0% | 102.59 0.0% 0.0% | 102.10 0.5% 0.5% | 102.09 0.5% 0.0% | 102.03 0.6% 0.1% |
| CHF/ USD 0.9058 -0.1% 0.3% | 0.9067 -0.1% -0.1% | 0.9091 -0.4% -0.3% | 0.9076 -0.2% 0.2% | 0.9089 -0.3% -0.1% | 0.9055 0.0% 0.4% |
| CHF/ EUR 1.2164 -0.1% 0.0% | 1.2169 | 1.2160 | 1.2146 | 1.2146 | 1.2144 |
| USD/ AUD 0.9314 1.0737 -0.9% 0.2% | 0.9334 1.0714 0.2% 0.2% | 0.9304 1.0748 -0.1% -0.3% | 0.9355 1.0689 0.4% 0.5% | 0.9271 1.0786 -0.5% -0.9% | 0.9277 1.0779 -0.4% 0.1% |
| 10Y Note 2.497 | 2.487 | 2.487 | 2.469 | 2.412 | 2.420 |
| 2Y Note 0.470 | 0.466 | 0.470 | 0.458 | 0.426 | 0.446 |
| German Bond 2Y 0.02 10Y 1.13 | 2Y 0.023 10Y 1.14 | 2Y 0.02 10Y 1.17 | 2Y 0.00 10Y 1.10 | 2Y 0.00 10Y 1.06 | 2Y 0.00 10Y 1.05 |
| DJIA 16493.37 -2.8% -0.4% | 16569.28 0.5% 0.5% | 16429.47 -0.4% -0.8% | 16443.34 -0.3% 0.1% | 16368.27 -0.8% -0.5% | 16553.93 0.4% 1.1% |
| Dow Global 2562.22 -2.6% -0.7% | 2571.39 0.4% 0.4% | 2553.41 -0.3% -0.7% | 2543.67 -0.7% -0.4% | 2528.69 1.3% -0.6% | 2532.94 -1.1% 0.2% |
| DJ Asia Pacific 1524.49 -0.9% -0.7% | 1527.10 0.2% 0.2% | 1515.87 -0.6% -0.7% | 1509.23 -1.0% -0.4% | 1508.68 -1.0% 0.0% | 1489.67 -2.3% -1.3% |
| Nikkei 15523.11 0.4% -0.6% | 15474.50 -0.3% -0.3% | 15320.31 -1.3% -1.0% | 15159.79 -2.3% -1.0% | 15232.37 -1.9% 0.5% | 14778.37 -4.8% -3.0% |
| Shanghai 2185.30 2.8% -0.7% | 2223.33 1.7% 1.7% | 2219.95 1.6% -0.2% | 2217.46 1.5% -0.1% | 2187.67 0.1% -1.3% | 2194.42 0.4% 0.3% |
| DAX 9210.08 -4.5% -2.1% | 9154.14 -0.6% -0.6% | 9189.74 -0.2% 0.4% | 9130.04 -0.9% -0.6% | 9038.97 -1.9% -1.0% | 9009.32 -2.2% -0.3% |
| DJ UBS Comm. NA | NA | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| WTI $/B 97.88 -4.1% -0.3% | 98.29 0.4% 0.4% | 97.38 -0.5% -0.9% | 96.92 -1.0% -0.5% | 97.34 -0.6% 0.4% | 97.65 -0.2% 0.3% |
| Brent $/B 104.84 -3.3% -1.1% | 105.41 0.5% 0.5% | 104.61 -0.2% -0.8% | 104.59 -0.2% 0.0% | 105.44 0.6% 0.8% | 105.02 0.2% -0.4% |
| Gold $/OZ 1293.6 -0.7% 1.0% | 1287.7 -0.5% -0.5% | 1284.0 -0.7% -0.3% | 1306.7 1.0% 1.8% | 1310.8 1.3% 0.3% | 1308.9 1.2% -0.1% |
Note: USD: US dollar; JPY: Japanese Yen; CHF: Swiss
Franc; AUD: Australian dollar; Comm.: commodities; OZ: ounce
Sources: http://www.bloomberg.com/markets/
http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_hps_marketdata
There is initial discussion of current and recent risk-determining events followed below by analysis of risk-measuring yields of the US and Germany and the USD/EUR rate.
1 First, risk determining events. Jon Hilsenrath, writing on “New view into Fed’s response to crisis,” on Feb 21, 2014, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702303775504579396803024281322?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection), analyzes 1865 pages of transcripts of eight formal and six emergency policy meetings at the Fed in 2008 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/fomchistorical2008.htm). If there were an infallible science of central banking, models and forecasts would provide accurate information to policymakers on the future course of the economy in advance. Such forewarning is essential to central bank science because of the long lag between the actual impulse of monetary policy and the actual full effects on income and prices many months and even years ahead (Romer and Romer 2004, Friedman 1961, 1953, Culbertson 1960, 1961, Batini and Nelson 2002). The transcripts of the Fed meetings in 2008 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/fomchistorical2008.htm) analyzed by Jon Hilsenrath demonstrate that Fed policymakers frequently did not understand the current state of the US economy in 2008 and much less the direction of income and prices. The conclusion of Friedman (1953) is that monetary impulses increase financial and economic instability because of lags in anticipating needs of policy, taking policy decisions and effects of decisions. This is a fortiori true when untested unconventional monetary policy in gargantuan doses shocks the economy and financial markets.
In testimony on the Semiannual Monetary Policy Report to the Congress before the Committee on Financial Services, US House of Representatives, on Feb 11, 2014, Chair Janet Yellen states (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20140211a.htm):
“Turning to monetary policy, let me emphasize that I expect a great deal of continuity in the FOMC's approach to monetary policy. I served on the Committee as we formulated our current policy strategy and I strongly support that strategy, which is designed to fulfill the Federal Reserve's statutory mandate of maximum employment and price stability. If incoming information broadly supports the Committee's expectation of ongoing improvement in labor market conditions and inflation moving back toward its longer-run objective, the Committee will likely reduce the pace of asset purchases in further measured steps at future meetings. That said, purchases are not on a preset course, and the Committee's decisions about their pace will remain contingent on its outlook for the labor market and inflation as well as its assessment of the likely efficacy and costs of such purchases. In December of last year and again this January, the Committee said that its current expectation--based on its assessment of a broad range of measures of labor market conditions, indicators of inflation pressures and inflation expectations, and readings on financial developments--is that it likely will be appropriate to maintain the current target range for the federal funds rate well past the time that the unemployment rate declines below 6-1/2 percent, especially if projected inflation continues to run below the 2 percent goal. I am committed to achieving both parts of our dual mandate: helping the economy return to full employment and returning inflation to 2 percent while ensuring that it does not run persistently above or below that level (emphasis added).”
Prior risk determining events are in an appendix below following Table III-1A. Current focus is on “tapering” quantitative easing by the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC). At the meeting on Jul 30, 2014, the FOMC decided additional tapering monthly bond purchases. Earlier programs are continued with an additional lower open-ended $25 billion of bond purchases per month, increasing the stock of $4,139,056 million “securities held outright” and bank reserves deposited at the Fed of $2,789,406 million (http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h41/current/h41.htm#h41tab1) (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20140730a.htm):
“The Committee currently judges that there is sufficient underlying strength in the broader economy to support ongoing improvement in labor market conditions. In light of the cumulative progress toward maximum employment and the improvement in the outlook for labor market conditions since the inception of the current asset purchase program, the Committee decided to make a further measured reduction in the pace of its asset purchases. Beginning in August, the Committee will add to its holdings of agency mortgage-backed securities at a pace of $10 billion per month rather than $15 billion per month, and will add to its holdings of longer-term Treasury securities at a pace of $15 billion per month rather than $20 billion per month. The Committee is maintaining its existing policy of reinvesting principal payments from its holdings of agency debt and agency mortgage-backed securities in agency mortgage-backed securities and of rolling over maturing Treasury securities at auction. The Committee's sizable and still-increasing holdings of longer-term securities should maintain downward pressure on longer-term interest rates, support mortgage markets, and help to make broader financial conditions more accommodative, which in turn should promote a stronger economic recovery and help to ensure that inflation, over time, is at the rate most consistent with the Committee's dual mandate.’
At the confirmation hearing on nomination for Chair of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Vice Chair Yellen (2013Nov14 http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20131114a.htm), states needs and intentions of policy:
“We have made good progress, but we have farther to go to regain the ground lost in the crisis and the recession. Unemployment is down from a peak of 10 percent, but at 7.3 percent in October, it is still too high, reflecting a labor market and economy performing far short of their potential. At the same time, inflation has been running below the Federal Reserve's goal of 2 percent and is expected to continue to do so for some time.
For these reasons, the Federal Reserve is using its monetary policy tools to promote a more robust recovery. A strong recovery will ultimately enable the Fed to reduce its monetary accommodation and reliance on unconventional policy tools such as asset purchases. I believe that supporting the recovery today is the surest path to returning to a more normal approach to monetary policy.”
There is sharp distinction between the two measures of unconventional monetary policy: (1) fixing of the overnight rate of fed funds at 0 to ¼ percent; and (2) outright purchase of Treasury and agency securities and mortgage-backed securities for the balance sheet of the Federal Reserve. Market are overreacting to the so-called “tapering” of outright purchases of $85 billion of securities per month for the balance sheet of the Fed. What is truly important is the fixing of the overnight fed funds at 0 to ¼ percent for which there is no end in sight as evident in the FOMC statement for Jul 30, 2014 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20140730a.htm):
“To support continued progress toward maximum employment and price stability, the Committee today reaffirmed its view that a highly accommodative stance of monetary policy remains appropriate. In determining how long to maintain the current 0 to 1/4 percent target range for the federal funds rate, the Committee will assess progress--both realized and expected--toward its objectives of maximum employment and 2 percent inflation. This assessment will take into account a wide range of information, including measures of labor market conditions, indicators of inflation pressures and inflation expectations, and readings on financial developments. The Committee continues to anticipate, based on its assessment of these factors, that it likely will be appropriate to maintain the current target range for the federal funds rate for a considerable time after the asset purchase program ends, especially if projected inflation continues to run below the Committee's 2 percent longer-run goal, and provided that longer-term inflation expectations remain well anchored” (emphasis added).
Perhaps one of the most critical statements on policy is the answer to a question of Peter Barnes by Chair Janet Yellen at the press conference following the meeting on Jun 18, 2014 (page 19 at http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20140618.pdf):
So I don't have a sense--the committee doesn't try to gauge what is the right level of equity prices. But we do certainly monitor a number of different metrics that give us a feeling for where valuations are relative to things like earnings or dividends, and look at where these metrics stand in comparison with previous history to get a sense of whether or not we're moving to valuation levels that are outside of historical norms, and I still don't see that. I still don't see that for equity prices broadly” (emphasis added).
How long is “considerable time”? At the press conference following the meeting on Mar 19, 2014, Chair Yellen answered a question of Jon Hilsenrath of the Wall Street Journal explaining “In particular, the Committee has endorsed the view that it anticipates that will be a considerable period after the asset purchase program ends before it will be appropriate to begin to raise rates. And of course on our present path, well, that's not utterly preset. We would be looking at next, next fall. So, I think that's important guidance” (http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20140319.pdf). Many focused on “next fall,” ignoring that the path of increasing rates is not “utterly preset.”
At a speech on Mar 31, 2014, Chair Yellen analyzed labor market conditions as follows (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20140331a.htm):
“And based on the evidence available, it is clear to me that the U.S. economy is still considerably short of the two goals assigned to the Federal Reserve by the Congress. The first of those goals is maximum sustainable employment, the highest level of employment that can be sustained while maintaining a stable inflation rate. Most of my colleagues on the Federal Open Market Committee and I estimate that the unemployment rate consistent with maximum sustainable employment is now between 5.2 percent and 5.6 percent, well below the 6.7 percent rate in February.
Let me explain what I mean by that word "slack" and why it is so important.
Slack means that there are significantly more people willing and capable of filling a job than there are jobs for them to fill. During a period of little or no slack, there still may be vacant jobs and people who want to work, but a large share of those willing to work lack the skills or are otherwise not well suited for the jobs that are available. With 6.7 percent unemployment, it might seem that there must be a lot of slack in the U.S. economy, but there are reasons why that may not be true.”
Another critical concern in the statement of the FOMC on Sep 18, 2013, is on the effects of tapering expectations on interest rates (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20130918a.htm):
“Household spending and business fixed investment advanced, and the housing sector has been strengthening, but mortgage rates have risen further and fiscal policy is restraining economic growth” (emphasis added).
Will the FOMC increase purchases of mortgage-backed securities if mortgage rates increase?
Perhaps one of the most critical statements on policy is the answer to a question of Peter Barnes by Chair Janet Yellen at the press conference following the meeting on Jun 18, 2014 (page 19 at http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20140618.pdf):
So I don't have a sense--the committee doesn't try to gauge what is the right level of equity prices. But we do certainly monitor a number of different metrics that give us a feeling for where valuations are relative to things like earnings or dividends, and look at where these metrics stand in comparison with previous history to get a sense of whether or not we're moving to valuation levels that are outside of historical norms, and I still don't see that. I still don't see that for equity prices broadly” (emphasis added).
In a speech at the IMF on Jul 2, 2014, Chair Yellen analyzed the link between monetary policy and financial risks (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20140702a.htm):
“Monetary policy has powerful effects on risk taking. Indeed, the accommodative policy stance of recent years has supported the recovery, in part, by providing increased incentives for households and businesses to take on the risk of potentially productive investments. But such risk-taking can go too far, thereby contributing to fragility in the financial system. This possibility does not obviate the need for monetary policy to focus primarily on price stability and full employment--the costs to society in terms of deviations from price stability and full employment that would arise would likely be significant. In the private sector, key vulnerabilities included high levels of leverage, excessive dependence on unstable short-term funding, weak underwriting of loans, deficiencies in risk measurement and risk management, and the use of exotic financial instruments that redistributed risk in nontransparent ways.”
Yellen (2014Jul14) warned again at the Committee on Banking, Housing and Urban Affairs on Jul 15, 2014:
“The Committee recognizes that low interest rates may provide incentives for some investors to “reach for yield,” and those actions could increase vulnerabilities in the financial system to adverse events. While prices of real estate, equities, and corporate bonds have risen appreciably and valuation metrics have increased, they remain generally in line with historical norms. In some sectors, such as lower-rated corporate debt, valuations appear stretched and issuance has been brisk. Accordingly, we are closely monitoring developments in the leveraged loan market and are working to enhance the effectiveness of our supervisory guidance. More broadly, the financial sector has continued to become more resilient, as banks have continued to boost their capital and liquidity positions, and growth in wholesale short-term funding in financial markets has been modest” (emphasis added).
Greenspan (1996) made similar warnings:
“Clearly, sustained low inflation implies less uncertainty about the future, and lower risk premiums imply higher prices of stocks and other earning assets. We can see that in the inverse relationship exhibited by price/earnings ratios and the rate of inflation in the past. But how do we know when irrational exuberance has unduly escalated asset values, which then become subject to unexpected and prolonged contractions as they have in Japan over the past decade? And how do we factor that assessment into monetary policy? We as central bankers need not be concerned if a collapsing financial asset bubble does not threaten to impair the real economy, its production, jobs, and price stability. Indeed, the sharp stock market break of 1987 had few negative consequences for the economy. But we should not underestimate or become complacent about the complexity of the interactions of asset markets and the economy. Thus, evaluating shifts in balance sheets generally, and in asset prices particularly, must be an integral part of the development of monetary policy” (emphasis added).
Bernanke (2010WP) and Yellen (2011AS) reveal the emphasis of monetary policy on the impact of the rise of stock market valuations in stimulating consumption by wealth effects on household confidence. What is the success in evaluating deviations of valuations of risk financial assets from “historical norms”? What are the consequences on economic activity and employment of deviations of valuations of risk financial assets from those “historical norms”? What are the policy tools and their effectiveness in returning valuations of risk financial assets to their “historical norms”?
The key policy is maintaining fed funds rate between 0 and ¼ percent. An increase in fed funds rates could cause flight out of risk financial markets worldwide. There is no exit from this policy without major financial market repercussions. There are high costs and risks of this policy because indefinite financial repression induces carry trades with high leverage, risks and illiquidity.
Professor Raguram G Rajan, governor of the Reserve Bank of India, which is India’s central bank, warned about risks in high valuations of asset prices in an interview with Christopher Jeffery of Central Banking Journal on Aug 6, 2014 (http://www.centralbanking.com/central-banking-journal/interview/2358995/raghuram-rajan-on-the-dangers-of-asset-prices-policy-spillovers-and-finance-in-india). Professor Rajan demystifies in the interview “competitive easing” by major central banks as equivalent to competitive devaluation. Rajan (2005) anticipated the risks of the world financial crisis. Professor John B. Taylor (2014Jul15, 2014Jun26) building on advanced research (Taylor (1993, 1998LB, 1999, 1998LB, 1999, 2007JH, 2008Nov, 2009, 2012JMCB, 2014Jan3) finds that a monetary policy rule would function best in promoting an environment of low inflation and strong economic growth with stability of financial markets. There is strong case for using rules instead of discretionary authorities in monetary policy (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/search?q=rules+versus+authorities http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/financial-irrational-exuberance.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/world-inflation-waves-united-states.html).
In testimony before the Committee on the Budget of the US Senate on May 8, 2014, Chair Yellen provides analysis of the current economic situation and outlook (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/yellen20140507a.htm):
“The economy has continued to recover from the steep recession of 2008 and 2009. Real gross domestic product (GDP) growth stepped up to an average annual rate of about 3-1/4 percent over the second half of last year, a faster pace than in the first half and during the preceding two years. Although real GDP growth is currently estimated to have paused in the first quarter of this year, I see that pause as mostly reflecting transitory factors, including the effects of the unusually cold and snowy winter weather. With the harsh winter behind us, many recent indicators suggest that a rebound in spending and production is already under way, putting the overall economy on track for solid growth in the current quarter. One cautionary note, though, is that readings on housing activity--a sector that has been recovering since 2011--have remained disappointing so far this year and will bear watching.
Conditions in the labor market have continued to improve. The unemployment rate was 6.3 percent in April, about 1-1/4 percentage points below where it was a year ago. Moreover, gains in payroll employment averaged nearly 200,000 jobs per month over the past year. During the economic recovery so far, payroll employment has increased by about 8-1/2 million jobs since its low point, and the unemployment rate has declined about 3-3/4 percentage points since its peak.
While conditions in the labor market have improved appreciably, they are still far from satisfactory. Even with recent declines in the unemployment rate, it continues to be elevated. Moreover, both the share of the labor force that has been unemployed for more than six months and the number of individuals who work part time but would prefer a full-time job are at historically high levels. In addition, most measures of labor compensation have been rising slowly--another signal that a substantial amount of slack remains in the labor market.
Inflation has been quite low even as the economy has continued to expand. Some of the factors contributing to the softness in inflation over the past year, such as the declines seen in non-oil import prices, will probably be transitory. Importantly, measures of longer-run inflation expectations have remained stable. That said, the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) recognizes that inflation persistently below 2 percent--the rate that the Committee judges to be most consistent with its dual mandate--could pose risks to economic performance, and we are monitoring inflation developments closely.
Looking ahead, I expect that economic activity will expand at a somewhat faster pace this year than it did last year, that the unemployment rate will continue to decline gradually, and that inflation will begin to move up toward 2 percent. A faster rate of economic growth this year should be supported by reduced restraint from changes in fiscal policy, gains in household net worth from increases in home prices and equity values, a firming in foreign economic growth, and further improvements in household and business confidence as the economy continues to strengthen. Moreover, U.S. financial conditions remain supportive of growth in economic activity and employment.”
In his classic restatement of the Keynesian demand function in terms of “liquidity preference as behavior toward risk,” James Tobin (http://www.nobelprize.org/nobel_prizes/economic-sciences/laureates/1981/tobin-bio.html) identifies the risks of low interest rates in terms of portfolio allocation (Tobin 1958, 86):
“The assumption that investors expect on balance no change in the rate of interest has been adopted for the theoretical reasons explained in section 2.6 rather than for reasons of realism. Clearly investors do form expectations of changes in interest rates and differ from each other in their expectations. For the purposes of dynamic theory and of analysis of specific market situations, the theories of sections 2 and 3 are complementary rather than competitive. The formal apparatus of section 3 will serve just as well for a non-zero expected capital gain or loss as for a zero expected value of g. Stickiness of interest rate expectations would mean that the expected value of g is a function of the rate of interest r, going down when r goes down and rising when r goes up. In addition to the rotation of the opportunity locus due to a change in r itself, there would be a further rotation in the same direction due to the accompanying change in the expected capital gain or loss. At low interest rates expectation of capital loss may push the opportunity locus into the negative quadrant, so that the optimal position is clearly no consols, all cash. At the other extreme, expectation of capital gain at high interest rates would increase sharply the slope of the opportunity locus and the frequency of no cash, all consols positions, like that of Figure 3.3. The stickier the investor's expectations, the more sensitive his demand for cash will be to changes in the rate of interest (emphasis added).”
Tobin (1969) provides more elegant, complete analysis of portfolio allocation in a general equilibrium model. The major point is equally clear in a portfolio consisting of only cash balances and a perpetuity or consol. Let g be the capital gain, r the rate of interest on the consol and re the expected rate of interest. The rates are expressed as proportions. The price of the consol is the inverse of the interest rate, (1+re). Thus, g = [(r/re) – 1]. The critical analysis of Tobin is that at extremely low interest rates there is only expectation of interest rate increases, that is, dre>0, such that there is expectation of capital losses on the consol, dg<0. Investors move into positions combining only cash and no consols. Valuations of risk financial assets would collapse in reversal of long positions in carry trades with short exposures in a flight to cash. There is no exit from a central bank created liquidity trap without risks of financial crash and another global recession. The net worth of the economy depends on interest rates. In theory, “income is generally defined as the amount a consumer unit could consume (or believe that it could) while maintaining its wealth intact” (Friedman 1957, 10). Income, Y, is a flow that is obtained by applying a rate of return, r, to a stock of wealth, W, or Y = rW (Ibid). According to a subsequent statement: “The basic idea is simply that individuals live for many years and that therefore the appropriate constraint for consumption is the long-run expected yield from wealth r*W. This yield was named permanent income: Y* = r*W” (Darby 1974, 229), where * denotes permanent. The simplified relation of income and wealth can be restated as:
W = Y/r (10
Equation (1) shows that as r goes to zero, r→0, W grows without bound, W→∞. Unconventional monetary policy lowers interest rates to increase the present value of cash flows derived from projects of firms, creating the impression of long-term increase in net worth. An attempt to reverse unconventional monetary policy necessarily causes increases in interest rates, creating the opposite perception of declining net worth. As r→∞, W = Y/r →0. There is no exit from unconventional monetary policy without increasing interest rates with resulting pain of financial crisis and adverse effects on production, investment and employment.
In delivering the biannual report on monetary policy (Board of Governors 2013Jul17), Chairman Bernanke (2013Jul17) advised Congress that:
“Instead, we are providing additional policy accommodation through two distinct yet complementary policy tools. The first tool is expanding the Federal Reserve's portfolio of longer-term Treasury securities and agency mortgage-backed securities (MBS); we are currently purchasing $40 billion per month in agency MBS and $45 billion per month in Treasuries. We are using asset purchases and the resulting expansion of the Federal Reserve's balance sheet primarily to increase the near-term momentum of the economy, with the specific goal of achieving a substantial improvement in the outlook for the labor market in a context of price stability. We have made some progress toward this goal, and, with inflation subdued, we intend to continue our purchases until a substantial improvement in the labor market outlook has been realized. We are relying on near-zero short-term interest rates, together with our forward guidance that rates will continue to be exceptionally low--our second tool--to help maintain a high degree of monetary accommodation for an extended period after asset purchases end, even as the economic recovery strengthens and unemployment declines toward more-normal levels. In appropriate combination, these two tools can provide the high level of policy accommodation needed to promote a stronger economic recovery with price stability.
The Committee's decisions regarding the asset purchase program (and the overall stance of monetary policy) depend on our assessment of the economic outlook and of the cumulative progress toward our objectives. Of course, economic forecasts must be revised when new information arrives and are thus necessarily provisional.”
Friedman (1953) argues there are three lags in effects of monetary policy: (1) between the need for action and recognition of the need; (2) the recognition of the need and taking of actions; and (3) taking of action and actual effects. Friedman (1953) finds that the combination of these lags with insufficient knowledge of the current and future behavior of the economy causes discretionary economic policy to increase instability of the economy or standard deviations of real income σy and prices σp. Policy attempts to circumvent the lags by policy impulses based on forecasts. We are all naïve about forecasting. Data are available with lags and revised to maintain high standards of estimation. Policy simulation models estimate economic relations with structures prevailing before simulations of policy impulses such that parameters change as discovered by Lucas (1977). Economic agents adjust their behavior in ways that cause opposite results from those intended by optimal control policy as discovered by Kydland and Prescott (1977). Advance guidance attempts to circumvent expectations by economic agents that could reverse policy impulses but is of dubious effectiveness. There is strong case for using rules instead of discretionary authorities in monetary policy (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/search?q=rules+versus+authorities http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/financial-irrational-exuberance.html http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/world-inflation-waves-united-states.html).
There is concern of declining inflation and appreciation of the euro. In the “Introductory statement to the press conference,” on May 8, 2014, the President of the European Central Bank Mario Draghi states (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pressconf/2014/html/is140508.en.html):
“We will maintain a high degree of monetary accommodation and act swiftly, if required, with further monetary policy easing. We firmly reiterate that we continue to expect the key ECB interest rates to remain at present or lower levels for an extended period of time. This expectation is based on an overall subdued outlook for inflation extending into the medium term, given the broad-based weakness of the economy, the high degree of unutilised capacity, and subdued money and credit creation. The Governing Council is unanimous in its commitment to using also unconventional instruments within its mandate in order to cope effectively with risks of a too prolonged period of low inflation. Further information and analysis concerning the outlook for inflation and the availability of bank loans to the private sector will be available in early June.”
On Jun 5, 2014, the European Central Bank introduced cuts in interest rates and a negative rate paid on deposits of banks (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pr/date/2014/html/pr140605.en.html):
“5 June 2014 - Monetary policy decisions
At today’s meeting the Governing Council of the ECB took the following monetary policy decisions:
- The interest rate on the main refinancing operations of the Eurosystem will be decreased by 10 basis points to 0.15%, starting from the operation to be settled on 11 June 2014.
- The interest rate on the marginal lending facility will be decreased by 35 basis points to 0.40%, with effect from 11 June 2014.
- The interest rate on the deposit facility will be decreased by 10 basis points to -0.10%, with effect from 11 June 2014. A separate press release to be published at 3.30 p.m. CET today will provide details on the implementation of the negative deposit facility rate.”
The ECB also introduced new measures of monetary policy on Jun 5, 2014 (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pr/date/2014/html/pr140605_2.en.html):
“5 June 2014 - ECB announces monetary policy measures to enhance the functioning of the monetary policy transmission mechanism
In pursuing its price stability mandate, the Governing Council of the ECB has today announced measures to enhance the functioning of the monetary policy transmission mechanism by supporting lending to the real economy. In particular, the Governing Council has decided:
- To conduct a series of targeted longer-term refinancing operations (TLTROs) aimed at improving bank lending to the euro area non-financial private sector [1], excluding loans to households for house purchase, over a window of two years.
- To intensify preparatory work related to outright purchases of asset-backed securities (ABS).”
The President of the European Central Bank (ECB) Mario Draghi analyzed the measures at a press conference (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pressconf/2014/html/is140605.en.html).
The President of the European Central Bank (ECB) Mario Draghi reaffirmed the policy stance at the press conference following the meeting on Feb 6, 2014 (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pressconf/2014/html/is140206.en.html): “As I have said several times we are willing to act and we stand ready to act. We confirmed our forward guidance, so interest rates will stay at the present or lower levels for an extended period of time.”
The President of the European Central Bank (ECB) Mario Draghi explained the indefinite period of low policy rates during the press conference following the meeting on Jul 4, 2013 (http://www.ecb.int/press/pressconf/2013/html/is130704.en.html):
“Yes, that is why I said you haven’t listened carefully. The Governing Council has taken the unprecedented step of giving forward guidance in a rather more specific way than it ever has done in the past. In my statement, I said “The Governing Council expects the key…” – i.e. all interest rates – “…ECB interest rates to remain at present or lower levels for an extended period of time.” It is the first time that the Governing Council has said something like this. And, by the way, what Mark Carney [Governor of the Bank of England] said in London is just a coincidence.”
The European Central Bank (ECB) lowered the policy rates on Nov 7, 2013 (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pr/date/2013/html/pr131107.en.html):
“PRESS RELEASE
7 November 2013 - Monetary policy decisions
At today’s meeting the Governing Council of the ECB took the following monetary policy decisions:
- The interest rate on the main refinancing operations of the Eurosystem will be decreased by 25 basis points to 0.25%, starting from the operation to be settled on 13 November 2013.
- The interest rate on the marginal lending facility will be decreased by 25 basis points to 0.75%, with effect from 13 November 2013.
- The interest rate on the deposit facility will remain unchanged at 0.00%.
The President of the ECB will comment on the considerations underlying these decisions at a press conference starting at 2.30 p.m. CET today.”
Mario Draghi, President of the ECB, explained as follows (http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pressconf/2013/html/is131107.en.html):
“Based on our regular economic and monetary analyses, we decided to lower the interest rate on the main refinancing operations of the Eurosystem by 25 basis points to 0.25% and the rate on the marginal lending facility by 25 basis points to 0.75%. The rate on the deposit facility will remain unchanged at 0.00%. These decisions are in line with our forward guidance of July 2013, given the latest indications of further diminishing underlying price pressures in the euro area over the medium term, starting from currently low annual inflation rates of below 1%. In keeping with this picture, monetary and, in particular, credit dynamics remain subdued. At the same time, inflation expectations for the euro area over the medium to long term continue to be firmly anchored in line with our aim of maintaining inflation rates below, but close to, 2%. Such a constellation suggests that we may experience a prolonged period of low inflation, to be followed by a gradual upward movement towards inflation rates below, but close to, 2% later on. Accordingly, our monetary policy stance will remain accommodative for as long as necessary. It will thereby also continue to assist the gradual economic recovery as reflected in confidence indicators up to October.”
The ECB decision together with the employment situation report on Fri Nov 8, 2013, influenced revaluation of the dollar. Market expectations were of relatively easier monetary policy in the euro area.
The statement of the meeting of the Monetary Policy Committee of the Bank of England on Jul 4, 2013, may be leading toward the same forward guidance (http://www.bankofengland.co.uk/publications/Pages/news/2013/007.aspx):
“At its meeting today, the Committee noted that the incoming data over the past couple of months had been broadly consistent with the central outlook for output growth and inflation contained in the May Report. The significant upward movement in market interest rates would, however, weigh on that outlook; in the Committee’s view, the implied rise in the expected future path of Bank Rate was not warranted by the recent developments in the domestic economy.”
A competing event is the high level of valuations of risk financial assets (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/01/peaking-valuation-of-risk-financial.html).
Matt Jarzemsky, writing on “Dow industrials set record,” on Mar 5, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887324156204578275560657416332.html), analyzes that the DJIA broke the closing high of 14,164.53 set on Oct 9, 2007, and subsequently also broke the intraday high of 14,198.10 reached on Oct 11, 2007. The DJIA closed at 16,553.93 on Fr Aug 8, 2014, which is higher by 16.9 percent than the value of 14,164.53 reached on Oct 9, 2007 and higher by 16.6 percent than the value of 14,198.10 reached on Oct 11, 2007. Values of risk financial are approaching or exceeding historical highs. Perhaps one of the most critical statements on policy is the answer to a question of Peter Barnes by Chair Janet Yellen at the press conference following the meeting on Jun 18, 2014 (page 19 at http://www.federalreserve.gov/mediacenter/files/FOMCpresconf20140618.pdf):
So I don't have a sense--the committee doesn't try to gauge what is the right level of equity prices. But we do certainly monitor a number of different metrics that give us a feeling for where valuations are relative to things like earnings or dividends, and look at where these metrics stand in comparison with previous history to get a sense of whether or not we're moving to valuation levels that are outside of historical norms, and I still don't see that. I still don't see that for equity prices broadly” (emphasis added).
In a speech at the IMF on Jul 2, 2014, Chair Yellen analyzed the link between monetary policy and financial risks (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/yellen20140702a.htm):
“Monetary policy has powerful effects on risk taking. Indeed, the accommodative policy stance of recent years has supported the recovery, in part, by providing increased incentives for households and businesses to take on the risk of potentially productive investments. But such risk-taking can go too far, thereby contributing to fragility in the financial system. This possibility does not obviate the need for monetary policy to focus primarily on price stability and full employment--the costs to society in terms of deviations from price stability and full employment that would arise would likely be significant. In the private sector, key vulnerabilities included high levels of leverage, excessive dependence on unstable short-term funding, weak underwriting of loans, deficiencies in risk measurement and risk management, and the use of exotic financial instruments that redistributed risk in nontransparent ways.”
Yellen (2014Jul14) warned again at the Committee on Banking, Housing and Urban Affairs on Jul 15, 2014:
“The Committee recognizes that low interest rates may provide incentives for some investors to “reach for yield,” and those actions could increase vulnerabilities in the financial system to adverse events. While prices of real estate, equities, and corporate bonds have risen appreciably and valuation metrics have increased, they remain generally in line with historical norms. In some sectors, such as lower-rated corporate debt, valuations appear stretched and issuance has been brisk. Accordingly, we are closely monitoring developments in the leveraged loan market and are working to enhance the effectiveness of our supervisory guidance. More broadly, the financial sector has continued to become more resilient, as banks have continued to boost their capital and liquidity positions, and growth in wholesale short-term funding in financial markets has been modest” (emphasis added).
Greenspan (1996) made similar warnings:
“Clearly, sustained low inflation implies less uncertainty about the future, and lower risk premiums imply higher prices of stocks and other earning assets. We can see that in the inverse relationship exhibited by price/earnings ratios and the rate of inflation in the past. But how do we know when irrational exuberance has unduly escalated asset values, which then become subject to unexpected and prolonged contractions as they have in Japan over the past decade? And how do we factor that assessment into monetary policy? We as central bankers need not be concerned if a collapsing financial asset bubble does not threaten to impair the real economy, its production, jobs, and price stability. Indeed, the sharp stock market break of 1987 had few negative consequences for the economy. But we should not underestimate or become complacent about the complexity of the interactions of asset markets and the economy. Thus, evaluating shifts in balance sheets generally, and in asset prices particularly, must be an integral part of the development of monetary policy” (emphasis added).
Bernanke (2010WP) and Yellen (2011AS) reveal the emphasis of monetary policy on the impact of the rise of stock market valuations in stimulating consumption by wealth effects on household confidence. What is the success in evaluating deviations of valuations of risk financial assets from “historical norms”? What are the consequences on economic activity and employment of deviations of valuations of risk financial assets from those “historical norms”? What are the policy tools and their effectiveness in returning valuations of risk financial assets to their “historical norms”?
The key policy is maintaining fed funds rate between 0 and ¼ percent. An increase in fed funds rates could cause flight out of risk financial markets worldwide. There is no exit from this policy without major financial market repercussions. There are high costs and risks of this policy because indefinite financial repression induces carry trades with high leverage, risks and illiquidity.
Professor Raguram G Rajan, governor of the Reserve Bank of India, which is India’s central bank, warned about risks in high valuations of asset prices in an interview with Christopher Jeffery of Central Banking Journal on Aug 6, 2014 (http://www.centralbanking.com/central-banking-journal/interview/2358995/raghuram-rajan-on-the-dangers-of-asset-prices-policy-spillovers-and-finance-in-india). Professor Rajan demystifies in the interview “competitive easing” by major central banks as equivalent to competitive devaluation. Rajan (2005) anticipated the risks of the world financial crisis. Professor John B. Taylor (2014Jul15, 2014Jun26) building on advanced research (Taylor (1993, 1998LB, 1999, 1998LB, 1999, 2007JH, 2008Nov, 2009, 2012JMCB, 2014Jan3) finds that a monetary policy rule would function best in promoting an environment of low inflation and strong economic growth with stability of financial markets. There is strong case for using rules instead of discretionary authorities in monetary policy (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/search?q=rules+versus+authorities http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/financial-irrational-exuberance.html).
In remarkable anticipation in 2005, Professor Raghuram G. Rajan (2005) warned of low liquidity and high risks of central bank policy rates approaching the zero bound (Pelaez and Pelaez, Regulation of Banks and Finance (2009b), 218-9). Professor Rajan excelled in a distinguished career as an academic economist in finance and was chief economist of the International Monetary Fund (IMF). Shefali Anand and Jon Hilsenrath, writing on Oct 13, 2013, on “India’s central banker lobbies Fed,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702304330904579133530766149484?KEYWORDS=Rajan), interviewed Raghuram G Rajan, who is the current Governor of the Reserve Bank of India, which is India’s central bank (http://www.rbi.org.in/scripts/AboutusDisplay.aspx). In this interview, Rajan argues that central banks should avoid unintended consequences on emerging market economies of inflows and outflows of capital triggered by monetary policy. Professor Rajan, in an interview with Kartik Goyal of Bloomberg (http://www.bloomberg.com/news/2014-01-30/rajan-warns-of-global-policy-breakdown-as-emerging-markets-slide.html), warns of breakdown of global policy coordination. Portfolio reallocations induced by combination of zero interest rates and risk events stimulate carry trades that generate wide swings in world capital flows.
Professor Ronald I. McKinnon (2013Oct27), writing on “Tapering without tears—how to end QE3,” on Oct 27, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702304799404579153693500945608?KEYWORDS=Ronald+I+McKinnon), finds that the major central banks of the world have fallen into a “near-zero-interest-rate trap.” World economic conditions are weak such that exit from the zero interest rate trap could have adverse effects on production, investment and employment. The maintenance of interest rates near zero creates long-term near stagnation. The proposal of Professor McKinnon is credible, coordinated increase of policy interest rates toward 2 percent. Professor John B. Taylor at Stanford University, writing on “Economic failures cause political polarization,” on Oct 28, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702303442004579121010753999086?KEYWORDS=John+B+Taylor), analyzes that excessive risks induced by near zero interest rates in 2003-2004 caused the financial crash. Monetary policy continued in similar paths during and after the global recession with resulting political polarization worldwide.
Second, Risk-Measuring Yields and Exchange Rate. The ten-year government bond of Spain was quoted at 6.868 percent on Aug 10, 2012, declining to 6.447 percent on Aug 17 and 6.403 percent on Aug 24, 2012, and the ten-year government bond of Italy fell from 5.894 percent on Aug 10, 2012 to 5.709 percent on Aug 17 and 5.618 percent on Aug 24, 2012. The yield of the ten-year sovereign bond of Spain traded at 2.576 percent on Aug 8, 2014, and that of the ten-year sovereign bond of Italy at 2.829 percent (http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_PRO_hps_marketdata). Risk aversion is captured by flight of investors from risk financial assets to the government securities of the US and Germany. Diminishing aversion is captured by increase of the yield of the two- and ten-year Treasury notes and the two- and ten-year government bonds of Germany. Table III-1A provides yields of US and German governments bonds and the rate of USD/EUR. Yields of US and German government bonds decline during shocks of risk aversion and the dollar strengthens in the form of fewer dollars required to buy one euro. The yield of the US ten-year Treasury note fell from 2.202 percent on Aug 26, 2011 to 1.459 percent on Jul 20, 2012, reminiscent of experience during the Treasury-Fed accord of the 1940s that placed a ceiling on long-term Treasury debt (Hetzel and Leach 2001), while the yield of the ten-year government bond of Germany fell from 2.16 percent to 1.17 percent. In the week of Aug 8, 2014, the yield of the two-year Treasury decreased to 0.446 percent and that of the ten-year Treasury decreased to 2.420 percent while the yield of the two-year bond of Germany fell to 0.00 percent and the ten-year yield eased to 1.05 percent; and the dollar appreciated at USD 1.3411/EUR. The zero interest rates for the monetary policy rate of the US, or fed funds rate, induce carry trades that ensure devaluation of the dollar if there is no risk aversion but the dollar appreciates in flight to safe haven during episodes of risk aversion. Unconventional monetary policy induces significant global financial instability, excessive risks and low liquidity. The ten-year Treasury yield of 2.420 percent is higher than consumer price inflation of 2.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2014 (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/07/world-inflation-waves-united-states.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/06/valuation-risks-world-inflation-waves.html and earlier http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2014/05/world-inflation-waves-squeeze-of.html) and the expectation of higher inflation if risk aversion diminishes. The one-year Treasury yield of 0.096 percent (http://online.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/mdc_bonds.html?mod=mdc_topnav_2_3002) is well below the 12-month consumer price inflation of 2.1 percent. Treasury securities continue to be safe haven for investors fearing risk but with concentration in shorter maturities such as the two-year Treasury. The lower part of Table III-1A provides the same flight to government securities of the US and Germany and the USD during the financial crisis and global recession and the beginning of the European debt crisis in the spring of 2010 with the USD trading at USD 1.192/EUR on Jun 7, 2010.
Table III-1A, Two- and Ten-Year Yields of Government Bonds of the US and Germany and US Dollar/EUR Exchange rate
| US 2Y | US 10Y | DE 2Y | DE 10Y | USD/ EUR | |
| 08/08/14 | 0.446 | 2.420 | 0.00 | 1.05 | 1.3411 |
| 08/01/14 | 0.470 | 2.497 | 0.02 | 1.13 | 1.3430 |
| 07/25/14 | 0.494 | 2.464 | 0.02 | 1.15 | 1.3431 |
| 07/18/14 | 0.478 | 2.484 | 0.02 | 1.15 | 1.3525 |
| 07/11/14 | 0.446 | 2.516 | 0.01 | 1.20 | 1.3608 |
| 07/04/14 | 0.502 | 2.641 | 0.02 | 1.26 | 1.3595 |
| 06/27/14 | 0.463 | 2.536 | 0.03 | 1.26 | 1.3649 |
| 06/20/14 | 0.458 | 2.609 | 0.03 | 1.34 | 1.3600 |
| 06/13/14 | 0.451 | 2.605 | 0.02 | 1.36 | 1.3540 |
| 06/06/14 | 0.405 | 2.598 | 0.05 | 1.35 | 1.3643 |
| 05/30/14 | 0.373 | 2.473 | 0.06 | 1.36 | 1.3632 |
| 05/23/14 | 0.345 | 2.532 | 0.06 | 1.41 | 1.3630 |
| 05/16/14 | 0.357 | 2.520 | 0.09 | 1.33 | 1.3694 |
| 05/09/14 | 0.385 | 2.624 | 0.13 | 1.45 | 1.3760 |
| 05/02/14 | 0.421 | 2.583 | 0.12 | 1.45 | 1.3873 |
| 04/25/14 | 0.432 | 2.668 | 0.17 | 1.48 | 1.3833 |
| 04/18/14 | 0.401 | 2.724 | 0.17 | 1.51 | 1.3813 |
| 04/11/14 | 0.357 | 2.628 | 0.16 | 1.50 | 1.3885 |
| 04/04/14 | 0.413 | 2.724 | 0.16 | 1.55 | 1.3704 |
| 03/28/14 | 0.448 | 2.721 | 0.14 | 1.55 | 1.3752 |
| 03/21/14 | 0.431 | 2.743 | 0.20 | 1.63 | 1.3793 |
| 03/14/14 | 0.340 | 2.654 | 0.15 | 1.54 | 1.3912 |
| 03/07/14 | 0.367 | 2.792 | 0.17 | 1.65 | 1.3877 |
| 02/28/14 | 0.323 | 2.655 | 0.13 | 1.62 | 1.3801 |
| 02/21/14 | 0.316 | 2.730 | 0.12 | 1.66 | 1.3739 |
| 02/14/14 | 0.313 | 2.743 | 0.11 | 1.68 | 1.3693 |
| 02/07/14 | 0.305 | 2.681 | 0.09 | 1.66 | 1.3635 |
| 1/31/14 | 0.330 | 2.645 | 0.07 | 1.66 | 1.3488 |
| 1/24/14 | 0.342 | 2.720 | 0.12 | 1.66 | 1.3677 |
| 1/17/14 | 0.373 | 2.818 | 0.17 | 1.75 | 1.3541 |
| 1/10/14 | 0.372 | 2.858 | 0.18 | 1.84 | 1.3670 |
| 1/3/14 | 0.398 | 2.999 | 0.20 | 1.94 | 1.3588 |
| 12/27/13 | 0.393 | 3.004 | 0.24 | 1.95 | 1.3746 |
| 12/20/13 | 0.377 | 2.891 | 0.22 | 1.87 | 1.3673 |
| 12/13/13 | 0.328 | 2.865 | 0.24 | 1.83 | 1.3742 |
| 12/6/13 | 0.304 | 2.858 | 0.21 | 1.84 | 1.3705 |
| 11/29/13 | 0.283 | 2.743 | 0.11 | 1.69 | 1.3592 |
| 11/22/13 | 0.280 | 2.746 | 0.13 | 1.74 | 1.3557 |
| 11/15/13 | 0.292 | 2.704 | 0.10 | 1.70 | 1.3497 |
| 11/8/13 | 0.316 | 2.750 | 0.10 | 1.76 | 1.3369 |
| 11/1/13 | 0.311 | 2.622 | 0.11 | 1.69 | 1.3488 |
| 10/25/13 | 0.305 | 2.507 | 0.18 | 1.75 | 1.3804 |
| 10/18/13 | 0.321 | 2.588 | 0.17 | 1.83 | 1.3686 |
| 10/11/13 | 0.344 | 2.688 | 0.18 | 1.86 | 1.3543 |
| 10/4/13 | 0.335 | 2.645 | 0.17 | 1.84 | 1.3557 |
| 9/27/13 | 0.335 | 2.626 | 0.16 | 1.78 | 1.3523 |
| 9/20/13 | 0.333 | 2.734 | 0.21 | 1.94 | 1.3526 |
| 9/13/13 | 0.433 | 2.890 | 0.22 | 1.97 | 1.3297 |
| 9/6/13 | 0.461 | 2.941 | 0.26 | 1.95 | 1.3179 |
| 8/23/13 | 0.401 | 2.784 | 0.23 | 1.85 | 1.3221 |
| 8/23/13 | 0.374 | 2.818 | 0.28 | 1.93 | 1.3380 |
| 8/16/13 | 0.341 | 2.829 | 0.22 | 1.88 | 1.3328 |
| 8/9/13 | 0.30 | 2.579 | 0.16 | 1.68 | 1.3342 |
| 8/2/13 | 0.299 | 2.597 | 0.15 | 1.65 | 1.3281 |
| 7/26/13 | 0.315 | 2.565 | 0.15 | 1.66 | 1.3279 |
| 7/19/13 | 0.300 | 2.480 | 0.08 | 1.52 | 1.3141 |
| 7/12/13 | 0.345 | 2.585 | 0.10 | 1.56 | 1.3068 |
| 7/5/13 | 0.397 | 2.734 | 0.11 | 1.72 | 1.2832 |
| 6/28/13 | 0.357 | 2.486 | 0.19 | 1.73 | 1.3010 |
| 6/21/13 | 0.366 | 2.542 | 0.26 | 1.72 | 1.3122 |
| 6/14/13 | 0.276 | 2.125 | 0.12 | 1.51 | 1.3345 |
| 6/7/13 | 0.304 | 2.174 | 0.18 | 1.54 | 1.3219 |
| 5/31/13 | 0.299 | 2.132 | 0.06 | 1.50 | 1.2996 |
| 5/24/13 | 0.249 | 2.009 | 0.00 | 1.43 | 1.2932 |
| 5/17/13 | 0.248 | 1.952 | -0.03 | 1.32 | 1.2837 |
| 5/10/13 | 0.239 | 1.896 | 0.05 | 1.38 | 1.2992 |
| 5/3/13 | 0.22 | 1.742 | 0.00 | 1.24 | 1.3115 |
| 4/26/13 | 0.209 | 1.663 | 0.00 | 1.21 | 1.3028 |
| 4/19/13 | 0.232 | 1.702 | 0.02 | 1.25 | 1.3052 |
| 4/12/13 | 0.228 | 1.719 | 0.02 | 1.26 | 1.3111 |
| 4/5/13 | 0.228 | 1.706 | 0.01 | 1.21 | 1.2995 |
| 3/29/13 | 0.244 | 1.847 | -0.02 | 1.29 | 1.2818 |
| 3/22/13 | 0.242 | 1.931 | 0.03 | 1.38 | 1.2988 |
| 3/15/13 | 0.246 | 1.992 | 0.05 | 1.46 | 1.3076 |
| 3/8/13 | 0.256 | 2.056 | 0.09 | 1.53 | 1.3003 |
| 3/1/13 | 0.236 | 1.842 | 0.03 | 1.41 | 1.3020 |
| 2/22/13 | 0.252 | 1.967 | 0.13 | 1.57 | 1.3190 |
| 2/15/13 | 0.268 | 2.007 | 0.19 | 1.65 | 1.3362 |
| 2/8/13 | 0.252 | 1.949 | 0.18 | 1.61 | 1.3365 |
| 2/1/13 | 0.26 | 2.024 | 0.25 | 1.67 | 1.3642 |
| 1/25/13 | 0.278 | 1.947 | 0.26 | 1.64 | 1.3459 |
| 1/18/13 | 0.252 | 1.84 | 0.18 | 1.56 | 1.3321 |
| 1/11/13 | 0.247 | 1.862 | 0.13 | 1.58 | 1.3343 |
| 1/4/13 | 0.262 | 1.898 | 0.08 | 1.54 | 1.3069 |
| 12/28/12 | 0.252 | 1.699 | -0.01 | 1.31 | 1.3218 |
| 12/21/12 | 0.272 | 1.77 | -0.01 | 1.38 | 1.3189 |
| 12/14/12 | 0.232 | 1.704 | -0.04 | 1.35 | 1.3162 |
| 12/7/12 | 0.256 | 1.625 | -0.08 | 1.30 | 1.2926 |
| 11/30/12 | 0.248 | 1.612 | 0.01 | 1.39 | 1.2987 |
| 11/23/12 | 0.273 | 1.691 | 0.00 | 1.44 | 1.2975 |
| 11/16/12 | 0.24 | 1.584 | -0.03 | 1.33 | 1.2743 |
| 11/9/12 | 0.256 | 1.614 | -0.03 | 1.35 | 1.2711 |
| 11/2/12 | 0.274 | 1.715 | 0.01 | 1.45 | 1.2838 |
| 10/26/12 | 0.299 | 1.748 | 0.05 | 1.54 | 1.2942 |
| 10/19/12 | 0.296 | 1.766 | 0.11 | 1.59 | 1.3023 |
| 10/12/12 | 0.264 | 1.663 | 0.04 | 1.45 | 1.2953 |
| 10/5/12 | 0.26 | 1.737 | 0.06 | 1.52 | 1.3036 |
| 9/28/12 | 0.236 | 1.631 | 0.02 | 1.44 | 1.2859 |
| 9/21/12 | 0.26 | 1.753 | 0.04 | 1.60 | 1.2981 |
| 9/14/12 | 0.252 | 1.863 | 0.10 | 1.71 | 1.3130 |
| 9/7/12 | 0.252 | 1.668 | 0.03 | 1.52 | 1.2816 |
| 8/31/12 | 0.225 | 1.543 | -0.03 | 1.33 | 1.2575 |
| 8/24/12 | 0.266 | 1.684 | -0.01 | 1.35 | 1.2512 |
| 8/17/12 | 0.288 | 1.814 | -0.04 | 1.50 | 1.2335 |
| 8/10/12 | 0.267 | 1.658 | -0.07 | 1.38 | 1.2290 |
| 8/3/12 | 0.242 | 1.569 | -0.02 | 1.42 | 1.2387 |
| 7/27/12 | 0.244 | 1.544 | -0.03 | 1.40 | 1.2320 |
| 7/20/12 | 0.207 | 1.459 | -0.07 | 1.17 | 1.2158 |
| 7/13/12 | 0.24 | 1.49 | -0.04 | 1.26 | 1.2248 |
| 7/6/12 | 0.272 | 1.548 | -0.01 | 1.33 | 1.2288 |
| 6/29/12 | 0.305 | 1.648 | 0.12 | 1.58 | 1.2661 |
| 6/22/12 | 0.309 | 1.676 | 0.14 | 1.58 | 1.2570 |
| 6/15/12 | 0.272 | 1.584 | 0.07 | 1.44 | 1.2640 |
| 6/8/12 | 0.268 | 1.635 | 0.04 | 1.33 | 1.2517 |
| 6/1/12 | 0.248 | 1.454 | 0.01 | 1.17 | 1.2435 |
| 5/25/12 | 0.291 | 1.738 | 0.05 | 1.37 | 1.2518 |
| 5/18/12 | 0.292 | 1.714 | 0.05 | 1.43 | 1.2780 |
| 5/11/12 | 0.248 | 1.845 | 0.09 | 1.52 | 1.2917 |
| 5/4/12 | 0.256 | 1.876 | 0.08 | 1.58 | 1.3084 |
| 4/6/12 | 0.31 | 2.058 | 0.14 | 1.74 | 1.3096 |
| 3/30/12 | 0.335 | 2.214 | 0.21 | 1.79 | 1.3340 |
| 3/2/12 | 0.29 | 1.977 | 0.16 | 1.80 | 1.3190 |
| 2/24/12 | 0.307 | 1.977 | 0.24 | 1.88 | 1.3449 |
| 1/6/12 | 0.256 | 1.957 | 0.17 | 1.85 | 1.2720 |
| 12/30/11 | 0.239 | 1.871 | 0.14 | 1.83 | 1.2944 |
| 8/26/11 | 0.20 | 2.202 | 0.65 | 2.16 | 1.450 |
| 8/19/11 | 0.192 | 2.066 | 0.65 | 2.11 | 1.4390 |
| 6/7/10 | 0.74 | 3.17 | 0.49 | 2.56 | 1.192 |
| 3/5/09 | 0.89 | 2.83 | 1.19 | 3.01 | 1.254 |
| 12/17/08 | 0.73 | 2.20 | 1.94 | 3.00 | 1.442 |
| 10/27/08 | 1.57 | 3.79 | 2.61 | 3.76 | 1.246 |
| 7/14/08 | 2.47 | 3.88 | 4.38 | 4.40 | 1.5914 |
| 6/26/03 | 1.41 | 3.55 | NA | 3.62 | 1.1423 |
Note: DE: Germany
Source: http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_hps_marketdata
http://www.bloomberg.com/markets/
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15/
Appendix: Prior Risk Determining Events. Current risk analysis concentrates on deciphering what the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) may decide on quantitative easing. The week of May 24 was dominated by the testimony of Chairman Bernanke to the Joint Economic Committee of the US Congress on May 22, 2013 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/bernanke20130522a.htm), followed by questions and answers and the release on May 22, 2013 of the minutes of the meeting of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) from Apr 30 to May 1, 2013 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/fomcminutes20130501.htm). Monetary policy emphasizes communication of policy intentions to avoid that expectations reverse outcomes in reality (Kydland and Prescott 1977). Jon Hilsenrath, writing on “In bid for clarity, Fed delivers opacity,” on May 23, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887323336104578501552642287218.html?KEYWORDS=articles+by+jon+hilsenrath), analyzes discrepancies in communication by the Fed. The annotated chart of values of the Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) during trading on May 23, 2013 provided by Hinselrath, links the prepared testimony of Chairman Bernanke at 10:AM, following questions and answers and the release of the minutes of the FOMC at 2PM. Financial markets strengthened between 10 and 10:30AM on May 23, 2013, perhaps because of the statement by Chairman Bernanke in prepared testimony (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/bernanke20130522a.htm):
“A premature tightening of monetary policy could lead interest rates to rise temporarily but would also carry a substantial risk of slowing or ending the economic recovery and causing inflation to fall further. Such outcomes tend to be associated with extended periods of lower, not higher, interest rates, as well as poor returns on other assets. Moreover, renewed economic weakness would pose its own risks to financial stability.”
In that testimony, Chairman Bernanke (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/testimony/bernanke20130522a.htm) also analyzes current weakness of labor markets:
“Despite this improvement, the job market remains weak overall: The unemployment rate is still well above its longer-run normal level, rates of long-term unemployment are historically high, and the labor force participation rate has continued to move down. Moreover, nearly 8 million people are working part time even though they would prefer full-time work. High rates of unemployment and underemployment are extraordinarily costly: Not only do they impose hardships on the affected individuals and their families, they also damage the productive potential of the economy as a whole by eroding workers' skills and--particularly relevant during this commencement season--by preventing many young people from gaining workplace skills and experience in the first place. The loss of output and earnings associated with high unemployment also reduces government revenues and increases spending on income-support programs, thereby leading to larger budget deficits and higher levels of public debt than would otherwise occur.”
Hilsenrath (op. cit. http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887323336104578501552642287218.html?KEYWORDS=articles+by+jon+hilsenrath) analyzes the subsequent decline of the market from 10:30AM to 10:40AM as Chairman Bernanke responded questions with the statement that withdrawal of stimulus would be determined by data but that it could begin in one of the “next few meetings.” The DJIA recovered part of the losses between 10:40AM and 2PM. The minutes of the FOMC released at 2PM on May 23, 2013, contained a phrase that troubled market participants (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/fomcminutes20130501.htm): “A number of participants expressed willingness to adjust the flow of purchases downward as early as the June meeting if the economic information received by that time showed evidence of sufficiently strong and sustained growth; however, views differed about what evidence would be necessary and the likelihood of that outcome.” The DJIA closed at 15,387.58 on May 21, 2013 and fell to 15,307.17 at the close on May 22, 2013, with the loss of 0.5 percent occurring after release of the minutes of the FOMC at 2PM when the DJIA stood at around 15,400. The concern about exist of the Fed from stimulus affected markets worldwide as shown in declines of equity indexes in Table III-1 with delays because of differences in trading hours. This behavior shows the trap of unconventional monetary policy with no exit from zero interest rates without risking financial crash and likely adverse repercussions on economic activity.
Financial markets worldwide were affected by the reduction of policy rates of the European Central Bank (ECB) on May 2, 2013. (http://www.ecb.int/press/pr/date/2013/html/pr130502.en.html):
“2 May 2013 - Monetary policy decisions
At today’s meeting, which was held in Bratislava, the Governing Council of the ECB took the following monetary policy decisions:
- The interest rate on the main refinancing operations of the Eurosystem will be decreased by 25 basis points to 0.50%, starting from the operation to be settled on 8 May 2013.
- The interest rate on the marginal lending facility will be decreased by 50 basis points to 1.00%, with effect from 8 May 2013.
- The interest rate on the deposit facility will remain unchanged at 0.00%.”
Financial markets in Japan and worldwide were shocked by new bold measures of “quantitative and qualitative monetary easing” by the Bank of Japan (http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2013/k130404a.pdf). The objective of policy is to “achieve the price stability target of 2 percent in terms of the year-on-year rate of change in the consumer price index (CPI) at the earliest possible time, with a time horizon of about two years” (http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2013/k130404a.pdf). The main elements of the new policy are as follows:
- Monetary Base Control. Most central banks in the world pursue interest rates instead of monetary aggregates, injecting bank reserves to lower interest rates to desired levels. The Bank of Japan (BOJ) has shifted back to monetary aggregates, conducting money market operations with the objective of increasing base money, or monetary liabilities of the government, at the annual rate of 60 to 70 trillion yen. The BOJ estimates base money outstanding at “138 trillion yen at end-2012) and plans to increase it to “200 trillion yen at end-2012 and 270 trillion yen at end 2014” (http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2013/k130404a.pdf).
- Maturity Extension of Purchases of Japanese Government Bonds. Purchases of bonds will be extended even up to bonds with maturity of 40 years with the guideline of extending the average maturity of BOJ bond purchases from three to seven years. The BOJ estimates the current average maturity of Japanese government bonds (JGB) at around seven years. The BOJ plans to purchase about 7.5 trillion yen per month (http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2013/rel130404d.pdf). Takashi Nakamichi, Tatsuo Ito and Phred Dvorak, wiring on “Bank of Japan mounts bid for revival,” on Apr 4, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887323646604578401633067110420.html), find that the limit of maturities of three years on purchases of JGBs was designed to avoid views that the BOJ would finance uncontrolled government deficits.
- Seigniorage. The BOJ is pursuing coordination with the government that will take measures to establish “sustainable fiscal structure with a view to ensuring the credibility of fiscal management” (http://www.boj.or.jp/en/announcements/release_2013/k130404a.pdf).
- Diversification of Asset Purchases. The BOJ will engage in transactions of exchange traded funds (ETF) and real estate investment trusts (REITS) and not solely on purchases of JGBs. Purchases of ETFs will be at an annual rate of increase of one trillion yen and purchases of REITS at 30 billion yen.
The European sovereign debt crisis continues to shake financial markets and the world economy. Debt resolution within the international financial architecture requires that a country be capable of borrowing on its own from the private sector. Mechanisms of debt resolution have included participation of the private sector (PSI), or “bail in,” that has been voluntary, almost coercive, agreed and outright coercive (Pelaez and Pelaez, International Financial Architecture: G7, IMF, BIS, Creditors and Debtors (2005), Chapter 4, 187-202). Private sector involvement requires losses by the private sector in bailouts of highly indebted countries. The essence of successful private sector involvement is to recover private-sector credit of the highly indebted country. Mary Watkins, writing on “Bank bailouts reshuffle risk hierarchy,” published on Mar 19, 2013, in the Financial Times (http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/7666546a-9095-11e2-a456-00144feabdc0.html#axzz2OSpbvCn8) analyzes the impact of the bailout or resolution of Cyprus banks on the hierarchy of risks of bank liabilities. Cyprus banks depend mostly on deposits with less reliance on debt, raising concerns in creditors of fixed-income debt and equity holders in banks in the euro area. Uncertainty remains as to the dimensions and structure of losses in private sector involvement or “bail in” in other rescue programs in the euro area. Alkman Granitsas, writing on “Central bank details losses at Bank of Cyprus,” on Mar 30, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887324000704578392502889560768.html), analyzes the impact of the agreement with the €10 billion agreement with IMF and the European Union on the banks of Cyprus. The recapitalization plan provides for immediate conversion of 37.5 percent of all deposits in excess of €100,000 to shares of special class of the bank. An additional 22.5 percent will be frozen without interest until the plan is completed. The overwhelming risk factor is the unsustainable Treasury deficit/debt of the United States (http://cmpassocregulationblog.blogspot.com/2013/02/united-states-unsustainable-fiscal.html). Another rising risk is division within the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) on risks and benefits of current policies as expressed in the minutes of the meeting held on Jan 29-30, 2013 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/monetarypolicy/files/fomcminutes20130130.pdf 13):
“However, many participants also expressed some concerns about potential costs and risks arising from further asset purchases. Several participants discussed the possible complications that additional purchases could cause for the eventual withdrawal of policy accommodation, a few mentioned the prospect of inflationary risks, and some noted that further asset purchases could foster market behavior that could undermine financial stability. Several participants noted that a very large portfolio of long-duration assets would, under certain circumstances, expose the Federal Reserve to significant capital losses when these holdings were unwound, but others pointed to offsetting factors and one noted that losses would not impede the effective operation of monetary policy.
Jon Hilsenrath, writing on “Fed maps exit from stimulus,” on May 11, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887324744104578475273101471896.html?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection), analyzes the development of strategy for unwinding quantitative easing and how it can create uncertainty in financial markets. Jon Hilsenrath and Victoria McGrane, writing on “Fed slip over how long to keep cash spigot open,” published on Feb 20, 2013 in the Wall street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887323511804578298121033876536.html), analyze the minutes of the Fed, comments by members of the FOMC and data showing increase in holdings of riskier debt by investors, record issuance of junk bonds, mortgage securities and corporate loans.
Jon Hilsenrath, writing on “Jobs upturn isn’t enough to satisfy Fed,” on Mar 8, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887324582804578348293647760204.html), finds that much stronger labor market conditions are required for the Fed to end quantitative easing. Unconventional monetary policy with zero interest rates and quantitative easing is quite difficult to unwind because of the adverse effects of raising interest rates on valuations of risk financial assets and home prices, including the very own valuation of the securities held outright in the Fed balance sheet. Gradual unwinding of 1 percent fed funds rates from Jun 2003 to Jun 2004 by seventeen consecutive increases of 25 percentage points from Jun 2004 to Jun 2006 to reach 5.25 percent caused default of subprime mortgages and adjustable-rate mortgages linked to the overnight fed funds rate. The zero interest rate has penalized liquidity and increased risks by inducing carry trades from zero interest rates to speculative positions in risk financial assets. There is no exit from zero interest rates without provoking another financial crash.
An important risk event is the reduction of growth prospects in the euro zone discussed by European Central Bank President Mario Draghi in “Introductory statement to the press conference,” on Dec 6, 2012 (http://www.ecb.int/press/pressconf/2012/html/is121206.en.html):
“This assessment is reflected in the December 2012 Eurosystem staff macroeconomic projections for the euro area, which foresee annual real GDP growth in a range between -0.6% and -0.4% for 2012, between -0.9% and 0.3% for 2013 and between 0.2% and 2.2% for 2014. Compared with the September 2012 ECB staff macroeconomic projections, the ranges for 2012 and 2013 have been revised downwards.
The Governing Council continues to see downside risks to the economic outlook for the euro area. These are mainly related to uncertainties about the resolution of sovereign debt and governance issues in the euro area, geopolitical issues and fiscal policy decisions in the United States possibly dampening sentiment for longer than currently assumed and delaying further the recovery of private investment, employment and consumption.”
Reuters, writing on “Bundesbank cuts German growth forecast,” on Dec 7, 2012, published in the Financial Times (http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/8e845114-4045-11e2-8f90-00144feabdc0.html#axzz2EMQxzs3u), informs that the central bank of Germany, Deutsche Bundesbank reduced its forecast of growth for the economy of Germany to 0.7 percent in 2012 from an earlier forecast of 1.0 percent in Jun and to 0.4 percent in 2012 from an earlier forecast of 1.6 percent while the forecast for 2014 is at 1.9 percent.
The major risk event during earlier weeks was sharp decline of sovereign yields with the yield on the ten-year bond of Spain falling to 5.309 percent and that of the ten-year bond of Italy falling to 4.473 percent on Fri Nov 30, 2012 and 5.366 percent for the ten-year of Spain and 4.527 percent for the ten-year of Italy on Fri Nov 14, 2012 (http://professional.wsj.com/mdc/public/page/marketsdata.html?mod=WSJ_PRO_hps_marketdata). Vanessa Mock and Frances Robinson, writing on “EU approves Spanish bank’s restructuring plans,” on Nov 28, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887323751104578146520774638316.html?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection), inform that the European Union regulators approved restructuring of four Spanish banks (Bankia, NCG Banco, Catalunya Banc and Banco de Valencia), which helped to calm sovereign debt markets. Harriet Torry and James Angelo, writing on “Germany approves Greek aid,” on Nov 30, 2012, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887323751104578150532603095790.html?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection), inform that the German parliament approved the plan to provide Greece a tranche of €44 billion in promised financial support, which is subject to sustainability analysis of the bond repurchase program later in Dec 2012. A hurdle for sustainability of repurchasing debt is that Greece’s sovereign bonds have appreciated significantly from around 24 percent for the bond maturing in 21 years and 20 percent for the bond maturing in 31 years in Aug 2012 to around 17 percent for the 21-year maturity and 15 percent for the 31-year maturing in Nov 2012. Declining years are equivalent to increasing prices, making the repurchase more expensive. Debt repurchase is intended to reduce bonds in circulation, turning Greek debt more manageable. Ben McLannahan, writing on “Japan unveils $11bn stimulus package,” on Nov 30, 2012, published in the Financial Times (http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/adc0569a-3aa5-11e2-baac-00144feabdc0.html#axzz2DibFFquN), informs that the cabinet in Japan approved another stimulus program of $11 billion, which is twice larger than another stimulus plan in late Oct and close to elections in Dec. Henry Sender, writing on “Tokyo faces weak yen and high bond yields,” published on Nov 29, 2012 in the Financial Times (http://www.ft.com/intl/cms/s/0/9a7178d0-393d-11e2-afa8-00144feabdc0.html#axzz2DibFFquN), analyzes concerns of regulators on duration of bond holdings in an environment of likelihood of increasing yields and yen depreciation.
First, Risk-Determining Events. The European Council statement on Nov 23, 2012 asked the President of the European Commission “to continue the work and pursue consultations in the coming weeks to find a consensus among the 27 over the Union’s Multiannual Financial Framework for the period 2014-2020” (http://www.consilium.europa.eu/uedocs/cms_Data/docs/pressdata/en/ec/133723.pdf) Discussions will continue in the effort to reach agreement on a budget: “A European budget is important for the cohesion of the Union and for jobs and growth in all our countries” (http://www.consilium.europa.eu/uedocs/cms_Data/docs/pressdata/en/ec/133723.pdf). There is disagreement between the group of countries requiring financial assistance and those providing bailout funds. Gabrielle Steinhauser and Costas Paris, writing on “Greek bond rally puts buyback in doubt,” on Nov 23, 2012, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887324352004578136362599130992.html?mg=reno64-wsj) find a new hurdle in rising prices of Greek sovereign debt that may make more difficult buybacks of debt held by investors. European finance ministers continue their efforts to reach an agreement for Greece that meets with approval of the European Central Bank and the IMF. The European Council (2012Oct19 http://www.consilium.europa.eu/uedocs/cms_data/docs/pressdata/en/ec/133004.pdf ) reached conclusions on strengthening the euro area and providing unified financial supervision:
“The European Council called for work to proceed on the proposals on the Single Supervisory Mechanism as a matter of priority with the objective of agreeing on the legislative framework by 1st January 2013 and agreed on a number of orientations to that end. It also took note of issues relating to the integrated budgetary and economic policy frameworks and democratic legitimacy and accountability which should be further explored. It agreed that the process towards deeper economic and monetary union should build on the EU's institutional and legal framework and be characterised by openness and transparency towards non-euro area Member States and respect for the integrity of the Single Market. It looked forward to a specific and time-bound roadmap to be presented at its December 2012 meeting, so that it can move ahead on all essential building blocks on which a genuine EMU should be based.”
Buiter (2012Oct15) finds that resolution of the euro crisis requires full banking union together with restructuring the sovereign debt of at least four and possibly total seven European countries. The Bank of Spain released new data on doubtful debtors in Spain’s credit institutions (http://www.bde.es/bde/en/secciones/prensa/Agenda/Datos_de_credit_a6cd708c59cf931.html). In 2006, the value of doubtful credits reached €10,859 million or 0.7 percent of total credit of €1,508,626 million. In Aug 2012, doubtful credit reached €178,579 million or 10.5 percent of total credit of €1,698,714 million.
There are three critical factors influencing world financial markets. (1) Spain could request formal bailout from the European Stability Mechanism (ESM) that may also affect Italy’s international borrowing. David Roman and Jonathan House, writing on “Spain risks backlash with budget plan,” on Sep 27, 2012, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10000872396390443916104578021692765950384.html?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection) analyze Spain’s proposal of reducing government expenditures by €13 billion, or around $16.7 billion, increasing taxes in 2013, establishing limits on early retirement and cutting the deficit by €65 billion through 2014. Banco de España, Bank of Spain, contracted consulting company Oliver Wyman to conduct rigorous stress tests of the resilience of its banking system. (Stress tests and their use are analyzed by Pelaez and Pelaez Globalization and the State Vol. I (2008b), 95-100, International Financial Architecture (2005) 112-6, 123-4, 130-3).) The results are available from Banco de España (http://www.bde.es/bde/en/secciones/prensa/infointeres/reestructuracion/ http://www.bde.es/f/webbde/SSICOM/20120928/informe_ow280912e.pdf). The assumptions of the adverse scenario used by Oliver Wyman are quite tough for the three-year period from 2012 to 2014: “6.5 percent cumulative decline of GDP, unemployment rising to 27.2 percent and further declines of 25 percent of house prices and 60 percent of land prices (http://www.bde.es/f/webbde/SSICOM/20120928/informe_ow280912e.pdf). Fourteen banks were stress tested with capital needs estimates of seven banks totaling €59.3 billion. The three largest banks of Spain, Banco Santander (http://www.santander.com/csgs/Satellite/CFWCSancomQP01/es_ES/Corporativo.html), BBVA (http://www.bbva.com/TLBB/tlbb/jsp/ing/home/index.jsp) and Caixabank (http://www.caixabank.com/index_en.html), with 43 percent of exposure under analysis, have excess capital of €37 billion in the adverse scenario in contradiction with theories that large, international banks are necessarily riskier. Jonathan House, writing on “Spain expects wider deficit on bank aid,” on Sep 30, 2012, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10000872396390444138104578028484168511130.html?mod=WSJPRO_hpp_LEFTTopStories), analyzes the 2013 budget plan of Spain that will increase the deficit of 7.4 percent of GDP in 2012, which is above the target of 6.3 percent under commitment with the European Union. The ratio of debt to GDP will increase to 85.3 percent in 2012 and 90.5 percent in 2013 while the 27 members of the European Union have an average debt/GDP ratio of 83 percent at the end of IIQ2012. (2) Symmetric inflation targets appear to have been abandoned in favor of a self-imposed single jobs mandate of easing monetary policy even after the economy grows again at or close to potential output. Monetary easing by unconventional measures is now apparently open ended in perpetuity as provided in the statement of the meeting of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) on Sep 13, 2012 (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/press/monetary/20120913a.htm):
“To support a stronger economic recovery and to help ensure that inflation, over time, is at the rate most consistent with its dual mandate, the Committee agreed today to increase policy accommodation by purchasing additional agency mortgage-backed securities at a pace of $40 billion per month. The Committee also will continue through the end of the year its program to extend the average maturity of its holdings of securities as announced in June, and it is maintaining its existing policy of reinvesting principal payments from its holdings of agency debt and agency mortgage-backed securities in agency mortgage-backed securities. These actions, which together will increase the Committee’s holdings of longer-term securities by about $85 billion each month through the end of the year, should put downward pressure on longer-term interest rates, support mortgage markets, and help to make broader financial conditions more accommodative.
To support continued progress toward maximum employment and price stability, the Committee expects that a highly accommodative stance of monetary policy will remain appropriate for a considerable time after the economic recovery strengthens.”
In fact, it is evident to the public that this policy will be abandoned if inflation costs rise. There is the concern of the production and employment costs of controlling future inflation.
(2) The European Central Bank (ECB) approved a new program of bond purchases under the name “Outright Monetary Transactions” (OMT). The ECB will purchase sovereign bonds of euro zone member countries that have a program of conditionality under the European Financial Stability Facility (EFSF) that is converting into the European Stability Mechanism (ESM). These programs provide enhancing the solvency of member countries in a transition period of structural reforms and fiscal adjustment. The purchase of bonds by the ECB would maintain debt costs of sovereigns at sufficiently low levels to permit adjustment under the EFSF/ESM programs. Purchases of bonds are not limited quantitatively with discretion by the ECB as to how much is necessary to support countries with adjustment programs. Another feature of the OMT of the ECB is sterilization of bond purchases: funds injected to pay for the bonds would be withdrawn or sterilized by ECB transactions. The statement by the European Central Bank on the program of OTM is as follows (http://www.ecb.int/press/pr/date/2012/html/pr120906_1.en.html):
“6 September 2012 - Technical features of Outright Monetary Transactions
As announced on 2 August 2012, the Governing Council of the European Central Bank (ECB) has today taken decisions on a number of technical features regarding the Eurosystem’s outright transactions in secondary sovereign bond markets that aim at safeguarding an appropriate monetary policy transmission and the singleness of the monetary policy. These will be known as Outright Monetary Transactions (OMTs) and will be conducted within the following framework:
Conditionality
A necessary condition for Outright Monetary Transactions is strict and effective conditionality attached to an appropriate European Financial Stability Facility/European Stability Mechanism (EFSF/ESM) programme. Such programmes can take the form of a full EFSF/ESM macroeconomic adjustment programme or a precautionary programme (Enhanced Conditions Credit Line), provided that they include the possibility of EFSF/ESM primary market purchases. The involvement of the IMF shall also be sought for the design of the country-specific conditionality and the monitoring of such a programme.
The Governing Council will consider Outright Monetary Transactions to the extent that they are warranted from a monetary policy perspective as long as programme conditionality is fully respected, and terminate them once their objectives are achieved or when there is non-compliance with the macroeconomic adjustment or precautionary programme.
Following a thorough assessment, the Governing Council will decide on the start, continuation and suspension of Outright Monetary Transactions in full discretion and acting in accordance with its monetary policy mandate.
Coverage
Outright Monetary Transactions will be considered for future cases of EFSF/ESM macroeconomic adjustment programmes or precautionary programmes as specified above. They may also be considered for Member States currently under a macroeconomic adjustment programme when they will be regaining bond market access.
Transactions will be focused on the shorter part of the yield curve, and in particular on sovereign bonds with a maturity of between one and three years.
No ex ante quantitative limits are set on the size of Outright Monetary Transactions.
Creditor treatment
The Eurosystem intends to clarify in the legal act concerning Outright Monetary Transactions that it accepts the same (pari passu) treatment as private or other creditors with respect to bonds issued by euro area countries and purchased by the Eurosystem through Outright Monetary Transactions, in accordance with the terms of such bonds.
Sterilisation
The liquidity created through Outright Monetary Transactions will be fully sterilised.
Transparency
Aggregate Outright Monetary Transaction holdings and their market values will be published on a weekly basis. Publication of the average duration of Outright Monetary Transaction holdings and the breakdown by country will take place on a monthly basis.
Securities Markets Programme
Following today’s decision on Outright Monetary Transactions, the Securities Markets Programme (SMP) is herewith terminated. The liquidity injected through the SMP will continue to be absorbed as in the past, and the existing securities in the SMP portfolio will be held to maturity.”
Jon Hilsenrath, writing on “Fed sets stage for stimulus,” on Aug 31, 2012, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10000872396390443864204577623220212805132.html?mod=WSJ_hp_LEFTWhatsNewsCollection), analyzes the essay presented by Chairman Bernanke at the Jackson Hole meeting of central bankers, as defending past stimulus with unconventional measures of monetary policy that could be used to reduce extremely high unemployment. Chairman Bernanke (2012JHAug31, 18-9) does support further unconventional monetary policy impulses if required by economic conditions (http://www.federalreserve.gov/newsevents/speech/bernanke20120831a.htm):
“Over the past five years, the Federal Reserve has acted to support economic growth and foster job creation, and it is important to achieve further progress, particularly in the labor market. Taking due account of the uncertainties and limits of its policy tools, the Federal Reserve will provide additional policy accommodation as needed to promote a stronger economic recovery and sustained improvement in labor market conditions in a context of price stability.”
Professor John H Cochrane (2012Aug31), at the University of Chicago Booth School of Business, writing on “The Federal Reserve: from central bank to central planner,” on Aug 31, 2012, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10000872396390444812704577609384030304936.html?mod=WSJ_hps_sections_opinion), analyzes that the departure of central banks from open market operations into purchase of assets with risks to taxpayers and direct allocation of credit subject to political influence has caused them to abandon their political independence and accountability. Cochrane (2012Aug31) finds a return to the proposition of Milton Friedman in the 1960s that central banks can cause inflation and macroeconomic instability.
Mario Draghi (2012Aug29), President of the European Central Bank, also reiterated the need of exceptional and unconventional central bank policies (http://www.ecb.int/press/key/date/2012/html/sp120829.en.html):
“Yet it should be understood that fulfilling our mandate sometimes requires us to go beyond standard monetary policy tools. When markets are fragmented or influenced by irrational fears, our monetary policy signals do not reach citizens evenly across the euro area. We have to fix such blockages to ensure a single monetary policy and therefore price stability for all euro area citizens. This may at times require exceptional measures. But this is our responsibility as the central bank of the euro area as a whole.
The ECB is not a political institution. But it is committed to its responsibilities as an institution of the European Union. As such, we never lose sight of our mission to guarantee a strong and stable currency. The banknotes that we issue bear the European flag and are a powerful symbol of European identity.”
Buiter (2011Oct31) analyzes that the European Financial Stability Fund (EFSF) would need a “bigger bazooka” to bail out euro members in difficulties that could possibly be provided by the ECB. Buiter (2012Oct15) finds that resolution of the euro crisis requires full banking union together with restructuring the sovereign debt of at least four and possibly total seven European countries. Table III-7 in IIIE Appendix Euro Zone Survival Risk below provides the combined GDP in 2012 of the highly indebted euro zone members estimated in the latest World Economic Outlook of the IMF at $4167 billion or 33.1 percent of total euro zone GDP of $12,586 billion. Using the WEO of the IMF, Table III-8 in IIIE Appendix Euro Zone Survival Risk below provides debt of the highly indebted euro zone members at $3927.8 billion in 2012 that increases to $5809.9 billion when adding Germany’s debt, corresponding to 167.0 percent of Germany’s GDP. There are additional sources of debt in bailing out banks. The dimensions of the problem may require more firepower than a bazooka perhaps that of the largest conventional bomb of all times of 44,000 pounds experimentally detonated only once by the US in 1948 (http://www.airpower.au.af.mil/airchronicles/aureview/1967/mar-apr/coker.html).
Chart III-1A of the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System provides the ten-year, two-year and one-month Treasury constant maturity yields together with the overnight fed funds rate, and the yield of the corporate bond with Moody’s rating of Baa. The riskier yield of the Baa corporate bond exceeds the relatively riskless yields of the Treasury securities. The beginning yields in Chart III-1A for Jan 2, 1962, are 2.75 percent for the fed fund rates and 4.06 percent for the ten-year Treasury constant maturity. On July 31, 2001, the yields in Chart III-1A are 3.67 percent for one month, 3.79 percent for two years, 5.07 percent for ten years, 3.82 percent for the fed funds rate and 7.85 percent for the Baa corporate bond. On July 30, 2007, yields inverted with the one-month at 4.95 percent, the two-year at 4.59 percent and the ten-year at 5.82 percent with the yield of the Baa corporate bond at 6.70 percent. Another interesting point is for Oct 31, 2008, with the yield of the Baa jumping to 9.54 percent and the Treasury yields declining: one month 0.12 percent, two years 1.56 percent and ten years 4.01 percent during a flight to the dollar and government securities analyzed by Cochrane and Zingales (2009). Another spike in the series is for Apr 4, 2006 with the yield of the corporate Baa bond at 8.63 and the Treasury yields of 0.12 percent for one month, 0.94 for two years and 2.95 percent for ten years. During the beginning of the flight from risk financial assets to US government securities (see Cochrane and Zingales 2009), the one-month yield was 0.07 percent, the two-year yield 1.64 percent and the ten-year yield 3.41. The combination of zero fed funds rate and quantitative easing caused sharp decline of the yields from 2008 and 2009. Yield declines have also occurred during periods of financial risk aversion, including the current one of stress of financial markets in Europe. The final point of Chart III1-A is for Aug 7, 2014, with the one-month yield at 0.03 percent, the two-year at 0.44 percent, the ten-year at 2.43 percent, the fed funds rate at 0.09 percent and the corporate Baa bond at 4.71 percent. There is an evident increase in the yields of the 10-year Treasury constant maturity and the Moody’s Baa corporate bond with subsequent decline in wide swings of portfolio reallocations.
Chart III-1A, US, Ten-Year, Two-Year and One-Month Treasury Constant Maturity Yields, Overnight Fed Funds Rate and Yield of Moody’s Baa Corporate Bond, Jan 2, 1962-Aug 7, 2014
Note: US Recessions in shaded areas
Source: Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System
http://www.federalreserve.gov/releases/h15
Tom Lauricella, writing on Mar 31, 2014, on “Stock investors see hints of a stronger quarter,” published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/news/articles/SB10001424052702304157204579473513864900656?mod=WSJ_smq0314_LeadStory&mg=reno64-wsj), finds views of stronger earnings among many money managers with positive factors for equity markets in continuing low interest rates and US economic growth. There is important information in the Quarterly Markets review of the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/public/page/quarterly-markets-review-03312014.html) for IQ2014. Alexandra Scaggs, writing on “Tepid profits, roaring stocks,” on May 16, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://online.wsj.com/article/SB10001424127887323398204578487460105747412.html), analyzes stabilization of earnings growth: 70 percent of 458 reporting companies in the S&P 500 stock index reported earnings above forecasts but sales fell 0.2 percent relative to forecasts of increase of 0.5 percent. Paul Vigna, writing on “Earnings are a margin story but for how long,” on May 17, 2013, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://blogs.wsj.com/moneybeat/2013/05/17/earnings-are-a-margin-story-but-for-how-long/), analyzes that corporate profits increase with stagnating sales while companies manage costs tightly. More than 90 percent of S&P components reported moderate increase of earnings of 3.7 percent in IQ2013 relative to IQ2012 with decline of sales of 0.2 percent. Earnings and sales have been in declining trend. In IVQ2009, growth of earnings reached 104 percent and sales jumped 13 percent. Net margins reached 8.92 percent in IQ2013, which is almost the same at 8.95 percent in IIIQ2006. Operating margins are 9.58 percent. There is concern by market participants that reversion of margins to the mean could exert pressure on earnings unless there is more accelerated growth of sales. Vigna (op. cit.) finds sales growth limited by weak economic growth. Kate Linebaugh, writing on “Falling revenue dings stocks,” on Oct 20, 2012, published in the Wall Street Journal (http://professional.wsj.com/article/SB10000872396390444592704578066933466076070.html?mod=WSJPRO_hpp_LEFTTopStories), identifies a key financial vulnerability: falling revenues across markets for United States reporting companies. Global economic slowdown is reducing corporate sales and squeezing corporate strategies. Linebaugh quotes data from Thomson Reuters that 100 companies of the S&P 500 index have reported declining revenue only 1 percent higher in Jun-Sep 2012 relative to Jun-Sep 2011 but about 60 percent of the companies are reporting lower sales than expected by analysts with expectation that revenue for the S&P 500 will be lower in Jun-Sep 2012 for the entities represented in the index. Results of US companies are likely repeated worldwide. Future company cash flows derive from investment projects. In IQ1980, real gross private domestic investment in the US was $951.6 billion of chained 2009 dollars, growing to $1,254.6 billion in IVQ1987 or 31.8 percent. Real gross private domestic investment in the US increased 3.3 percent from $2,605.2 billion of chained 2009 dollars in IVQ2007 to $2,691.8 billion in IIQ2014, which is stagnation in comparison with growth of 31.8 percent in the comparable first twenty quarters of expansion from IQ1983 to IVQ1987. Real private fixed investment fell 0.5 percent from $2,586.3 billion of chained 2009 dollars in IVQ2007 to $2,572.7 billion in IIQ2014. Growth of real private investment is mediocre for all but four quarters from IIQ2011 to IQ2012 (Section I).
The investment decision of United States corporations has been fractured in the current economic cycle in preference of cash. Undistributed corporate profits swelled 294.4 percent from $107.7 billion in IQ2007 to $424.8 billion in IQ2014 and changed signs from minus $55.9 billion in current dollars in IVQ2007. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA fell $26.6 billion in IQ2013 after increasing $34.9 billion in IVQ2012 and $13.9 billion in IIIQ2012. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA rebounded with $66.8 billion in IIQ2013 and $39.2 billion in IIIQ2013. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased $47.1 billion in IVQ2013. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA fell $198.3 billion in IQ2014. Profits after tax with IVA and CCA fell $1.7 billion in IQ2013 after increasing $40.8 billion in IVQ2012 and $4.5 billion in IIIQ2012. In IIQ2013, profits after tax with IVA and CCA increased $56.9 billion and $39.5 billion in IIIQ2013. In IVQ2013, profits after tax with IVA and CCA increased $33.8 billion. Profits after tax with IVA and CCA fell at $226.0 billion in IQ2014. Anticipation of higher taxes in the “fiscal cliff” episode caused increase of $120.9 billion in net dividends in IVQ2012 followed with adjustment in the form of decrease of net dividends by $103.8 billion in IQ2013, rebounding with $273.5 billion in IIQ2013. Net dividends fell at $179.0 billion in IIIQ2013 and increased at $90.5 billion in IVQ2013. Net dividends fell at $87.1 billion in IQ2014. There is similar decrease of $80.1 billion in undistributed profits with IVA and CCA in IVQ2012 followed by increase of $102.1 billion in IQ2013 and decline of $216.6 billion in IIQ2013. Undistributed profits with IVA and CCA rose at $218.6 billion in IIIQ2013 and fell at $56.7 billion in IVQ2013. Undistributed corporate profits swelled 294.4 percent from $107.7 billion in IQ2007 to $424.8 billion in IQ2014 and changed signs from minus $55.9 billion in current dollars in IVQ2007 (Section IA2). In IQ2013, corporate profits with inventory valuation and capital consumption adjustment fell $26.6 billion relative to IVQ2012, from $2047.2 billion to $2020.6 billion at the quarterly rate of minus 1.3 percent. In IIQ2013, corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased $66.8 billion from $2020.6 billion in IQ2013 to $2087.4 billion at the SAAR of 3.3 percent. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased $39.2 billion from $2087.4 billion in IIQ2013 to $2126.6 billion in IIIQ2013 at the SAAR of 1.9 percent. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA increased at $47.1 billion in IVQ2013 from $2126.6 billion in IIIQ2013 to $2173.7 billion in IVQ2013 at the SAAR of 2.2 percent. Corporate profits with IVA and CCA fell at $198.3 billion from $2173.7 billion in IVQ2013 to $1975.4 billion in IQ2014 at the SAAR of minus 9.1 percent (http://www.bea.gov/newsreleases/national/gdp/2014/pdf/gdp1q14_2nd.pdf). The investment decision of US business is fractured. The basic valuation equation that is also used in capital budgeting postulates that the value of stocks or of an investment project is given by:
Where Rτ is expected revenue in the time horizon from τ =1 to T; Cτ denotes costs; and ρ is an appropriate rate of discount. In words, the value today of a stock or investment project is the net revenue, or revenue less costs, in the investment period from τ =1 to T discounted to the present by an appropriate rate of discount. In the current weak economy, revenues have been increasing more slowly than anticipated in investment plans. An increase in interest rates would affect discount rates used in calculations of present value, resulting in frustration of investment decisions. If V represents value of the stock or investment project, as ρ → ∞, meaning that interest rates increase without bound, then V → 0, or
declines. Equally, decline in expected revenue from the stock or project, Rτ, causes decline in valuation.
There is mixed performance in equity indexes with several indexes in Table III-1 decreasing in the week ending on Aug 1, 2014, after wide swings caused by reallocations of investment portfolios worldwide. Stagnating revenues, corporate cash hoarding and declining investment are causing reevaluation of discounted net earnings with deteriorating views on the world economy and United States fiscal sustainability but investors have been driving indexes higher. DJIA increased 1.1 percent on Aug 8, increasing 0.4 percent in the week. Germany’s DAX decreased 0.3 percent on Aug 8 and decreased 2.2 percent in the week. Dow Global increased 0.2 percent on Aug 8 and decreased 1.1 percent in the week. Japan’s Nikkei Average decreased 3.0 percent on Aug 8 and decreased 4.8 percent in the week as the yen continues oscillating but relatively weaker and the stock market gains in expectations of success of fiscal stimulus by a new administration and monetary stimulus by a new board of the Bank of Japan. Dow Asia Pacific TSM decreased 1.3 percent on Aug 8 and decreased 2.3 percent in the week. Shanghai Composite that decreased 0.2 percent on Mar 8 and decreased 1.7 percent in the week of Mar 8, falling below 2000 to close at 1980.13 on Fri Nov 30 but closing at 2194.42 on Aug 8 for increase of 0.3 percent and increase of 0.4 percent in the week of Aug 8. There is deceleration with oscillations of the world economy that could affect corporate revenue and equity valuations, causing fluctuations in equity markets with increases during favorable risk appetite.
Commodities were mixed in the week of Aug 8, 2014. Table III-1 shows that WTI decreased 0.2 percent in the week of Aug 8 while Brent increased 0.2 percent in the week with turmoil in the Middle East. Gold decreased 0.1 percent on Aug 8 and increased 1.2 percent in the week.
Table III-2 provides an update of the consolidated financial statement of the Eurosystem. The balance sheet has swollen with the long-term refinancing operations (LTROs). Line 5 “Lending to Euro Area Credit Institutions Related to Monetary Policy” increased from €546,747 million on Dec 31, 2010, to €879,130 million on Dec 28, 2011 and €533,535 million on Aug 1, 2014, with some repayment of loans already occurring. The sum of line 5 and line 7 (“Securities of Euro Area Residents Denominated in Euro”) has reached €1,090,344 million in the statement of Aug 1, 2014, with marginal reduction. There is high credit risk in these transactions with capital of only €95,311 million as analyzed by Cochrane (2012Aug31).
Table III-2, Consolidated Financial Statement of the Eurosystem, Million EUR
| Dec 31, 2010 | Dec 28, 2011 | Aug 1, 2014 | |
| 1 Gold and other Receivables | 367,402 | 419,822 | 334,432 |
| 2 Claims on Non Euro Area Residents Denominated in Foreign Currency | 223,995 | 236,826 | 248,462 |
| 3 Claims on Euro Area Residents Denominated in Foreign Currency | 26,941 | 95,355 | 24,897 |
| 4 Claims on Non-Euro Area Residents Denominated in Euro | 22,592 | 25,982 | 18,526 |
| 5 Lending to Euro Area Credit Institutions Related to Monetary Policy Operations Denominated in Euro | 546,747 | 879,130 | 533,535 |
| 6 Other Claims on Euro Area Credit Institutions Denominated in Euro | 45,654 | 94,989 | 74,200 |
| 7 Securities of Euro Area Residents Denominated in Euro | 457,427 | 610,629 | 556,809 |
| 8 General Government Debt Denominated in Euro | 34,954 | 33,928 | 26,705 |
| 9 Other Assets | 278,719 | 336,574 | 242,118 |
| TOTAL ASSETS | 2,004, 432 | 2,733,235 | 2,0059,683 |
| Memo Items | |||
| Sum of 5 and 7 | 1,004,174 | 1,489,759 | 1,090,344 |
| Capital and Reserves | 78,143 | 81,481 | 95,311 |
Source: European Central Bank
http://www.ecb.int/press/pr/wfs/2011/html/fs110105.en.html
http://www.ecb.int/press/pr/wfs/2011/html/fs111228.en.html
http://www.ecb.europa.eu/press/pr/wfs/2014/html/fs140805.en.html
IIIE Appendix Euro Zone Survival Risk. Resolution of the European sovereign debt crisis with survival of the euro area would require success in the restructuring of Italy. Growth of the Italian economy would assure that success. A critical problem is that the common euro currency prevents Italy from devaluing the exchange to parity or the exchange rate that would permit export growth to promote internal economic activity, which could generate fiscal revenues for primary fiscal surpluses that ensure creditworthiness.
Professors Ricardo Caballero and Francesco Giavazzi (2012Jan15) find that the resolution of the European sovereign crisis with survival of the euro area would require success in the restructuring of Italy. Growth of the Italian economy would ensure that success. A critical problem is that the common euro currency prevents Italy from devaluing the exchange rate to parity or the exchange rate that would permit export growth to promote internal economic activity, which could generate fiscal revenues for primary fiscal surpluses that ensure creditworthiness. Fiscal consolidation and restructuring are important but of long-term gestation. Immediate growth of the Italian economy would consolidate the resolution of the sovereign debt crisis. Caballero and Giavazzi (2012Jan15) argue that 55 percent of the exports of Italy are to countries outside the euro area such that devaluation of 15 percent would be effective in increasing export revenue. Newly available data in Table III-3 providing Italy’s trade with regions and countries supports the argument of Caballero and Giavazzi (2012Jan15). Italy’s exports to the European Monetary Union (EMU), or euro area, are only 39.8 percent of the total in May 2014. Exports to the non-European Union area with share of 46.3 percent in Italy’s total exports are growing at minus 5.2 percent in Jan-May 2014 relative to Jan-May 2013 while those to EMU are growing at minus 1.1 percent.
Table III-3, Italy, Exports and Imports by Regions and Countries, % Share and 12-Month ∆%
| May 2014 | Exports | ∆% Jan-May 2014/ Jan-May 2013 | Imports | ∆% Jan-May 2014/ Jan-May 2013 |
| EU | 53.7 | 4.1 | 55.3 | -0.2 |
| EMU 17 | 39.8 | 3.1 | 44.3 | -1.1 |
| France | 10.8 | -0.4 | 8.4 | -1.5 |
| Germany | 12.4 | 4.7 | 14.7 | 1.6 |
| Spain | 4.4 | 3.0 | 4.5 | 2.0 |
| UK | 5.0 | 6.6 | 2.7 | -1.0 |
| Non EU | 46.3 | -2.0 | 44.7 | -5.2 |
| Europe non EU | 13.0 | -9.9 | 12.1 | -6.4 |
| USA | 6.9 | 6.2 | 3.2 | 10.0 |
| China | 2.5 | 10.6 | 6.4 | 1.8 |
| OPEC | 6.0 | -7.3 | 8.1 | -32.4 |
| Total | 100.0 | 1.3 | 100.0 | -2.5 |
Notes: EU: European Union; EMU: European Monetary Union (euro zone)
Source: Istituto Nazionale di Statistica
http://www.istat.it/it/archivio/128657
Table III-4 provides Italy’s trade balance by regions and countries. Italy had trade deficit of €56 million with the 17 countries of the euro zone (EMU 17) in May 2014 and cumulative surplus of €570 million in Jan-May 2014. Depreciation to parity could permit greater competitiveness in improving the trade surplus of €1546 million in Jan-May 2014 with Europe non-European Union, the trade surplus of €6455 million with the US and the trade surplus with non-European Union of €7279 million in Jan-Apr 2014. There is significant rigidity in the trade deficits in Jan-May 2014 of €5554 million with China and €87 million with members of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC). Higher exports could drive economic growth in the economy of Italy that would permit less onerous adjustment of the country’s fiscal imbalances, raising the country’s credit rating.
Table III-4, Italy, Trade Balance by Regions and Countries, Millions of Euro
| Regions and Countries | Trade Balance May 2014 Millions of Euro | Trade Balance Cumulative Jan-May 2014 Millions of Euro |
| EU | 1,223 | 6,791 |
| EMU 17 | -56 | 570 |
| France | 1,070 | 5,212 |
| Germany | -313 | -1,469 |
| Spain | -16 | 423 |
| UK | 871 | 4,141 |
| Non EU | 2,453 | 7,279 |
| Europe non EU | 146 | 1,546 |
| USA | 1,995 | 6,455 |
| China | -1,065 | -5,554 |
| OPEC | 68 | -87 |
| Total | 3,676 | 14,070 |
Notes: EU: European Union; EMU: European Monetary Union (euro zone)
Source: Istituto Nazionale di Statistica
http://www.istat.it/it/archivio/128657
Growth rates of Italy’s trade and major products are in Table III-5 for the period Jan-May 2014 relative to Jan-May 2013. Growth rates of cumulative imports relative to a year earlier are negative for energy with minus 16.7 percent. Exports of durable goods grew 3.8 percent and exports of capital goods increased 4.8 percent. The higher rate of growth of exports of 1.3 percent in Jan-May 2014/Jan-May 2013 relative to that of imports of minus 2.5 percent may reflect weak demand in Italy with GDP declining during nine consecutive quarters from IIIQ2011 through IIIQ2013 together with softening commodity prices. GDP increased marginally 0.1 percent in IVQ2013 and fell 0.1 percent in IQ2014.
Table III-5, Italy, Exports and Imports % Share of Products in Total and ∆%
| Exports | Exports | Imports | Imports | |
| Consumer | 31.0 | 3.3 | 27.3 | 1.8 |
| Durable | 6.0 | 3.8 | 2.9 | 7.6 |
| Non-Durable | 25.1 | 3.2 | 24.4 | 1.1 |
| Capital Goods | 32.3 | 4.8 | 20.3 | 2.8 |
| Inter- | 32.3 | -1.5 | 32.5 | -0.6 |
| Energy | 4.4 | -15.8 | 19.9 | -16.7 |
| Total ex Energy | 95.6 | 2.1 | 80.1 | 1.0 |
| Total | 100.0 | 1.3 | 100.0 | -2.5 |
Note: % Share for 2012 total trade.
Source: Istituto Nazionale di Statistica
http://www.istat.it/it/archivio/128657
Table III-6 provides Italy’s trade balance by product categories in May 2014 and cumulative Jan-May 2014. Italy’s trade balance excluding energy, generated surplus of €7912 million in May 2014 and €33,161 million cumulative in Jan-May 2014 but the energy trade balance created deficit of €4237 million in May 2014 and cumulative €19,091 million in Jan-May 2014. The overall surplus in May 2014 was €3676 million with cumulative surplus of €14,070 million in Jan-May 2014. Italy has significant competitiveness in various economic activities in contrast with some other countries with debt difficulties.
Table III-6, Italy, Trade Balance by Product Categories, € Millions
| May 2014 | Cumulative Jan-May 2014 | |
| Consumer Goods | 1,811 | 9,006 |
| Durable | 1,135 | 5,190 |
| Nondurable | 676 | 3,816 |
| Capital Goods | 5,365 | 21,720 |
| Intermediate Goods | 736 | 2,435 |
| Energy | -4,237 | -19,091 |
| Total ex Energy | 7,912 | 33,161 |
| Total | 3,676 | 14,070 |
Source: Istituto Nazionale di Statistica
http://www.istat.it/it/archivio/128657
Brazil faced in the debt crisis of 1982 a more complex policy mix. Between 1977 and 1983, Brazil’s terms of trade, export prices relative to import prices, deteriorated 47 percent and 36 percent excluding oil (Pelaez 1987, 176-79; Pelaez 1986, 37-66; see Pelaez and Pelaez, The Global Recession Risk (2007), 178-87). Brazil had accumulated unsustainable foreign debt by borrowing to finance balance of payments deficits during the 1970s. Foreign lending virtually stopped. The German mark devalued strongly relative to the dollar such that Brazil’s products lost competitiveness in Germany and in multiple markets in competition with Germany. The resolution of the crisis was devaluation of the Brazilian currency by 30 percent relative to the dollar and subsequent maintenance of parity by monthly devaluation equal to inflation and indexing that resulted in financial stability by parity in external and internal interest rates avoiding capital flight. With a combination of declining imports, domestic import substitution and export growth, Brazil followed rapid growth in the US and grew out of the crisis with surprising GDP growth of 4.5 percent in 1984.
The euro zone faces a critical survival risk because several of its members may default on their sovereign obligations if not bailed out by the other members. The valuation equation of bonds is essential to understanding the stability of the euro area. An explanation is provided in this paragraph and readers interested in technical details are referred to the Subsection IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation. Contrary to the Wriston doctrine, investing in sovereign obligations is a credit decision. The value of a bond today is equal to the discounted value of future obligations of interest and principal until maturity. On Dec 30, 2011, the yield of the 2-year bond of the government of Greece was quoted around 100 percent. In contrast, the 2-year US Treasury note traded at 0.239 percent and the 10-year at 2.871 percent while the comparable 2-year government bond of Germany traded at 0.14 percent and the 10-year government bond of Germany traded at 1.83 percent. There is no need for sovereign ratings: the perceptions of investors are of relatively higher probability of default by Greece, defying Wriston (1982), and nil probability of default of the US Treasury and the German government. The essence of the sovereign credit decision is whether the sovereign will be able to finance new debt and refinance existing debt without interrupting service of interest and principal. Prices of sovereign bonds incorporate multiple anticipations such as inflation and liquidity premiums of long-term relative to short-term debt but also risk premiums on whether the sovereign’s debt can be managed as it increases without bound. The austerity measures of Italy are designed to increase the primary surplus, or government revenues less expenditures excluding interest, to ensure investors that Italy will have the fiscal strength to manage its debt exceeding 100 percent of GDP, which is the third largest in the world after the US and Japan. Appendix IIIE links the expectations on the primary surplus to the real current value of government monetary and fiscal obligations. As Blanchard (2011SepWEO) analyzes, fiscal consolidation to increase the primary surplus is facilitated by growth of the economy. Italy and the other indebted sovereigns in Europe face the dual challenge of increasing primary surpluses while maintaining growth of the economy (for the experience of Brazil in the debt crisis of 1982 see Pelaez 1986, 1987).
Much of the analysis and concern over the euro zone centers on the lack of credibility of the debt of a few countries while there is credibility of the debt of the euro zone as a whole. In practice, there is convergence in valuations and concerns toward the fact that there may not be credibility of the euro zone as a whole. The fluctuations of financial risk assets of members of the euro zone move together with risk aversion toward the countries with lack of debt credibility. This movement raises the need to consider analytically sovereign debt valuation of the euro zone as a whole in the essential analysis of whether the single-currency will survive without major changes.
Welfare economics considers the desirability of alternative states, which in this case would be evaluating the “value” of Germany (1) within and (2) outside the euro zone. Is the sum of the wealth of euro zone countries outside of the euro zone higher than the wealth of these countries maintaining the euro zone? On the choice of indicator of welfare, Hicks (1975, 324) argues:
“Partly as a result of the Keynesian revolution, but more (perhaps) because of statistical labours that were initially quite independent of it, the Social Product has now come right back into its old place. Modern economics—especially modern applied economics—is centered upon the Social Product, the Wealth of Nations, as it was in the days of Smith and Ricardo, but as it was not in the time that came between. So if modern theory is to be effective, if it is to deal with the questions which we in our time want to have answered, the size and growth of the Social Product are among the chief things with which it must concern itself. It is of course the objective Social Product on which attention must be fixed. We have indexes of production; we do not have—it is clear we cannot have—an Index of Welfare.”
If the burden of the debt of the euro zone falls on Germany and France or only on Germany, is the wealth of Germany and France or only Germany higher after breakup of the euro zone or if maintaining the euro zone? In practice, political realities will determine the decision through elections.
The prospects of survival of the euro zone are dire. Table III-7 is constructed with IMF World Economic Outlook database (http://www.imf.org/external/ns/cs.aspx?id=28) for GDP in USD billions, primary net lending/borrowing as percent of GDP and general government debt as percent of GDP for selected regions and countries in 2014.
Table III-7, World and Selected Regional and Country GDP and Fiscal Situation
| GDP 2014 | Primary Net Lending Borrowing | General Government Net Debt | |
| World | 76,776 | ||
| Euro Zone | 13,416 | -0.1 | 73.2 |
| Portugal | 231 | 0.3 | 119.9 |
| Ireland | 230 | -0.7 | 103.5 |
| Greece | 249 | 1.5 | 169.3 |
| Spain | 1,415 | -2.8 | 65.7 |
| Major Advanced Economies G7 | 35,904 | -2.7 | 87.0 |
| United States | 17,528 | -3.2 | 82.3 |
| UK | 2,828 | -3.5 | 84.4 |
| Germany | 3,876 | 1.6 | 52.9 |
| France | 2,886 | -1.7 | 89.5 |
| Japan | 4,846 | -6.4 | 137.1 |
| Canada | 1,769 | -2.2 | 39.5 |
| Italy | 2,172 | 2.3 | 112.4 |
| China | 10,028 | -2.0* | 20.2** |
*Net Lending/borrowing**Gross Debt
Source: IMF World Economic Outlook http://www.imf.org/external/ns/cs.aspx?id=28
The data in Table III-7 are used for some very simple calculations in Table III-8. The column “Net Debt USD Billions 2014” in Table III-8 is generated by applying the percentage in Table III-7 column “General Government Net Debt % GDP 2014” to the column “GDP 2014 USD Billions.” The total debt of France and Germany in 2014 is $4633.4 billion, as shown in row “B+C” in column “Net Debt USD Billions 2014” The sum of the debt of Italy, Spain, Portugal, Greece and Ireland is $4307.7 billion, adding rows D+E+F+G+H in column “Net Debt USD billions 2014.” There is some simple “unpleasant bond arithmetic” in the two final columns of Table I-9. Suppose the entire debt burdens of the five countries with probability of default were to be guaranteed by France and Germany, which de facto would be required by continuing the euro zone. The sum of the total debt of these five countries and the debt of France and Germany is shown in column “Debt as % of Germany plus France GDP” to reach $8941.1 billion, which would be equivalent to 132.2 percent of their combined GDP in 2014. Under this arrangement, the entire debt of selected members of the euro zone including debt of France and Germany would not have nil probability of default. The final column provides “Debt as % of Germany GDP” that would exceed 230.7 percent if including debt of France and 164.0 percent of German GDP if excluding French debt. The unpleasant bond arithmetic illustrates that there is a limit as to how far Germany and France can go in bailing out the countries with unsustainable sovereign debt without incurring severe pains of their own such as downgrades of their sovereign credit ratings. A central bank is not typically engaged in direct credit because of remembrance of inflation and abuse in the past. There is also a limit to operations of the European Central Bank in doubtful credit obligations. Wriston (1982) would prove to be wrong again that countries do not bankrupt but would have a consolation prize that similar to LBOs the sum of the individual values of euro zone members outside the current agreement exceeds the value of the whole euro zone. Internal rescues of French and German banks may be less costly than bailing out other euro zone countries so that they do not default on French and German banks. Analysis of fiscal stress is quite difficult without including another global recession in an economic cycle that is already mature by historical experience.
Table III-8, Guarantees of Debt of Sovereigns in Euro Area as Percent of GDP of Germany and France, USD Billions and %
| Net Debt USD Billions 2014 | Debt as % of Germany Plus France GDP | Debt as % of Germany GDP | |
| A Euro Area | 9,820.5 | ||
| B Germany | 2,050.4 | $8941.1 as % of $3876 =230.7% $6358.1 as % of $3876 =164.0% | |
| C France | 2,583.0 | ||
| B+C | 4,633.4 | GDP $6,762.0 Total Debt $8941.1 Debt/GDP: 132.2% | |
| D Italy | 2,441.3 | ||
| E Spain | 929.7 | ||
| F Portugal | 277.0 | ||
| G Greece | 421.6 | ||
| H Ireland | 238.1 | ||
| Subtotal D+E+F+G+H | 4,307.7 |
Source: calculation with IMF data IMF World Economic Outlook databank
http://www.imf.org/external/ns/cs.aspx?id=28
There is extremely important information in Table III-9 for the current sovereign risk crisis in the euro zone. Table III-9 provides the structure of regional and country relations of Germany’s exports and imports with newly available data for Jun 2014. German exports to other European Union (EU) members are 58.7 percent of total exports in Jun 2014 and 58.6 percent in cumulative Jan-Jun 2014. Exports to the euro area are 37.3 percent of the total in Jun and 37.4 percent cumulative in Jan-Jun. Exports to third countries are 41.3 percent of the total in Jun and 41.4 percent cumulative in Jan-Jun. There is similar distribution for imports. Exports to non-euro countries are increasing 7.1 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2014, increasing 9.2 percent cumulative in Jan-Jun 2014 while exports to the euro area are increasing 0.3 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2014 and increasing 2.2 percent cumulative in Jan-Jun 2014. Exports to third countries, accounting for 41.3 percent of the total in Jun 2014, are decreasing 0.9 percent in the 12 months ending in Jun 2014 and decreasing 0.7 percent cumulative in Jan-Jun 2014, accounting for 41.4 percent of the cumulative total in Jan-Jun 2014. Price competitiveness through devaluation could improve export performance and growth. Economic performance in Germany is closely related to Germany’s high competitiveness in world markets. Weakness in the euro zone and the European Union in general could affect the German economy. This may be the major reason for choosing the “fiscal abuse” of the European Central Bank considered by Buiter (2011Oct31) over the breakdown of the euro zone. There is a tough analytical, empirical and forecasting doubt of growth and trade in the euro zone and the world with or without maintenance of the European Monetary Union (EMU) or euro zone. Germany could benefit from depreciation of the euro because of high share in its exports to countries not in the euro zone but breakdown of the euro zone raises doubts on the region’s economic growth that could affect German exports to other member states.
Table III-9, Germany, Structure of Exports and Imports by Region, € Billions and ∆%
| Jun 2014 | Jun 12-Month | Cumulative Jan-Jun 2014 € Billions | Cumulative Jan-Jun 2014/ | |
| Total | 93.4 | 1.1 | 558.3 | 2.4 |
| A. EU | 54.8 % 58.7 | 2.6 | 327.3 % 58.6 | 4.7 |
| Euro Area | 34.8 % 37.3 | 0.3 | 208.6 % 37.4 | 2.2 |
| Non-euro Area | 20.0 % 21.4 | 7.1 | 118.7 % 21.3 | 9.2 |
| B. Third Countries | 38.6 % 41.3 | -0.9 | 231.0 % 41.4 | -0.7 |
| Total Imports | 77.0 | 2.1 | 459.0 | 2.6 |
| C EU Members | 51.1 % 66.4 | 5.0 | 301.1 % 65.6 | 4.2 |
| Euro Area | 35.7 % 46.4 | 4.0 | 207.3 % 45.2 | 2.5 |
| Non-euro Area | 15.4 % 20.0 | 7.5 | 93.8 % 20.4 | 8.0 |
| D Third Countries | 25.8 % 33.5 | -3.2 | 157.9 % 34.4 | -0.3 |
Notes: Total Exports = A+B; Total Imports = C+D
Source: Statistisches Bundesamt Deutschland
https://www.destatis.de/EN/PressServices/Press/pr/2014/07/PE14_244_51.html
IIIF Appendix on Sovereign Bond Valuation. There are two approaches to government finance and their implications: (1) simple unpleasant monetarist arithmetic; and (2) simple unpleasant fiscal arithmetic. Both approaches illustrate how sovereign debt can be perceived riskier under profligacy.
First, Unpleasant Monetarist Arithmetic. Fiscal policy is described by Sargent and Wallace (1981, 3, equation 1) as a time sequence of D(t), t = 1, 2,…t, …, where D is real government expenditures, excluding interest on government debt, less real tax receipts. D(t) is the real deficit excluding real interest payments measured in real time t goods. Monetary policy is described by a time sequence of H(t), t=1,2,…t, …, with H(t) being the stock of base money at time t. In order to simplify analysis, all government debt is considered as being only for one time period, in the form of a one-period bond B(t), issued at time t-1 and maturing at time t. Denote by R(t-1) the real rate of interest on the one-period bond B(t) between t-1 and t. The measurement of B(t-1) is in terms of t-1 goods and [1+R(t-1)] “is measured in time t goods per unit of time t-1 goods” (Sargent and Wallace 1981, 3). Thus, B(t-1)[1+R(t-1)] brings B(t-1) to maturing time t. B(t) represents borrowing by the government from the private sector from t to t+1 in terms of time t goods. The price level at t is denoted by p(t). The budget constraint of Sargent and Wallace (1981, 3, equation 1) is:
D(t) = {[H(t) – H(t-1)]/p(t)} + {B(t) – B(t-1)[1 + R(t-1)]} (1)
Equation (1) states that the government finances its real deficits into two portions. The first portion, {[H(t) – H(t-1)]/p(t)}, is seigniorage, or “printing money.” The second part,
{B(t) – B(t-1)[1 + R(t-1)]}, is borrowing from the public by issue of interest-bearing securities. Denote population at time t by N(t) and growing by assumption at the constant rate of n, such that:
N(t+1) = (1+n)N(t), n>-1 (2)
The per capita form of the budget constraint is obtained by dividing (1) by N(t) and rearranging:
B(t)/N(t) = {[1+R(t-1)]/(1+n)}x[B(t-1)/N(t-1)]+[D(t)/N(t)] – {[H(t)-H(t-1)]/[N(t)p(t)]} (3)
On the basis of the assumptions of equal constant rate of growth of population and real income, n, constant real rate of return on government securities exceeding growth of economic activity and quantity theory equation of demand for base money, Sargent and Wallace (1981) find that “tighter current monetary policy implies higher future inflation” under fiscal policy dominance of monetary policy. That is, the monetary authority does not permanently influence inflation, lowering inflation now with tighter policy but experiencing higher inflation in the future.
Second, Unpleasant Fiscal Arithmetic. The tool of analysis of Cochrane (2011Jan, 27, equation (16)) is the government debt valuation equation:
(Mt + Bt)/Pt = Et∫(1/Rt, t+τ)st+τdτ (4)
Equation (4) expresses the monetary, Mt, and debt, Bt, liabilities of the government, divided by the price level, Pt, in terms of the expected value discounted by the ex-post rate on government debt, Rt, t+τ, of the future primary surpluses st+τ, which are equal to Tt+τ – Gt+τ or difference between taxes, T, and government expenditures, G. Cochrane (2010A) provides the link to a web appendix demonstrating that it is possible to discount by the ex post Rt, t+τ. The second equation of Cochrane (2011Jan, 5) is:
MtV(it, ·) = PtYt (5)
Conventional analysis of monetary policy contends that fiscal authorities simply adjust primary surpluses, s, to sanction the price level determined by the monetary authority through equation (5), which deprives the debt valuation equation (4) of any role in price level determination. The simple explanation is (Cochrane 2011Jan, 5):
“We are here to think about what happens when [4] exerts more force on the price level. This change may happen by force, when debt, deficits and distorting taxes become large so the Treasury is unable or refuses to follow. Then [4] determines the price level; monetary policy must follow the fiscal lead and ‘passively’ adjust M to satisfy [5]. This change may also happen by choice; monetary policies may be deliberately passive, in which case there is nothing for the Treasury to follow and [4] determines the price level.”
An intuitive interpretation by Cochrane (2011Jan 4) is that when the current real value of government debt exceeds expected future surpluses, economic agents unload government debt to purchase private assets and goods, resulting in inflation. If the risk premium on government debt declines, government debt becomes more valuable, causing a deflationary effect. If the risk premium on government debt increases, government debt becomes less valuable, causing an inflationary effect.
There are multiple conclusions by Cochrane (2011Jan) on the debt/dollar crisis and Global recession, among which the following three:
(1) The flight to quality that magnified the recession was not from goods into money but from private-sector securities into government debt because of the risk premium on private-sector securities; monetary policy consisted of providing liquidity in private-sector markets suffering stress
(2) Increases in liquidity by open-market operations with short-term securities have no impact; quantitative easing can affect the timing but not the rate of inflation; and purchase of private debt can reverse part of the flight to quality
(3) The debt valuation equation has a similar role as the expectation shifting the Phillips curve such that a fiscal inflation can generate stagflation effects similar to those occurring from a loss of anchoring expectations.
© Carlos M. Pelaez, 2009, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013, 2014.





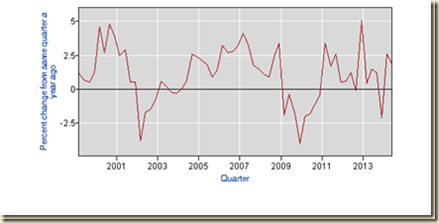

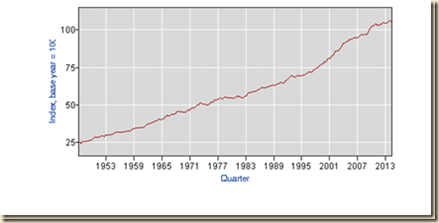
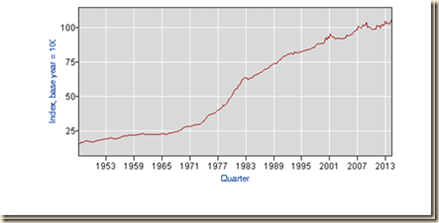


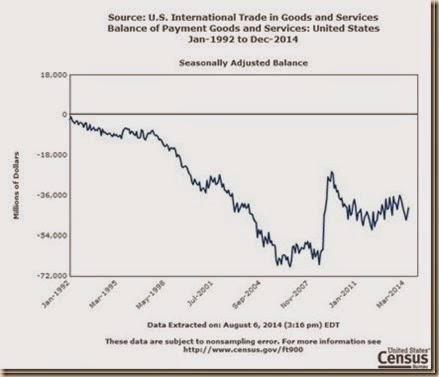
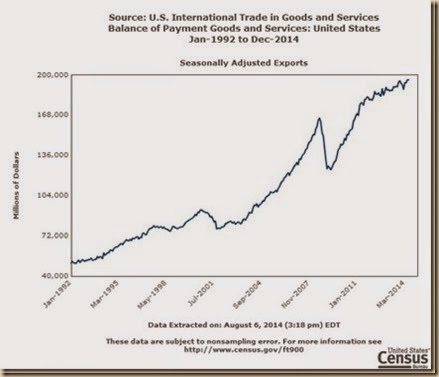
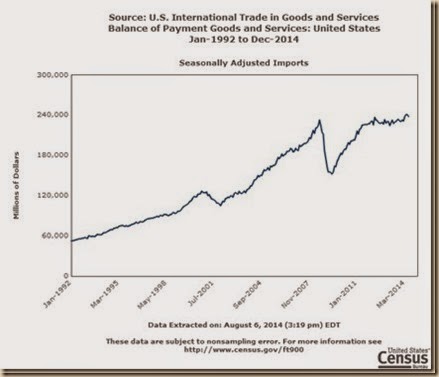








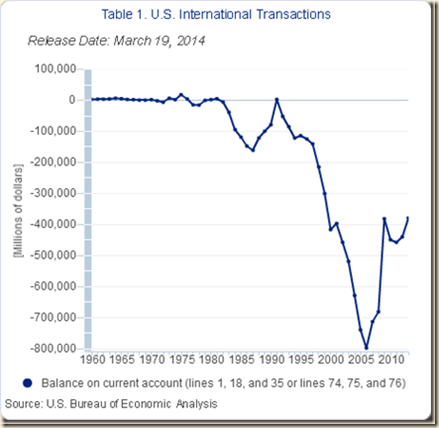



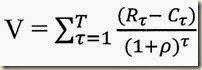

No comments:
Post a Comment